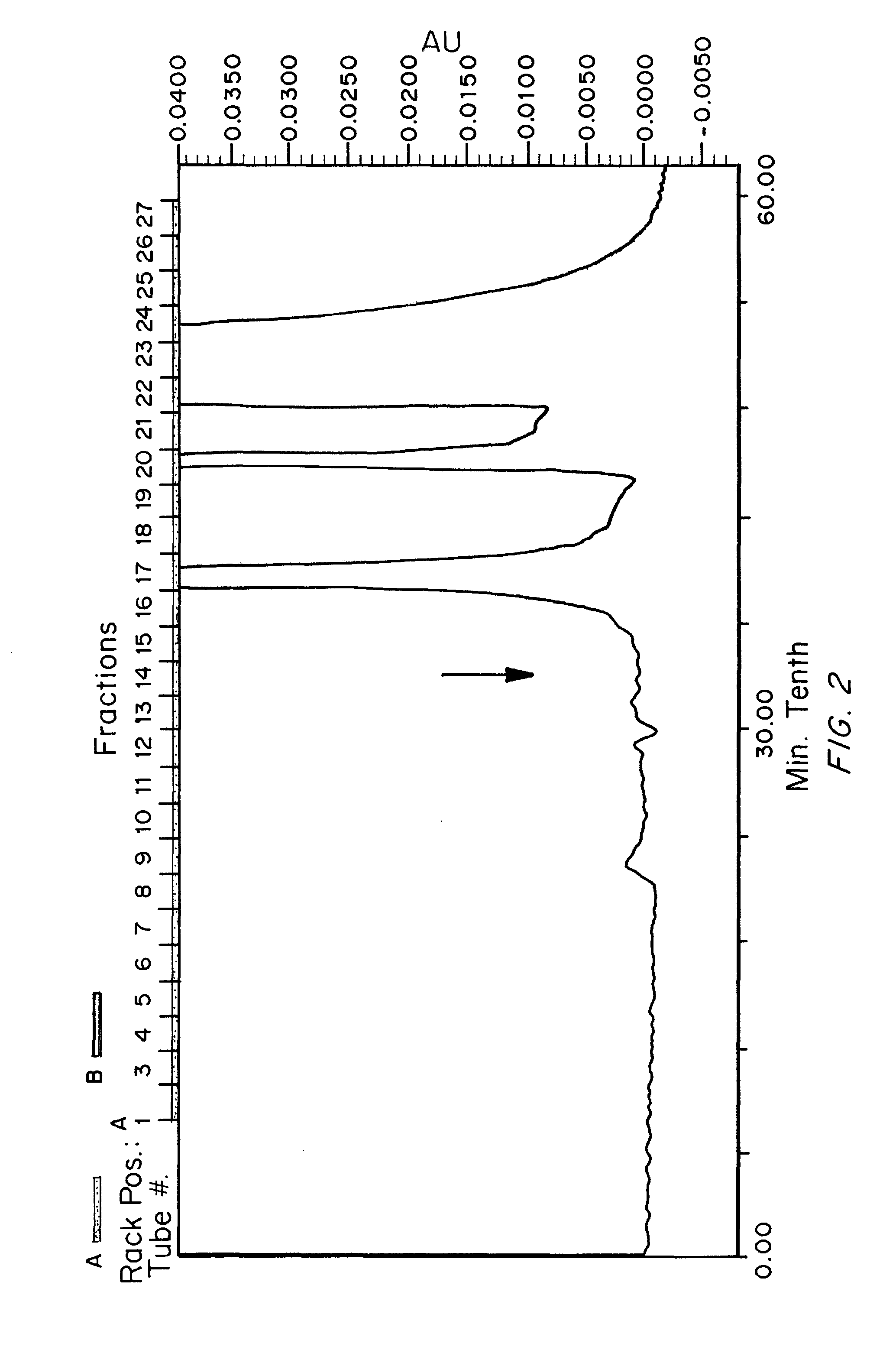
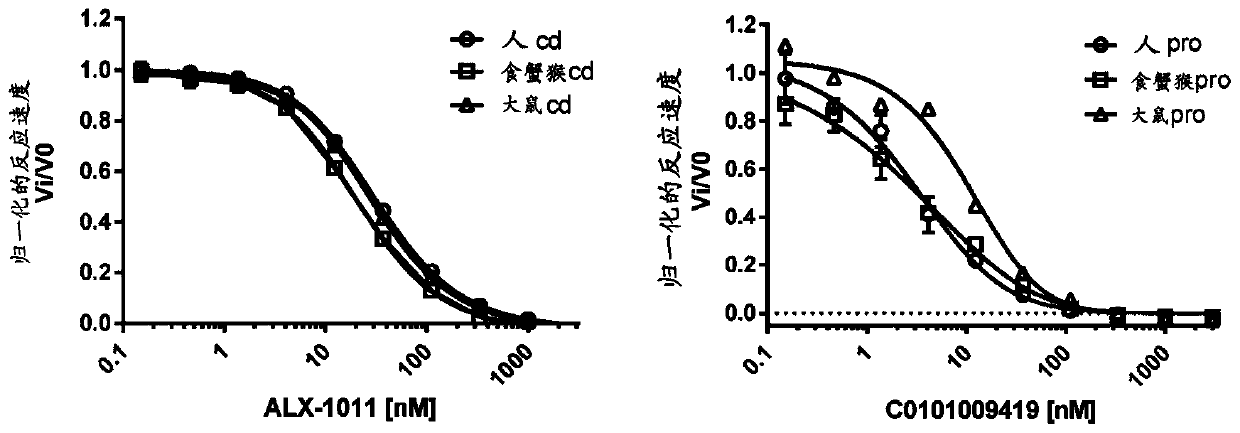
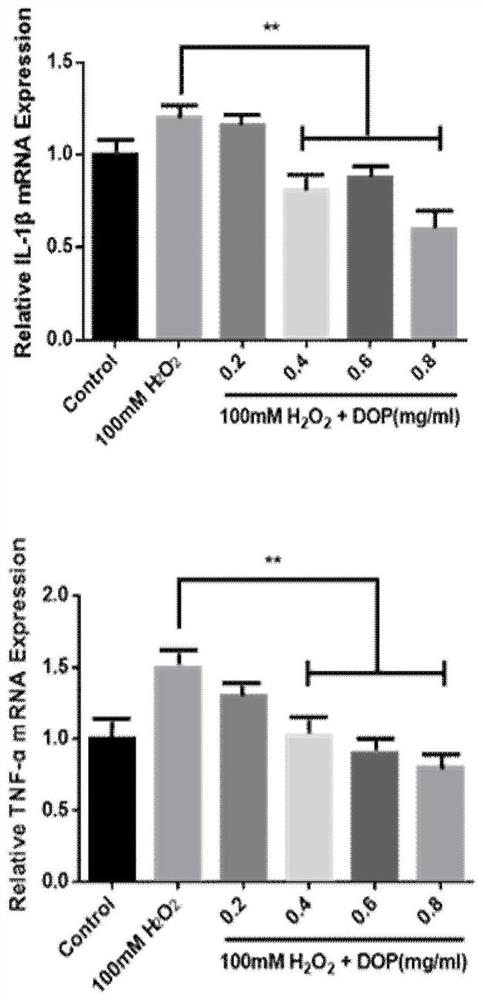
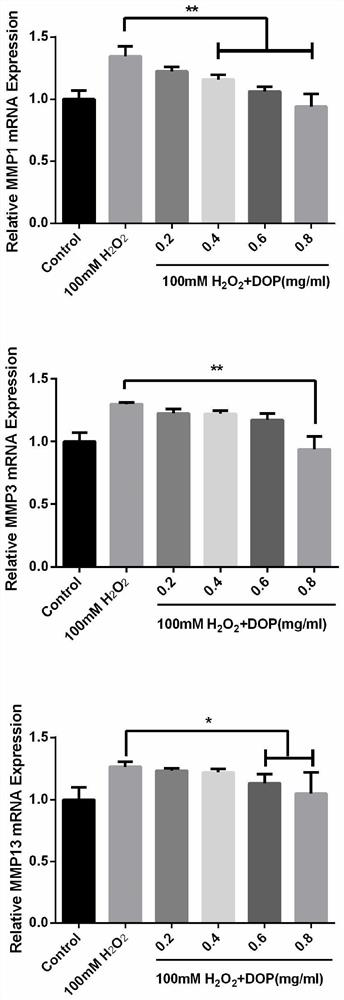
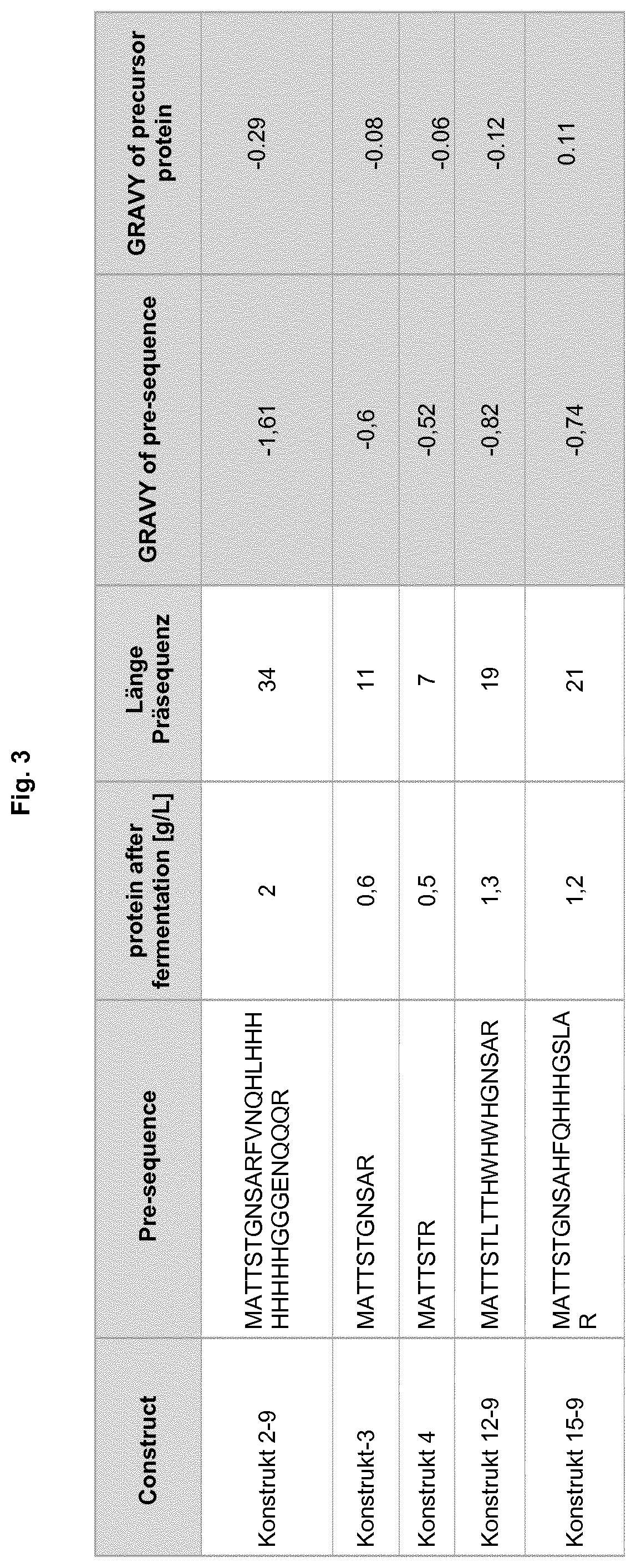
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Aggrecan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aggrecan (ACAN), also known as cartilage-specific proteoglycan core protein (CSPCP) or chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACAN gene. This gene is a member of the lectican (chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan) family. The encoded protein is an integral part of the extracellular matrix in cartilagenous tissue and it withstands compression in cartilage.
