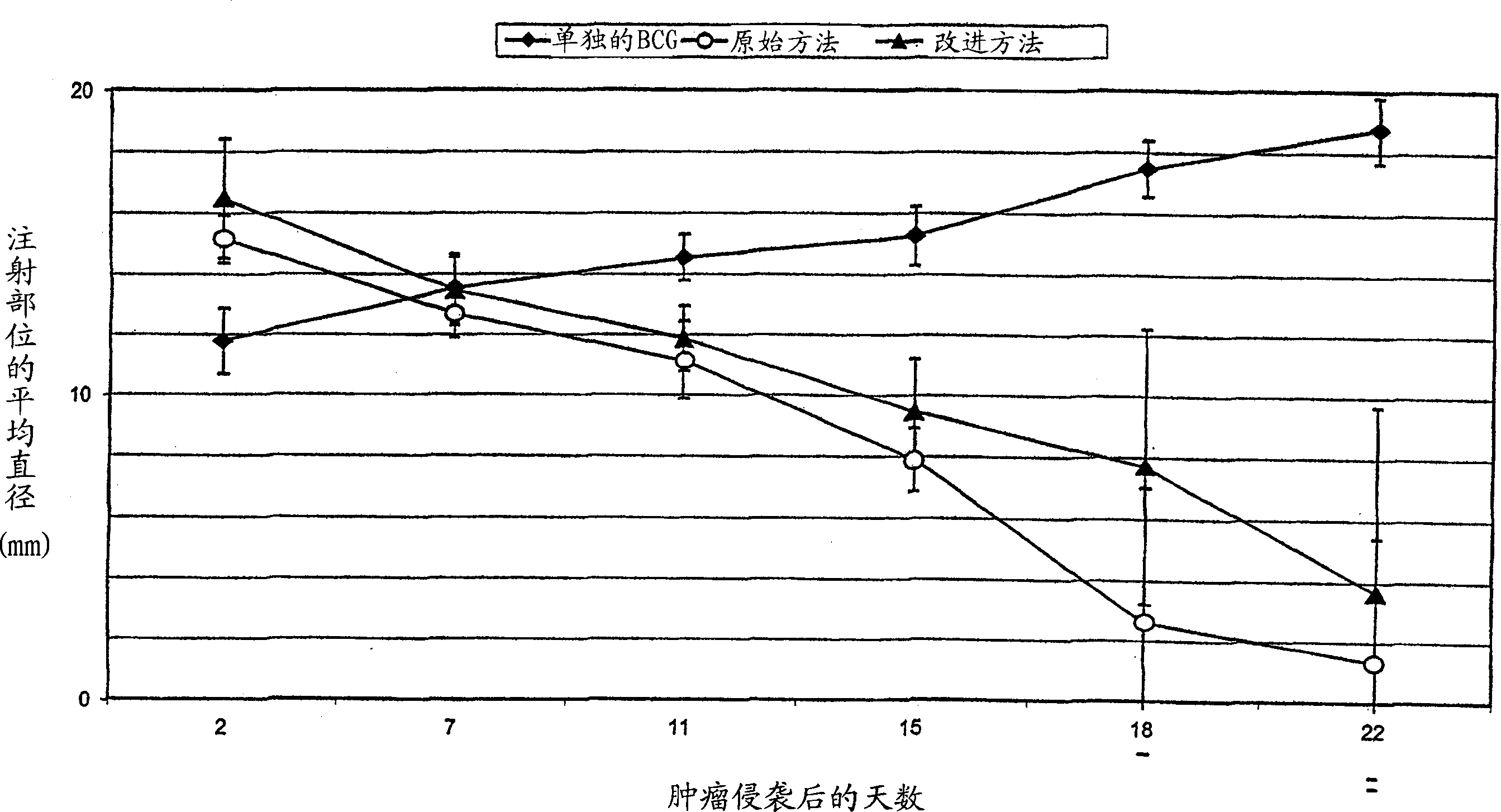
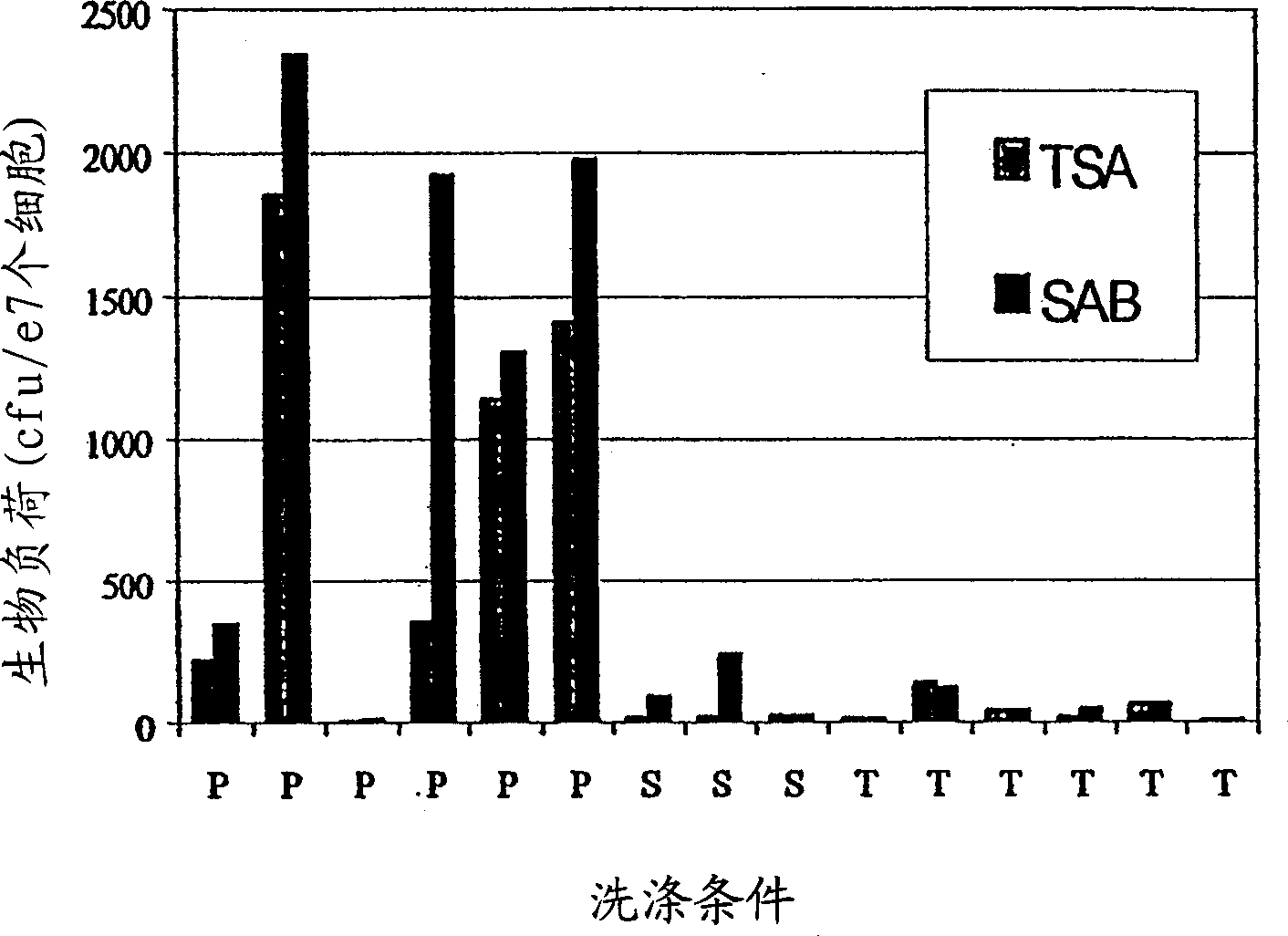
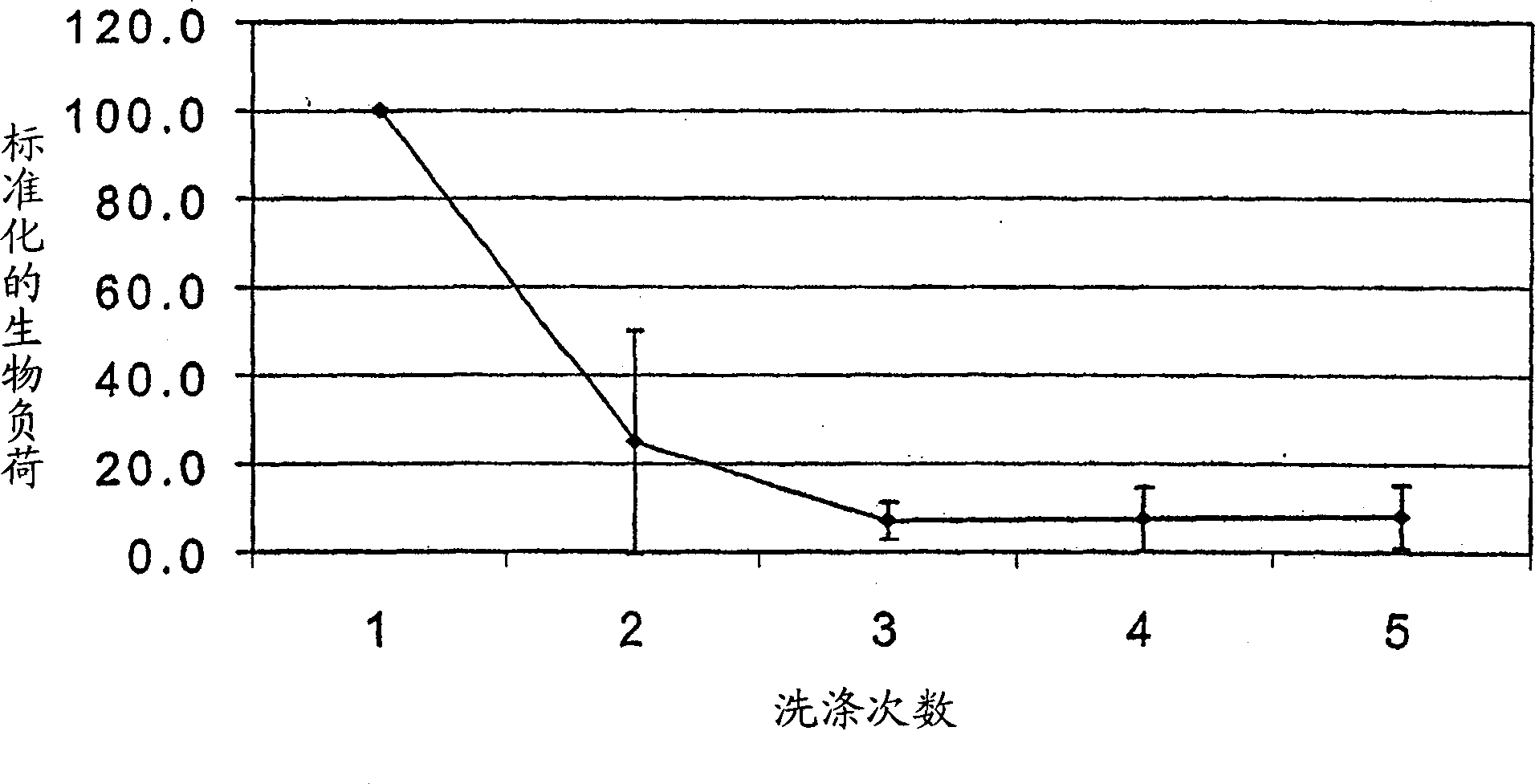
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Metastasis tumor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
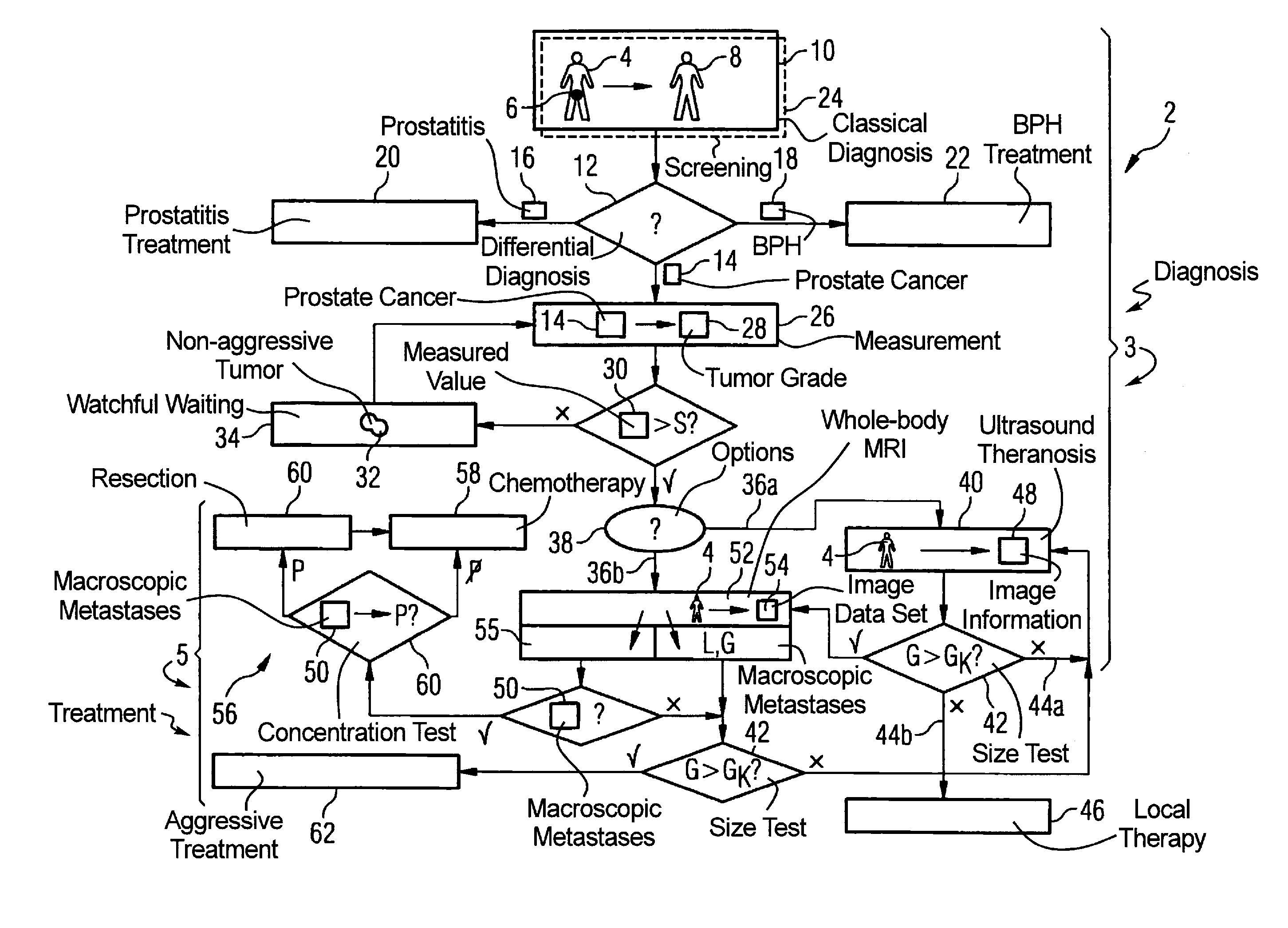
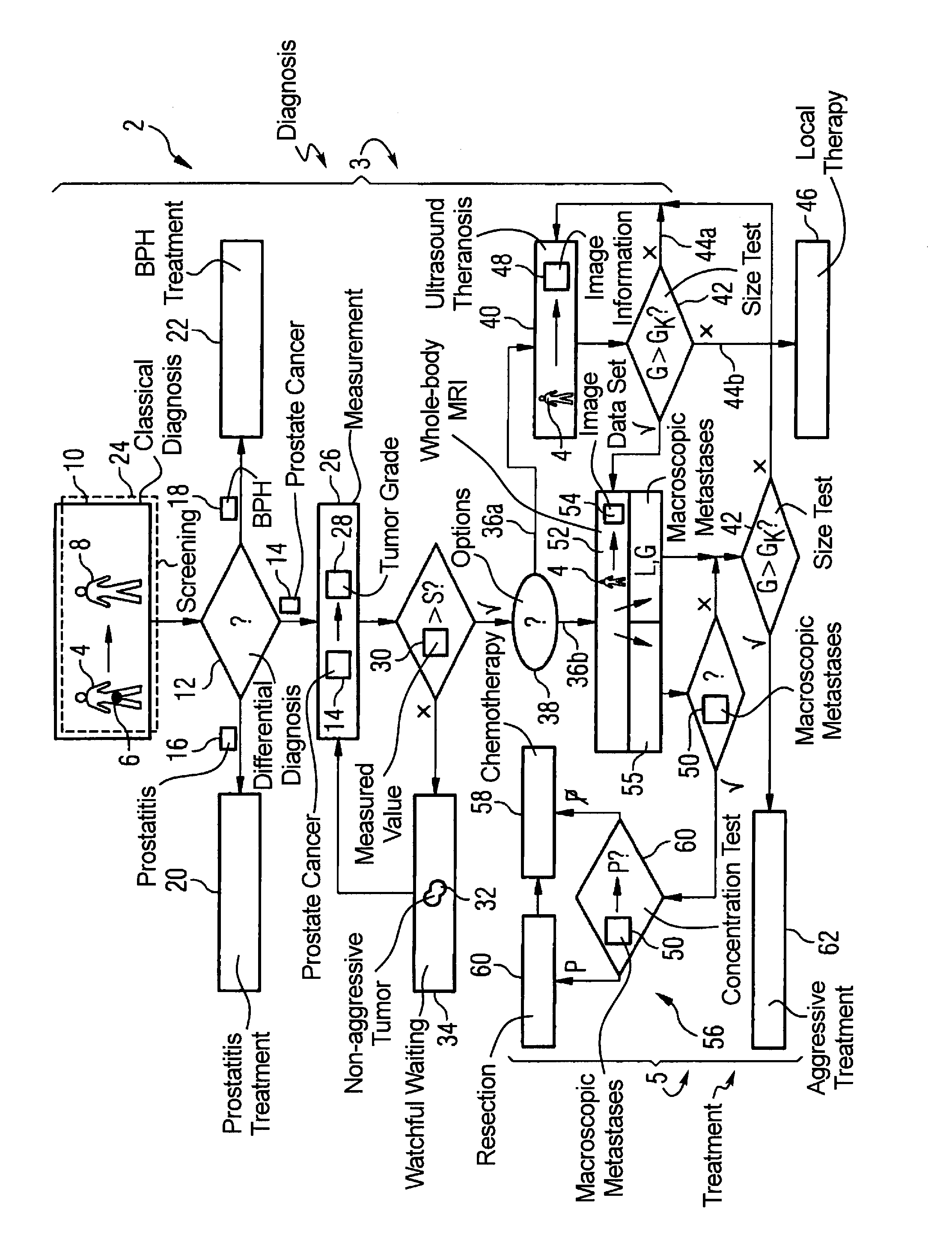
Method for diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20090062645A1Easy to useUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionLymphatic SpreadTumor therapy
In a method for diagnosis and treatment of a patient with a tumor relating to prostate cancer, the following steps are implemented. A differential diagnosis of prostate cancer versus prostatitis and / or BPH is conducted on a patient using a cost-effective diagnosis method. If prostate cancer is diagnosed in the patient using a cost-effective measurement method, a characteristic value for the tumor aggressiveness of the prostate cancer is determined. A watchful waiting treatment is implemented with the patient given a characteristic value below a predeterminable first limit value. The size and position of the tumor is determined using a cost-effective method given a characteristic value above the first limit value. A cost-effective ultrasonic theranosis or a conventional therapy is conducted for a size below a second predeterminable limit value. The presence of metastases in the patient is checked, with a cost-intensive method generating image information, for a size above the second limit value. A metastasis treatment is implemented in the event that metastases are present. In the event that no metastases are present, a tumor treatment based on the aforementioned image information generated is implemented.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Blood test to monitor the genetic changes of progressive cancer using immunomagnetic enrichment and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
InactiveUS20080113350A1Accurate measurementEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadGenetic Change
