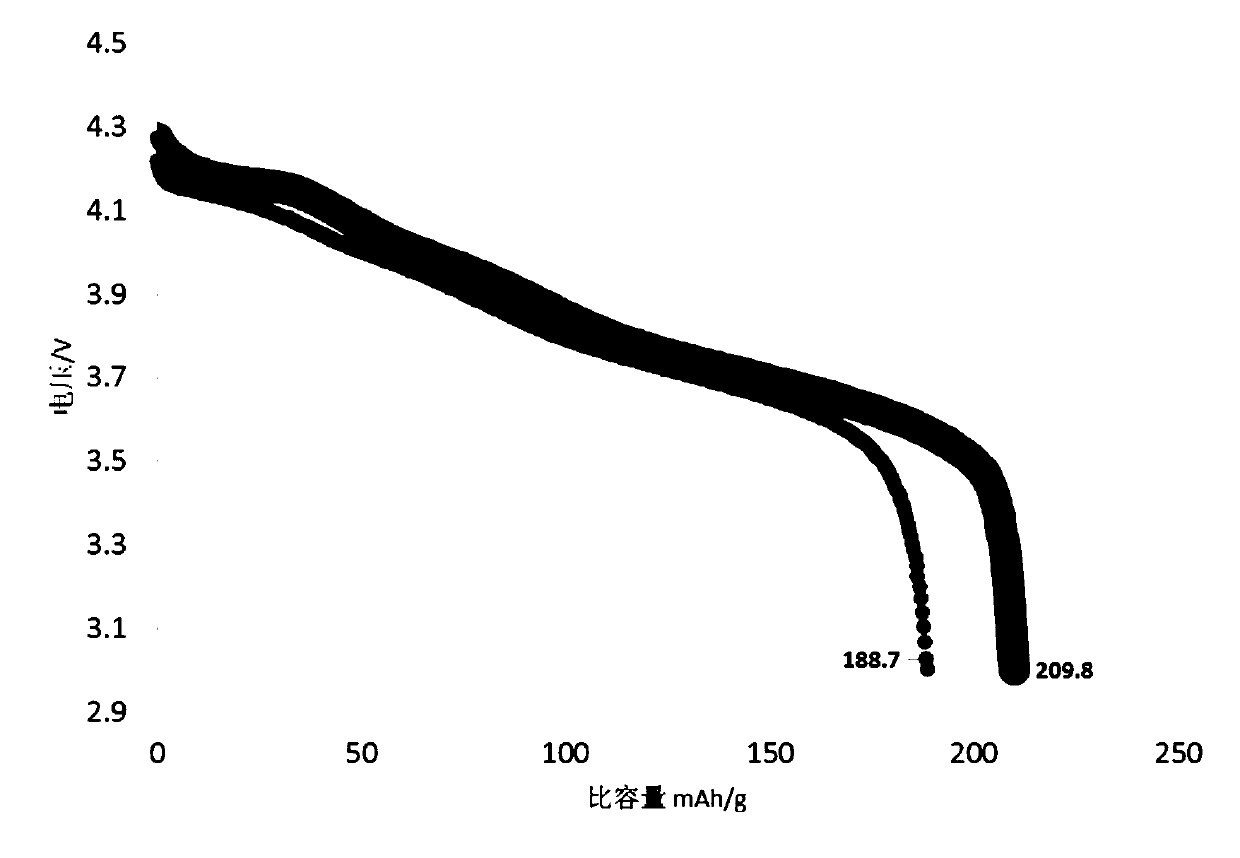
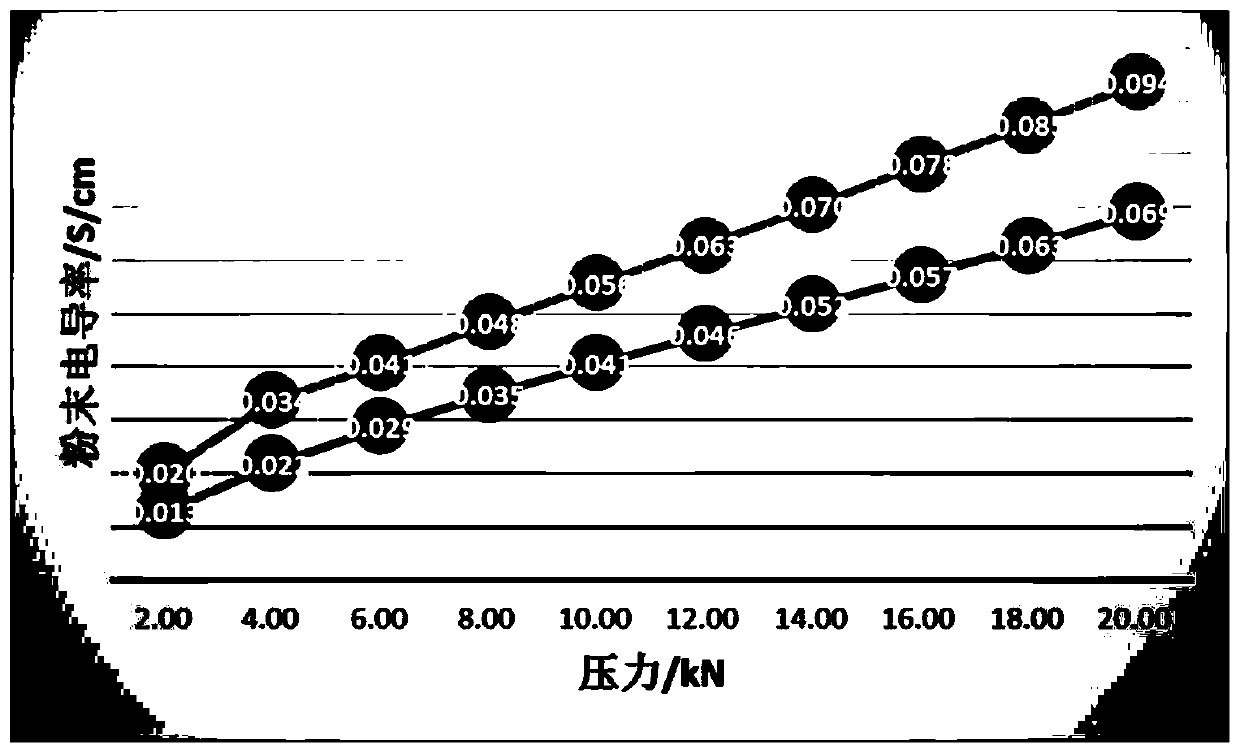
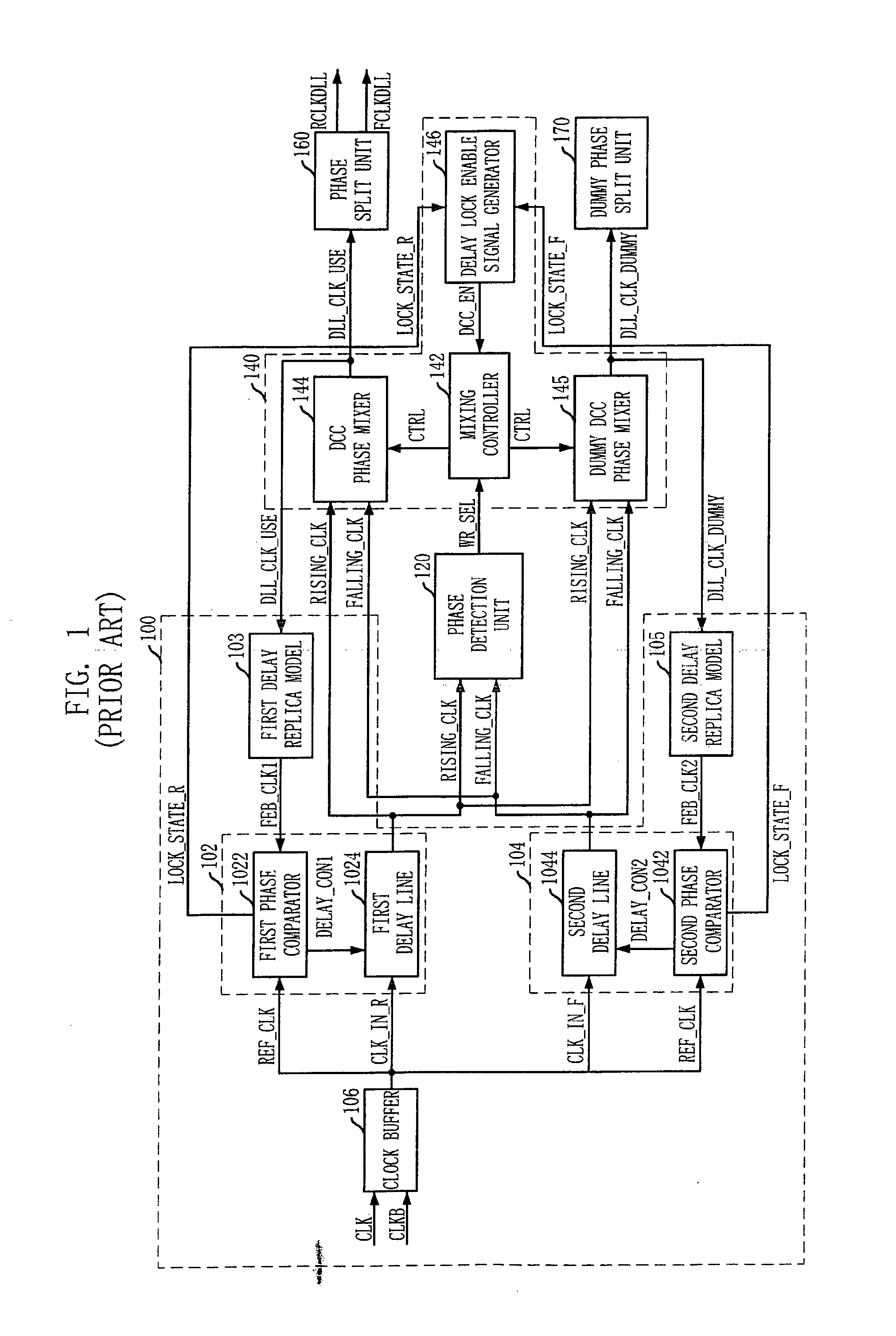
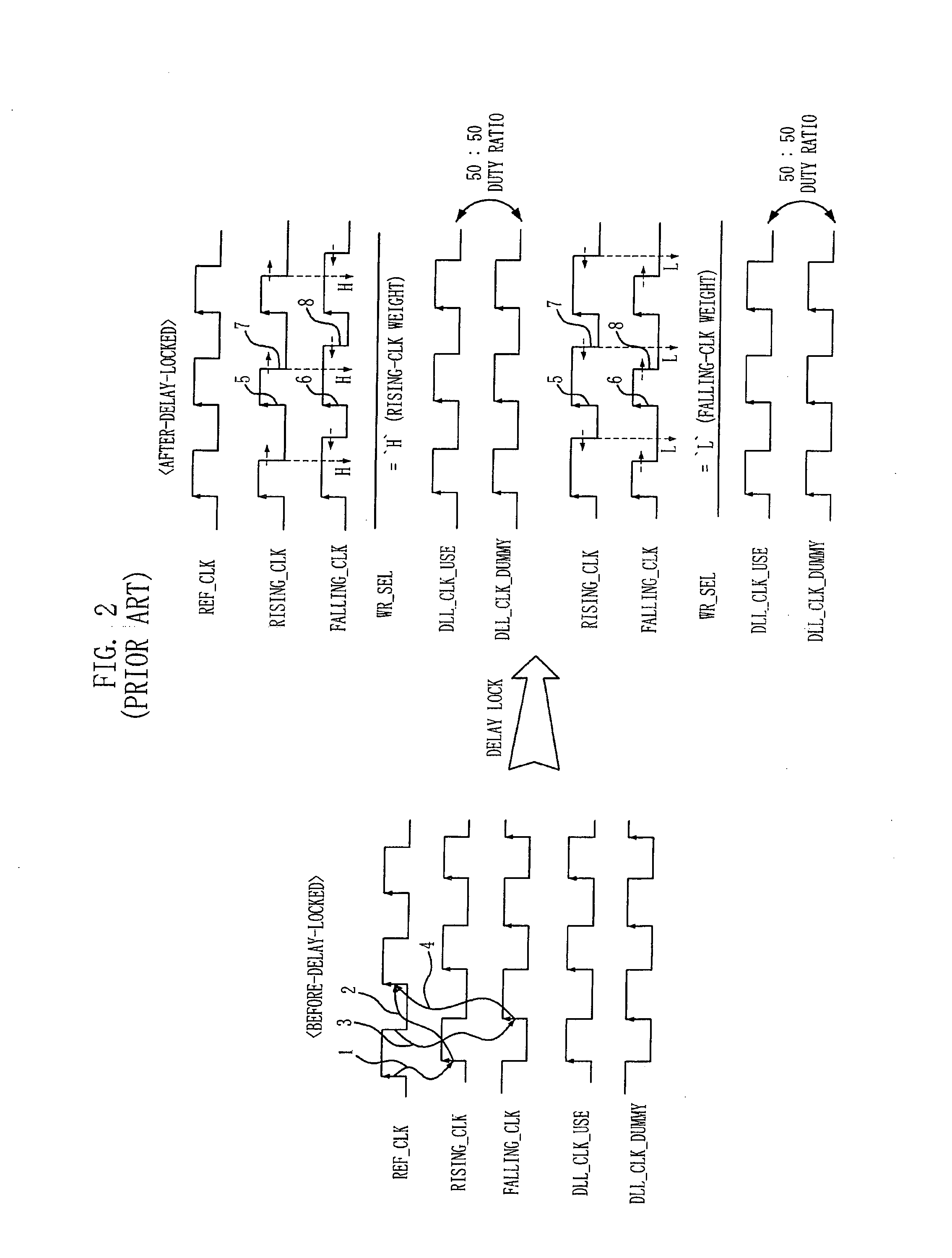
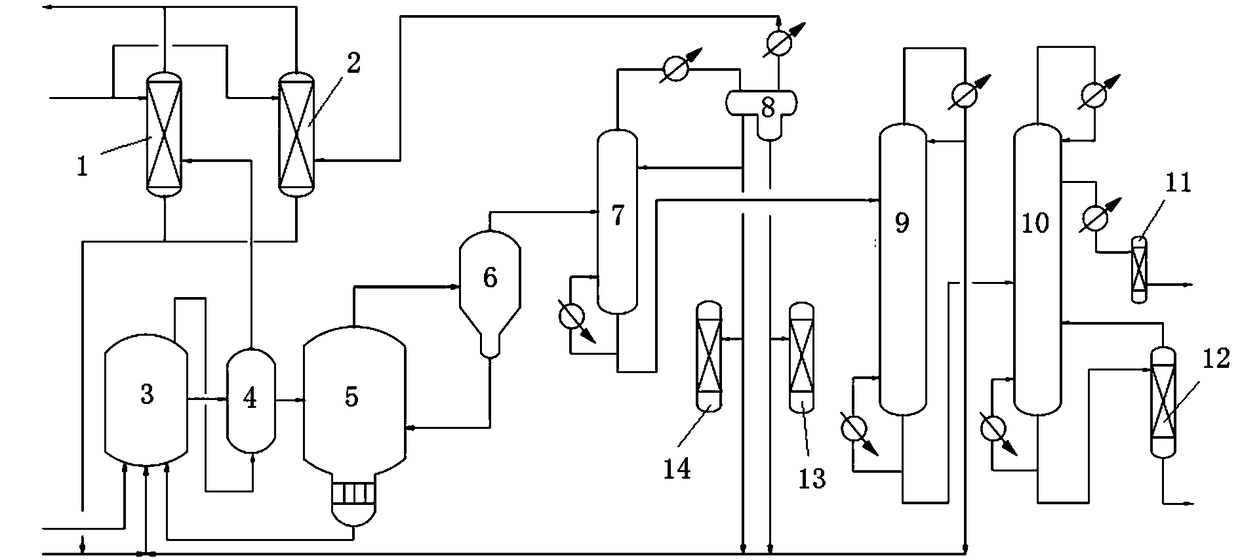
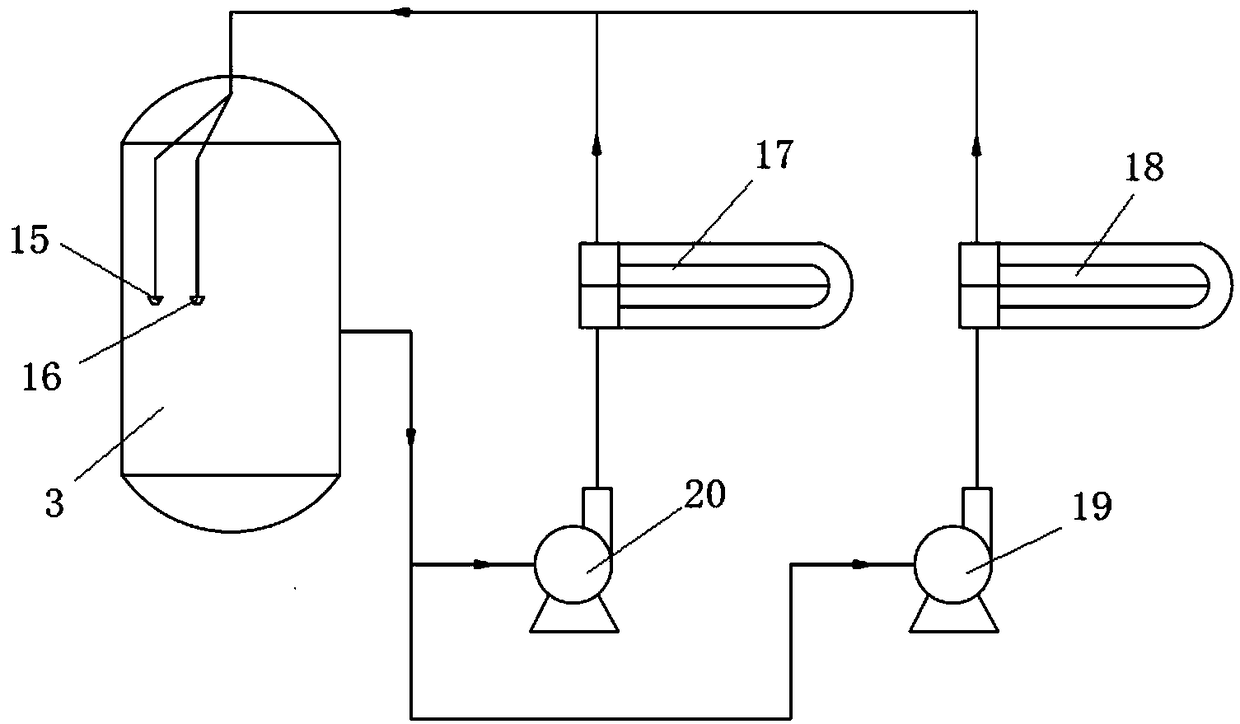
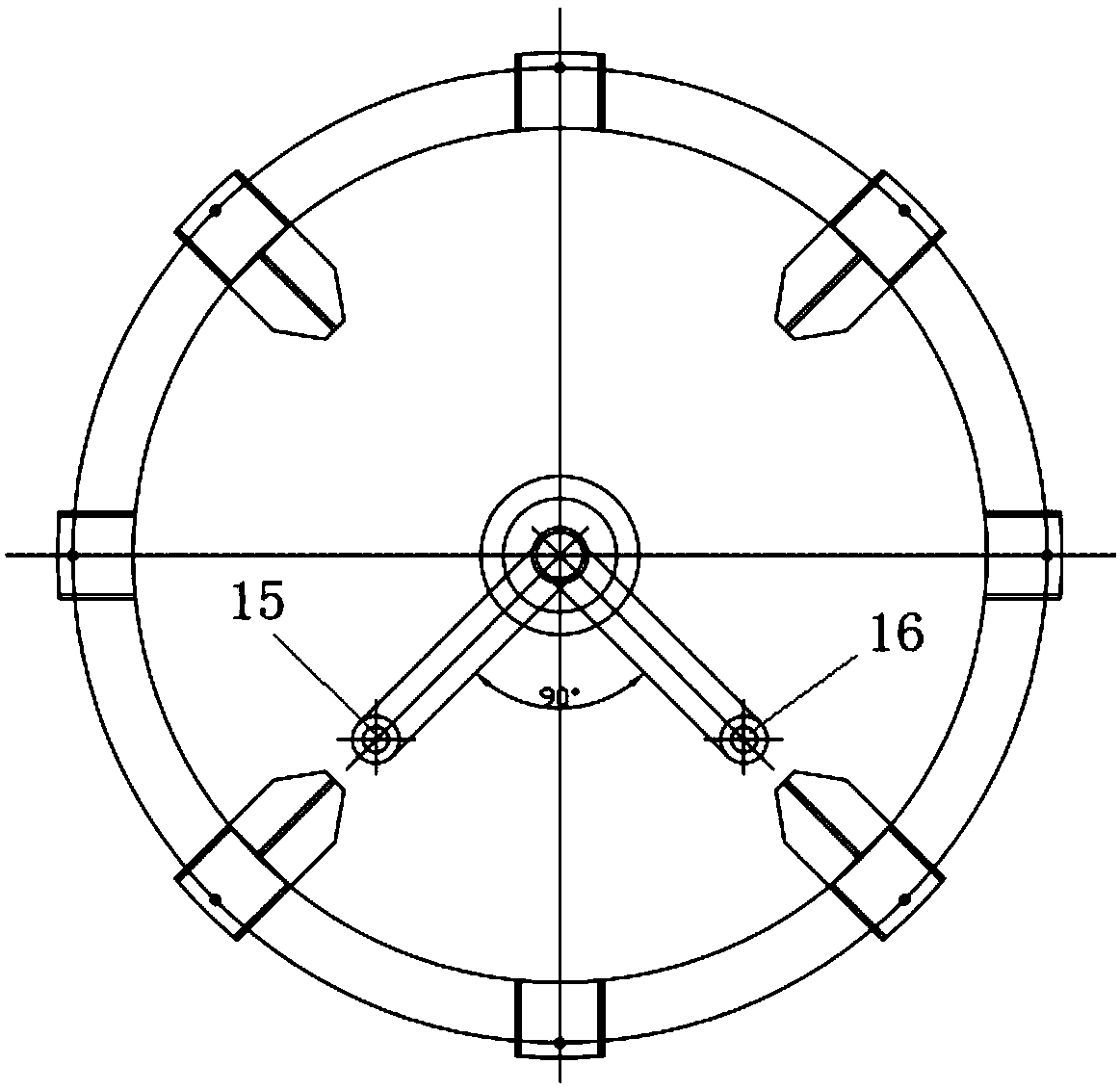
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
283 results about "Phase mixing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
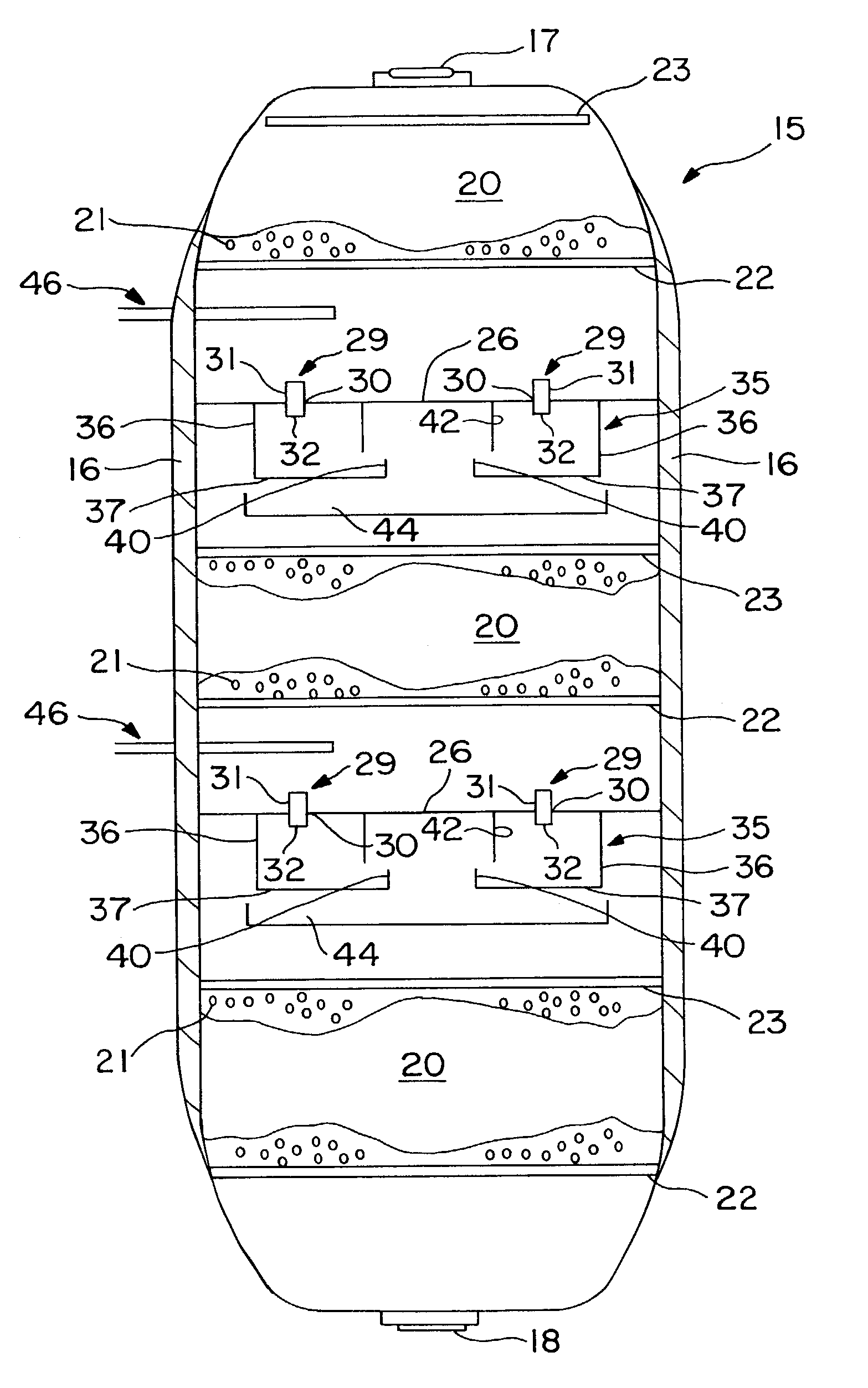
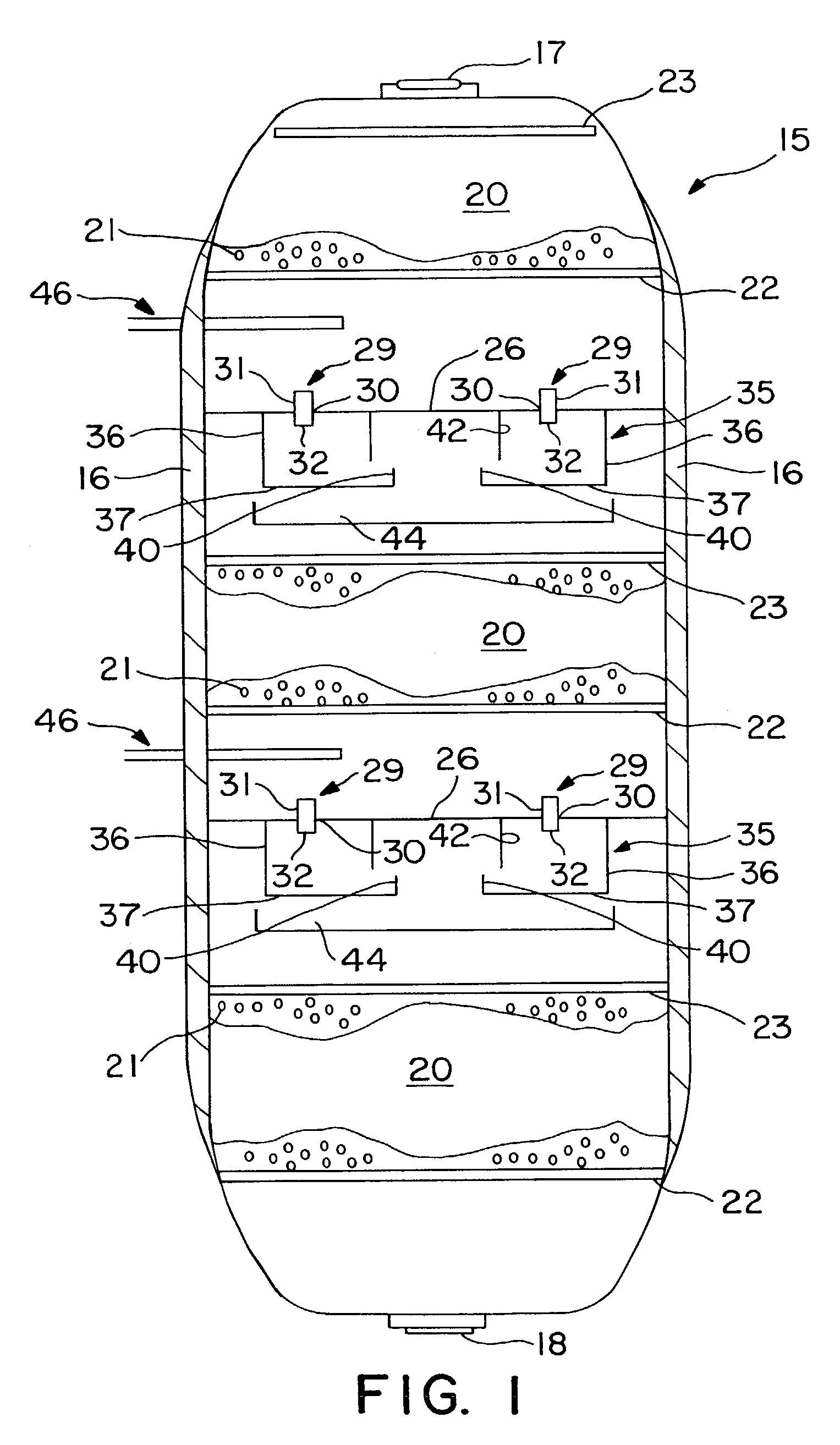
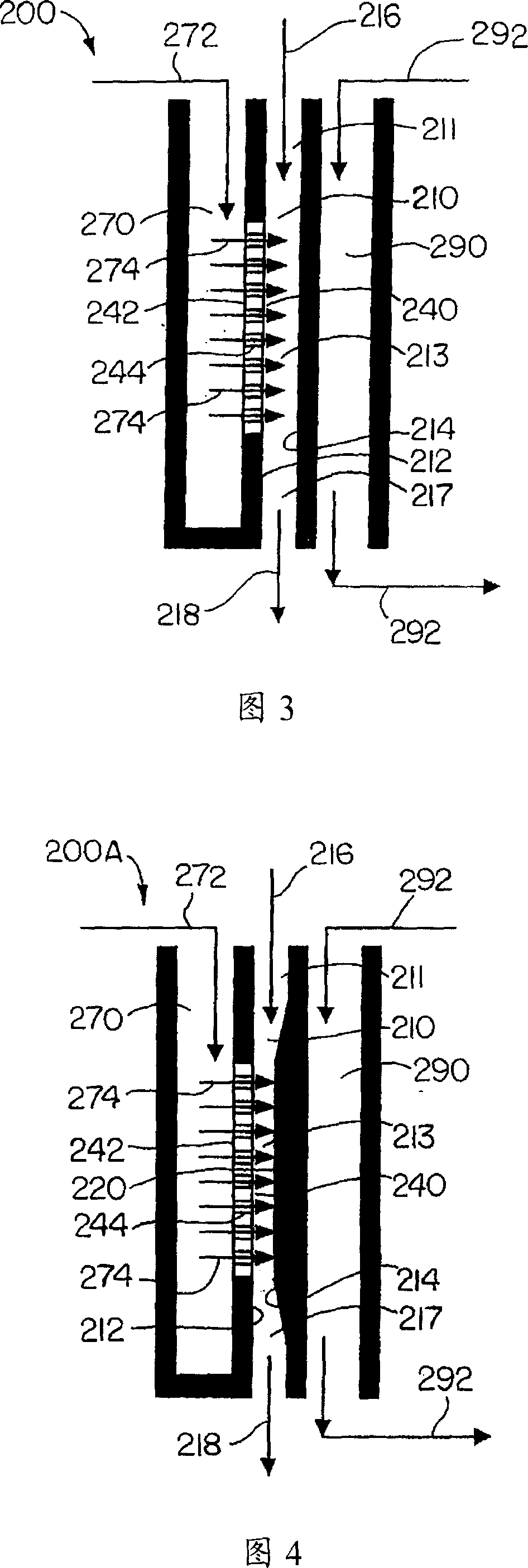
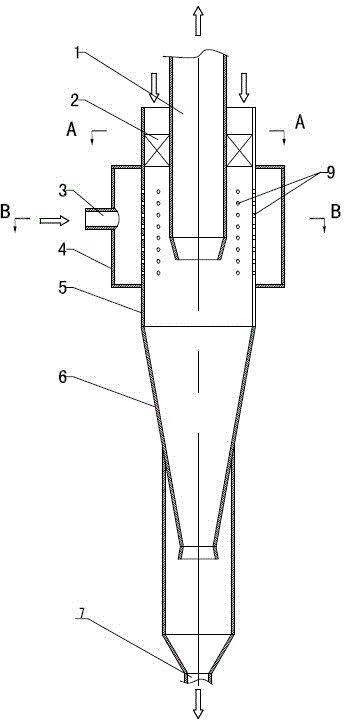
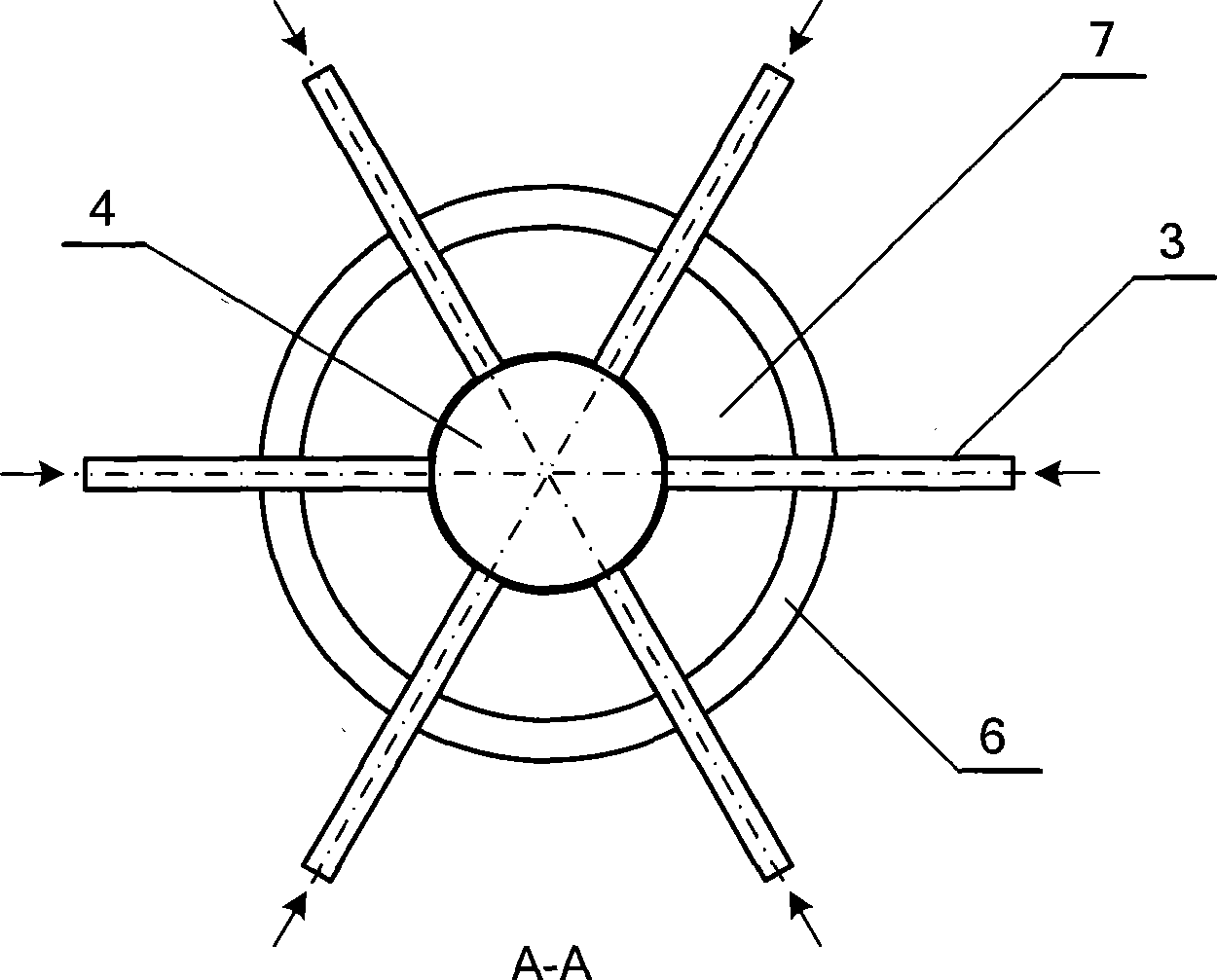
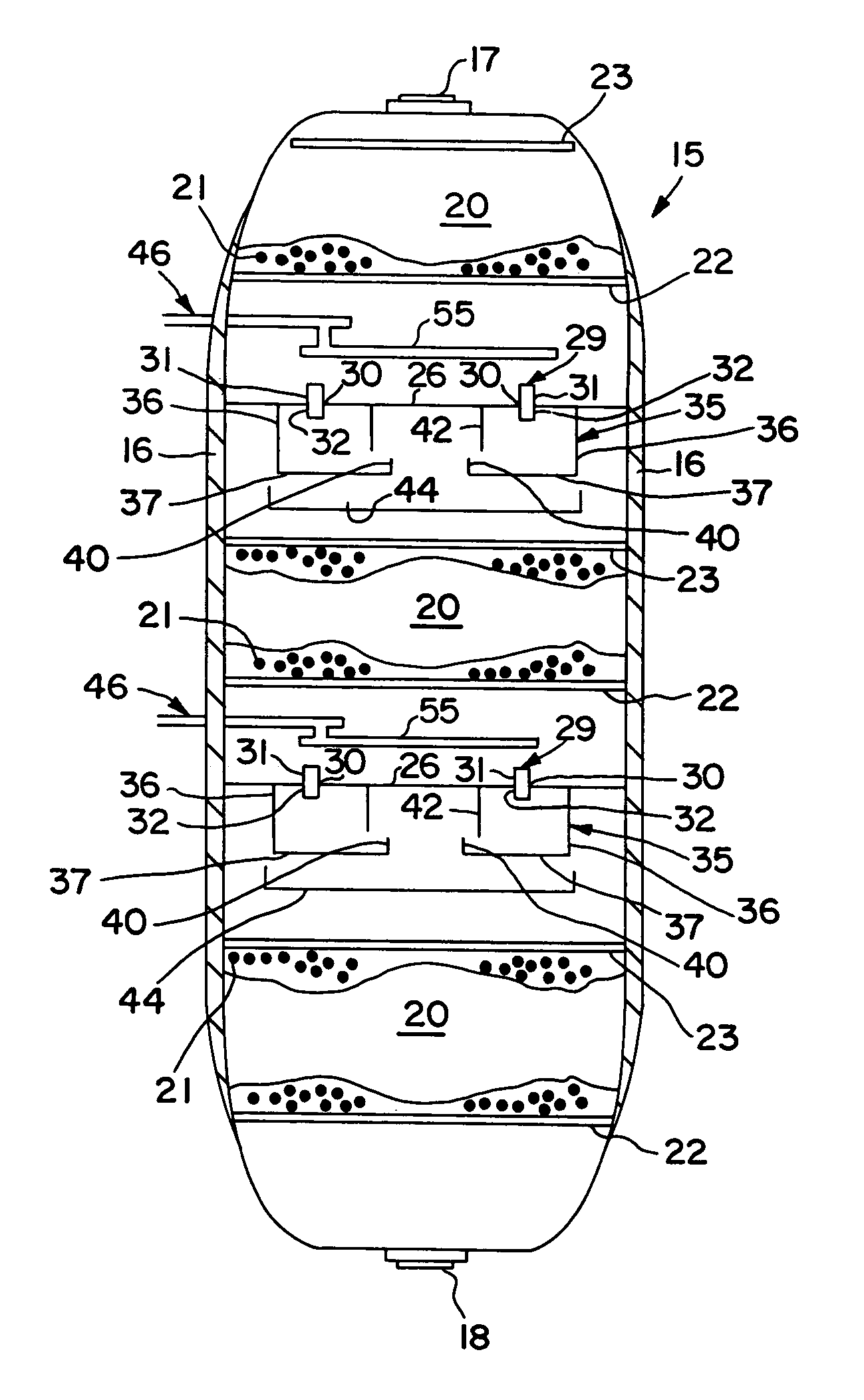
Multiphase mixing device with staged gas introduction
InactiveUS7052654B2Lower overall pressure dropImprove efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPhase mixingHybrid system
The present invention comprises a mixing system that provides improved mixing of quench gas and process fluids in a height constrained interbed space while not increasing pressure drop. In particular, the device improves the effectiveness of an existing mixing volume in mixing the gas phase of two-phase systems. The mixing system includes a horizontal collection tray, a mixing chamber positioned below the collection tray, at least one passageway extending through the collection tray into the mixing chamber, and a vapor slipstream passageway extending through the collection tray into the mixing chamber for directing a vapor slipstream from above the collection tray into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber and the collection tray define a two-phase mixing volume. The passageway conducts fluid containing at least some vapor from above the collection tray into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber preferably includes at least one outlet opening for the downward passage of fluid. The vapor slipstream passageway, optionally, comprises a plurality of inlets arranged to impart rotational movement to the vapor phase at a location within the mixing chamber where the vapor phase has substantially expended the kinetic energy of its initial entry into the mixing chamber. As a result of providing at least one additional passageway for a vapor slipstream, and optionally, including one or more baffles as described above, significant re-acceleration of the vapor phase is achieved in the mixing chamber resulting in improvements in mixing efficiency of both the vapor and liquid phases.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Method for three-phase extraction one-step separation of platinum, palladium and rhodium from leaching solution of precious metal catalyst
ActiveCN102002589AHigh separation selectivitySimple processProcess efficiency improvementPhosphateSolvent
