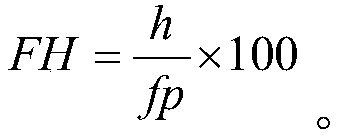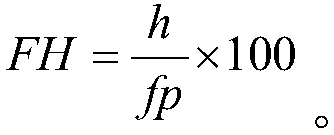Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149 results about "Bone development" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apoptosis inducing molecule II and methods of use
The present invention relates to a novel member of the TNF-Ligand superfamily. More specifically, isolated nucleic acid molecules are provided encoding a human Apoptosis Inducing Molecule II (AIM II). AIM II polypeptides are also provided, as are vectors, host cells and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of AIM II activity. Also provided are therapeutic methods for treating lymphadenopathy, aberrant bone development, autoimmune and other immune system diseases, graft versus host disease, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and to inhibit neoplasia, such as tumor cell growth.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Antibodies that block receptor protein tyrosine kinase activation, methods of screening for and uses thereof
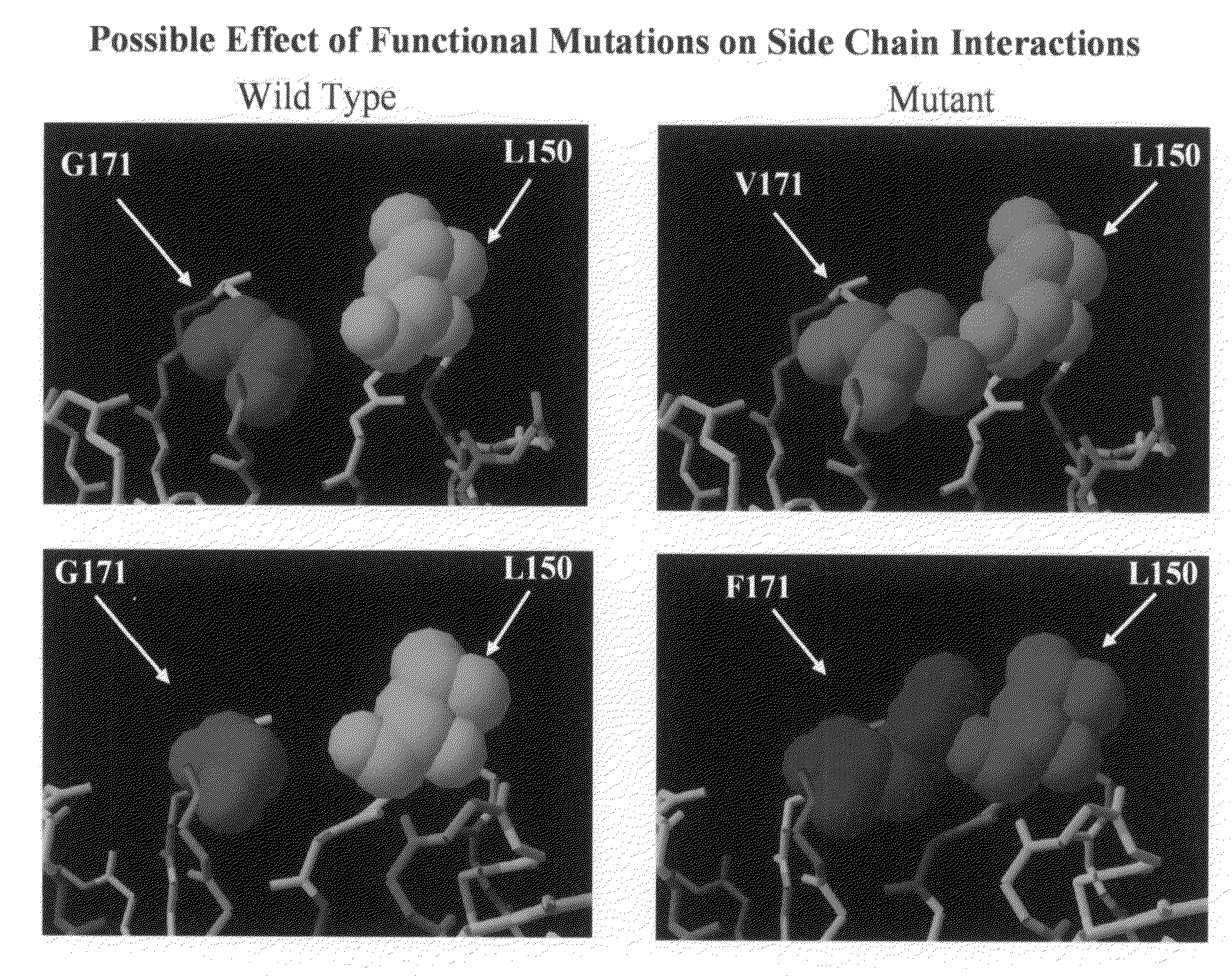
Molecules comprising the antigen-binding portion of antibodies that block constitutive and / or ligand-dependent activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase, such as fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), are found through screening methods, where a soluble dimeric form of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase is used as target for screening a library of antibody fragments displayed on the surface of bacteriophage. The molecules of the present invention which block constitutive activation can be administered to treat or inhibit skeletal dysplasia, craniosynostosis disorders, cell proliferative diseases or disorders, or tumor progression associated with the constitutive activation of a receptor protein tyrosine kinase.
Owner:FIBRON
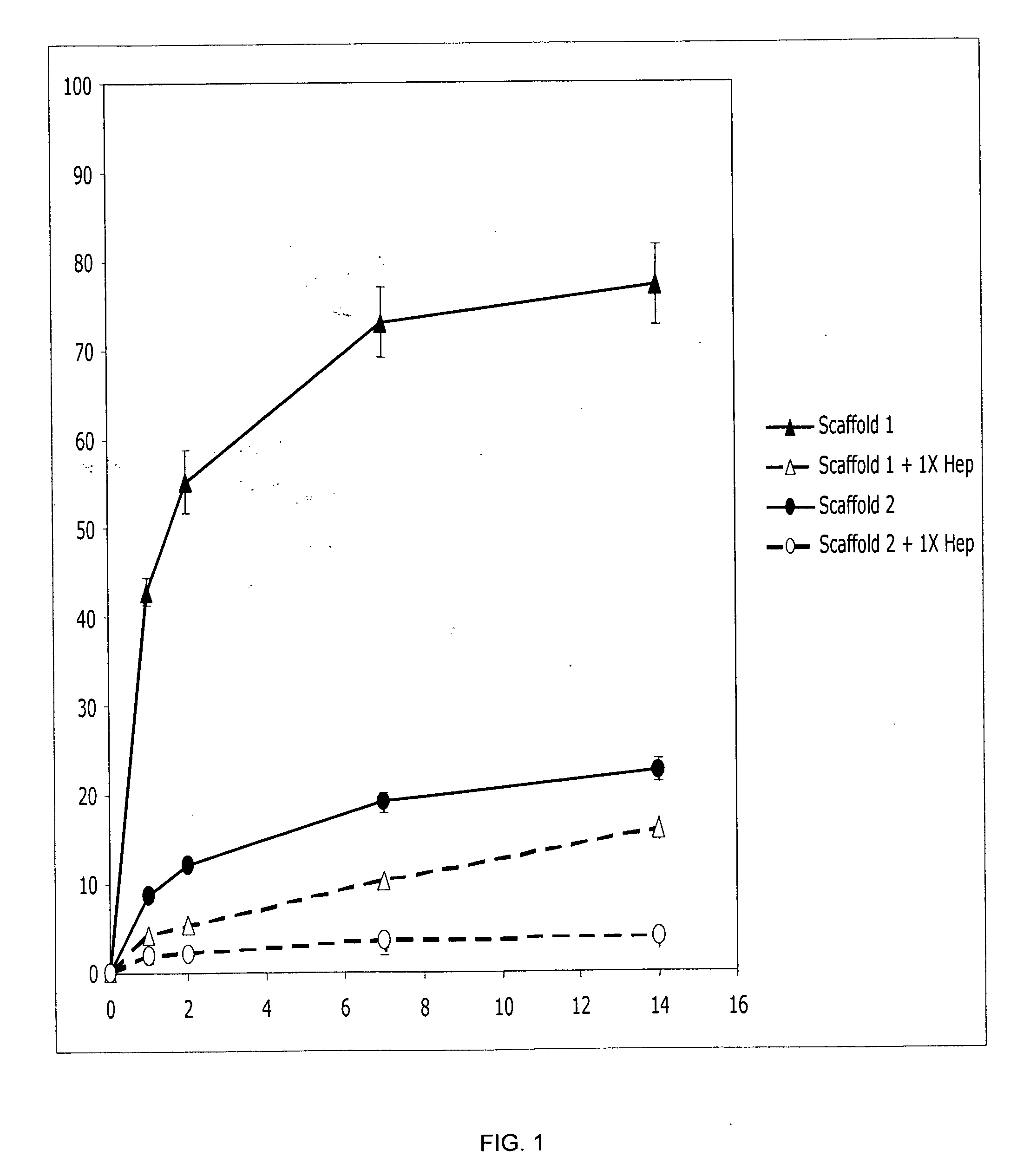
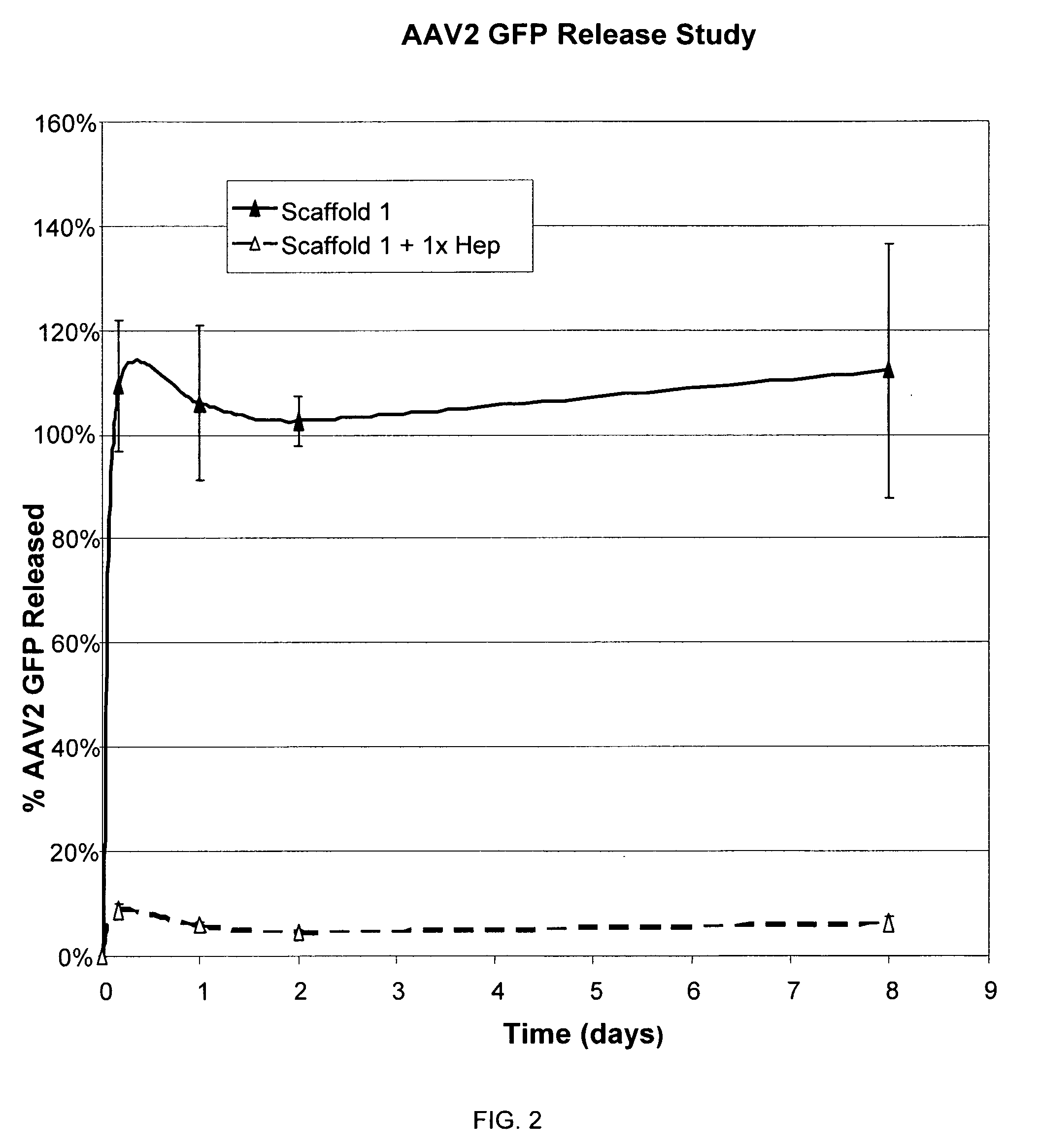
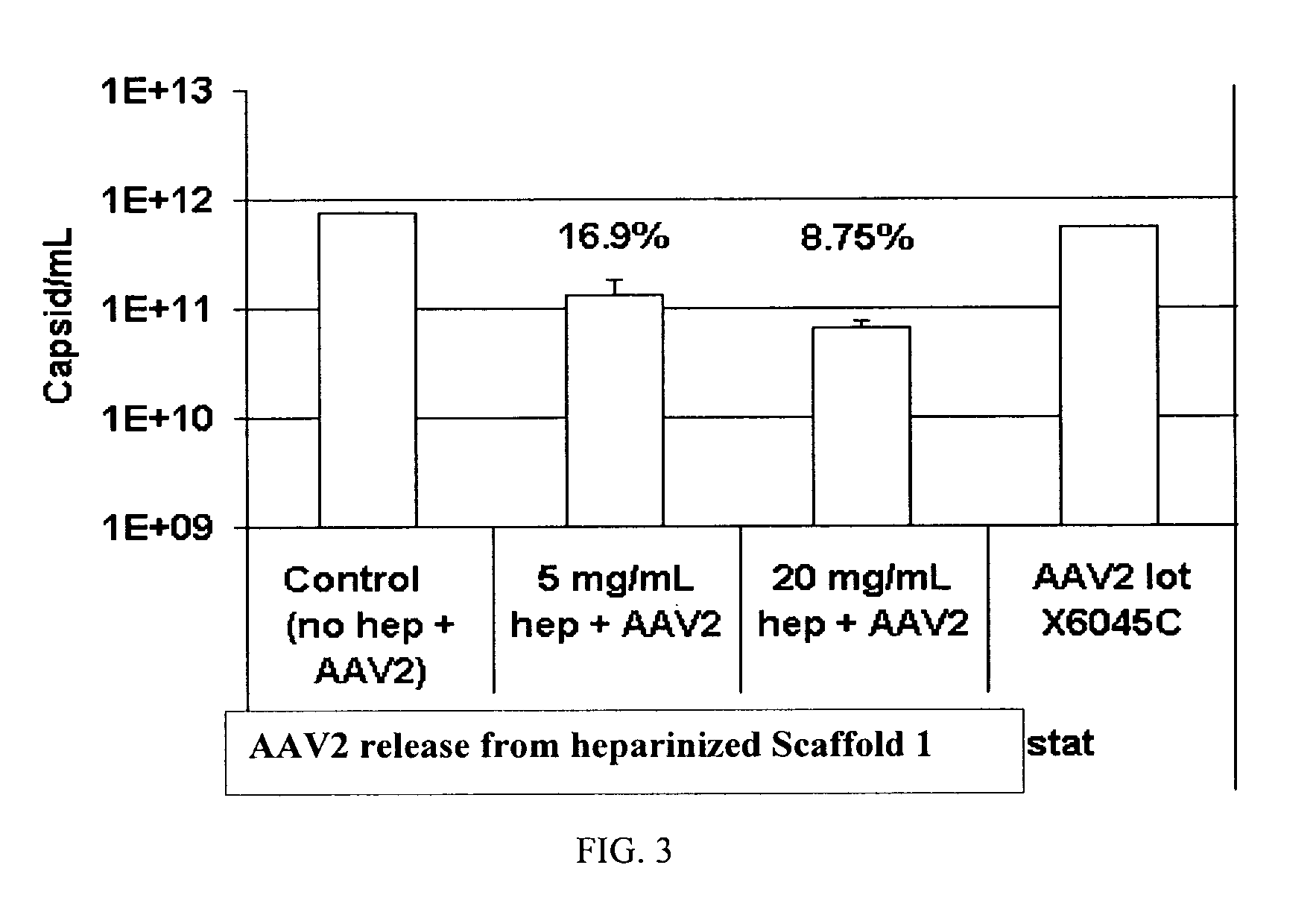
Prolonged delivery of heparin-binding growth factors from heparin-derivatized collagen
InactiveUS20090192079A1Improve biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic therapy composition manufactureMuscle tissueCollagen scaffold
