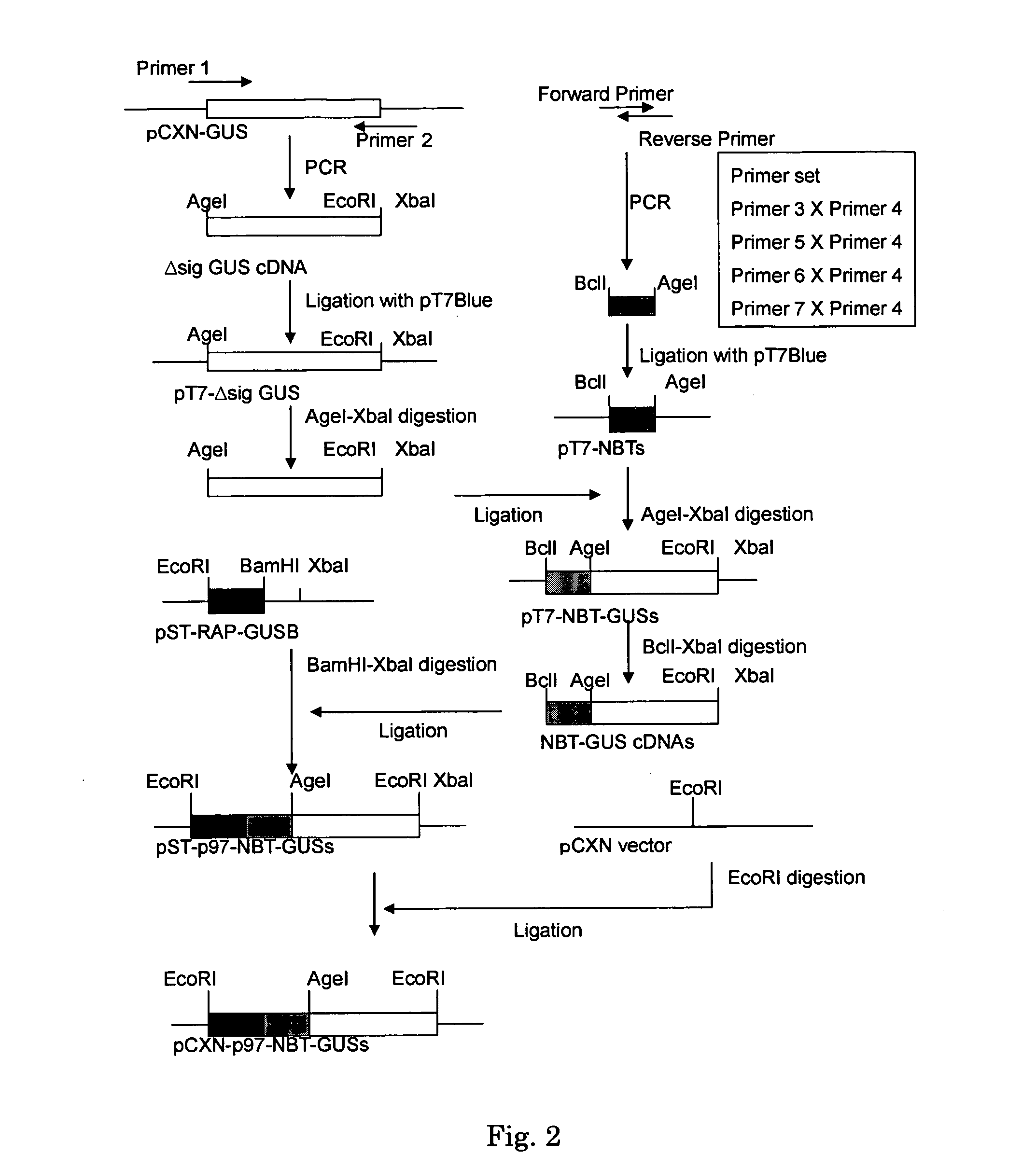
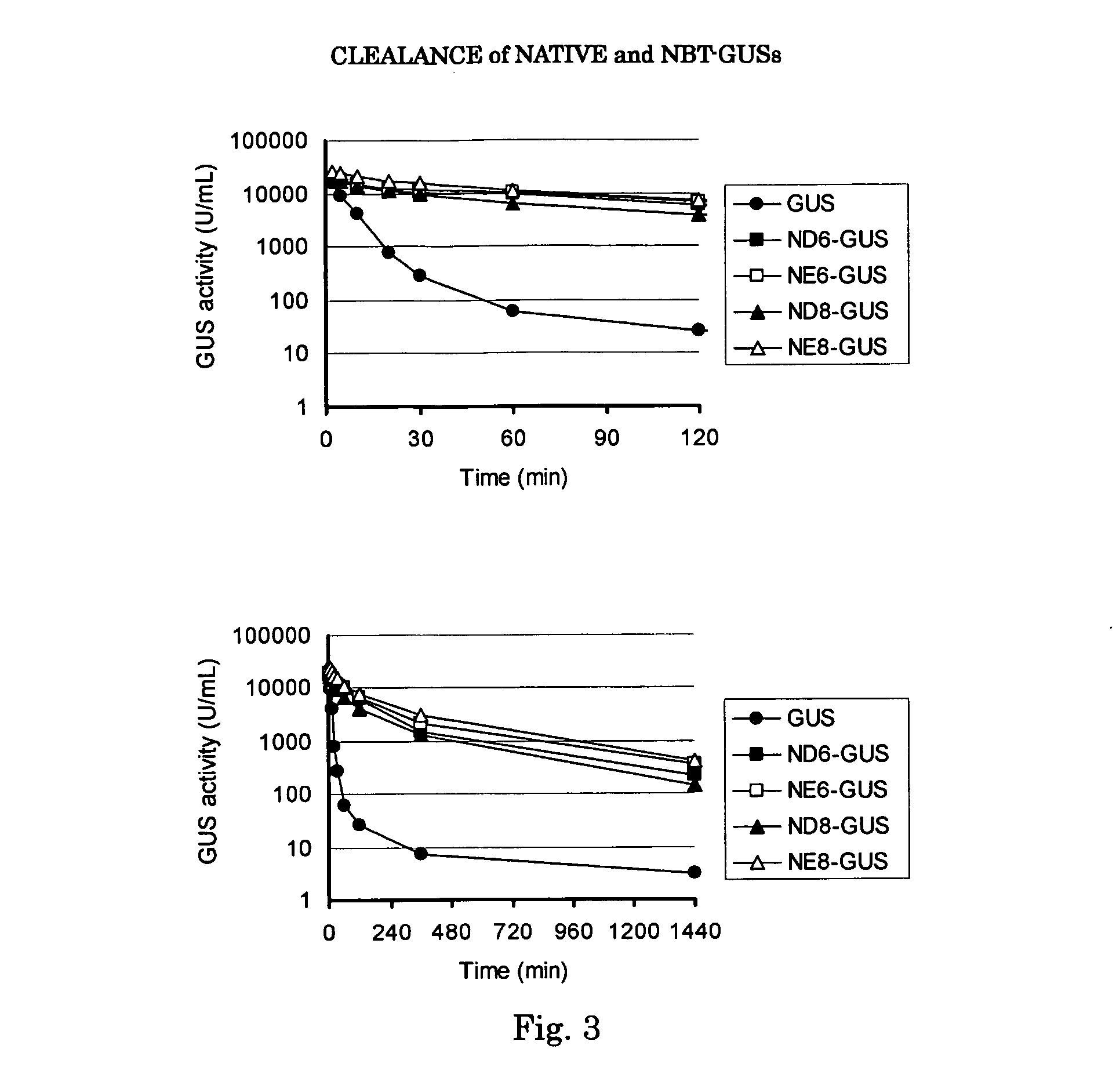
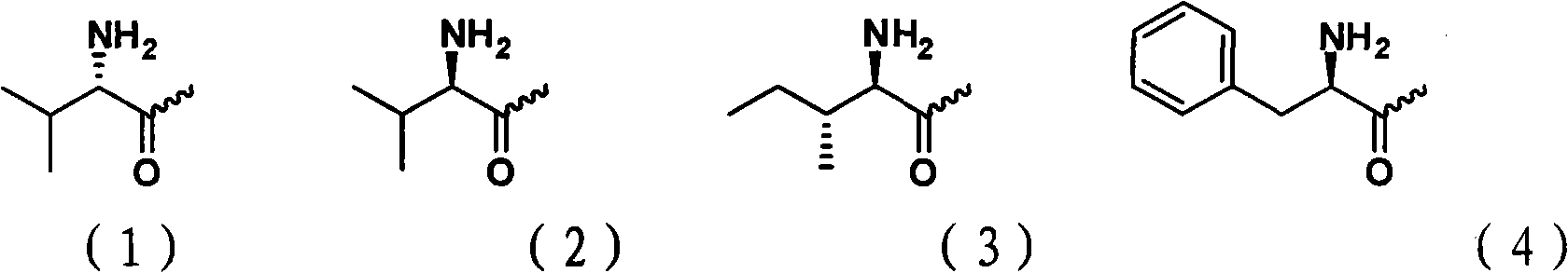
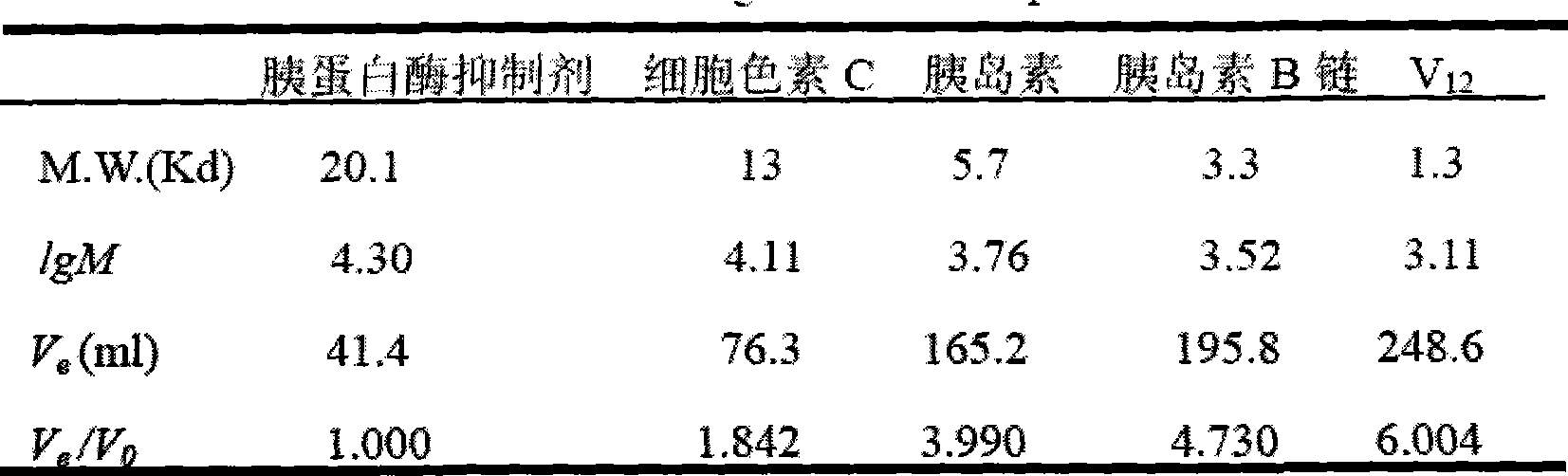
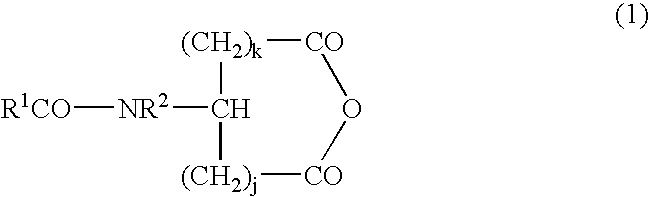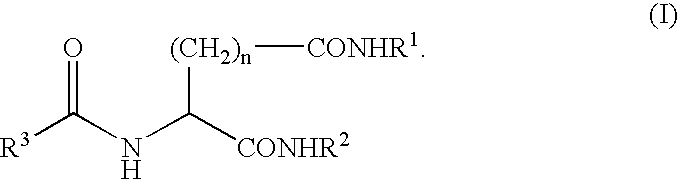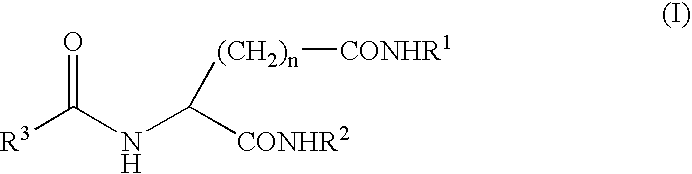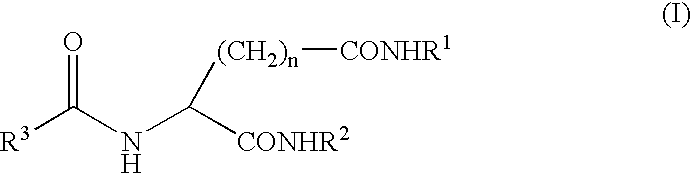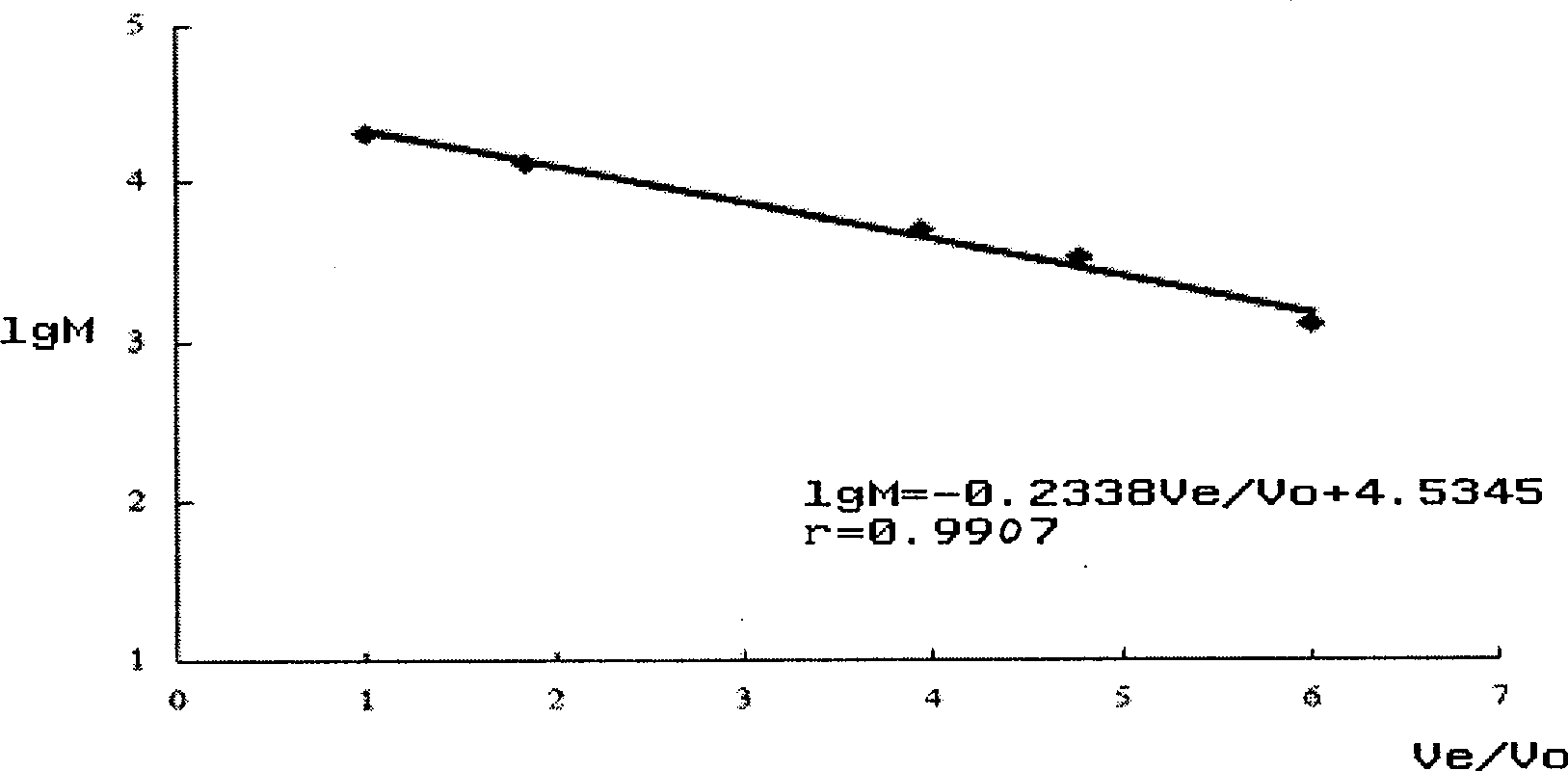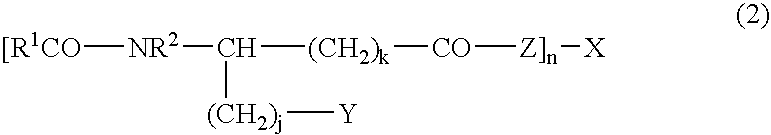Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
335 results about "Acidic amino acids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
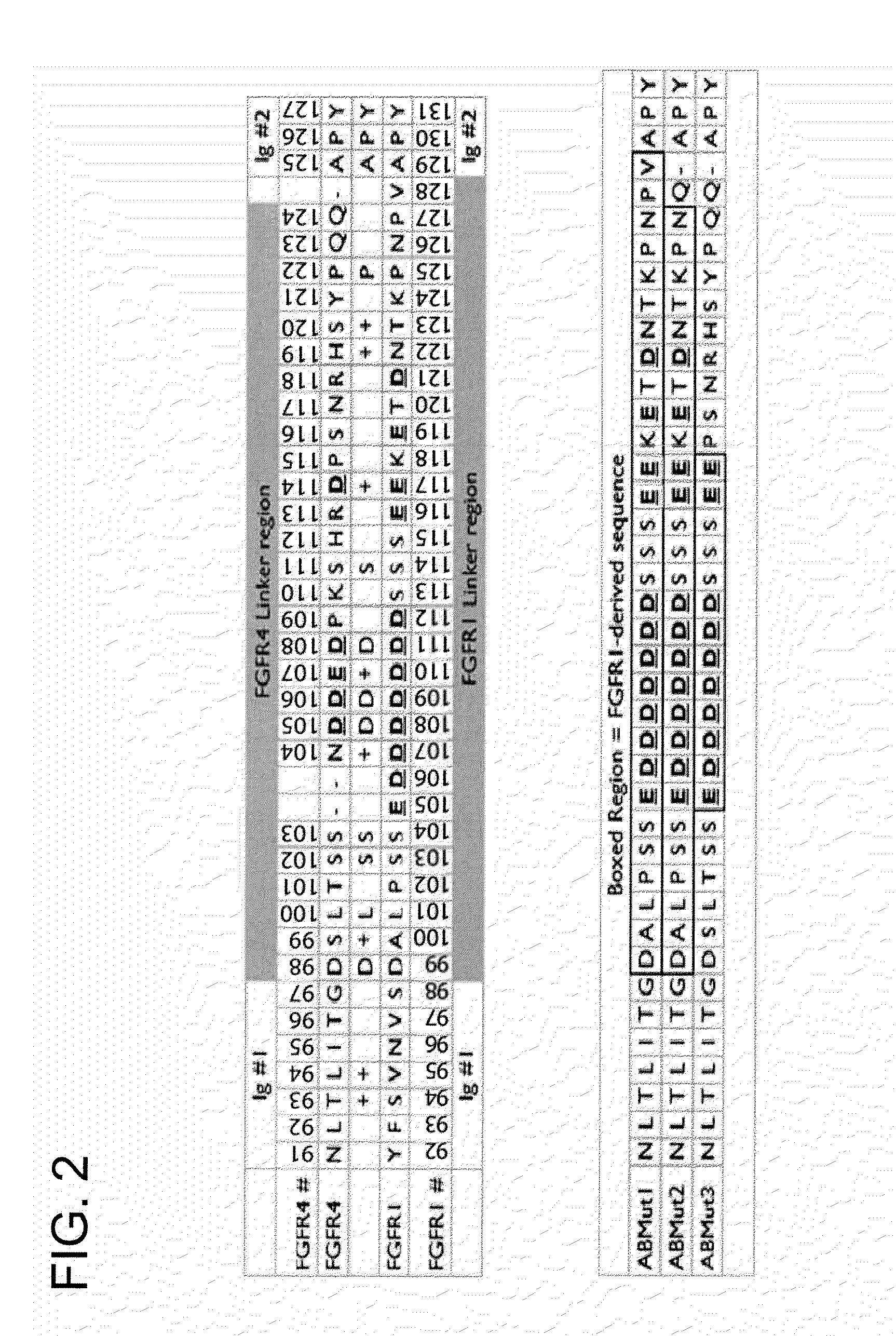
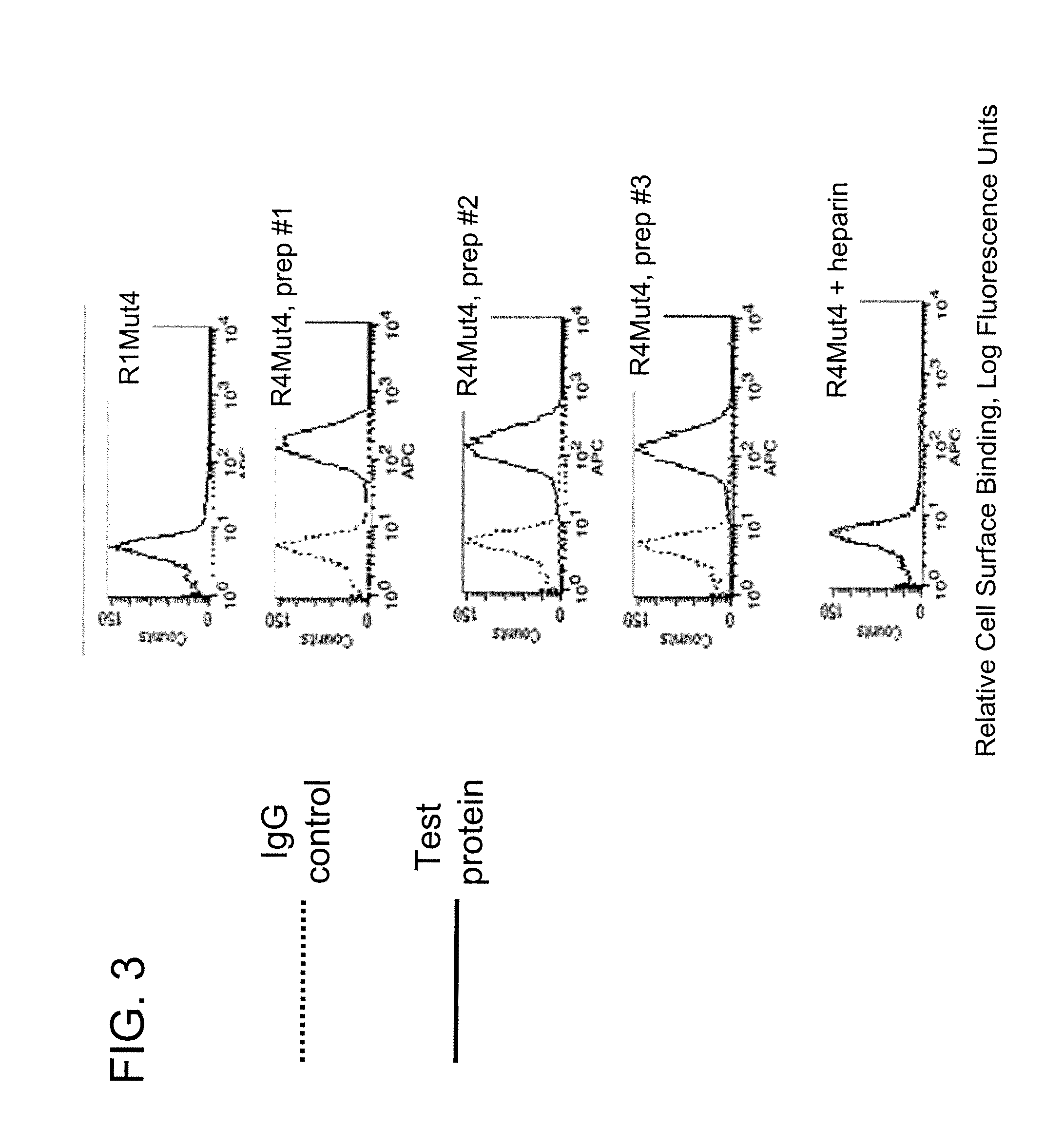
FGFR Extracellular Domain Acidic Region Muteins
InactiveUS20100087627A1Decreased ECM bindingImprove bioavailabilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) extracellular domain (ECD) acidic region muteins that have been engineered to exhibit decreased tissue binding by increasing the number of acidic amino acid residues within the D1-D2 linker region are provided. Polynucleotides encoding FGFR ECD acidic region muteins are also provided. Methods of making FGFR ECD acidic region muteins, and methods of using such molecules to treat proliferative disorders, including cancers, disorders of angiogenesis, and macular degeneration, are also provided.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
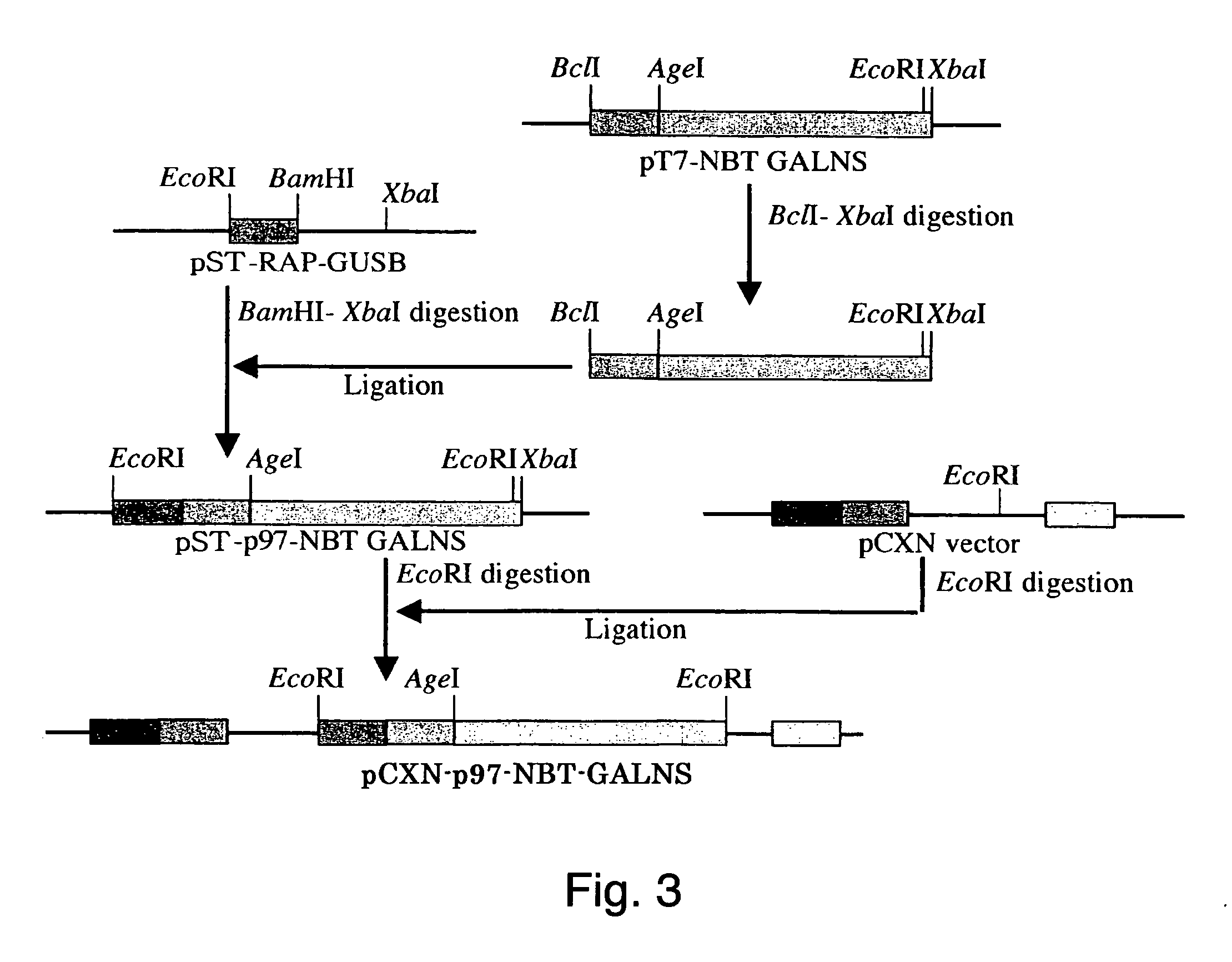
Proteins with an attached short peptide of acidic amino acids
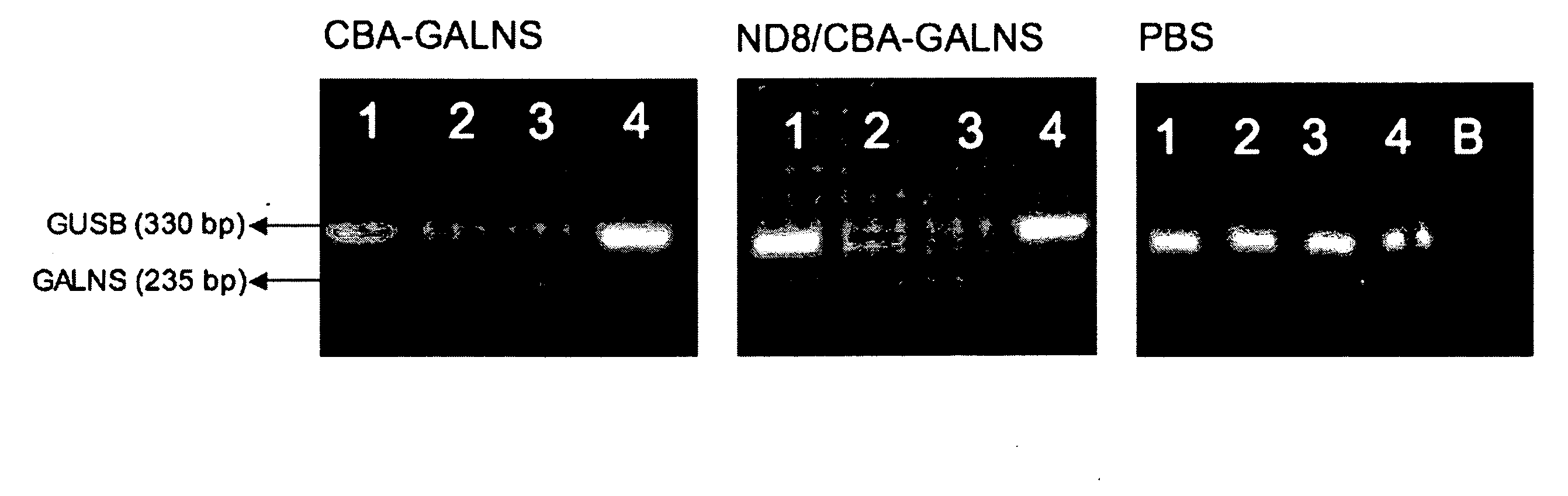
ActiveUS20050276796A1Improve stabilityImprove aimingPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSenses disorderN acetylgalactosamine 6 sulfate sulfataseBone tissue