The invention relates to a method for three-phase extraction one-step separation of platinum, palladium and rhodium from leaching solution of a precious metal catalyst, which belongs to the technical field of solvent extraction and separation of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium. The separation of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium can be completed by adding hydrochloride, sulfate, nitrate or phosphate of sodium, potassium, lithium or ammonium into two non-polar and polar organic phases which can not be mixed and water solution containing the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium, and carrying out phase mixing under room temperature for obtaining a three-phase system. The separation of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium can also be completed by adding a macromoleclar polymer and the hydrochloride, the sulfate, the nitrate or the phosphate containing the sodium, the potassium, the lithium or the ammonium into the water solution containing the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium according to proportion, further adding a non-polar organic solvent and carrying out the phase mixing under the room temperature for obtaining three phases. The method can simultaneously separate three phases of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium with high separation selectivity from the failure extraction solution of a vehicle catalyst during the extraction process, and effectively simplify the existing lengthy and tedious two-phase extraction and separation process.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiphase mixing process using microchannel process technology
The disclosed invention relates to a process for making a multiphase mixture, comprising: flowing a first fluid stream through a process microchannel, the first fluid stream comprising at least one liquid and / or at least one gas, the process microchannel having an apertured section; flowing a second fluid stream through the apertured section into the process microchannel in contact with the first fluid stream to form the multiphase mixture, the second fluid stream comprising at least one gas and / or at least one microbody-forming material, the first fluid stream forming a continuous phase in the multiphase mixture, the second fluid stream forming a discontinuous phase dispersed in the continuous phase.
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
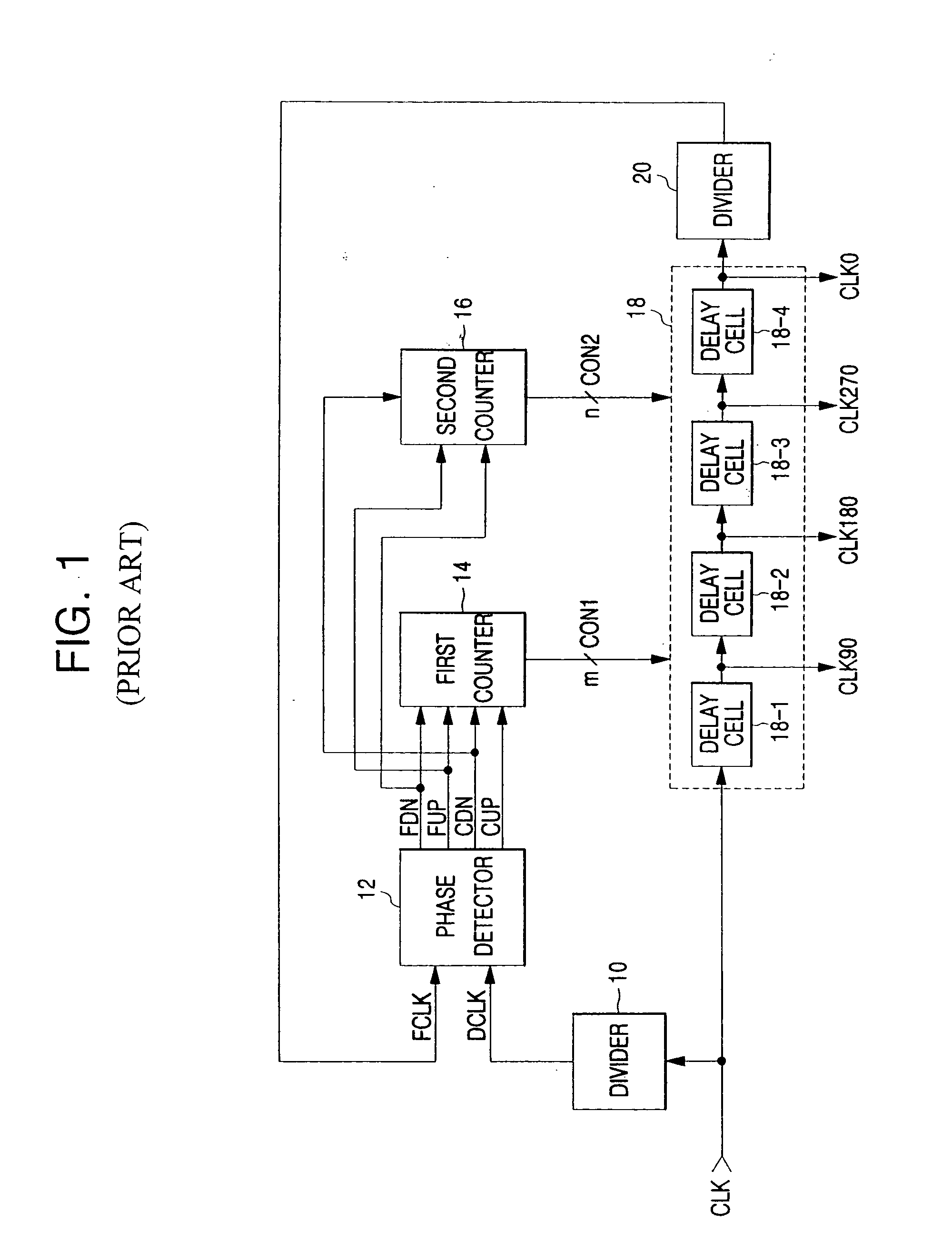
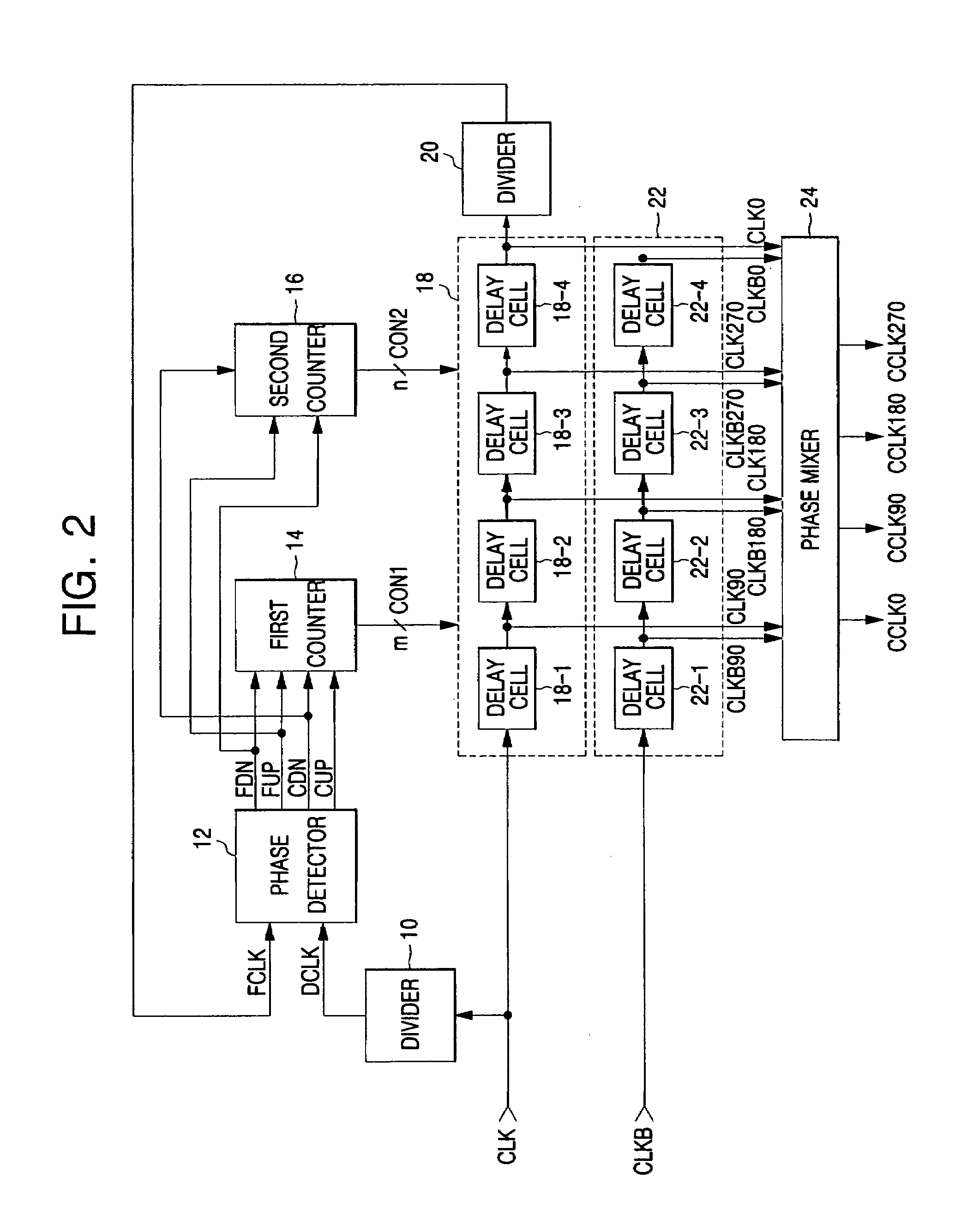
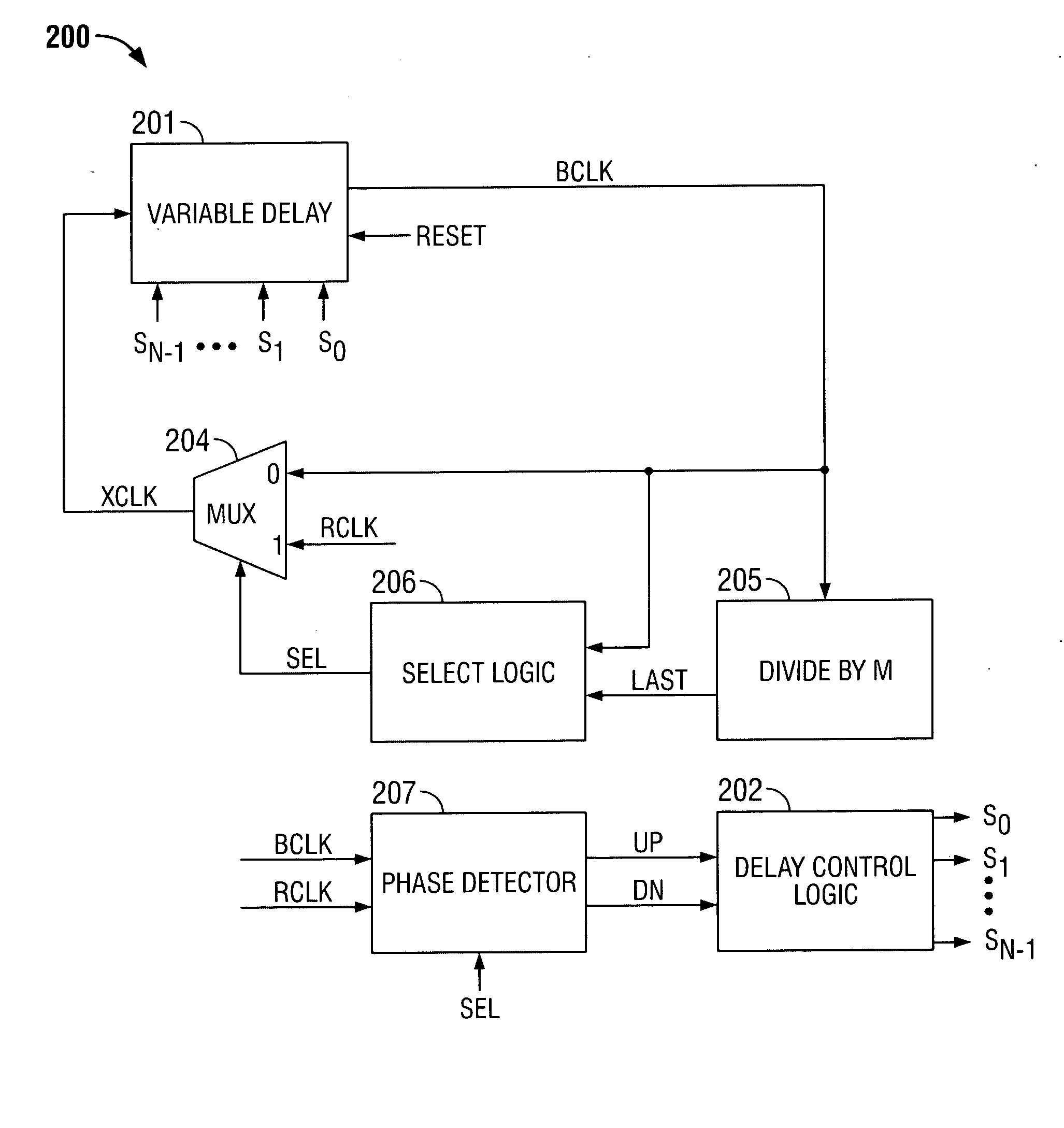
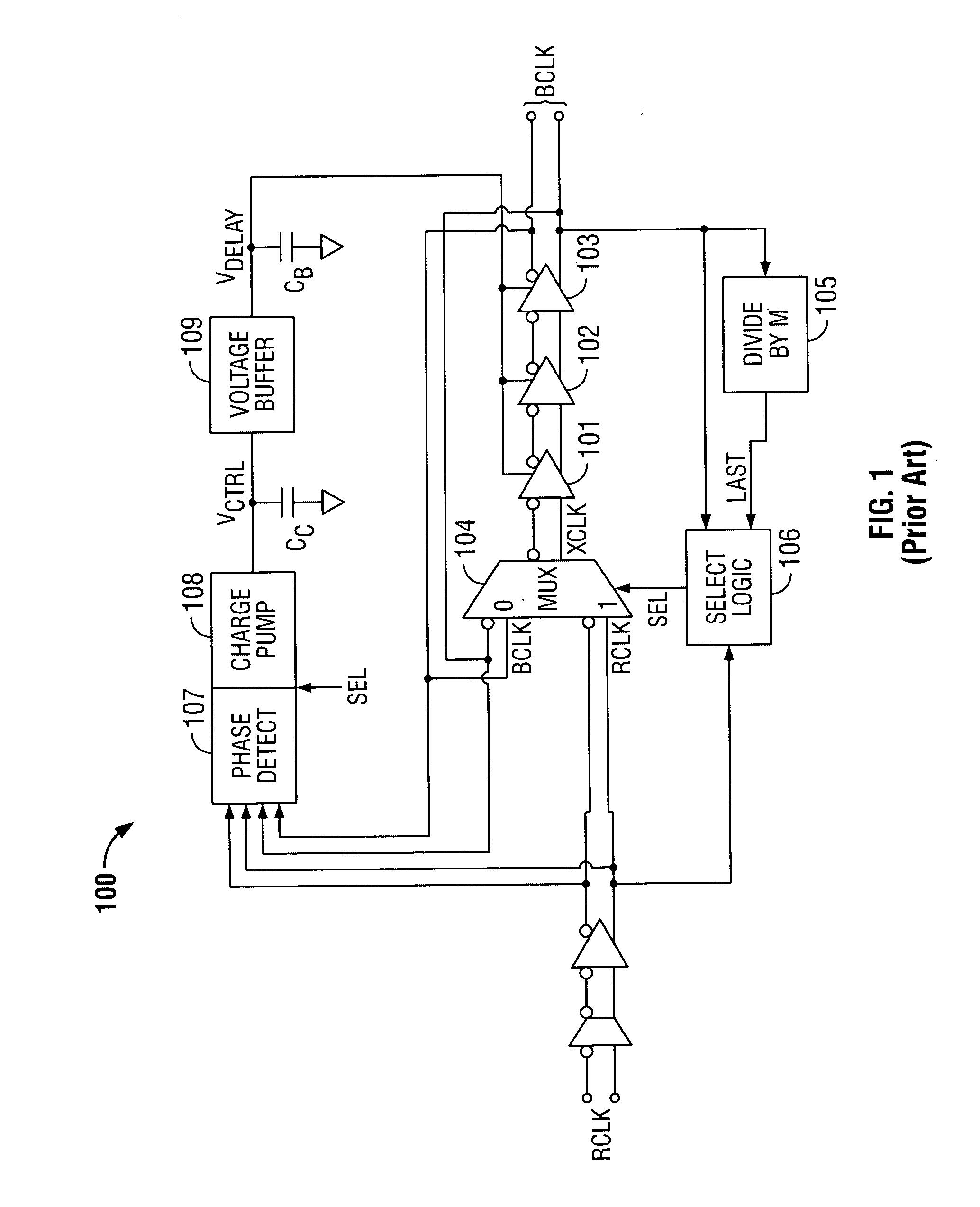
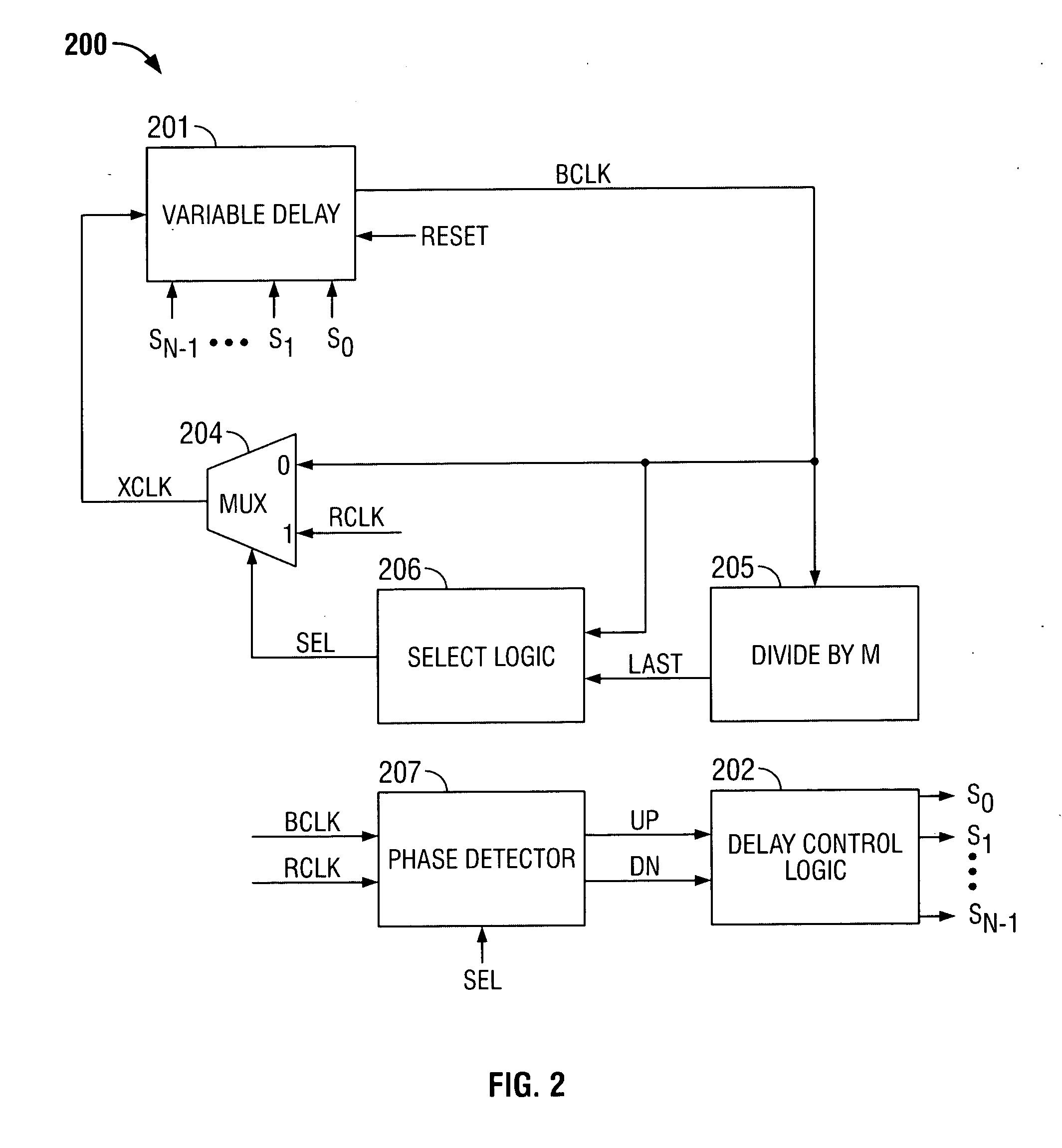
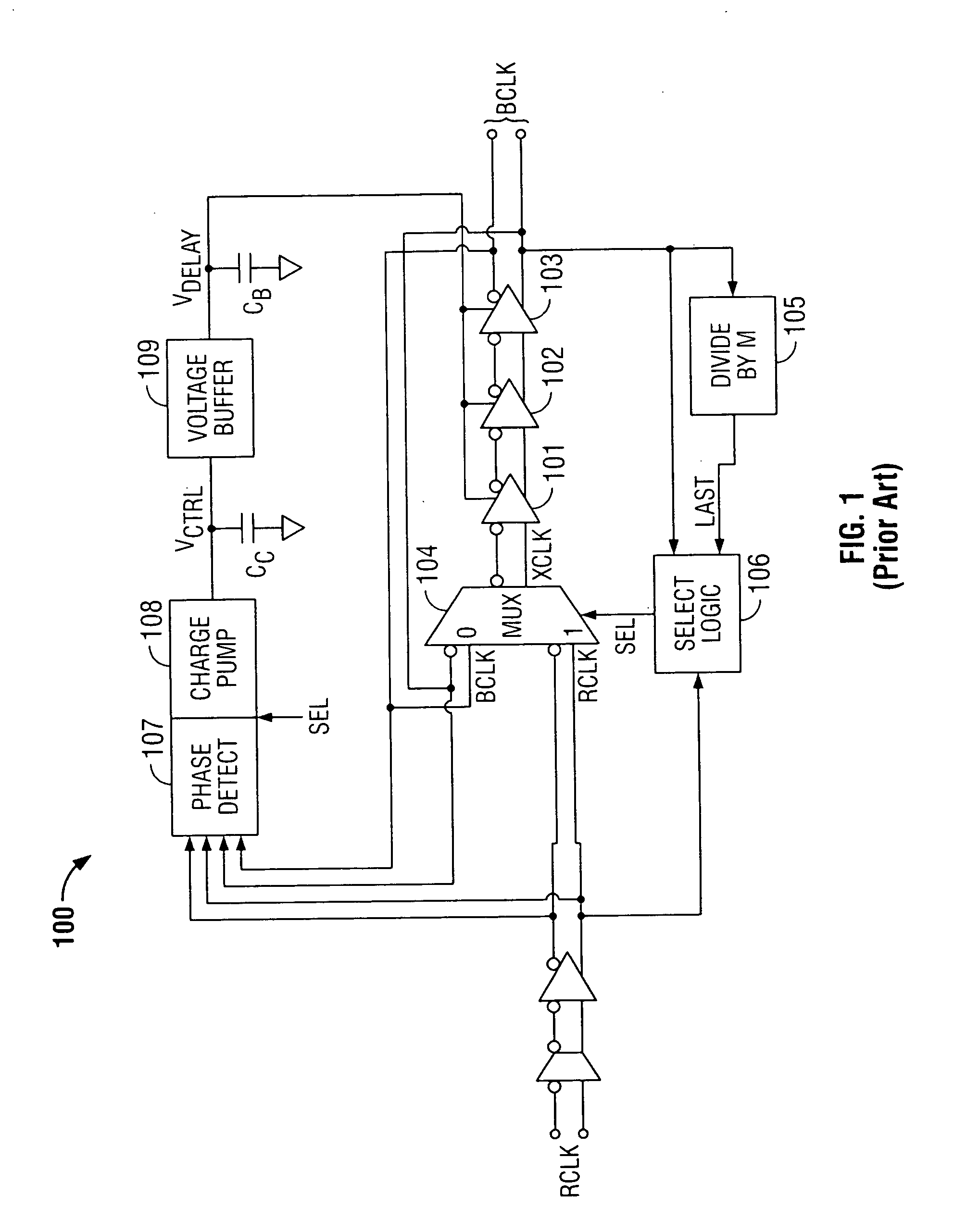
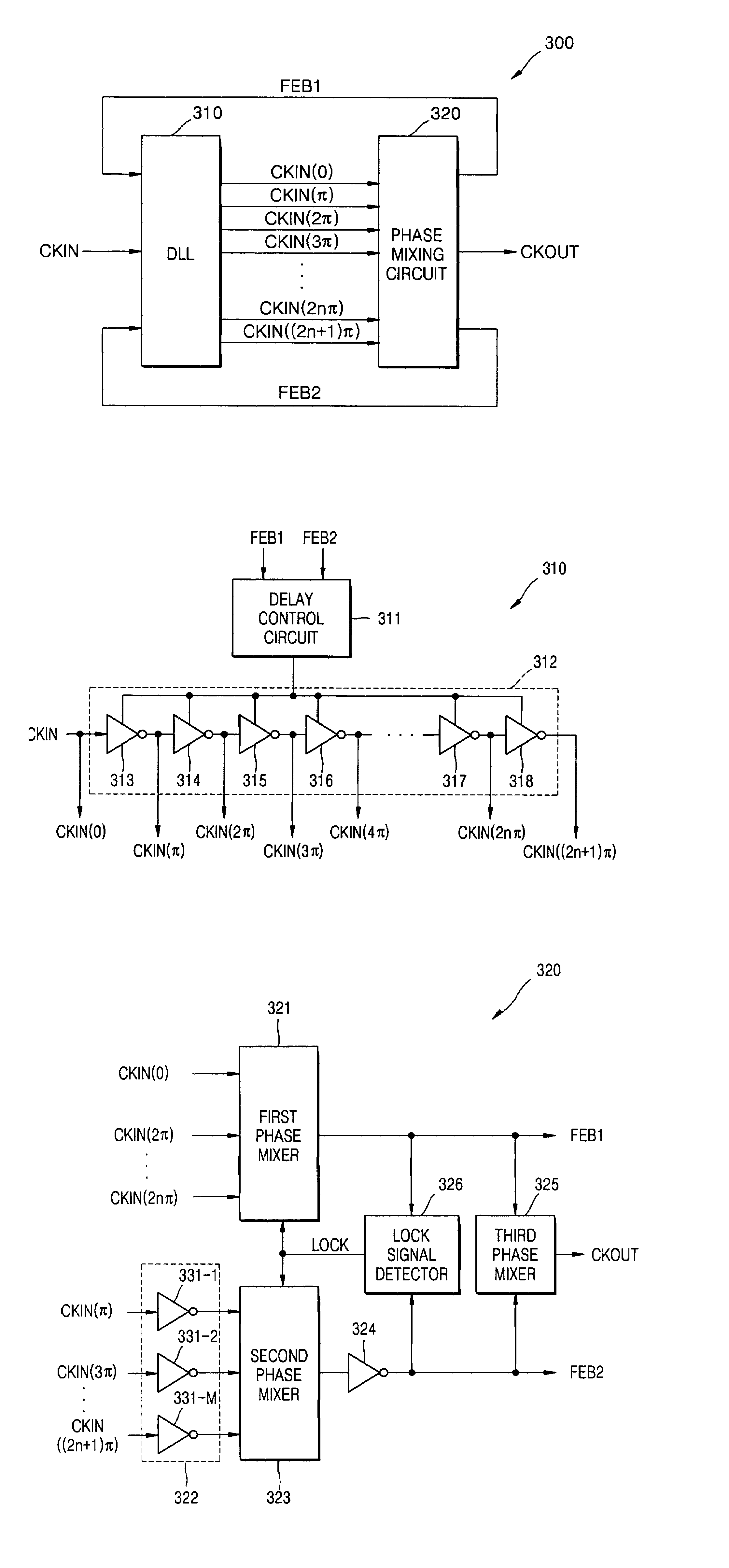
