Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
313 results about "Neural activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
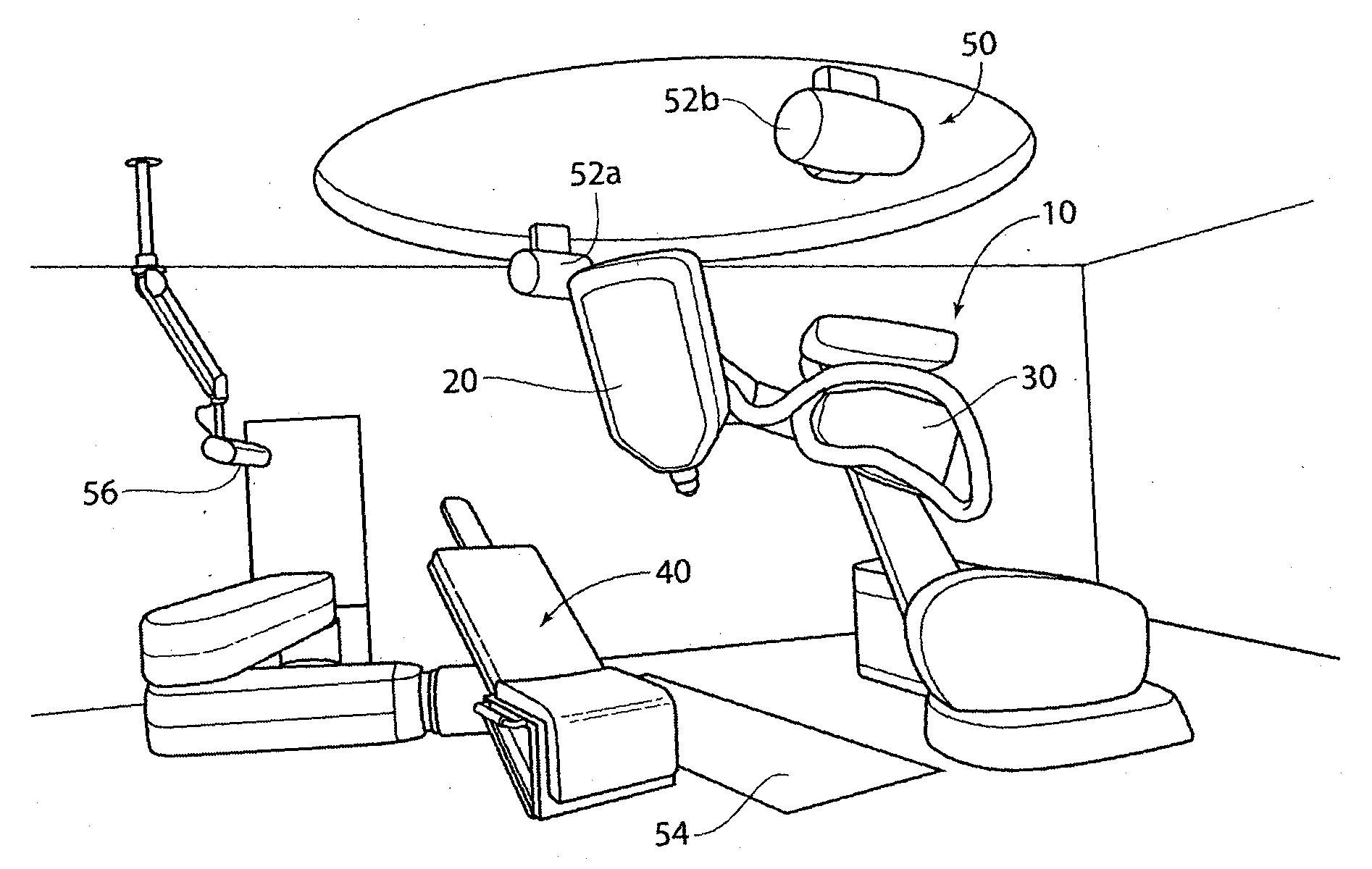
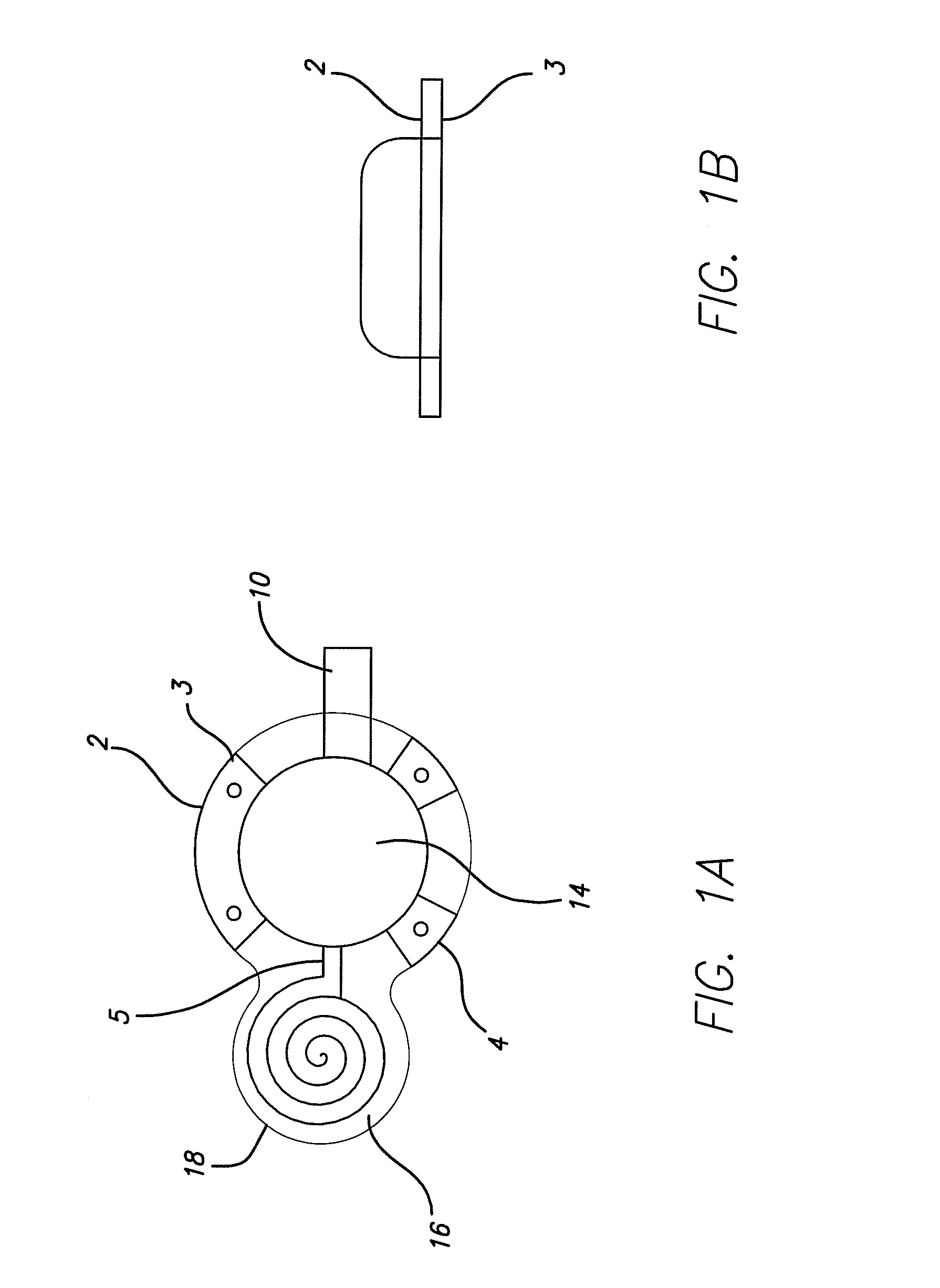
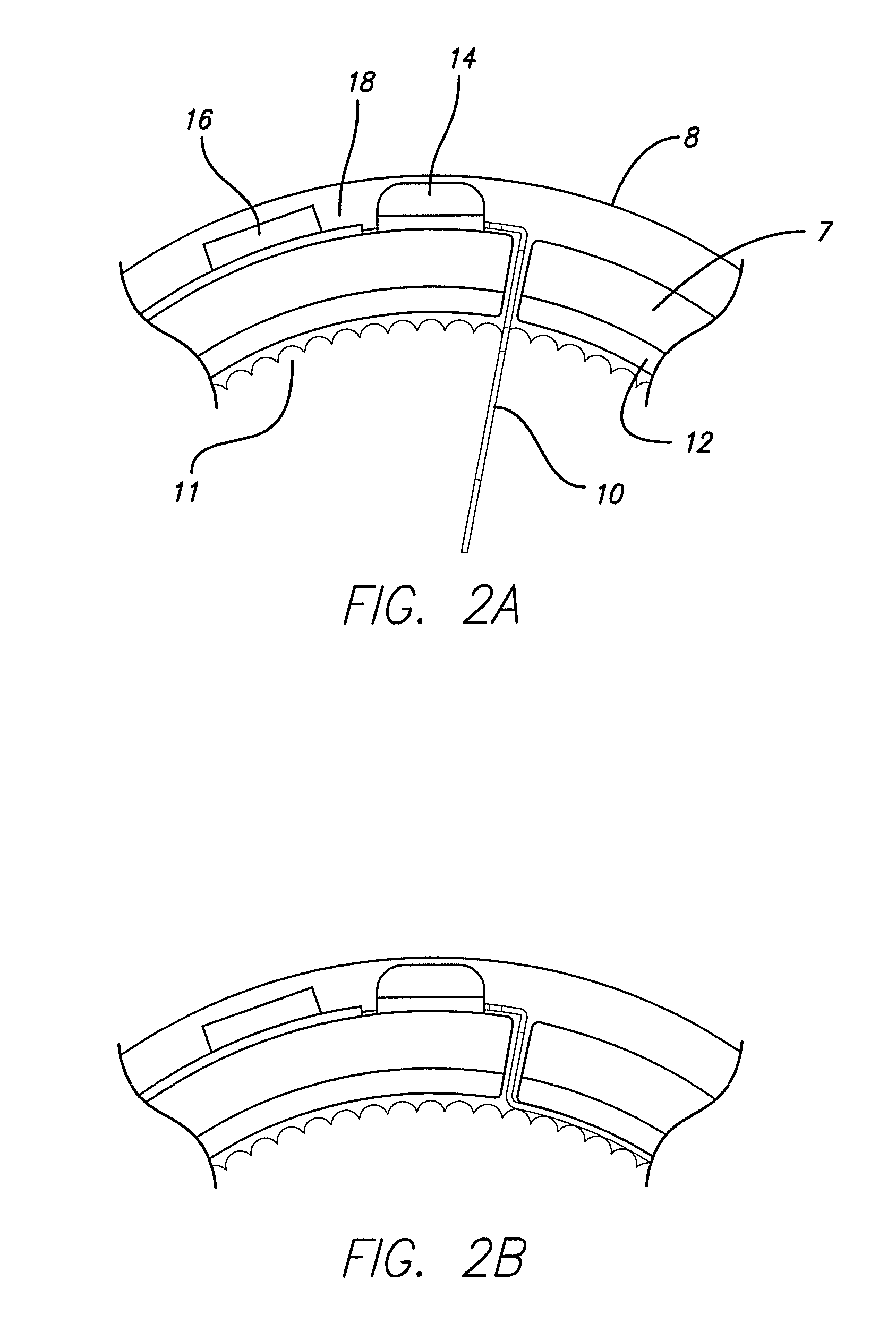
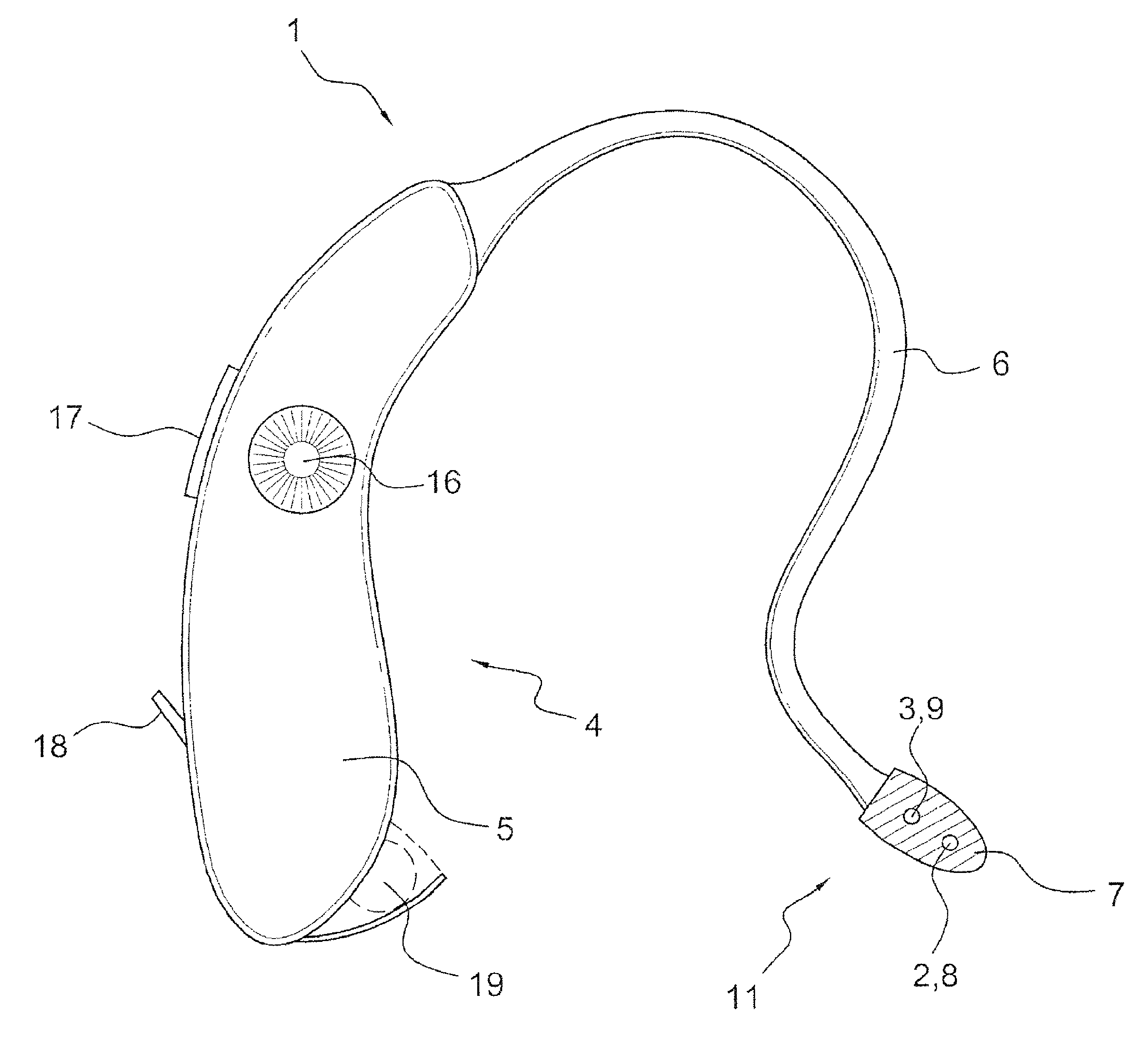
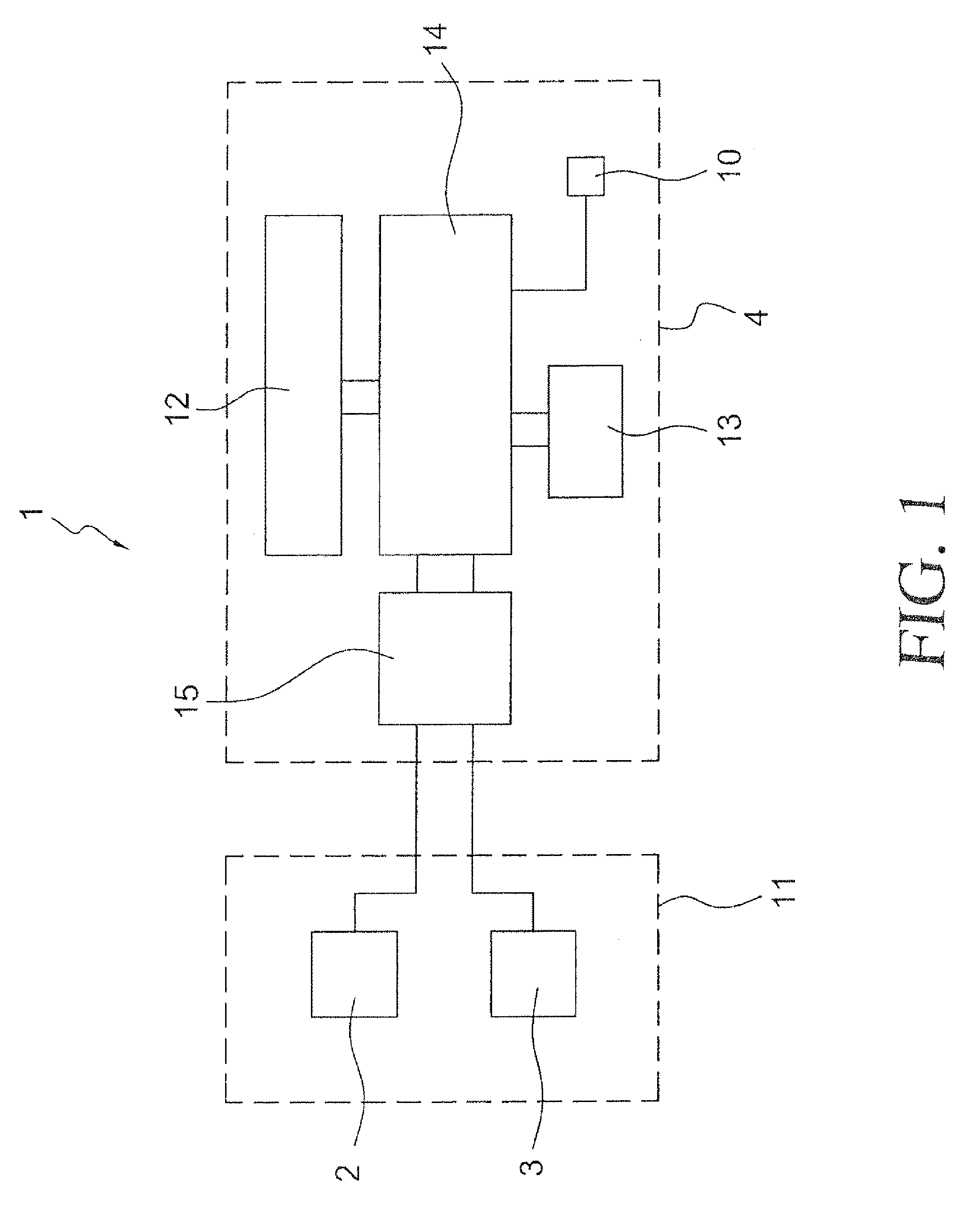
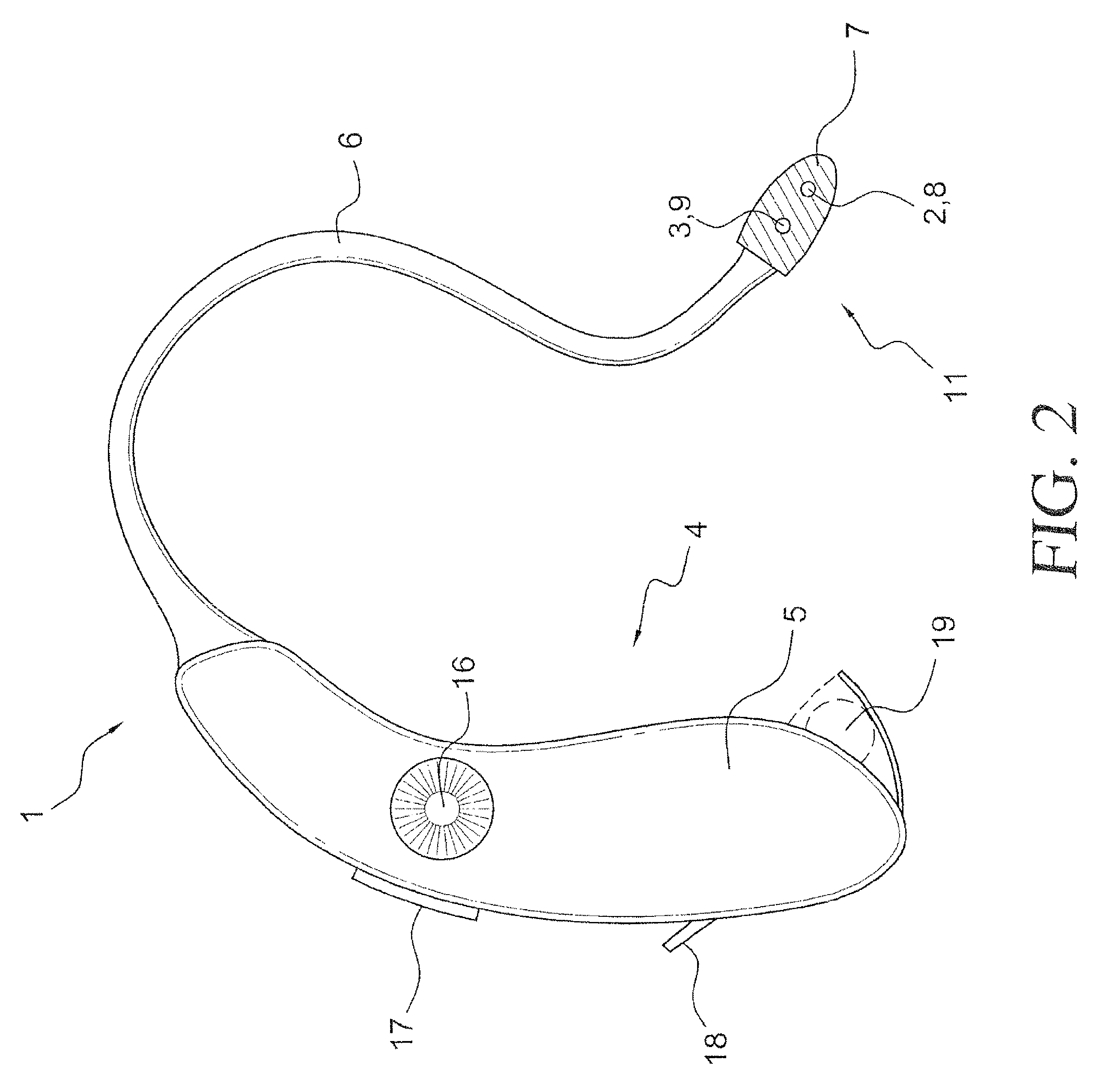
Methods and apparatus for renal neuromodulation via stereotactic radiotherapy
InactiveUS20110200171A1Precise positioningReduce and minimize exposureUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsDiseaseStereotactic radiotherapy
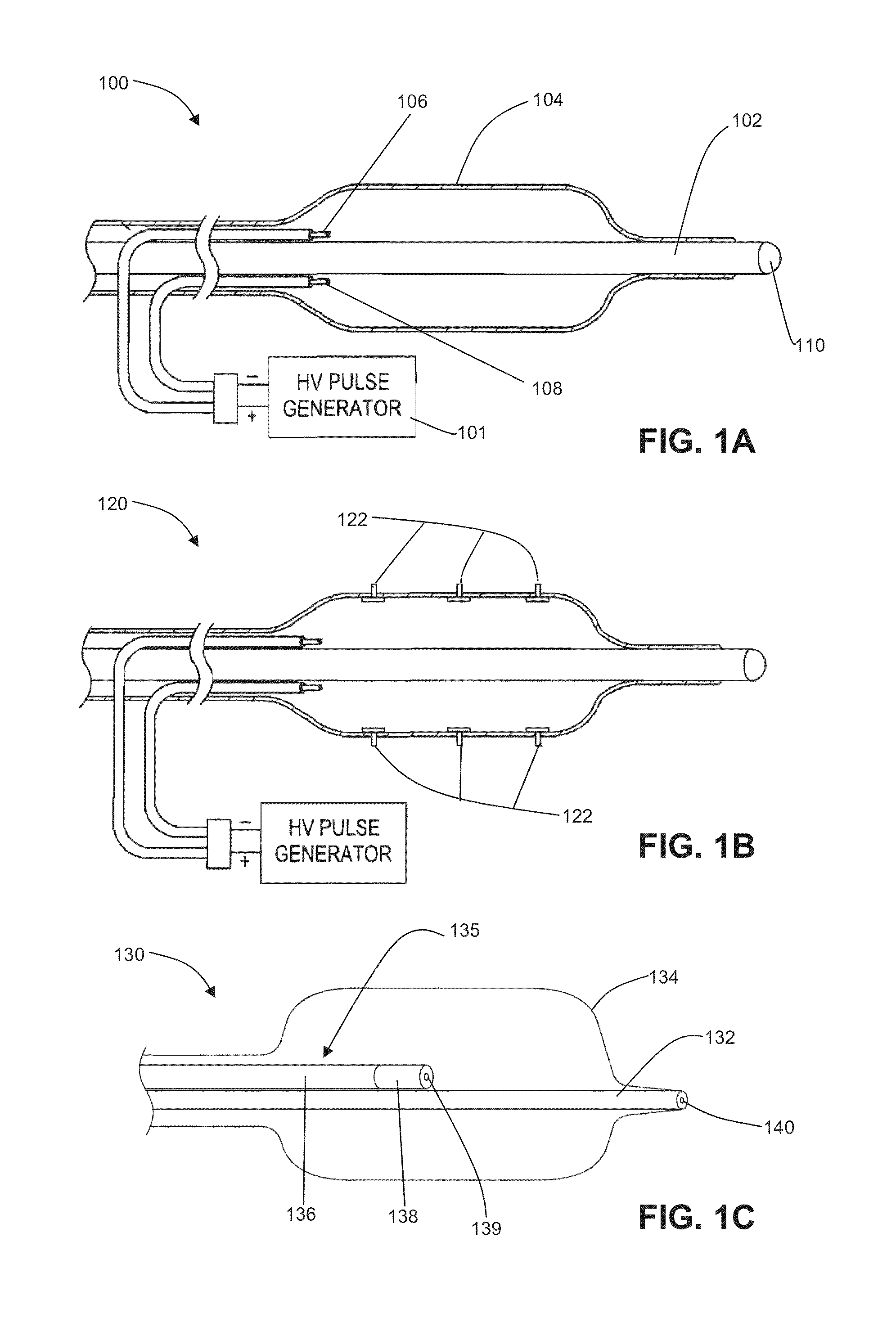
The present disclosure describes methods and apparatus for renal neuromodulation via stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of hypertension, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, insulin resistance, metabolic disorder or other ailments. Renal neuromodulation may be achieved by locating renal nerves and then utilizing stereotactic radiotherapy to expose the renal nerves to a radiation dose sufficient to reduce neural activity. A neural location element may be provided for locating target renal nerves, and a stereotactic radiotherapy system may be provided for exposing the located renal nerves to a radiation dose sufficient to reduce the neural activity, with reduced or minimized radiation exposure in adjacent tissue. Renal nerves may be located and targeted at the level of the ganglion and / or at postganglionic positions, as well as at pre-ganglionic positions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ARDIAN LUXEMBOURG SARL
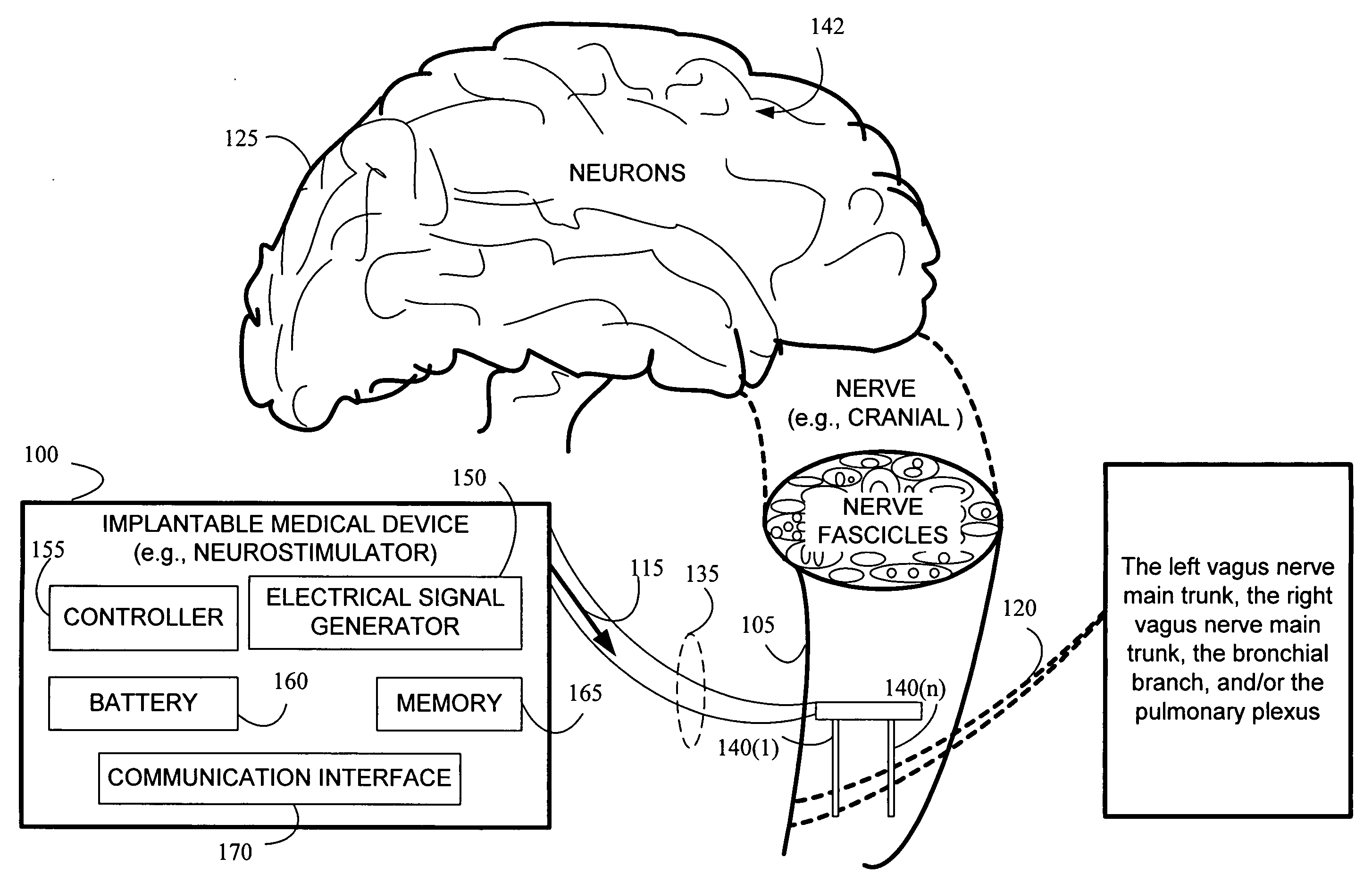
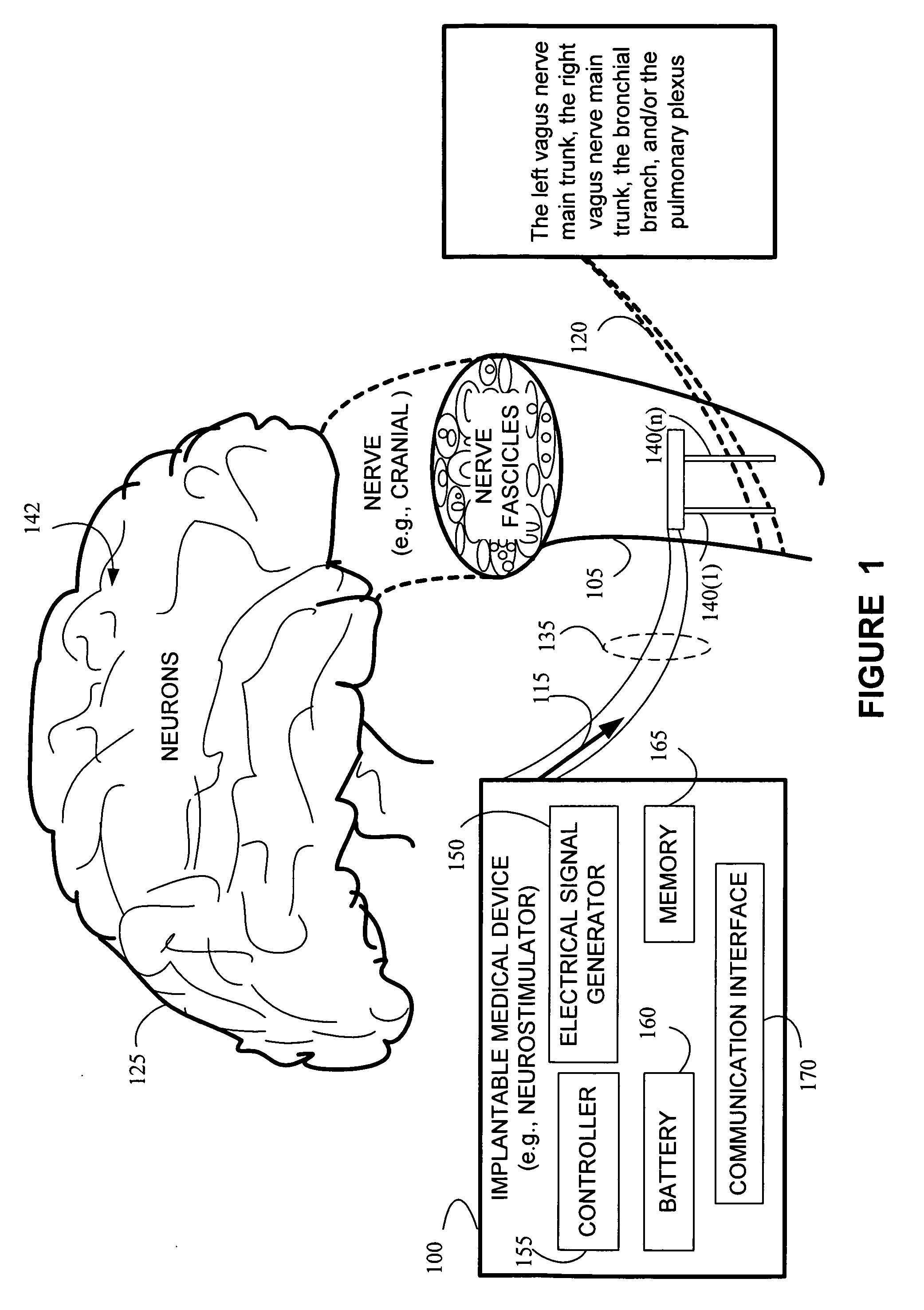
Stimulating cranial nerve to treat pulmonary disorder
A method for stimulating a portion of a vagus nerve of a patient to treat a pulmonary disorder is provided. At least one electrode is coupled to at least one portion of a left vagus nerve and / or a right vagus nerve of the patient. An electrical signal is applied to the portion of the vagus nerve using the electrode to treat the pulmonary disorder. The electrical signal may perform a blocking of an intrinsic neural activity on said at least one portion of the left vagus nerve and said right vagus nerve.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Neural blocking therapy
A method and apparatus are disclosed for treating a variety of conditions include treating a disorder associated with neural activity near a region of a brain. In such condition, the method includes placing an electrode to create a field near said region, creating said field with parameters selected to at least partially block neural activity within said field. For treating a tissue sensation, the method includes identifying a target area of tissue to be treated and placing an electrode to create a field near the target area, and creating the field with parameters selected to at least partially block neural activity within the target area. For treating a condition associated with neural activity of a spinal cord, the method includes placing an electrode to create a field near a nerve associated with the spinal cord, and creating the field with parameters selected to at least partially block neural activity within the nerve.