The present invention relates to a heparin-derivatized collagen matrix comprising a fragment of heparin covalently linked to a collagen scaffold, wherein the fragment of heparin has molecular weight of less than about 15 kDa, and at least one heparin-binding growth factor (HBGF) or heparin-binding adeno-associated virus (HB-AAV) or a combination thereof and methods for promoting bone growth, bone repair, cartilage repair, bone development, neo-angiogensis, wound healing, tissue engraftment and muscle tissue regeneration and / or tissue augmentation comprising administering a heparin-derivatized collagen matrix that includes at least one heparin-binding growth factor or heparin-binding adeno-associated virus or a combination thereof.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
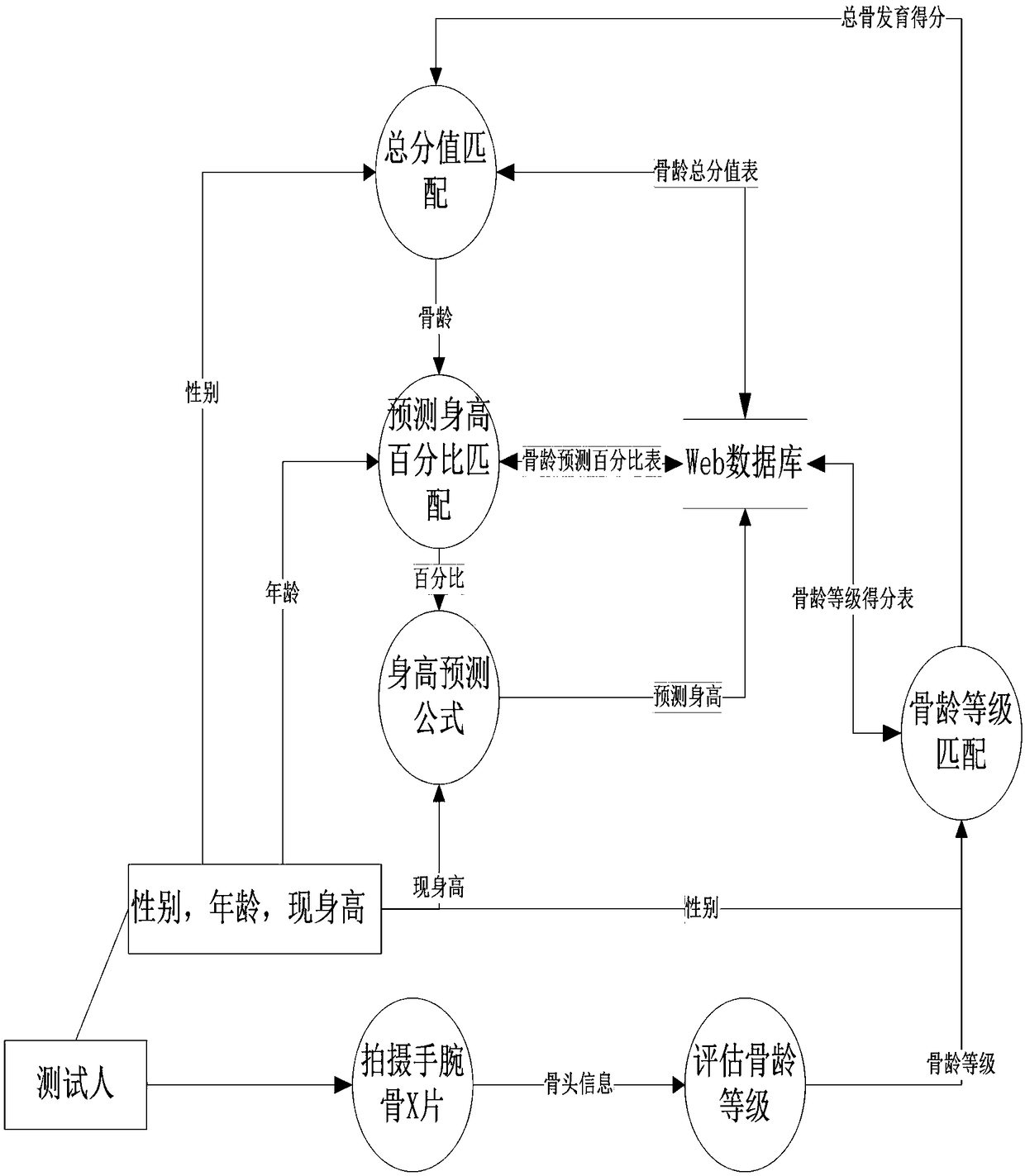
Web database based online bone age calculating and height predicating method
InactiveCN108836338AReduce the amount of calculationReduce error rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBone ageX-ray
The invention discloses a web database based online bone age calculating and height predicating method. The method comprises the following steps: dividing hand wrist and bone age level; recording thebase information of testing people; inputting shot hand and wrist X ray images; decoding bone data; calculating the bone age; and calculating the predicated height. The method is applicable to professors with evaluation experience; the works such as general sheet checking, recording and summing can be saved; a computer supports. Therefore, the repeating workload can be greatly decreased; the calculation accuracy is improved; various hand wrist bone development standard data can be stored on the basis of the web database, so that the completeness, the safety and the handleability of the data can be ensured; in addition, different predication results can be examined and compared based on different bone age evaluation standards during use; the web database is adopted, so that the characteristics of high efficiency and expandability are met while a new bone age evaluation standard is added; and the method is high in application and popularization value and economic benefit.
