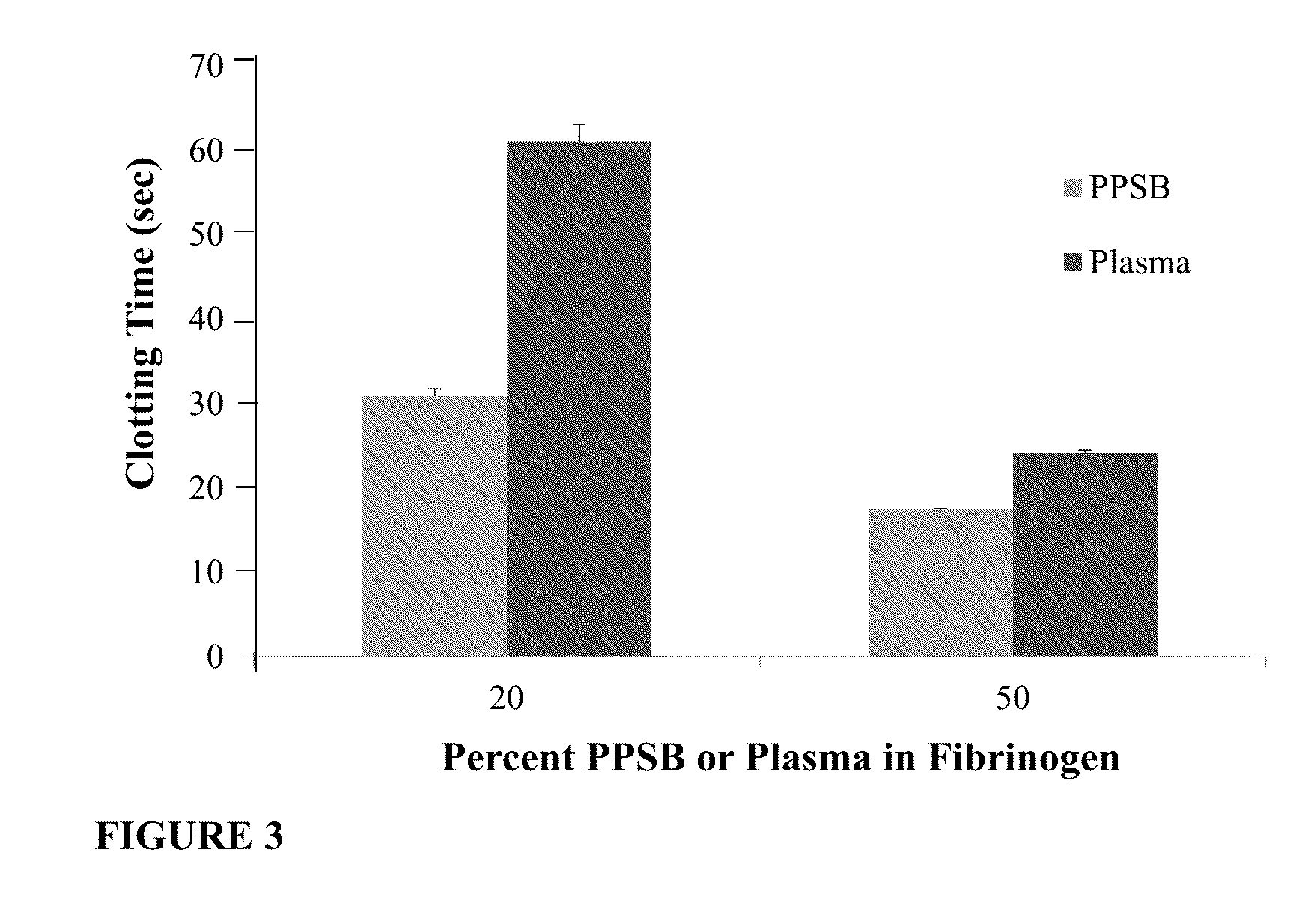
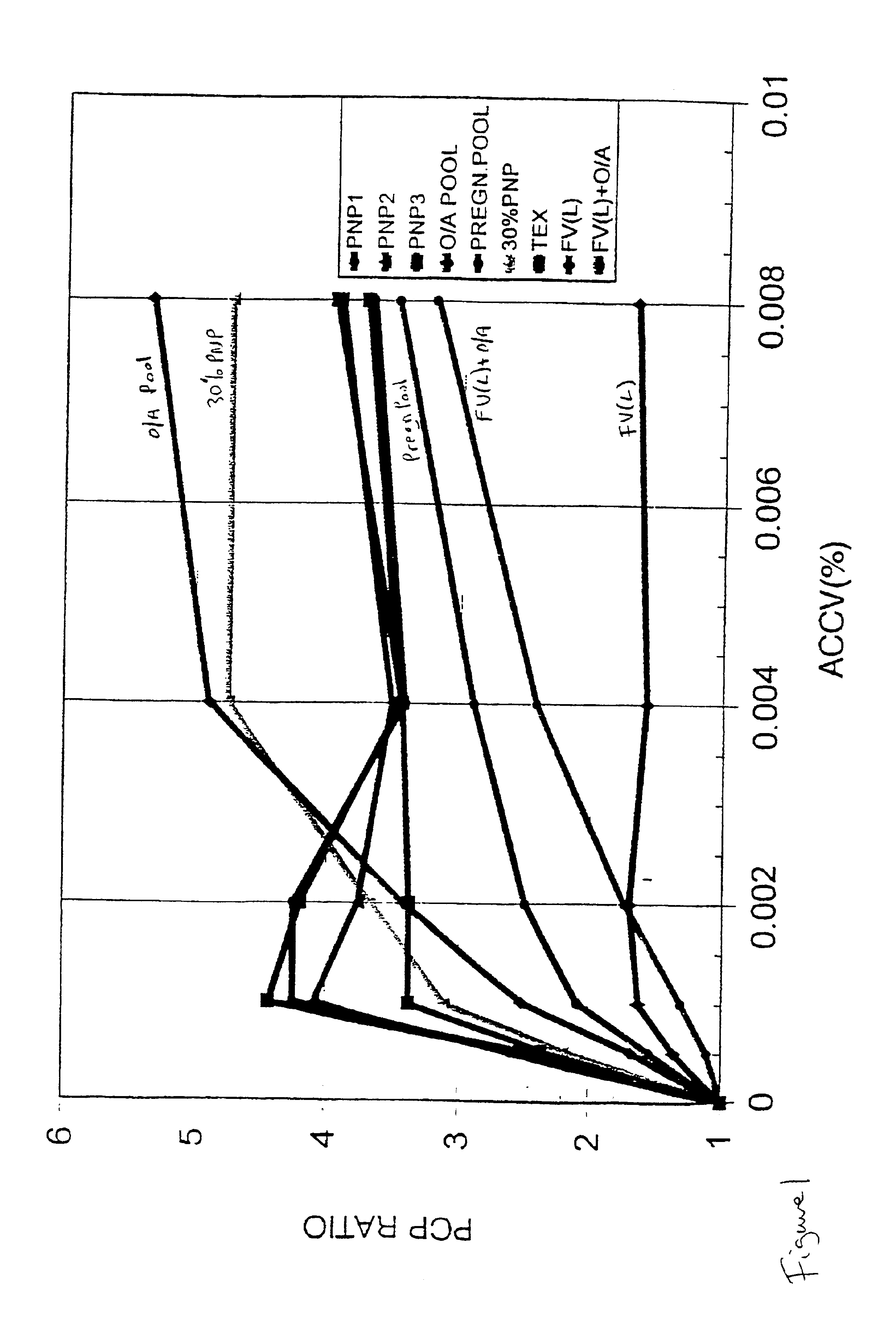
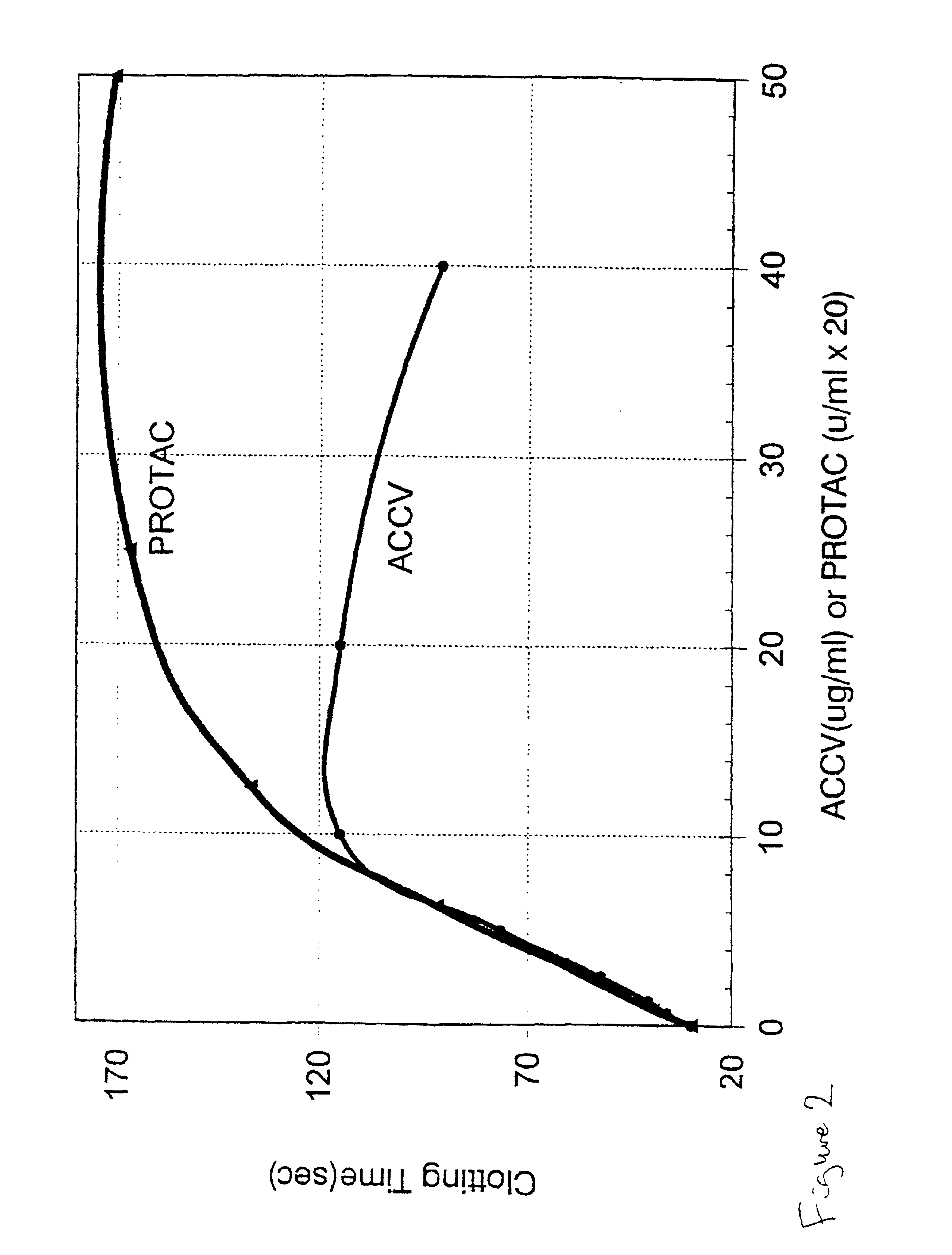
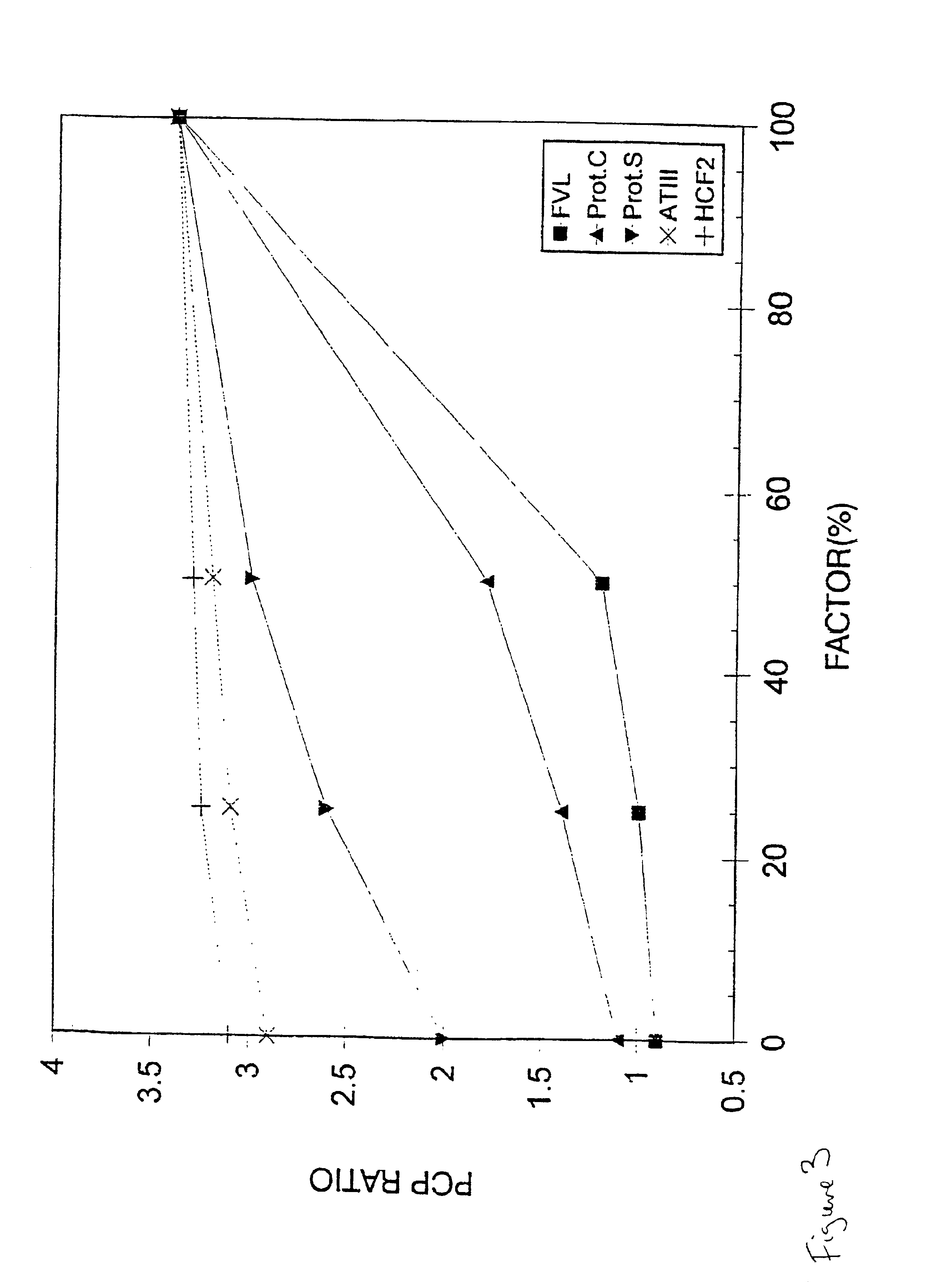
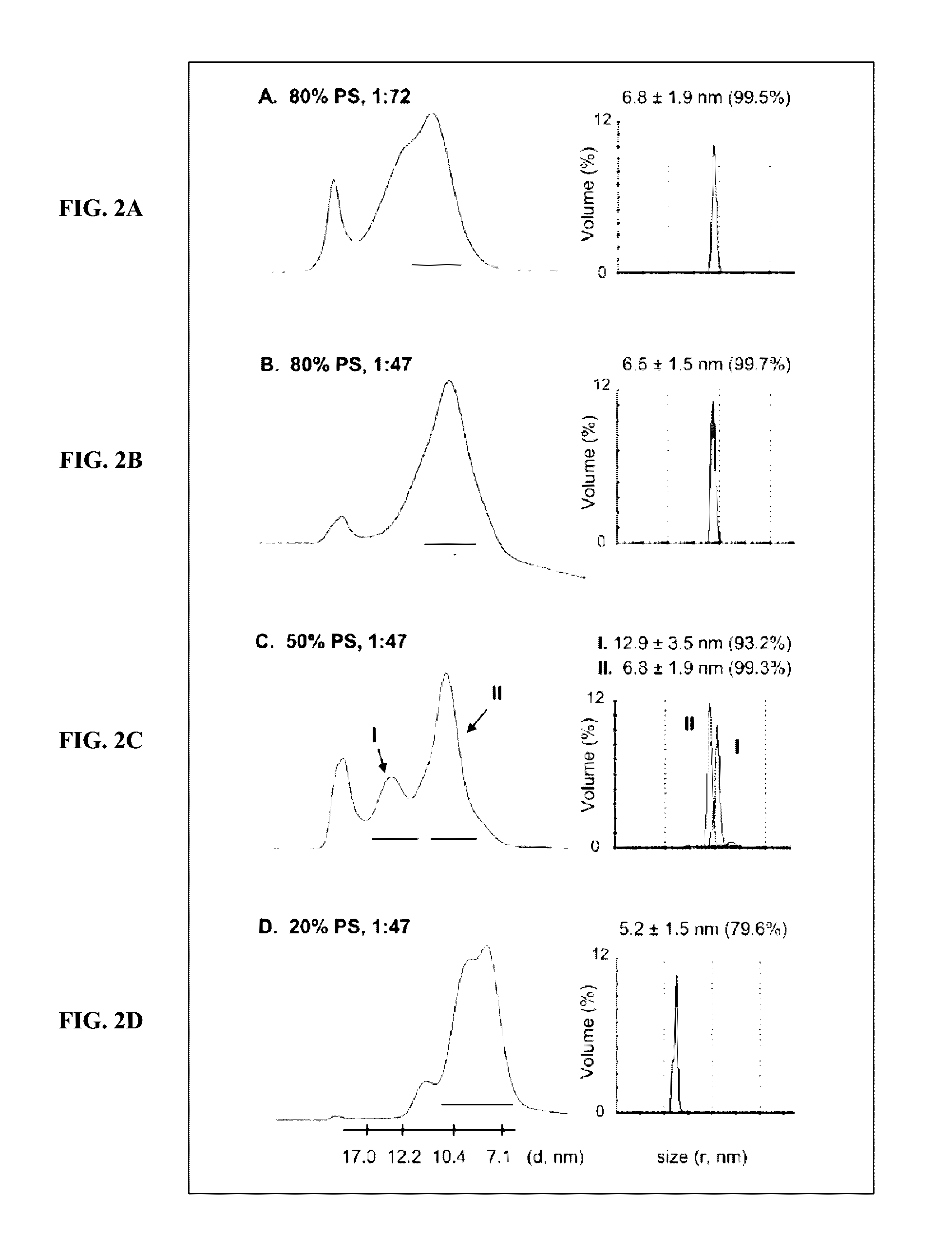
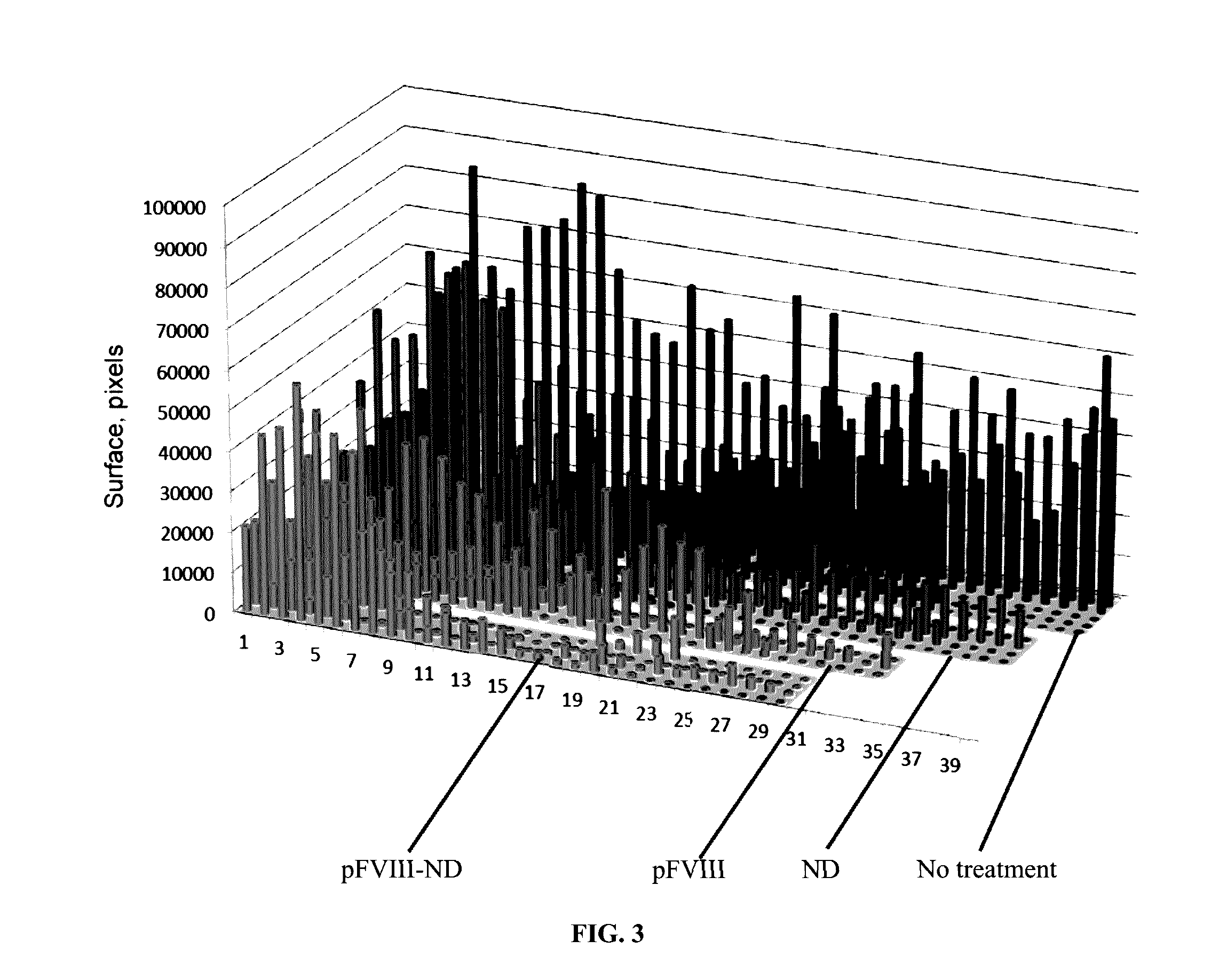
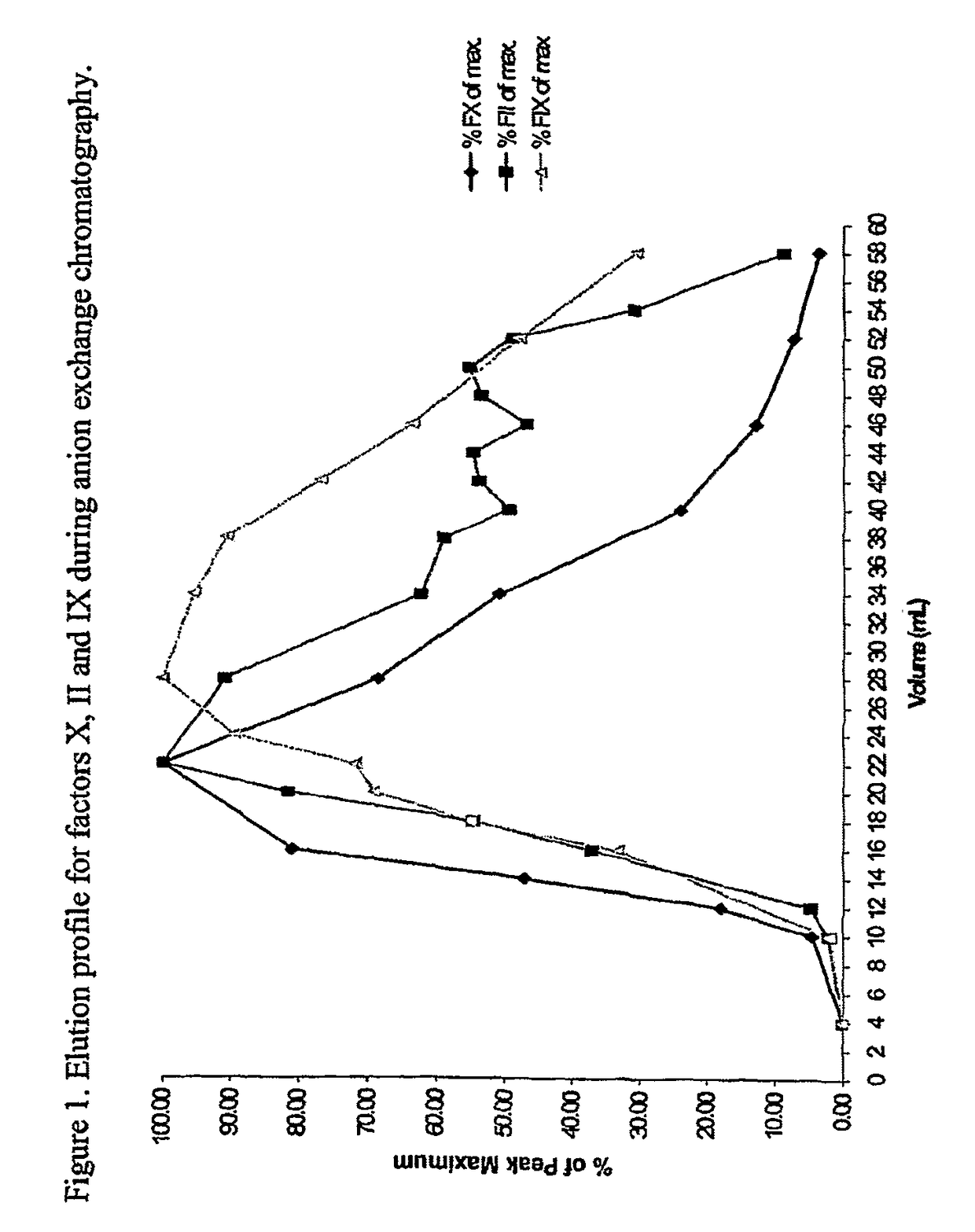
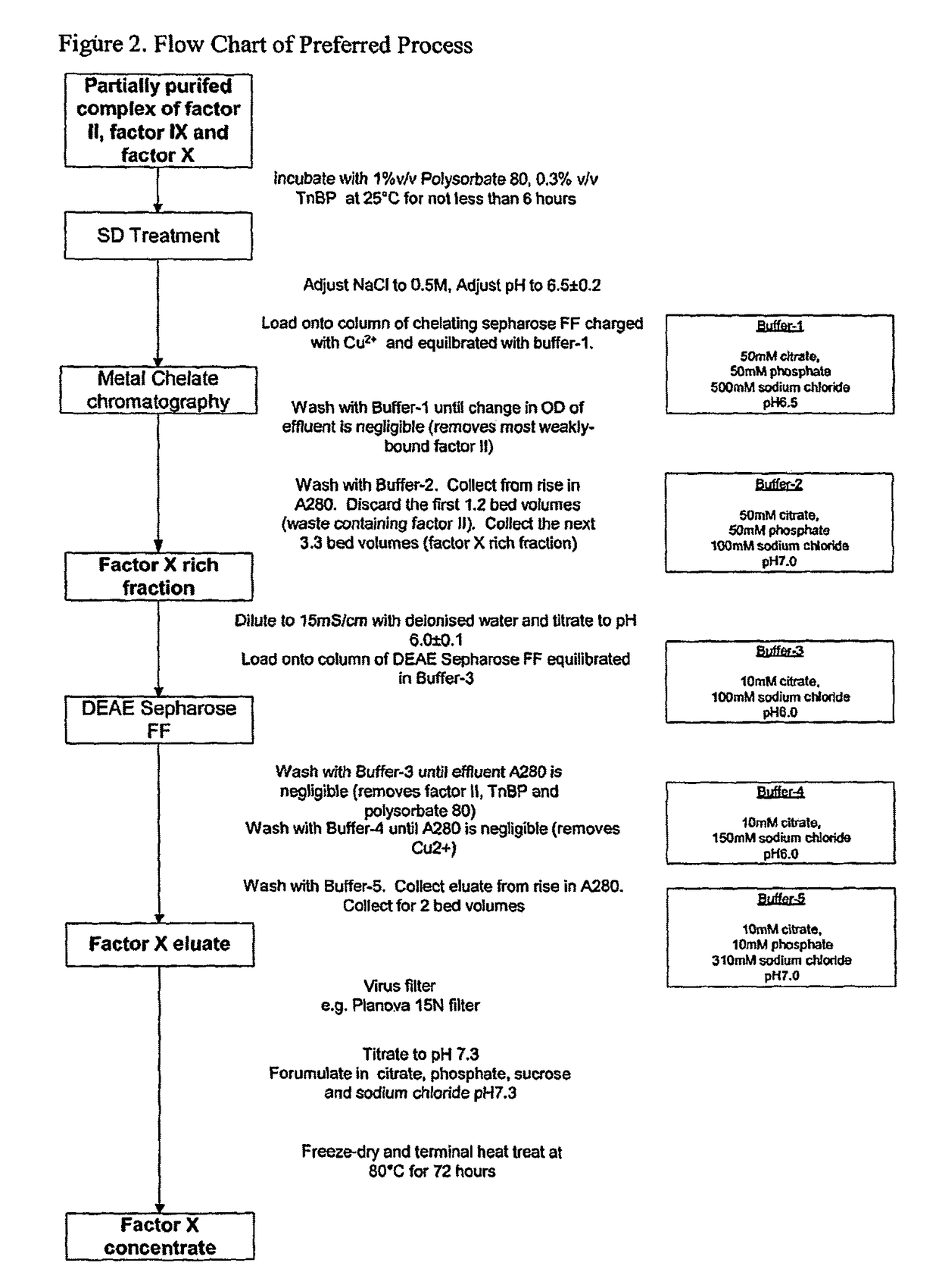
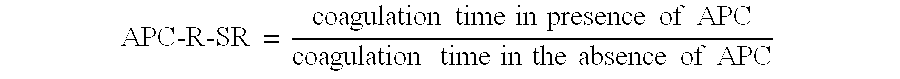Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Factor X" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
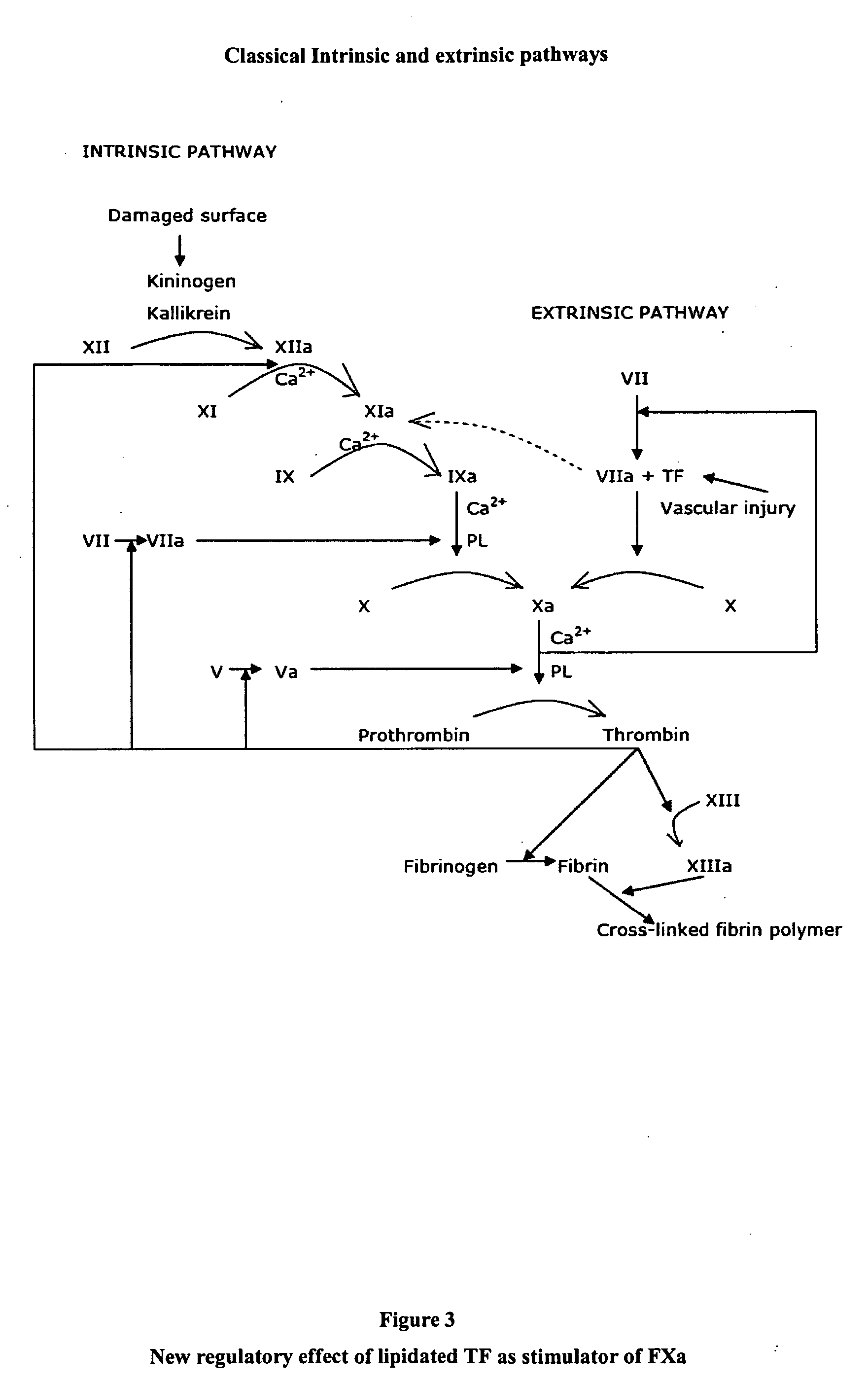
Factor X, also known by the eponym Stuart–Prower factor, is an enzyme (EC 3.4.21.6) of the coagulation cascade. It is a serine endopeptidase (protease group S1, PA clan). Factor X is synthesized in the liver and requires vitamin K for its synthesis.
