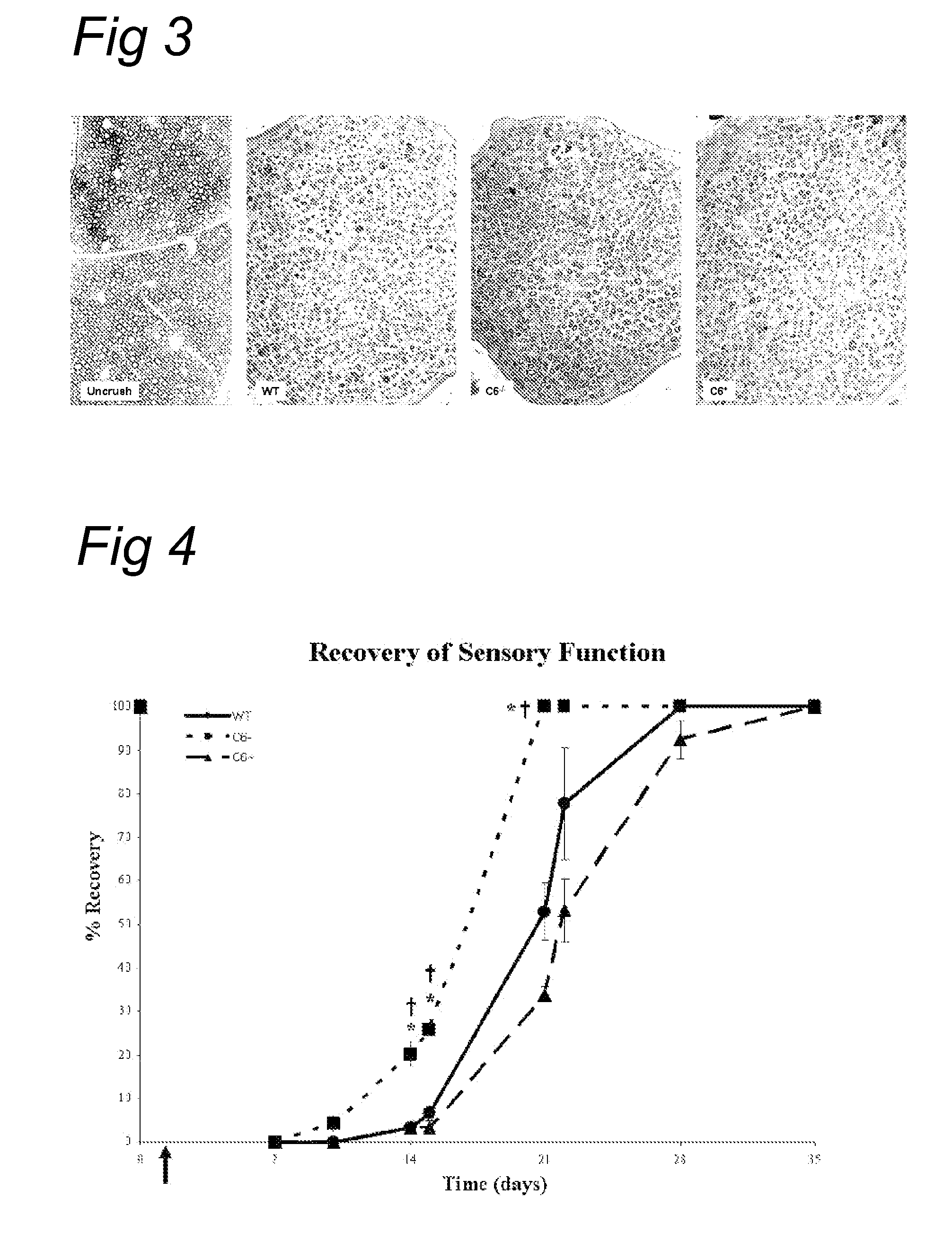
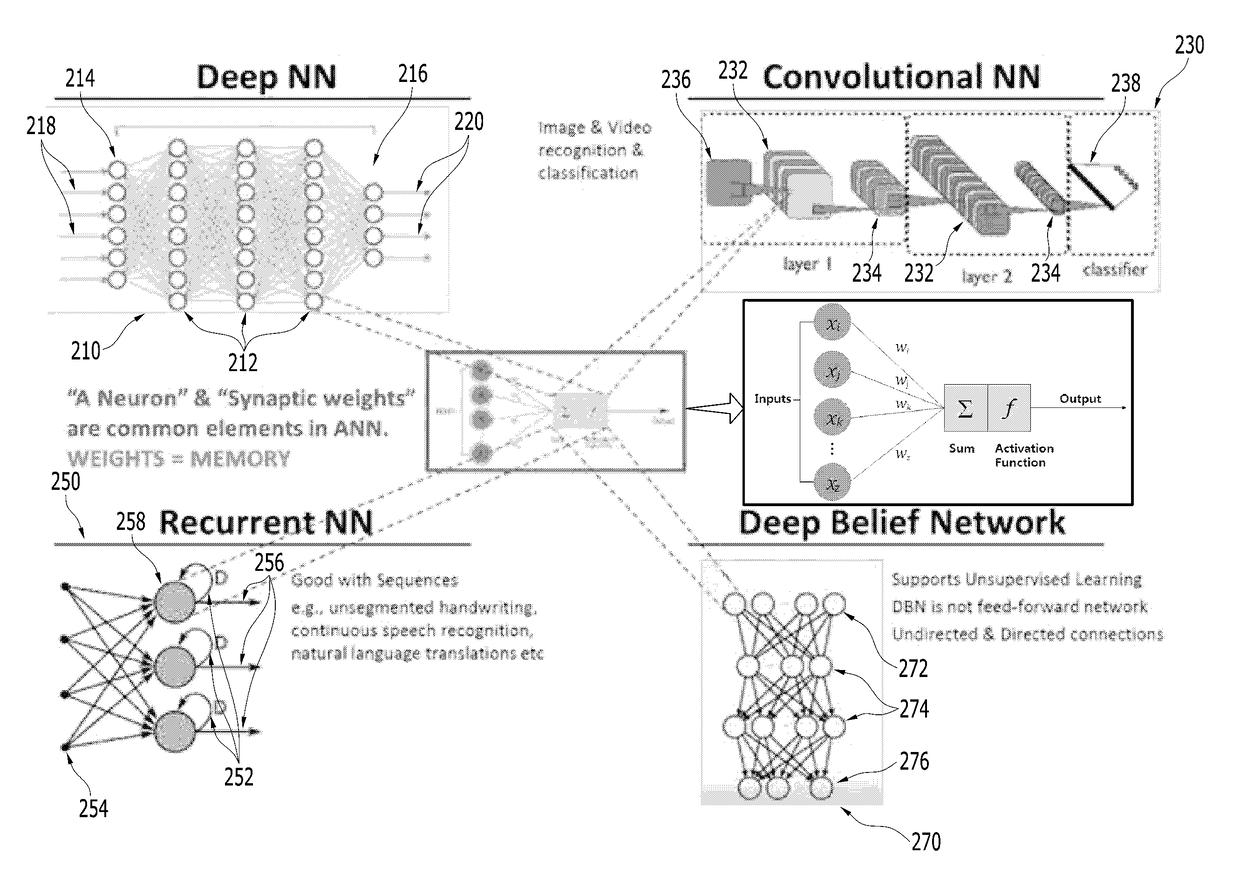
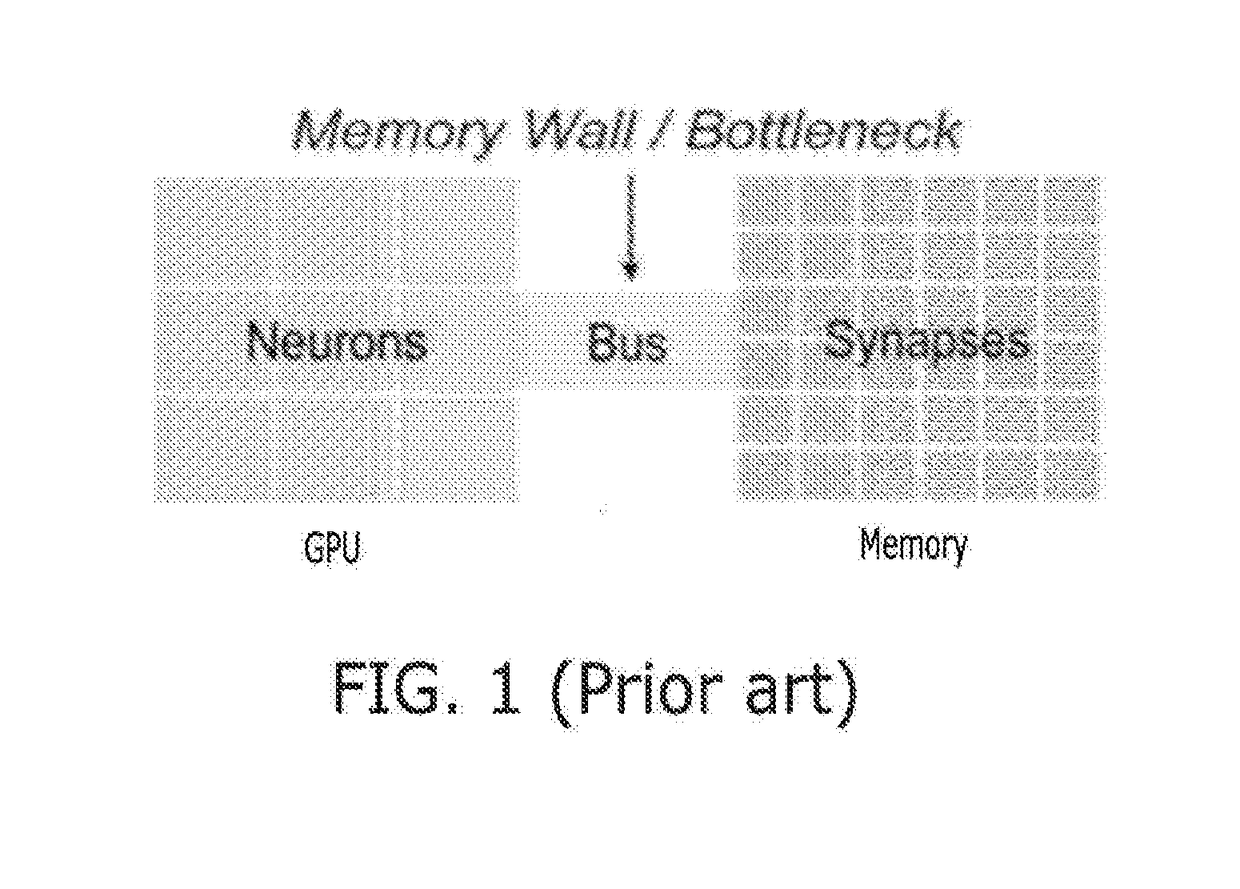
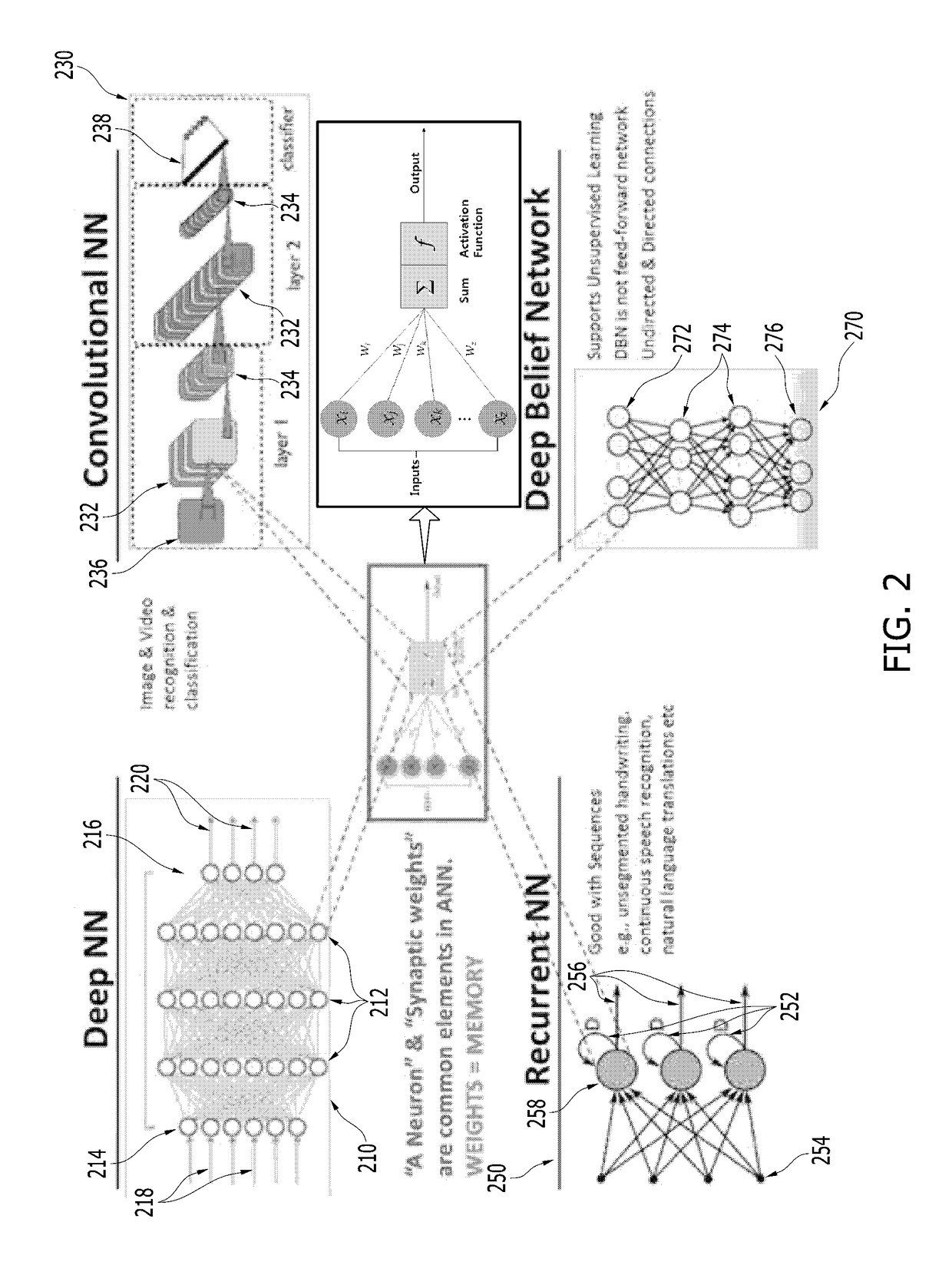
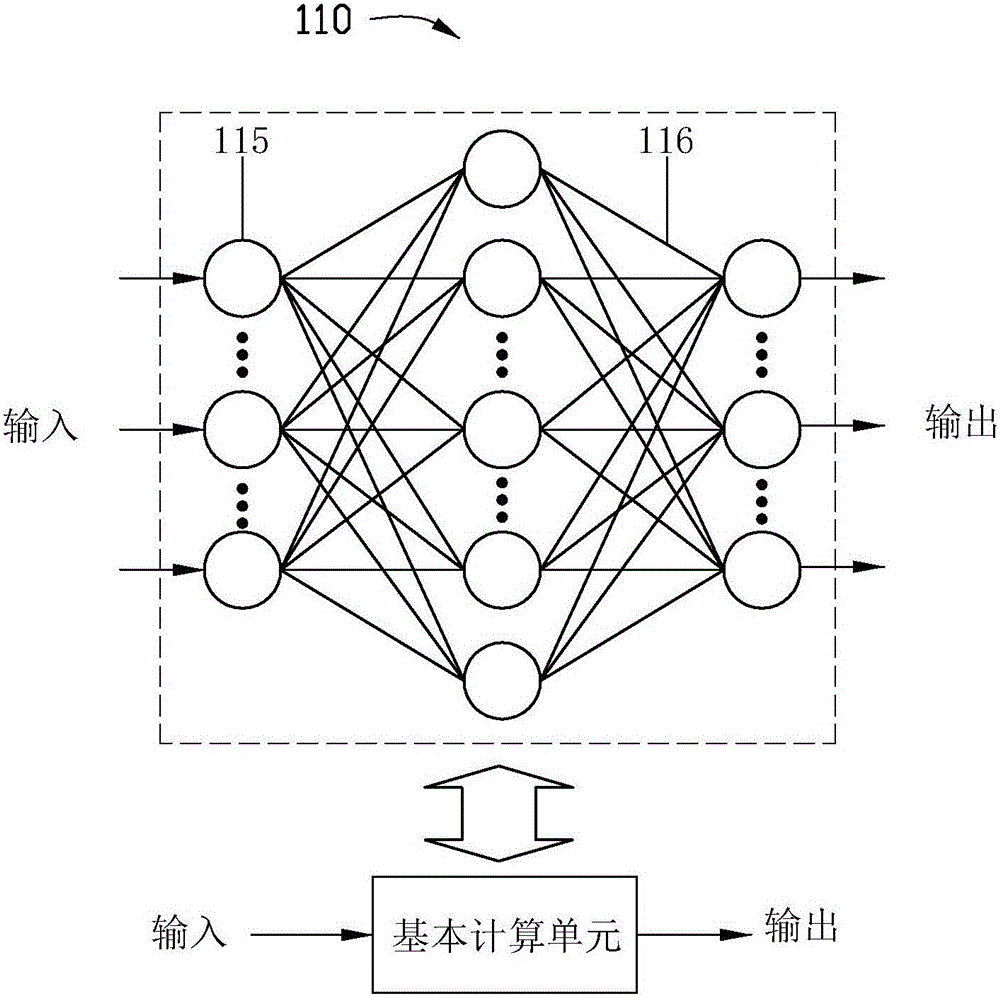
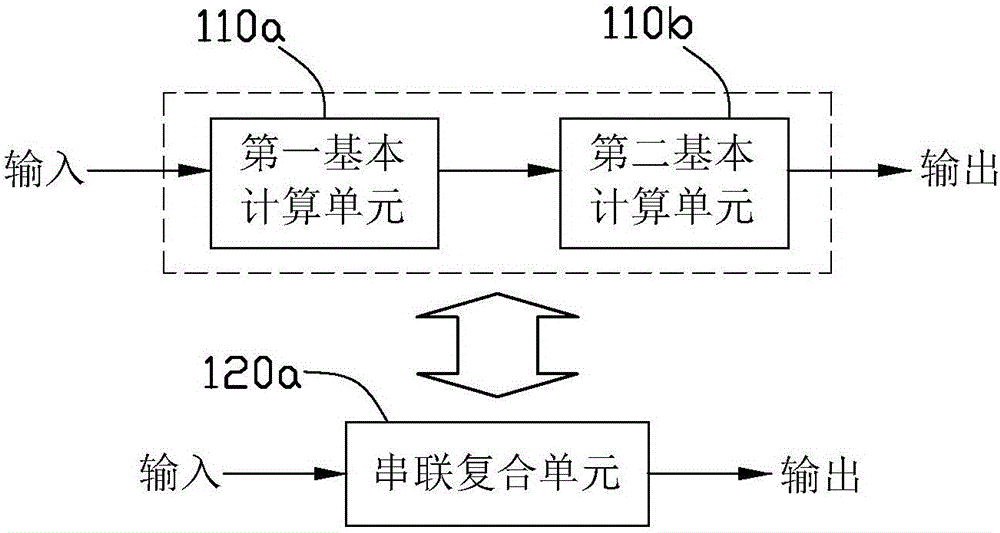
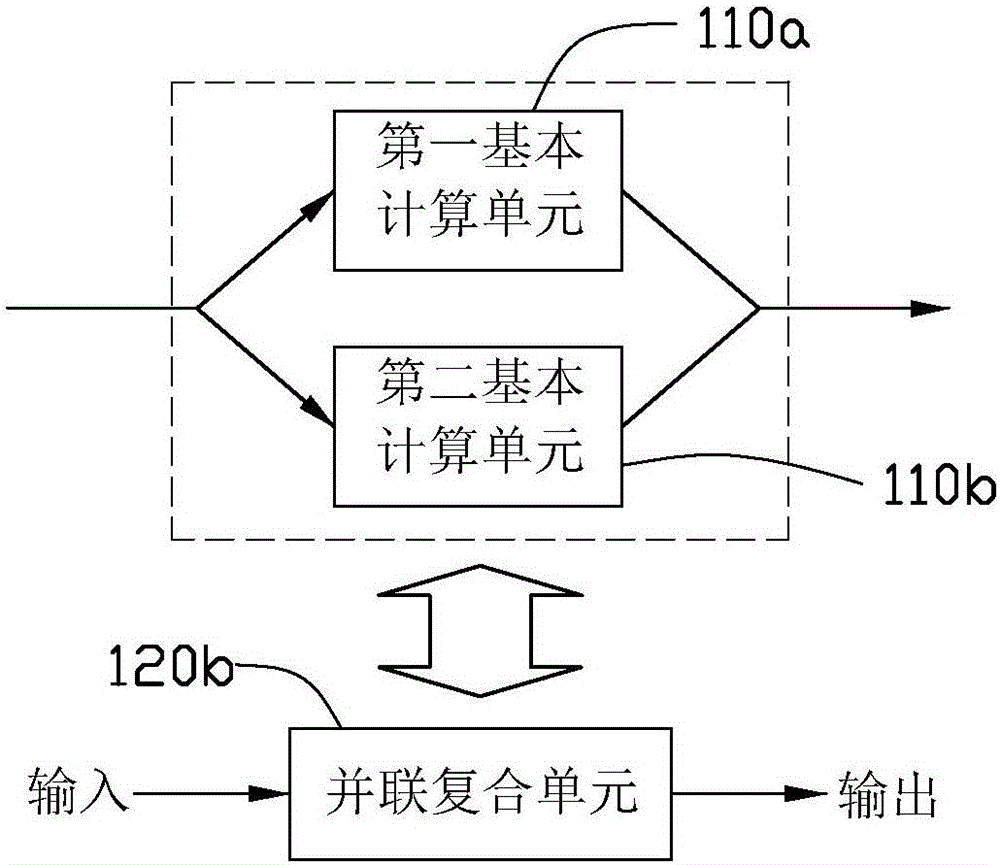
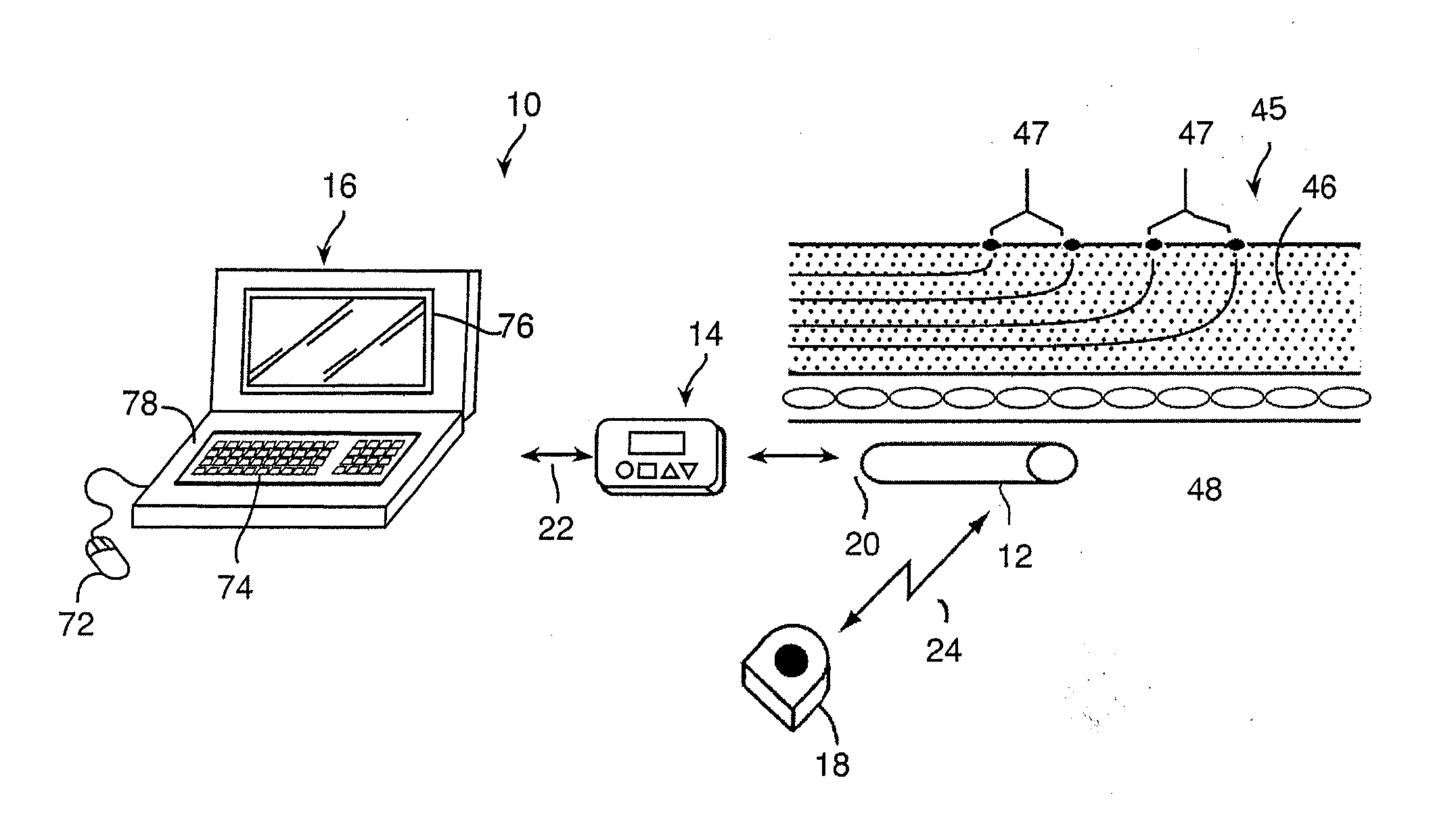
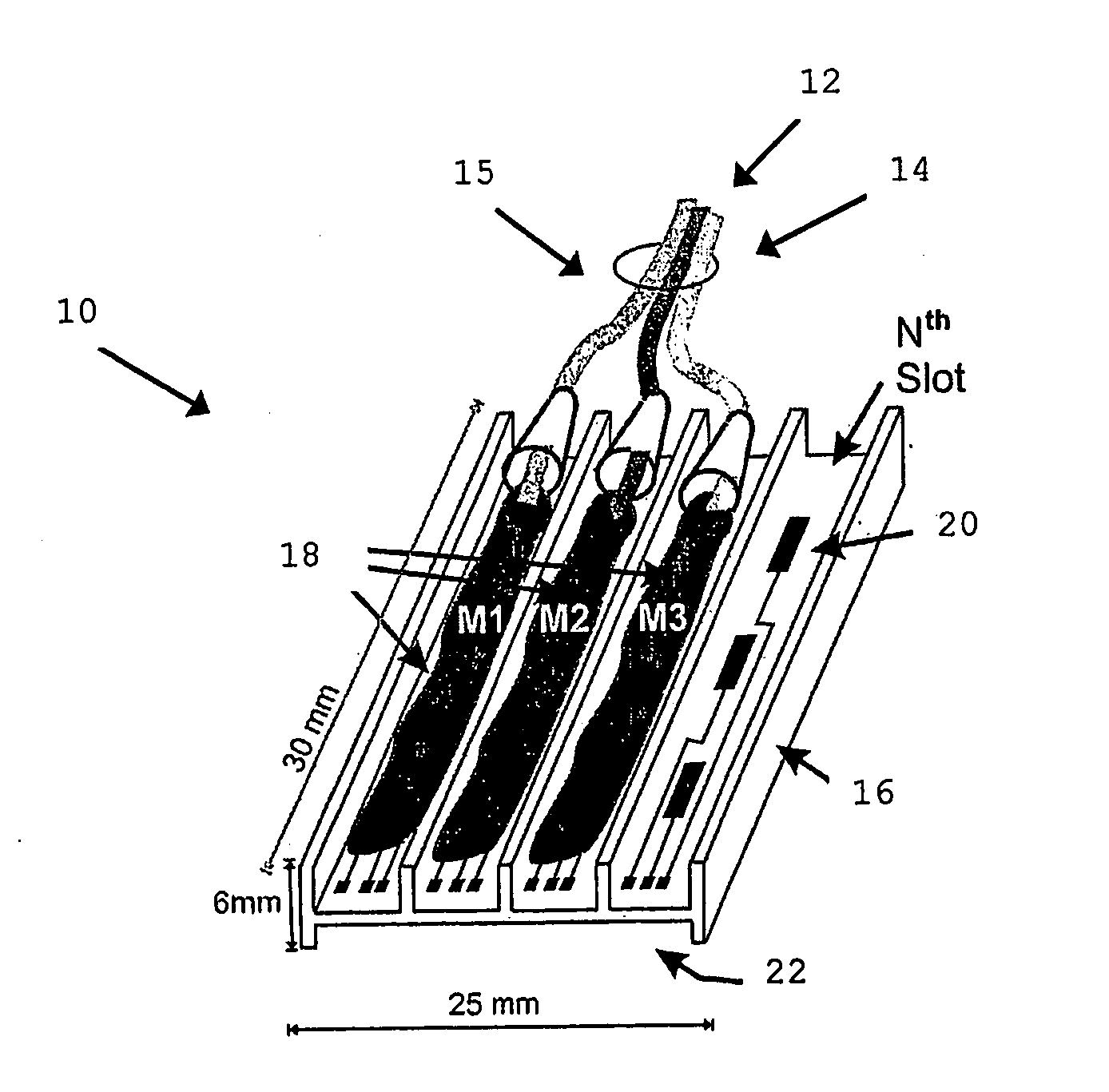
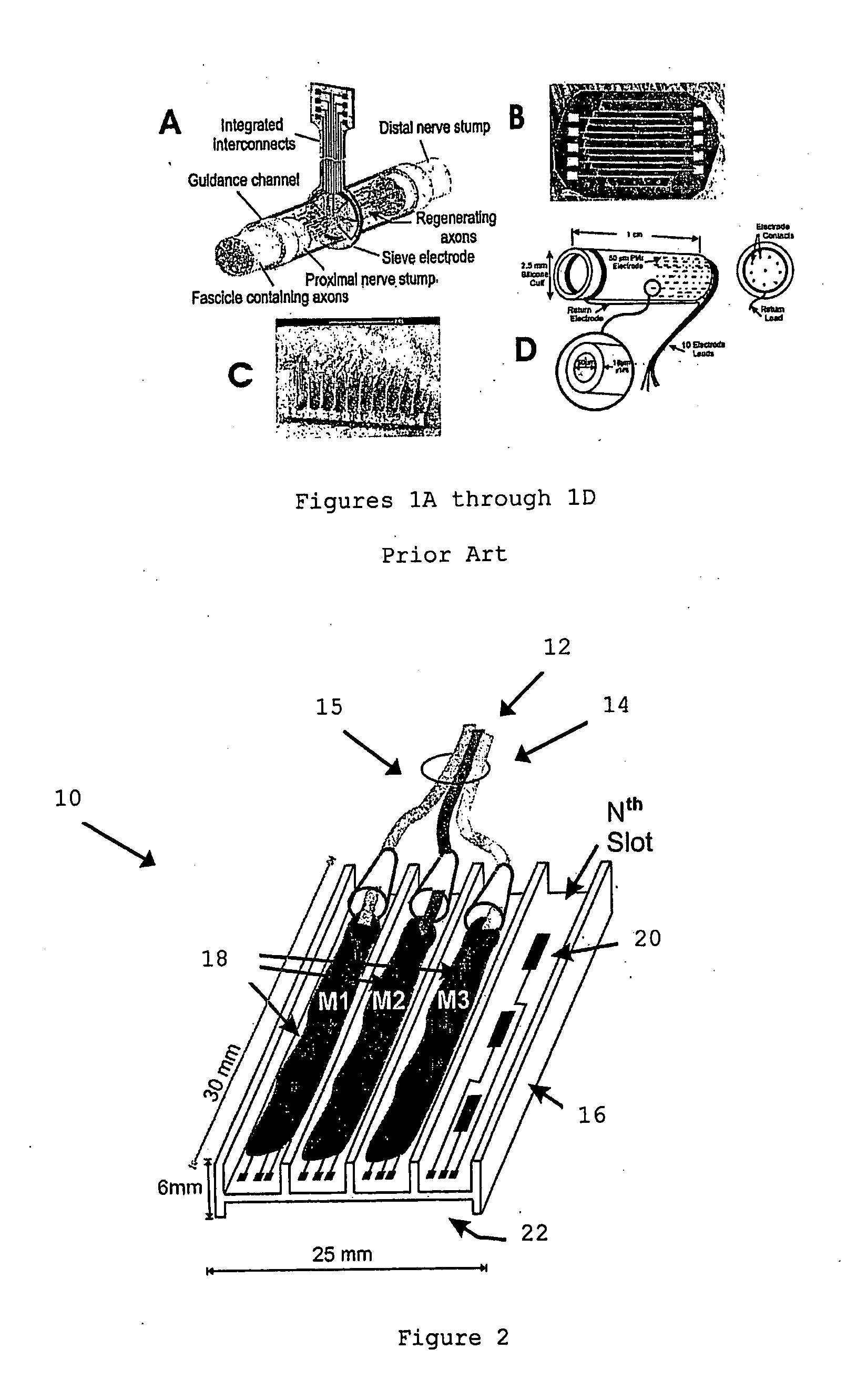
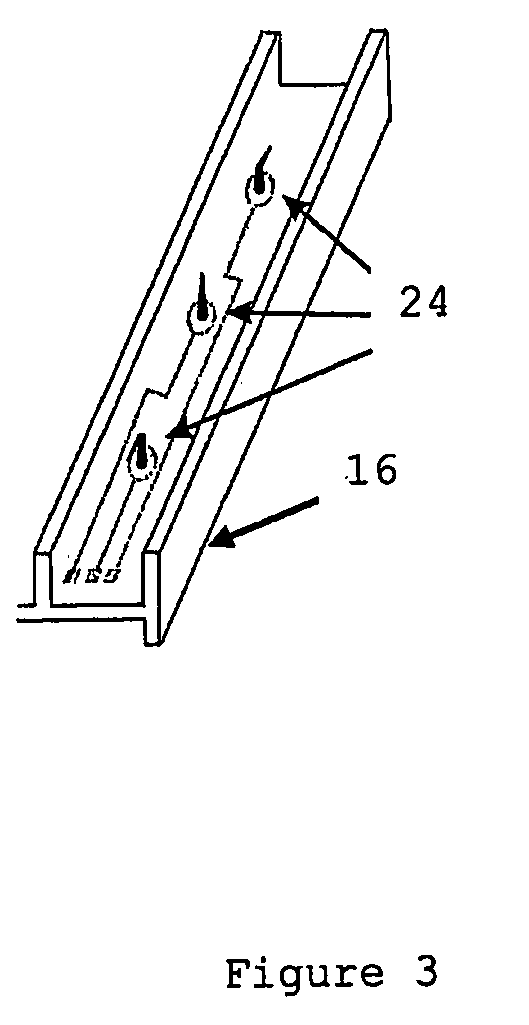
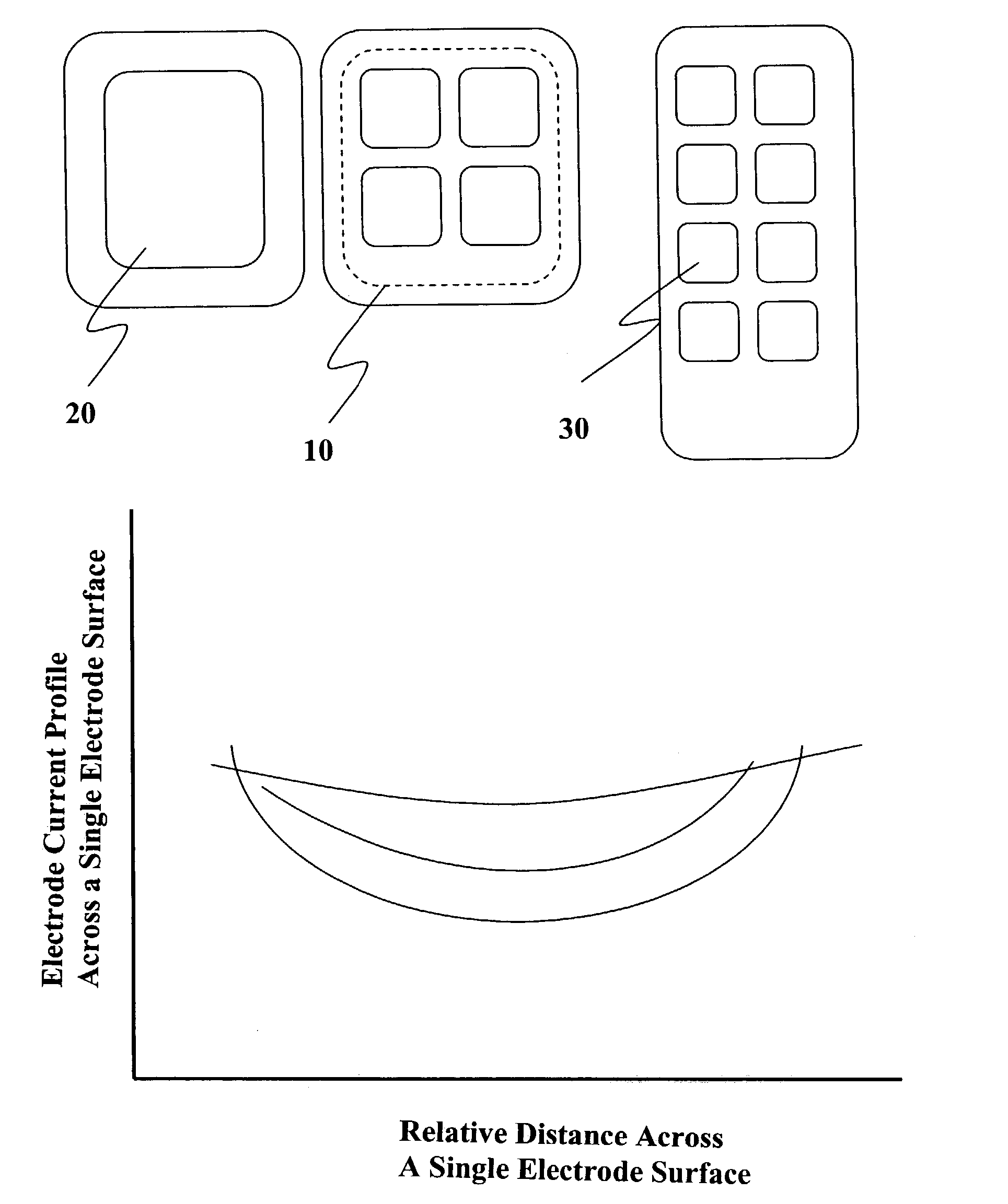
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
426 results about "Axon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
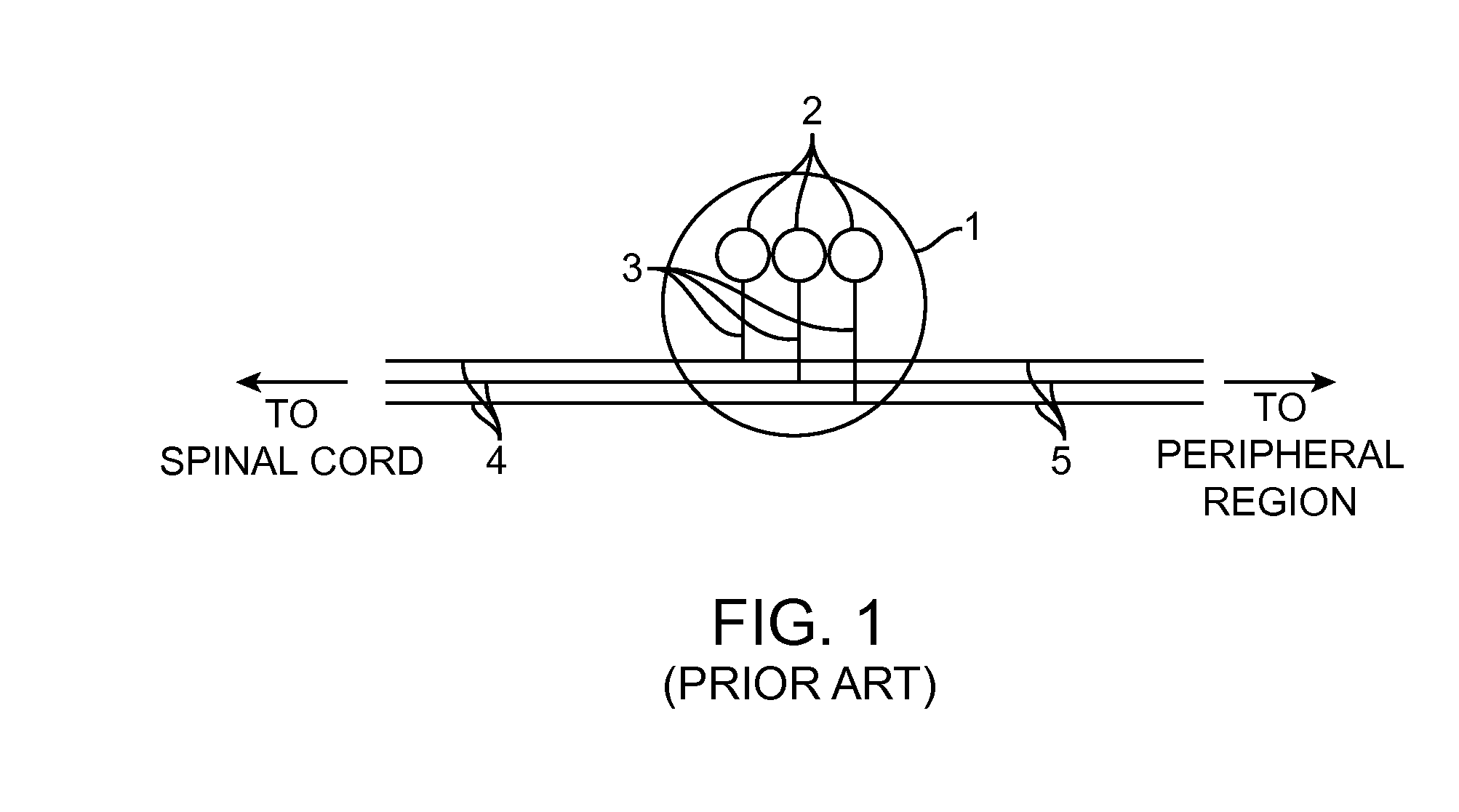
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction has caused many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types – group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. These groups include both sensory fibers and motor fibers. Another classification groups only the sensory fibers as Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.
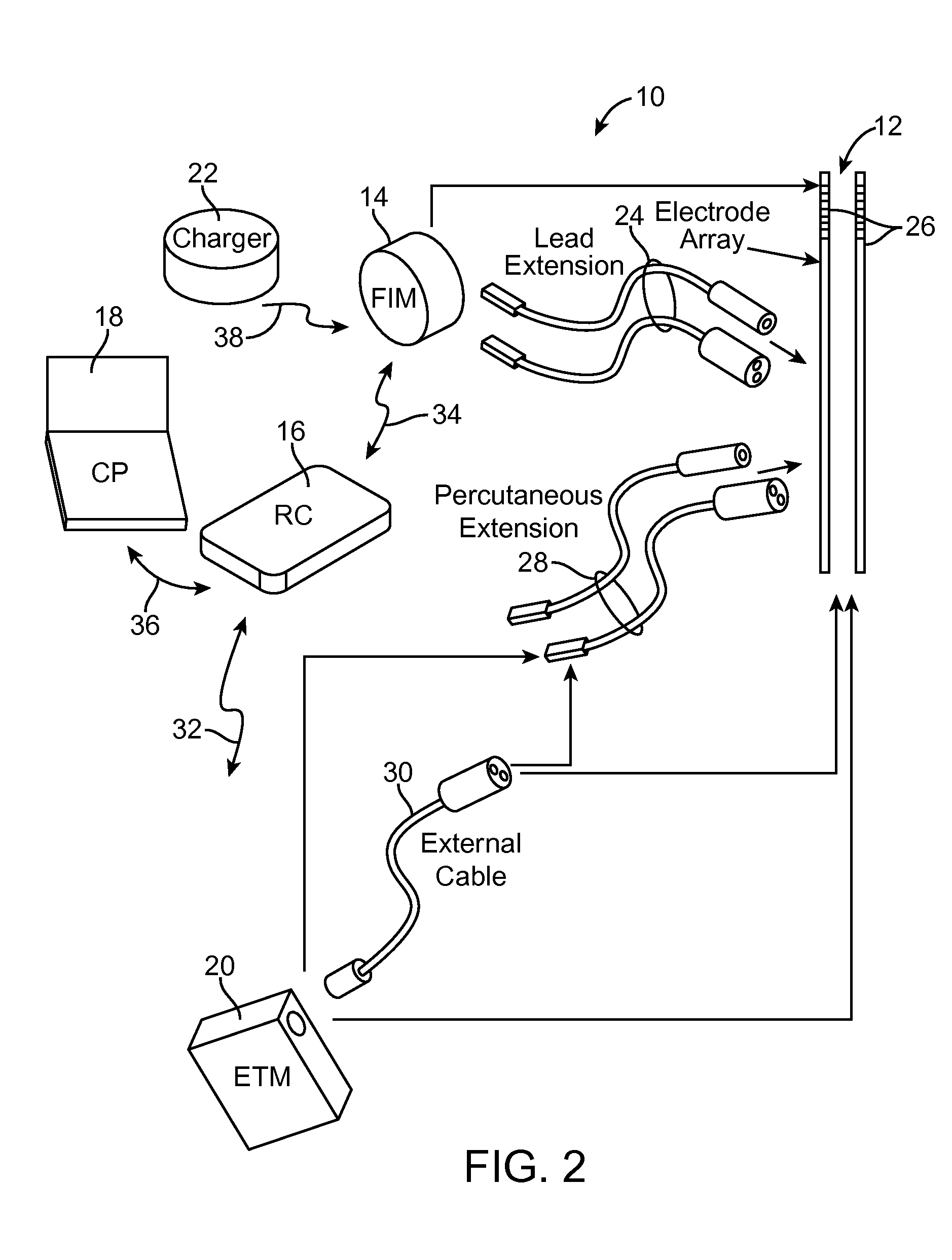
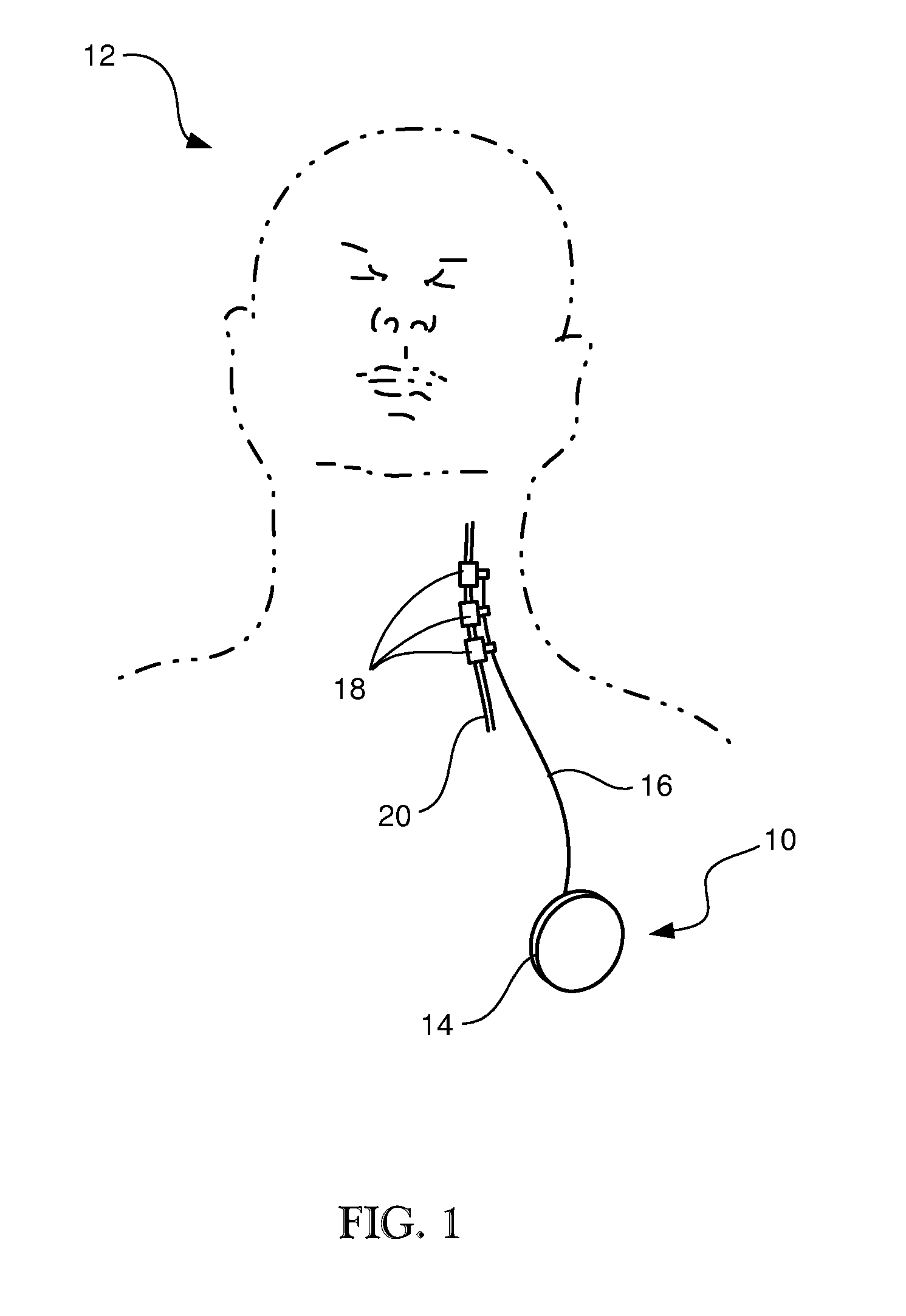
Actuation and control of limbs through motor nerve stimulation
InactiveUS6839594B2Easy to moveEasy to controlElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDriving currentPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
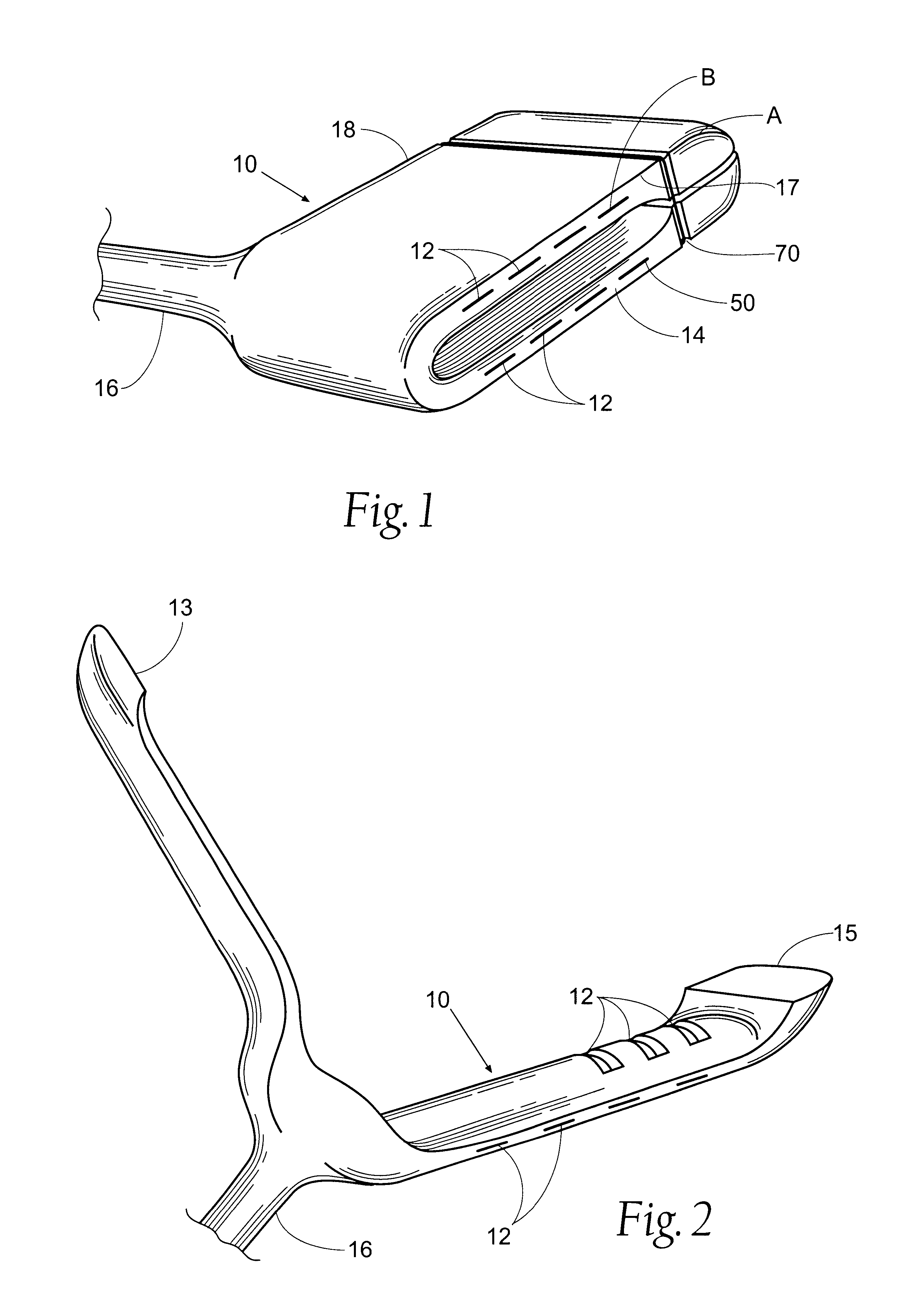
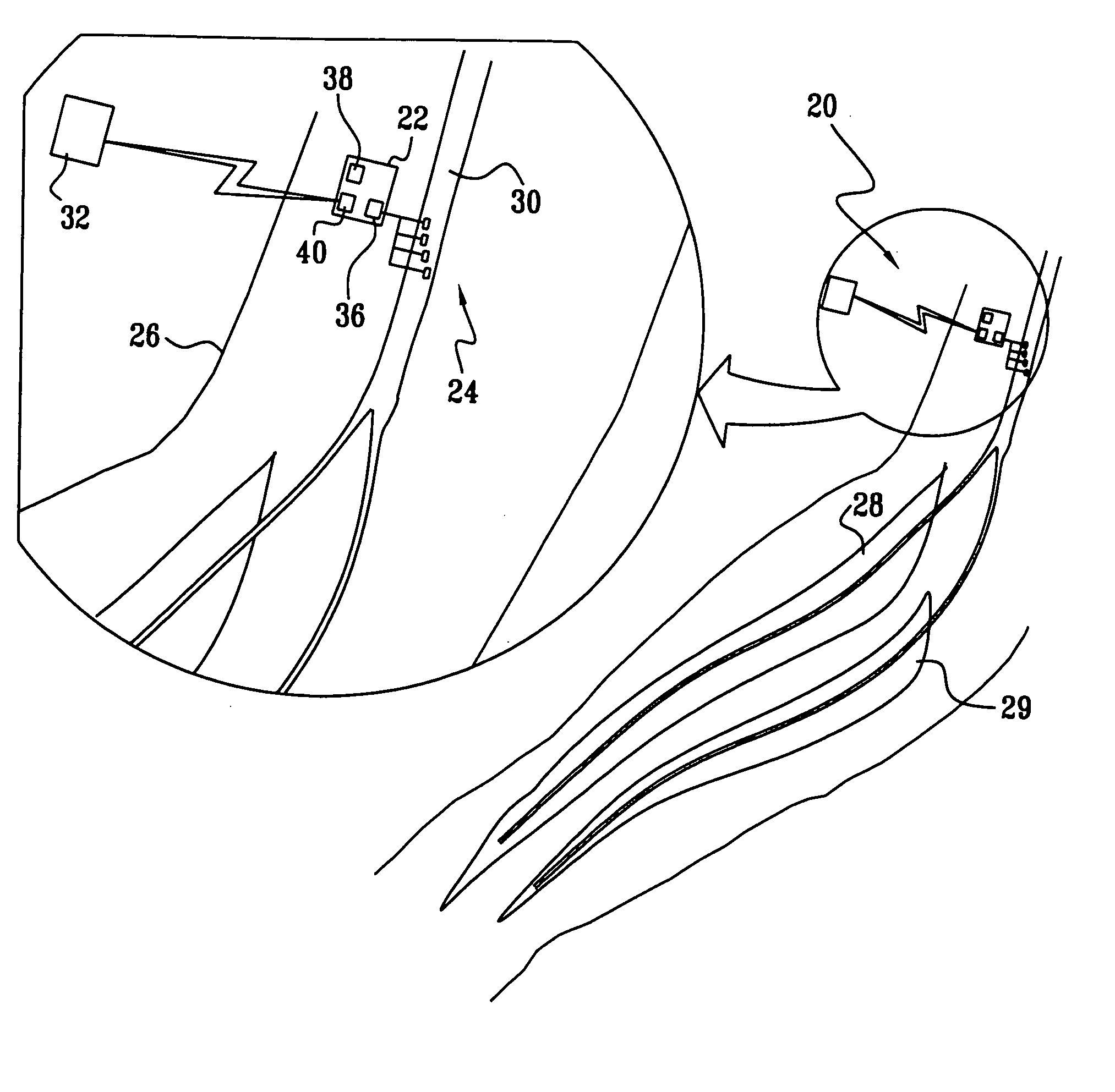
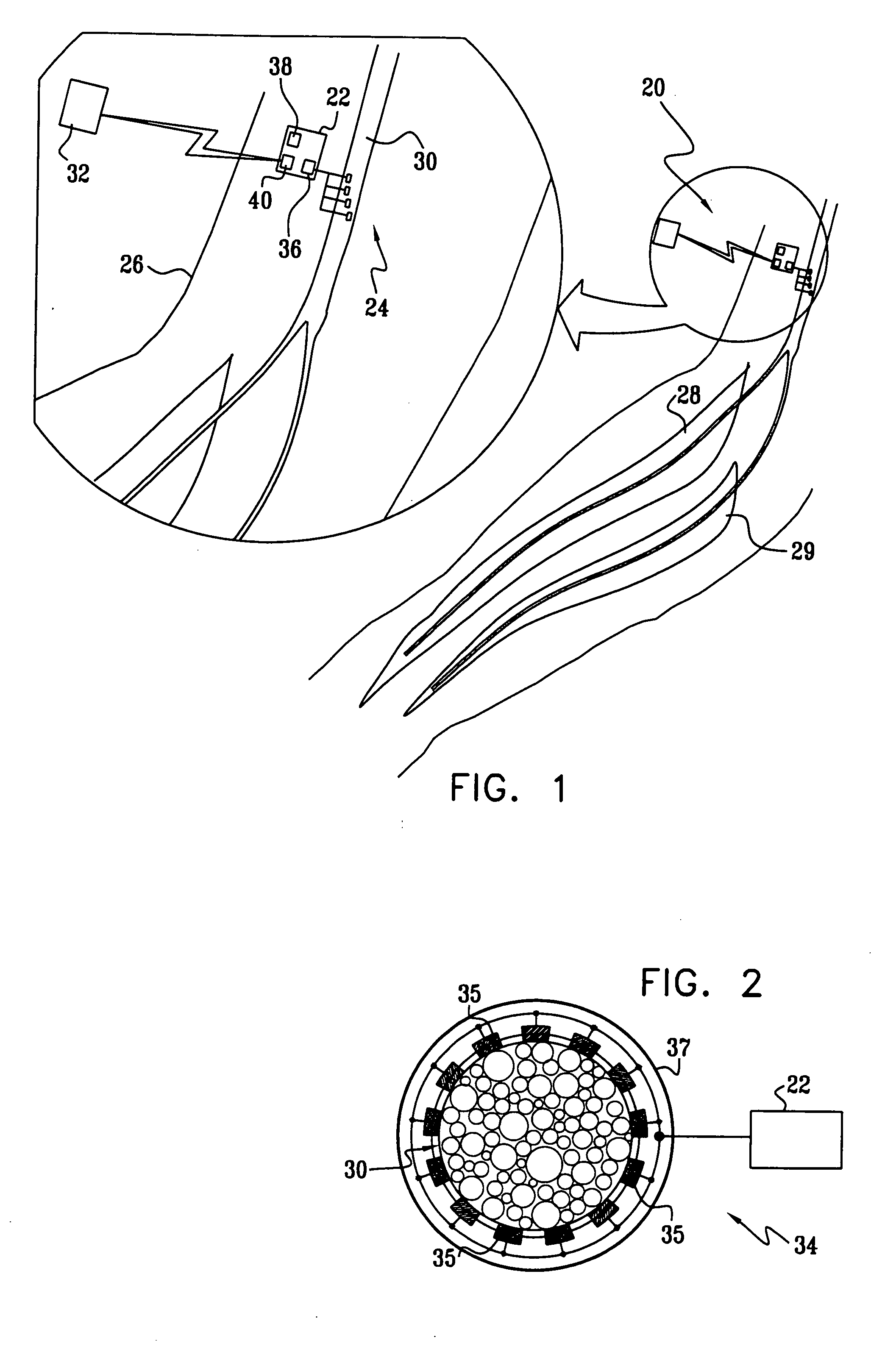
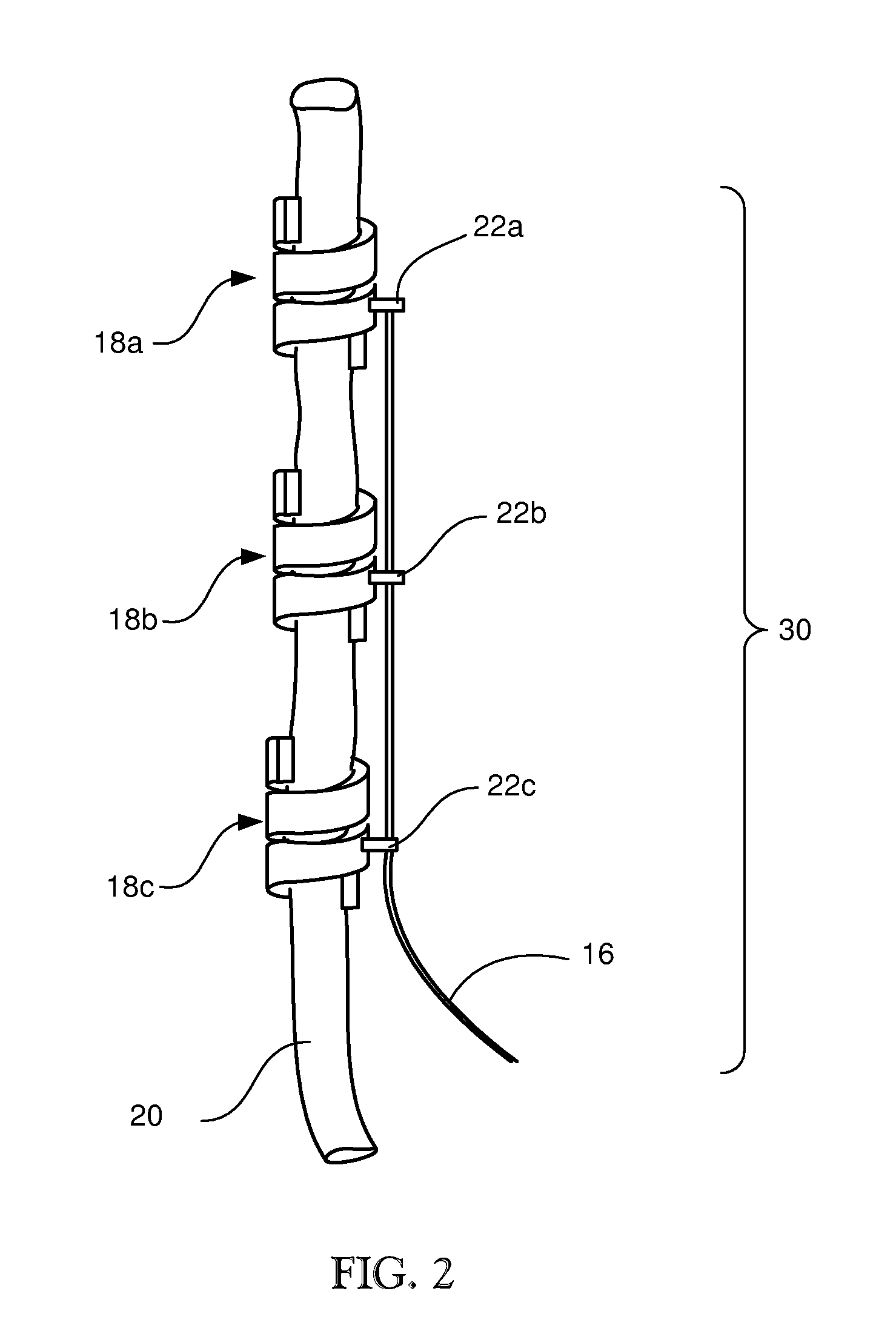
Flat interface nerve electrode and a method for use
A flat interface nerve electrode is provided along with a method for its use. The electrode provides a plurality of conductive elements embedded in a non-conductive cuff structure, which acts to gently and non-evasively redefine the geometry of a nerve through the application of a force so as to apply pressure to a nerve in a defined range, namely from 2 to 40 mmHG and more preferably from 15 to 30 mmHG and most preferably from 15 mmHG to 20 MMHG. This range is selected to minimize the reduction of blood flow within the tissue, which preferably is at least 70% of the initial value, more