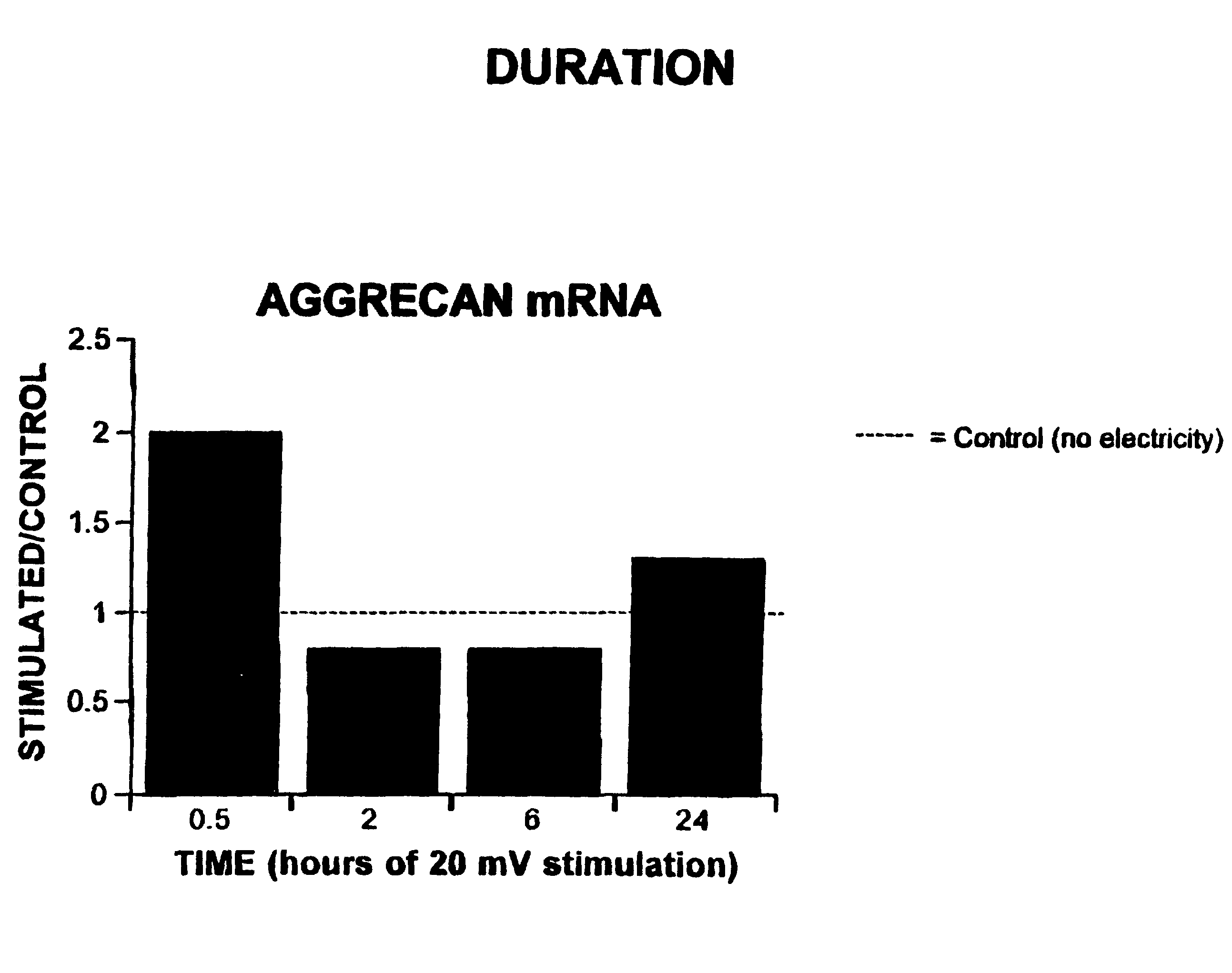
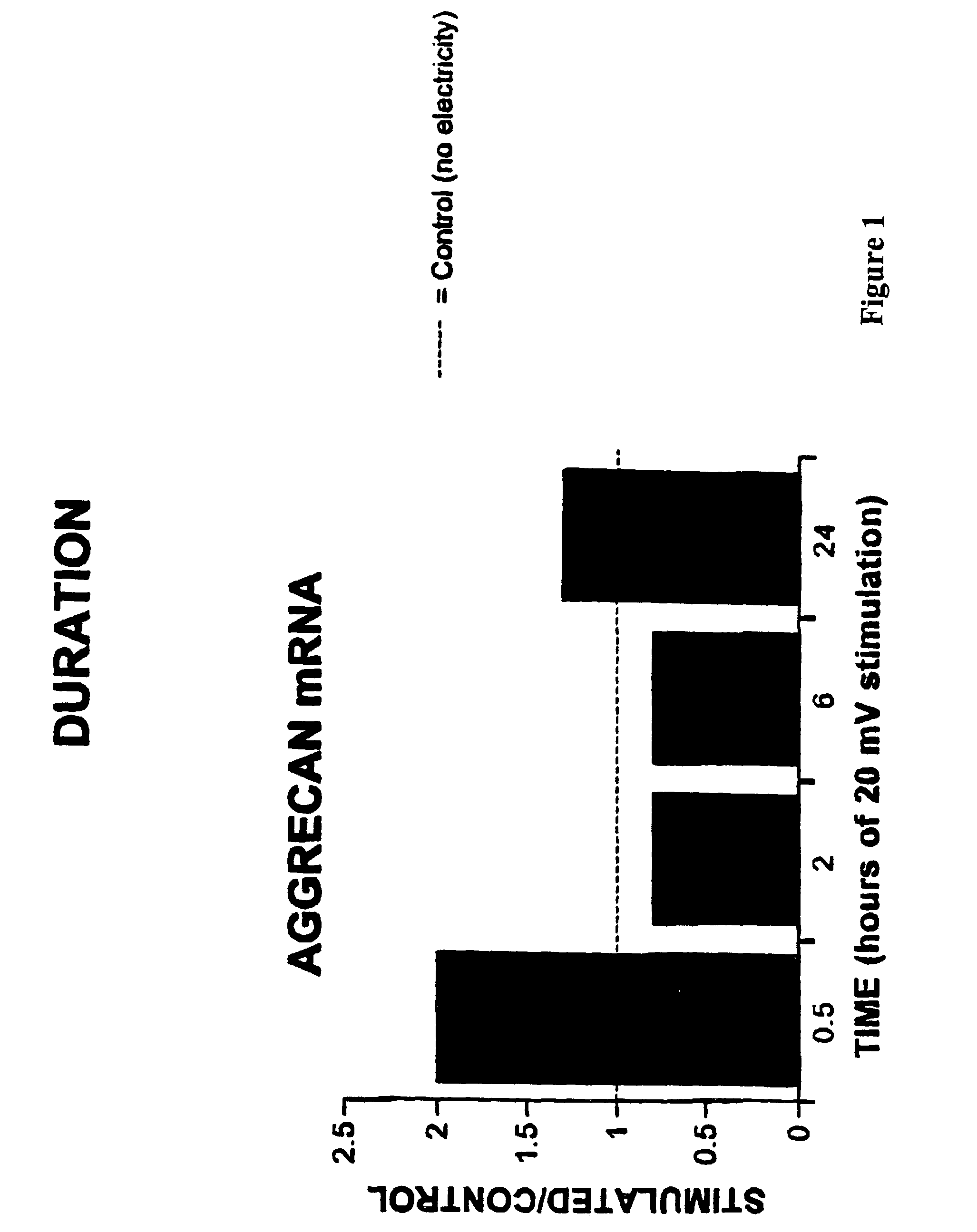
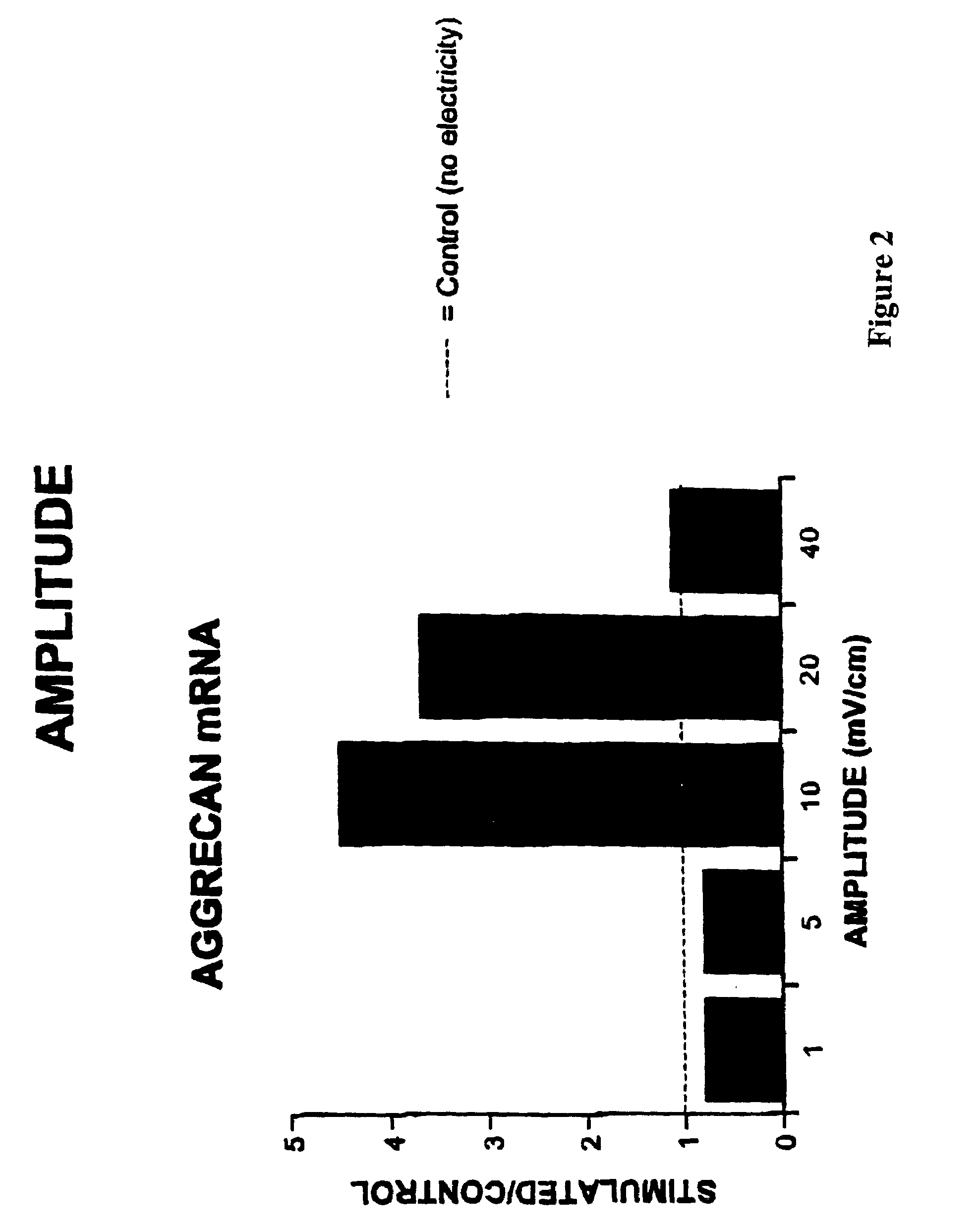
Regulation of aggrecan gene expression using specific and selective electrical and electromagnetic signals
Methods and devices for the regulation of aggrecan gene expression in cartilage cells via the application of fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals in the treatment of diseased or injured articular cartilage. By gene expression is meant the up regulation or down regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased cartilage tissue that include generating specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals that generate fields optimized for aggrecan gene expression and exposing cartilage tissue to the fields generated by specific and selective signals so as to regulate aggrecan gene expression in such cartilage tissue. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, cartilage injury, and cartilage defects.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
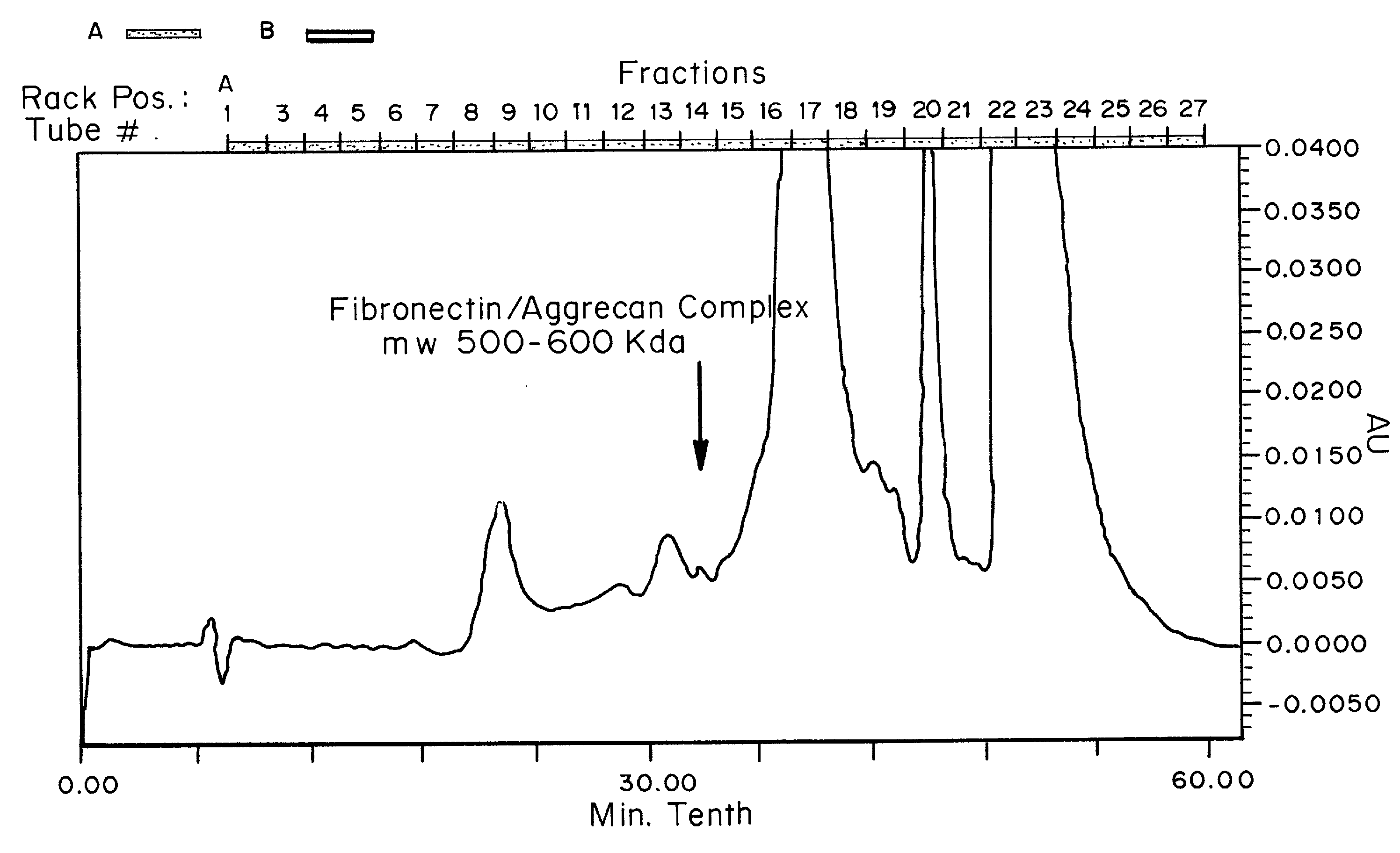
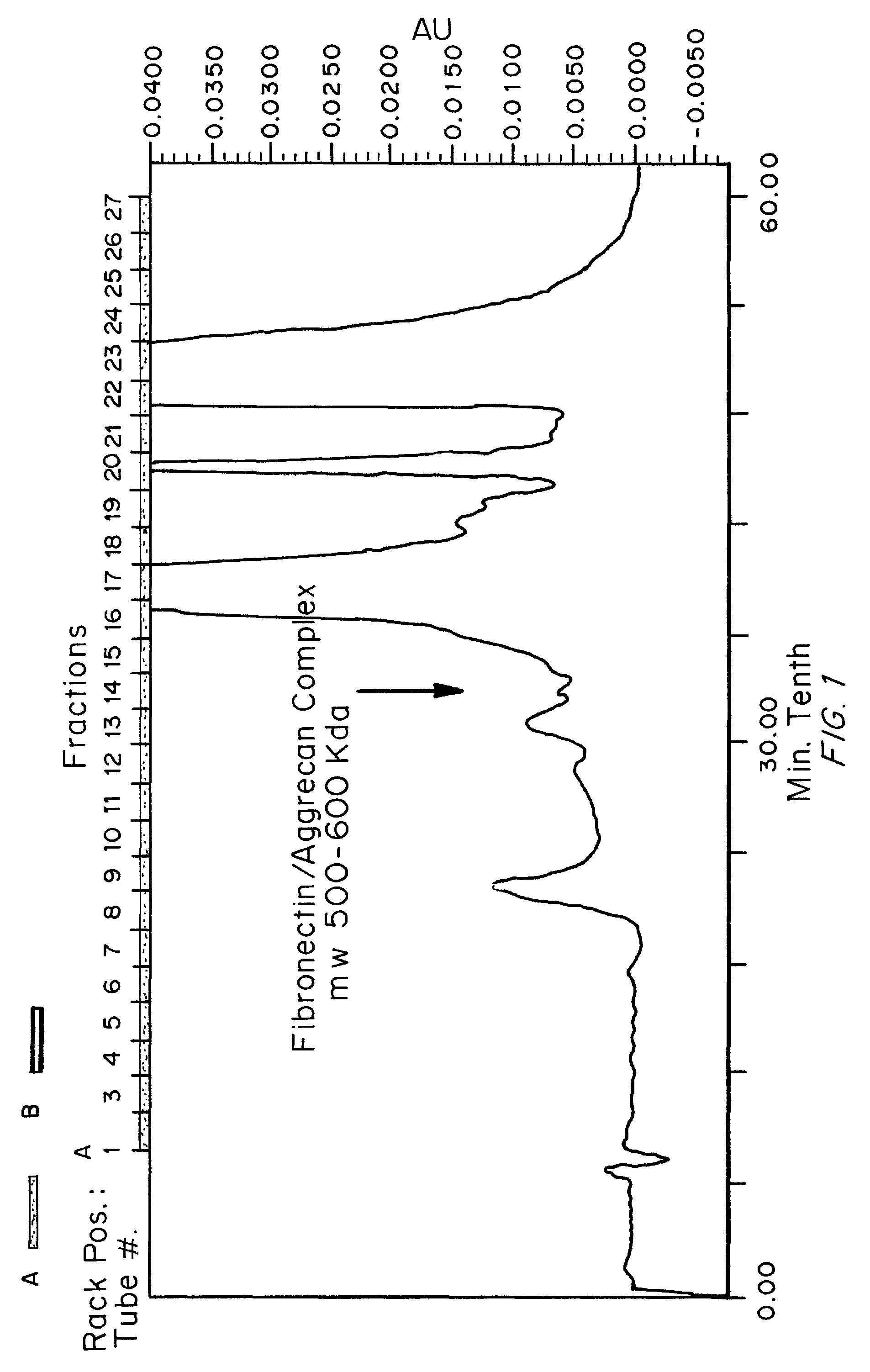
Biomarkers and methods for detecting and treating spinal and joint pain
ActiveUS20100098684A1Inhibit and reduce biological activityReduce formationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderJoint painSpinal column
Biomarkers, including isolated fibronectin-aggrecan complexes that correlate with spinal or joint pain and inflammation, and methods for their detection are provided. Also provided are methods for identifying treatment sites in the spine or joint for treatment of pain and inflammation by detecting the presence of, or increased levels of, fibronectin-aggrecan complexes. Methods for treating spinal or joint pain and inflammation are also provided.
