Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1027 results about "Fractionating column" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
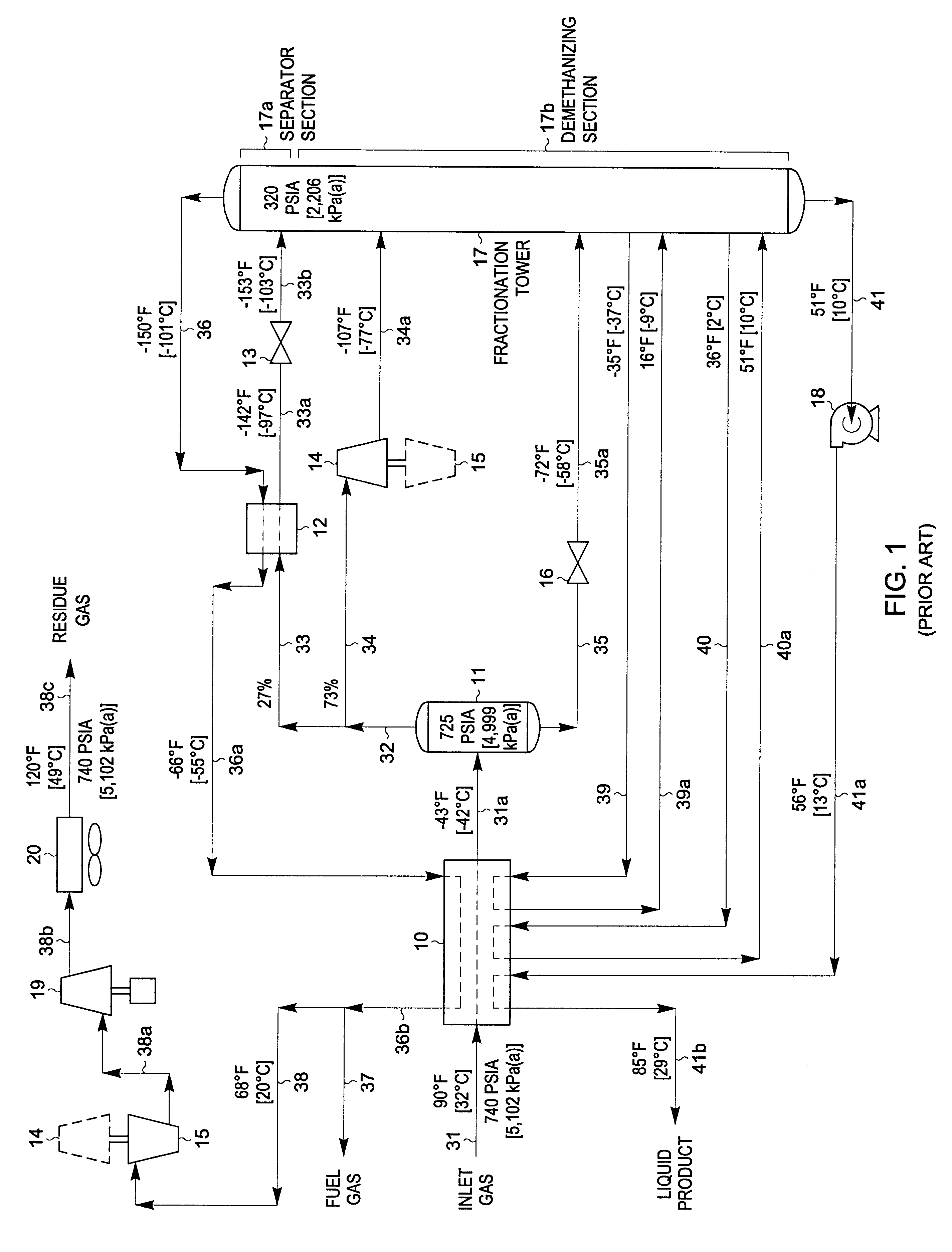
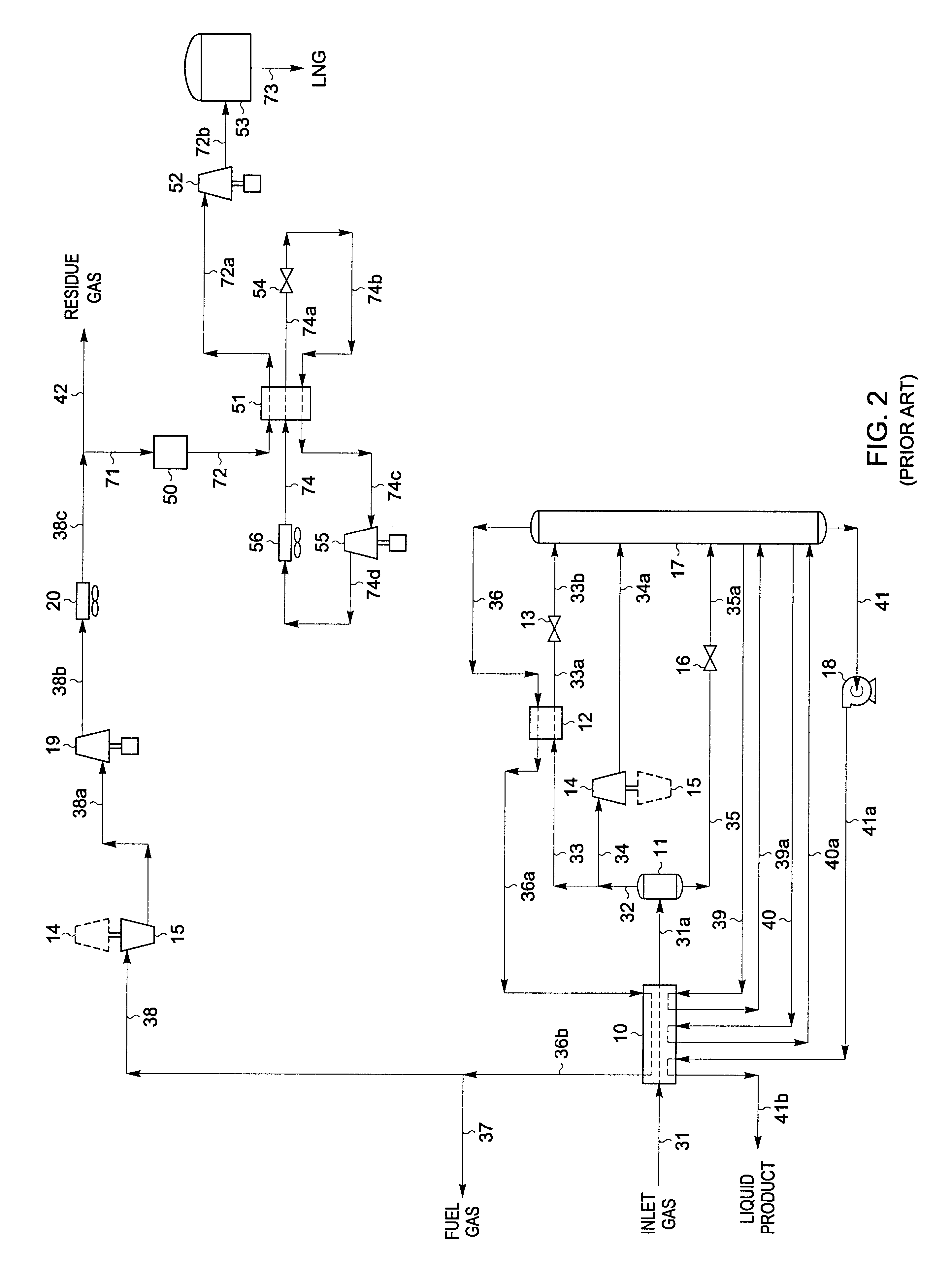
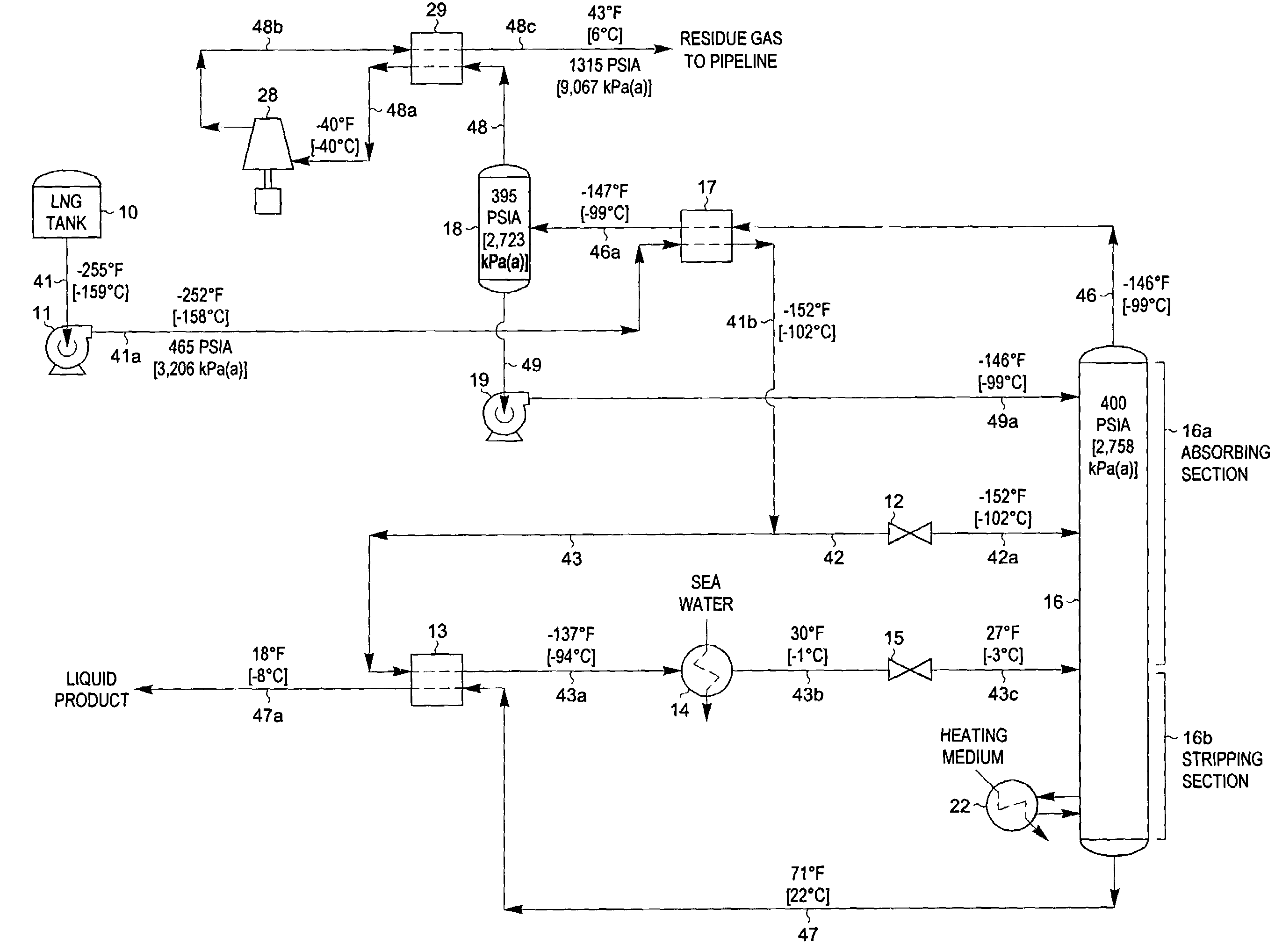
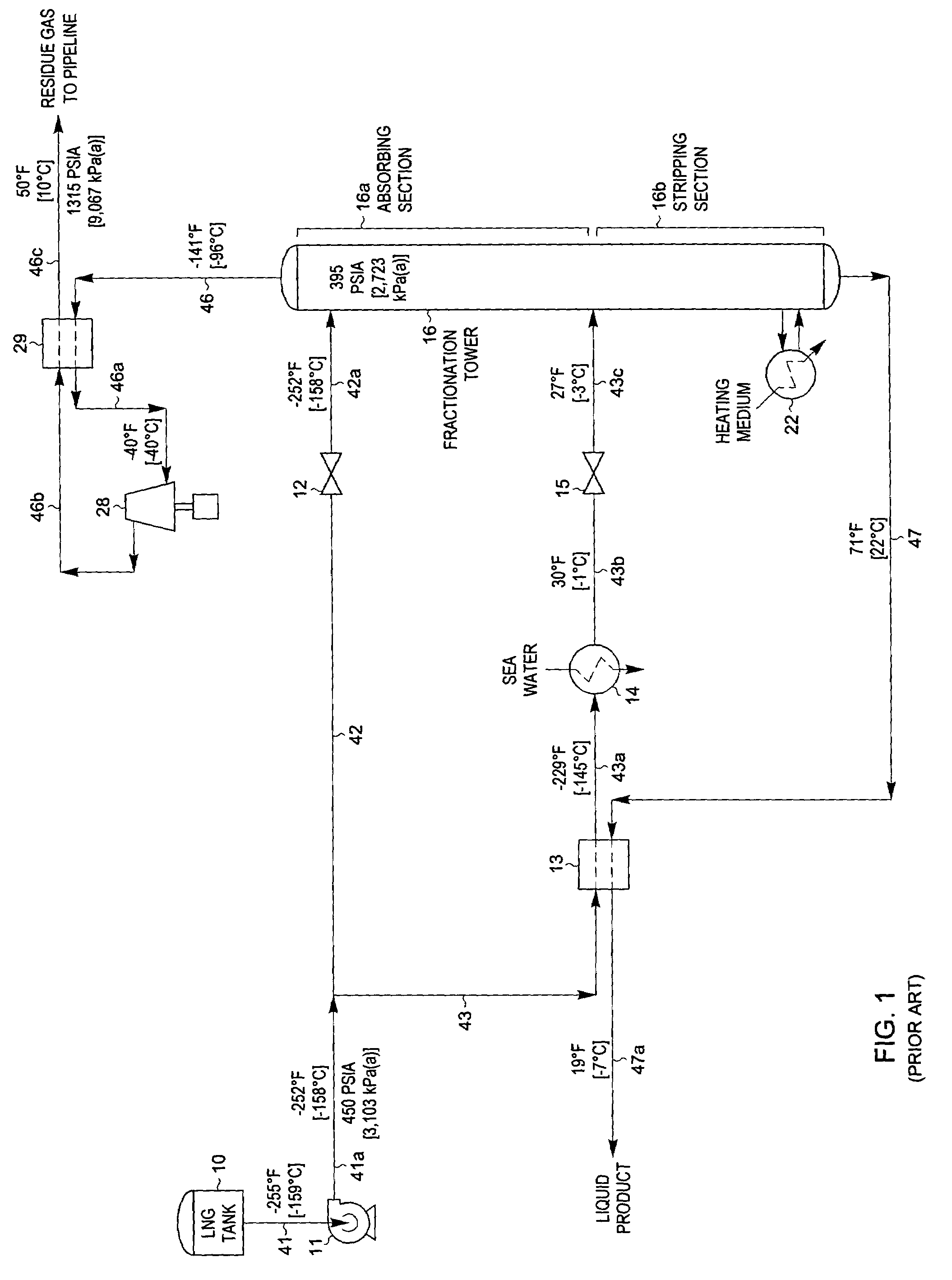
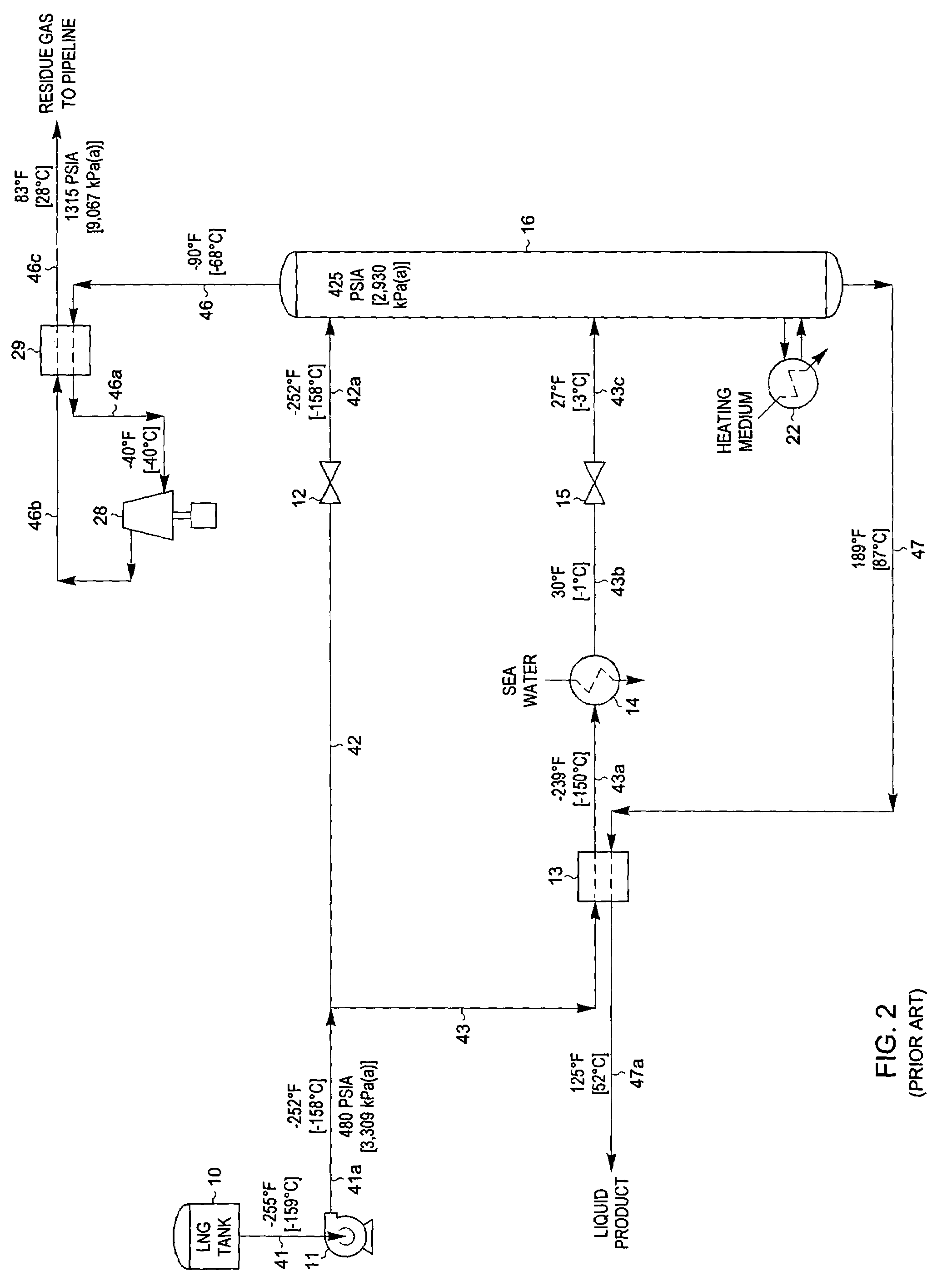
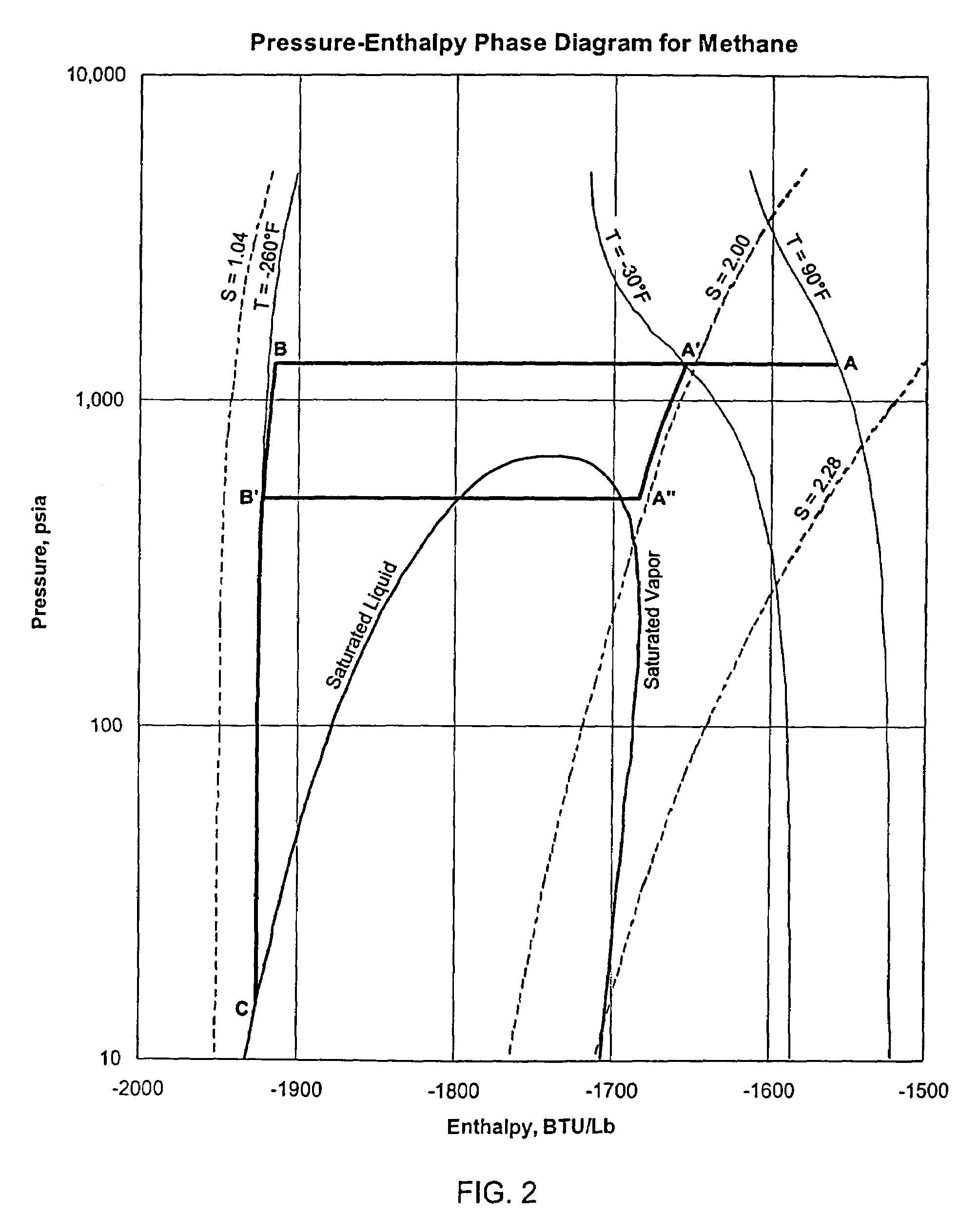
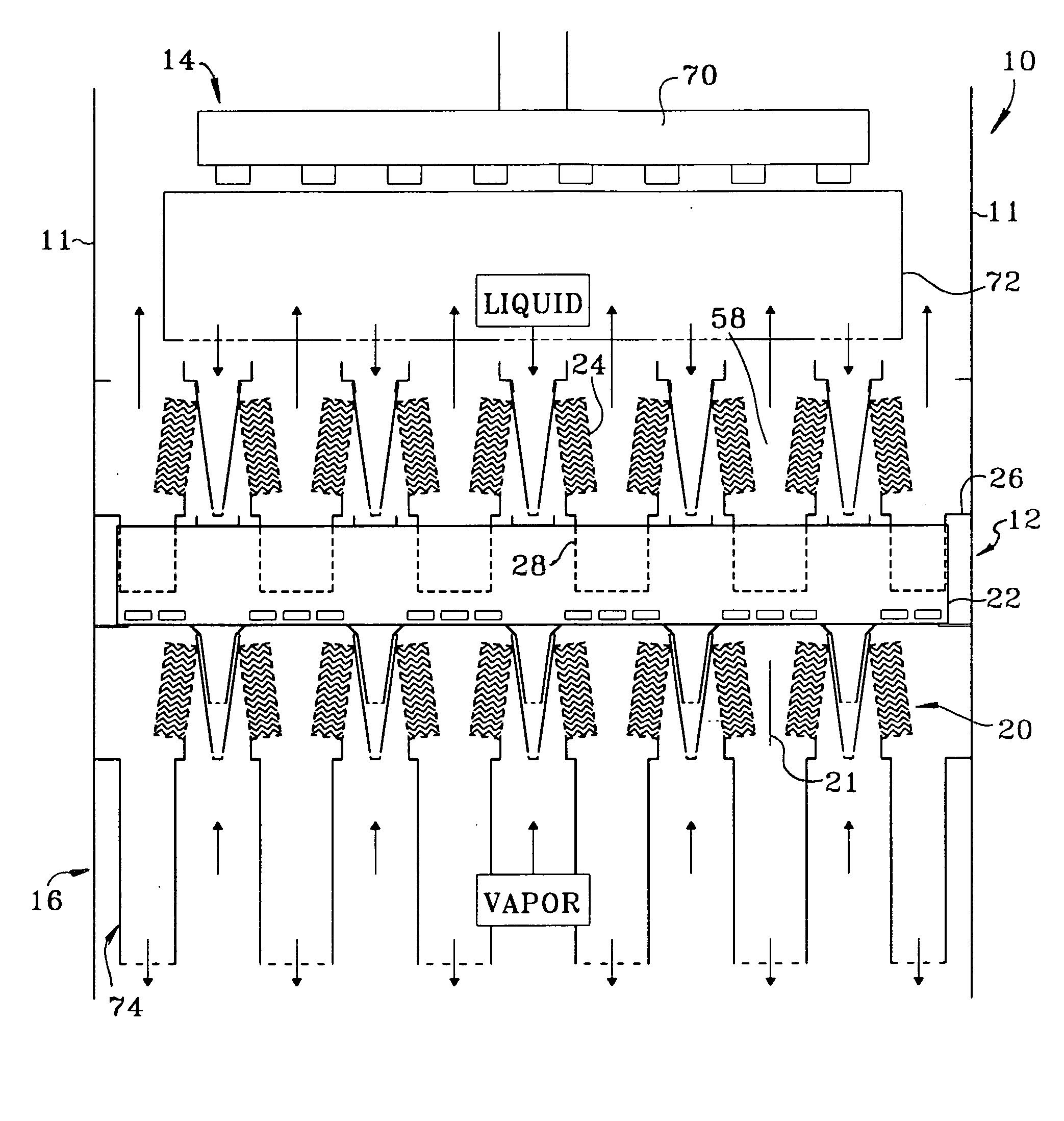
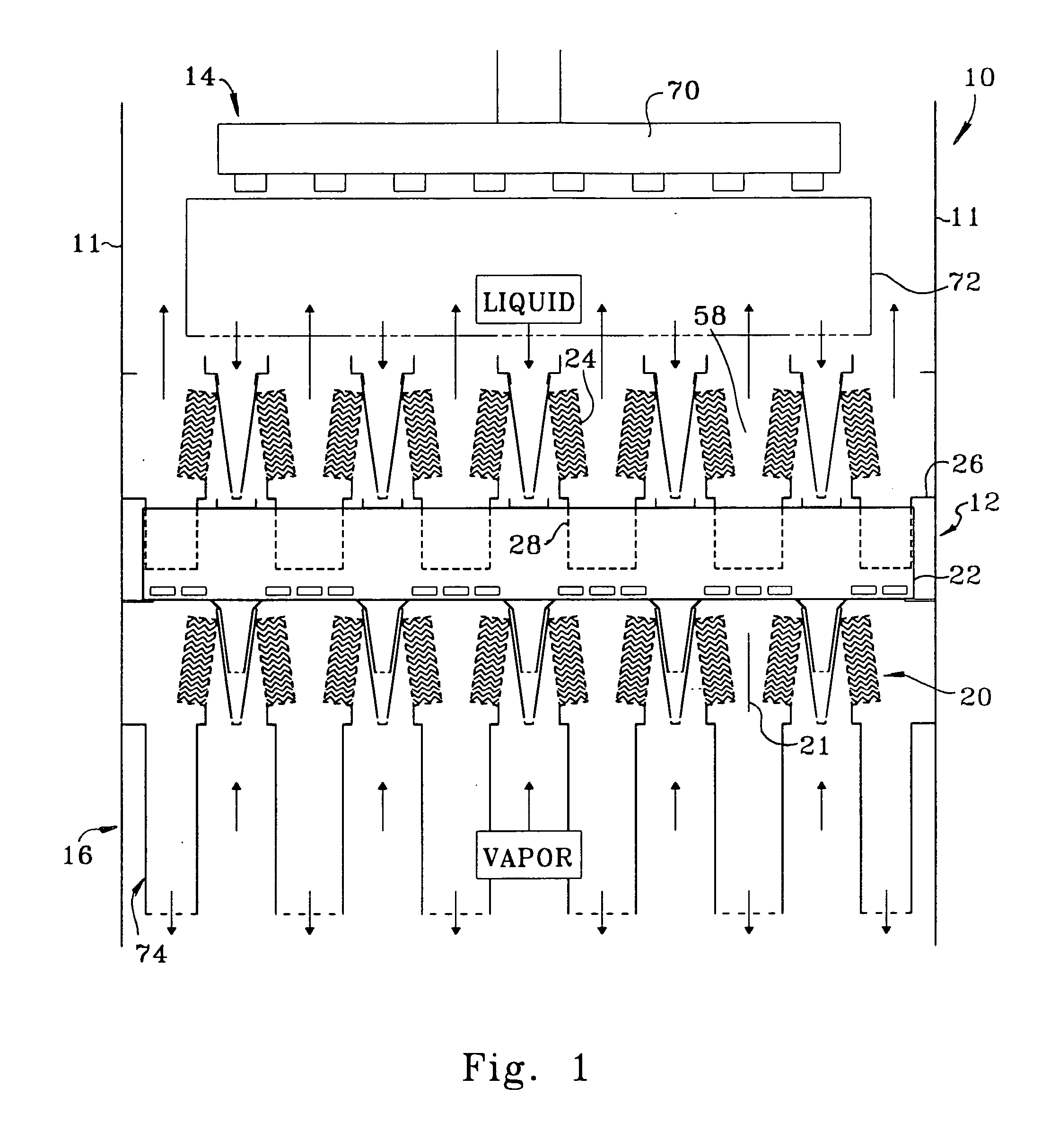
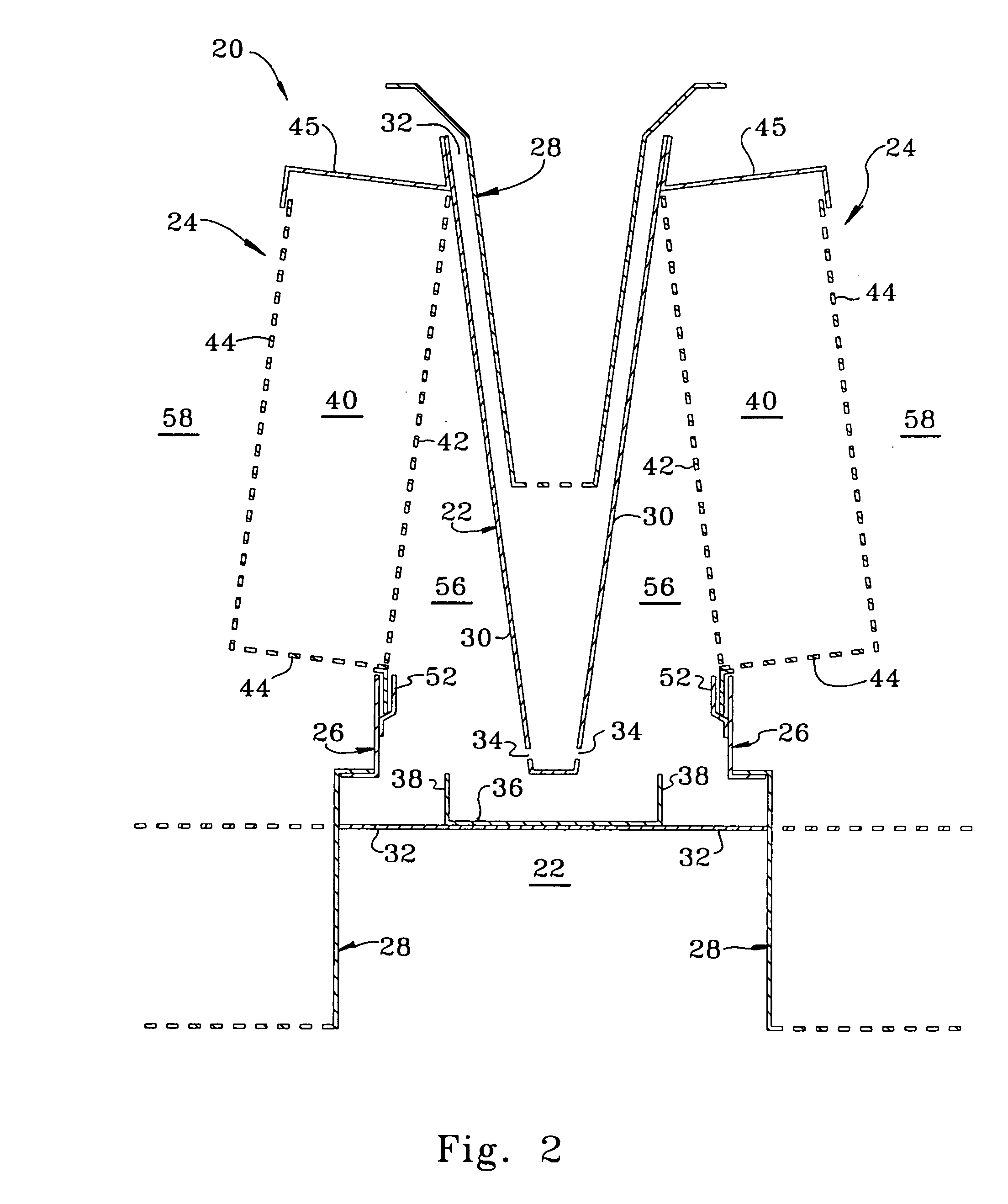
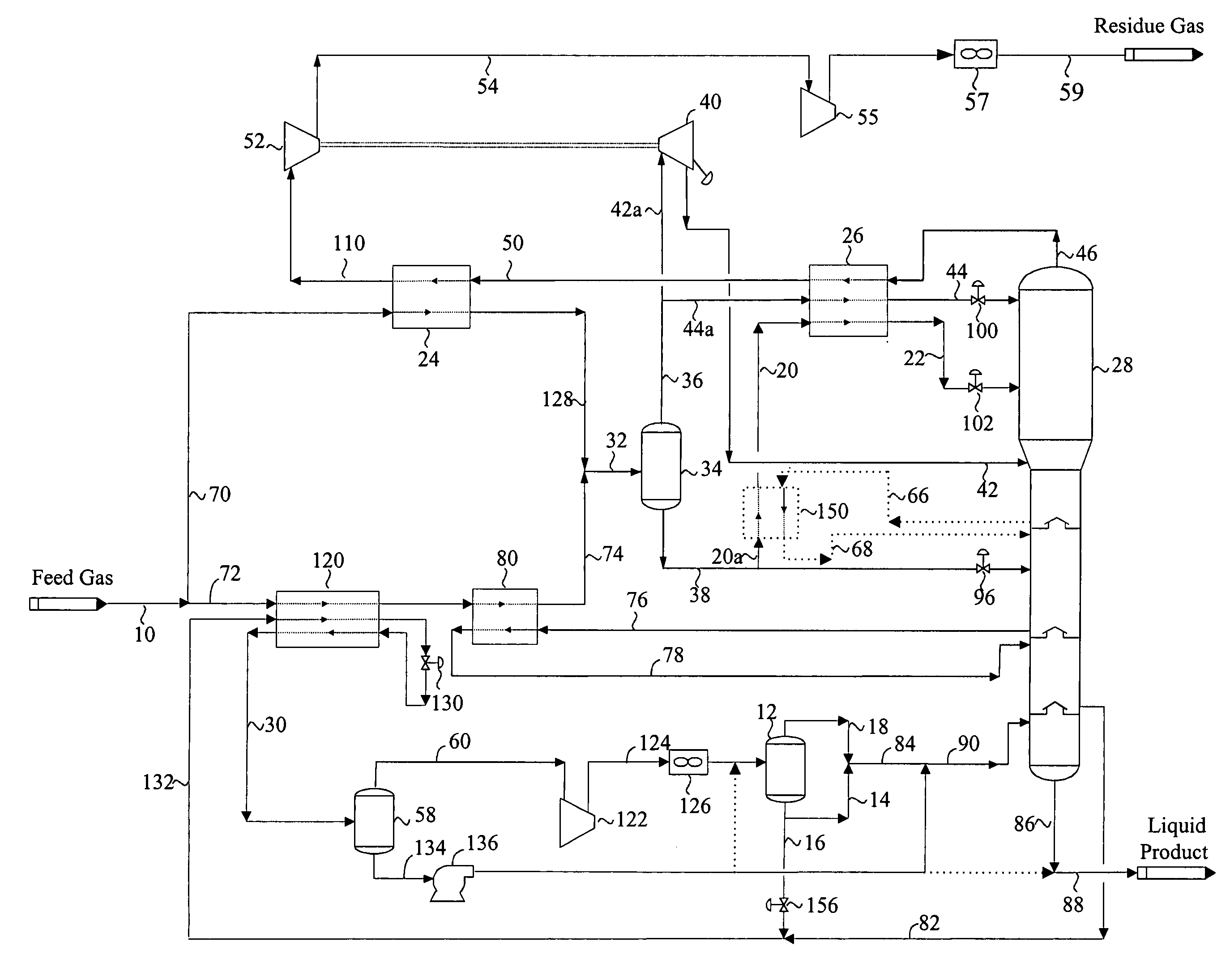
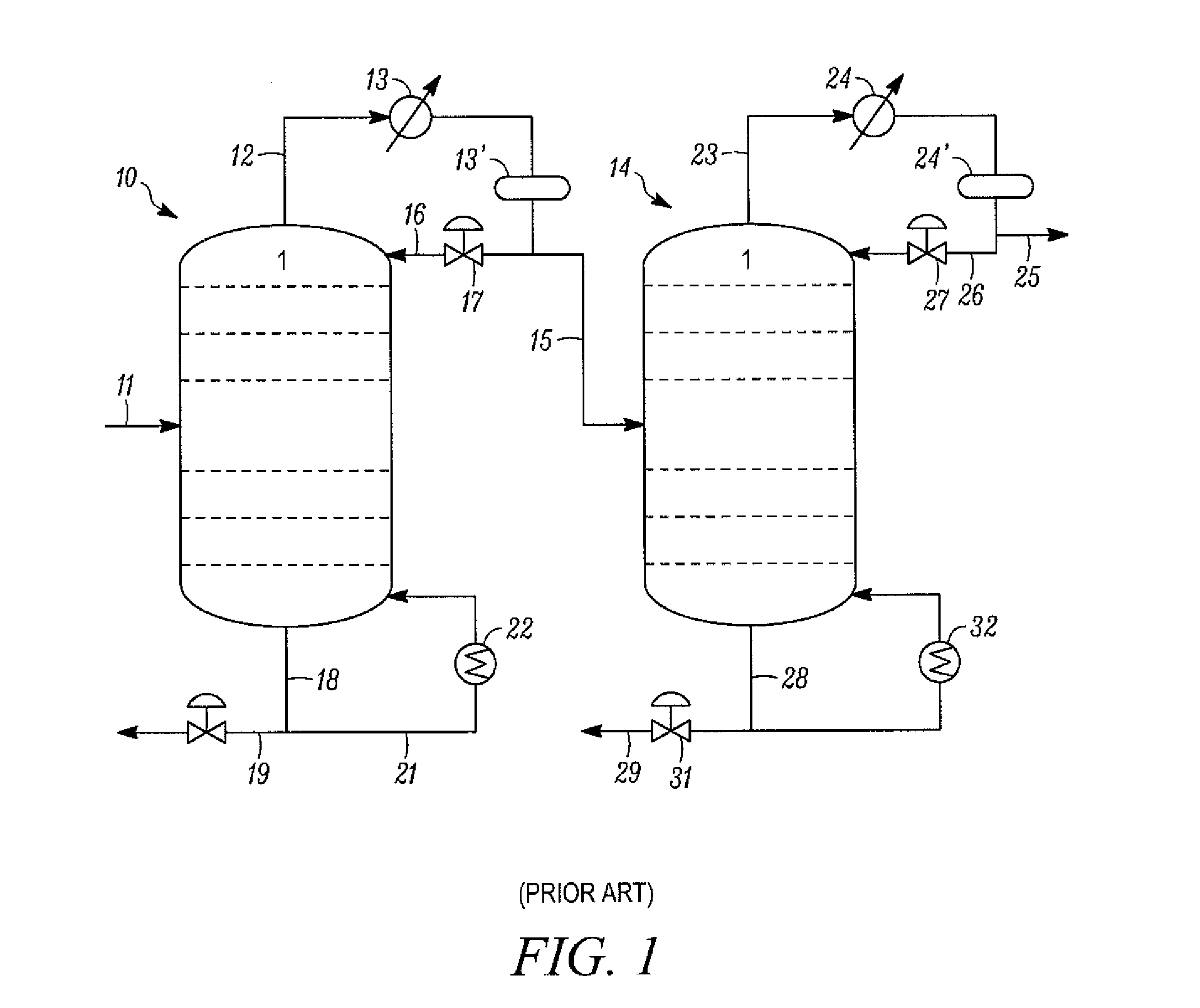
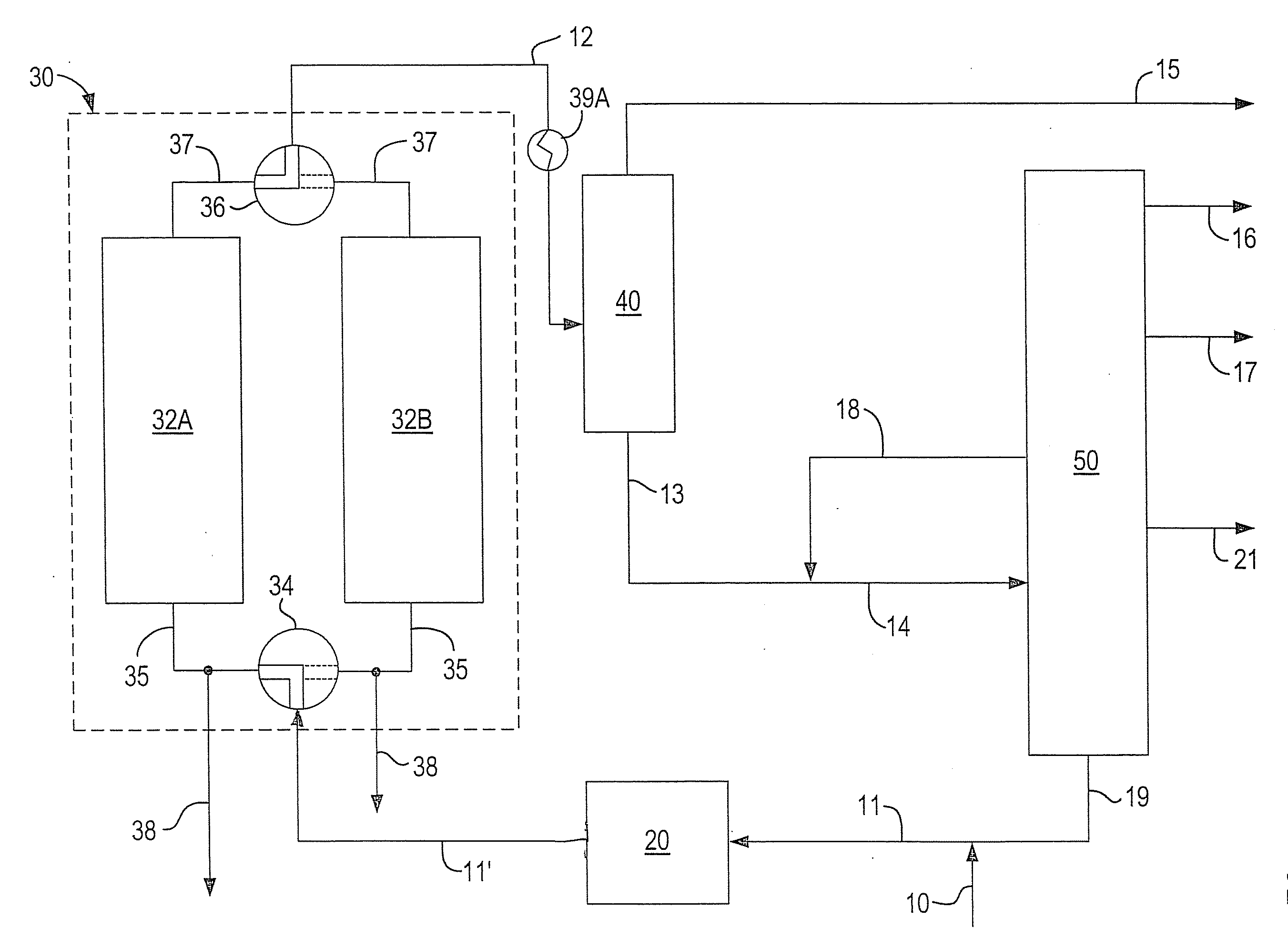
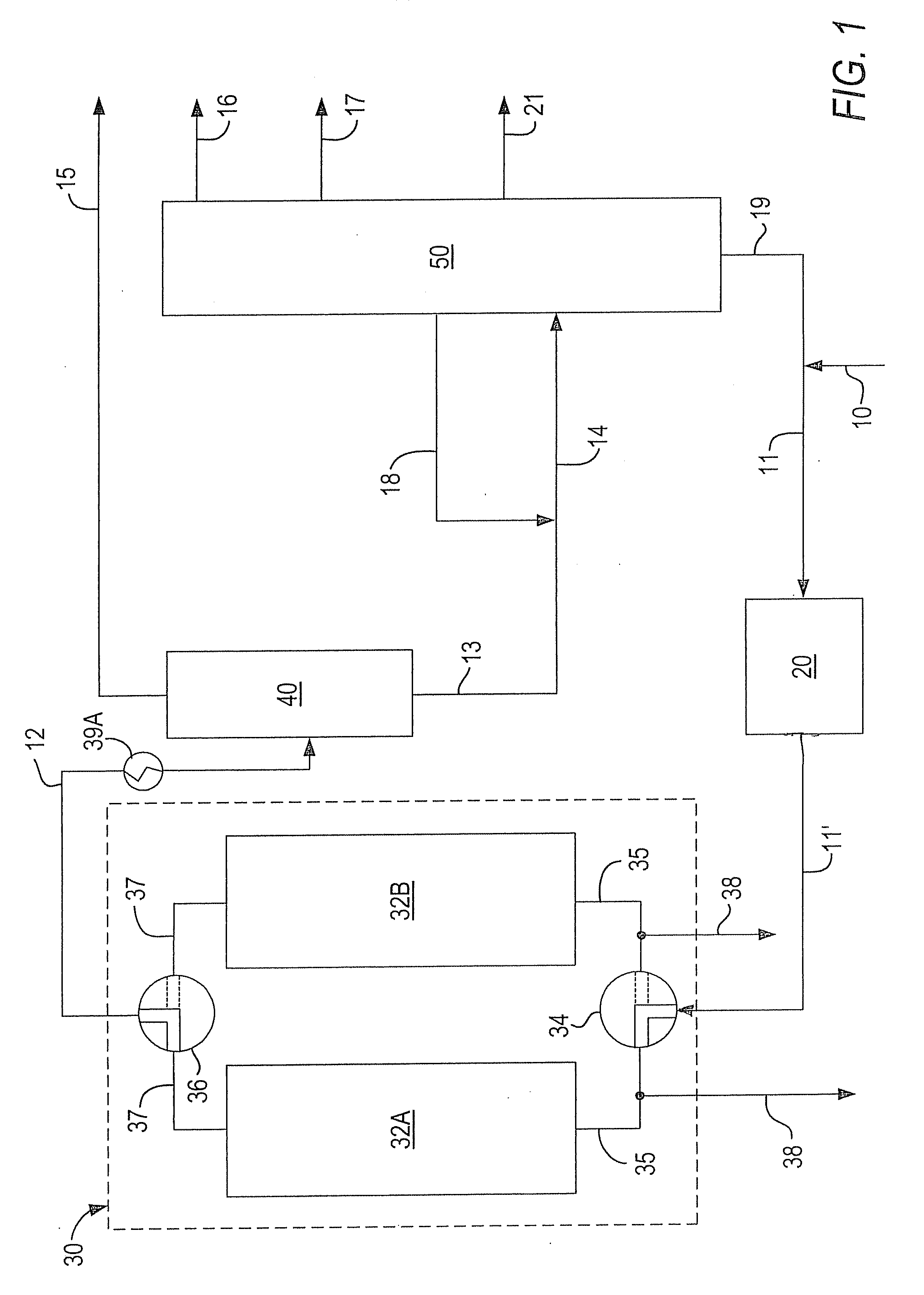
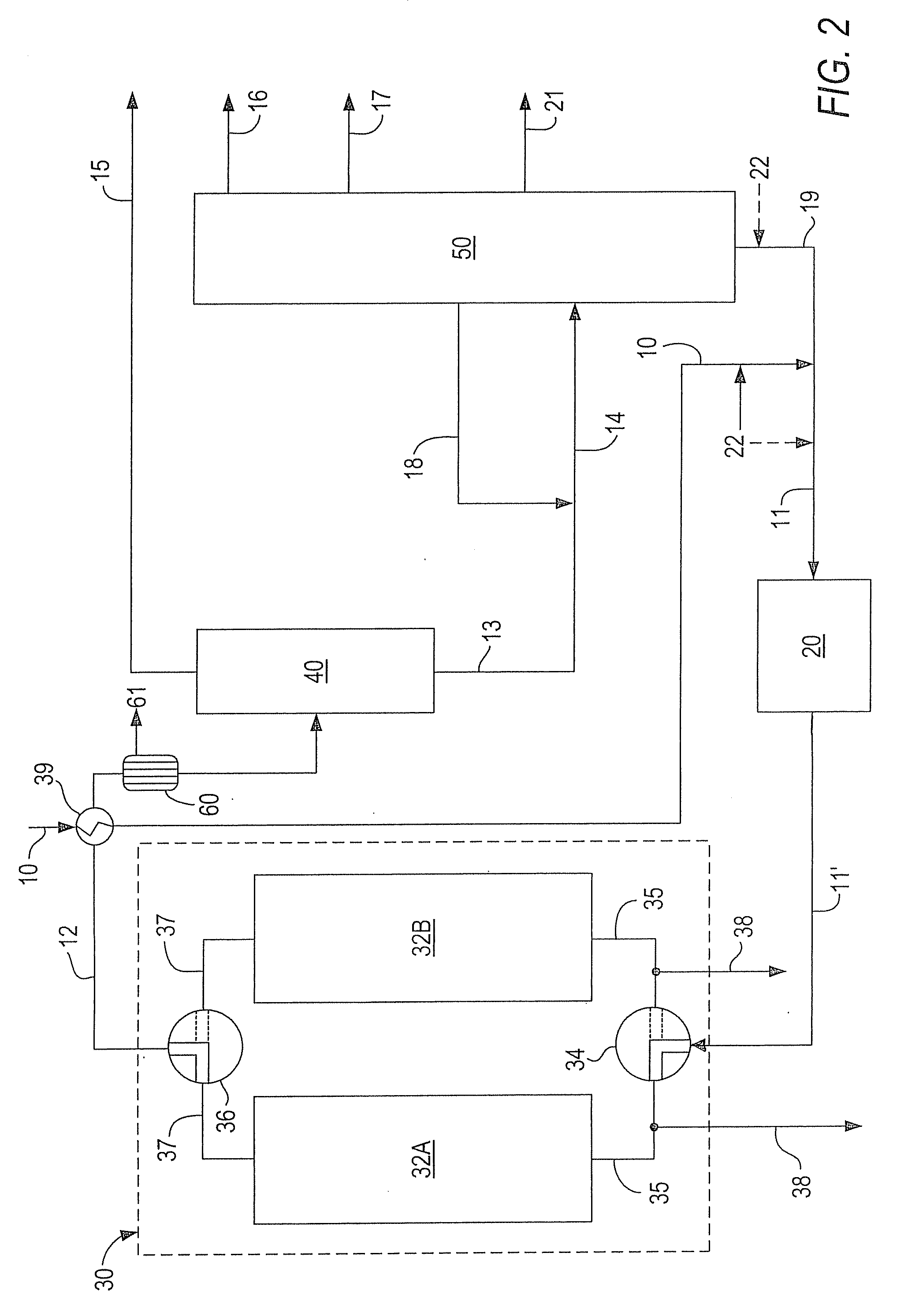
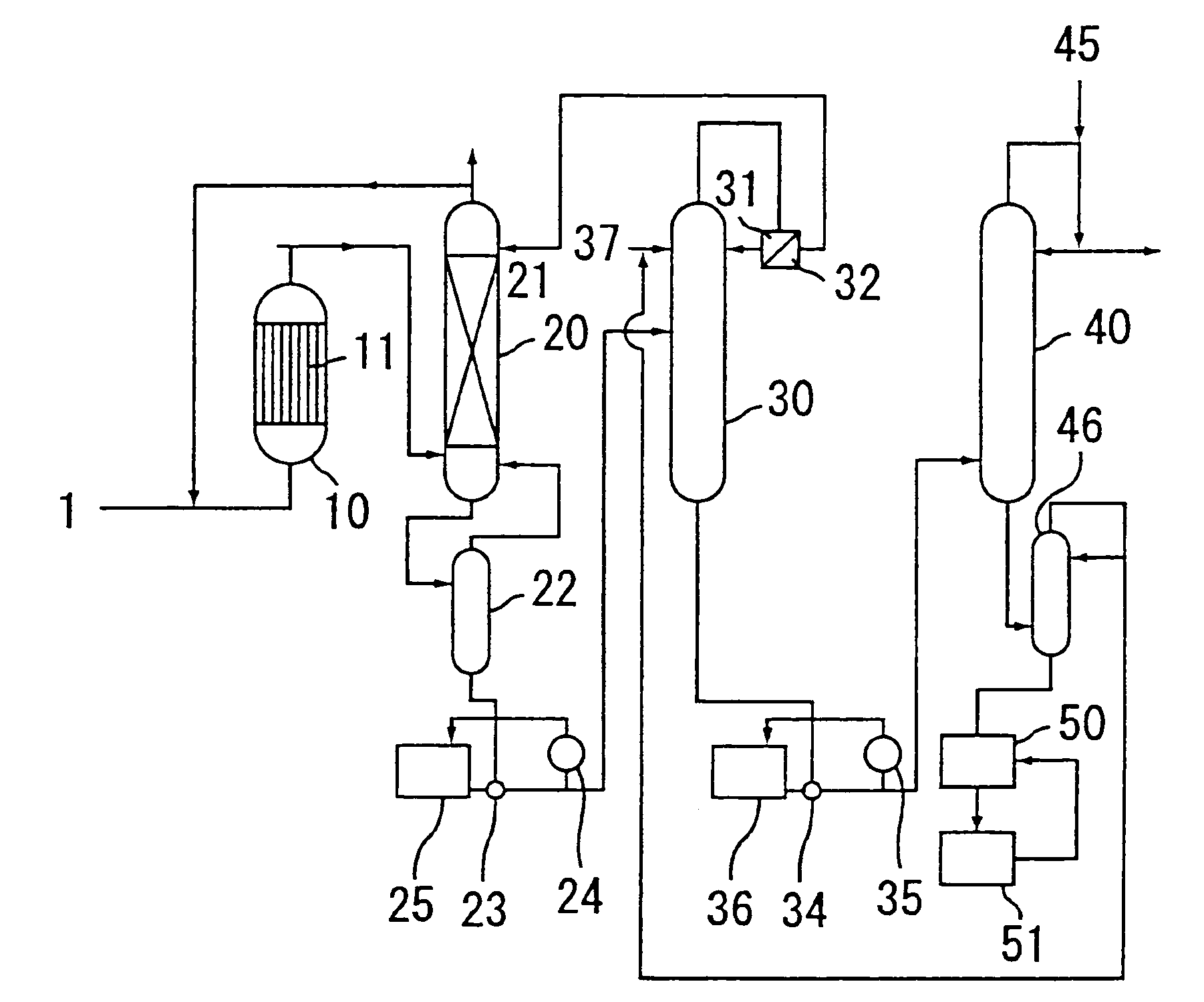
A fractionating column is an essential item used in distillation of liquid mixtures so as to separate the mixture into its component parts, or fractions, based on the differences in volatilities. Fractionating columns are used in small scale laboratory distillations as well as for large scale industrial distillations.
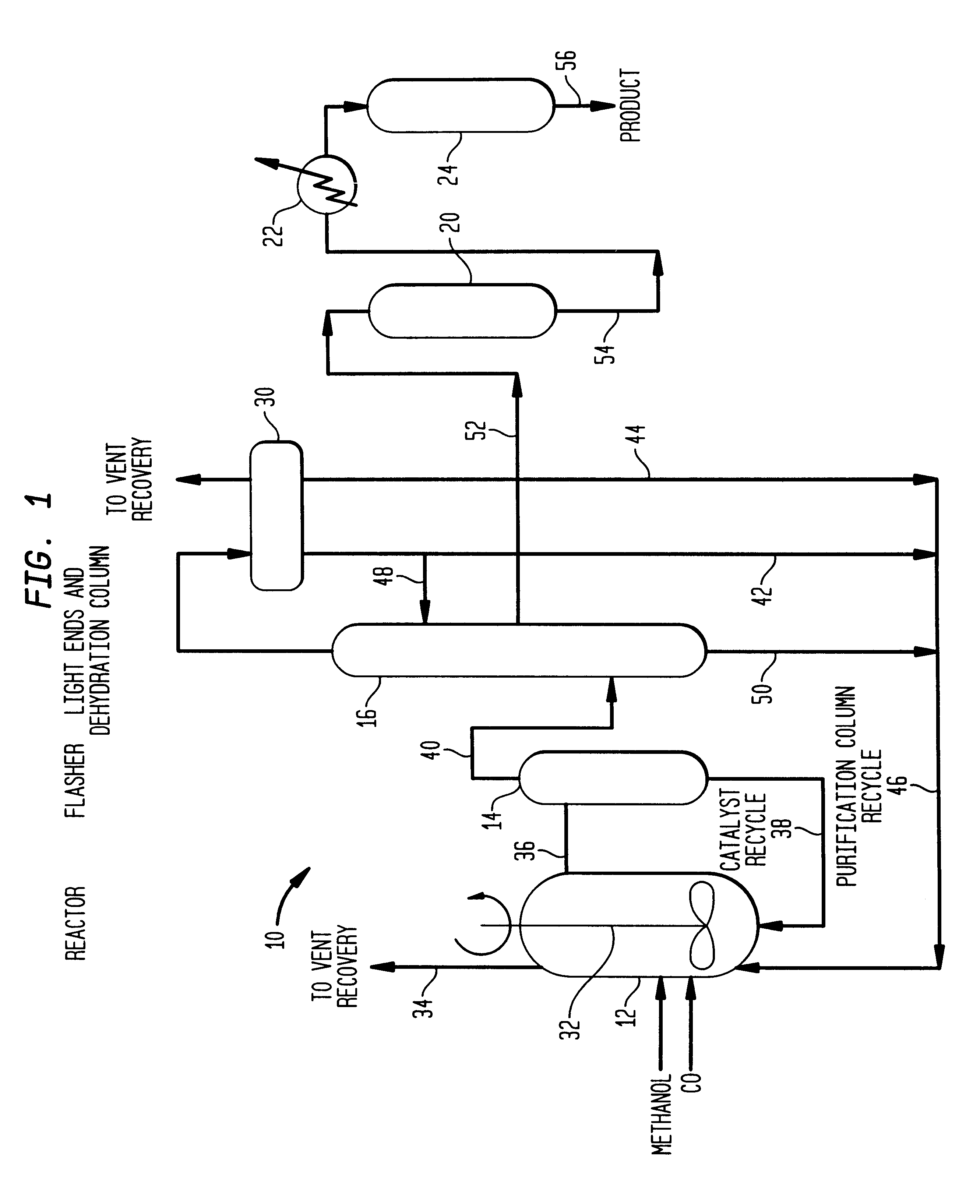
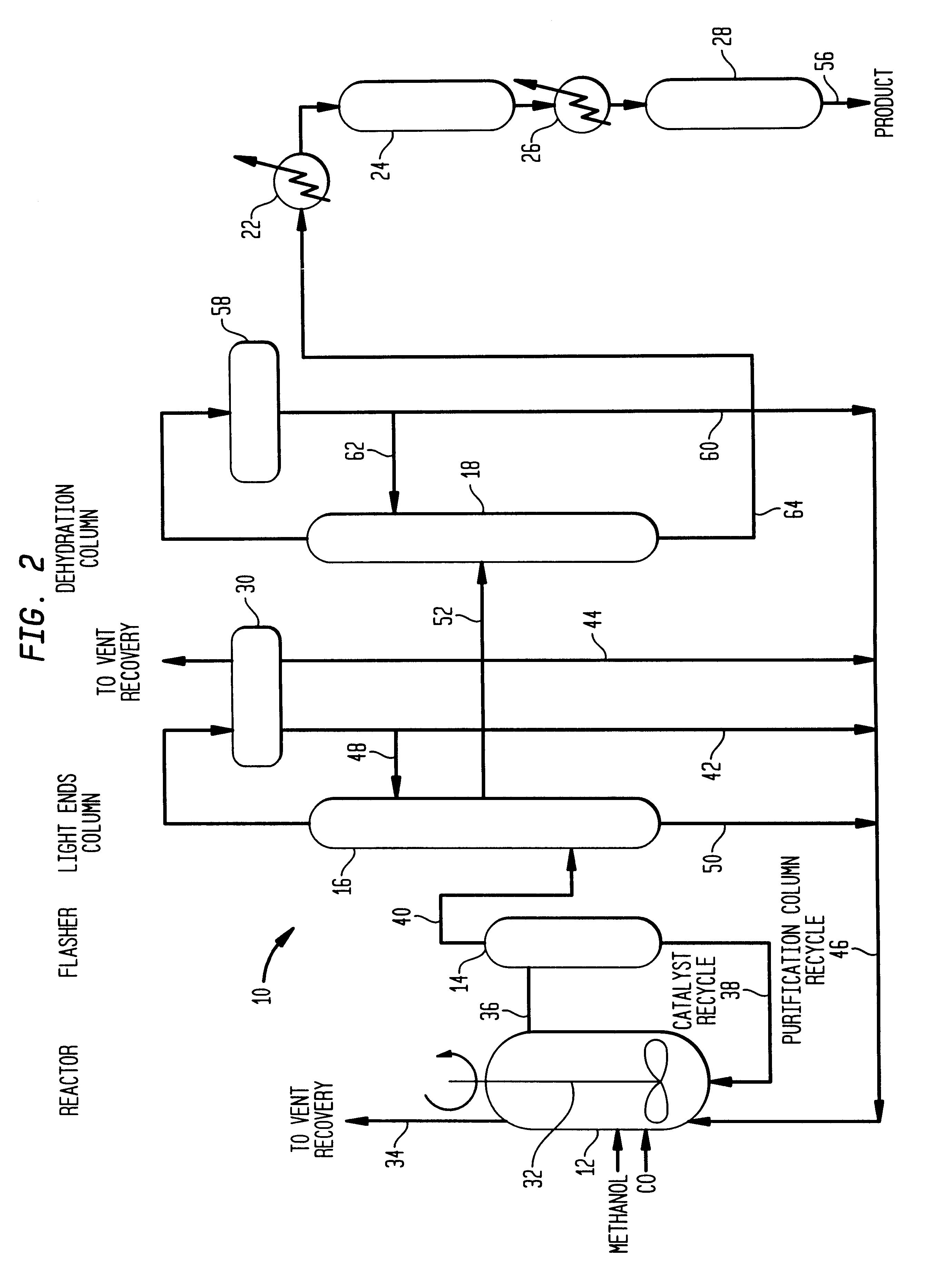
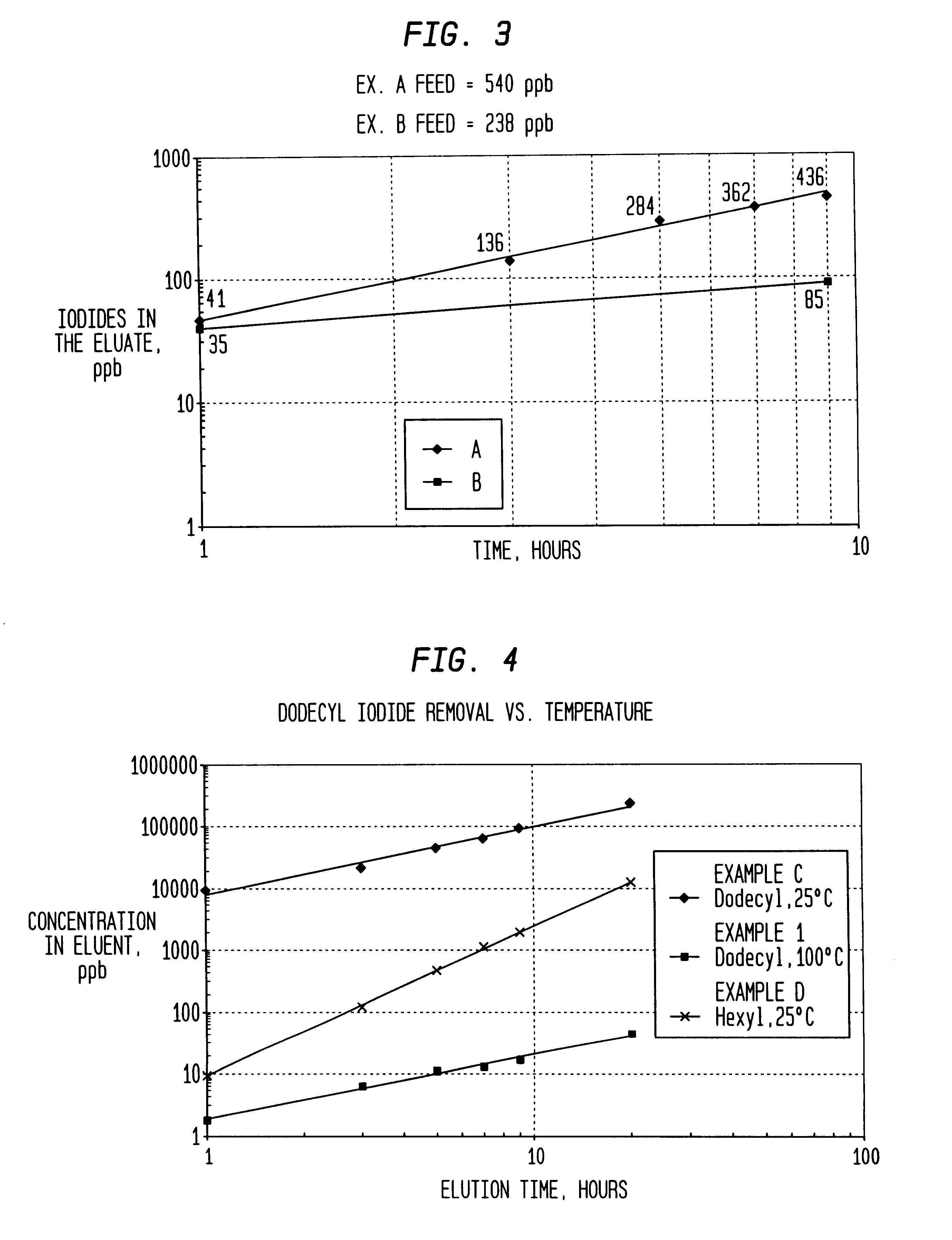
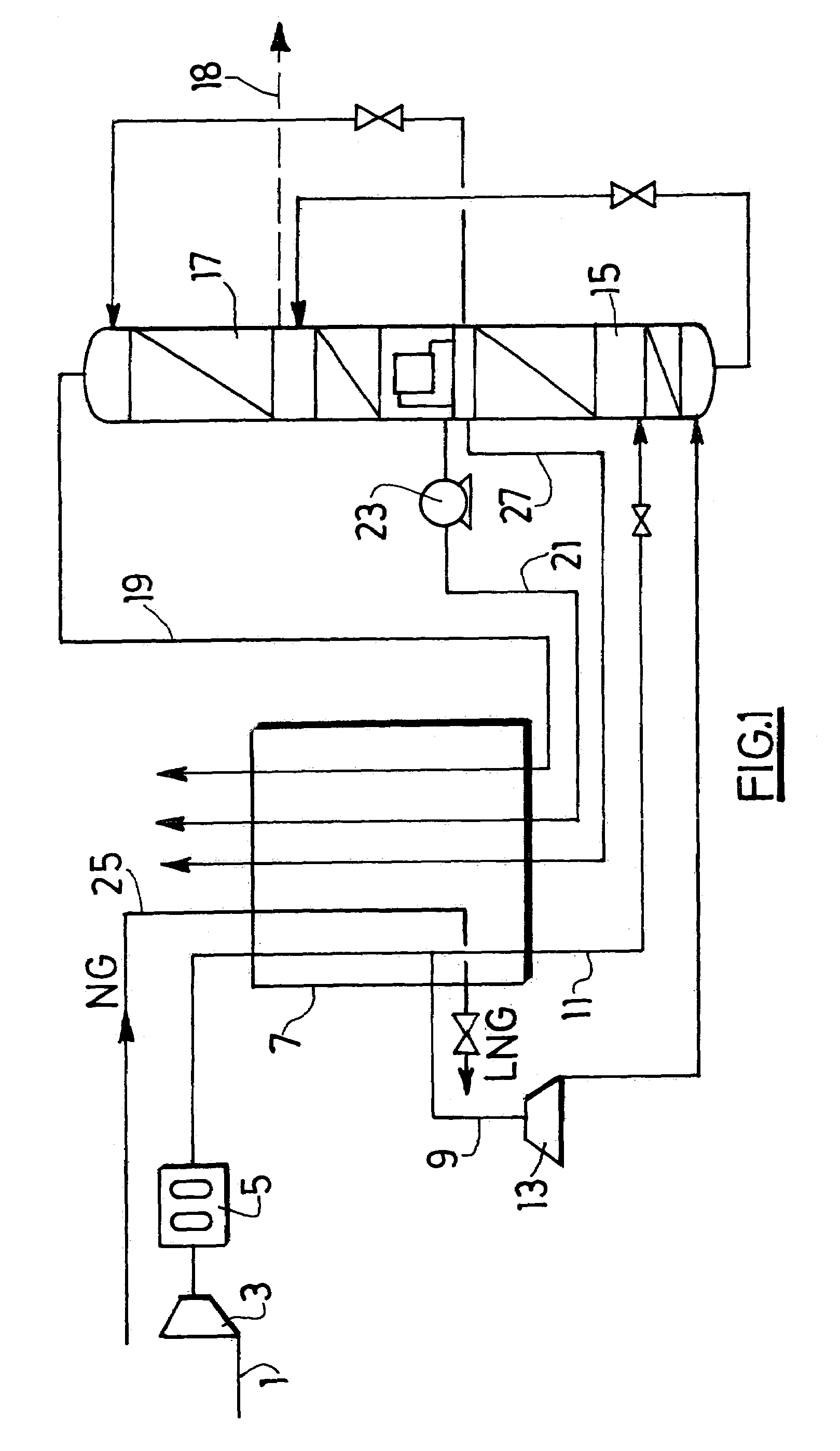
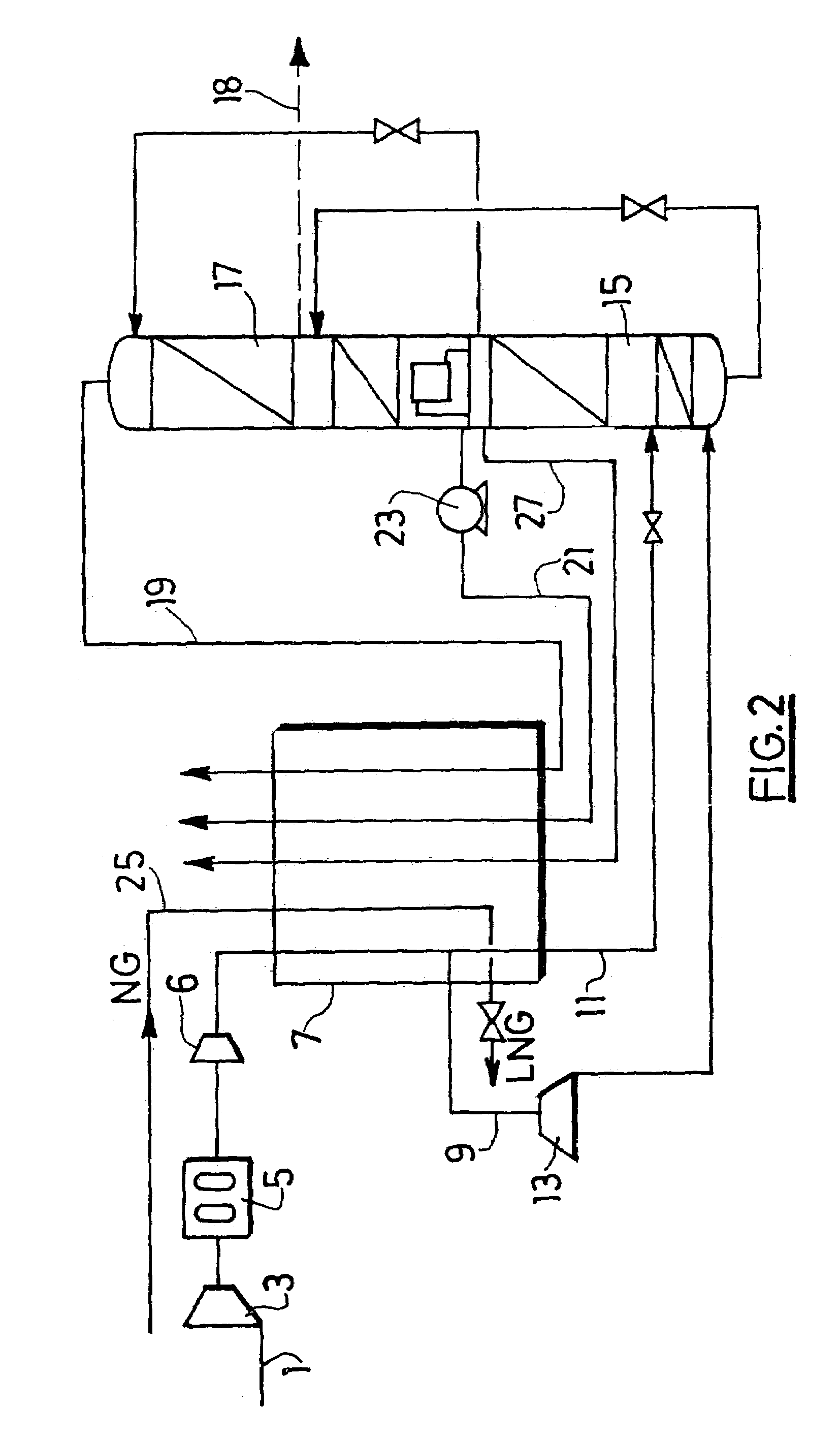
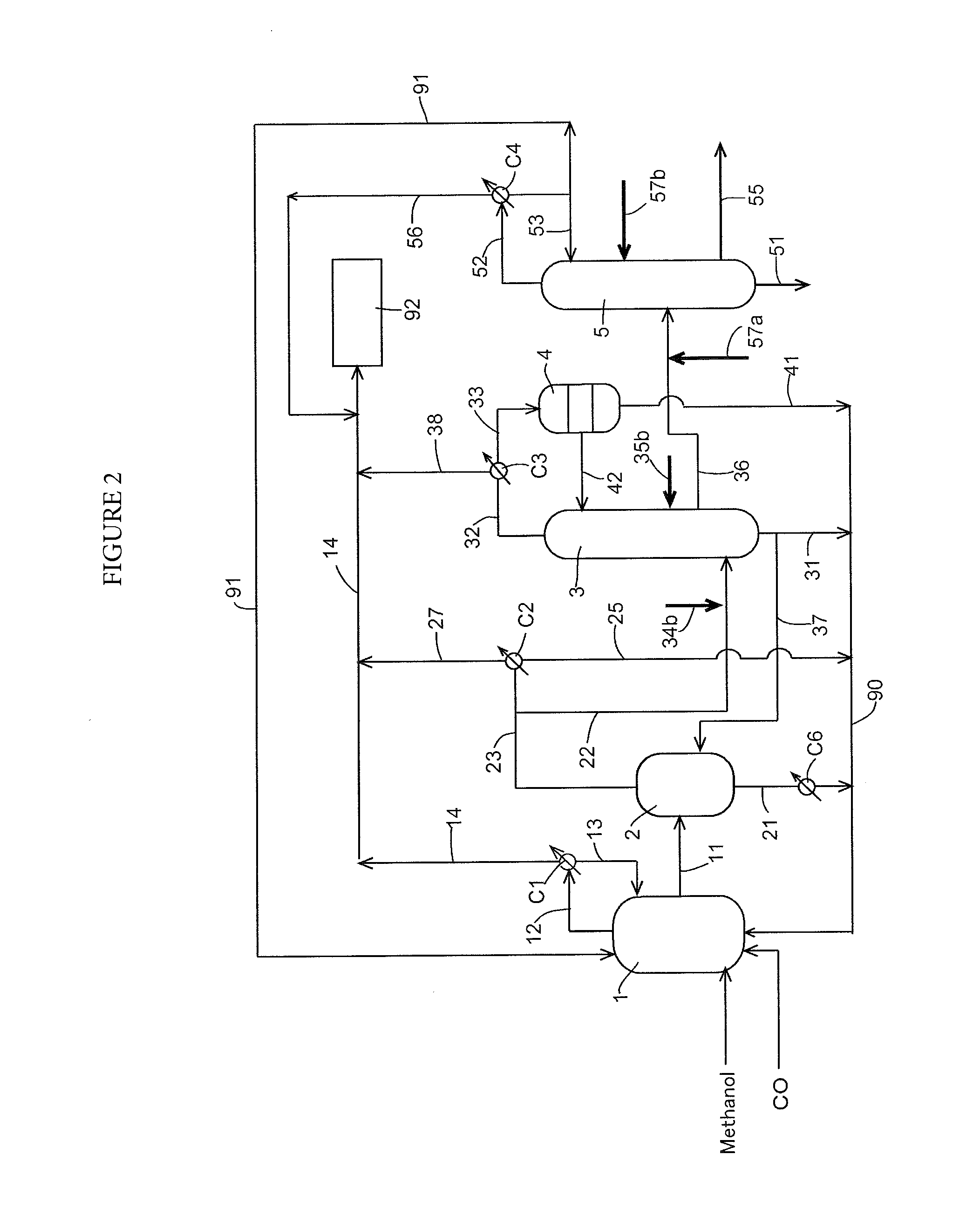
Low energy carbonylation process
