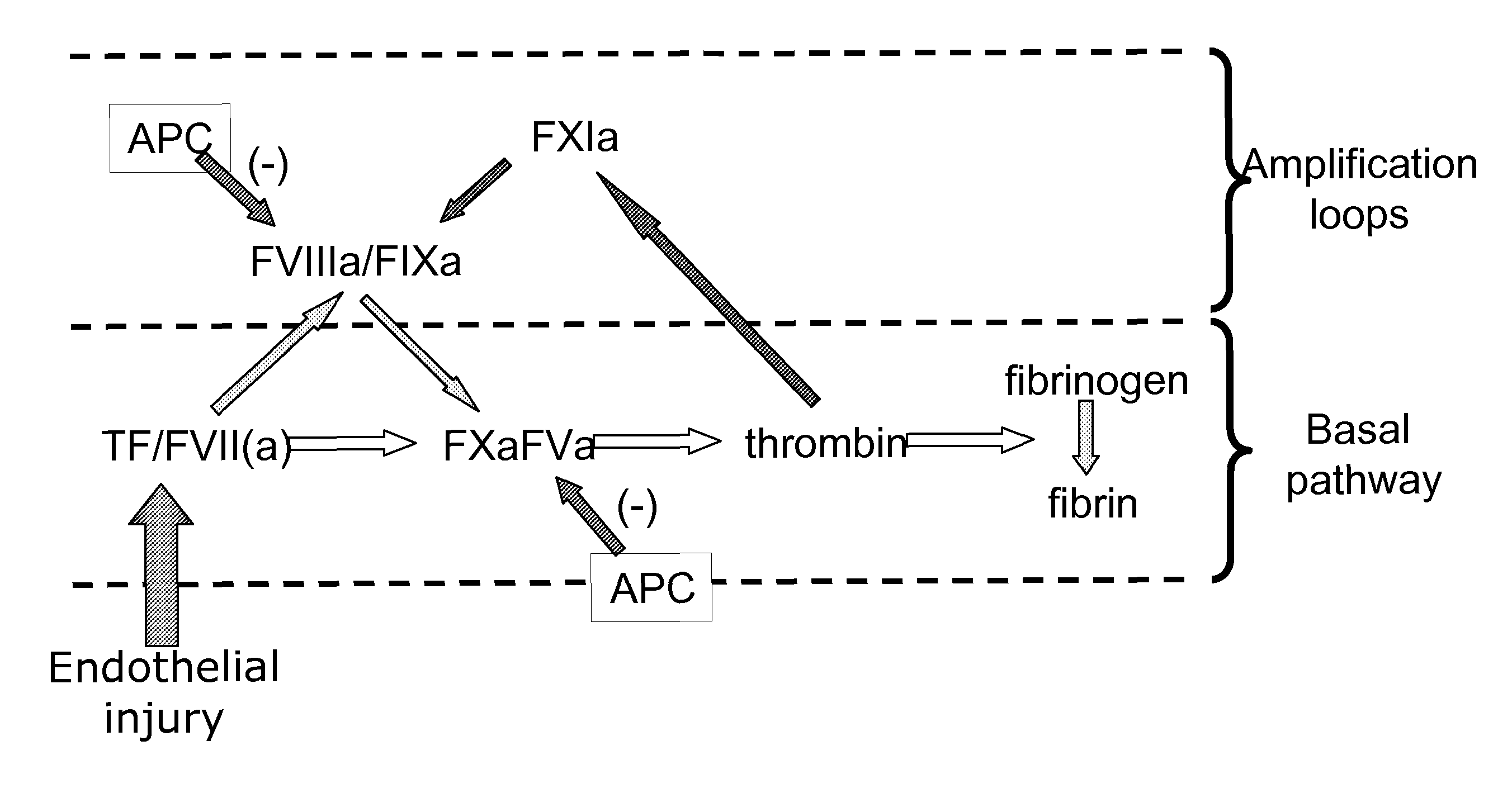