preferably 90% of the initial value. The cuff has an opening, which is elongated relative to the diameter of the nerve to which it is applied. Preferably, the cuff is constructed from an elastic bio-compatible material having top and bottom beam members configured to define a nerve opening. The cuff is open at one side and has a connection at the other side which results in a spring force being applied through the surfaces of the nerve opening to the subject nerve. During implantation the open sides of the cuff are closed so as to capture the nerve in the cuff. As the nerve is reshaped, specific nerve axons become more easily addressed through the epineurium by the embedded conductive elements.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
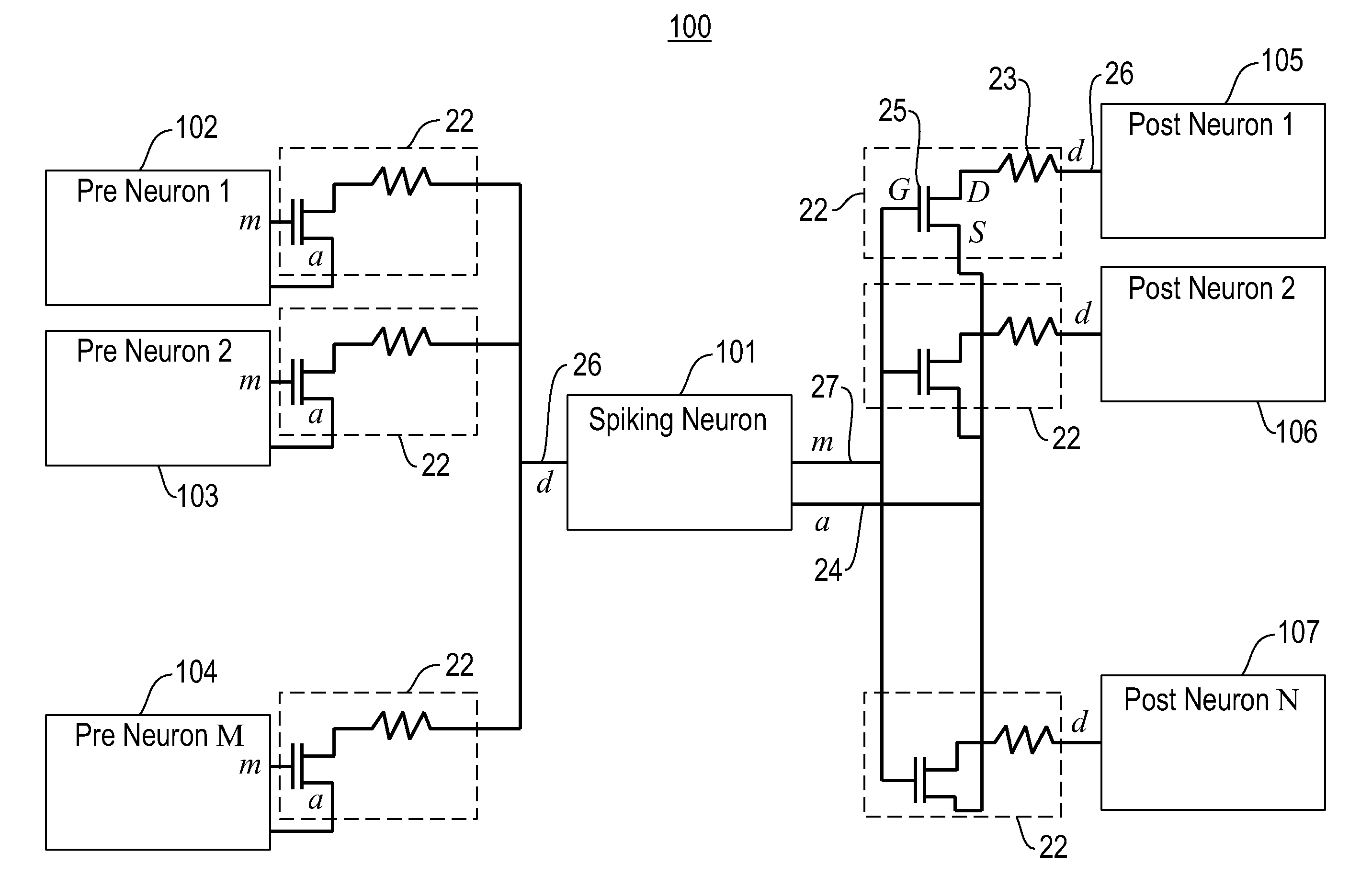
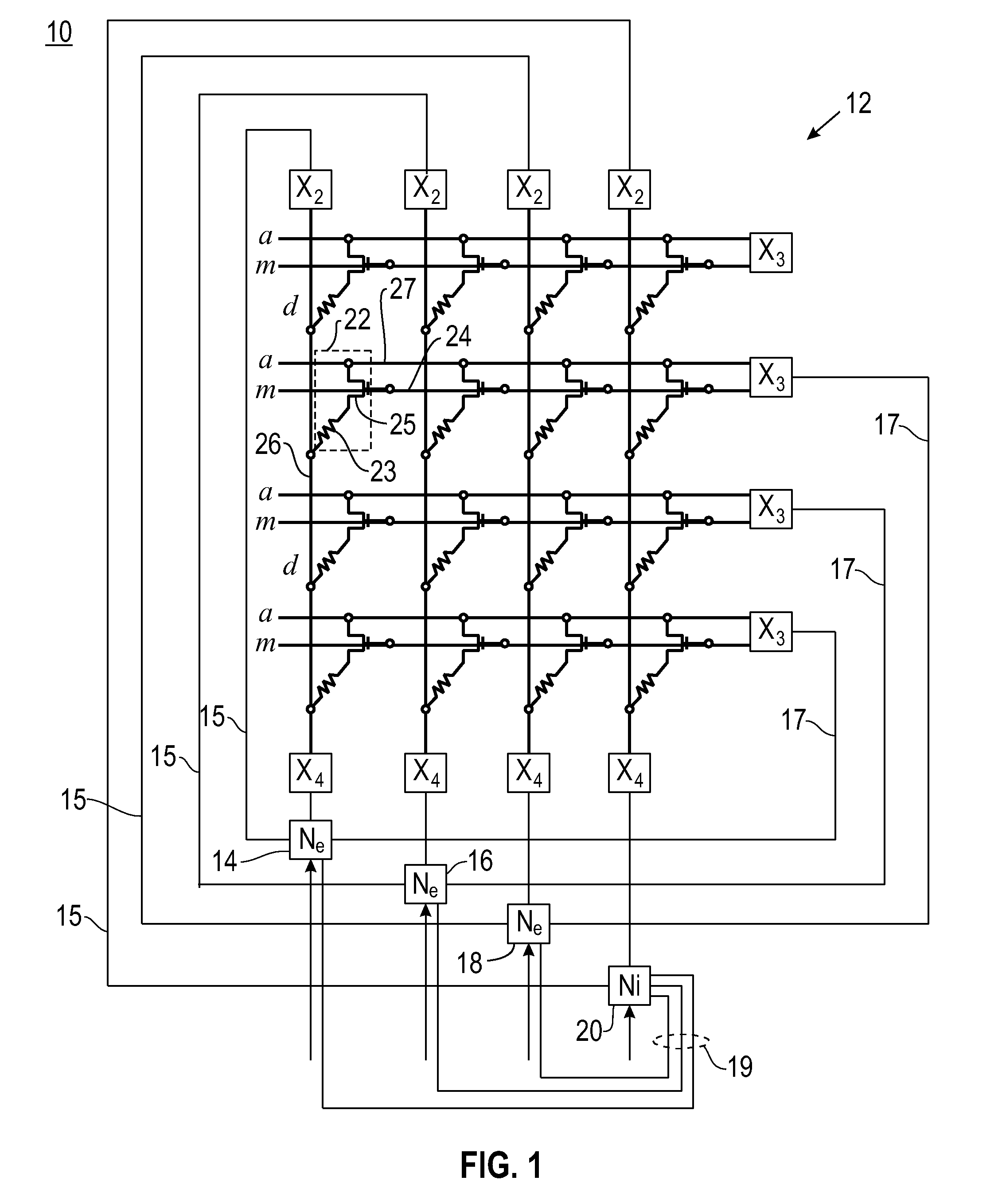
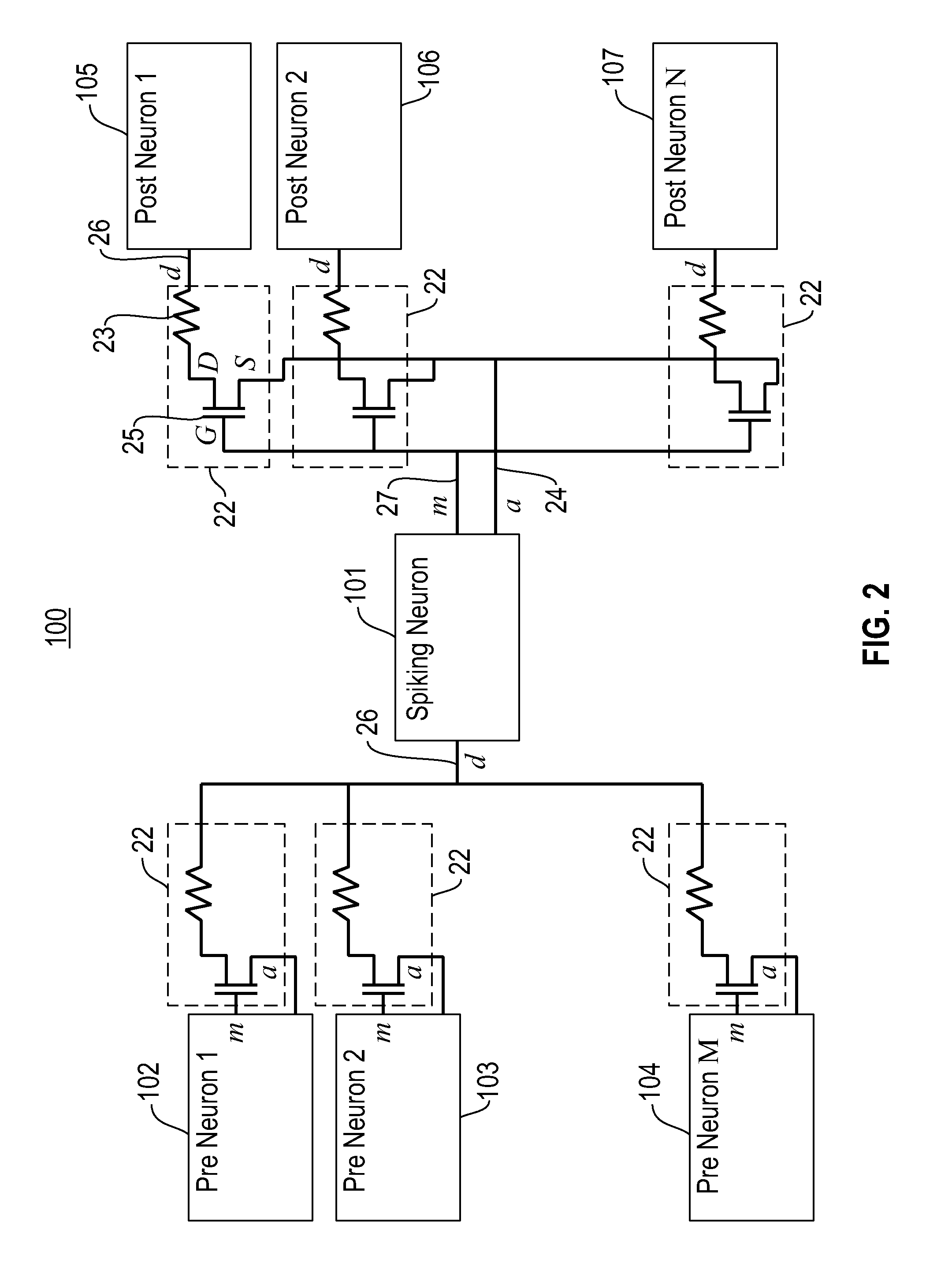
Producing spike-timing dependent plasticity in a neuromorphic network utilizing phase change synaptic devices
ActiveUS20120084241A1Digital computer detailsDigital storageSynaptic deviceSpike-timing-dependent plasticity
Embodiments of the invention relate to a neuromorphic network for producing spike-timing dependent plasticity. The neuromorphic network includes a plurality of electronic neurons and an interconnect circuit coupled for interconnecting the plurality of electronic neurons. The interconnect circuit includes plural synaptic devices for interconnecting the electronic neurons via axon paths, dendrite paths and membrane paths. Each synaptic device includes a variable state resistor and a transistor device with a gate terminal, a source terminal and a drain terminal, wherein the drain terminal is connected in series with a first terminal of the variable state resistor. The source terminal of the transistor device is connected to an axon path, the gate terminal of the transistor device is connected to a membrane path and a second terminal of the variable state resistor is connected to a dendrite path, such that each synaptic device is coupled between a first axon path and a first dendrite path, and between a first membrane path and said first dendrite path.