Owner:CYTONICS CORP
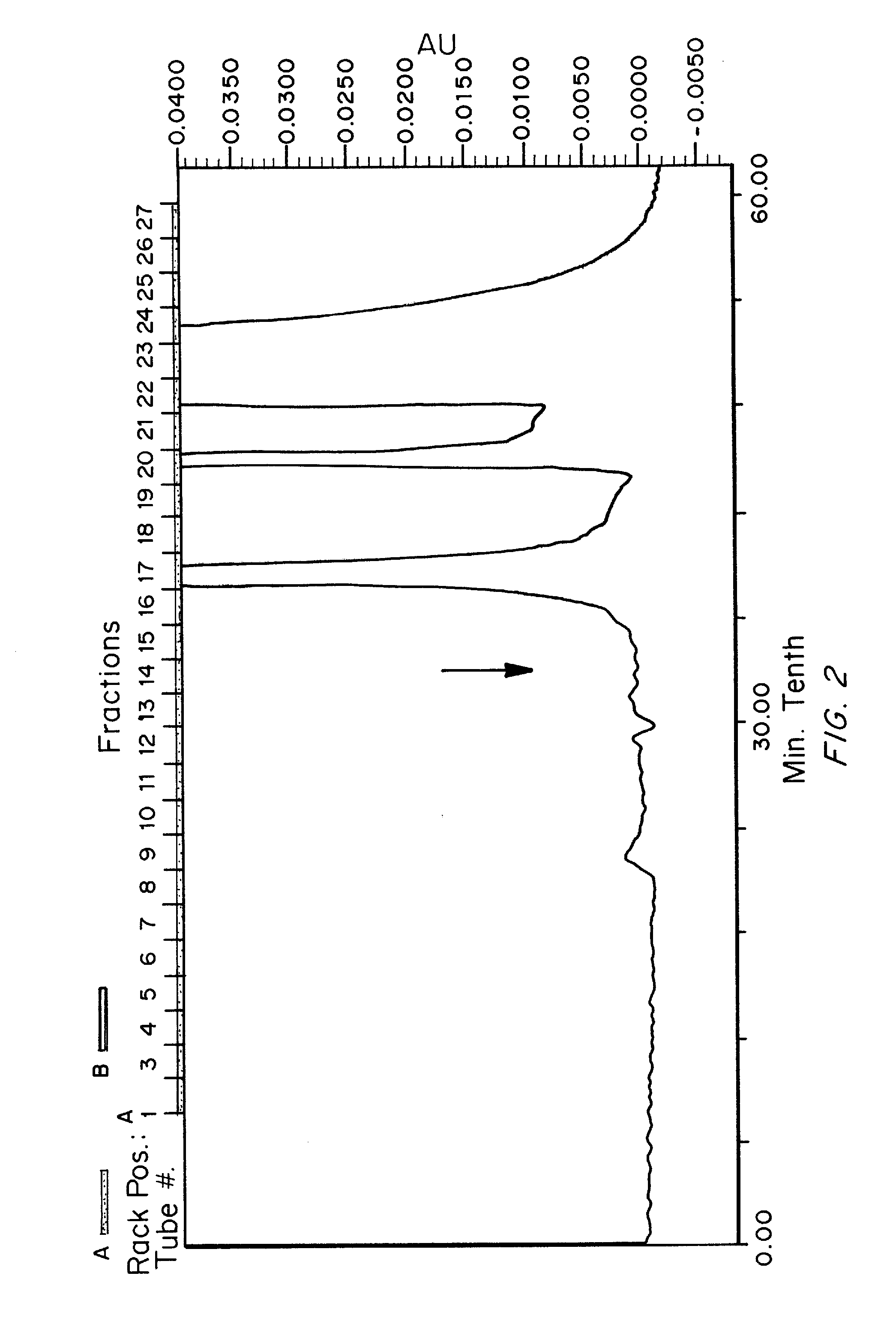
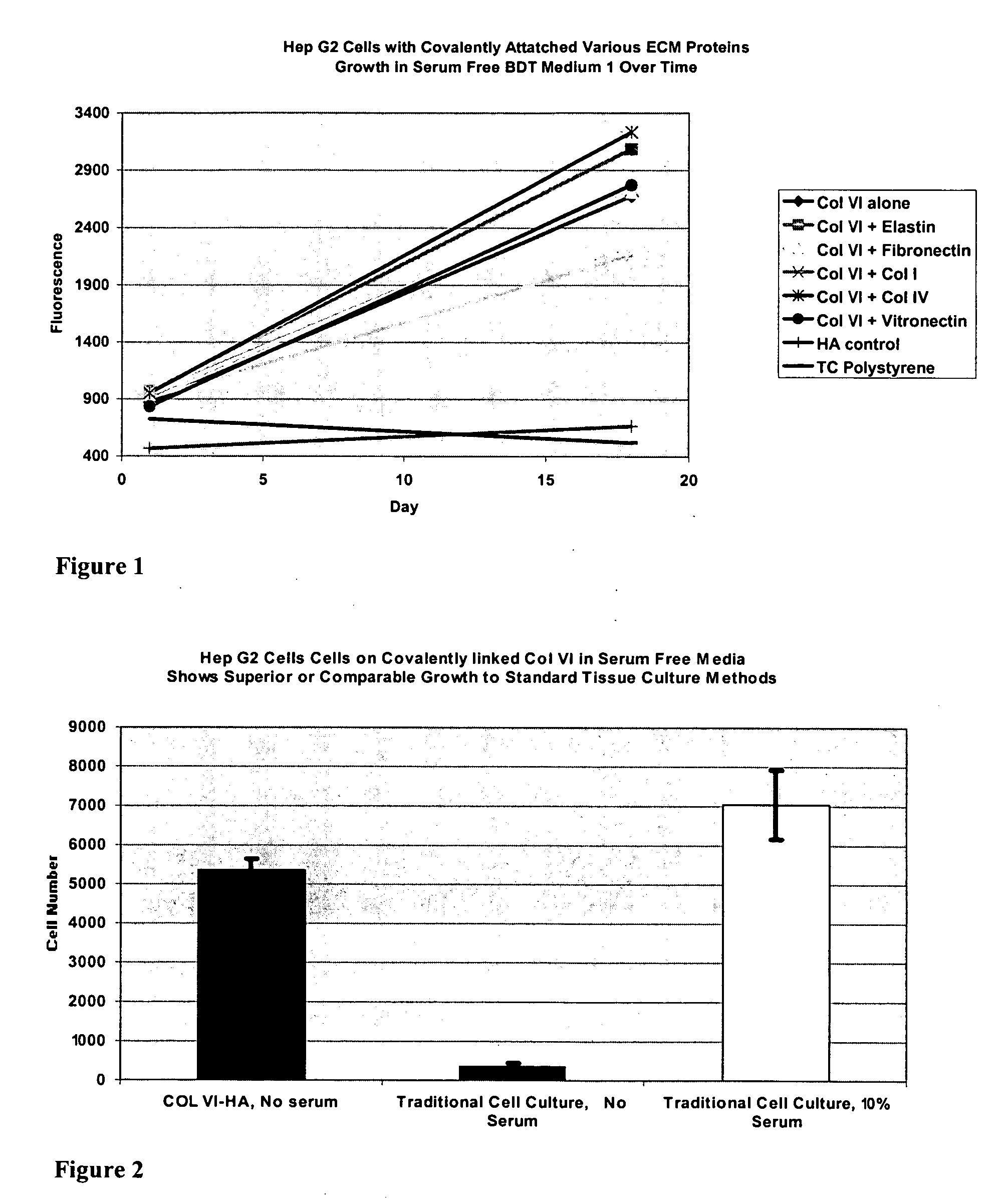
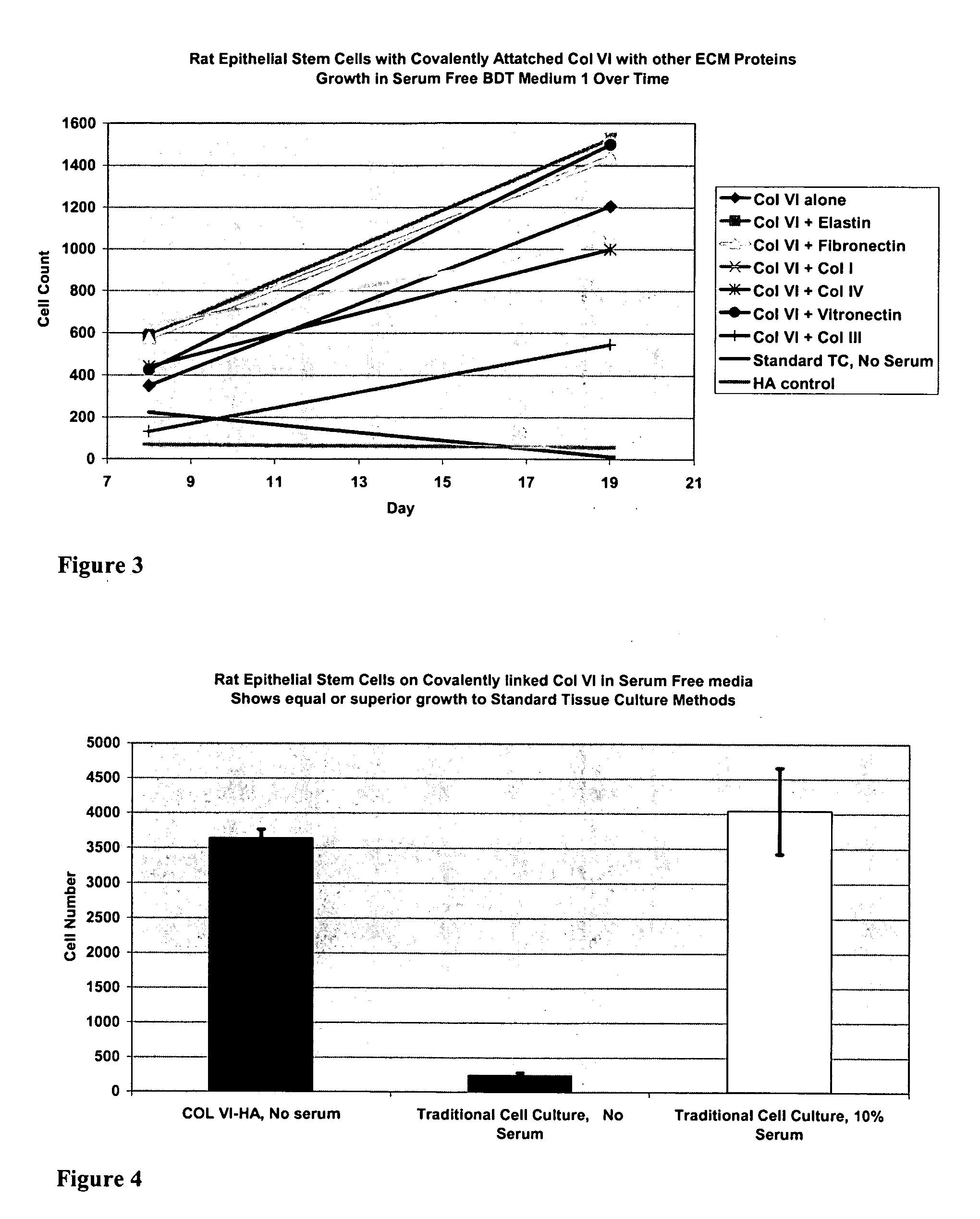
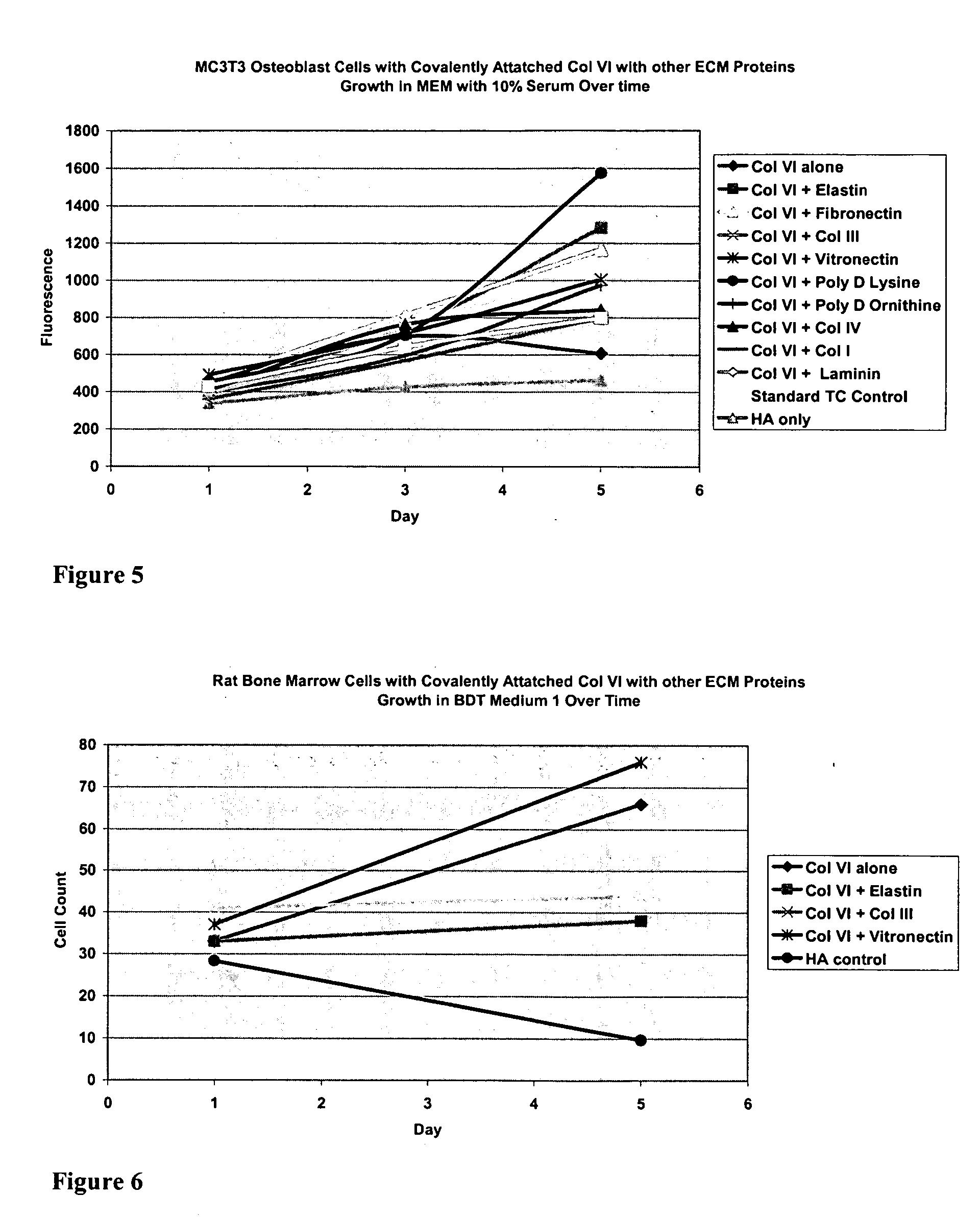
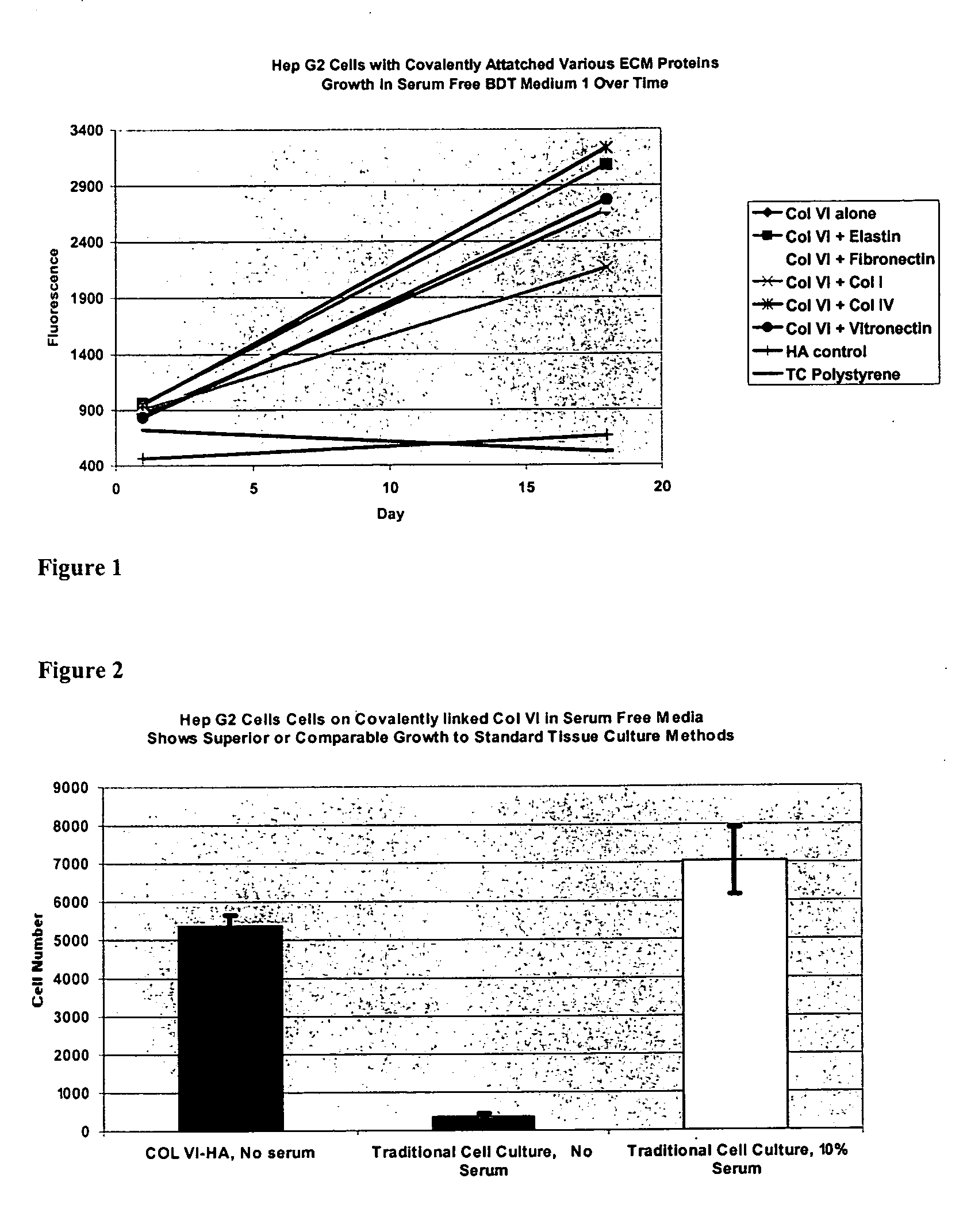
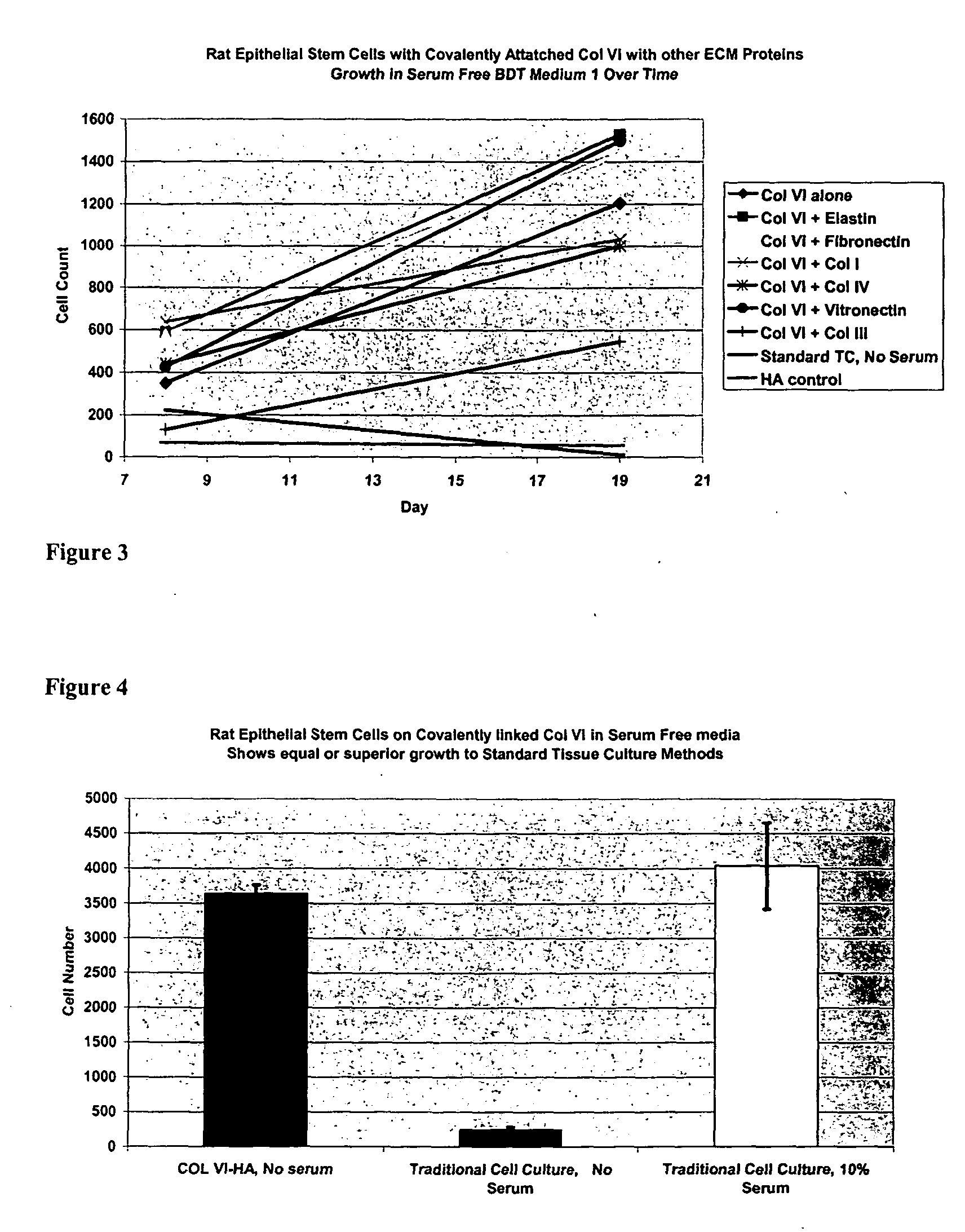
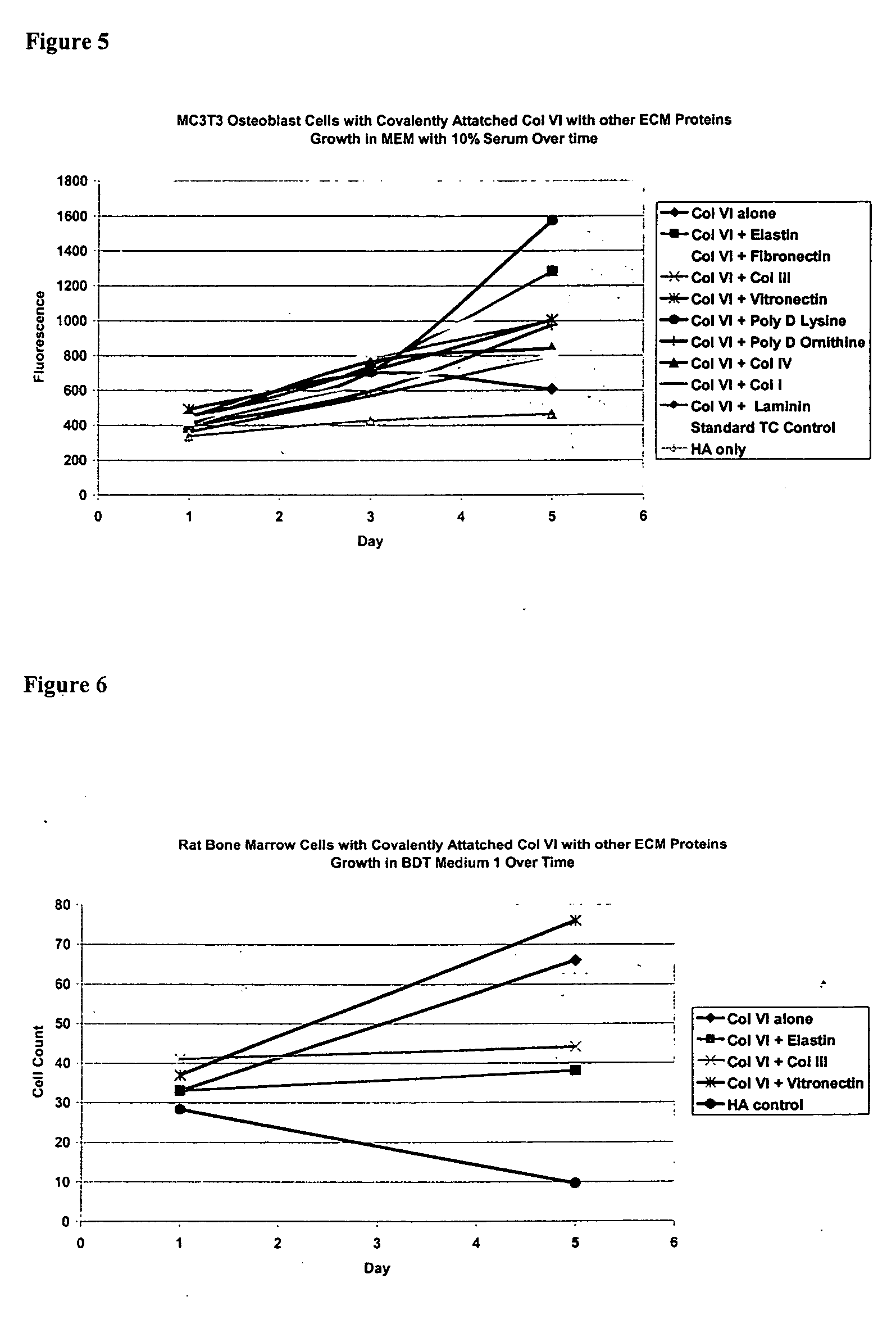
Covalently attached collagen VI for cell attachment and proliferation
Surfaces useful for cell culture comprise a support to which is bound a CAR material, and, bound to the CAR material, collagen VI or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof and, optionally, one or more other ECM proteins (or fragments or variants thereof) such as elastin, fibronectin, vitronectin, tenascin, laminin, entactin, aggrecan, decorin, collagen I, collagen III, and collagen IV. Also, optionally present on the surface is one or more polycationic polymers, such as poly-D-lysine or poly-D-ornithine. This surface is used in cell culture to promote cell attachment, survival, and / or proliferation of a number of different cell types such as (a) liver cells (e.g., HepG2 tumor cells, and a newly discovered line of rat liver epithelial stem cells) (b) osteoblasts, such as the murine cell line MC3T3 cell line and (c) primary bone marrow cells. Kits comprising the surfaces and additional reagents are also disclosed.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Covalently attached collagen VI for cell attachment and proliferation
InactiveUS20050058687A1Promote proliferationEasy SurvivalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCollagen VIPolymer
Surfaces useful for cell culture comprise a support to which is bound a CAR material, and, bound to the CAR material, collagen VI or a biologically active fragment or variant thereof and, optionally, one or more other ECM proteins (or fragments or variants thereof) such as elastin, fibronectin, vitronectin, tenascin, laminin, entactin, aggrecan, decorin, collagen I, collagen III, and collagen IV. Also, optionally present on the surface is one or more polycationic polymers, such as poly-D-lysine or poly-D-ornithine. This surface is used in cell culture to promote cell attachment, survival, and / or proliferation of a number of different cell types such as (a) liver cells (e.g., HepG2 tumor cells, and a newly discovered line of rat liver epithelial stem cells) (b) osteoblasts, such as the murine cell line MC3T3 cell line and (c) primary bone marrow cells. Kits comprising the surfaces and additional reagents are also disclosed.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
In vitro formation of congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques to identify anti-plaque therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's and Prion diseases
InactiveUS20020168753A1Test effectivenessCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderCongo redNeuroglycan C
Co-incubation of an amyloid protein with sulfated macromolecules as a method for the formation of amyloid plaques. The amyloid protein may be the beta-amyloid protein or the prion protein or the like. Amyoid plaque formation in one embodiment proceeds in vitro and desireably produces amyloid plaques that stain with Congo red and demonstrate a maltese-cross pattern when viewed under polarized light. The method also produces amyloid plaques that demonstrate an "amyloid star" appearance when viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Sulfated macromolecules include a sulfated proteoglycan selected from the group consisting of perlecan, ~220 kilodalton heparan sulfate proteoglyean, glypican, cerebroglycan, aggrecan, synaptoglycan (SV2PG), syndecan, N-syndecan (also known as syndecan-3), syndecan-1, syndecan-4, neurocan, phosphacan, decorin, biglycan, versican, amphiglycan, lumican, PG-M, PG-M (3), agrin, betaglycan, claustrin, brevican, appican, epican, neuroglycan-C, and fragments thereof. Thw sulfated macromolecule may be a sulfated glycosaminoglycan selected from the group consisting of heparin, heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, and