Delay locked loop and semiconductor memory device having the same
InactiveUS7202721B2Correction of phase differencePulse automatic controlPulse modulationPhase mixingPhase difference
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mixer settler for three-phase extraction
InactiveCN101991971AAchieve separationSolving Three-Phase Flow ProblemsLiquid solutions solvent extractionPhase mixingThree stage
The invention belongs to a liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase multi-stage continuous extraction device, and particularly relates to a mixer settler for three-phase extraction, which can extract the target component in one step and realizes high-level separation in a multi-component complex system. The mixer settler for three-phase extraction comprises a first-level mixer settler, a second-level mixer settler and a third-level mixer settler which have the same structure; and every mixer settler comprises a three-phase mixing chamber, a clarifying chamber, an intermediate-low phase mixing chamber, and the like. As an aqueous two-phase system, an intermediate phase and a salt-rich low phase rich in polymer are used as one phase under the condition of stirring to transfer mass during counterflow with the organic phase so that the problem of three-phase flow in the three-phase extraction process is solved and the multi-stage continuous extraction can be carried out. Under the circumference that the one-stage extraction separating effect is unsatisfactory in the multi-component complex system, the mixer settler for three-phase extraction can realize three-stage reverse flow continuous extraction and high-level multi-component separation according to the components. The invention successfully solves the problem of three-phase flow in the three-phase extraction process.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
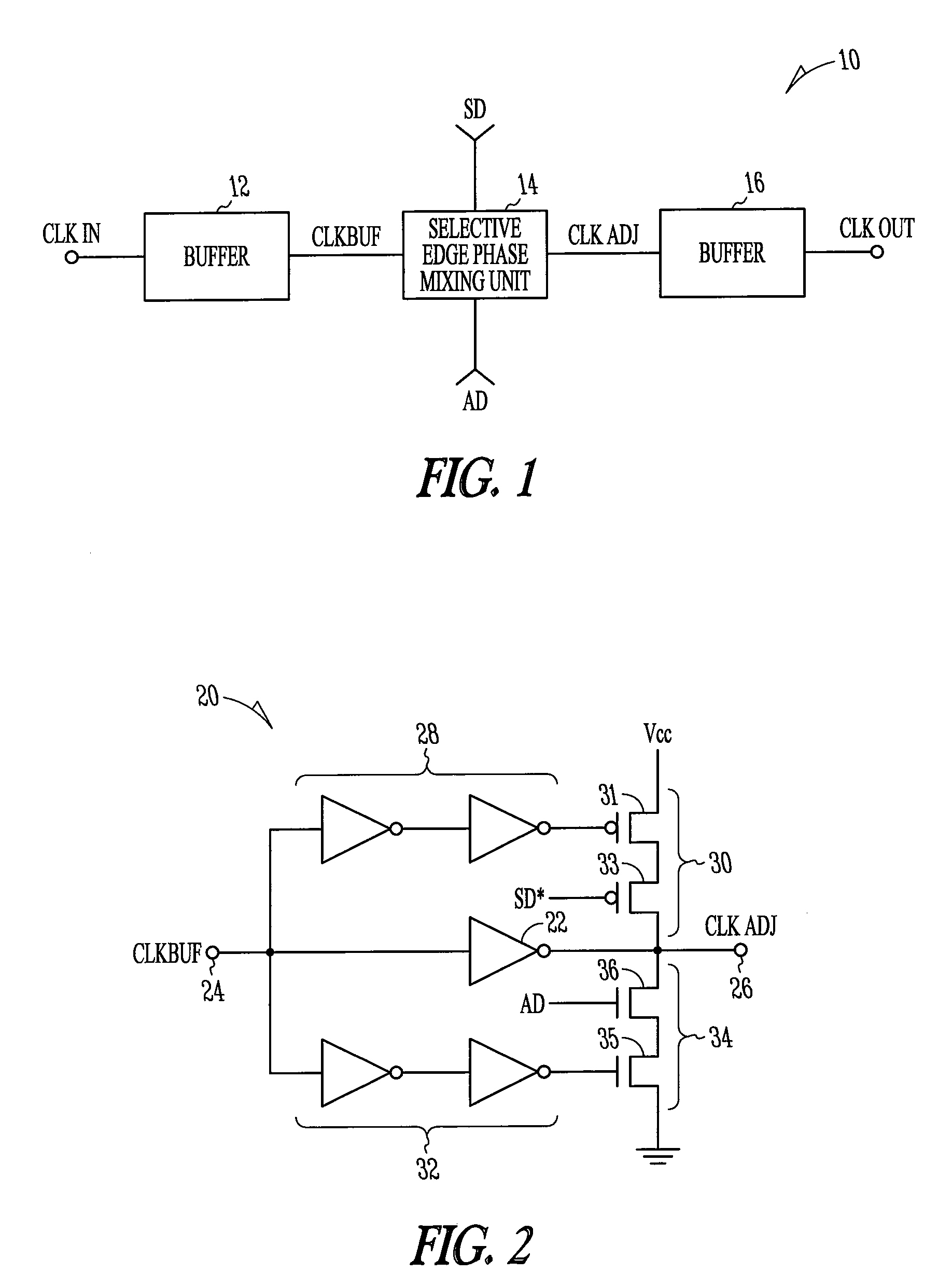
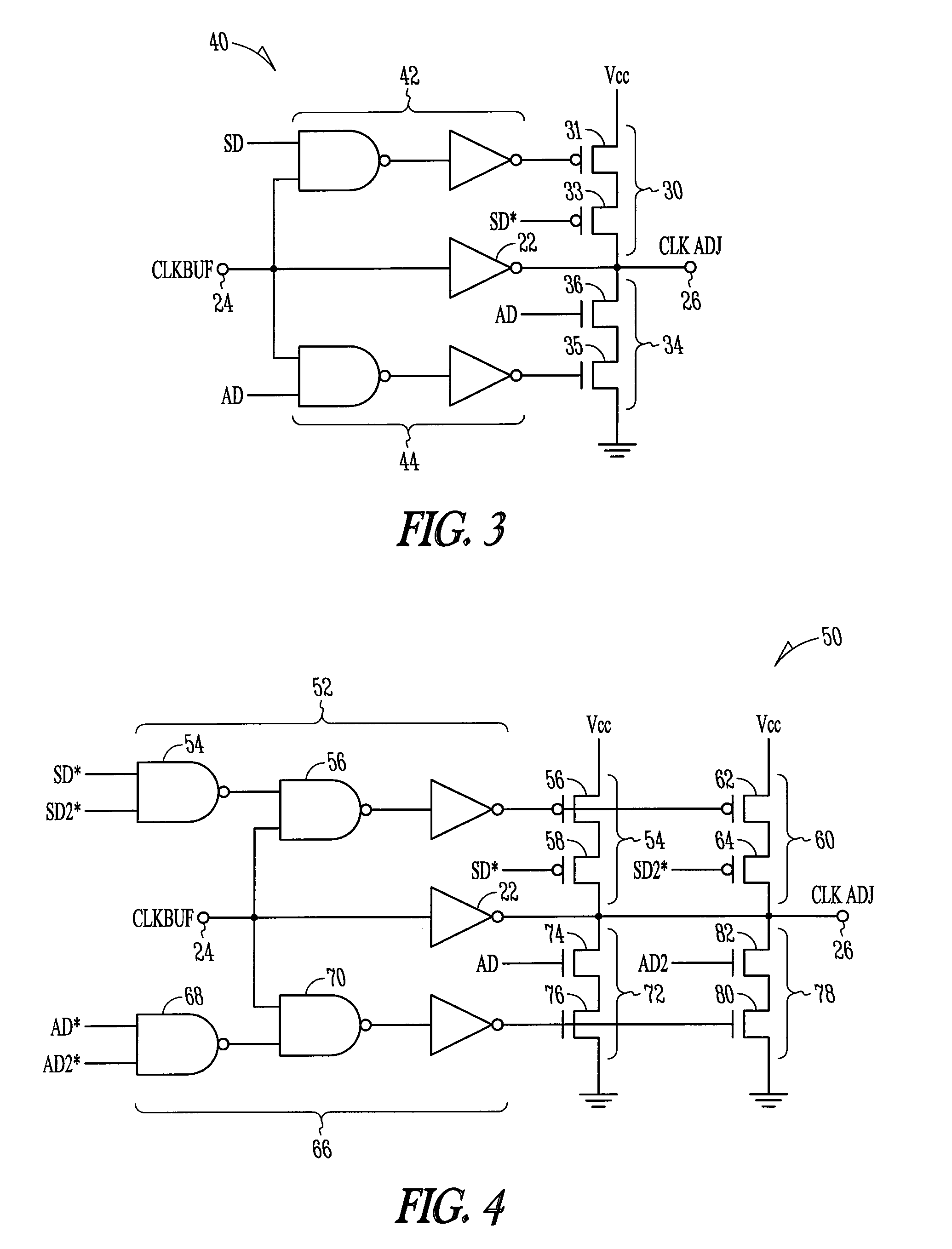
Selective edge phase mixing
Electronic apparatus, systems, and methods to implement selective edge phase mixing are disclosed. A selective edge phase mixing system includes a processor and memory device configured to perform operations in synchronization with transitions of an externally provided clock signal. A selective edge phase mixing unit for the memory device may include a first logic gate that receives the clock signal at an input port and receives first control signals, and pull-up circuits in communication with an output of the first logic gate and first control signals. A second logic gate receives the clock signal at the input port and receives second control signals. Pull-down circuits are coupled to the second logic gate and the second control signals, wherein the pull-up circuits and the pull-down circuits are coupled to the output port to provide a duty cycle corrected clock signal to the memory device. Additional apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Preparation method for high-tapping-density modified nickel-cobalt lithium manganate positive material