Disclosed are a fusion protein comprising enzyme N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase and a short peptide consisting of 4-15 acidic amino acids attached to the enzyme on its N-terminal side, a pharmaceutical composition containing the fusion protein, and a method for treatment of type A Morquio disease using the fusion protein. Compared with the native enzyme protein, the fusion protein exhibits higher transferability to bone tissues and improved, higher stability in the blood.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY +2
FGFR extracellular domain acidic region muteins
InactiveUS8338569B2Preventing tissue bindingGreater ECM bindingSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) extracellular domain (ECD) acidic region muteins that have been engineered to exhibit decreased tissue binding by increasing the number of acidic amino acid residues within the D1-D2 linker region are provided. Polynucleotides encoding FGFR ECD acidic region muteins are also provided. Methods of making FGFR ECD acidic region muteins, and methods of using such molecules to treat proliferative disorders, including cancers, disorders of angiogenesis, and macular degeneration, are also provided.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
Peptide having an extending action for half-life of object peptide in plasma
ActiveUS20100305031A1Improve securityLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHalf-lifeBlood plasma
A peptide of the following (I) or (II).(I) a peptide represented by the formula B, A-B, B-C or A-B-C in which A, B and C each is represented by the following (1), (2) and (3) and, when it is bonded to other object peptide, it is able to extent the half-life in plasma as compared with the object peptide where the physiological activity of the object peptide is still retained.(II) a peptide comprising a reversed sequence of the peptide of (I); a sequence which is represented by A-B in (I) and A or B is reversed; a sequence which is represented by B-C in (I) and B or C is reversed; or a sequence which is represented by A-B-C in (I) and A, B, C, A and B, B and C or A and C is reserved.