Owner:IBM CORP
Actuation and control of limbs through motor nerve stimulation
ActiveUS7628750B2ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDriving currentPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Apparatus for actuating a skeletal muscle of a patient is provided. The apparatus typically includes a plurality of electrodes, which are adapted to be placed in a vicinity of a motor nerve that innervates the skeletal muscle. A control unit, is preferably adapted to drive a current between two or more of the plurality of electrodes, and to configure the current such that a first subset of axons in the nerve is excited by the current and such that a second subset of axons in the nerve is not excited by the current.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Artificial neural canal
InactiveUS6090117AStay in shapePrevent intrusionTubular organ implantsTissue regenerationMedicineBlood capillary
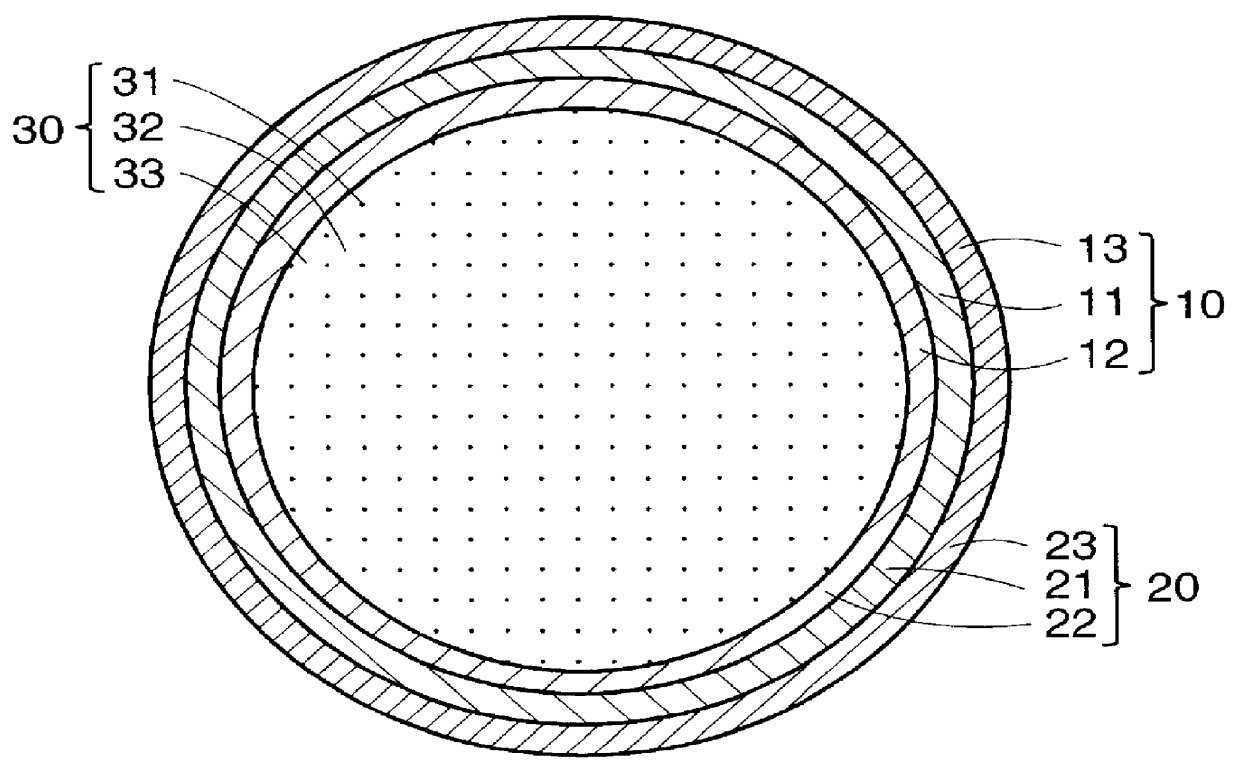
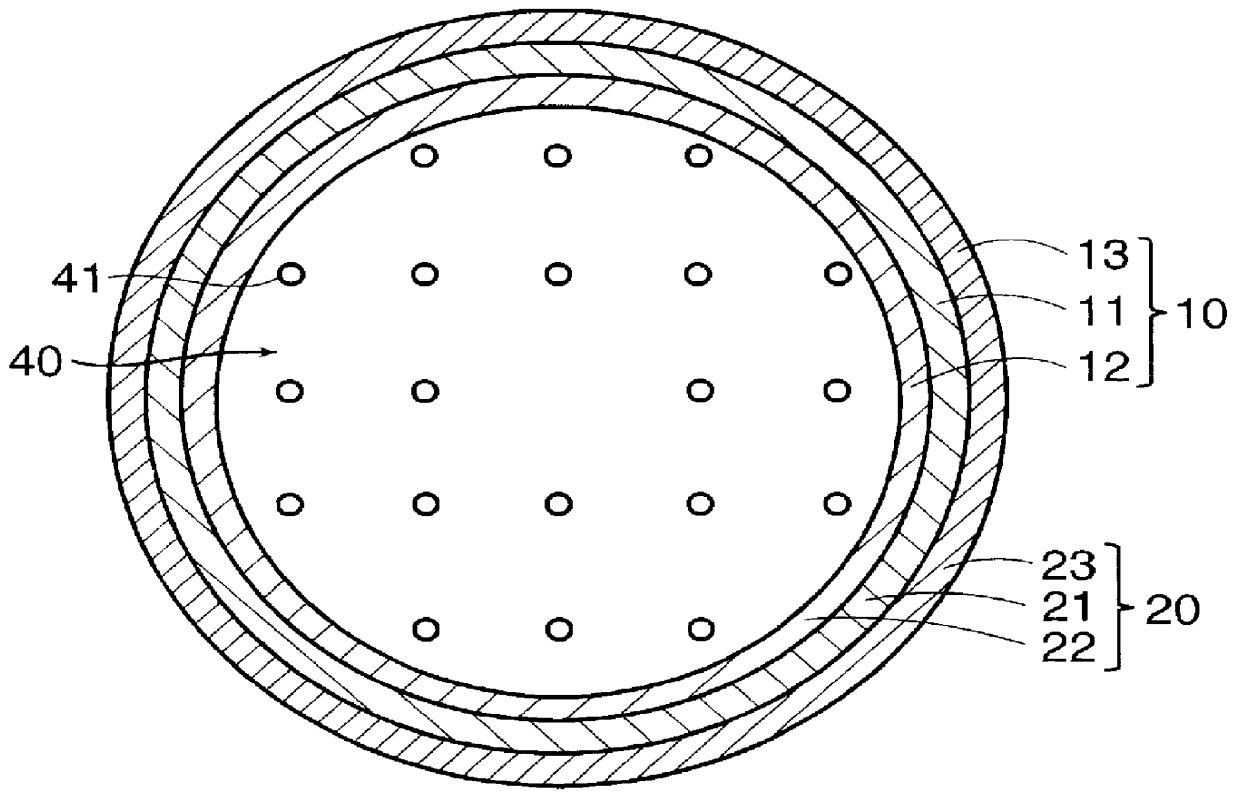
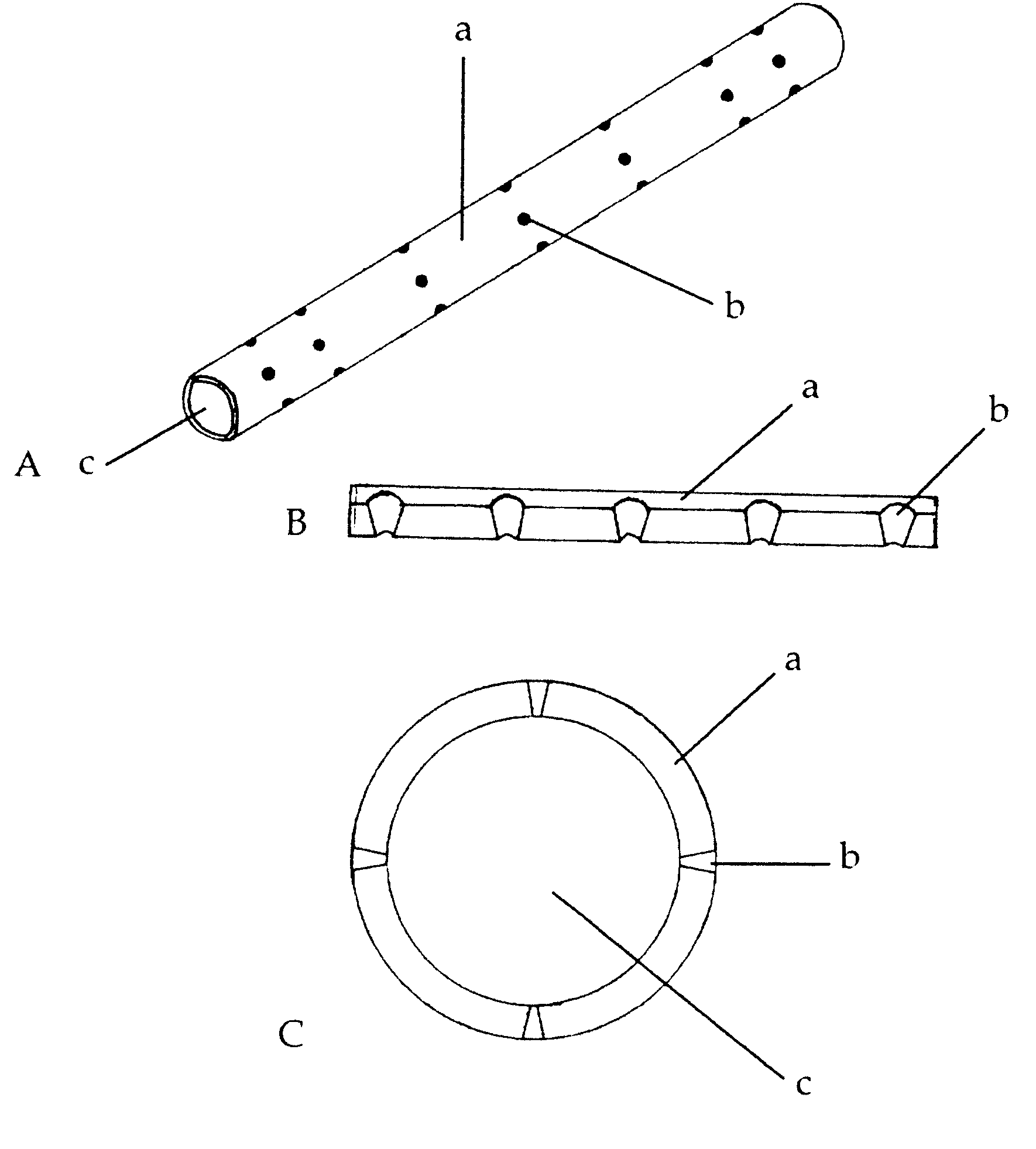
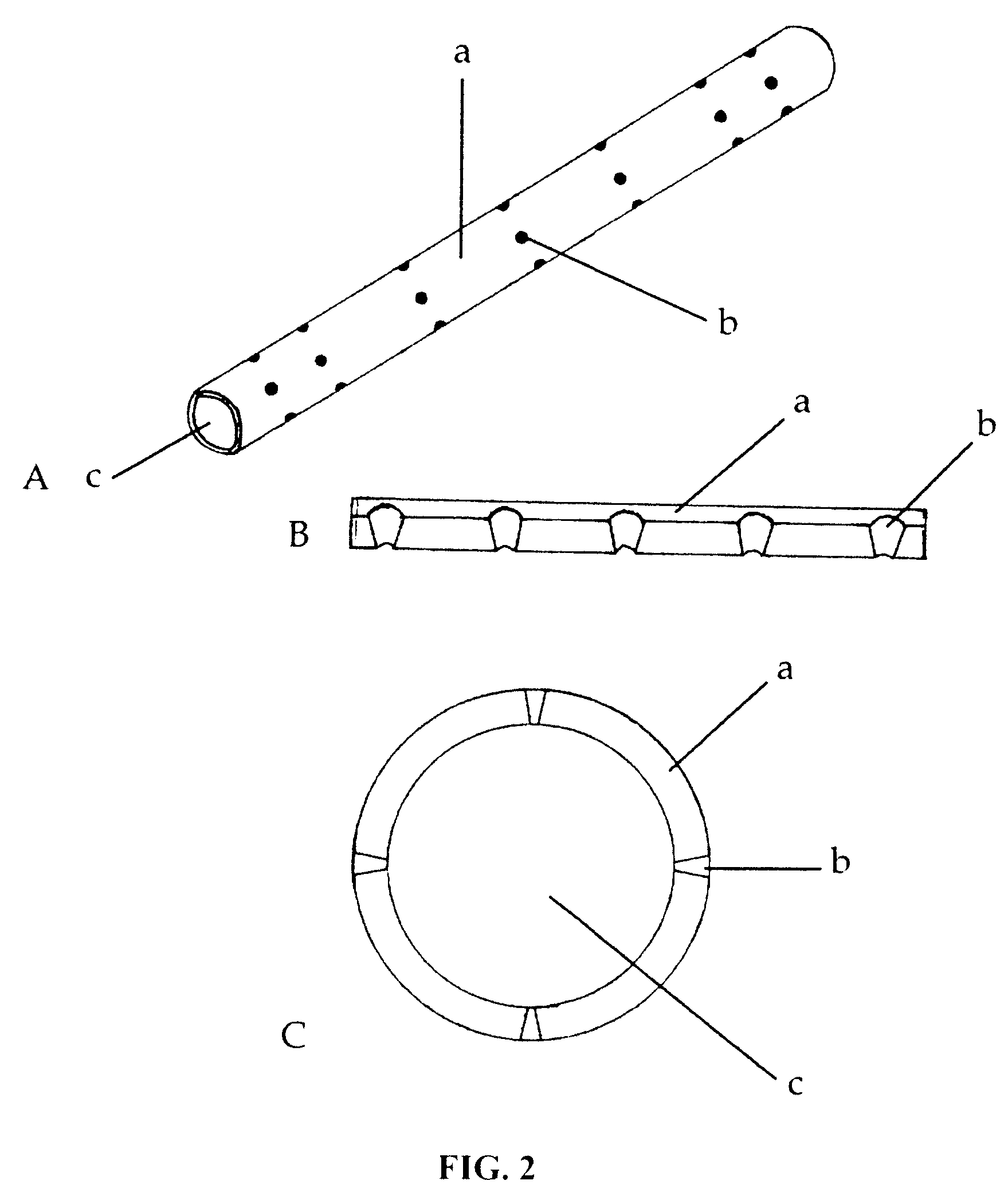
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 04203 Sec. 371 Date May 20, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date May 20, 1999 PCT Filed Nov. 19, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 22155 PCT Pub. Date May 28, 1998The present invention offers an artificial tube for nerve which can remain in the body until the nerve regenerates while does not remain as a foreign body in the body following nerve regeneration, and which induces axons regenerated from severed nerve stumps, can promote infiltration of blood capillaries from the body and regeneration of nerve tissue. The present invention comprises a tube 10 or 20 having coating layers 12, 13 or 22, 23 composed of gelatin or collagen on the inner and outer surfaces of a tube 11 or 21 composed of a material being biodegradable and absorbable in vivo, and a collagen body 30 or 40 having cavities 32, 33 or 41 which pass through said tube so as to be substantially parallel to the axis of said tube; wherein, said cavities are filled with a matrix gel.