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nickel-cobalt lithium manganatepositive material. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out coprecipitation reaction, drying, carrying out uniform rheological phase mixing, and calcining at high temperature so as to obtain high-tapping-density ball-shaped nickel-cobalt lithium manganate. The positive material prepared by adopting the method has the advantages of uniform element distribution, uniform particle size distribution, high tapping density, small specific surface area and good electrochemical property; a preparation process is simple, and the industrial production is easily realized; and the production cost also can be reduced and the stability of the quality of a product can be improved.
Owner:RUYUAN YAO AUTONOMOUS COUNTY DONGYANGGUANG FORMED FOIL CO LTD
Concentric pipe layered steam injection system and method
The invention discloses a concentric pipe layered steam injection system and a method. A cyclone and a phase mixing device are arranged in a steam inlet passage of a steam distributor of the concentric pipe layered steam injection system, the outlet end of the steam inlet passage is respectively connected with a first steam outlet passage and a second steam outlet through a dryness distribution chamber, an inner steam injection flow passage and an outer steam injection flow passage of a well opening device are respectively connected with a steam distributor through an inner steam injection opening and an outer steam injection opening, a concentric type layered steam injection pipe post is connected under the well opening device and realizes the steam injection to a first underground oil layer through the concentric steam distributor arranged on an outer steam injection pipe post, and the steam is injected to a second underground oil layer through an inner steam injection pipe post. The steam dryness from a boiler can be regulated, and in addition, the double-flow-passage layered steam injection is realized, so the accuracy of the steam injection quantity is ensured, simultaneously, certain compensation is provided for the thermal stress deformation generated by the pipe posts through high temperature in the well in the steam injection process, the steam injection effect is improved, and simultaneously, the occurrence of the condition of the pipe post damage is avoided.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Bubble atomizing nozzle and adjusting method of bubble atomizing nozzle