(1) A is a peptide comprising 1 to 14 of any amino acid(s)(2) B is a peptide represented by the formula 1:(Wk-Xl-Y-Zm-Wn)-(Wo-Xp-Y-Zq-Wr)s(In the formula 1, W is a basic amino acid; X and Z are any amino acids; Y is an acidic amino acid; k is 1 or 2; l is an integer of 4≧l≧0; m is an integer of 2≧m≧0; 4≧l+m≧0; n is 1 or 2; o is 1 or 2; p is an integer of 4≧p≧0; q is an integer of 2≧q≧0; 4≧p+q≧0; r is 1 or 2; and s is 0 or 1.)(3) C is a peptide comprising 2 to 14 of any amino acids.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Process for producing long chain N-acyl acidic amino acid
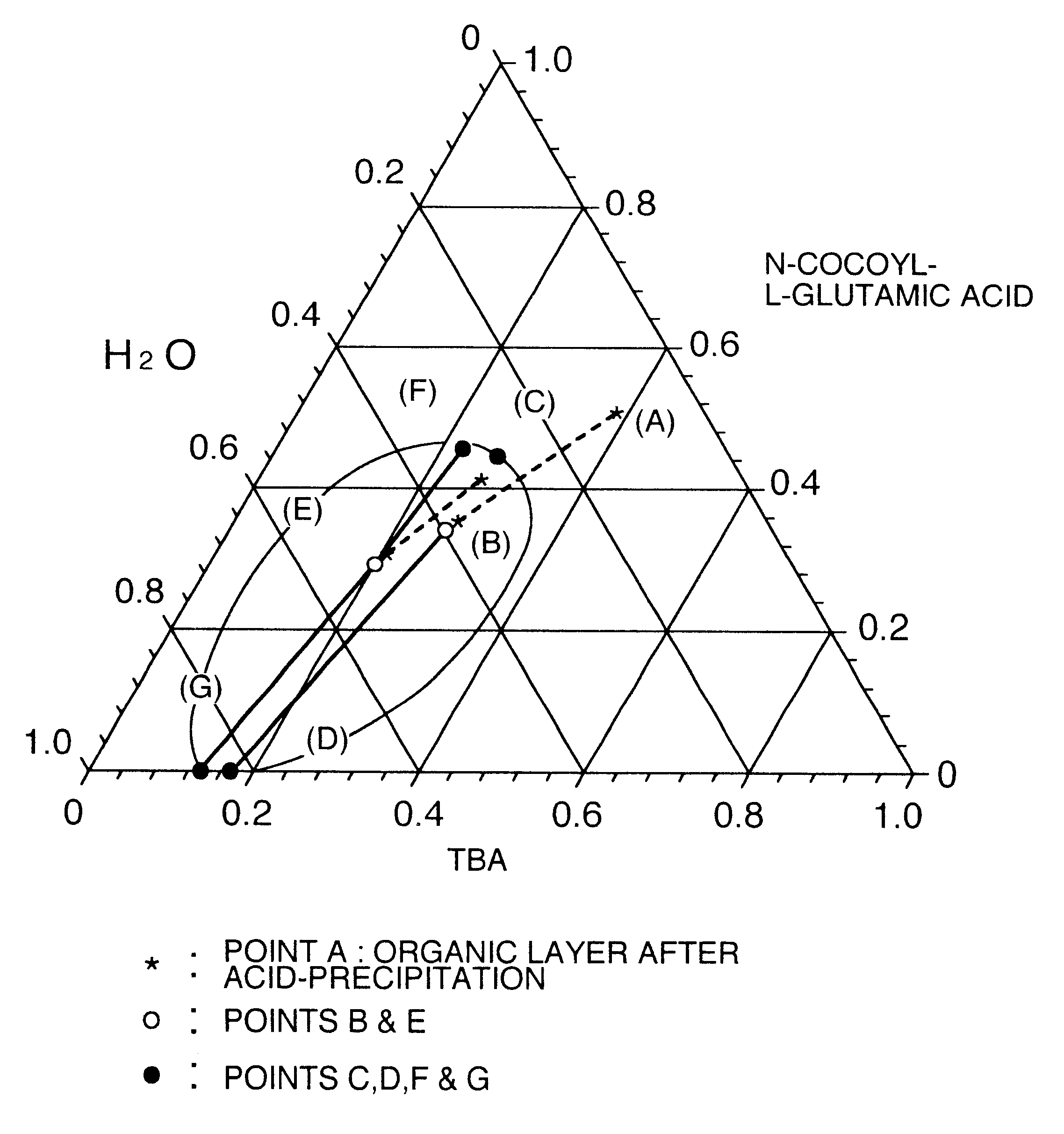
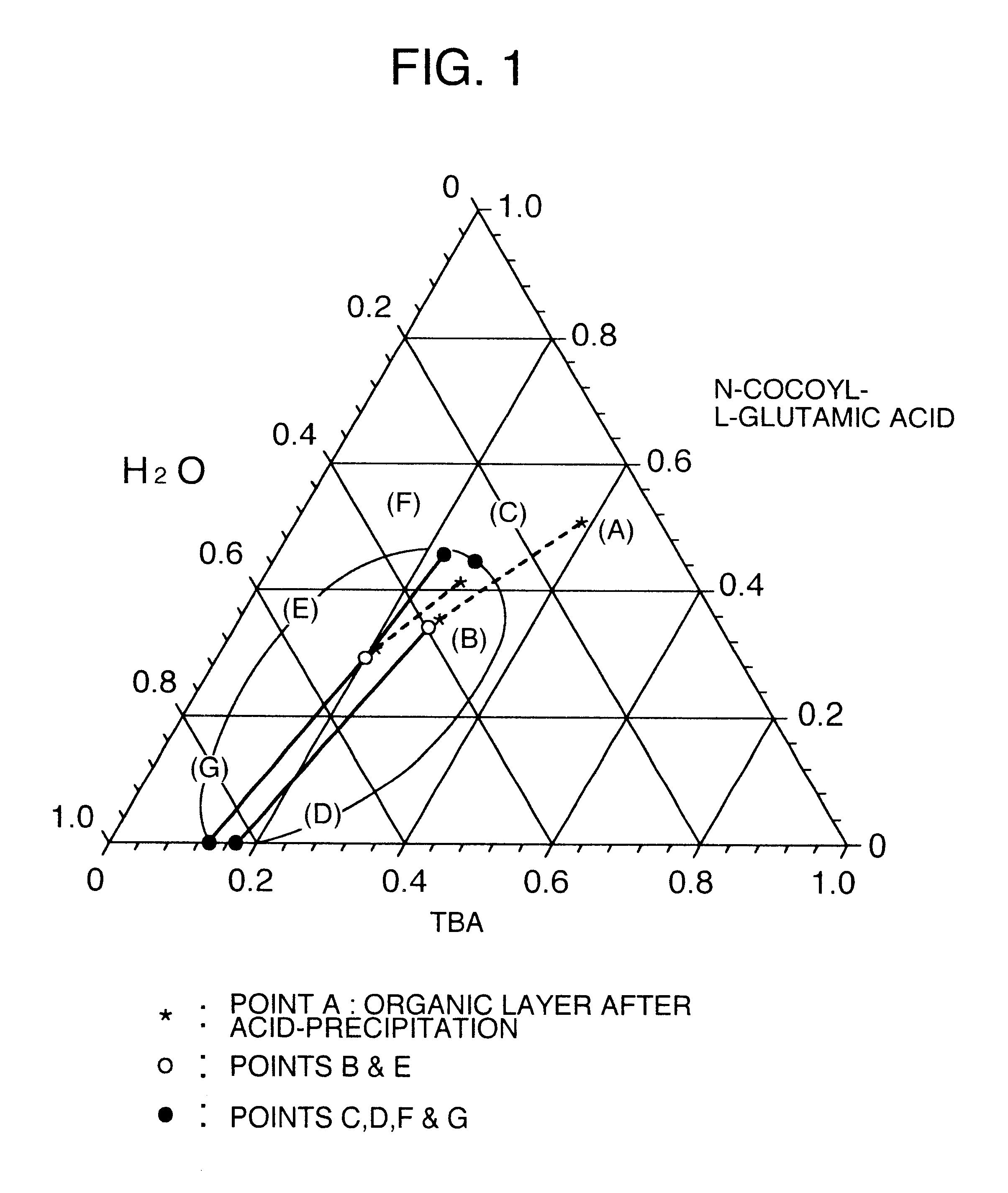
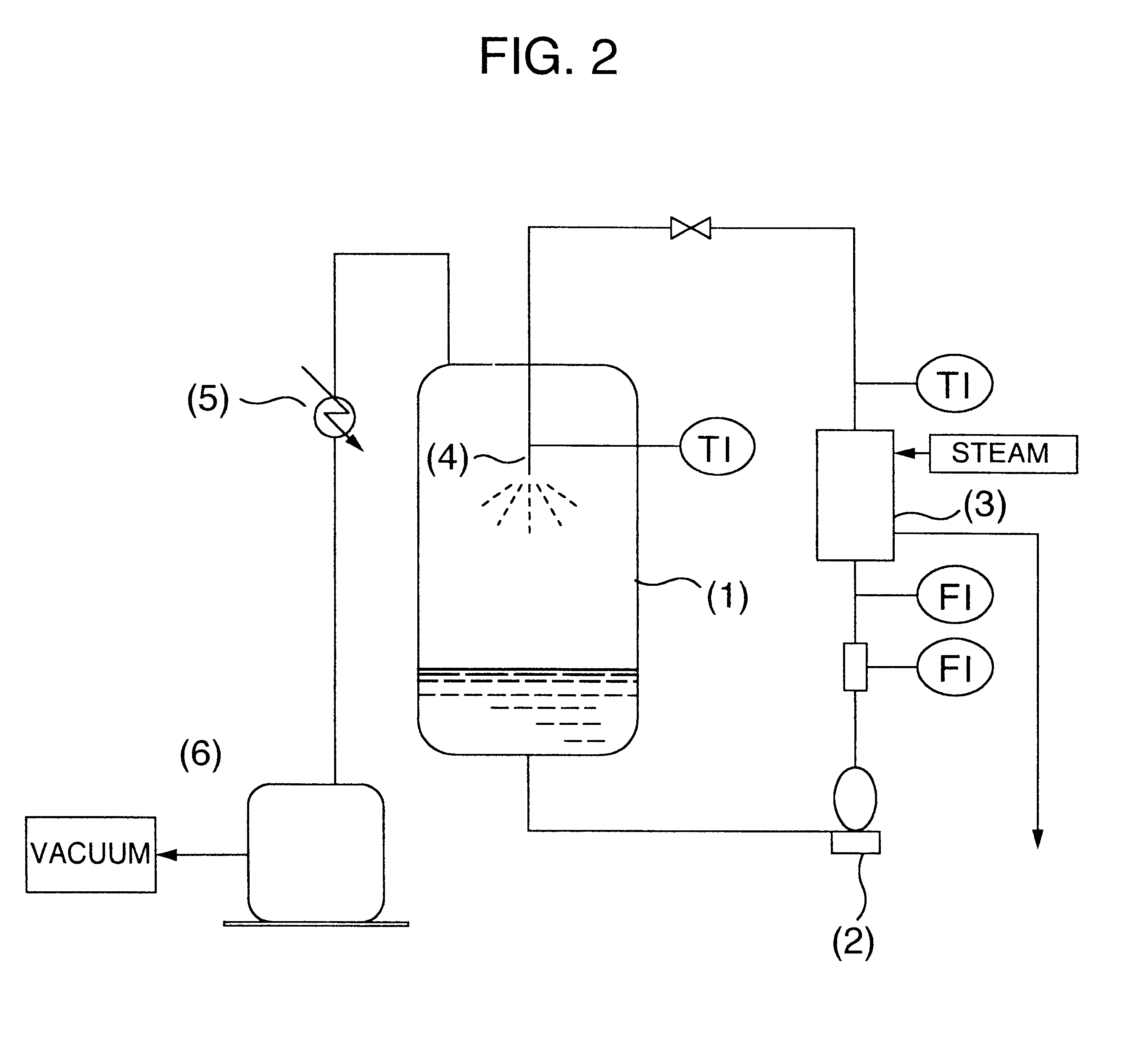
A process for producing a long chain N-acyl acidic amino acid removes impurities by separating a mixture composed of a long chain N-acyl acidic amino acid containing an inorganic salt and a medium containing water and tertiary butanol into an aqueous layer and an organic layer containing the long chain N-acyl acidic amino acid at a temperature of from 35 to 80° C.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI FINECHEM CO LTD
Protein appropriate for orientation-controlled immobilization and immobilization carrier on which the proteins are immobilized
InactiveUS20090299035A1Prepared efficiently and rapidlyFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAcidic amino acidsIsoelectric point
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel protein having the following amino acid sequence altered for specifically and efficiently binding a protein to an immobilization carrier via the carboxy terminus. The protein is used for immobilizing a portion represented by R1-R2 on an