Amplification and overexpression of theHER-2 oncogene in breast cancer is felt to be stable over the course of disease and concordant between the primary tumor and metastases. Therefore, patients with HER-2 negative primary tumors will rarely receive anti-HER-2 antibody therapy. A very sensitive blood test is used to capture circulating tumor cells (CTC's) and evaluate their HER-2 gene status by FISH evaluation. The HER-2 status of the primary tumor and corresponding CTC's is used to assess the ratio of CTC's as a reliable surrogate marker. HER-2 expression of 10 CTC's is sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of the HER-2 gene status for the whole population of CTC's in patients with recurrent breast cancer.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Radiolabeled peptides for the diagnosis and treatment of breast and prostate tumors and metastases of such tumors
InactiveUS20030224998A1Conveniently providedShort half-lifeCosmetic preparationsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBombesinReceptor
Compounds and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors, including breast and prostate tumors and metastases thereof using radiolabelled peptides that bind to GRP receptors. The peptides are Bombesin analogs wherein the first and optionally the third amino acid are modified.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
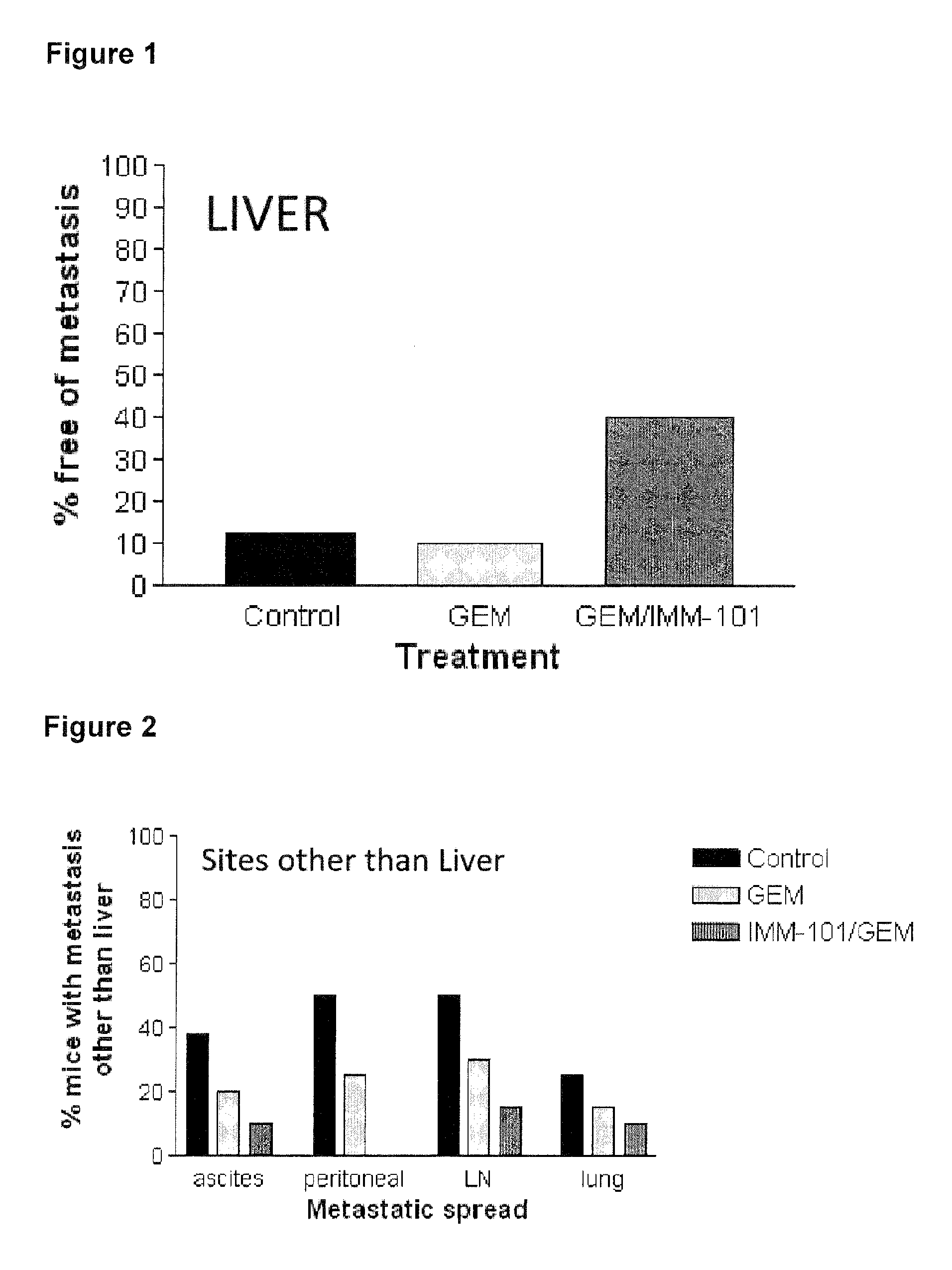
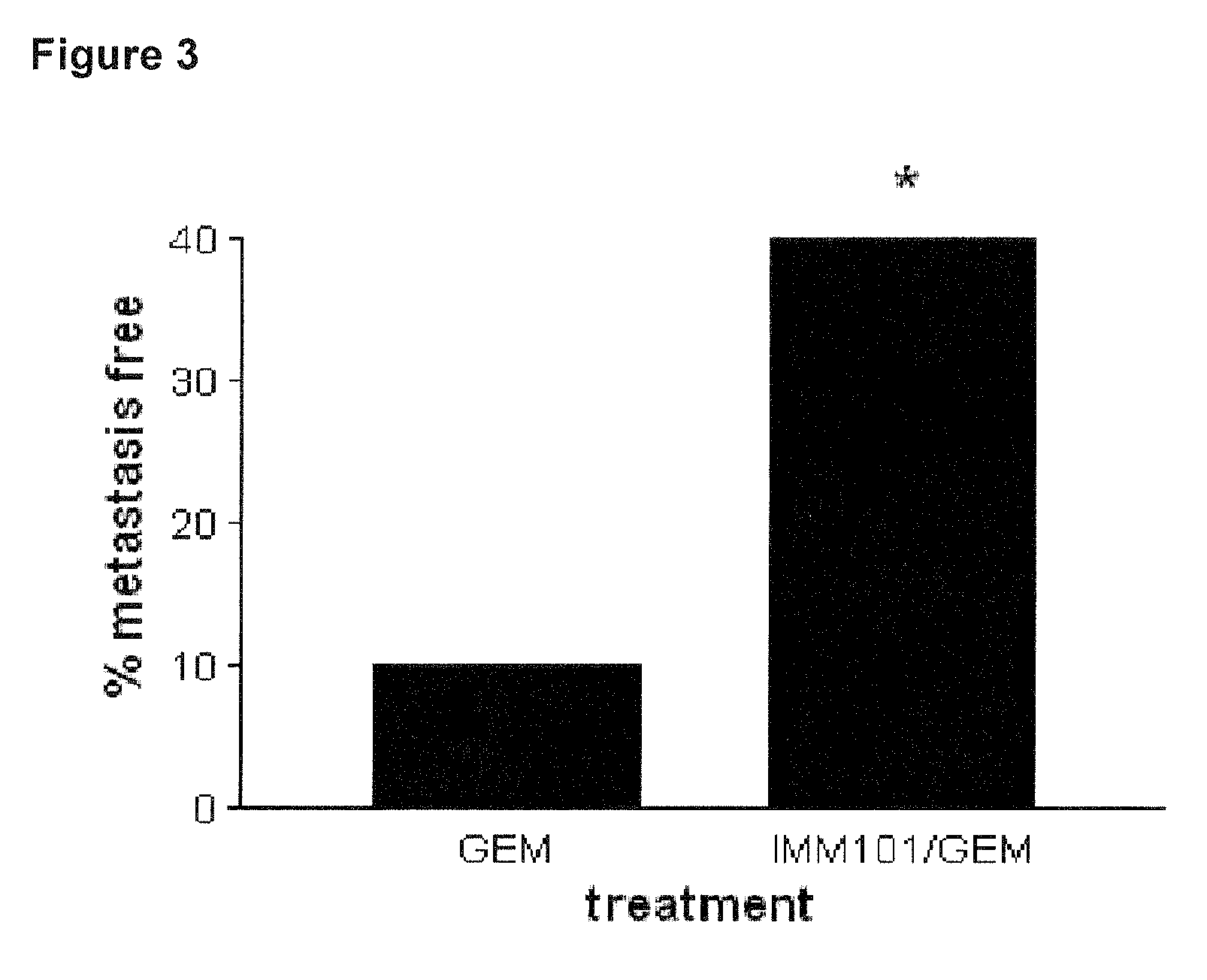
Cancer therapy
ActiveUS20130209517A1Great therapeutic responseBalanced immunoregulatoryBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsParanasal Sinus CarcinomaPyrimidine analogue
The present invention relates to a method of preventing, treating or inhibiting the development of tumors or metastases in a subject and to an immunomodulator for use in such therapy, in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent. An aspect the present invention is a method of preventing, treating, reducing, inhibiting and / or controlling the formation or establishment of metastasis of a primary neoplasia, tumor or cancer at one or more sites distinct from a primary neoplasia, tumor or cancer, in a subject intended to undergo chemotherapy, wherein the method comprises administering to the subject, a therapeutically effective amount of an antimetabolite pyrimidine analogue and an immunomodulator.
