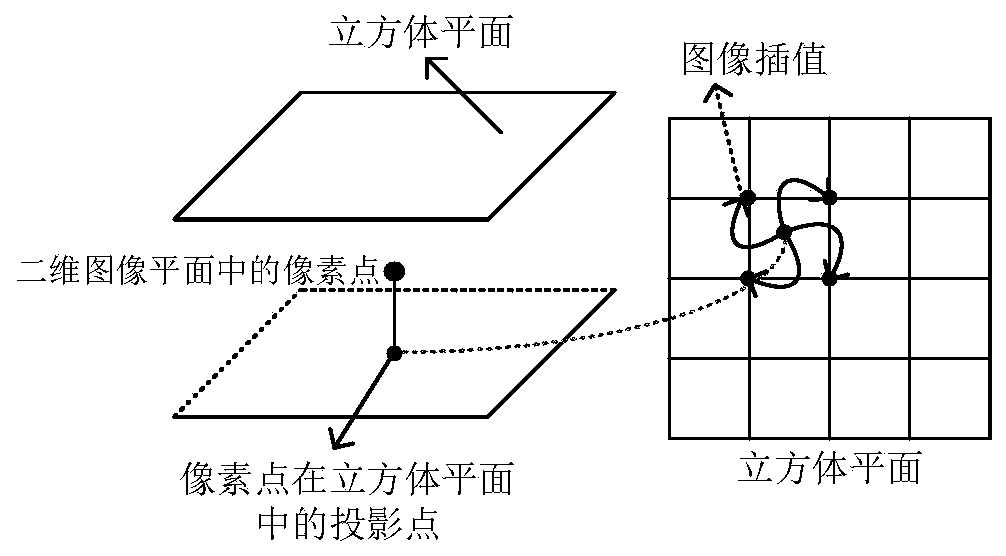
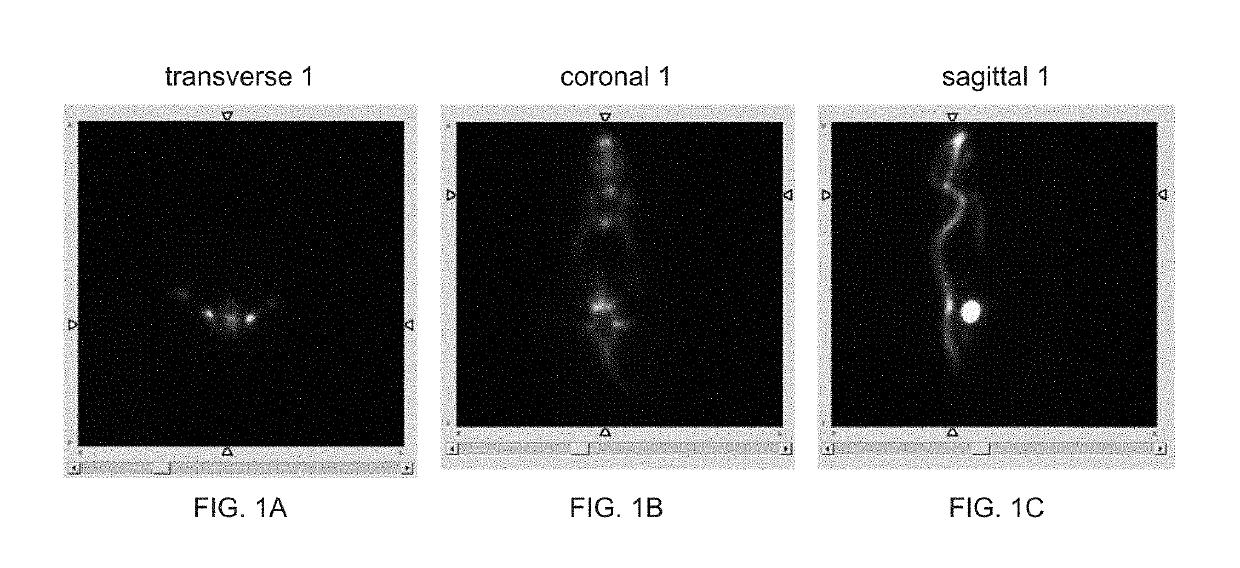
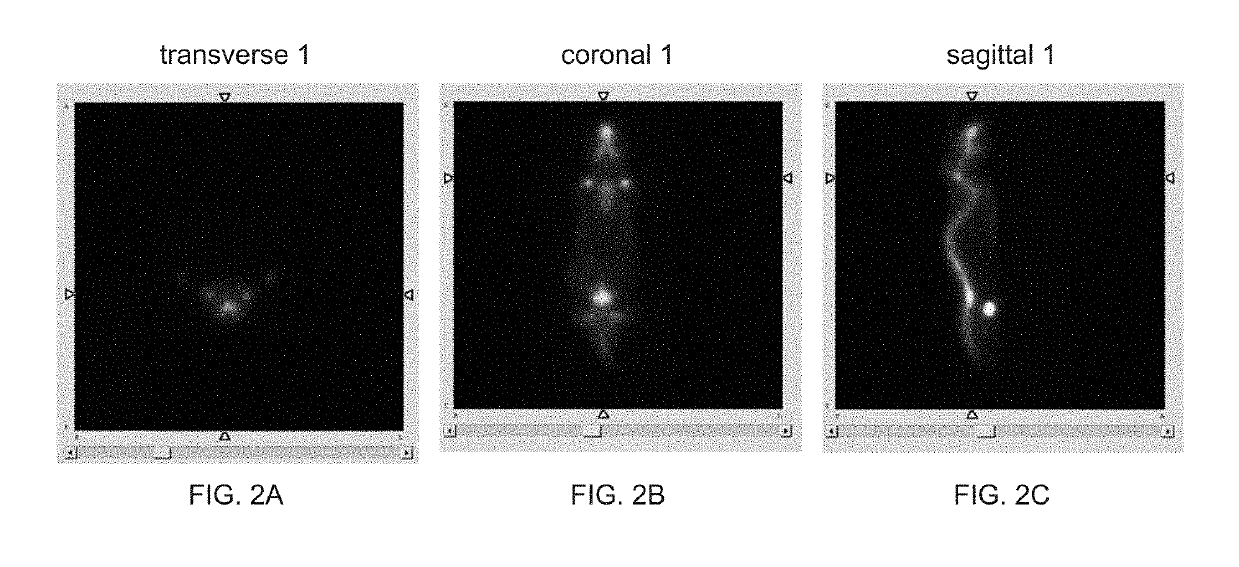
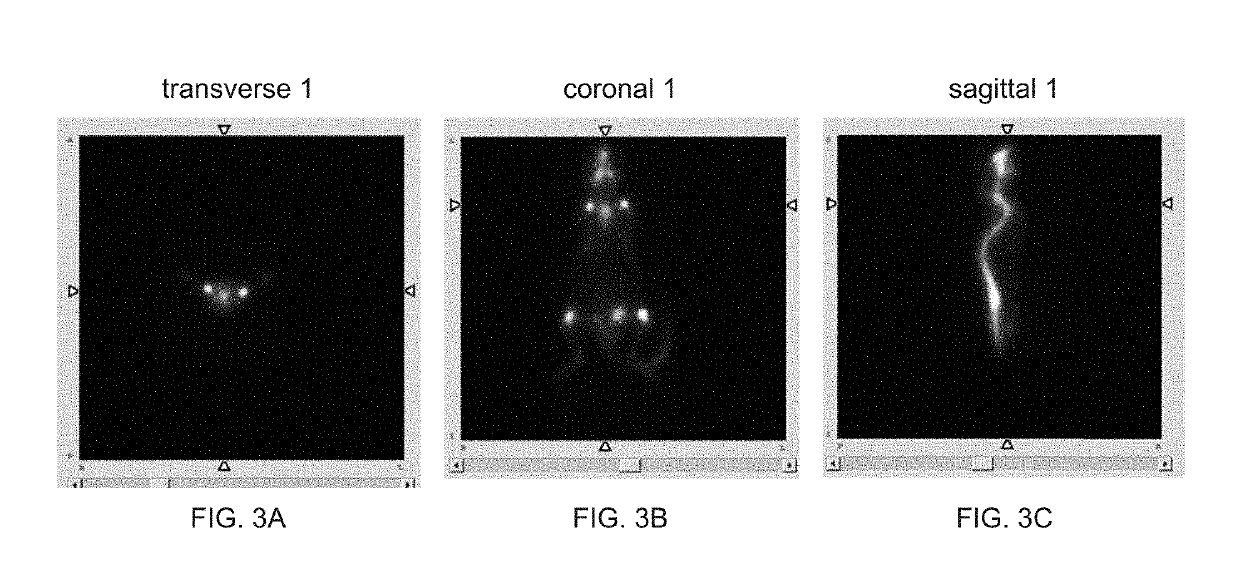
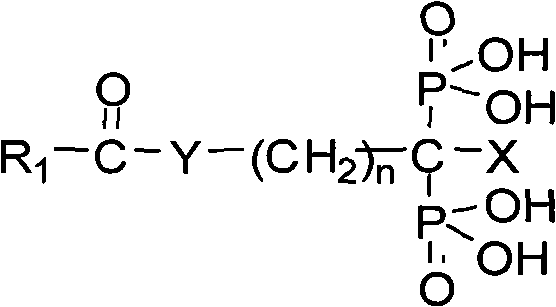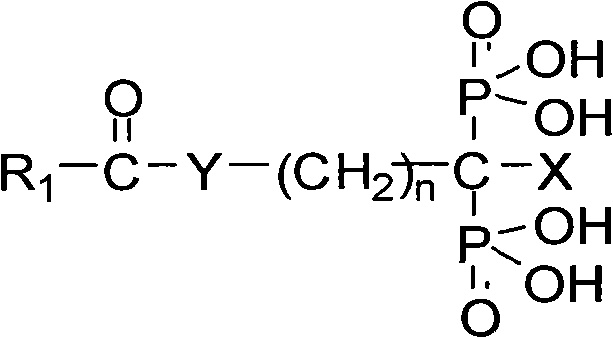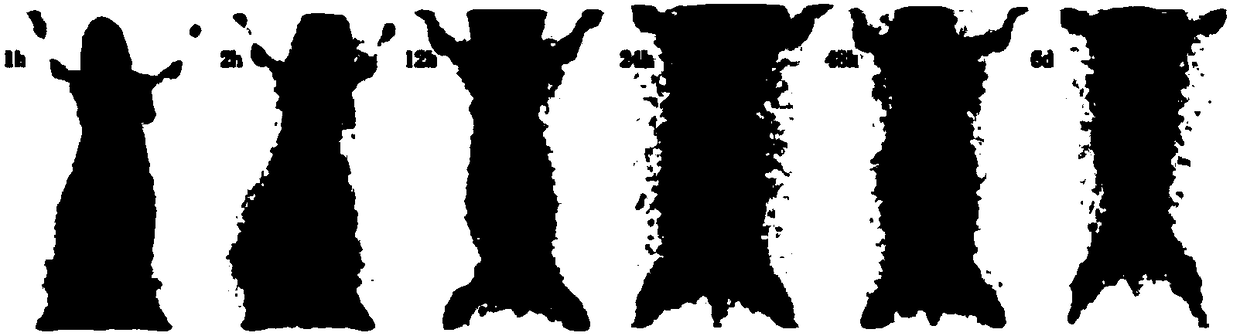Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Bone imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
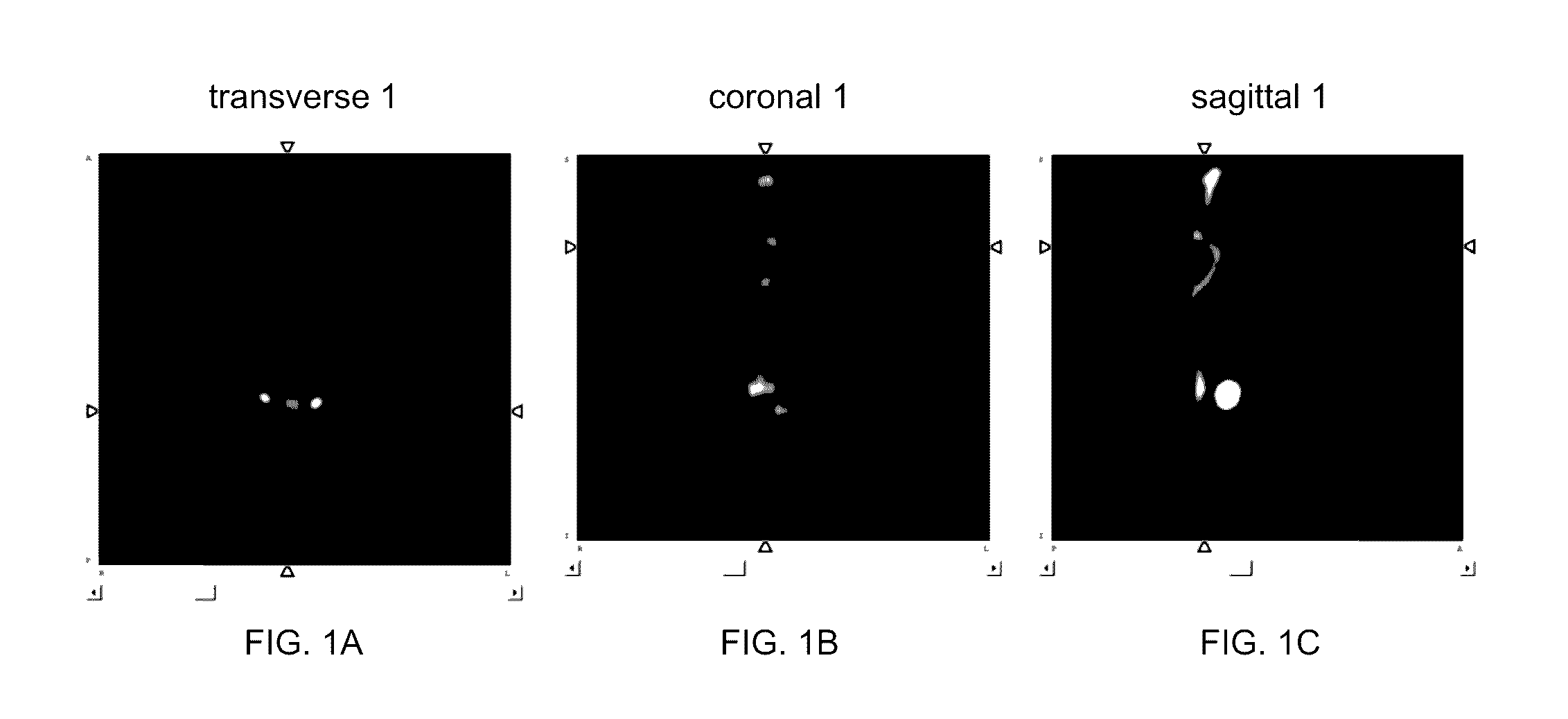
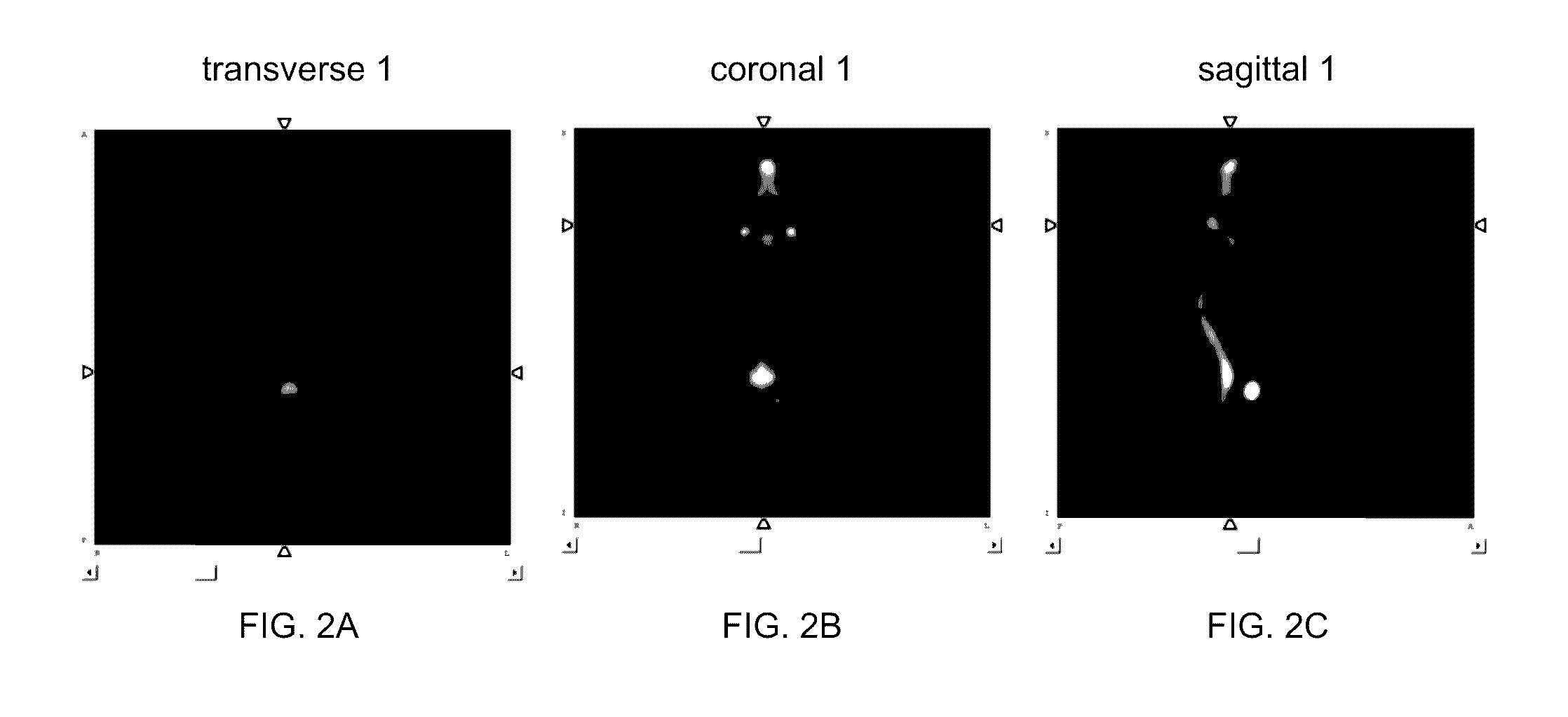
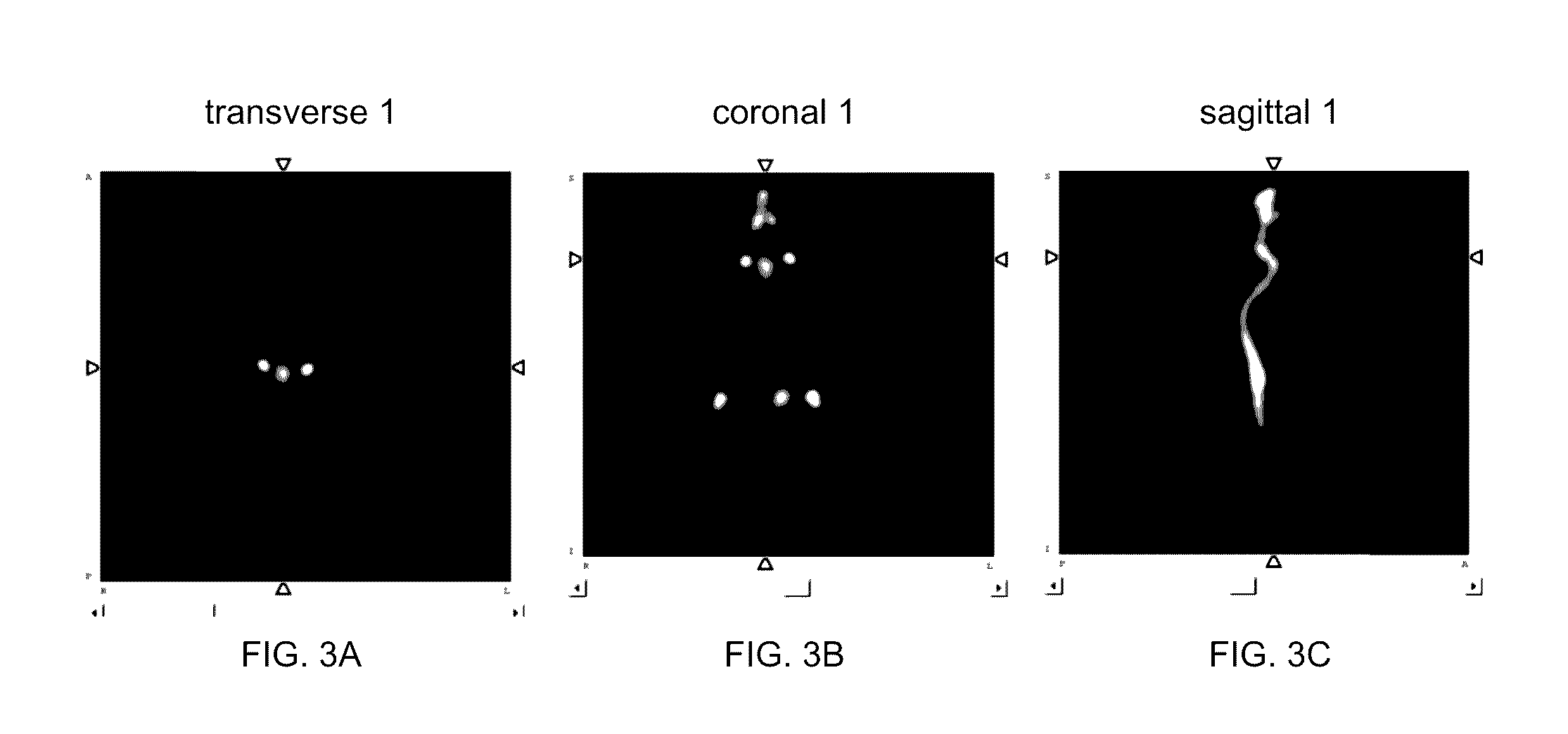
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy /sɪnˈtɪɡrəfi/ is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including; cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be visible in traditional X-ray images), and bone infection.