immobilization carrier, comprising the amino acid sequence represented by the general formula R1-R2-R3-R4-R5 [wherein:the sequences are oriented from the amino terminal side to the carboxy terminal side;the sequence of the R1 portion is the sequence of a subject protein to be immobilized and contains neither a lysine residue nor a cysteine residue;the sequence of the R2 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R2 portion is present, the sequence of the R2 portion is a spacer sequence composed of amino acid residues other than lysine and cysteine residues;the sequence of the R3 portion is composed of two residues of amino acid represented by cysteine-X (where X denotes an amino acid residue other than lysine or cysteine);the sequence of the R4 portion may be absent, but when the sequence of the R4 portion is present, the sequence of the R4 portion contains neither a lysine residue nor a cysteine residue, but contains an acidic amino acid residue capable of acidifying the isoelectric point of the entire protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by the general formula R1-R2-R3-R4-R5; andthe sequence of an R5 portion is an affinity tag sequence for protein purification.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Beta-glucuronidase with an attached short peptide of acidic amino acids
InactiveUS20070081986A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationBeta-glucuronidaseAcidic amino acids
Disclosed are a fusion protein comprising enzyme β-glucuronidase and short peptide consisting 4-15 acidic amino acids attached to the enzyme on its N-terminal side, pharmaceutical composition containing the fusion protein, and a method for treatment of type VII mucopolysaccharidosis using the fusion protein. Compared with the native enzyme, the fusion protein exhibits higher stability in the blood.