Owner:浙江康体汇科技有限公司 +1
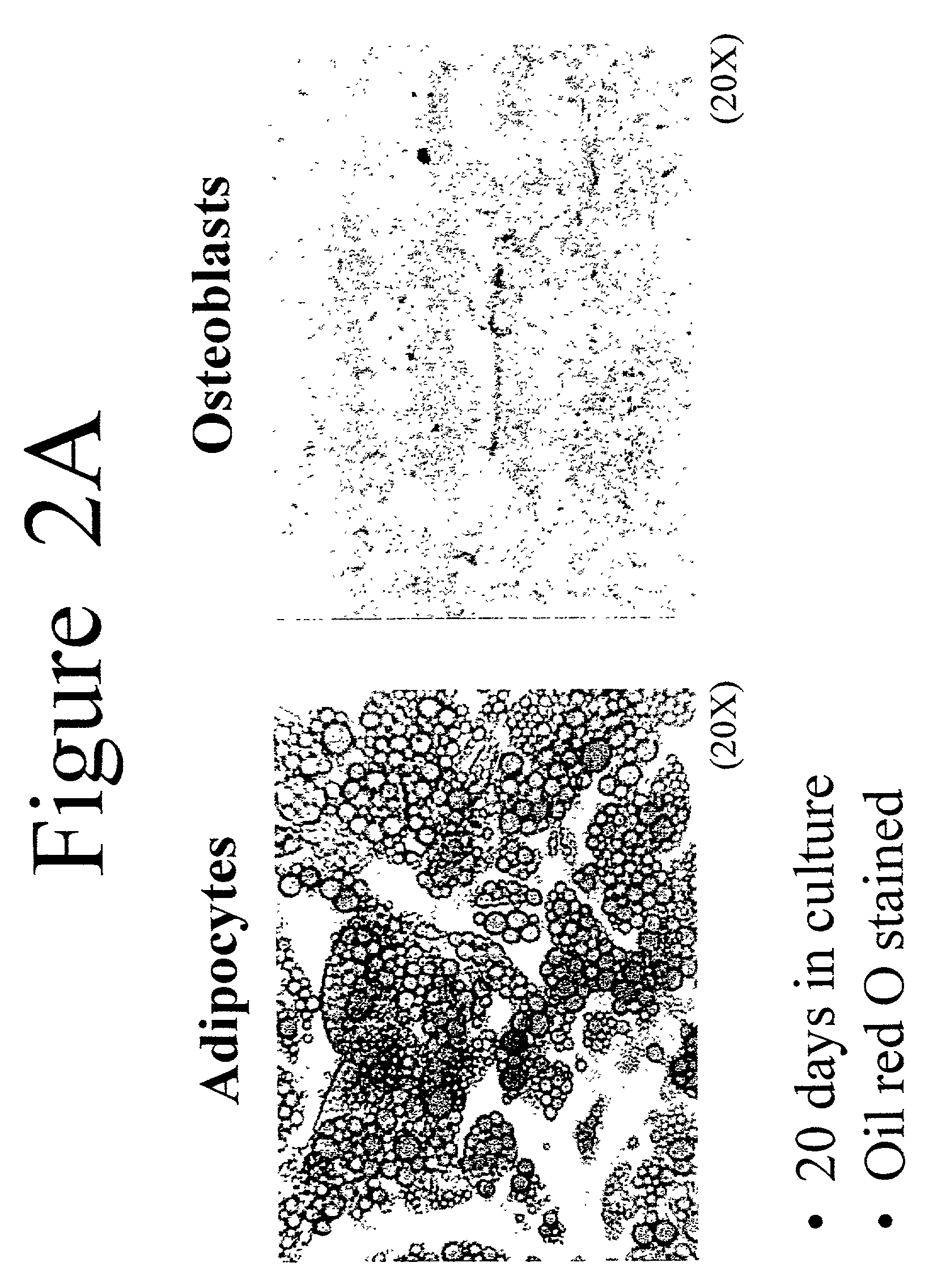
Differentiation of adipose stromal cells into osteoblasts and uses thereof
InactiveUS7179649B2Reinforce bone structureEnough timeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberBone structure
The invention provides methods and compositions for differentiating stromal cells from adipose tissue into cells having osteoblastic properties, and methods for improving a subject's bone structure. The methods comprise culturing stromal cells from adipose tissue in β-glycerophosphate and ascorbic acid and / or ascorbate-2-phosphate for a time sufficient to allow differentiation of said cells into osteoblasts. Such methods and compositions are useful in the production of osteoblasts for autologous transplantation into bone at a surgical site or injury. The compositions comprise adipose stromal cells, a medium capable of supporting the growth of fibroblasts and amounts of β-(glycerophosphate and ascorbic acid and / or ascorbic-2 phosphate sufficient to induce the differentiation of said stromal cells into osteoblasts.The invention further provides methods of identifying compounds that affect osteoblast differentiation. Such compounds are useful in the study of bone development and in the treatment of bone disorders, including bone fractures and osteoporosis.
Owner:COGNATE BIOSERVICES
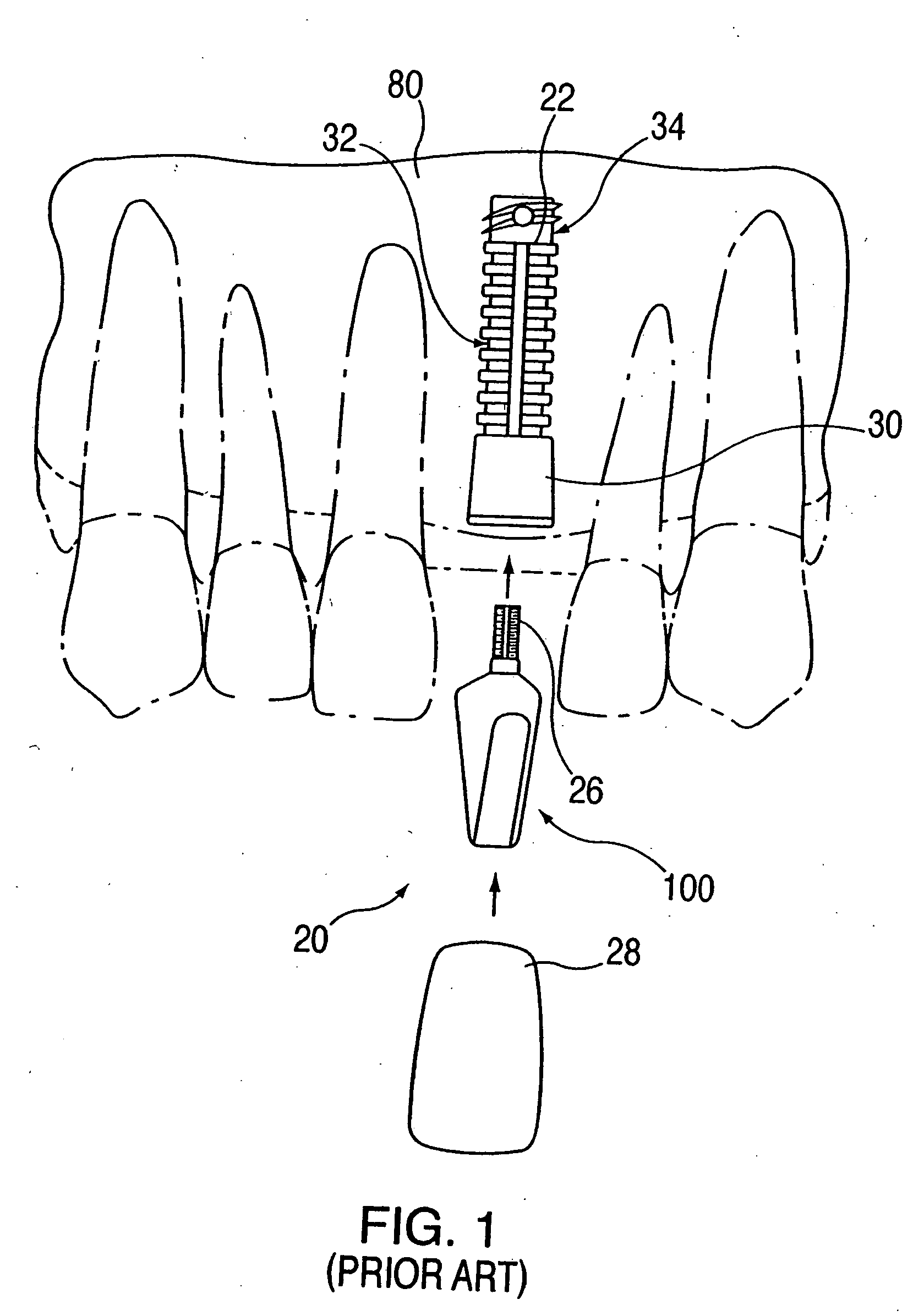
Combination distraction dental implant and method of use
InactiveUS20050084822A1Reduce in quantityEliminate needDental implantsFastenersSurgical operationCircular disc
A combination dental implant / prosthetic support and distractor for facilitating distraction osteogenesis comprises a basically cylindrical shaft having a set of threads on the outside surface and a smooth, distal tip which bears against the bone of the jaw of the patient. Rotation of the device in the mouth of the patient, after a suitable surgical cut is made, causes the adjacent tissue to move or ride up the screw threads to create space between the cut jaw segment and the balance of the jaw tissue. This space is then filled in by distraction osteogenesis. The implant / distractor is left in-situ, after the distraction is finished, for securement thereto of a dental prosthetic, either a bridge or crown. In an embodiment of the invention, a flat disc is placed in the blind bore drilled into the jaw such that the distal tip of the shaft of the combined implant / distractor, will bear against it. A protective cap and / or collar can be provided, suitable shaped, to protect the shaft / gum line from bacterial attack. Also, the shaft may be provided with an internal passageway and one or more radially extending branches. Growth-enhancing material can be passed through the passageway and branches to promote bone development and recovery. In another embodiment, a coronal member is provided, extra-osseously, to facilitate the distraction osteogenesis process. In one version of the device, fluting is provided to the exterior surface of the shaft so that bone growth is enhanced at that intersection. Also, the shaft can be provided with a flat disc at its head to reduce rocking of the device in the mouth.