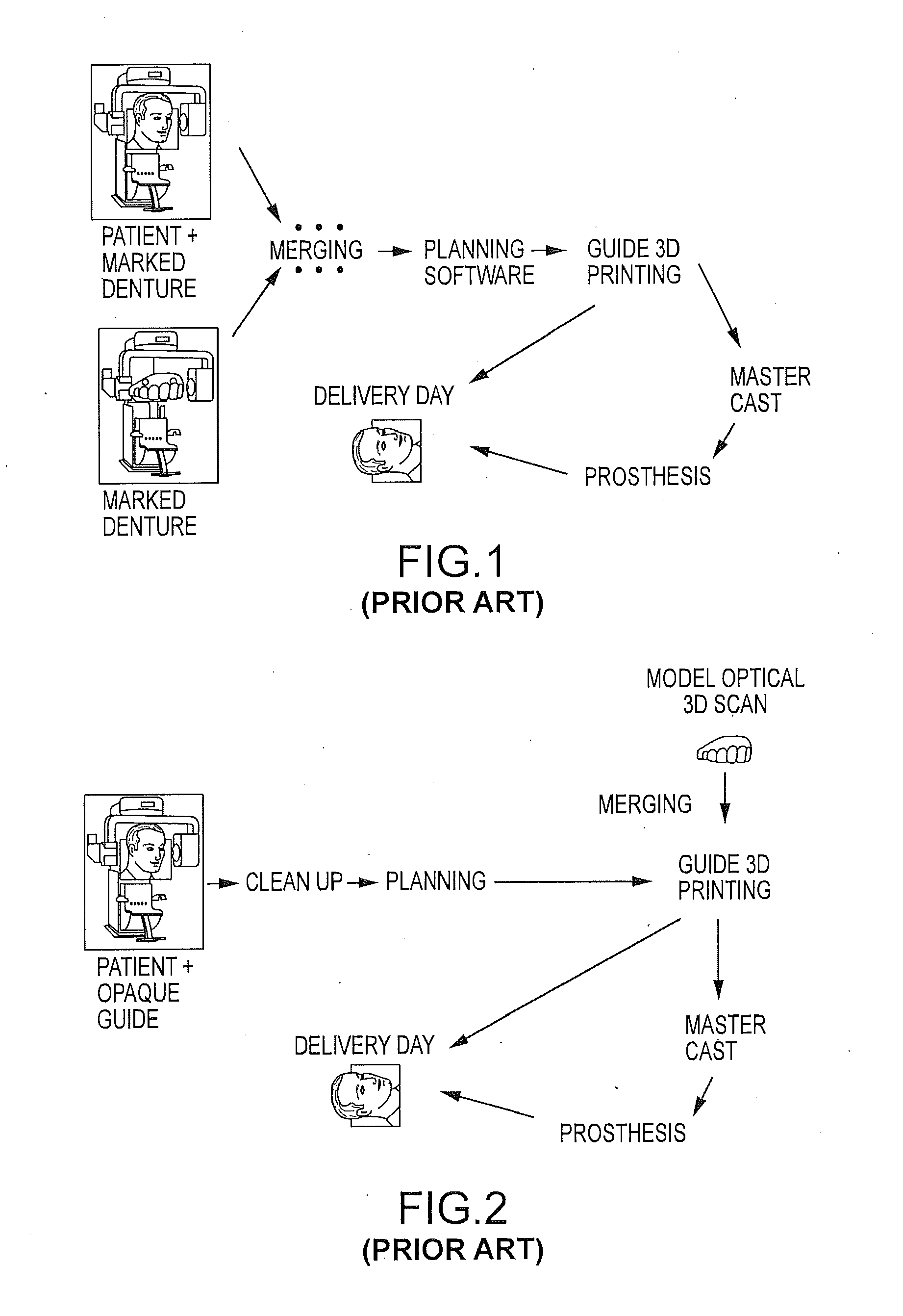
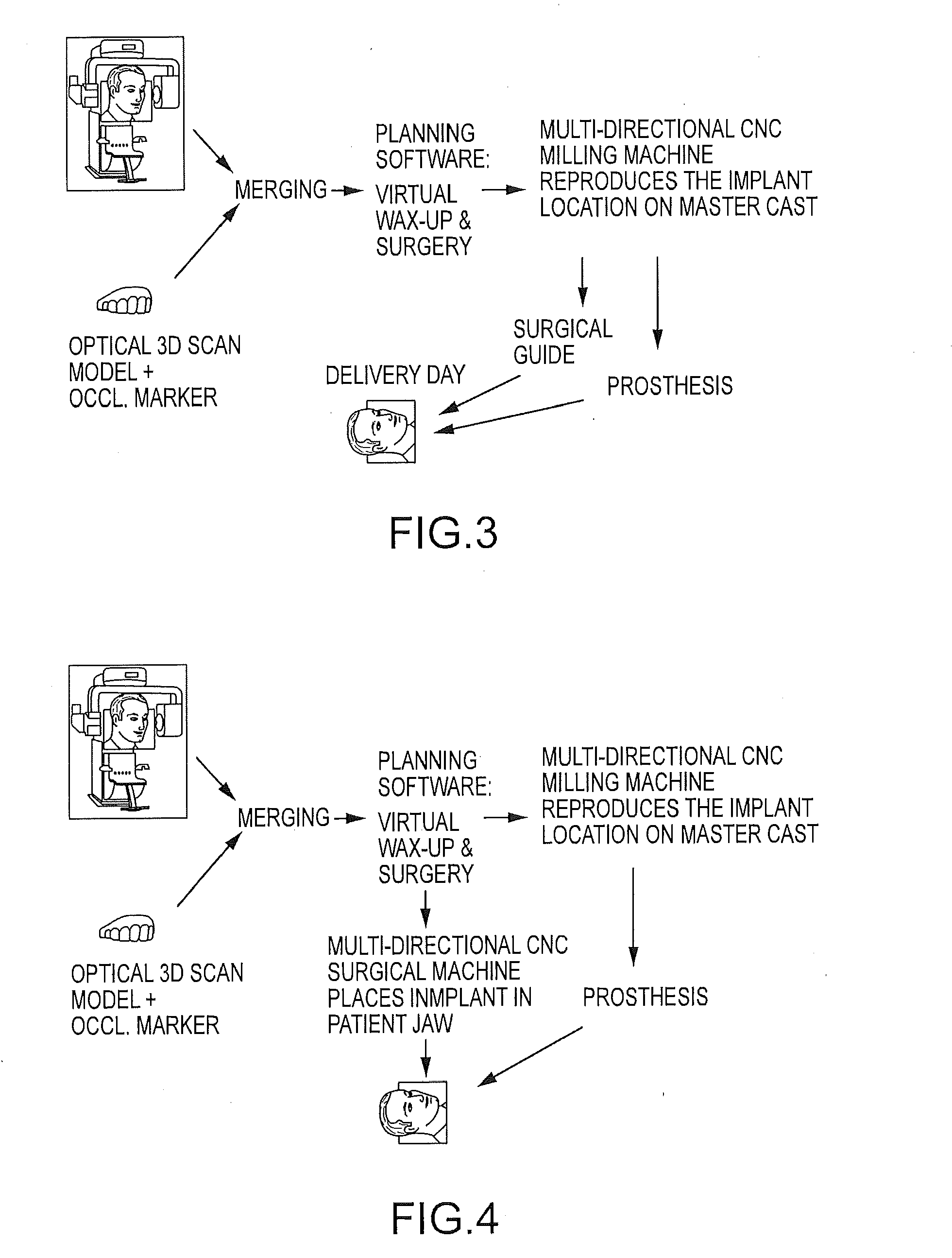
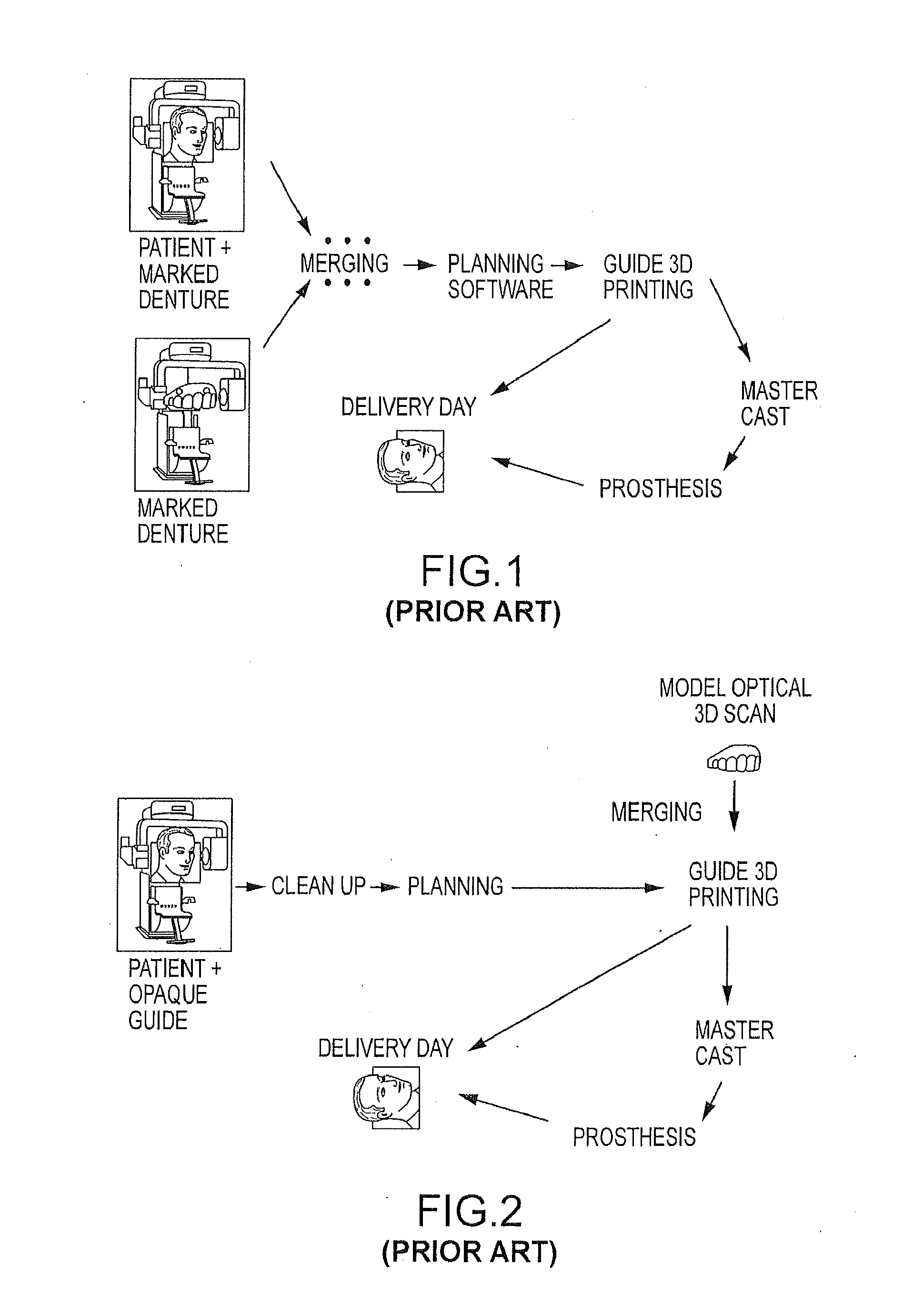
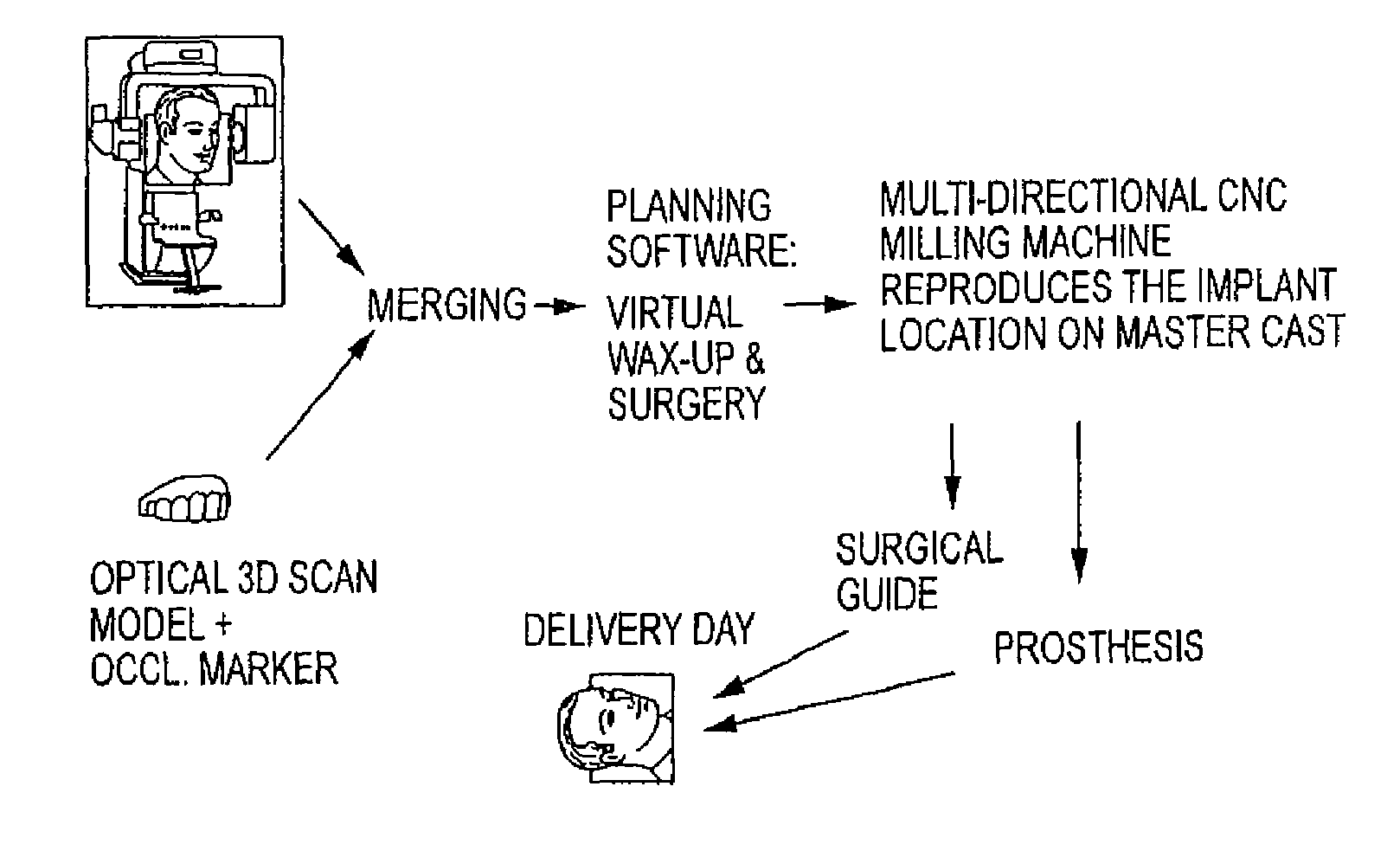
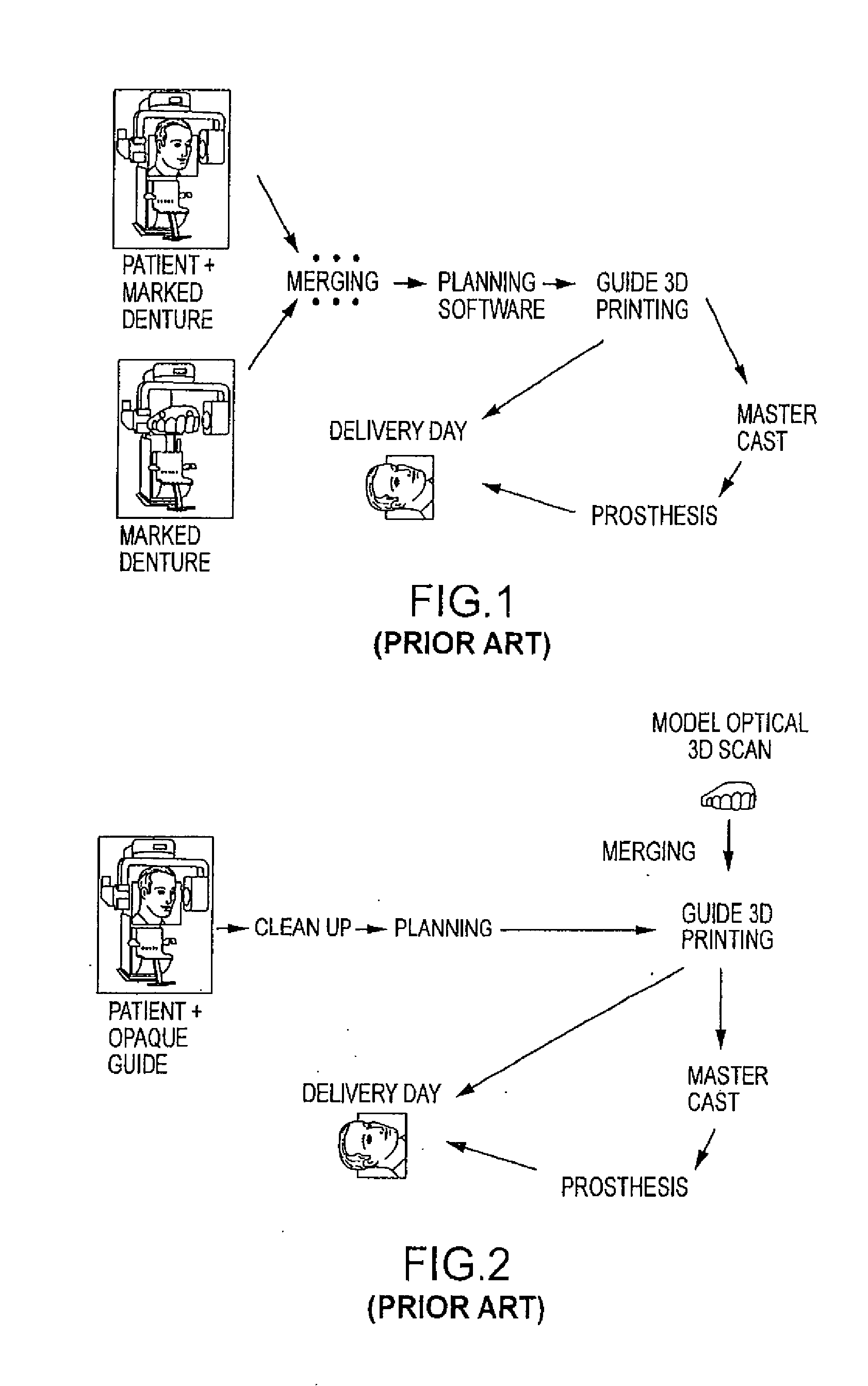
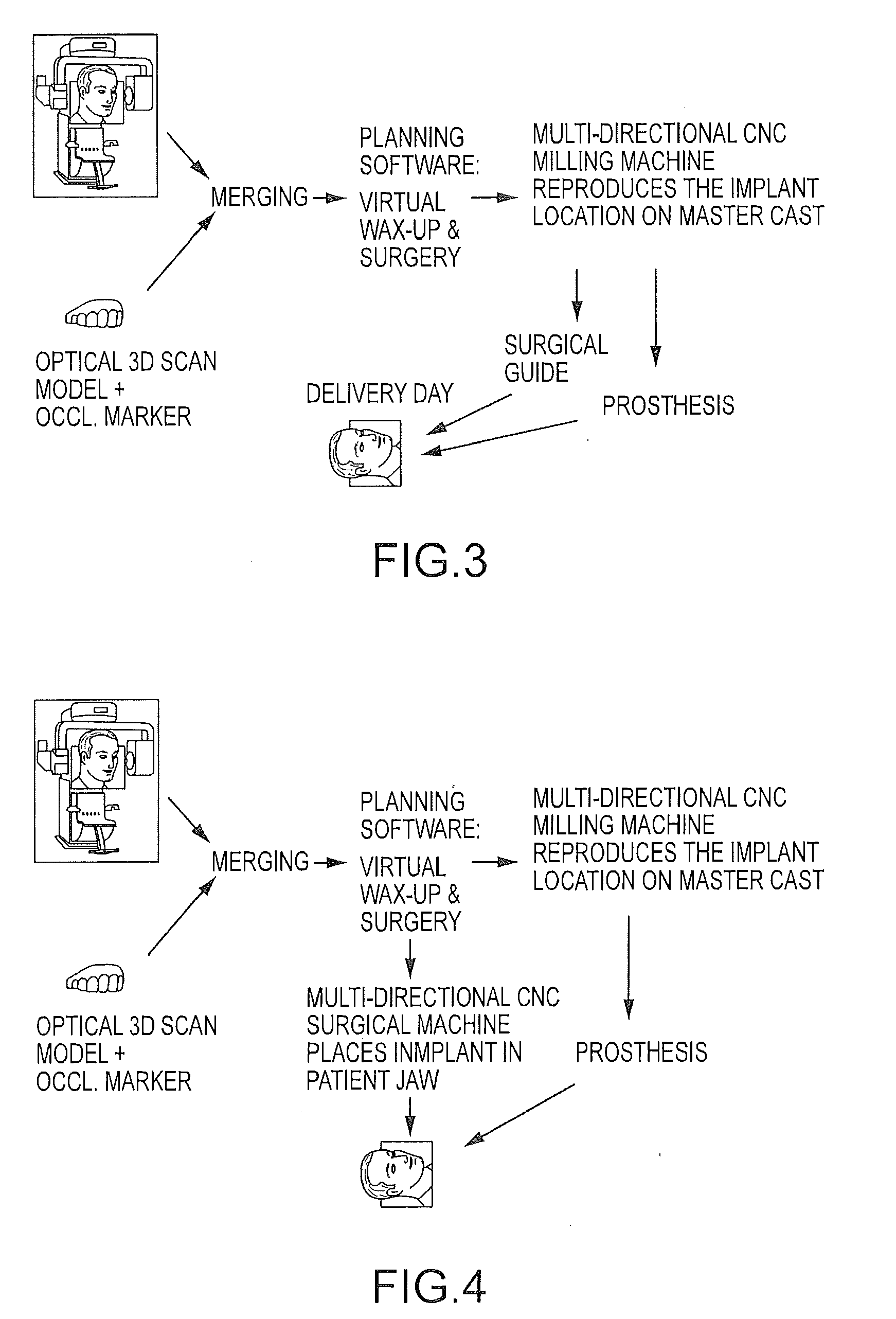
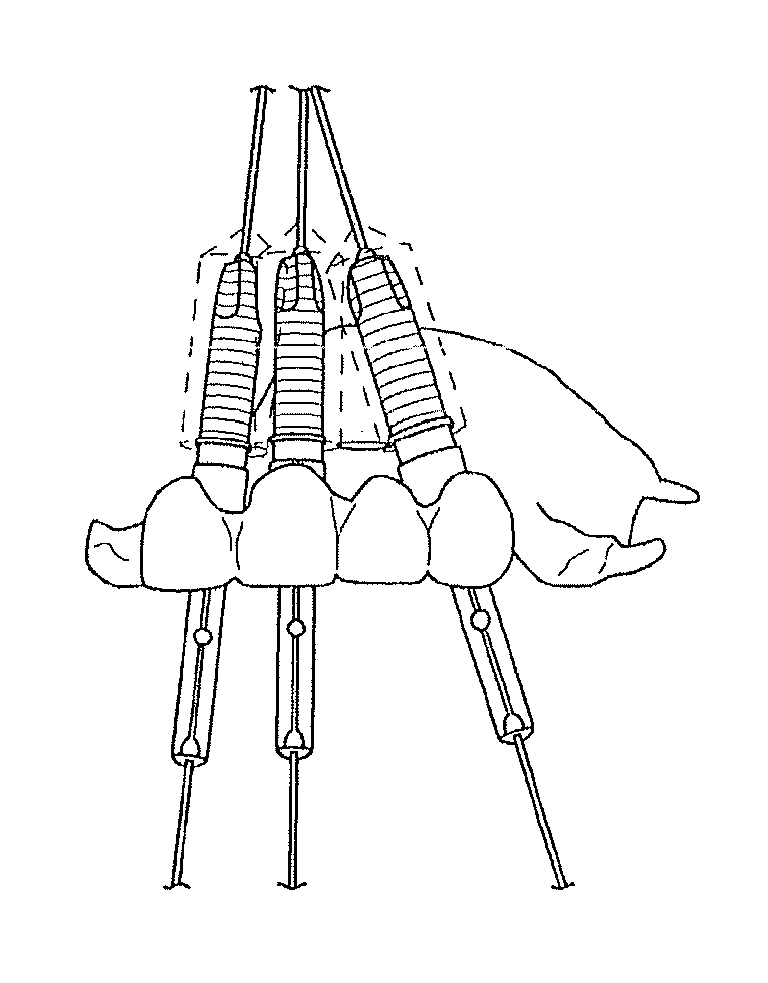
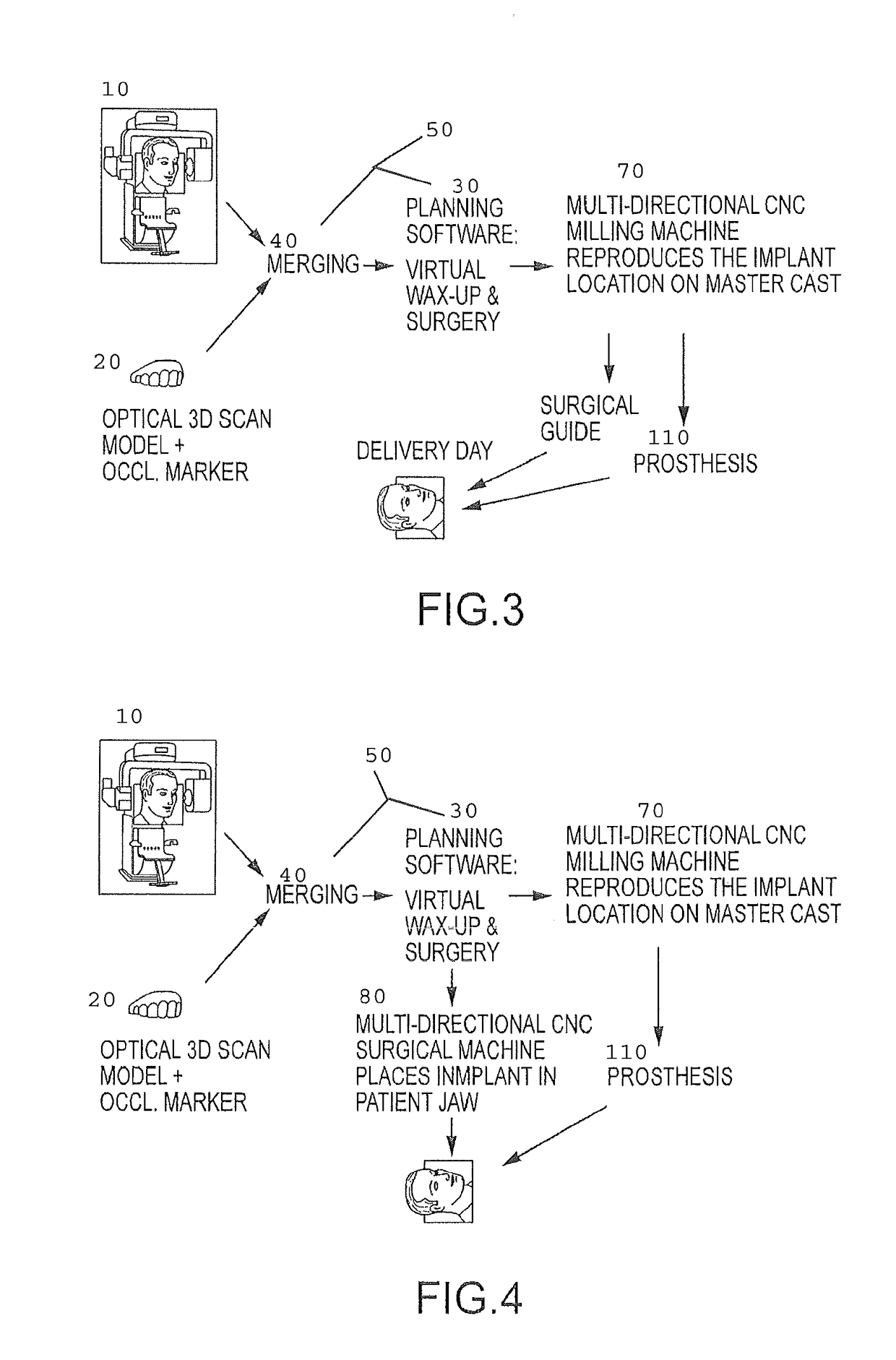
Assisted dental implant treatment
InactiveUS20090092948A1Diminished attractivenessEase of productionDental implantsImpression capsPhysical modelComputer module
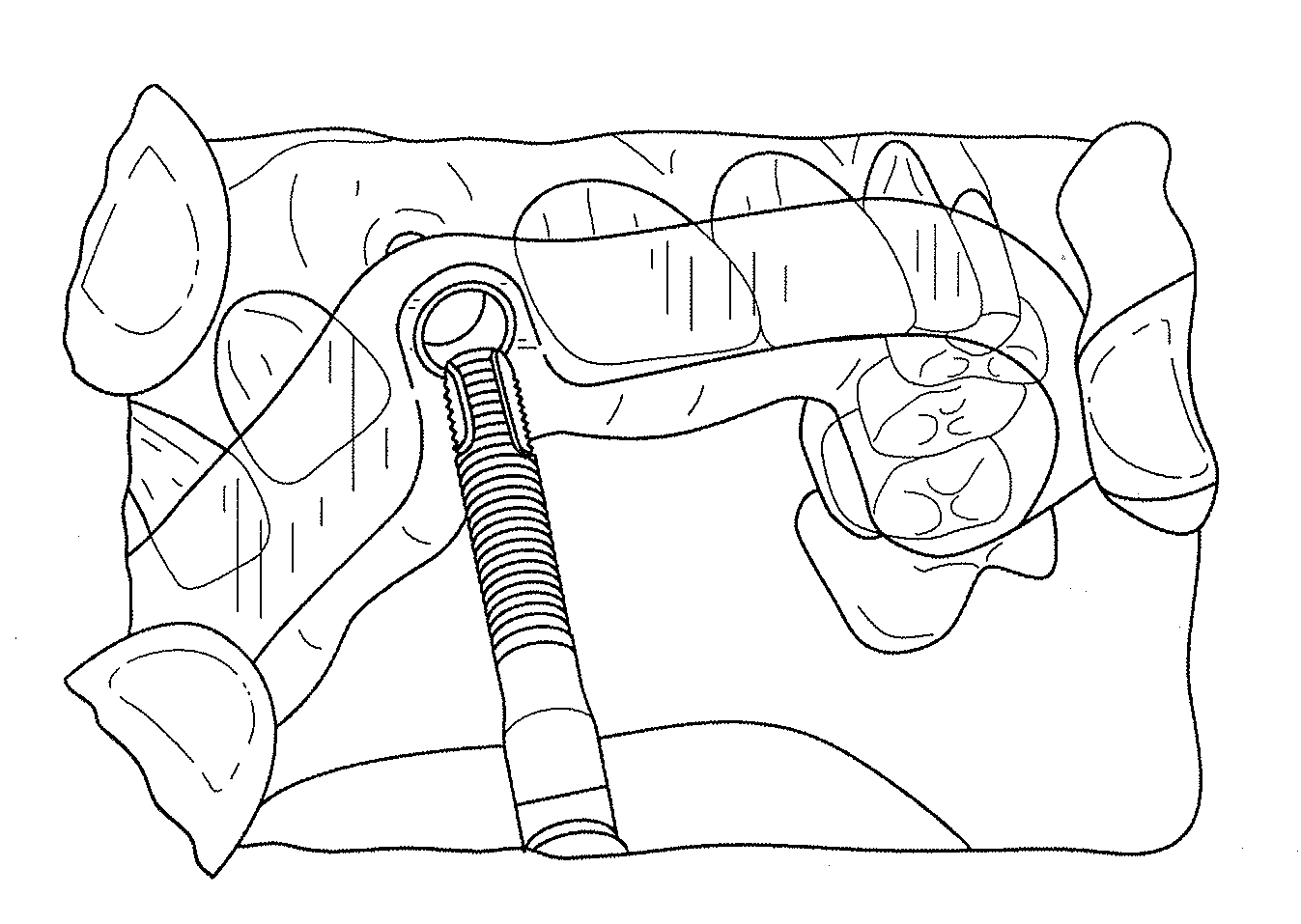
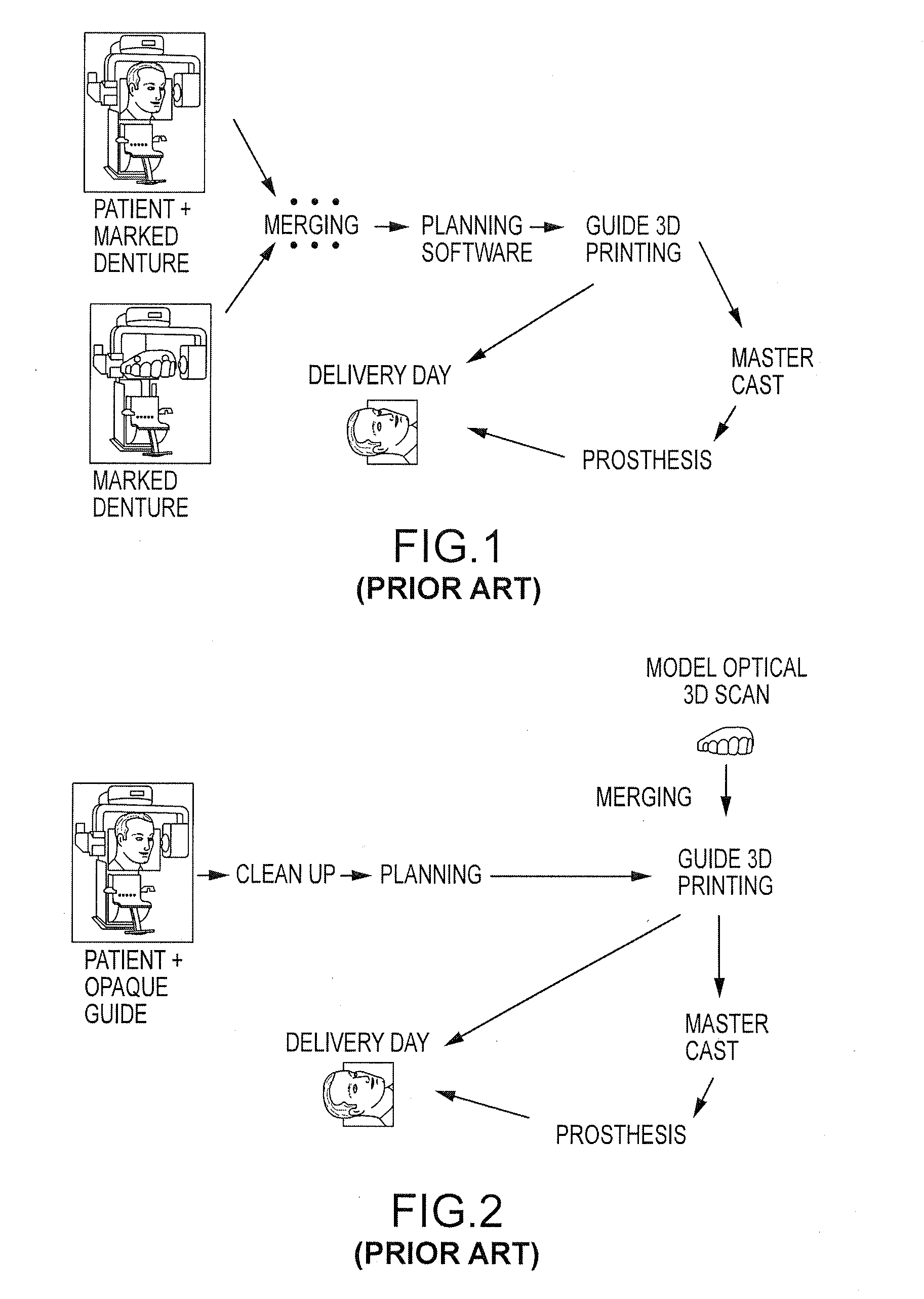
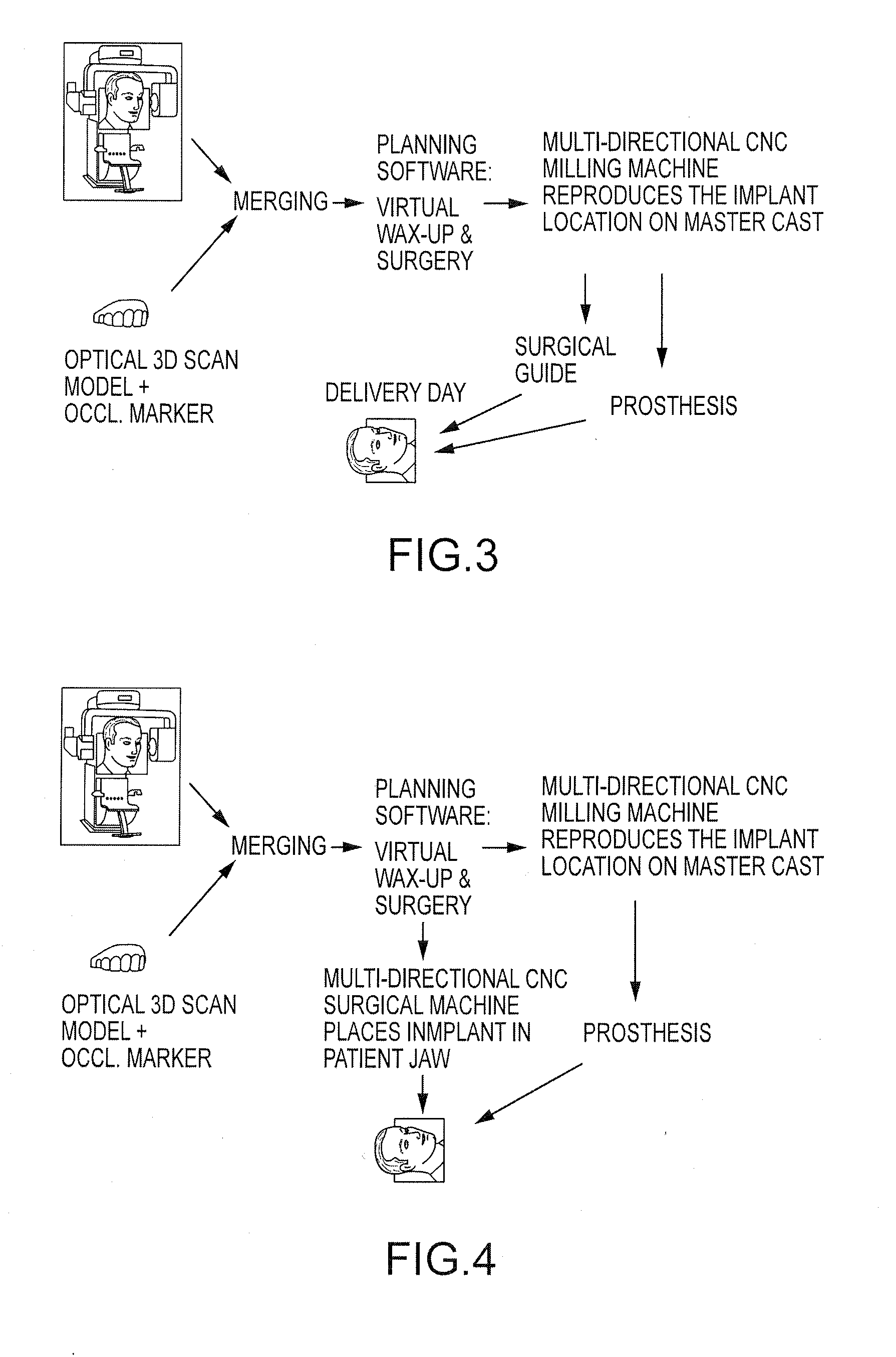
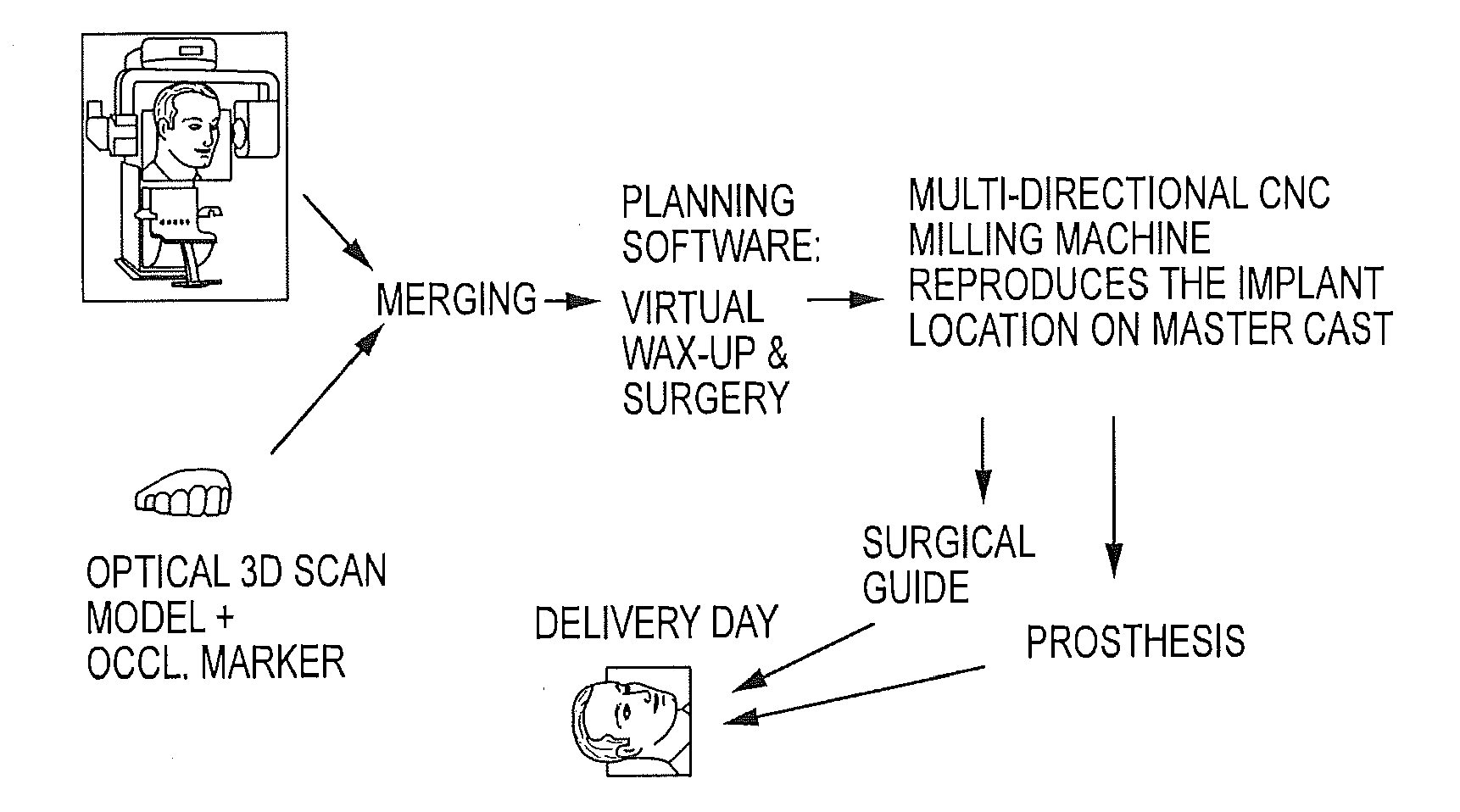
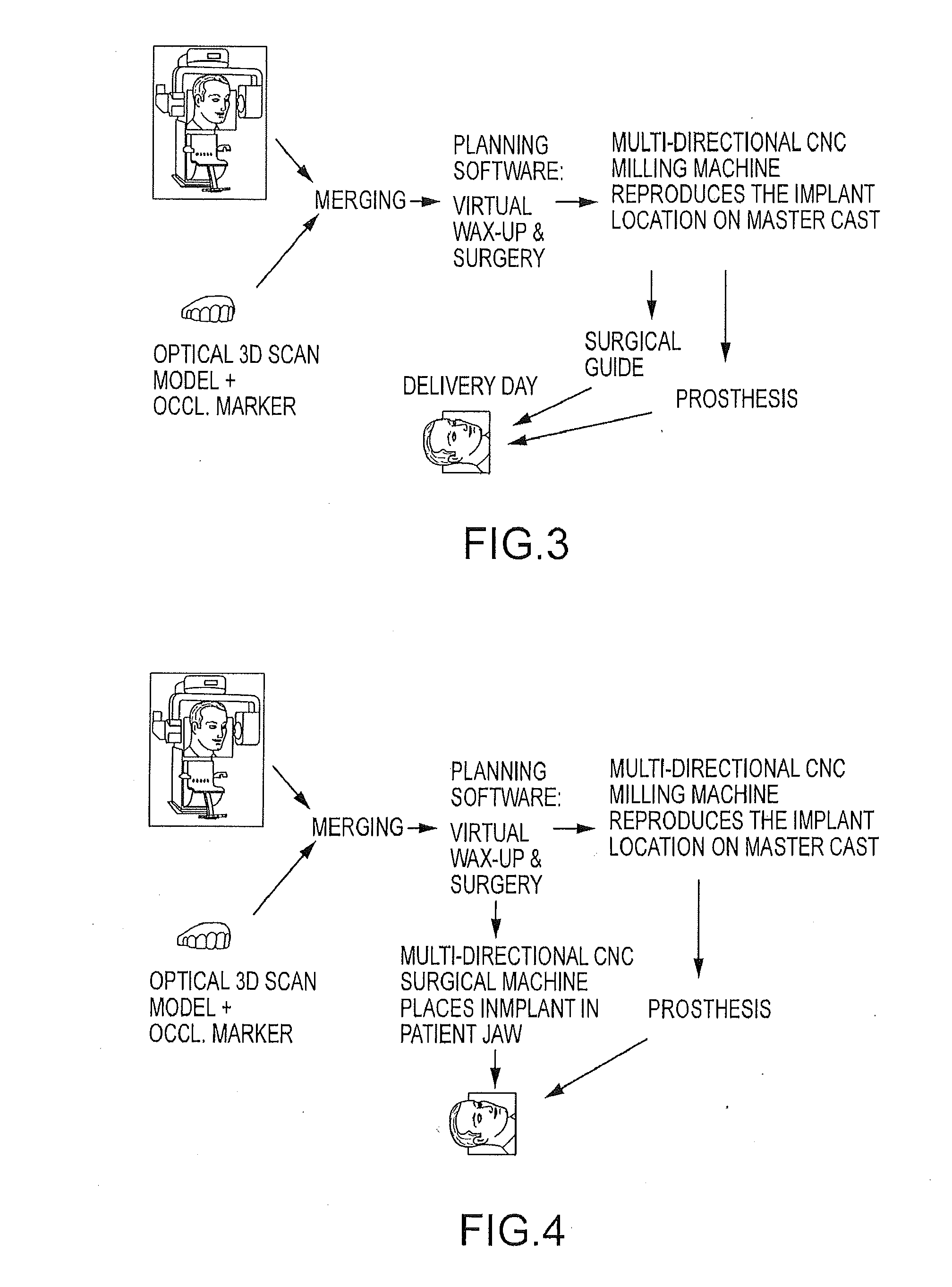
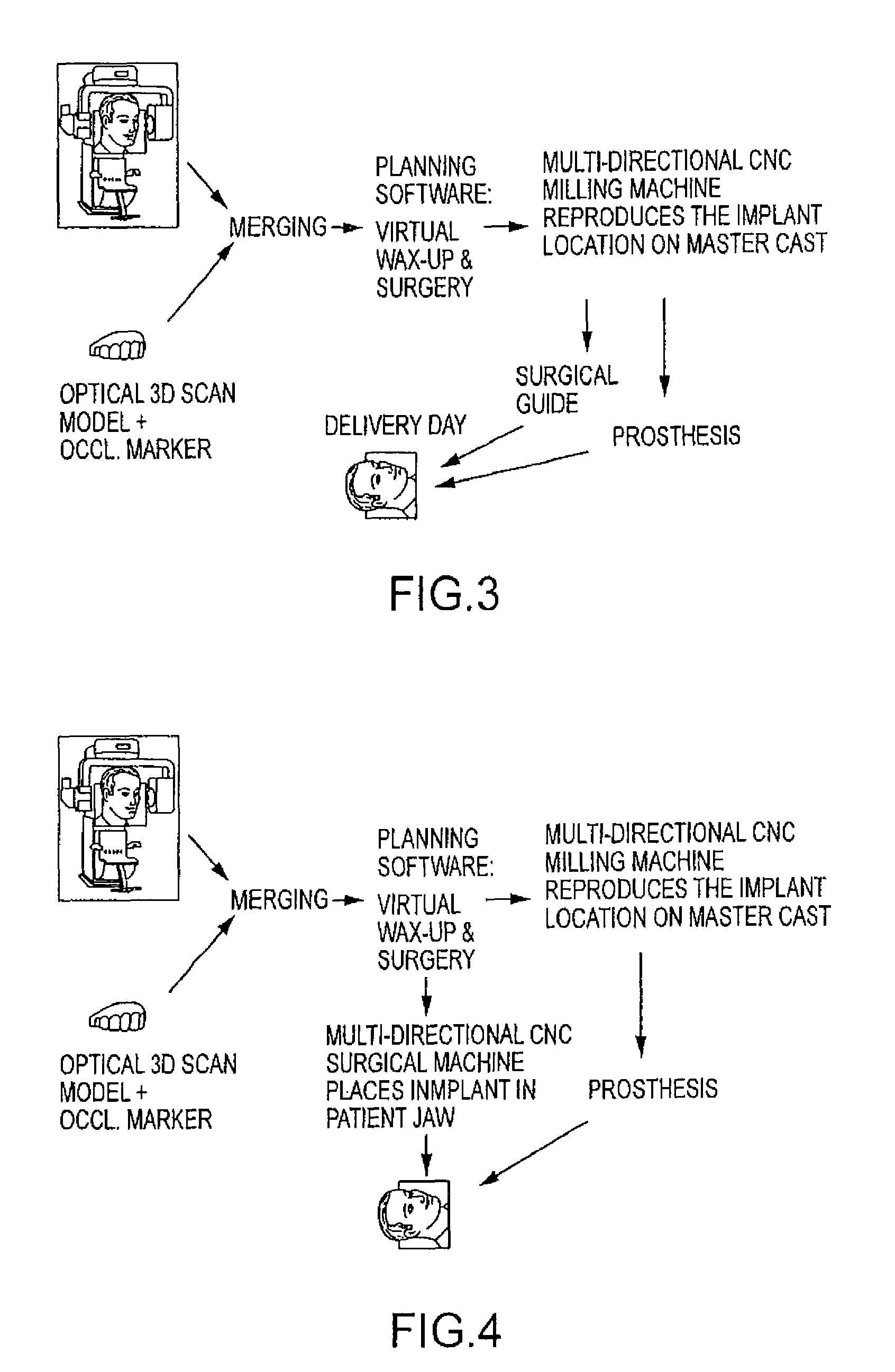
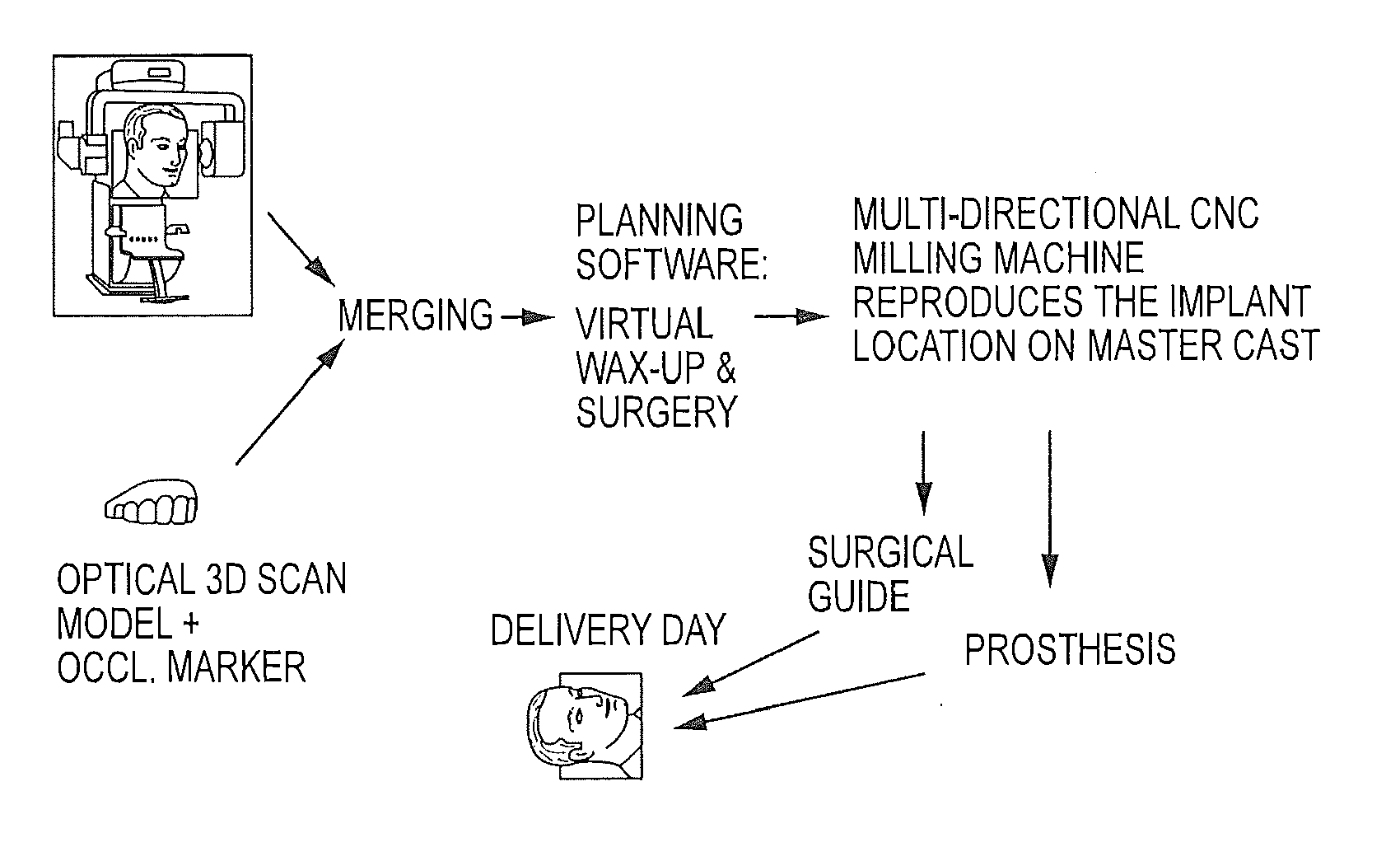
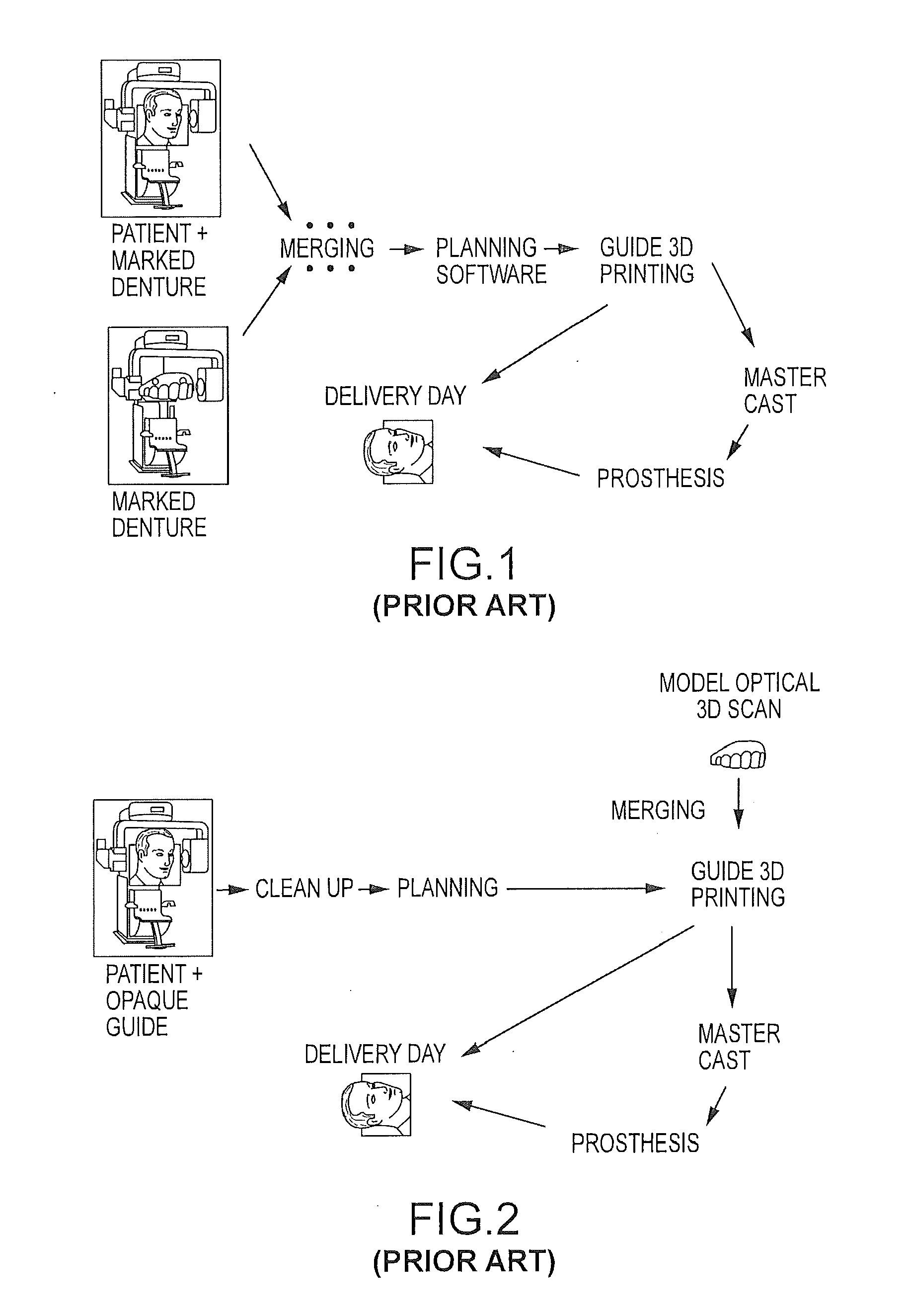
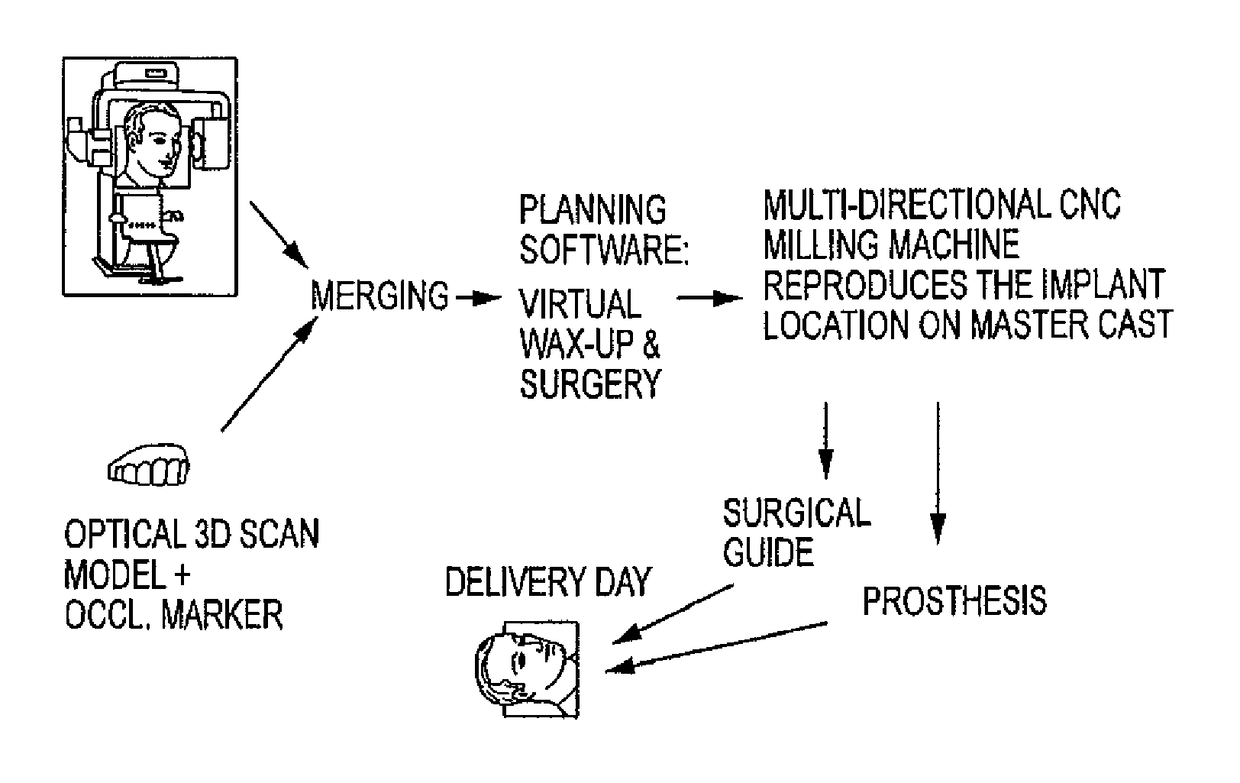
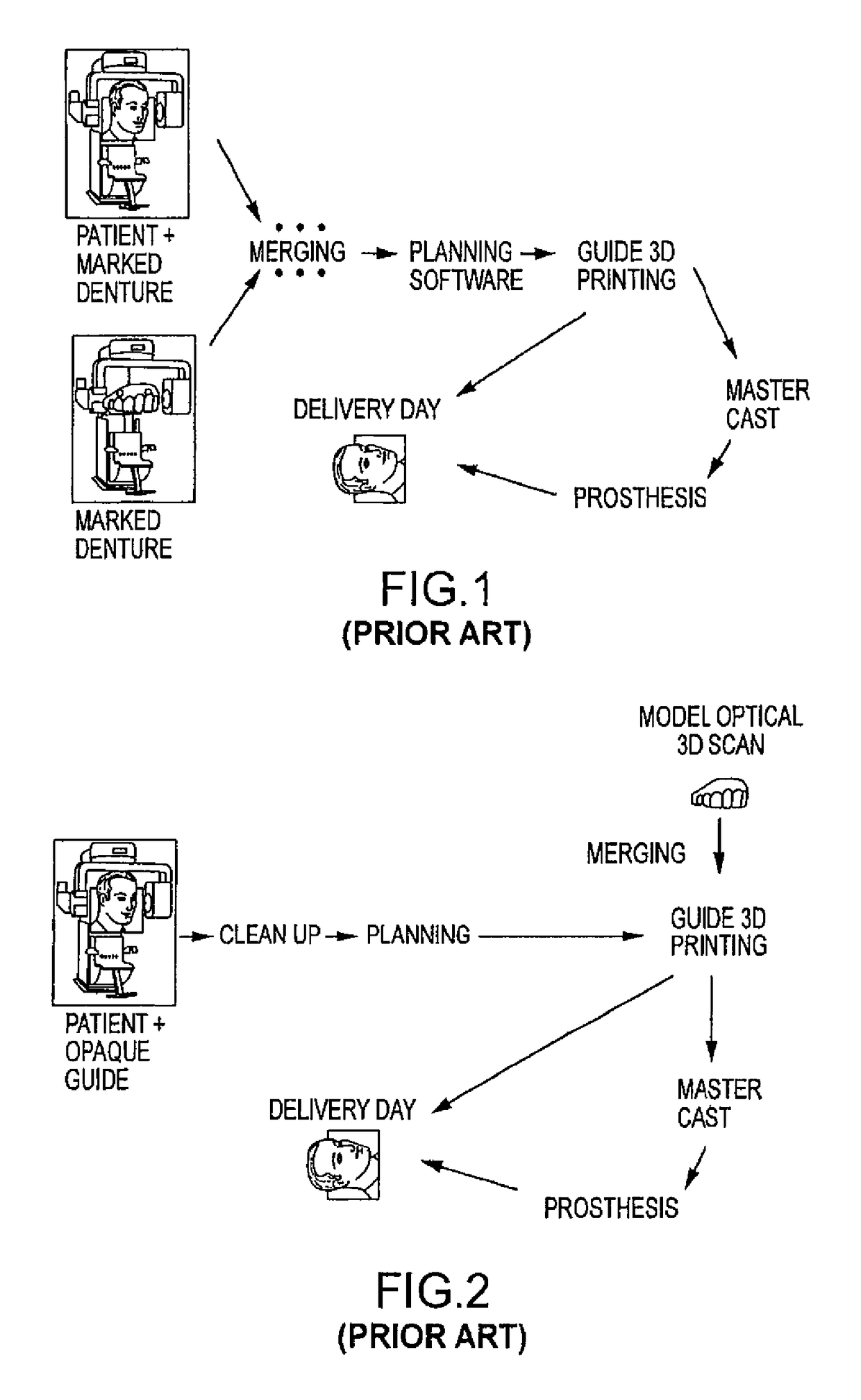
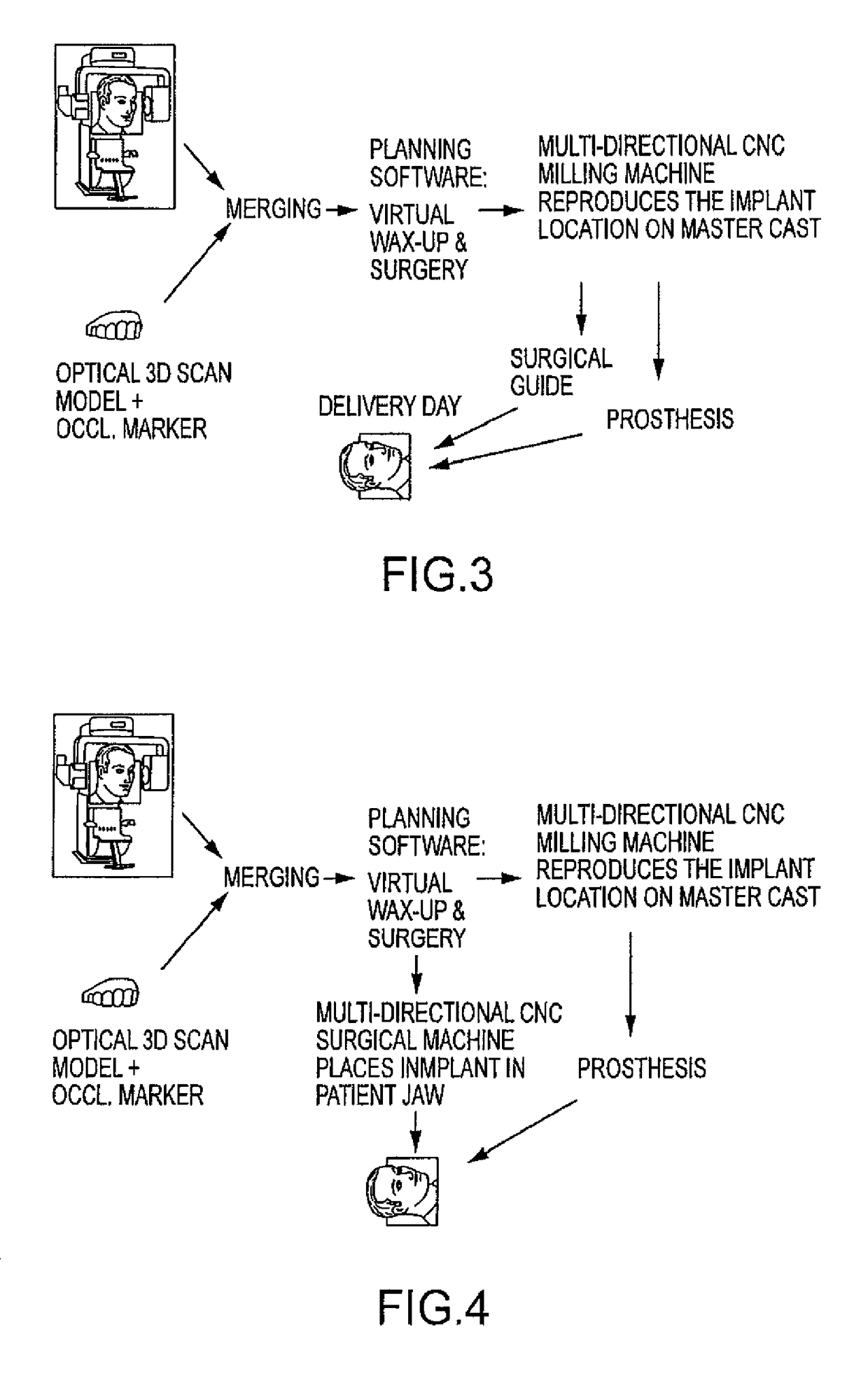
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
Assisted dental implant treatment and replication system
InactiveUS20110245951A1Diminished attractivenessEase of productionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProgramme controlPhysical modelDental implant
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
Assisted dental implant treatment
InactiveUS20120156638A1Diminished attractivenessEase of productionImpression capsDental articulatorsPhysical modelComputer module
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
Computer-Aided Method for Detection of Interval Changes in Successive Whole-Body Bone Scans and Related Computer Program Program Product and System
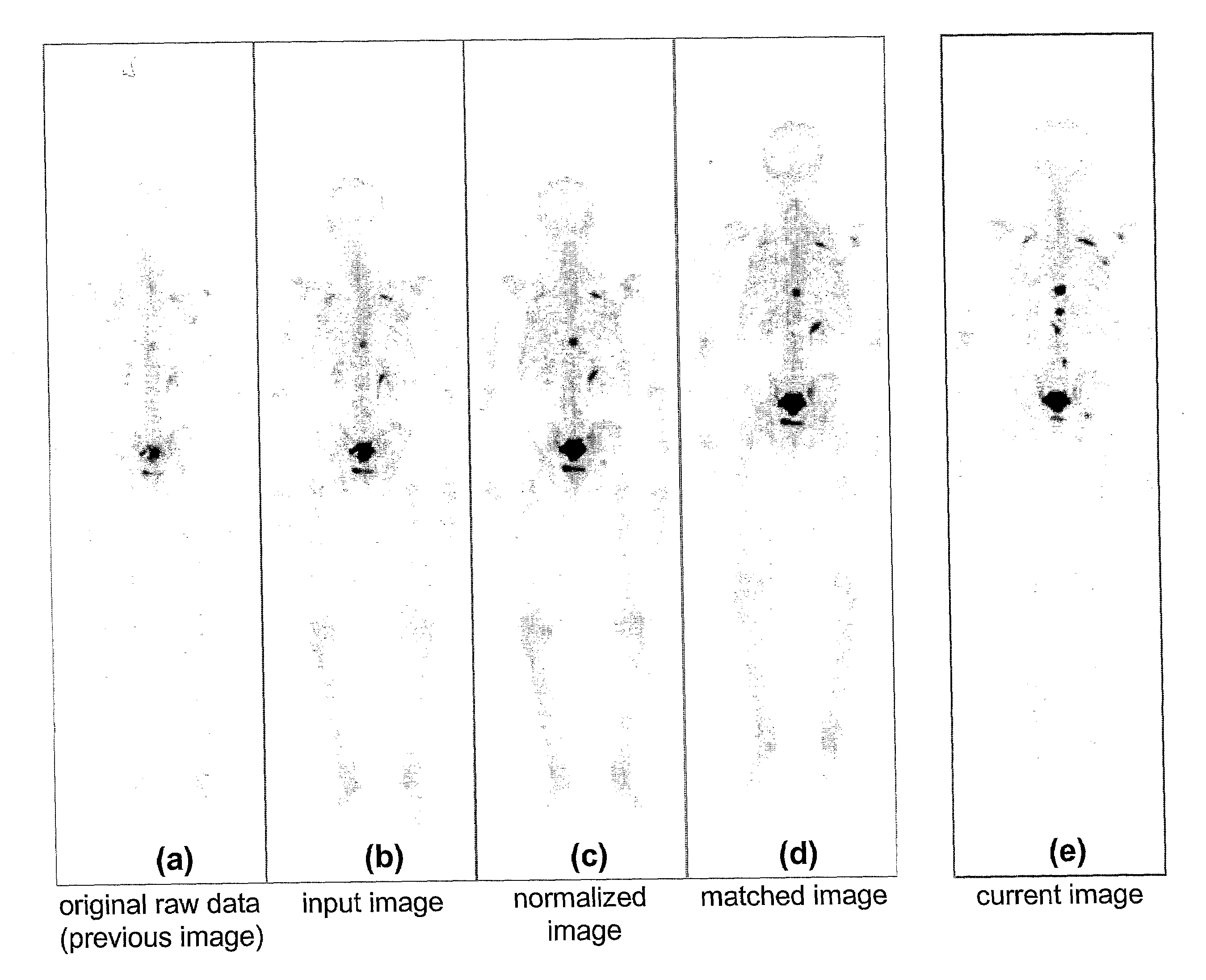
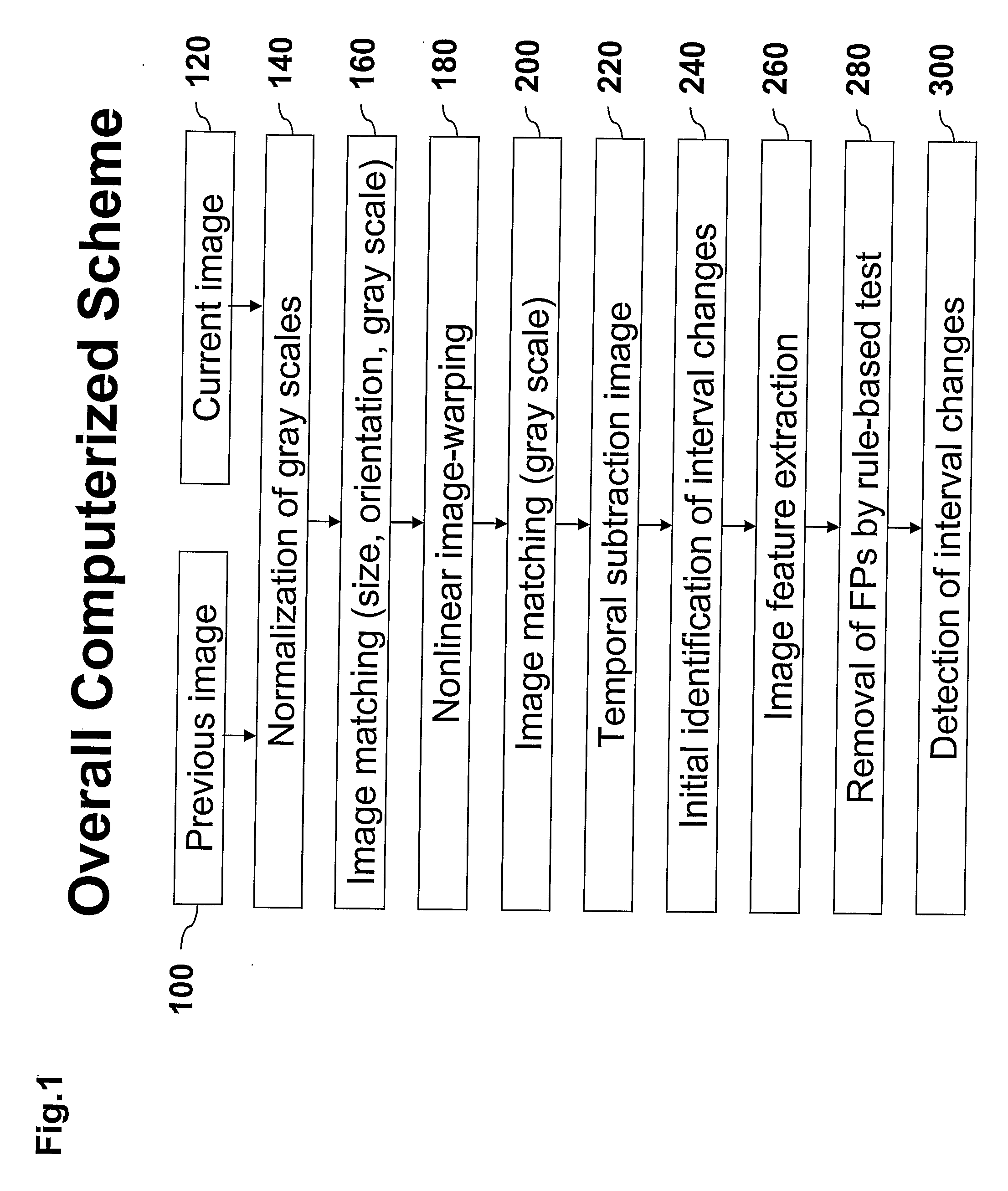
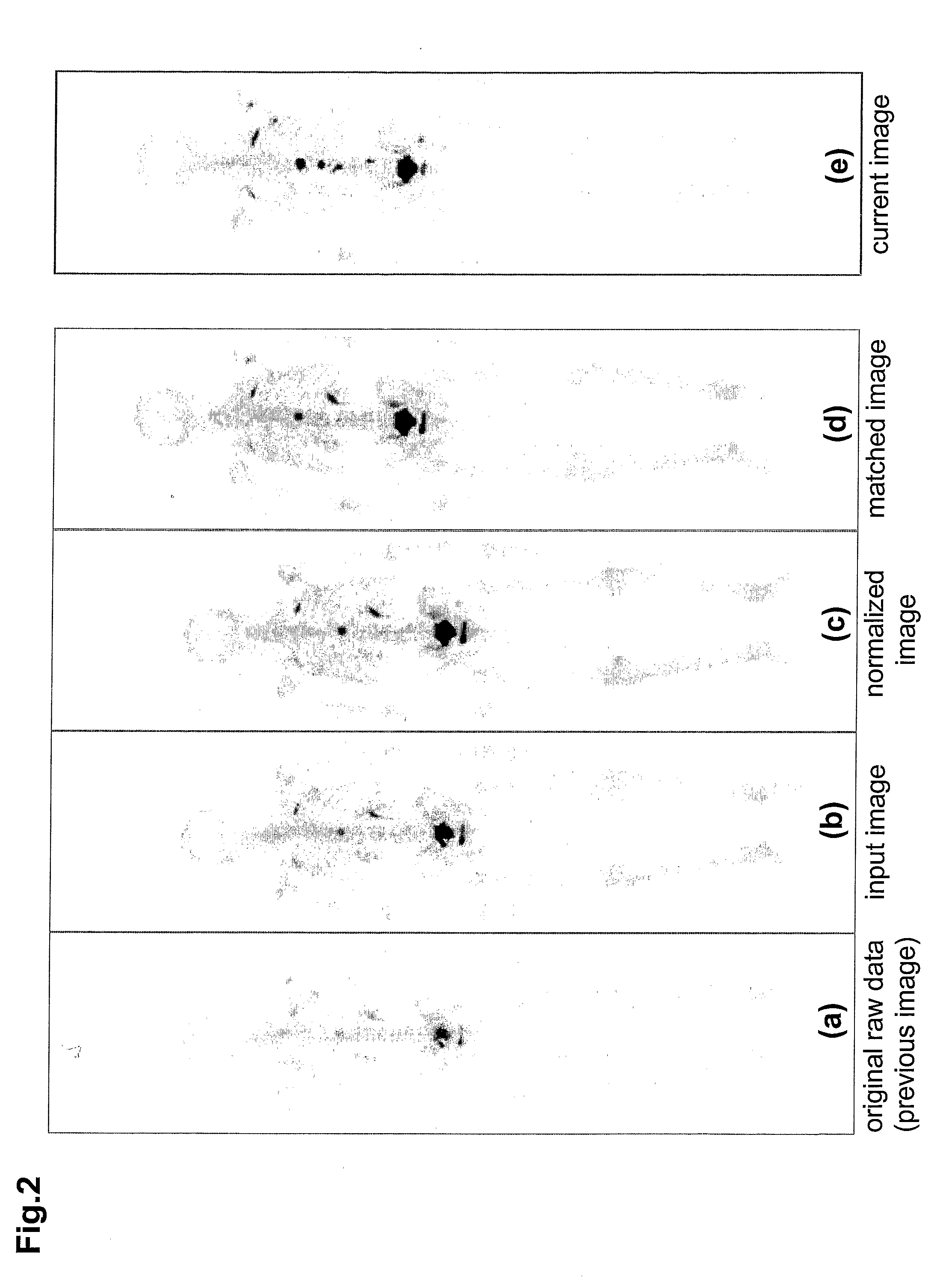
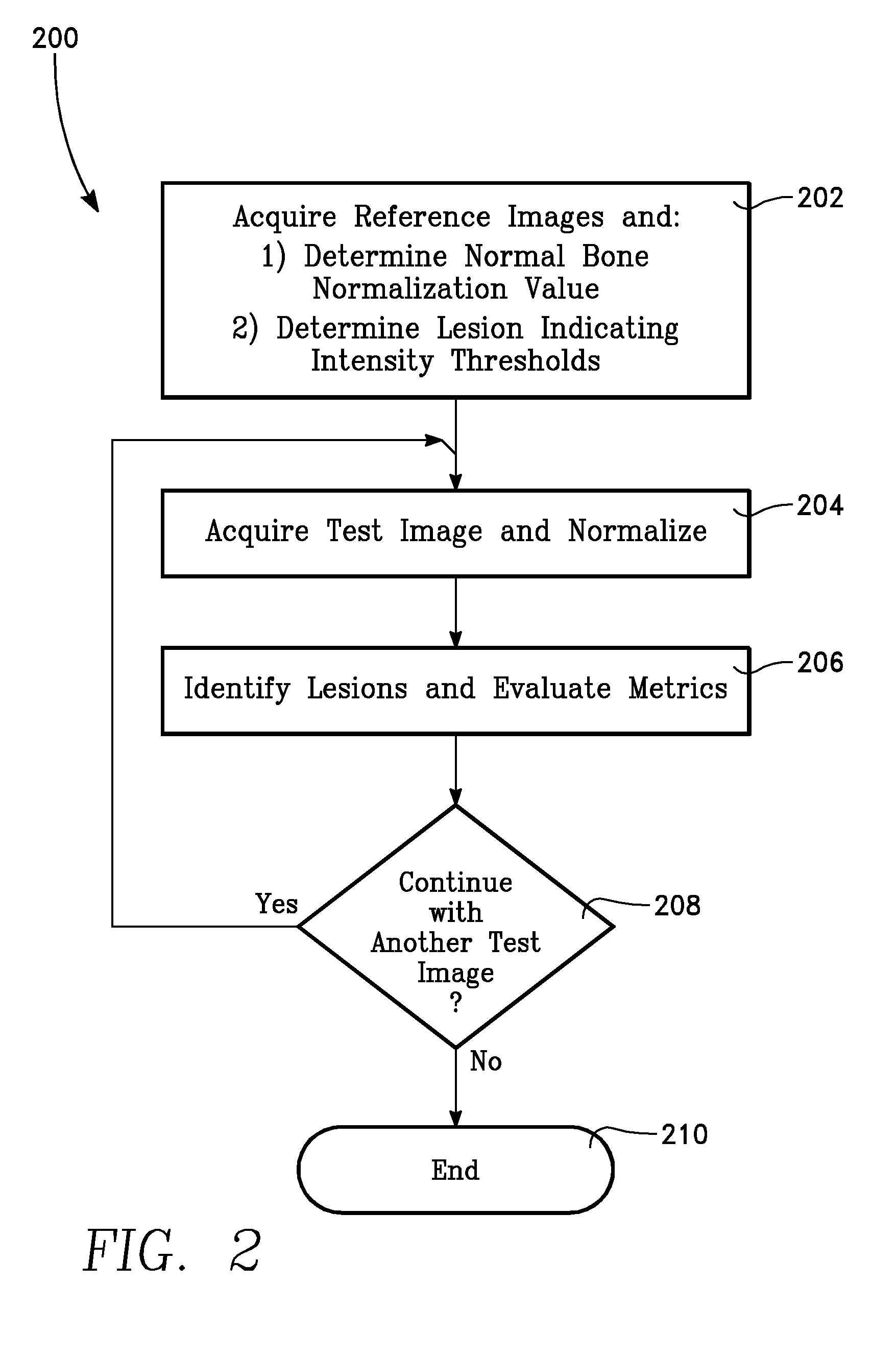