Owner:FLATHEAD PARTNERS LLC +1
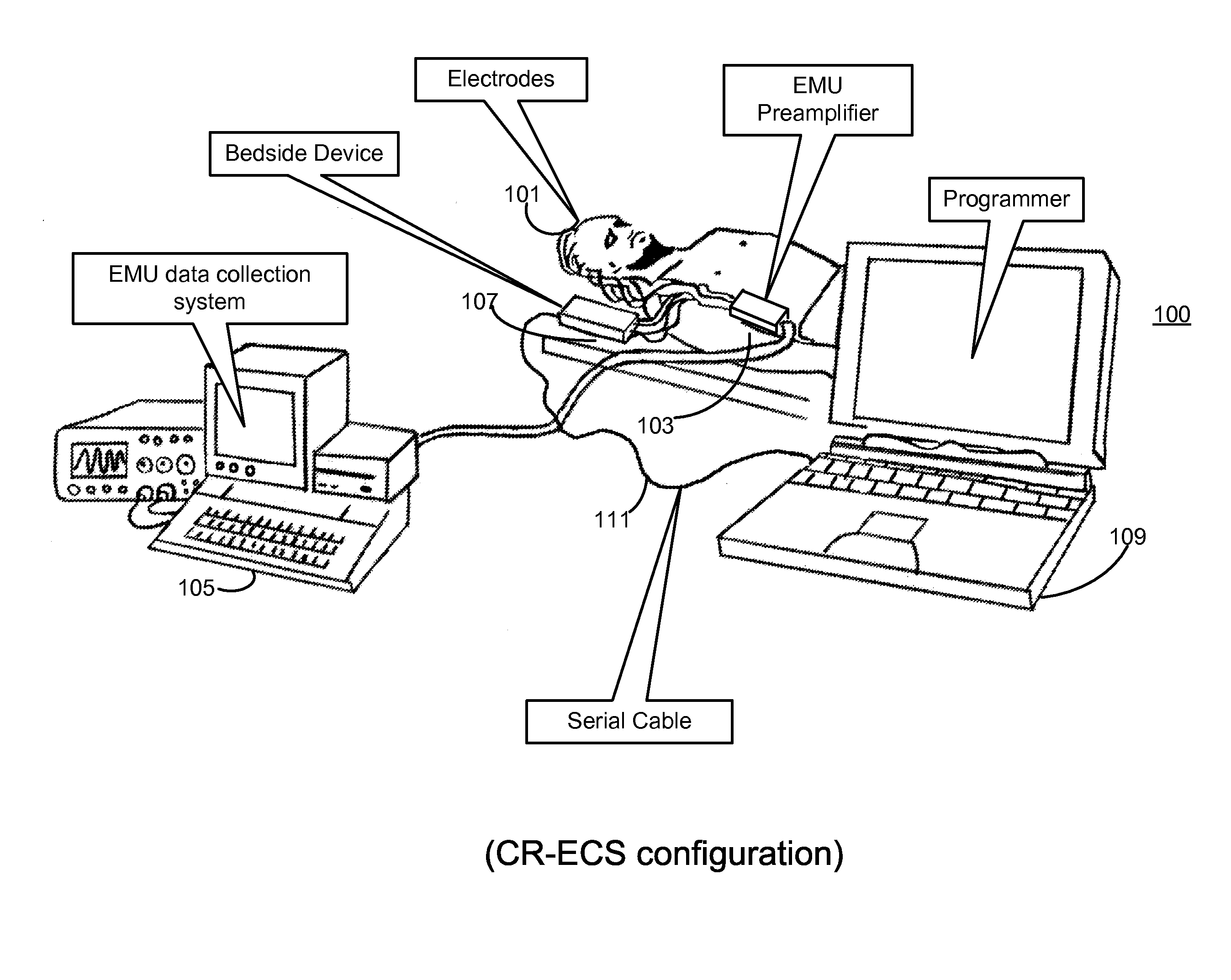
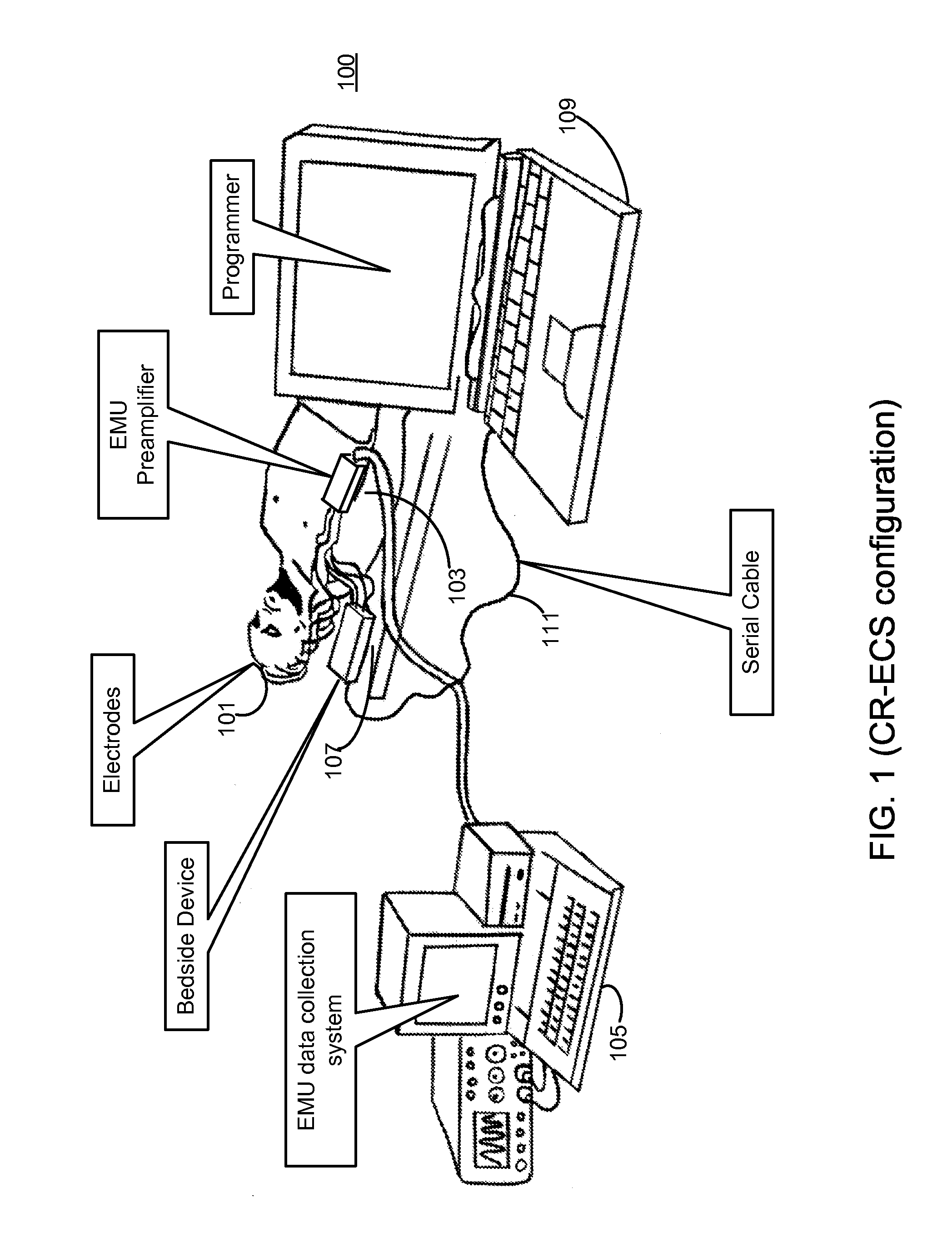
Measurement and analysis of trends in physiological and/or health data
InactiveUS7485095B2Reduce signal to noise ratioCompensates the low SNRElectrocardiographyCatheterData systemPostural orientation
System comprised of a portable medical device and method for registering at least one of electrocardiographic (ECG), magnetocardiographic (MCG), physical activity, body position, respiration, temperature, blood pressure, vasomotor activity, blood flow, neural activity, and other physiological, and health data, extracting and representing the most significant parameters from time series (trends) of said data. The system achieves the necessary sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) in order to miniaturize the device by collecting data of at least one fiducial point in a cardiac complex over a period of at least one, and preferably, several seconds, and extracting the underlying typical patterns from these data. Due to the miniaturization (pocket-size), the system can be implemented in a shape of a pen (or another miniature shape) that can be worn in a pocket.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
Measurement and analysis of trends in physiological and/or health data
InactiveUS20060122525A1Reduce signal to noise ratioCompensates the low SNRElectrocardiographyCatheterData systemPostural orientation
System comprised of a portable medical device and method for non-contact registering at least one of electrocardiographic (ECG), magnetocardiographic (MCG), physical activity, body position, respiration, temperature, blood pressure, vasomotor activity, blood flow, neural activity, and other physiological, and health data, extracting and representing the most significant parameters from time series (trends) of said data. The system achieves the necessary sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) in order to miniaturize the device by collecting data of at least one fiducial point in a cardiac complex over a period of at least one, and preferably, several seconds, and extracting the underlying typical patterns from these data. Due to the miniaturization (pocket-size), the system can be implemented in a shape of a pen (or another miniature shape) that can be worn in a pocket.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
Focused stimulation in a medical stimulation device
ActiveUS20060247735A1Narrowing of the stimulation regions minimizes or prevents this from occurringHead electrodesDeaf-aid setsCochlear implantationImplant electrode
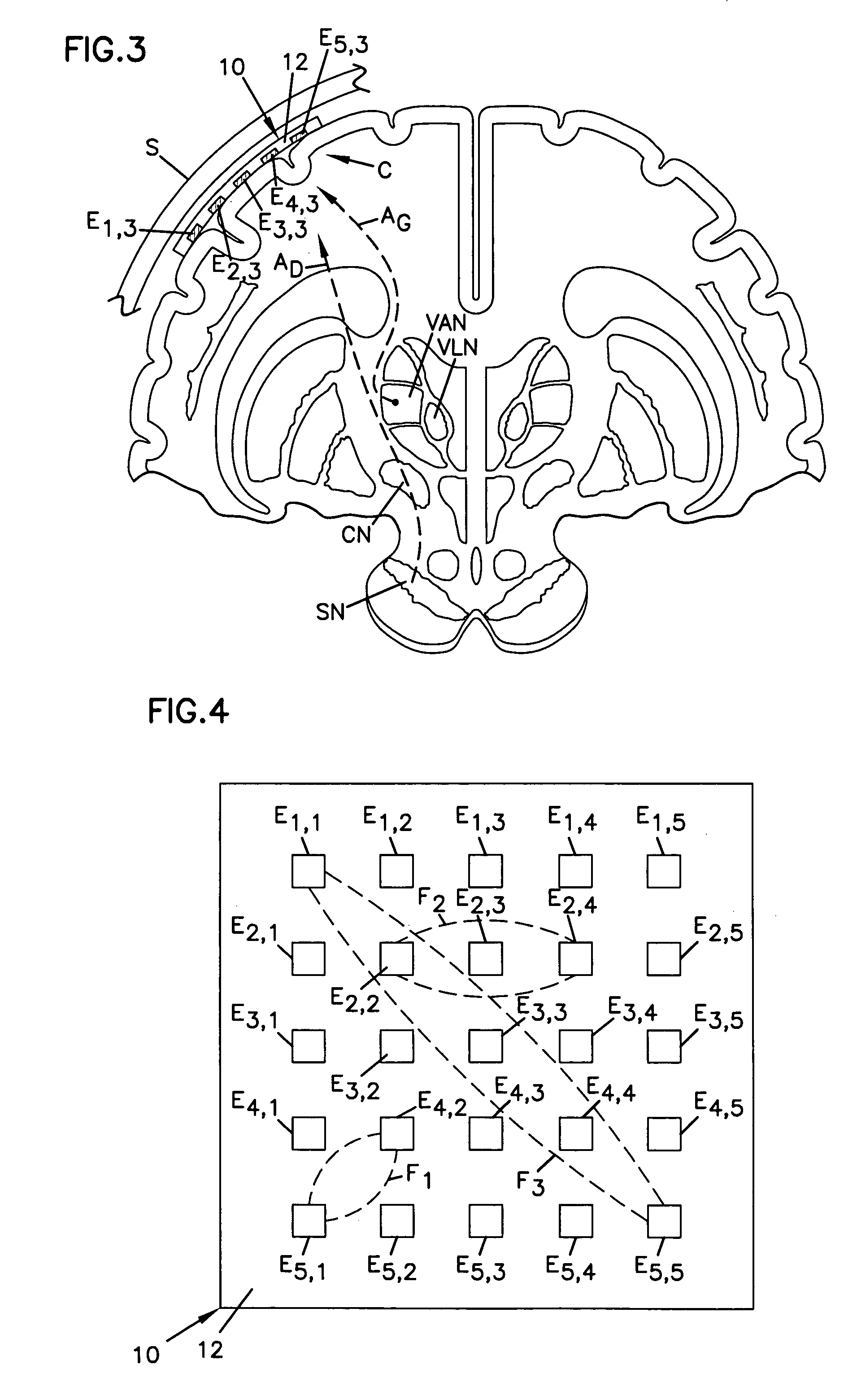
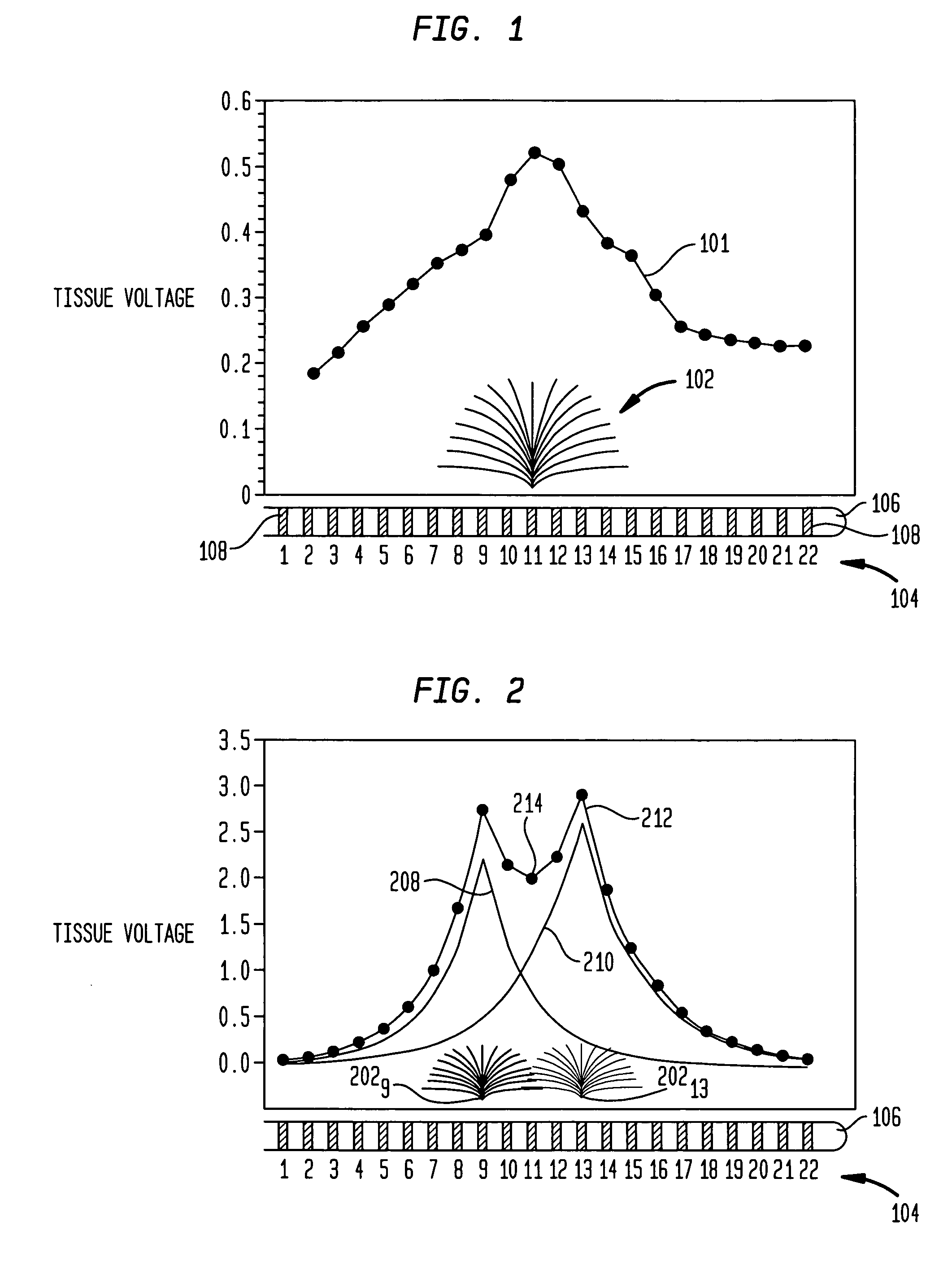
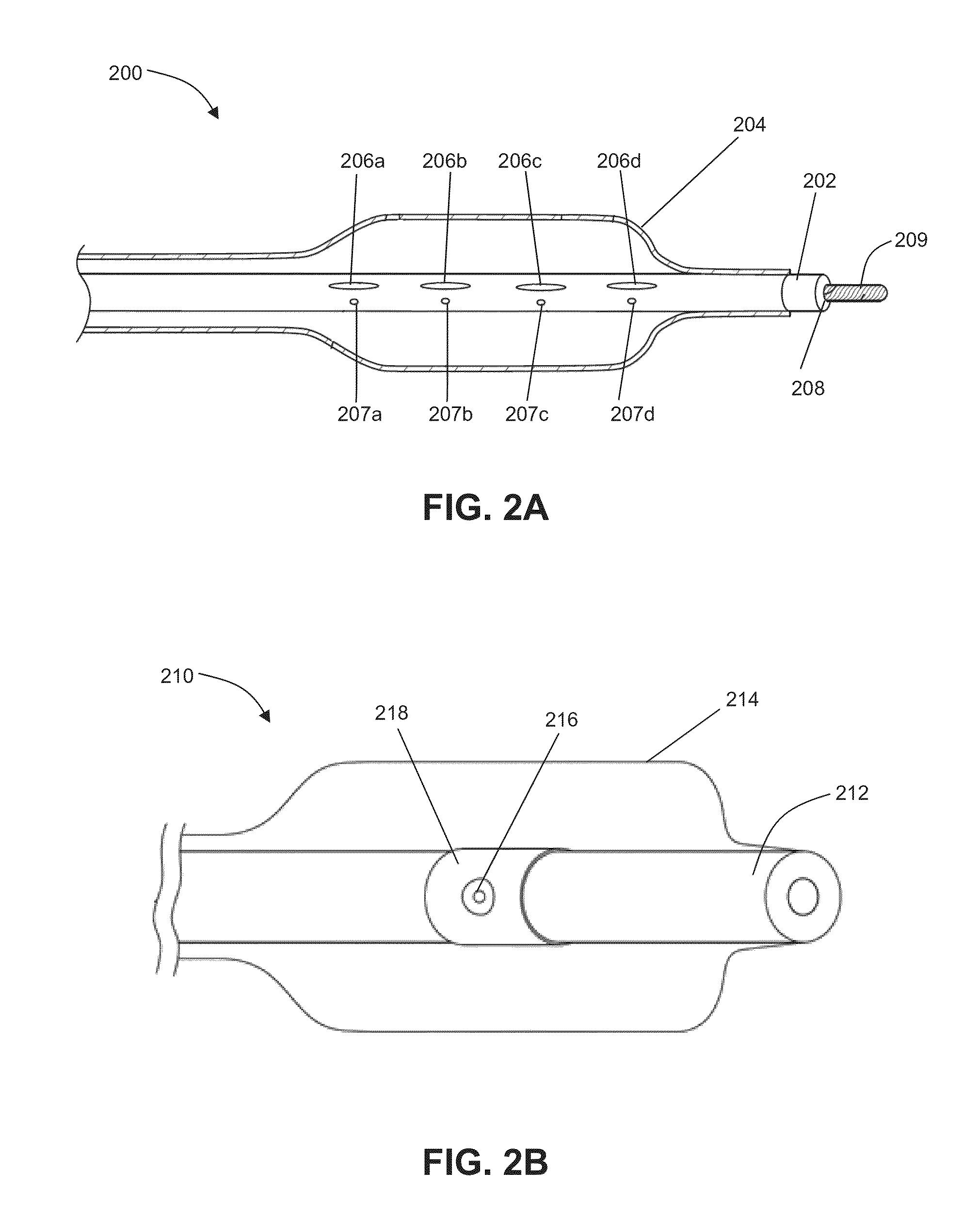
A medical stimulation device such as a cochlear implant configured to provide stimulation of one or more spatially-restricted contiguous portion(s) of the spiral array of auditory nerve fibers in the cochlear (“discrete stimulation regions”). Each discrete stimulation region is defined by the constructive and / or destructive interference of stimulating and limiting signals simultaneously applied to electrode channels of an implanted electrode array, the stimulating and limiting signals being determined based upon transimpedance measurements of intracochlear electrode channels of the implanted electrode array representing specific spread functions of an individual recipient. The stimulating signal is preferably applied through a targeted electrode channel; that is, one or more successive electrodes which is / are adjacent to the discrete stimulation region. The targeted electrode channel is selected to represent a sound based on the outputs of a sound processor to stimulate neural activity in the discrete stimulation region to thereby cause a percept of the represented sound. The size of the discrete stimulation region is defined by the limiting signal(s) applied to electrode channel(s) other than the targeted electrode channel, and which negate(s) current spread which would otherwise occur in response to the stimulating signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
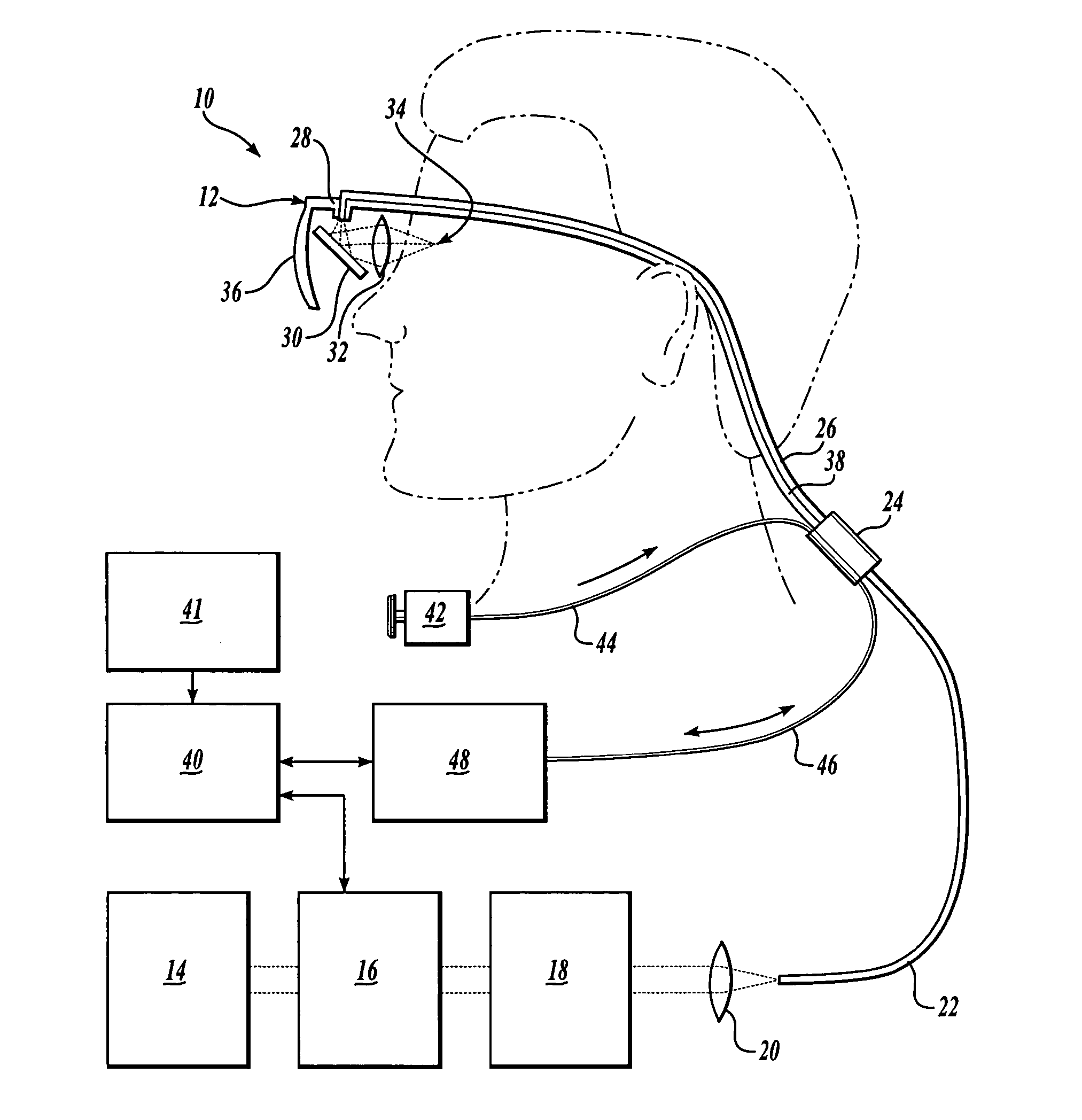
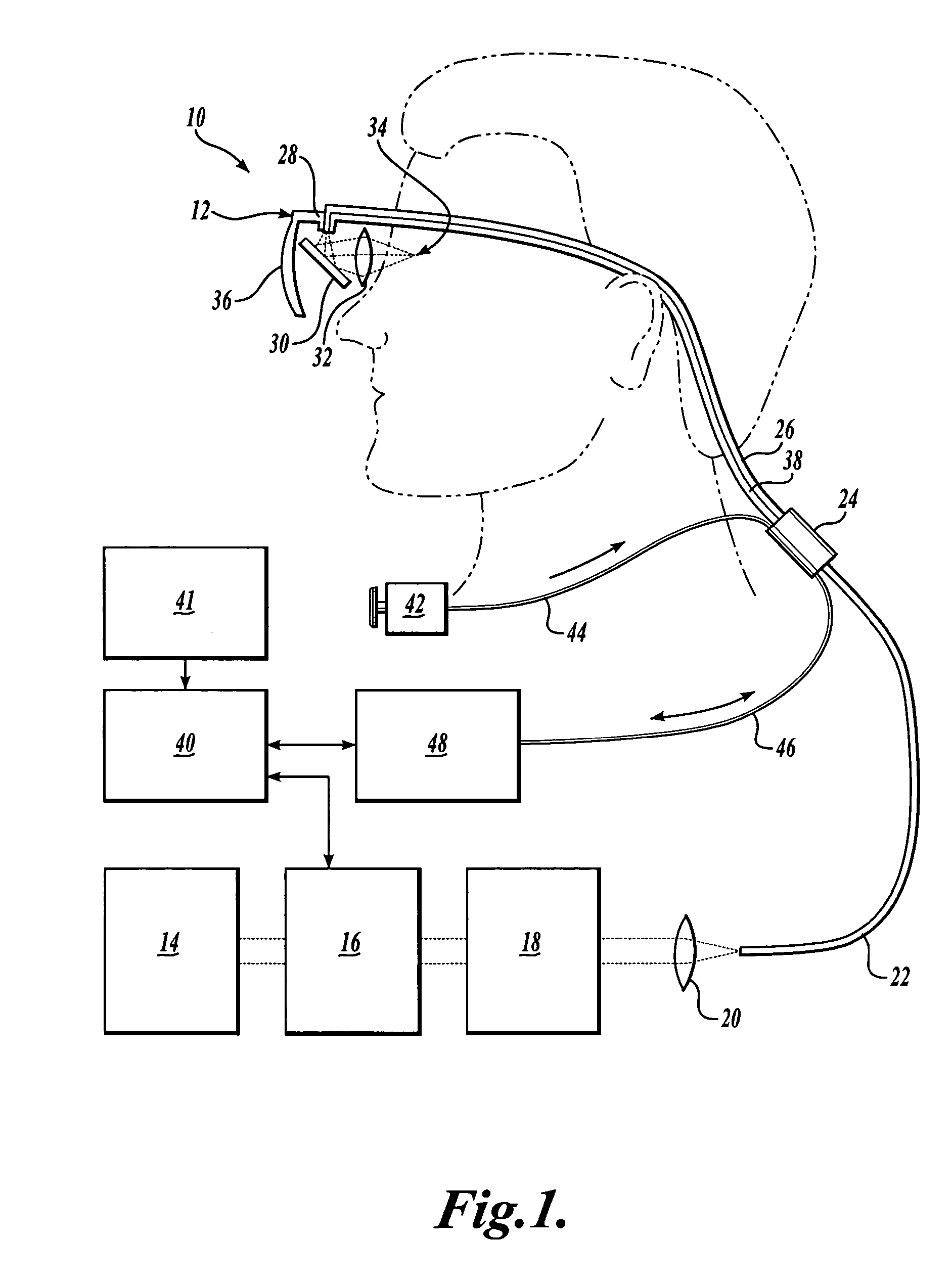
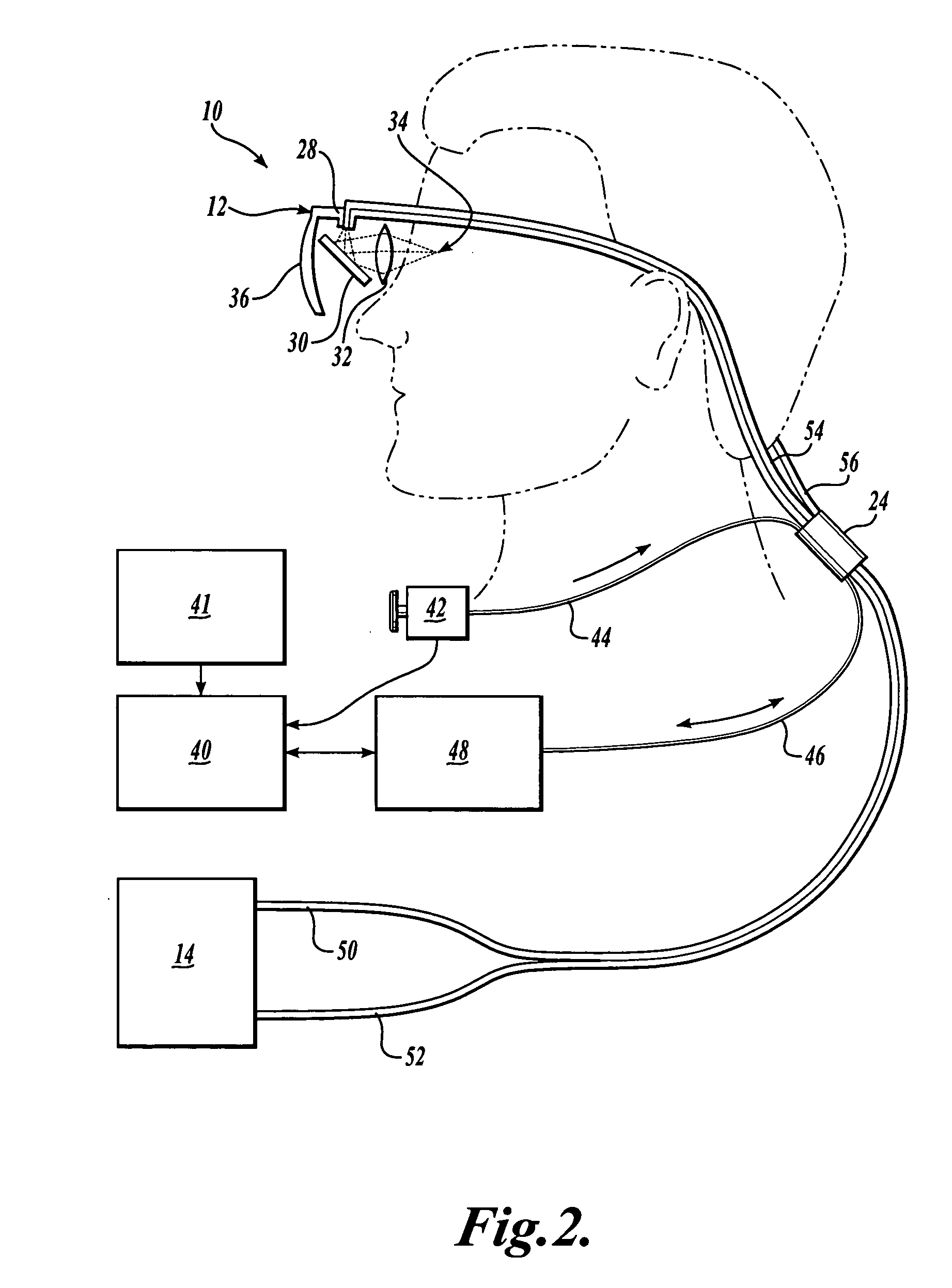
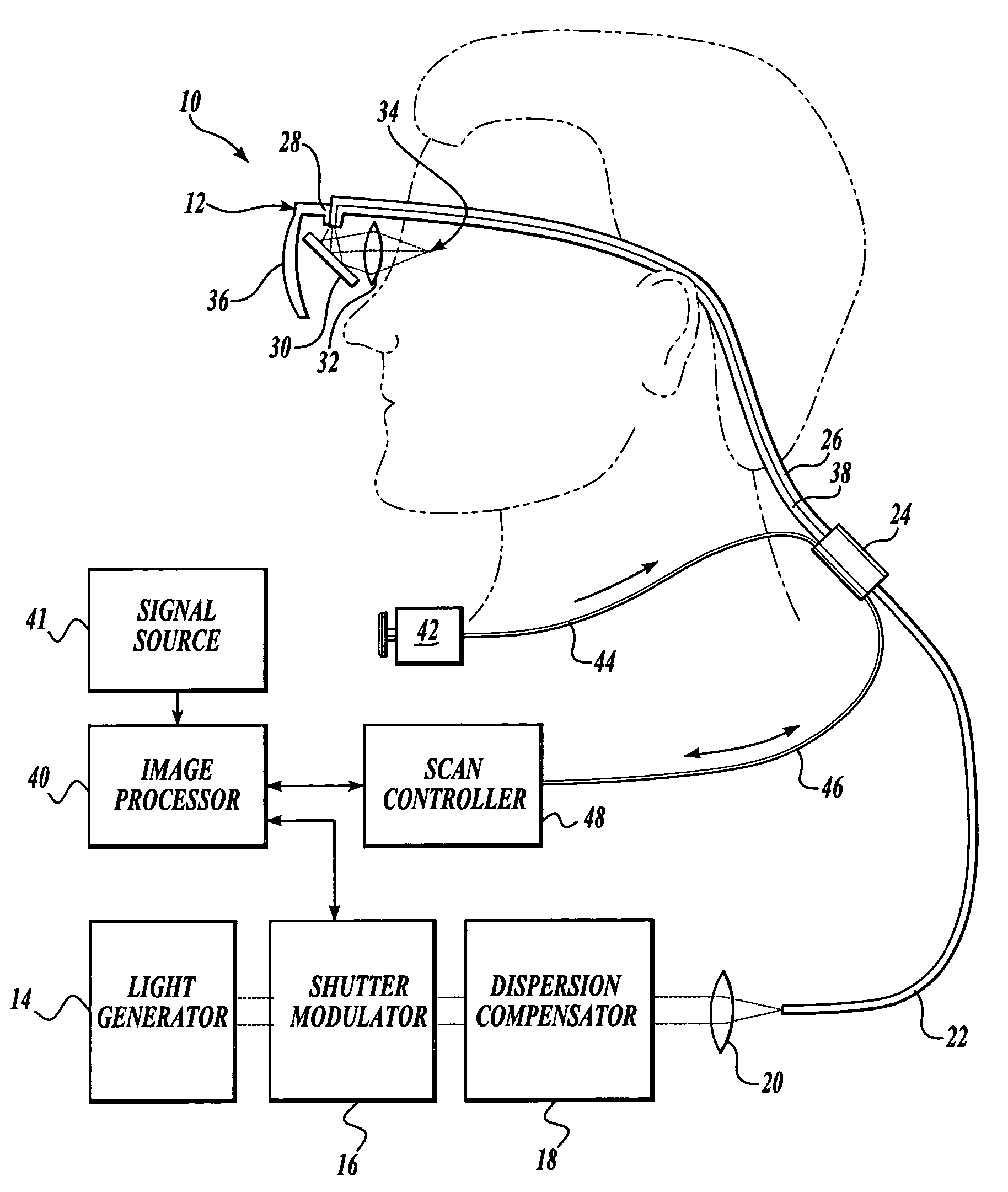
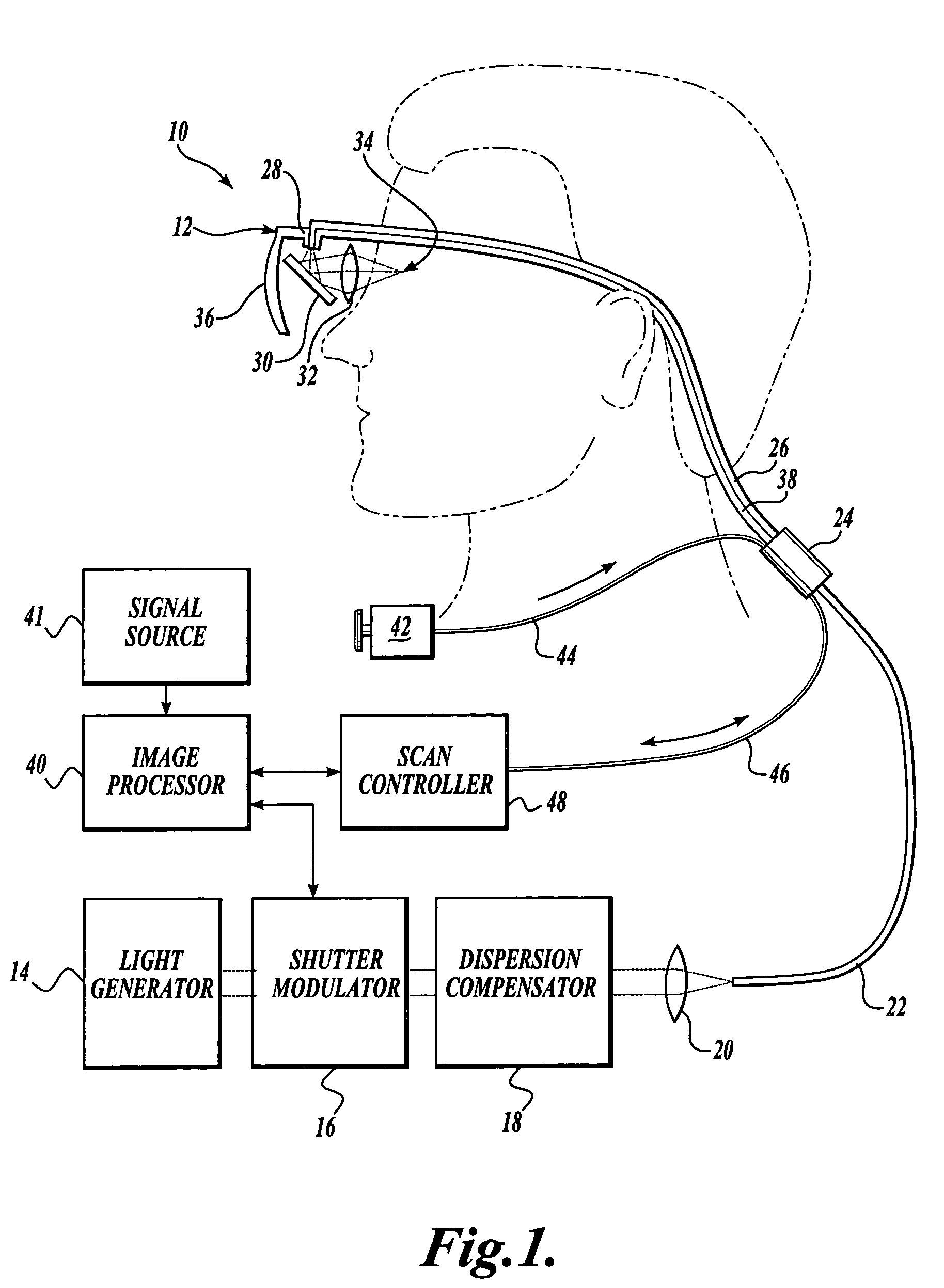