Owner:STUCKI MCCORMICK SUZANNE
Transgenic animal model of bone mass modulation
InactiveUS20090023905A1Optimization orderEasy to identifySugar derivativesBone-inducing factorOligonucleotide primersOsteopoikilosis
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to express the HBM protein in animal cells and transgenic animals. The present invention also relates to transgenic animals expressing the high bone mass gene, the corresponding wild-type gene, and mutants thereof. The invention provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Mutations in WNT-frizzled signaling pathways associated with osteoarthritis
InactiveUS20050130199A1Prevent and slow developmentSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDisease progressionSignal Pathways
This invention provides methods to identify individuals predisposed to developing osteoarthritis, to diagnose osteoarthritis, and to monitor the progression of the disease. The method also provides methods to identify modulators of bone development that affect a wnt / fzd signaling pathway and methods to prevent or treat osteoarthritis by administering the modulator of bone development.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
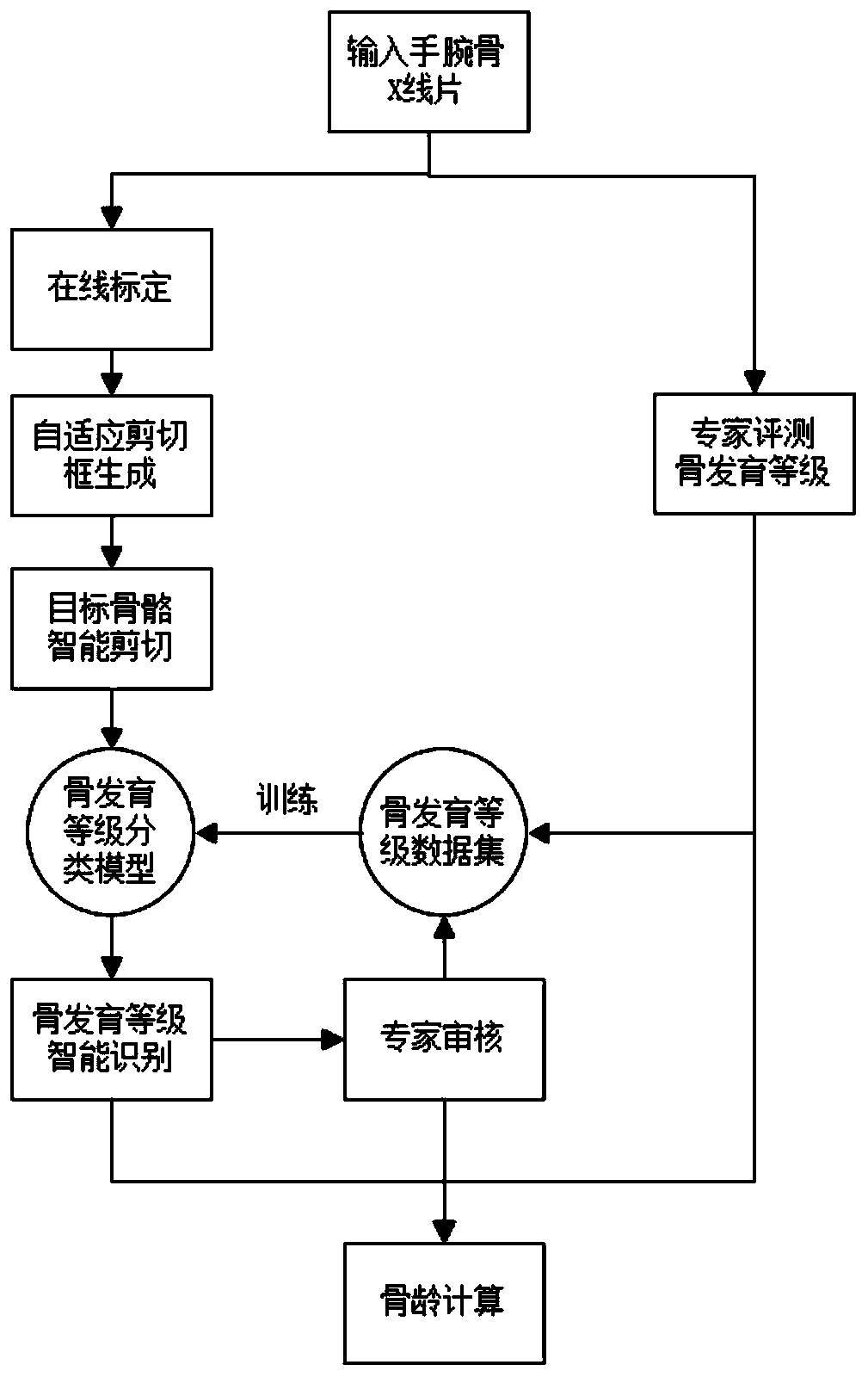
Bone age prediction method and system based on deep learning
InactiveCN110009605AAchieve forecastReduce workloadImage enhancementImage analysisPhysical medicine and rehabilitationBone age
The invention discloses a bone age prediction method based on deep learning. The bone age prediction method comprises the following steps: step 1, obtaining the size of a target bone self-adaptive shear frame according to the age, gender and present height; step 2, performing automatic shearing according to the size of the shear frame and the coordinates of the target bone center point to obtain atarget bone picture; step 3, inputting the picture obtained in the step 2 into a bone development grade classification model for recognition to obtain a predicted development grade of each bone; andstep 4, referring to the score table of each bone development stage of a CHN method and a CHN method bone development maturity score and bone age comparison table to obtain a final bone age predictionresult. The invention also provides a bone age prediction system based on deep learning. The method has better stability and accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for breeding zebra fish with wnt16 gene deletion through gene knockout
InactiveCN106191112AShorten the growth cycleGood medical researchPeptidesNucleic acid vectorState of artLiving body
The invention discloses a method for breeding zebra fish with wnt16 gene deletion through gene knockout. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that specific genes can be more efficiently and more accurately silenced in a genome of a living body, in addition, the preparation is simple, the cost is low, moreover, a plurality of sites on a target gene can be simultaneously shorn, and single genes of any number can be silenced. The method is used for carrying out the relevant researches on gene and skeletal development, also can be used for carrying out the exploration research of other aspects, is used for detecting that whether the deletion of the wnt16 gene has relevance with the development of other organs, such as the heart, or not, and has a very good medical research value, meanwhile, the zebra fish with the wnt16 gene knocked out has the obviously shortened growth cycle, and thus the commercial value is good.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Combination distraction dental implant and method of use
InactiveUS20070105068A1Reduce in quantityEliminate needDental implantsFastenersSurgical operationBone growth
A combination dental implant / prosthetic support and distractor for facilitating distraction osteogenesis comprises a basically cylindrical shaft having a set of threads on the outside surface and a smooth, distal tip which bears against the bone of the jaw of the patient. Rotation of the device in the mouth of the patient, after a suitable surgical cut is made, causes the adjacent tissue to move or ride up the screw threads to create space between the cut jaw segment and the balance of the jaw tissue. This space is then filled in by distraction osteogenesis. The implant / distractor is left in-situ, after the distraction is finished, for securement thereto of a dental prosthetic, either a bridge or crown. In an embodiment of the invention, a flat disc is placed in the blind bore drilled into the jaw such that the distal tip of the shaft of the combined implant / distractor, will bear against it. A protective cap and / or collar can be provided, suitable shaped, to protect the shaft / gum line from bacterial attack. Also, the shaft may be provided with an internal passageway and one or more radially extending branches. Growth-enhancing material can be passed through the passageway and branches to promote bone development and recovery. In another embodiment, a coronal member is provided, extra-osseously, to facilitate the distraction osteogenesis process. In one version of the device, fluting is provided to the exterior surface of the shaft so that bone growth is enhanced at that intersection. Also, the shaft can be provided with a flat disc at its head to reduce rocking of the device in the mouth.
Owner:STUCKI MCCORMICK SUZANNE
Remote online bone age interpretation system
The invention provides a remote online bone age interpretation system capable of realizing remote online interpretation for bone age films, and belongs to the field of health assessment. The bone age refers to bone development age, can reflect body development situations objectively and has great significance in the aspects of bone age judgment in athletic contests, evaluation of adolescents' growth and development, prediction of adult height, selection of athletes, auxiliary diagnosis of metabolic diseases and the like. However, the bone age interpretation is required to be carried out by professionals, besides, the popularizing rate of special bone age equipment is lower, the probability of time delays between X-ray film shooting and the interpretation is high, and the process from the X-ray film shooting at hospital to the interpretation of a bone age result by the professionals is tedious, time-consuming and labor-consuming. The remote online bone age interpretation system can realize multiple functions such as digitization of bone age film collection, automatic film uploading, online interpretation of the bone age films, immediate feedback of the interpretation result and the like, greatly facilitates bone age testing, and has substantial significance for general survey of growth and development level, rapid interpretation of the bone age result and the like.