InactiveUS6657078B2Weaken energyHigh purityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPropanoic acidIodide
A low energy process for producing acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol is disclosed. The process involves a rhodium-catalyzed system operated at less than about 14% water utilizing up to 2 distillation columns. The process is preferably controlled such that the product stream has a low level of propionic acid impurity and the level of aldehyde impurities is minimized by way of aldehyde removal or minimizing aldehyde generation. The level of iodides is controlled by contacting the product, at elevated temperatures, with ion exchange resins. In preferred embodiments, at least one silver or mercury exchanged macroreticular strong acid ion exchange resin is used to purify the product. The high temperature treatment provides the added benefit of controlling the Color Value (Pt-Co units) of the product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
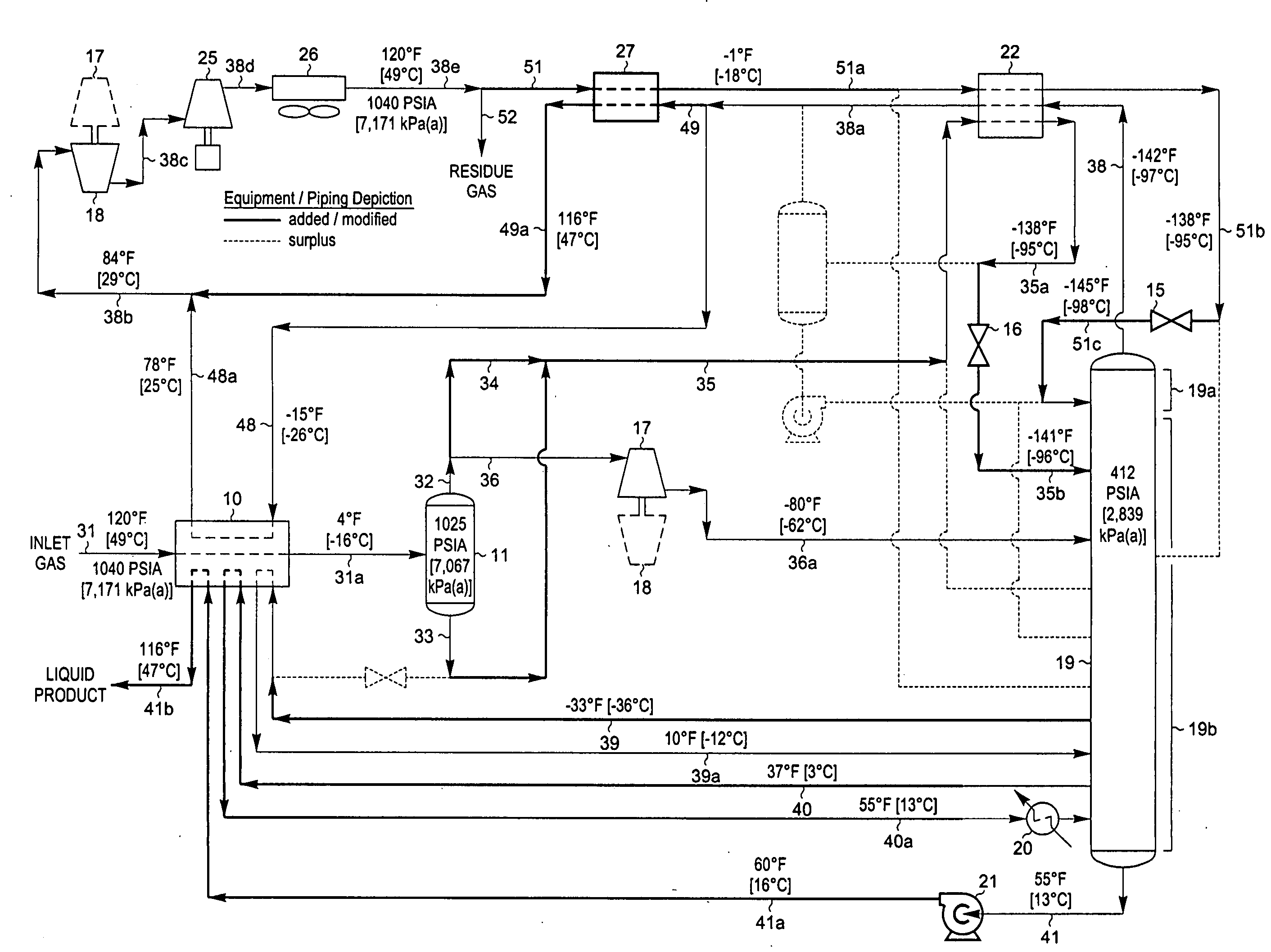
Hydrocarbon gas processing
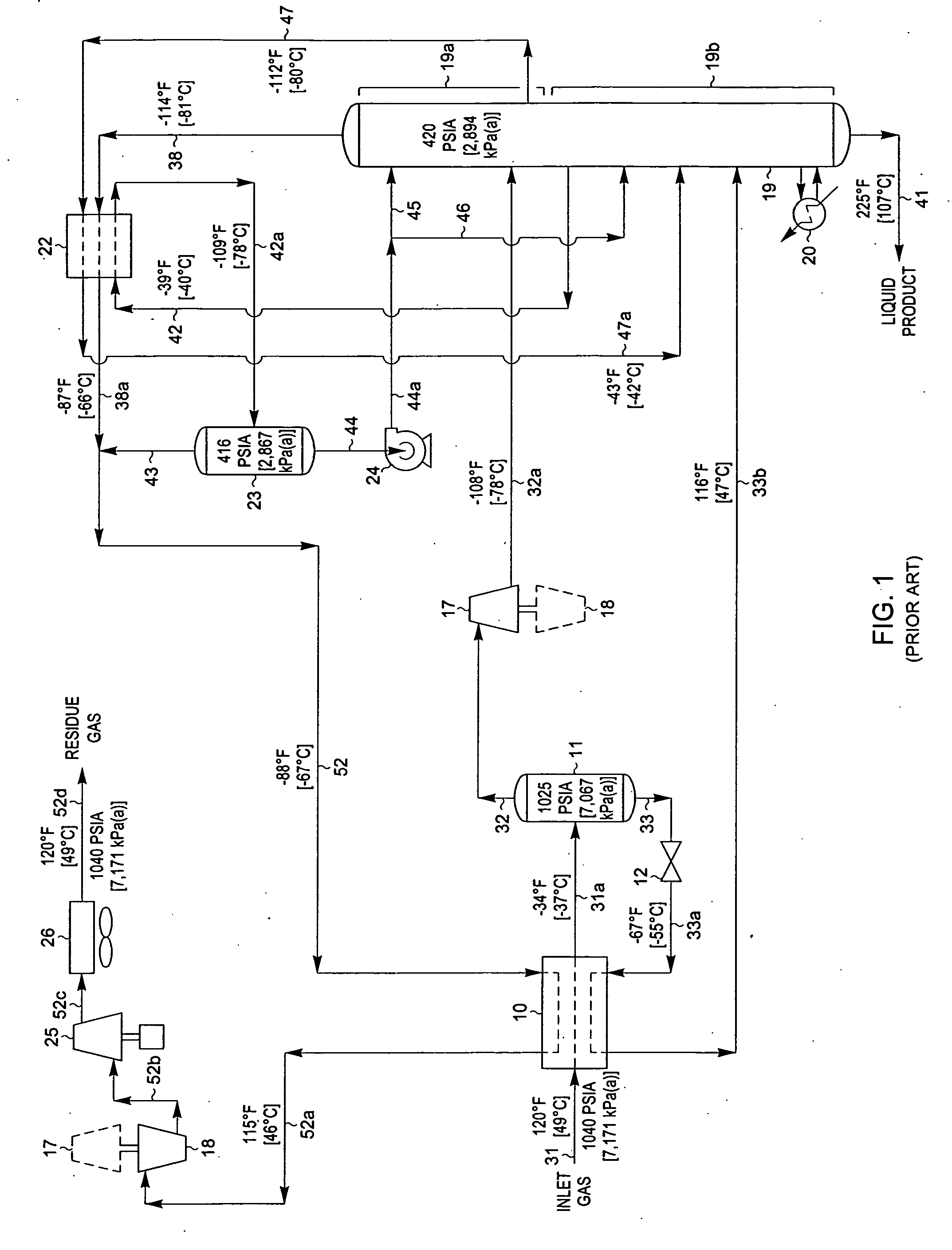
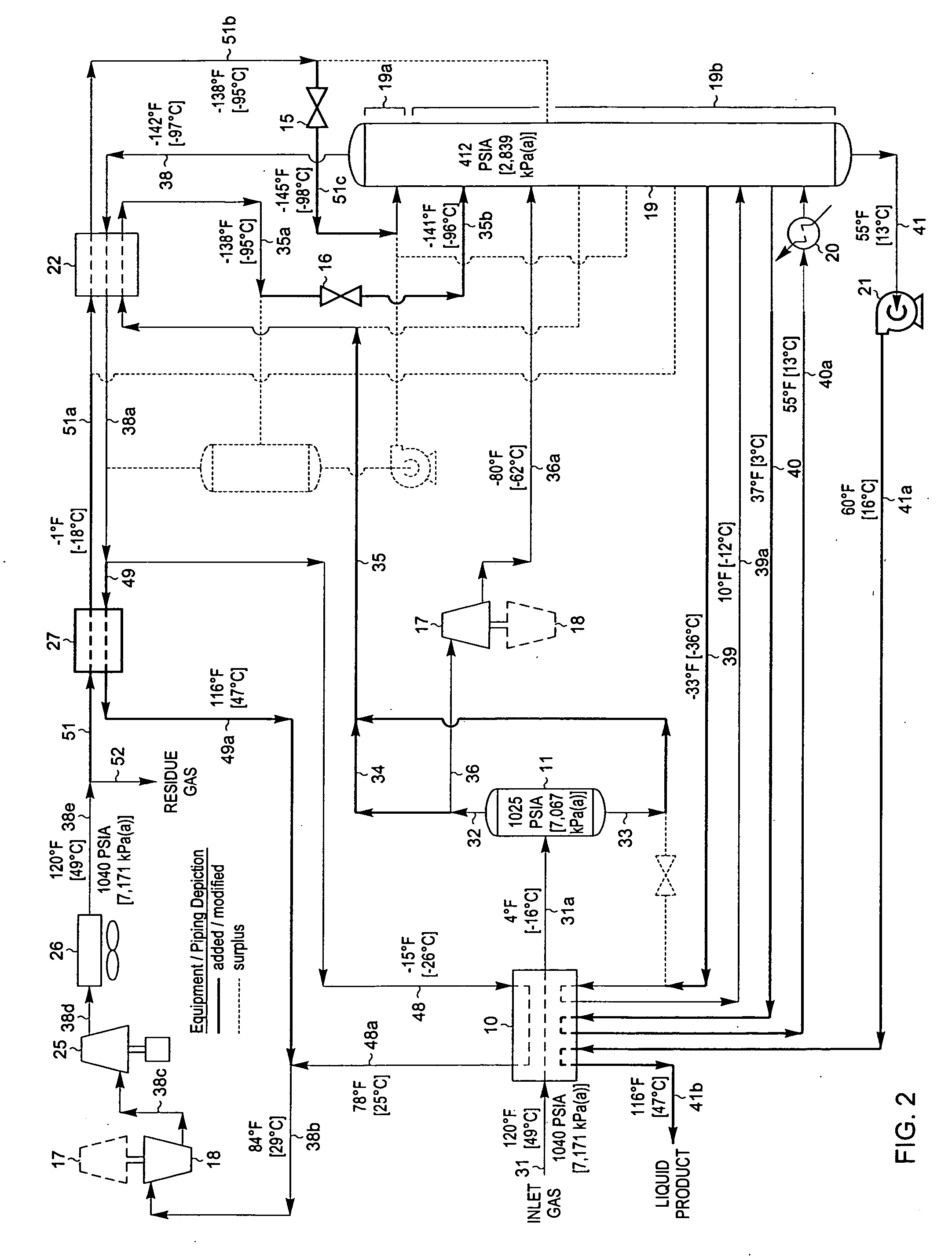
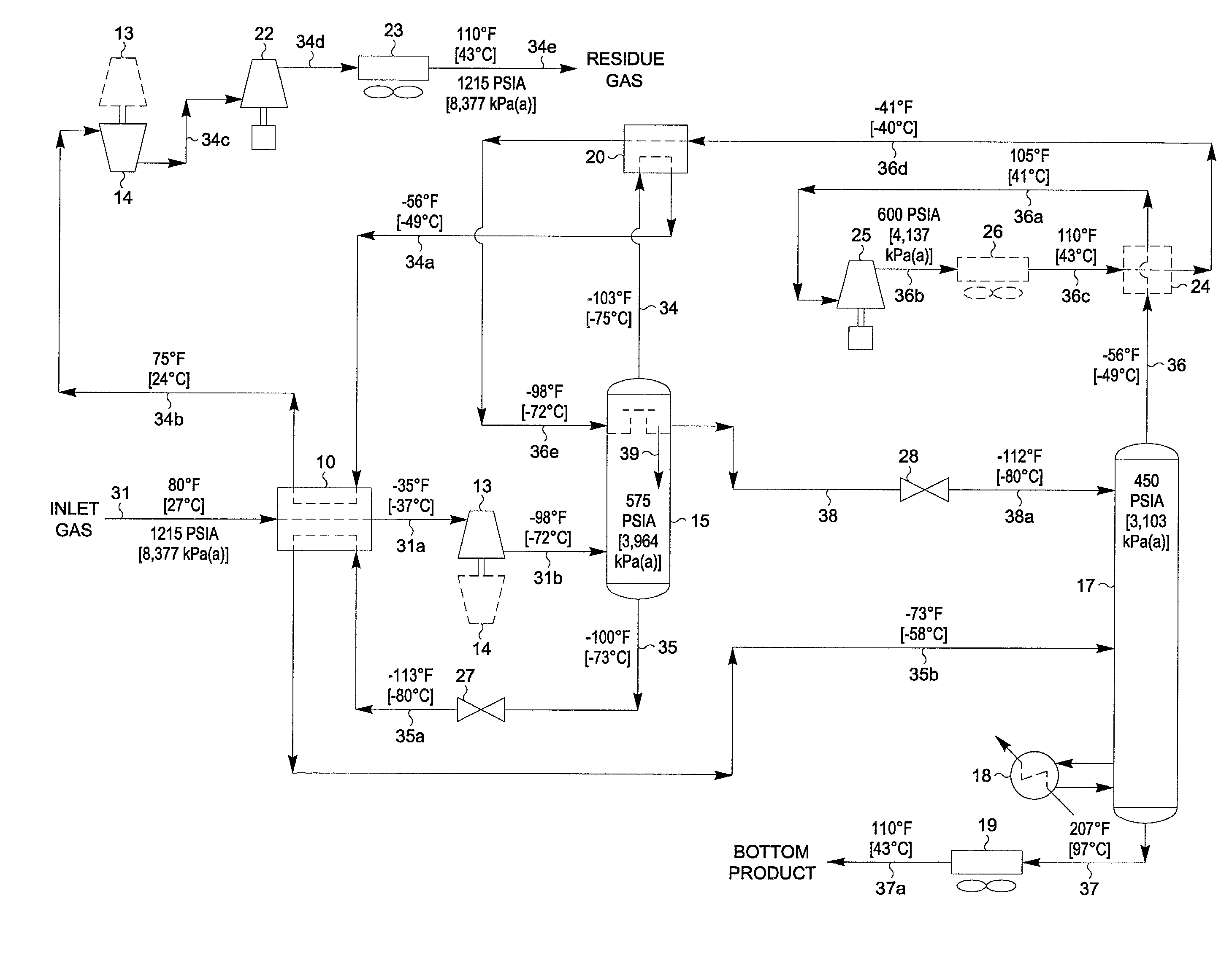
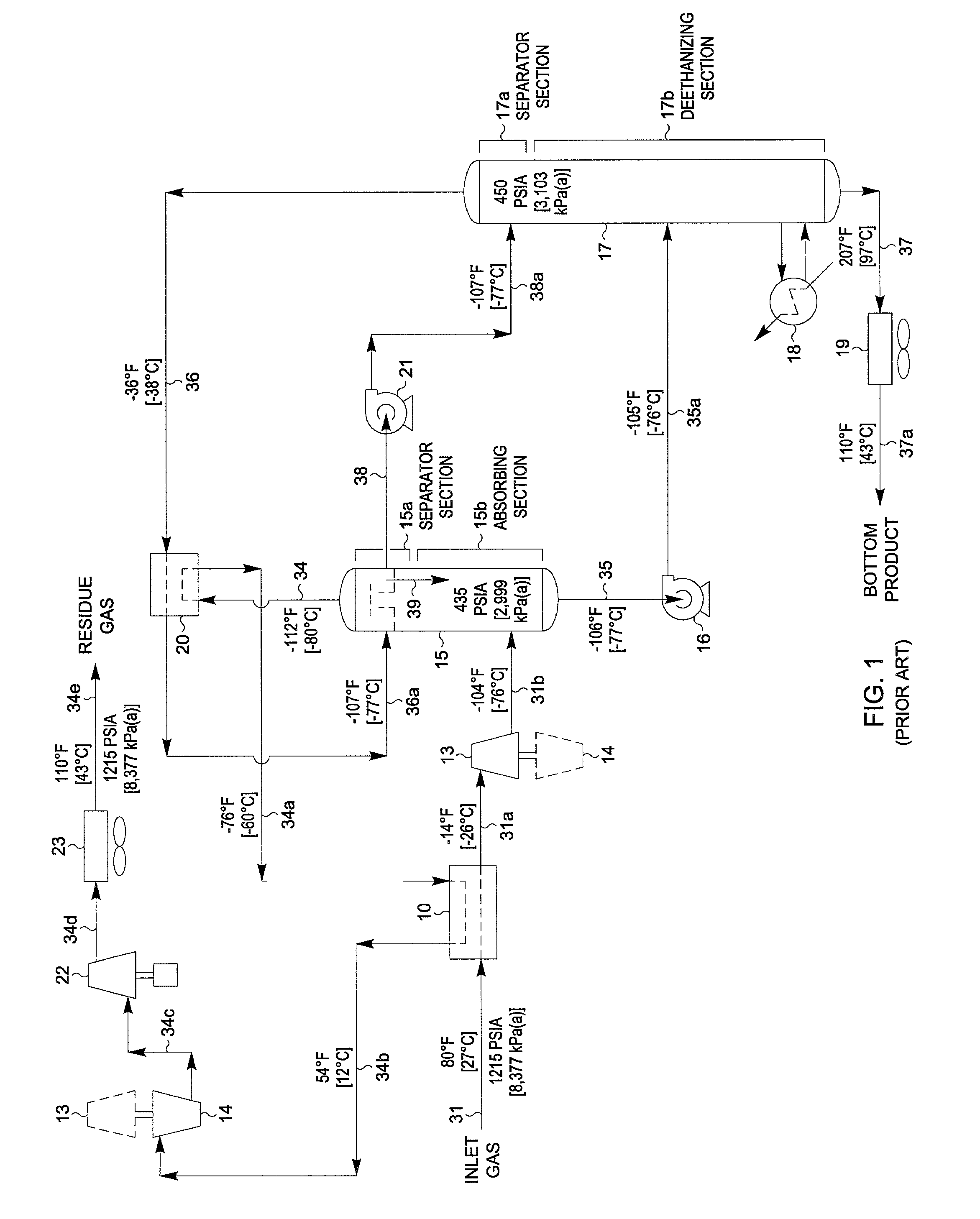
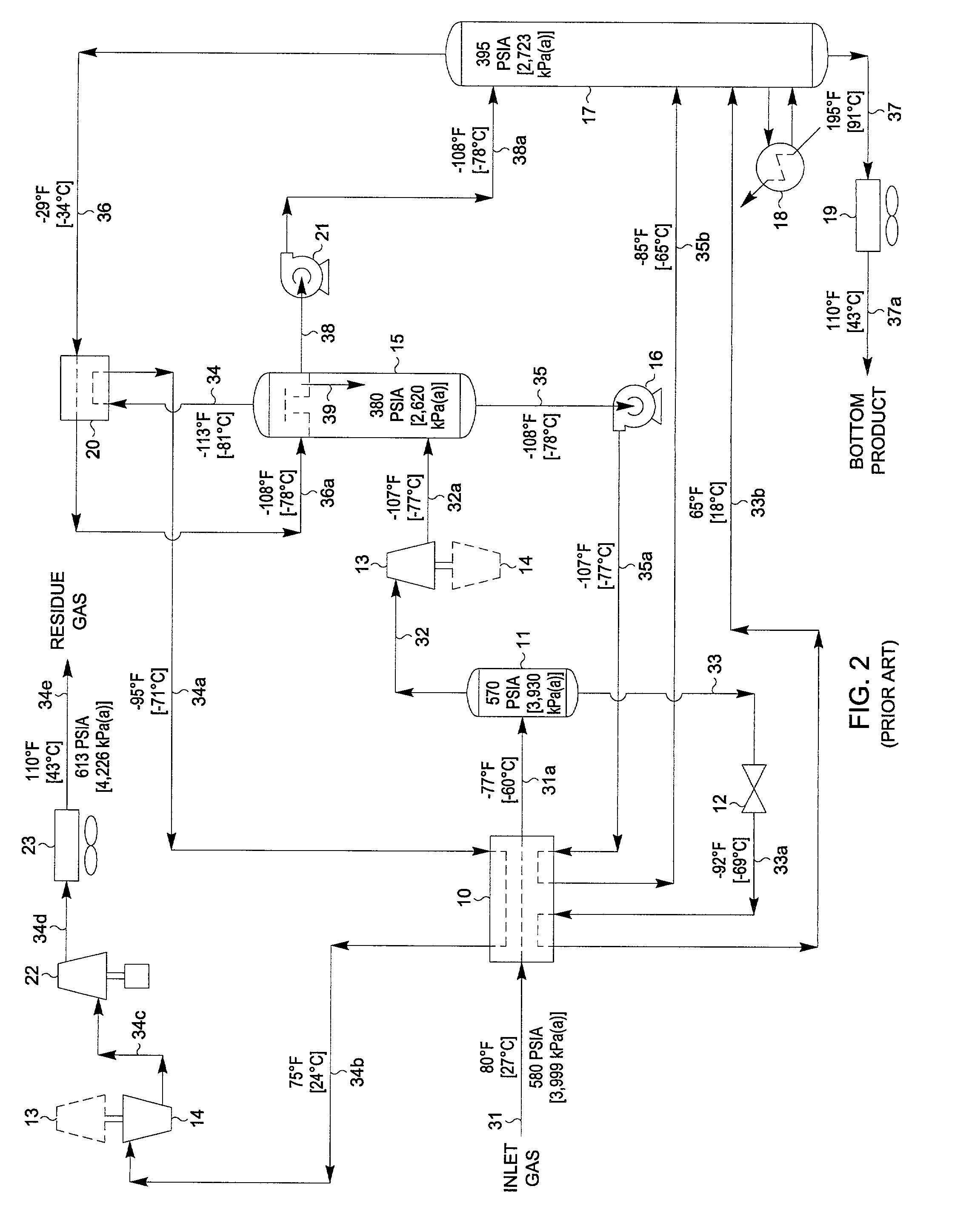
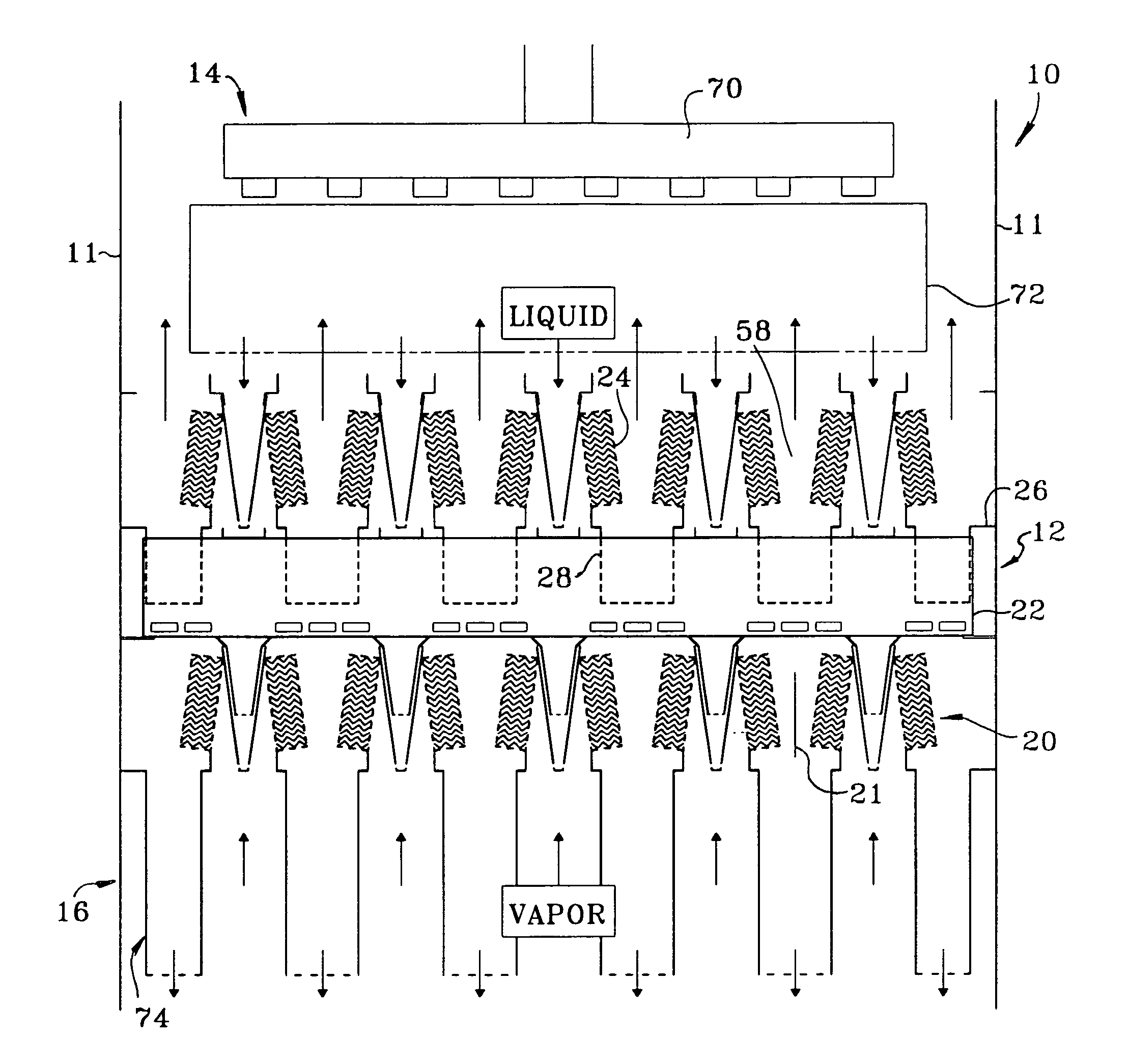
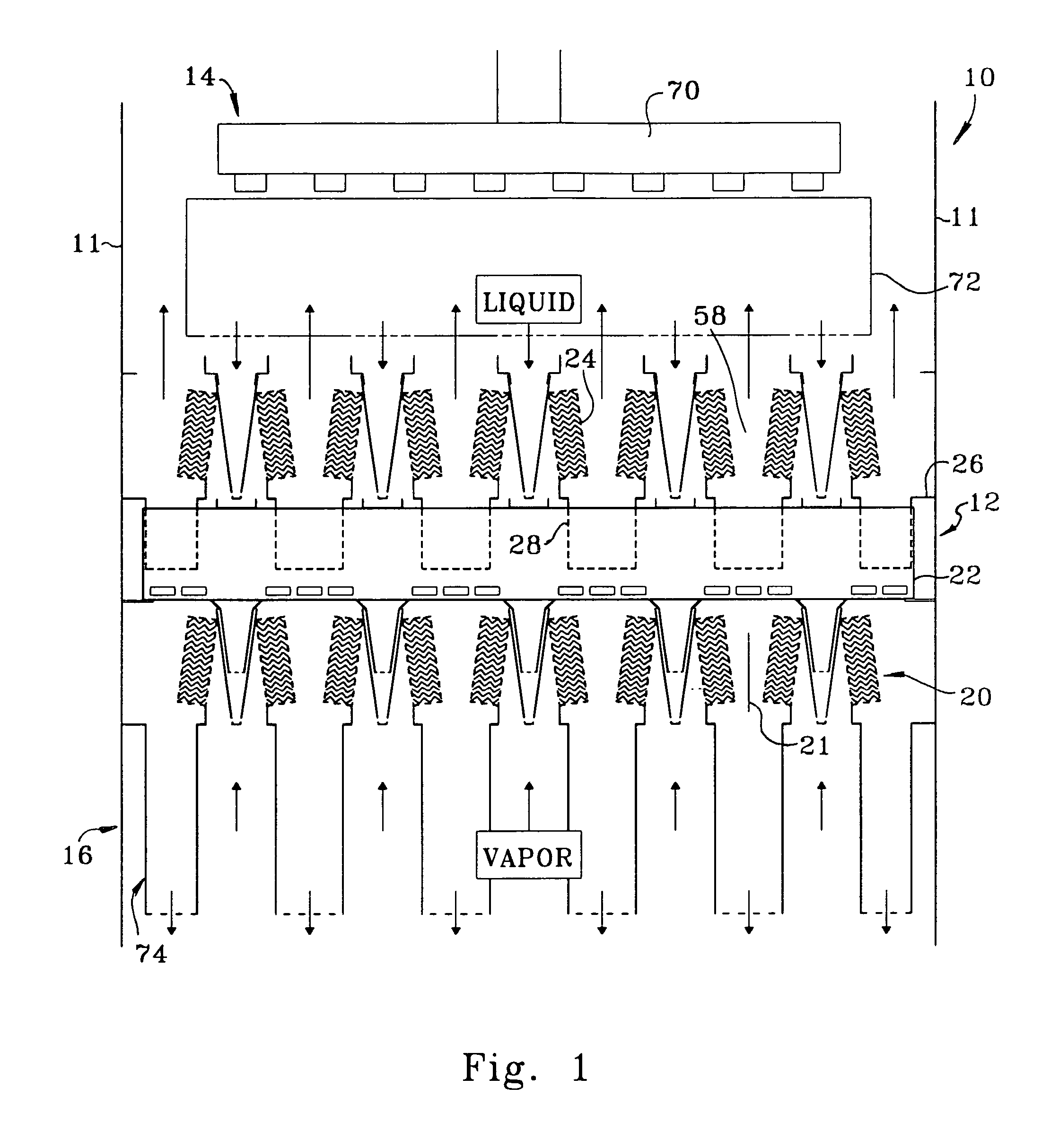
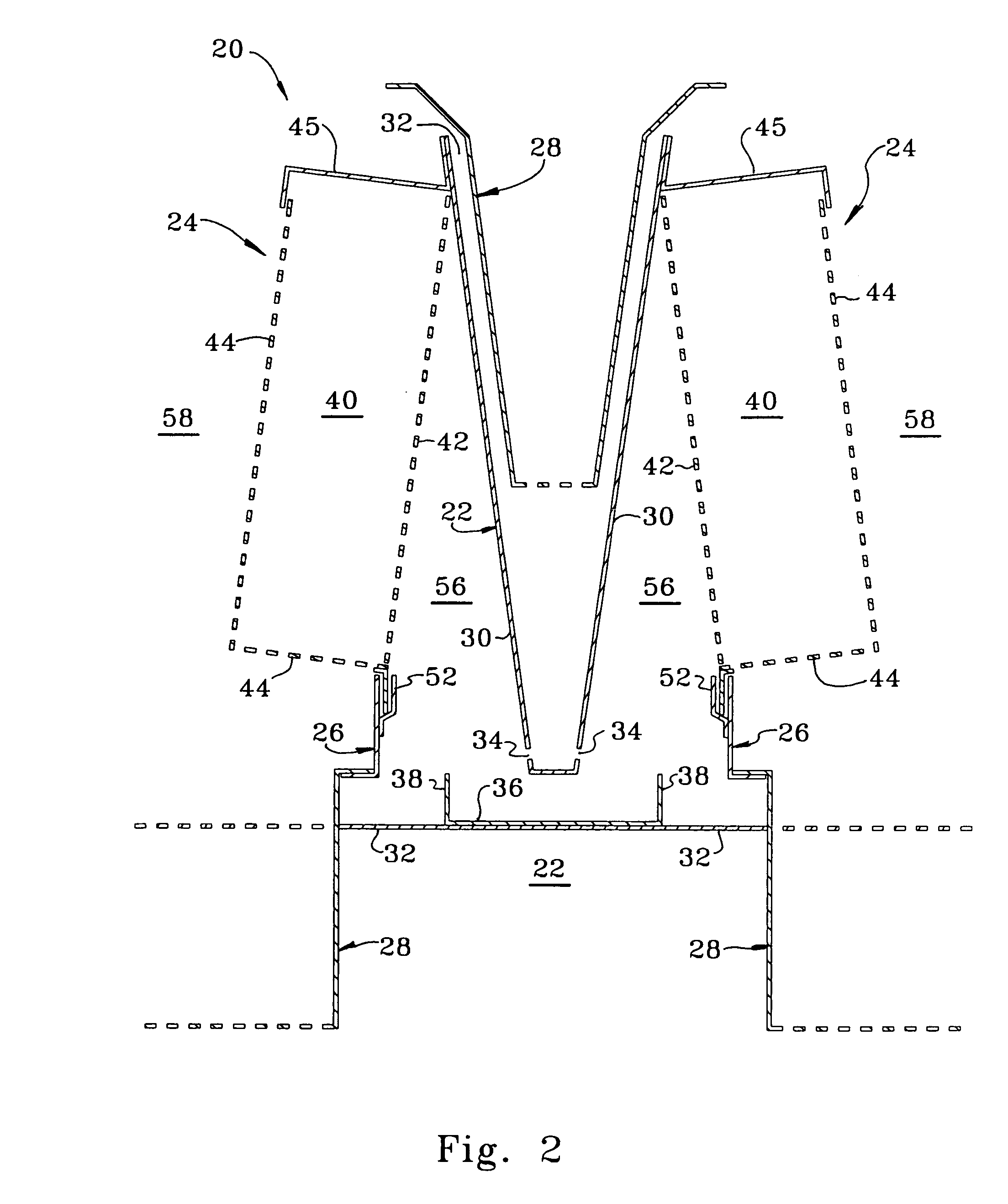
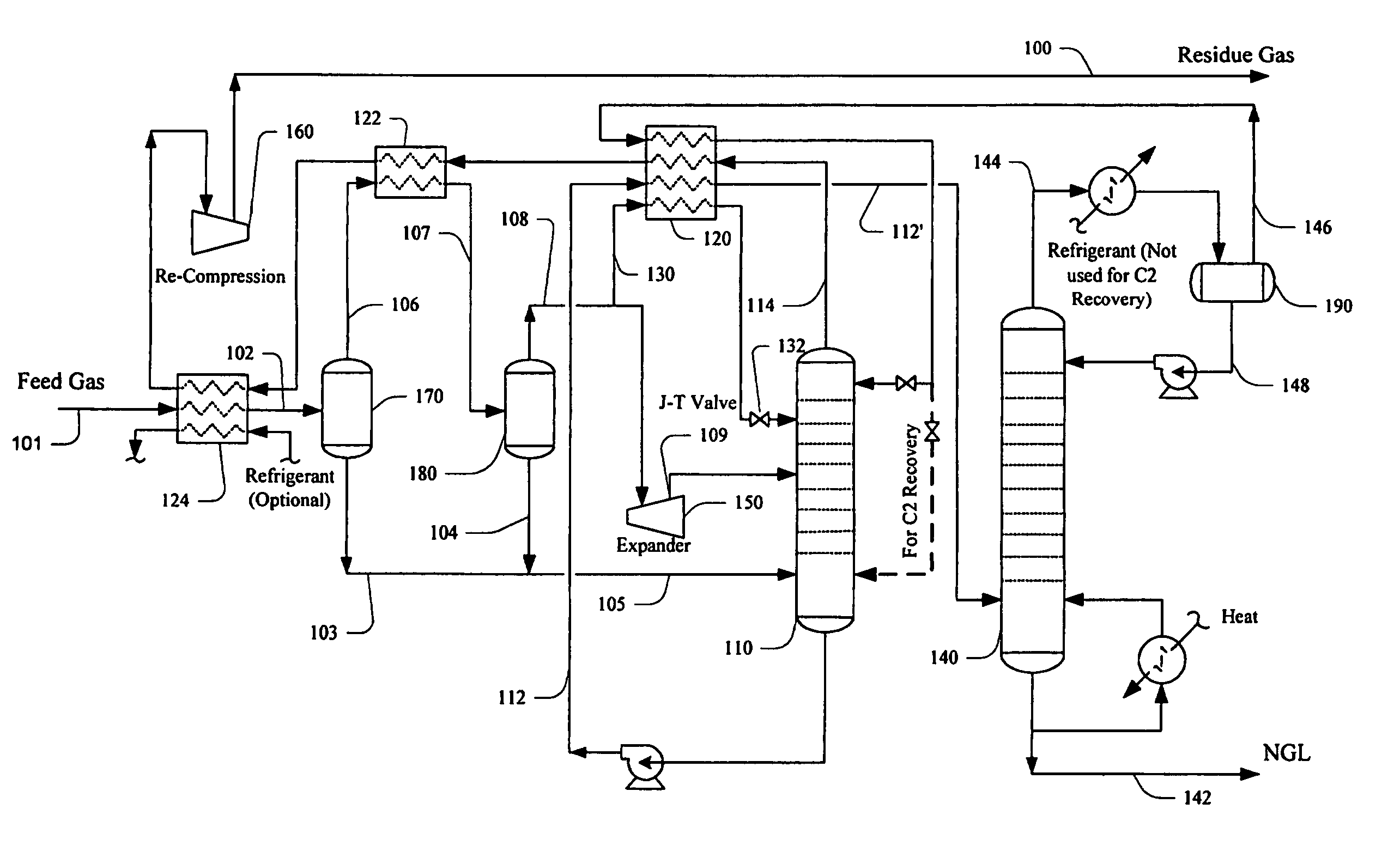