The invention relates to a bubble atomizing nozzle and an adjusting method of the bubble atomizing nozzle. The bubble atomizing nozzle comprises a multi-channel air intake structure consisting of two or more layers of sealing rings, or an external part of an air intake structure of a swirl groove, and an external part having a diffusion conical spray hole, a jackscrew hole and an air-liquid inlet quick mounting joint, wherein the internal part is directly inserted in the external part to assemble the nozzle; the internal part and the external part are sealed by an O-shaped rubber ring and fixed by a jackscrew; and a space between the internal part and the external part is a mixing chamber. The flowing resistance of the internal part is lower, so that the pressure of the mixing chamber can be kept in a higher range, and the atomizing efficiency of the nozzle is higher; a bubble flow formed in the air-liquid two-phase mixing process in the mixing chamber is uniform and stable, so that the stable atomizing effect is realized under the low-air-liquid mass flow ratio (between 0.07-0.1); and the working pressure is low, and the liquid flow is low, so that the stable atomization can be kept under the liquid flow of 3.5-6.0 kg / h and the absolute air-liquid inlet pressure of 0.36-0.40 MPa. The bubble atomizing nozzle is applied to such fields as chemical engineering, motive power and heating and ventilation.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH +1
High-nickel positive electrode material with uniform coating layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109950498AAvoid excessive churnHigh specific capacityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPhase mixingLithium
The invention discloses a high-nickel positive electrode material with a uniform coating layer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) performing fixed-phase mixing on a high-nickel positive electrode material, a lithium source and a nano coating material to be uniform and screening to obtain a mixture, and (2) placing the mixture in step (1) in a saggarand performing high-temperature sintering, cooling, crushing and sieving in a preheated muffle furnace oxygen atmosphere to obtain a uniform coating layer. According to the invention, the surface ofthe high-nickel positive electrode material is coated with an oxide coating layer, then an additional lithium source is added, and the positive electrode material with good stability and high specificcapacity is obtained through high-temperature sintering. According to the invention, the fixed-phase mixing of the coating material, the high-nickel positive electrode material and the lithium sourceis carried out, the operation is simple, the cost is low, and the mass production is easy to realize.