Owner:TOMATSU SHUNJI +5
Peptides whose uptake by cells is controllable
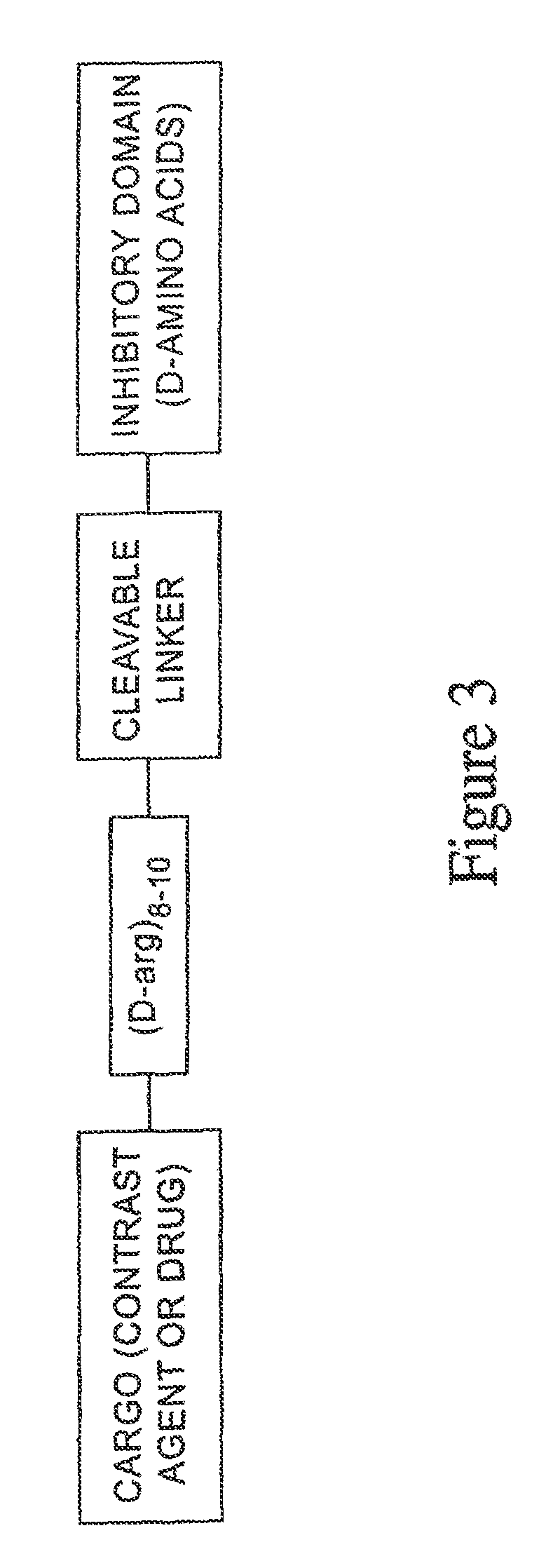
ActiveUS8642561B2Improve efficiencyDecrease possible side effect of treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunogenicityChemo therapy
A generic structure for the peptides of the present invention includes A-X-B-C, where C is a cargo moiety, the B portion includes basic amino acids, X is a cleavable linker sequence, and the A portion includes acidic amino acids. The intact structure is not significantly taken up by cells; however, upon extracellular cleavage of X, the B-C portion is taken up, delivering the cargo to targeted cells. Cargo may be, for example, a contrast agent for diagnostic imaging, a chemotherapeutic drug, or a radiation-sensitizer for therapy. Cleavage of X allows separation of A from B, unmasking the normal ability of the basic amino acids in B to drag cargo C into cells near the cleavage event. X is cleaved extracellularly, preferably under physiological conditions. D-amino acids are preferred for the A and B portions, to minimize immunogenicity and nonspecific cleavage by background peptidases or proteases.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Process for preparing gamma-amino butyric acid through enzymatic conversion
InactiveCN1635128ASimultaneous productionStrong specificityFermentationGlutamate decarboxylaseCombined method
The invention discloses an enzyme conversion method for preparing gamma-butyric acid. The preparation method comprises employing two mixed acidic amino acids of L-glutamic acid and L-aspartic acid as raw material, mixing the cells of Escherichia.coli AS1.505 with highly active L-glutamic acid decarboxylases and the conversion liquid containing the mixture of L-glutamic acid and L-aspartic acid, implementing enzymatic reaction under the temperature of 28~45íµ, then separating the conversion products by isoelectric point crystallization process or isoelectric point crystallization and ion exchange resin combined method to obtain high purity gamma-butyric acid and L-aspartic acid. The invention solves the problem of the highly effective separation of two acidic mixed amino acids, and obtains gamma-butyric acid with higher additional value, and has advantages of low price, simple operation, short conversion time, and low production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Novel composition containing acyl group
ActiveUS20050265951A1Reduce skin problemsSufficient surface activityCosmetic preparationsFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic solventAcyl group
According to the present invention, a process is provided for producing an acyl group-containing composition that includes a step of reacting a long chain N-acyl acidic amino acid anhydride with one or more compounds which have, per molecule, m functional groups of one kind or more selected from the group consisting of hydroxyl, amino and thiol groups in an aqueous solvent and / or a mixed solvent of water and an organic solvent (reaction step). The process makes it possible to produce an acyl group-containing composition that is free from coloration under moderate conditions.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI FINECHEM CO LTD
Inhibition of metal corrosion
InactiveUS6277302B1Prevent scalingLow toxicityOther chemical processesChemical inhibitorsPhysical chemistryAqueous solubility
A composition and method is disclosed for inhibiting the corrosion of metals in contact with an aqueous system capable of corroding the metal. The inventive composition contains a substantially water-soluble polymer of an acidic amino acid and at least one water-soluble salt of molybdenum or zinc. The composition is substantially non-toxic and environmentally acceptable and is supplied in a corrosion-inhibition amount to the otherwise metal-corrosive aqueous system.
Owner:DONLAR CORP
Crystals of insulin analogs and processes for their preparation
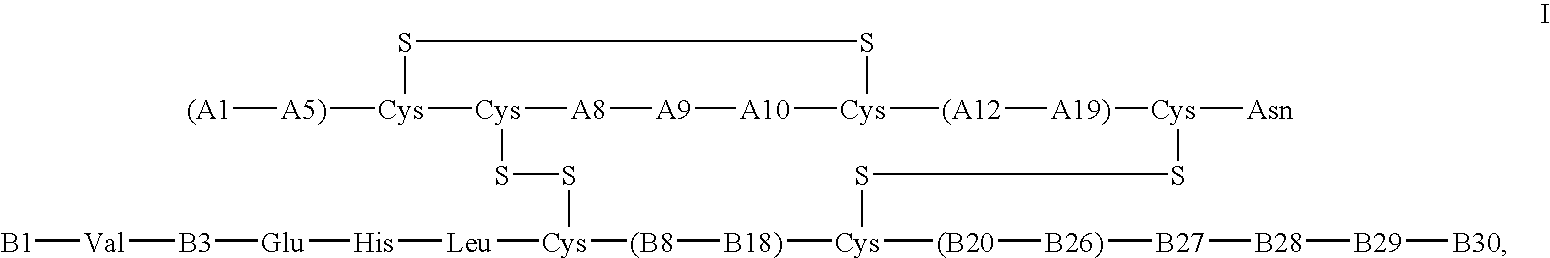
The invention relates to crystals of an insulin analog in which asparagine (Asn) in position B3 of the B chain is replaced by a naturally occurring basic amino acid residue and at least one amino acid residue in the positions B27, B28 or B29 of the B chain is replaced by another naturally occurring neutral or acidic amino acid residue, where phenylalanine (Phe) in position B1 of the B chain can optionally be absent, the crystals being present in the space group R3 (No. 146) with the cell axes A=81.5 ű1 Å and C=33.3 ű1 Å, their preparation and use, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising these crystals.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Delivery of therapeutic agents to the bone
This invention relates to compositions and methods of delivering therapeutic agents to bone. More specifically, the invention relates to endowing a large molecule vectors i.e., adeno virus, retrovirus, liposomes, micelles, natural and synthetic polymers, or combinations thereof, with the ability to target bone tissue in vivo and with improved stability in the blood, by attaching multiple copies of acid amino acid peptides. One preferred embodiment of the invention relates to endowing an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector with the ability to target bone-tissue in vivo and improve its stability, by the addition of multiple acidic amino acid peptides attached to the capsid of the viral vector.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Polishing agent for synthetic quartz glass substrate
InactiveUS20100243950A1Increase productionSmall feature sizeOther chemical processesLapping machinesColloidal silicaSilicon dioxide
Disclosed is a polishing agent for synthetic quartz glass substrates, which is characterized by containing a colloidal solution of a colloidal silica or the like having a colloid concentration of 20-50% by mass, and a polycarboxylic acid polymer, an acidic amino acid, a phenol or a glycosaminoglycan.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Gelling agent for oil
InactiveUS7244419B2Cosmetic preparationsFatty acid chemical modificationAspartic acid residueL-Aspartate
A compound represented by the following general formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 represent a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 26 carbon atoms, preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, R3 represents a hydrocarbon group having 7 to 10 carbon atoms, preferably a linear or branched alkyl group, n represents 1 or 2 provided that the acidic amino acid residue in the molecule is L-aspartic acid residue when n is 1 and said acidic amino acid residue is L-glutamic acid residue when n is 2, and a gelling agent for an oil comprising said compound
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Gelling agent
Gelling agents which contain at least one N-acyl-L-acidic amino acid dialkylamide represented by the following general formula (1): wherein R1 and R2 each independently represent a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 26 carbon atoms; R3 represents a hydrocarbon group having 7 to 10 carbon atoms; and n represents 1 or 2, such as N-2-ethylhexanoyl-L-glutamic acid dibutylamide; and at least one monohydric lower alcohol such as 3-methoxy-3-methylbutanol are useful for forming gel compositions with an oily base.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for preparing novel amino acid chelate
InactiveCN101671263AOrganic compound preparationCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesFood additiveSolubility
The invention relates to a method for preparing a novel food additive amino acid chelate, and the method comprises the following steps: acidic amino acid and calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide are chelated in a proper condition to obtain the calcium amino acid chelate; and the calcium amino acid chelate reacts with sulphates of zinc, iron, magnesium, copper, manganese and cobaltic to obtain the corresponding amino acid chelate. The amino acid micro-element chelate produced by the method is characterized in that the products are electric neutrality, do not carry other ions besides amino acid and microelements and have simple process, no environment pollution; the byproduct calcium sulphate is taken as raw auxiliary materials in food and medical fields. Due to the advantages of large dissolubility quality, stable properties, safety and effectiveness and no toxic side effect and the like, the stable amino acid micro-element chelate can bring new commercial opportunities for future healthcare products and medicinal markets.