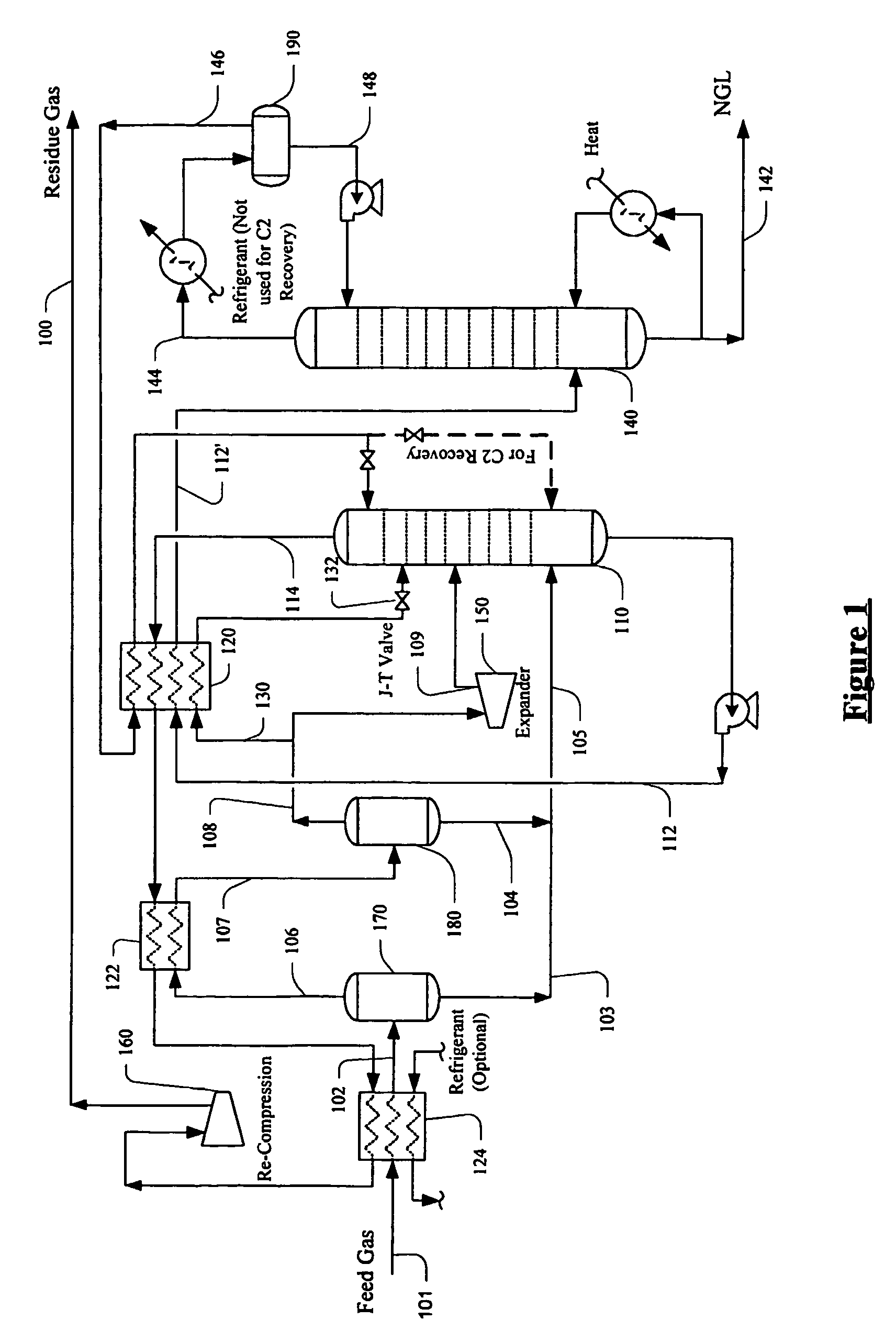
ActiveUS20060283207A1Reduce the valueReduce investmentSolidificationLiquefactionFractionationFractionating column
A process for the recovery of ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene, and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. The stream is cooled and is thereafter expanded to the fractionation tower pressure and supplied to the fractionation tower at a lower mid-column feed position. A distillation stream is withdrawn from the column below the feed point of the stream and is then directed into heat exchange relation with the tower overhead vapor stream to cool the distillation stream and condense at least a part of it, forming a condensed stream. At least a portion of the condensed stream is directed to the fractionation tower at an upper mid-column feed position. A recycle stream is withdrawn from the tower overhead after it has been warmed and compressed. The compressed recycle stream is cooled sufficiently to substantially condense it, and is then expanded to the pressure of the fractionation tower and supplied to the tower at a top column feed position. The quantities and temperatures of the feeds to the fractionation tower are effective to maintain the overhead temperature of the fractionation tower at a temperature whereby the major portion of the desired components is recovered.