Owner:NINGBO RONBAY LITHIUM BATTERY MATERIAL CO LTD
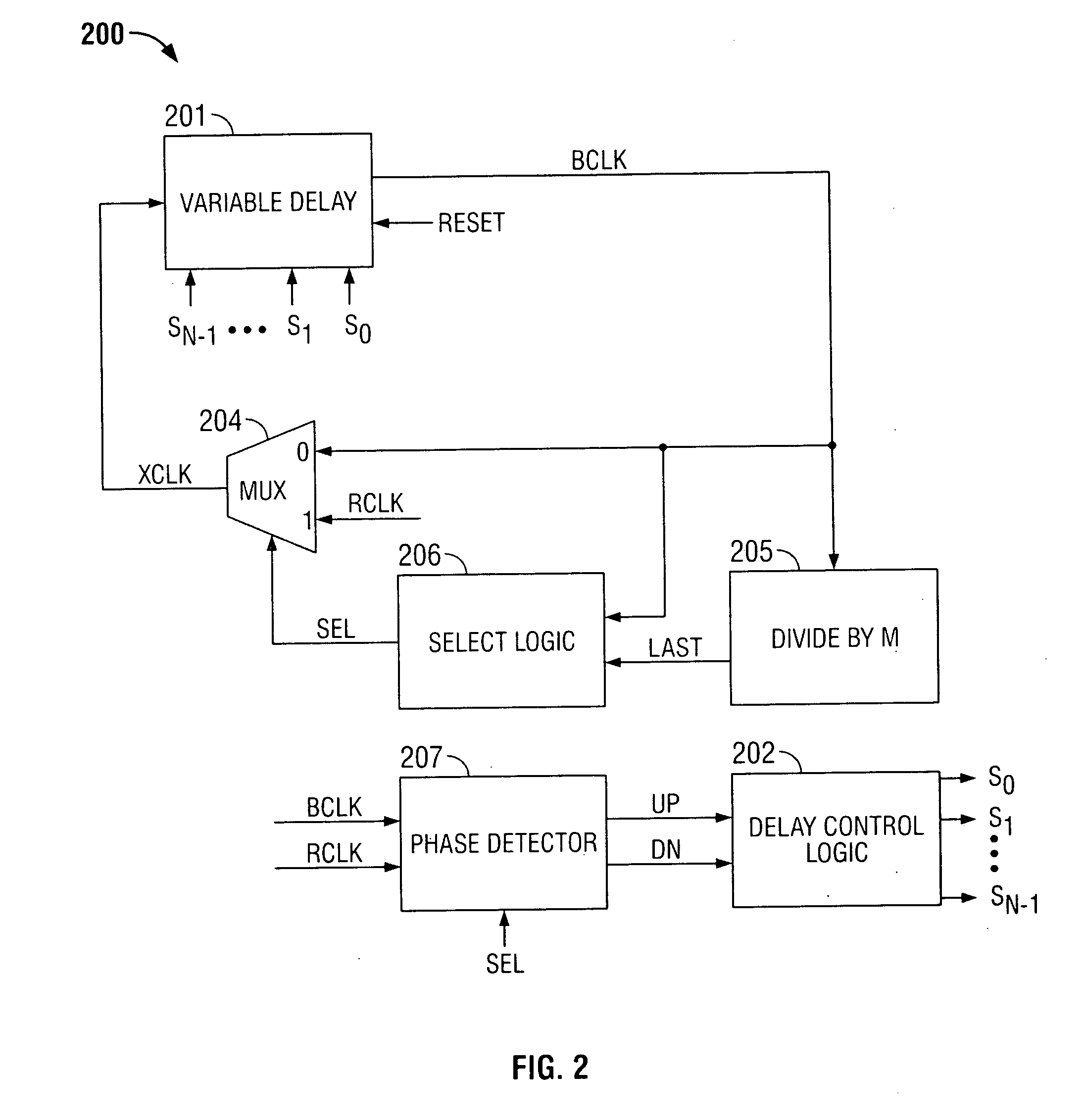
Delay locked loop and operating method thereof
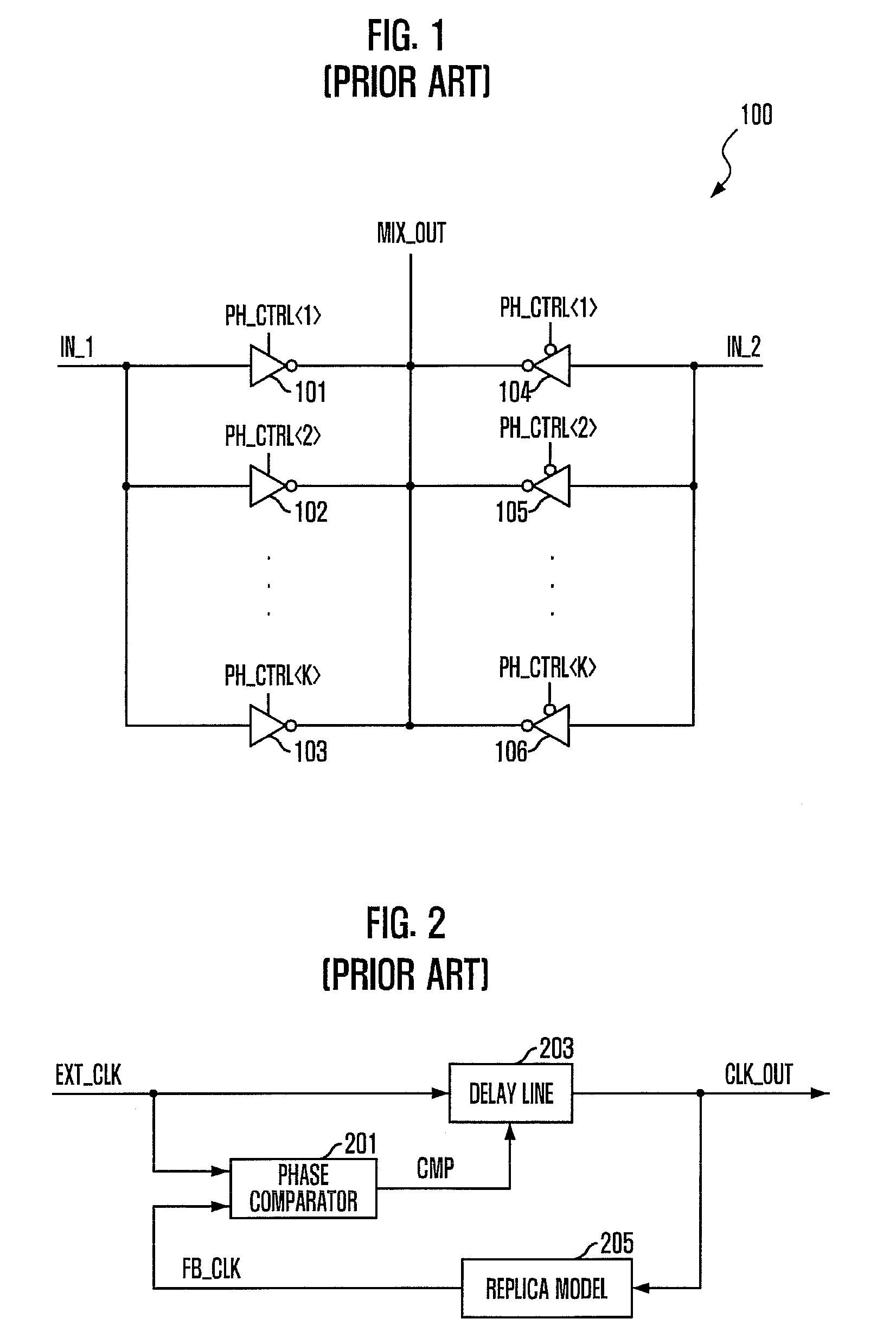
A delay locked loop (DLL) includes a delay-locking unit configured to generate first and second delay clocks corresponding to first and second clock edges of a reference clock for achieving a delay-locking; a phase detection unit configured to detect a phase difference between the first and second delay clocks to output a weight selection signal; a weight storage unit configured to store the weight selection signal obtained during a predetermined period from a point of time when the first and second delay clocks are delay locked; and a phase mixing unit configured to mix phases of the first and second delay clocks to output a DLL clock by applying a weight corresponding to the stored weight selection signal in the weight storage unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
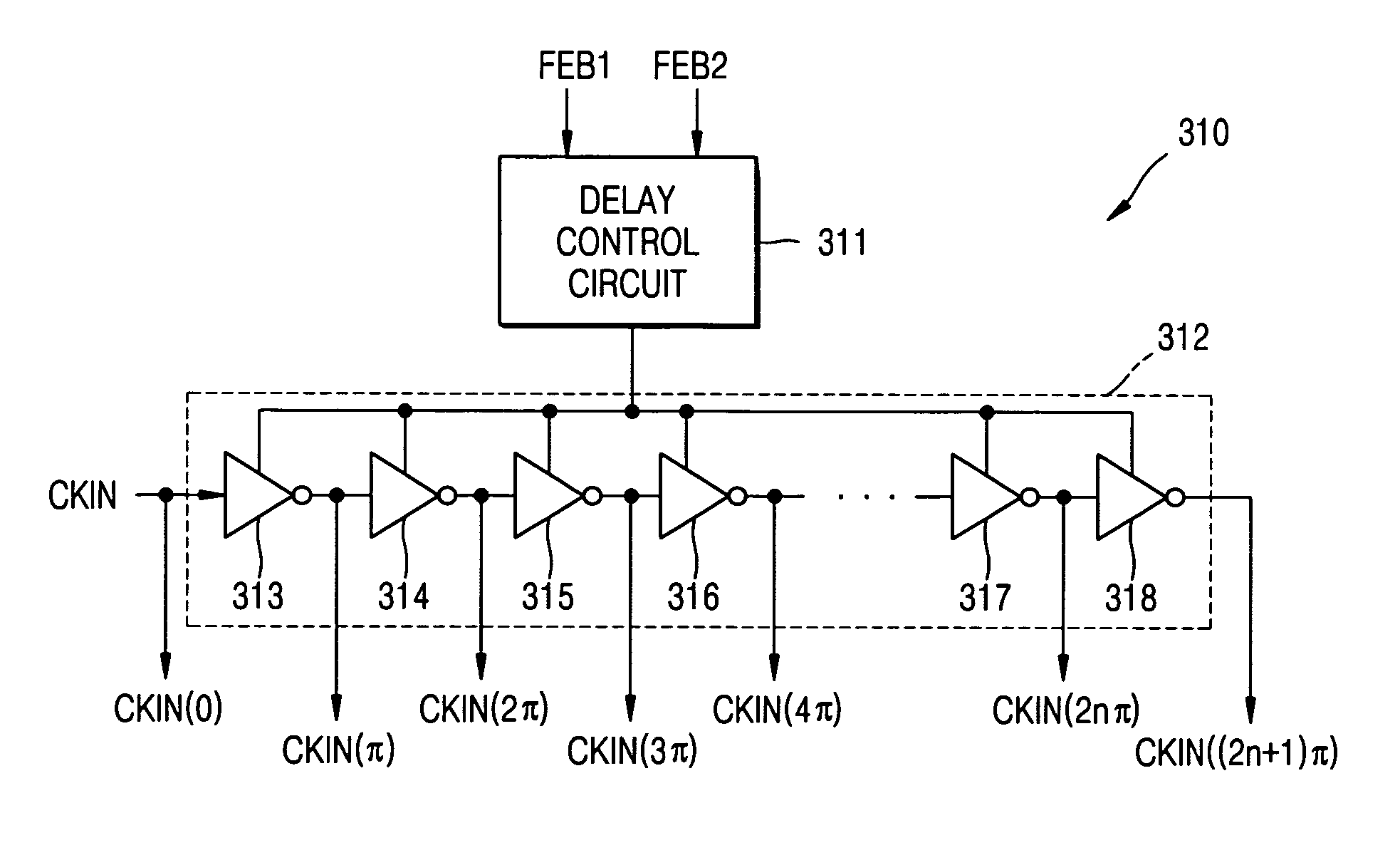
Digital frequency-multiplying DLLs
InactiveUS20050127964A1Reduce resolutionVary numberPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersPhase mixingDelayed time
Digital delay-locked loops (DLLs) and methods are provided for signal frequency multiplication. Analog delay elements of typical frequency-multiplying DLLs are replaced with digital and digitally-controlled elements including a variable delay line. The number of unit delay elements in the delay line can be selected to produce a desired output signal delay. Phase-mixing of multiple variable delay line outputs achieves finer delay-time adjustments.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Liquid-liquid heterogeneous mixing-reaction-separation integrated short-contact cyclone reactor
ActiveCN104971673AAchieve a high degree of dispersionFast mixingLiquid-liquid reaction processesPhase mixingThermodynamics
The invention relates to a liquid-liquid heterogeneous mixing-reaction-separation integrated short-contact cyclone reactor, belongs the field of liquid-liquid heterogeneous mixing equipment, and particularly relates to a short-contact cyclone reactor integrating mixed reaction and separation. The reactor is characterized in that a light phase liquid inlet pipe (3) is arranged at one side of an outer barrel (4), a material circulating structure (9) for communicating an inner cavity of an inner barrel (5) with an annular cavity is arranged on the wall of the inner barrel (5); a light phase overflow outlet pipe (1) is arranged on the inner upper part of the inner barrel (5) in a sleeving manner, an annular mixing cavity is formed between the light phase overflow outlet pipe (1) and the inner barrel (5), the upper part of the light phase overflow outlet pipe (1) extends out of the inner barrel (5), and a heavy phase underflow out pipe (7) is fixedly arranged on the lower part of the inner barrel (5) in a sleeving manner by a conical pipe (6). According to the invention, the integrated process of quick mixing, quick reaction and quick separation of heterogeneous liquid is realized, the equipment structure is compact, the handling capacity is large, continuous operation is realized, and the reactor has the advantages of being low in maintenance cost and strong in adaptability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Method for forming plural-layered coated film
InactiveUS20040228975A1Improve surface smoothnessPretreated surfacesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPhase mixingPolymer science
The present invention is to provide a method for forming a plural-layered coated film which is excellent in surface smoothness while phase mixing between an intermediate coating film and a base coating film is effectively prevented. The method comprises coating successively an aqueous intermediate coating paint, an aqueous base paint and a clear paint on an electrodeposition coated film in a wet-on-wet manner, and baking and curing them at the same time, wherein an intermediate coating film formed of the aqueous intermediate coating paint has a water absorption rate of coating film of 10% or less and a water dissolving rate of coating film of 5%, and the aqueous intermediate coating paint contains an acrylic resin emulsion, a urethane resin emulsion, and a curing agent.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT CO LTD
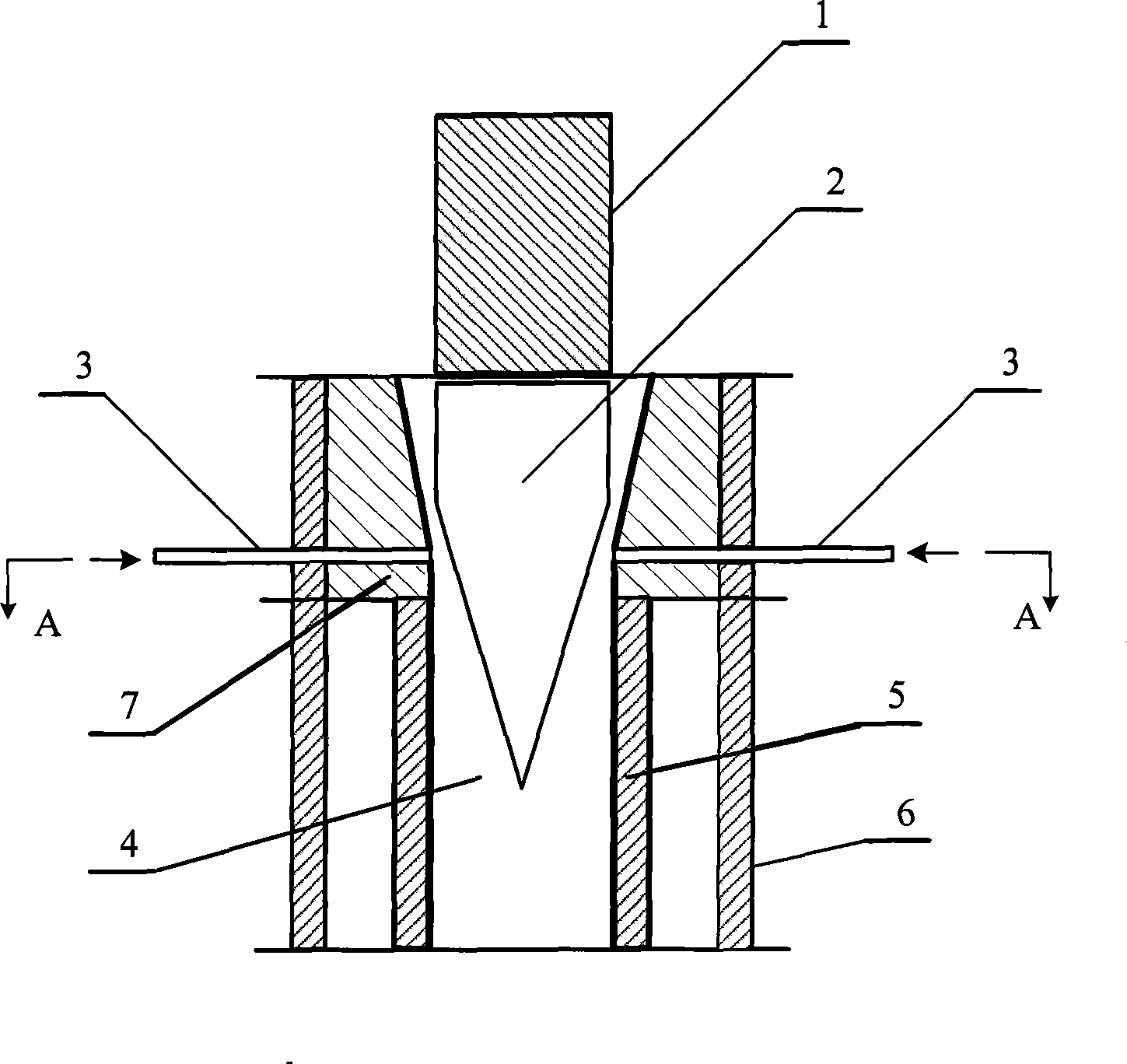
Nested type three-phase mixing nozzle of water, oil and gas and nozzle system with same
ActiveCN103522118AReduce precisionHigh surface finishLiquid spraying apparatusMaintainance and safety accessoriesSpray nozzleThree-phase
The invention provides a nested type three-phase mixing nozzle of water, oil and gas. The nested type three-phase mixing nozzle comprises a nozzle body, a nesting ring and a mixing chamber, and is characterized in that the nozzle body comprises a head portion, a middle portion and a bottom, the head portion of the nozzle body is a cone, and a spray hole is formed in the top end of the head portion of the nozzle body; the middle portion of the nozzle body is a cylinder, and at least two gas holes are evenly formed in the cylinder; the bottom of the nozzle body is of a thread structure; the nesting ring and the middle portion of the nozzle body are matched to form a clearance structure; an inner chamber with the top of a cone is arranged inside the nozzle body; the mixing chamber is arranged in the inner chamber and corresponds to the position of the middle portion of the nozzle body; a fluid channel communicated with the spray hole is further formed in the top of the inner chamber. The nozzle is arranged in a metal processing lubricating device, point lubricating is achieved, the problem that gas consumption is large in existing novel metal near-dry type processing lubricating is solved, meanwhile, a power source is saved, and the advantages of saving lubricating oil and being more environmentally friendly are achieved.
Owner:苏州金兆环保节能设备有限公司
Digital frequency-multiplying DLLs
InactiveUS20050285643A1Vary numberReduce resolutionPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersPhase mixingDelayed time
Digital delay-locked loops (DLLs) and methods are provided for signal frequency multiplication. Analog delay elements of typical frequency-multiplying DLLs are replaced with digital and digitally-controlled elements including a variable delay line. The number of unit delay elements in the delay line can be selected to produce a desired output signal delay. Phase-mixing of multiple variable delay line outputs achieves finer delay-time adjustments.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Preparation method of composite phase negative temperature coefficient thermal sensitive ceramic material
The invention relates to a preparation method of a composite phase negative temperature coefficient thermal sensitive ceramic material. In the method, based on La2O3, CaO, MnO2 and Ni2O3 are used as raw materials, perovskite phase LaCaMnO and spinel phase NiMnO powders are prepared by using an oxide solid phase method; drying, calcination, two-phase mixing and grinding, press molding and sintering are carried out on the powders; and then the ceramic material is prepared. The parameters of the composite phase negative temperature coefficient thermal sensitive ceramic material obtained by the method are as follows: B25 / 50 is (2600K-2962K)+ / -1.5%, and R 25 DEG C is (0.225omega-47omega)+ / -2%; and the composite phase negative temperature coefficient thermal sensitive ceramic material has the characteristics of high value B, low resistance, good consistency, high stability and repeatability, is suitable for inhibition of surge current and measurement, control and line compensation of temperature at low temperature.