fragments thereof. An in vivo assay is also presented for selecting a candidate therapeutic agent for inhibiting or disrupting amyloid plaque deposition or persistence. The assay includes a) pre-forming congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques in vitro following incubation of an amyloid protein and a selected sulfated macromolecule, b) using a first cannula and osmotic pump to continuously infuse for a selected duration the pre-formed congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques into a tissue or organ, c) changing the first cannulae and osmotic pump with a second cannulae and osmotic pump to administer the candidate therapeutic, and d) detecting the candidate therapeutic's ability to disrupt, reduce, or eliminate congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaque deposition / persistence in the tissue or organ.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Synergistic herbal composition for treatment of rheumatic and musculo-skeletal disorders (RMSDS)
InactiveUS20120021077A1Reduce denaturationReduce releaseBiocideAntipyreticHerbal preparationsDisease
The present invention deals with a synergistic herbal composition useful for treatment of rheumatic and musculo-skeletal disorders (RMSDs) comprising a base formulation (50-60%) and plant parts and / or extracts of the plant (40-50%) selected from the group consisting of Withania somnifera, Tribulus terrestris, Phyllanthus emblica and Boswellia serrata optionally along with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The herbal formulation is capable of causing simultaneous long term decrease in glycosaminoglycan (GAG) release and aggrecan by cartilage explants resulting in reduction of pain, inflammation, stiffness and low degeneration of bones, joints, muscles and other connective tissues. The present invention further deals with a process for the preparation of the said herbal formulation and a method of treating RMSDs using the formulation up to a high safety level and stable for a long durations.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Proteases and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050260733A1Altering cleavage activityCleavage activity can be modulatedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProteinase activityProteolysis
The present invention features methods of using ADAMTS-8 proteins or their functional derivatives to cleave aggrecan or other proteoglycan molecules. The present invention also features methods for identifying ADAMTS-8 modulators that are capable of inhibiting or enhancing ADAMTS-8 proteolytic activities. In addition, the present invention features pharmaceutical compositions comprising ADAMTS-8 proteins or their derivatives or modulators. These pharmaceutical compositions can be used to treat diseases that are characterized by deficiencies or abnormalities in proteoglycan cleavage or metabolism.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Soluble fgfr3 decoys for treating skeletal growth disorders
PendingUS20210009657A1Easy genetic manipulationReduce contentPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousDisease
Owner:THERACHON HLDG GMBH +3
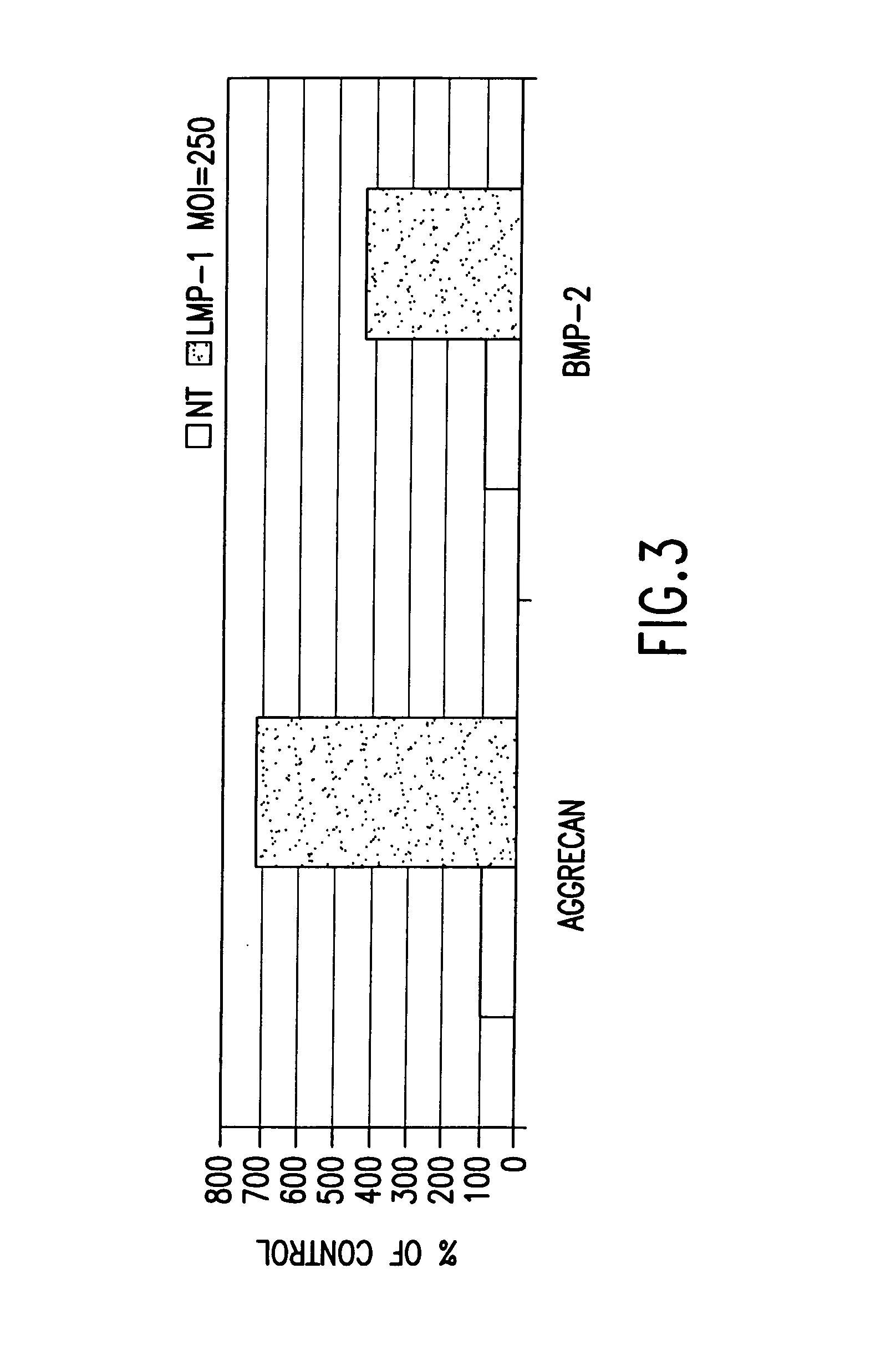
Methods of inducing or increasing the expression of proteoglycans such as aggrecan in cells
Methods of inducing the expression of a proteoglycan such as aggrecan in a cell are described. A method is described which includes transfecting a cell with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein operably linked to a promoter. The LIM mineralization protein can be rLMP, hLMP-1, hLMP-1s, or hLMP-3. Transfection maybe accomplished ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid. The method can be used to induce proteoglycan synthesis in osseous cells or to stimulate proteoglycan and / or collagen production in cells capable of producing proteoglycan and / or collagen (e.g., intervertebral disc cells including cells of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus).