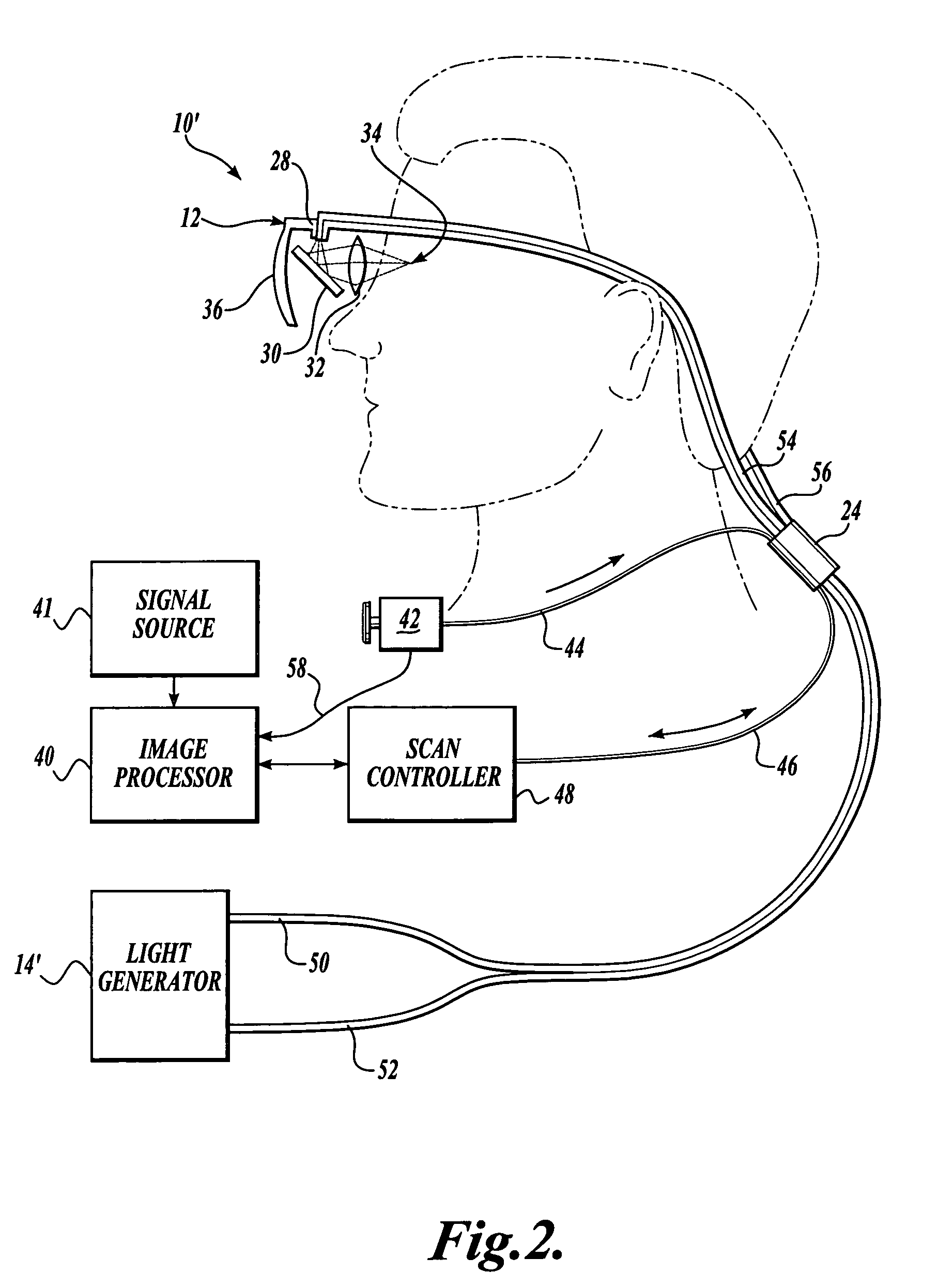
Scanning laser device and methods of use
InactiveUS20050015120A1Promote healthEasy SurvivalElectrotherapyDiagnosticsLight energyRetinal Neuron
In one aspect, the invention provides vision prosthesis systems. Exemplary vision prosthesis systems of the invention comprise a light energy generator operably connected to a wearable head piece comprising a device for directing light energy produced by the light energy generator onto a mammalian retina, wherein the light energy generator is tuned to emit light energy of sufficient power to modulate neural activity in the retina. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for irradiating neurons in the retina of the mammalian eye by directing light energy produced by a light energy generator onto a mammalian retina. The methods of the invention may be used to directly modulate the activity of retinal neurons or to introduce molecules into retinal cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
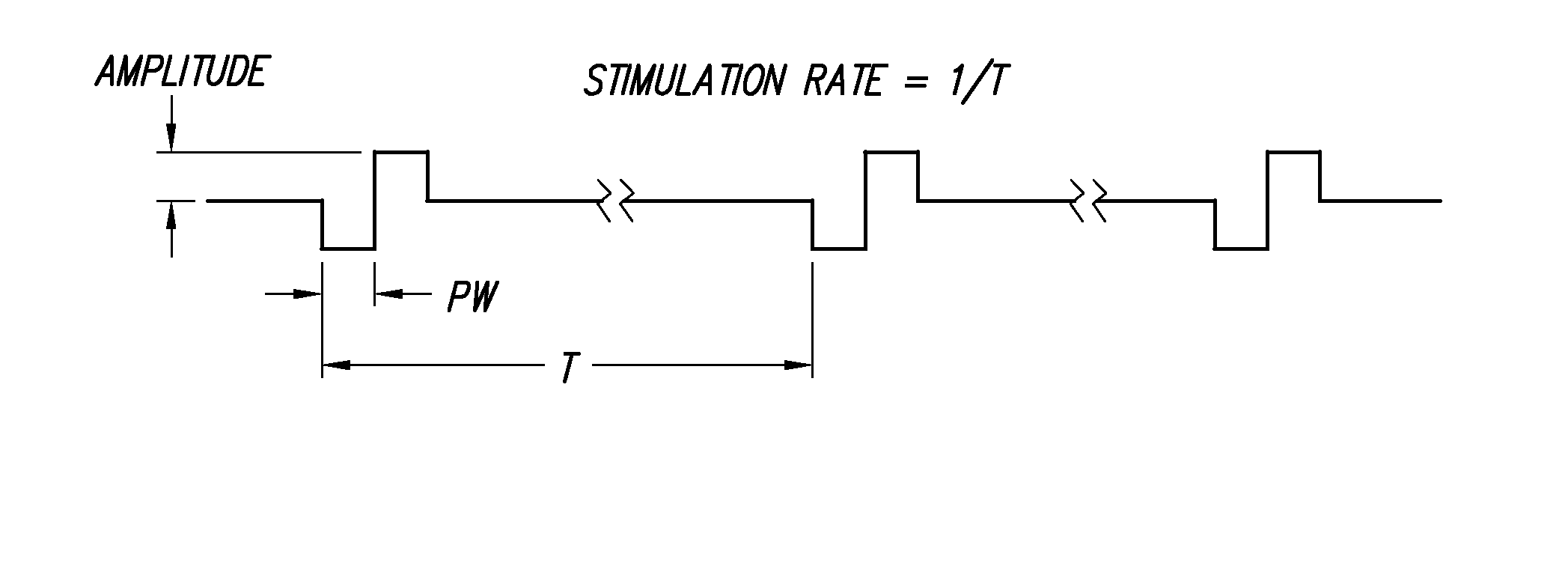
Gradual Recruitment of Muscle/Neural Excitable Tissue Using High-Rate Electrical Stimulation Parameters
InactiveUS20070244522A1Improve performanceIncrease rangeElectrotherapyArtificial respirationHigh rateElectrical dynamics
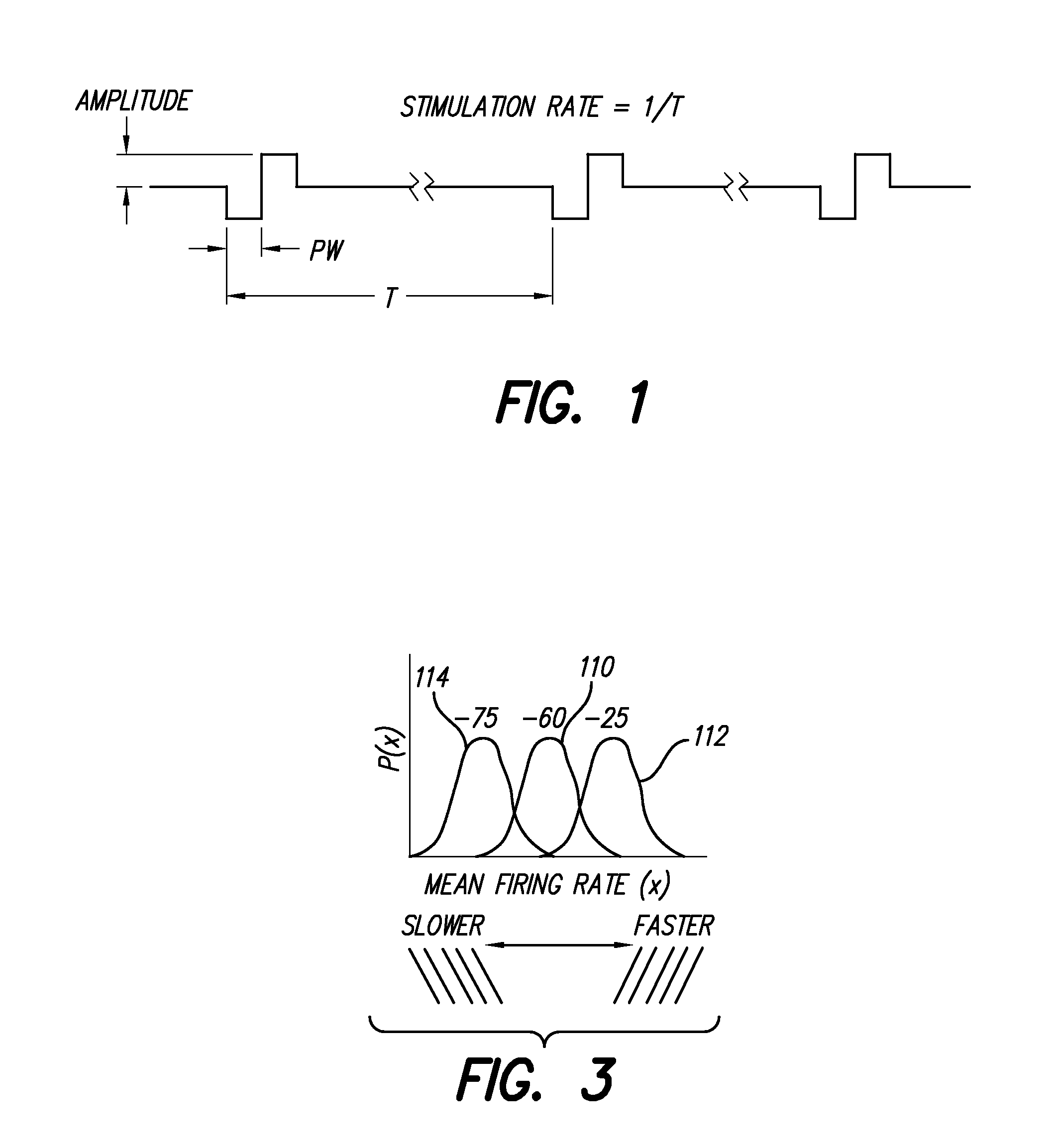
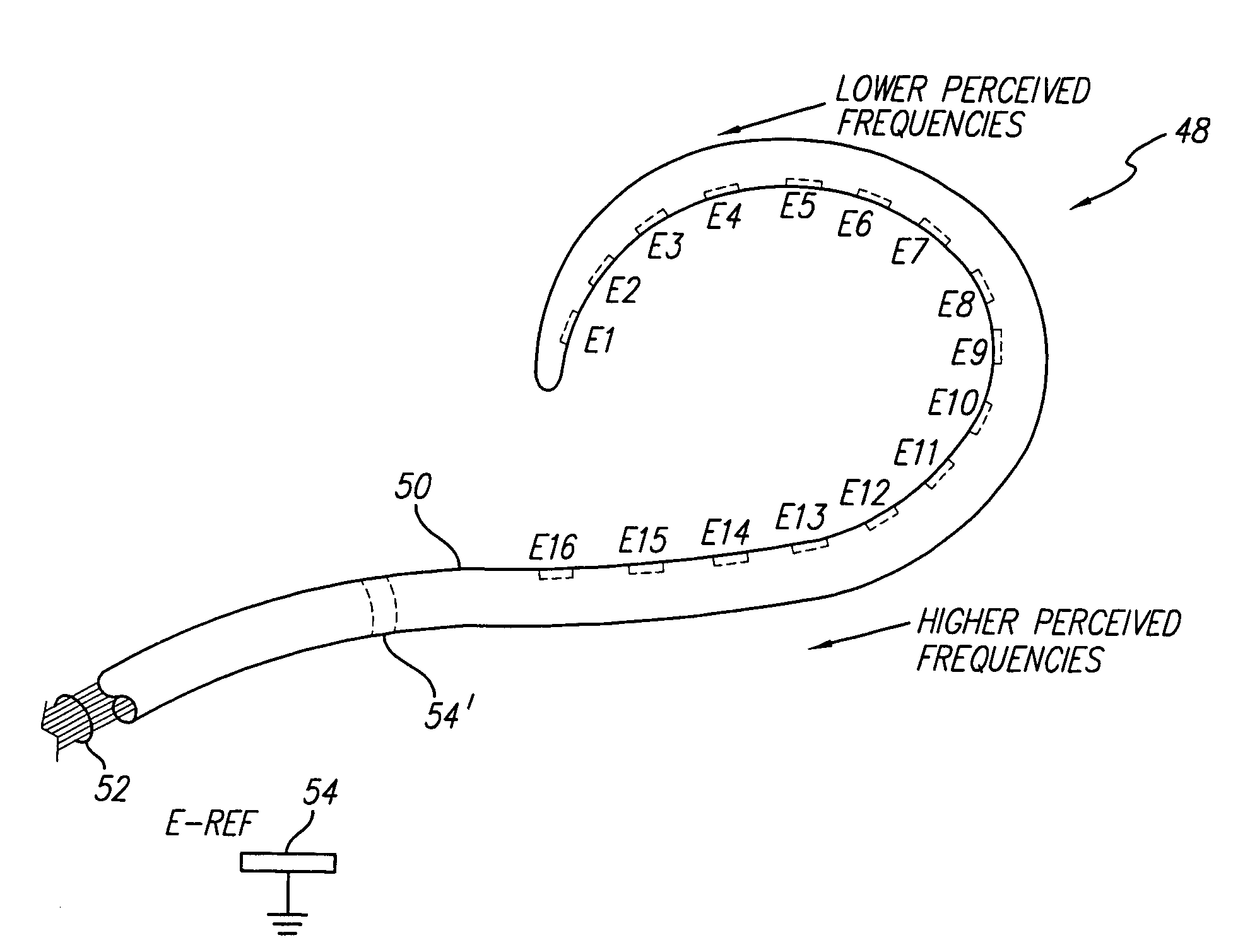
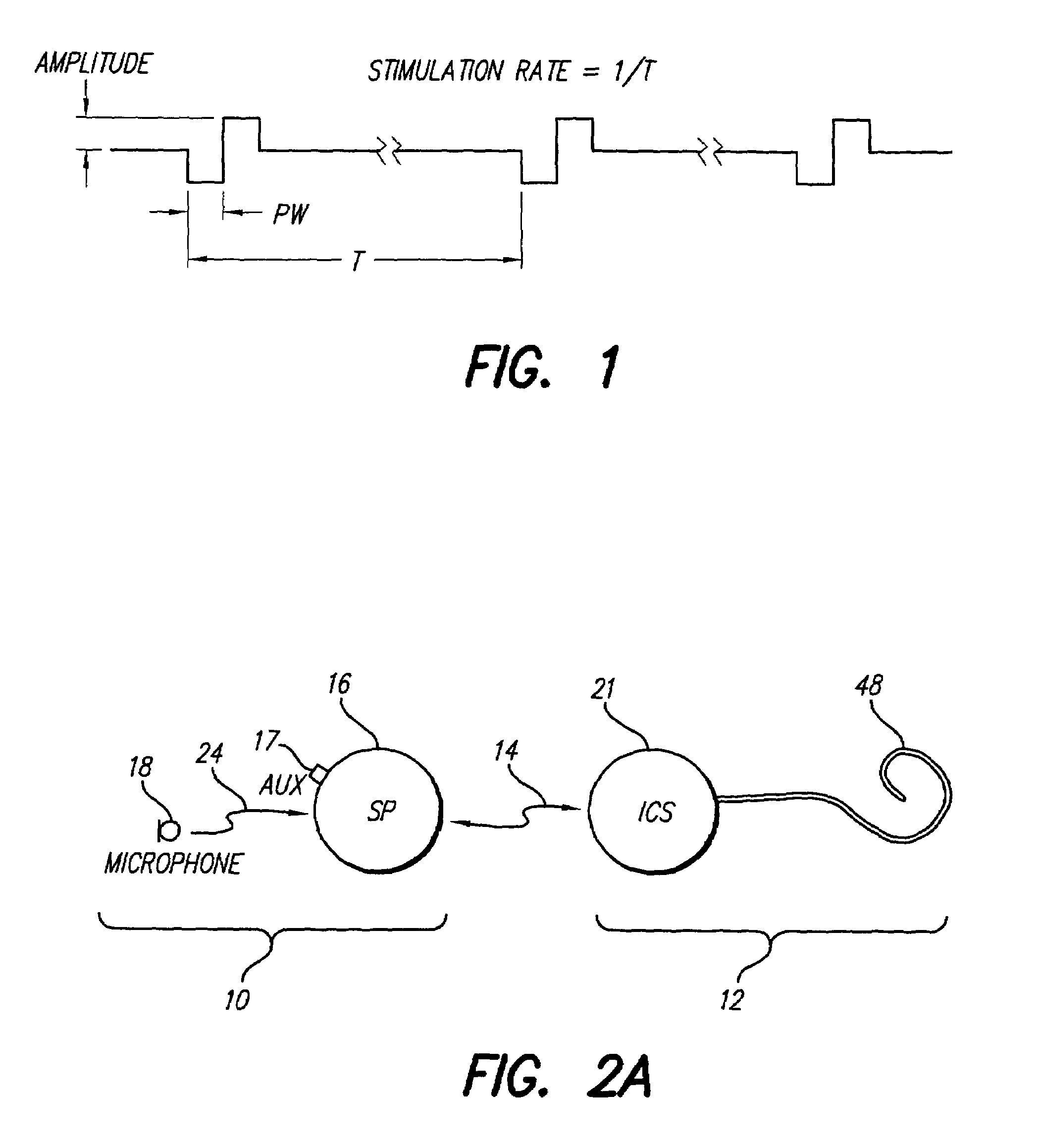
A neurostimulator system (170) stimulates excitable muscle or neural tissue through multiple electrodes (E1, E2, . . . En) fast enough to induce stochastic neural firing, thereby acting to restore “spontaneous” neural activity. The type of stimulation provided by the neurostimulator involves the use of a high rate, e.g., greater than about 2000 Hz, pulsatile stimulation signal generated by a high rate pulse generator (172). The stream of pulses generated by the high rate pulse generator is amplitude modulated in an output driver circuit (176) with control information, provided by a modulation control element (178). Such amplitude-modulated pulsatile stimulation exploits the subtle electro physiological differences between cells comprising excitable tissue in order to desynchronize action potentials within the population of excitable tissue. Such desynchronization induces a wider distribution of population thresholds, as well as a wider electrical dynamic range, thereby better mimicking biological recruitment characteristics.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Clustering of recorded patient neurological activity to determine length of a neurological event
Apparatus and method detect a detection cluster that is associated with a neurological event, such as a seizure, of a nervous system disorder and update therapy parameters that are associated with a treatment therapy. The occurrence of the detection cluster is detected when the maximal ratio exceeds an intensity threshold. If the maximal ratio drops below the intensity threshold for a time interval that is less than a time threshold and subsequently rises above the intensity threshold, the subsequent time duration is considered as being associated with the detection cluster rather than being associated with a different detection cluster. Consequently, treatment of the nervous system disorder during the corresponding time period is in accordance with one detection cluster. Treatment therapy may be provided by providing electrical stimulation, drug infusion or a combination. Therapy parameters may be updated for each mth successive group of applications of the treatment therapy or for each nth detection cluster.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
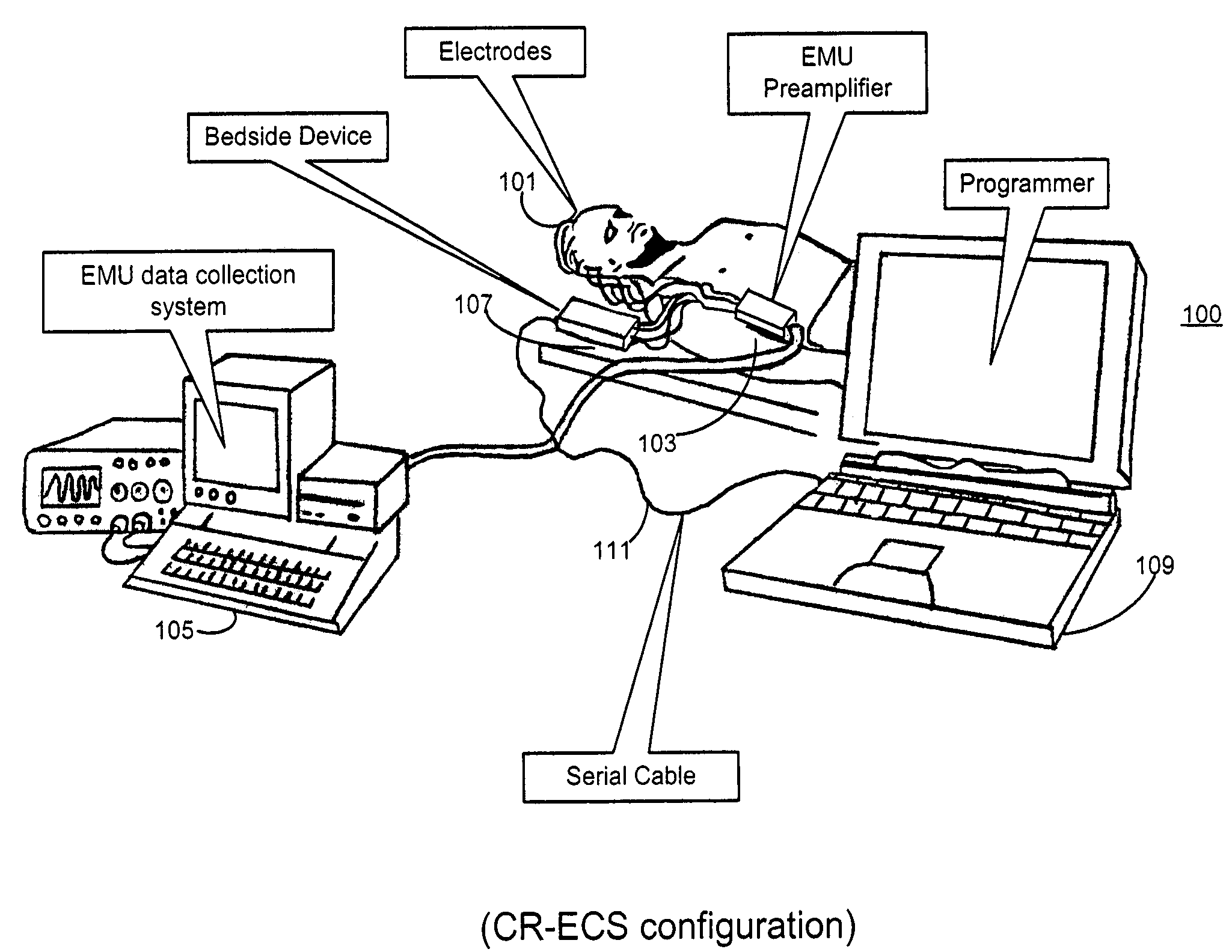
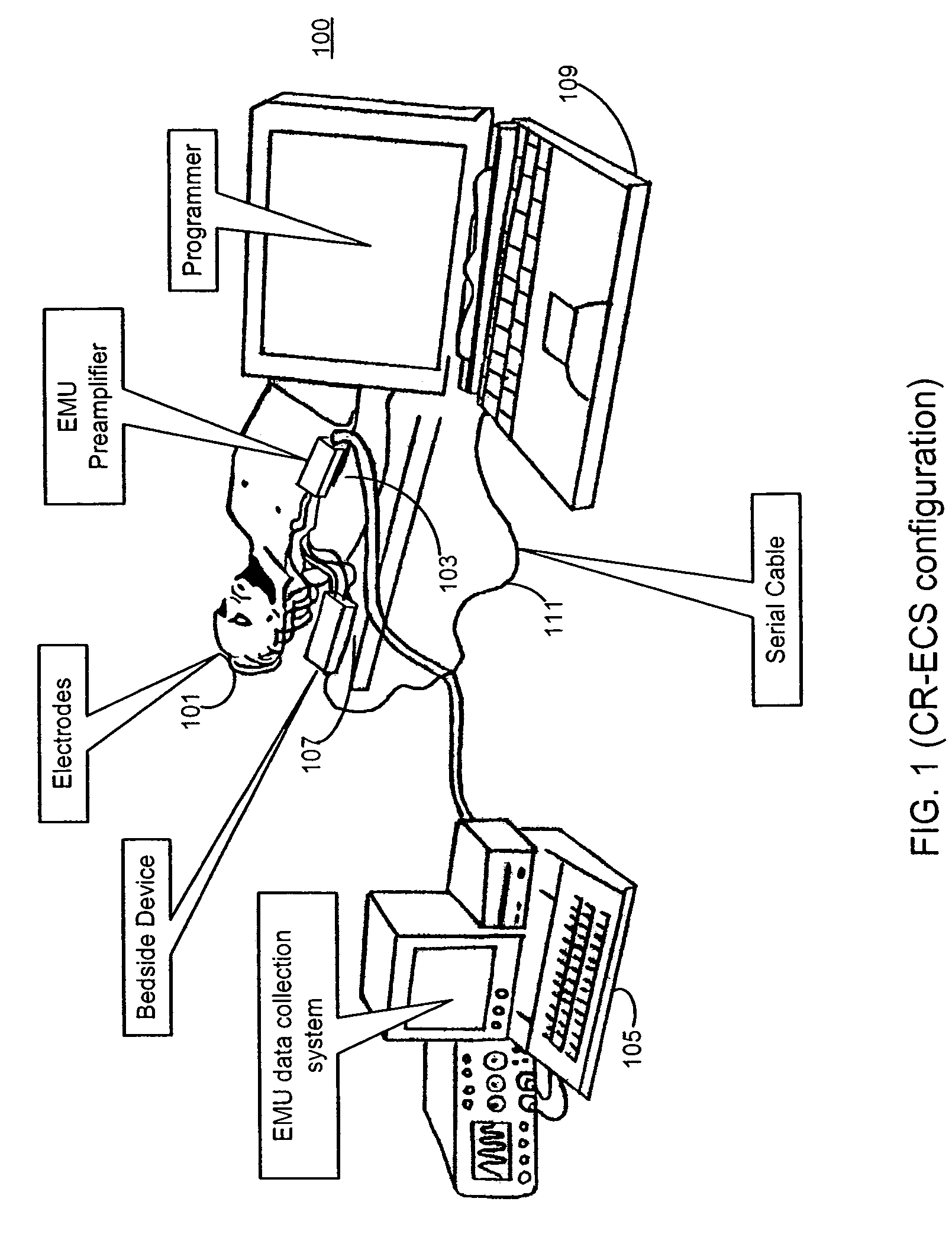
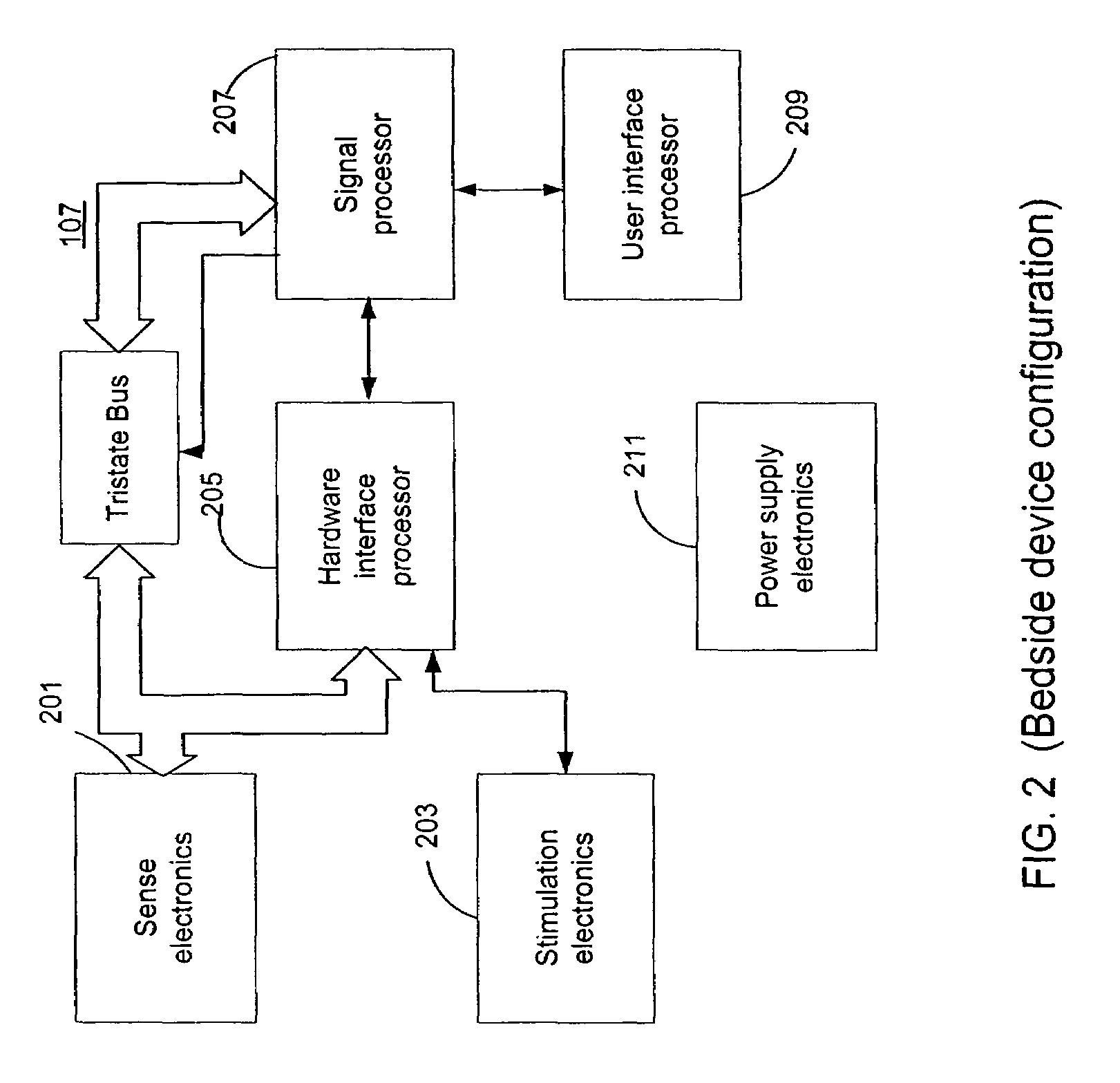
Cortical Implant System for Brain Stimulation and Recording
ActiveUS20150157862A1Shorter electrode arraysLess distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLaminating printed circuit boardsDiseaseEngineering
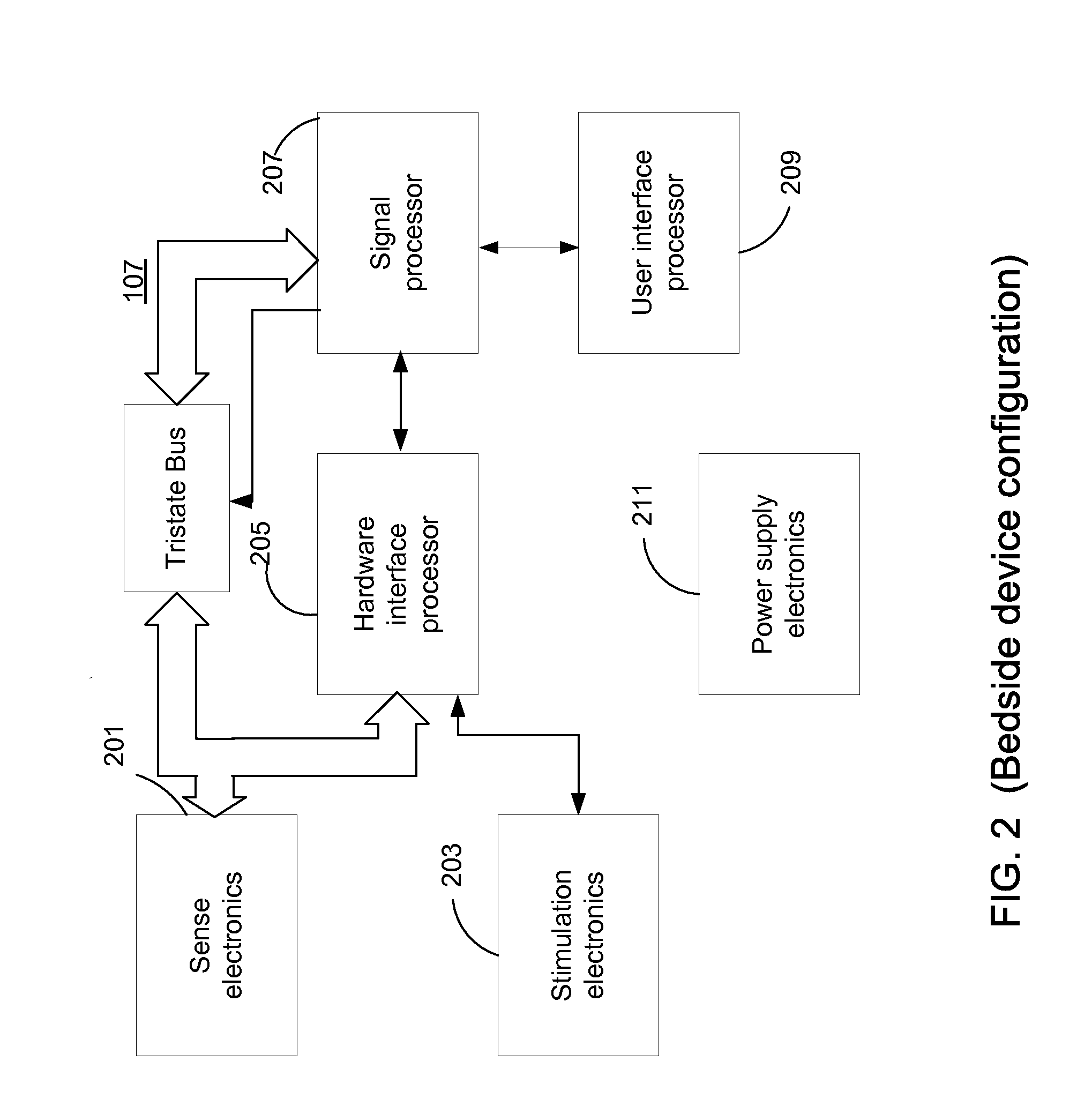
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. A brain stimulator, preferably a deep brain stimulator, stimulates the brain in response to neural recordings in a closed feedback loop. The device is advantageous in providing neuromodulation therapies for neurological disorders such as chronic pain, post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), major depression, or similar disorders. The invention and components thereof are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Apparatus and method for neural-signal capture to drive neuroprostheses or control bodily function