Owner:IMMODULON THERAPEUTICS
CA IX-specific inhibitors
InactiveUS20060057068A1Reduce acidificationIncrease aggressivenessOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthHypoxic cell
Therapeutic methods for inhibiting the growth of preneoplastic / neoplastic vertebrate cells that abnormally express MN protein are disclosed. Screening assays are provided for identifying compounds, preferably organic compounds, preferably aromatic and heterocylic sulfonamides, which inhibit the enzymatic activity of MN / CA IX and that are useful for treating patients with preneoplastic / neoplastic disease. Further, the CA IX-specific inhibitors when labeled or linked to an appropriate visualizing means can also be used diagnostically / prognostically for preneoplastic / neoplastic disease, and for imaging use, for example, to detect hypoxic precancerous cells, tumors and / or metastases, by selectively binding to activated CA IX, preferably CA IX activated under hypoxic conditions, and not to inactive CA IX. Such detection of hypoxic conditions can be helpful in determining effective treatment options, and in predicting treatment outcome and the prognosis of disease development. Still further, the CA IX-specific inhibitors can be used therapeutically to selectively target hypoxic cells expressing activated CA IX. The CA IX-specific inhibitors can be labelled or conjugated to radioisotopes for radiotherapy of hypoxic cells. Alternatively, the CA IX-specific inhibitors can be used for gene therapy coupled to vectors for targeted delivery to hypoxic preneoplastic / neoplastic cells expressing activated CA IX on their surfaces. In an alternative mode of the invention, CA IX-specific inhibitors may be used therapeutically to target acidic conditions of a tumor, e.g., to increase pHe in order to enhance the efficacy of weak base chemotherapeutic drugs.