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Mesenchymal stem cell induced differentiation and coating culture dish preparation
InactiveCN110241014AEfficient depositionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlcian blue stainUmbilical cord
The invention discloses mesenchymal stem cell induced differentiation and coating culture dish preparation. An agarose gel electrophoresis result shows that a culture group Aggrecan coated with no culture dish and type II collagen have no obvious expression, a group Aggrecan coated with a culture dish and type II collagen have obvious expression, it illustrates that the group coated with the culture dish has obvious expression of a cartilage marker, an xylan coated culture dish can be used for culturing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and inducing the mesenchymal stem cells into cartilage differentiation. An Aleian blue dyeing result shows that a control group is Aleian blue dying negative, the xylan group and the positive group are Aleian blue dyeing positive, it illustrates that the xylan group and the positive group both have obvious cartilage matrix protein glycan deposition, and it indicates that the xylan group and the positive group culture media can effectively induce human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into cartilage differentiation.
Owner:南京温博生物科技有限公司
Kits for biomarker detection and treatment selection
ActiveUS8338572B2Inhibit and reduce biological activityReduce formationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsJoint painBiomarker (petroleum)
Biomarkers, including isolated fibronectin-aggrecan complexes that correlate with spinal or joint pain and inflammation, and methods for their detection are provided. Also provided are methods for identifying treatment sites in the spine or joint for treatment of pain and inflammation by detecting the presence of, or increased levels of, fibronectin-aggrecan complexes. Methods for treating spinal or joint pain and inflammation are also provided.
Owner:CYTONICS CORP
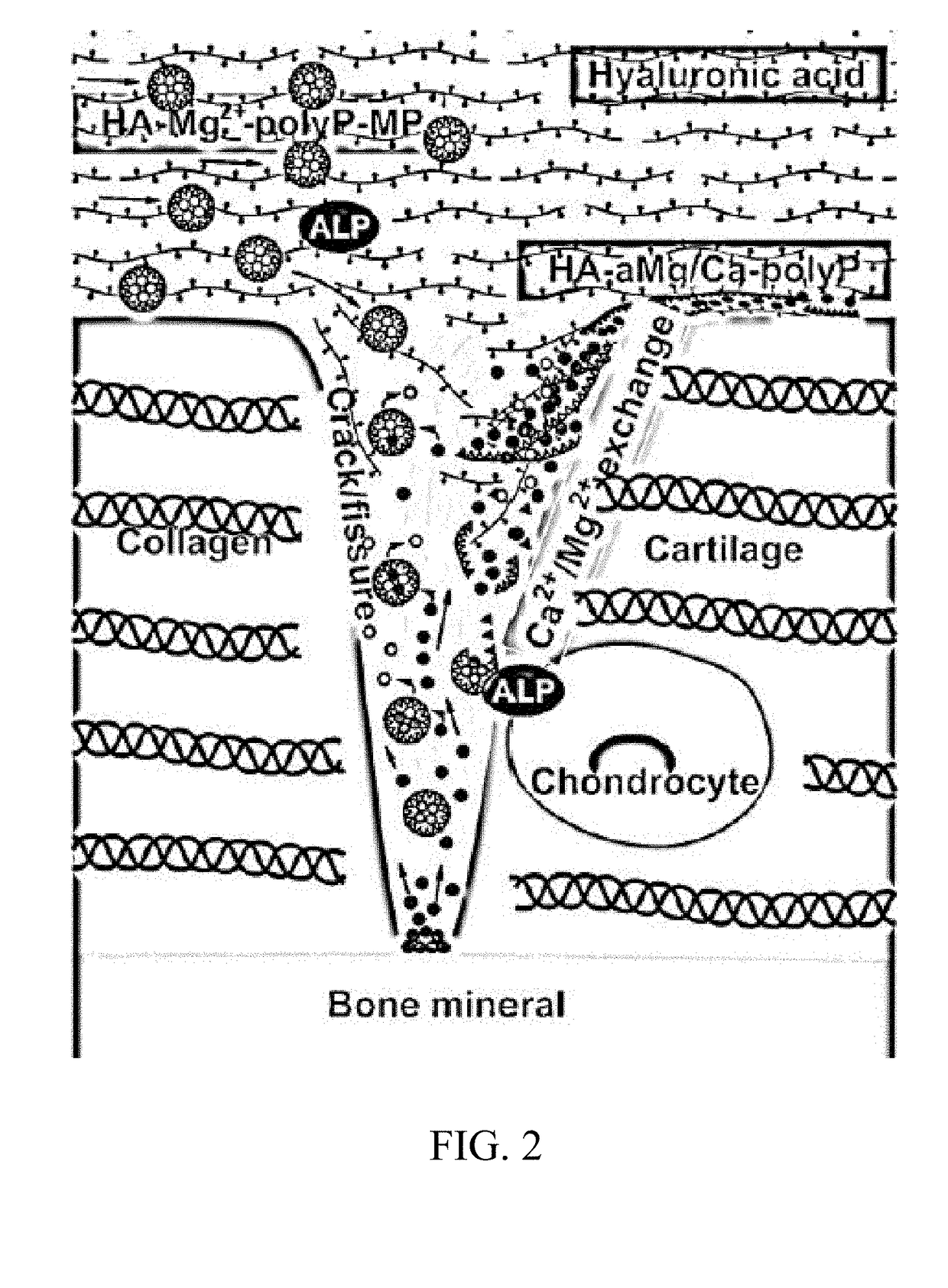
Amorphous hyaluronic acid-magnesium/calcium polyphosphate microparticles for cartilage regeneration and repair
InactiveUS20180015205A1Improve adhesionUpregulates expressionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBiomechanicsIon calcium
This invention concerns a biomimetic material based on energy-rich amorphous magnesium polyphosphate (Mg-polyP) microparticles that enhance cartilage synthesis and regeneration. One preferred formulation of the inventive material is a hyaluronic acid-Mg / Ca-polyP paste that can be produced from a water-soluble salt of polyP and water-soluble hyaluronic acid in the presence of water-insoluble / nearly insoluble calcium carbonate. Surprisingly, the inventor found that this cartilage-like material comprising amorphous Mg / Ca-polyP microparticles promotes the adhesion of chondrocytes and strongly upregulates the expression of the chondrocyte marker genes encoding alkaline phosphatase, collagen type 3A1, aggrecan and Sox9. The material through scavenging calcium ions (Mg2+ / Ca2+ exchange) and binding of the calcium-polyP to hyaluronic acid shows biomechanical properties, comparable to cartilage and thus can be used for prevention of calcium crystal formation in the synovial fluid and treatment of joint dysfunctions caused by osteoarthritis.
Owner:NANOTECMARIN
Methods of inducing or increasing the expression of proteoglycans such as aggrecan in cells
InactiveUS20070134218A1Prevent mineralizationDecrease osteocalcin productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideEukaryotic plasmids
Methods of inducing the expression of a proteoglycan such as aggrecan in a cell are described. A method is described which includes transfecting a cell with an isolated nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a LIM mineralization protein operably linked to a promoter. The LIM mineralization protein can be rLMP, hLMP-1, hLMP-1s, or hLMP-3. Transfection maybe accomplished ex vivo or in vivo by direct injection of virus or naked DNA, or by a nonviral vector such as a plasmid. The method can be used to induce proteoglycan synthesis in osseous cells or to stimulate proteoglycan and / or collagen production in cells capable of producing proteoglycan and / or collagen (e.g., intervertebral disc cells including cells of the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus).
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
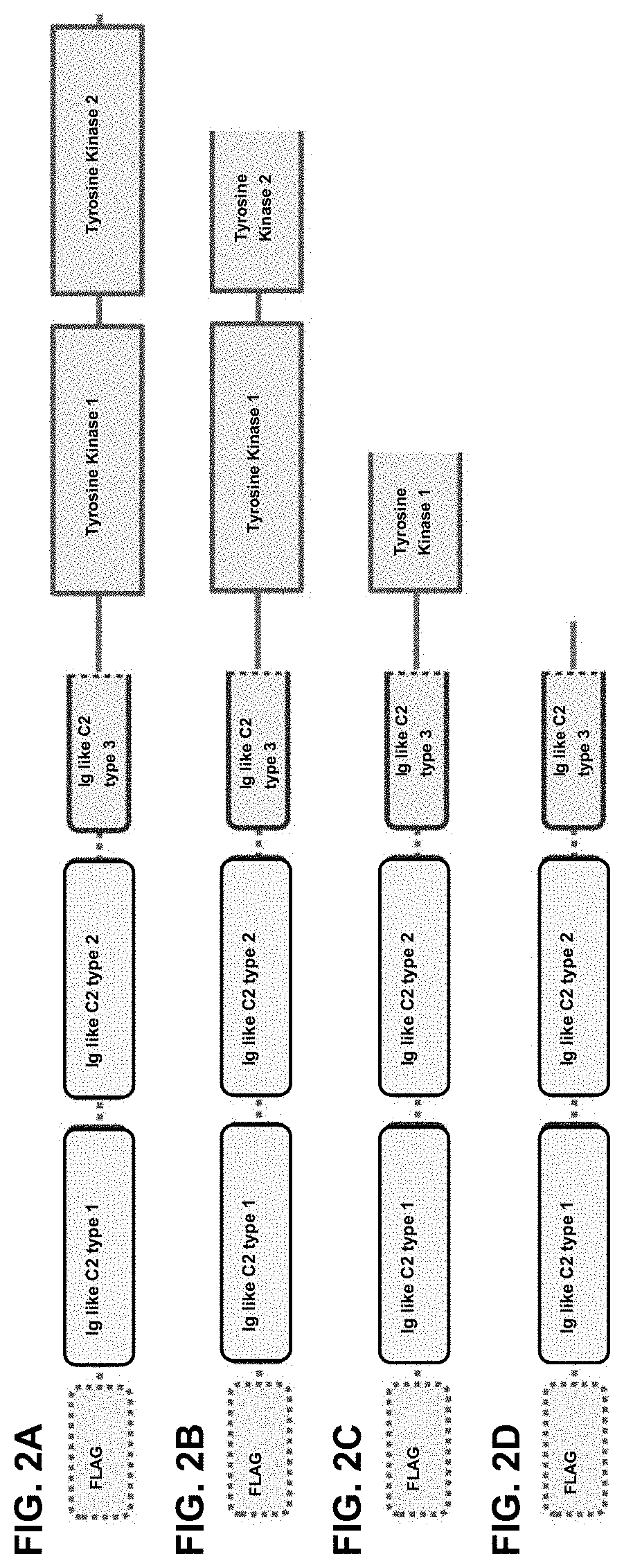
Aggrecan binding immunoglobulins
ActiveUS20200140532A1Good curative effectIncrease the number ofAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPharmaceutical drugIntravenous gammaglobulin
The present invention relates to immunoglobulins that specifically bind Aggrecan and more in particular to polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding such polypeptides; to methods for preparing such polypeptides; to compositions and in particular to pharmaceutical compositions that comprise such polypeptides, for prophylactic, therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. In particular, the immunoglobulins of the present invention inhibit the activity of Aggrecan.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH +1
ADAMTS-8 proteases and uses thereof
The present invention features methods of using ADAMTS-8 proteins or their functional derivatives to cleave aggrecan or other proteoglycan molecules. The present invention also features methods for identifying ADAMTS-8 modulators that are capable of inhibiting or enhancing ADAMTS-8 proteolytic activities. In addition, the present invention features pharmaceutical compositions comprising ADAMTS-8 proteins or their derivatives or modulators. These pharmaceutical compositions can be used to treat diseases that are characterized by deficiencies or abnormalities in proteoglycan cleavage or metabolism.