A method of producing an image to aid detection of a change in progress of a disease in a patient is described. In the method, a first image of a distribution of a radioisotope in the patient is obtained. A second image of the distribution of the radioisotope in the patient is also obtained. At least one of the first and second images are then normalized (1:140). One of the images is warped to match the other image using a multiple-segment matching method (1:160). The first image is subtracted from the second image to form a subtraction image (1:220). Finally, the resulting subtraction image is displayed.
Owner:SHIRAISHI JUNJI +4
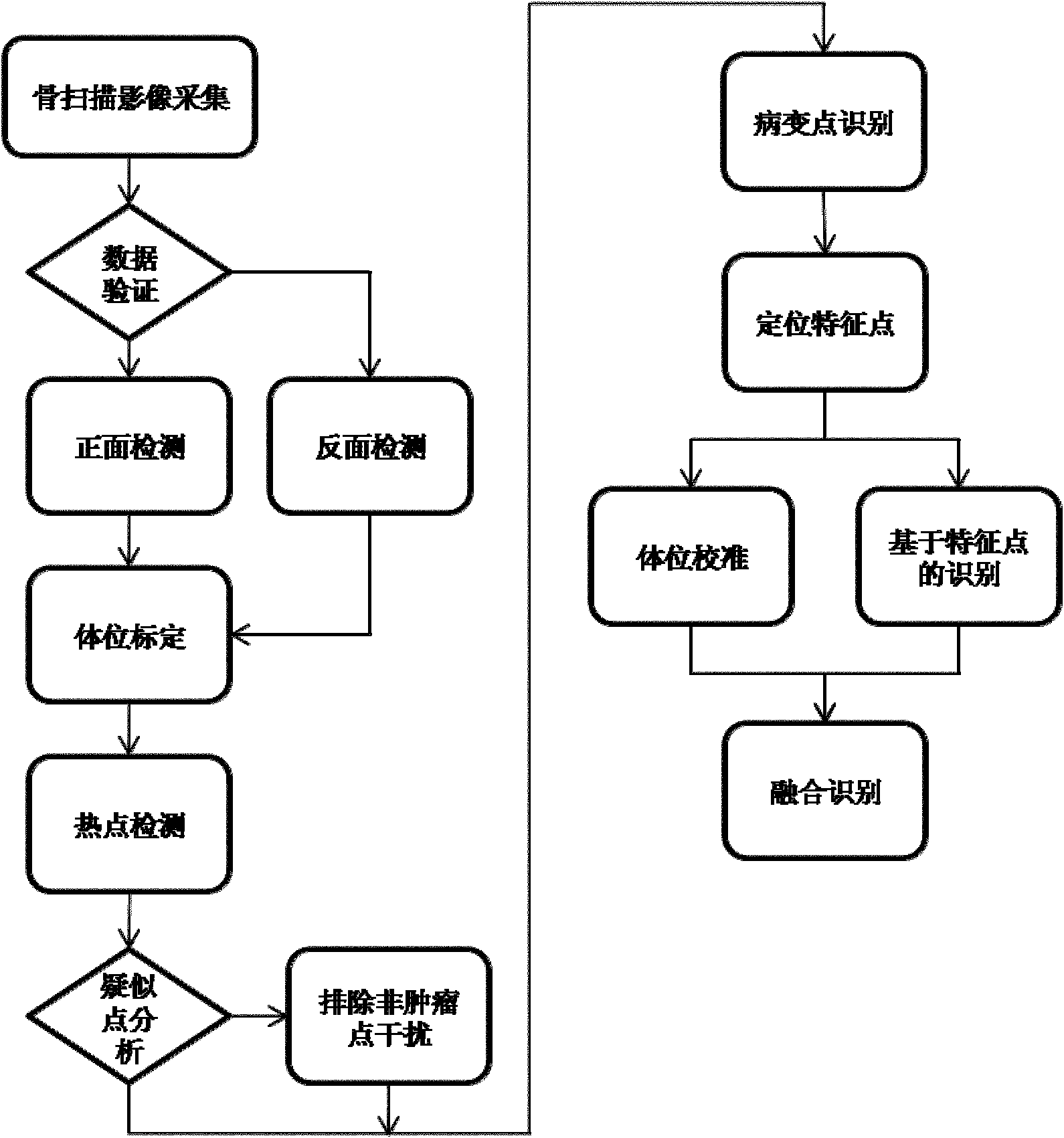
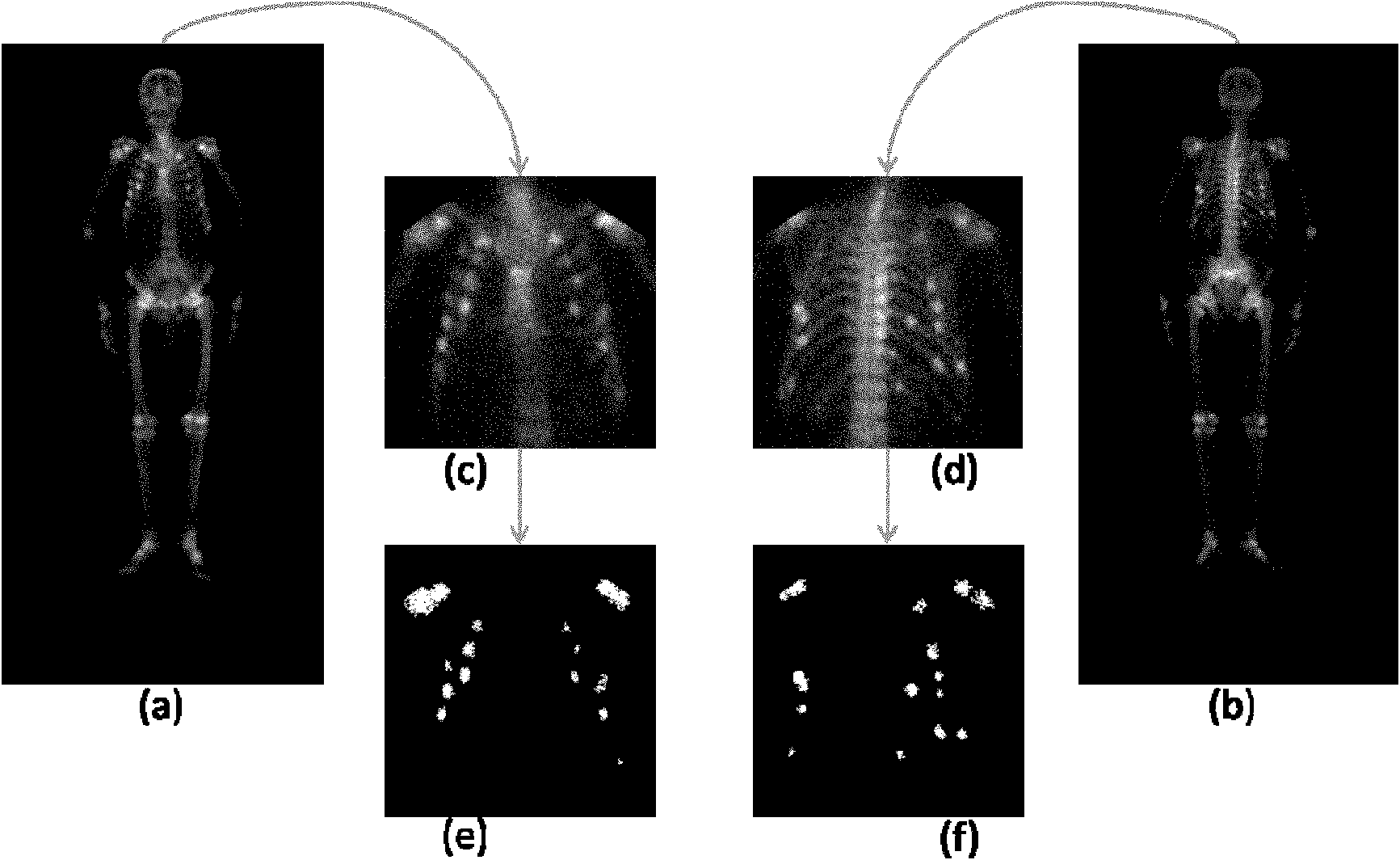
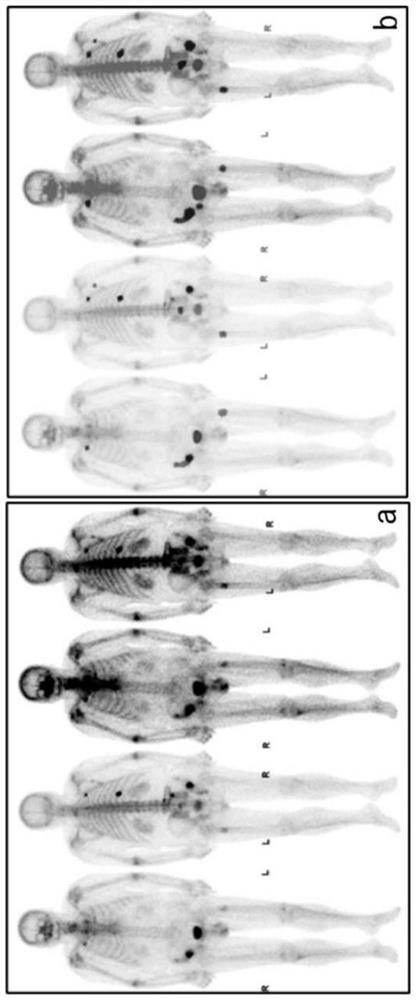
Method for recognizing image of carcinoma bone metastasis in bone scan
InactiveCN102096804APrecise positioningAccurate identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyLymphatic Spread
The invention provides a method for recognizing an image of carcinoma bone metastasis in bone scan in the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting positive information and negative information by extracting a whole body bone scan image of a human body; finding out a reference point according to image information, positioning a key part of the human body, and dividing the image into a plurality of main blocks; extracting a hot spot region by using an adaptive region-specific and characteristic-maximum-based (ARC) hot spot detection algorithm of each region; extracting a characteristic vector according to a hot spot detection result and the original image; using a support vector machine (SVM) training model according to the extracted characteristic vector; testing and modifying an obtained classifying model, and simultaneously performing checking, matching and human body calibration on a recognition result so as to obtain a correct diagnosis report. Compared with other methods of recognizing the image of carcinoma bone metastasis, the hot spot detection precision and patient recognition accuracy are improved, the blank in the new developing field of China is recovered, and a uniform diagnosis standard on carcinoma bone metastasis diagnosis in China is established.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Assisted dental implant treatment and replication system