Compositions and methods for treating coagulation related disorders
InactiveUS20060159675A1Initiate and prolong such disorderRelieve symptomsImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibacterial agentsDiseaseTissue factor
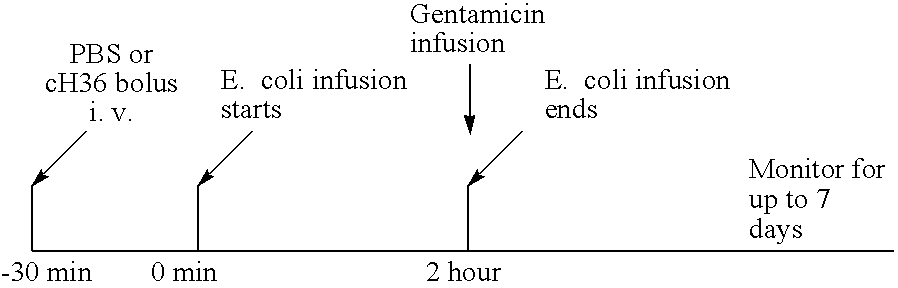
Disclosed are methods for preventing or treating sepsis, a sepsis-related condition or an inflammatory disease in a mammal. In one embodiment, the method includes administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of at least one humanized antibody, chimeric antibody, or fragment thereof that binds specifically to tissue factor (TF) to form a complex in which factor X or factor IX binding to the complex is inhibited and the administration is sufficient to prevent or treat the sepsis in the mammal. The invention has a wide spectrum of useful applications including treating sepsis, disorders related to sepsis, and inflammatory diseases such as arthritis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
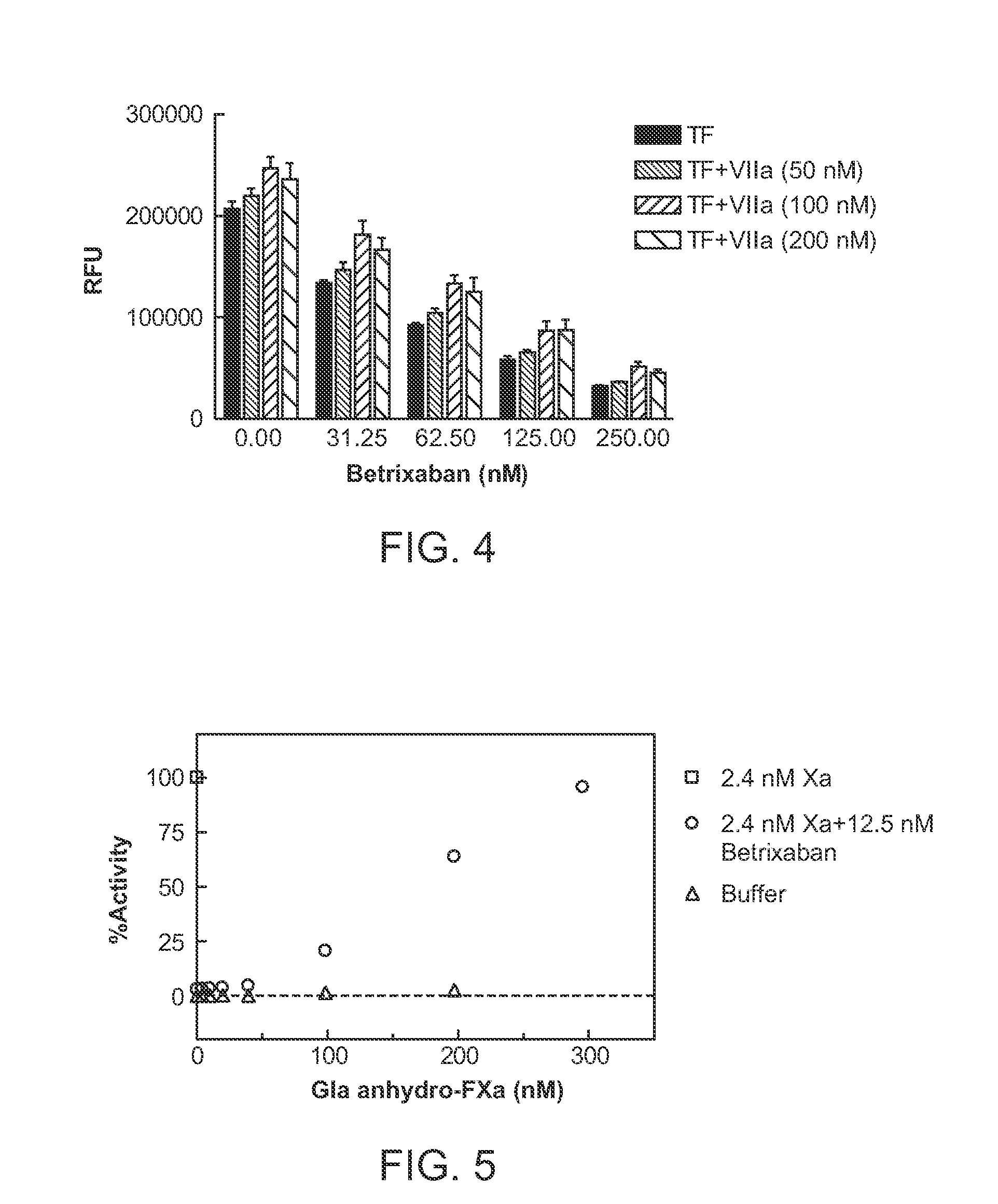
Antidotes for factor Xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS8268783B2Reduces and removes anticoagulant effectReduced activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFactor XAntidote
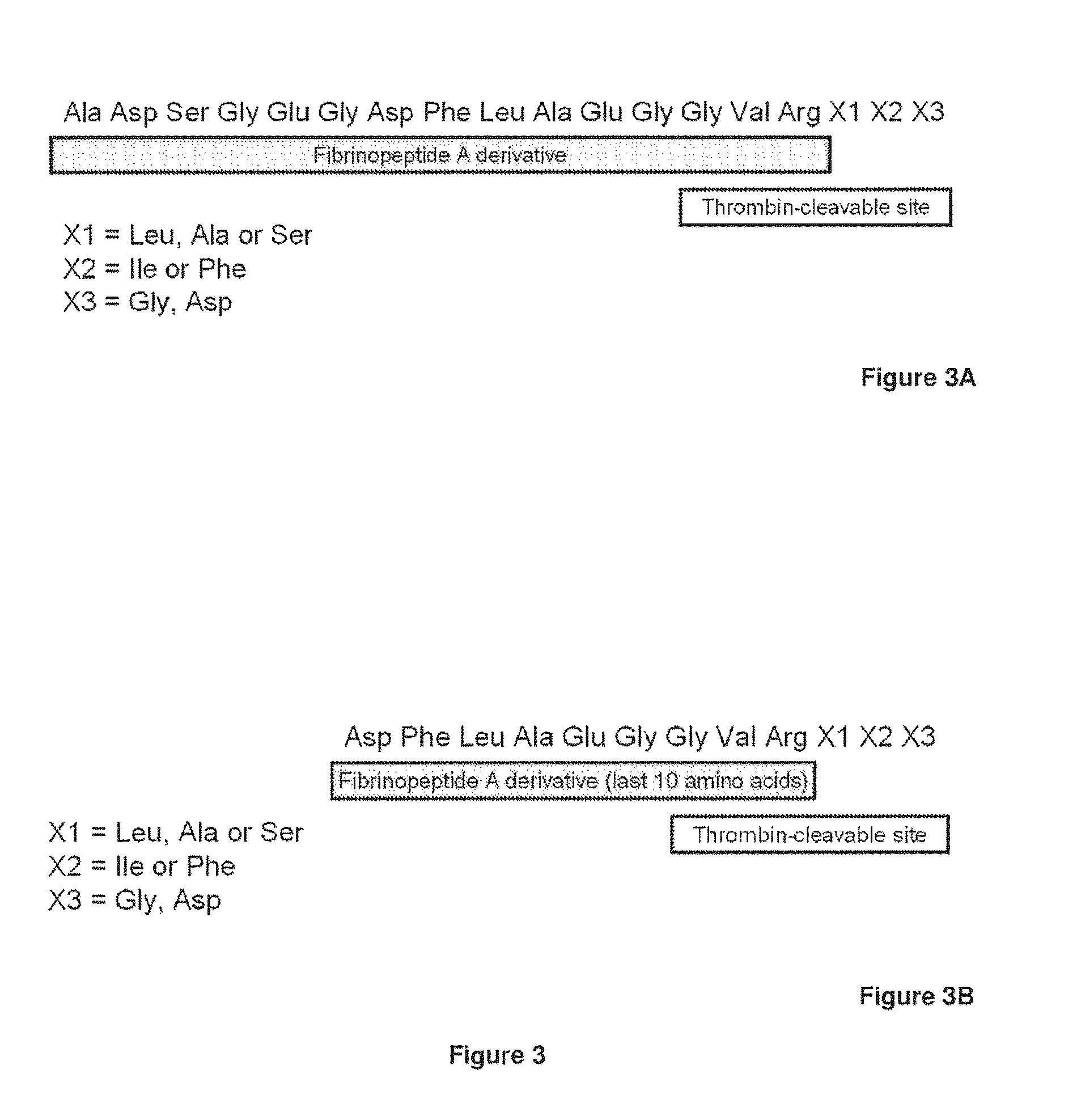
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor X and factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of reversing anticoagulation, stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Antidotes for factor xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20100255000A1Preventing and reducing bleedingReduces and removes anticoagulant effectPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesMedicineAntidote
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor X and factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of reversing anticoagulation, stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
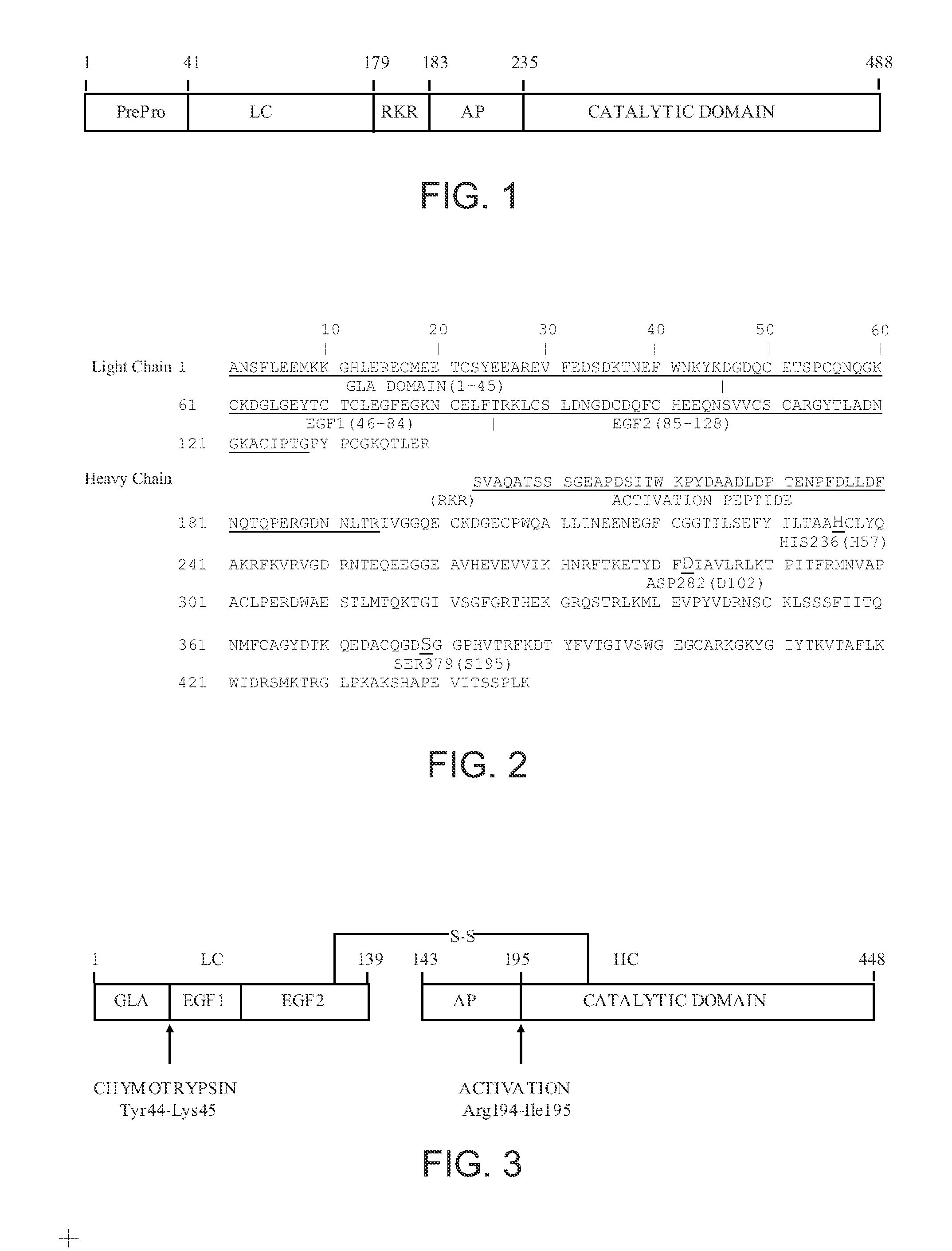
Factor X deletion mutants and analogues thereof
InactiveUS6562598B1Improve stabilityHigh stability and structural integrityFungiBacteriaFactor XAmino acid
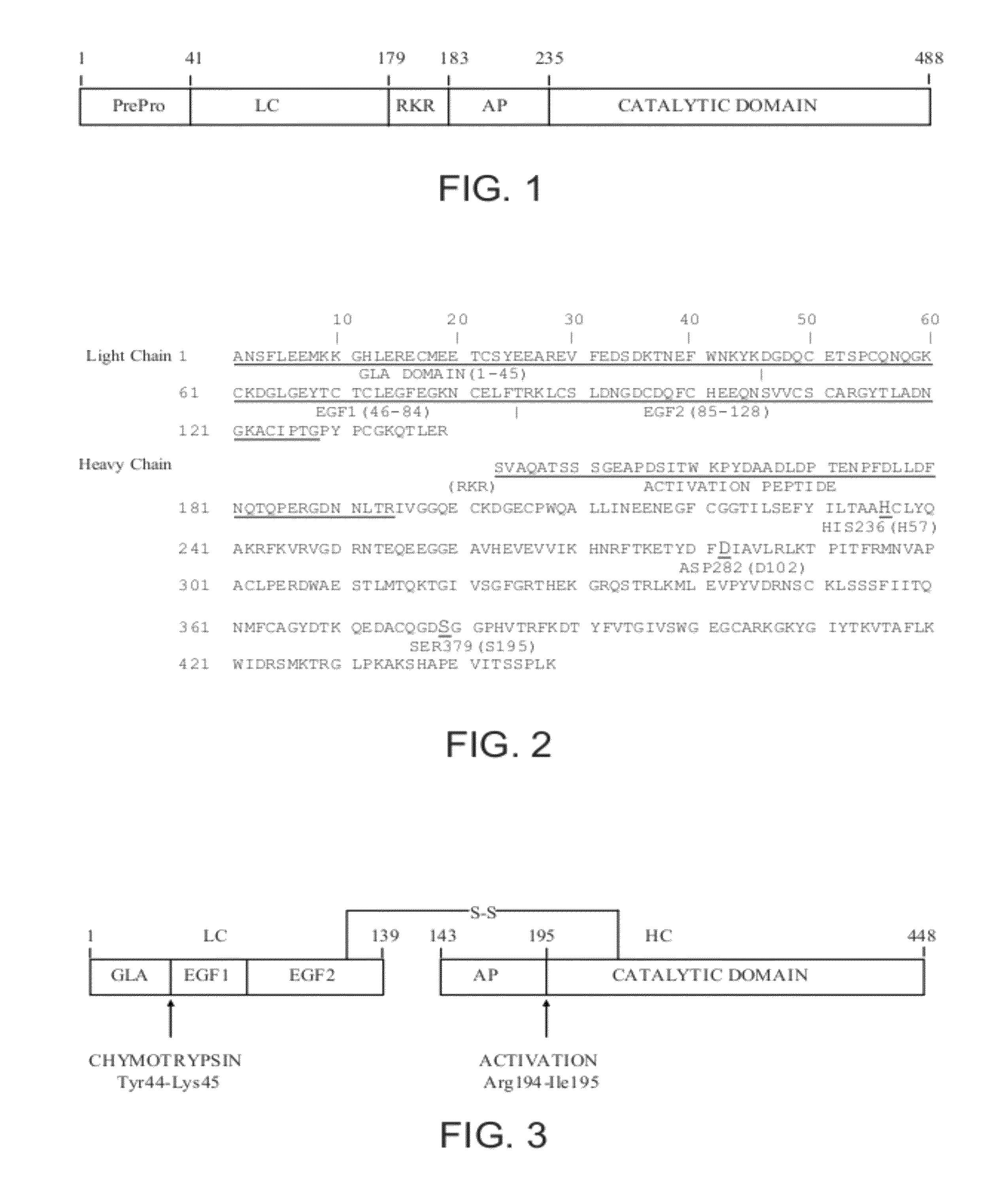
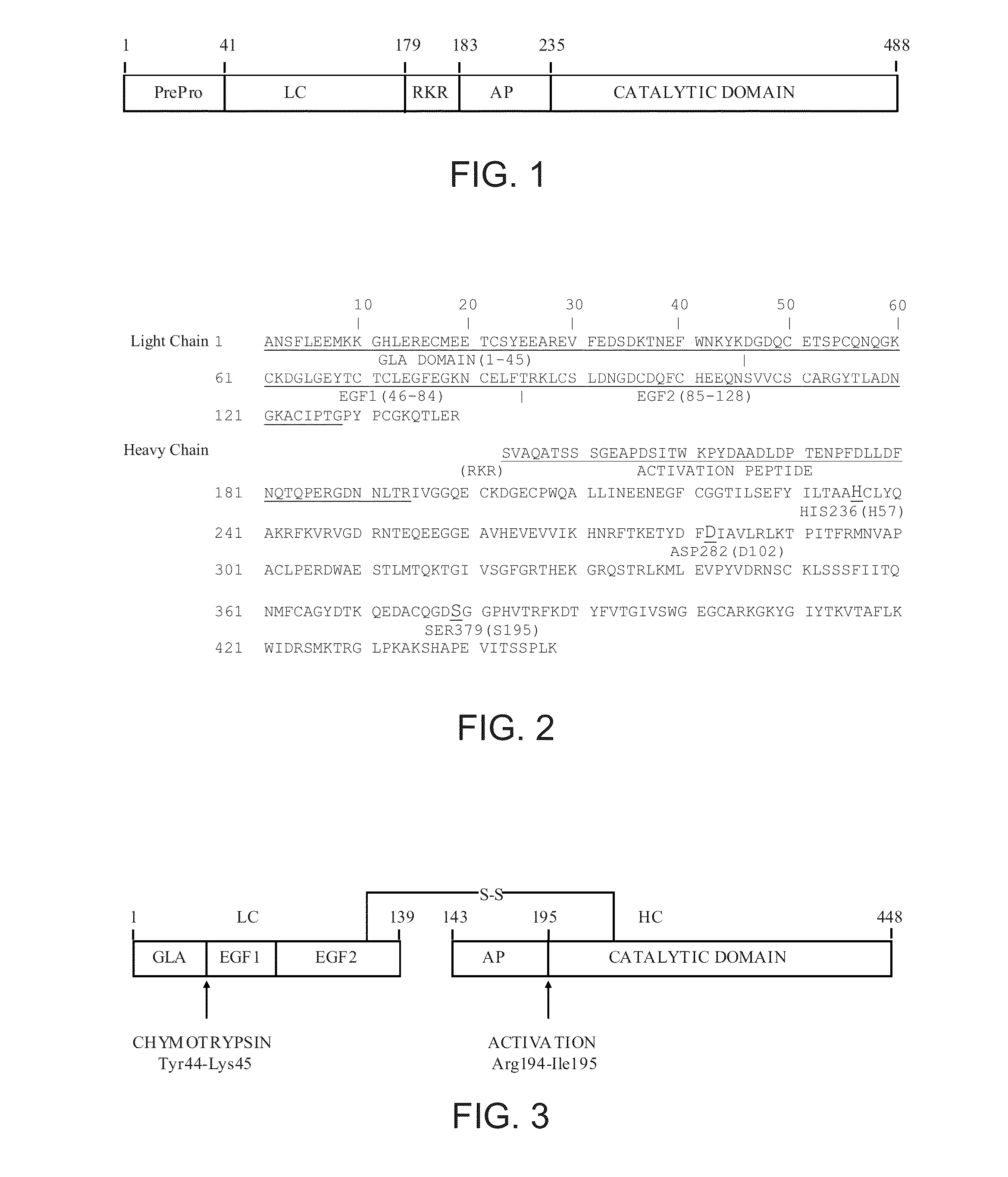
Factor XDELTA analogues are provided, as well as pharmaceutical preparations containing such analogues and methods of preparing such analogues. The factor XDELTA analogues have a deletion of the amino acids Arg180 to Arg234 and a modification in the region of the amino acid sequence between Gly173 and Arg179 of the factor X amino acid sequence. Such analogues can include a processing site not normally present in factor X, thus allowing for selective conversion of the analogue to an active form. The analogues and preparations have utility in the treatment of a number of blood coagulation disorders.
Owner:BAXALTA INC
Factor X analog with an improved ability to be activated
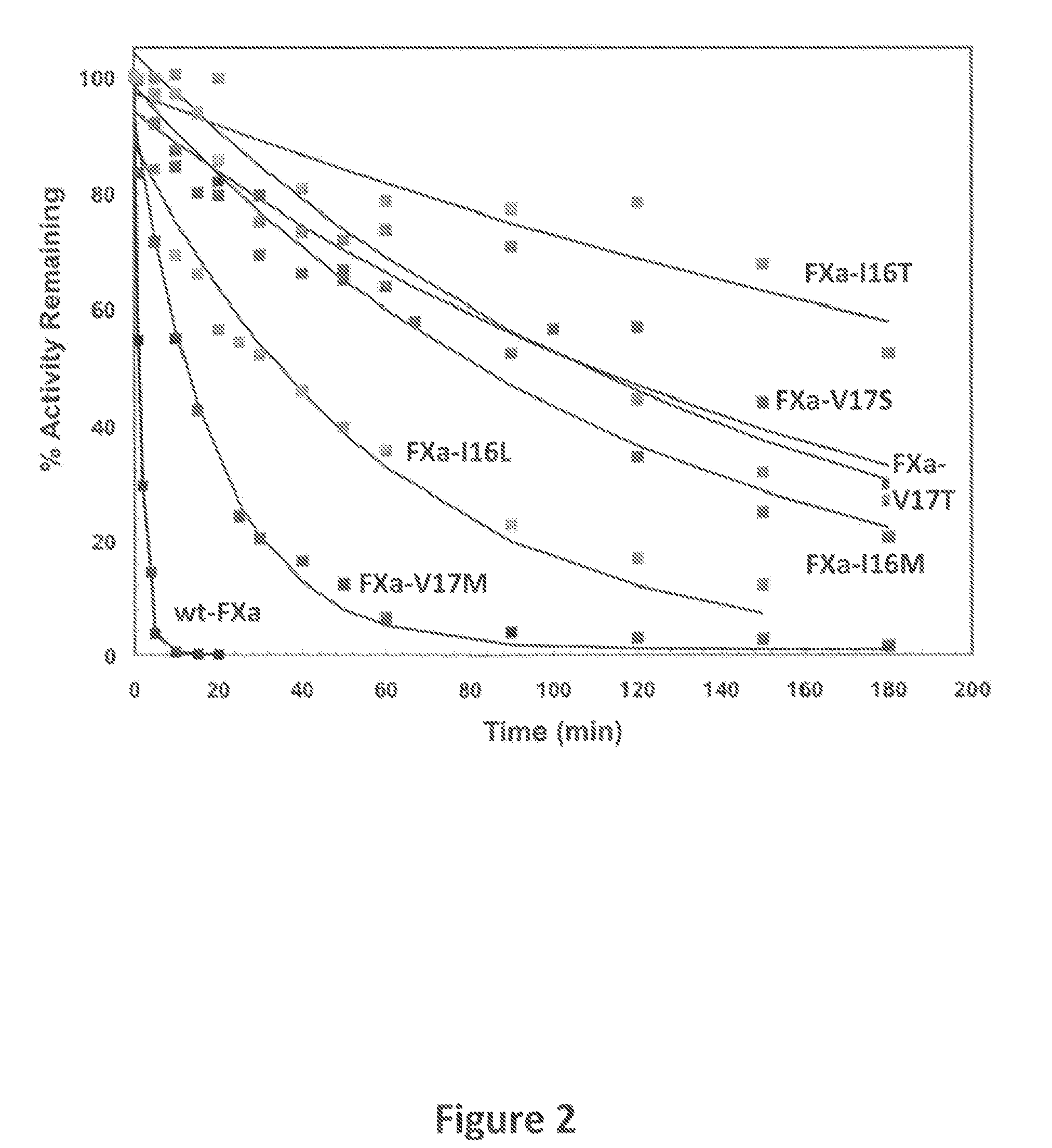
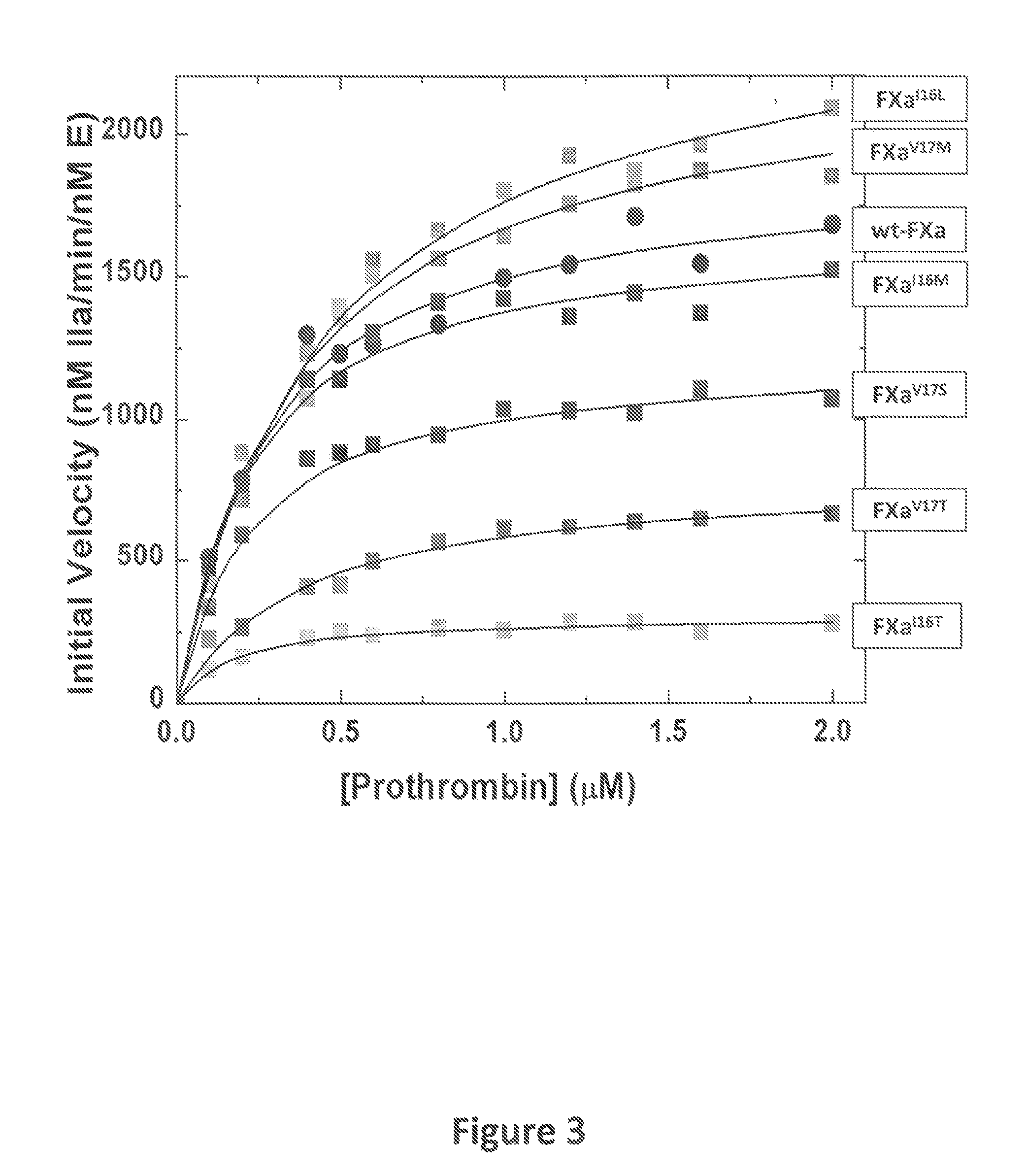
InactiveUS6958322B1Promote activationImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFactor XFactor ii
This invention describes a factor Xa analog which has a substitution of a minimum of one of the amino acid between Glu226 and Arg234 and possibly Ile235, relative to the amino acid numbering according to FIG. 1, a preparation containing the activated form of the factor X analog, and a method for the production of these molecules.