Owner:北京中国科学院老专家技术中心 +1
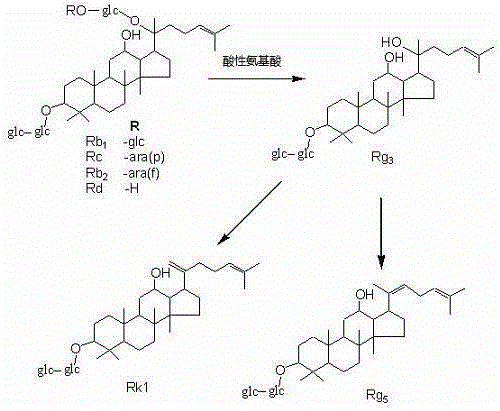
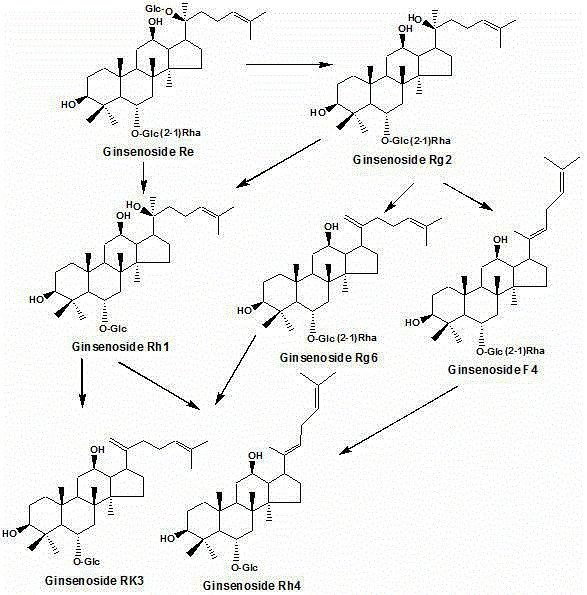
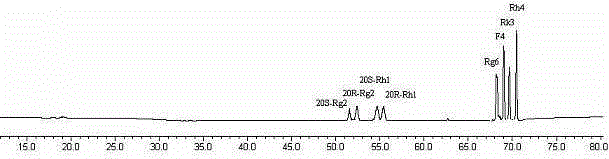
Method for preparing rare ginsenoside by hydrolyzing ginsenoside with acidic amino acid
ActiveCN105273032AOvercoming poor hydrolysis specificityLow overcoming rateSteroidsNeutral Amino AcidsNew medications
The invention discloses a method for preparing rare ginsenoside by hydrolyzing ginsenoside with acidic amino acid. Panoxadiol saponins are converted to generate 20R-Rg3, 20S-Rg3, Rg5 and Rk1, and panaxatriol saponins are converted to generate Rg6, F4, Rk3 and Rh4. Compared with an existing preparation process, the hydrolysis capacity of acidic amino acid is more than 10 times of that of neutral amino acid and that of basic amino acid and can better meet requirements of industrial preparation of rare ginsenoside, the defects that the hydrolysis specifity of ginsenoside is poor, the yield is low, the corrosion is high, environment pollution is caused, multiple byproducts are produced and the like due to the fact that a large amount of strong acid and strong base are used are overcome, ginseng resources are fully used, rare ginsenoside is extracted and enriched to the largest extent, the purpose of simple, quick, environment-friendly and low-cost enrichment of rare ginsenoside is achieved, and the method guarantees industrial production and preparation of new medicines.
Owner:JILIN YATAI PHARM CO LTD
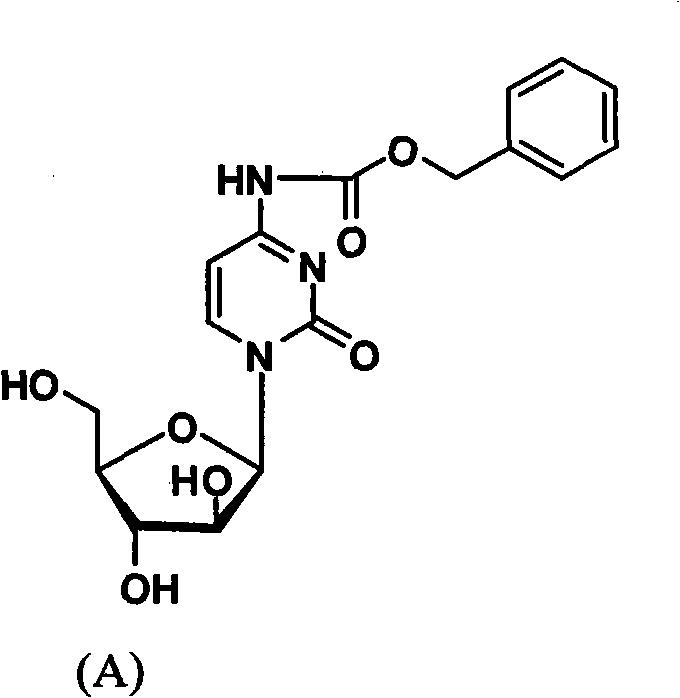
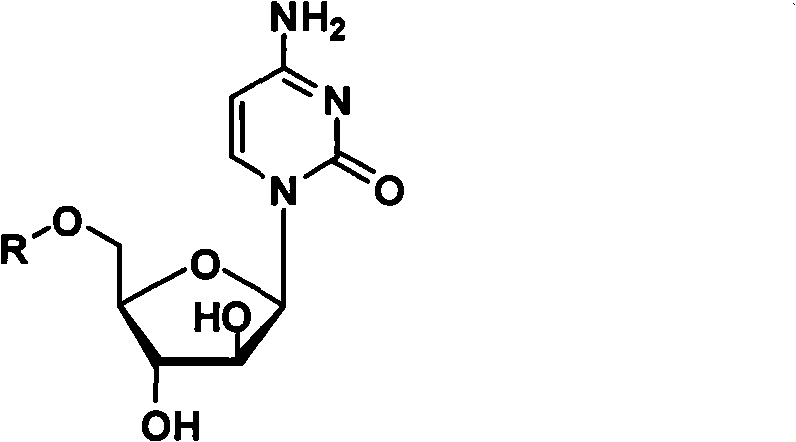
Cytarabine 5'-O-amino-acid ester, salts thereof and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101812105AGood membrane permeabilityIncrease Absolute BioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCytarabineSodium bicarbonate
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and discloses cytarabine 5'-O-amino-acid ester, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: slowly dropping carbobenzoxy chloride into a solution formed by cytarabine, sodium bicarbonate and N,N-dimethylacetylamide, and obtaining a compound A after reacting at room temperature; using the compound A and N-butyloxy formoxyl-amino acid as raw materials; adding a reagent to the solution to carry out an esterification reaction to obtain the cytarabine 5'-O-amino-acid ester; and then adding acid to obtain a finished product. The pharmaceutically acceptable salts comprise hydrochlorides, sulfates, formates, acetates, mesylates, propionates, butyrates, p-toluene sulphonates, phosphates, bisulfates, maleates, lactates, carbonates, bicarbonates, malonates, and salts formed with acidic amino acids, and the like. The invention can obviously improve the membrane permeability of the cytarabine so as to improve the bioavailability of the cytarabine.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Wood frog antibiotic peptides and preparation technology and its application in antiviral drug
ActiveCN101456910AGood antiviral effectNo hemolytic activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsArginineThreonine
The invention provides a wood frog antibiotic peptide and a preparation process thereof. The invention further discloses application of the antibiotic peptide in the preparation of antiviral medicines. The peptide is a basic polypeptide with the molecular weight range from 2 to 16 KDa and the isoelectric point from 8.9 to 9.5. The peptide consists of asparagic acid, glutamic acid, major serine, histidine, arginine, glycine, threonine, proline, alanine, Val, methionine, and the like, wherein the basic amino acid accounts for 23.99 percent of the gross amount, and the acidic amino acid accounts for 19.08 percent of the gross amount. The wood frog antiviral antibiotic peptide is a product obtained from natural resources. The wood frog antiviral antibiotic peptide has the good antiviral capability and simultaneously has the advantages of no hemolytic activity, no plasma coagulation activity, and the like. The wood frog antibiotic peptide can be used for preparing medicines for treating antiviral type flu, hepatitis B and AIDS.