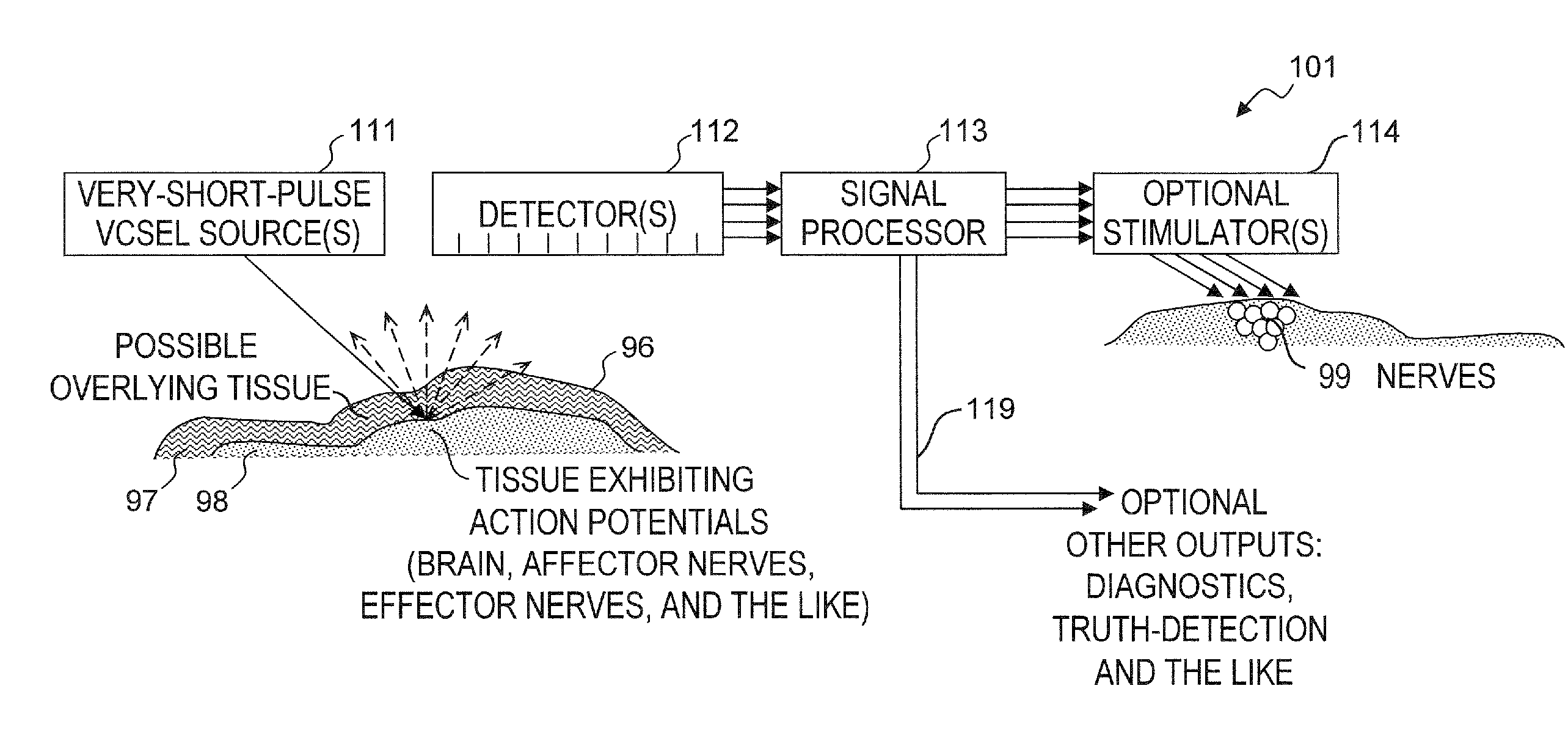
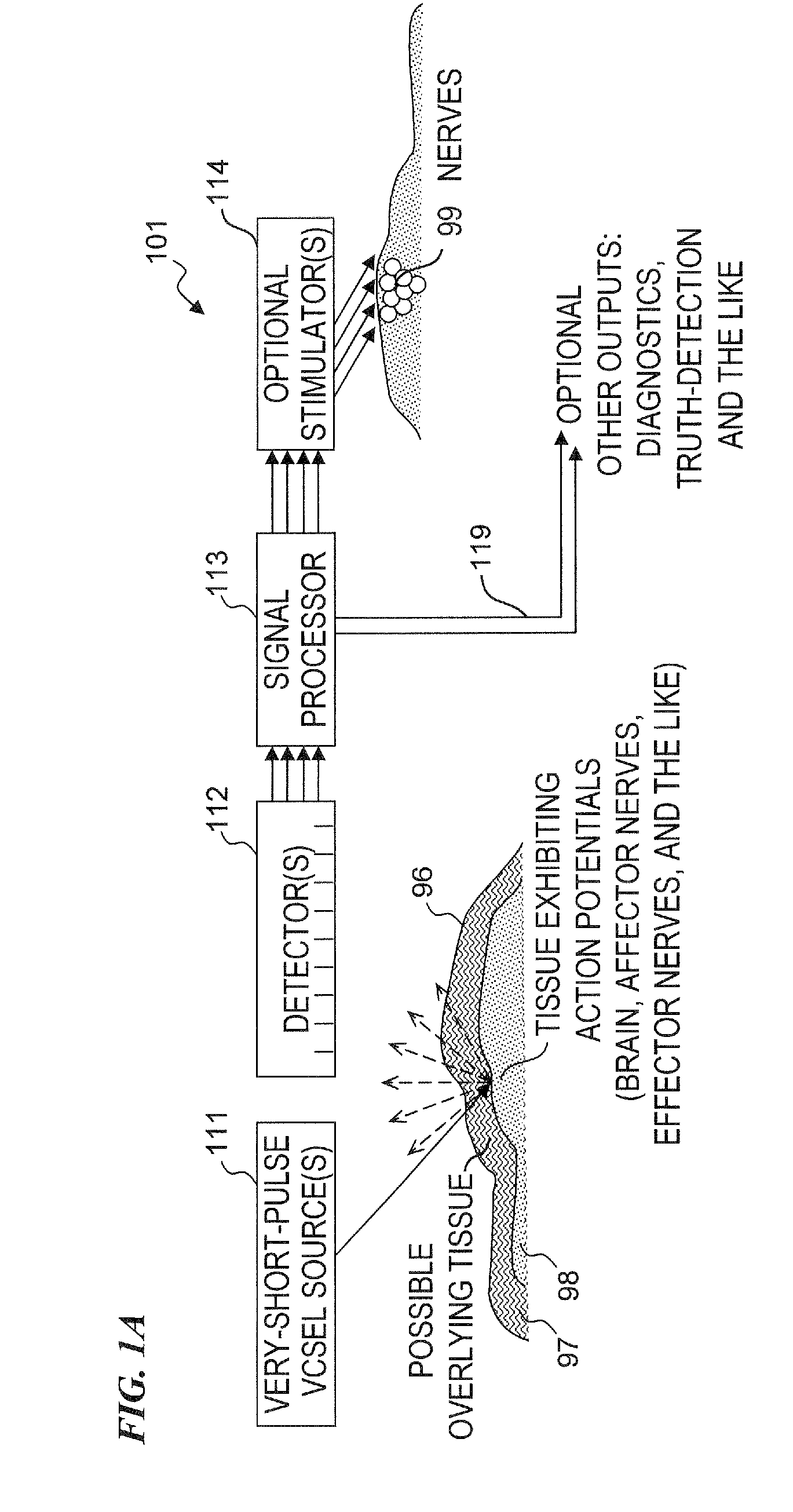
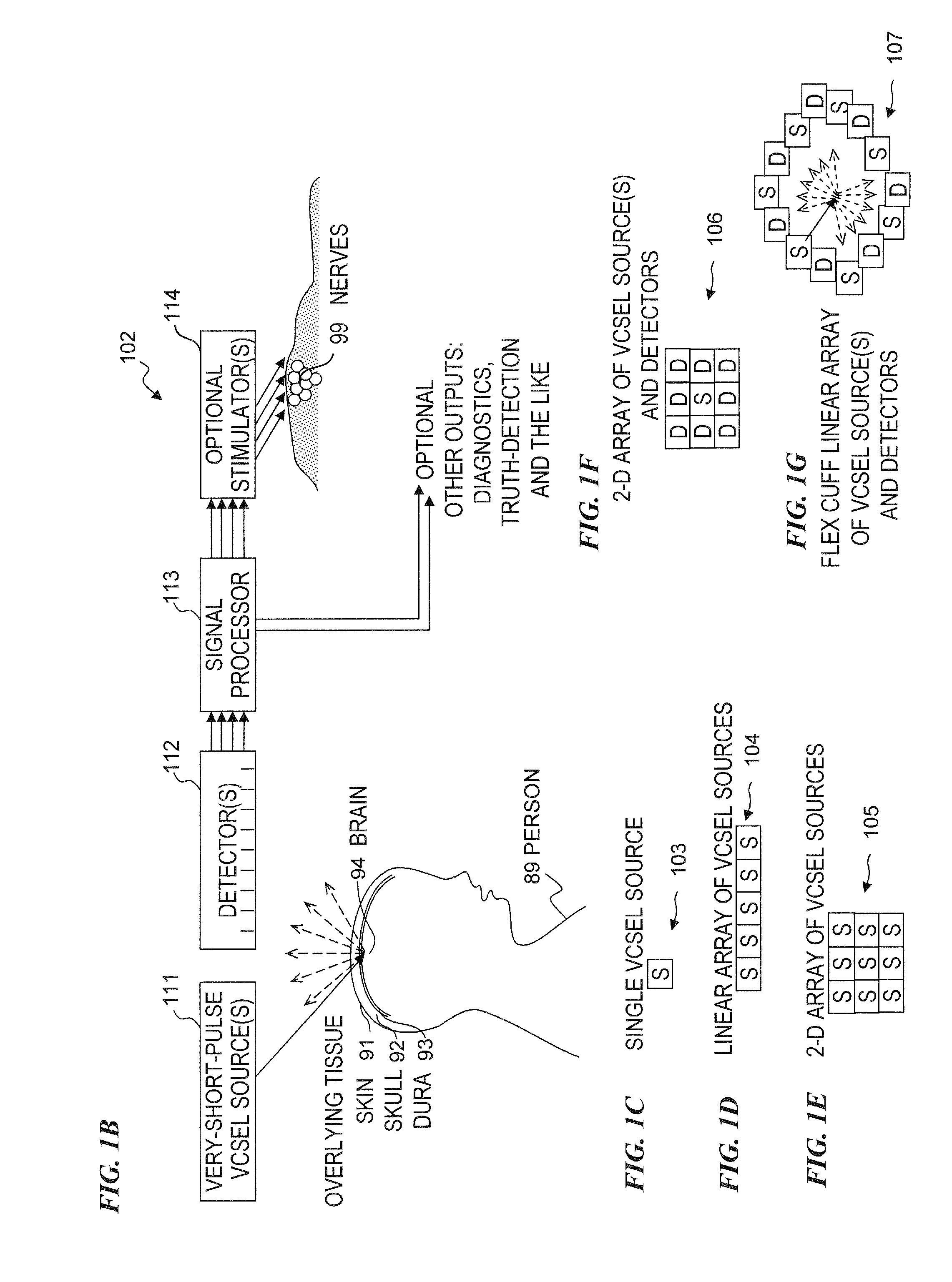
Method and apparatus for detecting nerve activity of an animal. Some embodiments include outputting a light pulse having a wavelength onto a volume of animal tissue such that the light pulse interacts with active nerves of the tissue; measuring a light signal resulting from the interaction of the light pulse with the tissue; transmitting an electrical signal based on the measured light signal; signal-processing the electrical signal; and outputting a response signal, which can optionally be used to control a prosthetic device, stimulate another nerve, or display / diagnose a condition. Some embodiments output a plurality of light wavelengths and / or pulses, which are optionally high-frequency intensity modulated. Some embodiments analyze DC, AC, and phase components of signals to spatially resolve locations of neural activity. Some embodiments output light pulse(s) and detect the resultant light from outside a human skull to detect neural activity of human brain tissue inside the skull.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Gradual Recruitment of Muscle/Neural Excitable Tissue Using High-Rate Electrical Stimulation Parameters
InactiveUS20070239226A1Wide dynamic rangeRaise the thresholdExternal electrodesArtificial respirationHigh rateElectrical dynamics
A neurostimulator system (170) stimulates excitable muscle or neural tissue through multiple electrodes (E1, E2, . . . En) fast enough to induce stochastic neural firing, thereby acting to restore “spontaneous” neural activity. The type of stimulation provided by the neurostimulator involves the use of a high rate, e.g., greater than about 2000 Hz, pulsatile stimulation signal generated by a high rate pulse generator (172). The stream of pulses generated by the high rate pulse generator is amplitude modulated in an output driver circuit (176) with control information, provided by a modulation control element (178). Such amplitude-modulated pulsatile stimulation exploits the subtle electro physiological differences between cells comprising excitable tissue in order to desynchronize action potentials within the population of excitable tissue. Such desynchronization induces a wider distribution of population thresholds, as well as a wider electrical dynamic range, thereby better mimicking biological recruitment characteristics.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Clustering of recorded patient neurological activity to determine length of a neurological event
ActiveUS20080033508A1Good curative effectElectroencephalographyImplantable neurostimulatorsDiseaseNervous system
Apparatus and method detect a detection cluster that is associated with a neurological event, such as a seizure, of a nervous system disorder and update therapy parameters that are associated with a treatment therapy. The occurrence of the detection cluster is detected when the maximal ratio exceeds an intensity threshold. If the maximal ratio drops below the intensity threshold for a time interval that is less than a time threshold and subsequently rises above the intensity threshold, the subsequent time duration is considered as being associated with the detection cluster rather than being associated with a different detection cluster. Consequently, treatment of the nervous system disorder during the corresponding time period is in accordance with one detection cluster. Treatment therapy may be provided by providing electrical stimulation, drug infusion or a combination. Therapy parameters may be updated for each mth successive group of applications of the treatment therapy or for each nth detection cluster.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
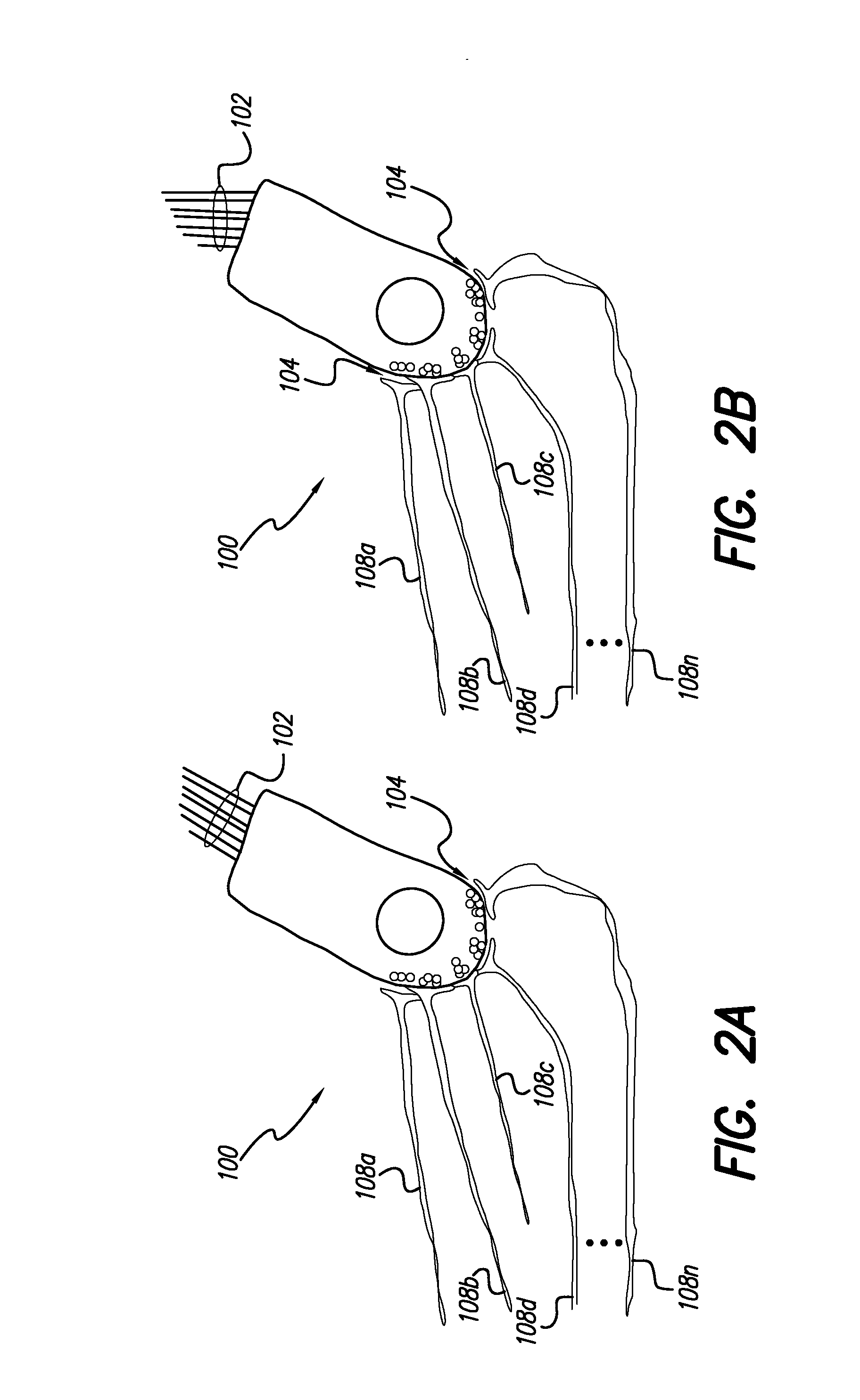
Implantable neural prosthetic device and methods of use