Owner:WYETH LLC
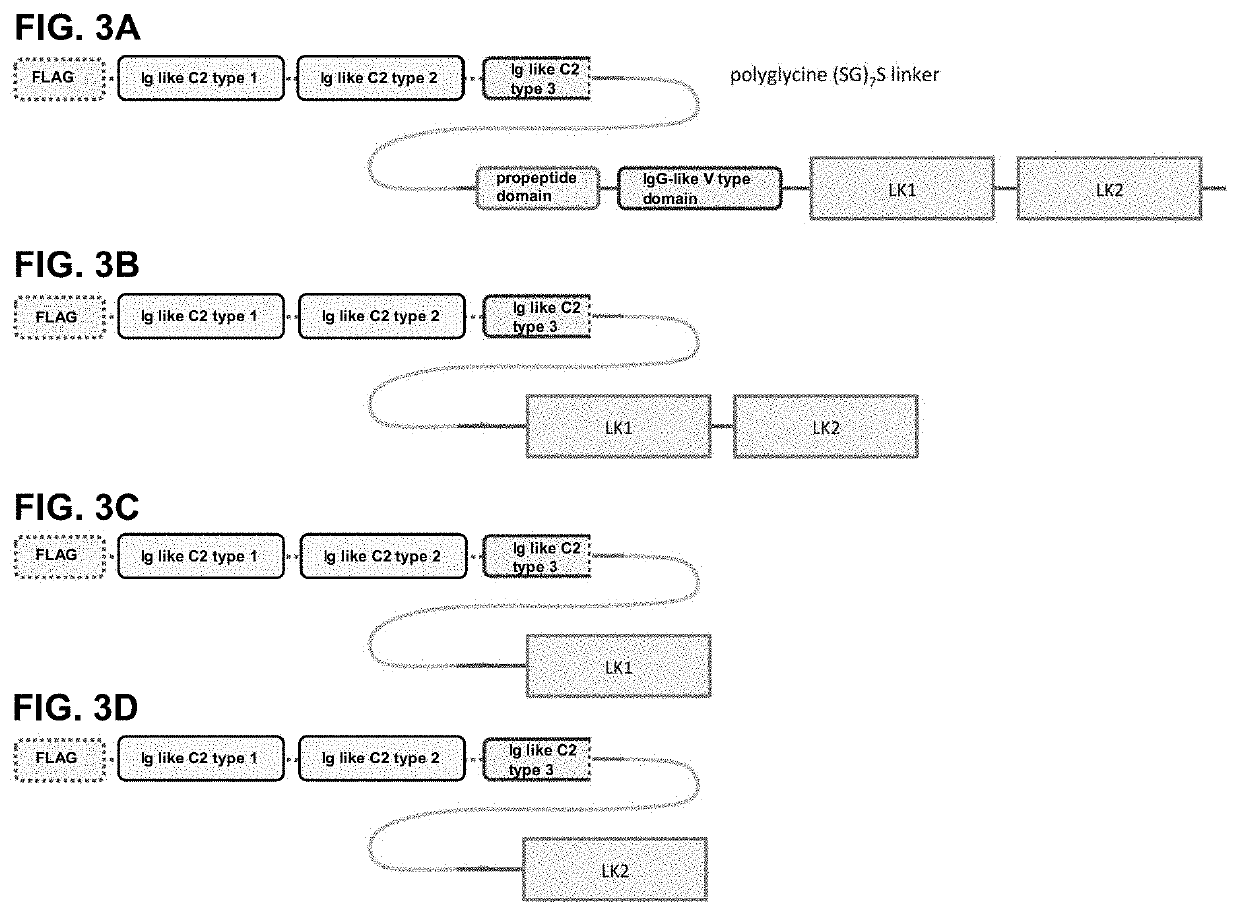
Polypeptides binding adamts5, mmp13 and aggrecan
PendingUS20210008160A1Improve stabilityLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPharmaceutical drugGlobulin
The present invention relates to polypeptides binding Aggrecan as well as ADAMTS5 and / or MMP13, more in particular to polypeptides that comprise or essentially consist of immunoglobulins binding Aggrecan as well as immunoglobulins binding ADAMTS5 and / or immunoglobulins binding MMP13 (also referred to herein as “polypeptides of the invention”, and “immunoglobulin(s) of the invention”, respectively). The invention also relates to constructs comprising such immunoglobulins, such as immunoglobulin single variable domains (ISVDs) or polypeptides as well as nucleic acids encoding such immunoglobulins or polypeptides (also referred to herein as “nucleic acid(s) of the invention”; to methods for preparing such immunoglobulins, polypeptides and constructs; to host cells expressing or capable of expressing such immunoglobulins or polypeptides; to compositions, and in particular to pharmaceutical compositions, that comprise such immunoglobulins, polypeptides, constructs, nucleic acids and / or host cells; and to uses of immunoglobulins, polypeptides, constructs, nucleic acids, host cells and / or compositions, in particular for prophylactic and / or therapeutic purposes, such as the prophylactic and / or therapeutic purposes mentioned herein. Other aspects, embodiments, advantages and applications of the invention will become clear from the further description herein.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
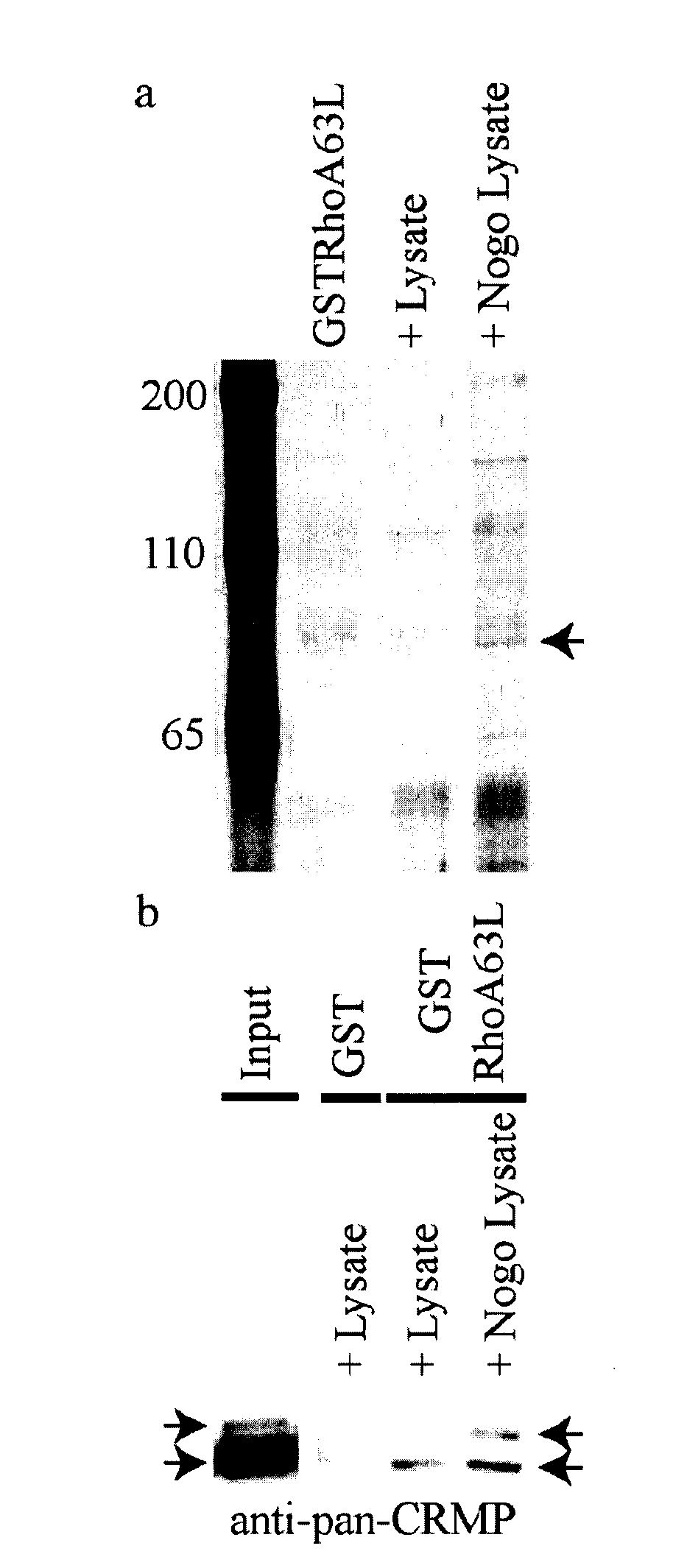
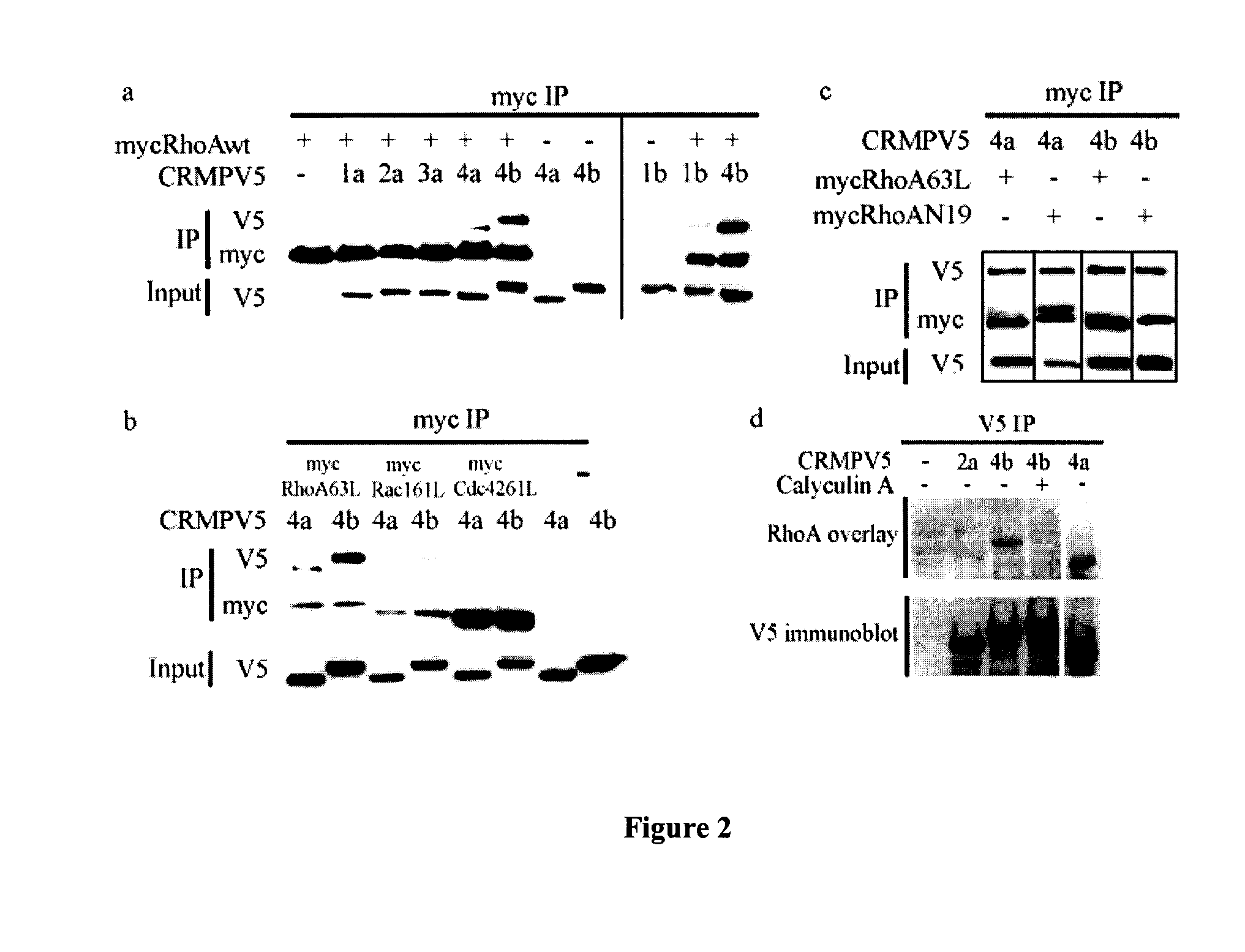
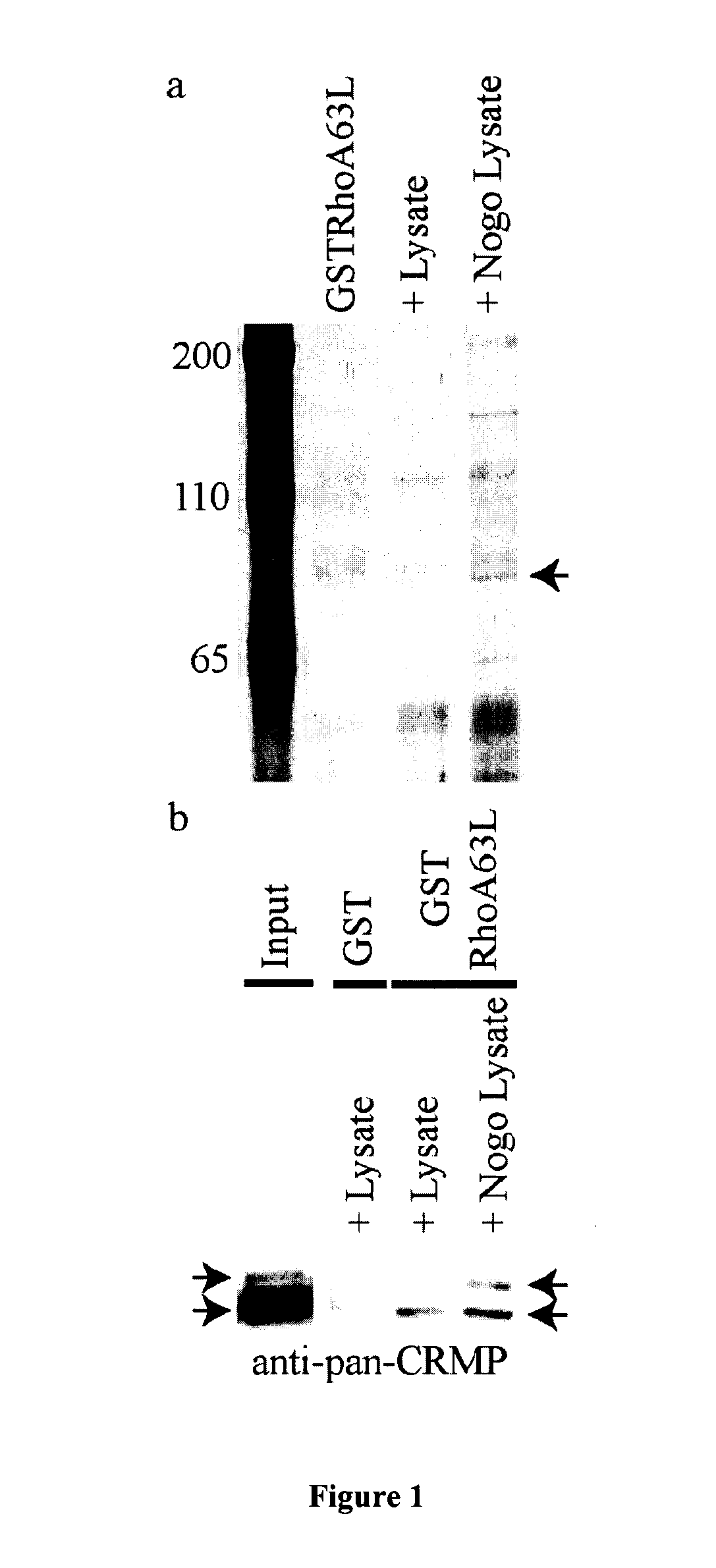
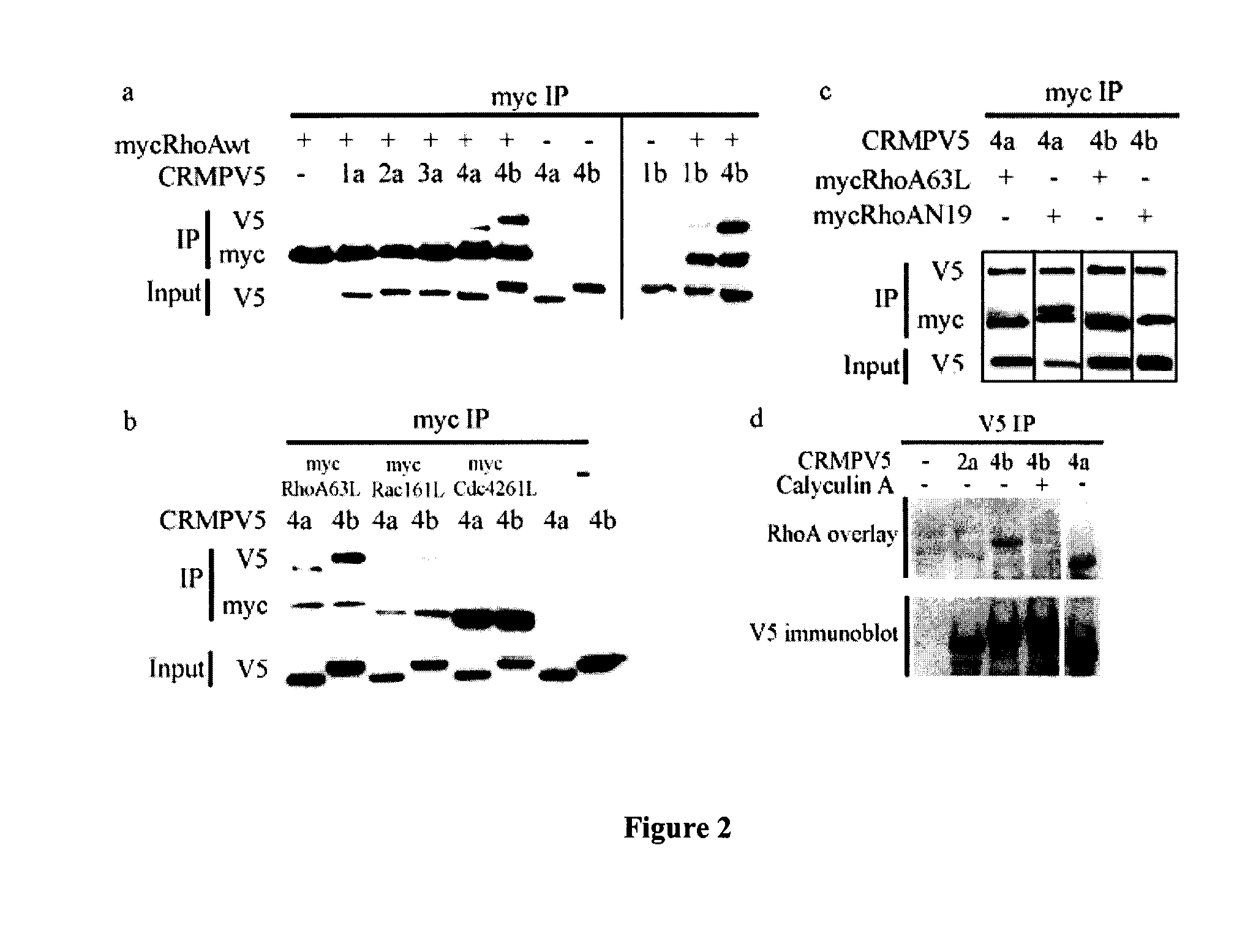
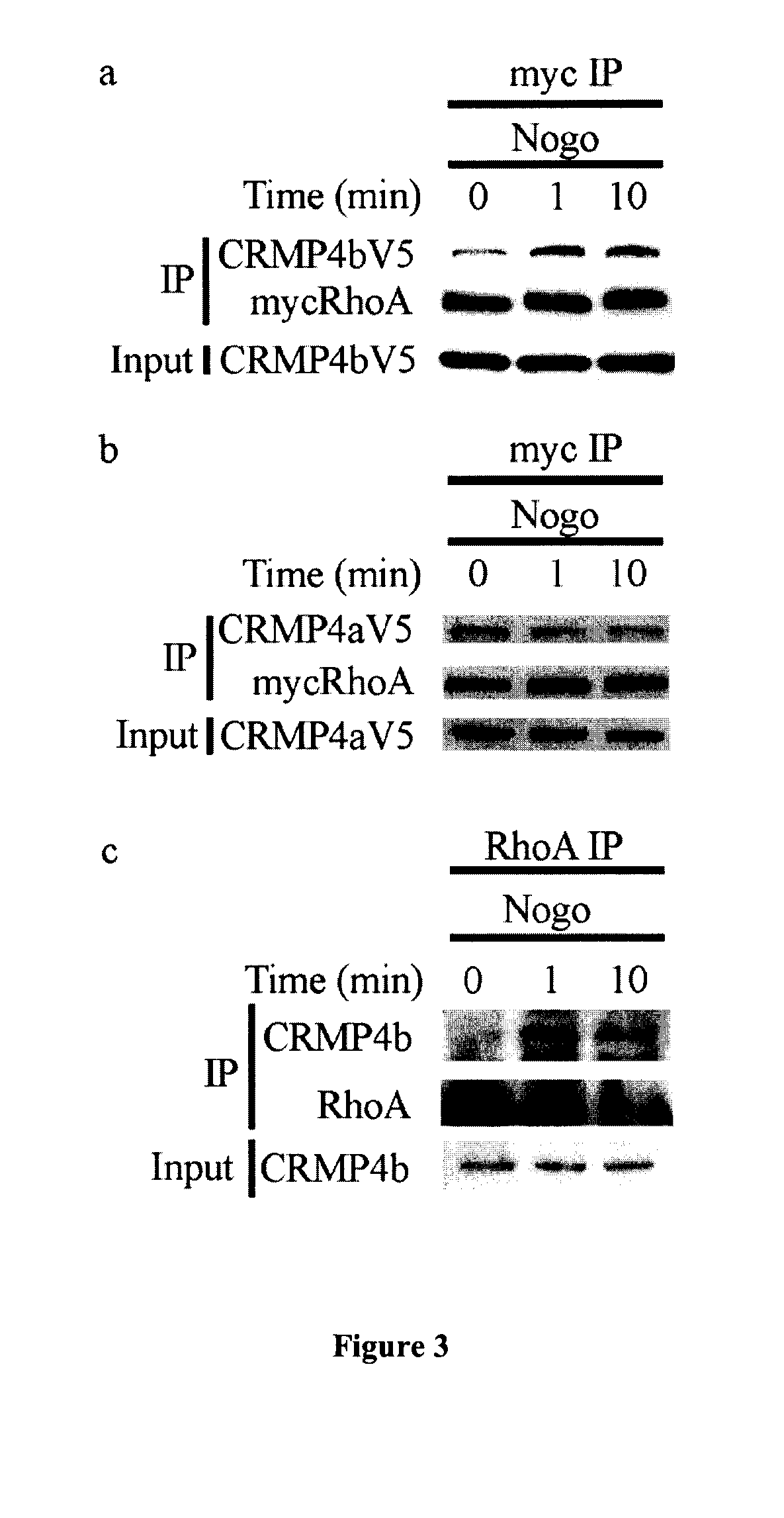
Identification of Crmp4 as a Convergent Regulator of Axon Outgrowth Inhibition
InactiveUS20090048169A1Promote regenerationCompound screeningNervous disorderCytoskeletonCo localization
The present invention relates to the identification of the cytosolic phosphoprotein CRMP4b as a protein that physically and functionally interacts with RhoA to mediate neurite outgrowth inhibition. siRNA-mediated knockdown of CRMP4 promotes neurite outgrowth on myelin substrates indicating a critical role for CRMP4 in neurite outgrowth inhibition. Disruption of CRMP4b-RhoA binding with a competitive inhibitor attenuates neurite outgrowth inhibition on myelin and aggrecan substrates. Stimulation of neuronal growth cones with Nogo leads to co-localization of CRMP4b and RhoA at discrete regions within the actin-rich central and peripheral domains of the growth cone indicative of a potential function in cytoskeletal rearrangements during neurite outgrowth inhibition. Together these data indicate that a RhoA-CRMP4b complex forms in response to inhibitory challenges in the growth cone environment and regulate cytoskeletal dynamics at distinct sites necessary for axon outgrowth inhibition. Competitive inhibition of CRMP4b-RhoA binding suggests a novel, highly specific therapeutic avenue for promoting regeneration following CNS injury.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