Owner:INST OF VIROLOGY SLOVAK ACAD OF SCI +1
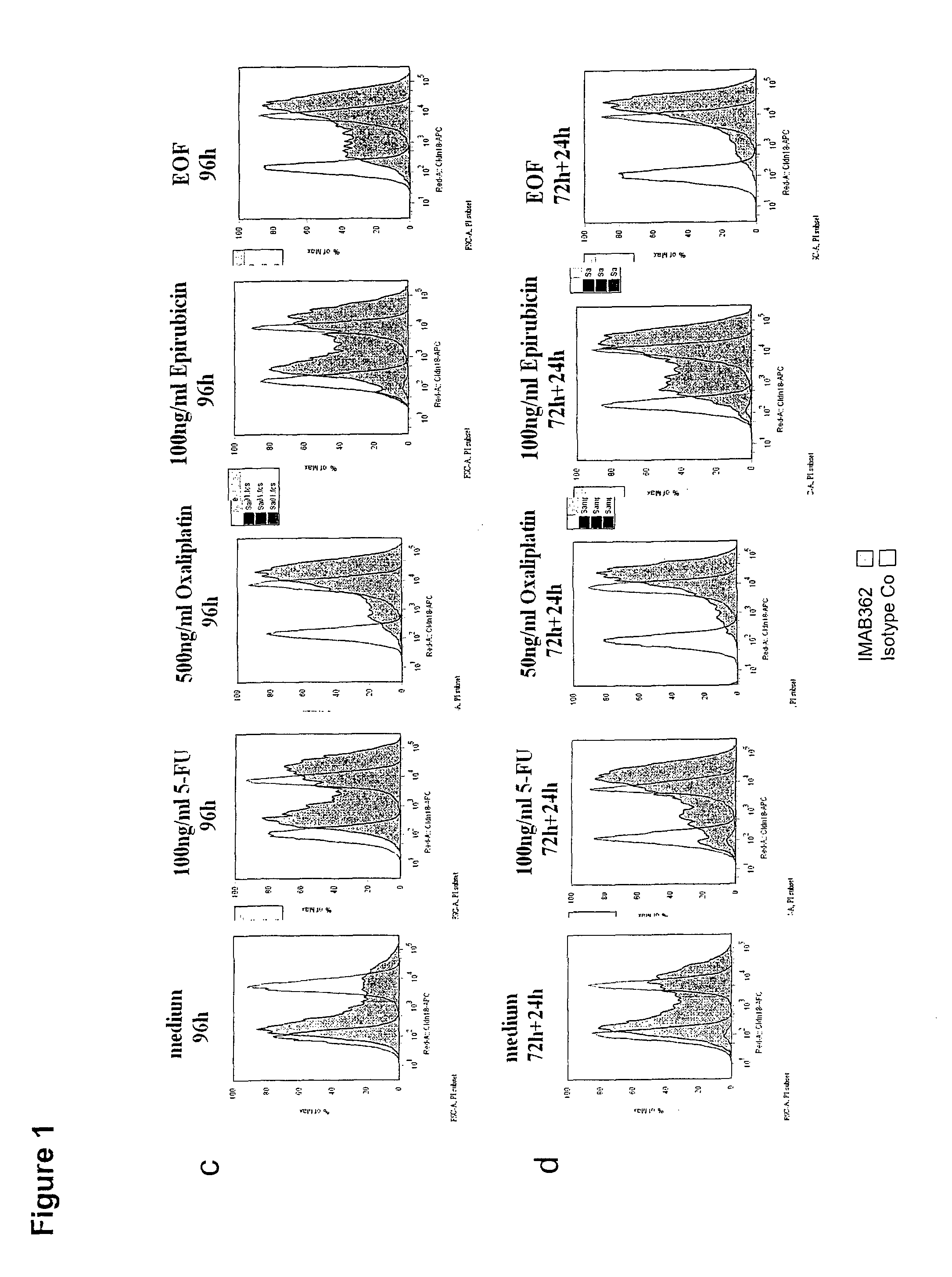
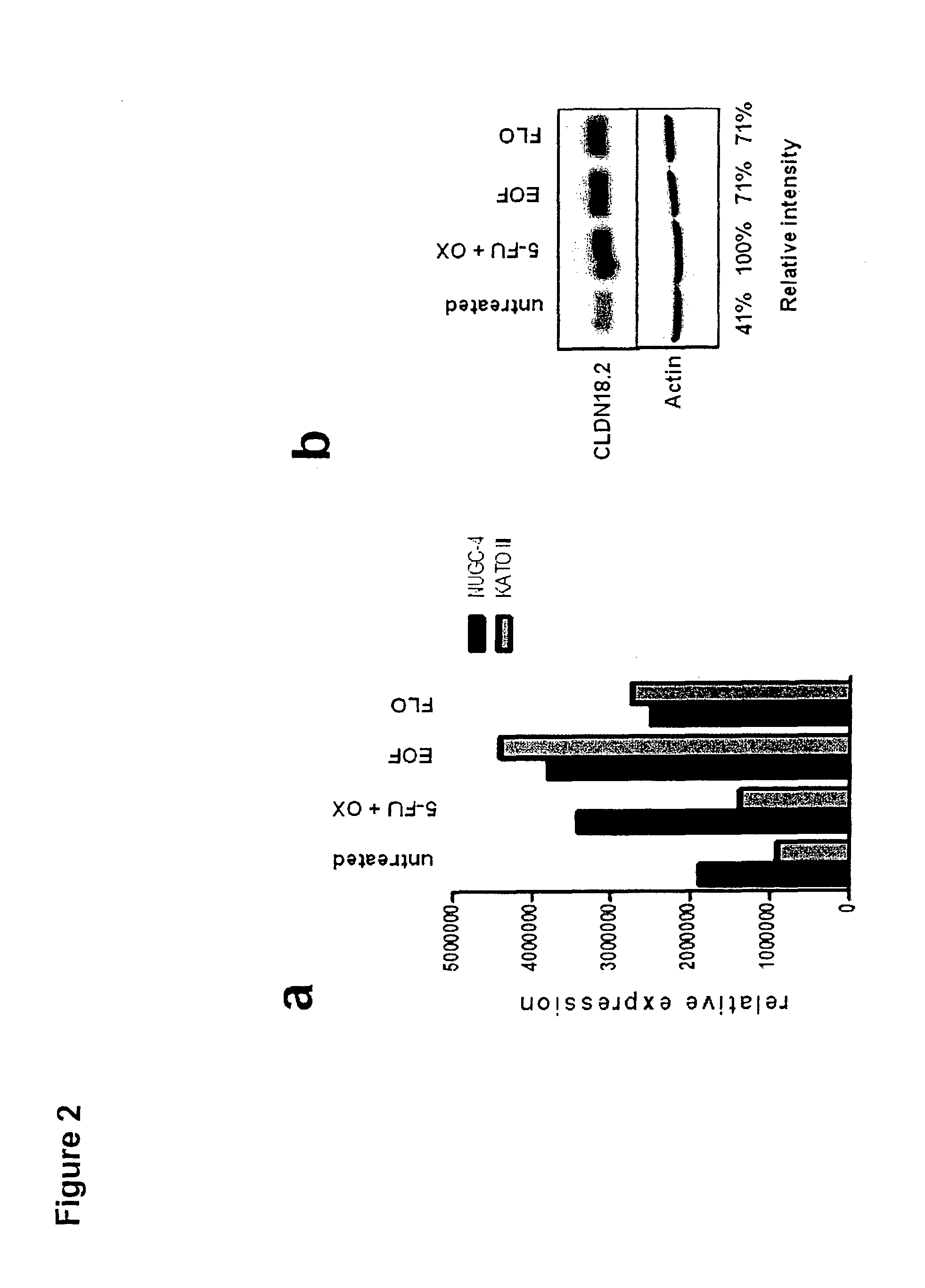
Combination therapy involving antibodies against claudin 18.2 for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20150132253A1Effectively preventingEffectively treatingHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCombined Modality Therapy
The present invention provides a combination therapy for effectively treating and / or preventing diseases associated with cells expressing CLDN18.2, including cancer diseases such as gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, hepatic cancer, head-neck cancer, and cancer of the gallbladder and metastases thereof.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC +1
Method for expansion of tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes for immunotherapy of patients with specific cancer types
ActiveUS7951365B2Conducive to survivalRaise the ratioBiocideInanimate material medical ingredientsDiseasePresent method
Methods for treating a patient suffering from a neoplastic disease are disclosed and described. A number of diseases can be treated under the present methods, including without limitation gall bladder cancer, hepato cellular cancer, ovarian cancer, small intestine cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, breast cancer, kidney cancer, pancreas cancer, prostate cancer, carcinoid cancer, leiomyosarcoma, or metastasis thereof. A general method for providing such treatment may include: 1) identifying in a patient one or more sentinel and / or metinel lymph nodes draining the neoplasm; 2) resecting the one or more nodes and, optionally all or part of the tumour or metastasis; 3) isolating tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes from said lymph nodes; 4) in vitro expanding said tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes; and 5) administering the thus obtained tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes to the patient.
Owner:SENTOCLONE INT AB
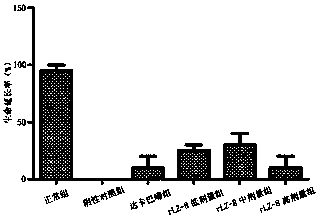
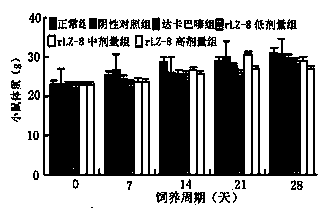
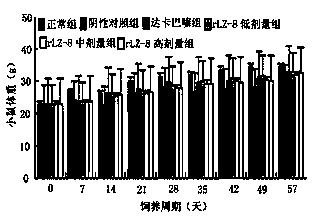
Application of recombined ganoderma lucidum immnoregulation protein (rLZ-8) in preparation of medicine for treating melanin tumor
InactiveCN103417953ATransfer of controlGuaranteed quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsFungi medical ingredientsMelanomaMetastasis tumor
The invention relates to application of recombined ganoderma lucidum immnoregulation protein (rLZ-8) in preparation of medicine for treating melanin tumor. In-situ tumor and metastatic tumor experiment animal models are used to research anti-tumor effect of rLZ-8, and the results show that the rLZ-8 can evidently inhibit in-situ tumor growing and metastasis forming of the melanin tumor.