Owner:ACMEWAY BEIJING HEALTH TECH CO LTD
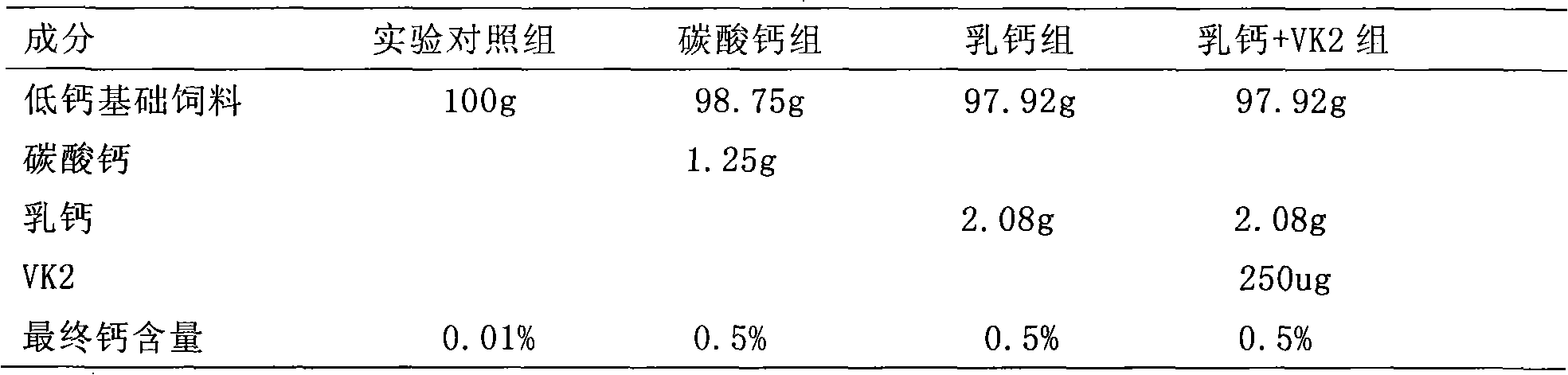
Nutrition composition and application thereof
The invention discloses a nutrition composition and application thereof. The nutrition composition comprises the following active ingredients in percentage by weight: 5-94.7 percent of calcium, 0.0001-0.02 percent of vitamin k, 5-94.7 percent of oil and 0.01-0.4 percent of antioxidant. The nutrition composition greatly enhances the bioavailability of the calcium, has multiple health care functions, and has obvious functions on controlling cancers, cardiac, cerebral and vascular diseases, diabetes, rheumatic disease, dermatitis, depression, dementia praecox, Alzheimer's disease, allergy, asthma, nephropathy, senium and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, enhancing intelligence and immunity, protecting eyesight, promoting skeleton growth and preventing osteoporosis, thereby being suitable for being taken by various people and being a difunctional product which has the function of calcium and memory simultaneous supplement and can satisfy the need by the development of infant body and brain.
Owner:上海厚品系统管理技术有限公司
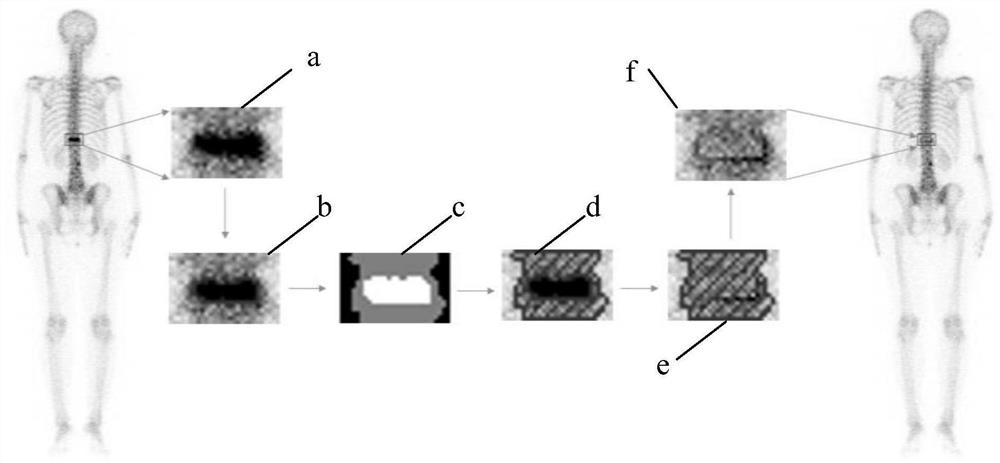
Whole-body bone imaging bone segmentation method based on image set registration
ActiveCN112102339AWork lessSave manpower and material resourcesImage enhancementImage analysisBone lesionBone scans
The invention discloses a whole-body bone imaging bone segmentation method based on atlas registration. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring original whole-body bone imaging data collected by professional equipment; subjecting the original whole-body bone imaging data to preprocessing including pollution detection processing, pollution repair processing, standardization processing,registration processing and regularization processing; and according to a deformation segmentation template stored in the system, carrying out segmentation processing on the preprocessed whole-body bone development image to obtain a segmentation result of whole-body bone development. By means of the method, bone positioning can be conducted on an image obtained through single whole-body bone scanning examination, a basis is provided for bone lesion positioning, development quality is improved by automatically reducing a difference through bone development pollution detection and a pollution repair algorithm, and the development difference between different whole-body bone scans is solved; and rapid, accurate and intelligent positioning of the whole-body bone imaging skeleton is achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Dovelet feed
InactiveCN104336415ASmall particlesSuitable for eatingAnimal feeding stuffCalcium in biologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a dovelet feed. The dovelet feed can effectively improve the immunity and the survival rate of dovelets, contains no antibiotics or antiseptics, and improves the quality of adult doves. The dovelet feed comprises, by weight, 8 parts of sorghum, 7 parts of soybean, 4 parts of brown rice, 6 parts of wheat, 3 parts of pea, 1 part of vitamin D, 2 parts of bone meal and 2 parts of vitamin A; and soybeans and peas are ground, and then are uniformly mixed with other ingredients. The dovelet feed has rich nutrition and fine particles, is suitable for dovelets to eat, and is conducive to digestion. A variety of vitamins are added to promote calcium absorption and bone development and benefit hair growth; and purslane powder and Semen Plantaginis powder have a certain anti-inflammatory effect, are natural herbs, and are beneficial and harmless.
Owner:XUZHOU MINGWEI FEED
Differentiation of adipose stromal cells into osteoblasts and uses thereof
The invention provides methods and compositions for differentiating stromal cells from adipose tissue into cells having osteoblastic properties, and methods for improving a subject's bone structure. The methods comprise culturing stromal cells from adipose tissue in β-glycerophosphate and ascorbic acid and / or ascorbate-2-phosphate for a time sufficient to allow differentiation of said cells into osteoblasts. Such methods and compositions are useful in the production of osteoblasts for autologous transplantation into bone at a surgical site or injury. The compositions comprise adipose stromal cells, a medium capable of supporting the growth of fibroblasts and amounts of β-glycerophosphate and ascorbic acid and / or ascorbic-2 phosphate sufficient to induce the differentiation of said stromal cells into osteoblasts. The invention further provides methods of identifying compounds that affect osteoblast differentiation. Such compounds are useful in the study of bone development and in the treatment of bone disorders, including bone fractures and osteoporosis.
Owner:COGNATE BIOSERVICES
High-fecundity meat-type Anhui white goat lamb breeding technology
InactiveCN106719405AImprove efficiencyFeeding method scienceFood processingAnimal feeding stuffWeaningObserved Survival
The invention discloses a high-fecundity meat-type Anhui white goat lamb breeding technology. A complete feeding management system is made according to specific physiology and growth characteristics of Anhui white goats and includes sterilization, heat insulation, milk drinking, feed supplementing, weaning, sanitation, epidemic prevention and the like of newly born lambs. The breeding technology is scientific in feeding method and appropriate in management and can guide farmers to scientifically feed the goats, and breeding benefits of the goats are improved. According to the breeding technology, by a scientific and effective management mode, the survival rate of the lambs is increased, bone development is facilitated, and subsequent growth and development of the lambs are greatly facilitated.