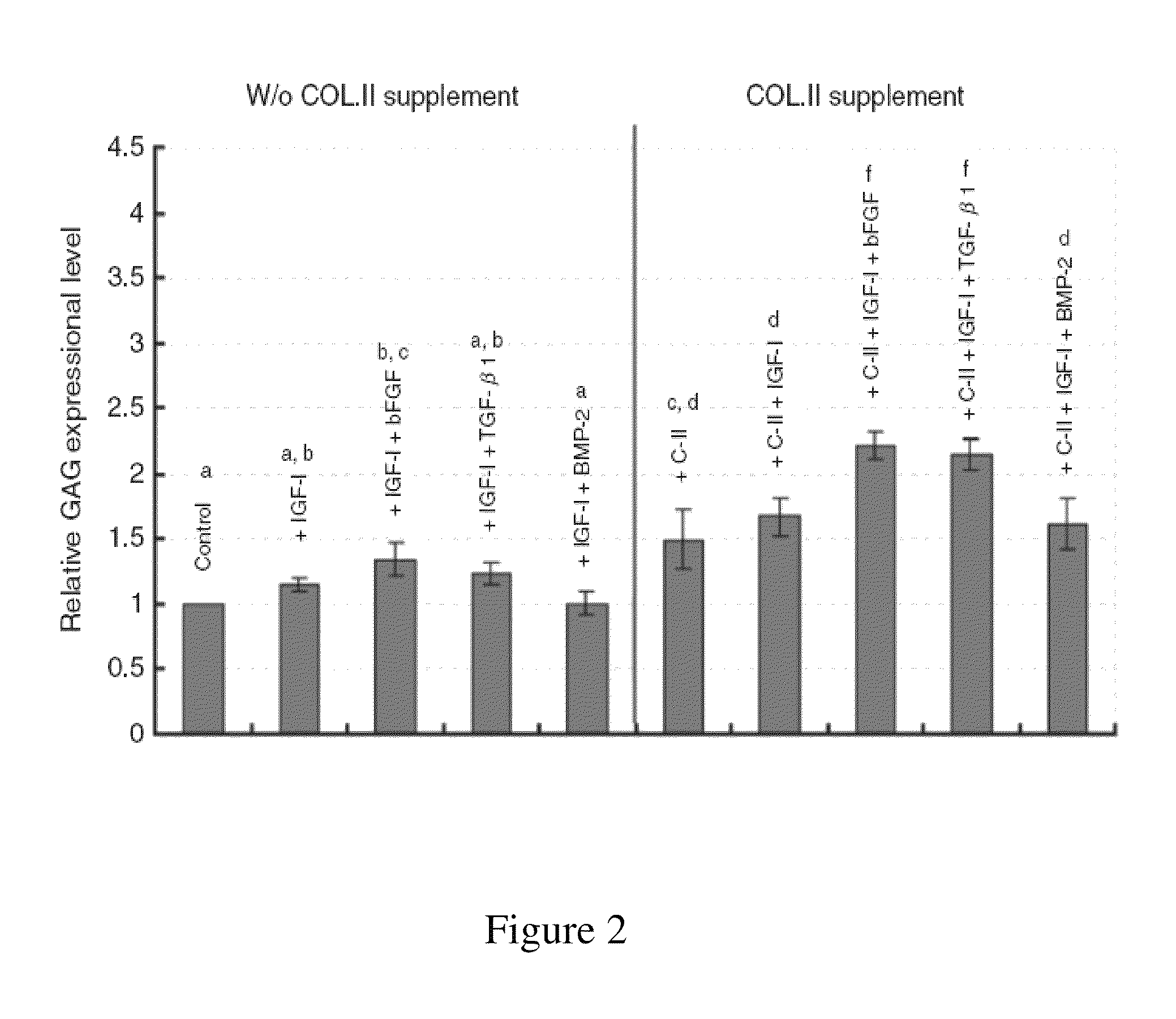
Method to restore cartilaginous phenotype of chondrocytes after cultured and expanded in vitro
The present invention provides a method for restoring native chondrocyte phenotype and functions of, and / or increasing type II collagen as well as aggrecan mRNA expression levels and GAG accumulation level in dedifferentiated chondrocytes which have been subcultured and expanded in vitro, which comprising culturing the said dedifferentiated chondrocytes in vitro with a medium comprising type II collagen, or its biologically active peptide fragment(s) or analogs with or without growth factor(s), wherein the type II collagen or its biologically active peptide fragment(s) or analogs are effective to restore chondrocyte phenotype and functions of, and / or to increase type II collagen and aggrecan expression levels and GAG accumulation level in the said dedifferentiated chondrocytes.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
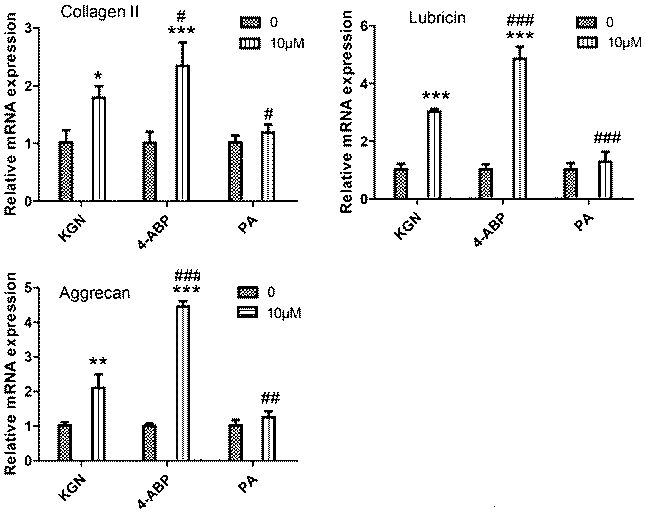
Application of small molecule compound 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) in promoting stem cell proliferation and cartilage differentiation
PendingCN110747162APromote healingReduce processOrganic active ingredientsCulture processAggrecanTissue engineering
The invention discloses application of small molecule compound 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) in promoting stem cell proliferation and cartilage differentiation. Experiments prove that the 4-ABP can promoteproliferation of mesenchymal stem cells (including bone marrow, fat, umbilical cords, placenta, joint tissue and joint fluid as well as mesenchymal stem cells derived from tissue cells such as inducedpluripotent stem cells and cartilage differentiation, and can increase the gene expression levels of Collagen II, Aggrecan and Lubricin of stem cells and expression content of corresponding protein.Therefore, the invention proves that the 4-ABP has functions of promoting proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage differentiation and is expected to become a regeneration and repair stimulation preparation or auxiliary preparation for stem cell medicated cartilage injury and diseases. The 4-ABP can be applied to MSC preparation related to cartilage regeneration and tissue engineeringand induced differentiation at the early stage of transplantation as a small molecule preparation, and lays a foundation for developing novel technical schemes and technical measures related to prevention and tretament of cartilage tissue injury and diseases.