Neural stimulation devices are described that detect the neural activity from the spinal cord in a semi-invasive manner, where the device comprises at least one antenna array comprising an antenna. The antenna of the array is in electrical communication with the spinal cord of the patient. A device comprising more than one antenna array can be used to detect the neural signal strength, as well as the velocity and directionality of the signal.
Owner:CENT NERVOUS SYST
Cortical Interface for Motor Signal Recording and Sensory Signal Stimulation
ActiveUS20120296444A1Small sizeIncrease the number ofHead electrodesPrinted circuit aspectsSensory FeedbacksProsthesis
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to the at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that is / are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. The output signals provide control for a motor prosthesis and the inputs signals provide sensory feedback for the motor prosthesis. The invention, or components thereof, is / are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
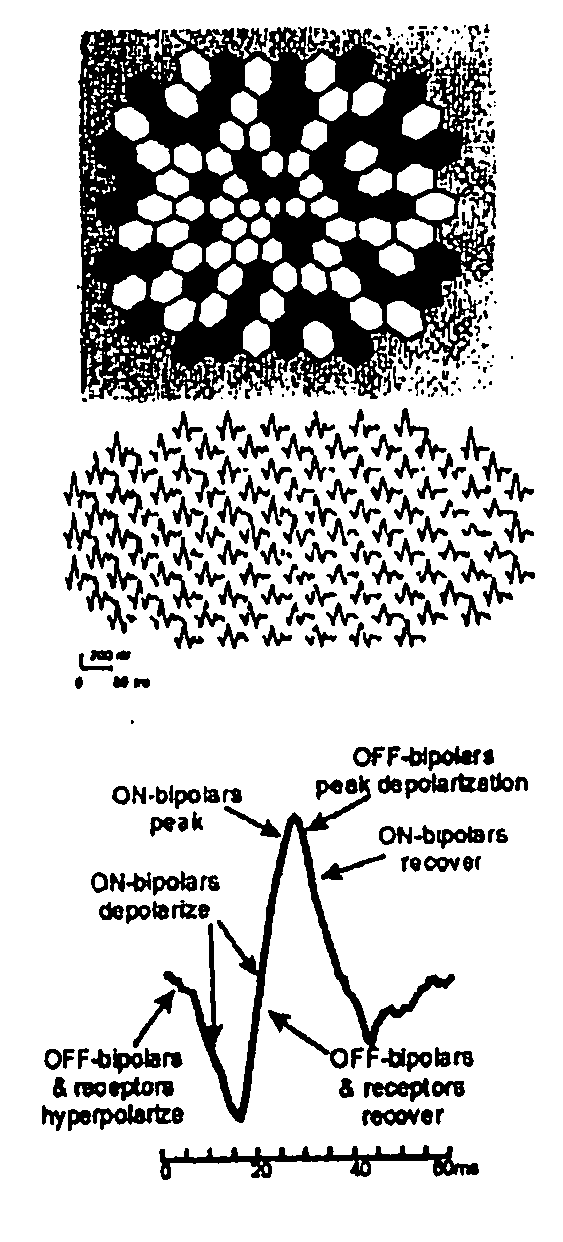
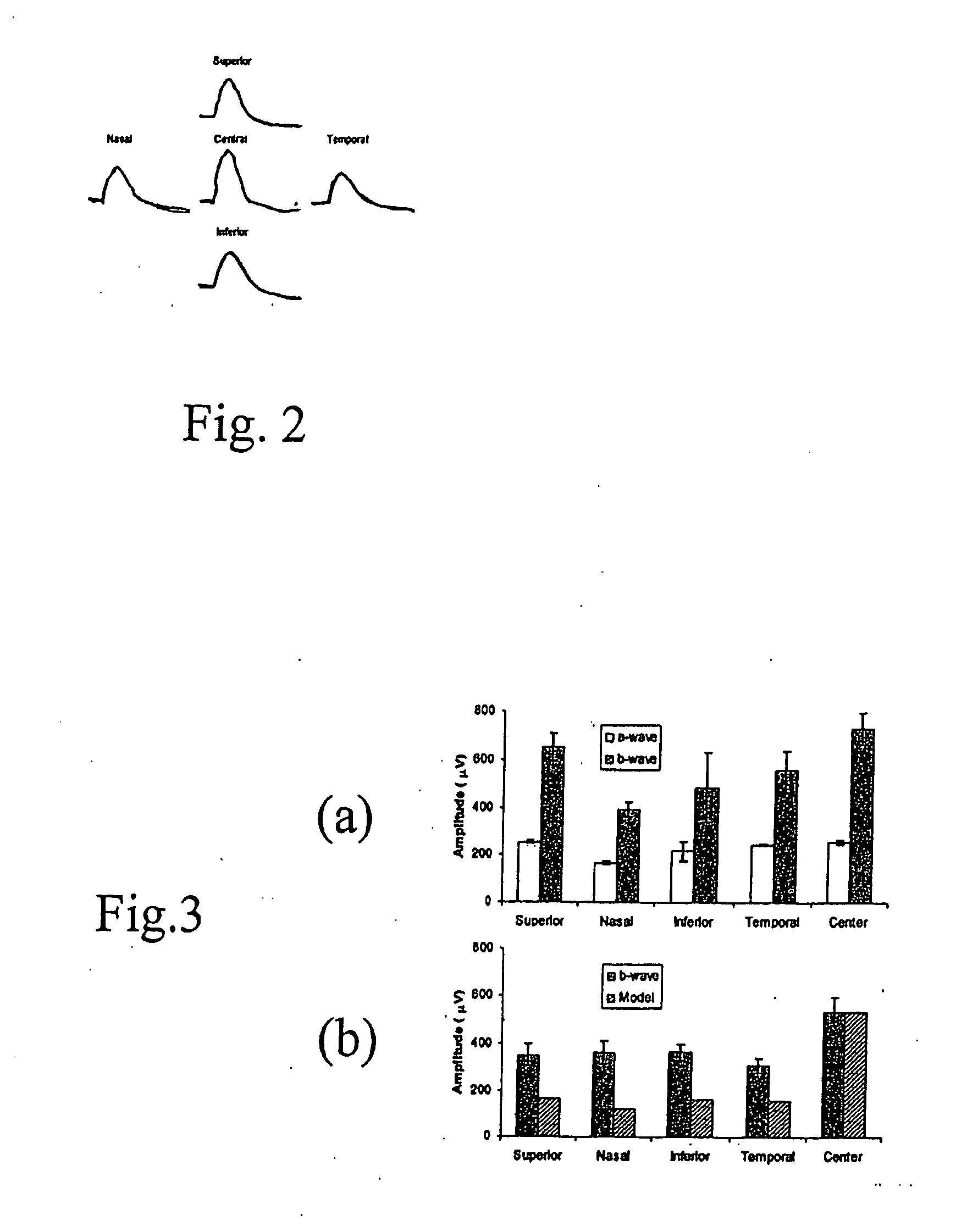
Mapping retinal function using corneal electrode array
A system and method for obtaining information about the spatial distribution of photoreceptor activity and neural activity in the retina using simultaneously recorded multiple biopotential signals. The information thus gathered is used to assess retinal dysfunction due to trauma or disease. The biopotential signals are recorded from the surface of the eye and head using a plurality of electrodes, including those integral to a contact lens. The biopotential signals are recorded before, during and after the presentation of an optical stimulus to the subject eye. The recorded biopotential signals are then analyzed and interpreted to reveal the distribution of photoreceptor activity and neural activity across the retina. The analysis and interpretation of the biopotential signals is quantitative, and makes use of an electromagnetic model of the subject eye. The subject may be animal or human.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Retroactive information searching enabled by neural sensing
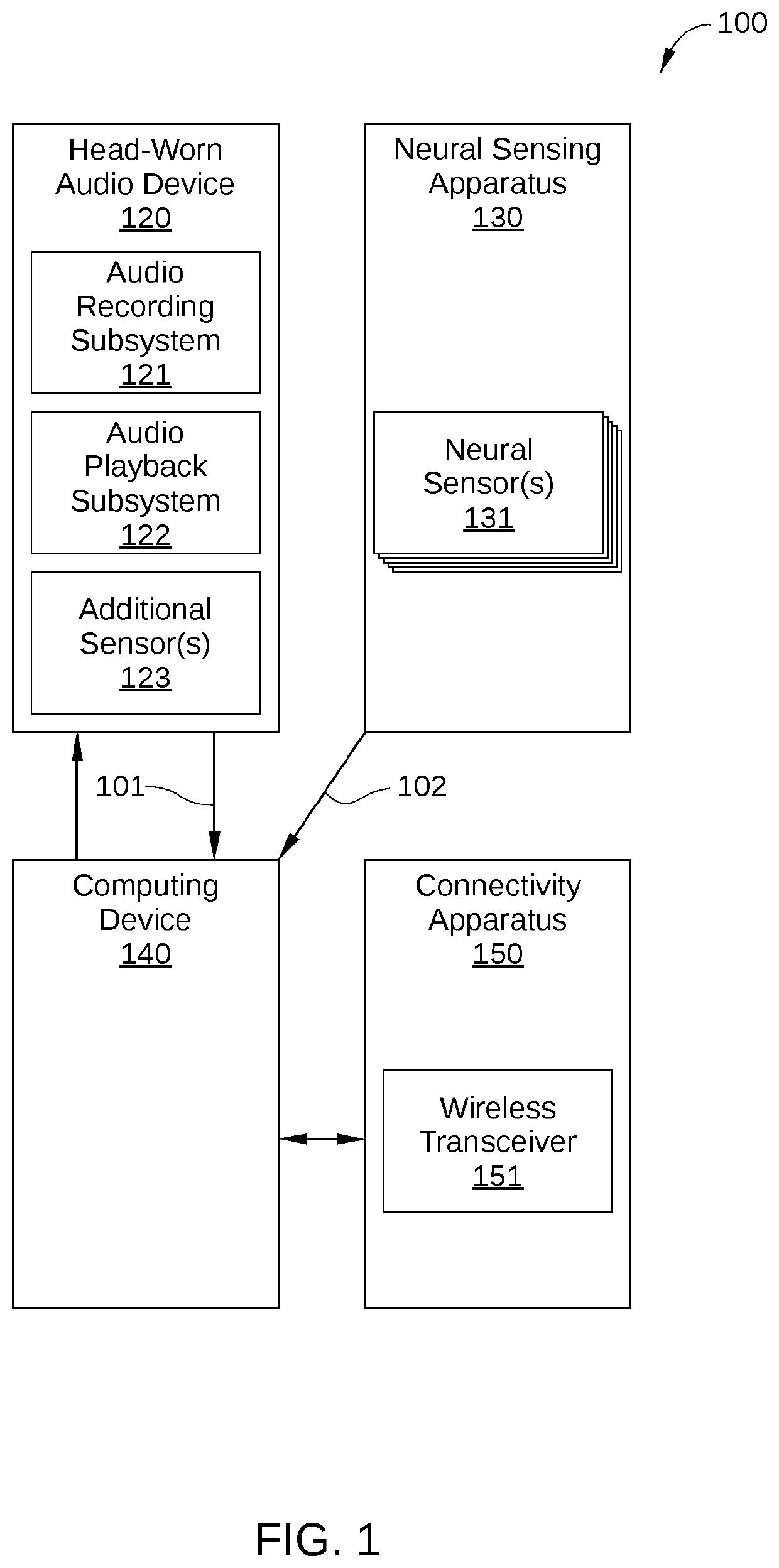
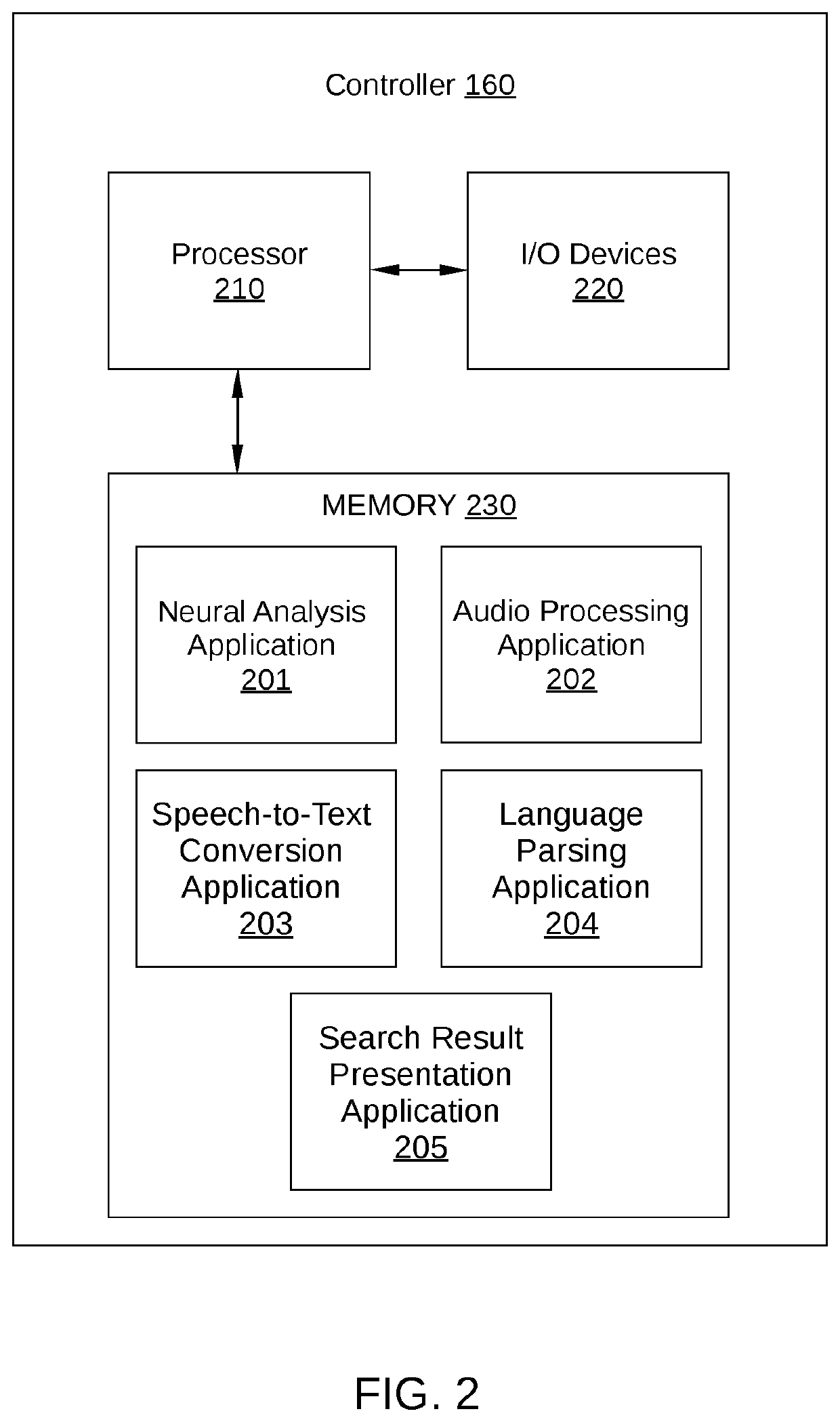
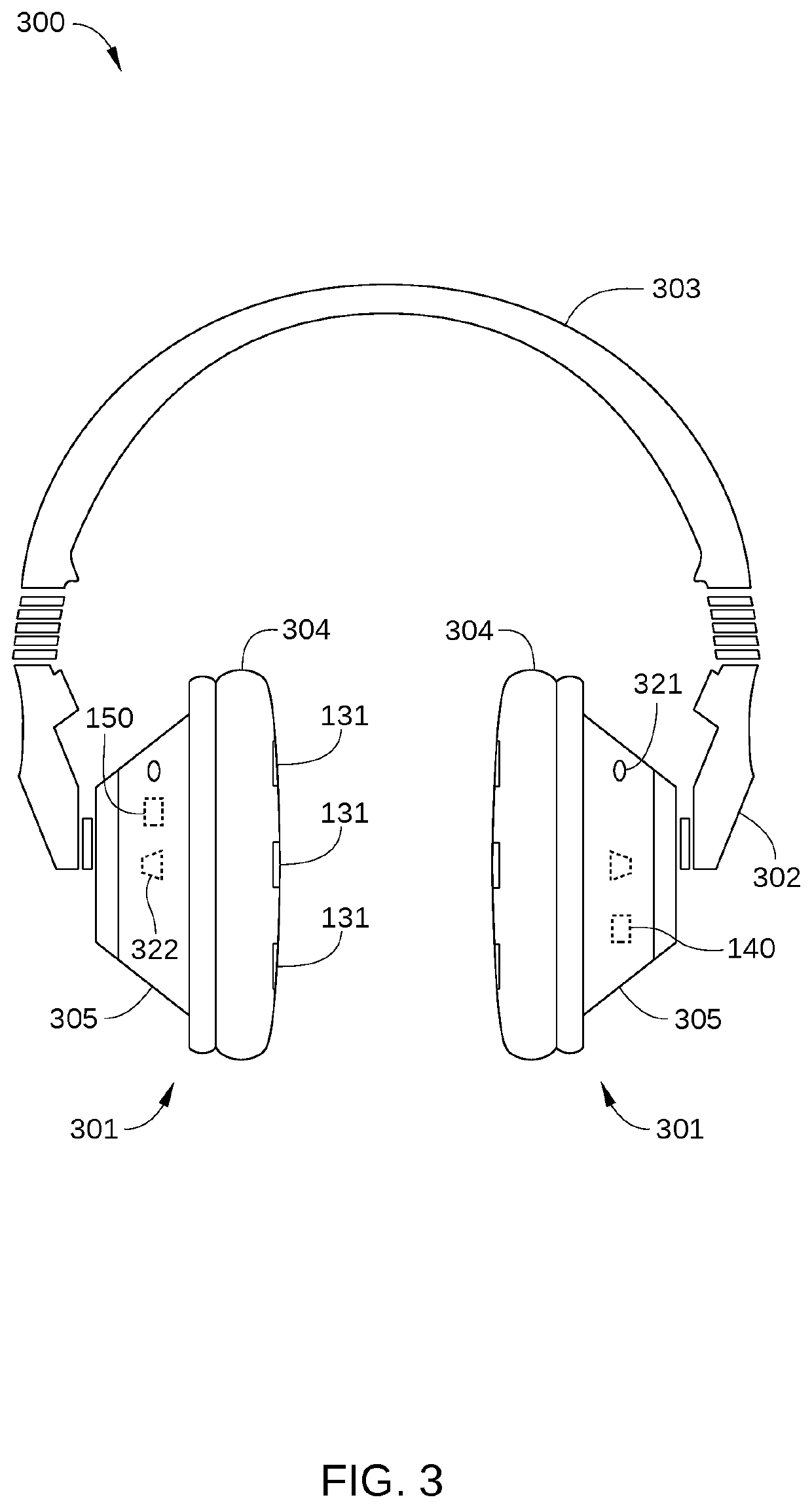
ActiveUS20200034492A1Provide informationNatural language translationInput/output for user-computer interactionOutput deviceInformation searching
A method for retrieving information includes detecting a first neural activity of a user, wherein the first neural activity corresponds to a key thought of the user; in response to detecting the first neural activity, generating a search query based on speech occurring prior to detecting the first neural activity; retrieving information based on the search query; and transmitting the information to one or more output devices.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
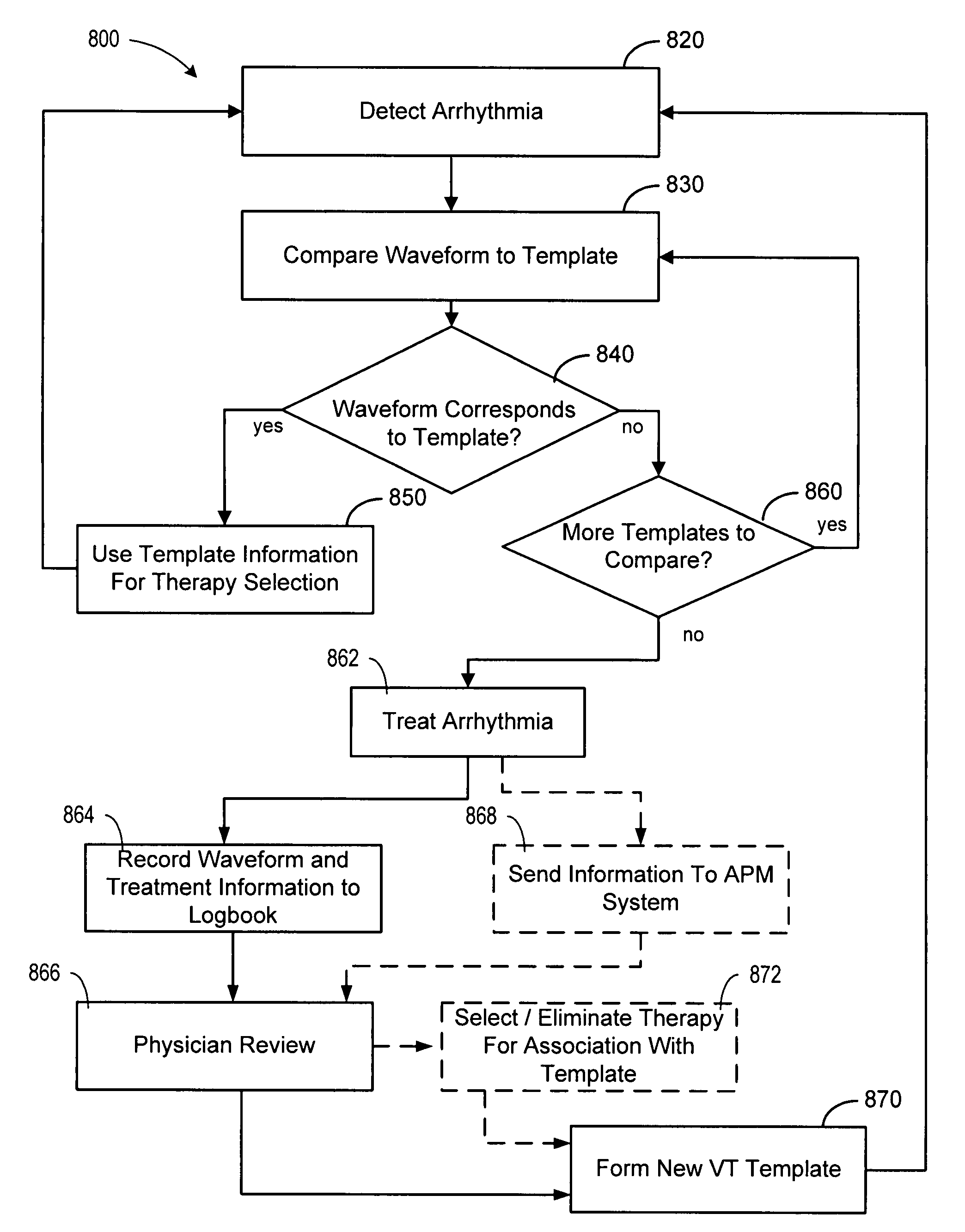
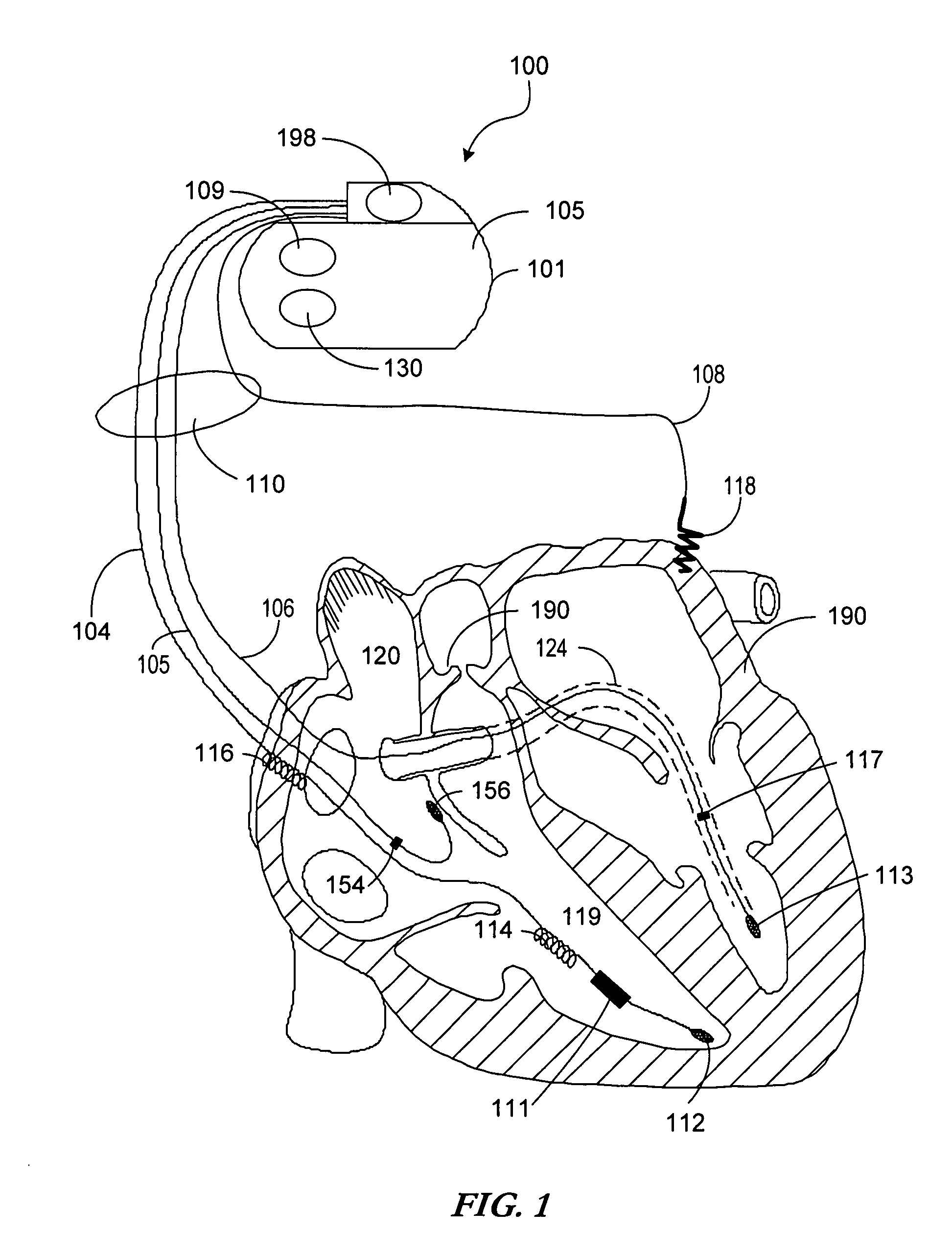
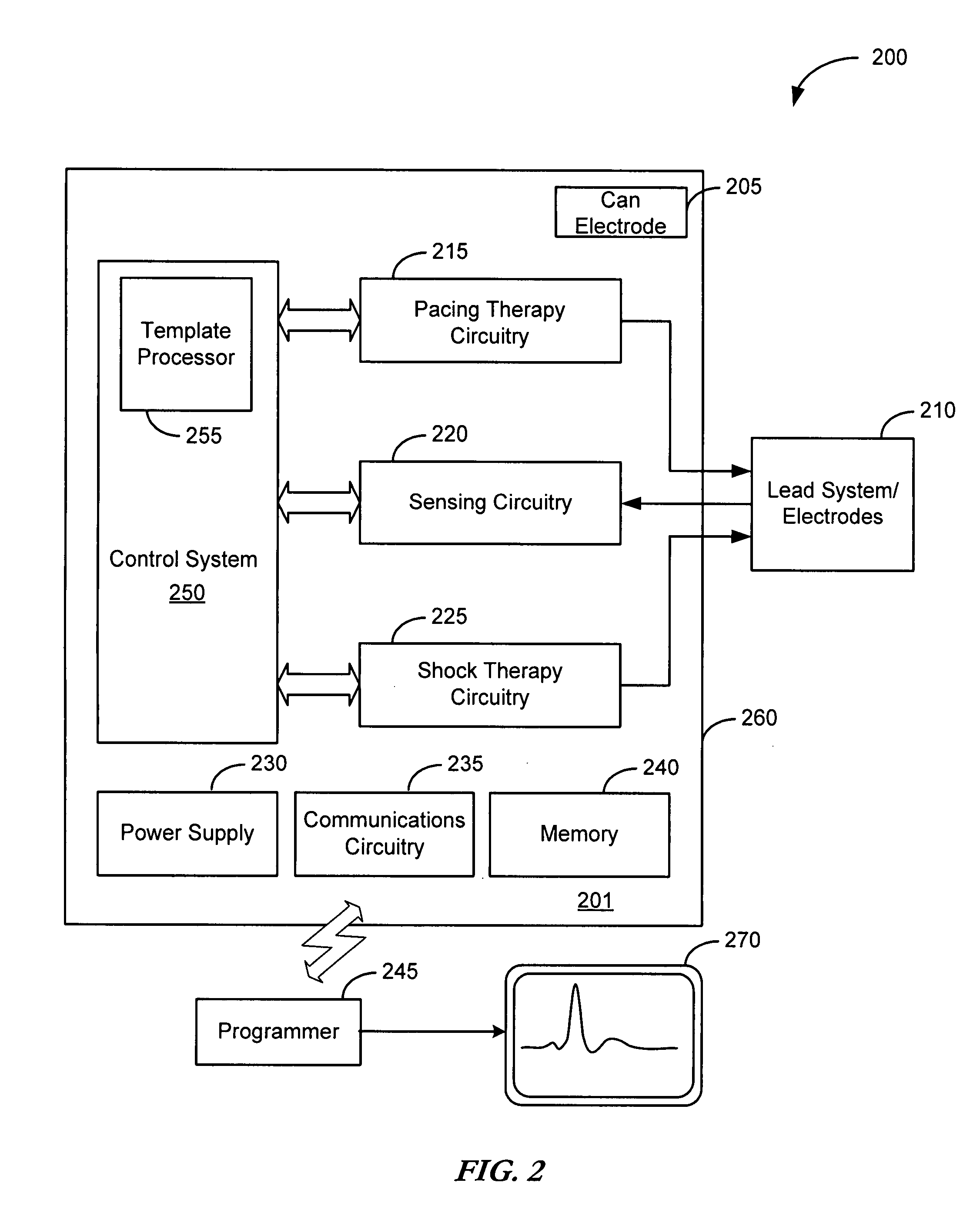
Cardiac tachyarrhythmia therapy selection based on patient response information
Cardiac treatment methods and devices providing templates representative of past tachyarrythmia events, each template associated with a therapy. A cardiac waveform is detected, and if it corresponds to a particular template associated with a previous therapy that was satisfactory in terminating a past event, the previous therapy is delivered again. If unsatisfactory, the previous therapy is eliminated as an option. If, for example, the previous therapy was an antitachycardia pacing therapy unsatisfactory in terminating the past tachyarrythmia event, delivery of the antitachycardia pacing therapy is eliminated as an option. Instead of ATP therapy, one or more of a cardioversion, defibrillation, or alternate anti-tachycardia pacing therapy may be associated with the particular template. Cardiac waveforms and templates may correspond in terms of one or more of morphology, timing, drug regimen, medication, neural activity, patient activity, hemodynamic status, cardiac tissue impedance, transthoracic impedance, or other information corresponding to the episode.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Scanning laser device and methods of use