Owner:BAXALTA INC
Electrochemical Determination of Factor XA Inhibitors
ActiveUS20090236238A1Current maximum and retardedMaximum and retarded reactionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFactor XFactor ii
Methods and devices for determining factor Xa inhibitors, in particular heparins and fractionated or low-molecular-weight heparins, as well as direct factor Xa inhibitors in blood samples. The methods include contacting a blood sample with a detection reagent that contains at least one thrombin substrate having a peptide residue that can be cleaved by thrombin and is amidically bound via the carboxyl end to an electrogenic substance, and with a known amount of factor X reagent and an activator reagent which induces the conversion of factor X into factor Xa. Subsequently, in a second step, the amount or activity of the electrogenic substance that is cleaved from the thrombin substrate by the factor Xa-mediated thrombin activation and / or the time course thereof is determined as the measurement signal using electrochemical methods. In a third step, the amount of the factor Xa inhibitor in the sample of the blood to be analyzed or a measured quantity that correlates therewith, in particular a clotting time that correlates therewith, is determined on the basis of this measurement signal.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Compositions and Methods for Modulating Hemostasis
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Serine protease derivatives and uses in the prevention or the treatment of blood coagulation disorders
ActiveUS8436144B2Extended half-lifePromote recoveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsZymogenWAS PROTEIN
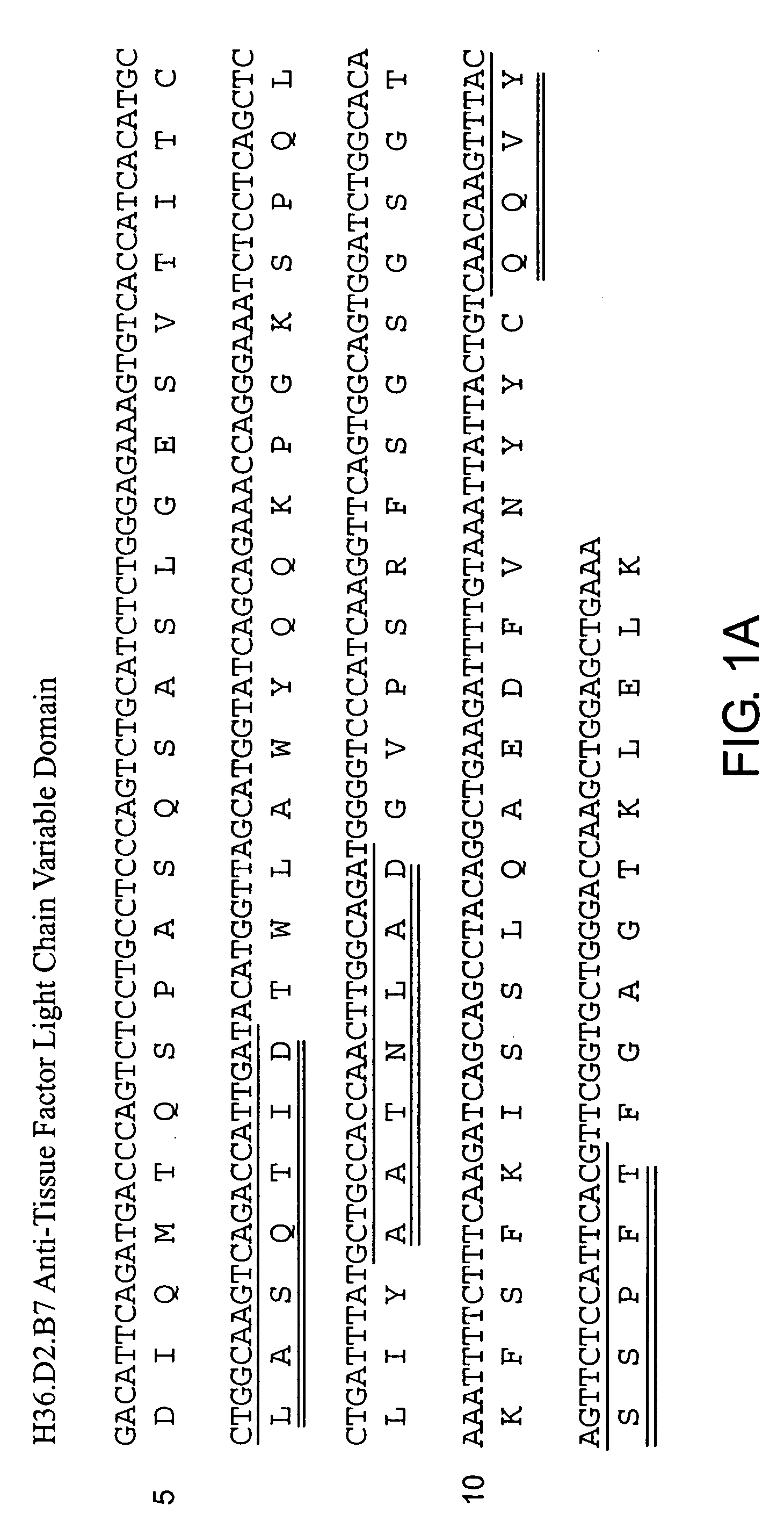
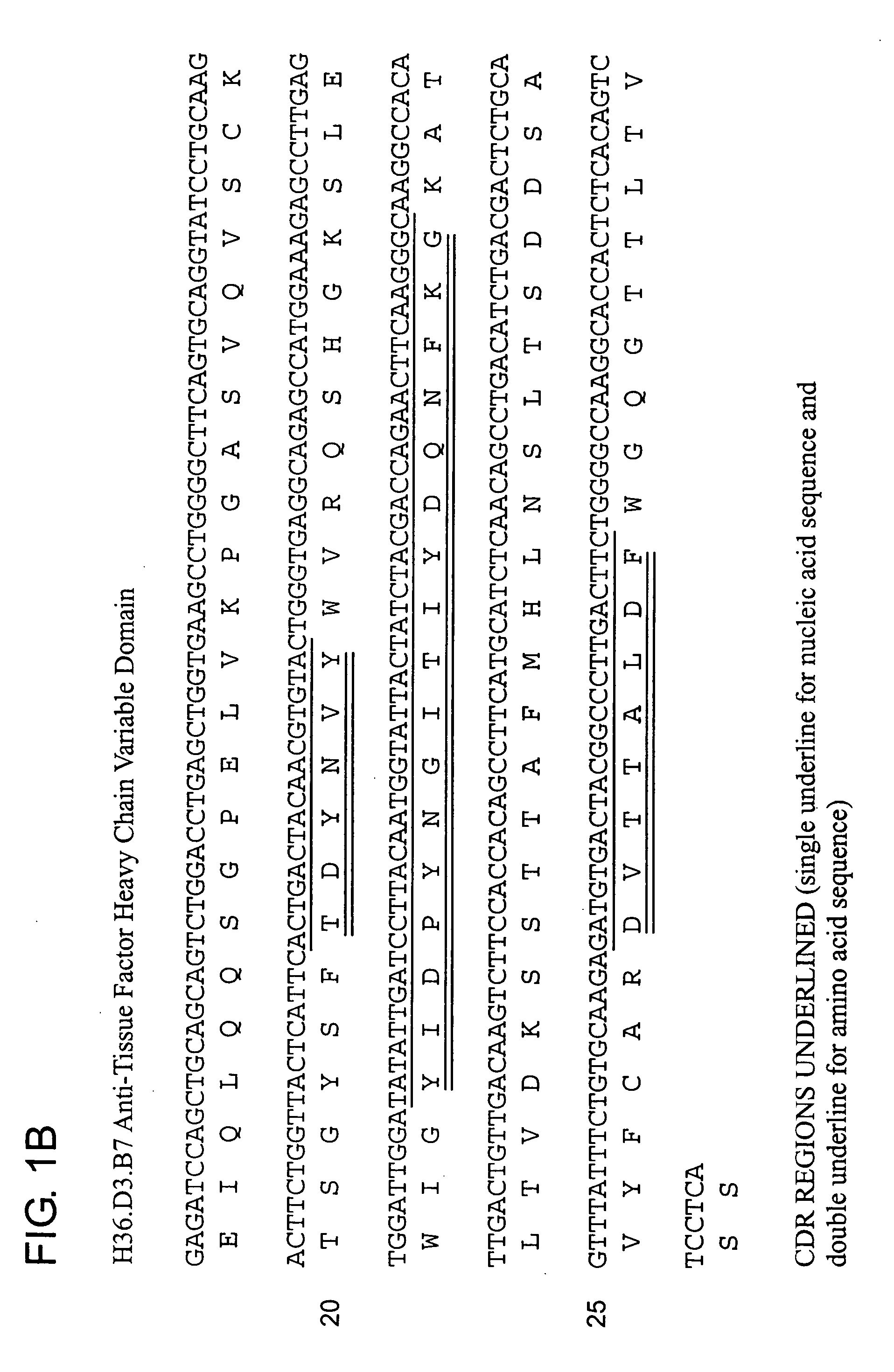
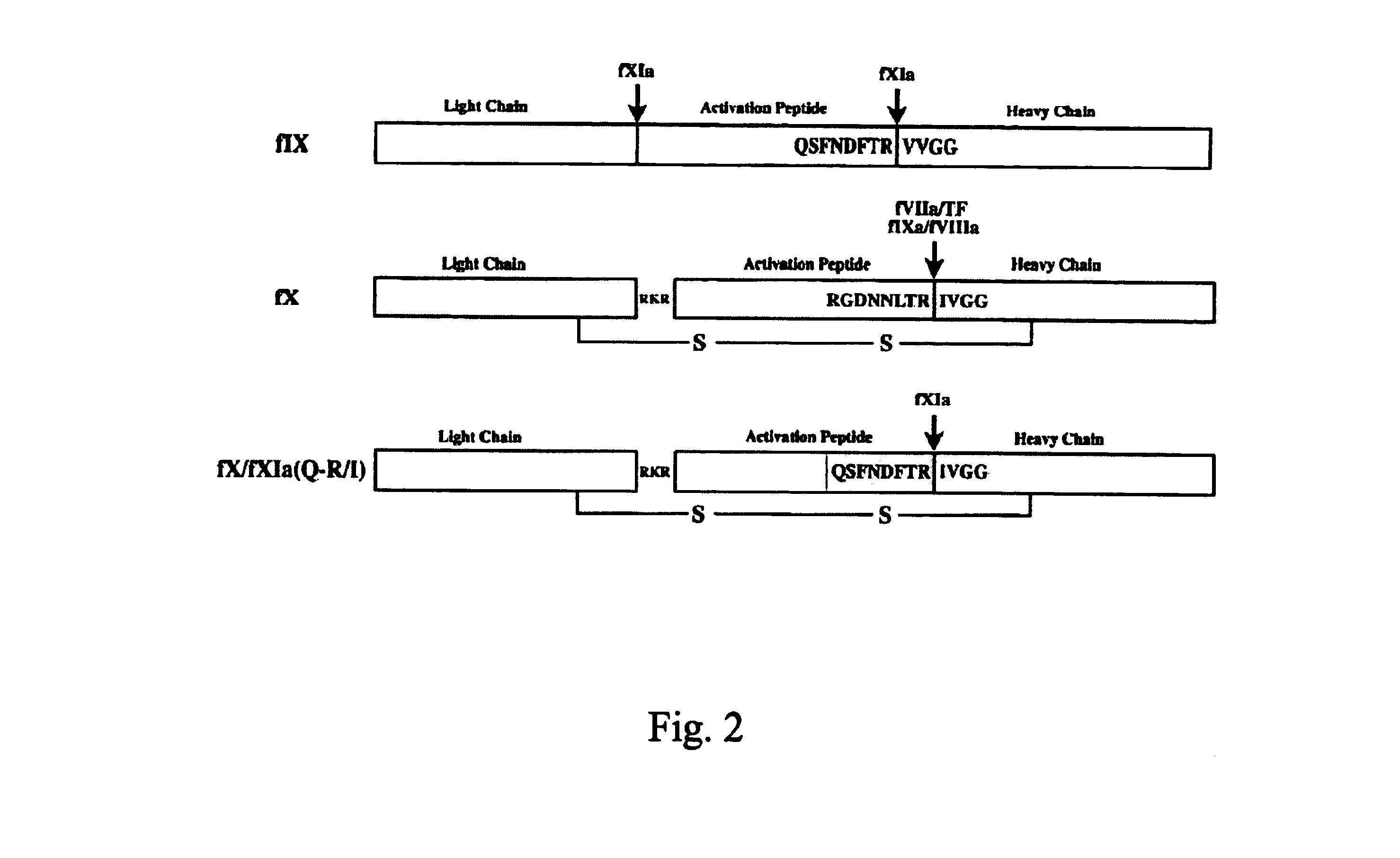
The present invention relates to chimeric derivatives of serine protease zymogen containing the activation peptide of factor X or a fragment thereof for improving the half-life of said derivatives. Preferably, said chimeric derivatives are protein C and factor X derivatives. The invention also relates to said derivatives for the prevention or treatment of blood coagulation disorders.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Serine protease derivatives and uses in the prevention or the treatment of blood coagulation disorders
ActiveUS20110293597A1Extended half-lifePromote recoveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsActivation peptideZymogen
The present invention relates to chimeric derivatives of serine protease zymogen containing the activation peptide of factor X or a fragment thereof for improving the half-life of said derivatives. Preferably, said chimeric derivatives are protein C and factor X derivatives. The invention also relates to said derivatives for the prevention or treatment of blood coagulation disorders.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Compositions and methods for treating coagulation related disorders
InactiveUS20090136501A1Initiate and prolong such disorderRelieve symptomsAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Disclosed are methods for preventing or treating sepsis, a sepsis-related condition or an inflammatory disease in a mammal. In one embodiment, the method includes administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of at least one humanized antibody, chimeric antibody, or fragment thereof that binds specifically to tissue factor (TF) to form a complex in which factor X or factor IX binding to the complex is inhibited and the administration is sufficient to prevent or treat the sepsis in the mammal. The invention has a wide spectrum of useful applications including treating sepsis, disorders related to sepsis, and inflammatory diseases such as arthritis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Antidotes for factor xa inhibitors and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20130129693A1Reduces and removes anticoagulant effectReduced activityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesMedicineAntidote
The present invention relates antidotes to anticoagulants targeting factor Xa. The antidotes are factor X and factor Xa protein derivatives that bind to the factor Xa inhibitors thereby substantially neutralizing them but do not assemble into the prothrombinase complex. The derivatives describe herein lack or have reduced intrinsic coagulant activity. Disclosed herein are methods of reversing anticoagulation, stopping or preventing bleeding in a patient that is currently undergoing anticoagulant therapy with a factor Xa inhibitor.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Compositions and methods for modulating hemostasis
ActiveUS9371522B2Modulate hemostasisPeptide/protein ingredientsDermatological disorderFactor XHemostasis
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
One component fibrin glue comprising zymogens
ActiveUS20150174215A1Eliminate cumbersome stepsPrevents and reduces premature activationOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesZymogenFibrin glue
Provided herein is a single component sealant formulation (e.g. in a liquid form), methods for its preparation, and use. The formulation includes fibrinogen; vitamin K-dependent clotting zymogens comprising at least Factor II (FII) and Factor X (FX).
Owner:ETHICON INC +1
Method for determining the coagulation potential of a plasma sample
InactiveUS6838251B1Enhanced interactionShorten clotting timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFactor XProtein activation
A method of determining the coagulation potential of a plasma sample be pre-incubating the plasma sample with a reagent such that endogenous protein C in the plasma is at least partially converted into activated protein C by the reagent, adding factor Xa which is progressively inactivated by antithrombin III / heparin cofactor 2 during the preincubation, adding an exogenous reagent which activates factor X to Xa or prothrombin to thrombin in a factor V-dependent manner, monitoring a reaction indicative of the rate of coagulation of the plasma sample, comparing that rate of coagulation control, or the equivalent rate determined for an individual without impaired coagulation control, or the equivalent rate determined for the plasma sample in the absence of protein C activator, and determining the coagulation potential of the plasma sample from one or other of the compairsons.