Owner:SHOUXIAN LINHUAI ANIMAL HUSBANDRY BREEDING CO LTD
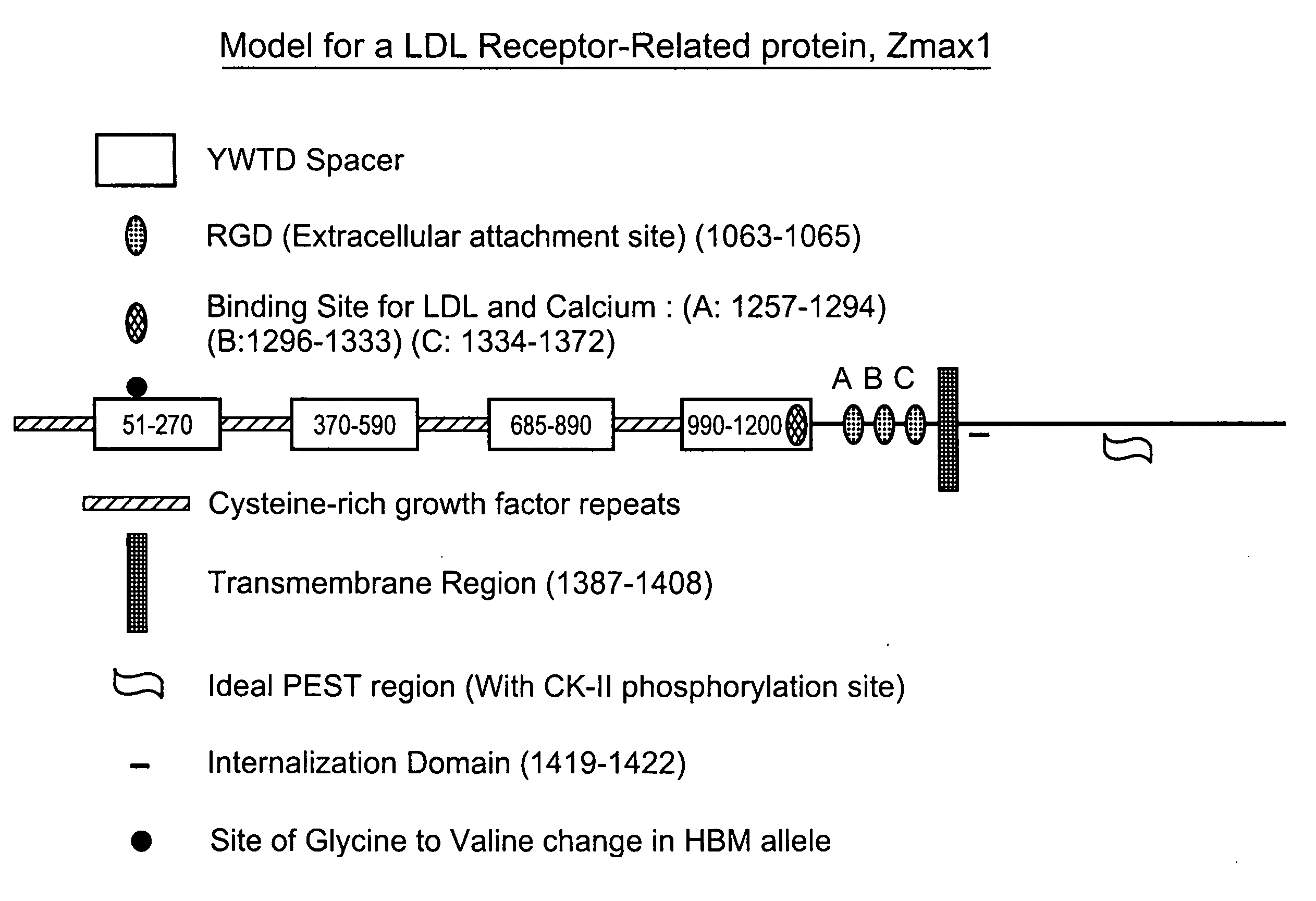
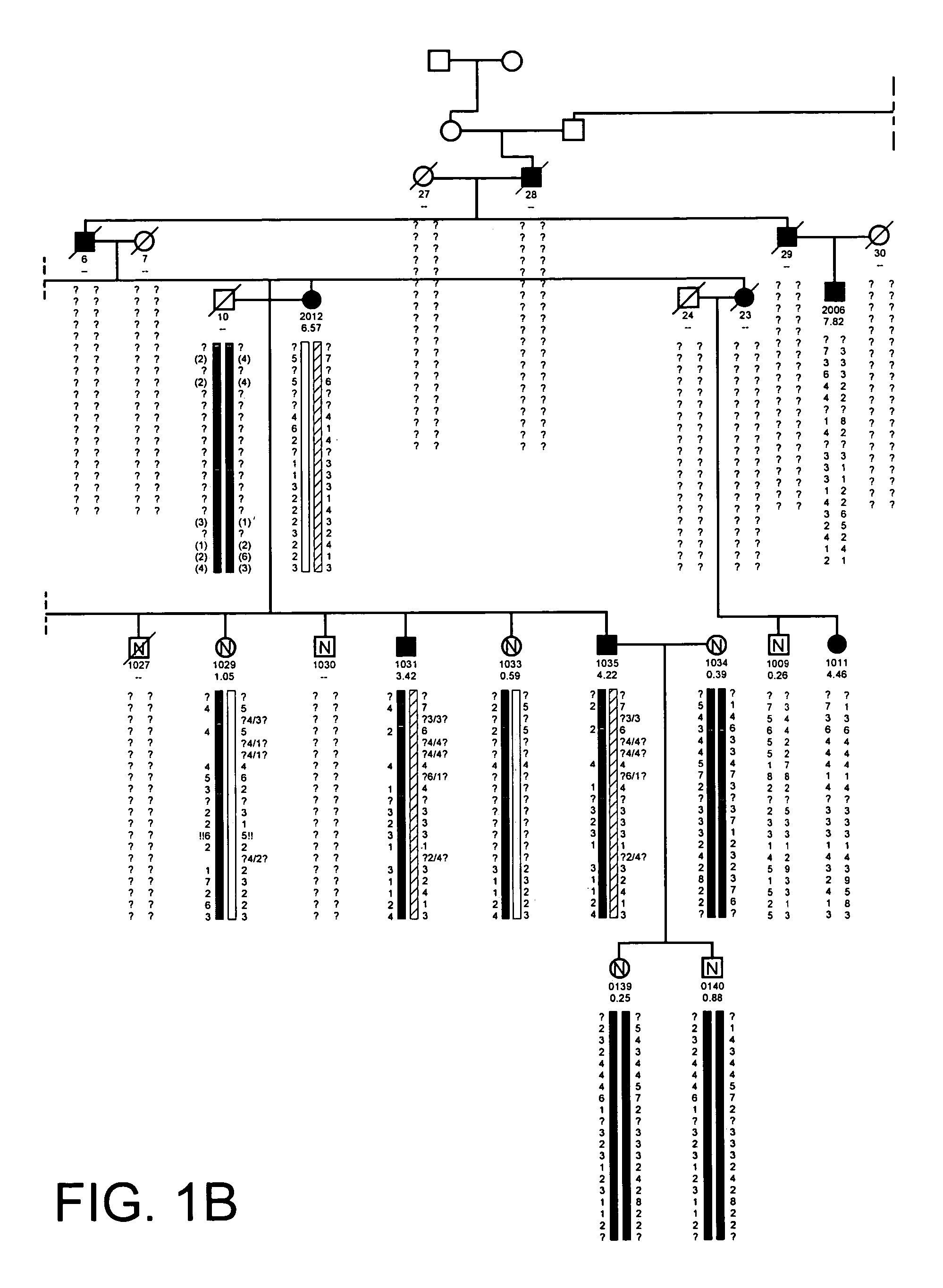
HBM variants that modulate bone mass and lipid levels
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to express an HBM-like polypeptide derived from HBM, LRP5 or LRP6 in animal cells and transgenic animals. The present invention also relates to transgenic animals expressing the HBM-like polypeptides. The invention provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development and lipid modulation. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:GENOME THERAPEUTICS +1
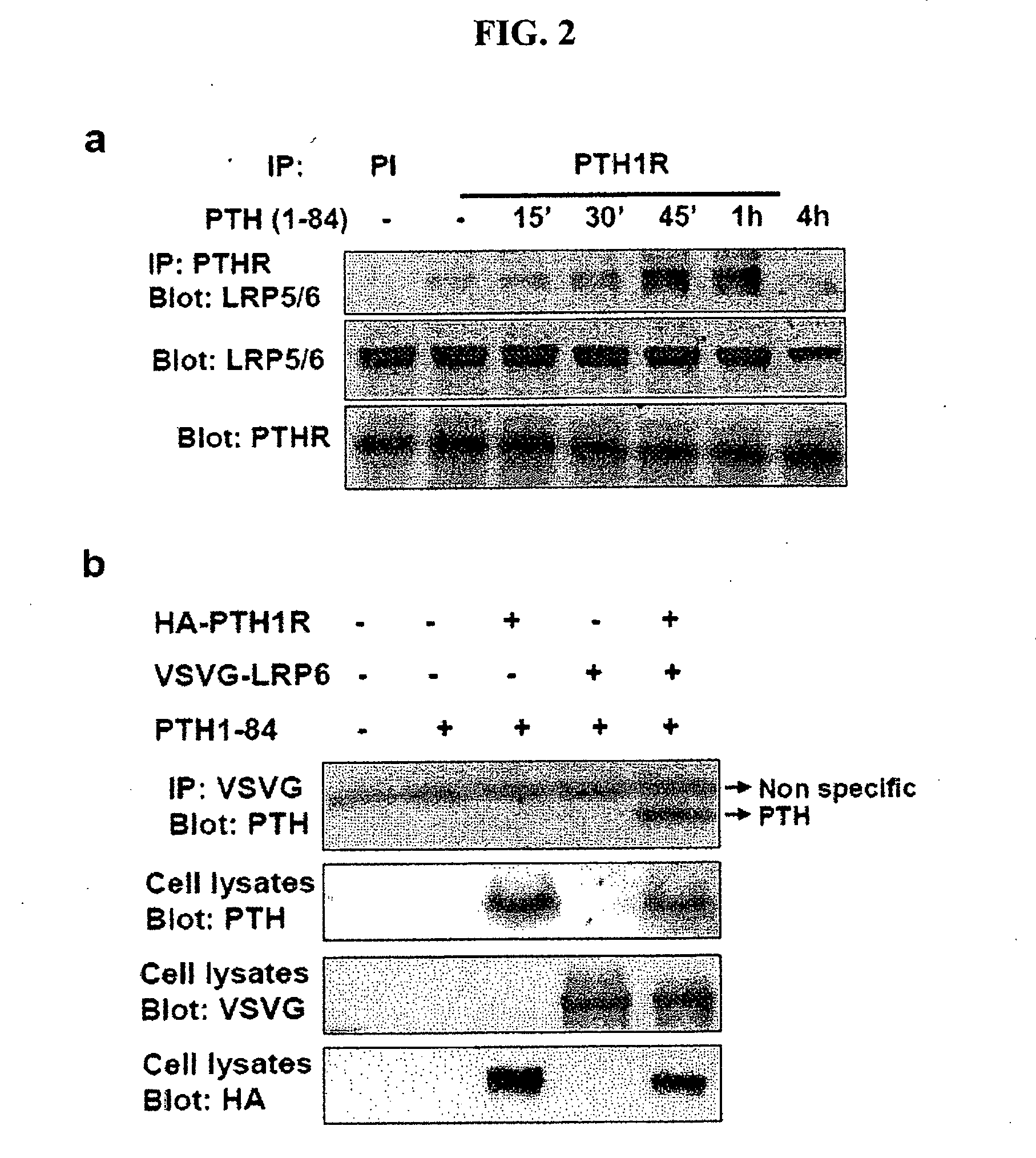
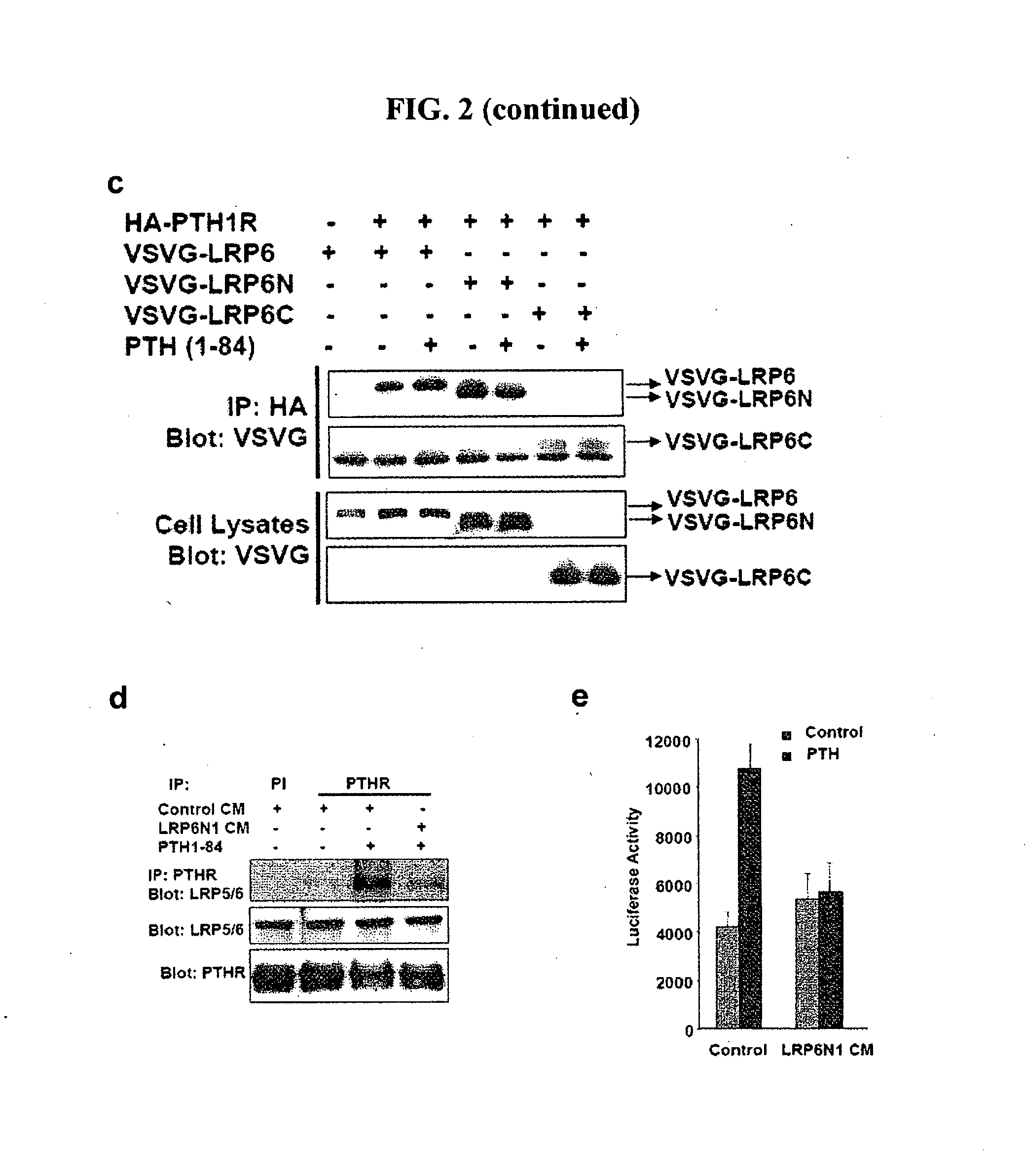
Compositions and Methods for Improving Bone Mass Through Modulation of Novel Receptors of PTH and Fragments Thereof
InactiveUS20100160220A1Enhanced interactionReduce interactionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNephropathyLRP5
The present invention relates to the discovery of novel receptors for the signaling of PTH and / or fragments of PTH, and the role of cPTH in bone development. The novel PTH receptors identified are selected from the group consisting of LRP5 / 6, TGFβRII, BMPRII (long form and short form), ActRIIA, and ActRIIB. Specifically, the present invention provides a novel screening tool for identifying compounds that improve bone mass by affecting certain pathways that promote or downregulate bone-forming activity. This promotion of bone-forming activity could provide for treatments for bone-loss or bone density disorders and / or kidney disease. The invention further encompasses the compounds, PTH ligands, and fragments of PTH ligands described herein; pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, PTH ligands, or fragments of PTH ligand; and methods of increasing bone density using the compounds, PTH ligands, or fragments of PTH ligands.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Bone Age Assessment And Height Prediction Model, System Thereof And Prediction Method Thereof
The present disclosure provides a bone age assessment and height prediction system including an image capturing unit and a non-transitory machine readable medium. The image capturing unit is for obtaining a target x-ray image data of a subject. The non-transitory machine-readable medium is for storing a program for assessing the development of the bones of a hand and the bone age of the subject, and predicting the adult height of the subject when executed by a processing unit. Therefore, the bone age assessment and height prediction system of the present disclosure can effectively improve the accuracy and sensitivity of the bone age assessment and the height prediction, and the time for assessing the bone age and predicting the height can be further shorten.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIV HOSPITAL
Method for breeding chicken on hillside
InactiveCN107114308AIncrease pleasureHigh reuse rateFood processingClimate change adaptationDiseaseLeg muscle