Owner:TAPIC INT
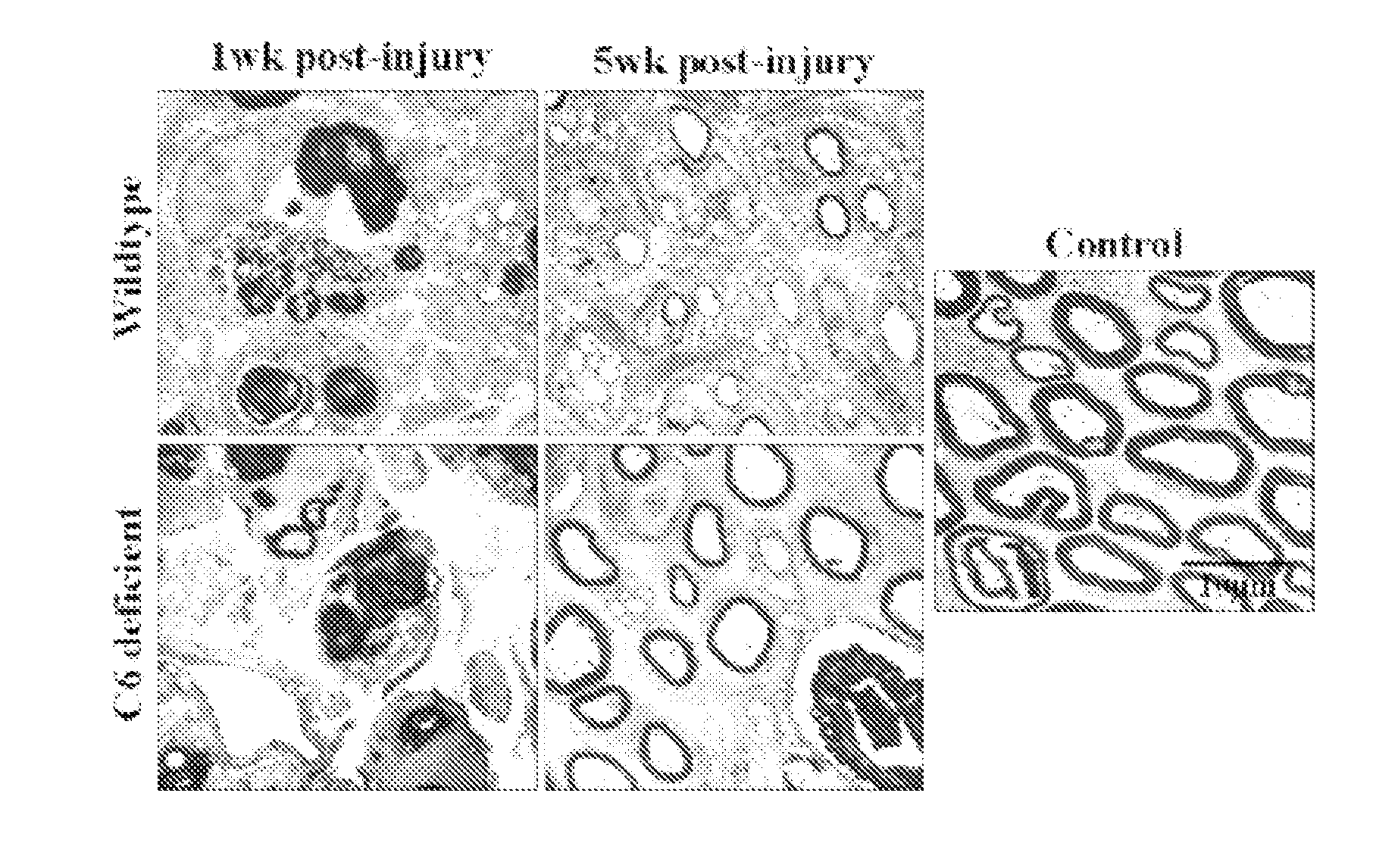
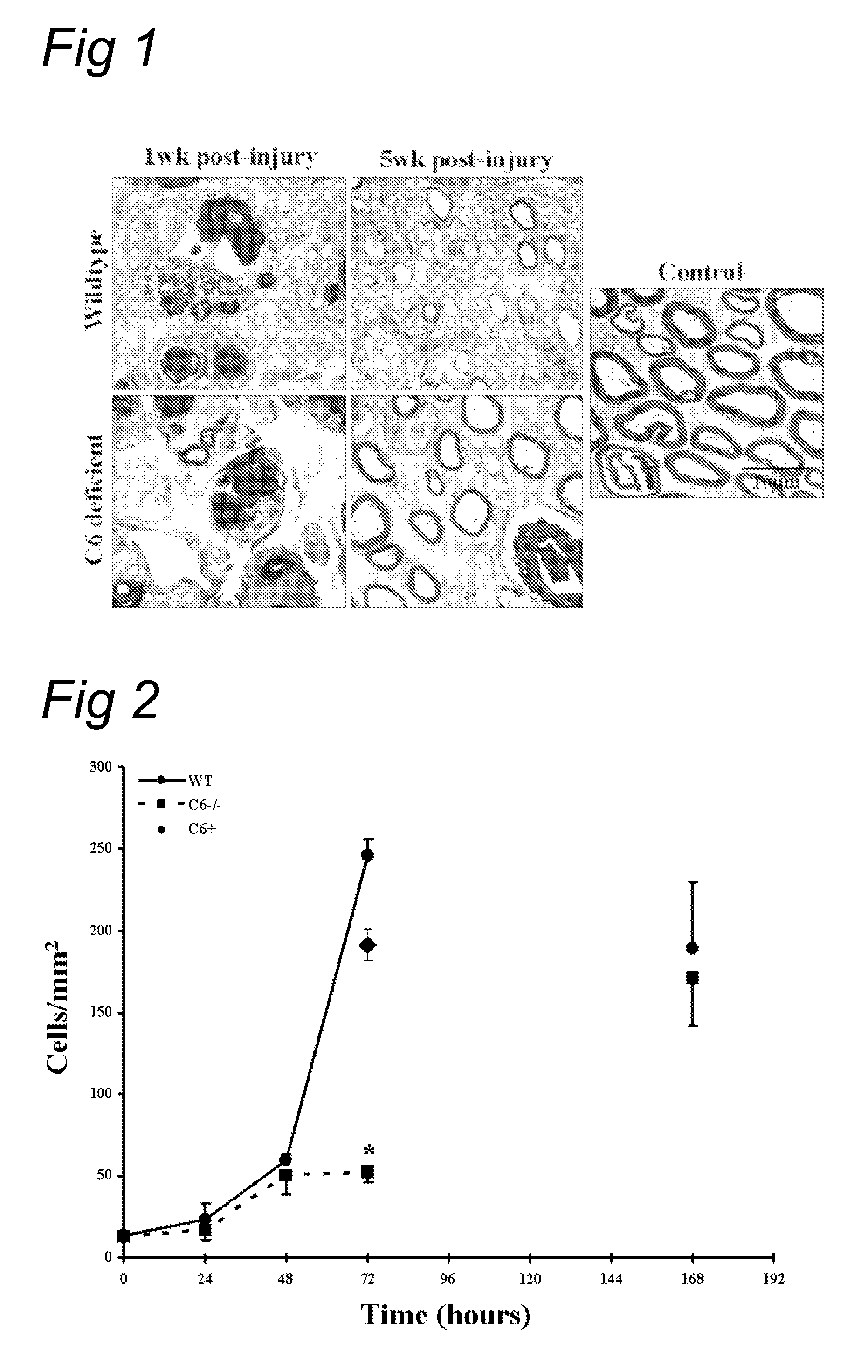
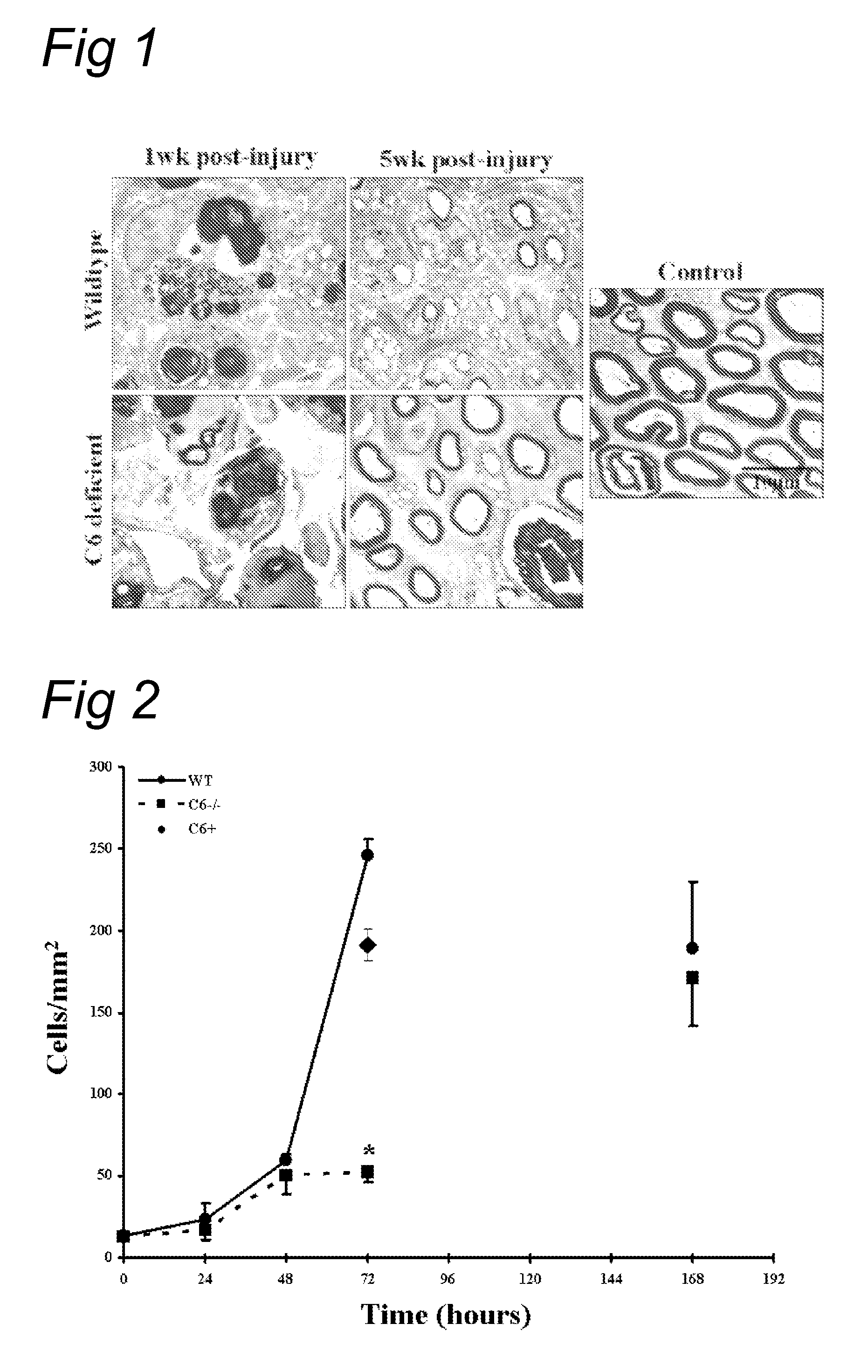
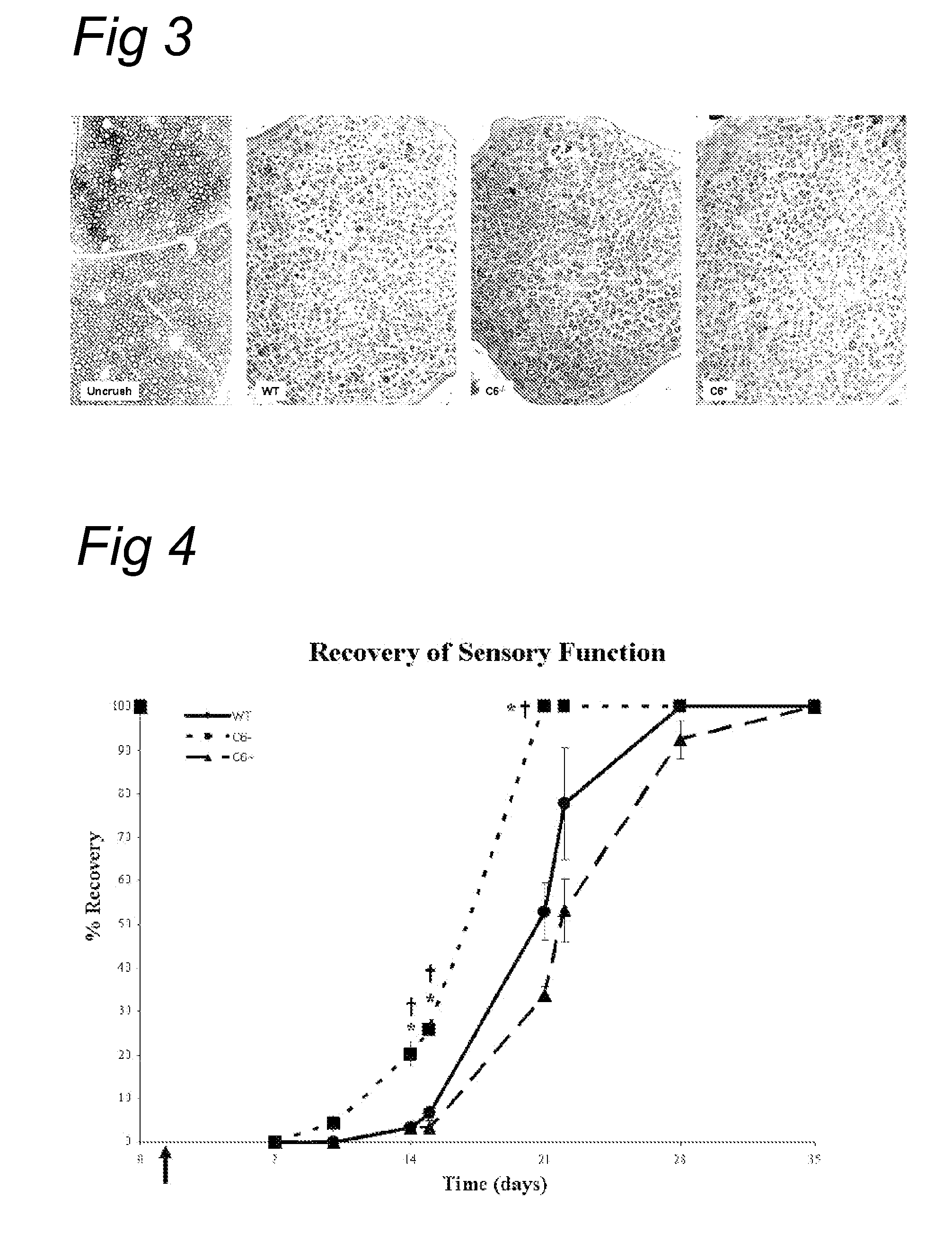
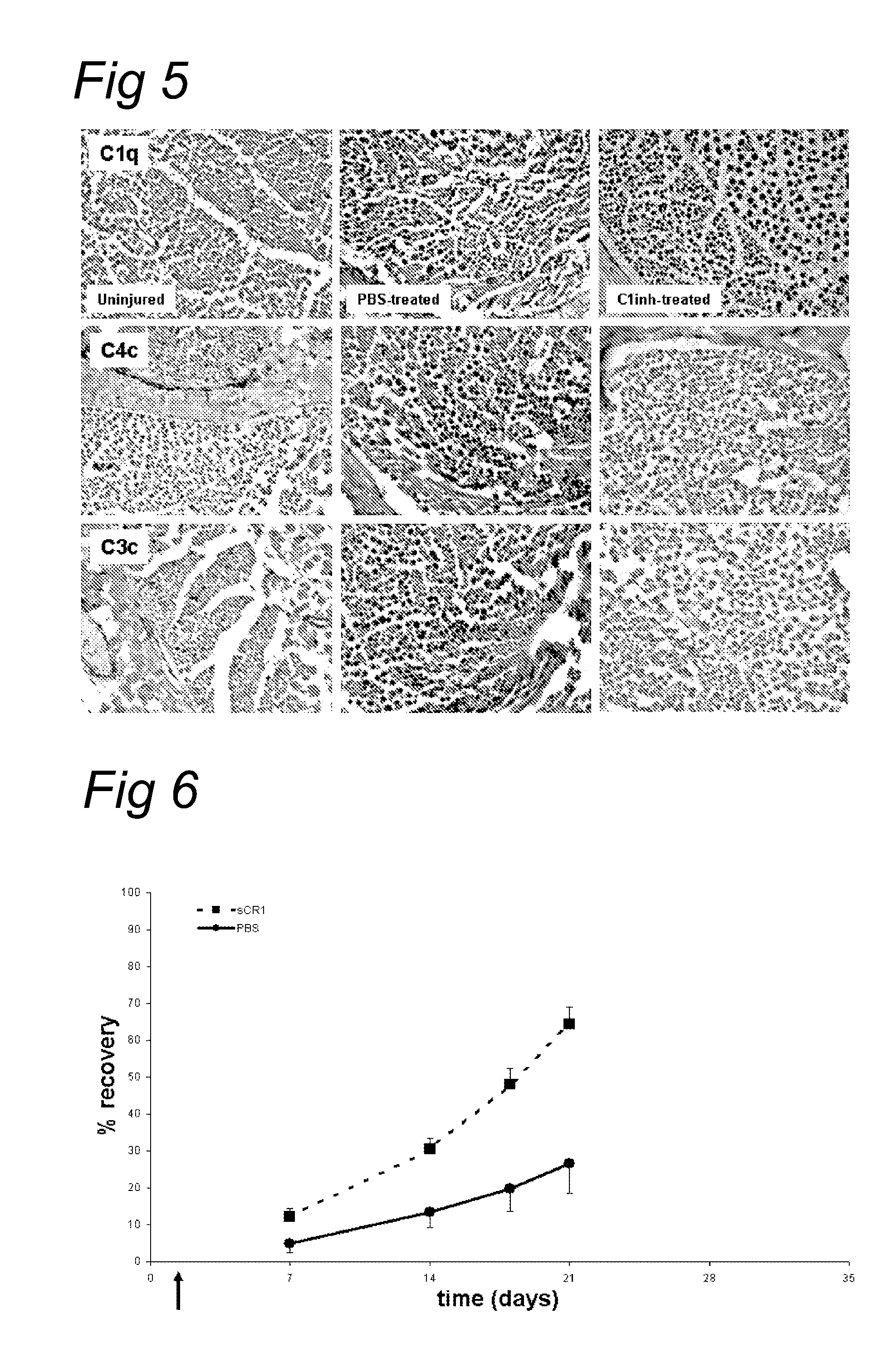
Complement inhibition for improved nerve regeneration
ActiveUS20100143344A1Improve regenerative abilityPromote regenerationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to methods and medicaments used for treating conditions that require axonal regeneration, e.g. in mammals affected by injury or disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. The medicaments used in these methods facilitate axonal regeneration by inhibition of the complement system. Conditions requiring axonal regeneration that may be treated in accordance with the invention include physical injuries as well as neurodegenerative disorders of the peripheral or central nervous system.
Owner:REGENESANCE
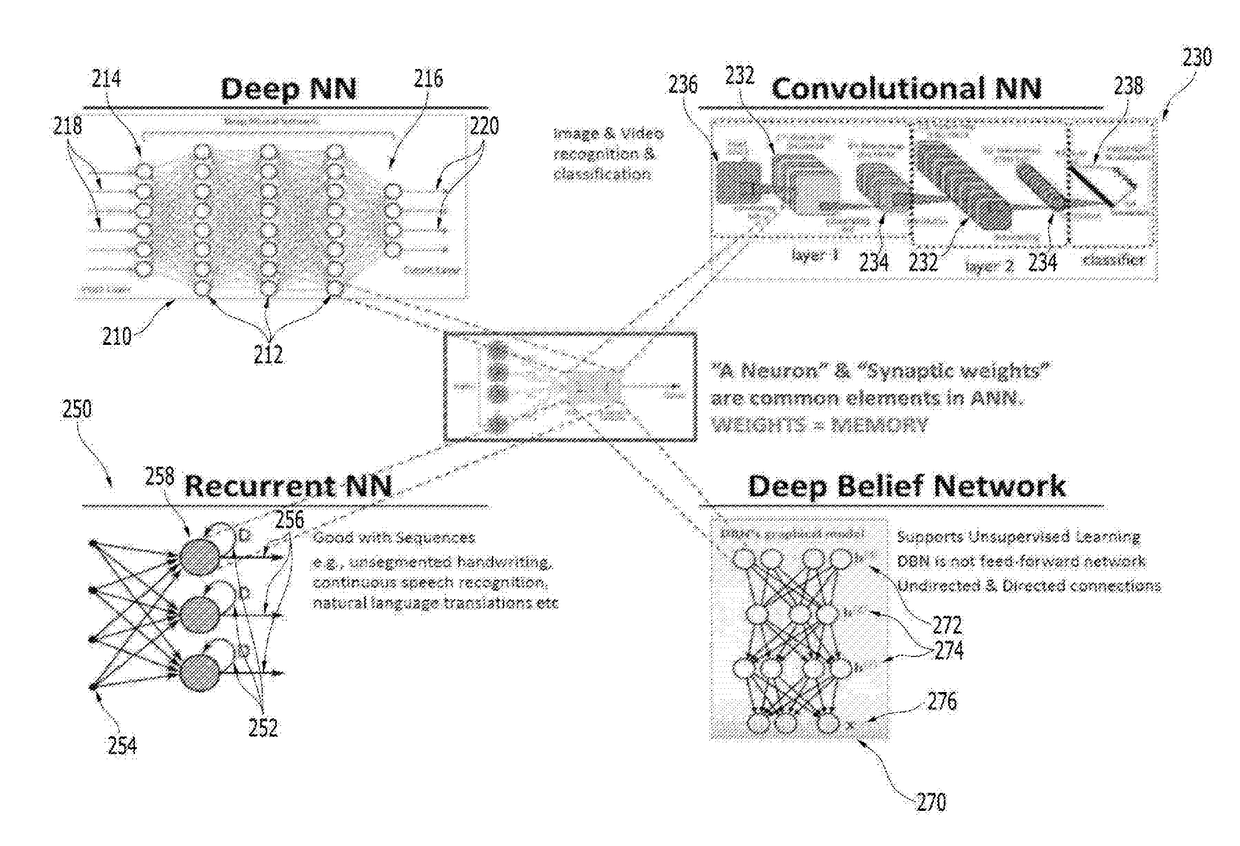
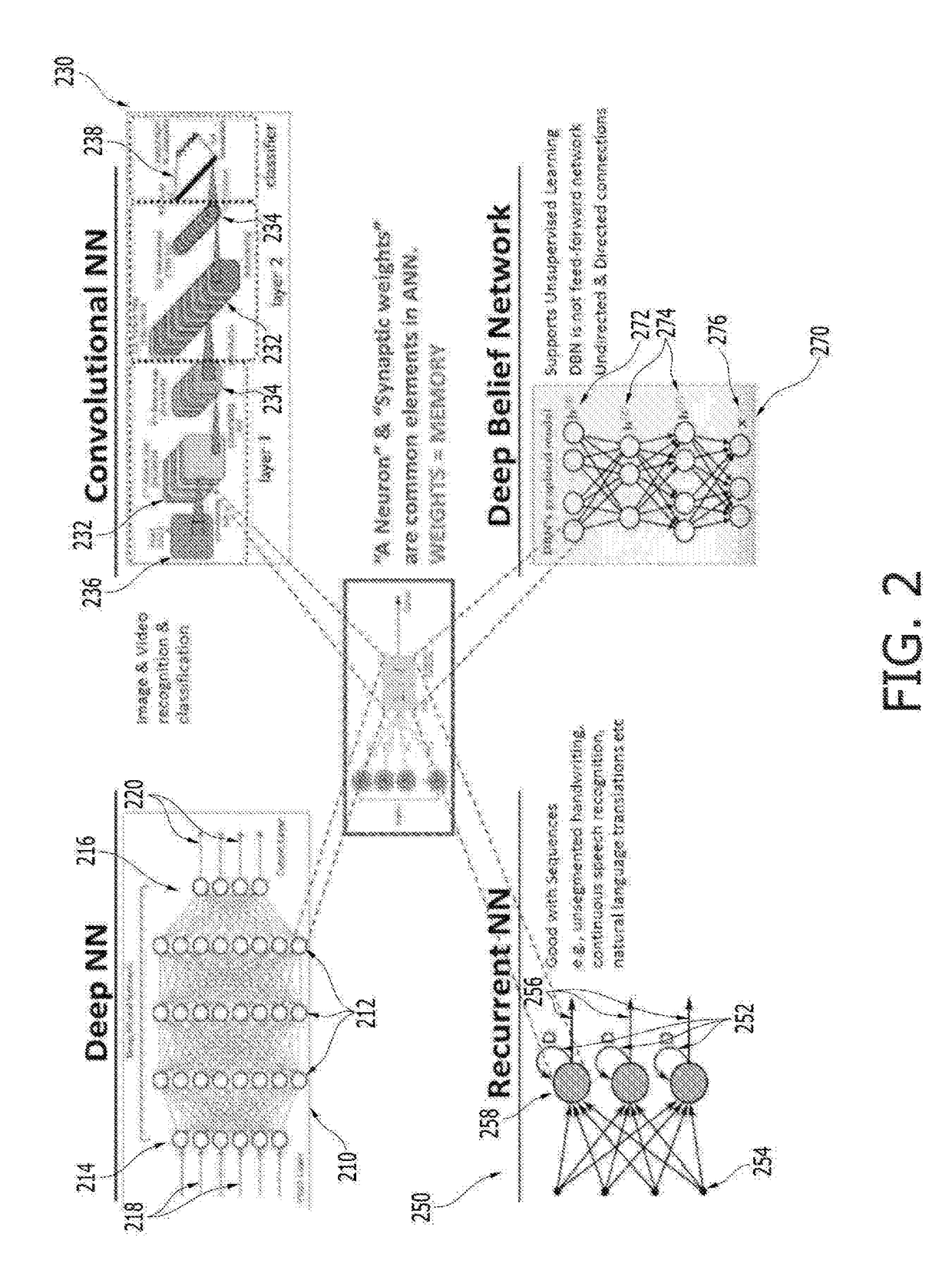
Neural network hardware accelerator architectures and operating method thereof
ActiveUS20180075344A1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital storageTimestampNeural network system
A memory-centric neural network system and operating method thereof includes: a processing unit; semiconductor memory devices coupled to the processing unit, the semiconductor memory devices contain instructions executed by the processing unit; a weight matrix constructed with rows and columns of memory cells, inputs of the memory cells of a same row are connected to one of Axons, outputs of the memory cells of a same column are connected to one of Neurons; timestamp registers registering timestamps of the Axons and the Neurons; and a lookup table containing adjusting values indexed in accordance with the timestamps, the processing unit updates the weight matrix in accordance with the adjusting values.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Neural network hardware accelerator architectures and operating method thereof
ActiveUS20180075339A1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital storageTimestampNeural network system
A memory-centric neural network system and operating method thereof includes: a processing unit; semiconductor memory devices coupled to the processing unit, the semiconductor memory devices contain instructions executed by the processing unit; weight matrixes including a positive weight matrix and a negative weight matrix constructed with rows and columns of memory cells, inputs of the memory cells of a same row are connected to one of Axons, outputs of the memory cells of a same column are connected to one of Neurons; timestamp registers registering timestamps of the Axons and the Neurons; and a lookup table containing adjusting values indexed in accordance with the timestamps, the processing unit updates the weight matrixes in accordance with the adjusting values.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