Owner:STAGO
Depolymerized glycosaminoglycan from Thelenota ananas and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS8809300B2Special structureGood anticoagulant potencyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFucosylationDepolymerization
Disclosed is a depolymerized glycosaminoglycan from Thelenota ananas (dTHG), weight average molecular weight of which is about 8000˜20000 Da, and monosaccharide components of which are acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), glucuronic acid (GlcUA), fucose (Fuc) or their sulfates (expressed as —OSO3−), in which molar ratio of GalNAc:GlcUA:Fuc:—OSO3− is about 1:(1±0.3):(1±0.3):(3.5±0.5). Said dTHG is a potent endogenous inhibitor of factor X, which has good anticoagulant and antithrombotic activity, and can be used for the prevention and / or treatment of thrombotic diseases. Also provided is a method for preparing said dTHG, which comprises steps of 1) extracting and obtaining fucosylated glycosaminoglycan (THG) from the body wall of Thelenota ananas; 2) depolymerizing THG to obtain dTHG by method of peroxide depolymerization or method of peroxide depolymerization catalyzed by catalyst of the fourth period transition metal ions; 3) removing impurities with lower and / or higher molecular weight in dTHG.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEPTUNUS PHARM CO LTD
Antibodies for inhibiting blood coagulation and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20090041766A1High anticoagulant activityInhibit blood coagulationImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFungiAntibody Binding SiteFactor X
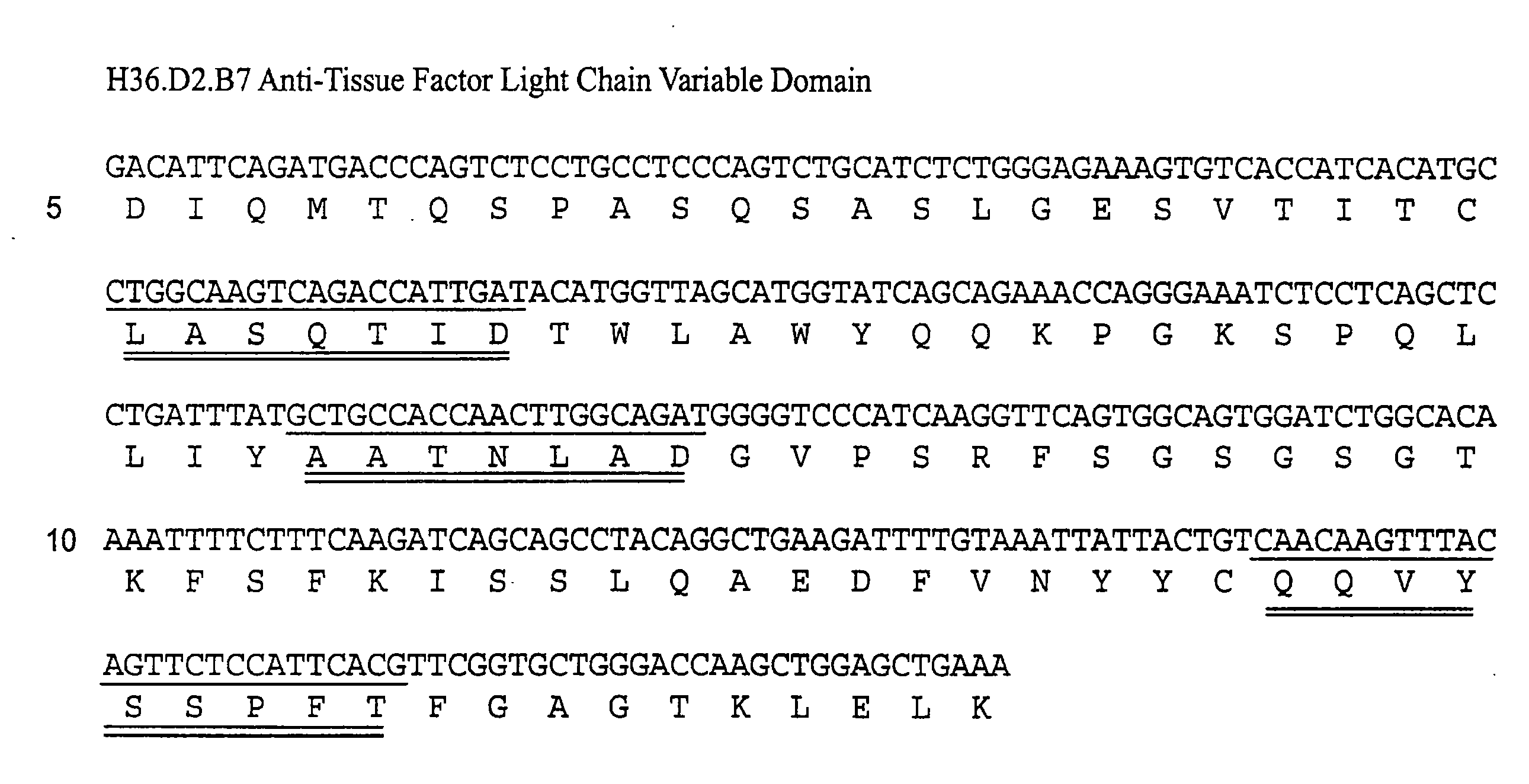
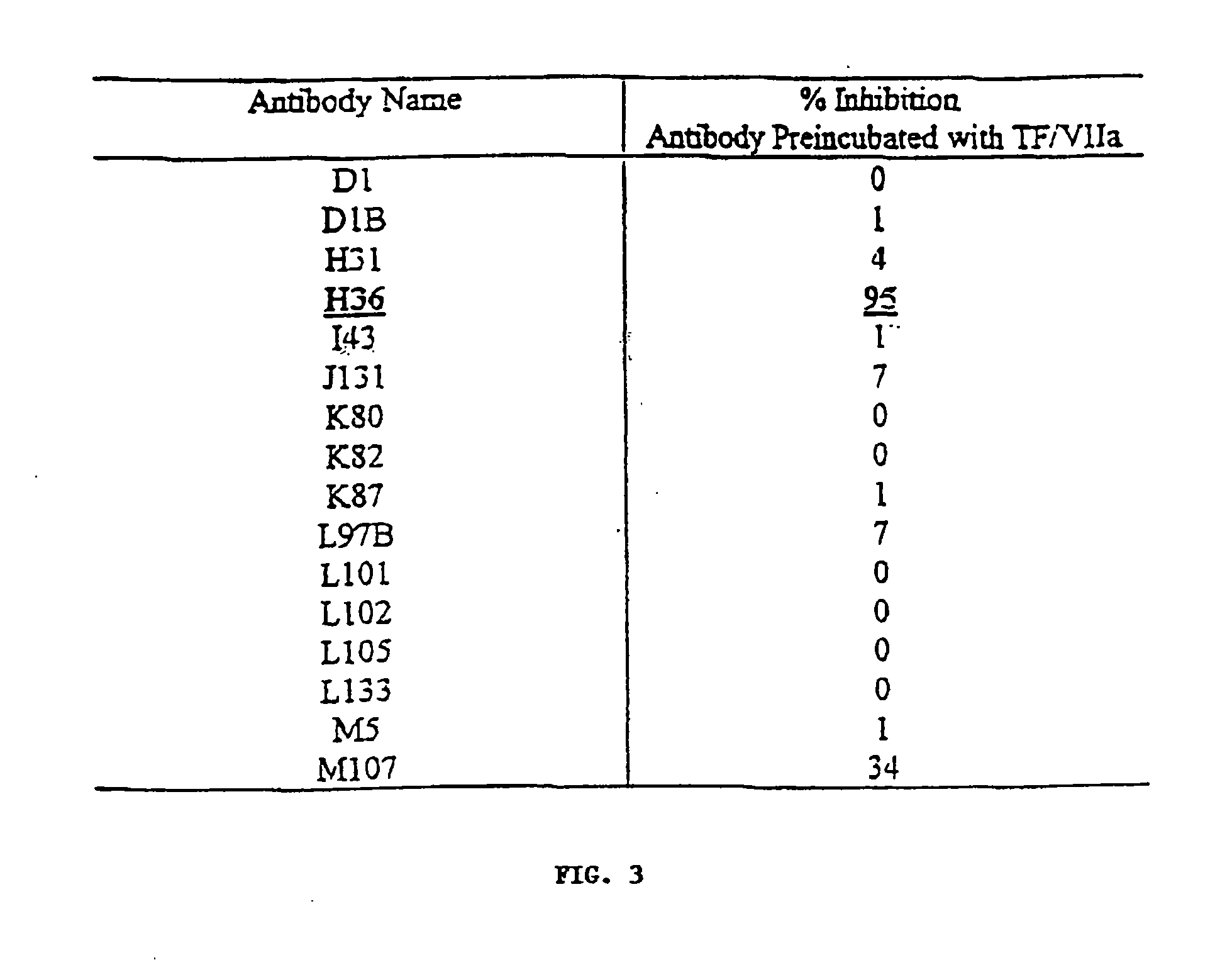
The invention includes antibodies that provide superior anti-coagulant activity by binding native human TF with high affinity and specificity. Antibodies of the invention can effectively inhibit blood coagulation in vivo. Antibodies of the invention can bind native human TF, either alone or present in a TF:VIIa complex, effectively preventing factor X binding to TF or that complex, and thereby reducing blood coagulation. Preferred antibodies of the invention specifically bind a conformational epitope predominant to native human TF, which epitope provides an unexpectedly strong antibody binding site.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Integrated process for the production of therapeutics (human albumin, intravenous immunoglobulins, clotting factor viii and clotting factor ix) from human plasma
ActiveUS20150210737A1Low costImprove affordabilityHydrolasesChemical industryFractionationHuman albumin
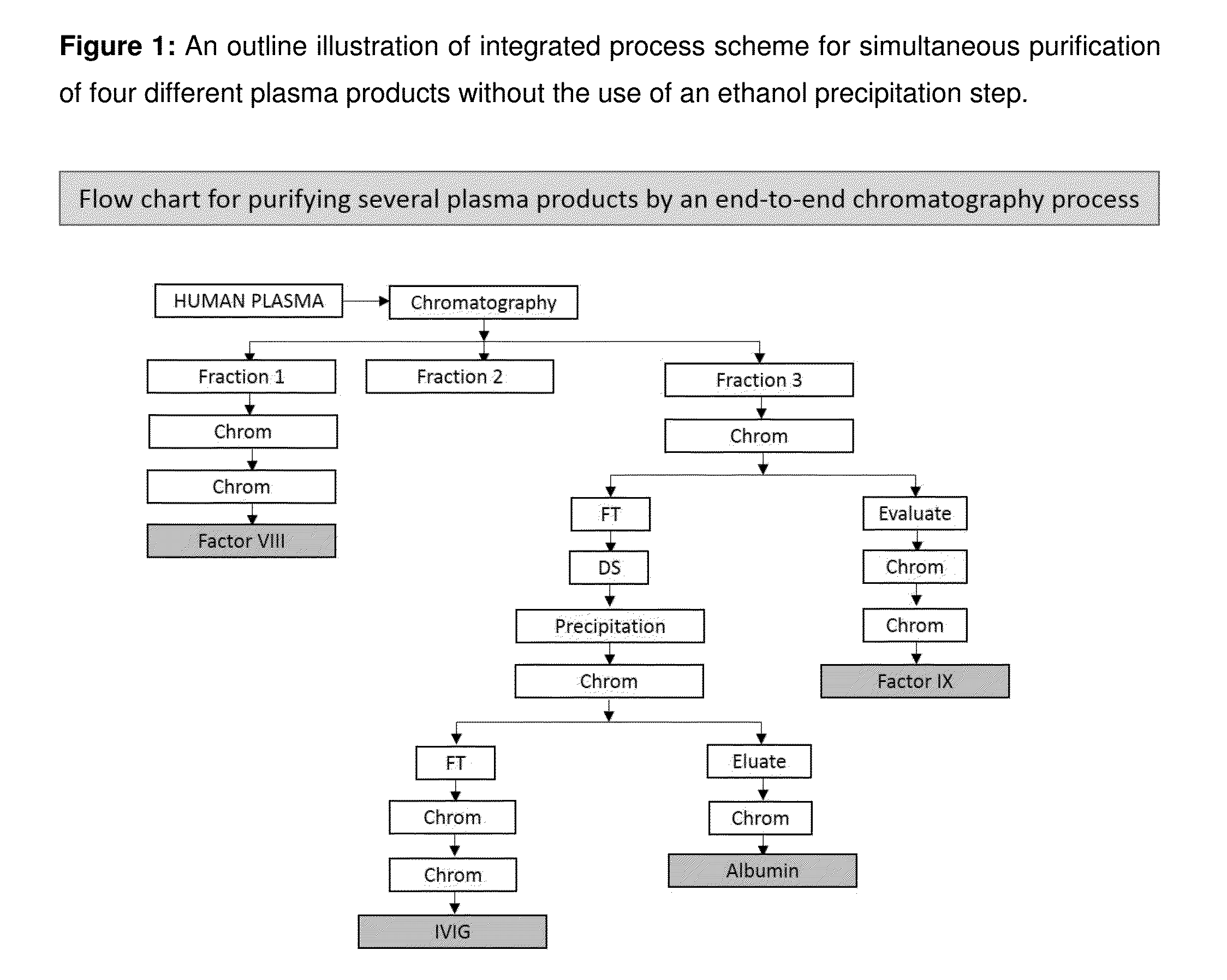
The invention relates to an integrated scheme for fractionation and purification of plasma products (human albumin, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), clotting factor VIII and clotting factor IX) by sequential chromatography and virus reduction steps. The therapeutically administrable protein IVIG has purity levels exceeding 98%, aggregates and dimers at less than 0.2%, Fc function of >90% and anti-complementary activity of less than 0.5 CH50 per mg of Ig. The distribution of IgG isomers is comparable to the ranges seen in normal plasma. Human albumin for therapeutic use, purified by this integrated scheme has an electrophoretic purity of close to 100%, with monomers exceeding 98%. The levels of aluminium and pre-kallikrein activator are below the detection limit for the respective tests. The Factor IX preparations have a specific activity of ≧200 IU / mg. The impurity levels of Factor-II, Factor VII, Factor X are at least 10-fold lesser (≦0.5% instead of 5%) and the heparin impurity of ≦0.01 IU (against 0.5 IU limit for this impurity) is 50-fold lesser the specified pharmacopoeial limits.The purification carried out by an all-chromatography scheme, avoids the use of ethanol precipitation in the entire manufacturing process of the said four plasma products. The invention describes an integrated process for purifying four different proteins from human plasma to high therapeutic grade purity levels, with a potential to purify more therapeutic proteins from a given plasma sample by incorporating additional chromatography steps in the sequence.
Owner:ICHOR BIOLOGICS PTE LTD
Antibodies for inhibiting blood coagulation and methods of use thereof
InactiveCN1599624AHigh anticoagulant activityPrevent coagulationImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntigenFactor X
The invention includes antibodies that provide superior anti-coagulant activity by binding native human TF with high affinity and specificity. Antibodies of the invention can effectively inhibit blood coagulation in vivo. Antibodies of the invention can bind native human TF, either alone or present in a TF:FVIIa complex, effectively preventing factor X or FIX binding to TF or that complex, and thereby reducing blood coagulation. Preferred antibodies of the invention specifically bind a conformational epitope predominant to native human TF, which epitope provides an unexpectedly strong antibody binding site. Also provided are humanized antibodies and fragments thereof that bind to the TF.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Coagulation proteins, coagulation-anticoagulation protein complexes, derivatives thereof and their uses
InactiveUS20070025979A1Enhance dissolving said blood clotHigh dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsFibrinogenSide effectFactor X
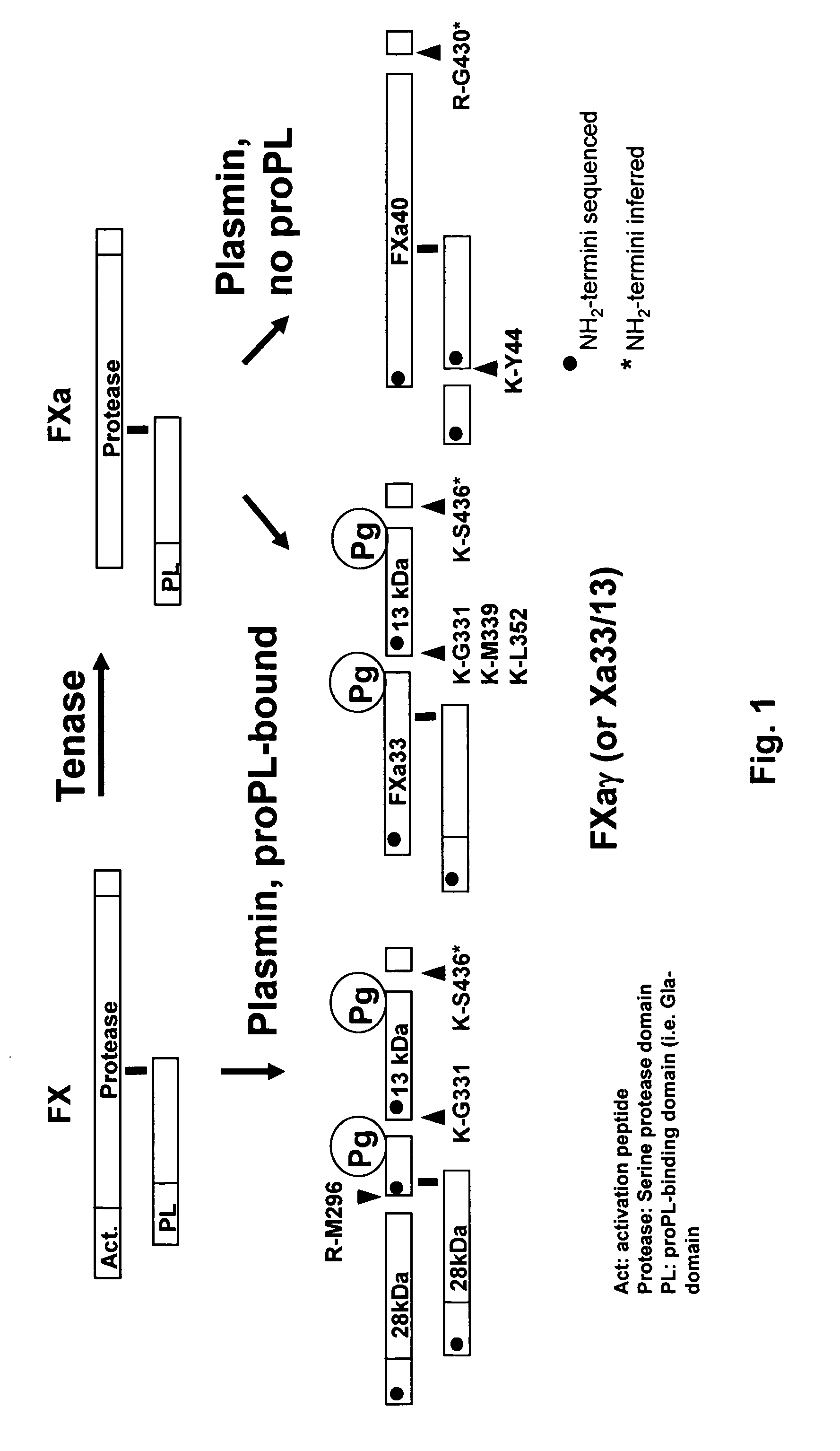
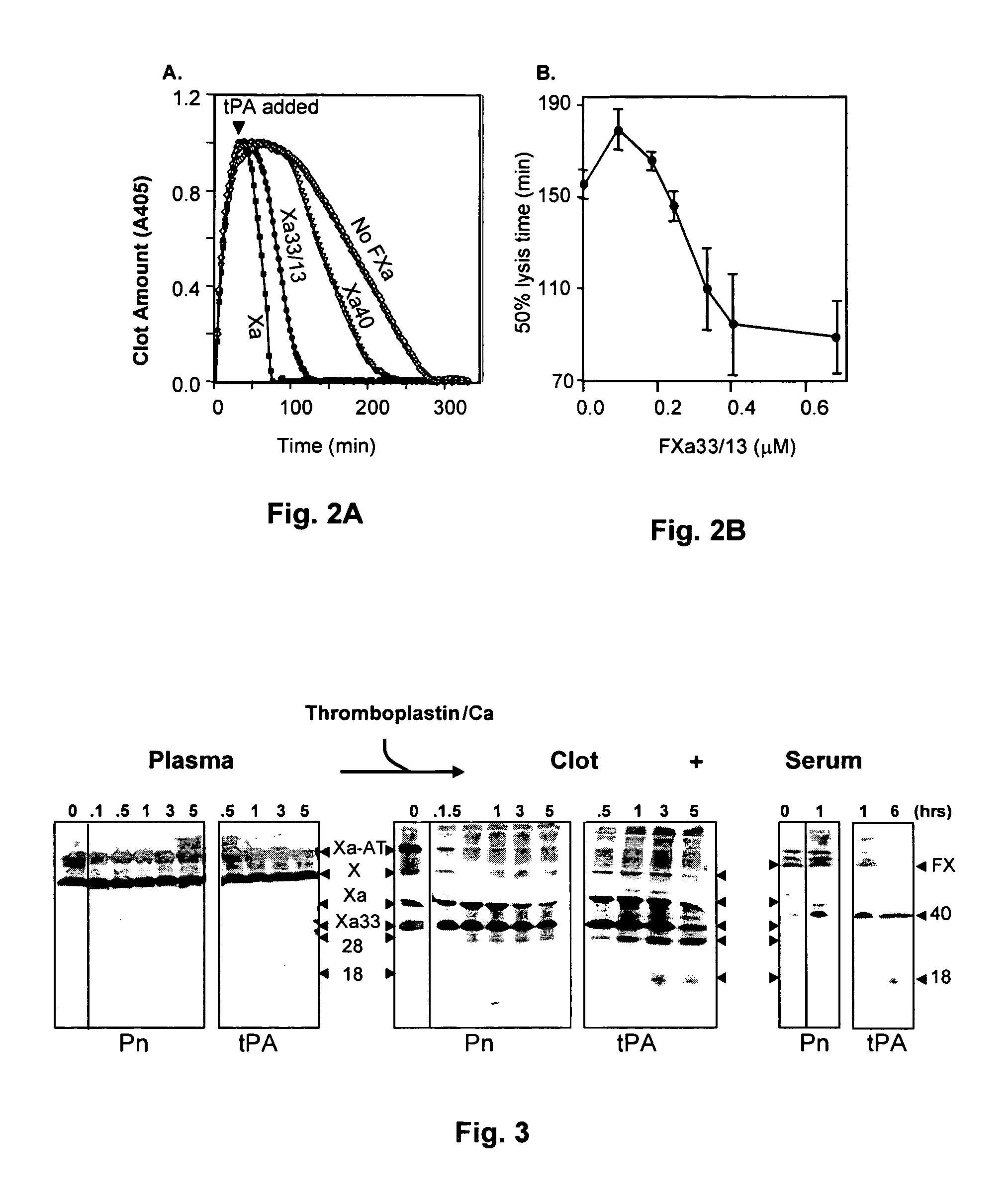
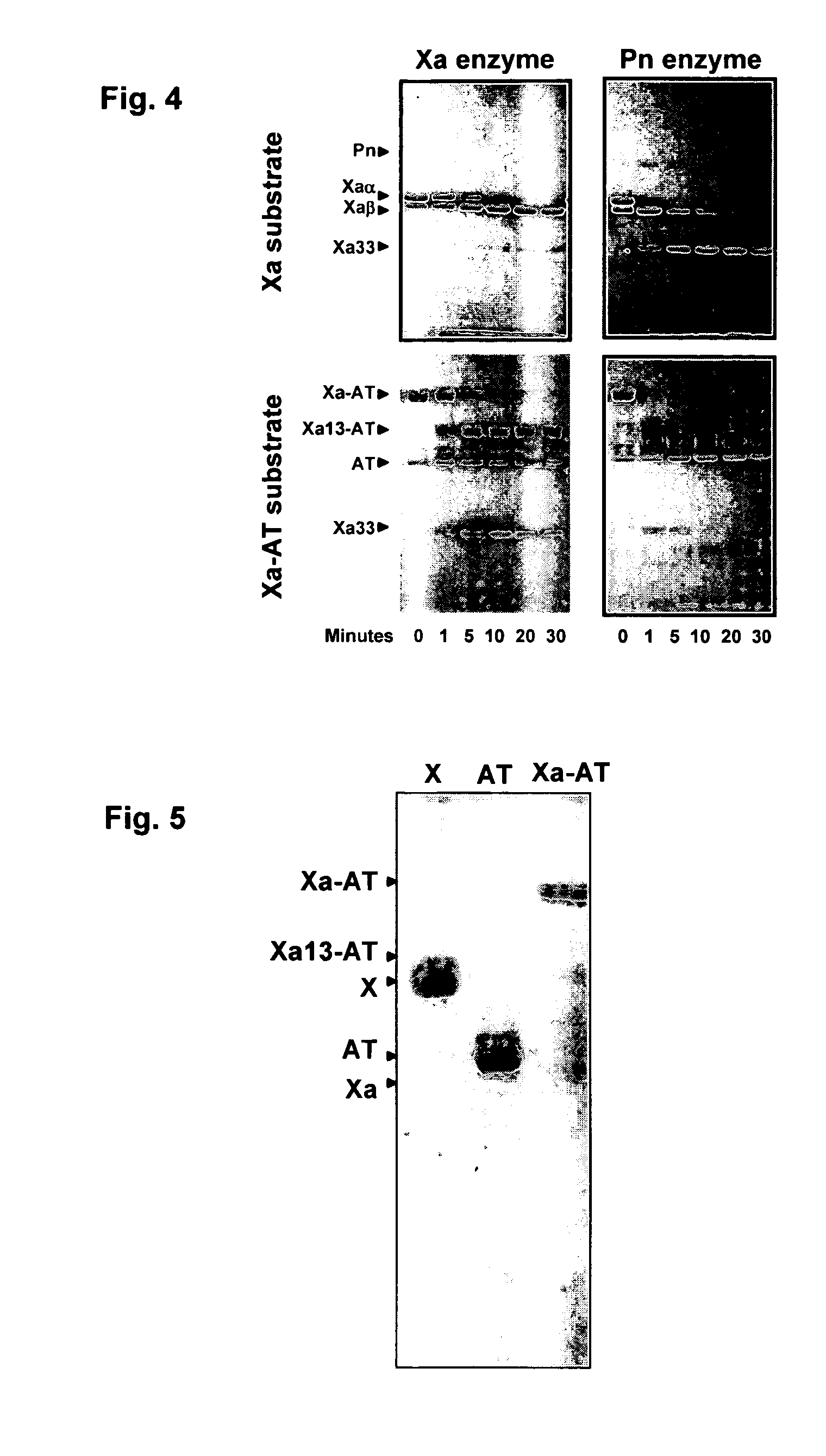
The present invention relates to the use of coagulation proteins and complexes thereof with anticoagulation proteins for the lysis of blood clots or other applications affected by accelerated plasmin production. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for accelerating the dissolution of a blood clot through the administration of at least one coagulation protein, with or without being in complex with a serpin, comprising a basic C-terminal amino acid, wherein the coagulation protein may be a derivative of Factor X or Factor V or a combination thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and prophylaxis of blood clots are also provided, wherein, the methods and products of the present invention advantageously accelerate clot dissolution while potentially minimizing the adverse side-effects, such as hemorrhaging, seen with other clot dissolving agents. The present invention also provides a method for detecting a fibrinolytic potential in a subject.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Method for detecting quality of Angelica