Owner:张喜田 +1
Method for expansion of tumour-reactive t-lymphocytes for immunotherapy of patients with specific cancer types
ActiveUS20090022695A1Conducive to survivalRaise the ratioBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCancer type
Methods for treating a patient suffering from a neoplastic disease are disclosed and described. A number of diseases can be treated under the present methods, including without limitation gall bladder cancer, hepato cellular cancer, ovarian cancer, small intestine cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, breast cancer, kidney cancer, pancreas cancer, prostate cancer, carcinoid cancer, leiomyosarcoma, or metastasis thereof. A general method for providing such treatment may include: 1) identifying in a patient one or more sentinel and / or metinel lymph nodes draining the neoplasm; 2) resecting the one or more nodes and, optionally all or part of the tumour or metastasis; 3) isolating tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes from said lymph nodes; 4) in vitro expanding said tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes; and 5) administering the thus obtained tumour-reactive T-lymphocytes to the patient.
Owner:SENTOCLONE INT AB
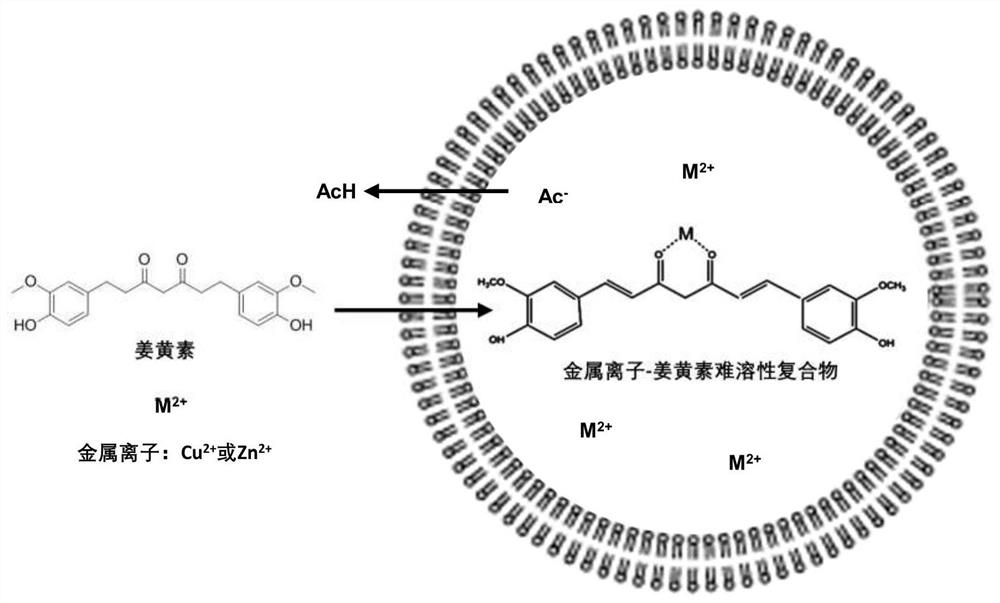
Curcumin active drug-loading liposome and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112451487AHigh encapsulation efficiencyPrevent leakageKetone active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCholesterolPhospholipid
The invention relates to the field of liposome drug delivery, in particular to a curcumin active drug-loading liposome and a preparation method thereof. The curcumin active drug-loading liposome is prepared from the following components of curcumin, phospholipid, cholesterol (Chol), a metal ion salt solution and an external water phase buffer solution, wherein the weight ratio of the curcumin to total phospholipid (the sum of phospholipid and cholesterol) is 0.5-1:10, the metal ion salt solution can be a sulfate, gluconate or acetate solution of copper ions or zinc ions, and the concentrationof the copper ions or the zinc ions in the metal ion salt solution is 50-300 mM. The curcumin active drug-loading liposome and the preparation method thereof have the characteristics that a curcumin active drug-loading liposome preparation with petal-like conformation is successfully prepared for the first time, cell experiments show that the curcumin active drug-loading liposome preparation has stronger active oxygen production capability and stronger tumor cell inhibition activity, and tumor-bearing mouse experiments show that the preparation has remarkable subcutaneous tumor growth inhibiting and metastatic tumor progress relieving effects.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Cancer therapy
ActiveUS8617520B2Safe, better tolerated and effective methodImprove responseBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsParanasal Sinus CarcinomaPyrimidine analogue
The present invention relates to a method of preventing, treating or inhibiting the development of tumors or metastases in a subject and to an immunomodulator for use in such therapy, in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent. An aspect the present invention is a method of preventing, treating, reducing, inhibiting and / or controlling the formation or establishment of metastasis of a primary neoplasia, tumor or cancer at one or more sites distinct from a primary neoplasia, tumor or cancer, in a subject intended to undergo chemotherapy, wherein the method comprises administering to the subject, a therapeutically effective amount of an antimetabolite pyrimidine analogue and an immunomodulator.