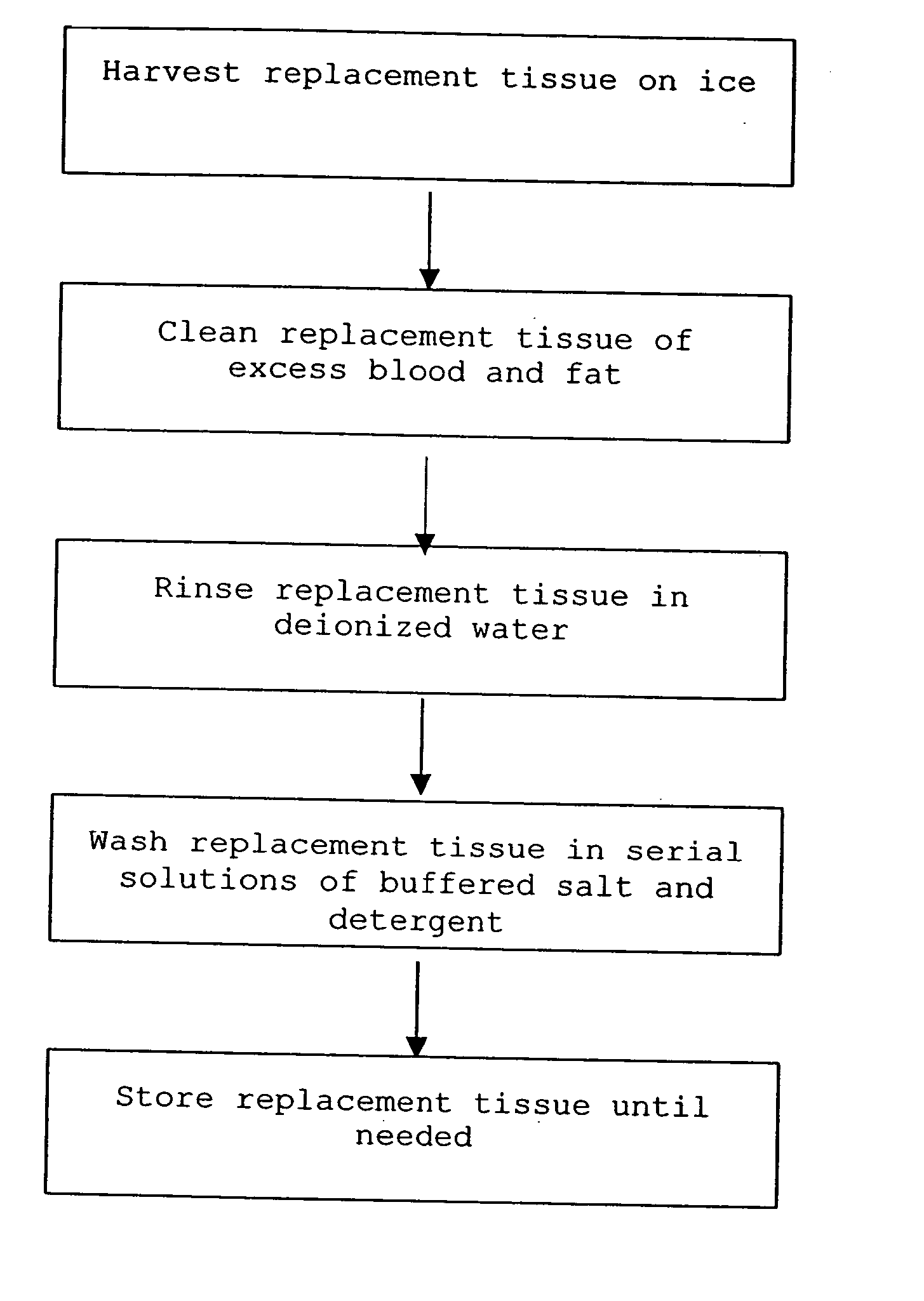
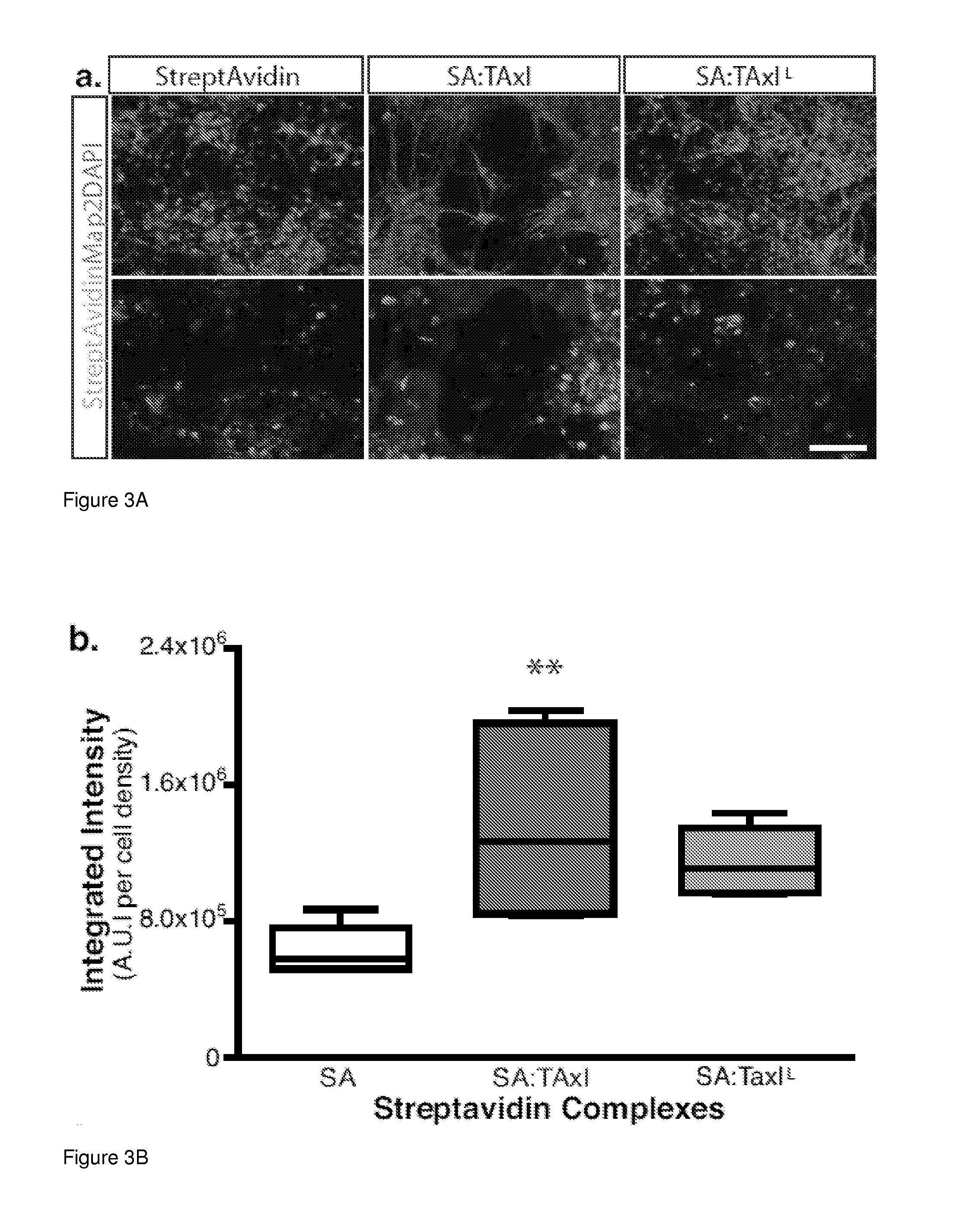
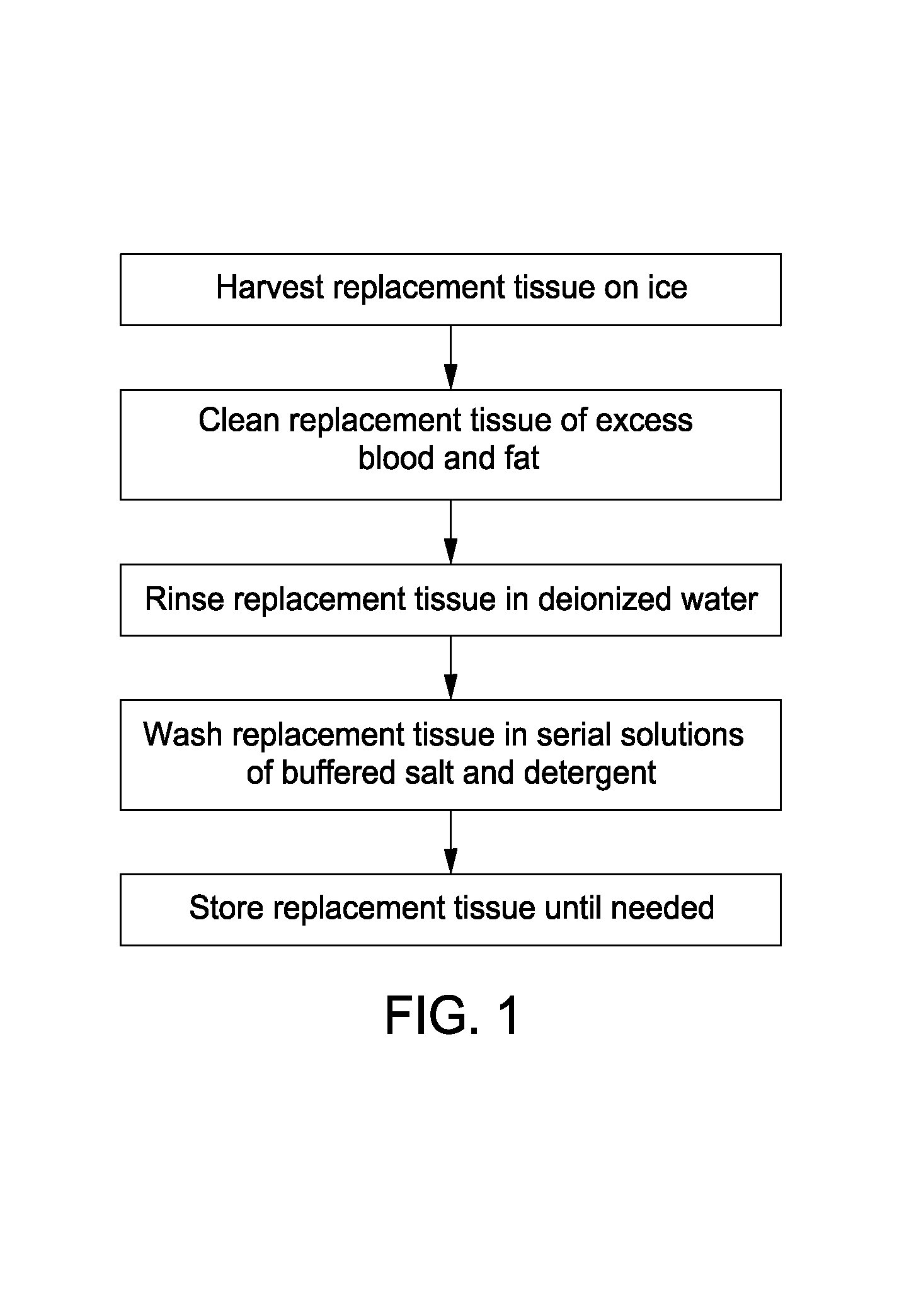
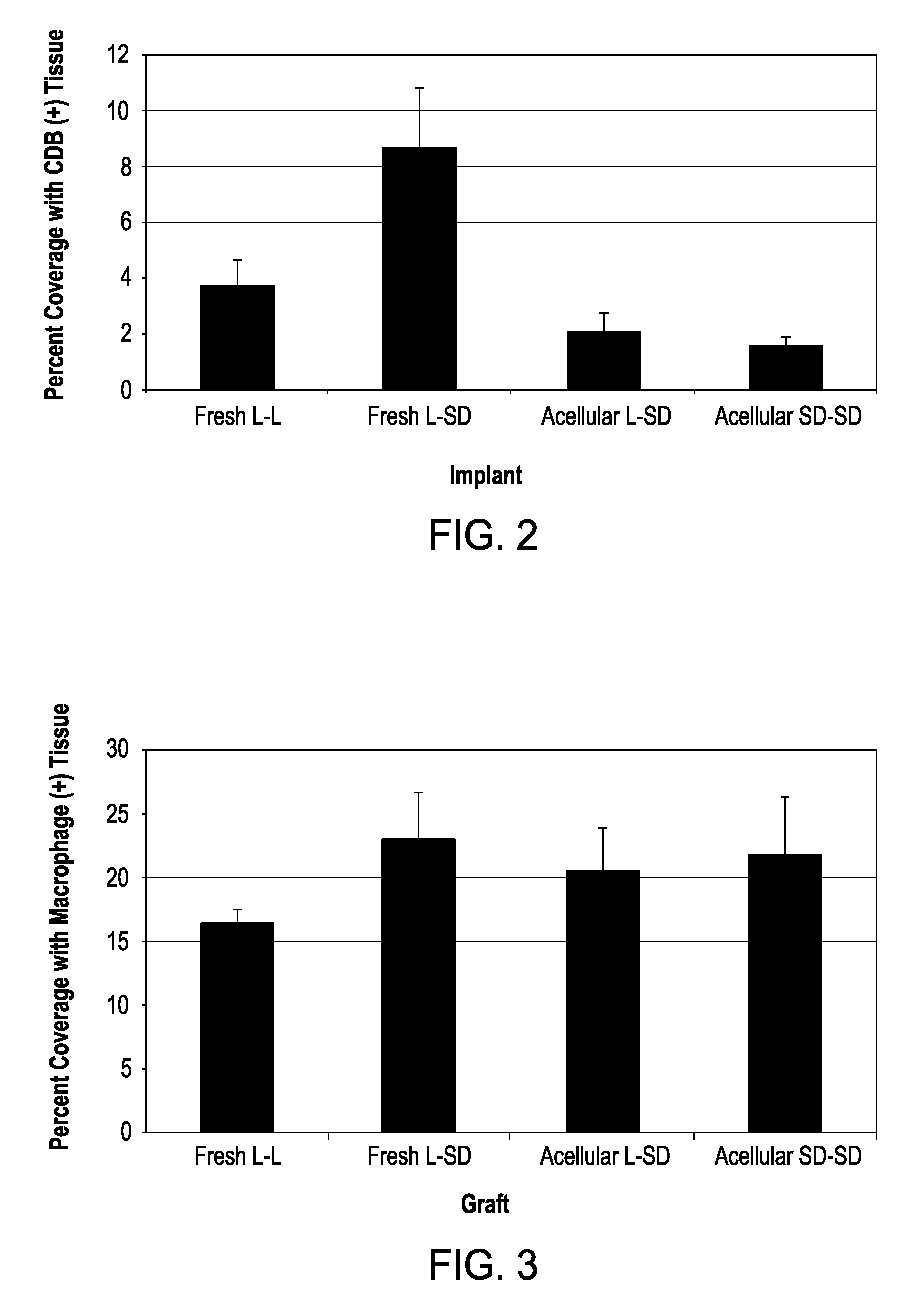
Cell-free tissue replacement for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20050043819A1Less remodelingPrevent penetrationPowder deliveryTissue regenerationCell freeNerve graft
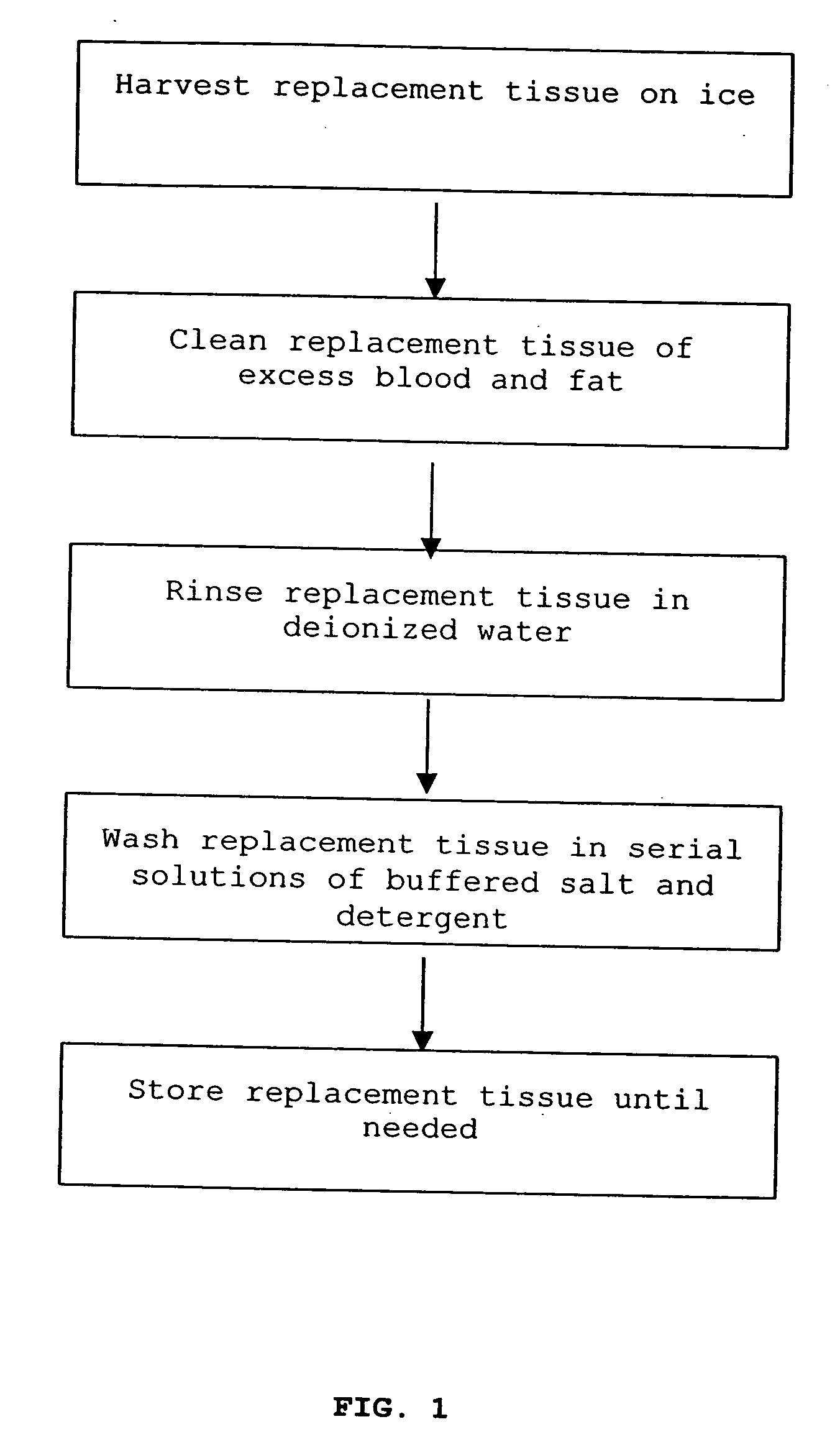
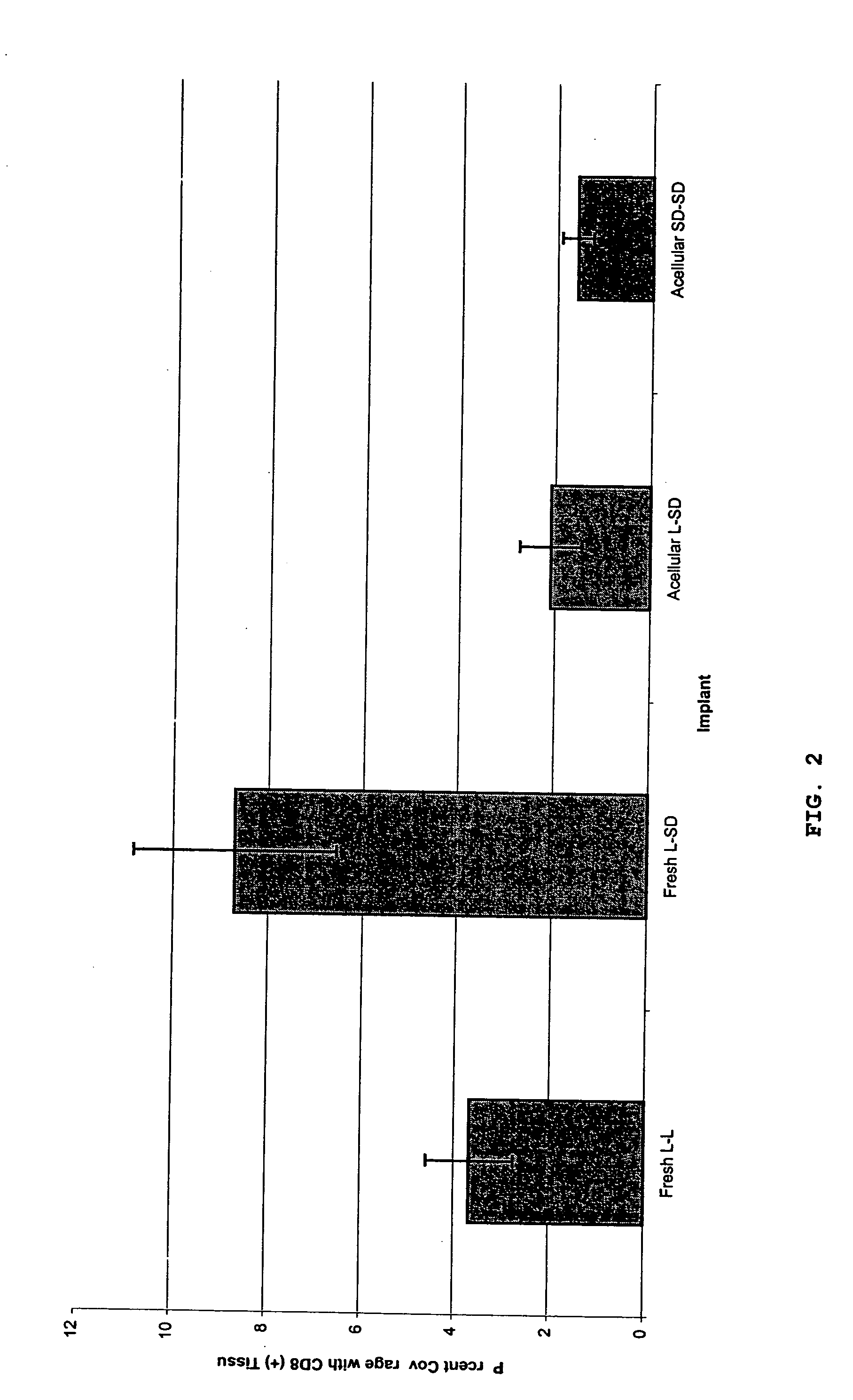
The present invention is a natural, cell-free tissue replacement that does not require difficult or extensive preparation made by washing tissue replacement in a solution including one or more sulfobetaines and an anionic surface-active detergent and washing the tissue replacement in serial solutions of the buffered salt to remove excess detergent. The natural, cell-free tissue replacement may be a nerve graft that supports axonal regeneration, guides the axons toward the distal nerve end and / or is immunologically tolerated. Other forms of the invention are a composition and kit prepared by the method of making a native, cell-free tissue replacement. The present invention may be modified for use in diagnostic, therapeutic, and prophylactic applications.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
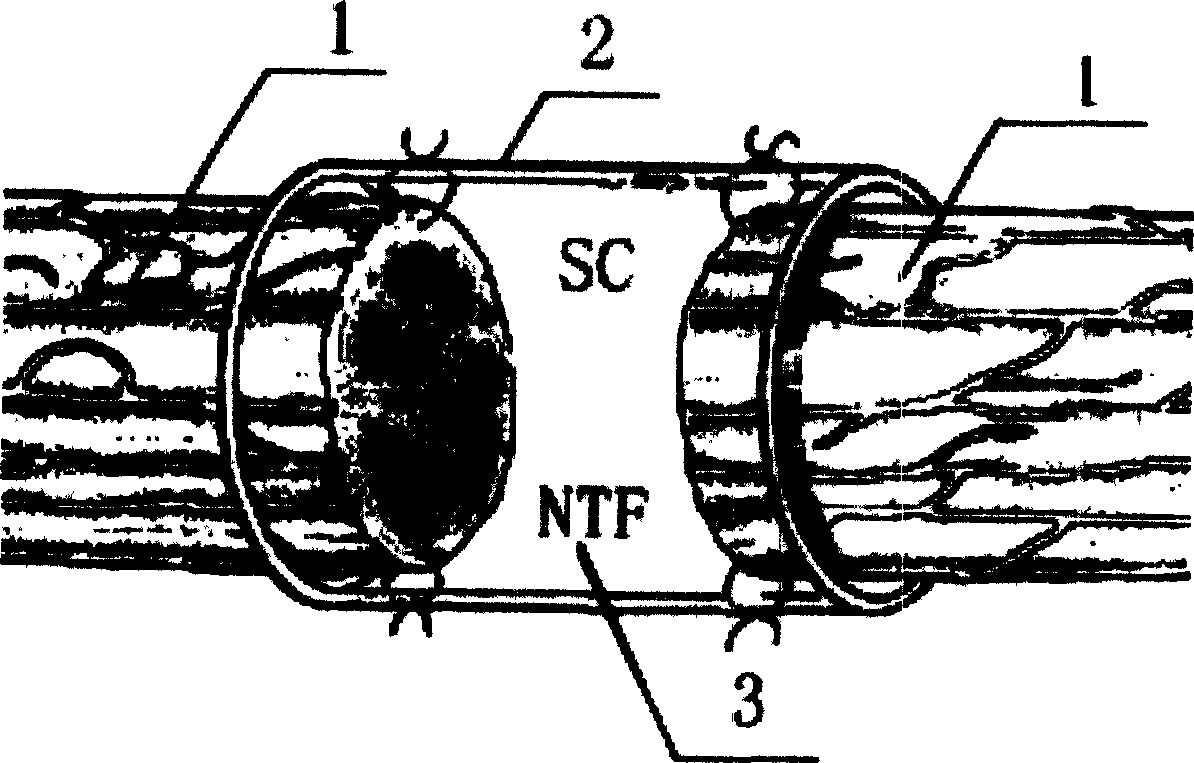
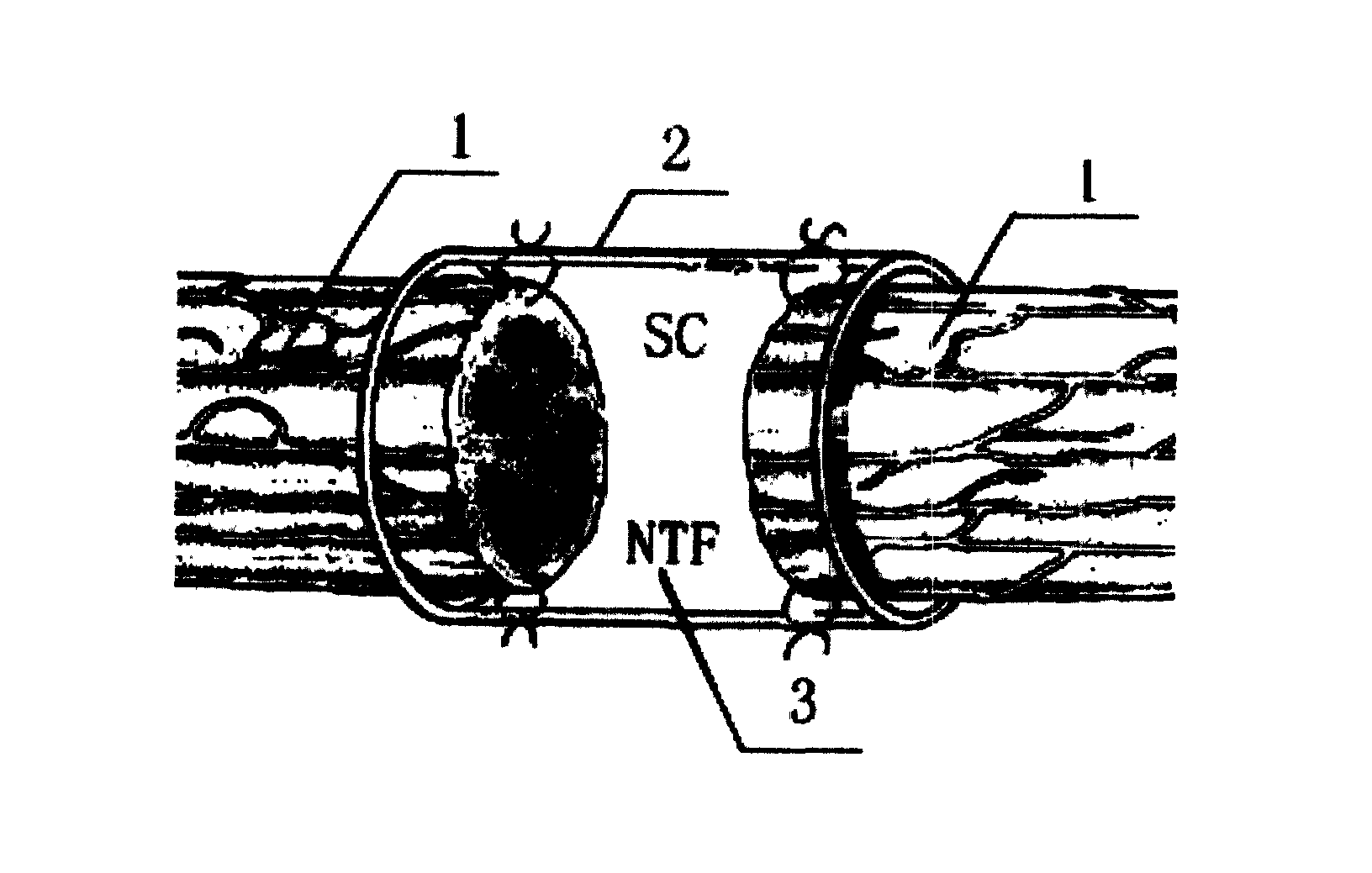
Tissue engineering peripheral nerve used for repairing peripheral nerve defect and its preparation method
A tissue-engineered peripheral nerve for reparing the demaged peripheral nerve is composed of neural canal and neuroglia cells or stem cells, and is prepared through preparing neural canal, preparing neurotrophic factor release controllable microspheres, and configuring the tissue-engineered peripheral nerve.
Owner:STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL NO 4 ARMY MEDICAL COLLEGE PLA
Complement inhibition for improved nerve regeneration
ActiveUS8703136B2Improve regenerative abilityPromote regenerationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to methods and medicaments used for treating conditions that require axonal regeneration, e.g. in mammals affected by injury or disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. The medicaments used in these methods facilitate axonal regeneration by inhibition of the complement system. Conditions requiring axonal regeneration that may be treated in accordance with the invention include physical injuries as well as neurodegenerative disorders of the peripheral or central nervous system.