Owner:UOP LLC
Ethane plus and HHH process for NGL recovery
InactiveUS7219513B1Good fractionation effectHeavy componentSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnPetrochemical
The present invention relates to methods for separating and recovering ethane, propane and heavier components from a feed gas, e.g. raw natural gas or a refinery or petroleum plant gas stream or a petrochemical plant gas stream. These methods employ a common new concept which is the use of the turbo-expander shaft compressor to generate the reflux requirement for the cryogenic absorber or distillation columns. The power of the turbo-expander which is absorbed by the shaft compressor is always high enough so that reflux generation by a specific gas compression through the expander shaft compressor and subsequent cooling, condensation and sub-cooling can always be easily maintained. The present invention allows for higher cryogenic absorber pressure and a lower demethanizer / de-ethanizer column pressure thus eliminating the common cryogenic pump at absorber bottom. The present invention ultimately results in a lower residue compression and utilities consumption. The present invention as such allows for a higher 99+% recovery of NGL from the feed gas stream.
Owner:MOSTAFA HUSSEIN MOHAMED ISMAIL
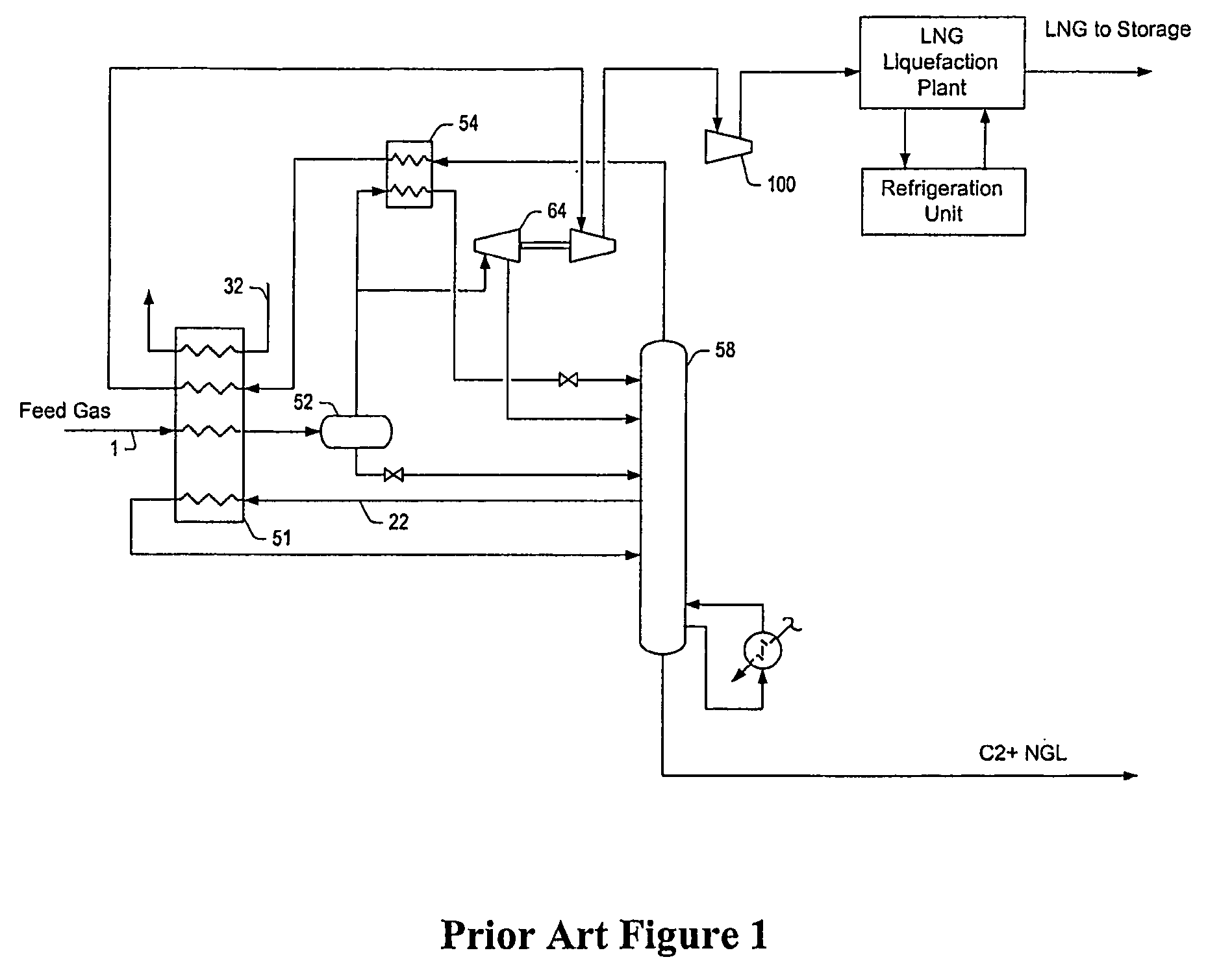
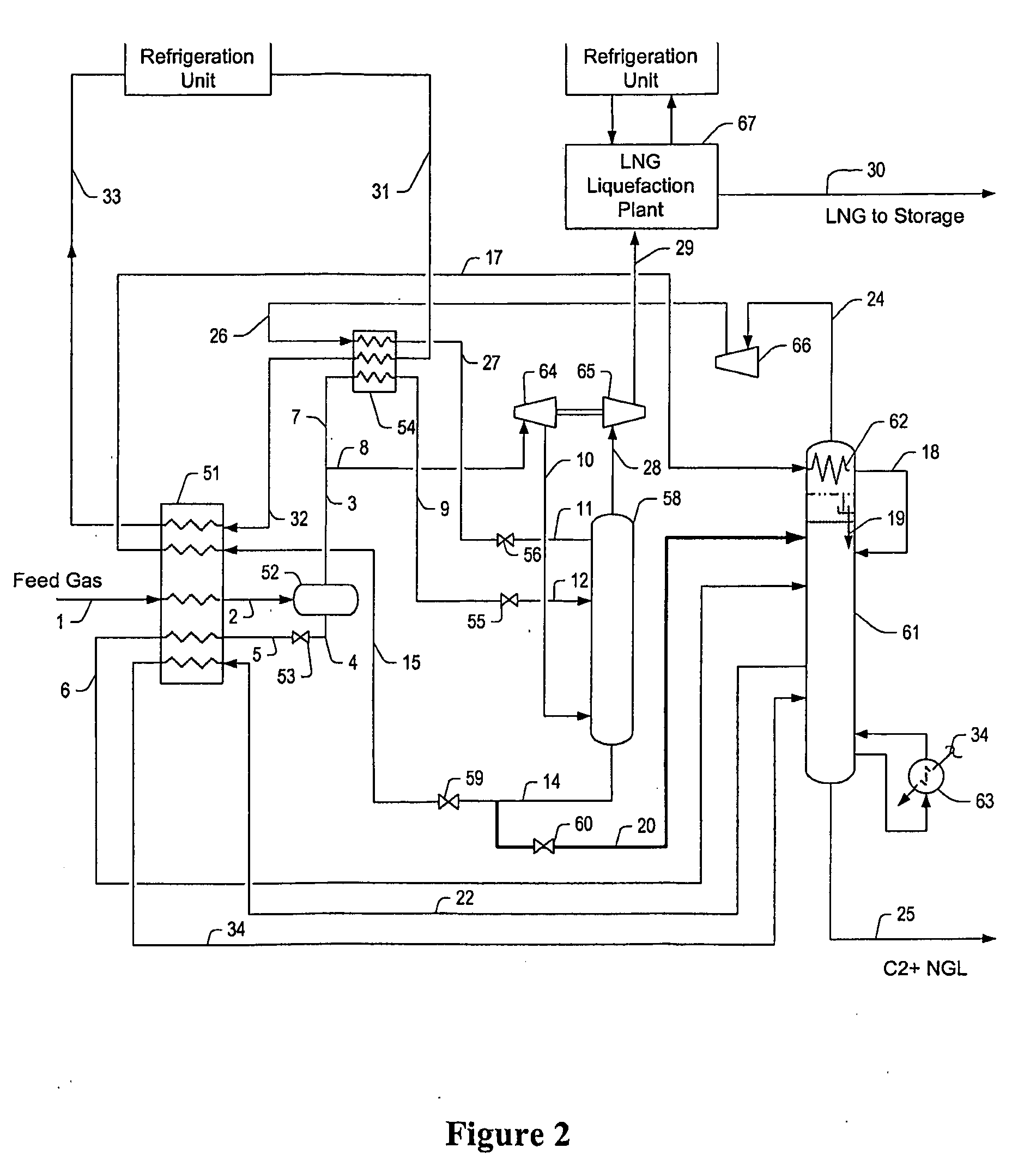
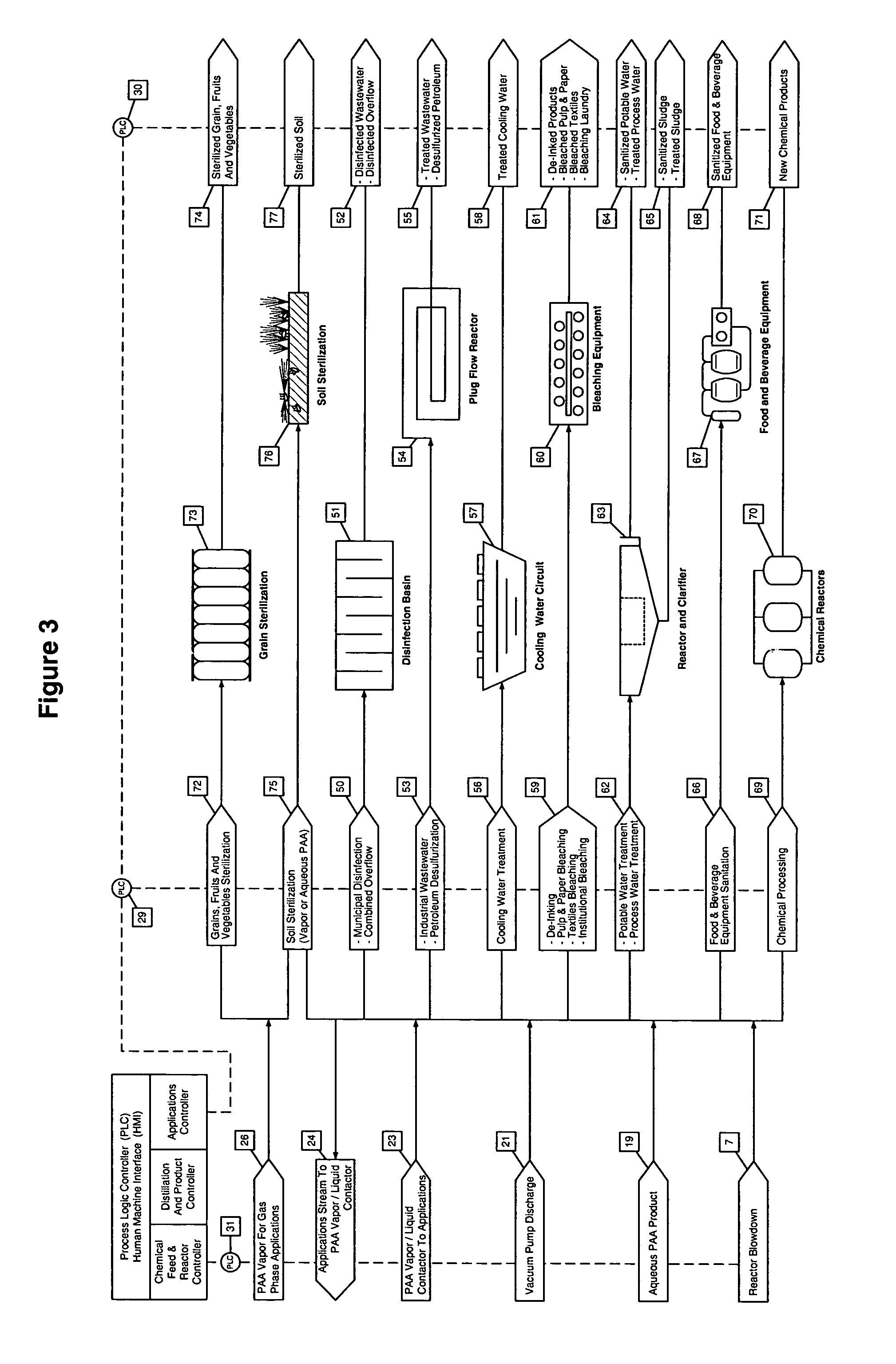
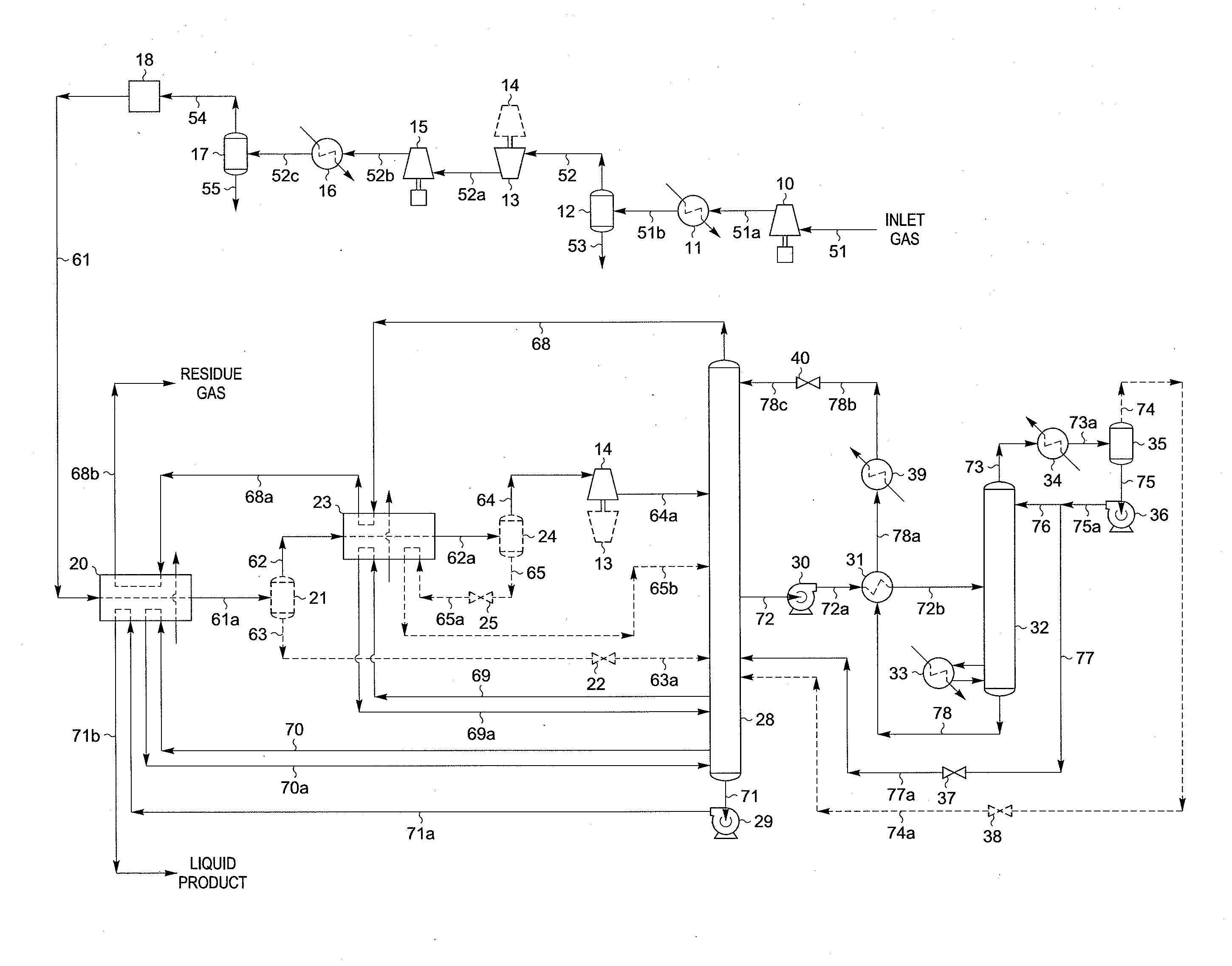
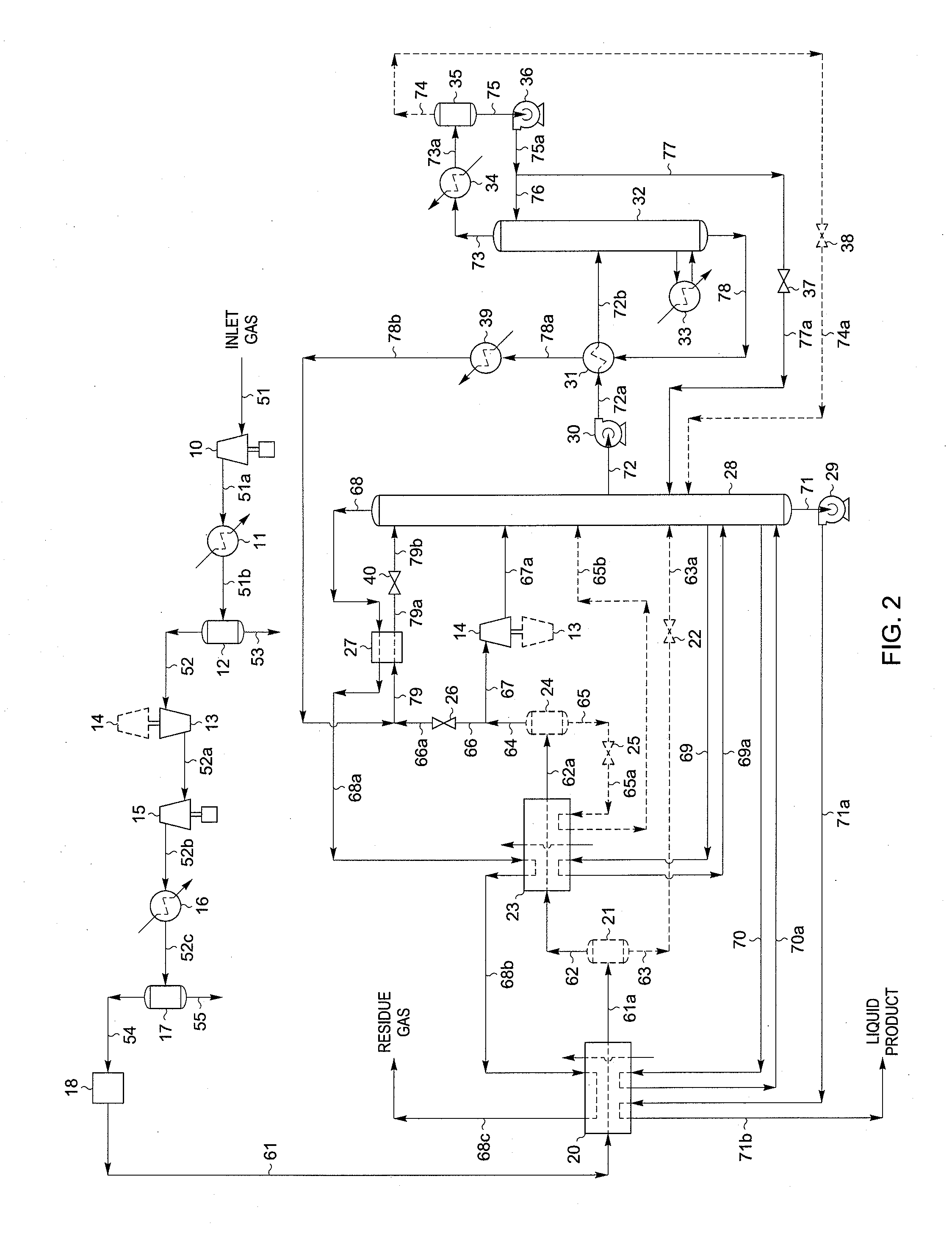
LNG production in cryogenic natural gas processing plants
A process for liquefying natural gas in conjunction with processing natural gas to recover natural gas liquids (NGL) is disclosed. In the process, the natural gas stream to be liquefied is taken from one of the streams in the NGL recovery plant and cooled under pressure to condense it. A distillation stream is withdrawn from the NGL recovery plant to provide some of the cooling required to condense the natural gas stream. The condensed natural gas stream is expanded to an intermediate pressure and supplied to a mid-column feed point on a distillation column. The bottom product from this distillation column preferentially contains the majority of any hydrocarbons heavier than methane that would otherwise reduce the purity of the liquefied natural gas, and is routed to the NGL recovery plant so that these heavier hydrocarbons can be recovered in the NGL product. The overhead vapor from the distillation column is cooled and condensed, and a portion of the condensed stream is supplied to a top feed point on the distillation column to serve as reflux. A second portion of the condensed stream is expanded to low pressure to form the liquefied natural gas stream.
Owner:ORTLOFF ENGINEERS
Hydrocarbon gas processing
A process for the recovery of propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream is disclosed. The stream is cooled and / or expanded to partially condense it, then separated to provide a first vapor stream. The first vapor stream is directed into a contacting device whereby vapors and liquids are formed. The liquids are directed to a distillation column operating at lower pressure wherein a second vapor stream is separated to recover a product containing the major portion of the C3 components and heavier hydrocarbon components. The second vapor stream is directed into heat exchange relation with the vapors to cool the second vapor stream and condense at least a part of it, forming a condensed stream. At least a portion of the condensed stream is directed to the contacting device to intimately contact the first vapor stream; the remaining portion (if any) of the condensed stream can be supplied to the distillation column as its top feed. The quantities and temperatures of the feeds to the contacting device and the distillation column are effective to maintain the overhead temperatures of the contacting device and the distillation column at temperatures whereby the major portion of the desired components is recovered.
Owner:ELCOR CORP
Combined air separation natural gas liquefaction plant
ActiveUS7143606B2Increase power consumptionIncrease the number ofSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnProcess engineering
In an integrated process and apparatus for the separation of air by cryogenic distillation and liquefaction of natural gas in which at least part of the refrigeration required to liquefy the natural gas is derived from at least one cryogenic air distillation plant comprising a main heat exchanger (7) and distillation columns (15, 17), wherein the natural gas (25) liquefies by indirect heat exchange in a heat exchanger (7, 32, 34) with a cold fluid (21, 26), the cold fluid being sent to the heat exchanger at least partially in liquid form and undergoing at least a partial vaporisation in the heat exchanger.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Method using solar energy, microwaves and plasmas to produce a liquid fuel and hydrogen from biomass or fossil coal
ActiveUS20100258429A1Promote gasificationImproving thermal inertiaElectrical coke oven heatingSolar heating energySludgeFractionating column
A system uses thermal solar energy coupled with microwaves and plasma for producing carbon monoxide (CO) and dihydrogen (H2) from carbonated compounds (biomass, domestic waste, sludge from waste water, fossil coal), wherein the obtained gaseous mixture yields, amongst others, hydrocarbon fuels (olefins, paraffin), esters, and alcohols via a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. In a first step the carbonated compounds are roasted and pyrolized to produce char and dry coal, and a mixture of superheated gases containing CO2, steam, tars and non-condensable volatile materials. The method includes in a second step, and from the pyrolyis products (char or coal, gas mixture), generating a syngas substantially containing a mixture of carbon monoxide and dihydrogen, the mixture being used in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis units. After the Fischer-Tropsch step, the synthesis products are separated in a distillation column after heating in solar furnaces of mixed furnaces (solar / microwave).