Owner:IMMODULON THERAPEUTICS
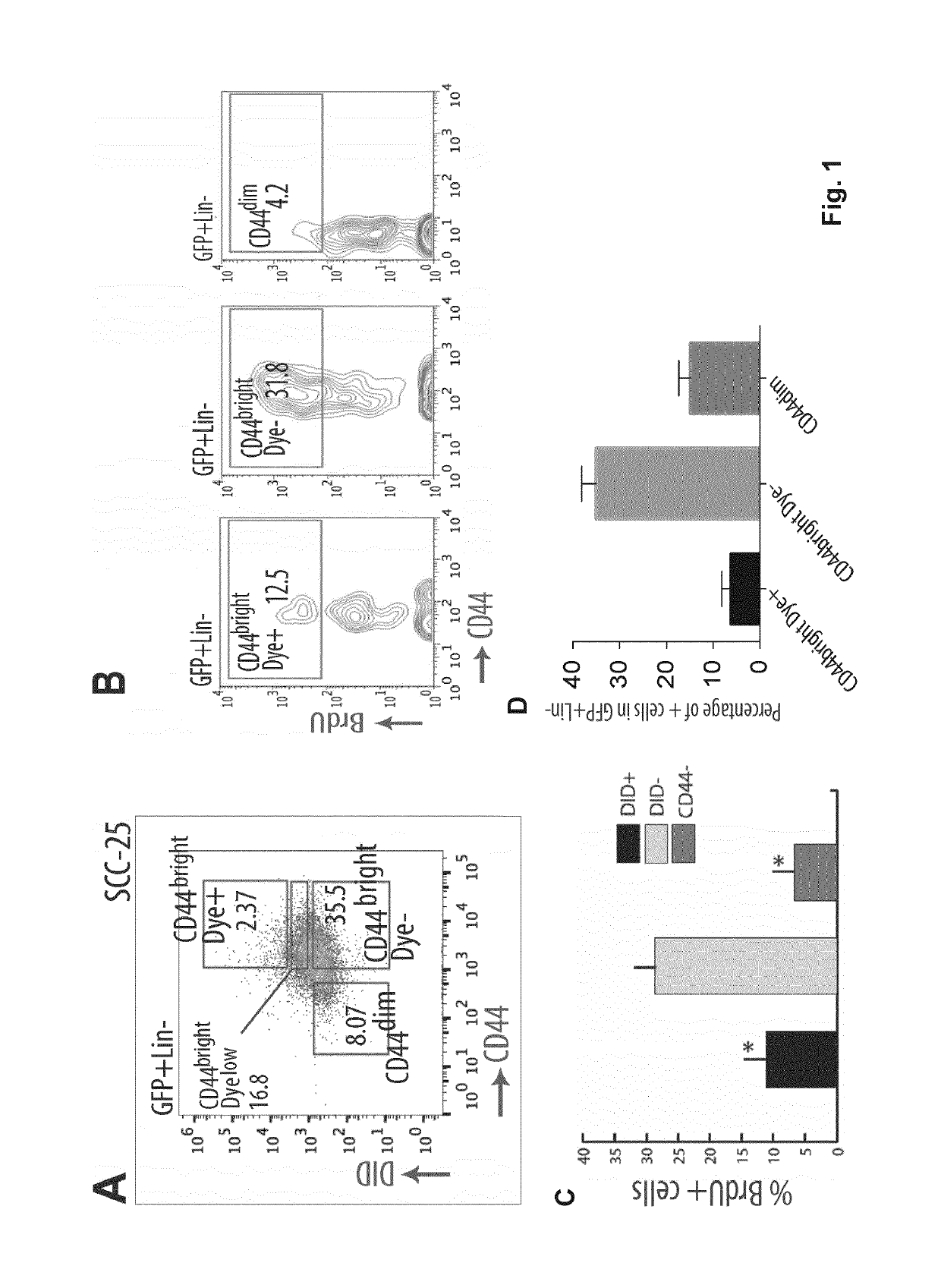
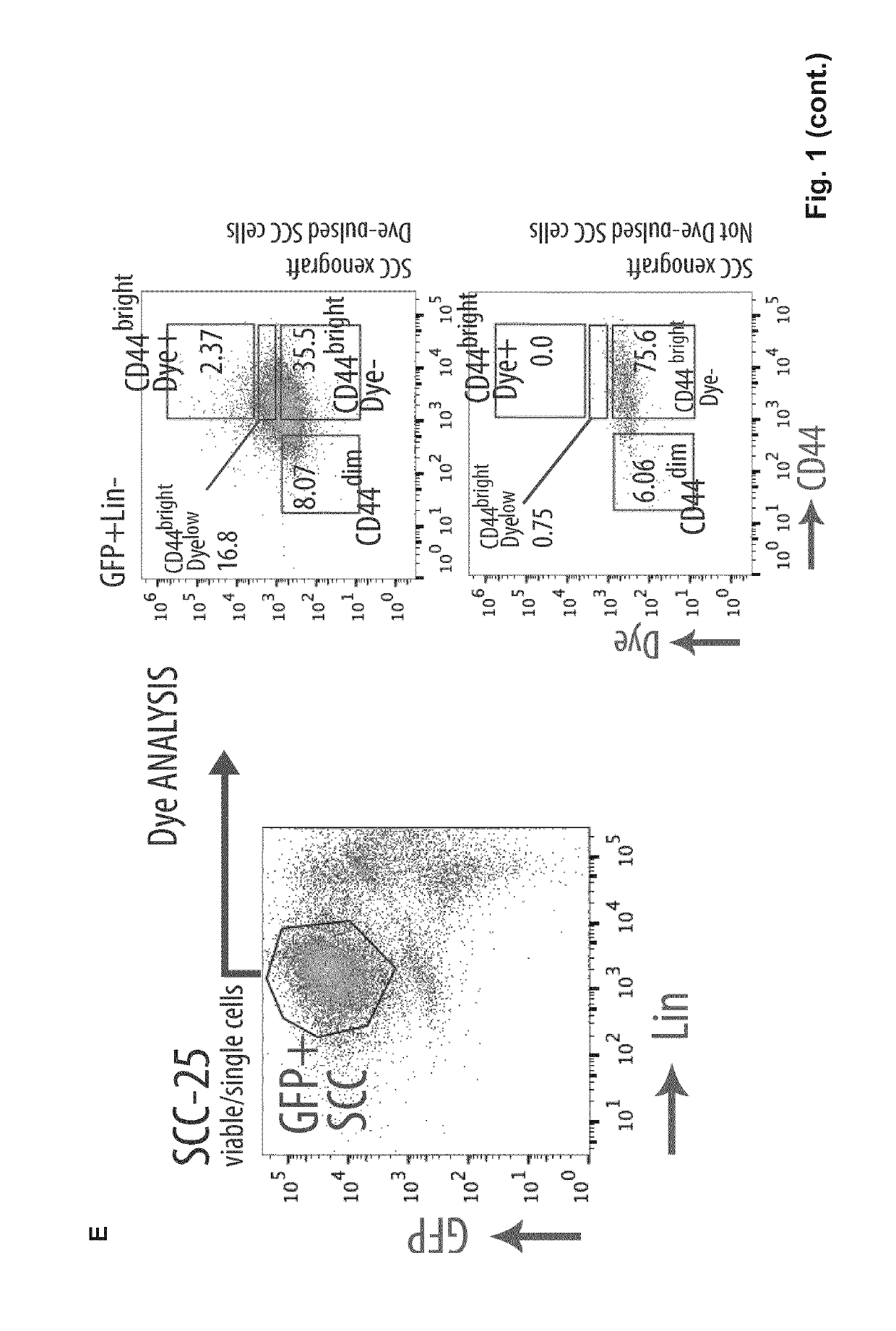
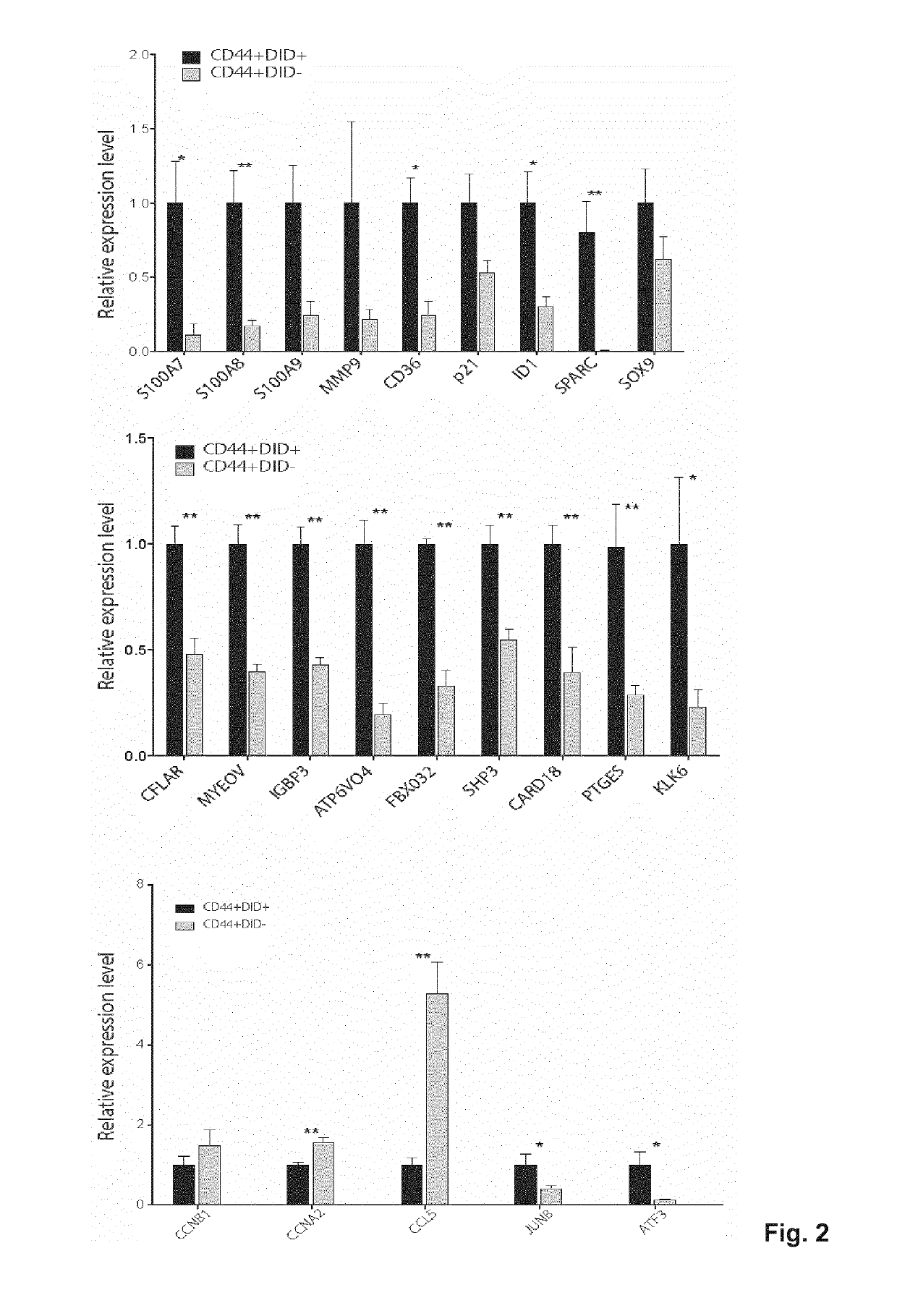
Targeting metastasis stem cells through a fatty acid receptor (CD36)
ActiveUS20190106503A1Diminish of metastasis growthPromote growthCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLipid formationLymphatic Spread
Metastasis stem cells are targeted through a fatty acid receptor. Blockers or inhibitors of CD36 activity or expression are for the treatment of oral squamous cell cancer (OSCC), particularly for the treatment of generated metastases and for diminishing generation from primary tumors. Apart from shRNAs, anti-CD36 antibodies are provided as blockers or inhibitors, especially those that block the binding of CD36 to oxidized LDL and fatty acids and their incorporation into cells, because the promotion of their transport is indicated as the mechanism by which CD36 promote metastases dissemination and growth. A method identifies candidates to anticancer agents, particularly for OSCC metastasis, among those that promote in CD36+ cells, in vivo or in vitro, effects associated to CD36 depletion or blocking such as decrease of growth accumulation of lipid droplets and decrease of size in the case of metastases.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE RECERCA BIOMEDICA (IRB BARCELONA) +1
Construction and application of near-infrared light activated macrophage-nano prodrug targeted drug delivery system
ActiveCN113456613AHigh drug loadingHigh activityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic active ingredientsNanocarriersCarboxylic acid
According to the invention, a carboxylated platinum prodrug is designed and synthesized, and a coordination nano core is prepared by utilizing the coordination effect of ions and the prodrug. Lipid is wrapped outside the nano-core, and a photosensitizer is dispersed in the nano-core to construct the prodrug nano-carrier. A nano prodrug is loaded by utilizing the phagocytic function of macrophages (BMDM), so that a near-infrared light (NIR) activated macrophage-nano prodrug delivery system is prepared. The system has the characteristics of high drug loading capacity, light-operated activation and retention of self activity and functions, and efficient and synchronous drug delivery of primary tumors and metastatic tumors can be realized after intravenous injection. Meanwhile, after primary tumors are irradiated by NIR, drugs can be triggered to be released quickly, chemotherapy-photodynamic combined therapy is achieved, and the purposes of killing tumor cells and activating an immune system are achieved. Through combination of three modes of chemotherapy, photodynamic and immunization, dual treatment of primary and metastatic tumors is finally realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Sterile immunogenic non-tumorigenic tumor cell compositions and methods
InactiveCN1774255AStay aliveMaintain metabolic activityMammal material medical ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsCell AggregationsMetastasis tumor
This invention relates to methods of removing bioburden from an aggregate of cells to obtain sterile cells that remain viable and immunogenic for the production of vaccines. This invention further relates to a method of eliciting an immune response to prevent a recurrence of metastases that involves preparing and administering a sterile vaccine derived from solid tumors. The vaccine is prepared by excising a solid tumor from a cancer patient, digesting the tumor cells with an enzyme to obtain dissociated cells, irradiating the dissociated cells to render the cells non-tumorigenic, and sterilizing the cells.