The invention relates to the field of chicken breeding, and discloses a method for breeding chicken on a hillside. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a breeding field and improving products to be planted and bred to reasonably utilize resources, save breeding cost, improve recycling rate of resources and ensure that the whole circulating chain can improve the pleasant feeling of chicken; (2) leading chicks on a hillside by hen in advance to improve the adaptive capacity of the chicks, promote bone development and improve the lean rate; (3) independently stocking in the rapid chick growth period to prevent disease infection, and comprehensively utilizing manufacture resources of each breeding field to reduce breeding cost; and (4) massively supplying vegetable and animal protein to remarkably improve the dressing percentage and obtain chicken having content of various amino acid and trace elements in chicken meat to be higher than those of chicken bred by a conventional breeding method since chicks reaching the age in 60 days are in the optimized moment for improving breast muscle yield and leg muscle yield.
Owner:枞阳县恒祥生态农业有限公司
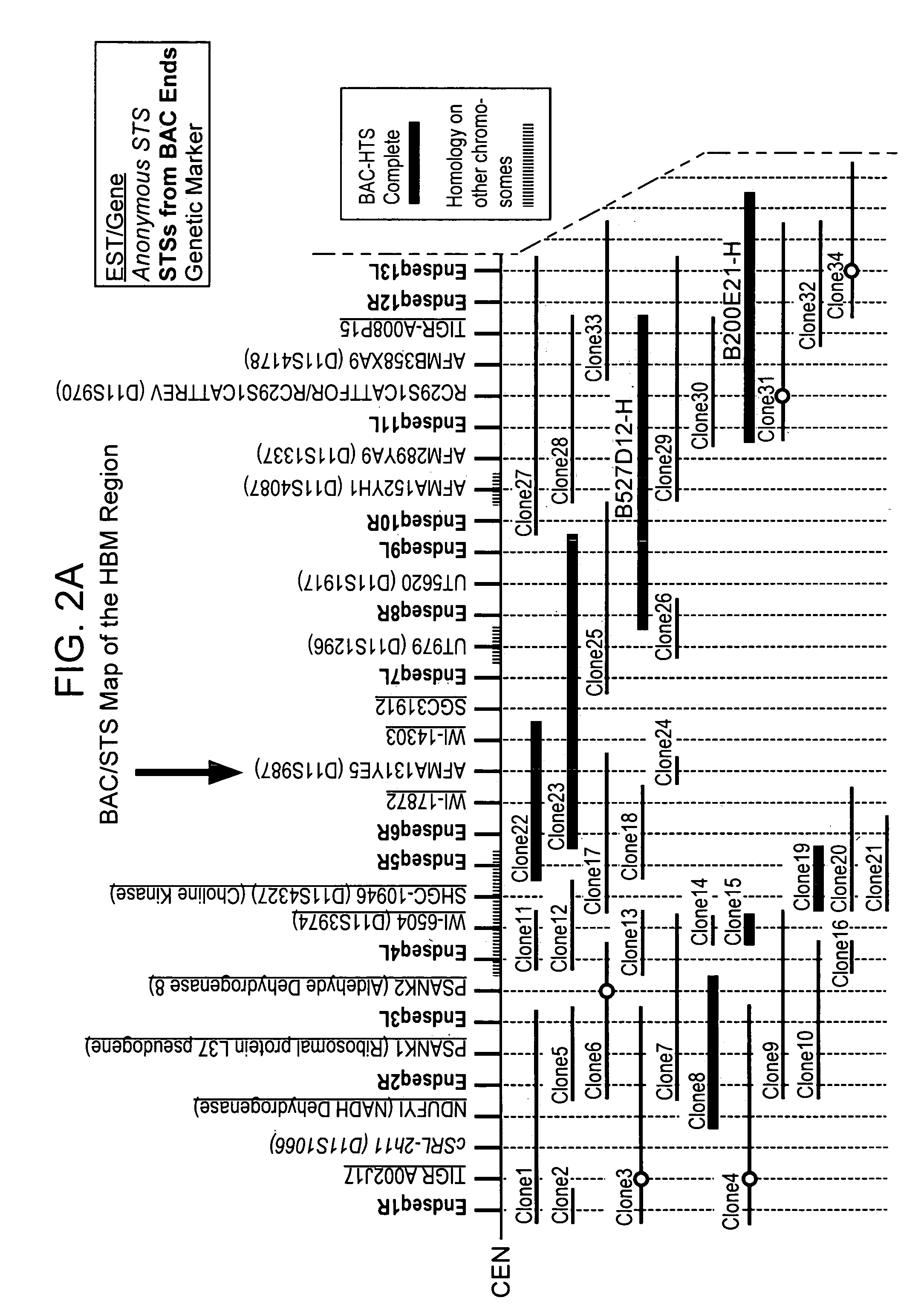
High bone mass gene of 11q13.3
InactiveUS20050142617A1Optimization orderEasy to identifyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseWild type
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to isolate and detect a high bone mass gene and a corresponding wild-type gene, and mutants thereof. The present invention also relates to the high bone mass gene, the corresponding wild-type gene, and mutants thereof. The genes identified in the present invention are implicated in bone development. The invention also provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:GENOME THERAPEUTICS
Breeding method for increasing survival rate of forcibly-weaned lambs
ActiveCN106359297AHigh growth indexFast growthFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceObserved Survival
The invention relates to the technical field of poultry cultivation, in particular to a breeding method for increasing the survival rate of forcibly-weaned lambs. The breeding method comprises the following steps: forcibly weaning the lambs aged 10 days; after weaning, performing adaptation period management, internal organ development promoting management and bone development promoting management and respectively feeding different diets during management. According to the breeding method for increasing the survival rate of the forcibly-weaned lambs, provided by the invention, the lambs aged 10 days can be quickly weaned, and after weaning, the good development of various signs of the lambs can be ensured. When the breeding method provided by the invention is adopted for performing weaning management on the lambs aged 10 days, the overall incidence of various diseases during management is lower than 0.03 percent, the development indexes of internal organs are higher, the bone development is faster, and the weight increasing speed is high.