Owner:UGOLIN NICOLAS
Integrating a methanol to olefin reaction system with a steam cracking system
InactiveUS20050038304A1Shorten the counting processReduce the amount requiredThermal non-catalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystOxygenateFractionating column
The present invention provides an integrated system for producing ethylene and propylene from an oxygenate to olefin (OTO) reaction system and a steam cracking system. In a preferred embodiment, at least a portion of an effluent stream from a steam cracking furnace is combined with at least a portion of an effluent stream from an OTO reaction system. Preferably the combined effluent stream is processed by one or more quench units, compression units, and / or fractionation columns. By integrating a steam cracking system with an OTO reaction system, equipment count can be reduced at a significant commercial savings. Compressor efficiency per pound of ethylene and propylene can also be advantageously increased over conventional steam cracking systems. Moreover, the amount of pollutants produced per pound of ethylene and propylene produced can be significantly reduced over the amount of pollutants produced per pound of ethylene and propylene produced in a steam cracking system.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Co-current vapor-liquid contacting apparatus
ActiveUS7424999B2Easily redistributedIncrease capacityCombination devicesLiquid degasificationVapor liquidFractionating column
Owner:UOP LLC
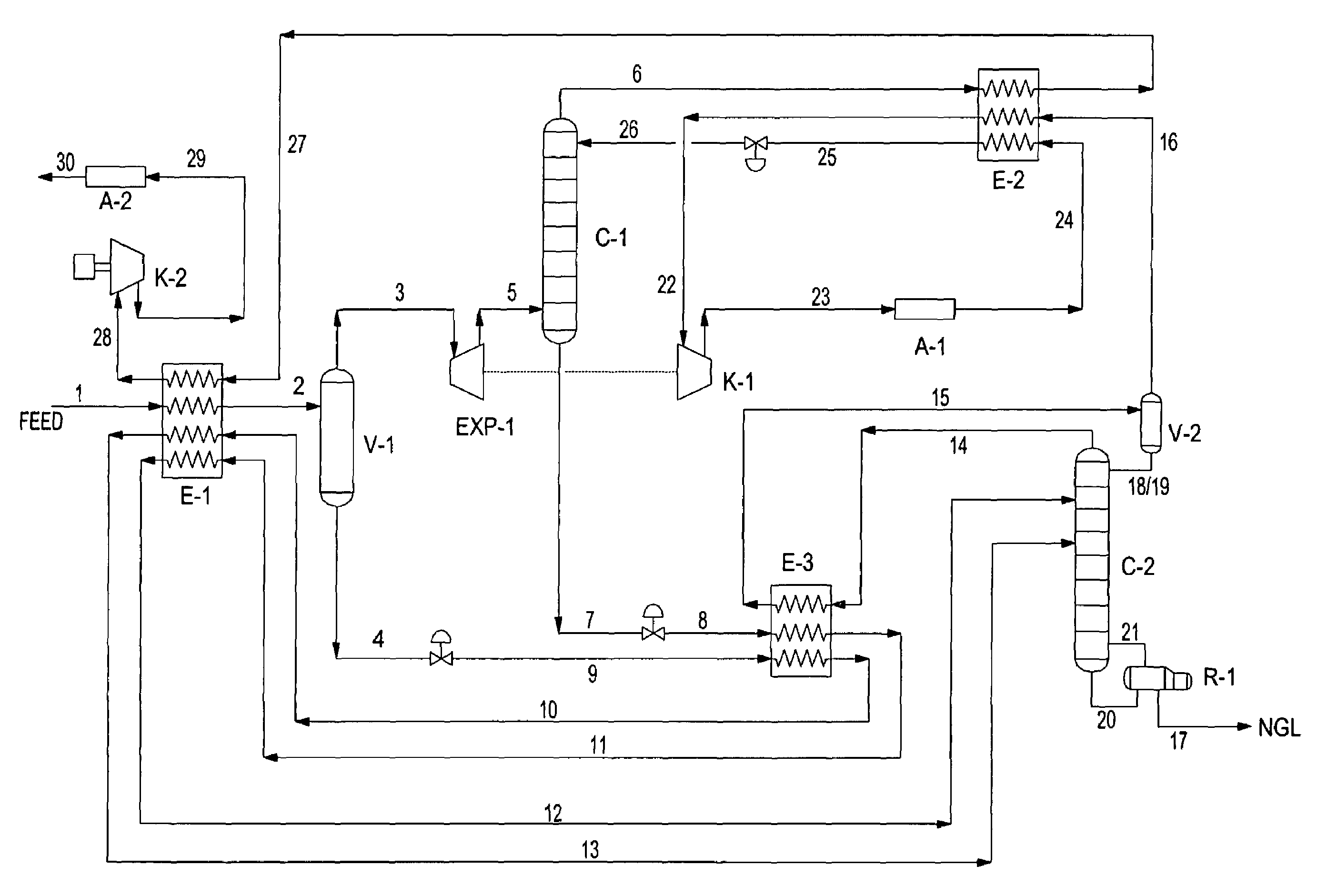
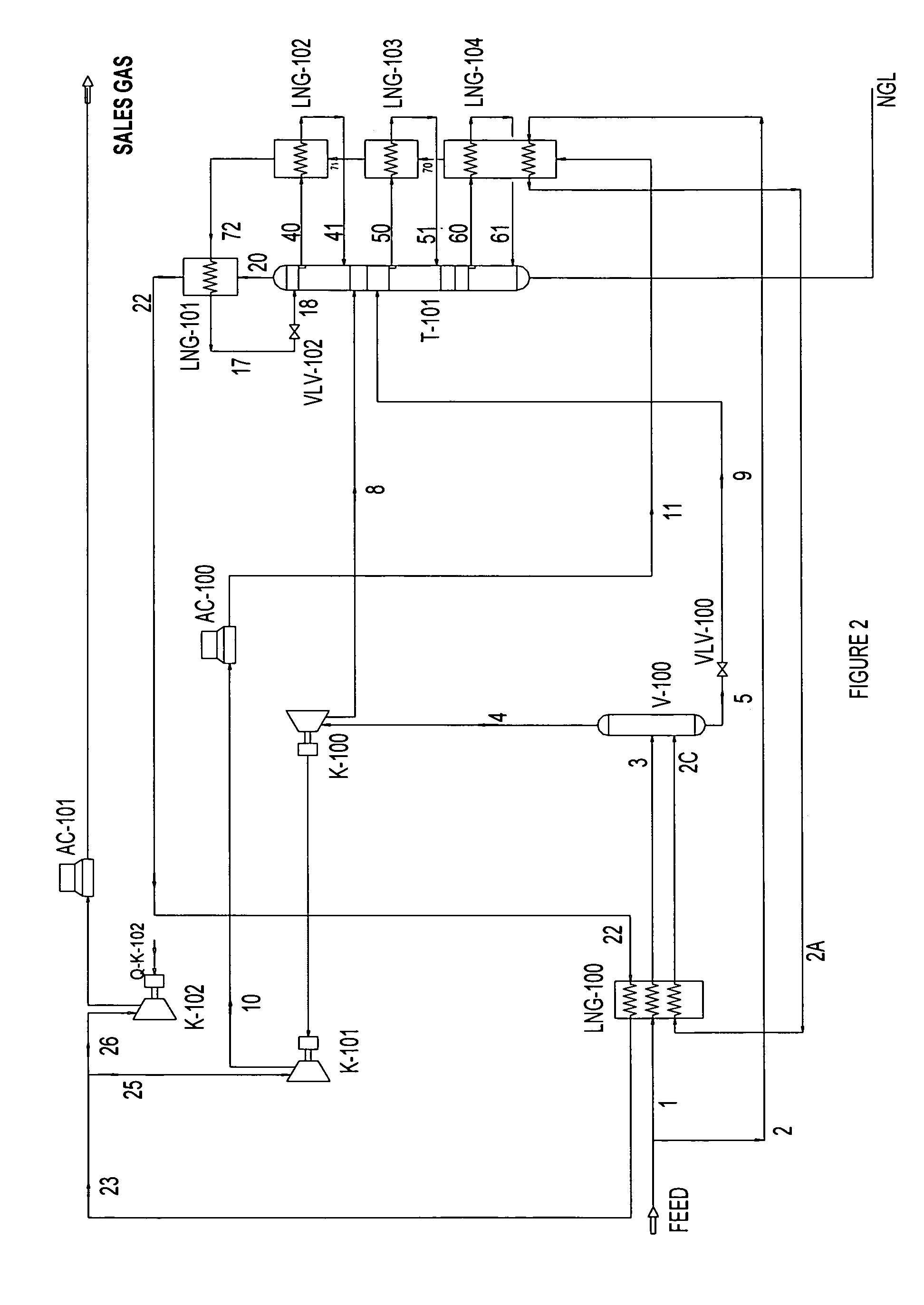
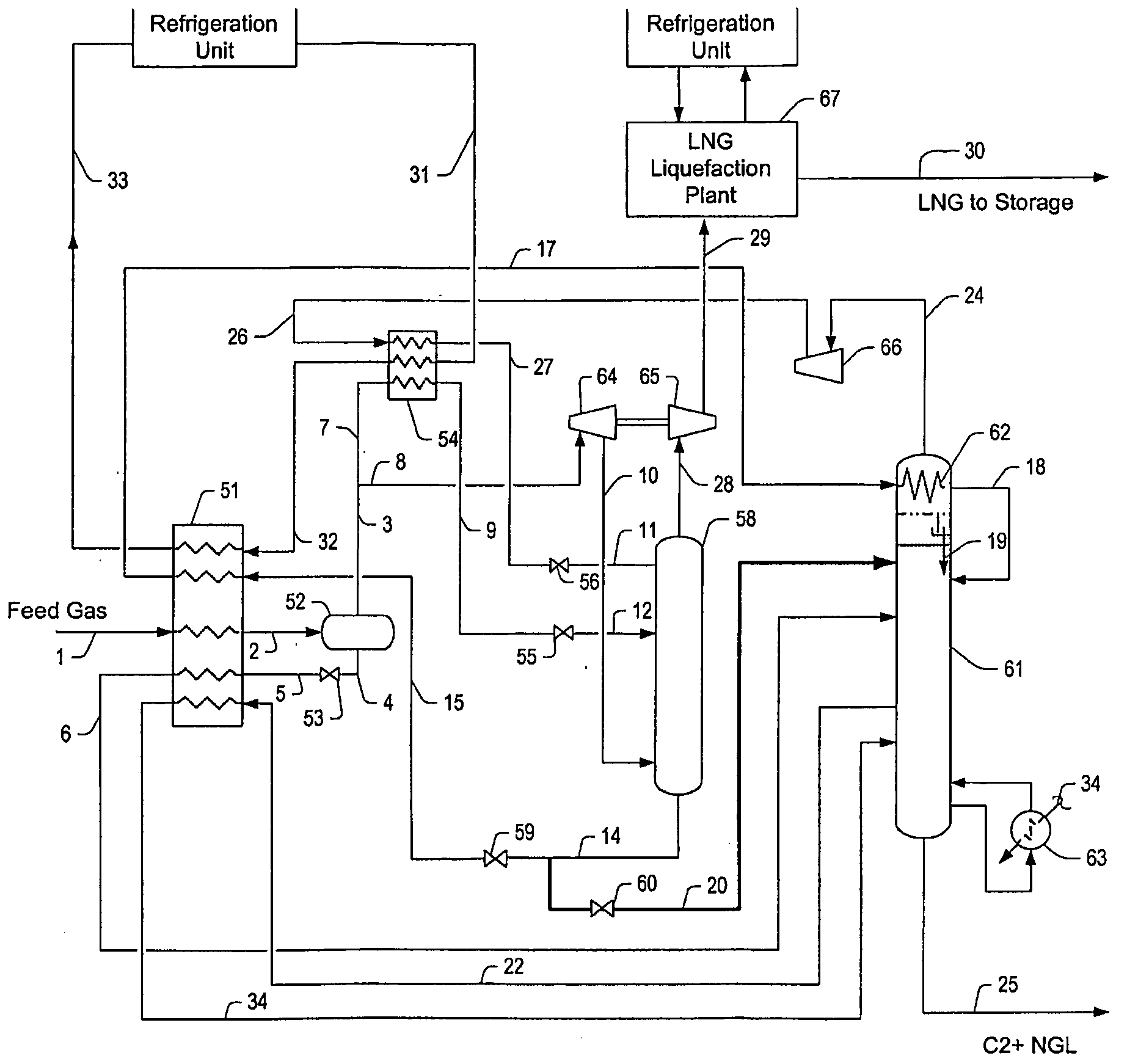
Intergrated Ngl Recovery and Lng Liquefaction
Contemplated plants include a refluxed absorber and a distillation column, wherein the absorber is operated at a higher pressure than the distillation column to thereby produce a cryogenic pressurized lean gas. The lean gas is further compressed to a pressure suitable for liquefaction using energy from feed gas vapor expansion. Desired separation of C2 products is ensured by temperature control of the absorber and distillation column using flow ratios of various streams within the plant, and by dividing the separation process into two portions at different pressures.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
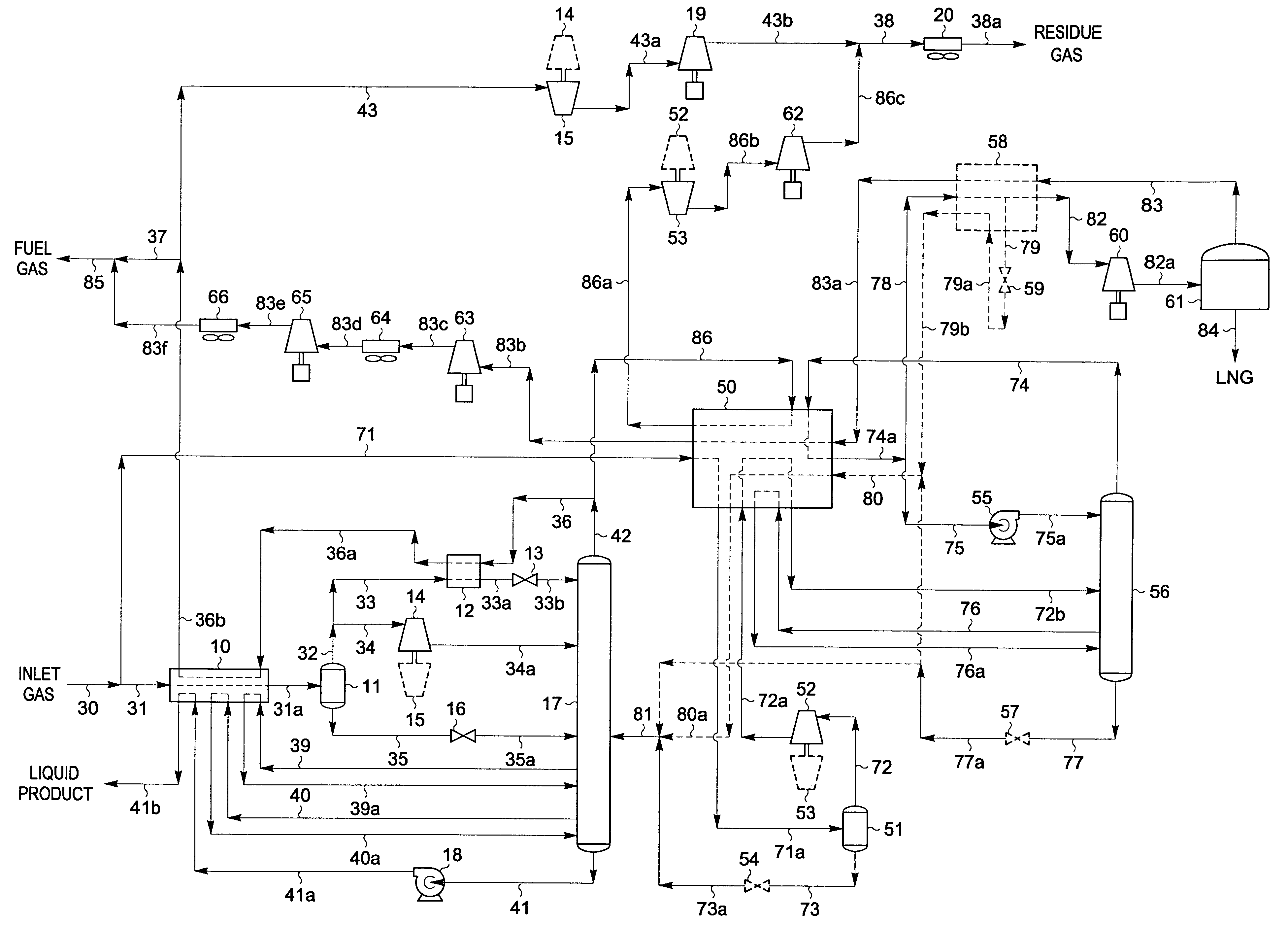
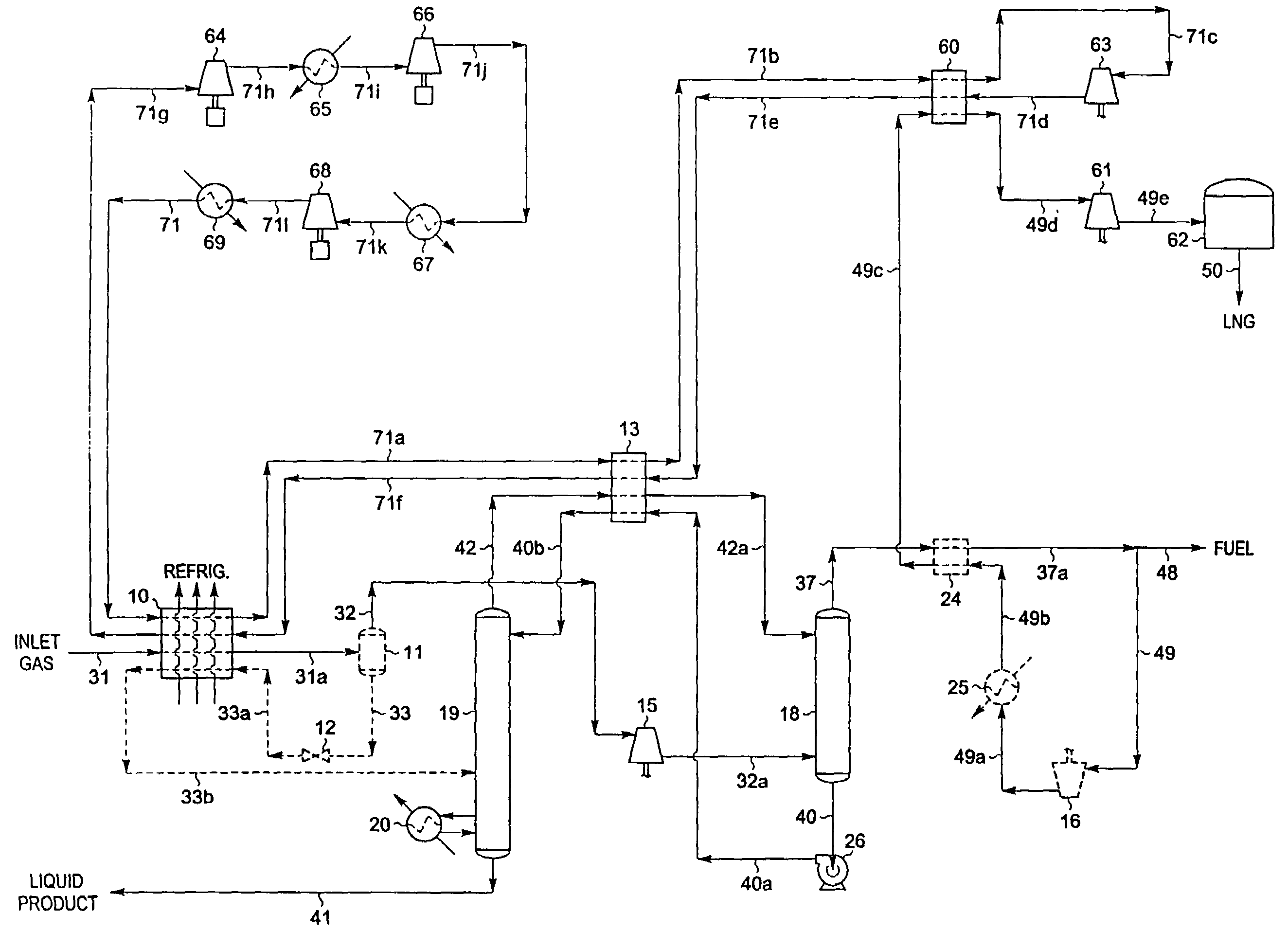
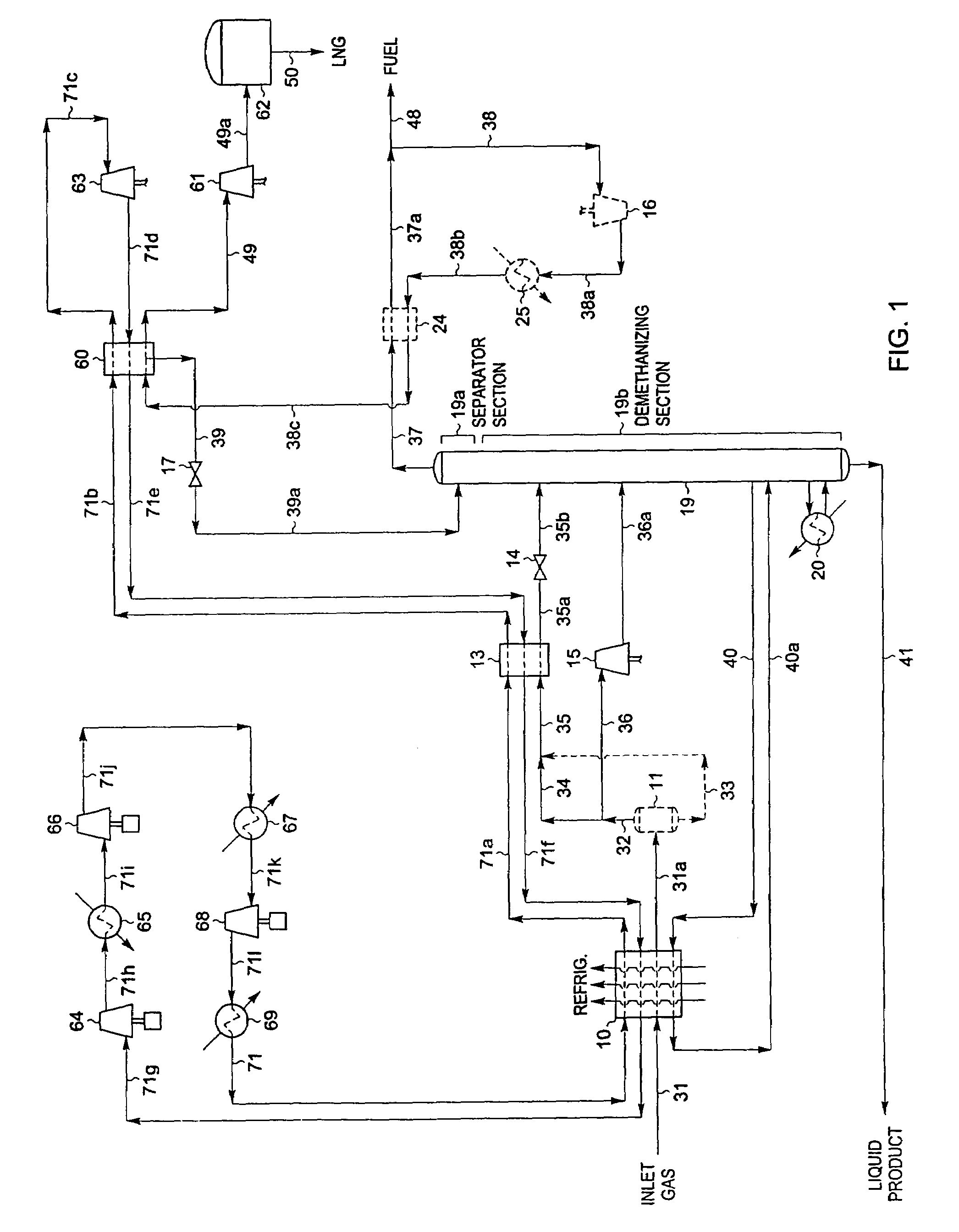
Integrated NGL recovery in the production of liquefied natural gas
Process for the liquefaction of natural gas and the recovery of components heavier than methane wherein natural gas is cooled and separated in a first distillation column into an overhead vapor enriched in methane and a bottoms stream enriched in components heavier than methane, wherein the first distillation column utilizes a liquefied methane-containing reflux stream. This reflux stream may be provided by a condensed portion of the overhead vapor or a portion of totally condensed overhead vapor that is subsequently warmed. The bottoms stream may be separated in one or more additional distillation columns to provide one or more product streams, any of which are partially or totally withdrawn as recovered hydrocarbons. A stream of unrecovered liquid hydrocarbons may be combined with either the condensed portion of the overhead vapor or a portion of totally condensed overhead vapor that is subsequently warmed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Liquefied natural gas processing
Owner:UOP LLC +1
Combined cryogenic distillation and PSA for argon production
ActiveUS7501009B2Improvements in the refining of crude argonSpeed up the processSolidificationLiquefactionParticulatesFiltration
A method and apparatus for producing high purity argon by combined cryogenic distillation and adsorption technologies is disclosed. Crude argon from a distillation column or a so-called argon column is passed to a system of adsorption vessels for further purification. Depressurization gas from adsorption is introduced back, in a controlled manner, to the distillation column and / or a compressor or other means for increasing pressure. Particulate filtration and getter purification may optionally be used.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
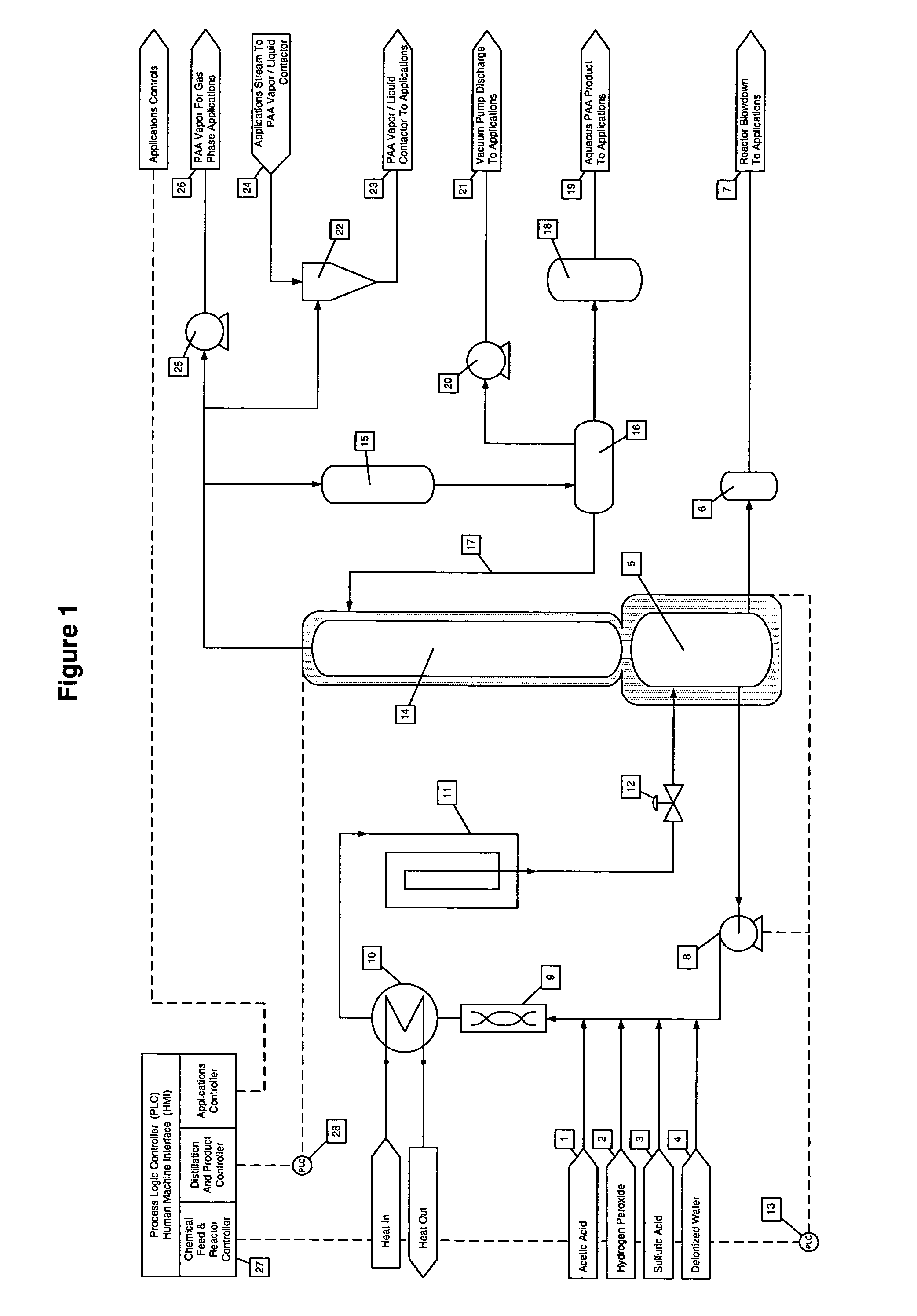
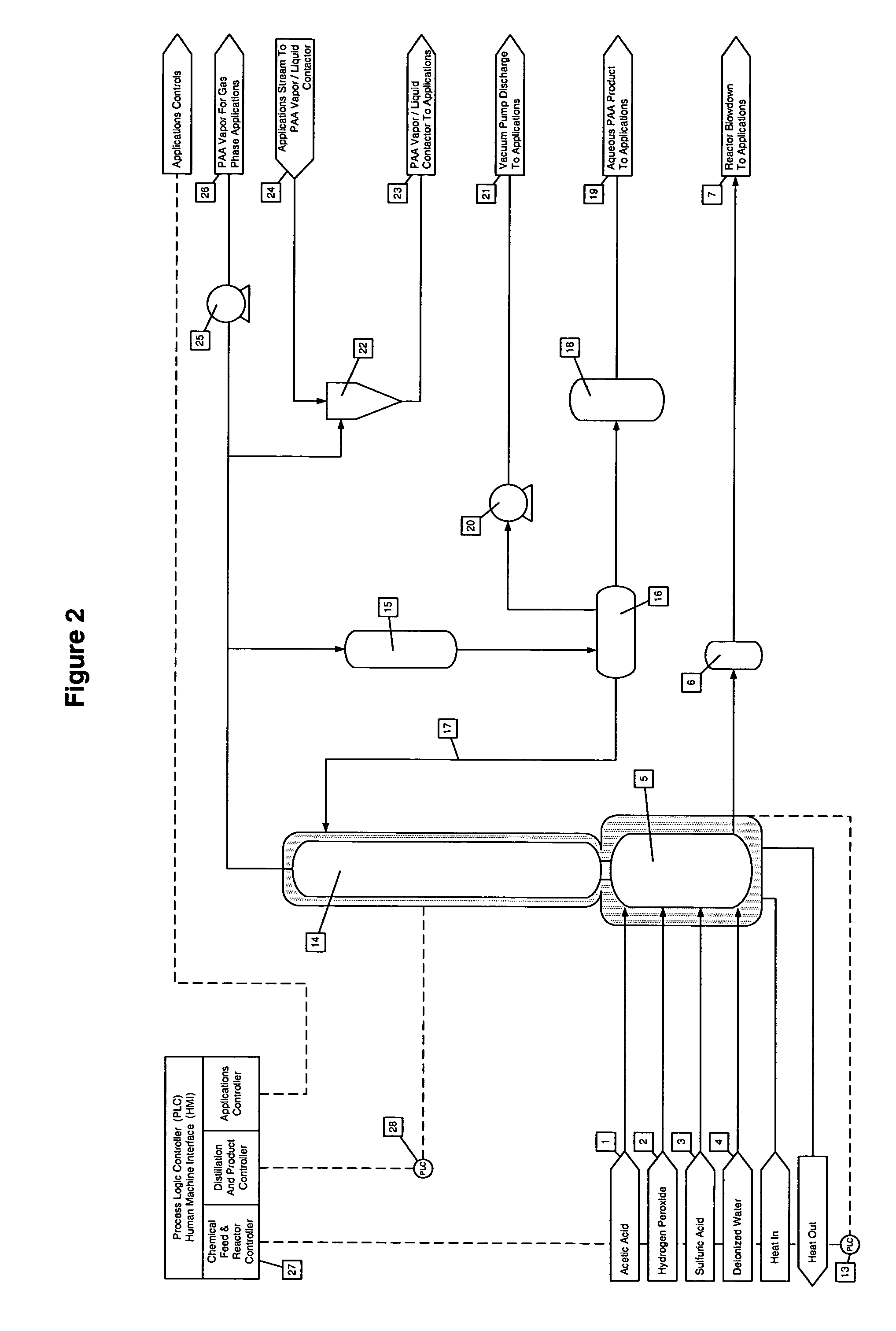
Continuous process for on-site and on-demand production of aqueous peracteic acid
ActiveUS7012154B2Low costSmall inventoryOrganic compound preparationOther chemical processesAcetic acidGas phase
Owner:ADVANCED PAA SOLUTIONS INC
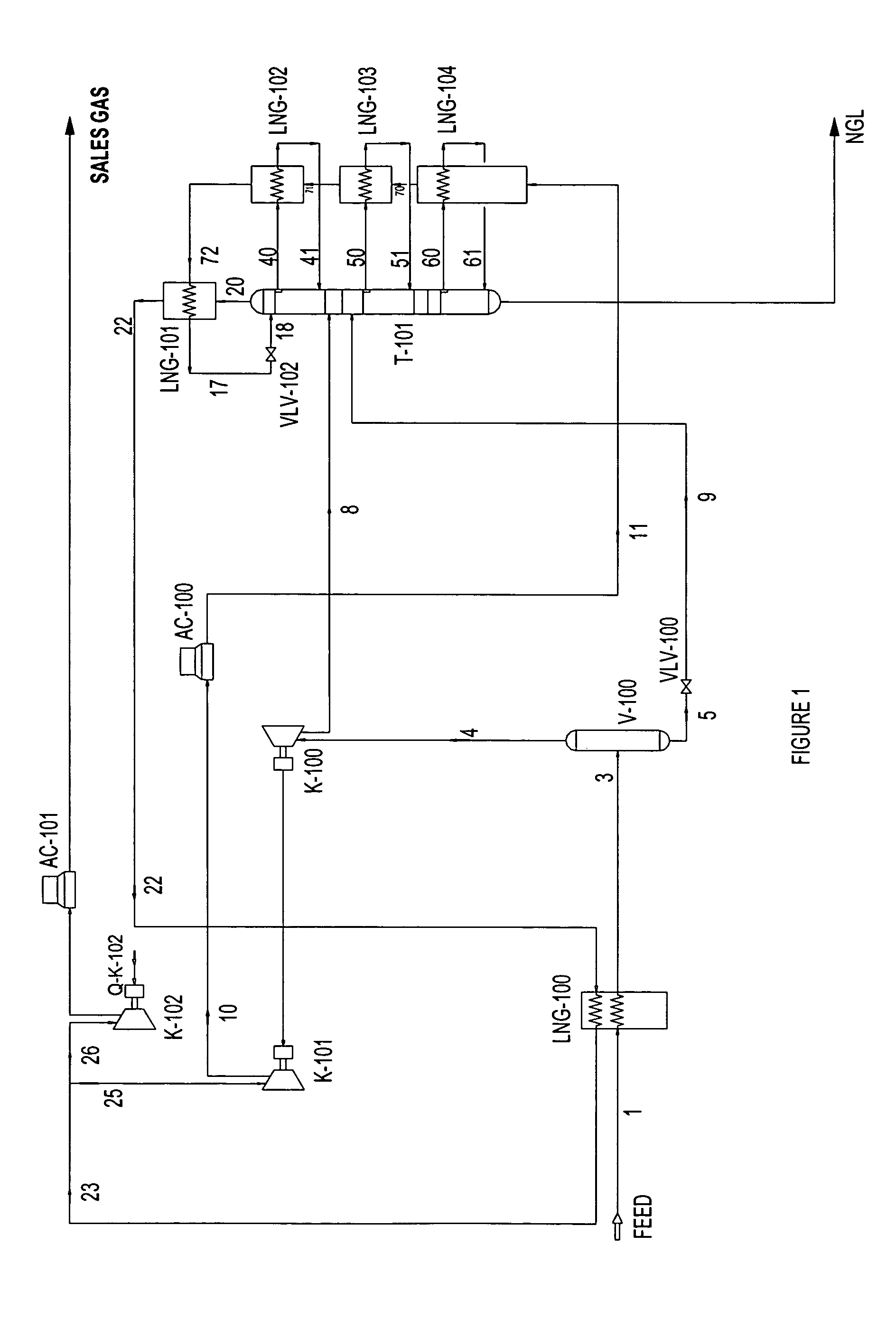
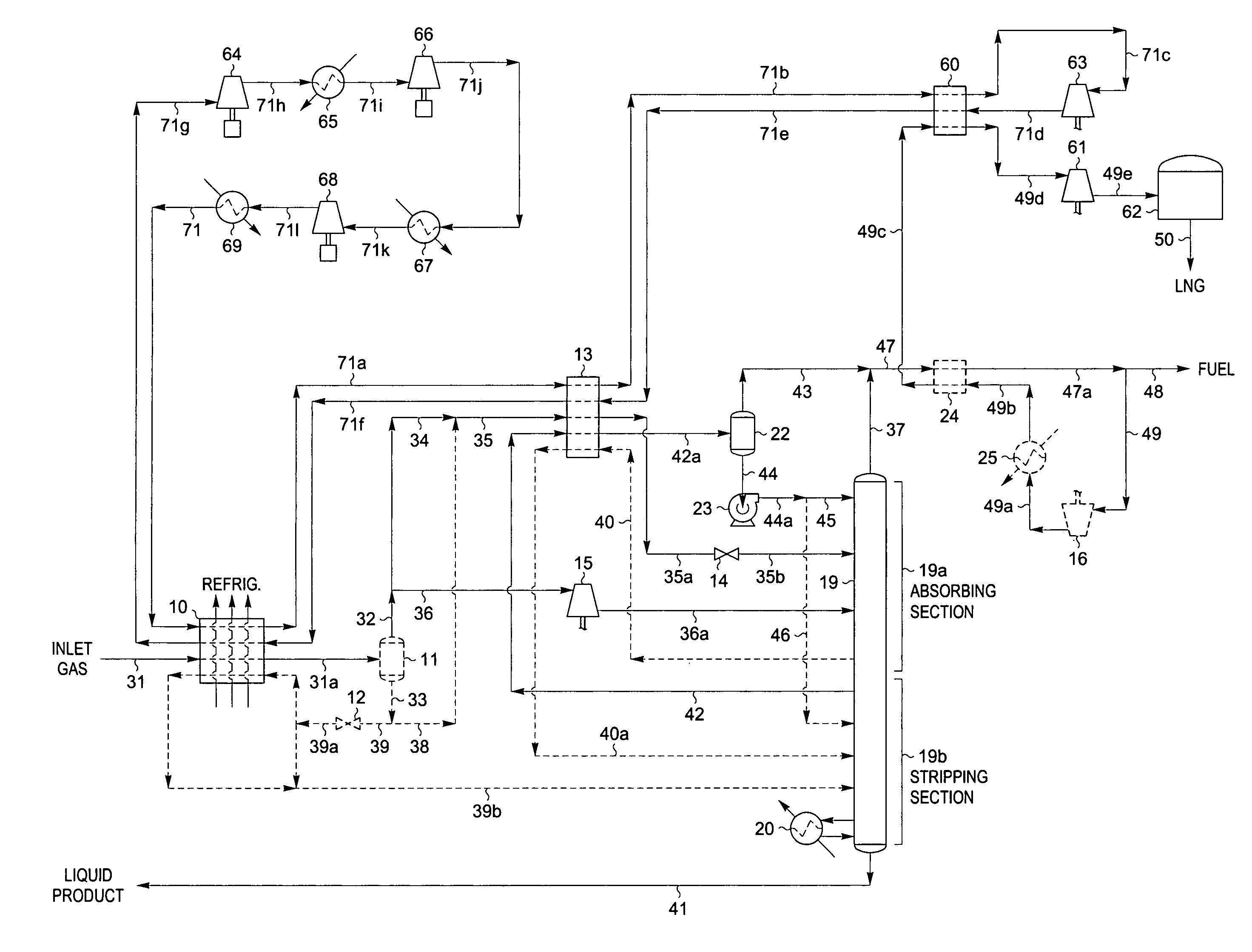
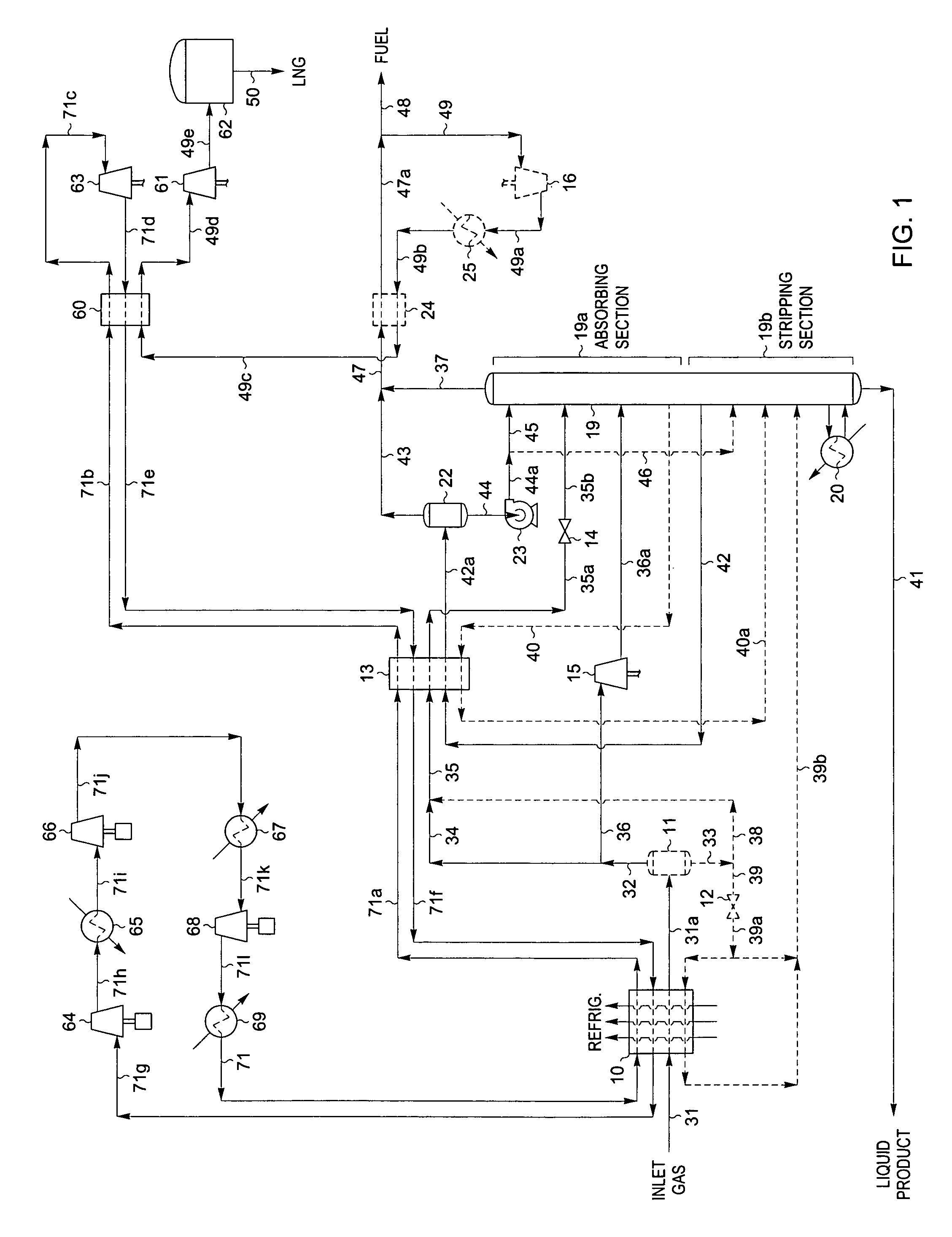
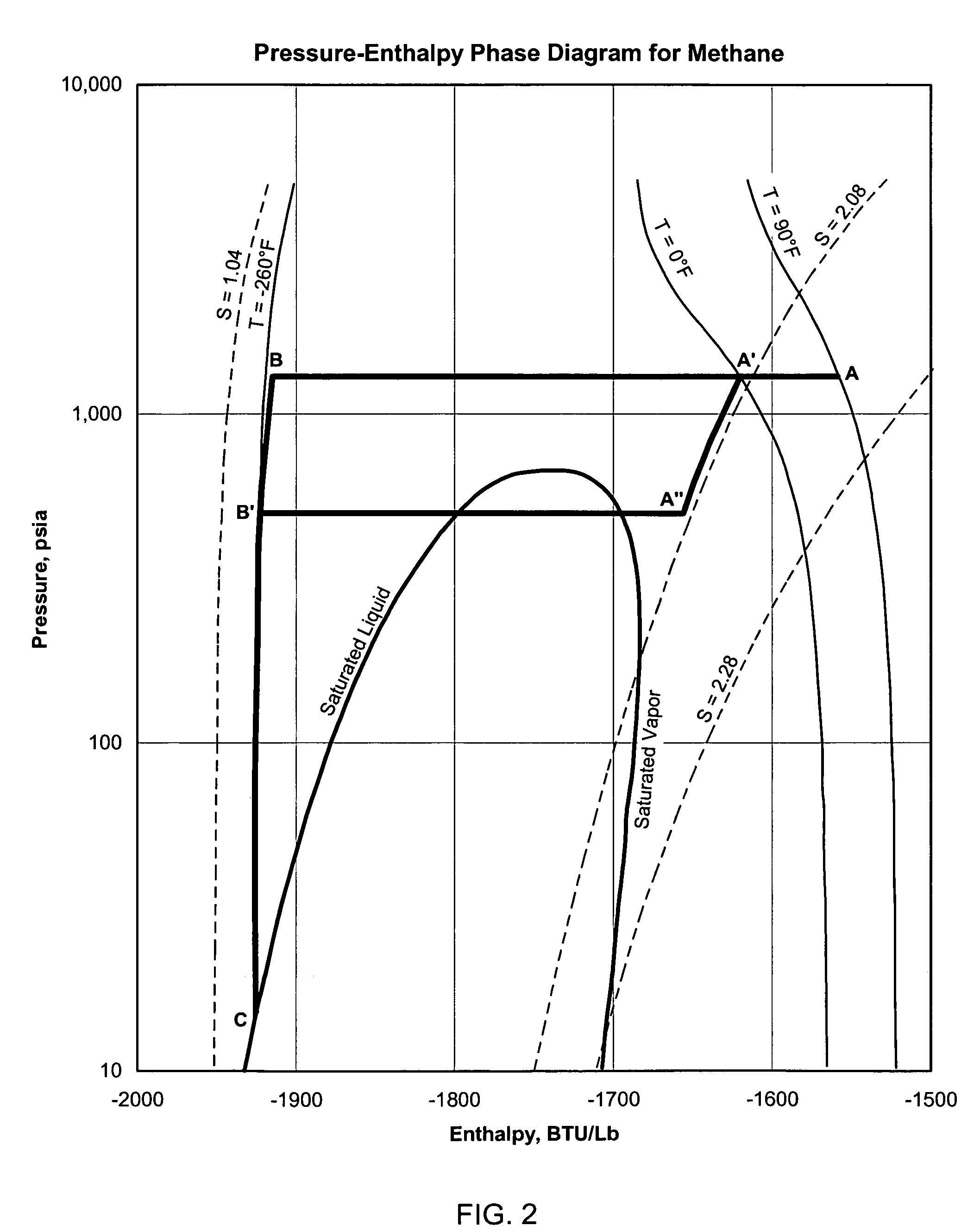
Natural gas liquefaction
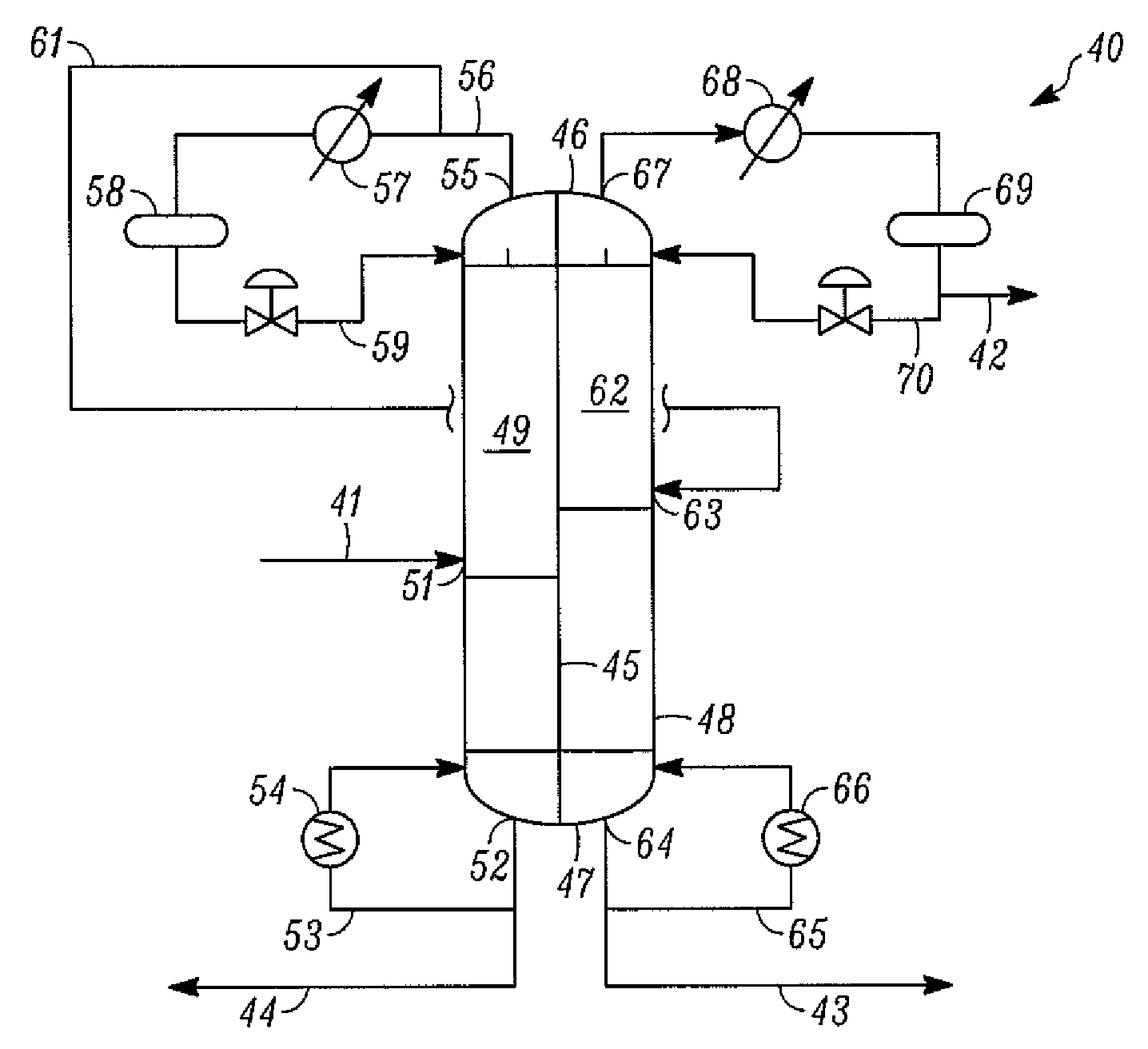
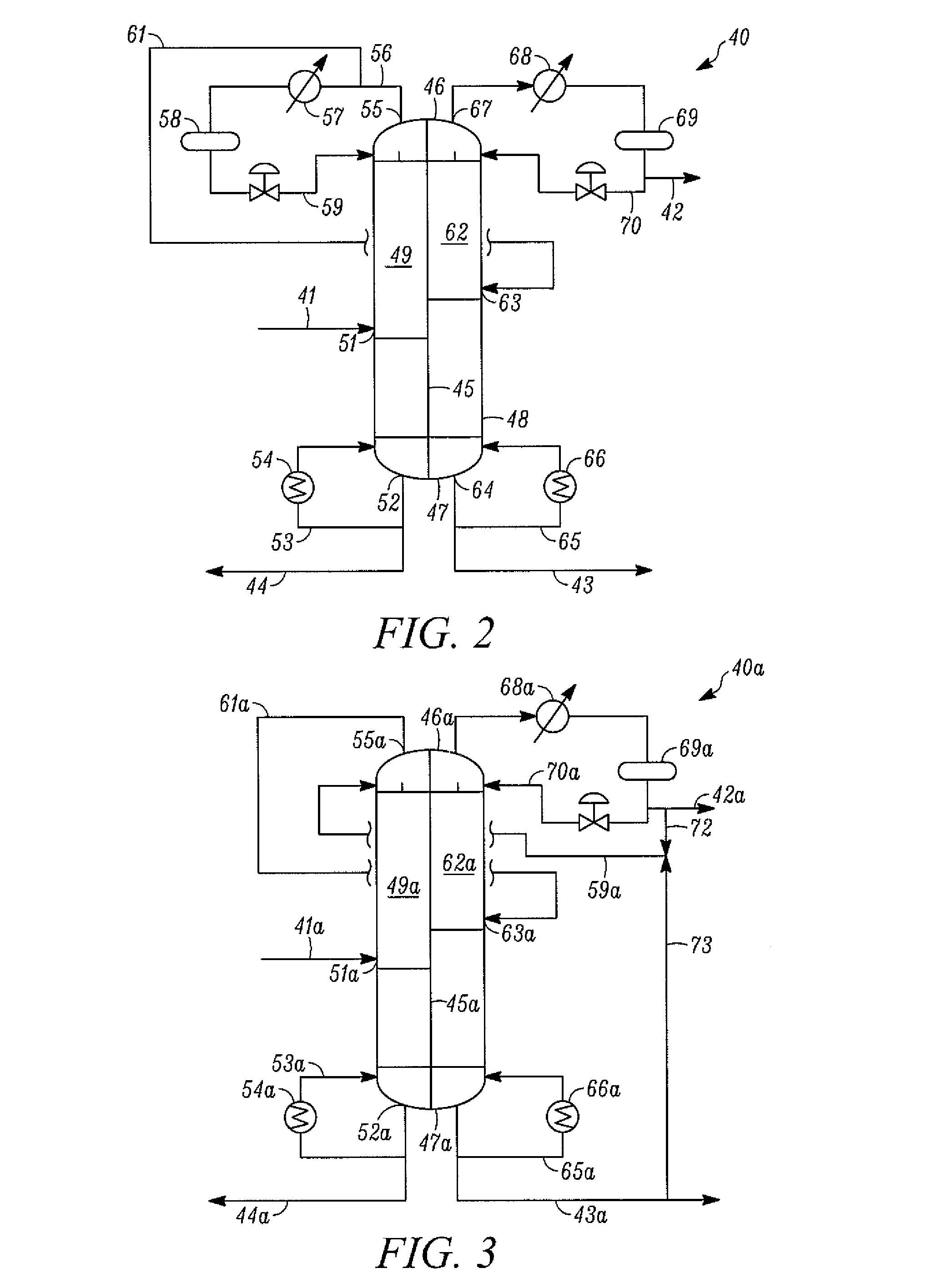
A process for liquefying natural gas in conjunction with producing a liquid stream containing predominantly hydrocarbons heavier than methane is disclosed. In the process, the natural gas stream to be liquefied is partially cooled and divided into first and second streams. The first stream is further cooled to condense substantially all of it, expanded to an intermediate pressure, and then supplied to a distillation column at a first mid-column feed position. The second stream is also expanded to intermediate pressure and is then supplied to the column at a second lower mid-column feed position. A distillation stream is withdrawn from the column below the feed point of the second stream and is cooled to condense at least a part of it, forming a reflux stream. At least a portion of the reflux stream is directed to the distillation column as its top feed. The bottom product from this distillation column preferentially contains the majority of any hydrocarbons heavier than methane that would otherwise reduce the purity of the liquefied natural gas. The residual gas stream from the distillation column is compressed to a higher intermediate pressure, cooled under pressure to condense it, and then expanded to low pressure to form the liquefied natural gas stream.