Owner:中科传感(佛山)科技有限公司
Dual phase rubber composition and tire with nanocomposite-containing sidewall thereof
This invention relates to a dual phase rubber composition and pneumatic tire with a rubber sidewall thereof, namely a dual phased non-black colored rubber composition composed of a first pre-formed elastomer phase comprised of butyl-type rubber and EPDM rubber containing a dispersion therein of reinforcing filler comprised of a particulate amorphous precipitated silica and a second pre-formed elastomer phase comprised of a nanocomposite of natural rubber containing a dispersion therein of exfoliated clay platelets. Said exfoliated clay platelets may be substantially oriented within the tire sidewall in a parallel direction to each and may also be substantially oriented in an annular direction about the axis of the tire. The tire sidewall rubber composition may contain at least one additional elastomer which may be included in either or both of said elastomer phases. Such tire sidewall rubber composition may contain a non-black colorant pigment, such as for example a white colored titanium dioxide pigment. The dual phased tire sidewall rubber composition is prepared by a phase mixing process comprised of pre-blending said butyl-type rubber and EPDM rubber together with said precipitated silica reinforcing filler to form a pre-mix thereof, and thereafter mixing therewith said nanocomposite as a pre-formed blend of natural rubber and exfoliated clay platelets.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
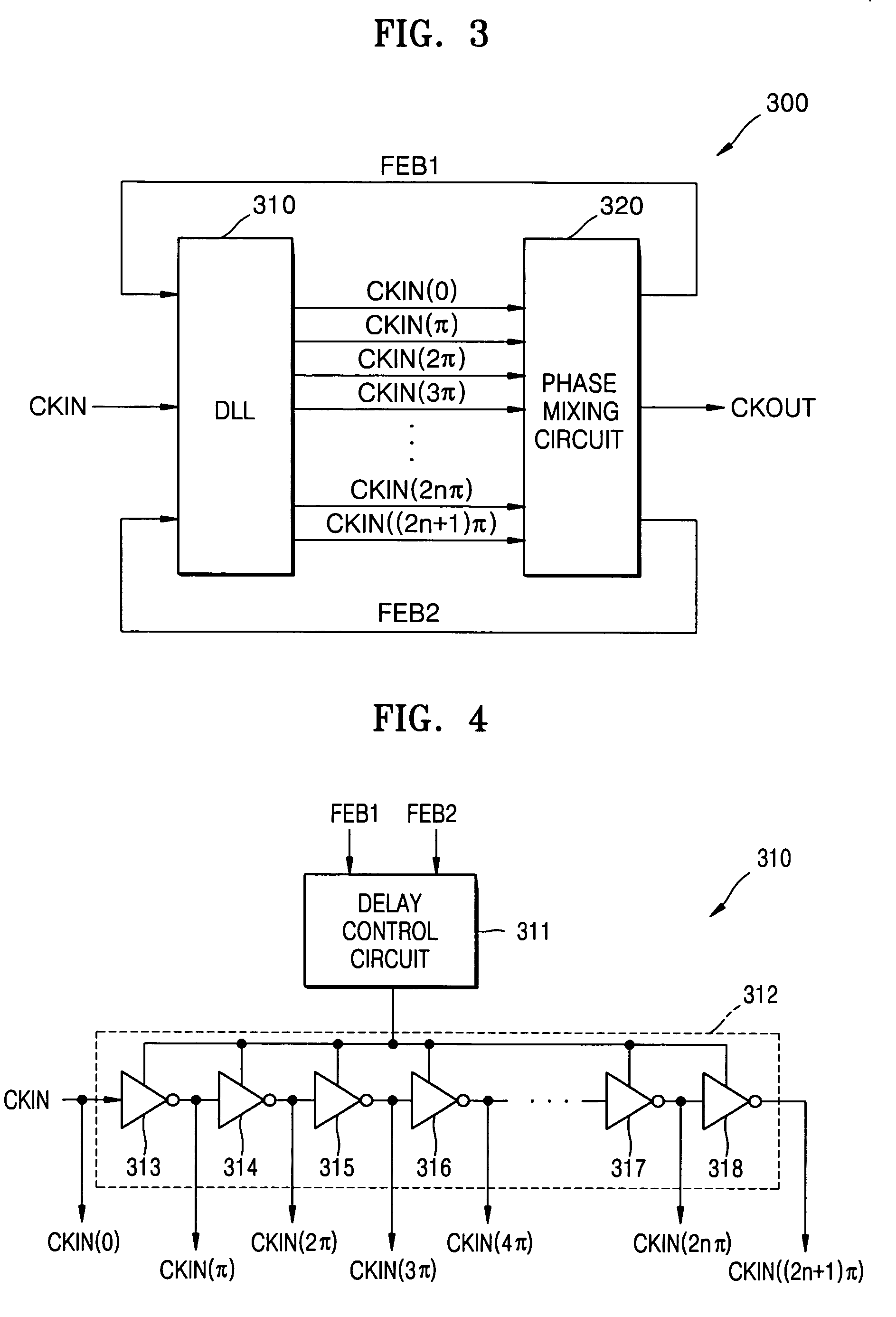
Clock signal generation circuits and methods using phase mixing of even and odd phased clock signals
InactiveUS20050189979A1Pulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase mixingDelay-locked loop
A clock signal generation circuit includes a Delay Locked Loop (DLL) that, responsive to an input clock signal and first and second feedback clock signals, generates a plurality of phased clock signals time-shifted with respect to one another. The clock signal generation circuit further includes a phase mixer that receives the plurality of phased clock signals, that phase mixes first and second groups of the plurality of phased clock signals to generate the respective first and second feedback signals, and that phase mixes the first and second feedback signals to generate an output clock signal. The phased plurality of clock signals may be separated by substantially uniform delays, the first group of clock signals may include signals delayed even numbers of delays with respect to the input clock signal, and the second group of clock signals may include signals delayed odd numbers of delays with respect to the input clock signal. Each of the substantially uniform delays may be approximately one-half of a period of the input clock signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cataplasm matrix and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101690818ALong storage timeHigh peel strengthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSheet deliveryPhase mixingAcetic acid
The invention discloses a cataplasm matrix and a preparation method thereof. The matrix comprises part of neutralized sodium polyacrylate, dihydroxyaluminium, glycerol, disodium edetate dehydrate, polyvinylpyrrolidone, crospolyvinylpyrrolidone, dihydroxybutanedioic acid, DMDMH, polysorbate 80 and purified water. The preparation method comprises three steps, namely oil phase preparation, aqueous phase preparation and oil-aqueous phase mixing. The matrix has excellent peel strength and sticky consistency, features long water preservation, is difficult to fall off when being stuck on the skin and is free of residue after being uncovered.
Owner:SUZHOU HENGXING MEDICAL MATERIAL
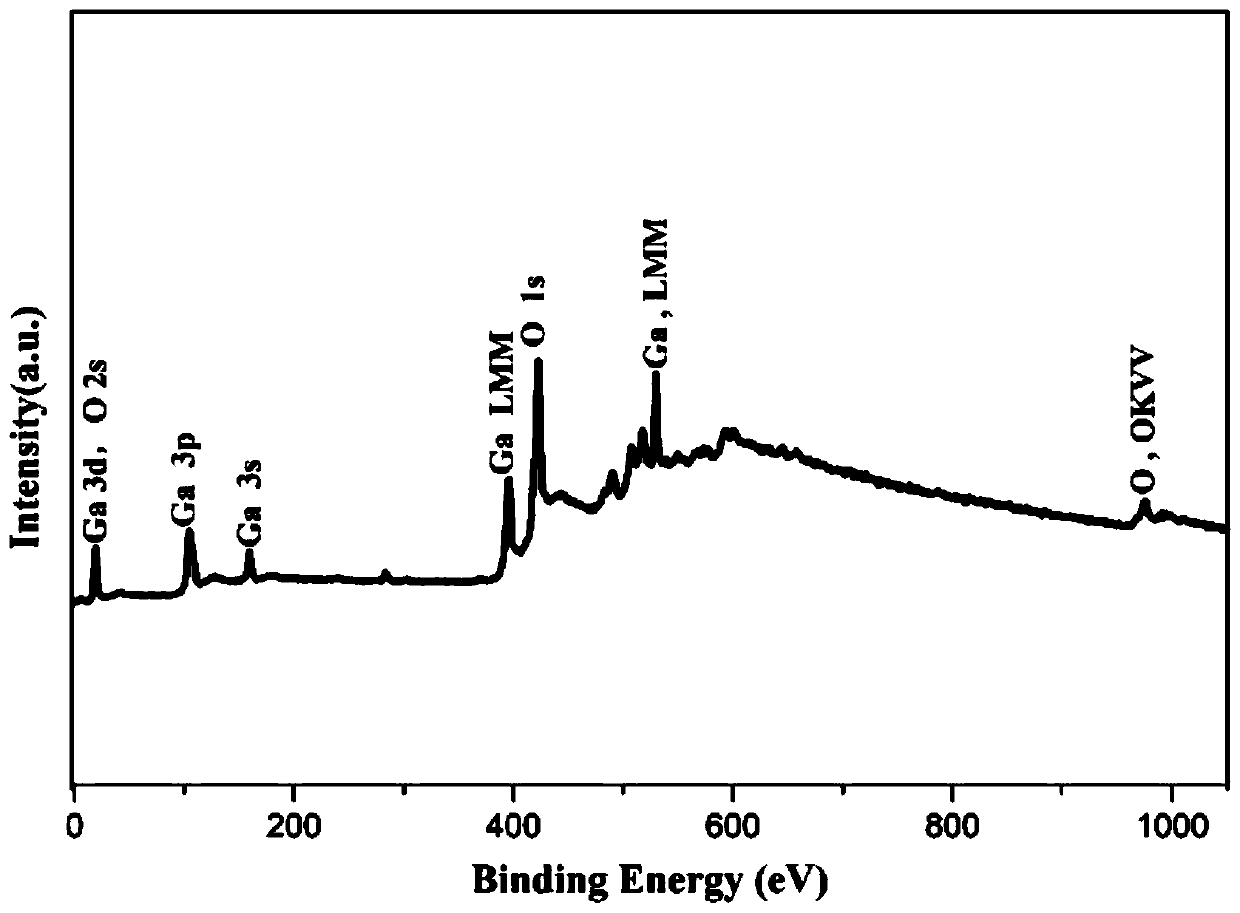
Method for preparing beta-Ga2O3 film
ActiveCN110195217AHigh activityImprove crystal qualityChemical vapor deposition coatingPhase mixingGas phase
The invention provides a method for preparing beta-Ga2O3 film and belongs to the technical field of micro-electronics. The problems of phase mixing and poor crystalline quality during preparation of the beta-Ga2O3 film are solved. The method comprises the steps that atomic layer deposition is reinforced through plasma, Ga2O3 film is grown on sapphire substrate, then high-temperature annealing recrystallization is conducted, metastable Ga2O3 is converted into stable Ga2O3, and finally the beta-Ga2O3 film is grown through metal organic chemical vapor deposition technology. The method for preparing the single-phase beta-Ga2O3 film can lay the foundation for preparing thick beta-Ga2O3 materials and devices.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Phase mixer and delay locked loop including the same
ActiveUS20100164571A1Increase jitterPreventing increase of jitterPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase mixingDelay-locked loop
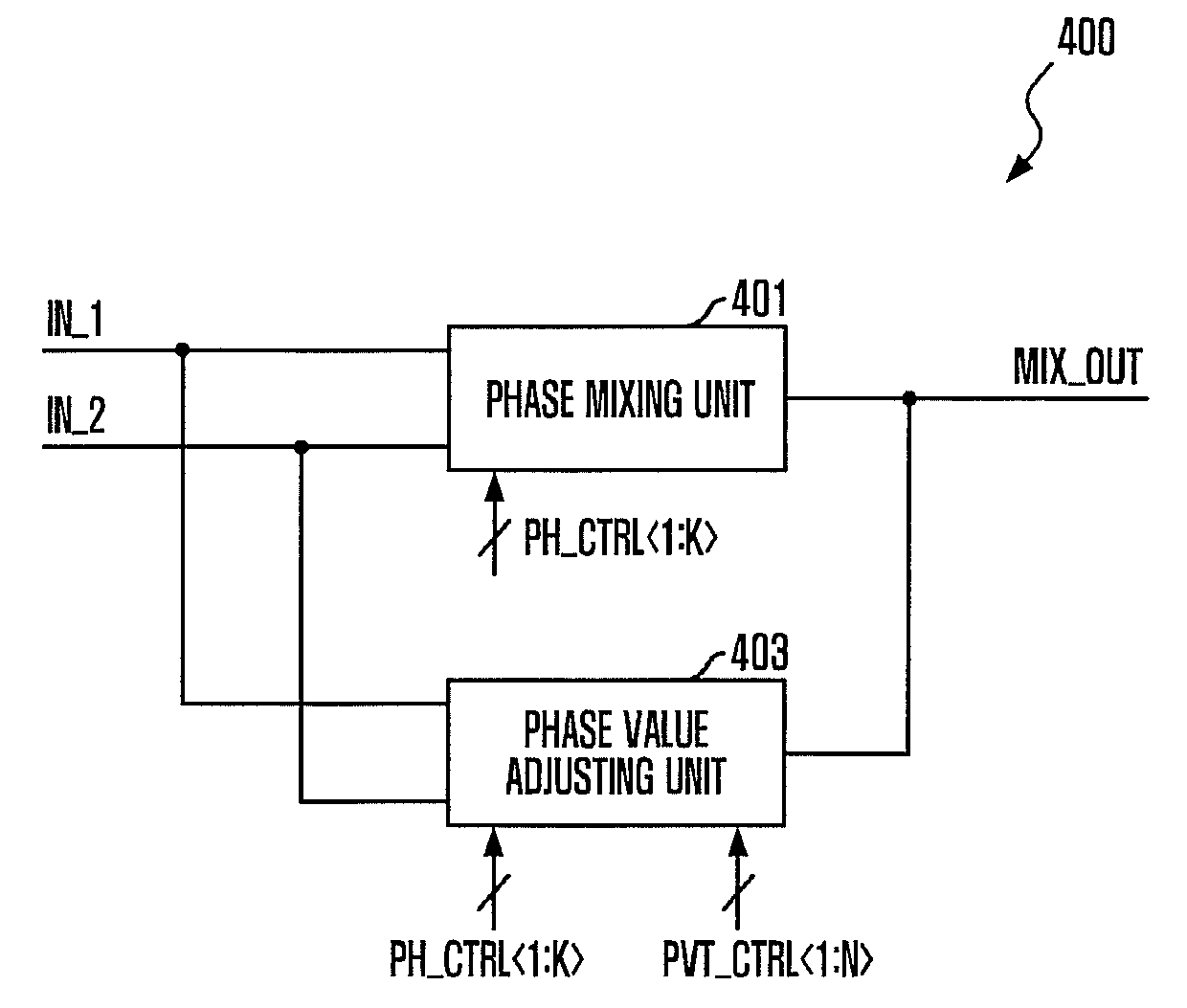
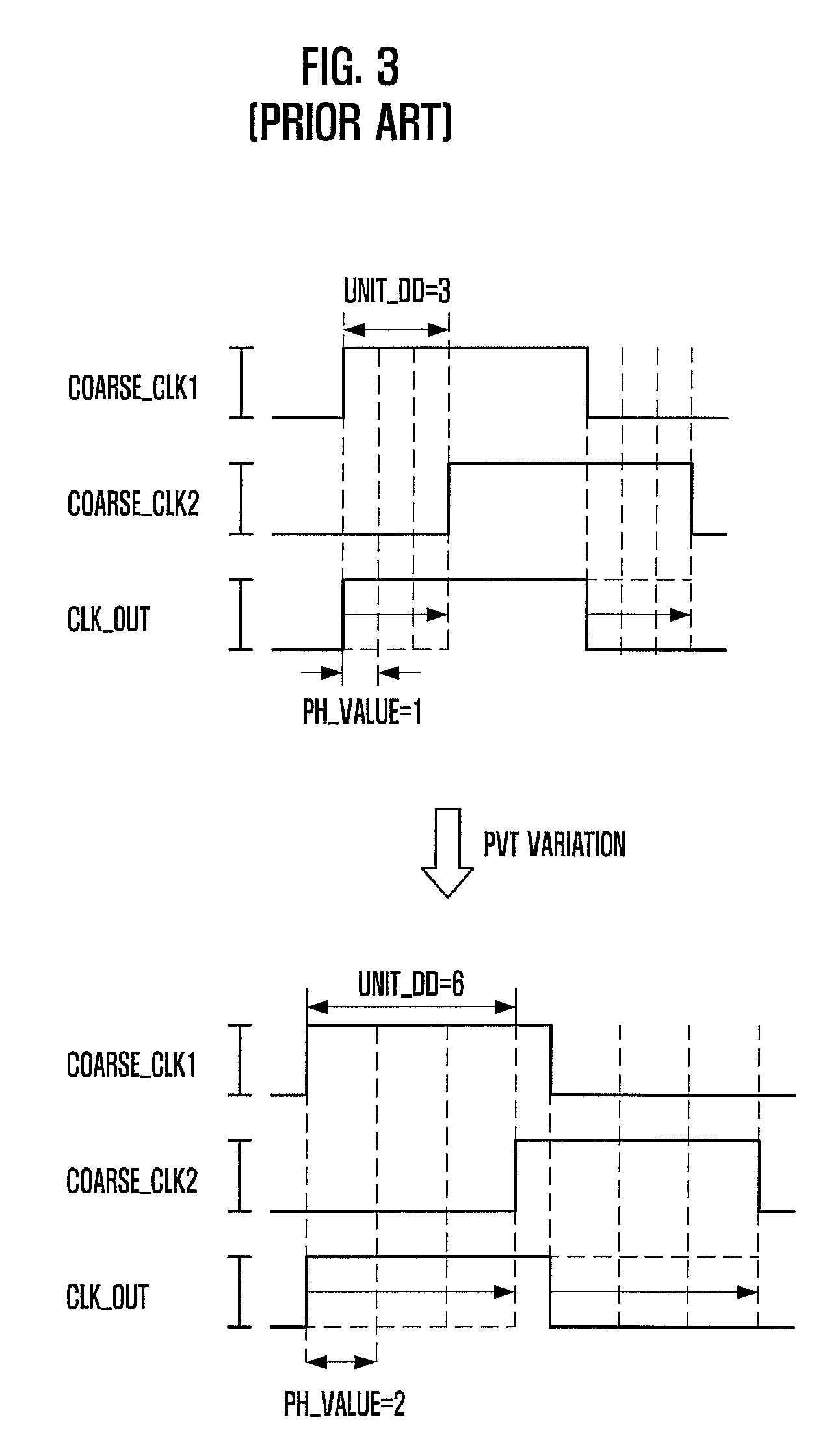
A phase mixer includes a phase mixing unit configured to mix a phase of a first input signal and a phase of a second input signal in response to a phase control signal and output a phase mixed signal whose phase is varied by one or more units of a unit phase value, and a phase value adjusting unit configured to control an operation of the phrase mixing unit so that the unit phase value is adjusted in response to a code signal coding at least one of a process, voltage, or temperature (PVT) variation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Coal powder entrance structure applied to reactor for producing acetylene with plasma coal cracking
The invention discloses a coal dust inlet structure applied to preparing an acetylene reactor by plasma coal pyrolysis, belonging to the technical field of industrial gas-solid two-phase mixing and reacting efficiently and rapidly. The outlet cross section of the coal dust spray head of the inlet structure is wide and flat; a long axis of the outlet cross section of the coal dust spray head forms a cut angle alpha with the cross section of the reactor channel; the coal dust spray heads are in central symmetrical distribution at the inner wall of the reactor channel; tangent of intersection of circumference surface of the cross section of the reactor channel inner wall where the coal dust spray heads are arranged and central line of the coal dust spray head forms an angle beta with the central line of the coal dust spray head; the central line of the coal dust spray head forms a cut angle gamma with the cross section of the reactor channel. The invention provides a coal dust inlet structure applied to preparing the acetylene reactor by plasma coal pyrolysis; by the structure, the coal dust sprayed by the coal dust spray heads can be well mixed with high temperature plasma jet, thereby effectively improving yield of acetylene and lessening coking of the reactor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for forming plural-layered coated film
The present invention is to provide a method for forming a plural-layered coated film which is excellent in surface smoothness while phase mixing between an intermediate coating film and a base coating film is effectively prevented. The method comprises coating successively an aqueous intermediate coating paint, an aqueous base paint and a clear paint on an electrodeposition coated film in a wet-on-wet manner, and baking and curing them at the same time, wherein an intermediate coating film formed of the aqueous intermediate coating paint has a water absorption rate of coating film of 10% or less and a water dissolving rate of coating film of 5%, and the aqueous intermediate coating paint contains an acrylic resin emulsion, a urethane resin emulsion, and a curing agent.