Owner:杨继刚
Transgenic animal model of bone mass modulation
InactiveUS7514594B2Optimization orderEasy to identifyAnimal cellsBone-inducing factorOligonucleotide primersWild type
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to express the HBM protein in animal cells and transgenic animals. The present invention also relates to transgenic animals expressing the high bone mass gene, the corresponding wild-type gene, and mutants thereof. The invention provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Food for promoting growth of children and preparation method of food
InactiveCN108968033APromote growthPromote absorptionFood ingredient functionsIntestinal structureCalcium in biology
The invention discloses a food for promoting growth of children and a preparation method of the food and belongs to the field of foods. The food for promoting growth of the children is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-20 parts of purple yam rhizome, 2-10 parts of poria cocos and 1-10 parts of gorgon fruit. The food is complete in nutrition and is beneficial to coordinating intestines and stomach of the children, protecting eyesight, promoting absorption of nutrition and calcium, enhancing children immunity, promoting bone development and thus promoting healthy growth of the children. The preparation method mixes the raw materials of the food for promoting growth of the children according to a ratio, is simple in formula, convenient to operate and low in costand is suitable for scale production.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU HESHI AGRI DEV
Ship inhibition to combat obesity
The present invention relates to the use of SHIP1 inhibitors and pan-SHIP1 / 2 inhibitors in various methods, including, without limitation: (i) a method to treat obesity or reduce body fat of an obese subject; (ii) a method to limit bone development in a subject suffering from an osteopetrotic or sclerotic disease; (iii) a method to treat or prevent diabetes; (iv) a method to reduce glucose intolerance or insulin resistance; and (v) a method to lower cholesterol.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
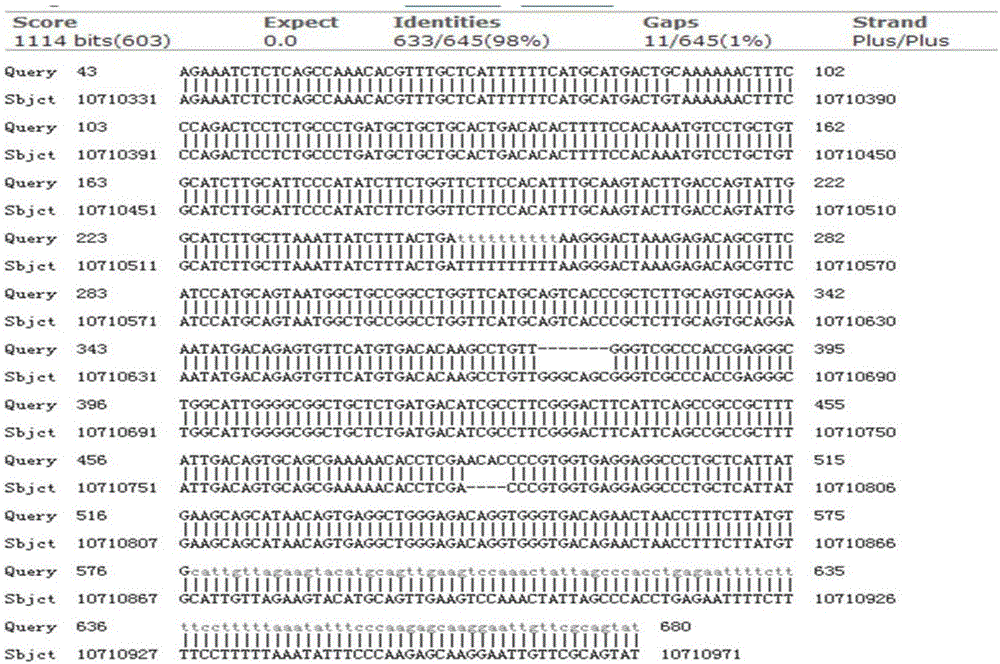
DNA library for detecting and diagnosing pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders and application thereof
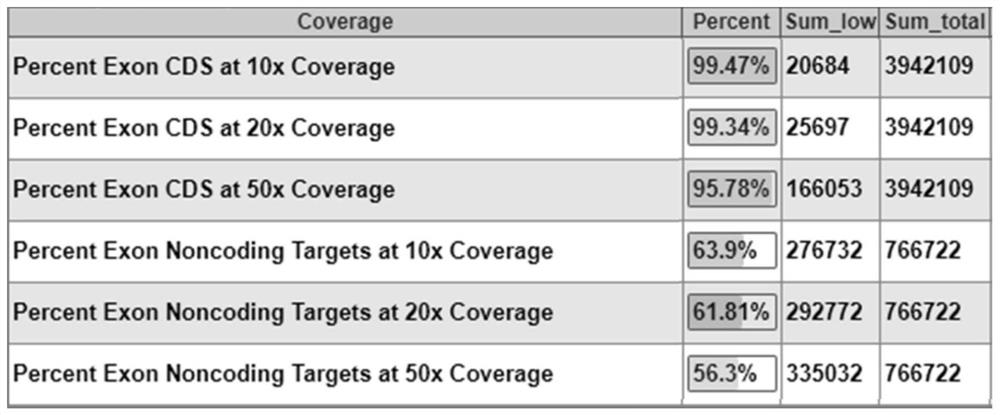
PendingCN112813156AAccurate detectionAids in Clinical Genetic CounselingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBone densityA-DNA
The invention relates to a DNA library for detecting and diagnosing pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders through a targeted high-throughput sequencing technology and application thereof. The library comprises 507 pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders. According to the invention, 507 pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders are preferably selected, a probe pool is designed, a target region library for 507 pathogenic genes of skeletal development disorders is established, and the library utilizes the high-throughput sequencing technology for sequencing to find pathogenic mutations, thereby providing genetic and molecular biological bases for clinical diagnosis. The DNA library provided by the invention has the characteristics of accuracy, rapidness, flexibility and low cost. The 507 genes involved in the invention include pathogenic genes of genetic diseases with skeletal development disorders as clinical manifestations, such as collagen dysplasia, metaphysic dysplasia, osteogenesis imperfecta and bone density reduction, mucopolysaccharide storage disease, cartilage dysplasia and the like, and have important significance and clinical value for diagnosis, differential diagnosis and accurate treatment of skeletal development disorders.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compound premix additive for improving bone development of replacement gilts
InactiveCN105192371AReduce elimination rateHeat concentrationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseDL-methionine
The invention discloses a compound premix additive for improving bone development of replacement gilts. The compound premix additive is prepared from, by weight, 30-40 parts of vitamin complex, 40-60 parts of trace element composite, 30-40 parts of choline chloride, 40-60 parts of L-lysine hydrochloride, 10-15 parts of DL-methionine, 5-10 parts of L-threonine, 120-150 parts of calcium hydrophosphate, 120-150 parts of monocalcium phosphate, 250-280 parts of limestone powder, 90-110 parts of salt and 85-265 parts of bran. By adoption of the compound premix additive, bone toughness and strength of the replacement gilts can be improved, reserve quantity of nutrients such as vitamins, trace elements and the like in the replacement gilts is increased, and accordingly occurrence rate of the foot-and-leg disease of the gilts is decreased, health of feet and legs of the gilts is protected, and lives of the gilts are prolonged.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Application of bovine bone collagen peptide in preparation of children's drinks to enhance bone development
InactiveCN110074290ASmall molecular weightIncrease supplyFood ingredient functionsProtein food ingredientsAbsorption rateProtein C
The invention provides an application of bovine bone collagen peptide in preparation of children's drinks to enhance bone development, and relates to the new medical application field of bovine bone collagen peptide. In the application of bovine bone collagen peptide in preparation of children's health care products or drinks to enhance bone development in the invention, the bone collagen in bovine bone collagen peptide may effectively prevent and improve osteoporosis; eliminate joint pain, keep off and reduce joint swelling, deformation and stiffness; accelerate fracture healing, and improvebone toughness; and keep off calcium loss and increase calcium absorption rate.
Owner:山东薇薇朵生物科技有限公司
Processing method of candid nutritious rhizoma dioscoreae cirrhosae
The present invention discloses a processing method of candid nutritious rhizoma dioscoreae cirrhosae and belongs to the field of food processing. The processing method is characterized by comprising the following processing processes of rhizoma dioscoreae cirrhosae selecting, washing, peeling, slice cutting, color protecting, hardening, washing, hot bleaching, sugaring, baking and sugar powder coating. Beneficial effects are as follows: the product is delicate and crisp in mouthfeel, crisp and tender, crisp and refreshing, has a special fragrant and waxy flavor of the rhizoma dioscoreae cirrhosae, is beneficial to improving immune function of human body and promoting bone development, has effects of clearing heat and relieving toxins, and stopping bleeding and activating blood, and is suitable for people at all ages.
Owner:安徽智联管理咨询有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com