Owner:UOP LLC
Twin reflux process and configurations for improved natural gas liquids recovery
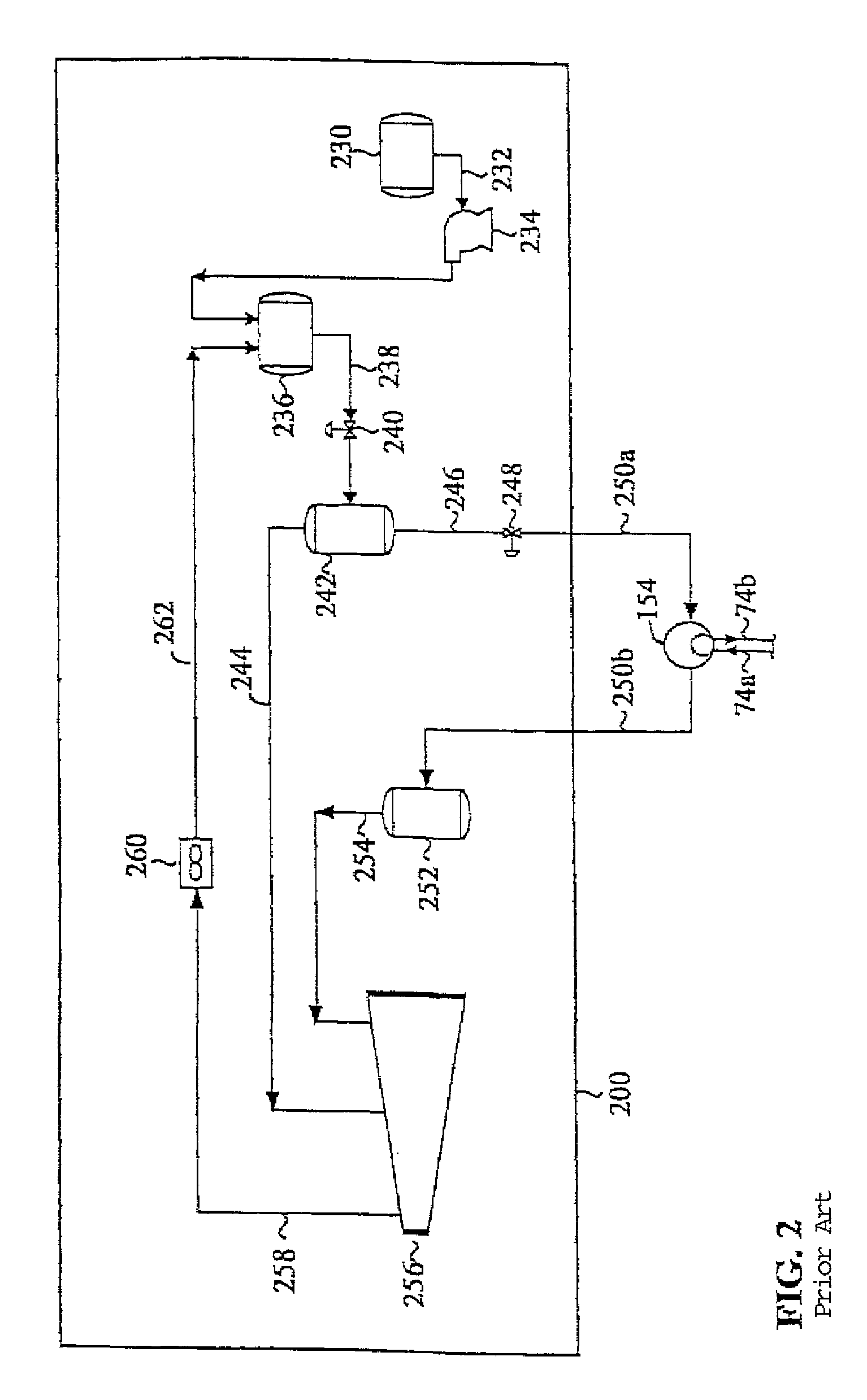
InactiveUS7051553B2Improve throughputReduce pressureSolidificationLiquefactionRefluxFractionating column
A two-column NGL recovery plant includes an absorber (110) and a distillation column (140) in which the absorber (110) receives two cooled reflux streams, wherein one reflux stream (107) comprises a vapor portion of the NGL and wherein the other reflux stream (146) comprises a lean reflux provided by the overhead (144) of the distillation column (140). Contemplat configurations are especially advantageous in a upgrade of an existing NGL plant and typically exhibit C3 recovery of at least 99% and C2 recovery of at least 90%.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
Natural gas liquefaction
A process for liquefying natural gas in conjunction with producing a liquid stream containing predominantly hydrocarbons heavier than methane is disclosed. In the process, the natural gas stream to be liquefied is partially cooled, expanded to an intermediate pressure, and supplied to a distillation column. The bottom product from this distillation column preferentially contains the majority of any hydrocarbons heavier than methane that would otherwise reduce the purity of the liquefied natural gas. The residual gas stream from the distillation column is compressed to a higher intermediate pressure, cooled under pressure to condense it, and then expanded to low pressure to form the liquefied natural gas stream.
Owner:ORTLOFF ENGINEERS
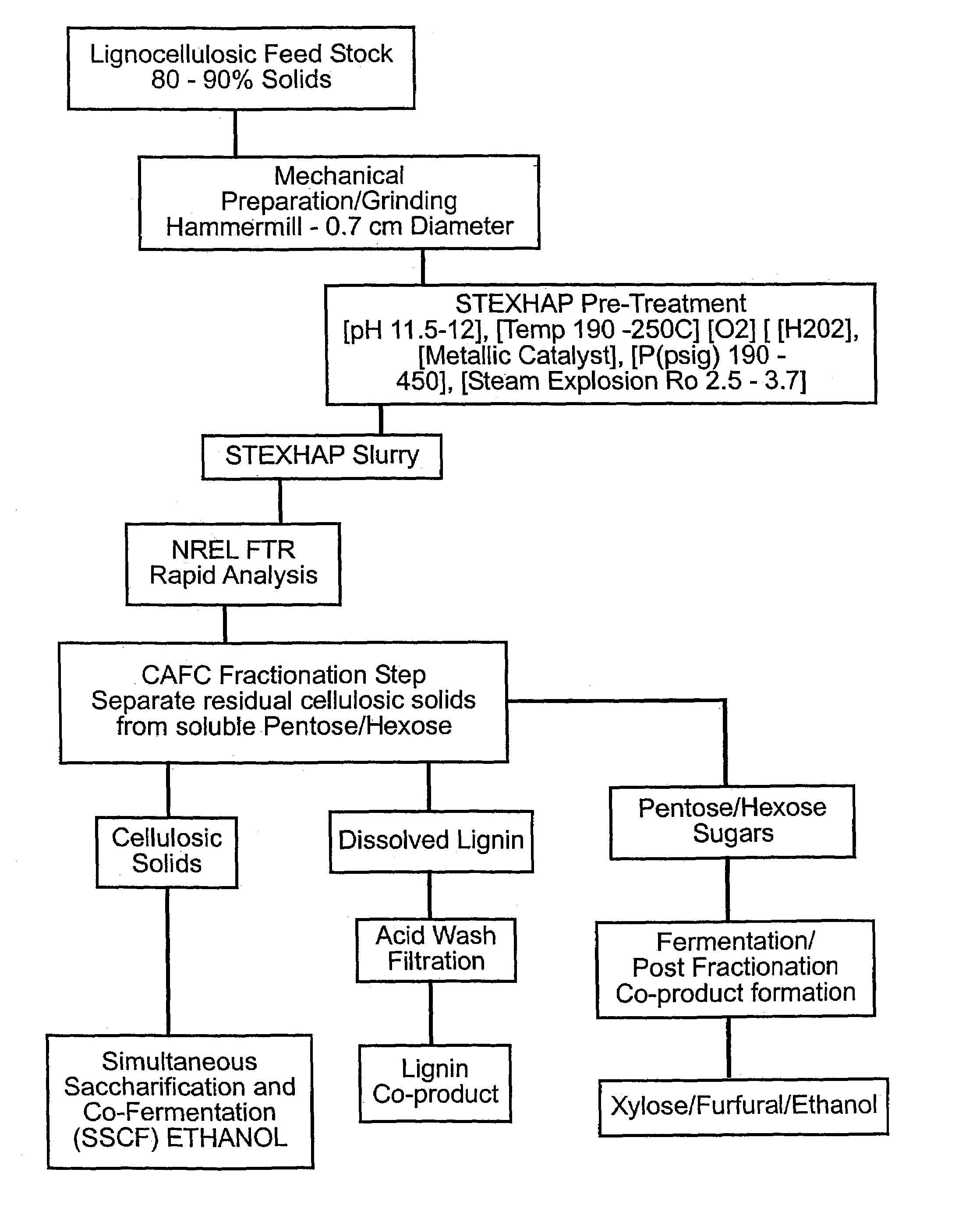
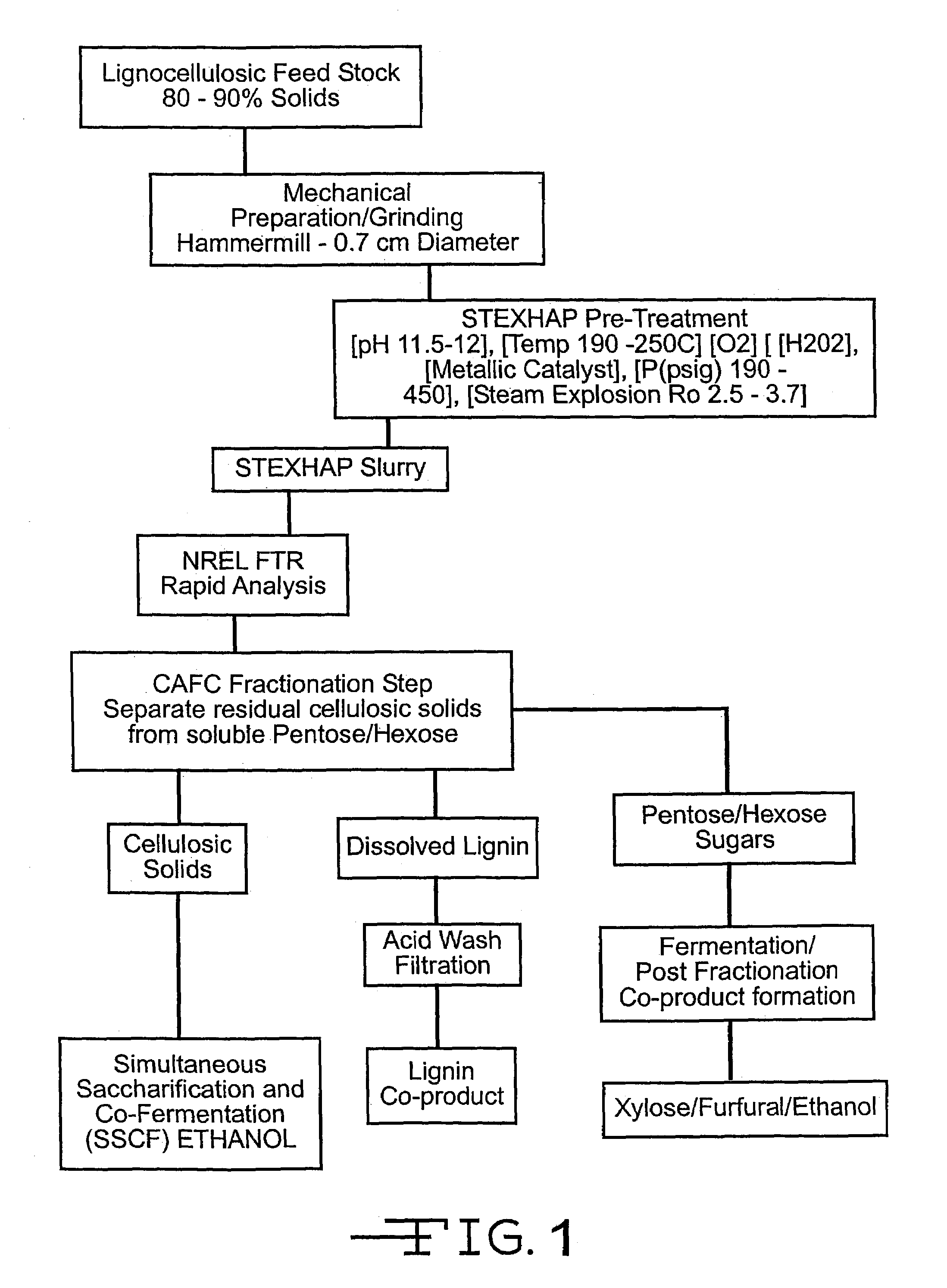
Process of treating lignocellulosic material to produce bio-ethanol
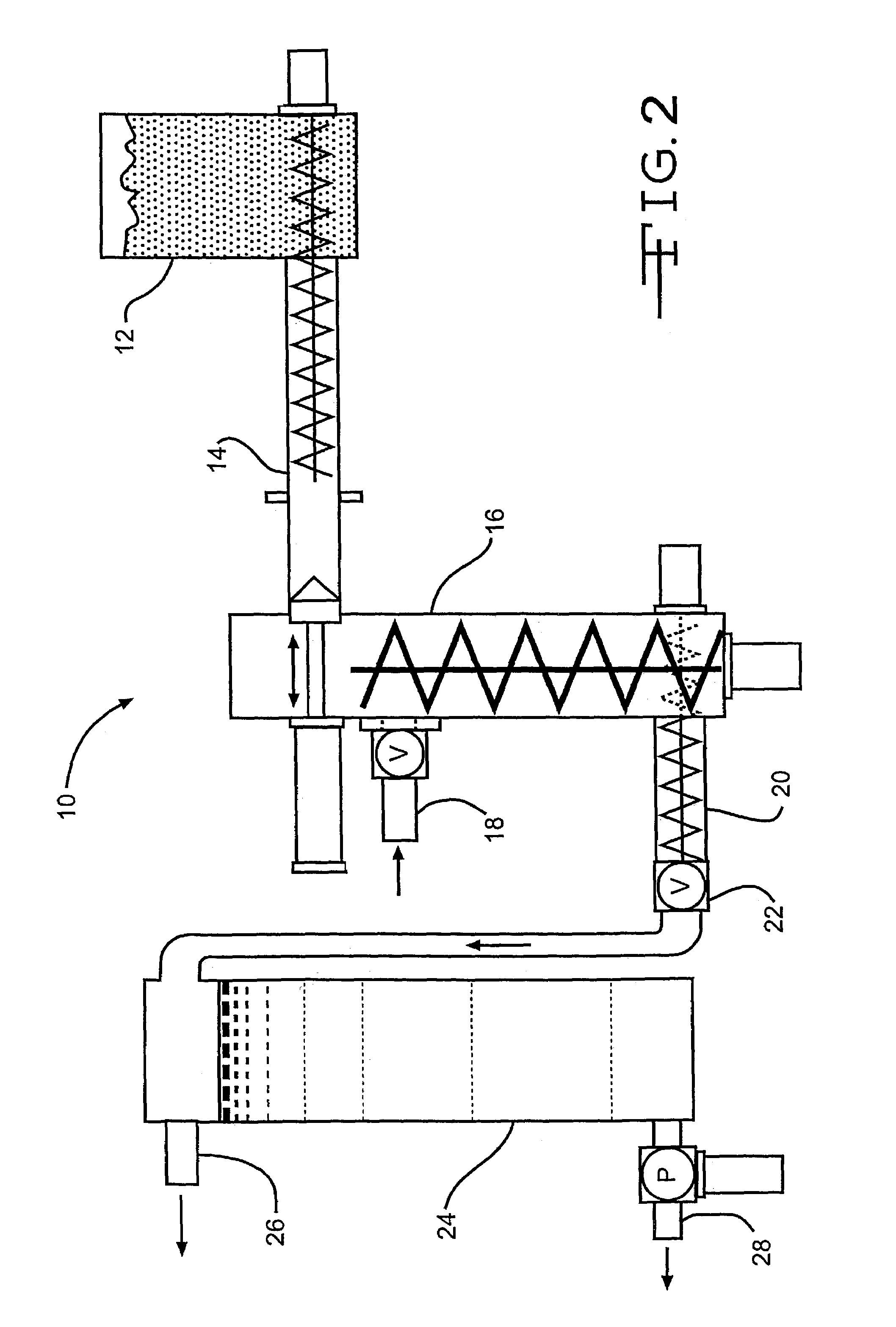
InactiveUS7189306B2Separation efficiency can be improvedEasy to separatePretreatment with water/steamPulp liquor regenerationSide productCo product
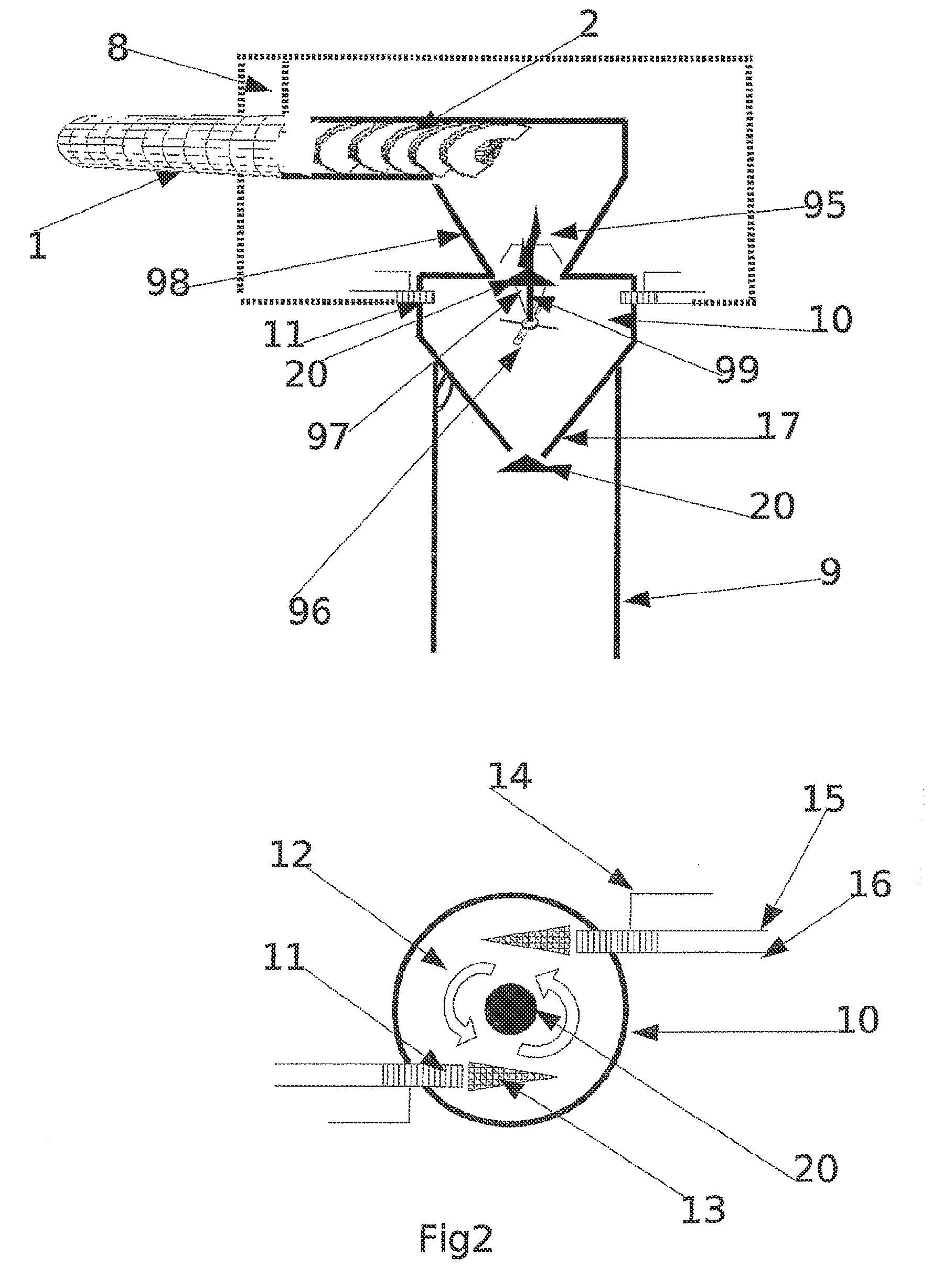
This invention relates to a process of treating a lignocellulosic material to produce bio-ethanol. The process includes the steps of: (a) exposing the lignocellulosic material to conditions including a pH not less than about 8, and steam at a first pressure, to produce a step (a) product; (b) explosively discharging the step (a) product to a second pressure less than the first pressure to produce a step (b) product; and (c) further processing the step (b) product to produce bio-ethanol and other co-products. In another embodiment, the invention relates to a conical auger fractionation column. The fractionation column includes a column body having an input and an output. A conical filter is positioned inside the column body, the filter having a larger diameter end directed toward the input and a smaller diameter end directed toward the output. A conical auger is positioned inside the conical filter, the conical auger having an outer diameter which is approximately the same as an inner diameter of the conical filter. The auger and filter are adapted to cooperate to separate cellulosic solids from a liquid stream in a process of producing bio-ethanol from a lignocellulosic material.
Owner:GERVAIS GIBSON W
Automatic control system for unit operation
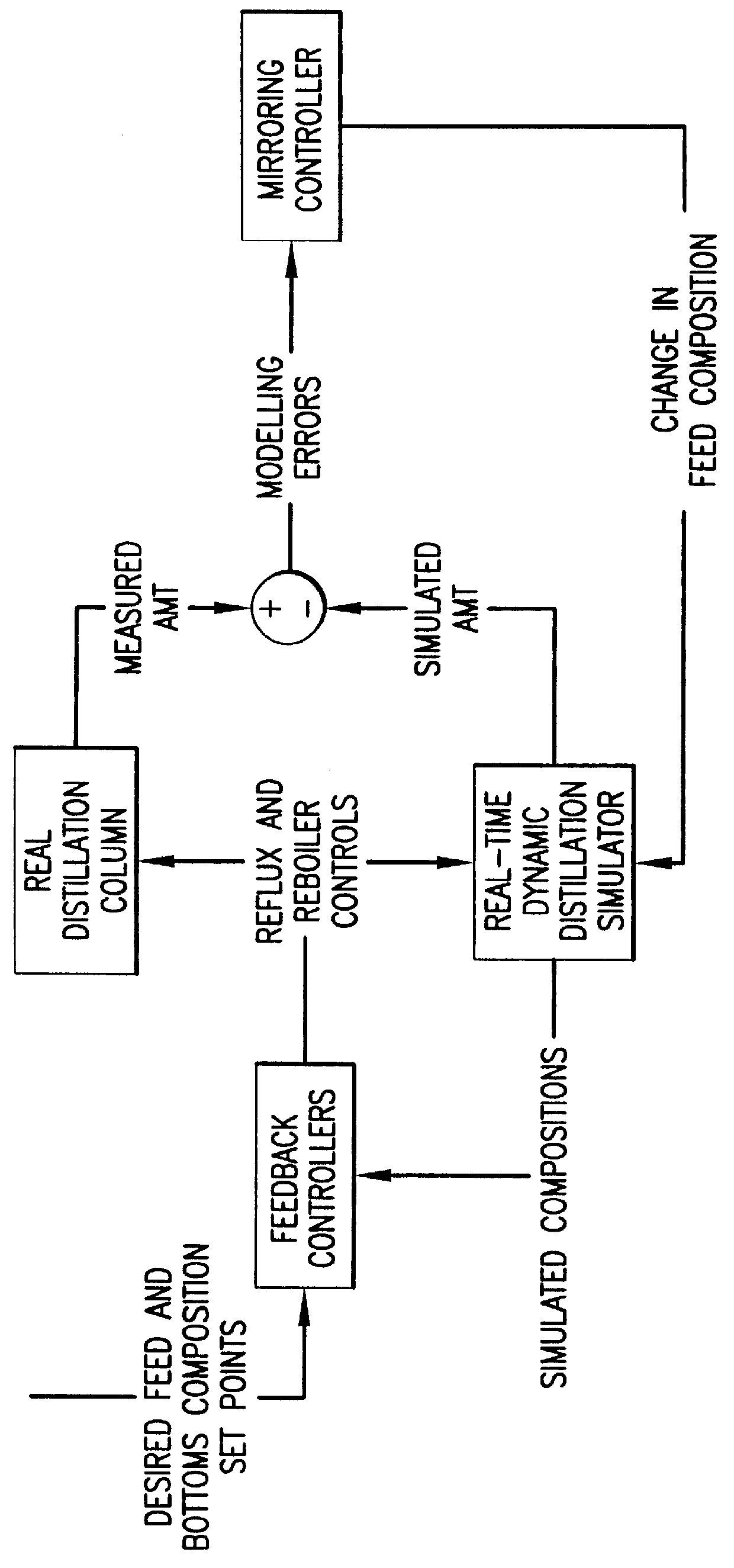
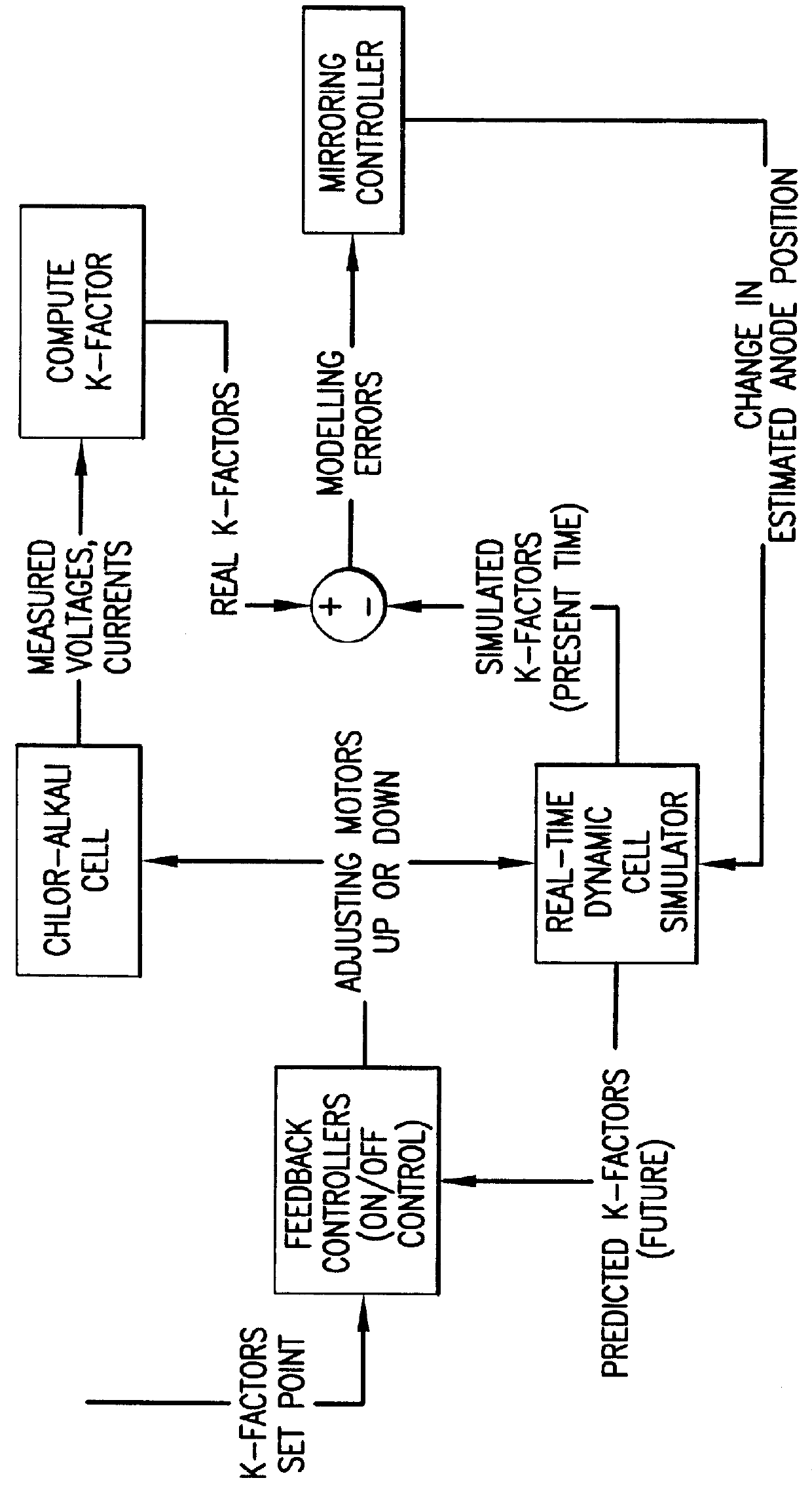
InactiveUS6088630AImprove stabilityAccurate predictionSampled-variable control systemsPhotography auxillary processesAutomatic controlAutomatic train control
Automatic control systems, and corresponding processes, for controlling either an anode adjuster in a chlor / alkali cell or at least one average middle temperature of a distillation column wherein the combination of feedback control from at least one real unit operation variable and an embedded real-time dynamic simulation of that variable are used.