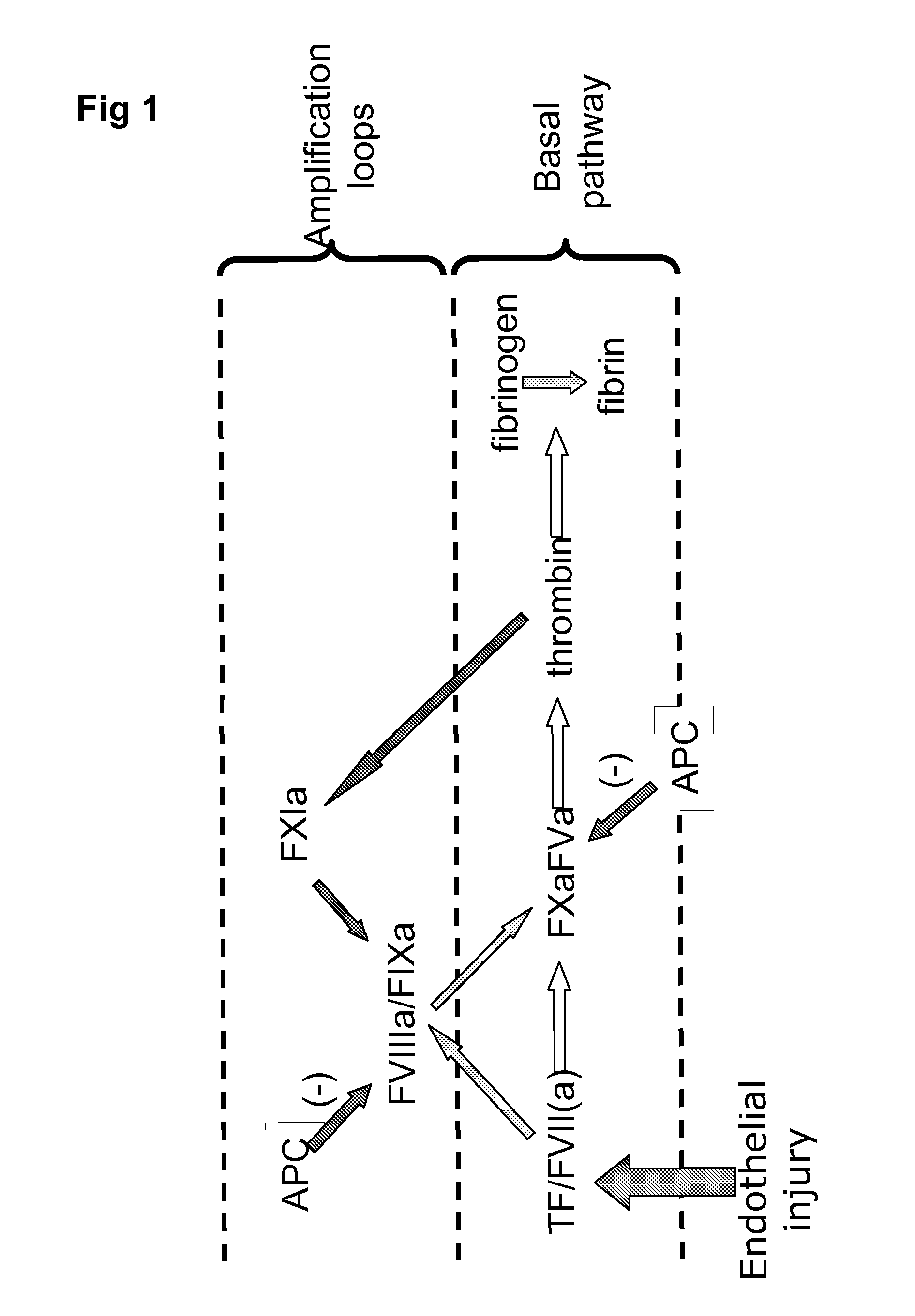