In one aspect, the invention provides vision prosthesis systems. Exemplary vision prosthesis systems of the invention comprise a light energy generator operably connected to a wearable head piece comprising a device for directing light energy produced by the light energy generator onto a mammalian retina, wherein the light energy generator is tuned to emit light energy of sufficient power to modulate neural activity in the retina. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for irradiating neurons in the retina of the mammalian eye by directing light energy produced by a light energy generator onto a mammalian retina. The methods of the invention may be used to directly modulate the activity of retinal neurons or to introduce molecules into retinal cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Clustering of recorded patient neurological activity to determine length of a neurological event
Apparatus and method detect a detection cluster that is associated with a neurological event, such as a seizure, of a nervous system disorder and update therapy parameters that are associated with a treatment therapy. The occurrence of the detection cluster is detected when the maximal ratio exceeds an intensity threshold. If the maximal ratio drops below the intensity threshold for a time interval that is less than a time threshold and subsequently rises above the intensity threshold, the subsequent time duration is considered as being associated with the detection cluster rather than being associated with a different detection cluster. Consequently, treatment of the nervous system disorder during the corresponding time period is in accordance with one detection cluster. Treatment therapy may be provided by providing electrical stimulation, drug infusion or a combination. Therapy parameters may be updated for each mth successive group of applications of the treatment therapy or for each nth detection cluster.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
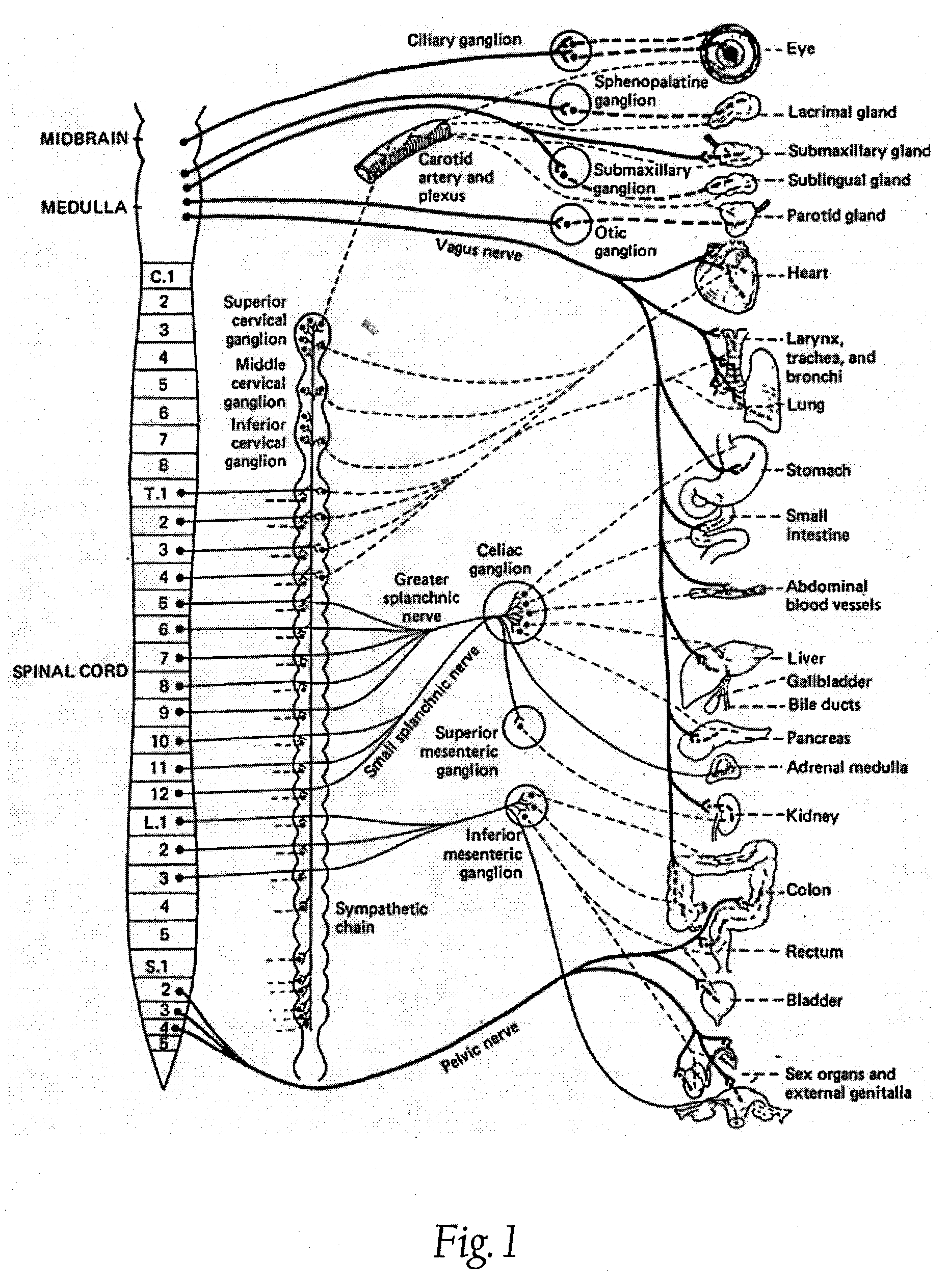
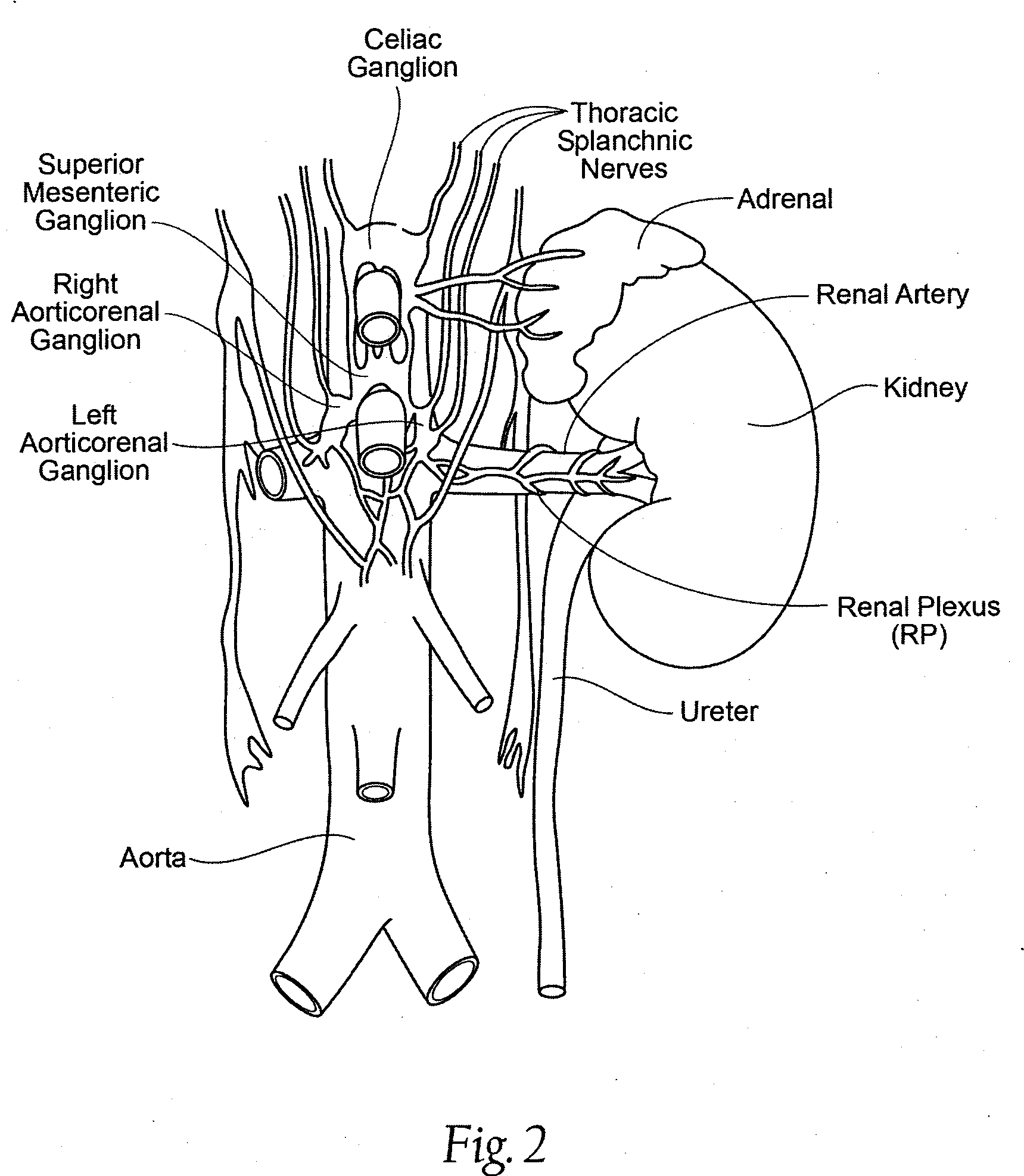
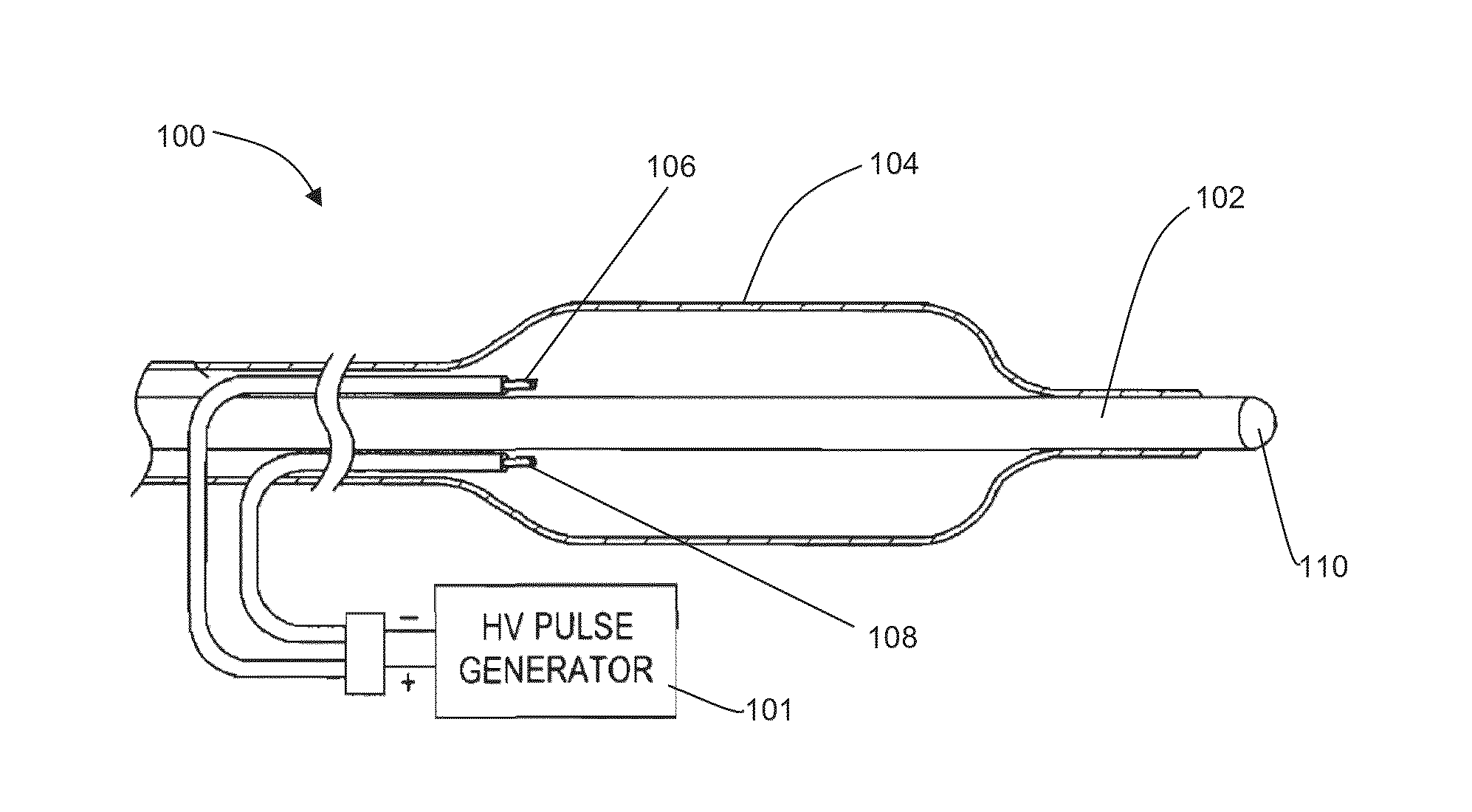
Shockwave nerve therapy system and method
ActiveUS20140046229A1Reduce and block activationModulate neural activitySurgeryChiropractic devicesBaroreceptor functionBiological activation
Disclosed herein are intravascular systems and methods for modulating the activation of neural activity using shock wave devices. Such systems and methods may be used to modulate the activity of the renal plexus and / or baroreceptors of the carotid sinus for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Spatial decimation stimulation in an implantable neural stimulator, such as a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7039466B1High rate stimulationReduce power levelElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationElectrode array
A cochlear implant system, or other neural stimulation system, has the capability to stimulate fast enough to induce stochastic neural firing so as to restore “spontaneous” neural activity. The stimulation rate applied to the more distally-located electrodes of an electrode array connected to the implant system is reduced from the stimulation rate applied to the more proximally-located electrodes. Thus, in the case of a cochlear implant system, the apically-located regions within the cochlea are stimulated at a reduced rate in order to conserve power. Pulse widths of the reduced-rate pulses may further be increased, and amplitudes reduced, to further conserve power. As needed, a low-level random conditioner stimulation signal may be applied to the apical regions of the cochlea in order to ensure the occurrence of random neural firings.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Treatment of clinical applications with neuromodulation
InactiveUS20110082326A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMedicineMagnetic brain stimulation
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method to enhance neural tissue operation
The invention relates to a method for modulation, augmentation and / or stimulation of neural tissue and / or neural tissue related functionality with stimulating neural tissue and / or neural tissue related functionality with stimuli by which neural activity related local perfusion changes, electro-neuro-chemical, biochemical, neural modulative or neuroplastical responses and / or alterations in ‘metabolism supply lines-neural tissue’ interaction processes in vertebrates can be triggered and / or influenced.