InactiveUS9259291B2Diminished attractivenessEase of productionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProgramme controlPhysical modelComputer module
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
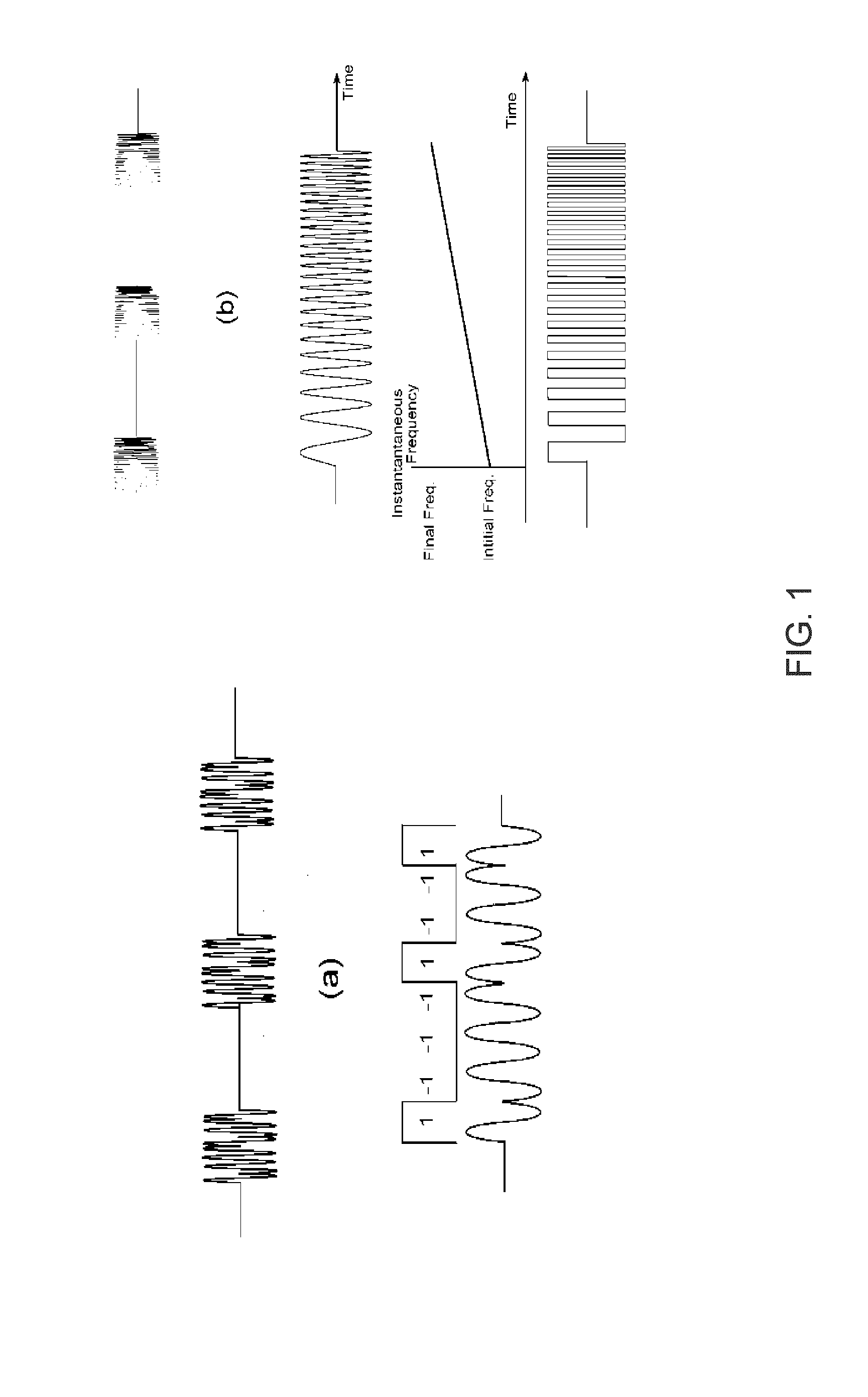
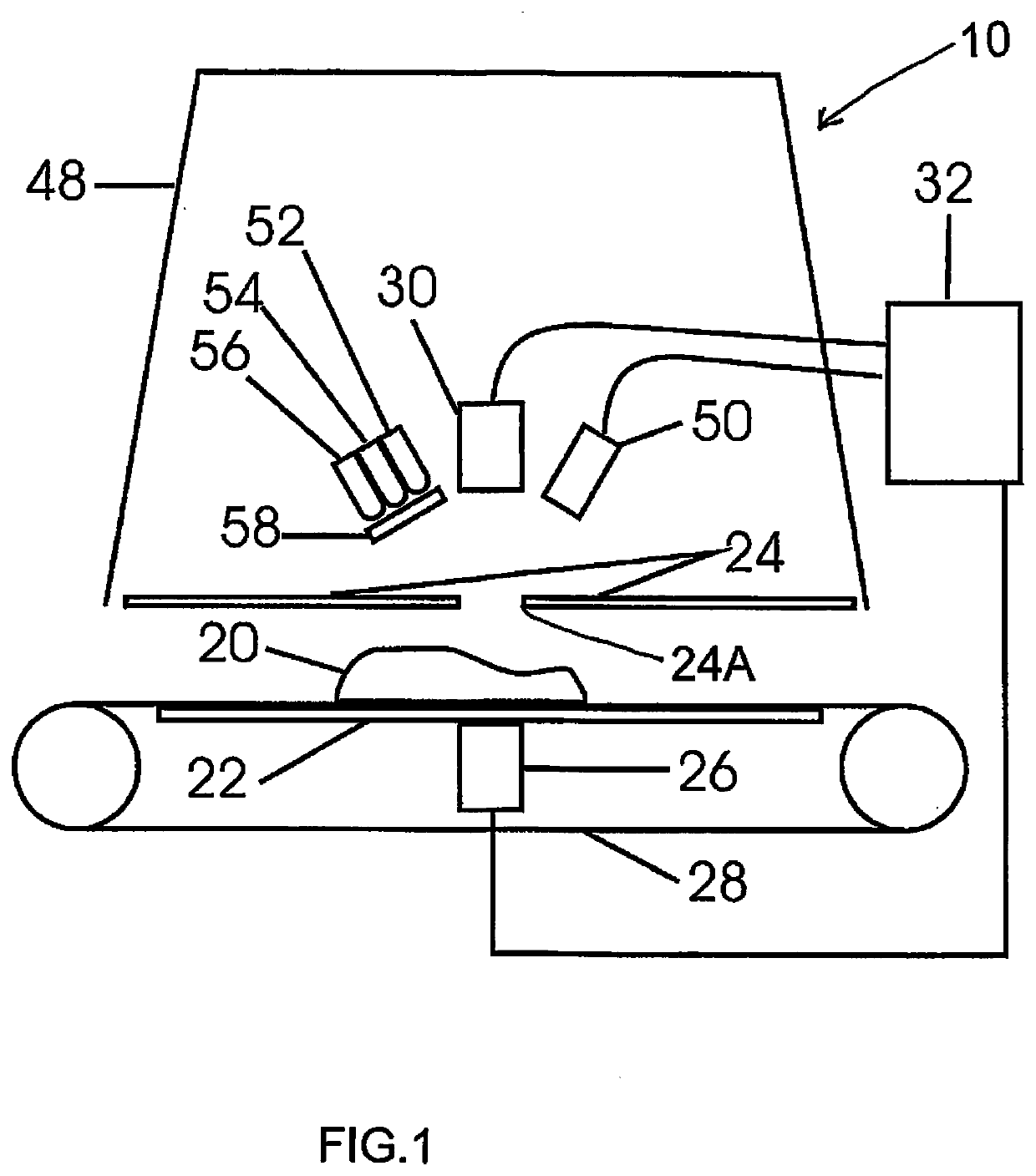
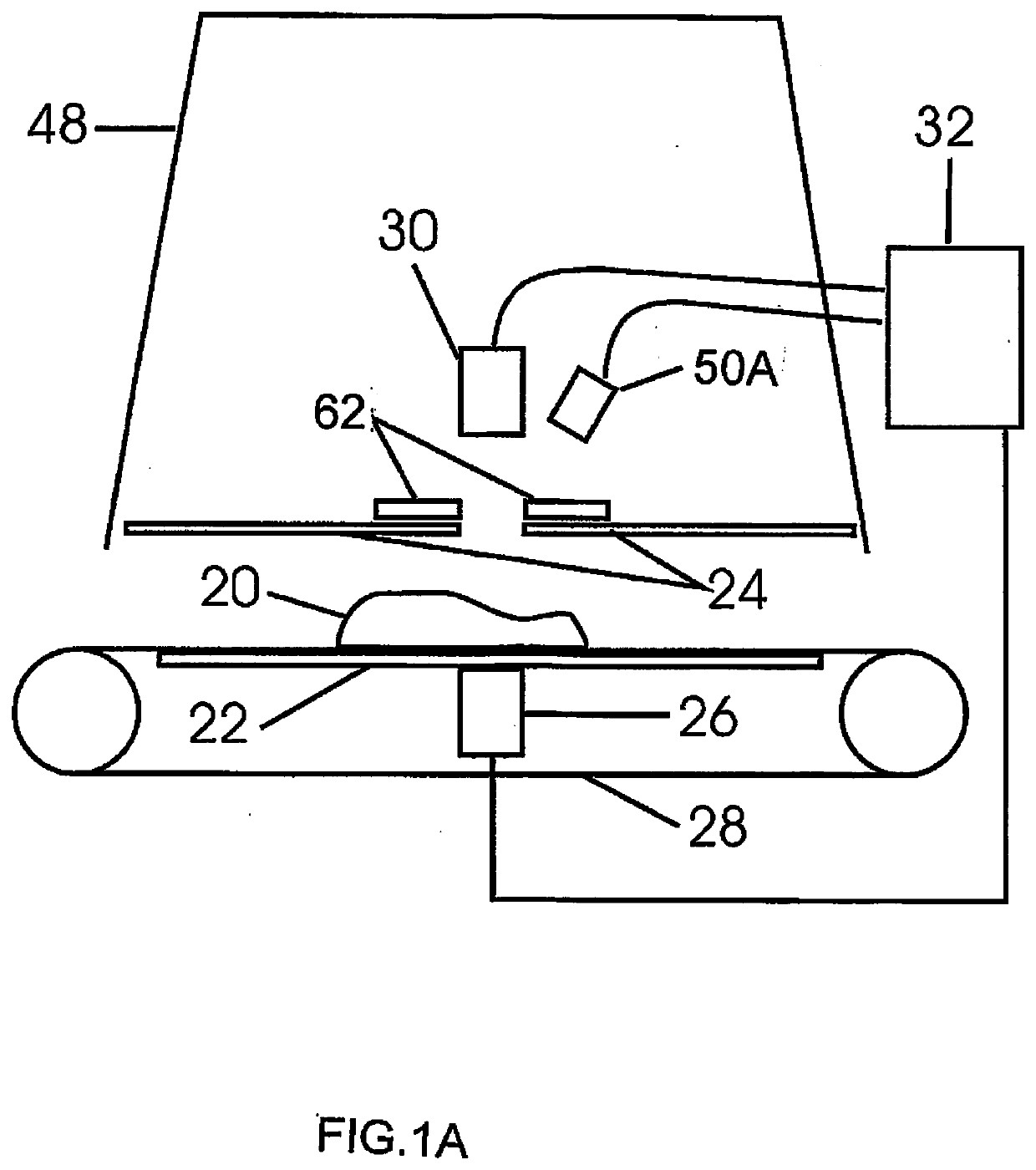
Method and Device for Bone Scan in Meat
InactiveUS20170205385A1Increase probabilityMinimizes and eliminates specular reflectanceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRaman scatteringForeign matterUltrasound Identification
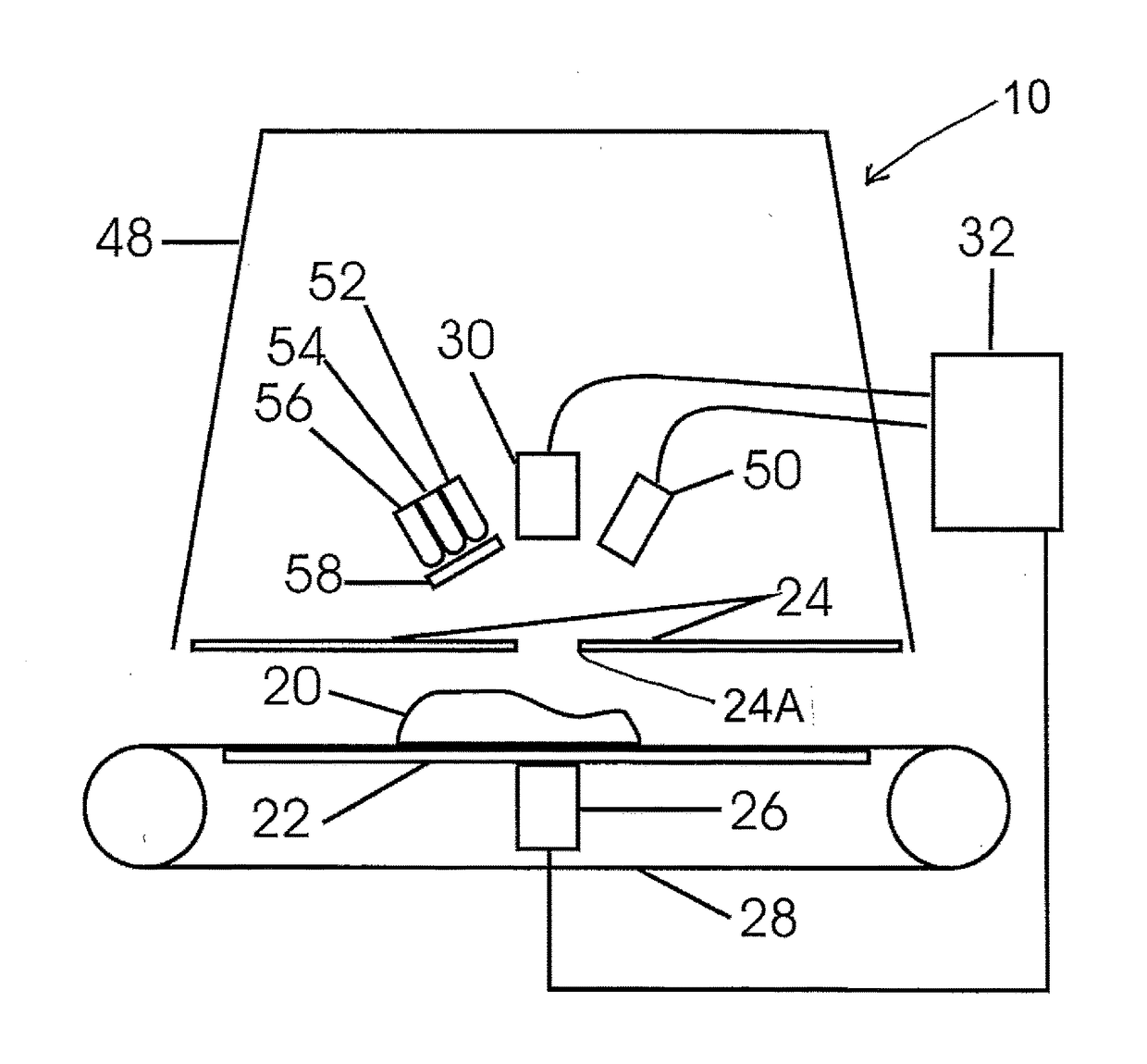
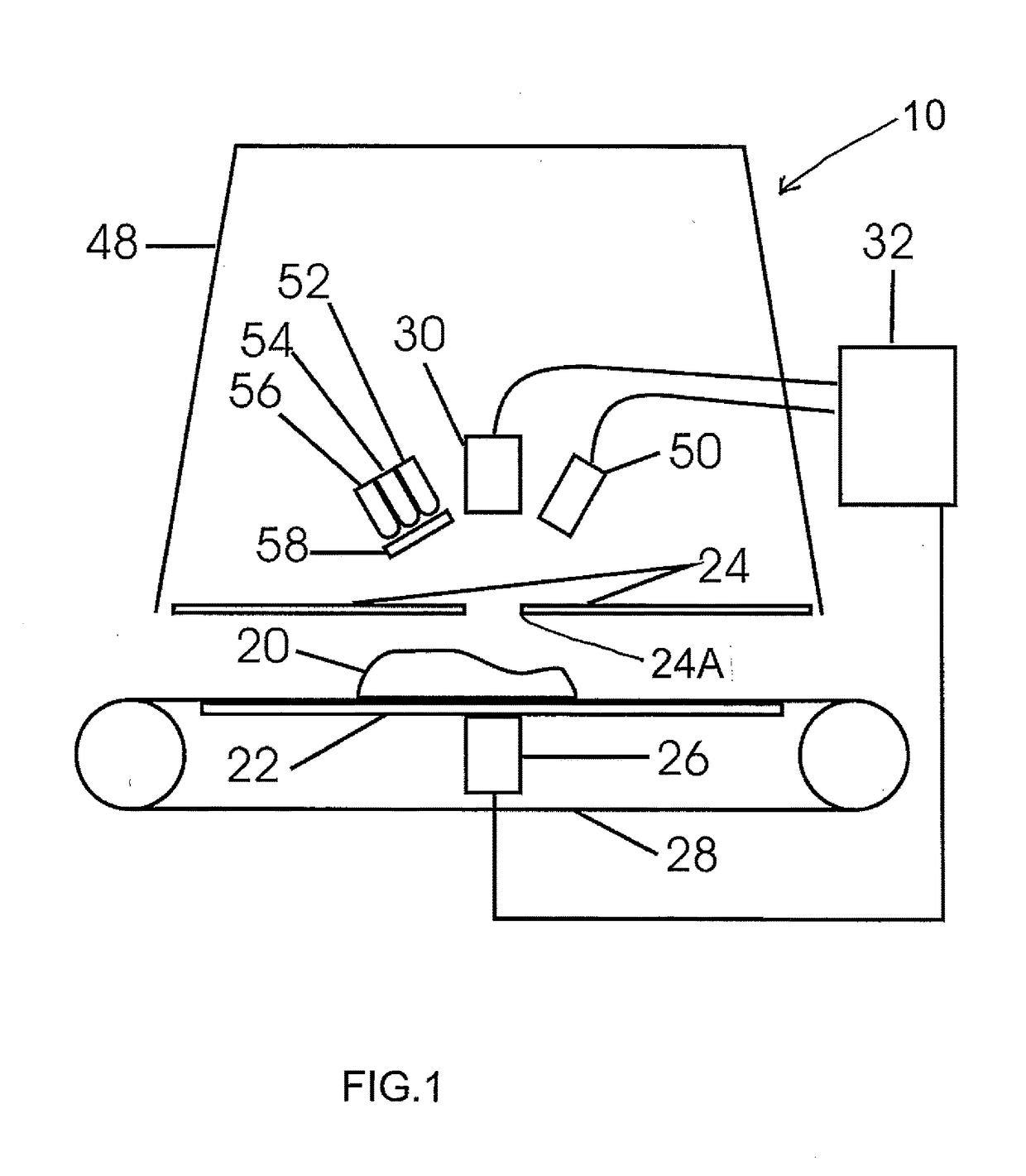
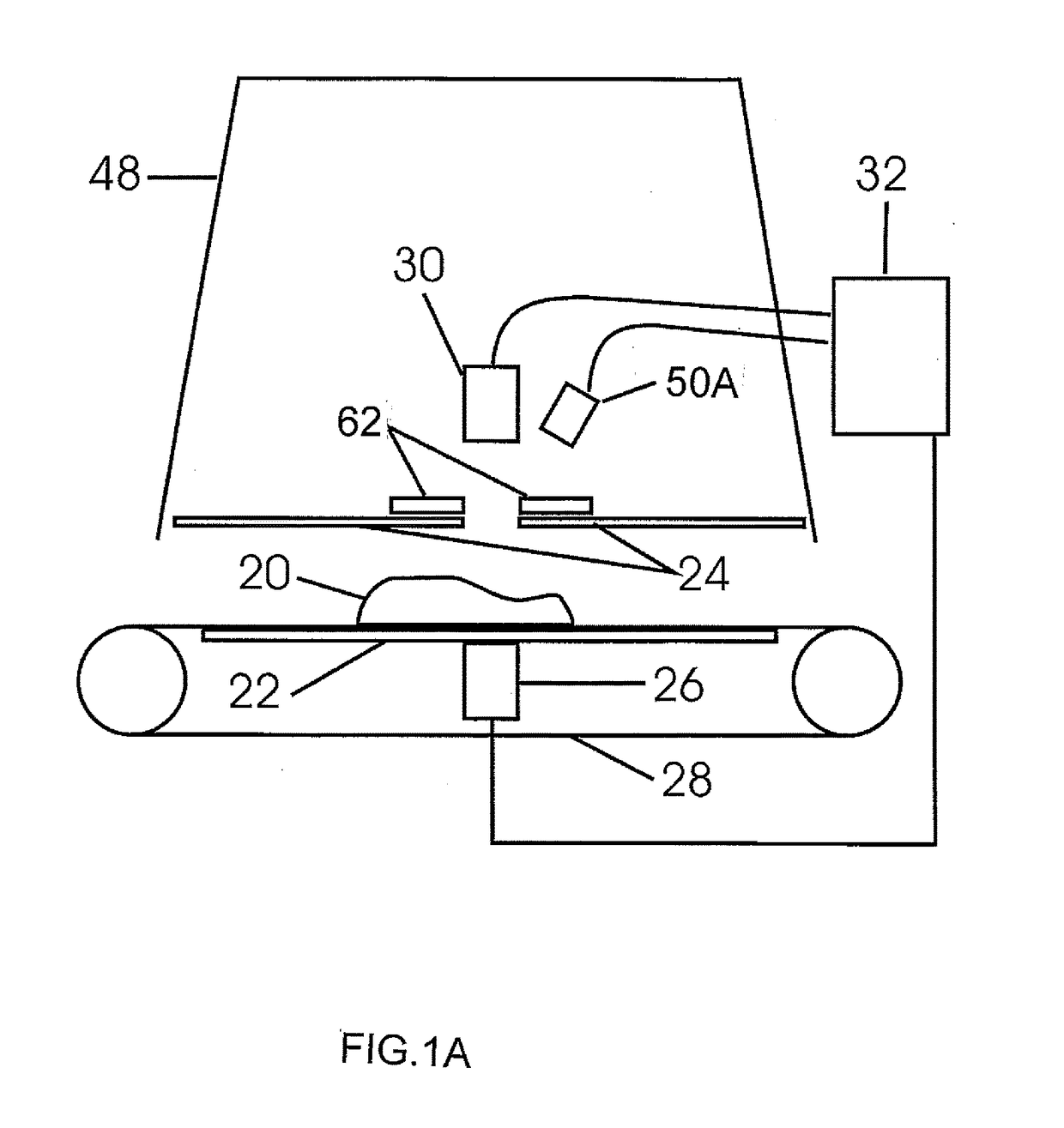
A method and device for detection of bone in meat identifies fragments larger than about 1 mm using spectral optical imaging and ultrasound. Spectral imaging can detect foreign material proximate to the surface and ultrasound can detect material within the sample. The sample is irradiated by light and reflected light or Raman scattered light measured. The sample is similarly irradiated by ultrasound and reflected or transmitted sound waves give a set of amplitude data points, which include temporal delay. These data points are then processed by statistical methods to derive a set of vectors in n-dimensional space, which are compared to a calibrated data set of derived vectors which have distinct identifying loci for each type of surface, are indicative of the presence or absence of defects.
Owner:7386819 MANITOBA LTD
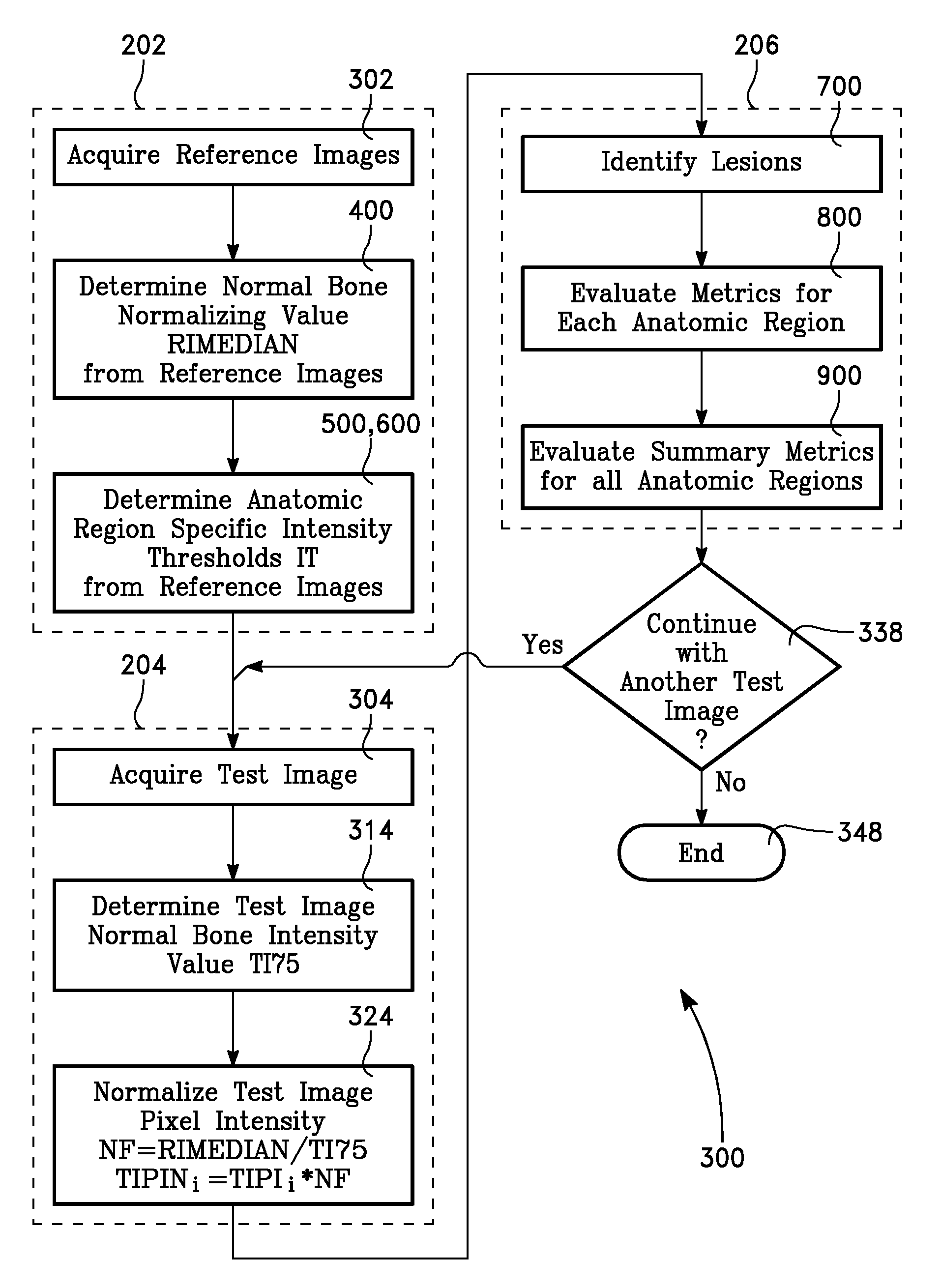
Computer-aided bone scan assessment with automated lesion detection and quantitative assessment of bone disease burden changes