Owner:TONGHUA KANGYUAN BIOLOGICAL TECH
Low temperature-stable creamy wash composition
Creamy wash composition containing (A) at least one N-long-chain-acyl acidic amino acid or a salt thereof, (B) at least one polyhydric alcohol, (C) at least one nonionic surfactant, (D) at least one salt of a divalent or higher cation and a monovalent or higher anion, and (E) water are stable at a low temperature and exhibit good foaming properties and a good feeling upon use.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Stable oral solid drug composition
InactiveUS20050026981A1Easy to getRemarkable effectPowder deliveryBiocideCarboxylic acidBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
This invention is aimed to provide a stabilized formulation of ramosetron or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof under a temperature / humidity condition, especially at a low content and relates to a stable oral solid drug composition of ramosetron or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, which is characterized by containing one or two or more members selected from the group consisting of an aliphatic carboxylic acid or an ester thereof, a hydroxycarboxylic acid or an ester thereof, an acidic amino acid, an enolic acid, an aromatic carboxyl compound or an ester thereof, and a carboxyl group-containing high-molecular substance, and to a stabilization method of the same. Also, this invention relates to a therapeutic agent of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome containing from 0.002 to 0.02 mg of ramosetron hydrochloride as a daily dose or an equivalent molar amount of ramosetron or its pharmaceutically acceptable other salt as an active ingredient.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
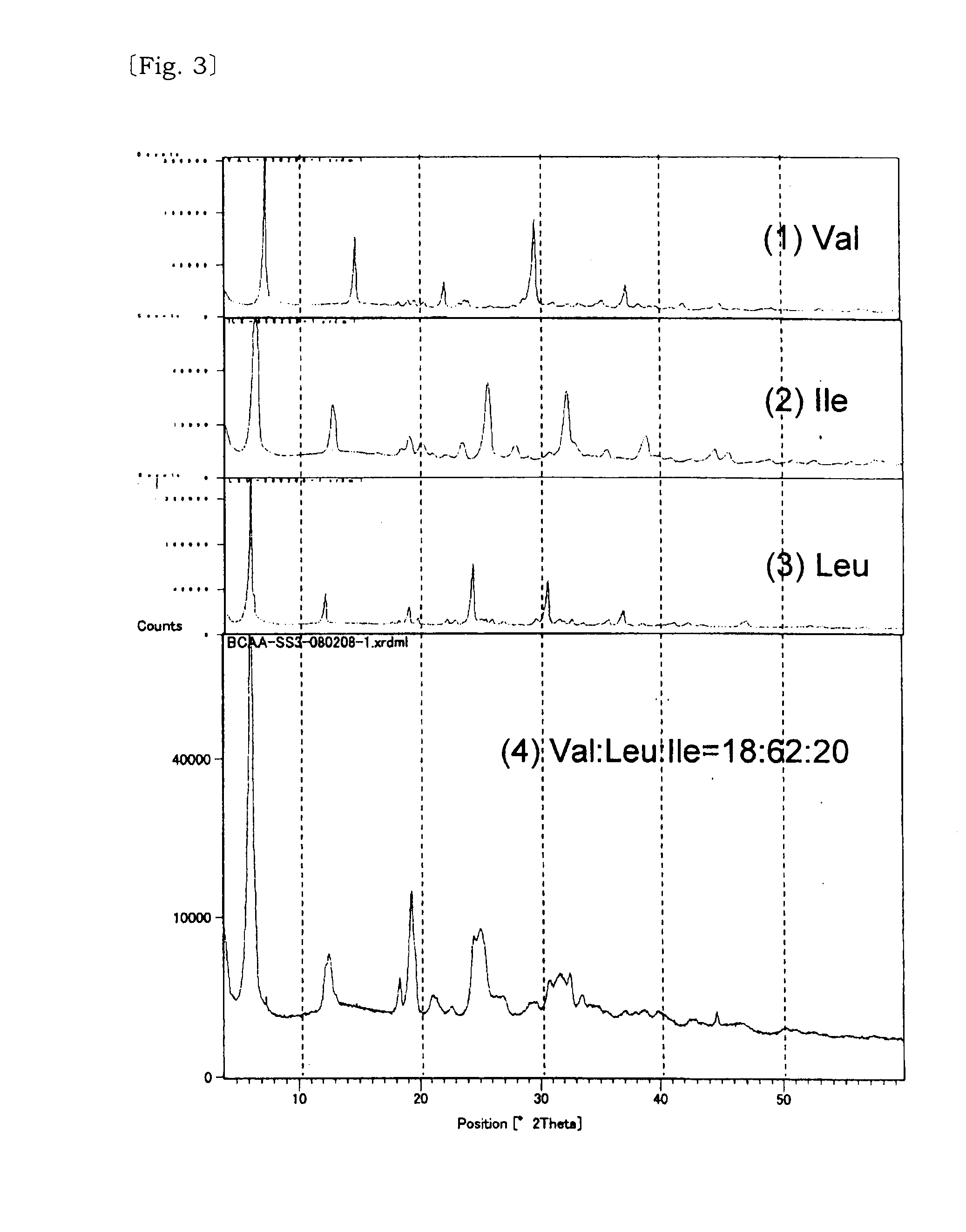
Solid solution of valine, isoleucine, leucine and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20110257236A1Reduce bitternessImprove dissolution rateBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCrystallographyTert-leucine
[Problem] A valine, isoleucine, leucine mixture which is excellent in the reduction of bitter taste and improved dissolution speed is provided.[Solving Means] The above problem is solved by a solid solution composed of three amino acids of valine, isoleucine, leucine, and a solid solution composed of these and at least one of acid selected from the group consisting of neutral aliphatic amino acid, neutral hydroxy amino acid, neutral acid amide amino acid, acidic amino acid, basic amino acid, hydroxy acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
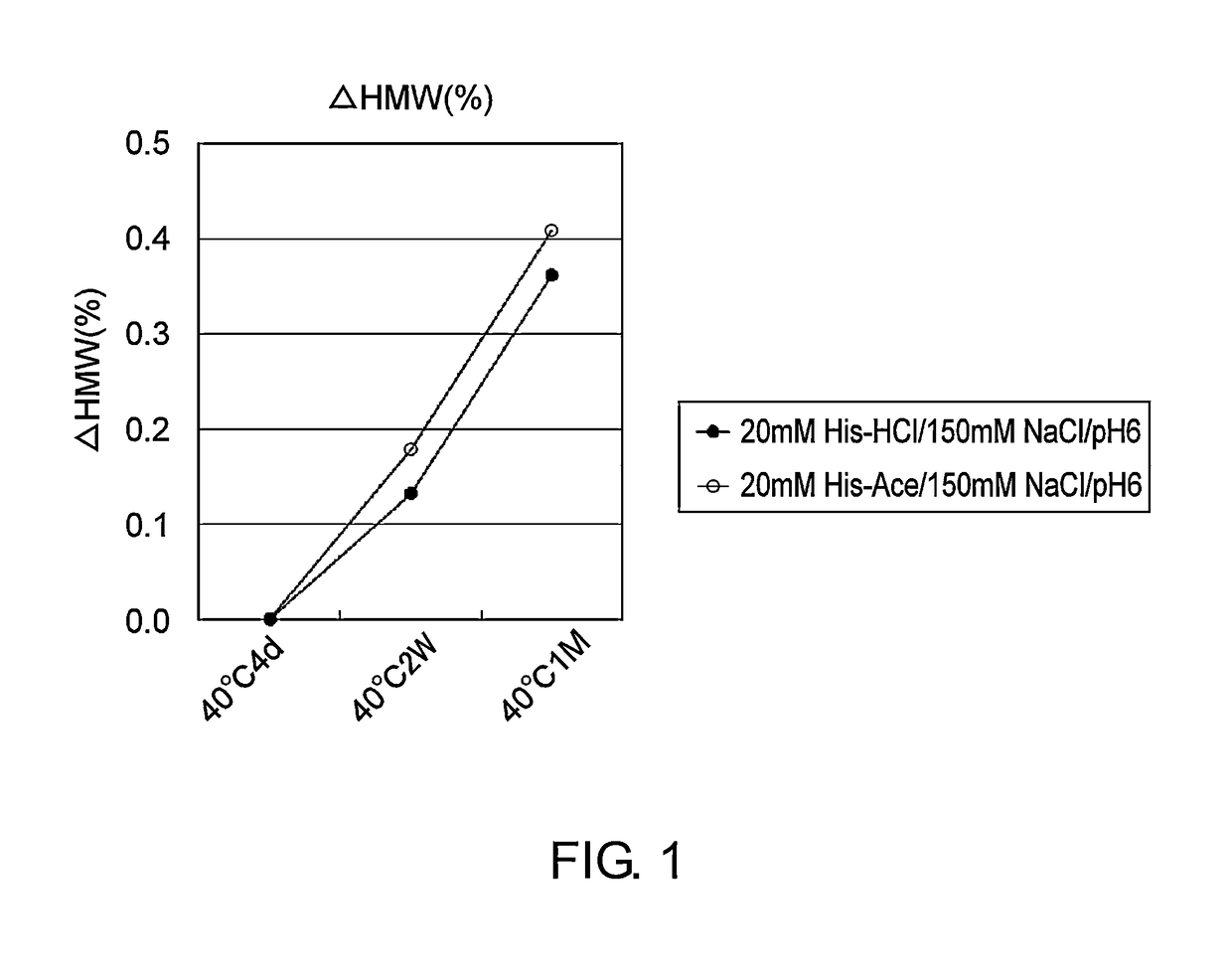
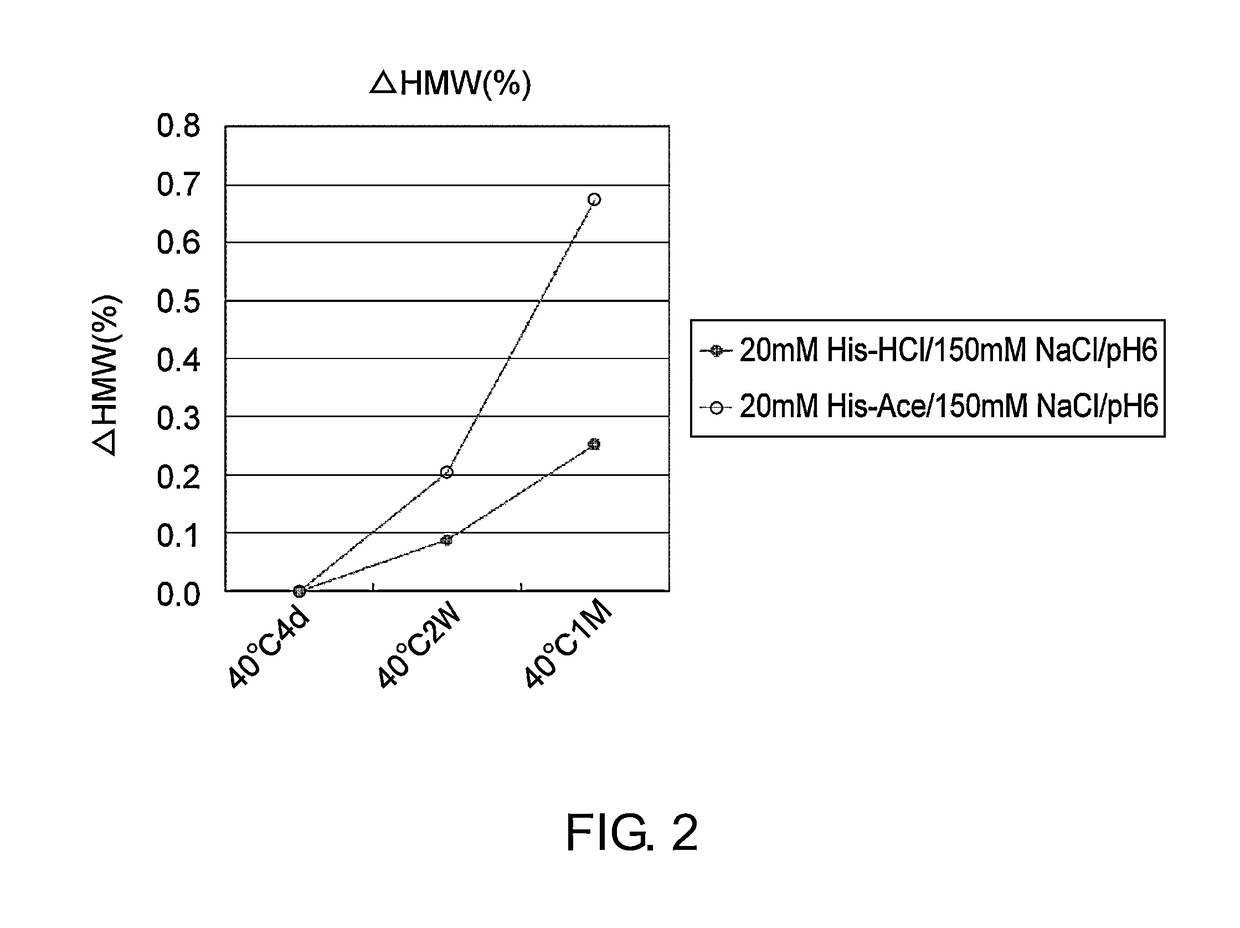
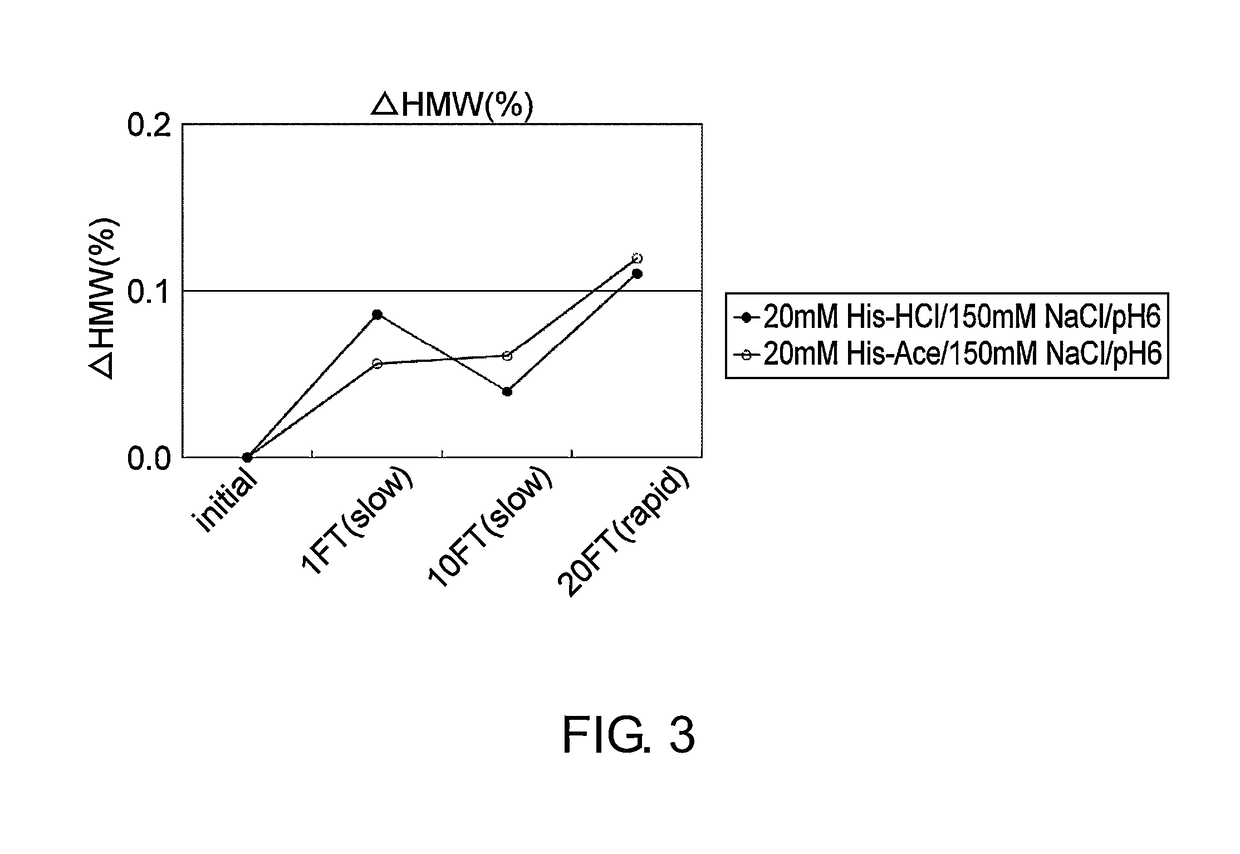
Stabilized antibody-containing liquid formulations
ActiveUS10022319B2Improve stabilityStable storageAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsArginine glutamateSignificant Stabilization
An objective of the present invention is to provide stable antibody-containing formulations which are suitable for subcutaneous administration and in which aggregation formation is suppressed during long-term storage.The present inventors discovered that a significant stabilization effect was achieved by using an acidic amino acid, aspartic acid or glutamic acid as a counter ion species in histidine buffer or tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, specifically by using histidine-aspartate buffer or histidine-glutamate buffer, or tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-aspartate or tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-glutamate as a buffer. The present inventors also discovered that a significant stabilization effect was achieved by using an acidic amino acid, aspartic acid or glutamic acid, as a counter ion species to a basic amino acid such as arginine, specifically by using arginine-aspartate or arginine-glutamate.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Soil improvement agent for saline-alkali land
InactiveCN107236548ALower pH valueAvoid churnAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesSodium BentoniteAlkali soil