Owner:CERBOMED GMBH
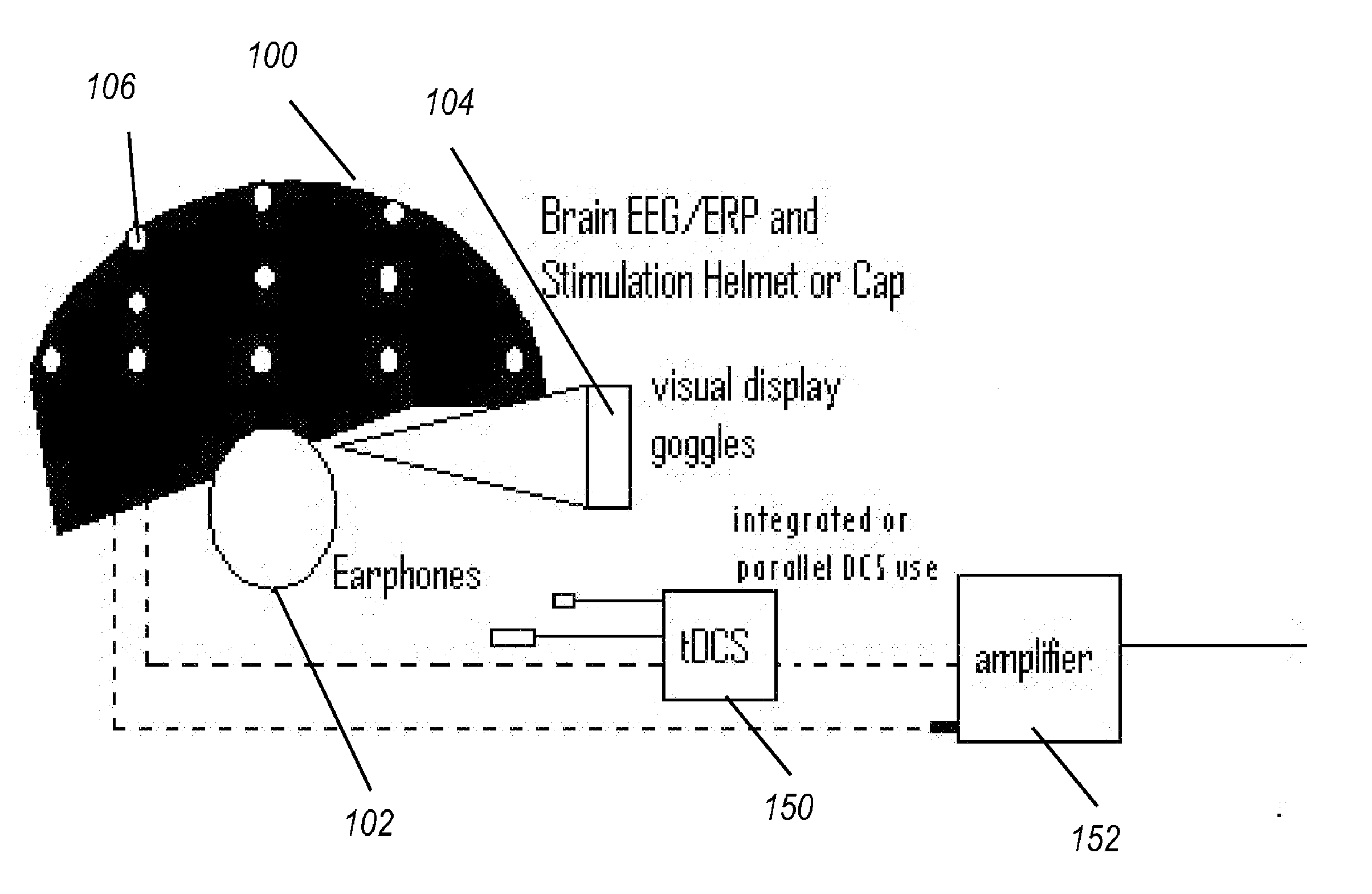
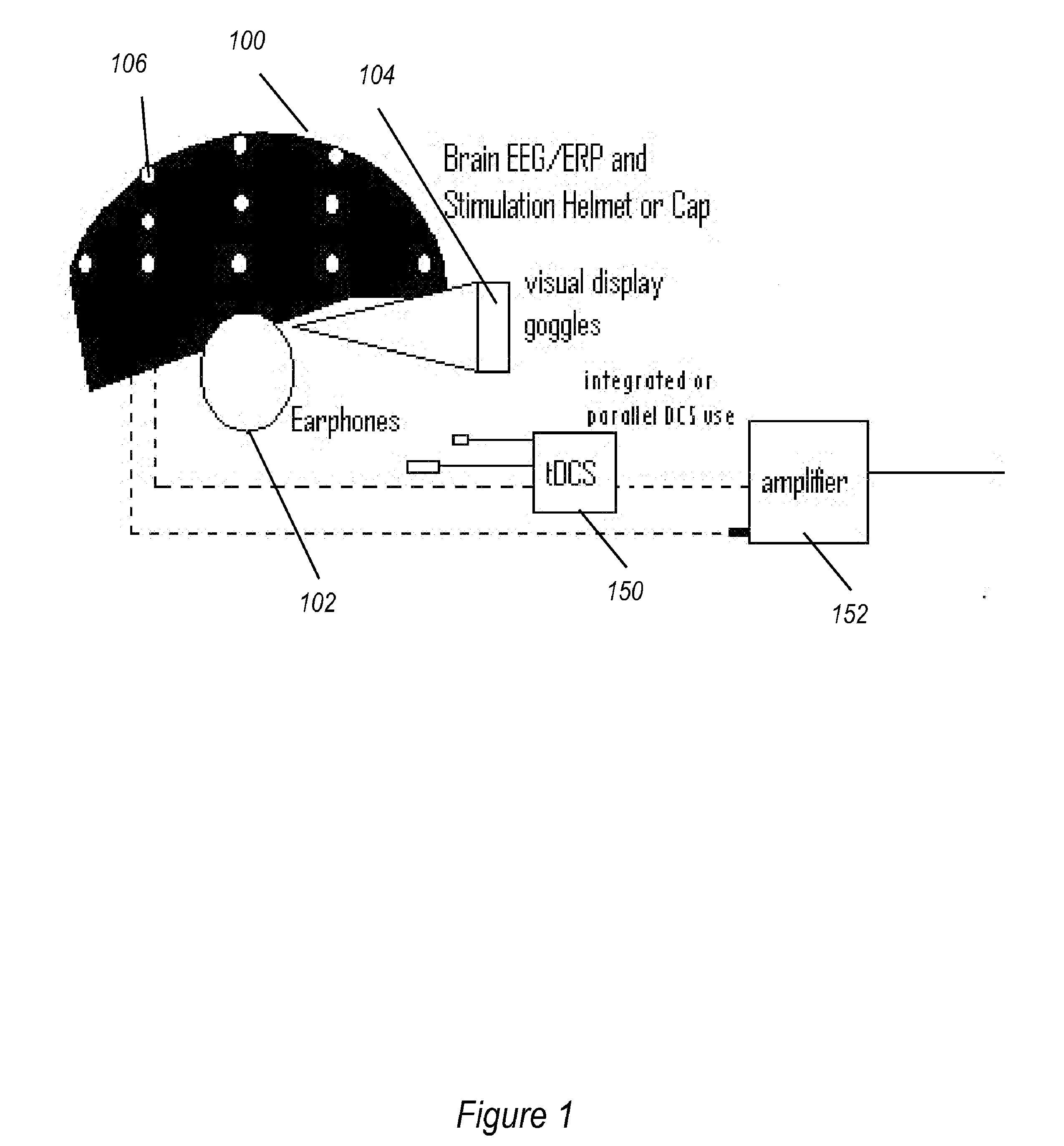
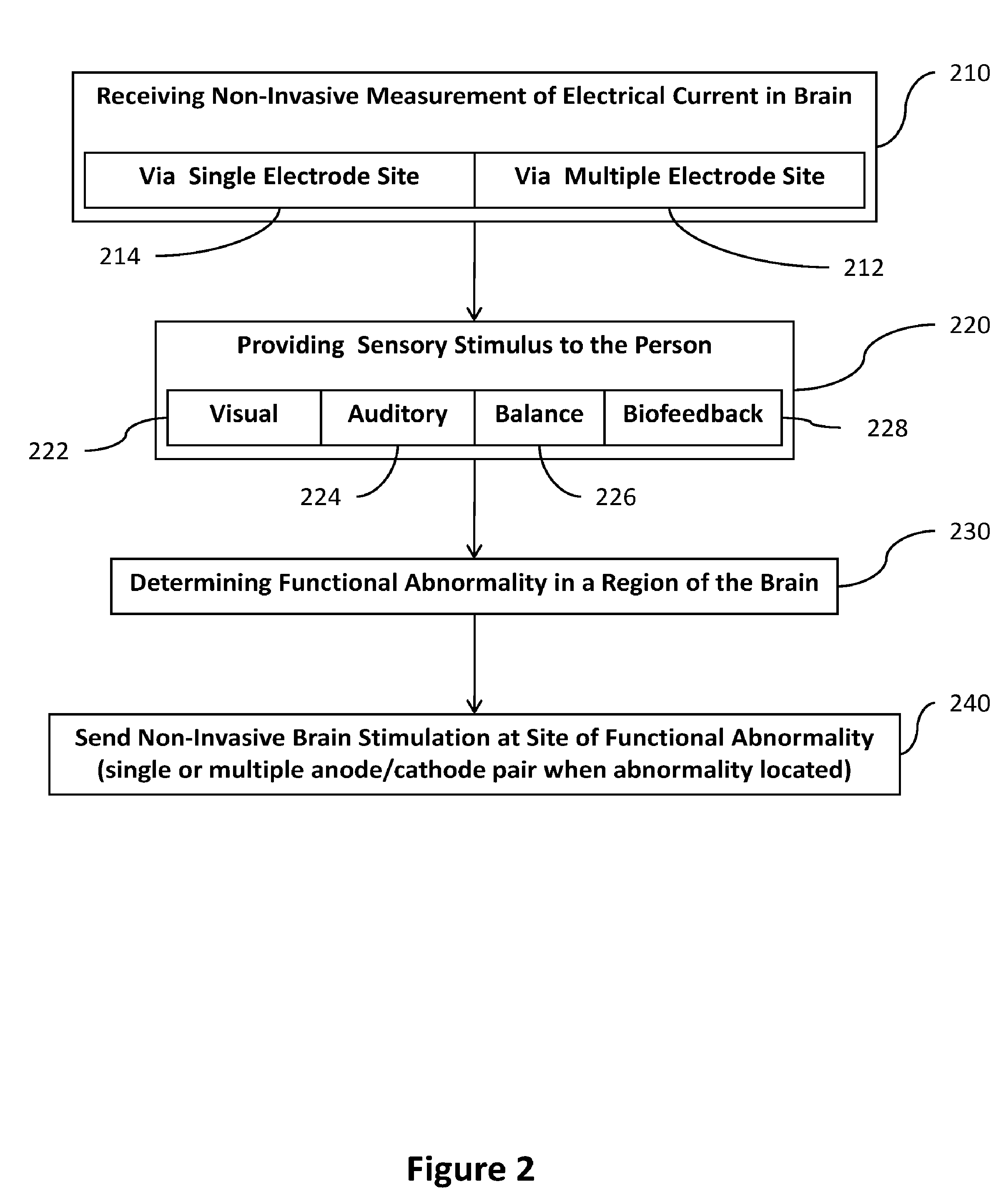
Transcranial stimulation device and method based on electrophysiological testing
Embodiments of the disclosed technology provide a combination electroencephalography and non-invasive stimulation devices. Upon measuring an electrical anomaly in a region of a brain, various non-invasive stimulation techniques are utilized to correct neural activity. Stimulation techniques include transcranial direct current stimulation, transcranial alternating current stimulation and transcranial random noise stimulation, low threshold transcranial magnetic stimulation and repetitive transcranial magnet stimulation. Devices of the disclosed technology may utilize visual, balance, auditory, and other stimuli to test the subject, analyze necessary brain stimulations, and administer stimulation to the brain.
Owner:EVOKE NEUROSCI
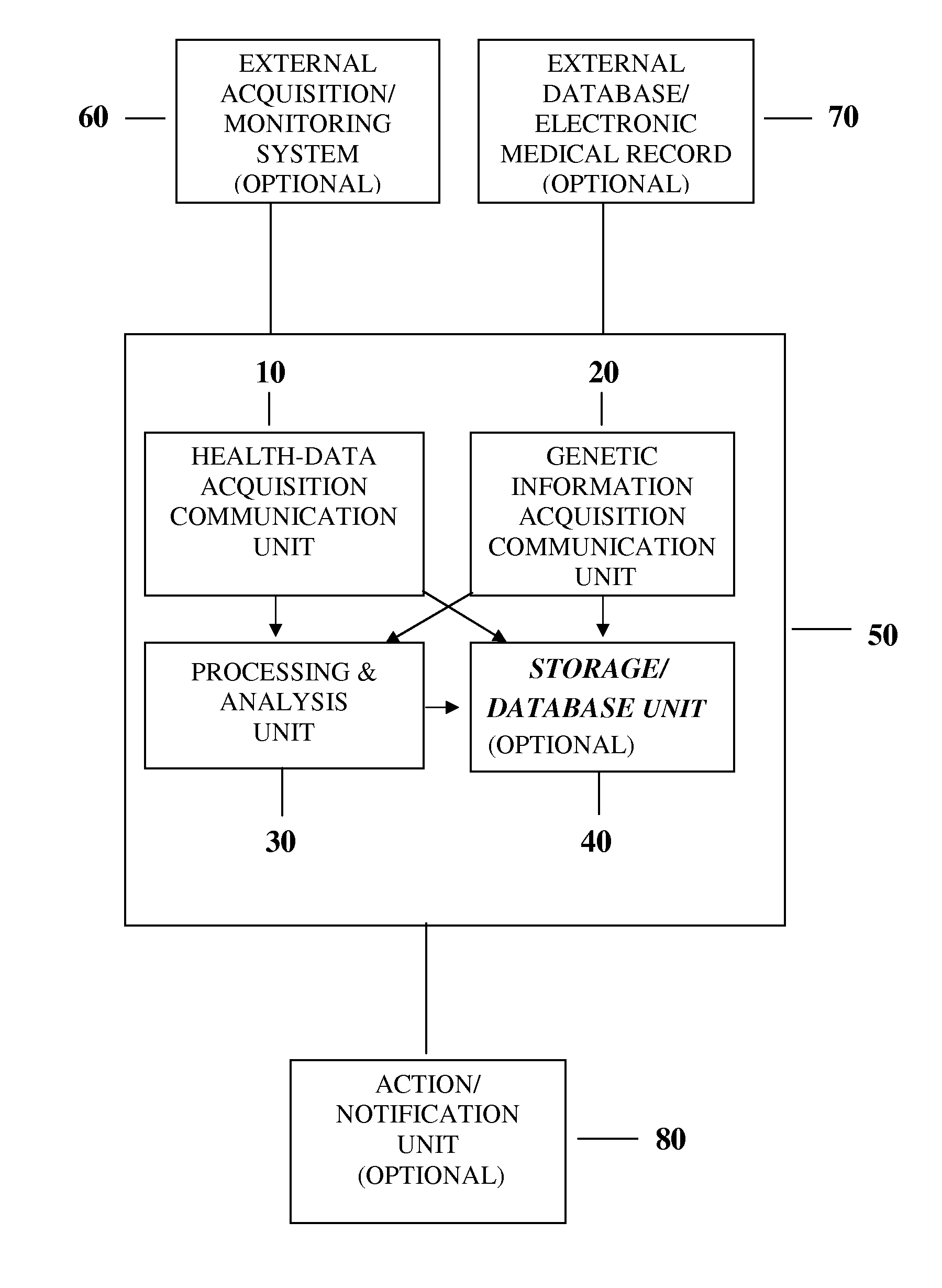
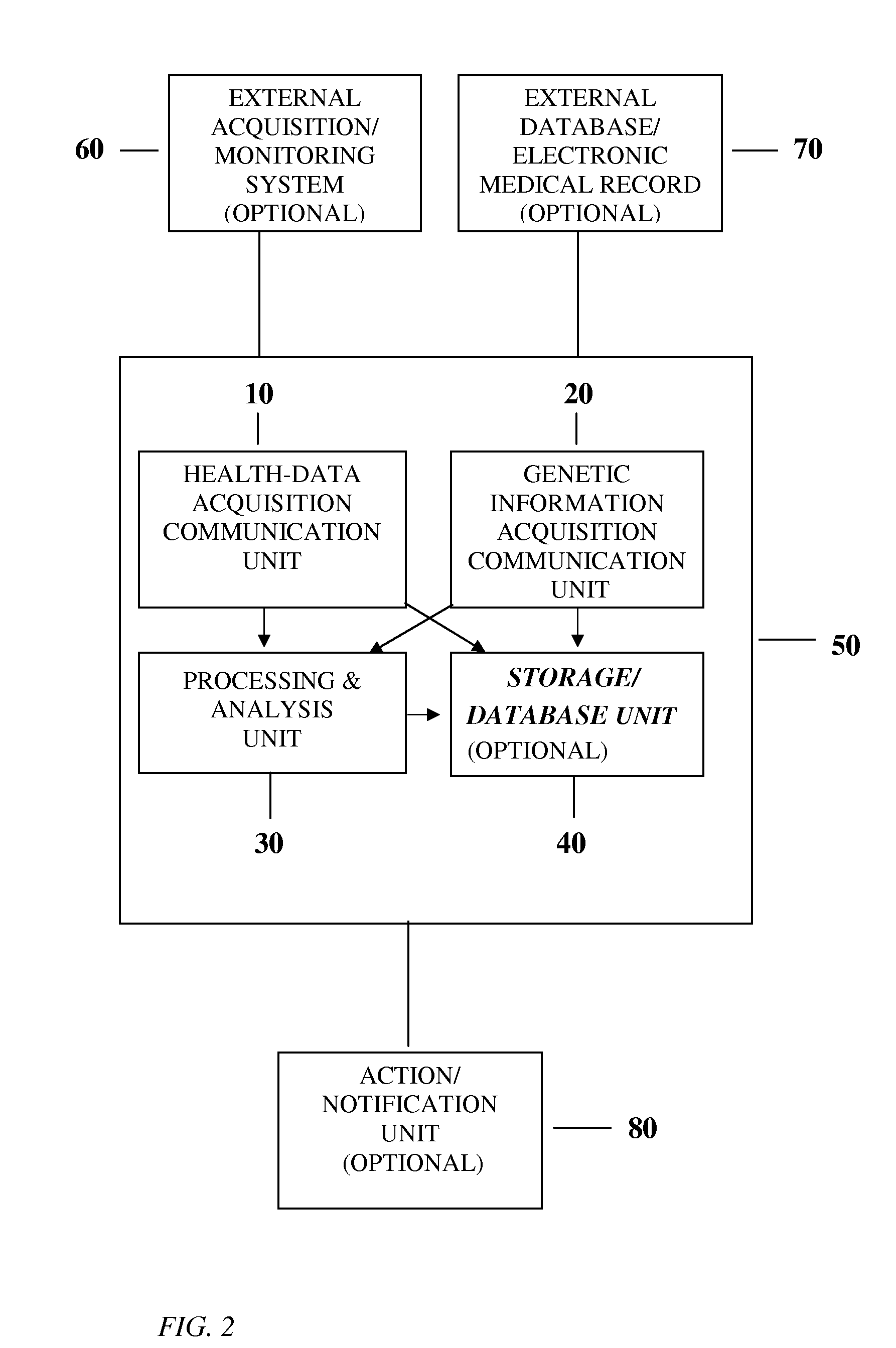
Health Data Dynamics, Its Sources and Linkage with Genetic/Molecular Tests
ActiveUS20110190598A1Easy to analyzeImprove accuracyData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisHolter monitorNeural activity
Method and system for the analysis and source localization of the dynamical patterns in medical and health data, and linking such dynamical patterns with the individual's genetic and / or molecular data. The invention makes use of optimally positioned sensors (sensor arrays) providing input data for signal processing, time-series analysis, pattern recognition and mathematical modeling to facilitate dynamical tracking of systemic arterial pressure without a pressure cuff, local vascular activity, electrocardiographic (ECG), respiratory, physical, muscular, gastrointestinal and neural activity, temperature and other physiological / health data. The invention also facilitates separation of local signals (such as local aneurisms or local vascular activity) from non-local, central or systemic patterns (e.g. systemic blood pressure). In addition, the invention improves identification of dynamical patterns associated with a specific genotype / disorder for screening, personalized risk assessment, diagnosis and treatment control. The system can be implemented in a specialized processor, such as an ambulatory blood pressure monitor, Electrocardiograph, Holter monitor located outside subject's body or implanted inside the body, mobile / cell phone or Smart Phone / Personal Digital Assistant, computer or computer network (the Internet), including wireless or mobile network. The system can be also linked to the electronic health / medical records and other databases.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
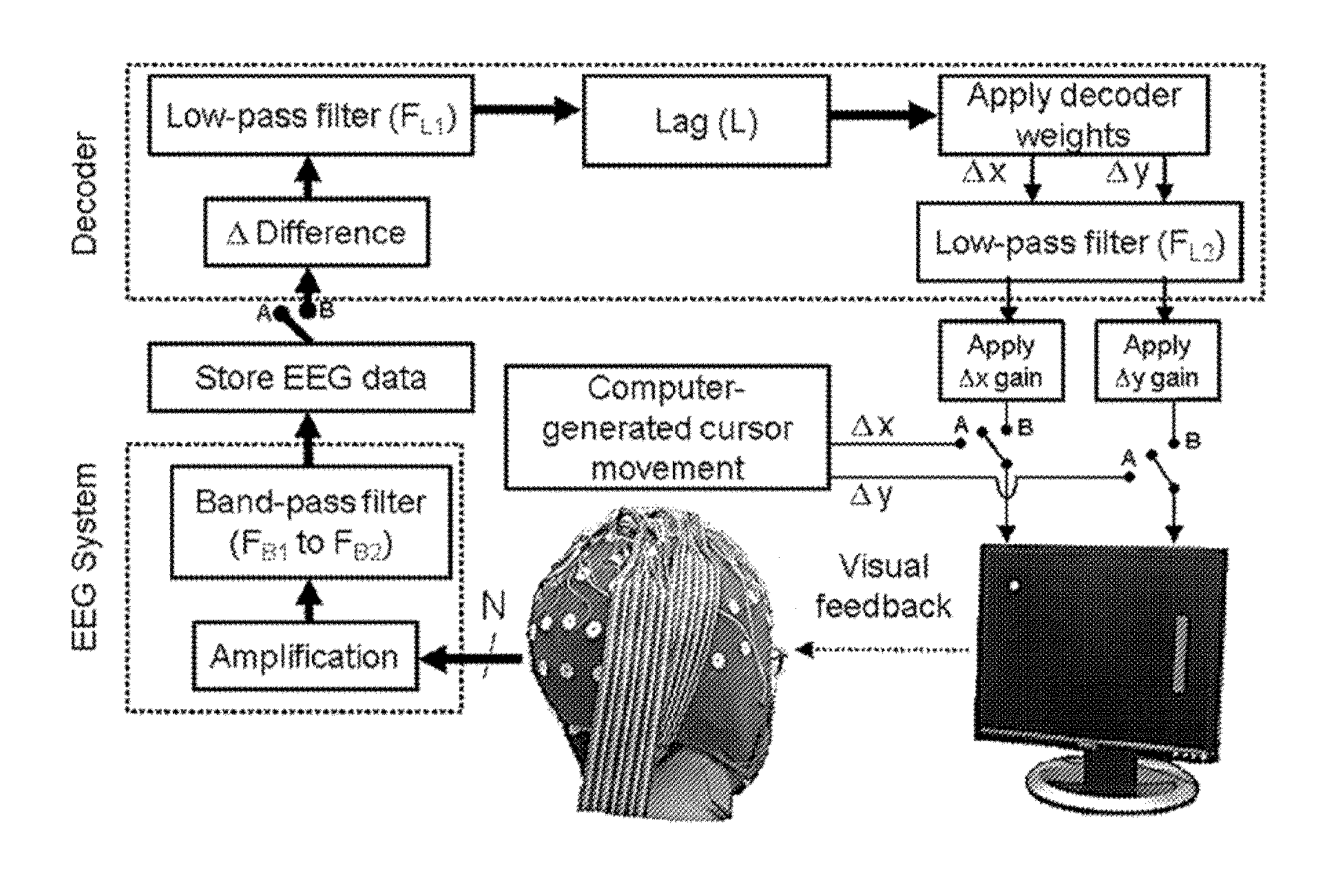
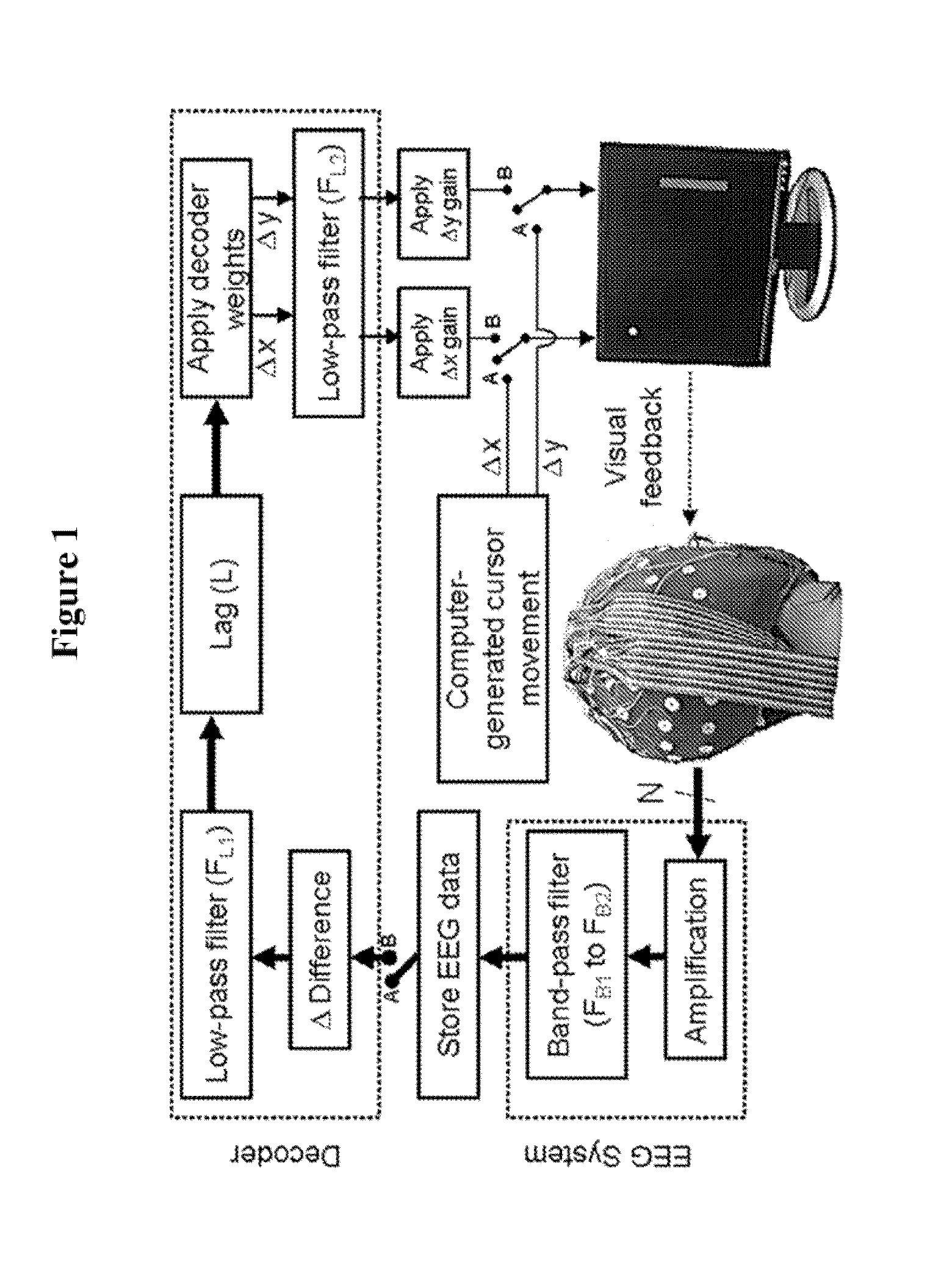
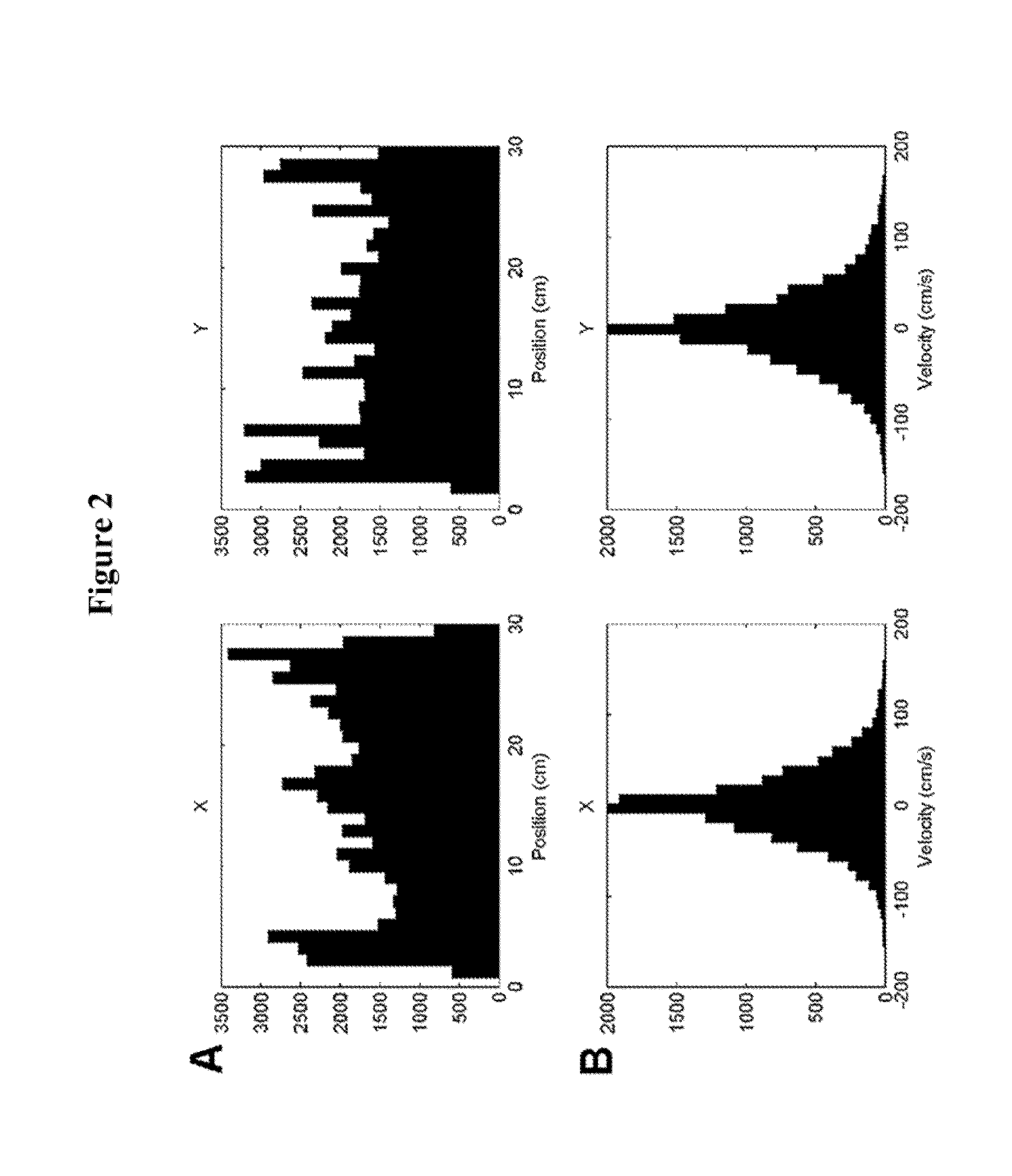
Time Domain-Based Methods for Noninvasive Brain-Machine Interfaces
ActiveUS20140058528A1Reduce training timeContinuous controlElectroencephalographySensorsTime domainBrain computer interfacing
A noninvasive brain computer interface (BCI) system includes an electroencephalography (EEG) electrode array configured to acquire EEG signals generated by a subject. The subject observes movement of a stimulus. A computer is coupled to the EEG electrode array and configured to collected and process the acquired EEG signals. A decoding algorithm is used that analyzes low-frequency (delta band) brain waves in the time domain to continuously decode neural activity associated with the observed movement.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