InactiveUS9002081B2Accurate segmentation and quantificationLow variabilityImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineLesion detection
A computer aided bone scan assessment system and method provide automated lesion detection and quantitative assessment of bone disease burden changes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cone-beam CT multi-directional scanning apparatus
PendingCN107157506AChange the status quo of low image resolution accuracyHigh Mass Density AccuracyComputerised tomographsTomographySagittal planeStanding Positions
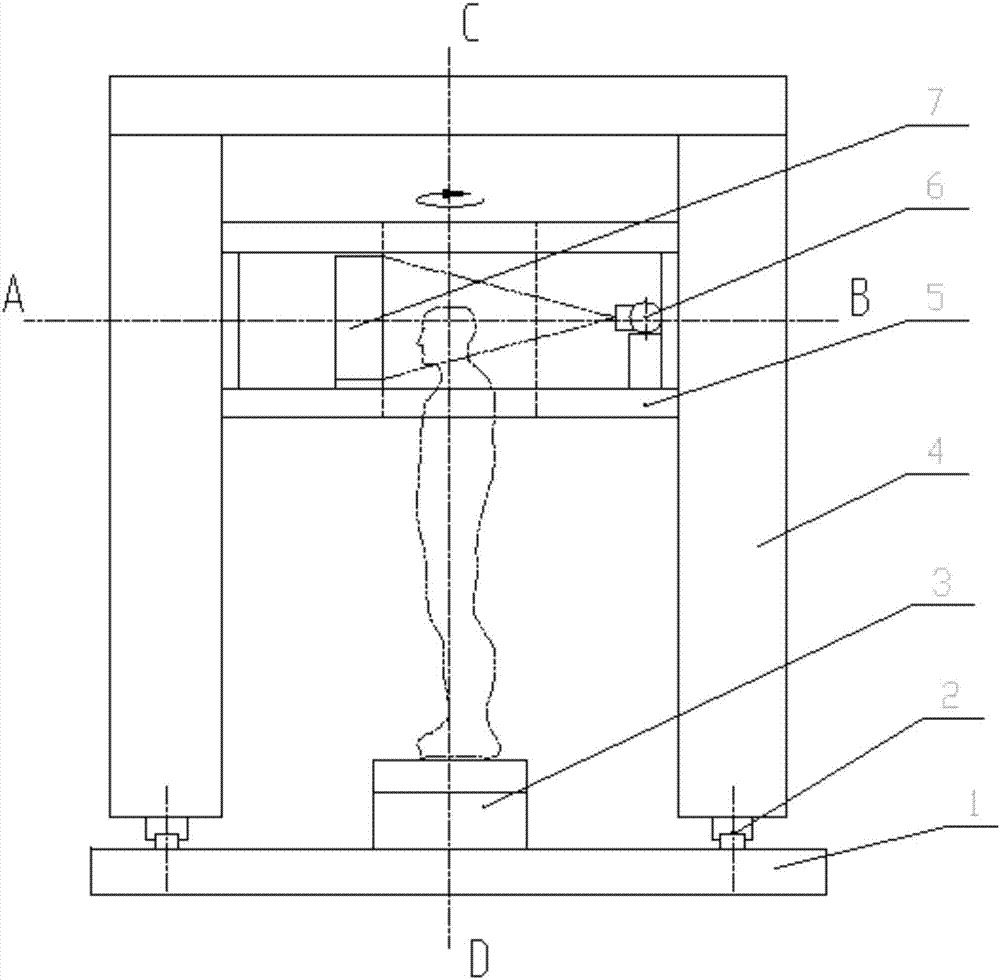
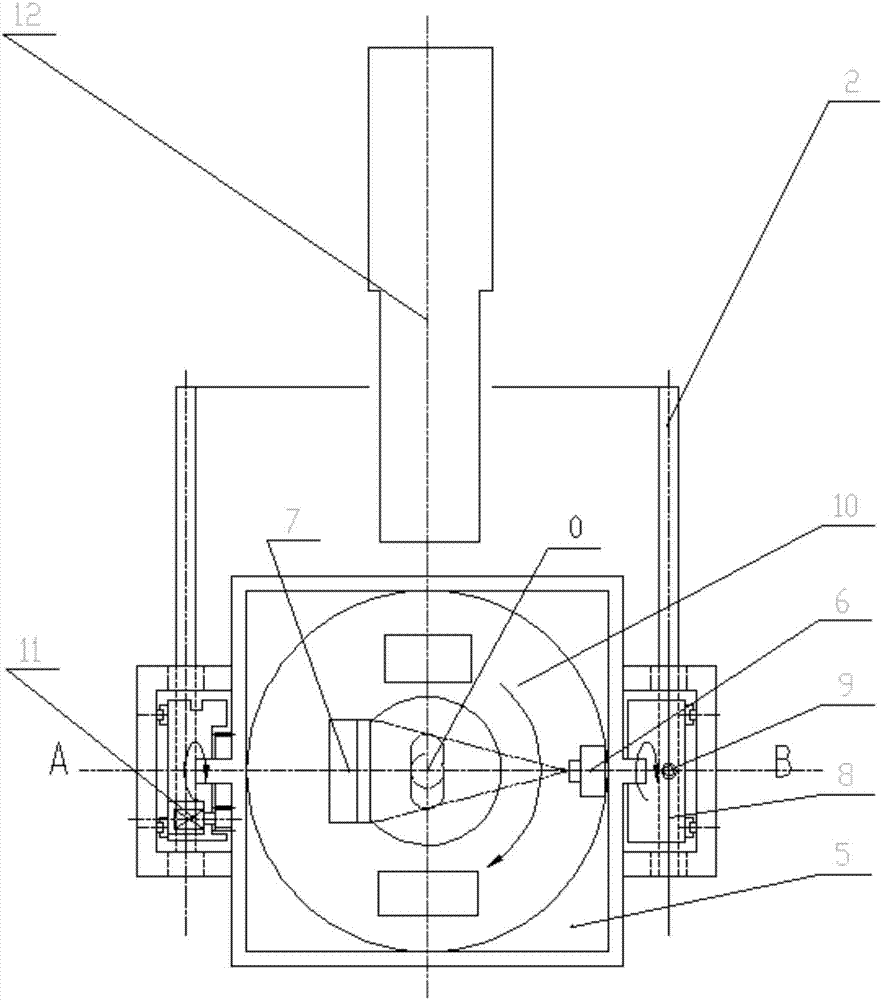
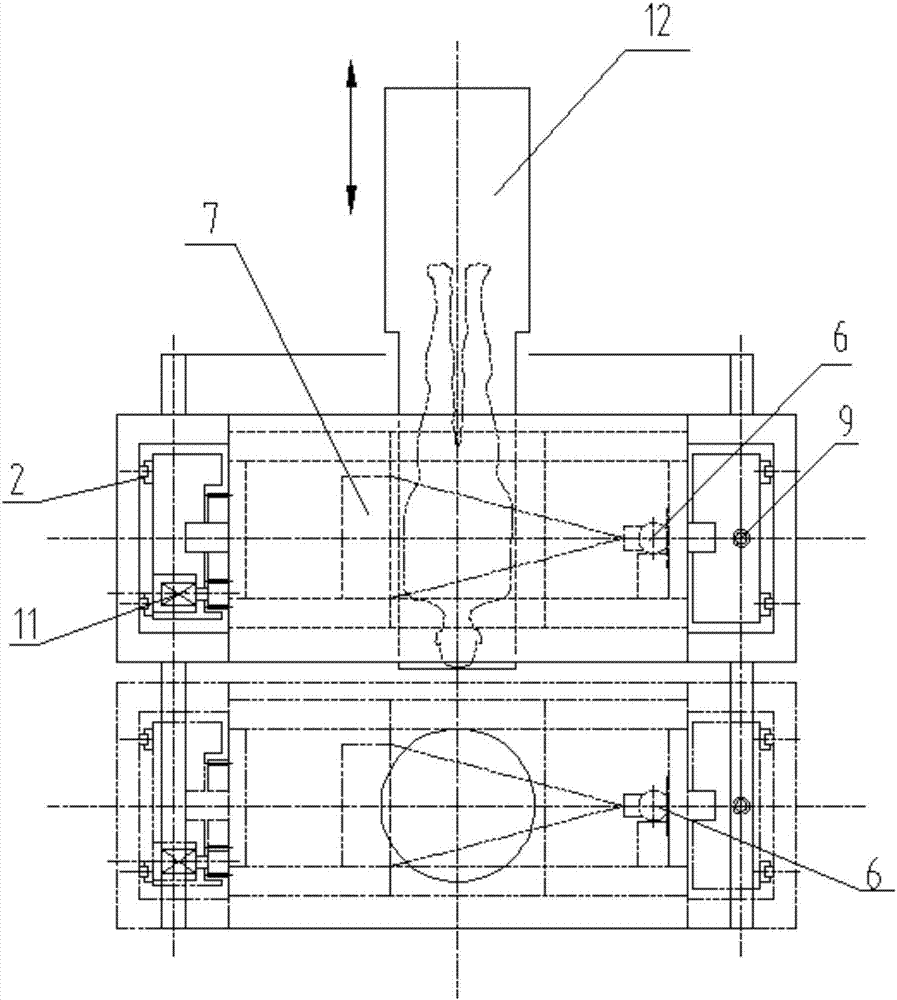
The invention discloses a cone-beam CT multi-directional scanner, which comprises a host machine frame, a cone-beam CT scanning device, a scanning frame and a rotary drive device; the cone-beam CT scanning device is installed on the frame body of the scanning frame, The scanning frame is connected with the host frame through a rotary driving device, so that the scanning frame can turn over inside the host frame. When flipped to a horizontal state, the human body can be scanned in a standing position; when the flipped to a vertical state, a human body can be scanned in a supine position. The cone-beam CT multi-directional scanner of the present invention can change the current situation that it is impossible to obtain three-dimensional bone image data in the upright position of the human body, and can also change the current situation that the image resolution accuracy of the sagittal plane of the CT image is relatively low. Three-dimensional cone-beam CT imaging and two-dimensional DR shaping can be performed in the standing and lying positions to obtain high-quality three-dimensional images of the human skeletal system and soft tissues with high-quality spatial precision and high-quality density precision.