Owner:REGENESANCE
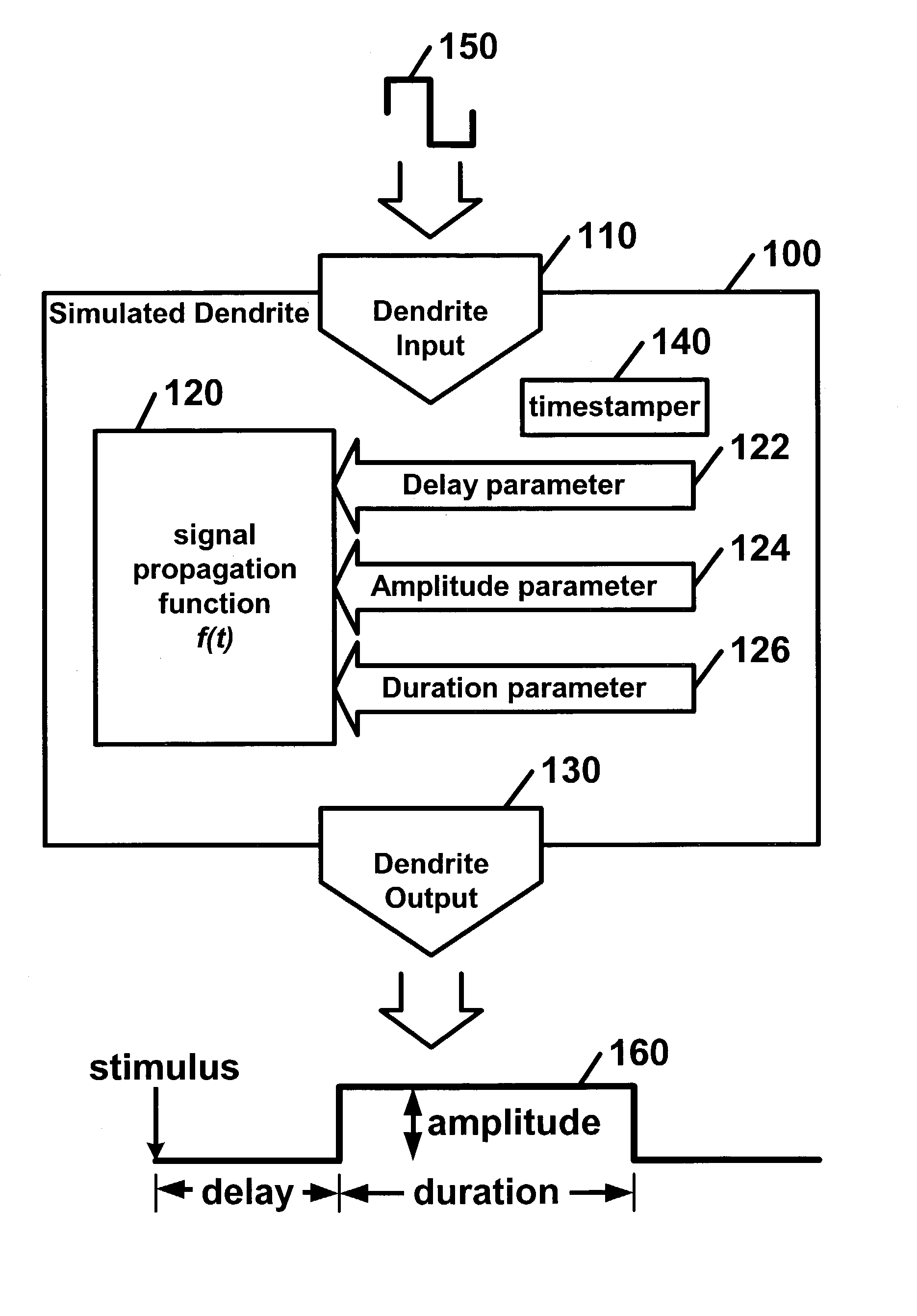
Neural processor
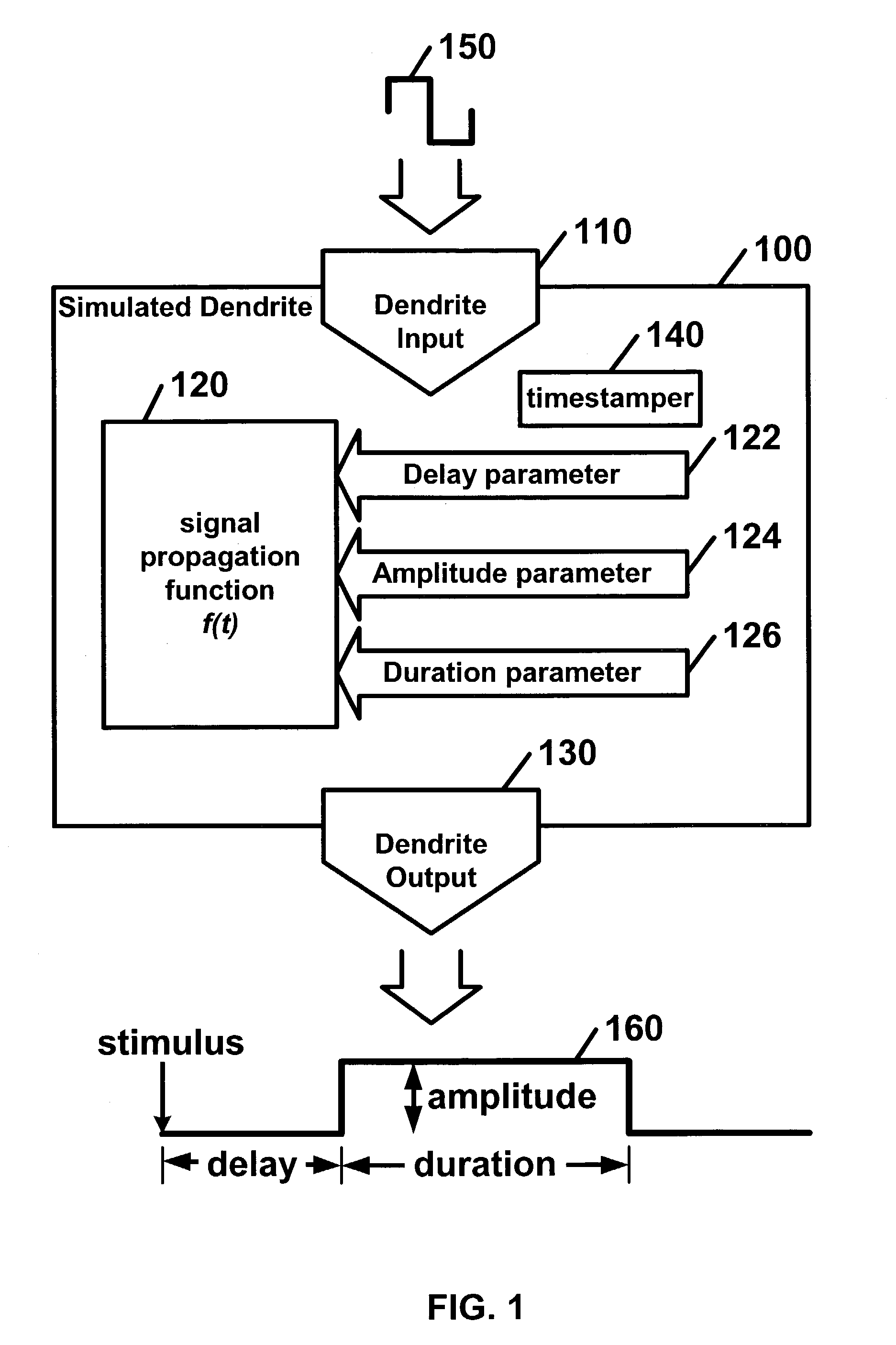
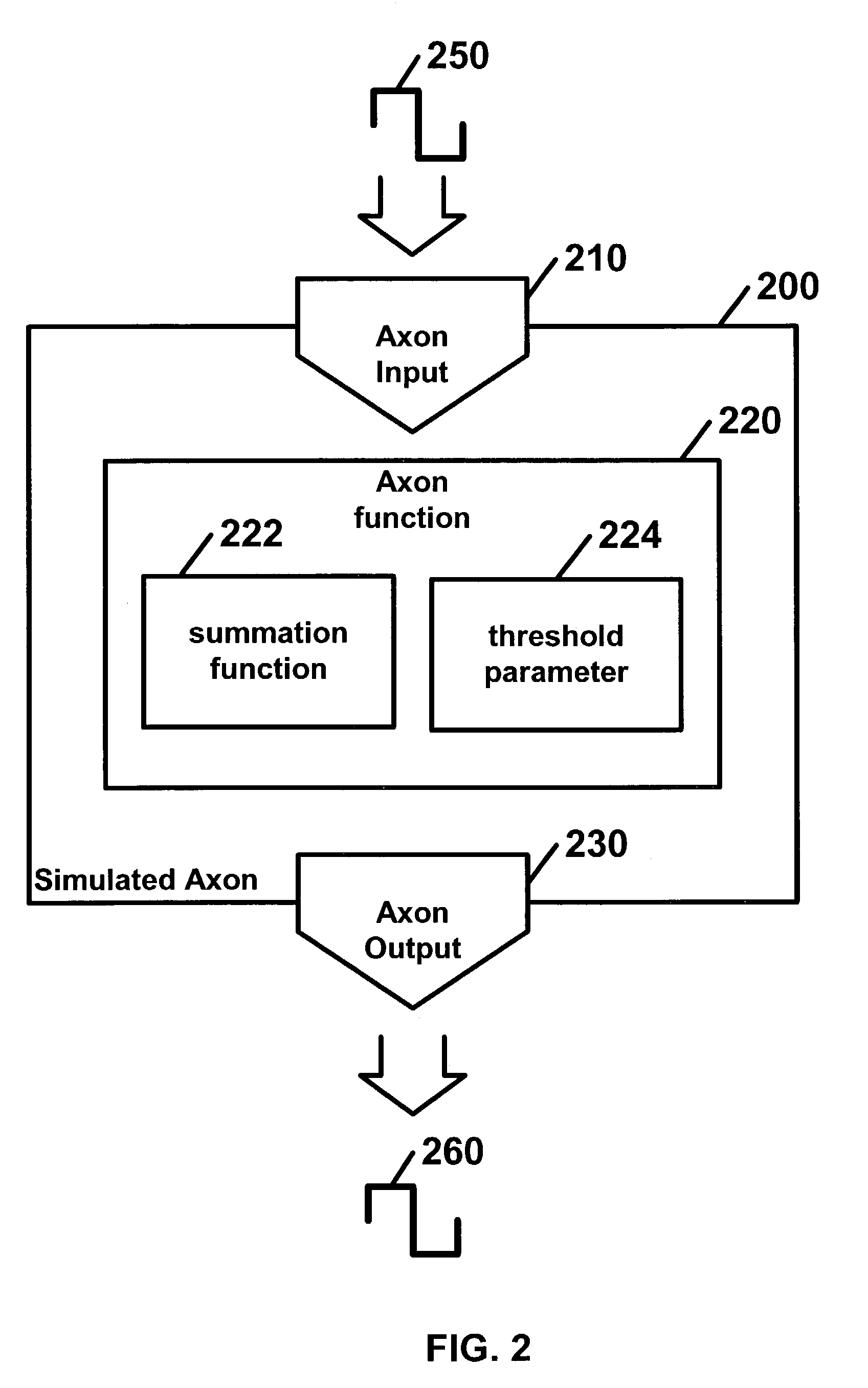
InactiveUS7174325B1Simple methodLarge structureDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesDendriteNeural processing
Disclosed is a digital neural processor comprising at least one neural processing element. The neural processing elements including at least one simulated dendrite and a simulated axon. Each of the simulated dendrites may include: a dendrite input capable of receiving at least one dendrite input signal and a dendrite signal propagation function capable of calculating a dendrite output signal in discrete time steps from each dendrite input signal. The signal propagation function may further include a delay parameter; a duration parameter; and an amplitude parameter. The simulated axon includes an axon input capable of receiving dendrite output signals, an axon function, capable of calculating an axon output signal from dendrite output signal(s) and an axon output capable of outputting the axon output signal.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
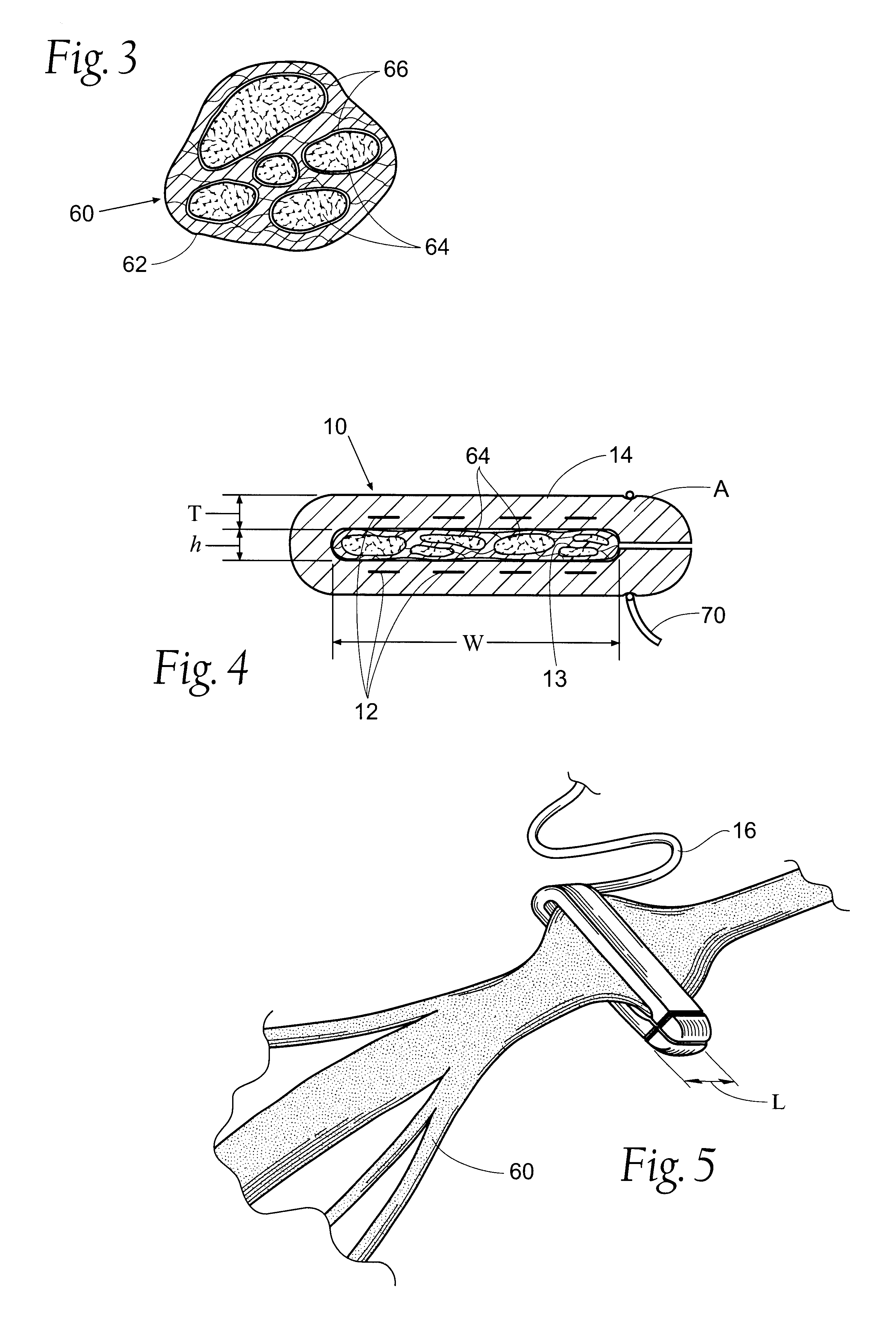
A Biomimetic Synthetic Nerve Implant
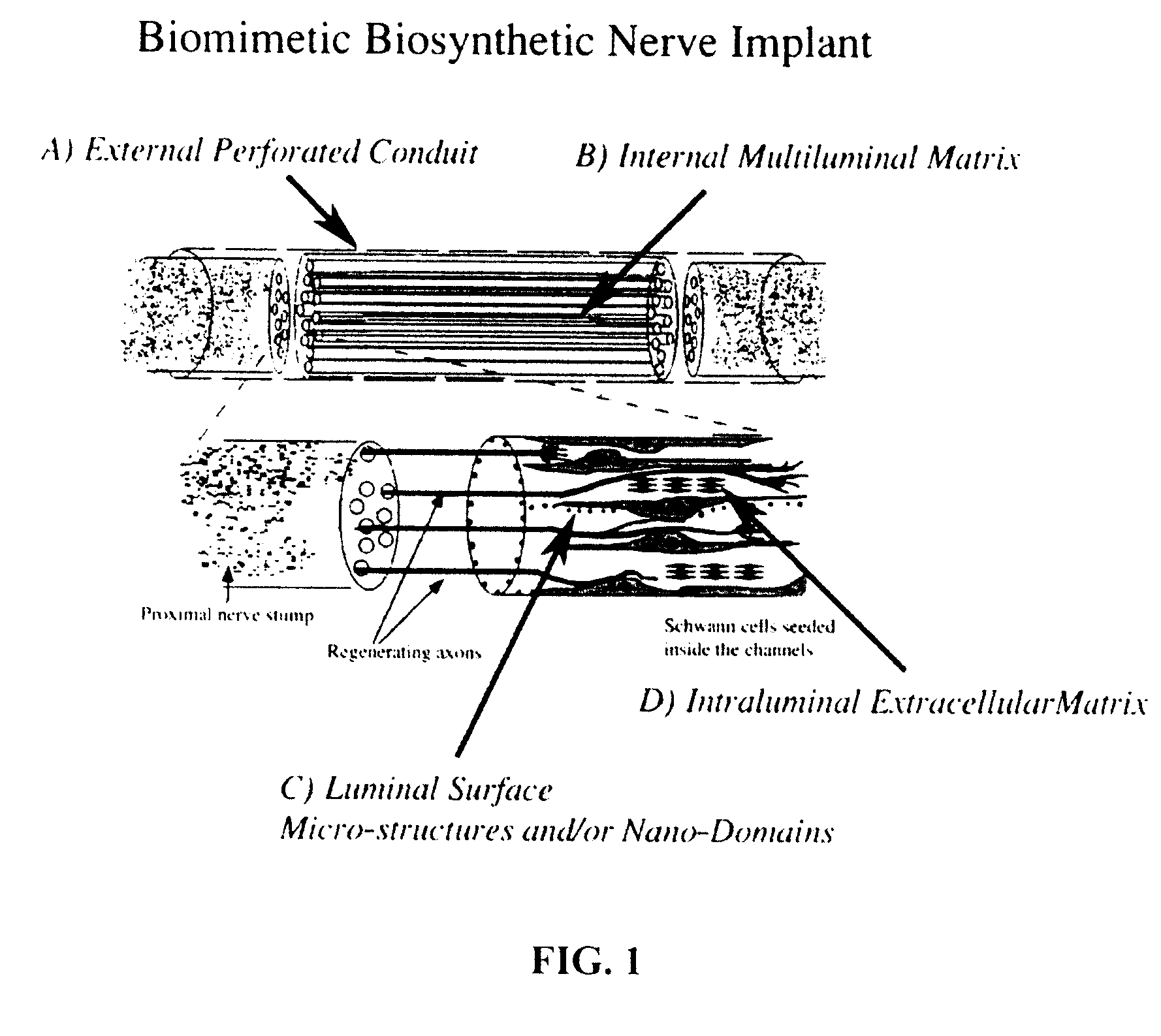
InactiveUS20070100358A2Enhanced and directed nerve regenerationPromotes and directs nerve regenerationElectrotherapyTissue regenerationAnatomical structuresSpinal cord
A biomimetic biosynthetic nerve implant (BNI) that uses a hydrogel-based, transparent, multi-channel matrix as a 3-D substrate for nerve repair is disclosed. Novel scaffold-casting devices were designed for reproducible fabrication of grafts containing several micro-conduits, and further tested in vivo using a sciatic nerve animal model and repair of the adult hemitransected spinal cord. At 16 weeks post-injury of the sciatic nerve, empty tubes formed a single nerve cable. In sharp contrast, animals that received the multi-luminal BNI showed multiple nerve cables within the available microchannels, better resembling the multi-fascicular anatomy and ultra structure of the normal nerve. In the injured spinal cord, the BNI loaded with genetically engineered Schwann cells were able to demonstrate survival of the grafted cells inside the BNI, and robust axonal regeneration through the implant up to 45 days after repair.
Owner:TEXAS SCOTTISH RITE HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN
Method for treating ALS via the increased production of factor h
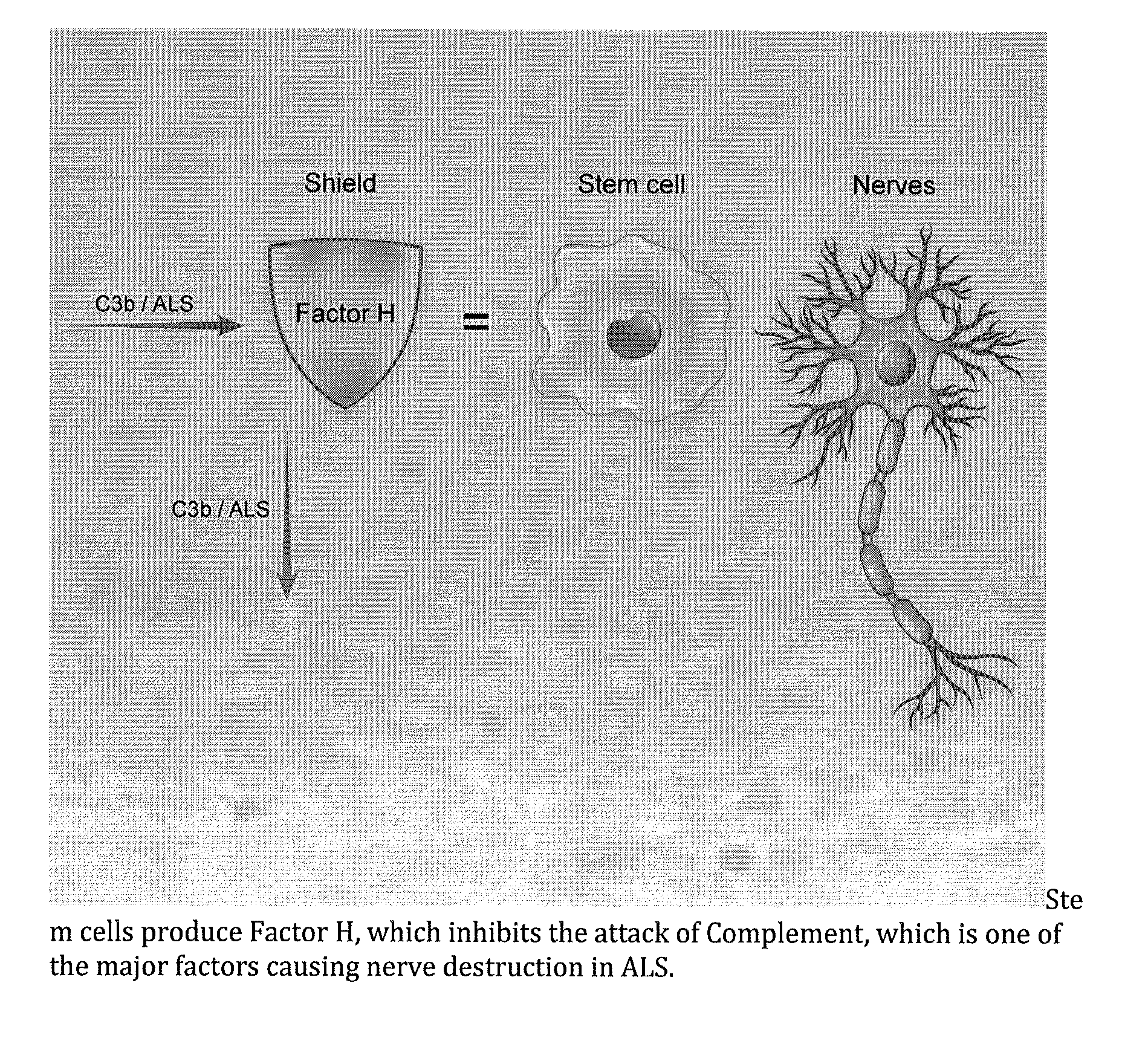
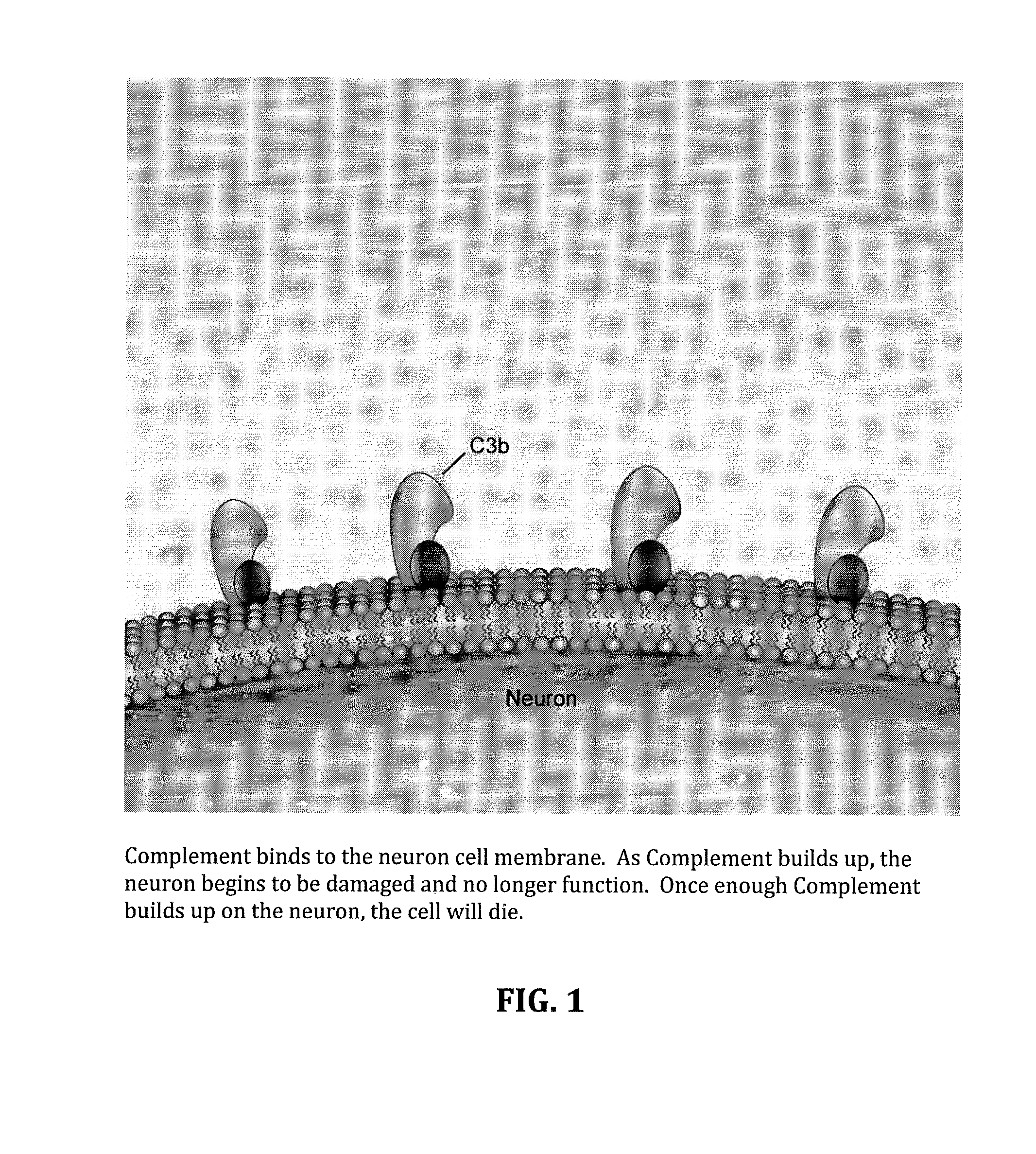
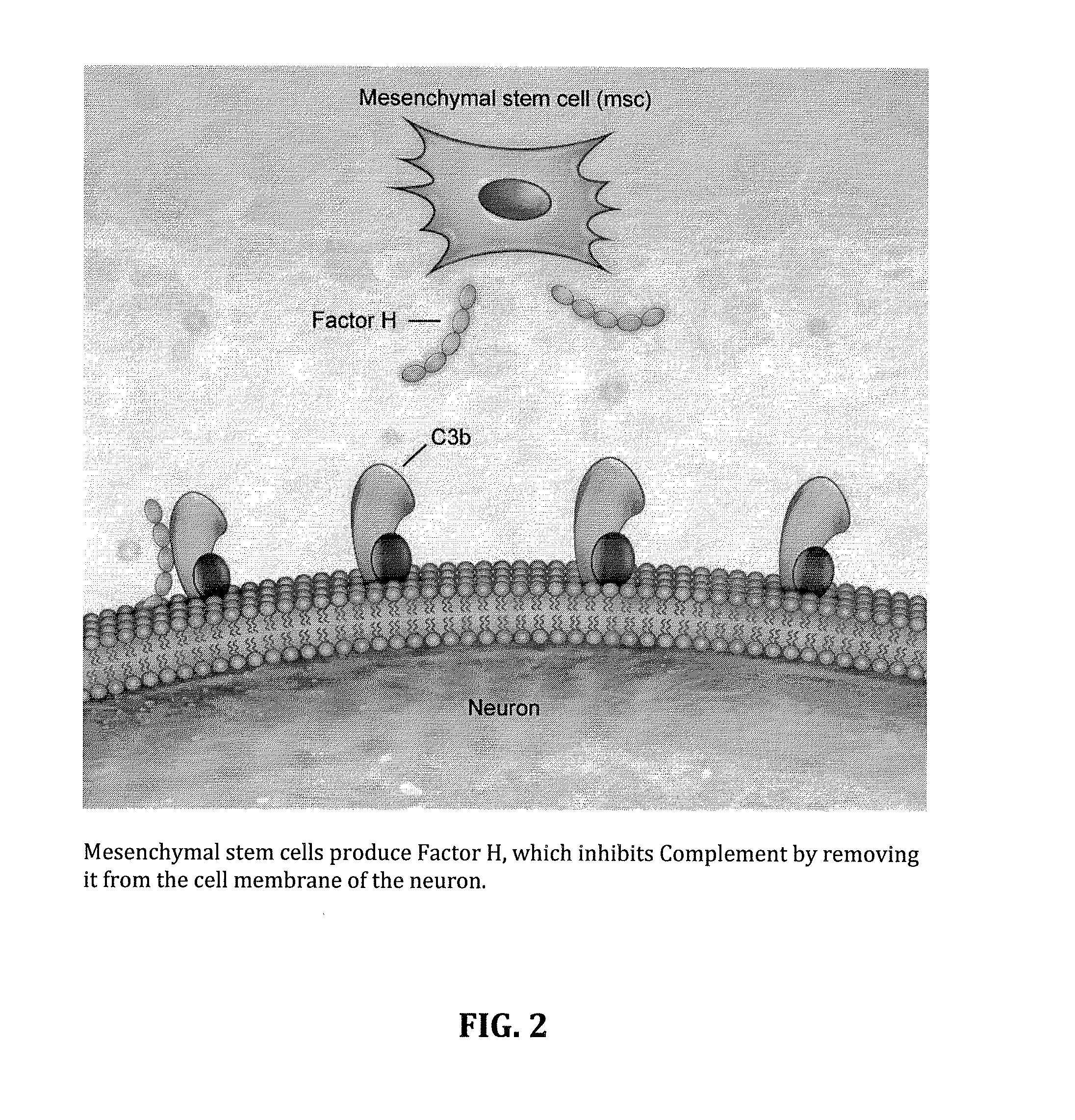
InactiveUS20140234275A1Improve satisfactionInhibition effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWhole bodyPrimary motor neuron
Methods and systems for the treatment for ALS incorporating stem cells harvested from the subject to be treated. These stem cells may be genetically altered with the addition of several genes of interest. Then, the patient will receive systemic gene therapy for the muscles and directed specifically at motor neurons. In this multi-pronged treatment approach, the stem cells provide immune regulation and the regeneration of motor neurons. And, the new motor neurons carry the added genes, which are protective against motor neuron death from ALS. The systemic therapy increases the amount of genes, which further reduces the effects of ALS. Additional gene therapy administered in the muscle will be further protective of the axon, while maintaining muscle mass and function.
Owner:BIOVIVA USA
Multi-mode neural morphological network core
ActiveCN105095967AReal-time computingGuaranteed accuracyPhysical realisationNerve networkSynaptic weight
Provided in the invention is a multi-mode neural morphological network core comprising a mode register, an axon input unit, a synaptic weight storage unit, a dendrite unit and a neuron computing unit. According to the multi-mode neural morphological network core, both artificial neural network computing and impulsive neural network computing can be carried out; and switching between an artificial neural network operation mode and an impulsive neural network operation mode can be realized according to demands.