Owner:深圳丹伦基因科技有限公司
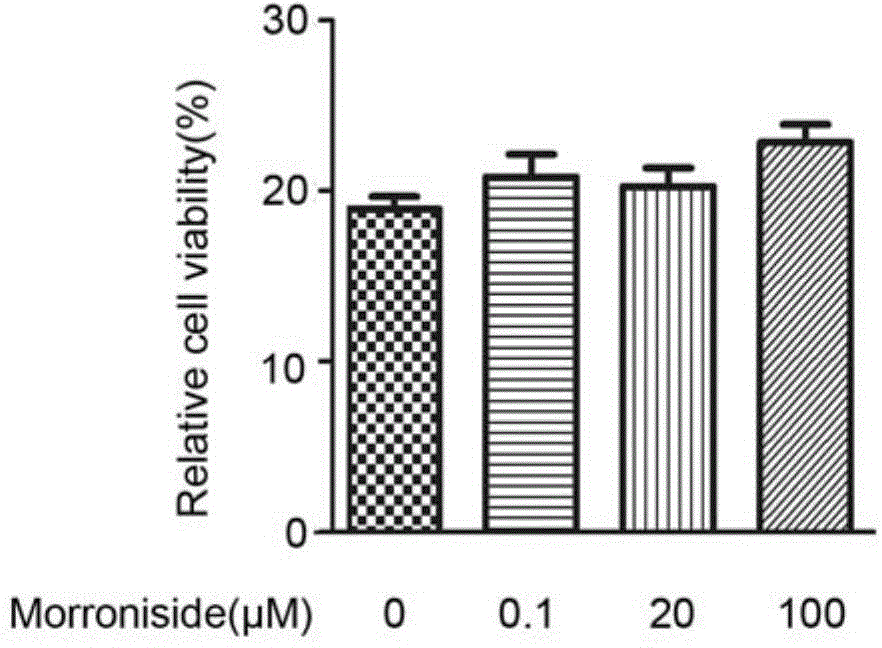
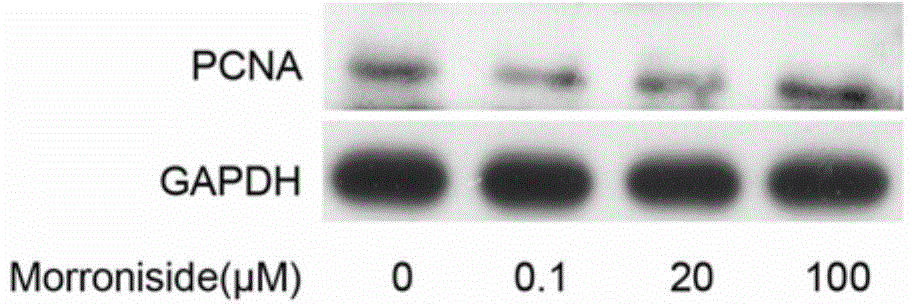
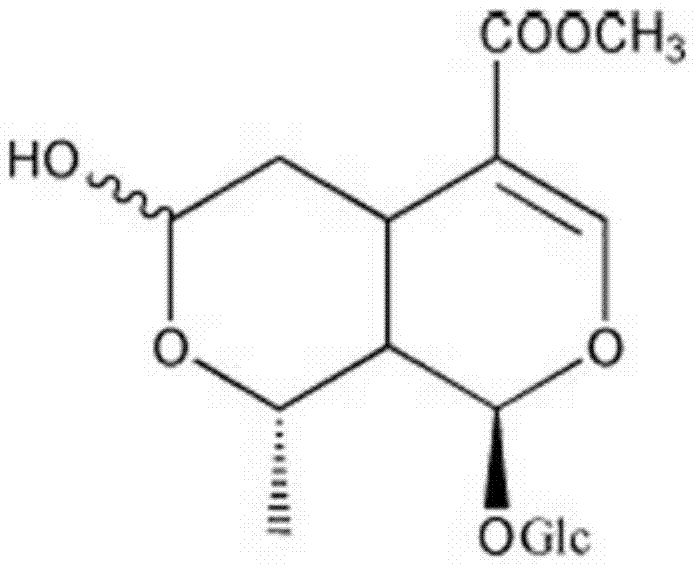
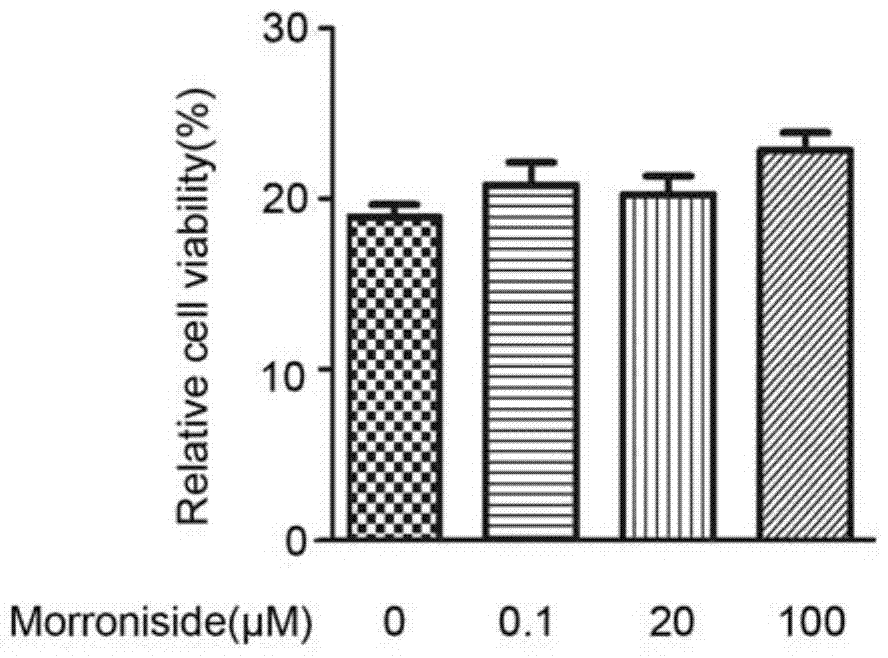
Application of morroniside to preparation of osteoarthritis treating drugs
InactiveCN104606216AConducive to survivalReduce apoptotic activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention discloses application of morroniside to preparation of osteoarthritis treating drugs and relates to application of the morroniside. The morroniside can be used for promoting the in-vitro cultured human osteoarthritis chondrocytes to survive, weakening the chondrocyte index of the chondrocytes, improving the expression levels of II type collagen and proteoglycan Aggrecan in extracellular matrixes of the in-vitro cultured human osteoarthritis chondrocytes, improving the phosphorylation levels of intracellular protein kinase B (PKB / Akt) and extracellular regulated protein kinase of the human osteoarthritis chondrocytes, effectively promoting the survival of the human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and weakening the apoptosis activity of the human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. According to the application, the injury of the osseous tissues in osteoarthritis models of experimental rats is effectively reduced, the cartilage layer thickness is increased and the extracellular polysaccharides content of the cartilage is improved.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL XIAMEN UNIV
The application of Monide in the preparation of the treatment of osteoarthritis drugs
InactiveCN104606216BConducive to survivalReduce apoptotic activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL XIAMEN UNIV
Device and method to treat or prevent joint degeneration
InactiveUS20200085855A1Enhance proprioceptionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsGlucosamine SulfateEngineering
A method for the delivery of aggrecan precursors to the joint of a subject, comprising the steps of: a) applying a composition comprising one or more aggrecan precursors chosen from the list comprising hyaluronic acid, glucosamine sulfate and / or chondroitin sulfate to the skin of the subject on or near a joint, wherein the composition is applied between the skin and a flexible magnetic film.
Owner:INT SCI
Acellular Bioactive Scaffold Device and Methods of Fabrication and Treatment Relating Thereto
PendingUS20200222190A1Promote cell growthWell formedAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsCentrifugationBioactive scaffold
An implantable acellular polymeric scaffold device functionalized with aggrecan is provided. Also provided are methods of fabricating a polymeric scaffold device, including methods of fabricating the scaffold device via 3D printing. Methods of treating a cartilage defect in a subject in need thereof comprise application of the disclosed scaffold device in combination with microfracture procedures. A specialized lid for a centrifugation well plate is also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Immunomodulatory agent and uses therefor
Disclosed are immunomodulatory agents that are useful for treating or preventing joint damage. More particularly, immunomodulators are disclosed for use in eliciting an antigen-specific tolerogenic response to an aggrecan polypeptide including citrullinated forms thereof to treat or prevent joint damage, including joint damage in subjects with early RA or incipient RA.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Polypeptides binding adamts5, mmp13 and aggrecan
PendingCN110997717APeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMedicinePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to polypeptides binding Aggrecan as well as ADAMTS5 and / or MMP13, more in particular to polypeptides that comprise or essentially consist of immunoglobulins binding Aggrecan as well as immunoglobulins binding ADAMTS5 and / or immunoglobulins binding MMP13 (also referred to herein as polypeptides of the invention, and immunoglobulin(s) of the invention, respectively). The invention also relates to constructs comprising such immunoglobulins, such as immunoglobulin single variable domains (ISVDs) or polypeptides as well as nucleic acids encoding such immunoglobulins orpolypeptides (also referred to herein as nucleic acid(s) of the invention; to methods for preparing such immunoglobulins, polypeptides and constructs; to host cells expressing or capable of expressing such immunoglobulins or polypeptides; to compositions, and in particular to pharmaceutical compositions, that comprise such immunoglobulins, polypeptides, constructs, nucleic acids and / or host cells; and to uses of immunoglobulins, polypeptides, constructs, nucleic acids, host cells and / or compositions, in particular for prophylactic and / or therapeutic purposes, such as the prophylactic and / or therapeutic purposes mentioned herein. Other aspects, embodiments, advantages and applications of the invention will become clear from the further description herein.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH +1
Assay of isomerised and/or optically inverted proteins and protein fragments
In an in vitro diagnostic test for osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, the amount or presence in a sample of anisomerised or optically inverted protein fragment is measured which derives from perlecan, bigylcan, decorin, fibrillin-1 or protocadherin or which is a specific sequence from aggrecan, type II collagen, COMP or CILP.
Owner:NORDIC BIOSCI DIAGNOSTICS
Application of dendrobium officinale polysaccharide in preparation of medicine for treating osteoarthritis
ActiveCN109045061BReduce apoptosisReduce degradationOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses an application of dendrobium officinale polysaccharide in preparing medicine for treating osteoarthritis. The dendrobium officinale polysaccharide of the present invention is used in the preparation of osteoarthritis drugs that inhibit the expression of cell inflammatory factors IL-1β, TNF-α, matrix metalloproteinase 1, matrix metalloproteinase 3, and matrix metalloproteinase 13 that degrade the extracellular matrix of cartilage, It can also be used in the preparation of osteoarthritis drugs that promote the expression of cartilage extracellular matrix type II collagen and aggrecan. The present invention discovers for the first time that Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides have significant effects in treating osteoarthritis and protecting cartilage. In the present invention, Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects, and improve the activity of antioxidant enzymes by scavenging free radicals, active oxygen, and active nitrogen. To reduce the apoptosis of chondrocytes and alleviate the damage of oxidative stress to cartilage. Therefore, Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide, as an active ingredient, has important social and economic significance in the preparation of medicines for treating osteoarthritis.
Owner:NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL
Expression and folding in the manufacturing process of CD-RAP by using a CD-RAP precursor protein
The present invention relates to a CD-RAP precursor protein comprising a pre-sequence and CD-RAP, and its use in manufacturing of native CD-RAP. The present invention further relates to a composition comprising CD-RAP and at least one positively charged amino acid and a buffer, pharmaceuticals comprising said composition, their use in methods of treating and / or preventing cartilage disease or injury in patients suffering from aggrecan degradation, and / or increased influx of water into the cartilage, and / or decreased CD-RAP expression, as well as methods of producing said composition and methods of storing CD-RAP in said composition. The present invention further relates to a composition comprising liposomes comprising encapsulated CD-RAP or a variant thereof, its use in methods of treating joint disease or injury, and methods of producing such liposomal composition as well as storing CD-RAP therein.
Owner:BIONET PHARMA GMBH
CRMP4b inhibitory peptide
InactiveUS7935349B2Promote regenerationCompound screeningNervous disorderCo localizationCytoskeleton
The present invention relates to the identification of the cytosolic phosphoprotein CRMP4b as a protein that physically and functionally interacts with RhoA to mediate neurite outgrowth inhibition. siRNA-mediated knockdown of CRMP4 promotes neurite outgrowth on myelin substrates indicating a critical role for CRMP4 in neurite outgrowth inhibition. Disruption of CRMP4b-RhoA binding with a competitive inhibitor attenuates neurite outgrowth inhibition on myelin and aggrecan substrates. Stimulation of neuronal growth cones with Nogo leads to co-localization of CRMP4b and RhoA at discrete regions within the actin-rich central and peripheral domains of the growth cone indicative of a potential function in cytoskeletal rearrangements during neurite outgrowth inhibition. Together these data indicate that a RhoA-CRMP4b complex forms in response to inhibitory challenges in the growth cone environment and regulate cytoskeletal dynamics at distinct sites necessary for axon outgrowth inhibition. Competitive inhibition of CRMP4b-RhoA binding suggests a novel, highly specific therapeutic avenue for promoting regeneration following CNS injury.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
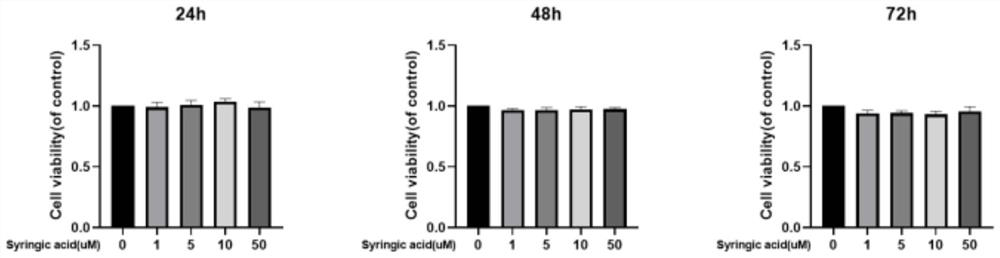
Application of syringic acid in preparation of medicine for treating osteoarthritis caused by cartilage degradation
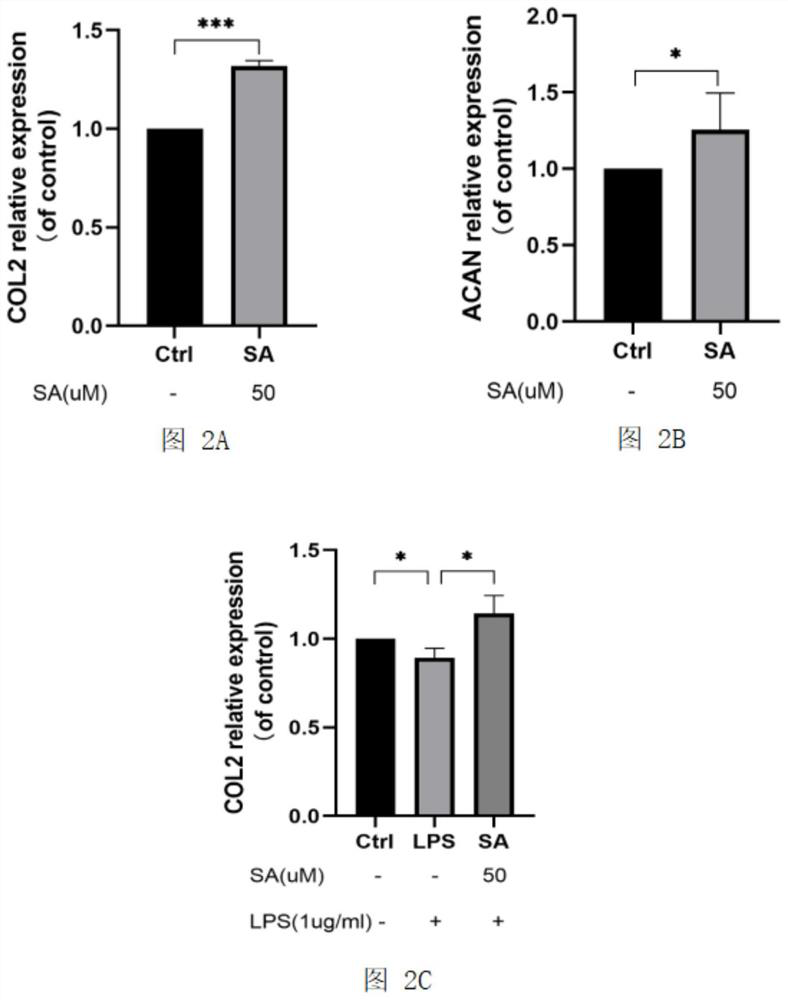
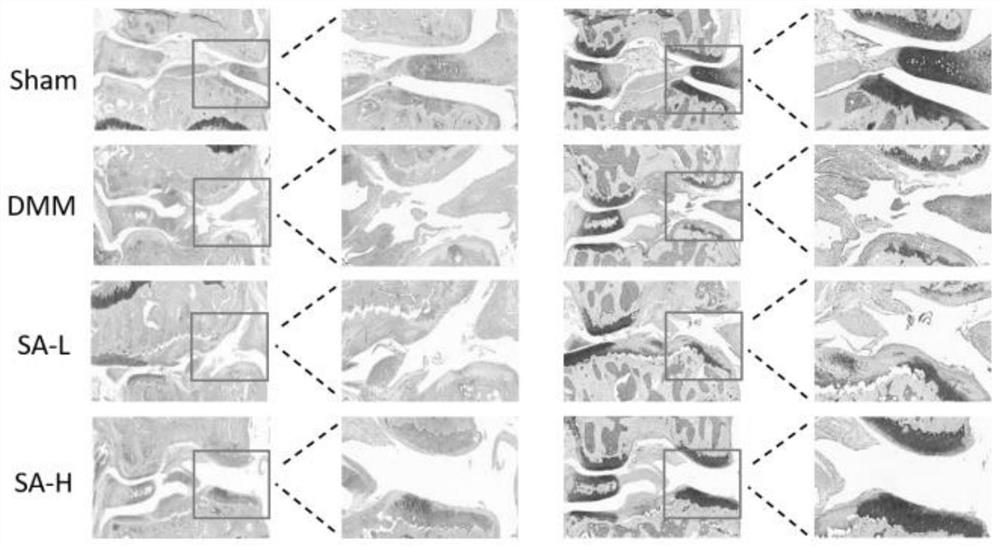
PendingCN114306303ALow immunogenicityEasy to synthesizeOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticArticular surfacePharmacology
The invention relates to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines, in particular to application of syringic acid in preparation of a medicine for treating osteoarthritis caused by cartilage degradation. The syringic acid (3, 5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid) can promote expression of cartilage cell type II collagen and aggregation proteoglycan in vitro, can relieve the progress of osteoarthritis caused by meniscus resection in vivo, relieves articular cartilage abrasion, has a protective effect on articular cartilage, and can be used for preparing a medicine for treating osteoarthritis. The method has important significance for treating or preventing osteoarthritis caused by cartilage degradation.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com