Owner:OLIN CORP
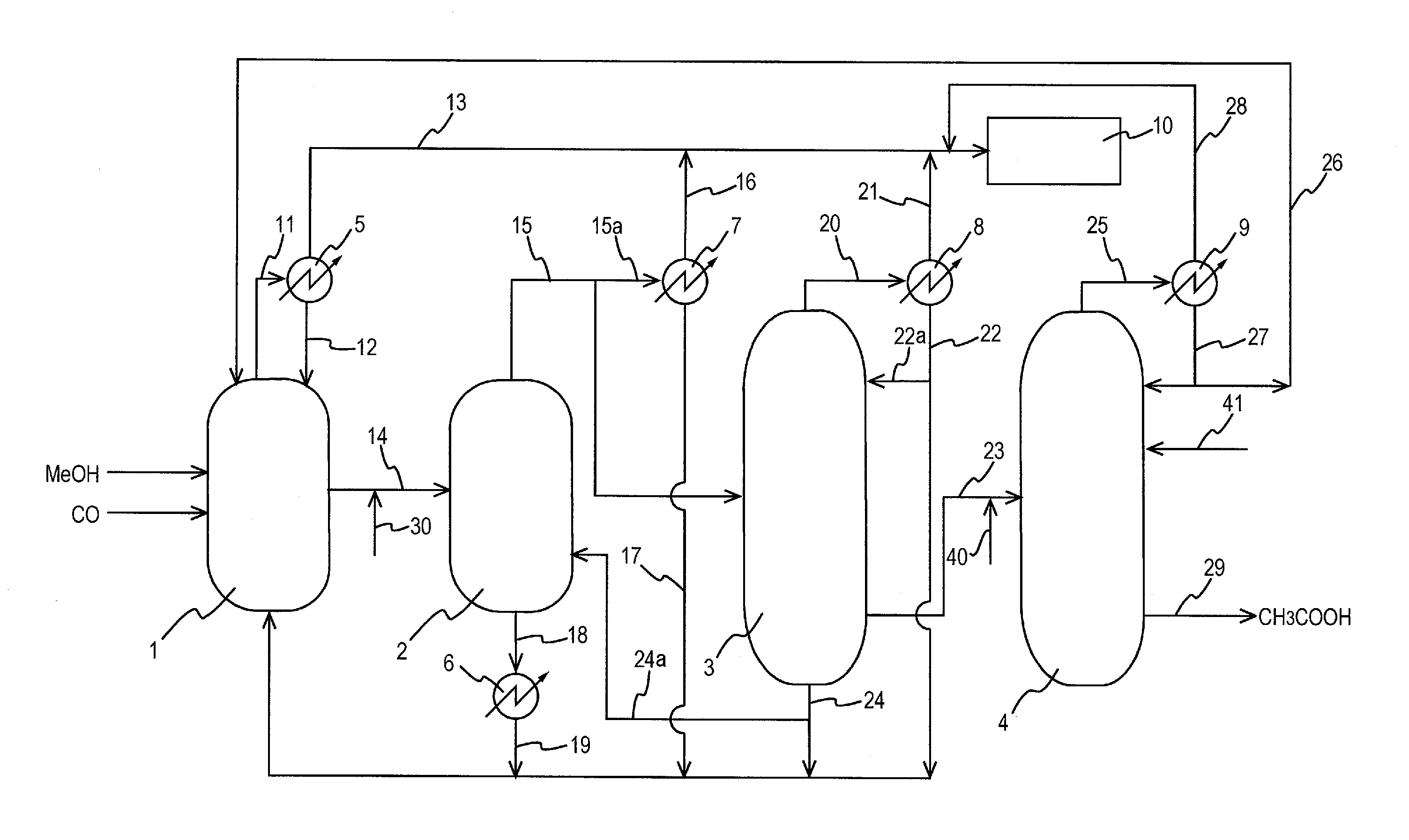
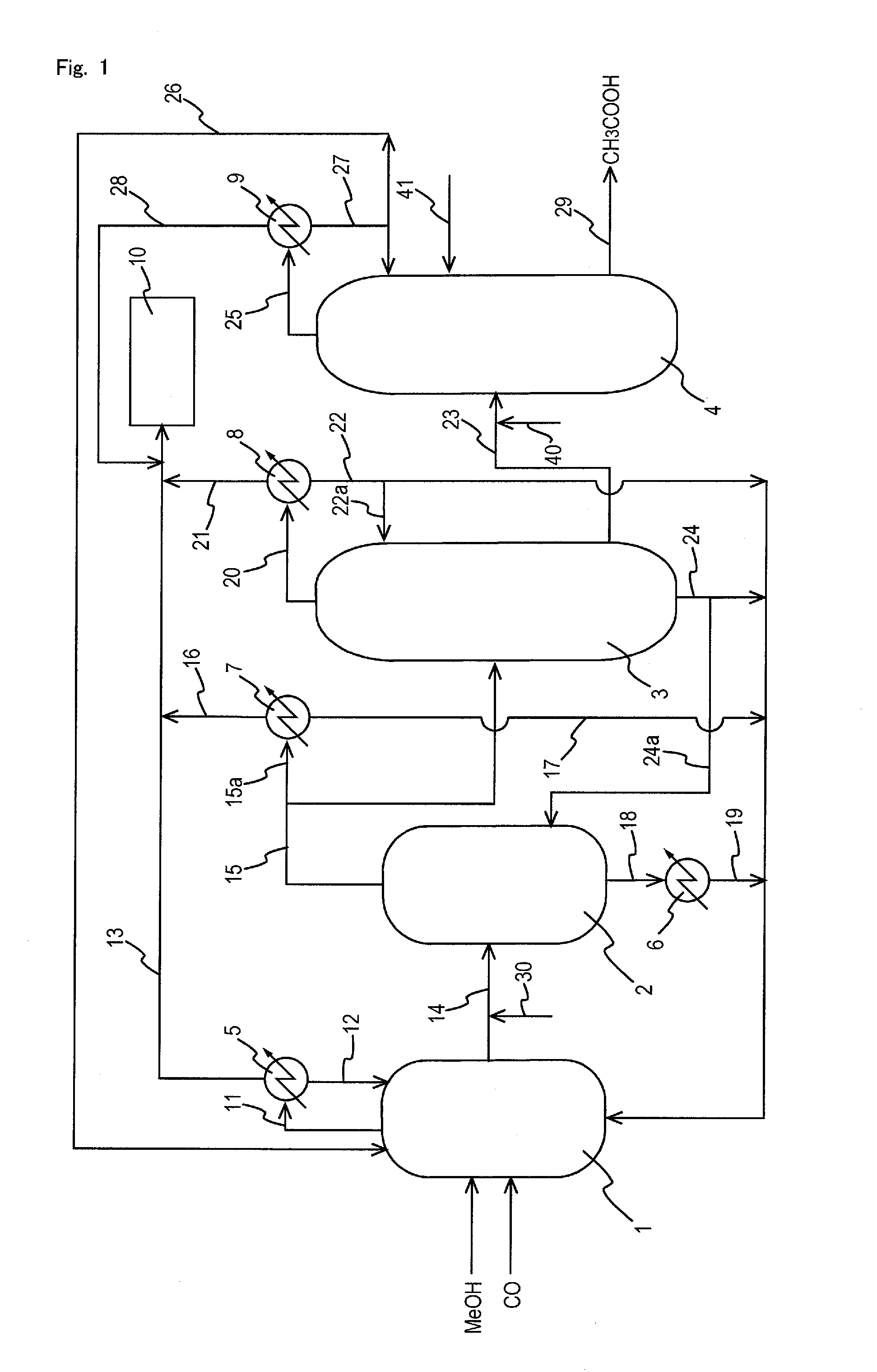
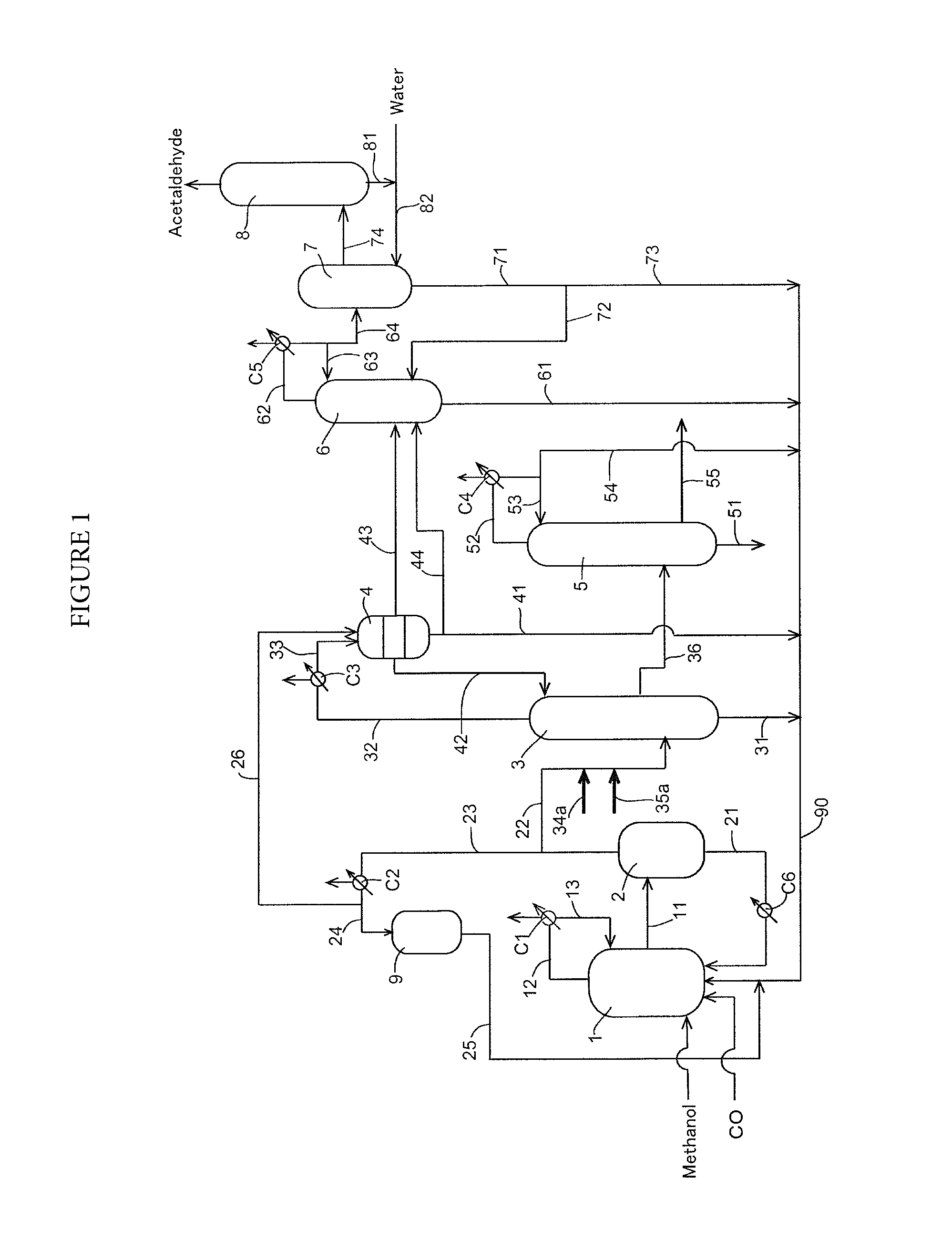
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130264186A1Improve concentrationEfficient executionOrganic chemistry methodsDistillation separationBoiling pointFractionating column
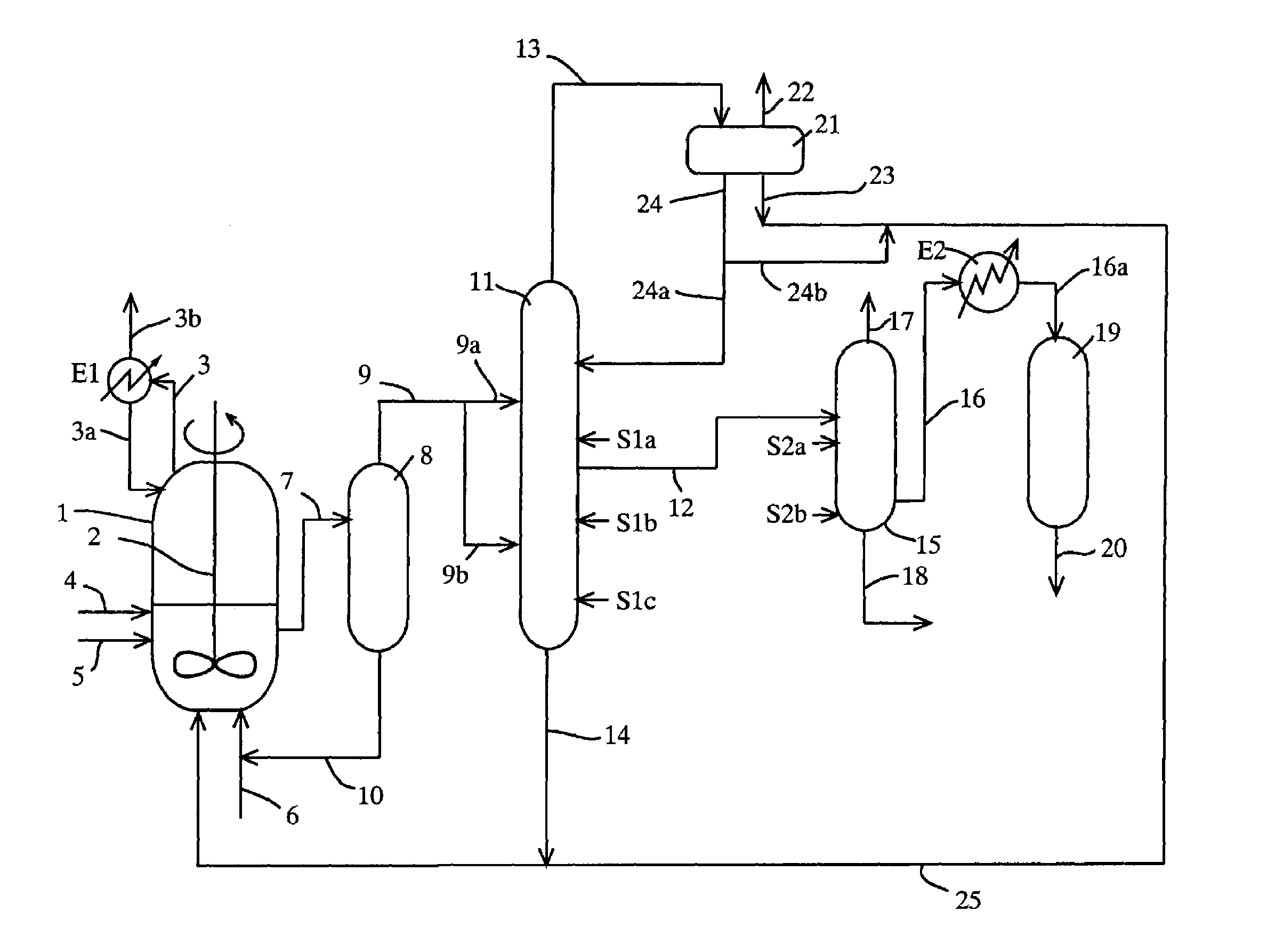
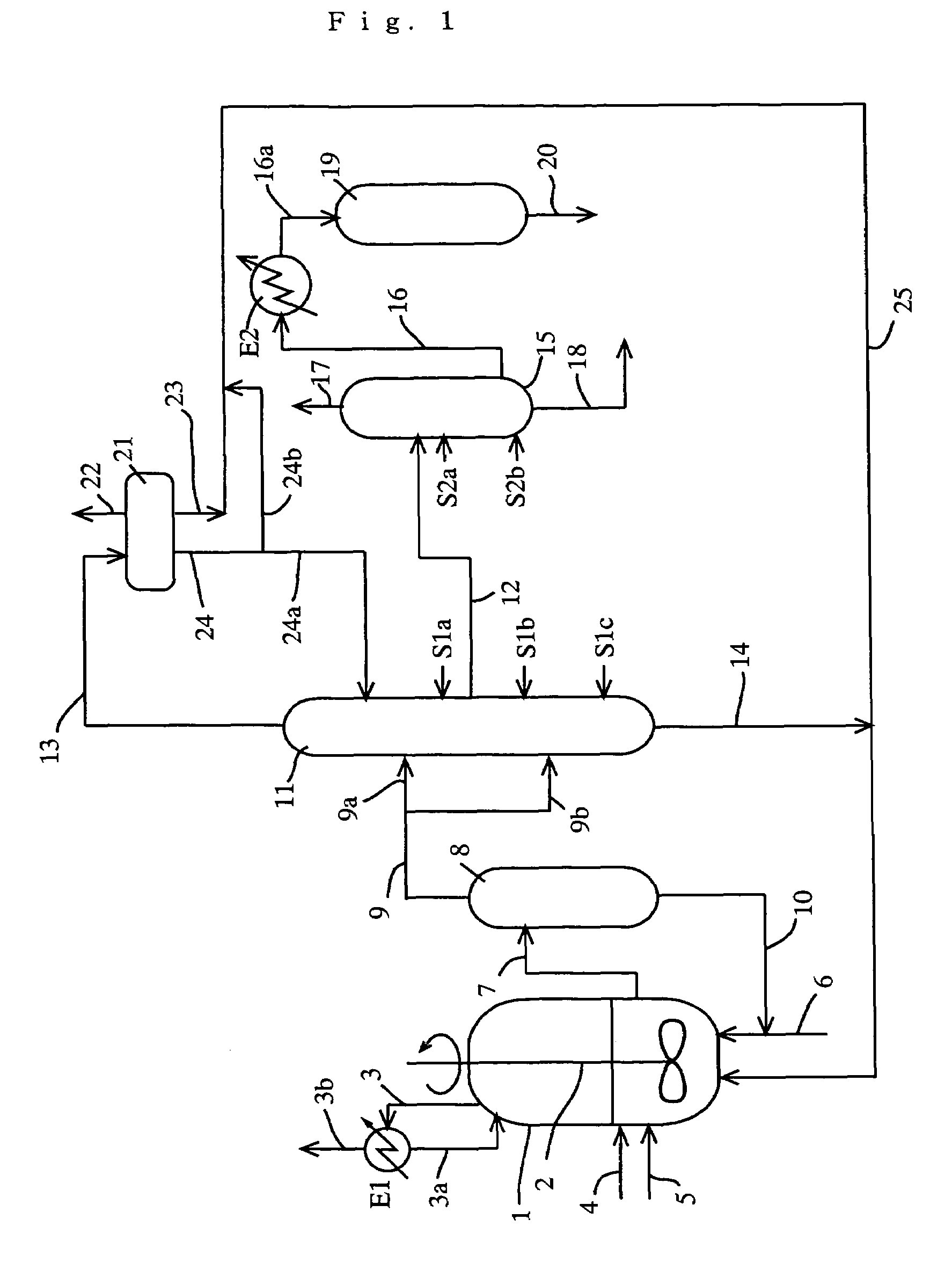
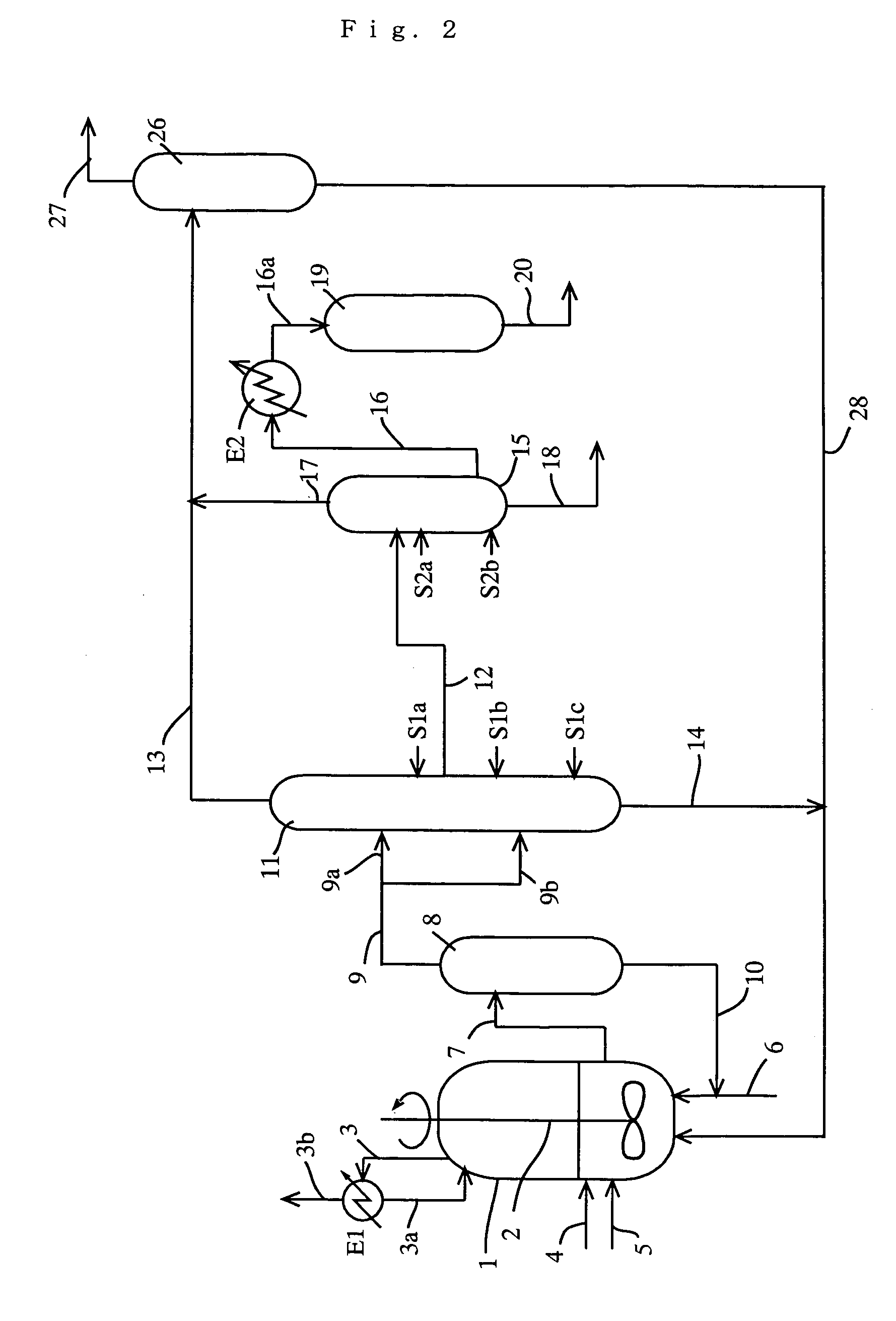
Acetic acid is produced while efficiently inhibiting condensation of hydrogen iodide in a distillation column (second distillation column) for purifying crude acetic acid by further distillation.A process for producing acetic acid comprises an acetic acid collection step for feeding a first distillation column with a volatile component at least containing acetic acid, methyl acetate, methyl iodide, water, and hydrogen iodide, separating a first lower boiling point component as an overhead, and collecting a first liquid stream mainly containing acetic acid, and an acetic acid purification step for feeding a second distillation column with the first liquid stream, further separating a second lower boiling point component as an overhead, and collecting a second liquid stream containing acetic acid, wherein an alkali component is added or mixed to the first liquid stream in the manners (1) and / or (2) for distilling a liquid object to be treated containing the first liquid stream and the alkali component in the second column: (1) the alkali component is added to or mixed with the first liquid stream before the first liquid stream is fed to the second column, (2) in the second column, the alkali component is added or mixed at the same height level as or at a height level upper than a height level at which the first liquid stream is fed.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for producing carboxylic acid
InactiveUS7678940B2Efficient separationHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationHydrogen halideAlcohol
A process for producing a purified carboxylic acid having “n+1” carbon atoms comprises feeding a carboxylic acid stream containing a carboxylic acid having “n+1” carbon atoms, a hydrogen halide, a lower boiling point (bp) component, a higher bp component, and others to a first distillation column; separating a lower bp fraction containing part of the lower bp component and a higher bp fraction containing part of the higher bp component in the first column; withdrawing a side stream containing at least the carboxylic acid by side cut from the first column; feeding the side stream to a second distillation column; separating a lower bp fraction containing part of the lower bp component and a higher bp fraction containing part of the higher bp component in the second column; and withdrawing a side stream containing the carboxylic acid by side cut from the second column to recover a purified carboxylic acid; and the process further comprises feeding at least one first component (A) selected from the group consisting of an alcohol, corresponding to the carboxylic acid, having “n” carbon atom(s), and an ester of the alcohol with the carboxylic acid to the first column, and if necessary water. Such a process ensures reduction of the concentration of the hydrogen halide in the purified carboxylic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Co-current vapor-liquid contacting apparatus
ActiveUS20070137482A1Easily redistributedIncrease capacityCombination devicesTransportation and packagingVapor liquidFractionating column
The invention is a high capacity and high efficiency co-current vapor-liquid contacting apparatus for use in distillation columns and other vapor-liquid contacting processes. The apparatus is characterized by an arrangement of modules in horizontal stages rather than tray-like construction. The modules define a co-current contacting volume and in an exemplary configuration the modules include a liquid distributor, a demister, a receiving pan and a duct. The modules of one stage are rotated to be non-parallel with respect to the modules of an inferior stage, a superior stage, or both. Variations relate to the design of the individual elements such as the demister, liquid distributor, ducts, and contacting volumes, and the overall arrangement of the apparatus.
Owner:UOP LLC
Internal refrigeration for enhanced NGL recovery
InactiveUS7257966B2Improve efficiency and economyEasy to separateSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnPetrochemical
The present invention is directed to methods for improving the efficiency of processes for the recovery of natural gas liquids from a gas feed, e.g., raw natural gas or a refinery or petrochemical plant gas stream. These methods may be employed with most, if not all, conventional separation methods using distillation towers, e.g., a demethanizer and / or deethanizer column. The methods of the present invention involve installing an internal refrigeration system consisting of an open cycle refrigerant withdrawn from a distillation column and a closed cycle refrigerant derived from the open cycle refrigeration system. A separator is installed downstream of the recycle compressor discharge cooler in the open cycle refrigeration scheme. At least a portion of liquid withdrawn from this separator is used as a closed cycle refrigerant by indirect heat exchange with the inlet gas or other process streams. Thus a closed refrigeration cycle enhances the performance of the open refrigeration cycle.