Owner:XIAN LIREN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Assisted dental implant treatment
InactiveUS20110256508A1Diminished attractivenessEase of productionImpression capsTeeth fillingPhysical modelComputer module
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
Assisted dental implant treatment
InactiveUS9901416B2Diminished attractivenessEase of productionImpression capsBoring toolsPhysical modelDental implant
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
Assisted dental implant treatment
InactiveUS9901417B2Diminished attractivenessEase of productionImpression capsDental toolsPhysical modelDental implant
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
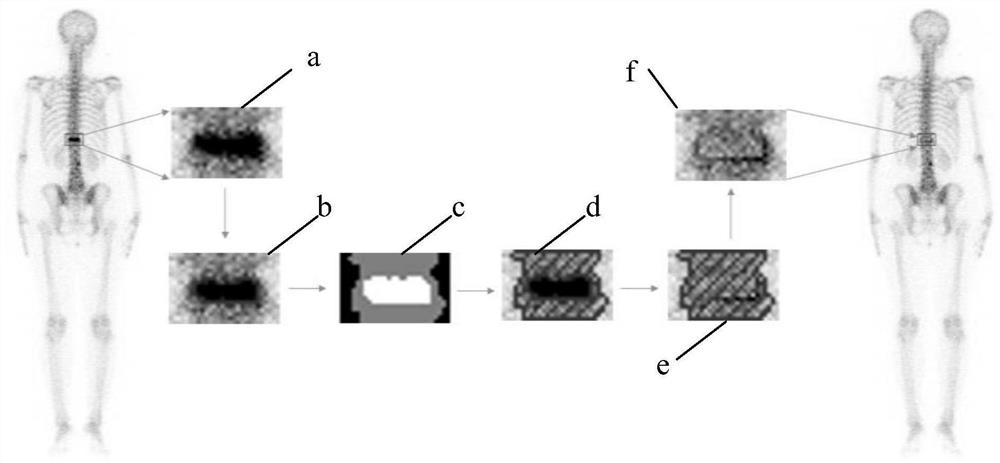
Whole-body bone imaging bone segmentation method based on image set registration
ActiveCN112102339AWork lessSave manpower and material resourcesImage enhancementImage analysisBone lesionBone scans
The invention discloses a whole-body bone imaging bone segmentation method based on atlas registration. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring original whole-body bone imaging data collected by professional equipment; subjecting the original whole-body bone imaging data to preprocessing including pollution detection processing, pollution repair processing, standardization processing,registration processing and regularization processing; and according to a deformation segmentation template stored in the system, carrying out segmentation processing on the preprocessed whole-body bone development image to obtain a segmentation result of whole-body bone development. By means of the method, bone positioning can be conducted on an image obtained through single whole-body bone scanning examination, a basis is provided for bone lesion positioning, development quality is improved by automatically reducing a difference through bone development pollution detection and a pollution repair algorithm, and the development difference between different whole-body bone scans is solved; and rapid, accurate and intelligent positioning of the whole-body bone imaging skeleton is achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Systems and methods for automated and interactive analysis of bone scan images for detection of metastases
ActiveUS20200337658A1Improve analysisAdditional processing stepsImage enhancementMedical data miningImaging processingImage segmentation
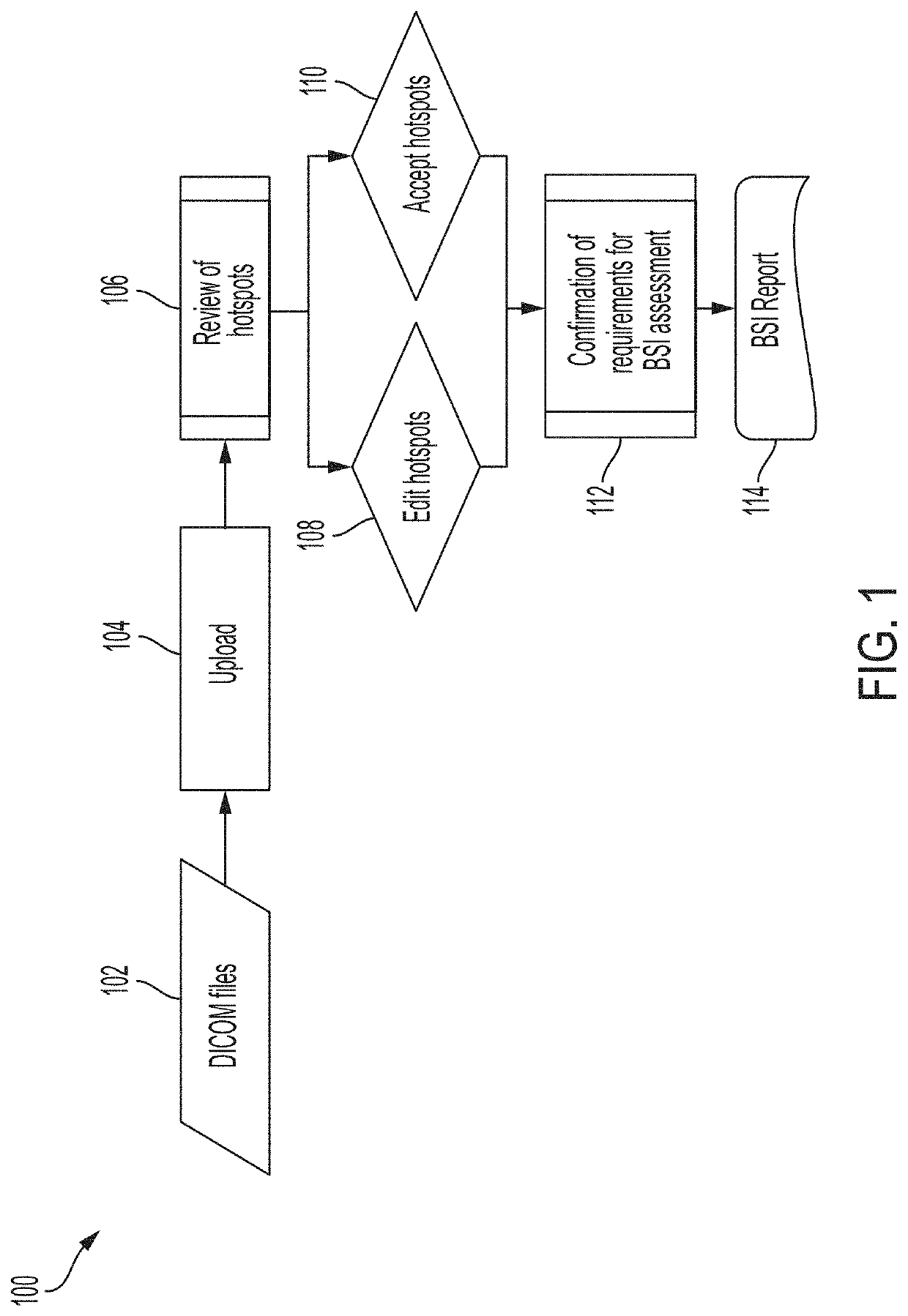
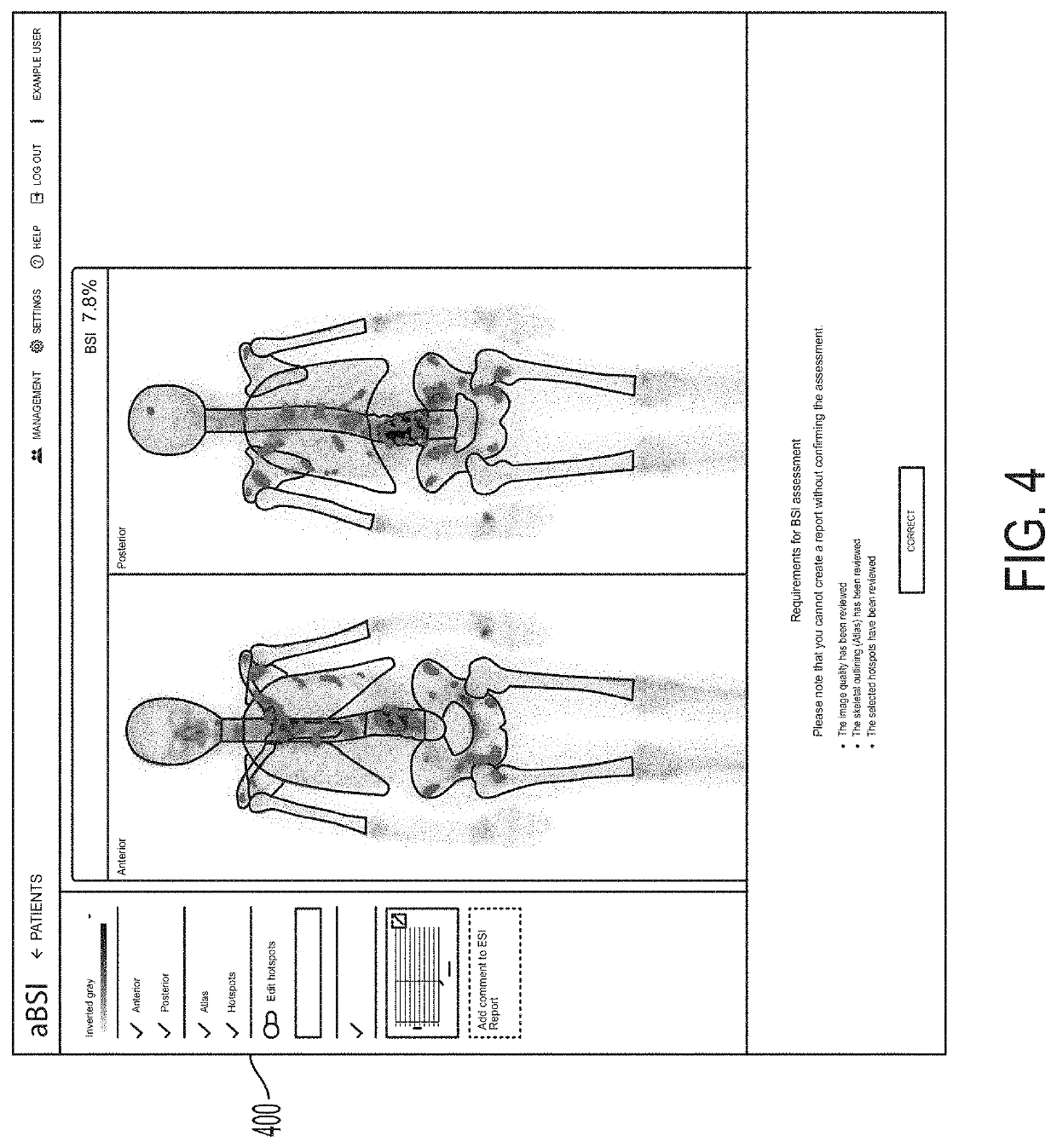
Presented herein are systems and methods that provide for improved computer aided display and analysis of nuclear medicine images. In particular, in certain embodiments, the systems and methods described herein provide improvements to several image processing steps used for automated analysis of bone scan images for assessing cancer status of a patient. For example, improved approaches for image segmentation, hotspot detection, automated classification of hotspots as representing metastases, and computation of risk indices such as bone scan index (BSI) values are provided.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC +1
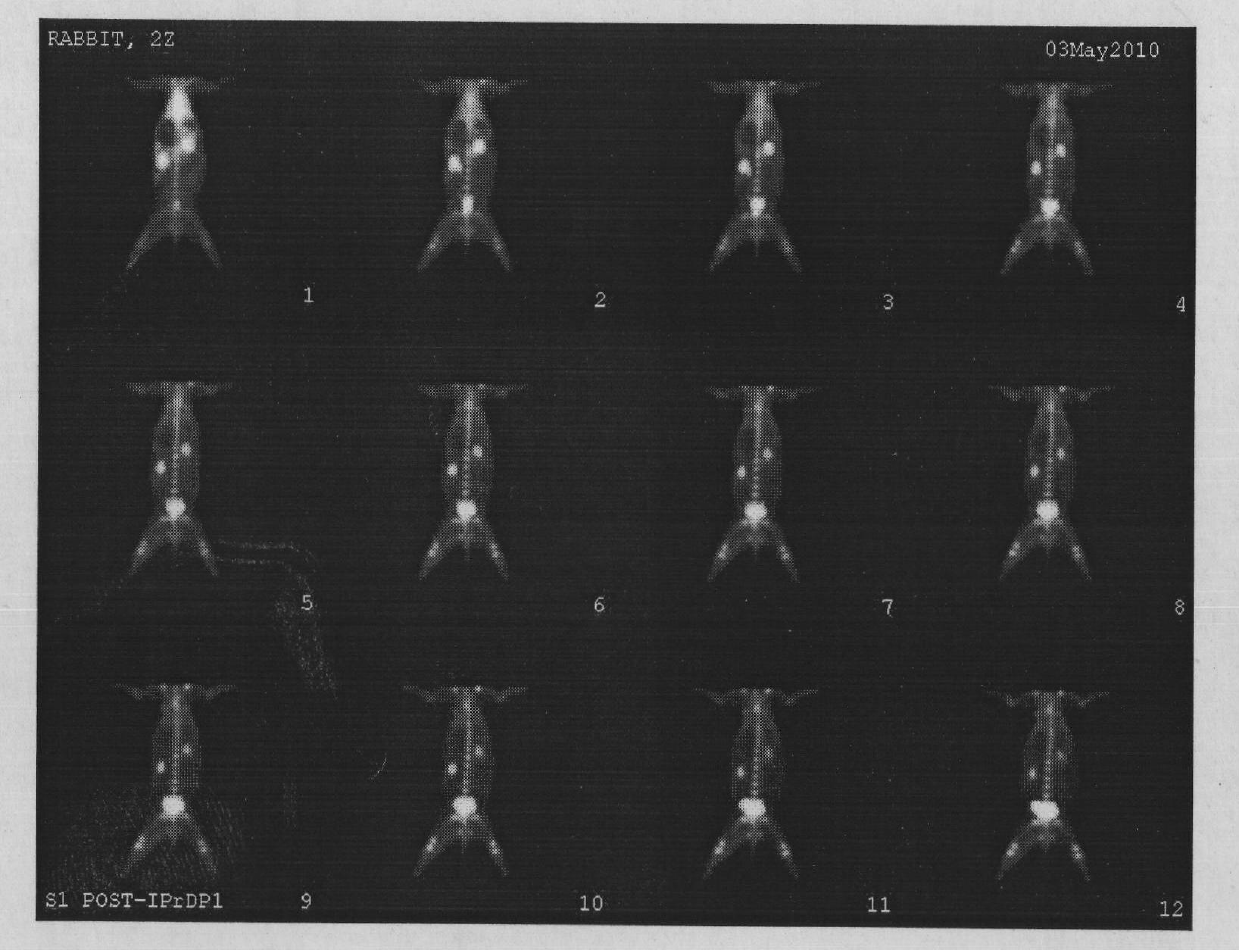
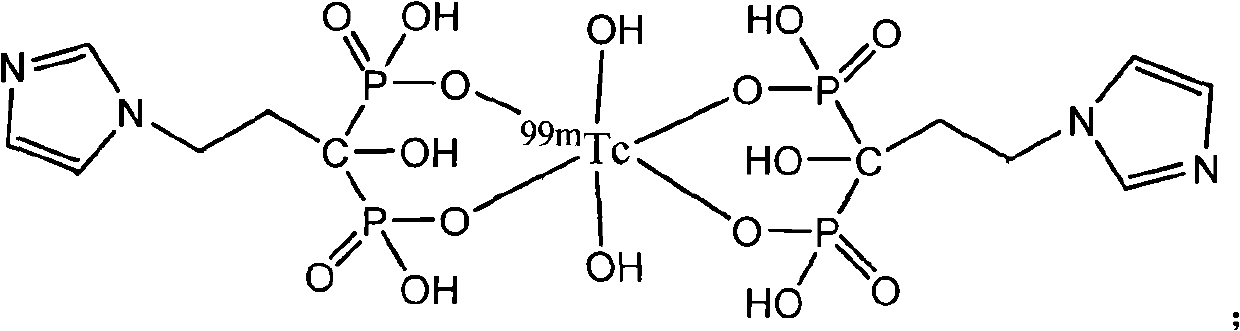
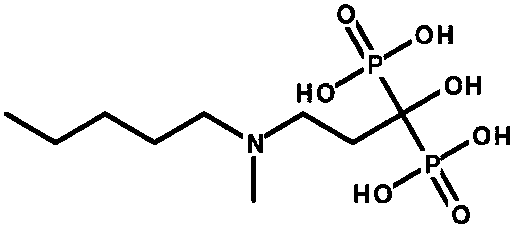
Bone-seeking 99mTc-IPrDP coordination compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101985456AImprove performanceExtension armRadioactive preparation carriersGroup 7/17 element organic compoundsClearance rate99mTc-IPrDP
The invention relates to a bone-seeking 99mTc-IPrDP coordination compound, belonging to the fields of radiopharmaceuticals and nuclear medicine. The structural formula of the bone-seeking 99mTc-IPrDP coordination compound is shown in the specification. The preparation method of the coordination compound is as follows: mixing ligand IPrDP, reducing agent, pH buffer solution and pertechnetic acid (99mTcO<4->) solution to react to obtain an IPrDP coordination compound labeled by technetium-99m. The 99mTc-IPrDP coordination compound is used for nuclear medical diagnostic imaging. Through comparison, the product provided by the invention has the advantages of good product specificity, high bone / tissue intake (Am, bone) (% ID / g) and (Am, bone / Am, blood) and good tissue clearance rate, thus being expected to become novel bone imaging agent.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
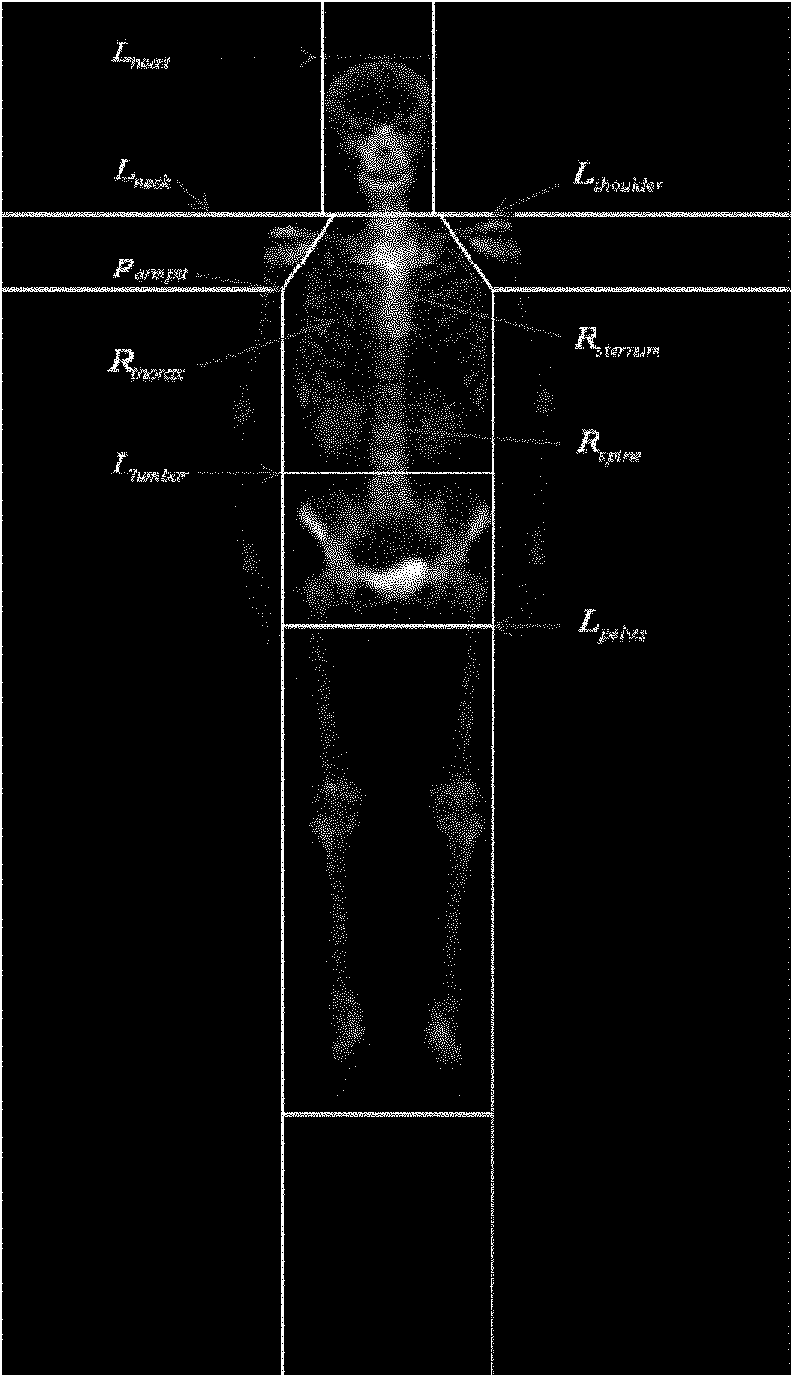
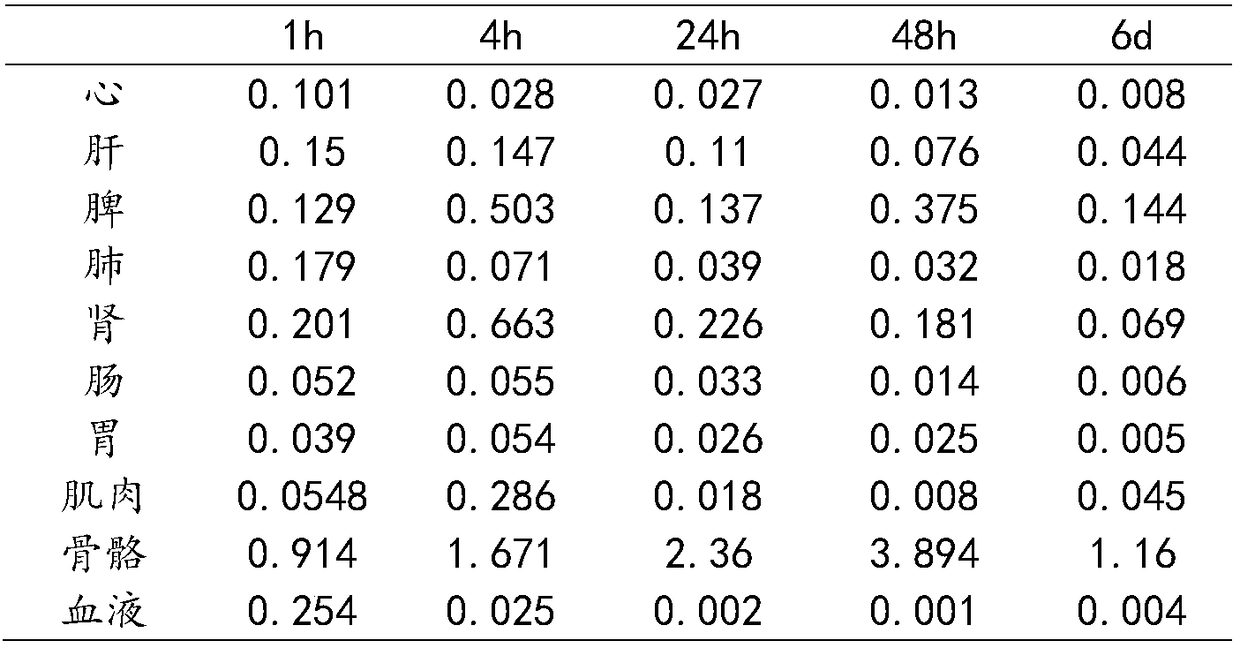
Human body part segmentation method and system based on SPECT imaging