Owner:LYNXI TECH CO LTD
Method for selectively performing local and radial peripheral stimulation
InactiveUS20120041511A1Reduce eliminateElectrotherapyLocal control/monitoringSide effectControl system
A control system for use with a neurostimulator comprises a user interface for receiving an input from a user and a controller. The user interface has a first control and a second control. The controller is configured for, in response to actuating the first control, operating the neurostimulation control system in a PNFS programming mode, and for, in response to actuating the second control, operating the neurostimulation control system in a PNS programming mode. A method of providing therapy to a patient comprises initially conveying pulsed electrical current at a pulse width into a peripheral tissue region of the patient to create a side effect via stimulation of one of a nerve ending and neural axon, and subsequently conveying pulsed electrical current at an adjusted pulse width into the peripheral tissue region to create a therapeutic effect via stimulation of the other one of the nerve ending and neural axon.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
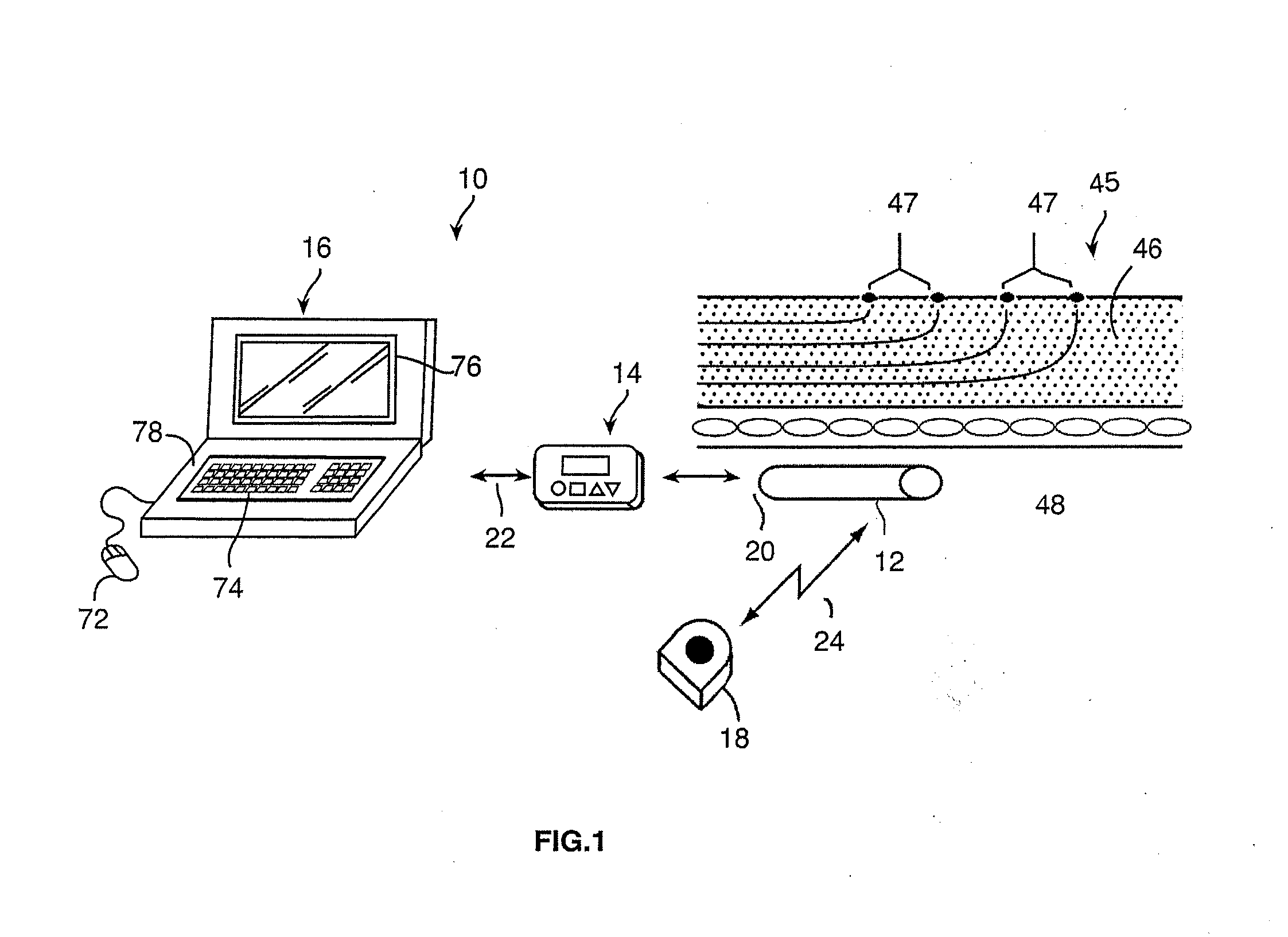
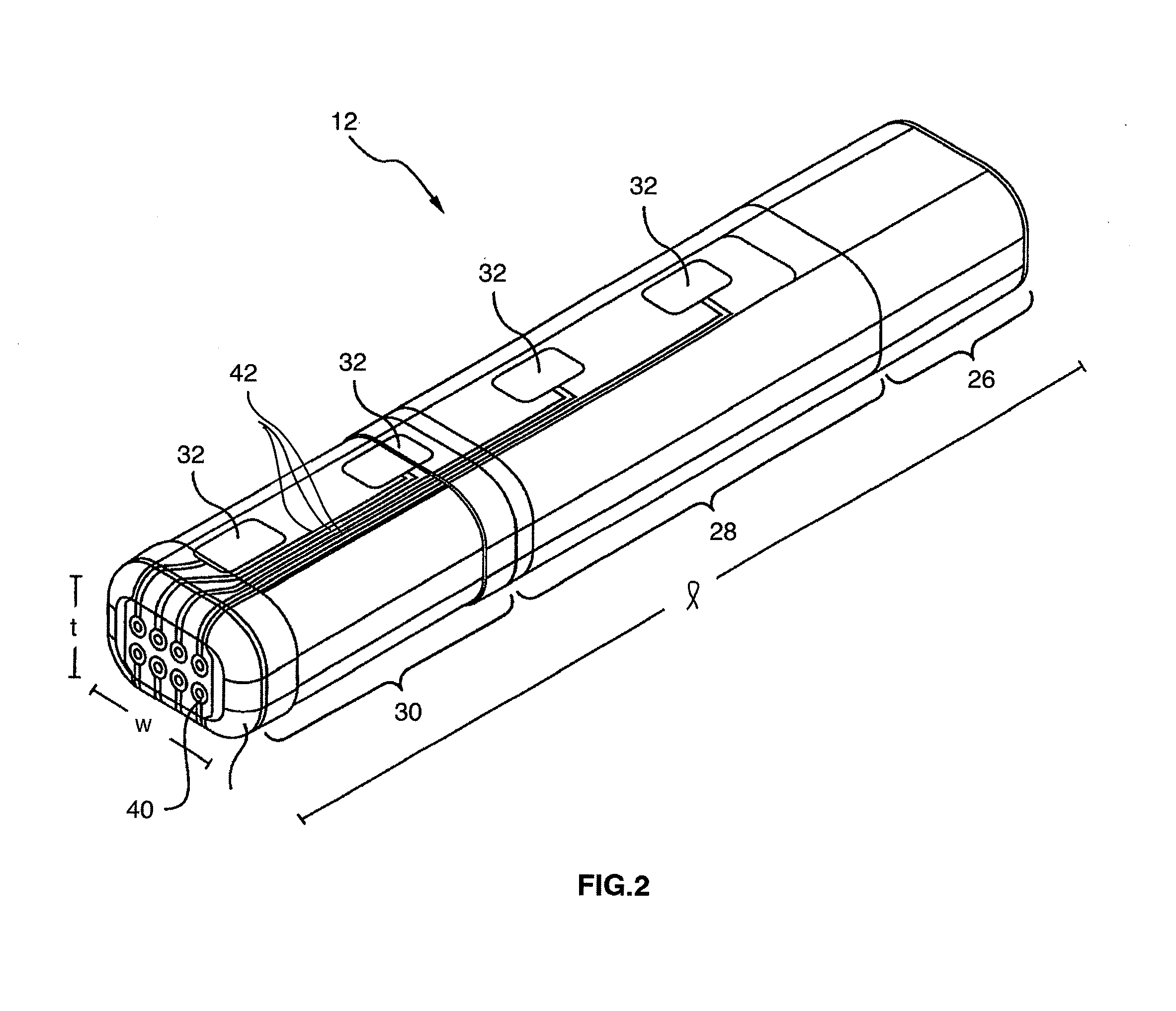
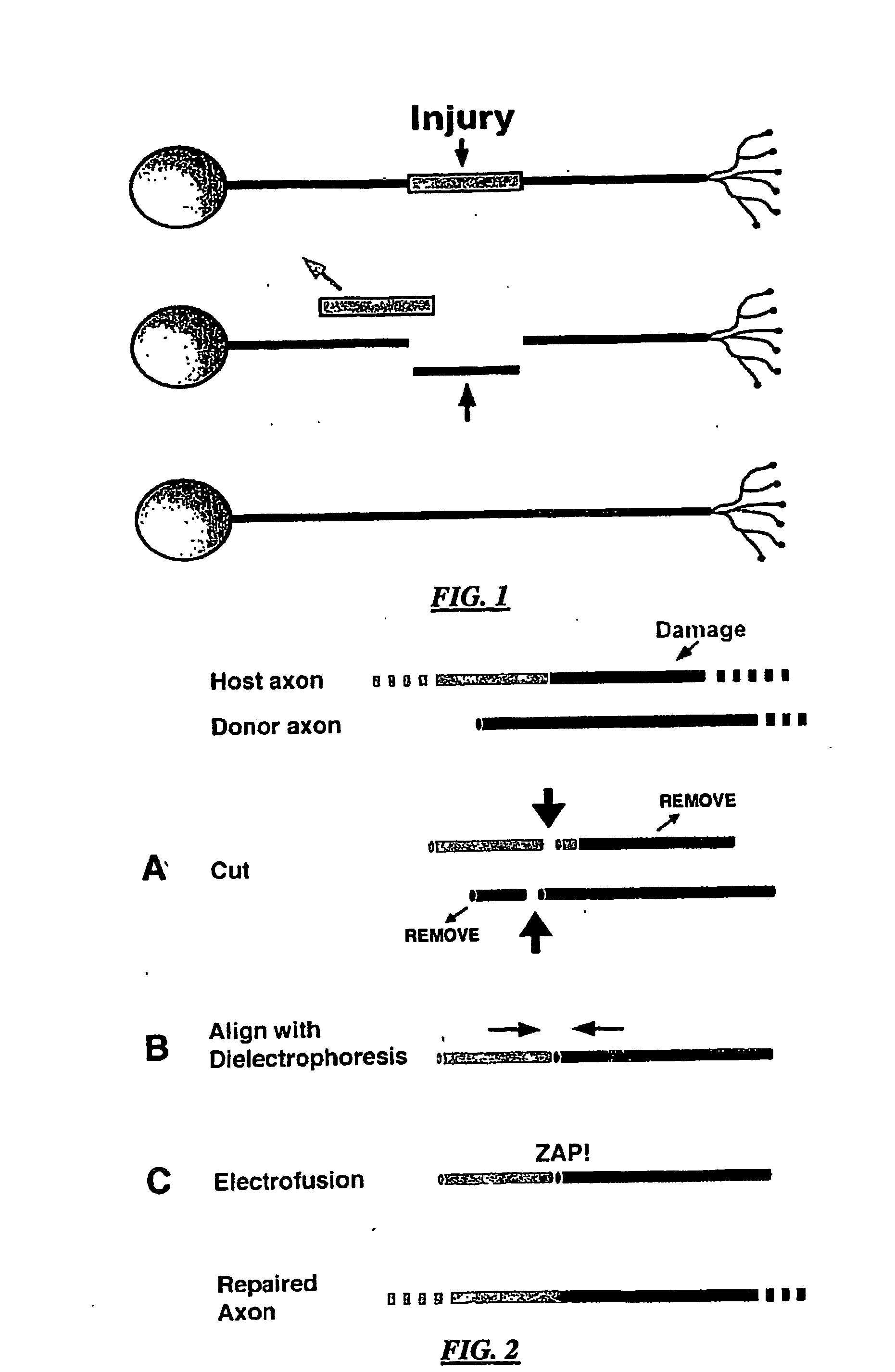
Method and system for nerve repair, nanoknife, mems platform and uses thereof
Method and systems for nerve repair and for microfabrication. In specific embodiments, nerve repair is accomplished by repairing axons. In further embodiments, a modular, 3D system having very small dimentions is described. In further embodiments, a method ans system for performing surgery on axons is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
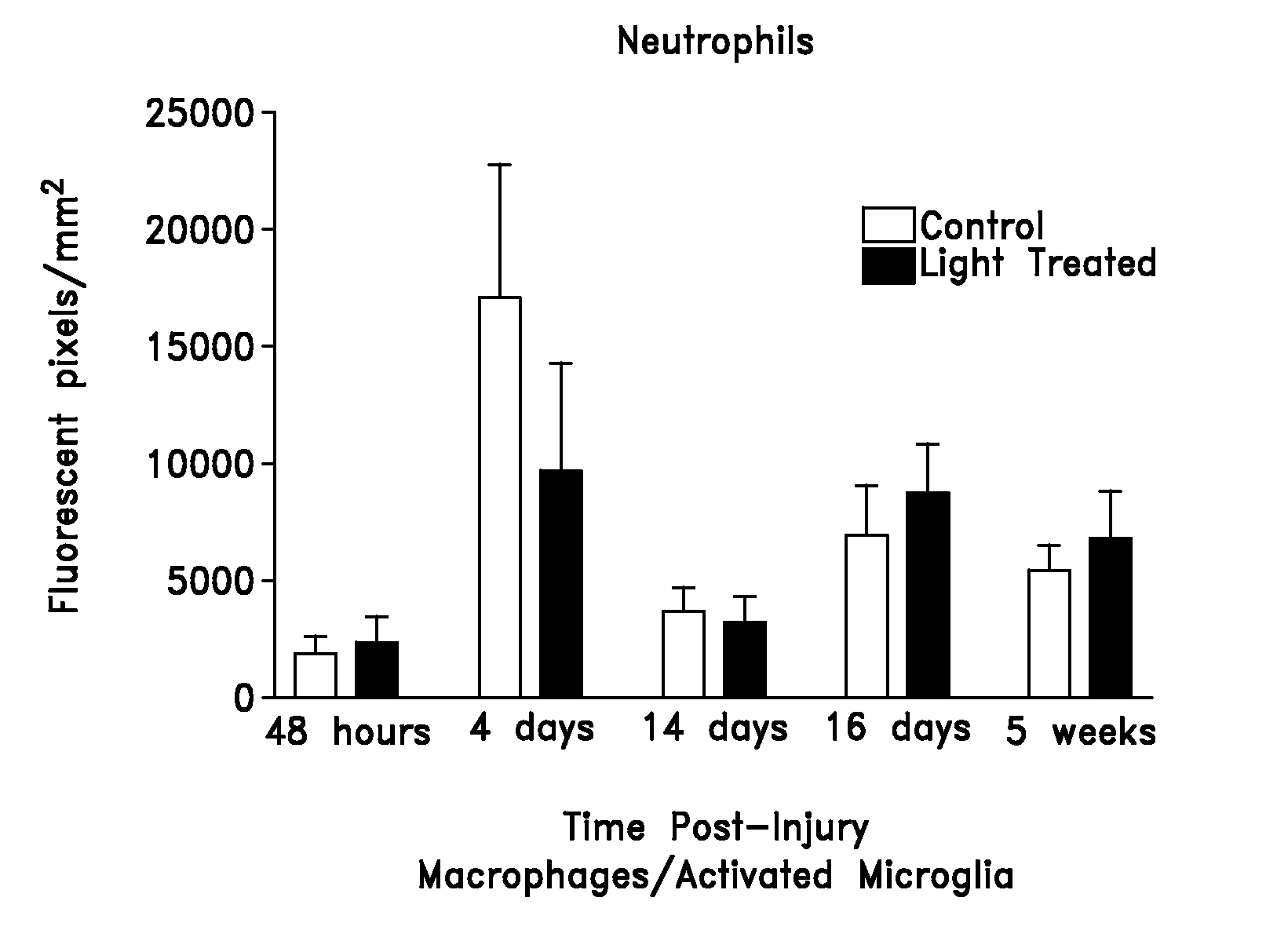
Light promotes regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury
The present invention relates generally to the treatment of SCI by stimulating axon regeneration within the central nerve system. One aspect of the present invention provides methods of treating SCI with low power laser irradiation (LPLI). Another aspect of the present invention provides methods of treating SCI by modulating a gene activity to stimulate axon regeneration. In this regard, the present invention also provides compositions that modulate genes expression relating to the neuron-regeneration after SCI. Another aspect of the present invention provides methods for evaluating the effectiveness of a treatment for SCI.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC +1
Long Term Bi-Directional Axon-Electronic Communication System
InactiveUS20080228240A1Restoring function to disabledElectromyographyInternal electrodesNerve muscleBidirectional communication
A long term bi-directional axon-electronic communication system that provides signaling capability at the level of individual nerve fascicles, bundles of axon and even axons is disclosed. The bi-directional communication system is a modular approach for achieving a chronic enduring interface to peripheral or central nerve atoms for the purpose of restoring function to disabled persons or animals with sensory and / or motor impairments. One embodiment of the communication system includes a multi-channeled nerve-muscle graft chamber for making the nerve-muscle connection. Another embodiment includes a regeneration based microtube nerve interface for bi-directional communication. The interface communication system permits amputees to obtain simultaneous control of multi-degree of freedom powered prostheses by means of naturally produced neural activity from the stamps of the amputated nerves in their residual limbs.
Owner:EDELL DAVID J +1
Apparatus and method for repair of spinal cord injury
InactiveUS6975907B2Lightweight productionDissipate any toxic productSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesPower flowMedicine
An apparatus for stimulating regeneration and repair of damaged spinal nerves, comprising at least two electrodes placed intravertebrally near the site of spinal axon injury and delivering DC current thereto. A method for stimulating regeneration and repair of damaged spinal nervous tissue, comprising placing electrodes intravertebrally near the site of spinal cord injury and applying DC current at a level sufficient to induce regeneration and repair of damaged spinal axons but less than the current level at which tissue toxicity occurs.
Owner:DYNAMED SYST
Retrograde transport peptide and use of same for delivery to central nervous system
Transport peptides, alone or attached to a cargo moiety, are capable of targeted axonal import into the spinal cord and other structures of the central nervous system. The transport peptides can be used to deliver therapeutic agents and other molecules of interest from the periphery to the central nervous system, providing a means to detect, treat or prevent neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, chronic pain and other conditions via minimally invasive techniques of administration.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
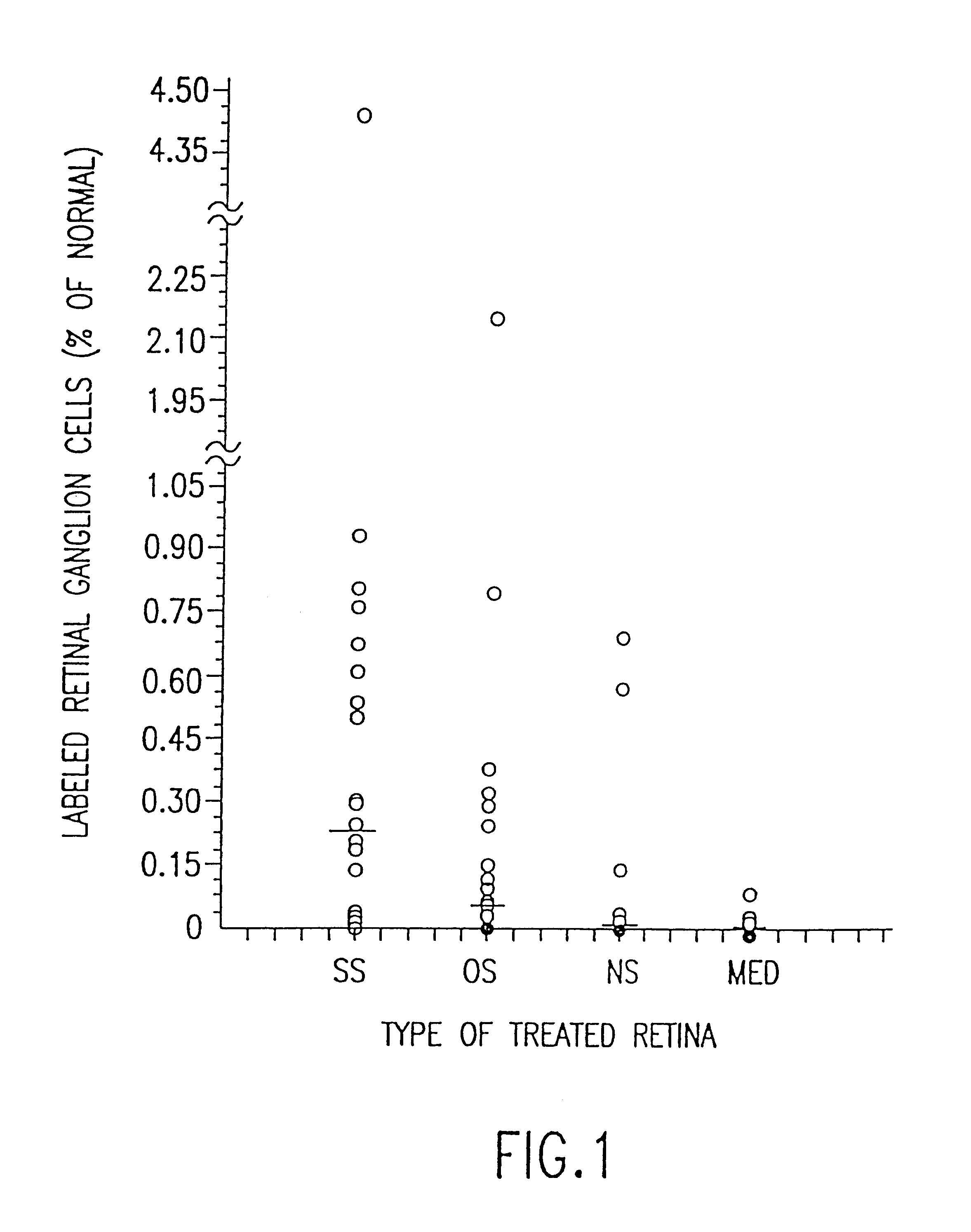
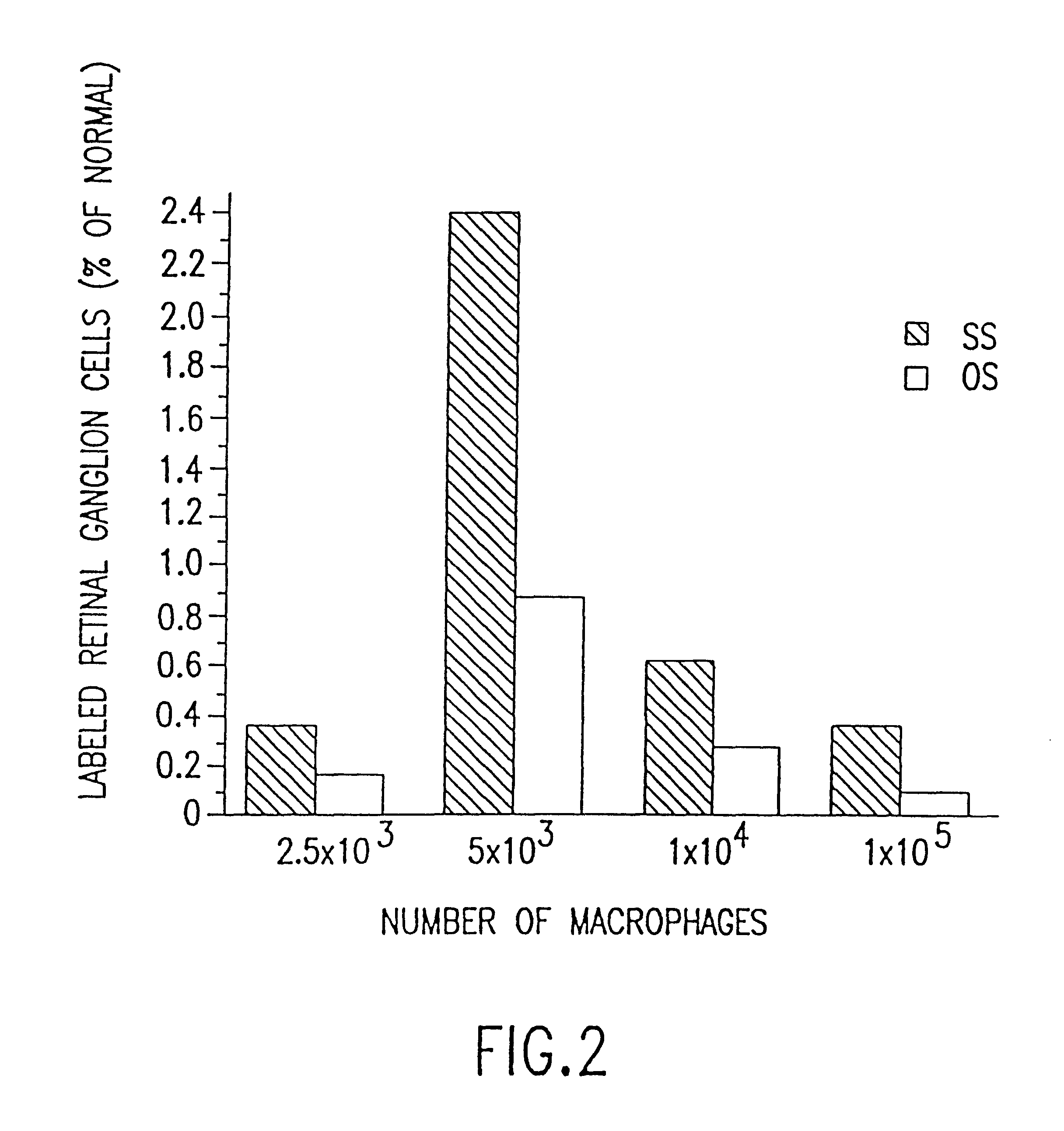
Mononuclear phagocytes and their use to promote axonal regeneration
InactiveUS6267955B1Increase capacityEnhance phagocytic activityBiocideNervous disorderPhagocyteDisease
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the use of allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes to promote axonal regeneration in the central nervous system of a mammal. In one embodiment, allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are cultured together with stimulatory tissue, such as skin, dermis or at least one nerve segment, and are subsequently administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. In an alternative embodiment, autologous monocytes, preferably stimulated autologous monocytes, are administered into the central nervous system of a mammal at or near a site of injury or disease. CNS administration of mononuclear phagocytes may optionally be combined with administration of an adjuvant factor (e.g. aFGF) to the CNS, anti-inflammatory therapy of the mammal, or both. Methods for screening stimulatory tissue and cells and methods and compositions for cryopreserved allogeneic mononuclear phagocytes are also disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Cell-free tissue replacement for tissue engineering
InactiveUS7402319B2Prevent penetrationLoss of functionPowder deliveryTissue regenerationCell freeNerve graft
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
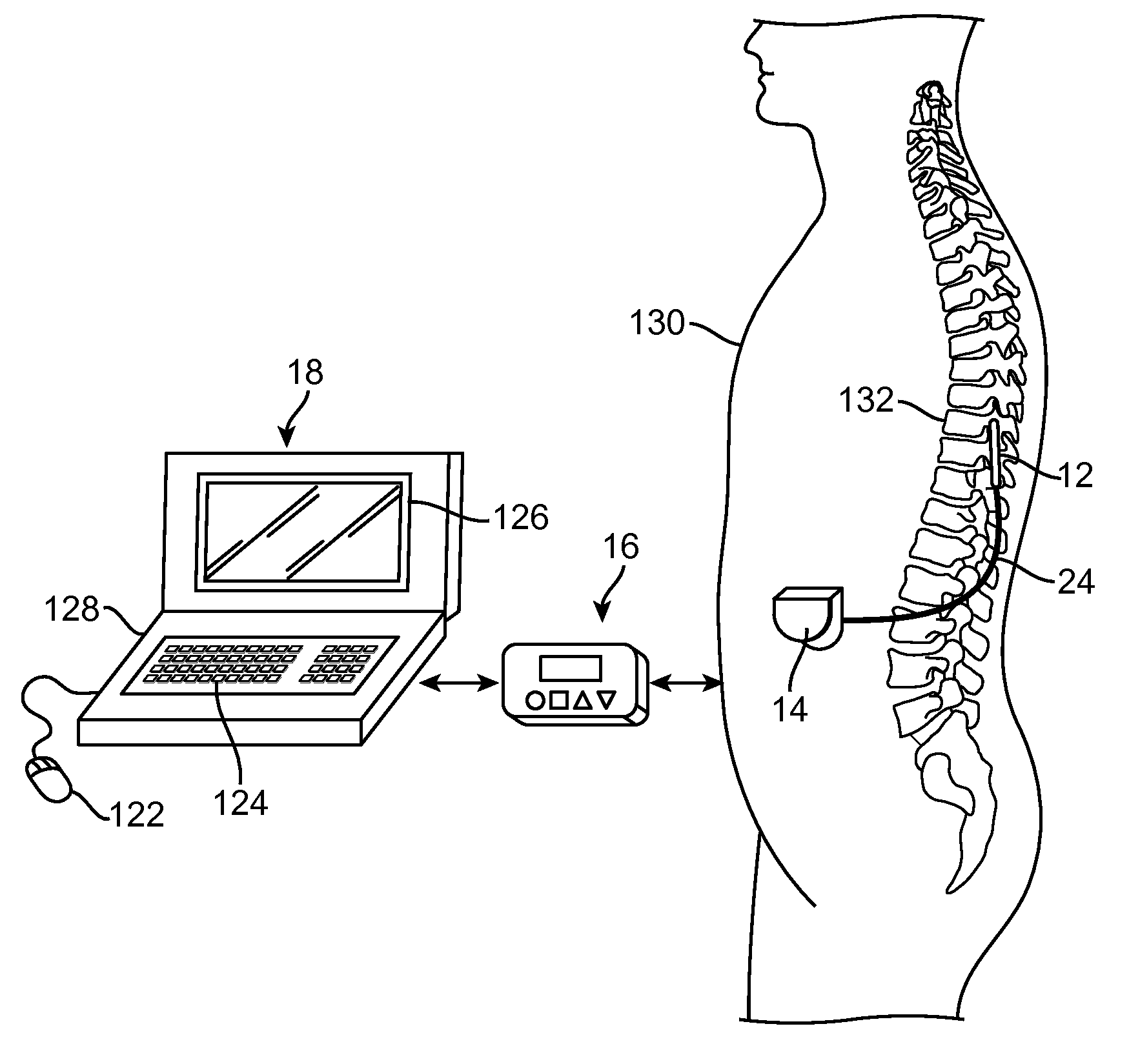
Electrical stimulation method for modulation on sensory information around dorsal root ganglia
A method of treating a patient with an ailment, comprises delivering first energy to a dorsal root ganglia (DRG), thereby modulating the DRG, and delivering second energy to at least one of a central neural axon extending from the DRG and a peripheral neural axon extending from the DRG, thereby modulating the at least one of the central neural axon and the peripheral neural axon.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Actuation and control of limbs through motor nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20050171577A1ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDriving currentPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Non-invasive brain injury evaluation
InactiveUS20090292198A1Medical simulationIntracranial pressure measurementDiffuse axonal injuryAbnormal tissue growth
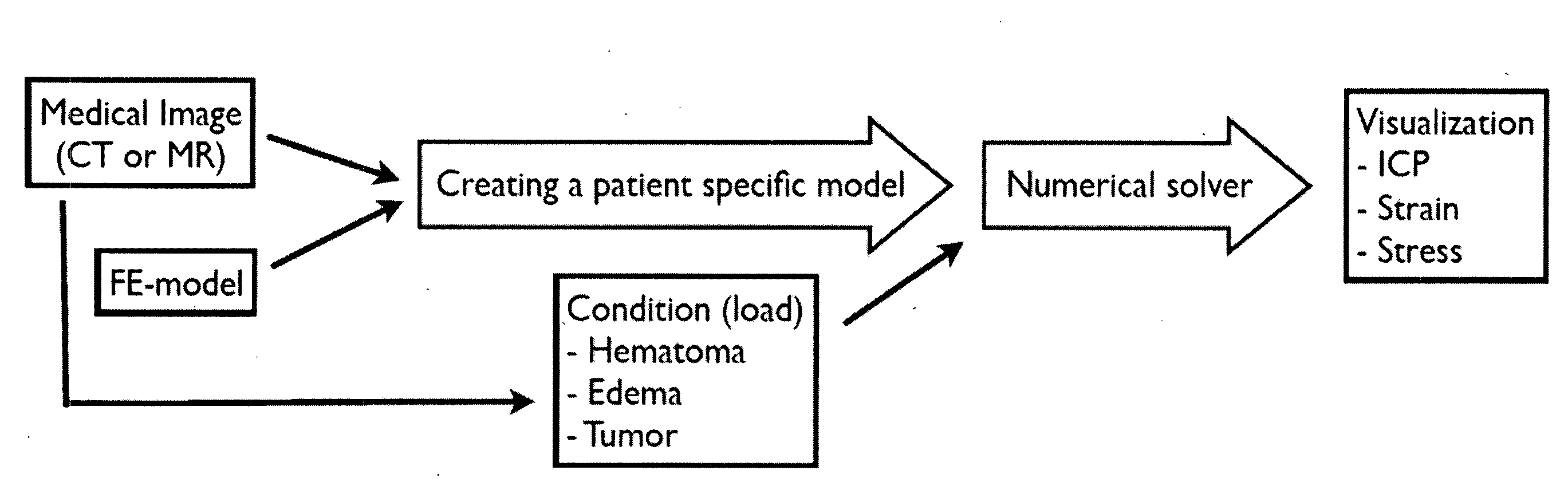
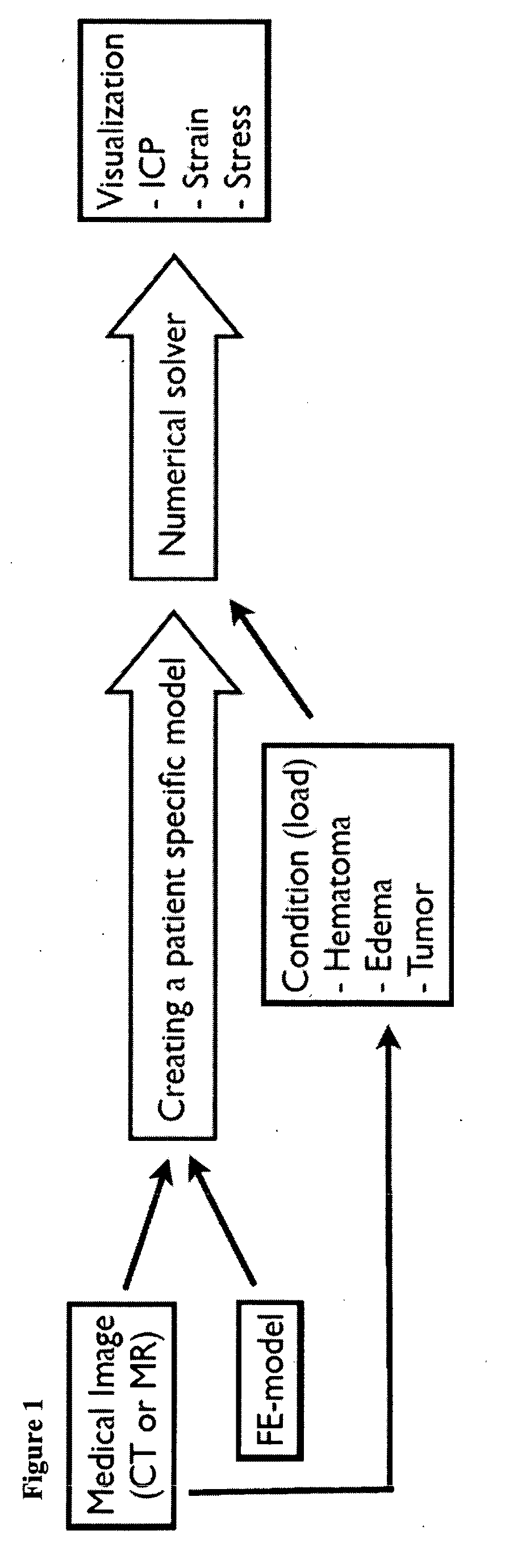
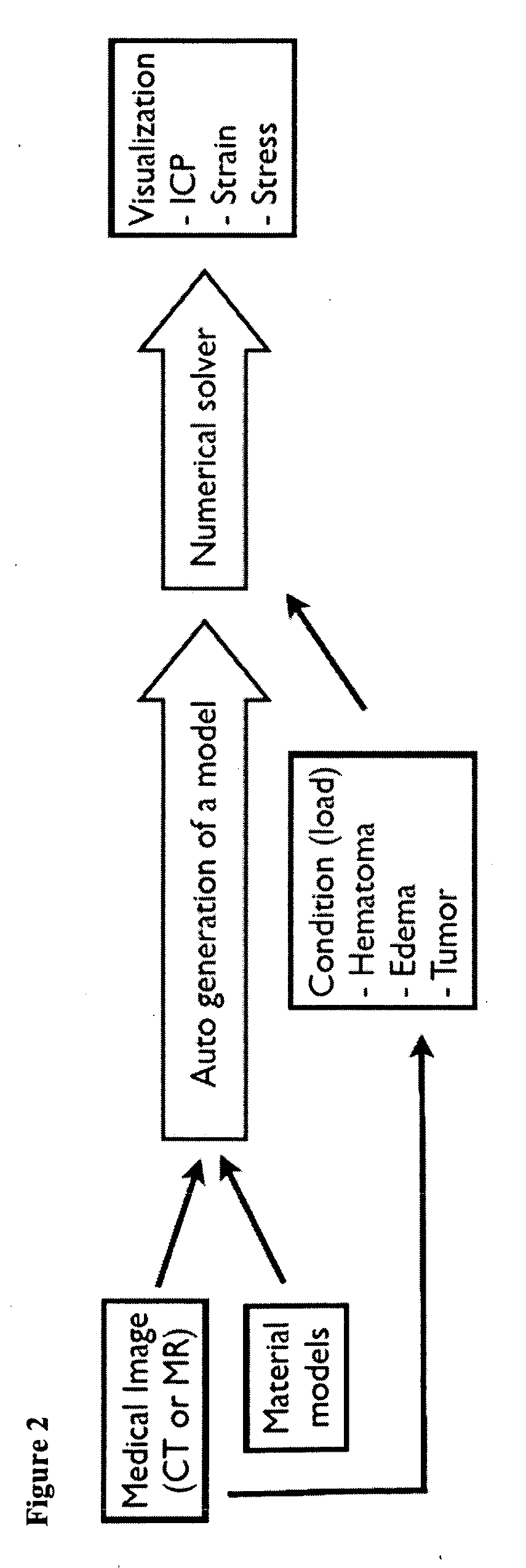
A non-invasive method for measuring intracranial pressure (ICP) is provided. A numerical model such as finite element model is developed in order to calculate the ICP, strain or stress for patients who suffers from hematoma, edema or tumor. The method can further provide local maximum principle strain that can provide information about possible subsequent brain injury, such as diffuse axonal injury, in sensitive region of the brain. Based on computer tomography or magnetic resonance images an individual diagnosis and treatment plan can be formed for each patient.