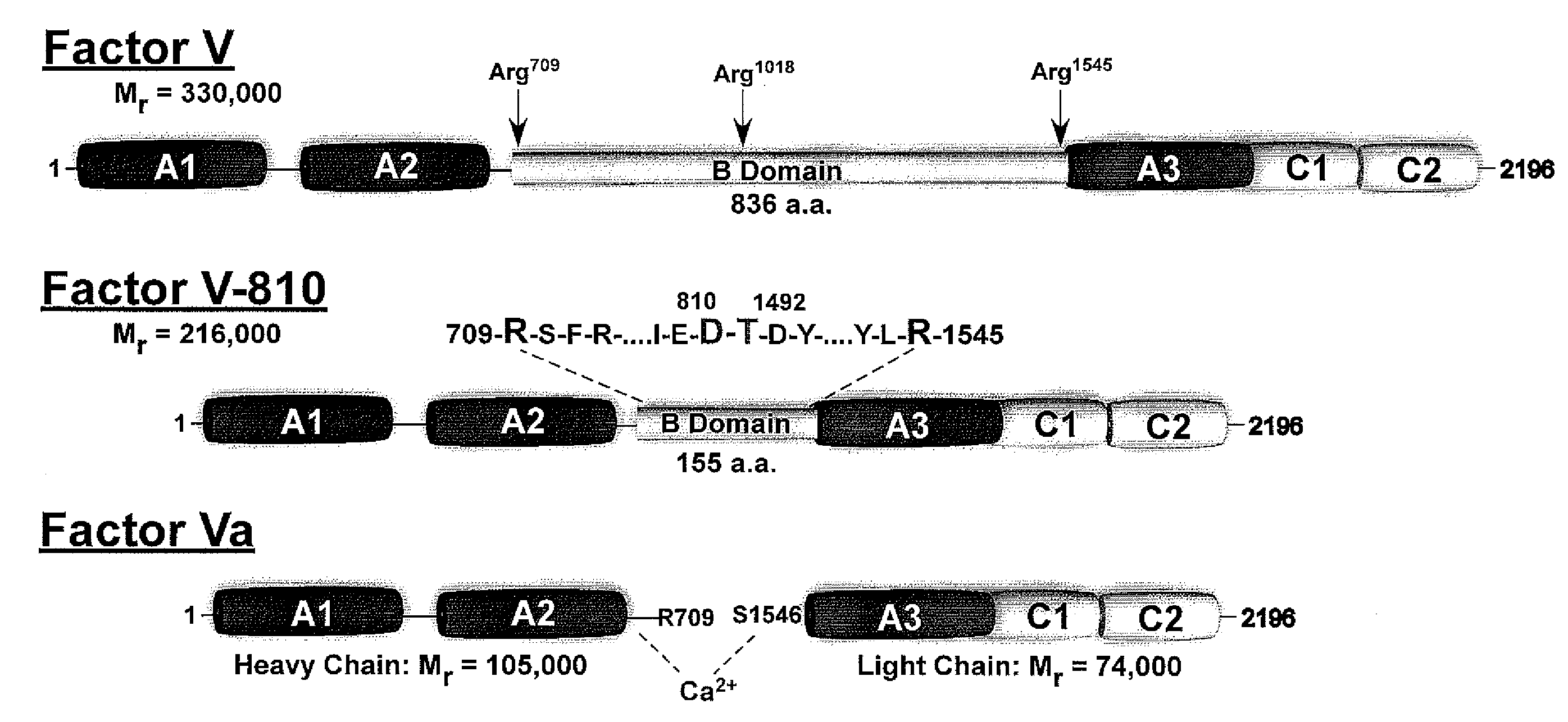