Owner:INTRACEL RESOURCES
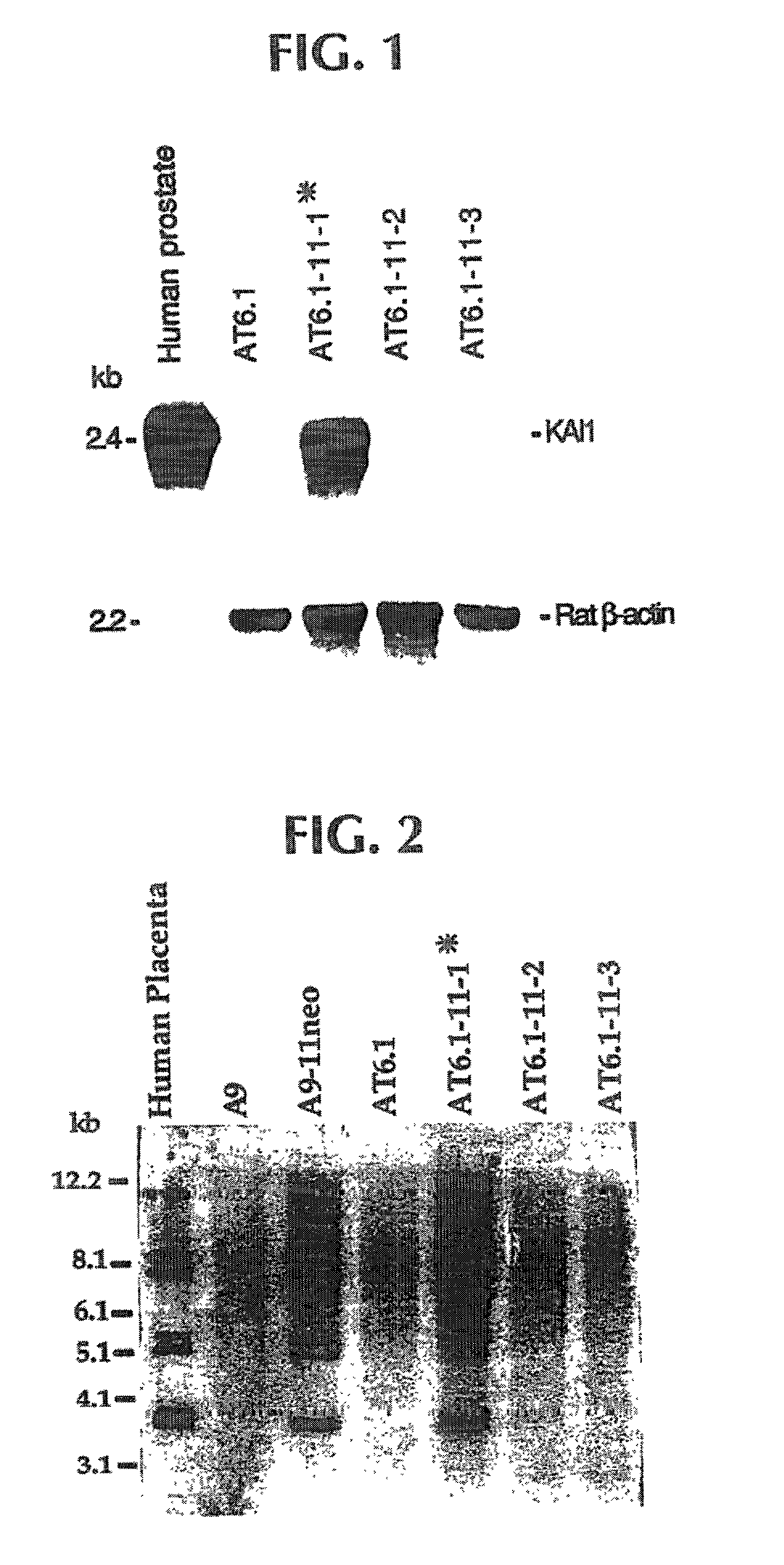
Diagnostic methods and gene therapy using reagents derived from the human metastasis suppressor gene KAI1
InactiveUS6204000B1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGenetic material ingredientsSuppressorMetastasis tumor
The isolation and characterization of a metastasis tumor suppressor gene KAI1 is disclosed and diagnostic methods and gene therapy approaches utilizing reagents derived from the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the KAI1 gene are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
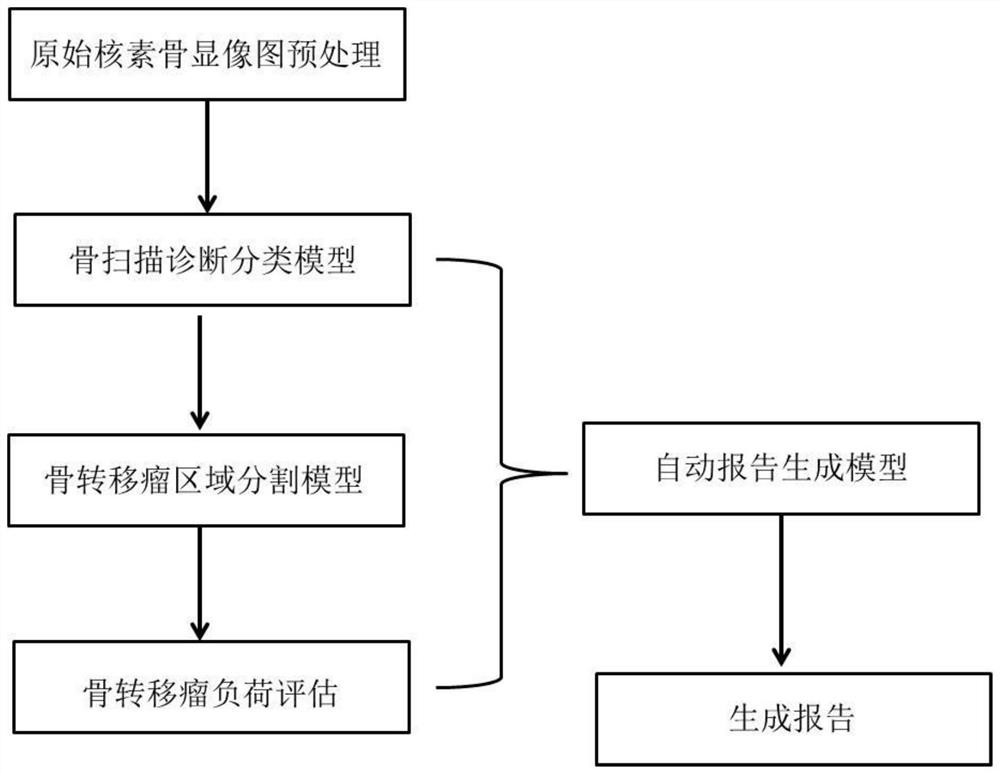
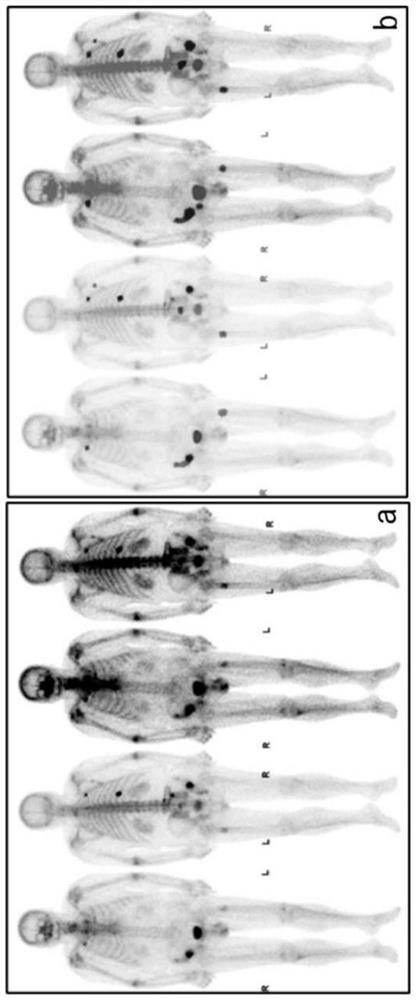
Diagnosis method for bone metastasis tumor in nuclide bone imaging based on deep learning
PendingCN112635067AQuantitatively accurateObjective and accurate quantitativeMedical simulationImage enhancementTumor LoadMetastasis tumor
The invention provides a method for diagnosing bone metastases in nuclide bone imaging based on deep learning. The method relates to a bone scanning diagnosis classification model, a bone metastasis tumor region segmentation model and a bone metastasis tumor load evaluation and automatic report generation model. By the adoption of the method, the bone metastasis tumor can be judged, automatic region segmentation can be conducted, the recognition accuracy is high, and full-automatic analysis from original image input to report generation is preliminarily achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Transcriptome-based tumor metastasis gene detection system
The invention provides a transcriptome-based tumor metastasis gene detection system. The transcriptome-based tumor metastasis gene detection system comprises an integration module, a recognition module, an analysis module and a marking module, wherein the integration module is used for integrating a Read counting matrix to obtain a statistical magnitude file of differential expression degree of each gene; the recognition module is used for recognizing the differential expression genes and comparing the differential degree between functions under tumor primary and metastasis conditions; the analysis module is used for analyzing a gene expression mode and classifying and analyzing the expression mode; the marking module is used for marking tumor metastasis genes; the integration module, the recognition module, the analysis module and the marking module are connected in sequence. The transcriptome-based tumor metastasis gene detection system is used for mining the tumor metastasis related genes from high-throughput data, and analyzing the abnormal changes of transcriptomes in primary and metastasis tumors and the dynamic changes of tumor metastasis marker gene expression modes in the metastasis process.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Peptide-Based Compounds and Their Uses for Tumor Imaging and Targeting
InactiveUS20170128596A1High tumor-to-background contrastStrong tumor-specific signal intensityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAbnormal tissue growthTumor targeting
The present invention relates to peptide-based compounds comprising (i) at least one peptide comprising the amino acid sequence of TKDNNLLGRFELXG wherein X is S or T and (ii) at least one label and / or drug. The present invention further relates to the use of said peptide-based compounds for tumor imaging and / or tumor targeting. The present invention further relates to the use of said peptide-based compounds as carrier of tumor therapeutic(s). The present invention further relates to methods for the in vitro and / or in vivo visualization, identification and / or detection of tumor cells and / or metastases as well as to methods for the treatment of cancer. The present invention further relates to a screening method for anti-tumor compounds.
Owner:KLINIKUM REKHTS DER IZAR DER TEKHNISHEN UNIV MYUNKHEN +1
Combination therapy involving antibodies against claudin 18.2 for treatment of cancer
ActiveUS9433675B2High affinityStrong specificityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseEsophageal cancer
The present invention provides a combination therapy for effectively treating and / or preventing diseases associated with cells expressing CLDN18.2, including cancer diseases such as gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, hepatic cancer, head-neck cancer, and cancer of the gallbladder and metastases thereof.