The invention discloses a soil improvement agent for a saline-alkali land. The soil improvement agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100-200 parts of humic acid, 50-100 parts of algae mud, 50-100 parts of biochar, 1-5 parts of a biological fungicide, 1-5 parts of a biological enzyme agent, 50-100 parts of pine needle meal, 50-100 parts of brewer's grain, 20-50 parts of sulfur slag, 20-50 parts of bentonite, 100-200 parts of chicken manure, 30-50 parts of straw, 20-30 parts of feather meal and 20-30 parts of earthworm powder. The sulfur ions and sulfuric acid contained in the added sulfur slag are firstly separated out by hot water, are attached to the biological fungicide by virtue of the biological fungicide and then are bound with ions in the saline-alkali land. By further adding an acidic amino acid chelating solution and a bamboo vinegar solution, the pH value of the saline-alkali land is decreased; and by adding the biochar, coconut chaff and rice bran, moisture and water preservation effects are achieved, and soil erosion is prevented.
Owner:钟春明
Composition containing acyl group
ActiveUS7488841B2Solve the lack of activityReduce skin problemsCosmetic preparationsOrganic compound preparationAcyl groupOrganosolv
Owner:ASAHI KASEI FINECHEM CO LTD
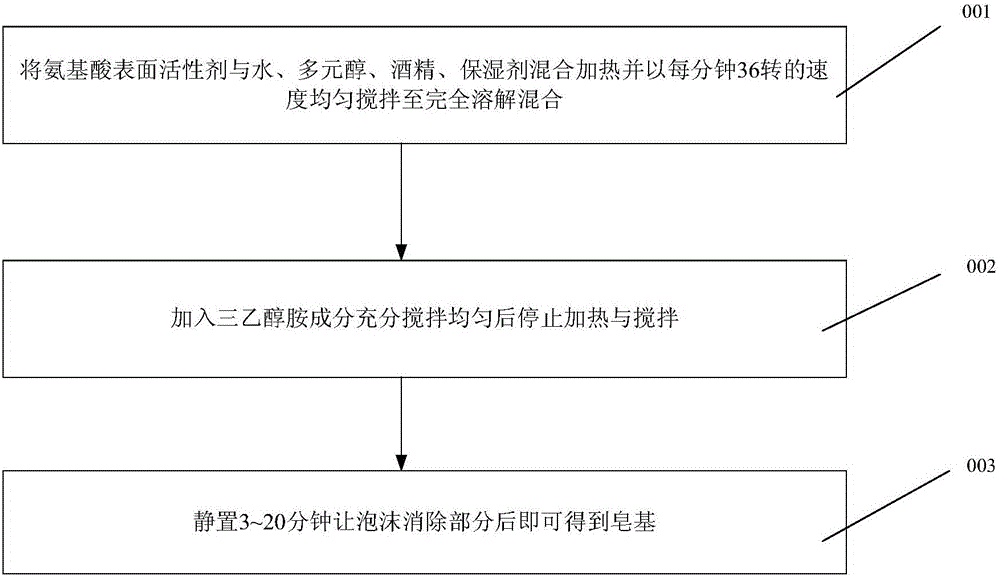
Method for producing composite faintly acid amino acid soap bases
InactiveCN104983594AImprove securityFine foamCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAlcoholAcidic amino acids
The invention provides a method for producing composite faintly acid amino acid soap bases. The method for producing the composite faintly acid amino acid soap bases comprises the steps of conducting saponification action with 18%-46% of amino acid surfactant, 10%-31% of water, 12%-29% of triethanolamine, 12%-25% of polyhydric alcohols, 4%-15% of ethyl alcohol and 0.08%-17% of humectant, and obtaining the soap bases. The composite faintly acid amino acid soap bases have the advantages that the PH value of the soap bases is close to that of skin, the PH value is equal to or less than 6.4, and tension or discomfort does not happen to skin after washing. Foam generated through the soap bases is excellent in quality, meanwhile, the appearance of the soap bases is clear and transparent just like crystal, the production process is easy to operate and control comparatively, and the popularization is facilitated. The amino acid surfactant is high in safety to environment and living bodies and has endophilicity to skin and hair.
Owner:罗晓安
Preparation method and application of N-acyl acidic amino acid or salt thereof
ActiveCN103435509ASatisfaction conversion rateLow costCosmetic preparationsOrganic compound preparationNeutral Amino AcidsSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of N-acyl acidic amino acid or a salt thereof. According to the preparation method, fatty acyl chloride and an amino acid are subjected to an amidation reaction under an alkaline condition. The preparation method is characterized in that in the amidation reaction, water is used as a solvent, an acidic amino acid or a salt thereof is used as a main raw material and a small amount of a neutral amino acid or a salt thereof is used as an auxiliary raw material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: under a stirring condition, dropping the fatty acyl chloride into the aqueous solution of the acidic amino acid or the salt thereof; adding an alkali to adjust the pH value of the reaction solution; after a certain amount of fatty acyl chloride is dropped, adding the aqueous solution of the neutral amino acid or the salt thereof, continue to drop the fatty acyl chloride until the dropping is finished and stirring to maintain the reaction. According to the preparation method, the mixed amino acid and the fatty acyl chloride react under a water-phase system, so that the conversion rates of the mixed amino acid and the fatty acyl chloride can be remarkably increased and the amount of residual amino acids is greatly reduced. The product can be directly used as a surfactant after being treated simply, and thus the cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING HUASHI NEW MATERIAL
Oral care compositions for promoting gum health
ActiveUS20190298620A1Deep penetrationAdd depthCosmetic preparationsImpression capsMouth careMedicine
Oral care compositions comprising an acidic amino acid and stannous ion source are provided for promoting Gum Health of a user.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Novel coronavirus recombinant antigen coating solution and pretreatment method and application thereof and product
Owner:ZHUHAI LIVZON DIAGNOSTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com