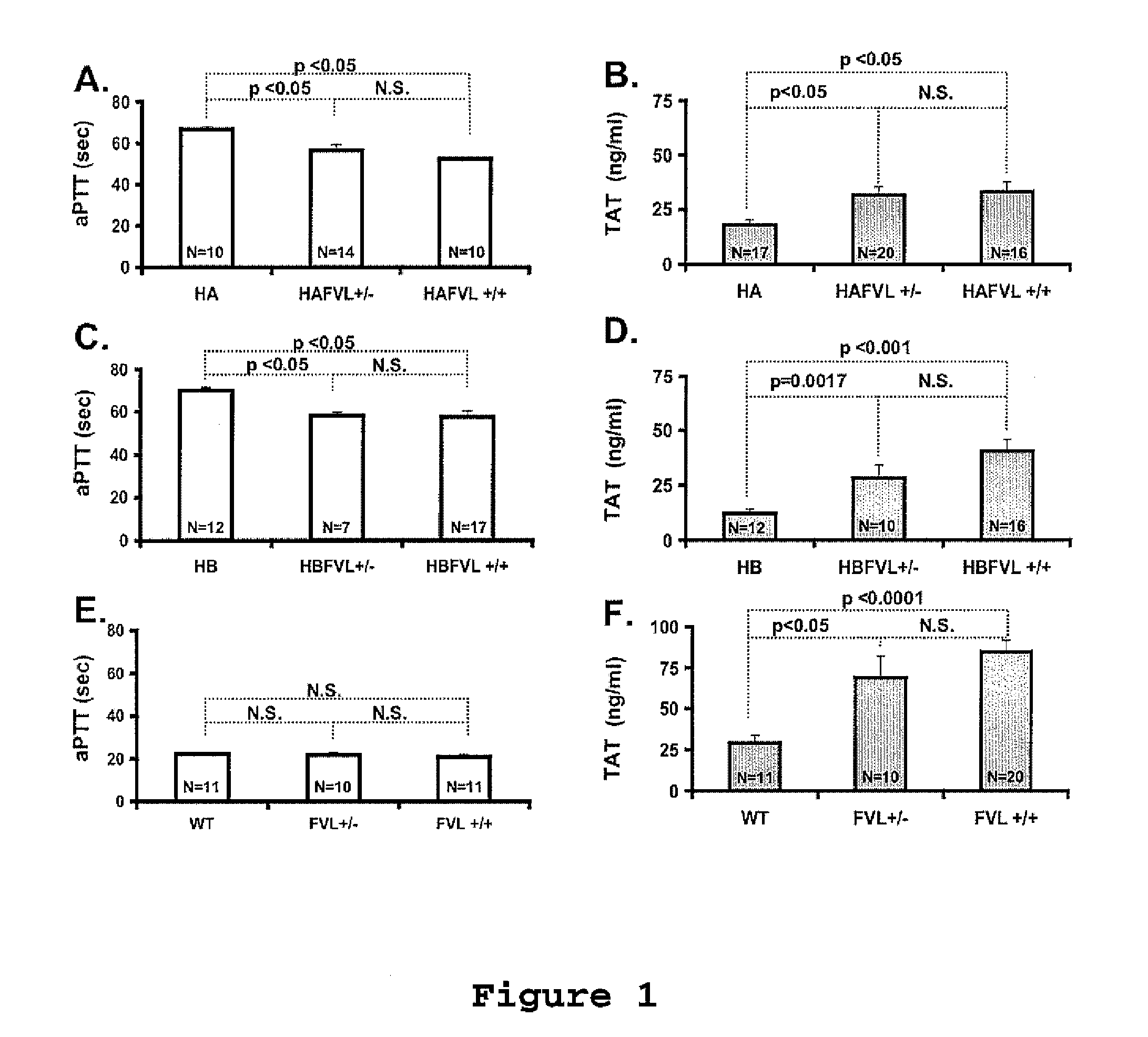