ActiveCN110376310AFully reflect the efficacy of the characterizationWell supported by scientific dataComponent separationLipid formationFactor X
The invention discloses a method for detecting the quality of Angelica. Pharmacokinetics parameter screening standards such as a lipid-water partition coefficient, an oral bioavailability and a drug-forming property of each matching compound are referred, a compound group with excellent pharmacokinetics and high safety are subjected to second screening, and compounds are taken as 'pharmaceutical component group' associated with the efficacy of the Angelica. Then a measured in vitro / in vivo biological activity of the Angelica is used as a monitoring factor Y and the Angelica 'pharmaceutical component group' is taken as an observation factor X according to the 'substance-efficacy' interaction of the Angelica, a partial least squares regression model of the Angelica biological activity and the 'pharmaceutical component group' is established, components which are positively correlated with the Angelica biological activity and have a high correlation coefficient are found, and the components are taken as a 'quality marker' for the quality evaluation of the Angelica. Finally, a method for determining the content of the 'quality marker' of the Angelica is established by the liquid-mass spectrometry technology, and an industrialization path is provided for the overall quality traceability and control of Angelica medicinal materials or decoction pieces.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Stimulators of Factor X activated (FXa) as new topical antihemorrhagic agents
InactiveUS20070032424A1Quickly initiate thrombin formationPotent hemostasicOrganic active ingredientsFactor VIIFactor XCompound (substance)
The activated coagulation Factor X (FXa) stimulating agents may be used in the treatment of hemorrhages in a subject. Compounds and combinations are described which are particularly useful for the topical treatment of hemorrhaging in healthy subjects or in patients with hemorrhagic diathesis.
Owner:THROMBOTARGETAB CORP
Host Defense Factor X (HDFX)
The present invention relates to compositions and methods useful in medical prophylaxis and treatment of a mammalian subject before and after exposure of the subject to potentially lethal pathogens and other insults. More specifically, the present invention provides an isolated a natural host defense factor, or “HDFX”, which enhances an animal subject's ability to withstand infection by any pathogen and a variety of insults. Pharmaceutical compositions containing HDFX and therapeutic methods involving administration of HDFX are also provided.
Owner:RES FOUND OF STATE OF UNIV OF NEW YORK THE
Stimulators of Factor X activated (FXa) as new topical antihemorrhagic agents
InactiveUS7772371B2Promote rapid formationPotent hemostasicFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor XFactor ii
The activated coagulation Factor X (FXa) stimulating agents may be used in the treatment of hemorrhages in a subject. Compounds and combinations are described which are particularly useful for the topical treatment of hemorrhaging in healthy subjects or in patients with hemorrhagic diathesis.
Owner:THROMBOTARGETAB CORP
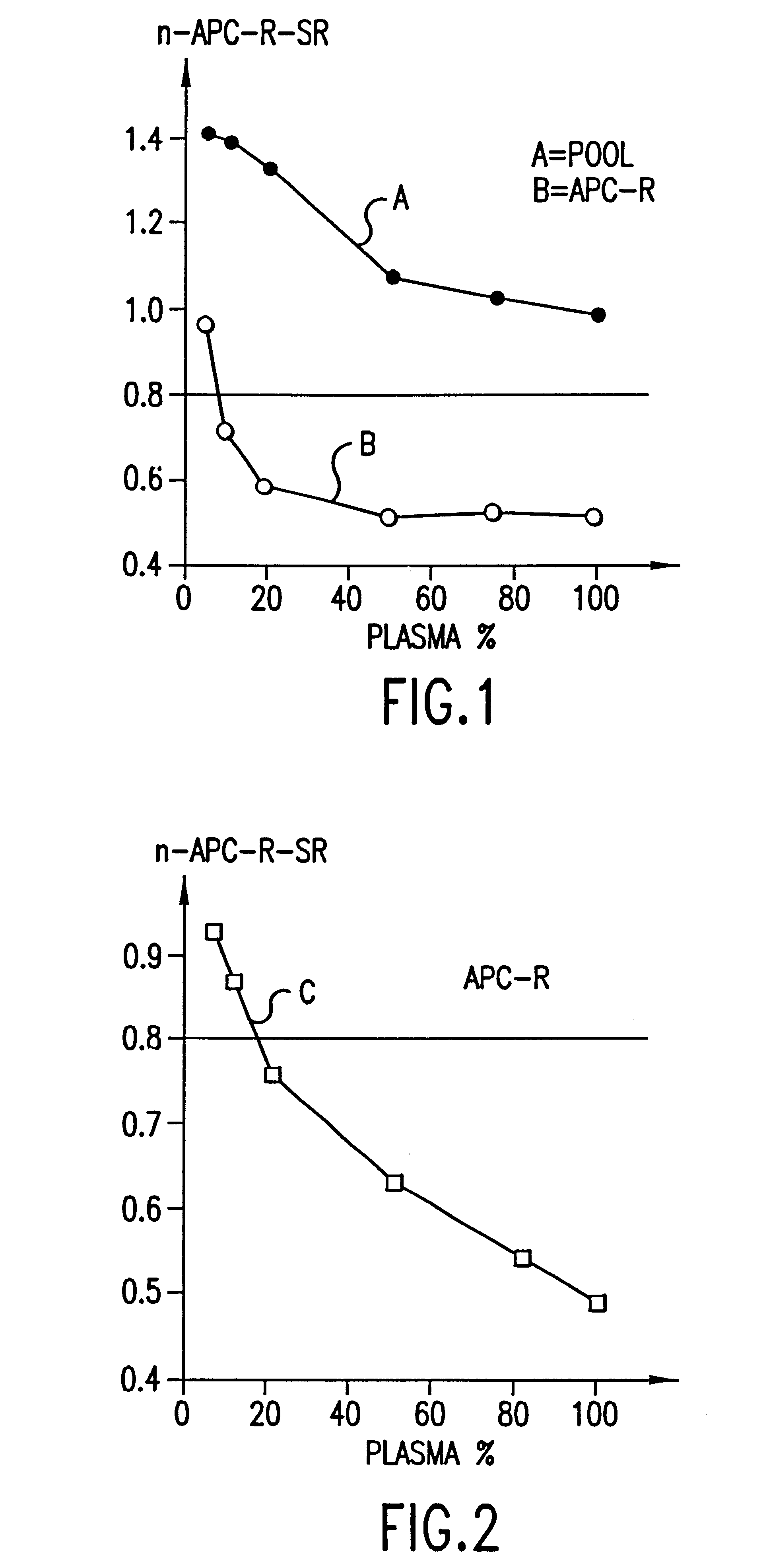
Process for determining a resistance to activated protein C
InactiveUS6251619B1Reduce in quantityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPrairie rattlesnakeFactor X
A process for determining a resistance to activated protein C of a test specimen of human plasma following the steps of: (1) mixing together (a) the test specimen of human plasma, (b) a reactant deficient in factor V which supplies at least most of the coagulation factors other than factor V, and (c) the venom of Crotalus viridis helleri which specifically activates factor X to Xa, and incubating the mixture of (a), (b) and (c) for at least one minute at a temperature of between 10 and 45° C.; (2) introducing into the incubated mixture(i) Ca2+ or (ii) Ca2++exogenic activated protein C; and (3) determining the coagulation time (i) in the absence of activated protein C and (ii) in the presence of activated protein C. Steps (1) to (3) are repeated, but replacing, in step (1), the test specimen with a normal plasma as control and correlating resistance to activated protein C by comparing the determinations made in steps for the test specimen and for the normal plasma. The initiation of coagulation is caused by activating factor X to Xa using the venom of Crotalus viridis helleri in the presence of (i) Ca2+ or (ii) Ca2++ exogenic activated protein C.
Owner:DIAGNOSTICA STAGO SA
Cell growth regulating factor X and its prepn process
InactiveCN1506052APromote regenerationPromote repairOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal disorderFactor XArthritis
The present invention is one kind of natural cell growth regulating factor X and its preparation process. The preparation process includes screening Gram-positive coccus or bacillus and Gram-negative coccus or bacillus, freeze preserving coccus or bacillus strain, conventional culture of the coccus or bacillus strain at 4-38 deg.c, once filtering to eliminate harmful bacteria while leaving beneficial thallus segment, extracting natural gene, adding kudzu vine juice into the natural gene, safety test, preparing into solution or powder, and sealing. The cell growth regulating factor X has the functions of stimulating and strengthening immunity, strengthening TC, repairing and reforming necrotic, degenerative, atrophic, fibrillated and calcified histiocyte, regenerating capillary vessel, so that it can treat sclerotic arthritis and titanic rachitis and shape normal joint and skeleton.