ActiveCN112950595AAchieve precise segmentationSmall amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyChest cavity
The invention relates to a human body part segmentation method and system based on SPECT imaging, based on a bone imaging data matrix, a human body region is extracted from a bone imaging image to obtain effective information of the bone imaging data matrix, the calculation amount is reduced, and the segmentation precision is improved. Then the human body area is divided into a head area, a chest area, a pelvic bone area and a leg area based on the data matrix corresponding to the human body area and human morphological characteristics, then the chest area is divided into a trunk area, a left upper limb and a right upper limb based on the data matrix corresponding to the chest area, and finally based on the data matrix corresponding to the leg area, the leg area is divided into the left lower limb and the right lower limb, so that the human body is divided into the head, the trunk, the four limbs, the pelvis and other parts, accurate segmentation of the human body parts is achieved, and accurate segmentation of the head, the trunk, the four limbs, the pelvis and other parts can be effectively conducted on any SPCET bone imaging image.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Computer-Aided Bone Scan Assessment With Automated Lesion Detection And Quantitative Assessment Of Bone Disease Burden Changes
InactiveUS20140105471A1Low variabilityAccurate segmentation and quantificationImage enhancementImage analysisLesion detectionComputer aid
A computer aided bone scan assessment system and method provide automated lesion detection and quantitative assessment of bone disease burden changes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
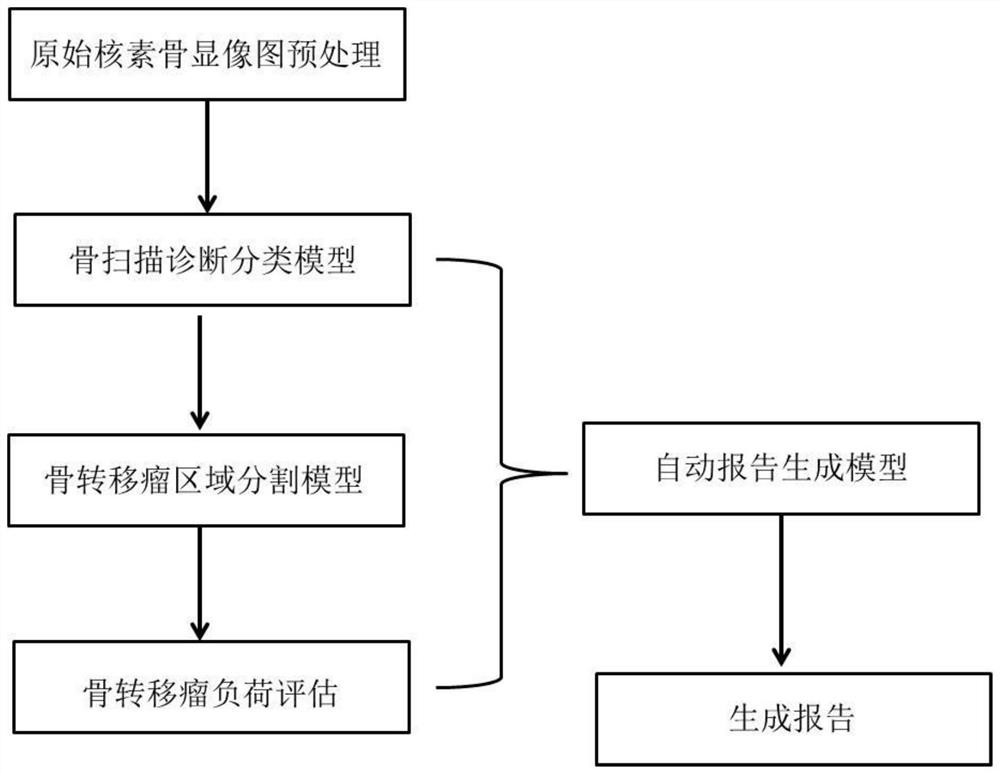
Diagnosis method for bone metastasis tumor in nuclide bone imaging based on deep learning
PendingCN112635067AQuantitatively accurateObjective and accurate quantitativeMedical simulationImage enhancementTumor LoadMetastasis tumor
The invention provides a method for diagnosing bone metastases in nuclide bone imaging based on deep learning. The method relates to a bone scanning diagnosis classification model, a bone metastasis tumor region segmentation model and a bone metastasis tumor load evaluation and automatic report generation model. By the adoption of the method, the bone metastasis tumor can be judged, automatic region segmentation can be conducted, the recognition accuracy is high, and full-automatic analysis from original image input to report generation is preliminarily achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Novel bone seeking <99m>Tc complex, preparation thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN101653614AHigh initial intakeExtended stayRadioactive preparation carriersImaging agentOxygen
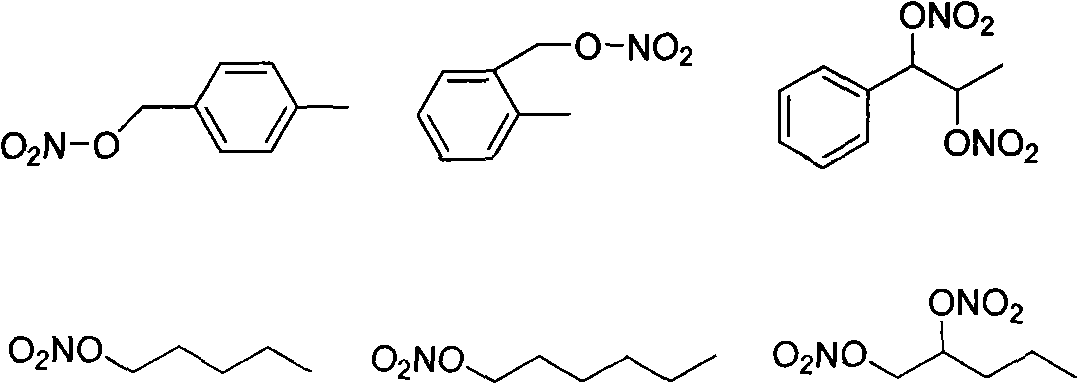
The invention discloses a novel bone seeking complex. The complex comprises a nuclide <99m>Tc and a ligand, wherein the ligand is a diphosphate derivative containing NO-donors and has a general formula represented by the following formula, wherein R1 is an aliphatic hydrocarbon, an aromatic ring or a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic ring containing 1 to 2 NO-donors; X is a group of -H, -OH, -NH2 and the like; Y is oxygen, sulfur or amino; and n is an integer between 2 and 9. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the complex and application of the complex as a bone imaging agent. Compared with the current bone imaging agent <99m>Tc-MDP widely used in the clinic at home and abroad, the bone imaging agent has high bone tissue initial stage uptake, long stay time and low non-target tissue uptake, particularly low liver uptake, and is expected to become a novel bone imaging agent with better performance.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method of Quantifying Cancer Treatment
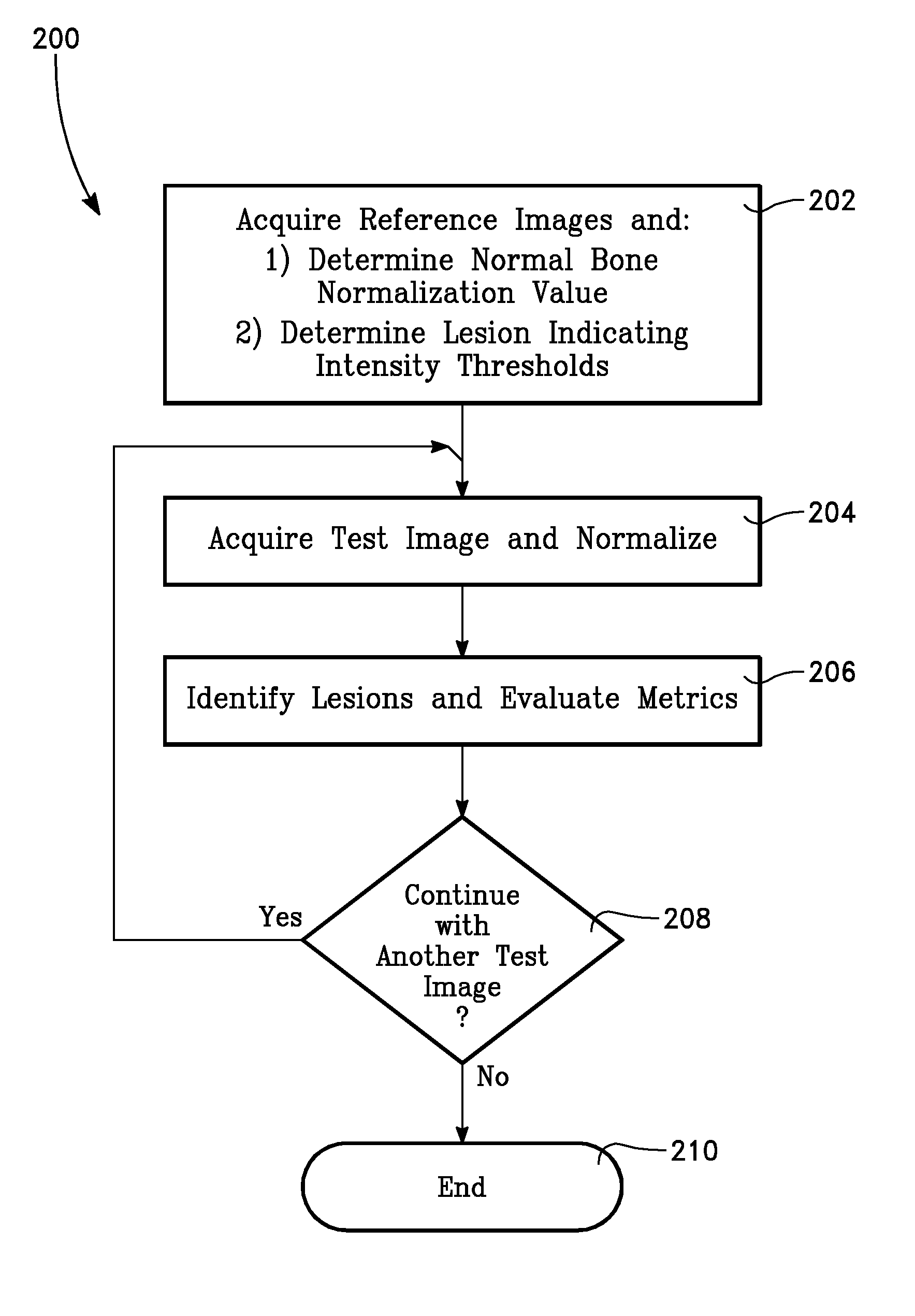
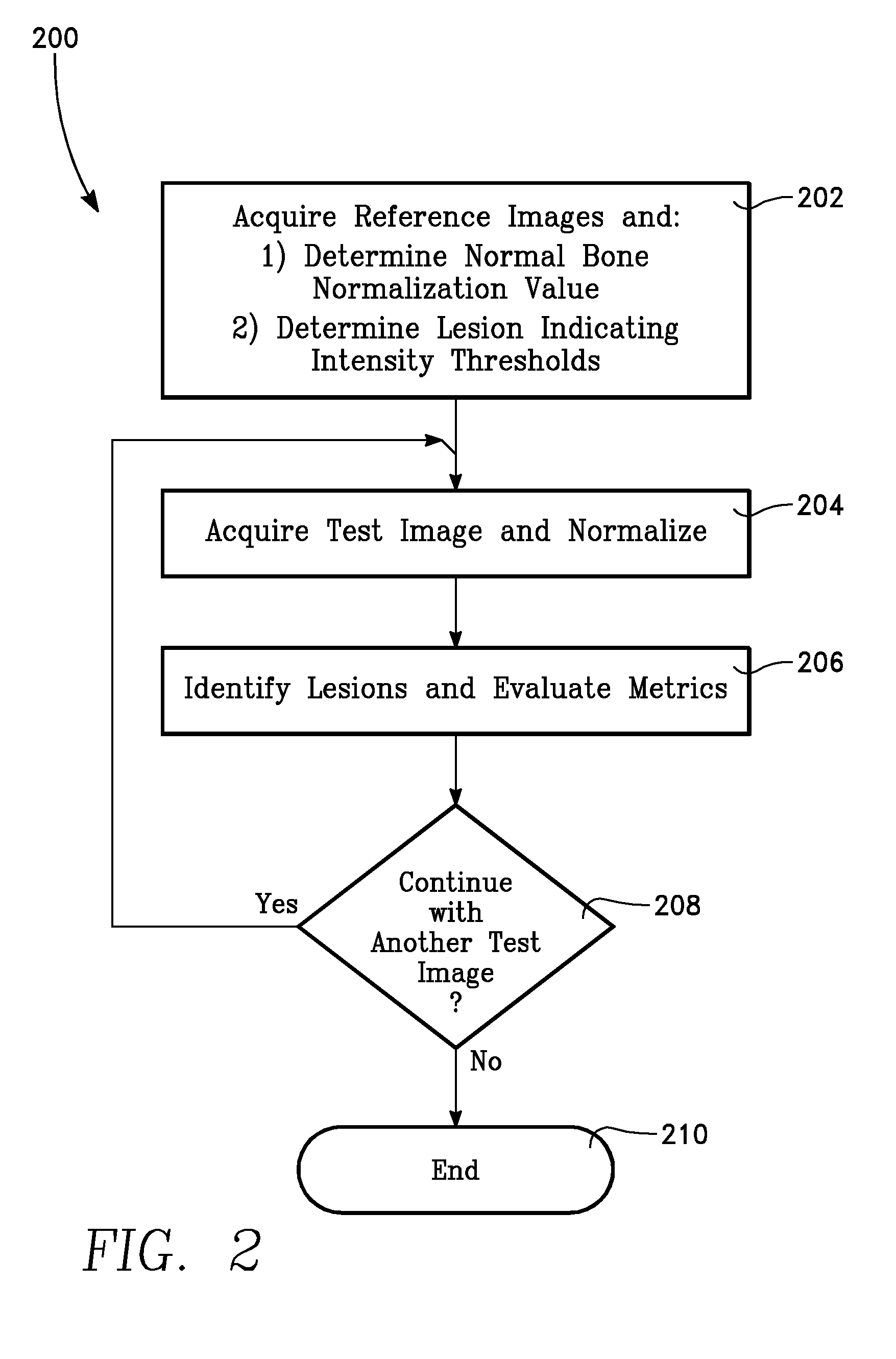
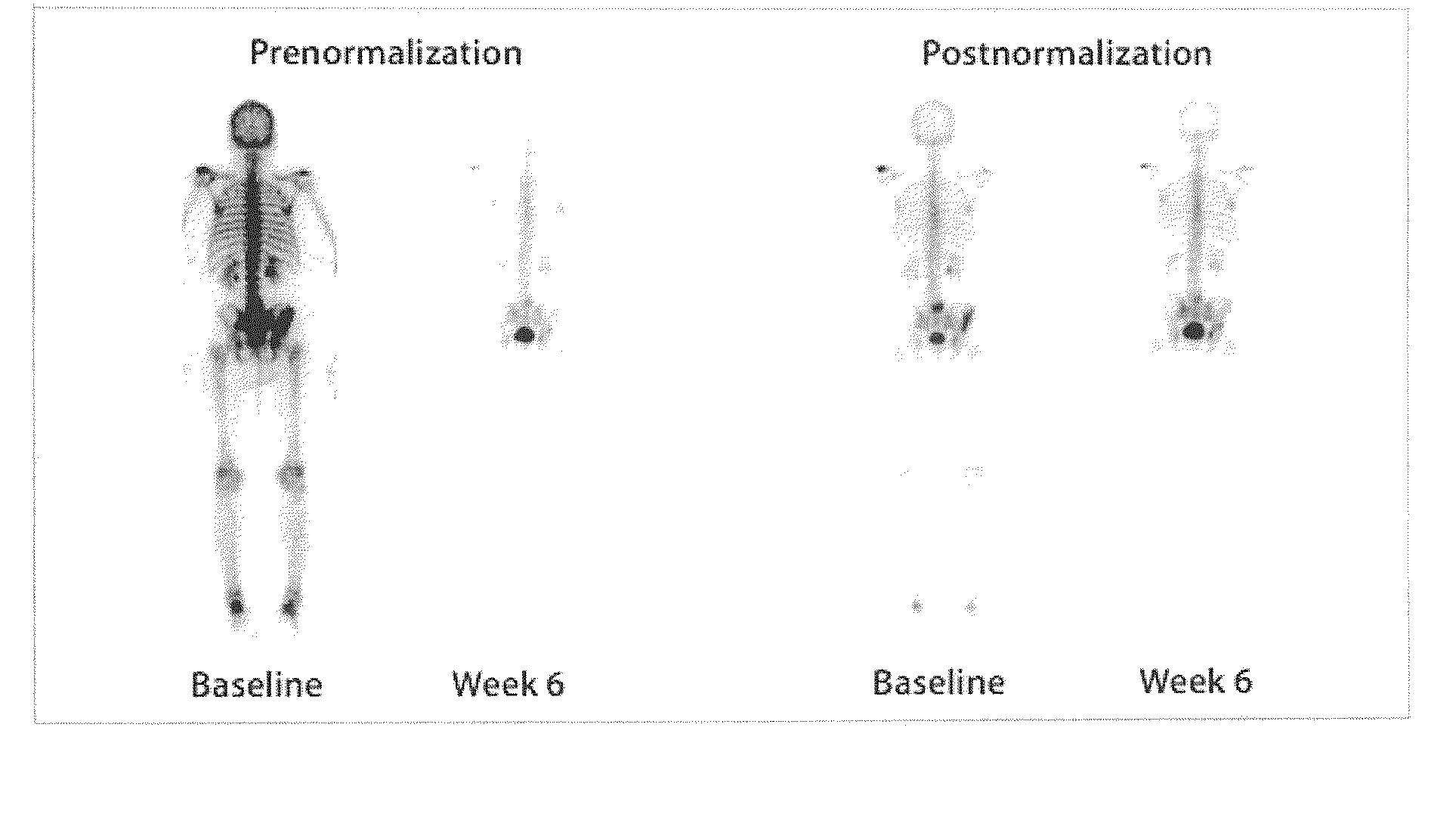
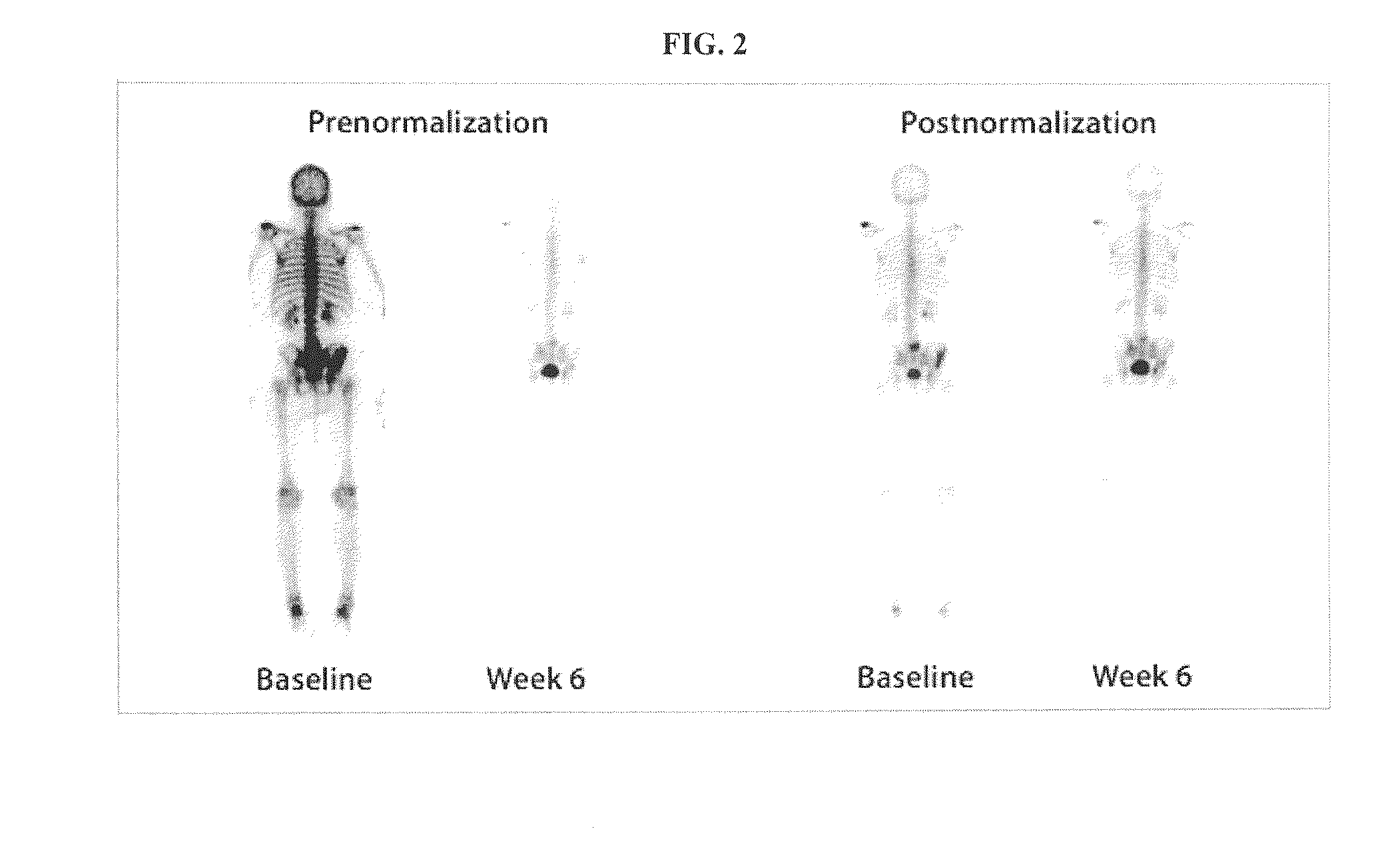
InactiveUS20140330170A1Improve survivalRelieve painHealth-index calculationPerson identificationLesion countComputer aid
This invention is directed to a method for quantifying cancer treatment response in patients with bone metastases using computer aided bone scan assessment, comprising:(a) obtaining a bone scan image;(b) normalizing the obtained bone scan image to identify normalized bone scan lesions; and(c) quantitatively assessing the normalized bone scan lesions using bone scan lesion area, bone scan intensity, or bone scan lesion count.