Owner:นิปปอน เพนท์ ออโตโมทีฟ โคทติ้งส์ โค แอลทีดี
Clock signal generation circuits and methods using phase mixing of even and odd phased clock signals
A clock signal generation circuit includes a Delay Locked Loop (DLL) that, responsive to an input clock signal and first and second feedback clock signals, generates a plurality of phased clock signals time-shifted with respect to one another. The clock signal generation circuit further includes a phase mixer that receives the plurality of phased clock signals, that phase mixes first and second groups of the plurality of phased clock signals to generate the respective first and second feedback signals, and that phase mixes the first and second feedback signals to generate an output clock signal. The phased plurality of clock signals may be separated by substantially uniform delays, the first group of clock signals may include signals delayed even numbers of delays with respect to the input clock signal, and the second group of clock signals may include signals delayed odd numbers of delays with respect to the input clock signal. Each of the substantially uniform delays may be approximately one-half of a period of the input clock signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
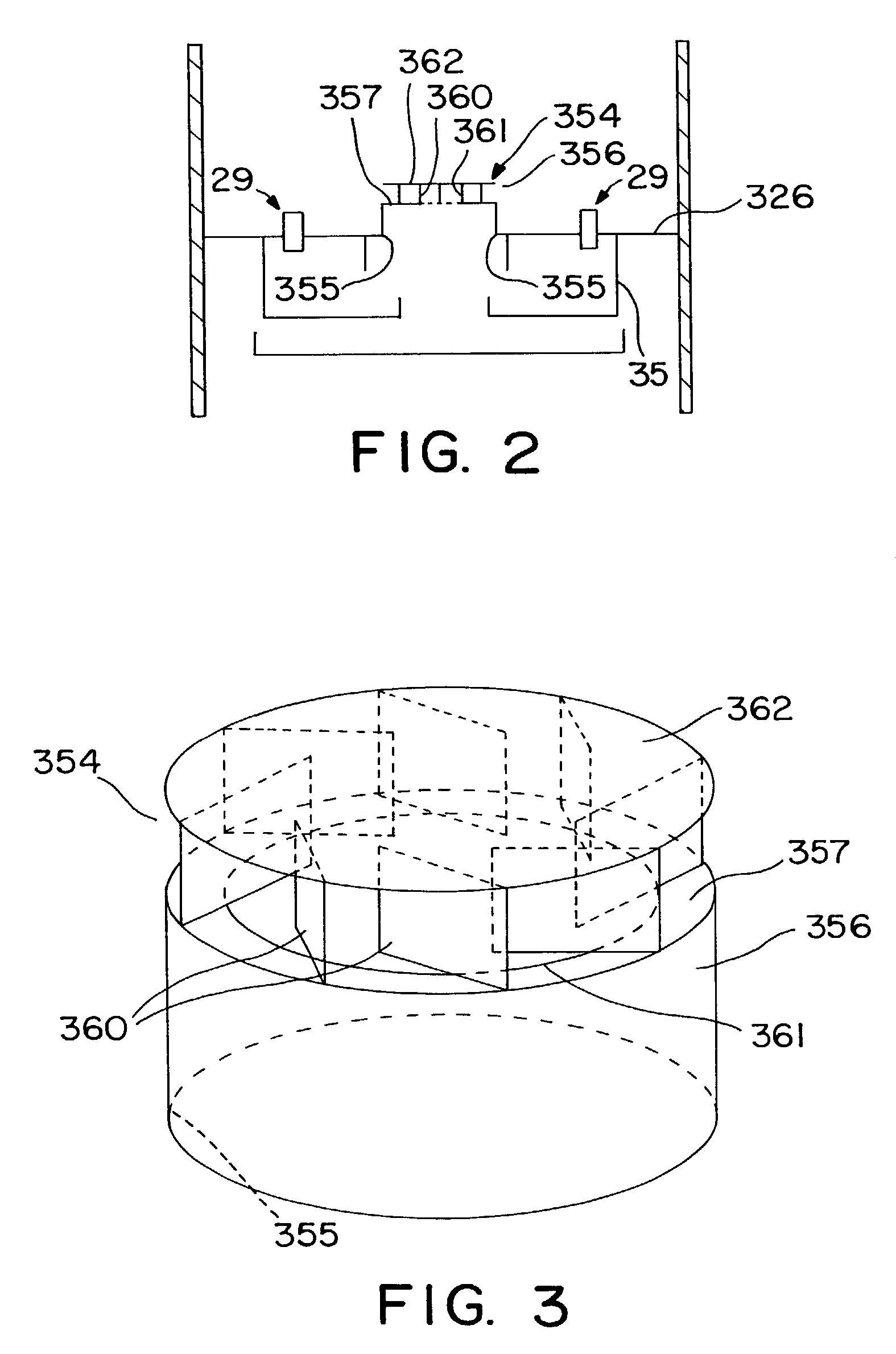
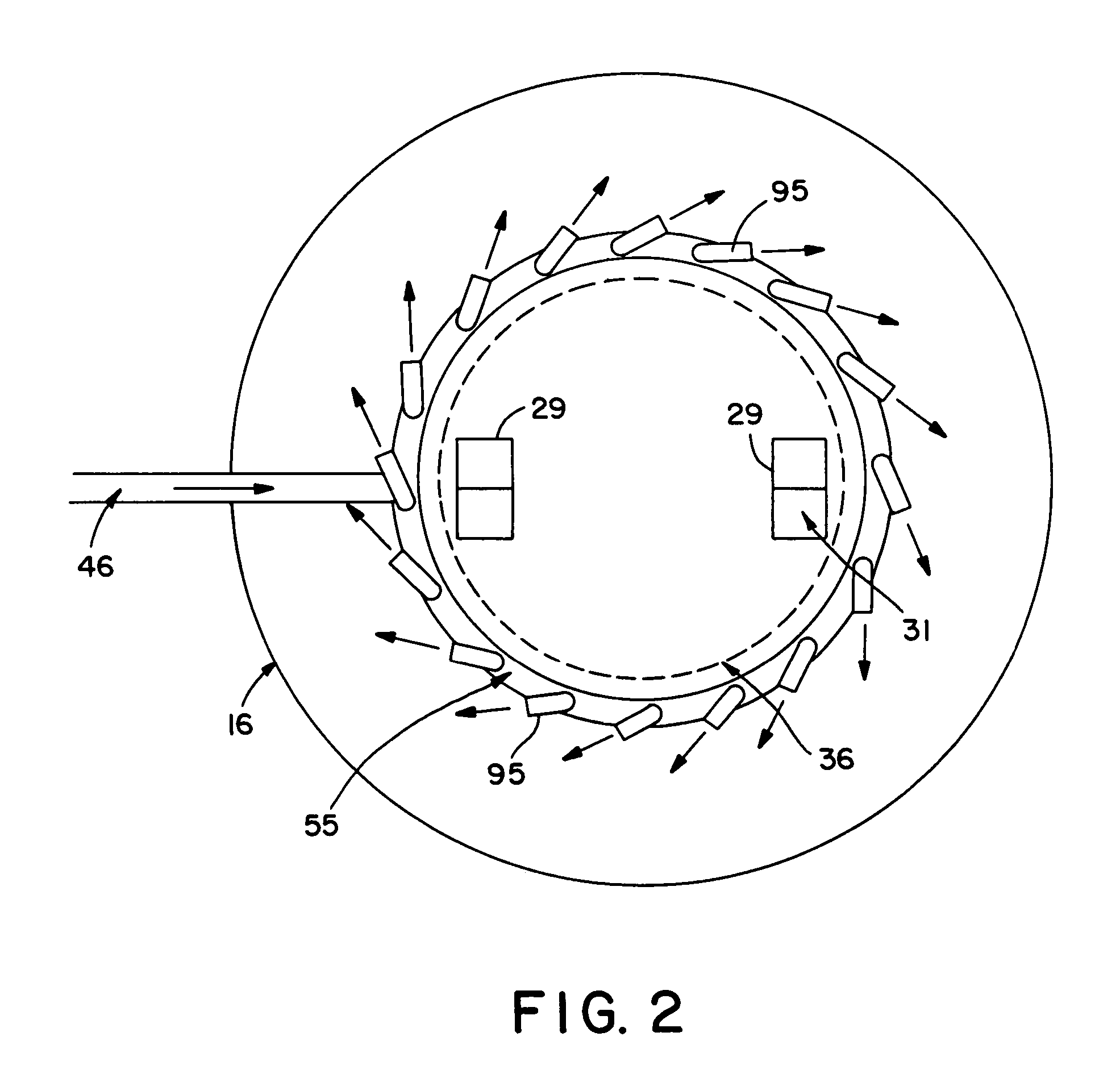
Multiphase mixing device with improved quench injection for inducing rotational flow
InactiveUS7074372B2Easy injectionImprove mixing efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsFlow mixersPhase mixingHybrid system
A mixing system is disclosed which provides improved multiphase mixing through the use of a novel quench injection means. The mixing system comprises a horizontal collection tray, a mixing chamber positioned below the collection tray, and at least one passageway extending through the collection tray into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber and the collection tray define a two-phase mixing volume. The passageway conducts fluid from above the collection tray into the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber preferably includes at least one outlet opening for the downward passage of fluid. In particular, mixing of quench fluid is significantly improved when quench is introduced into a region above the collection tray and where a preferred direction of quench injection is selected to cause a rotational current on the collection tray.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Vibrating screen plate tower for continuous production of liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase extraction
InactiveCN102233200ASolve flow problemsSimple extraction processLiquid solutions solvent extractionPhase mixingThree-phase
The invention relates to a vibrating screen plate tower for continuous production of liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase extraction. A cylindrical tower body comprises a light-phase clarification outer tank connected to the upper part of the cylindrical tower body and a tower bottom clarification tank connected to the lower part; a spindle leads to the lower part of the cylindrical tower body from the exterior of the light-phase clarification outer tank; the upper part and the lower part of the cylindrical tower body are provided with a conical liquid baffle and a light-phase distributor which are arranged on the spindle respectively; a middle screen plate is arranged in the middle of the spindle; a heavy-phase guide cylinder is arranged inside the light-phase clarification outer tank; a heavy-phase mixing chamber is arranged inside the heavy-phase guide cylinder; a bottom liquid outlet of the heavy-phase guide cylinder is positioned at the conical liquid baffle; a polymer phase distributor and an aqueous phase distributor are arranged on a polymer phase conduit and an aqueous phase conduit in the heavy-phase mixing chamber; a tower top screen plate is fixedly arranged on the spindle in the heavy-phase mixing chamber; a sealing ring is arranged between the spindle and the heavy-phase mixing chamber; and two layers of deflection baffles which are arranged in a staggered mode are fixedly arranged on the spindle in the tower bottom clarification tank. The vibrating screen plate tower has high mass transfer efficiency and high controllability.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Energy-efficient dispersion-mixing method for large-phase-ratio system and application of method
ActiveCN109569346AFully dispersedEnsure stability and continuityTransportation and packagingChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPhase mixingMicro nano
The invention provides an energy-efficient dispersion-mixing method for a large-phase-ratio system and an application of the method. The method includes forming continuous phase fluid into film-shapedflowing through a falling film mixing unit; forming dispersed phase fluid into micro-nano scale droplets through a super-gravity dispersing unit; and mixing the droplets with the continuous phase fluid flowing in a film shape. By arrangement of the super-gravity dispersing unit, the dispersed phase fluid is firstly dispersed into the micro-nano scale liquid droplets, the falling film mixing unitenables the continuous phase fluid to form a flowing liquid film, and then the droplets and the liquid film are impacted through the super-gravity dispersing unit; compared with the traditional mixingmethod, the dispersed phase fluid is uniformly mixed in a small liquid droplet mode and stirred at the same time; the dispersed phase fluid is fully dispersed before mixing, and then is mixed with the continuous phase, so that the disturbance of the two-phase mixing interface is increased, the mixing efficiency is improved, and the dispersion degree is high; and in addition, the falling film unitfurther crushes the liquid droplets dispersed and impacted on the liquid film, so that the energy utilization rate is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Production device and production method for synthesizing acetic acid by low-pressure carbonylation of methanol
ActiveCN109134233AEnsure continuityGuarantee stabilityCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionChemical/physical processesPhase mixingAcetic acid
The invention discloses a production device and a production method for synthesizing acetic acid by low-pressure carbonylation of methanol. A fluid stirring device arranged on the production device provided by the invention changes the situation that a mechanical stirring shaft seal and a transmission device are easy to damage in an operation process, eliminates dynamic seal points, and greatly improves the safe and stable operation of a system. At the same time, by matching with a CO distributor, the CO gas distribution in a reactor is more uniform, the gas-liquid two-phase mixing effect is improved, the reaction rate is increased, the reaction state of the system is optimized, and the production capacity of the device is increased from 300,000 tons per year to 600,000 tons per year.
Owner:YANKUANG GRP CO LTD
Industrial production method for simultaneously extracting tea seed oil and tea saponin
ActiveCN104479853AGood miscibilityEasy extractionSugar derivativesFatty-oils/fats refiningCamellia oleiferaSolvent
The invention discloses an industrial production method for simultaneously extracting tea seed oil and tea saponin. The industrial production method comprises the following steps: softening camellia seeds at a low temperature and separating shells and kernels to obtain camellia seed kernels; puffing the camellia seed kernels at a low temperature; extracting with an ether and alcohol homogeneous-phase mixing solvent to obtain homogeneous-phase mixing solvent extract; recycling the solvent from the homogeneous-phase mixing solvent extract; washing with water and separating by a centrifugal machine to obtain an alcohol phase and an ether phase; after recycling the solvent from the alcohol phase, separating the solvent by a foam separation tower and drying in vacuum to obtain the finished-product tea saponin; and after recycling the solvent from the ether phase, refining to obtain the tea seed oil, and adding alkali liquid to remove soap, de-coloring, deodorizing and winterizing in sequence to obtain the finished-product tea seed oil. According to the industrial production method, low-molecular-weight ether and low-molecular-weight alcohol can be mutually dissolved so that a homogeneous-phase mutually-soluble system is formed, and the tea seed oil and the tea saponin are effectively extracted; and meanwhile, tea seed meal with higher protein content also can be obtained, an application range of the camellia seeds is further expanded, the investment of extraction equipment is effectively reduced and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:CHENGUANG BIOTECH GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com