Owner:NIBIE
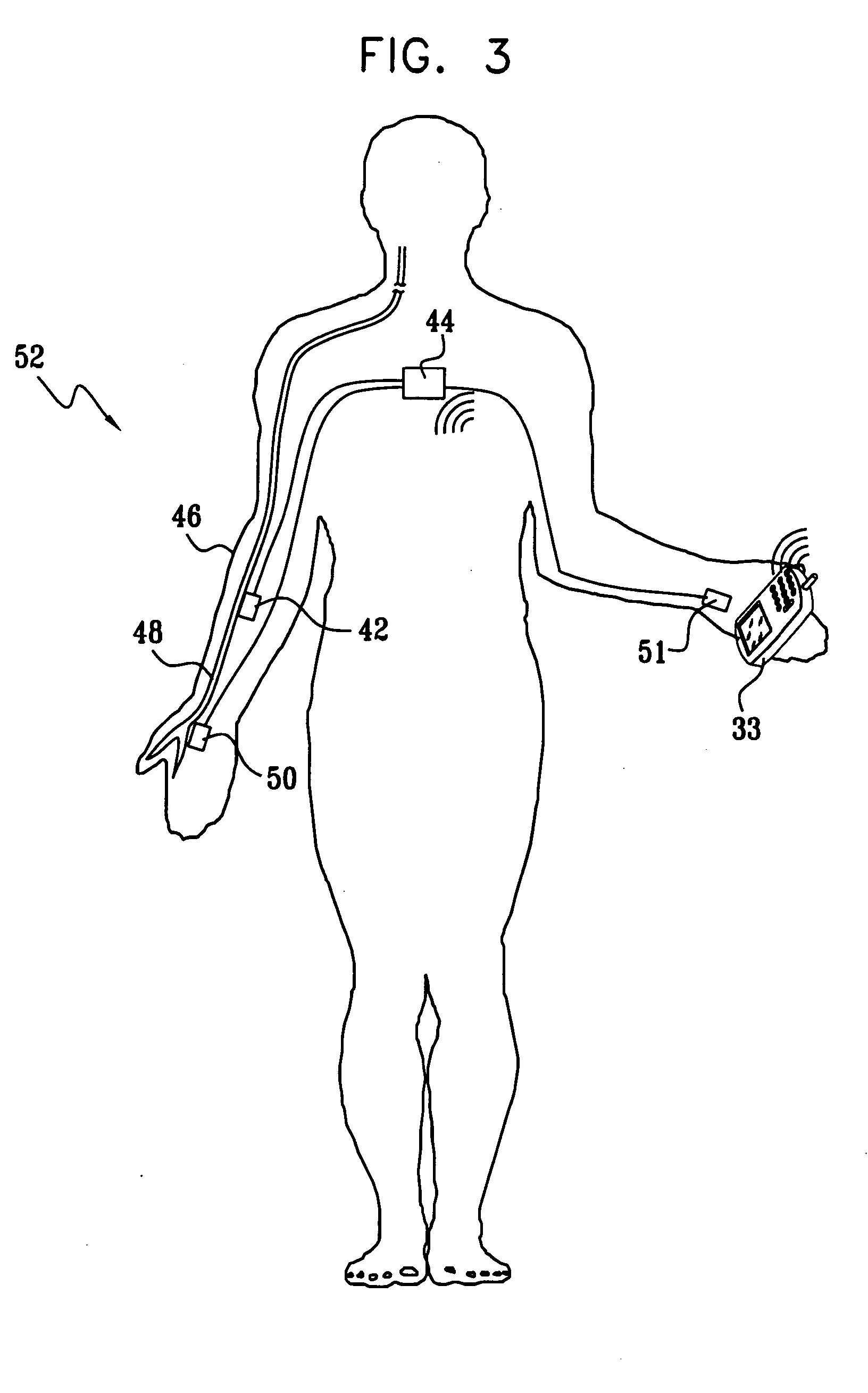
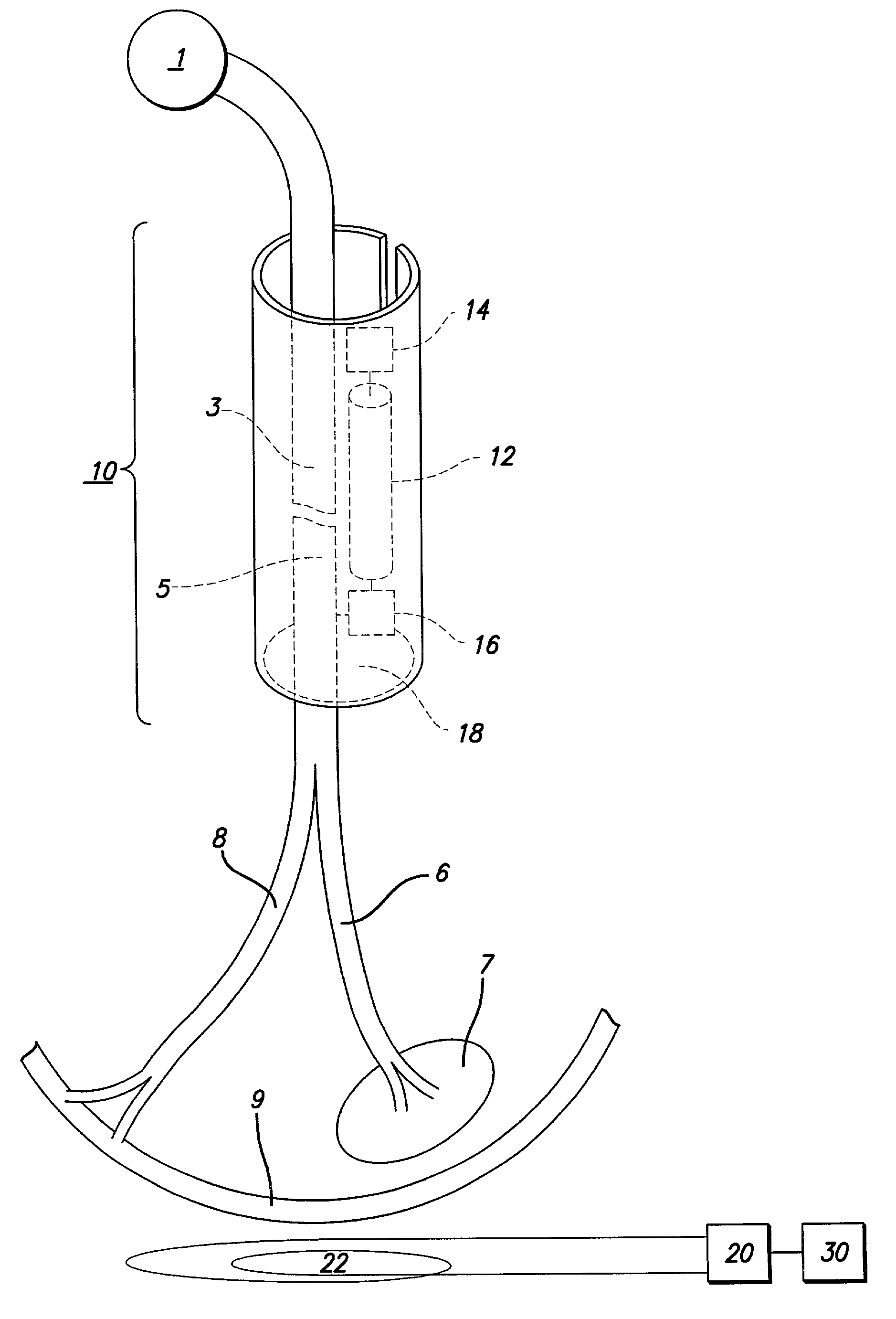
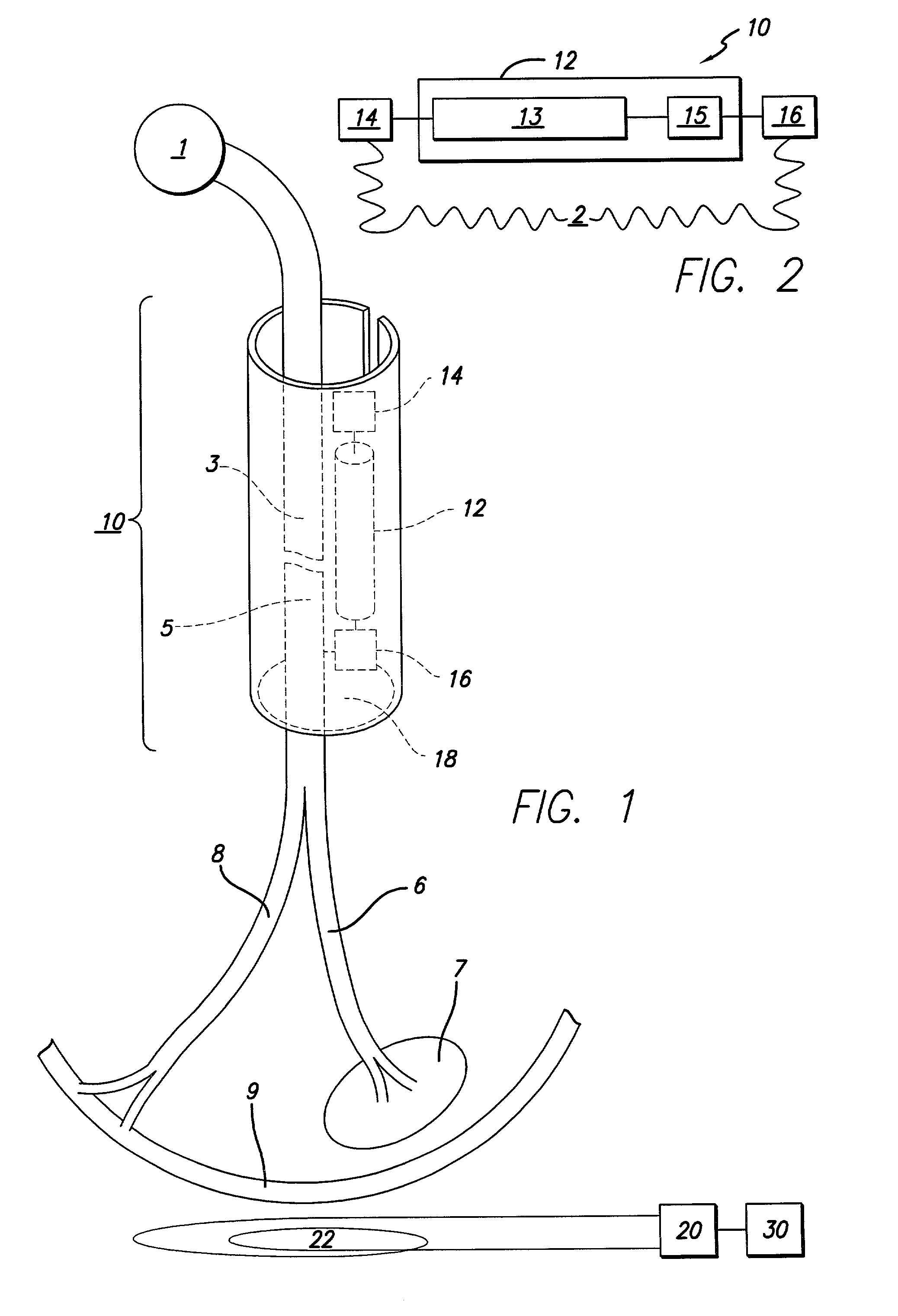
Helical electrode for nerve stimulation
ActiveUS8478428B2Stimulated is largeGood curative effectSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesPower flowElectrical conductor
A helical electrode for nerve stimulation includes an insulative helical substrate, having an inner surface, configured to wrap around a nerve. An electrical conductor is disposed upon the inner surface of the substrate. The conductor defines a helix of about one revolution and produces an electric field in which an injected current in similar axons varies by no more than about 25%. The conductor may include tapered end sections, which may be counter-tapered.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
System and method for providing recovery from muscle denervation
Recovery from peripheral nerve and nerve plexus injuries is usually slow and incomplete because the regenerating motor axons often head erroneously toward sensory receptors rather than muscle fibers and because the target muscles atrophy while waiting for the slow process of reinnervation. Research has suggested that electrical stimulation with different waveforms and temporal patterns at different times during the regeneration process might improve the clinical outcome through various mechanisms, but a practical means to deliver such stimulation has been lacking. This invention teaches the use of miniature electrical stimulators that can be implanted alongside the injured nerve(s) at the time of surgical repair and that can be powered and controlled by transmission of radiofrequency energy from outside the body so as to provide a variety of electrical stimuli at different times during the recovery process.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
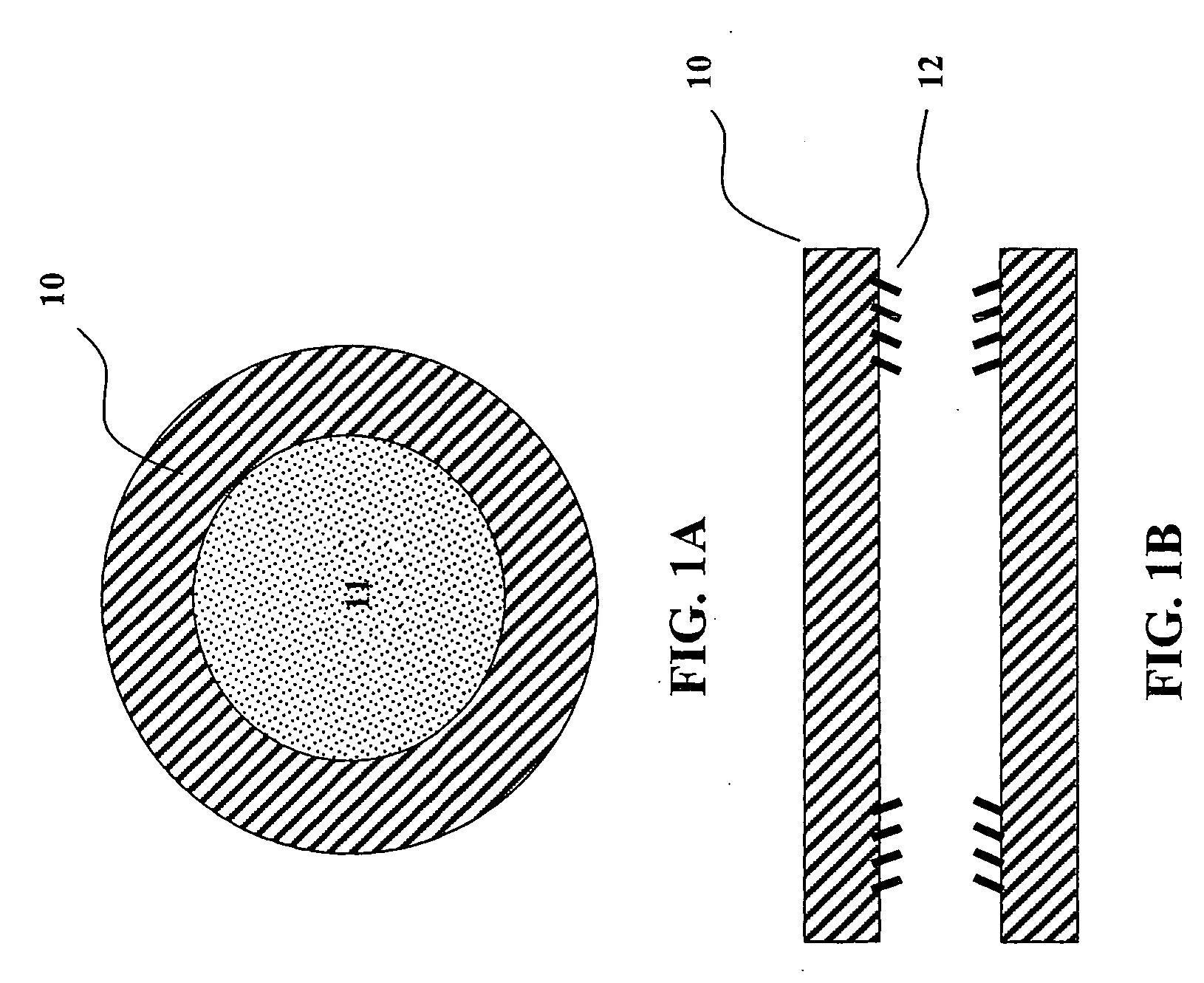
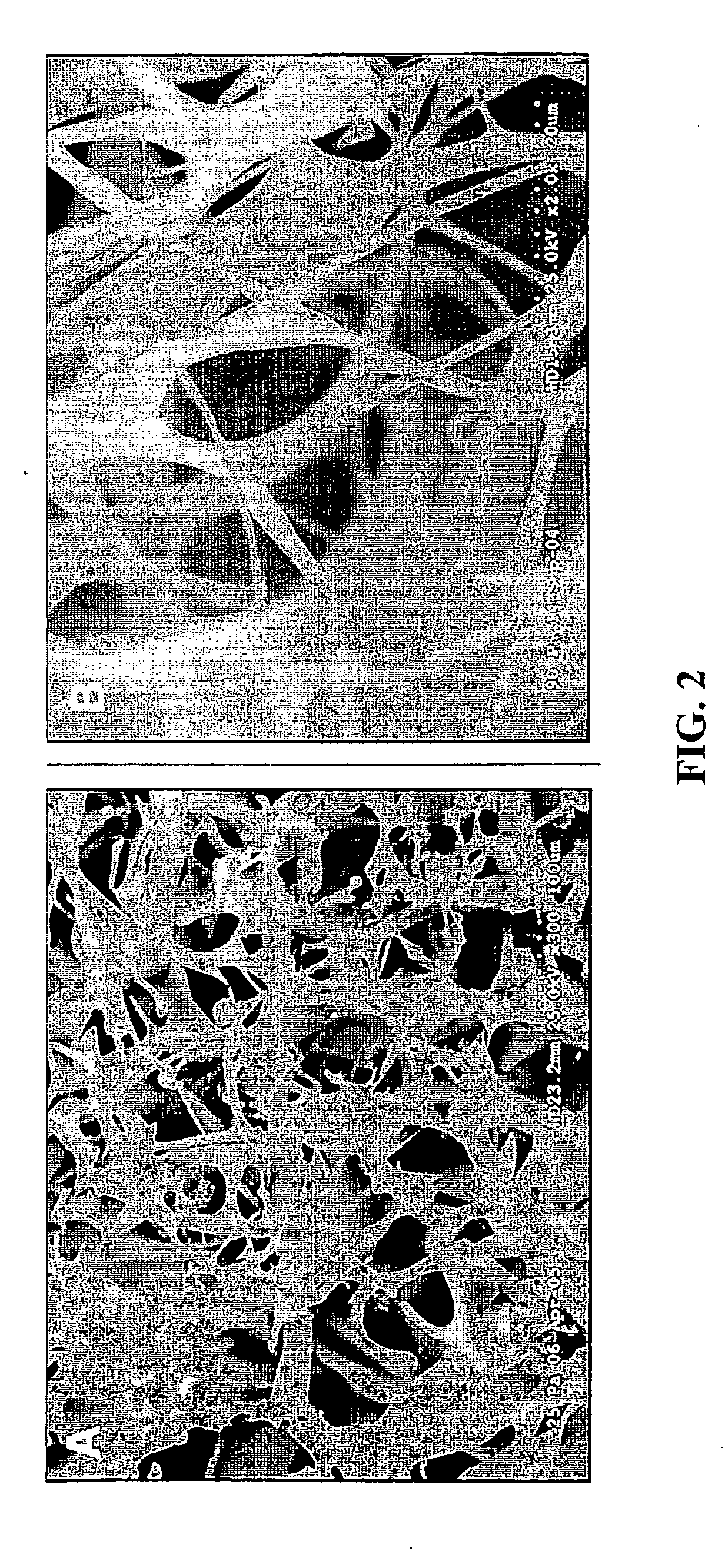
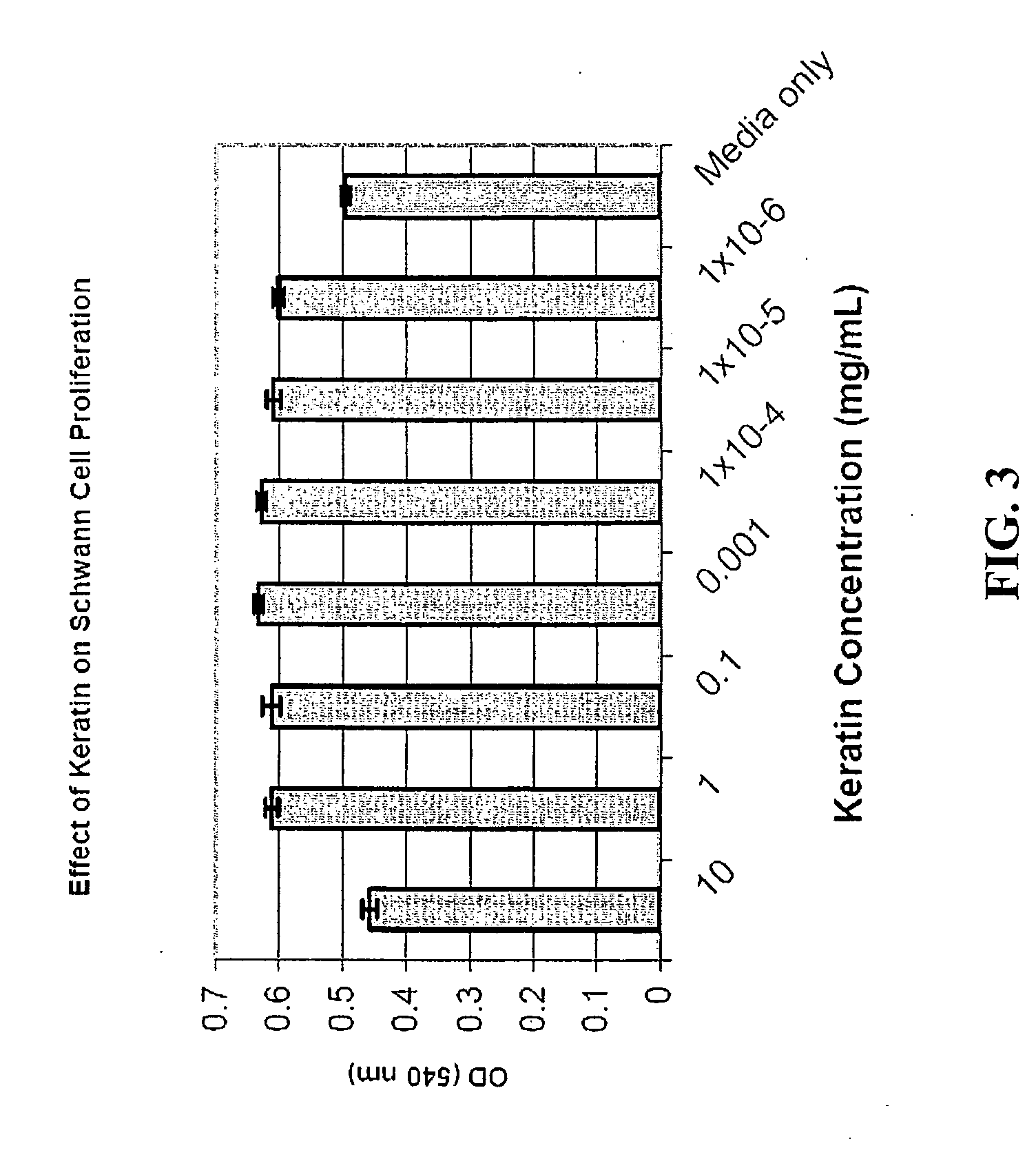
Nerve regeneration employing keratin biomaterials
A keratin hydrogel matrix serves as an effective acellular scaffold for axonal regeneration and facilitates functional nerve recovery.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Use of Epineural Sheath Grafts for Neural Regeneration and Protection
ActiveUS20110087338A1Minimal inflammatory reactionBlunt dissectorsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsNeurulationNeural regeneration
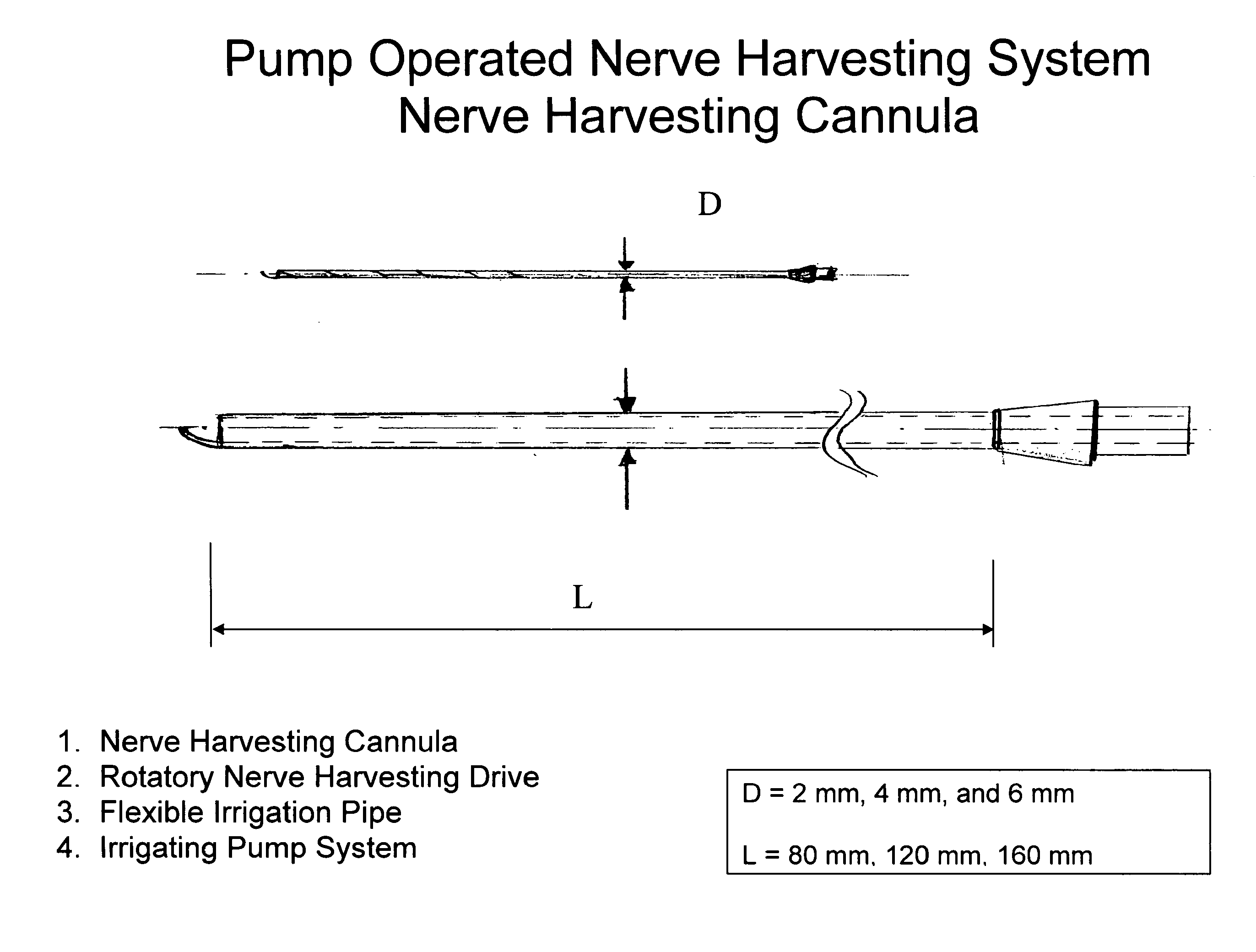
Described herein is conduit material that causes minimal inflammatory reaction, and serves as a structural guide for regenerating nerve tissue (e.g., axons). Thus, the invention is directed to methods of treating a nerve injury in an individual in need thereof. The methods employ an isolated, naturally occurring epineural sheath, and can be used, for example, to regenerate nerve tissue in an individual in need thereof. Also provided herein is a device for harvesting an epineural sheath.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com