Covalent organic framework material and preparation method and application thereof
A covalent organic framework and group technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as retention and lack of tumor targeting, and achieve high safety, improved therapeutic effect, and high biological safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0172] Example 1: Synthesis of Carborane Covalent Organic Framework Materials
[0173] Synthesis of Monomeric B-CHO as Carborane Covalent Organic Framework Materials
[0174]
[0175] (1). Synthesis of compound 1
[0176] 4-iodobenzaldehyde (5.00g, 21.55mmol), p-toluenesulfonic acid (0.82g, 4.30mmol), ethylene glycol (14.45g, 215.50mmol) and molecular sieve (sodium-type A molecular sieve, spherical 3mm ~ 5mm) dissolved in CHCl 3 (50 mL), the mixture was heated to 80°C and stirred overnight. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, water and NaHCO 3 (1M) was washed, and the aqueous layer was extracted with chloroform. Combined organic layers in NaSO 4 Dry over, filter and evaporate in vacuo to remove volatile compounds. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography using a mixture of n-hexane and dichloromethane (1:2, v:v) as eluent to obtain compound 1 as a white solid (0.75 g, 50%). 1 H NMR (400MHz, chloroform-d) δ7.72(d, J=8.3Hz, 2H...
Embodiment 2
[0189] Example 2: Characterization of Covalent Organic Frameworks
[0190] 1. Characterization of XRD
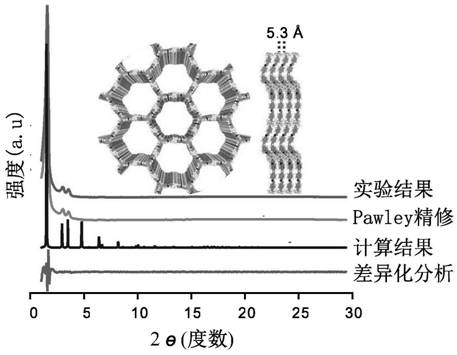
[0191] To explore the crystallinity of the polymerized product, organic solvents of TAPB and B-CHO at a molar ratio of 2:3 were added to different solvents (2.5 mL) containing HAc (0.15 mL, 12 M), and the crystalline product was precipitated. Experimental test results such as image 3 As shown in Table 1, the reaction solvent plays a key role in the formation of the crystalline B-COF structure. The crystallinity of the polymerization product obtained in o-dichlorobenzene solvent is higher than that using other conventional reaction solvents. Moreover, the crystallinity of B-COF gradually increased when the reaction temperature was increased by 50 °C from room temperature. Under the action of polystyrene microsphere template additive, the B-COF obtained better crystallinity after etching away the template with toluene.
[0192] Table 1: Optimal conditions for B-COF (R.T m...
Embodiment 3
[0216] Example 3: Defects caused by boron neutron capture reaction
[0217] 1. Irradiation in test tube experiments found that drug release was accelerated
[0218] Experimental process such as Figure 16 depicted in .
[0219] In brief, considering the high correlation between pharmacokinetics and immunological responses, the release profile of DSPE-IMD@B-COF before and after thermal neutron irradiation was preliminarily explored. Here, using the IHNI-1 neutron flux 1.9×10 9 (cm -2 the s -1 ) thermal neutron irradiation for 30 min to treat DSPE-IMD@B-COF to monitor its release efficiency. Place the test tube at the neutron beam outlet of the BNCT to receive neutron irradiation, and compare the changes in the release of small molecule drugs before and after irradiation ( Figure 16 ). A control group was set up, and the non-neutron irradiation group was a control experiment.
[0220] The effect of neutrons on drug release was evaluated by calculating the cumulative rel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com