Owner:IPSI
Apparatus and Methods for Separating Butene-1 from a Mixed C4 Feed
ActiveUS20080161618A1Reduce constructionLow costSolvent extractionDistillation in boilers/stillsButeneFractionating column
A process is disclosed for recovering 1-butene from a feed steam comprising n-butane, isobutane and butene isomers using a single, divided wall distillation column. The disclosed process includes introducing the feed steam into an inlet of a first side of a distillation column, wherein the distillation column comprises a top, a bottom and a center dividing wall extending between the bottom and the top of the column and dividing the column into the first side and a second side. The process includes taking off an isobutane stream from the top of the second side of column, taking off a 1-butene stream as a bottoms stream from the second side of the column, and taking off a combination 2-butene and n-butane stream as a bottom stream from the first side of column.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for delayed coking of whole crude oil
ActiveUS20120298552A1Enhance thermal cracking reactionReduce coke yieldThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingNaphthaFractionating column
An improved delayed coking process utilizing a coking unit and a coking unit product fractionating column which includes the steps of:heating a mixture of a fresh whole crude oil feedstream and the bottoms from the coking unit product fractionator in a furnace to a coking temperature in the range of 480° C. to 530° C. / 896° F. to 986° F.;introducing the heated mixed whole crude oil and bottoms feedstream directly into the delayed coking unit;optionally passing the vaporized liquid and gaseous coking unit product stream into a flash unit;recovering a light product gas stream that includes H2S, NH3 and C1 to C4 hydrocarbons from the flash unit;transferring the bottoms from the flash unit to the coking unit product fractionating column;recovering as separate side streams from the fractionating column naphtha, light gas oil and heavy gas oil;recycling a portion of the heavy gas oil by introducing it into the fractionating column optionally with the bottoms from the flash unit;mixing the fractionating column bottoms with the whole crude oil feedstream to form the mixed feedstream; andintroducing the mixed whole crude oil and fractionating column bottoms feedstream into the furnace.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process for producing aliphatic carboxylic acid
InactiveUS7319168B2Guaranteed uptimeShorten the timeOrganic compound preparationFractional distillationFractionating columnCarboxylic acid
It is an object of the present invention to provide a process for producing aliphatic carboxylic acid, which can stabilize operation of a distillation column upon production of aliphatic carboxylic acid by reducing a water content in an aqueous aliphatic carboxylic acid solution by a distillation column, and can shorten a time during the non-steady state such as at starting up of distillation column operation. The present invention is directed to a process for producing aliphatic carboxylic acid, which comprises an azeotropic distillation step of supplying an aqueous aliphatic carboxylic acid solution and an azeotropic solvent to an azeotropic distillation column to perform distillation, separating an azeotrope containing the azeotropic solvent and water as a distillate, and recovering aliphatic carboxylic acid with a reduced water content as bottom liquid, characterized in that a target value of an amount of the azeotropic solvent to be supplied is set depending on an amount of water in the aqueous aliphatic carboxylic acid solution supplied to the azeotropic distillation column, and the amount of the azeotropic solvent to be supplied is controlled at the target value.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
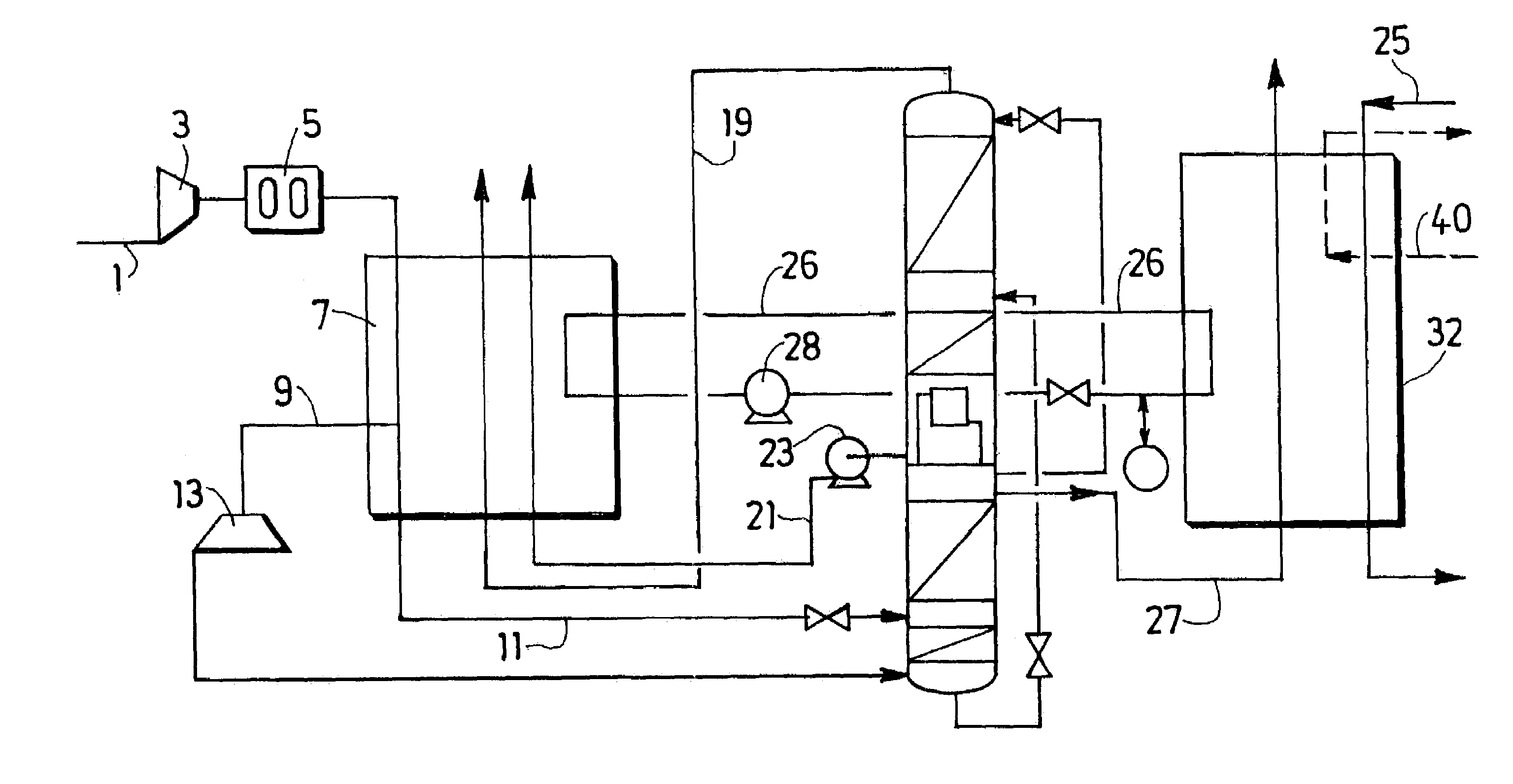
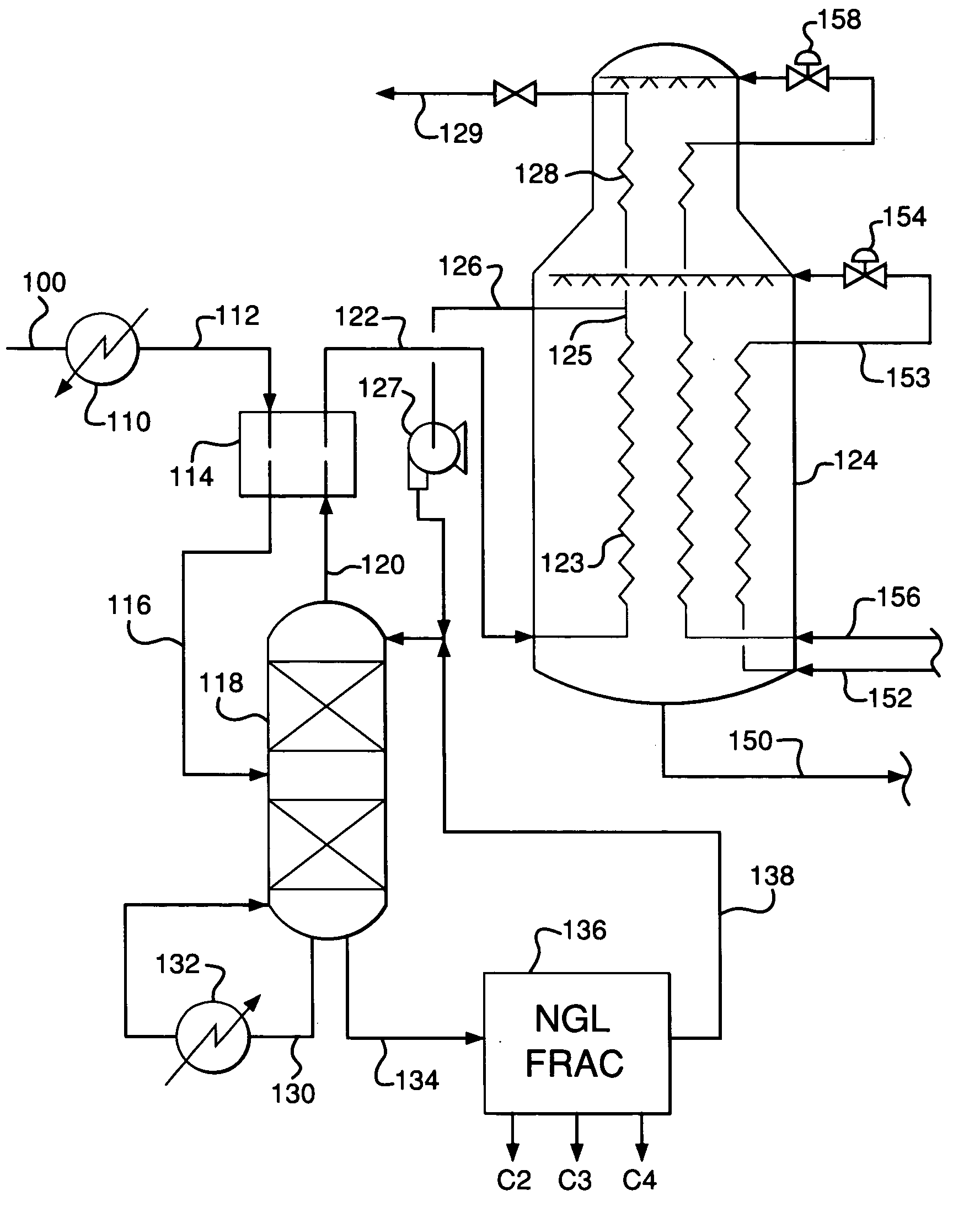
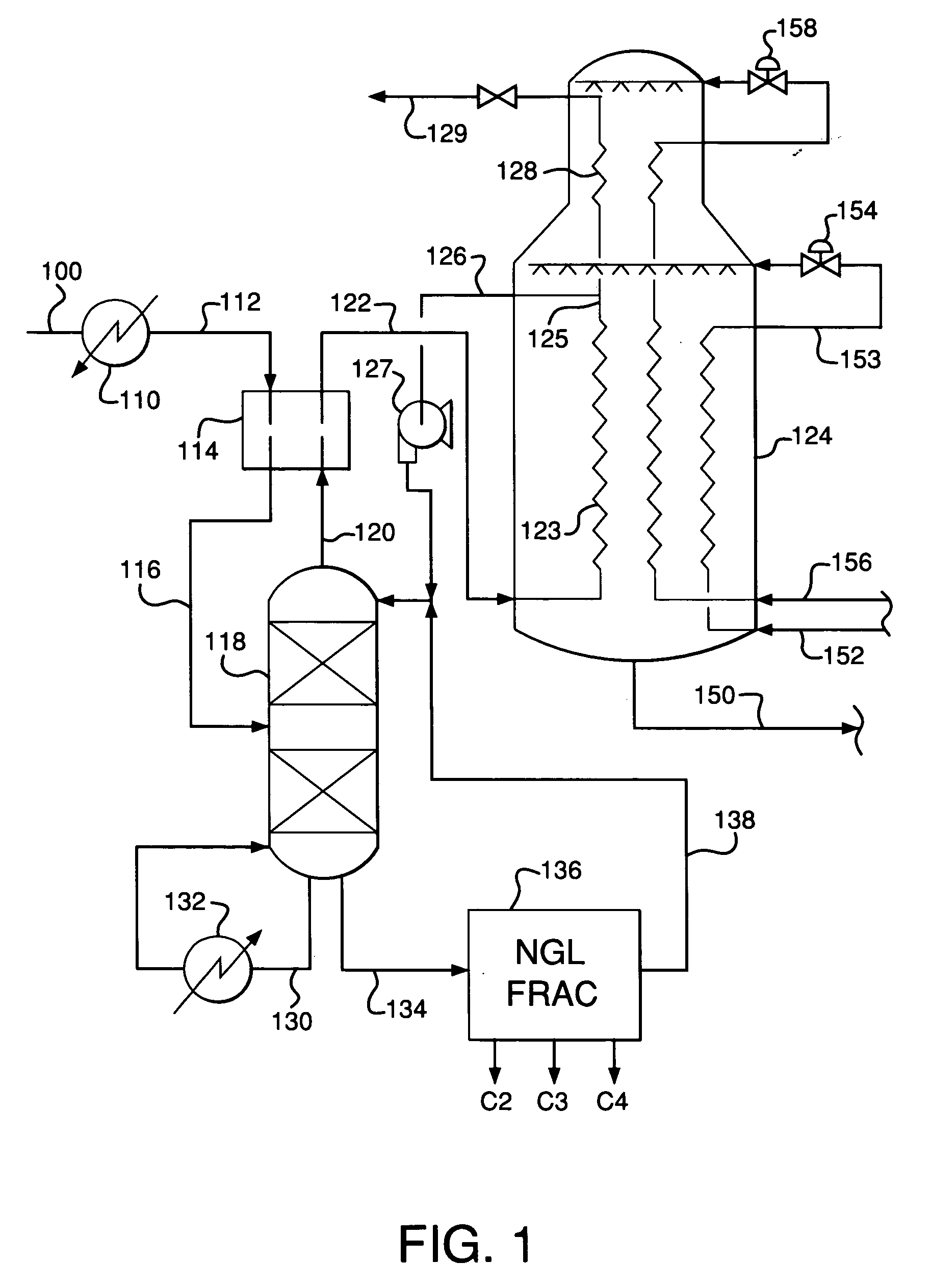
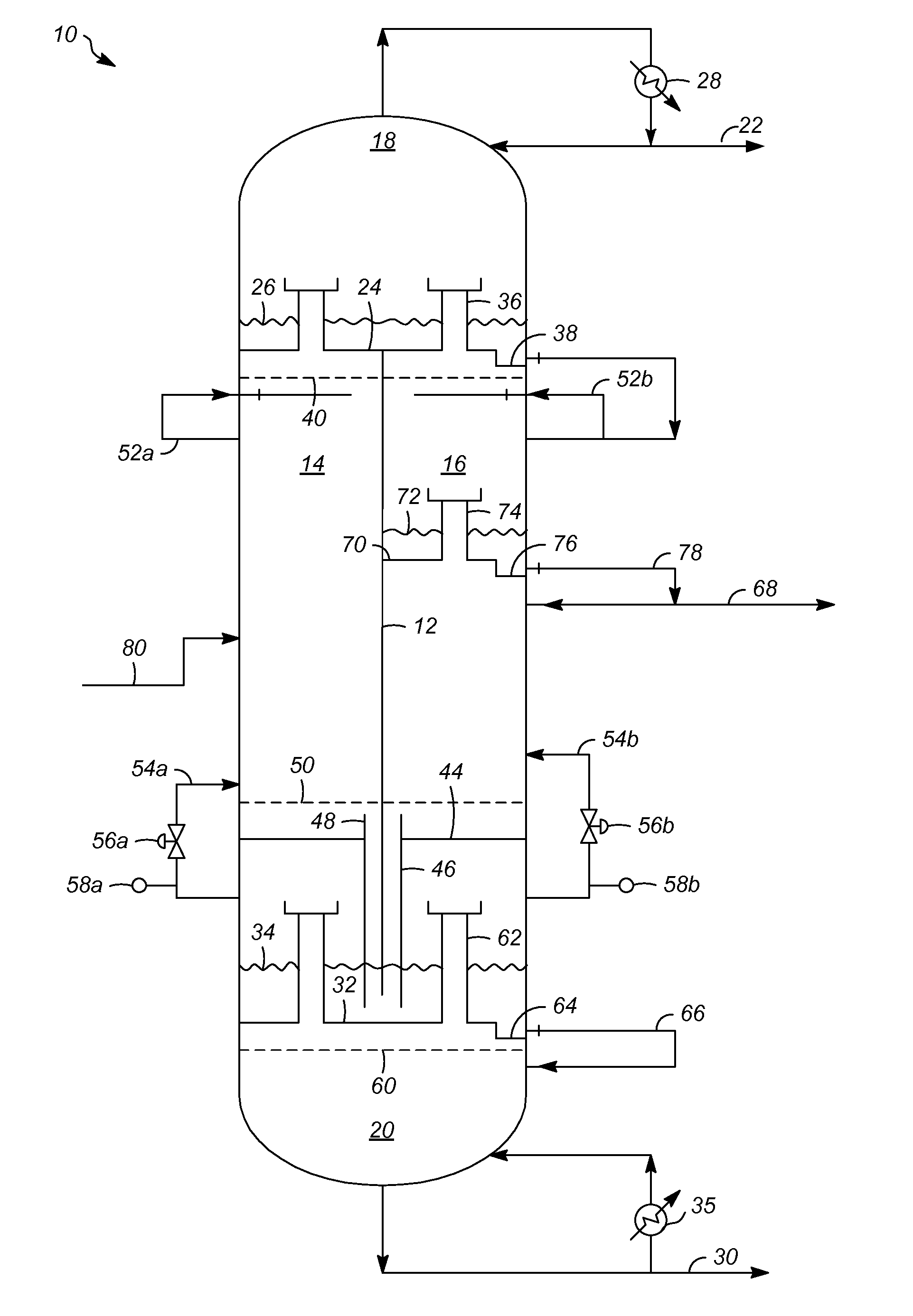
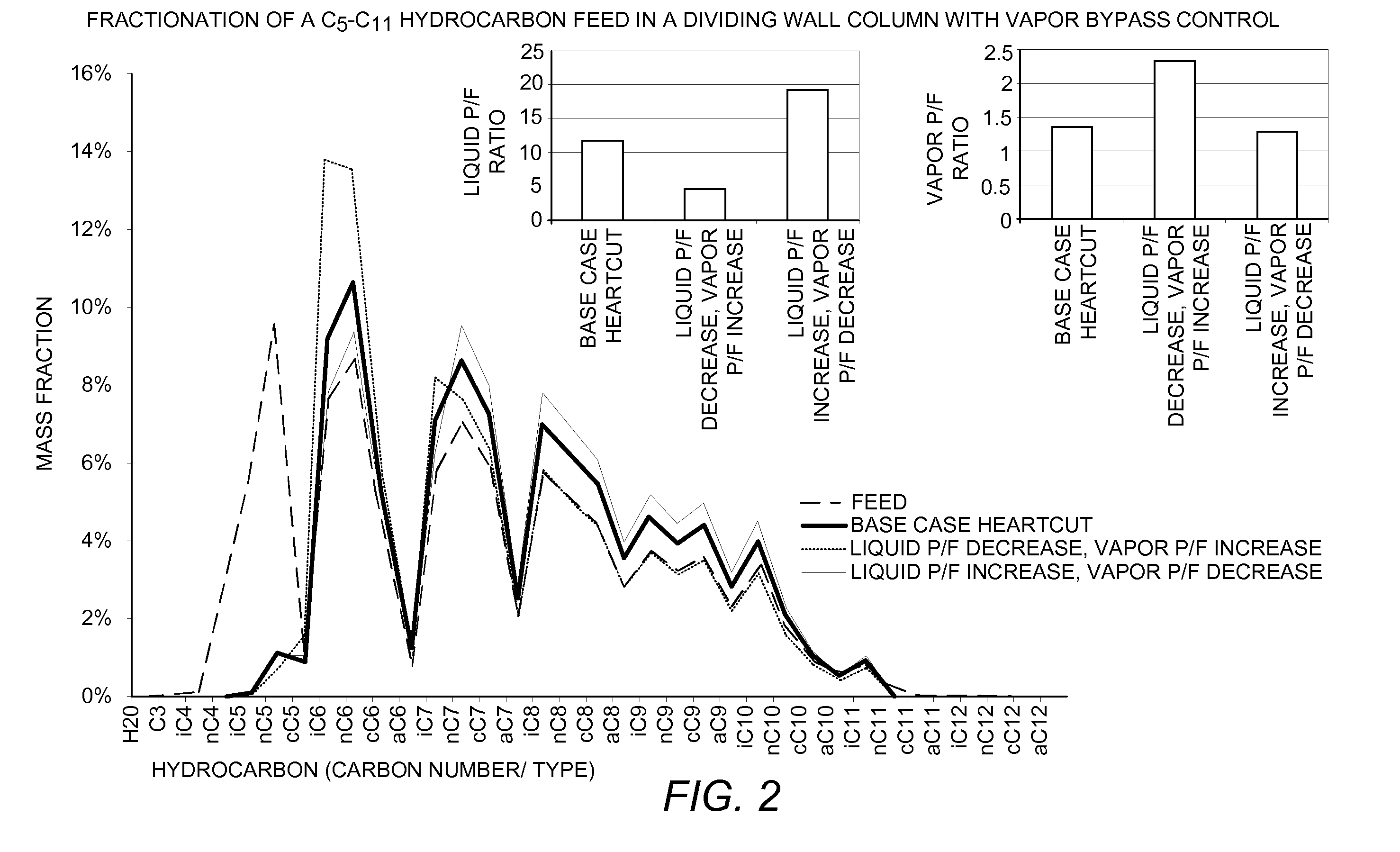
Vapor and liquid flow control in a dividing wall fractional distillation column
ActiveUS20120103013A1Good flexibilityEfficient changeSolidificationLiquefactionFractional distillationStreamflow
Dividing wall fractional distillation columns and methods of operating these columns with greater flexibility, especially in terms of the ability to adjust the composition of the heartcut, intermediate or sidecut product fraction, are described. In particular, this composition may be advantageously “biased” toward higher or lower molecular weight components, depending on operating needs. Changes in feedstock composition may also be managed more effectively. These benefits are obtained by varying the flow rate of vapor and liquid to each side of the dividing wall. The vapor flowrate rising from an undivided portion of the column interior below the dividing wall is varied to the feed and / or product sections on opposite sides of the dividing wall. Also, the liquid flowrate falling from an undivided portion of the column interior above the dividing wall is varied to the feed and / or product sections on opposite sides of the dividing wall.
Owner:UOP LLC
Integrated Controlled Freeze Zone (CFZ) Tower and Dividing Wall (DWC) for Enhanced Hydrocarbon Recovery
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for the operation of a distillation tower containing a controlled freezing zone and at least one distillation section. The process and tower design are utilized for the additional recovery of hydrocarbons from an acid gas. In this process, a separation process is utilized in which a multi-component feedstream is introduced into an apparatus that operates under solids forming conditions for at least one of the feedstream components. The freezable component, although typically CO2, H2S, or another acid gas, can be any component that has the potential for forming solids in the separation system. A dividing wall is added to at least a portion of the lower distillation section of the apparatus to effect the separation of at least some fraction of the hydrocarbons in that portion of the tower.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
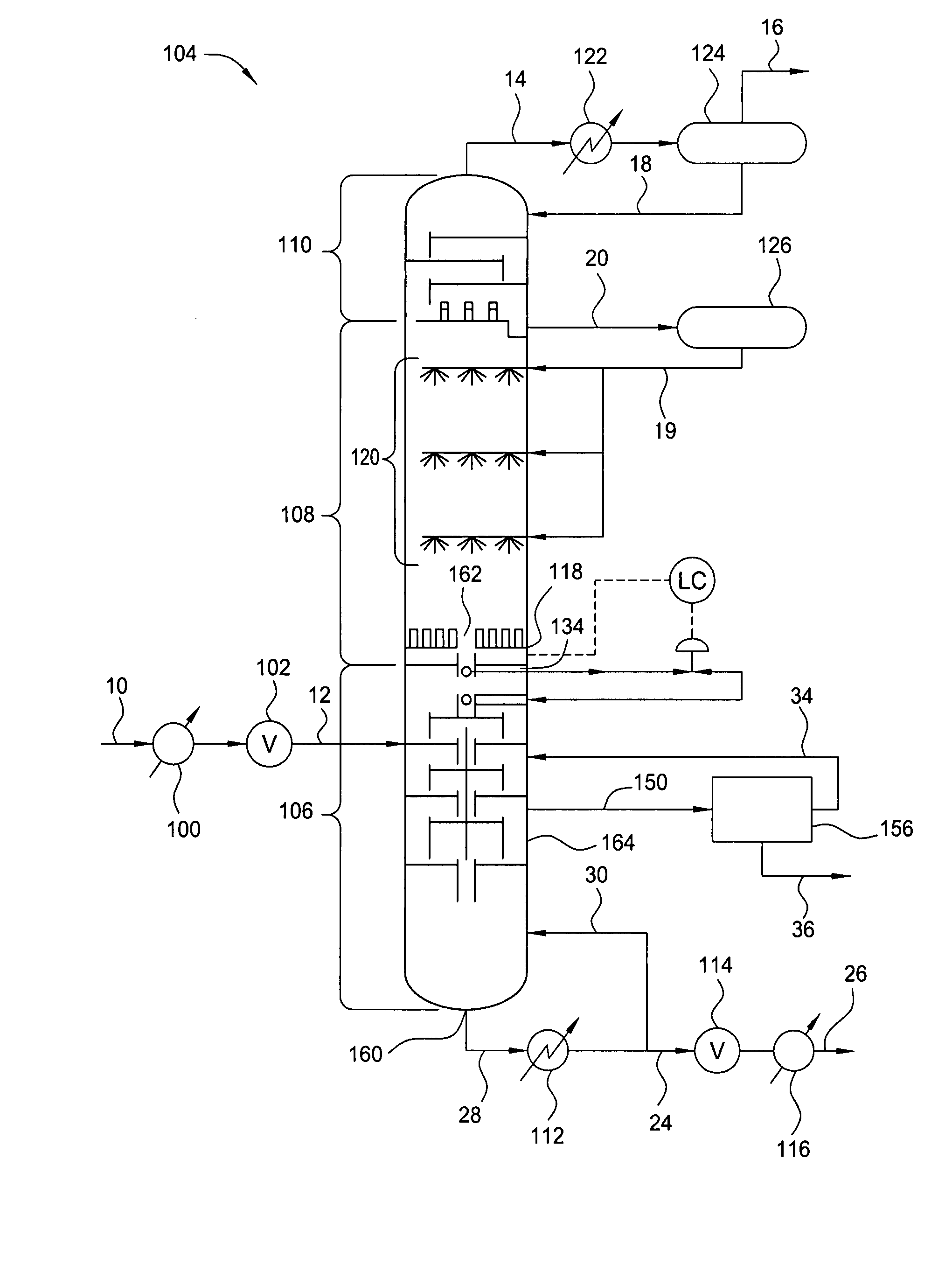
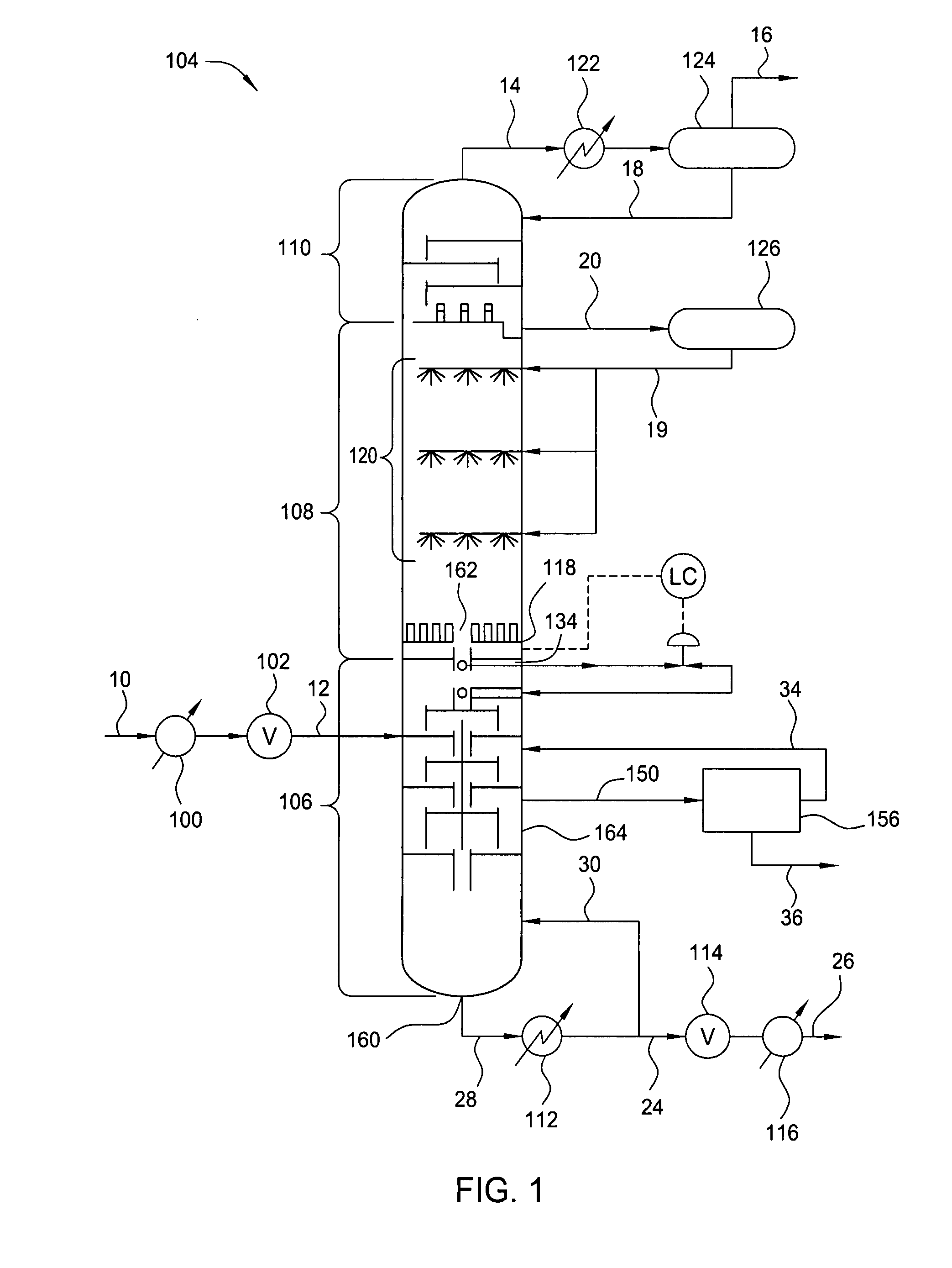
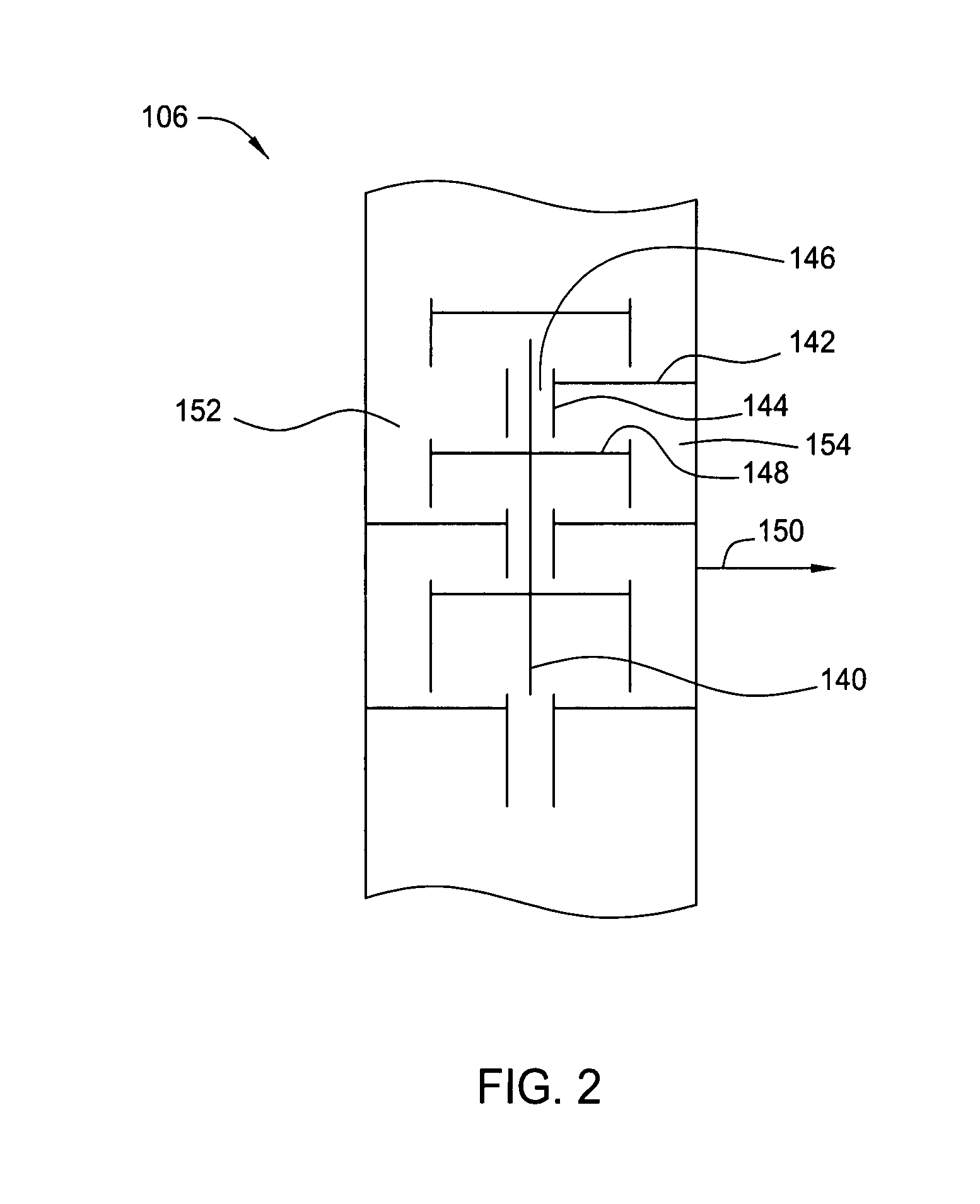
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS9006483B2Avoid pollutionEnsure stable and continuous operationOrganic compound preparationDistillation separationWater concentrationAcetic acid ear
A production process of acetic acid according to the present invention inhibits concentration of hydrogen iodide and improves a liquid-liquid separation of an overhead from a distillation column. Acetic acid is produced by distilling a mixture containing hydrogen iodide, water, acetic acid and methyl acetate in a first distillation column (3) to form an overhead and a side cut stream or bottom stream containing acetic acid, cooling and condensing the overhead in a condenser (C3) to form separated upper and lower phases in a decanter (4). According to this process, a zone having a high water concentration is formed in the distillation column above the feed position of the mixture by feeding a mixture having a water concentration of not less than an effective amount to not more than 5% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 4.5% by weight) and a methyl acetate concentration of 0.5 to 9% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 8% by weight) as the mixture to the distillation column and distilling the mixture. In the zone having a high water concentration, hydrogen iodide is allowed to react with methyl acetate to produce methyl iodide and acetic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
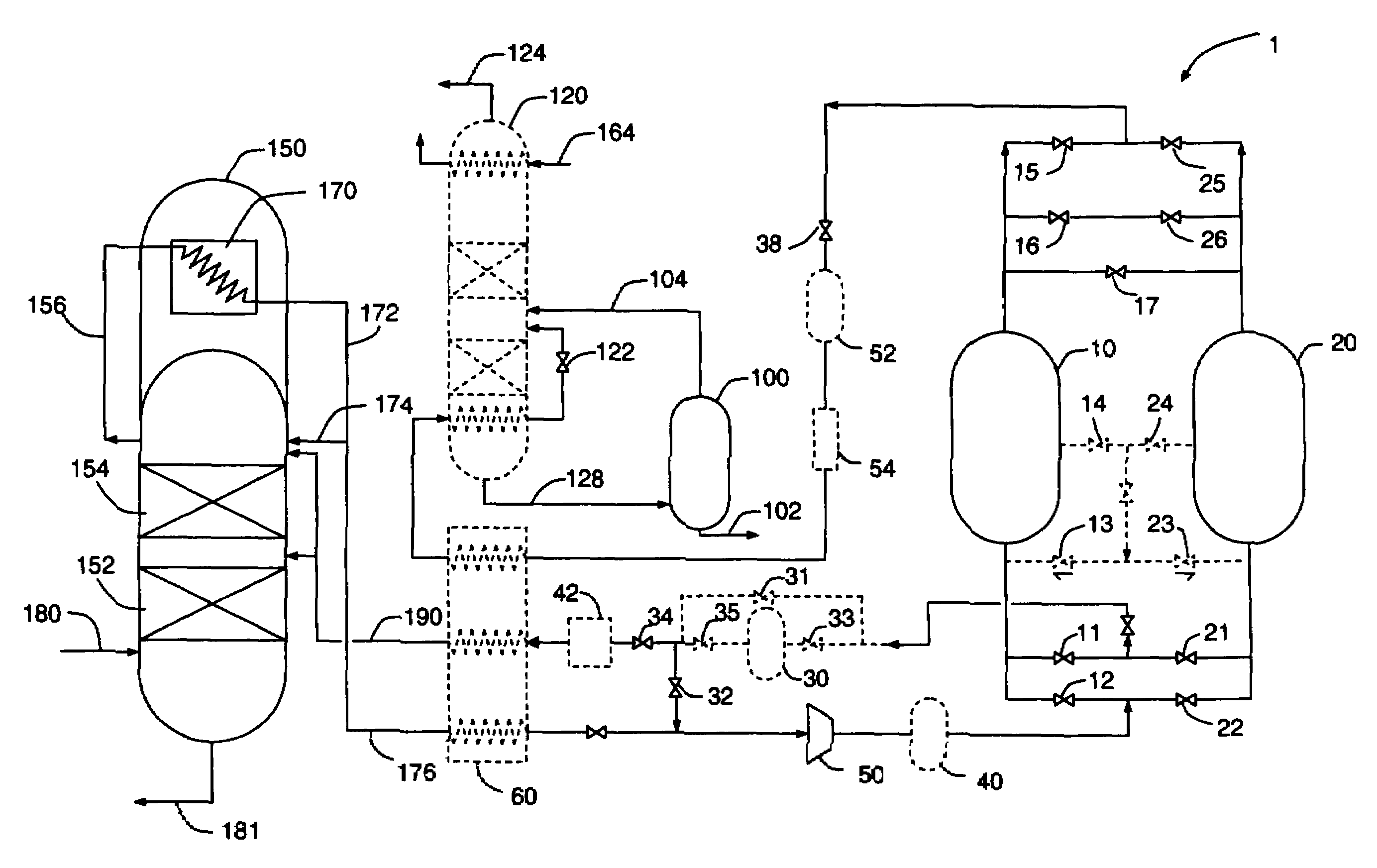
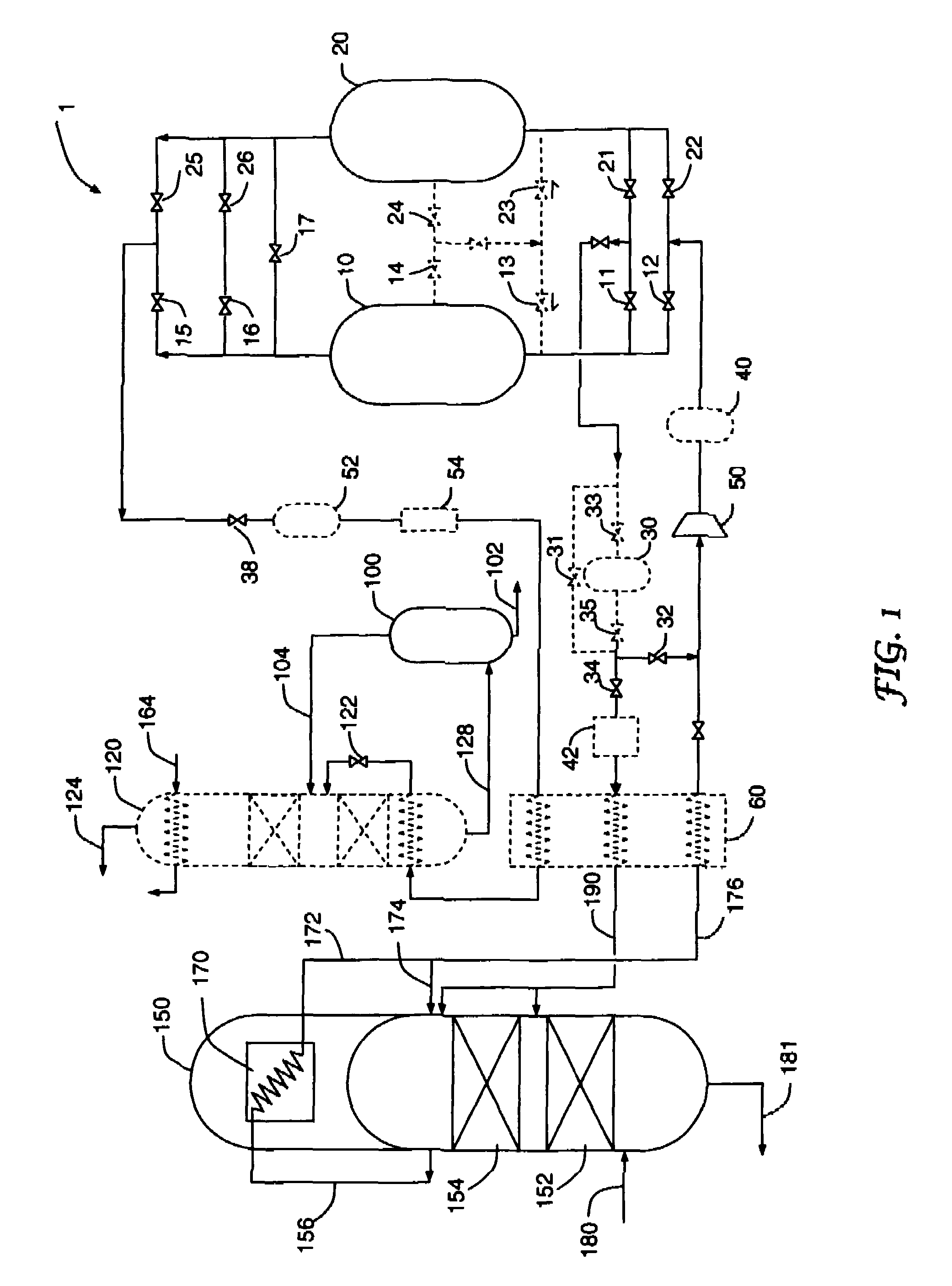
Hydrocarbon gas processing
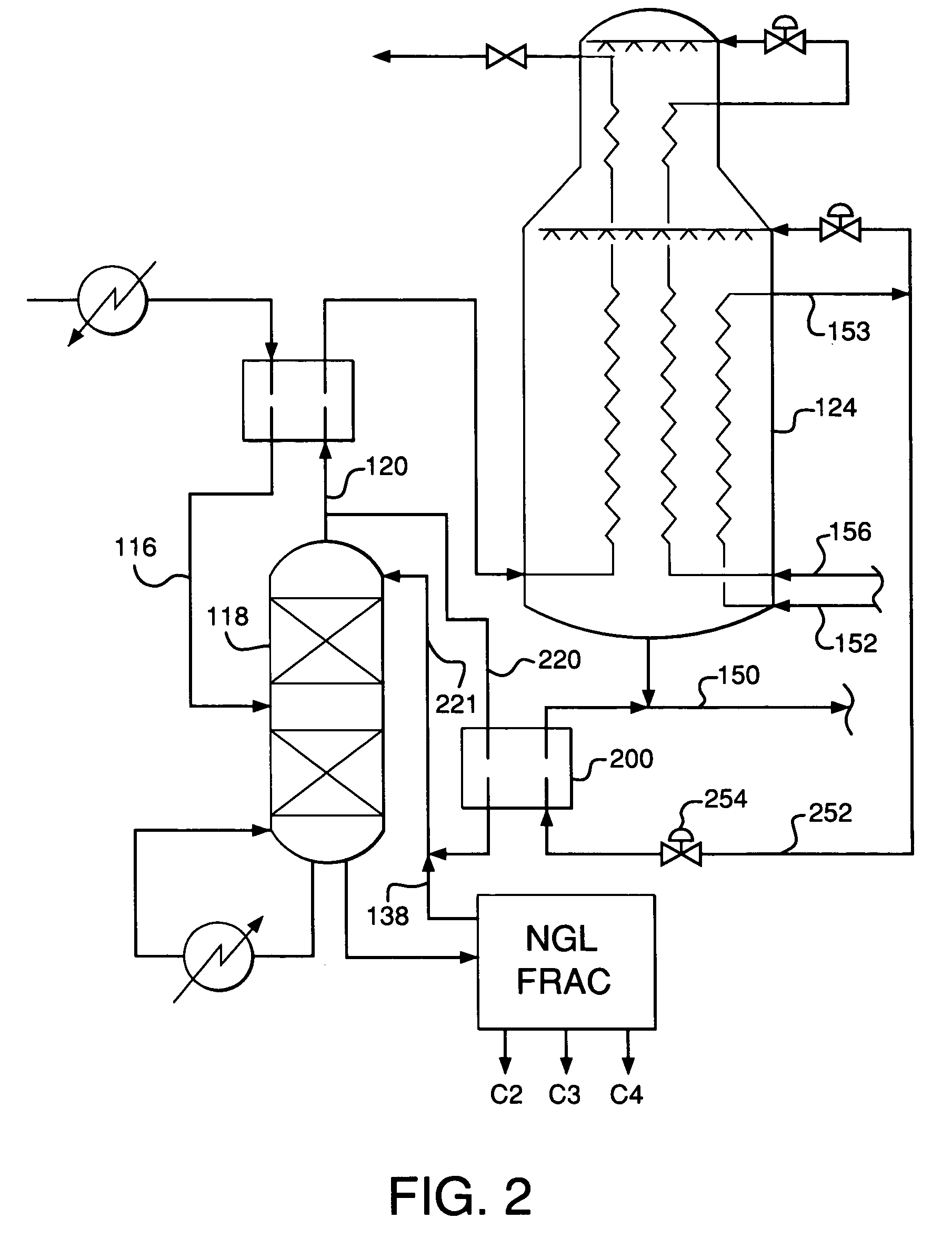
A process and an apparatus are disclosed for recovering ethane, ethylene, and heavier hydrocarbon components from a hydrocarbon gas stream. The stream is cooled, expanded to lower pressure, and supplied to a first fractionation tower at a mid-column feed position. A distillation liquid stream is withdrawn from the first fractionation tower below the feed position of the expanded stream, heated, and directed into a second fractionation tower that produces an overhead vapor stream and a bottom liquid stream. The overhead vapor stream is cooled to condense it, with a portion of the condensed stream directed to the second fractionation tower as its top feed and the remainder directed to the first fractionation tower at a lower column feed position. The bottom liquid stream from the second fractionation tower is cooled and directed to the first fractionation tower as its top feed.
Owner:UOP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com