Owner:TRON TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVERSITAETSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV MAINZ GEMEINNUETZIGE GMBH +1
Use of VEGFR-2 inhibitors for treating metastatic cancer
InactiveCN101883578AGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetastasis tumorOncology
The present application provides compositions and methods for treating metastatic cancer. Patients having or at risk of developing metastases may be treated. Compositions useful for the invention include VEGFR-2 specific inhibitors.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Nanoscale platinum compounds and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9393227B2Improvement therapeutic indexSustains the potency of the active agentOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryLymphatic SpreadMedicine
The invention is directed to biocompatible conjugated polymer nanoparticles including a copolymer backbone, a plurality of sidechains covalently linked to said backbone, and a plurality of platinum compounds dissociably linked to said backbone. The invention is also directed to dicarbonyl-lipid compounds wherein a platinum compound is dissociably linked to the dicarbonyl compound. The invention is also directed to methods of treating cancer or metastasis. The methods includes selecting a subject in need of treatment for cancer or metastasis and administering to the subject an effective amount of any of the nanoparticles, compounds, or compositions of the invention.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Radioactive label tEB-TMTP1 compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109705193AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsProduction rateMetastasis tumor
The invention discloses a radioactive label tEB-TMTP1 compound. Through modification with DOTA and NOTA bifunctional chelating agents, DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 and NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 are synthetized, radioactive metal nuclides of radioactive nuclides 68Ga, 64Cu and 177Lu and the like are respectively labelled, and a nuclear medicine diagnosis and treatment probe of specific target high-metastasis tumors is synthetized. The probe designed and synthesized from the radioactive label tEB-TMTP1 compound disclosed by the invention has two advantages that firstly the labelling steps are simple, higher labelling production rate is achieved, and a foundation is laid for clinical application; secondly, the obtained DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe and the obtained NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe have excellent pharmacokinetics nature,the half life of the DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe and the obtained NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe in bodies can be notably prolonged, the DOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe and the obtained NOTA-tEB-TMTP1 probe can circulate in thebodies for a long term, tumor part ingestion is increased, and target treatment on high-metastasis tumors can be realized.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XIAMEN UNIV
Novel stem cells, method for screening same, kit and application thereof
InactiveCN102796699AEliminate distractionsThe method is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementMammal material medical ingredientsScreening methodMixed Cellular Population
The invention belongs to the technical field of cells and discloses novel adult stem cells, a method for screening the same, a kit and application thereof. Biopsy samples, in vitro tissue samples, and cell line samples of normal tissues and tumors, precancerous tissues and tumors, carcinogenic tissues and metastatic tumors or cancer tissues of rodent, human or other mammals are screened by using chemotherapeutics and cell markers which are combined so as to obtain the stem cell groups. Moreover, the invention also discloses a method for screening and identifying the stem cells from the mixed cell groups, and the kit; and the method and the kit have the advantages of strong specificity, simplicity, convenience, quickness, practicality and effectiveness. The novel stem cells, the method for screening the same and the kit can be applied to clinic treatment, basis and application research, treatment, tissue engineering, medicine screening, and repairing and regeneration of diseased tissues and organs which loose functions well, and have wide prospect.
Owner:李福生 +1
Anticancer sustained-release gel injection containing neonatal blood vessel inhibitor
InactiveCN101283975APharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsRofecoxibResidual Tumors
A sustained-release gel injection comprises angiogenesis inhibitor, amphiphilic block copolymer, solvent and release regulator, wherein the mixture of amphiphilic block copolymer and solvent has temperature sensitive gelatinization characteristic, and can automatically become non-flowing degradable water insoluble gel, which can locally and slowly release drug at tumor foci for several weeks to several months, after injection into body. The preparation can be injected into or around tumor for treating solid tumors at different stages and metastatic tumors with remarkably reduced systemic toxicity of drug. The angiogenesis inhibitor is selected from alemtuzumab,ibritumomab, bevacizumab, rituximab, gemtuzumab ozogamicin, panitumumab, trastuzumab, celebrex, refecoxib, tositumomab, endostatain, engiostatin, toxitumomab, and cetuximab. The preparation has effects of controlling residual tumor cell relapse after operation and tumor can not be excised via operation, controlling complications at late stage of tumor, and enhancing treatment effect of chemotherapy and radiotherapy (particularly radioactive particles).
Owner:济南基福医药科技有限公司
Covalent organic framework material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114015066AHigh biosecurityImprove securityEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTreatment effectTopical treatment
The invention provides a covalent organic framework material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The covalent organic framework material comprises a structural unit with a regular hexagonal topological structure, and the structural unit comprises a compound as shown in a formula I and a compound comprising a core group and an arm group which are connected through an imine bond. By adopting the multifunctional boron capsule with high biocompatibility, BNCT and immunotherapy can be combined, the systemic anti-tumor treatment effect is achieved by enhancing the BNCT of local tumors, and wide prospects are shown in the aspect of treating far-end metastatic tumors through the local BNCT.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Curcuminoids in Combination Docetaxel for the Treatment of Cancer and Tumour Metastasis
The present invention relates to a curcuminoid for enhancing the clinical efficacy of Docetaxel for the treatment of cancers and metastases.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
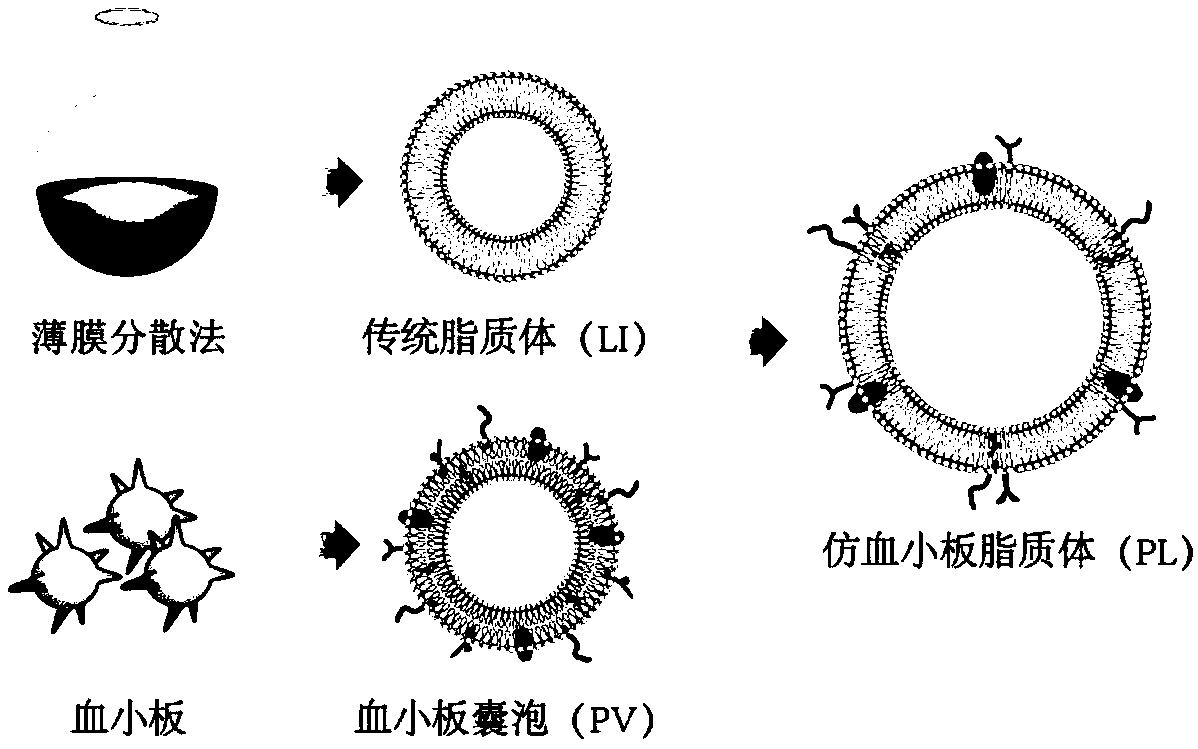
Platelet-like liposome drug delivery system, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111374945APossess natural targeting functionHas a natural targeting effectPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMetastasis tumorPlatelet
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical preparations, and relates to a targeted drug delivery system, specifically to a platelet-like liposome drug delivery system, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The drug delivery system is prepared from a platelet membrane and a traditional liposome through extrusion membrane-filtering and fusing. The drug delivery system has the advantages of both natural targeting of a platelet and in-vivo long circulation of a lipidosome; in-vitro adhesion experiment results prove that the platelet-like lipidosome has the adhesion capacity similar to the adhesion capacity of a pure platelet vesicle to collagen and fibrinogen; in-vitro targeting experiment results prove that the platelet-like liposome has good targeting similar to the targeting of the pure platelet vesicle to tumor cells; pharmacokinetic experiment results prove that the platelet-like lipidosome has long in-vivo circulation time close to the in-vivo circulation time of a traditional lipidosome; and in-vivo targeting experiment results prove that the platelet-like lipidosome has a targeting effect significantly higher than the targeting effect of a traditional lipidosome and the pure platelet vesicle on residual tumors and metastatic tumors.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating cancer pain caused by bone metastasis and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111588825AThe improvement of symptom score is goodAntipyreticAnalgesicsSide effectOncology
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating cancer pain caused by bone metastasis and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine compositions. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from, by mass, 10-50 parts of milkvetch roots, 10-50 parts of glossy privet fruits, 5-35 partsof herba taxilli, 5-35 parts of radix aucklandiae, 5-35 parts of radix sophorae subprostratae, 5-35 parts of spina gleditsiae, 5-35 parts of pseudobulbus cremastrae seu pleiones, 5-30 parts of rhizomasparganii, 5-30 parts of rhizoma curcumae, 5-30 parts of spica prunellae, 5-35 parts of cortex moutan, 5-35 parts of caulis spatholobi and 5-30 parts of radix glycyrrhizae preparata. The traditionalChinese medicine composition can achieve the analgesic effect and is free of side effects on the human body.
Owner:CHONGQING TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE HOSPITAL
Diagnostic methods and gene therapy using reagents derived from the human metastasis suppressor gene KAI1
InactiveUS20020058257A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementSuppressorMetastasis tumor
The isolation and characterization of a metastasis tumor suppressor gene KAI1 is disclosed and diagnostic methods and gene therapy approaches utilizing reagents derived from the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the KAI1 gene are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Methods for large tissue labeling, clearing and imaging
PendingCN110998277ADetailed inspectionReduce in quantityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansWHOLE ANIMALTumour metastasis
The present invention relates to methods for preparing an animal tissue for fluorescence microscopy, to an animal tissue obtainable by said methods, to methods for analyzing said animal tissues, and to methods for the detection of metastases, for analyzing the biodistribution of a biopharmaceutical drug, and for analyzing the biodistribution of nanoparticles. The methods for preparing an animal tissue according to the present invention encompass whole-body labeling, clearing and imaging methods. The methods of the invention are advantageous in that they, for instance, allow the visualization of single cells within mammalian tissues including pig and human brains, tumor metastases at the single cell level and of the distribution of biopharmaceutical drugs (e.g. the distribution of cancer-targeting therapeutic antibodies in whole animals such as intact mice) at single cell level in whole mouse.
Owner:DEEP PICTION GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com