Owner:谢旭明
Covalent factor VII-tissue factor complex
InactiveCN101466400ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue factorBlood coagulation factor VIII
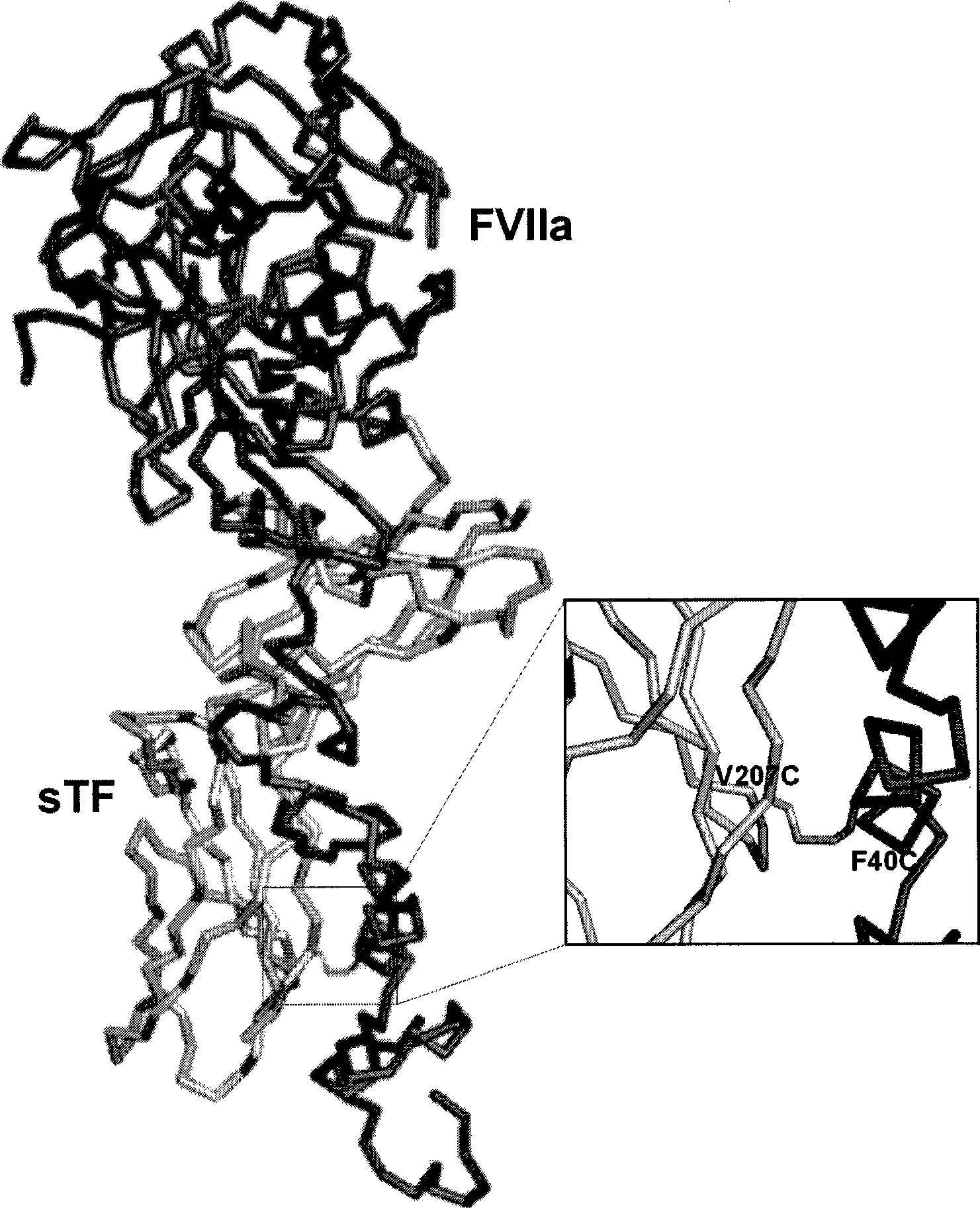
The present invention relates to novel covalent complexes of a Factor VII polypeptide and a Tissue Factor polypeptide, in particular to such complexes which are functionally active and which have an enhanced proteolytic activity towards Factor X compared to the corresponding free Factor VII polypeptide as well as methods for production of these novel complexes.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Lipid nanodiscs and nanorods as modulators of clotting factor function in vivo
InactiveUS20160367677A1High expressionStable and firmPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLipid formationFactor X
The present invention includes composition and methods of using a lipid nanodisk or nanotube composition comprising a lipid composition of phosphatidylserine and galactosylceramide and a membrane-bound Factor VIII protein, a membrane-bound Factor IX protein, a membrane-bound Factor VIII-Factor IX protein complex, or a membrane-bound Factor V-Factor X protein complex in or about the lipid nanodisks or nanotubes.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for preparing factor X, activated factor X, inactivated factor X and inactivated factor Xa, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising same
ActiveUS9956272B2Easy to separateHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor XAntibody Affinity Chromatography
Methods for preparing Factor X, activated Factor X, inactivated factor X and inactivated factor Xa, compositions comprising Factor X and Factor Xa, inactivated Factor X and inactivated Factor Xa and methods of medical treatment using Factor X, Factor Xa, activated Factor X and inactivated Factor Xa are disclosed. The preparation methods comprise a chromatography step using an immobilised metal ion affinity chromatography substrate.
Owner:BIO PRODUCTS LABORATORY
Compositions useful as fibrin sealants
InactiveCN1260720AInhibition of polymerizationReduce transmissionSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineFactor X
Novel fibrin monomer compositions which are solutions including additional coharvested components, such as prothrombin and Factor XIII, are useful in fibrin sealant applications. Preferably, the compositions are autologous to the patient receiving the sealant and these compositions may also include coharvested plasminogen, Factor X, antithrombin III and / or fibronectin.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
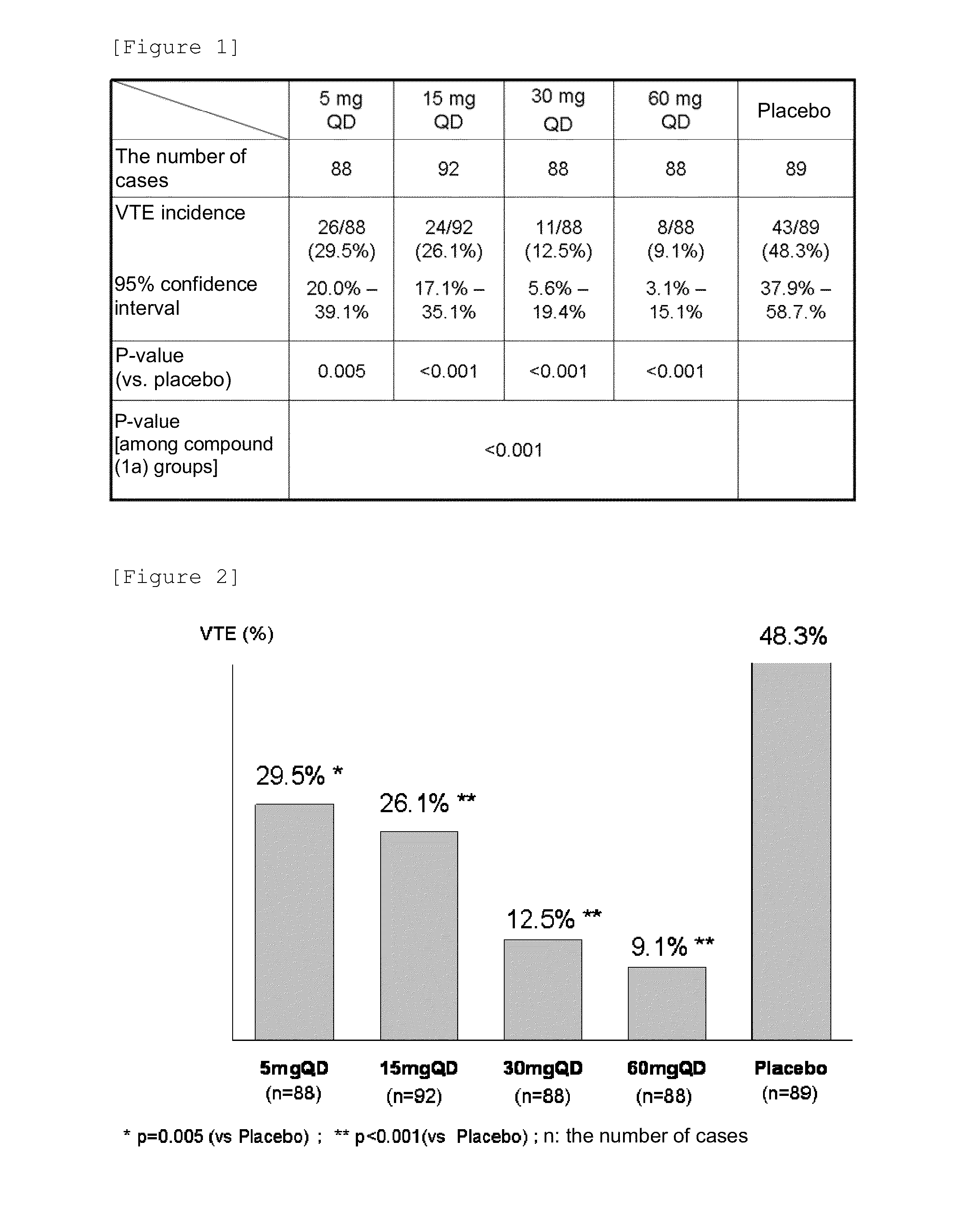
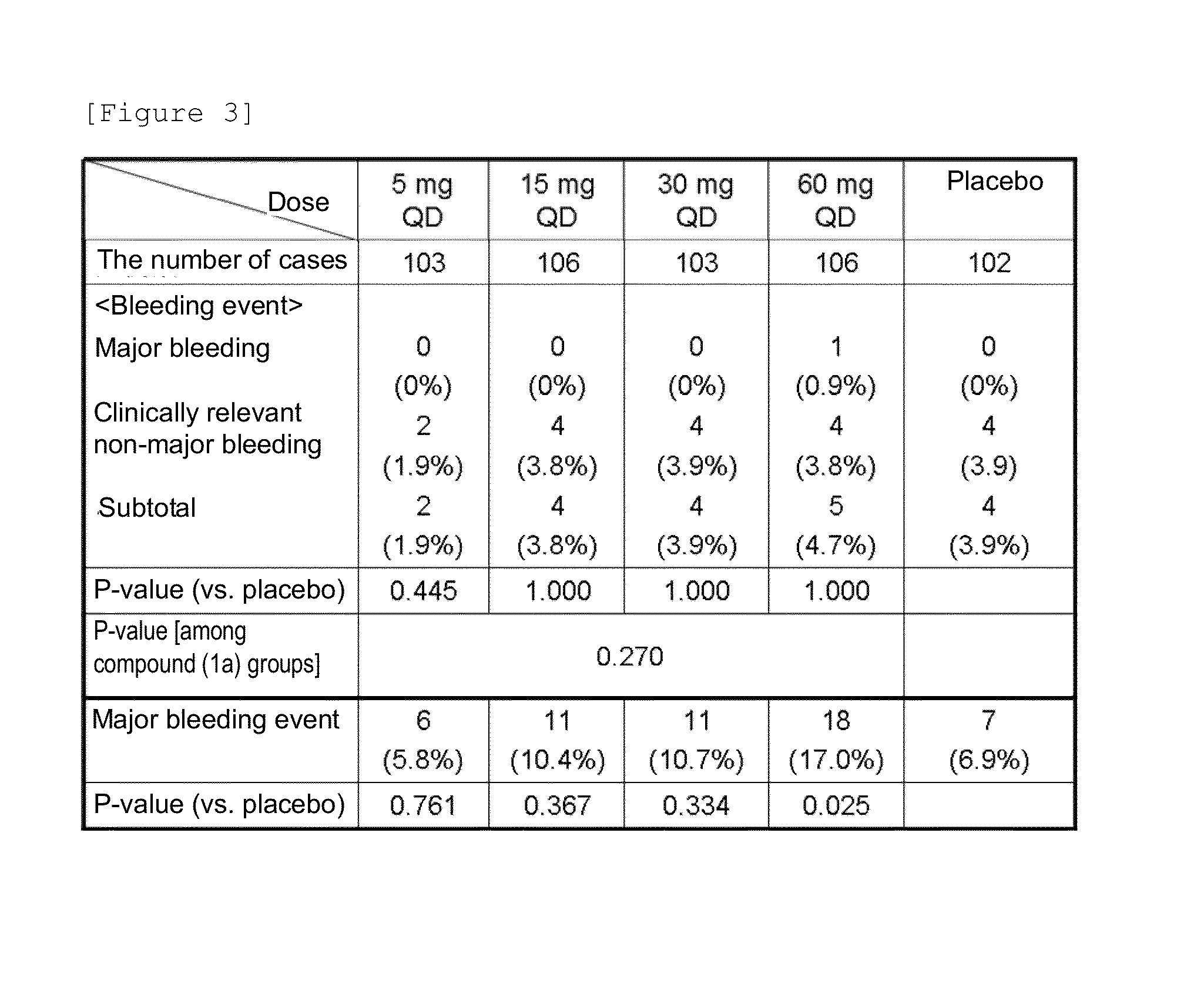
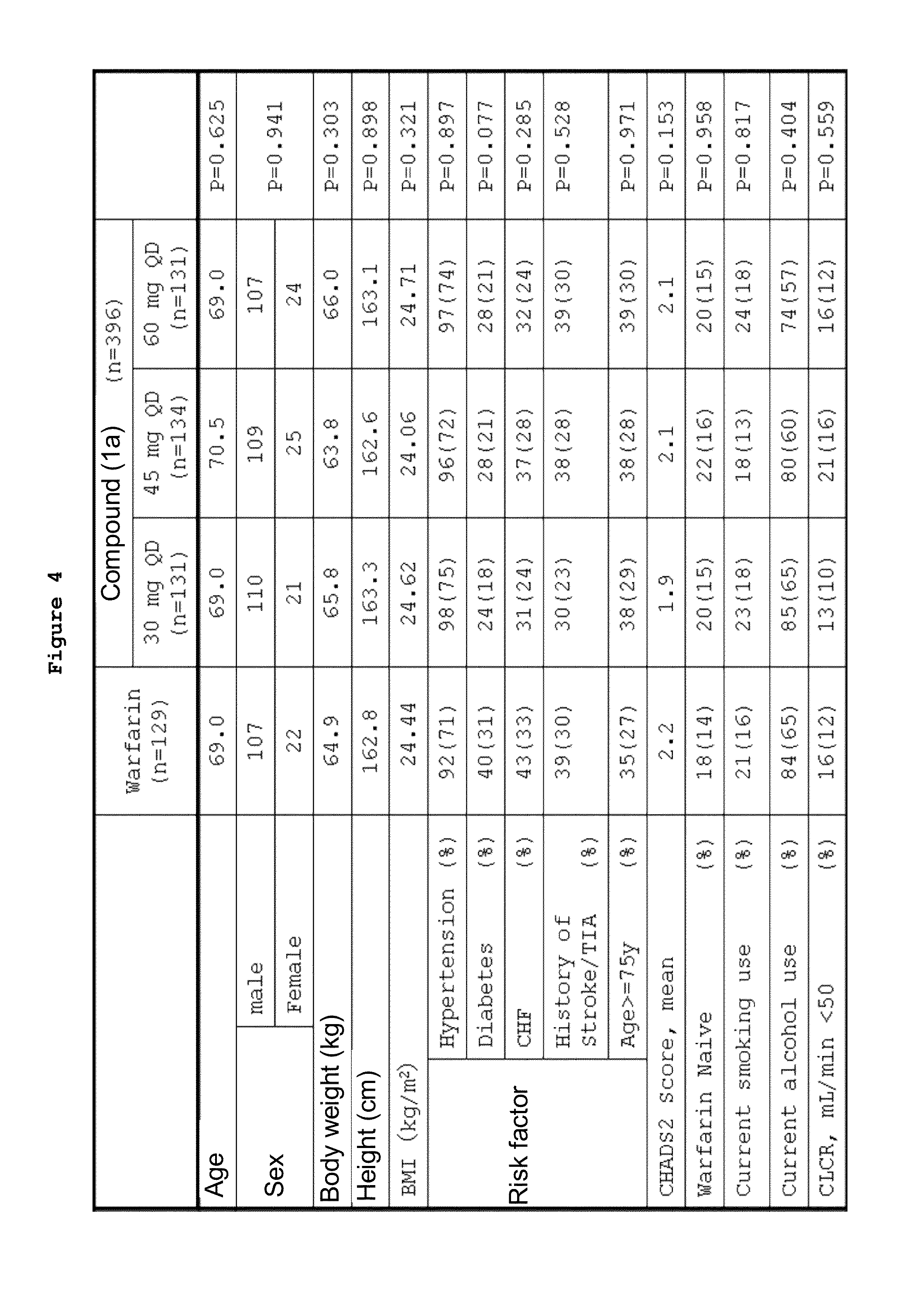
ACTIVATED BLOOD COAGULATION FACTOR X (FXa) INHIBITOR
InactiveUS20130184308A1Effective treatmentReduce riskBiocideOrganic chemistryAnticoagulant AgentBlood Coagulation Factor X
An object of the present invention is to provide an activated blood coagulation factor X (FXa) inhibitor that reduces the risk of bleeding caused by the treatment of thromboembolism. The present invention provides an oral anticoagulant agent comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1):or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, or a hydrate thereof, as an active ingredient, wherein (A) a factor involved in the risk of bleeding caused by the anticoagulant agent is selected as a dose determinant; (B) a reference value of the dose determinant is set; (C) the dose determinant of a patient in need of administration is measured; and (D) the dose of the anticoagulant agent is selected with the reference value as an index.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com