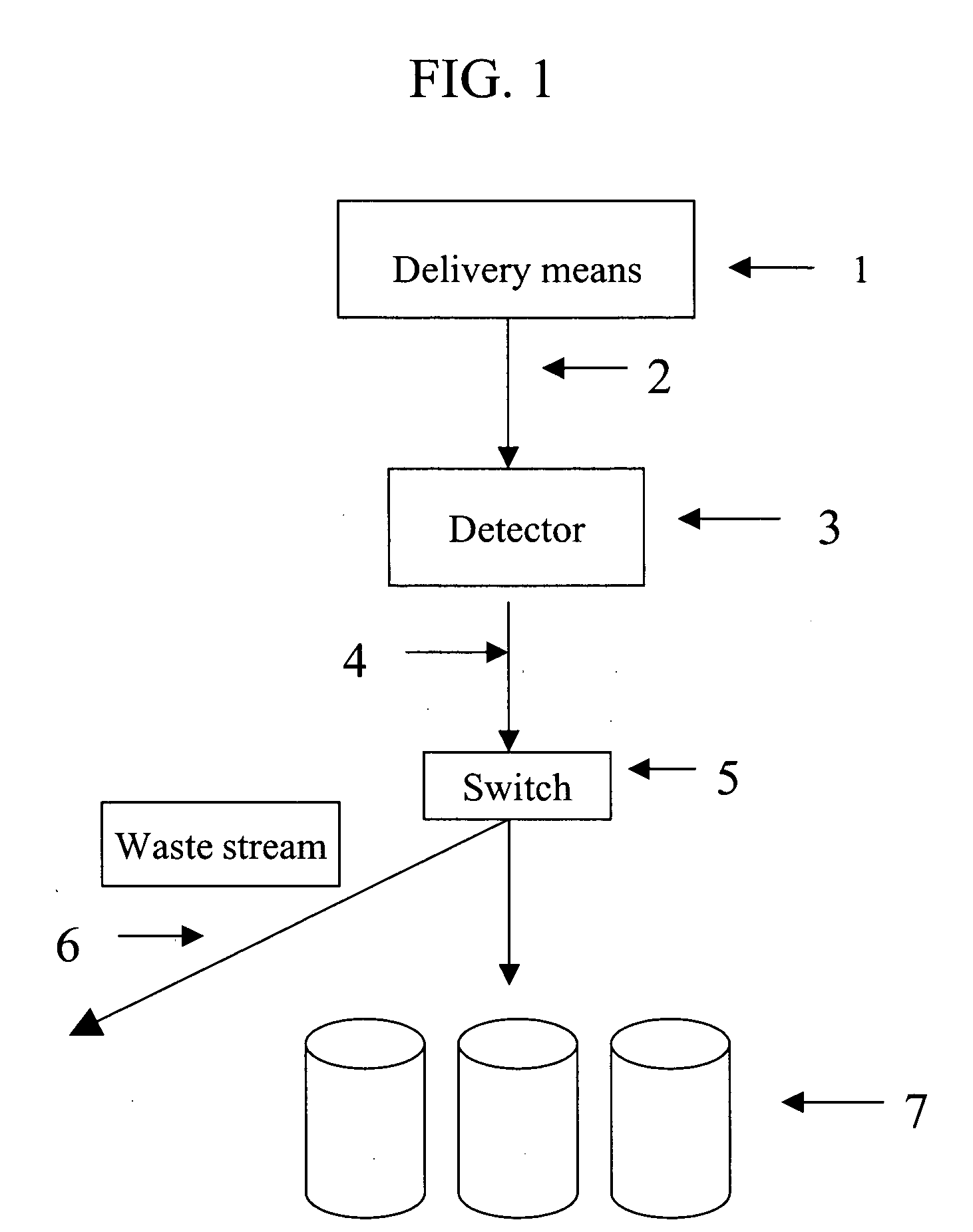
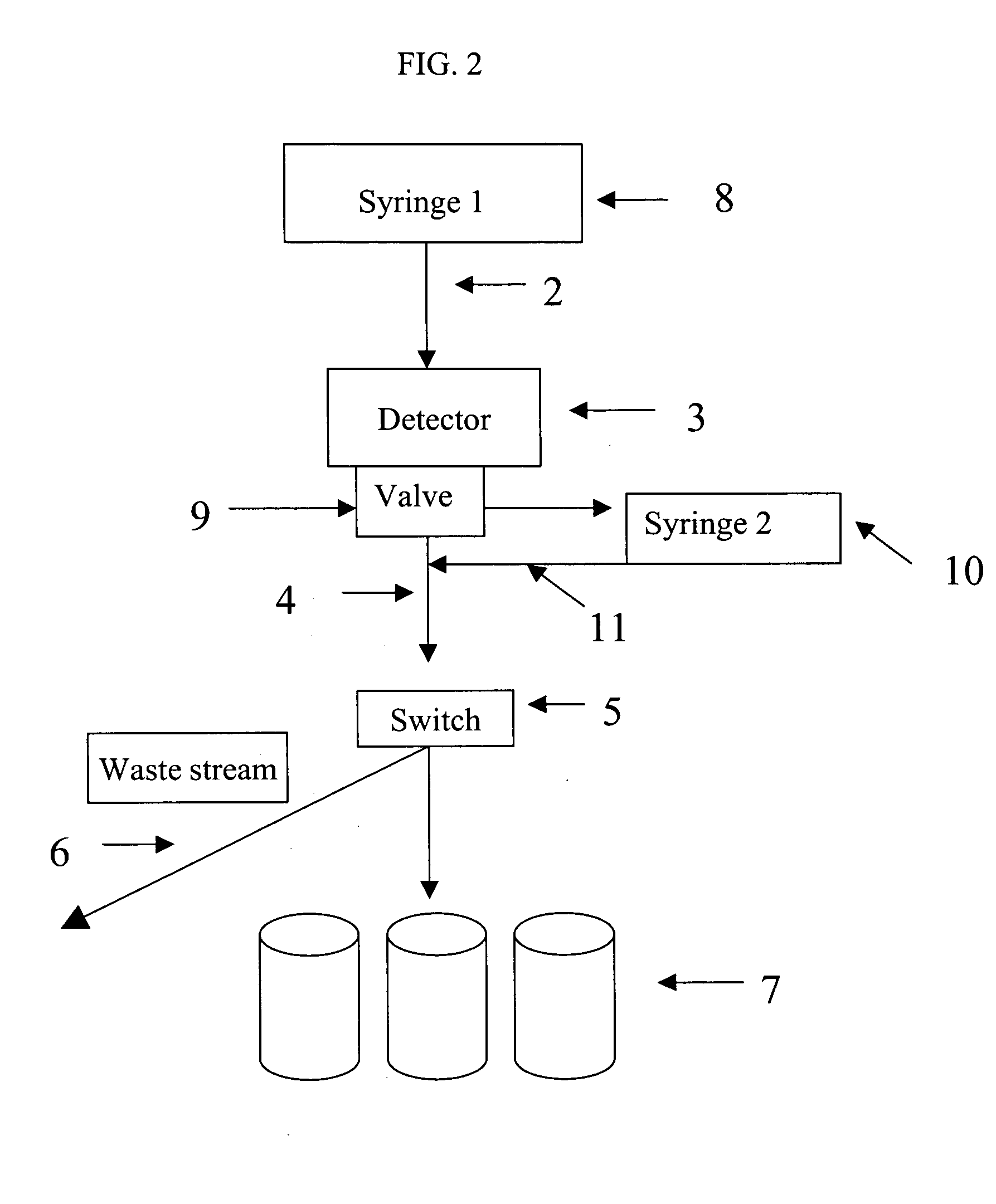
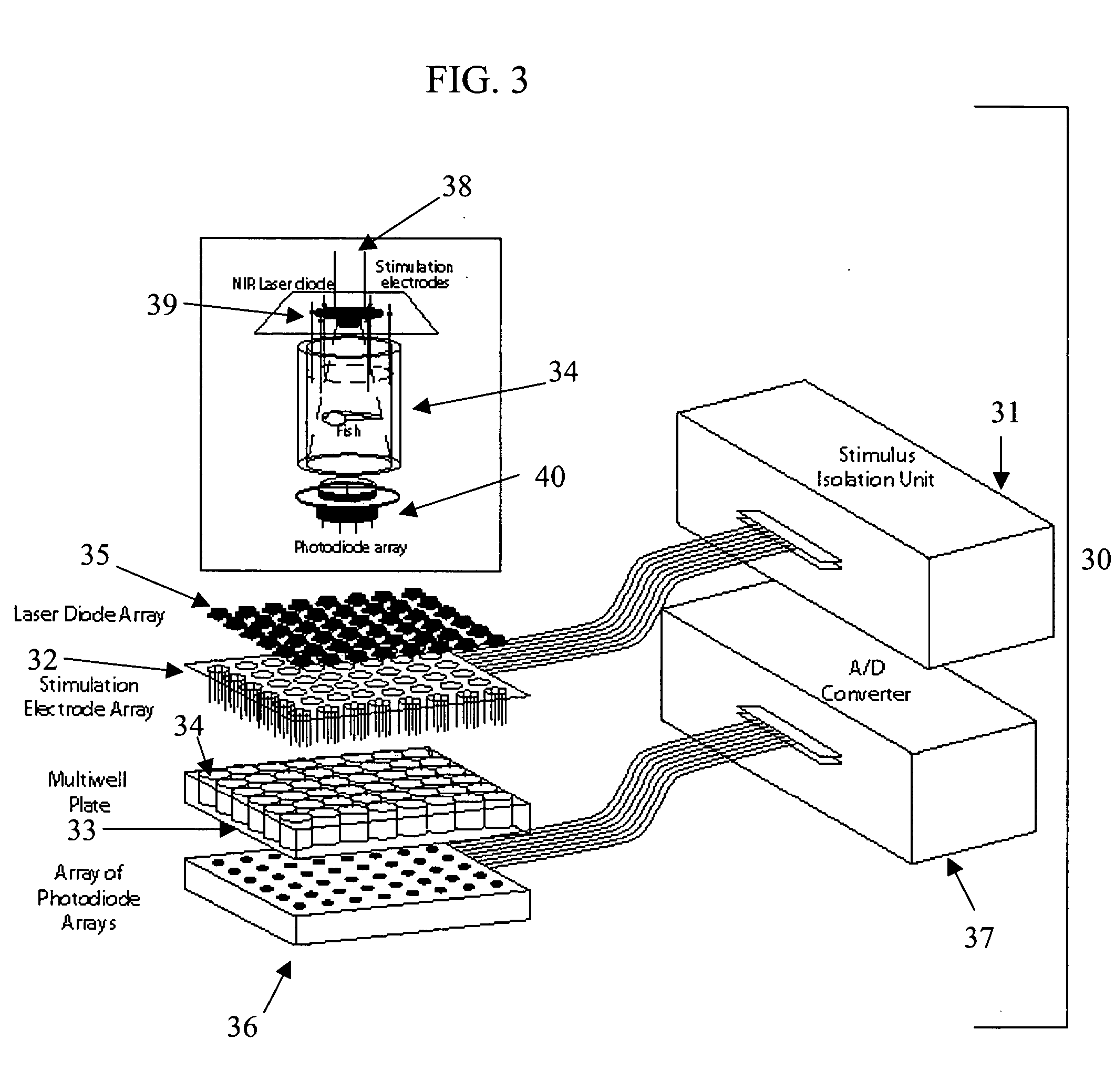
Method and system for screening compounds for muscular and/or neurological activity in animals
Screening methods and instrumentation for candidate pharmacological agents are applied to discover compounds with muscular and / or neurological activity. The method comprises the use of teleost fish, such as the medaka (Oryzias latipes), which may be stimulated with chemical agents or an electric field to produce, for example, seizure activity and / or convulsive activity. The convulsive behavior may be recorded optically and electrically. Antagonism of the convulsive behavior is produced by application of candidate pharmacological agents to the well containing the fish. The method may include stimulation and antagonism in a plurality of sample wells with a repetitive or simultaneous application of threshold electric fields. The methods and instrumentation can be applied to the study of other serious neurological diseases such as neuropathic pain. In addition the process of assaying the protection of animals to convulsant agents the assay measures pharmacological safety parameters including sedation and cognitive impairment.
Owner:MURPHY RANDALL +1
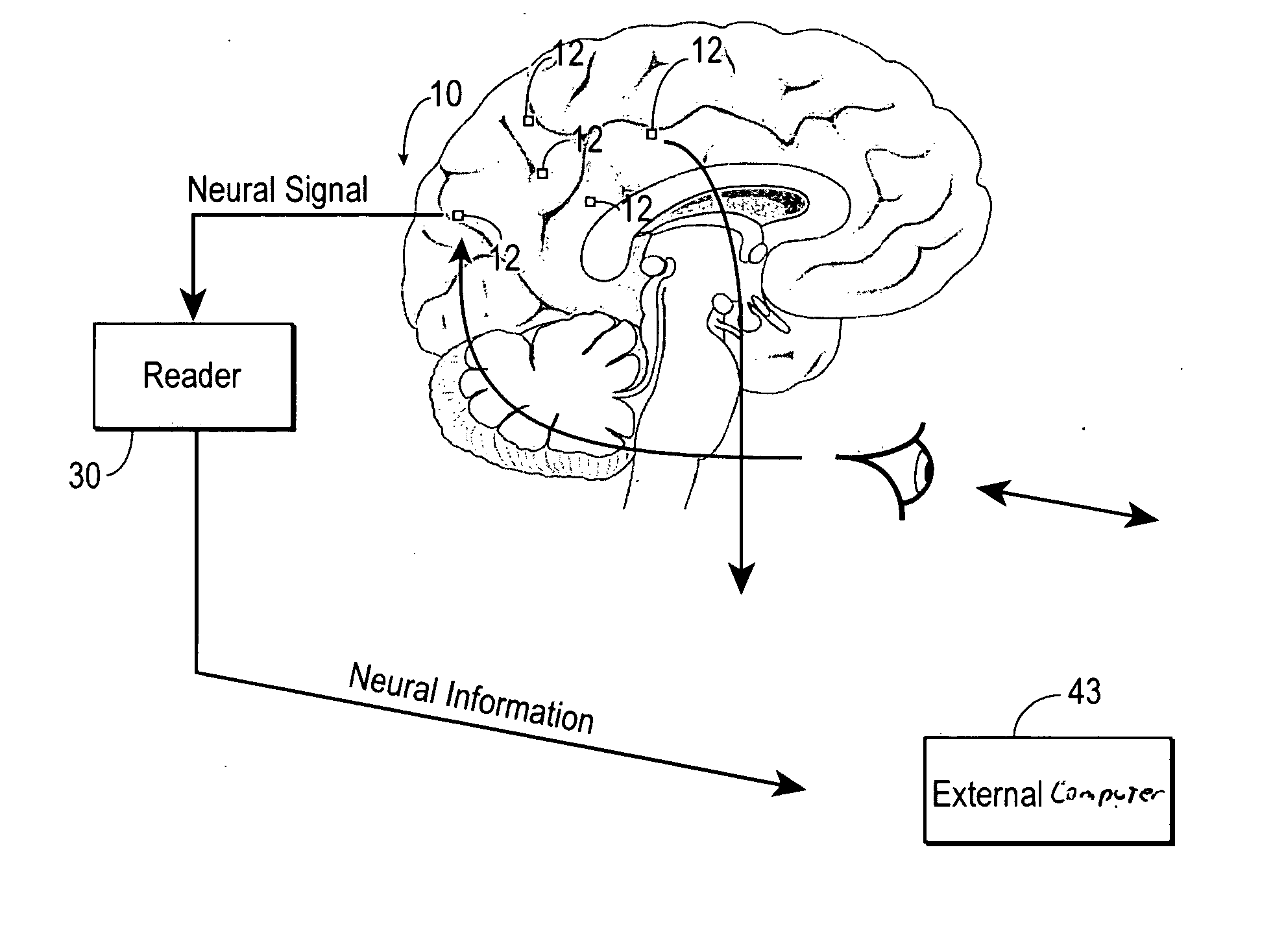
Brian machine interface device
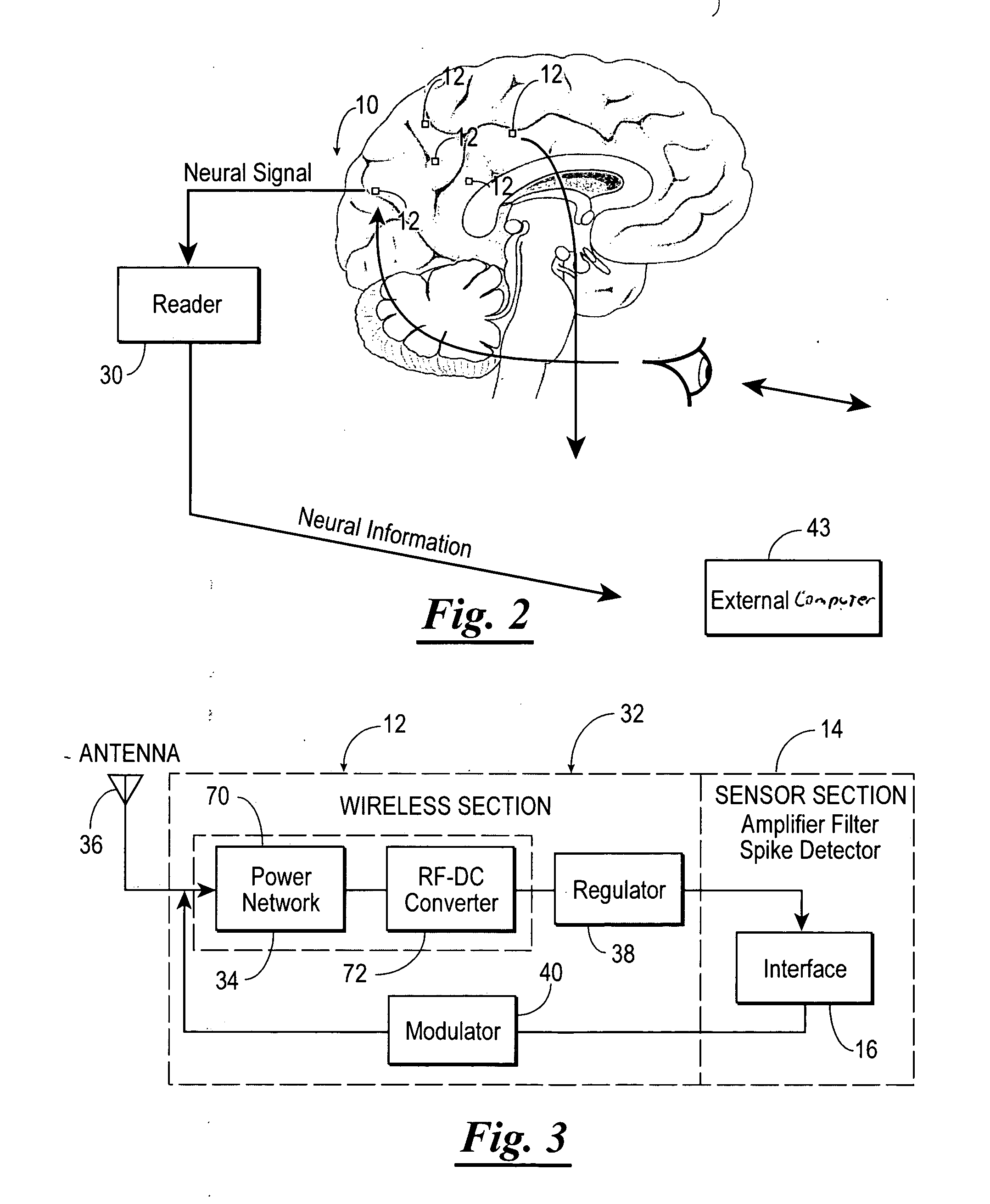
A distributed real-time wireless neural interface including a reader and an array of distinct recording devices. The reader outputs and receives radio-frequency signals. The array of distinct recording devices include a wireless section and a sensor section. The wireless section includes an rf power converter, an antenna, a regulator, and a modulator. The rf power converter converts radio frequency signals into power signals. The antenna receives the radio-frequency signals output by the reader and provides the radio-frequency signals to the rf power converter wherein the rf power converter converts such radio-frequency signals to power signals. The regulator receives the power signals and regulates such power signals to provide stable power signals. The modulator receives the power signals and is in communication with the antenna for utilizing the antenna to communicate with the reader. The sensor section receives the stable power signals. The sensor section is adapted to detect neural activity and provide output signals containing information indicative of such neural activity to the modulator of the wireless section whereby the modulator communicates the information in the output signals to the reader.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Monitoring Brain Neural Potentials
ActiveUS20160287126A1Eliminate needElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyMedicineBiomarker (petroleum)
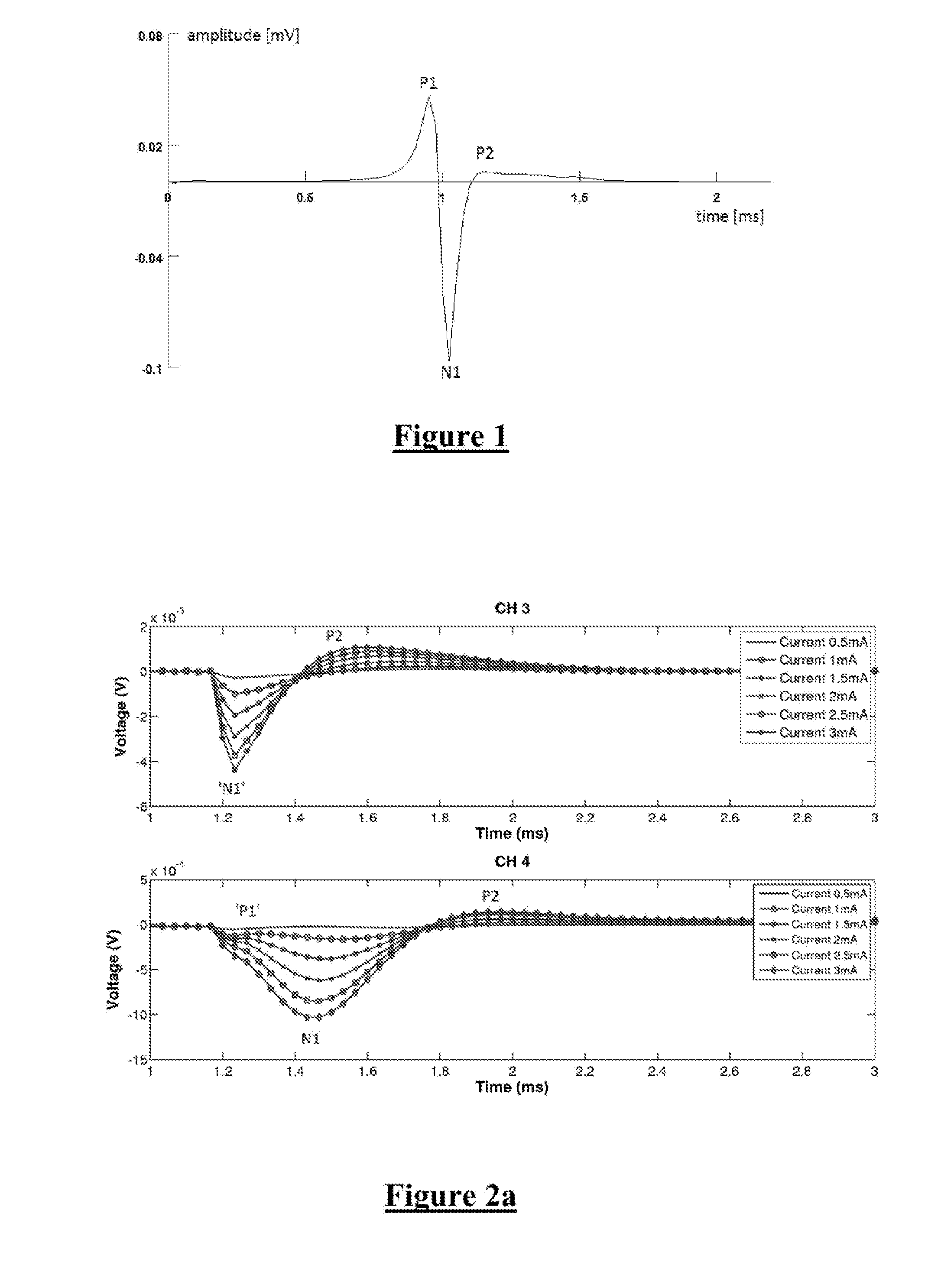
Neural activity in the brain arising from a stimulus is monitored. A stimulus is applied to a target structure of the brain and a neural measurement is obtained from at least one electrode implanted in contact with the target structure. The neural measurement is configured to capture a measure of any late response arising in the target structure, typically being a neural response arising after conclusion of an ECAP, such as in the period 1.5-10 ms after stimulus onset. The late response(s) can be a useful biomarker such as of therapeutic ranges of deep brain stimulation, disease progression, medication efficacy, and intra-operative changes.
Owner:CLOSED LOOP MEDICAL PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com