Owner:EXELIXIS INC
HBED-Bisphosphonates, Radiometal Conjugates and Their Use as Theranostic Agents
ActiveUS20170022224A1Group 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMedicineBisphosphonate
The present invention relates to compounds according to Formula I or Formula II, which are potential bone imaging agents. Certain compounds labeled with 68Ga displayed excellent bone uptake and retention. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutical acceptable carrier and a compound of Formula I or Formula II or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:FIVE ELEVEN PHARMA INC
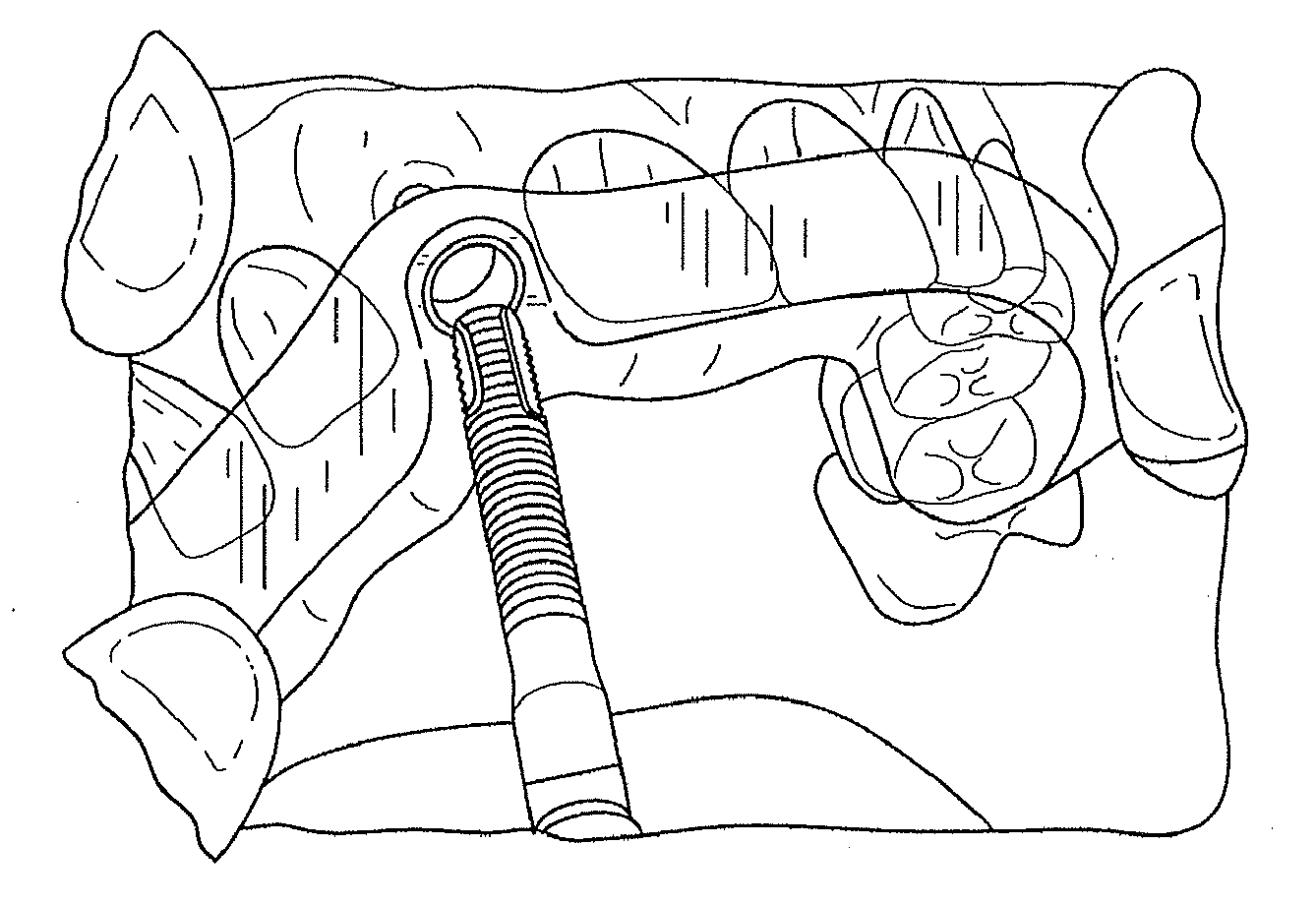
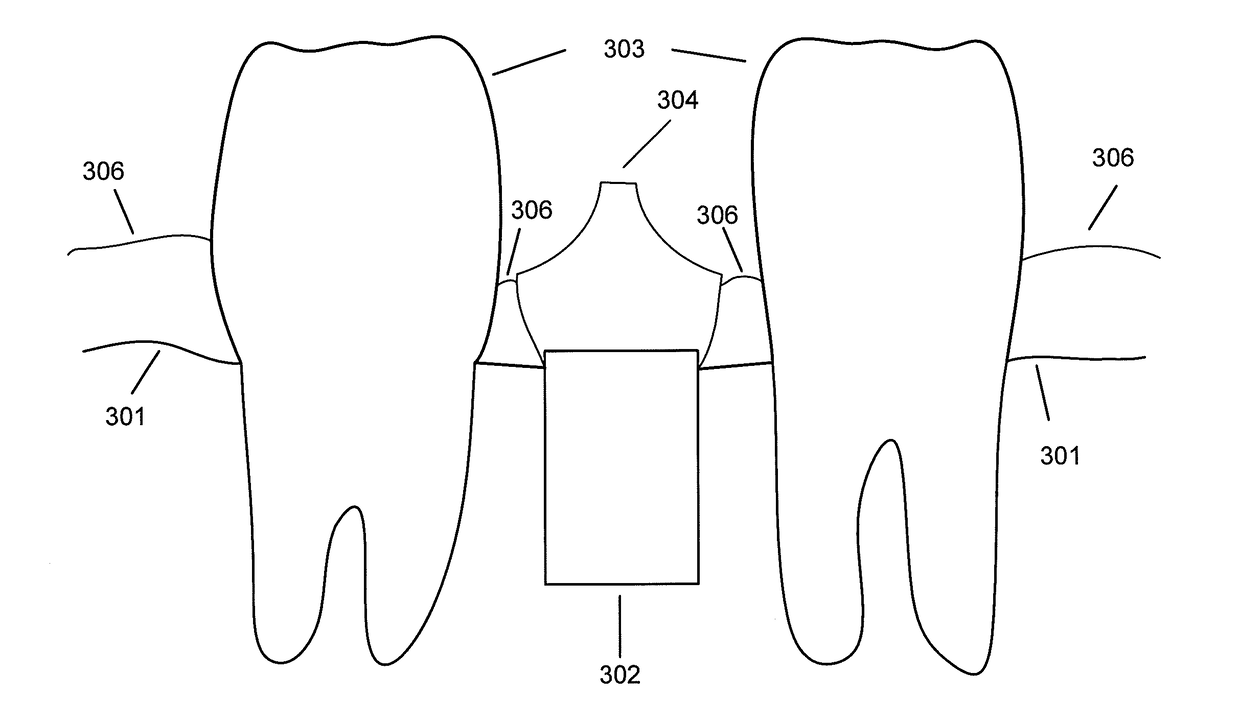
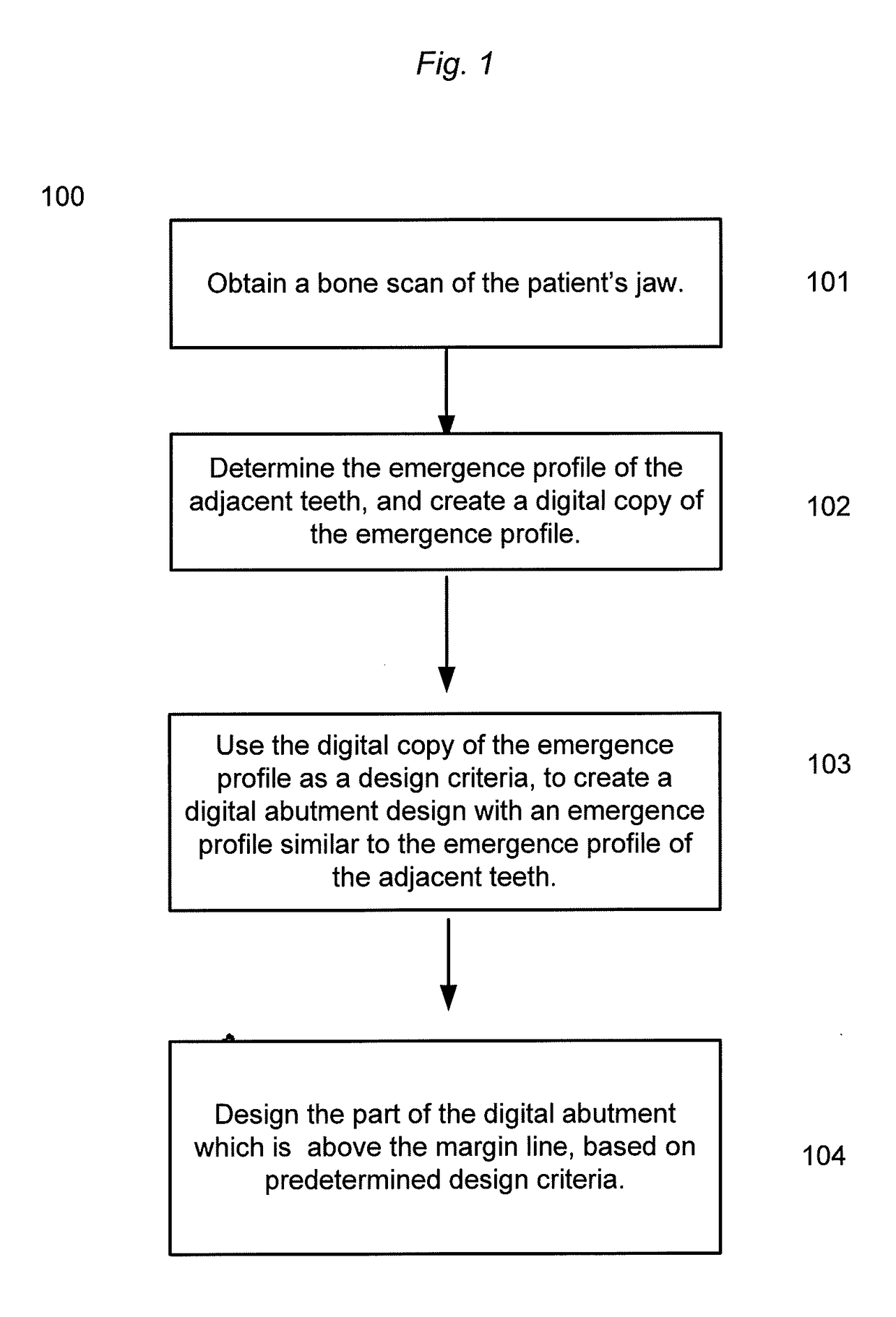
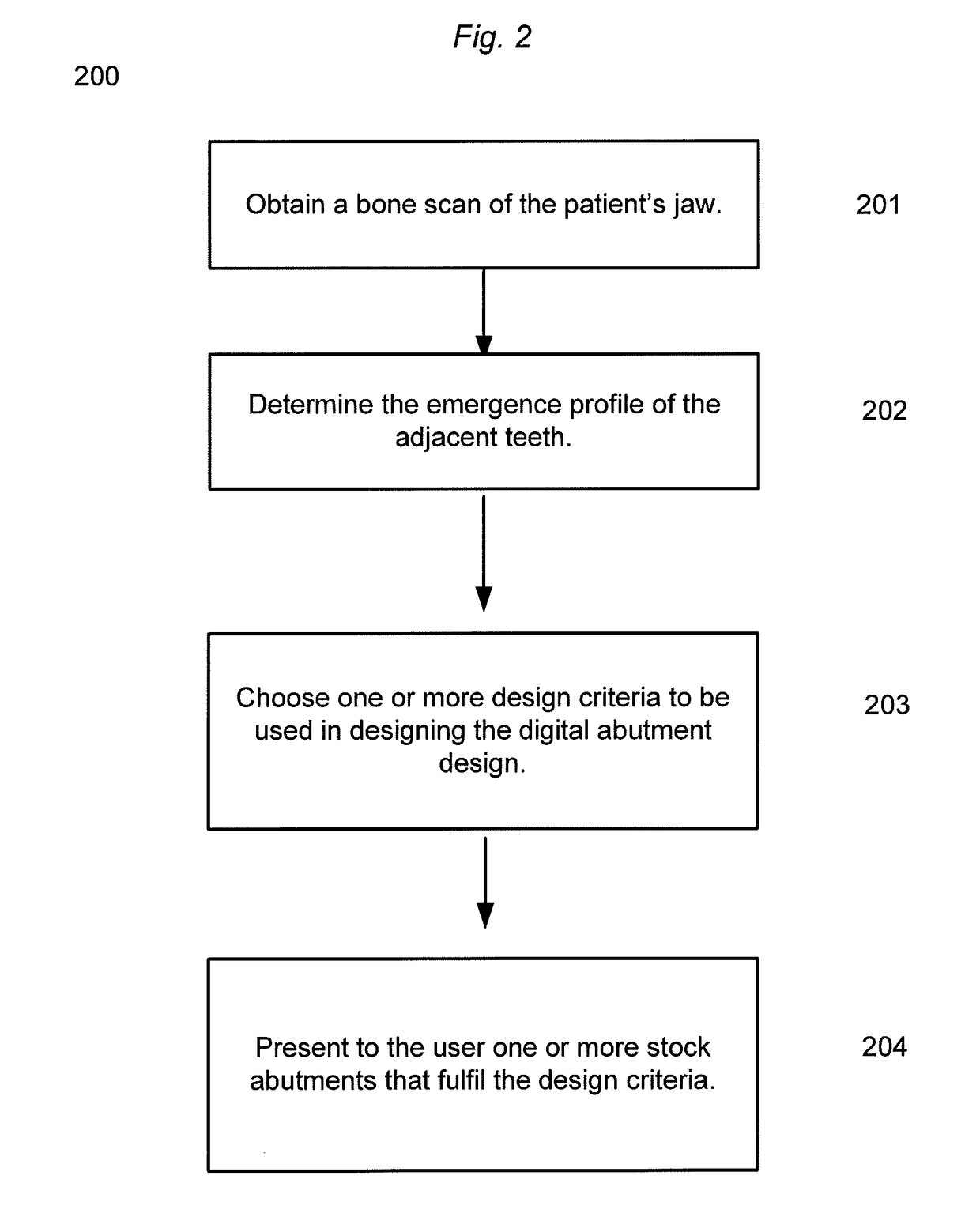
Using a cbct bone scan to design a dental abutment
Disclosed is a method of creating a digital abutment design of a customized dental abutment, the including comprising: obtaining a bone scan comprising a digital representation of at least a part of a patient's jaw including the surface of the jawbone; and designing the digital abutment design of the customized dental abutment; wherein the design of the digital abutment design is at least partly based on fulfilling a set of predefined design criteria including the relationship between the digital representation of the jawbone and the digital abutment design.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
Device and method for bone imaging
InactiveUS9050396B2Difference in positionImprove assessmentSurgeryDiagnostic markersMedical imagingBiomedical engineering
Owner:HALIFAX BIOMEDICAL
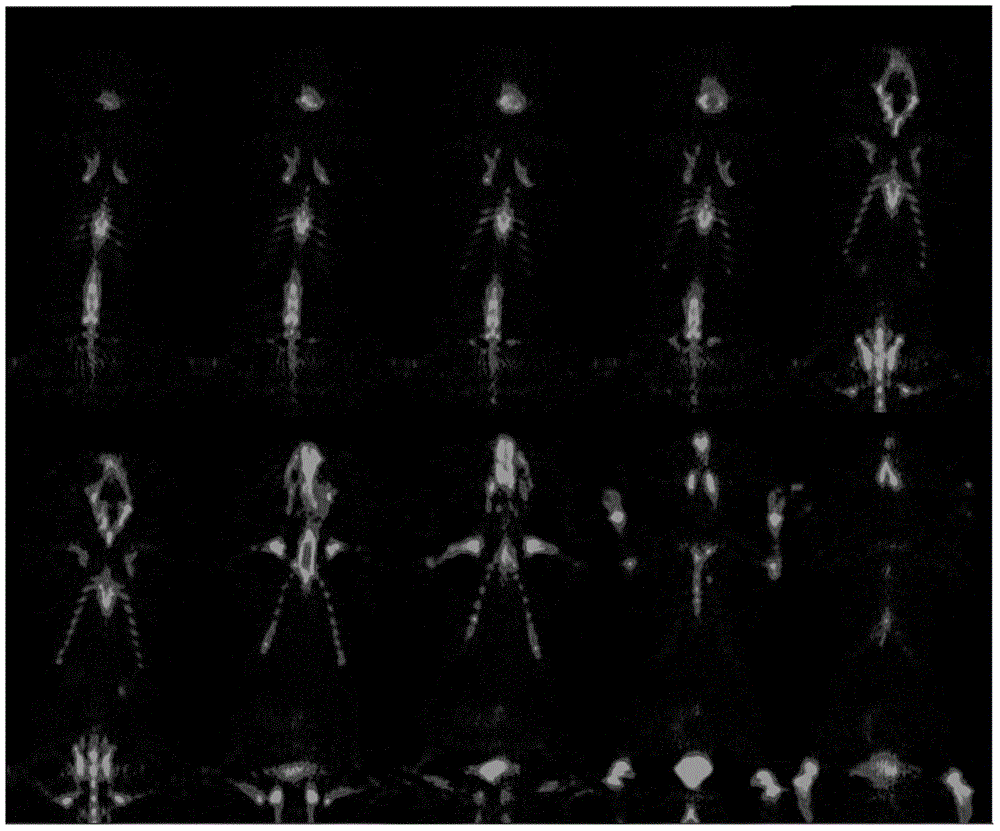
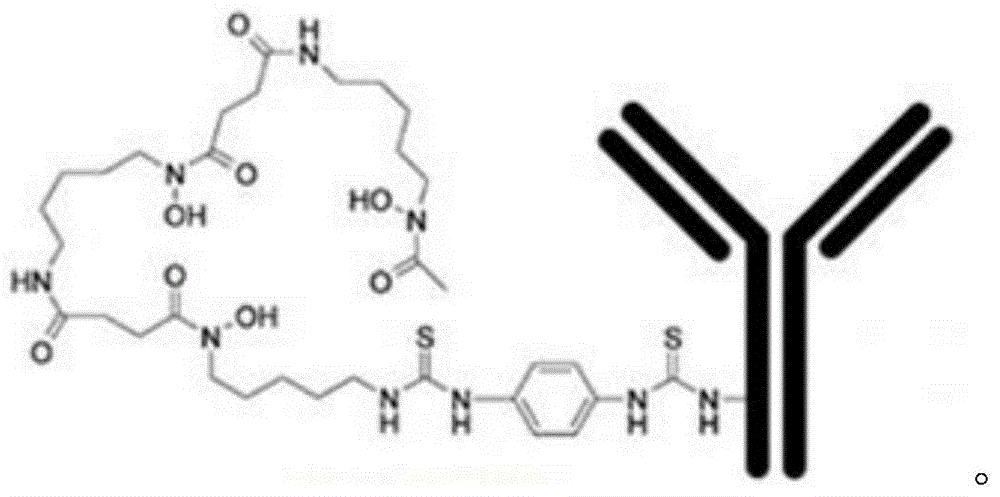
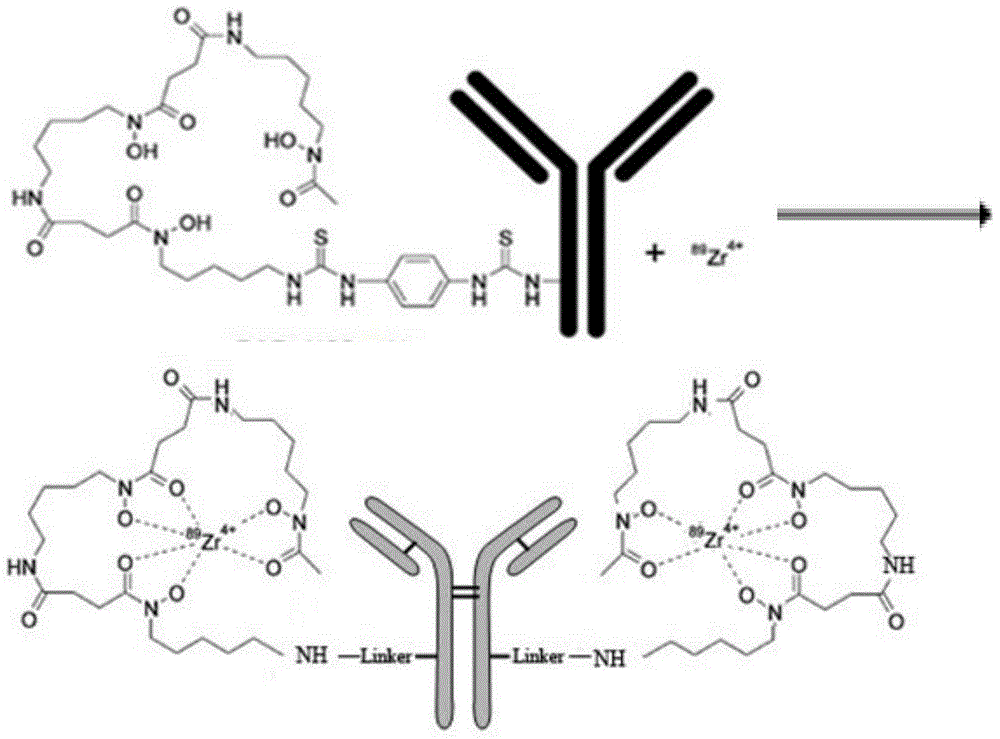
Mark product of <89>Zr marked denosumab, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104645364AHigh resolutionNo deposition in boneRadioactive preparation carriersDenosumabMedicine
The invention relates to a mark product of <89>Zr marked denosumab. The mark product is [<89>Zr]-Df-Bz-NCS-denosumab; and Df-Bz-NCS-denosumab is marked by adopting <89>Zr. The mark product disclosed by the invention is accurate and reliable in development result, proper in half-life period, good in specificity, targeting property and in-vitro stability and higher in radioactive chemical purity; a good imaging effect can be realized; for bone imaging, the mark product is capable of responding internal metabolism conditions of drugs objectively and accurately; and therefore, osteoporosis and solid tumour osseous metastasis can be diagnosed earlier.
Owner:NANJING PET TRACER
Preparation capable of bone imaging and bone metastases tumor curing and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108514645AGood treatment effectPlay a therapeutic roleOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLarge doseImaging agent
The invention provides a preparation capable of bone imaging and bone metastases tumor curing, and belongs to the technical field of bone metastases tumor curing. The preparation is <177>Lu-ibandronicacid. The invention further provides a preparation method of the preparation. According to the preparation method, ibandronic acid is added into a <177>LuCl3 solution, the solution pH is adjusted bymeans of hydrochloric acid, after reaction is carried out at a certain temperature for a certain time, sterilization is conducted, and filtering is conducted to obtain the preparation. According to the preparation capable of bone imaging and bone metastases tumor curing and the preparation method, by combining a radionuclide <177> Lu and the ibandronic acid, the preparation <177>Lu-ibandronic acidcapable of bone imaging and achieving bone metastases tumor curing is provided; the <177> Lu is a bone-seeking imaging agent, a large dose of the <177> Lu has curing action on bone metastases, and the ibandronic acid also has higher action on curing bone metastases, so that the <177>Lu-ibandronic acid preparation can bring the curing action of the radionuclide <177> Lu and the ibandronic acid onthe bone metastases tumor into play better.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
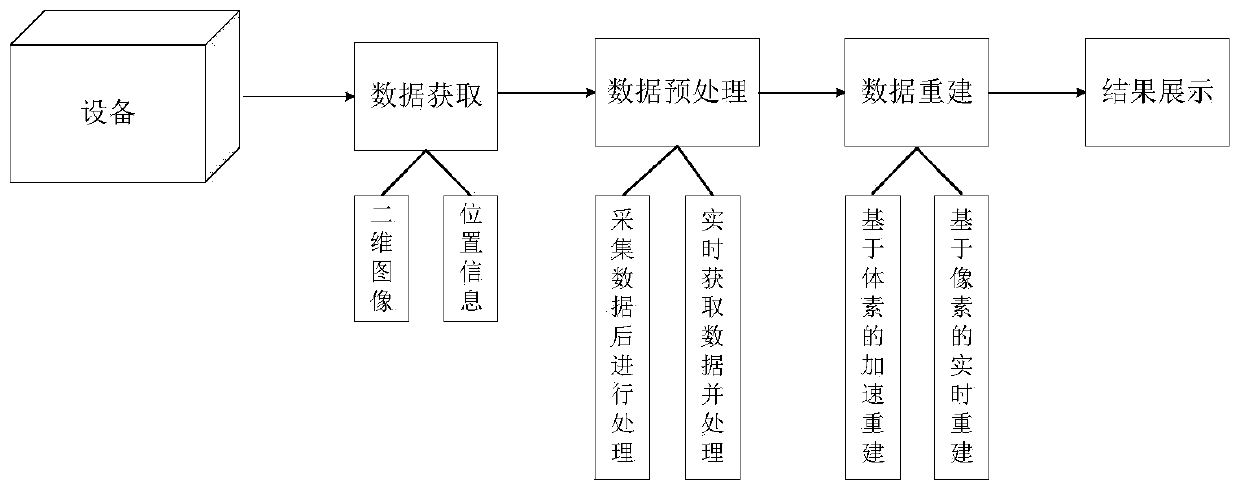
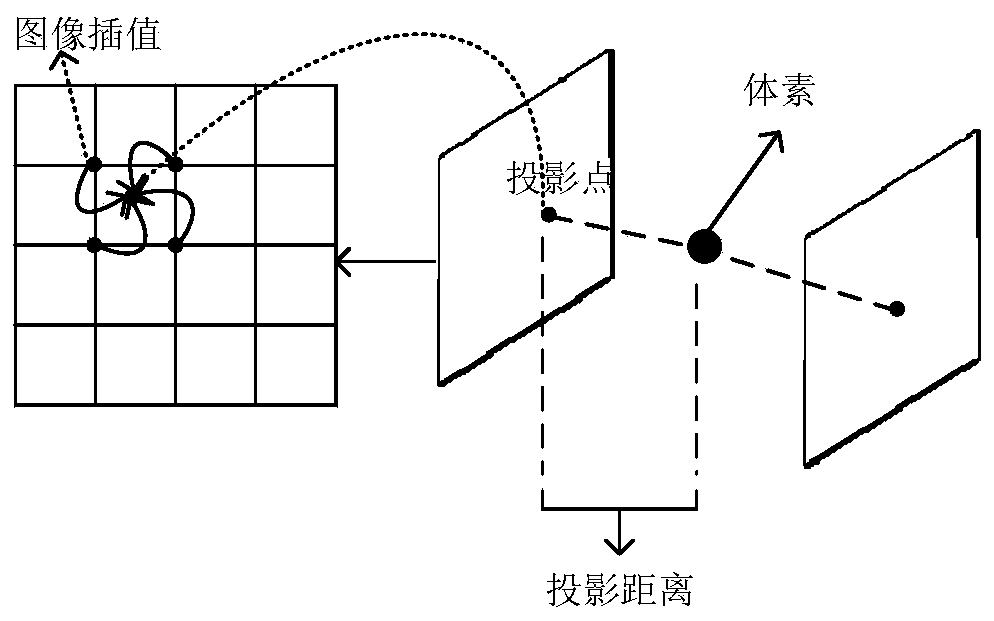
Unconstrained scanning and voxel-based three-dimensional real-time bone imaging method
ActiveCN110969694ASpeed up the rebuilding processFit bone contoursImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionVoxelReconstruction algorithm
The invention provides an unconstrained scanning and voxel-based three-dimensional real-time bone imaging method. According to the method, a voxel-based reconstruction algorithm in a traditional three-dimensional reconstruction technology is applied to skeletal system imaging, a traditional projection method used in the algorithm is optimized and accelerated, and an FDP method is proposed to achieve a real-time reconstruction effect. Because the method provided by the invention is a voxel-based reconstruction algorithm, large-area and large-range imaging (covering the whole back area of a general adult) can be carried out. The method is different from a traditional stacked scanning reconstruction method for three-dimensional bone imaging to the greatest extent. Finally, the technology provided by the invention is also suitable for general non-real-time reconstruction, and is used for accelerating the whole reconstruction process.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
HBED-bisphosphonates, radiometal conjugates and their use as theranostic agents
ActiveUS10253052B2Group 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMedicineBisphosphonate
The present invention relates to compounds according to Formula I or Formula II, which are potential bone imaging agents. Certain compounds labeled with 68Ga displayed excellent bone uptake and retention. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a pharmaceutical acceptable carrier and a compound of Formula I or Formula II or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:FIVE ELEVEN PHARMA INC
Ultrasound bone imaging assembly
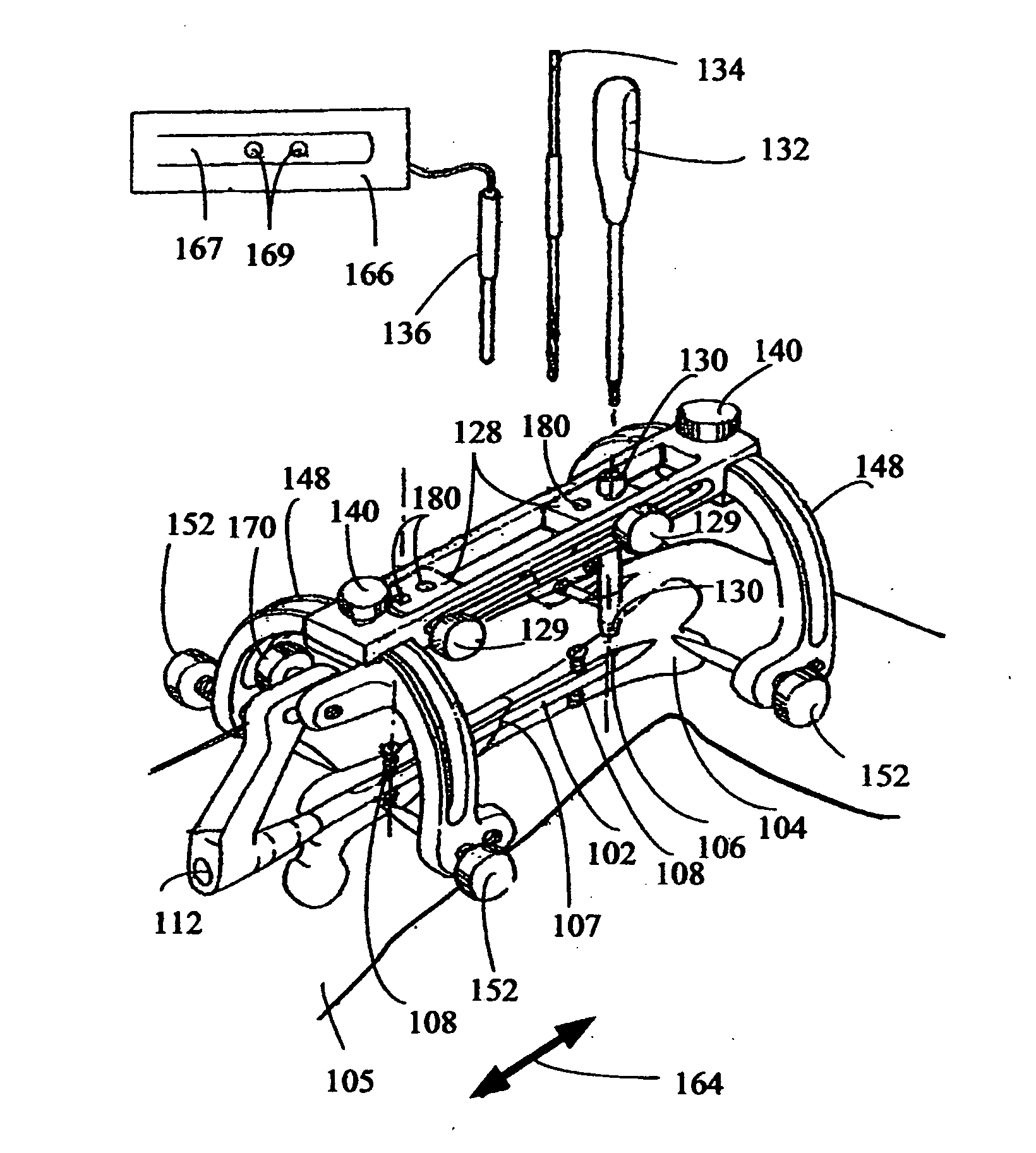
InactiveUS20130066205A1Reduce fracturesPromote lowerOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsBiomedical engineeringUltrasound probe
A device for orienting a bone cutting tool with respect to a locking screw hole of an intramedullary nail inserted within a bone is provided. The device includes a device body which is configured with a cutting path for a cutting device and a distal end portion which is adapted for positioning against a surface of the bone. The device also includes an ultrasound probe holder which serves for aligning the cutting path with the screw locking feature using at least one ultrasound signal of at least one ultrasound probe attached to the device.
Owner:LASTER ZVI +4
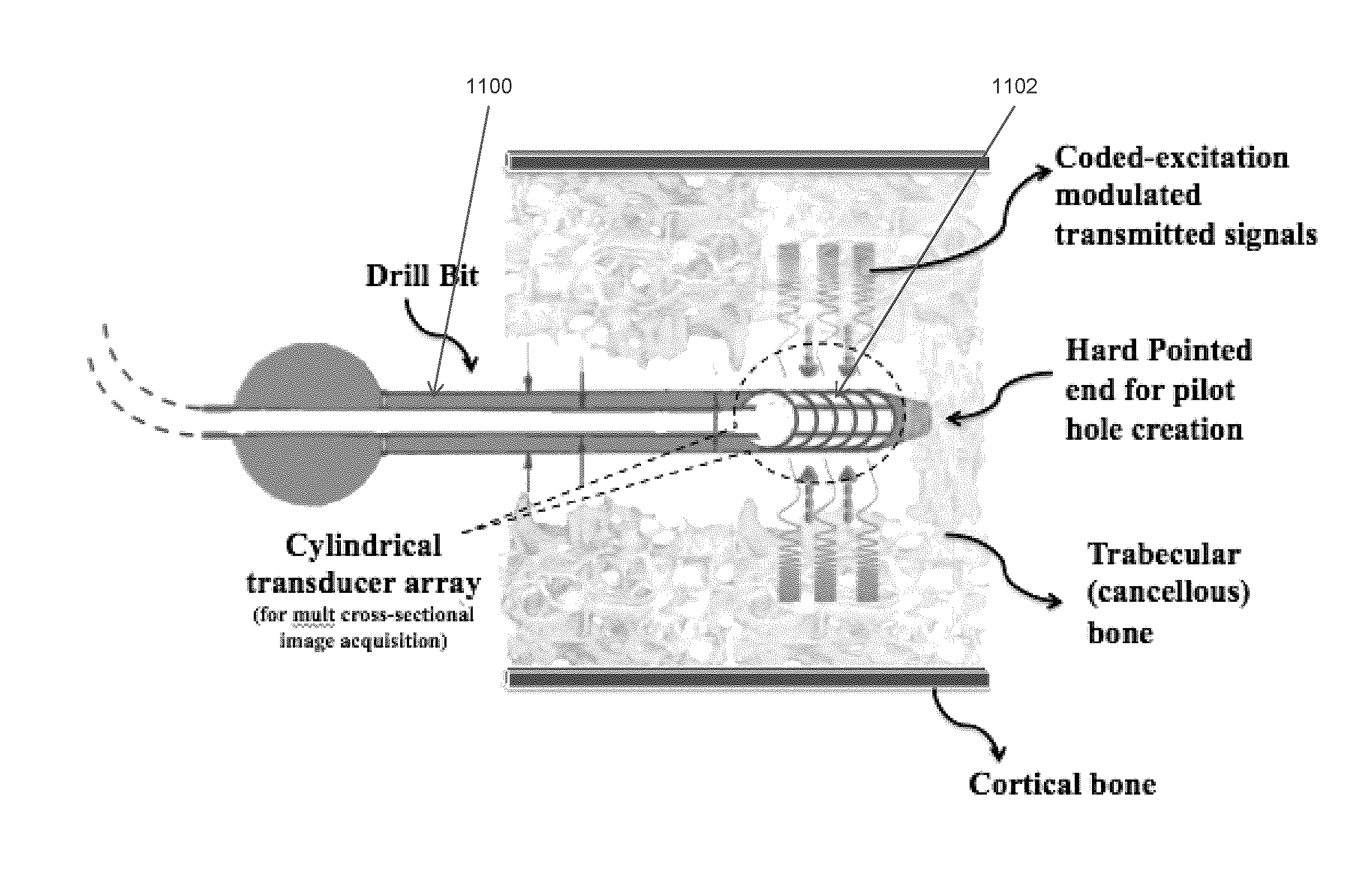
Ultrasonic signal processing for bone sonography
InactiveUS20160120501A1Internal osteosythesisOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationUltrasound sonography
Owner:MANBACHI AMIR +1
Method for Bone Scan in Meat
ActiveUS20200217831A1Slow changePrevent buildupAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRaman scatteringBone scansRaman scattering
A method and device for detection of bone in meat identifies fragments larger than about 1 mm using spectral optical imaging and ultrasound. Spectral imaging can detect foreign material proximate to the surface and ultrasound can detect material within the sample. The sample is irradiated by light and reflected light or Raman scattered light measured. The sample is similarly irradiated by ultrasound and reflected or transmitted sound waves give a set of amplitude data points, which include temporal delay. These data points are then processed by statistical methods to derive a set of vectors in n-dimensional space, which are compared to a calibrated data set of derived vectors which have distinct identifying loci for each type of surface, are indicative of the presence or absence of defects.
Owner:7386819 MANITOBA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com