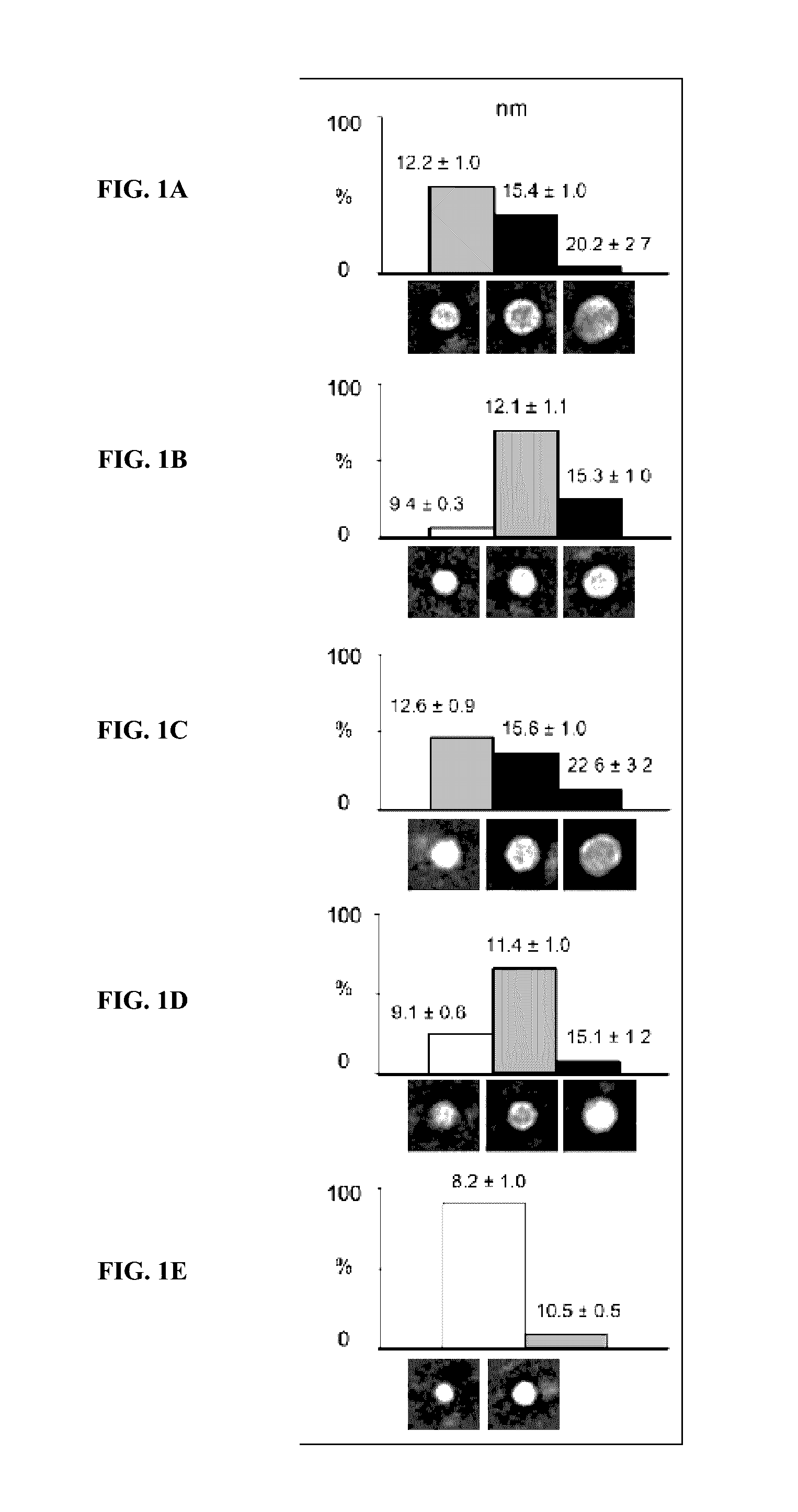
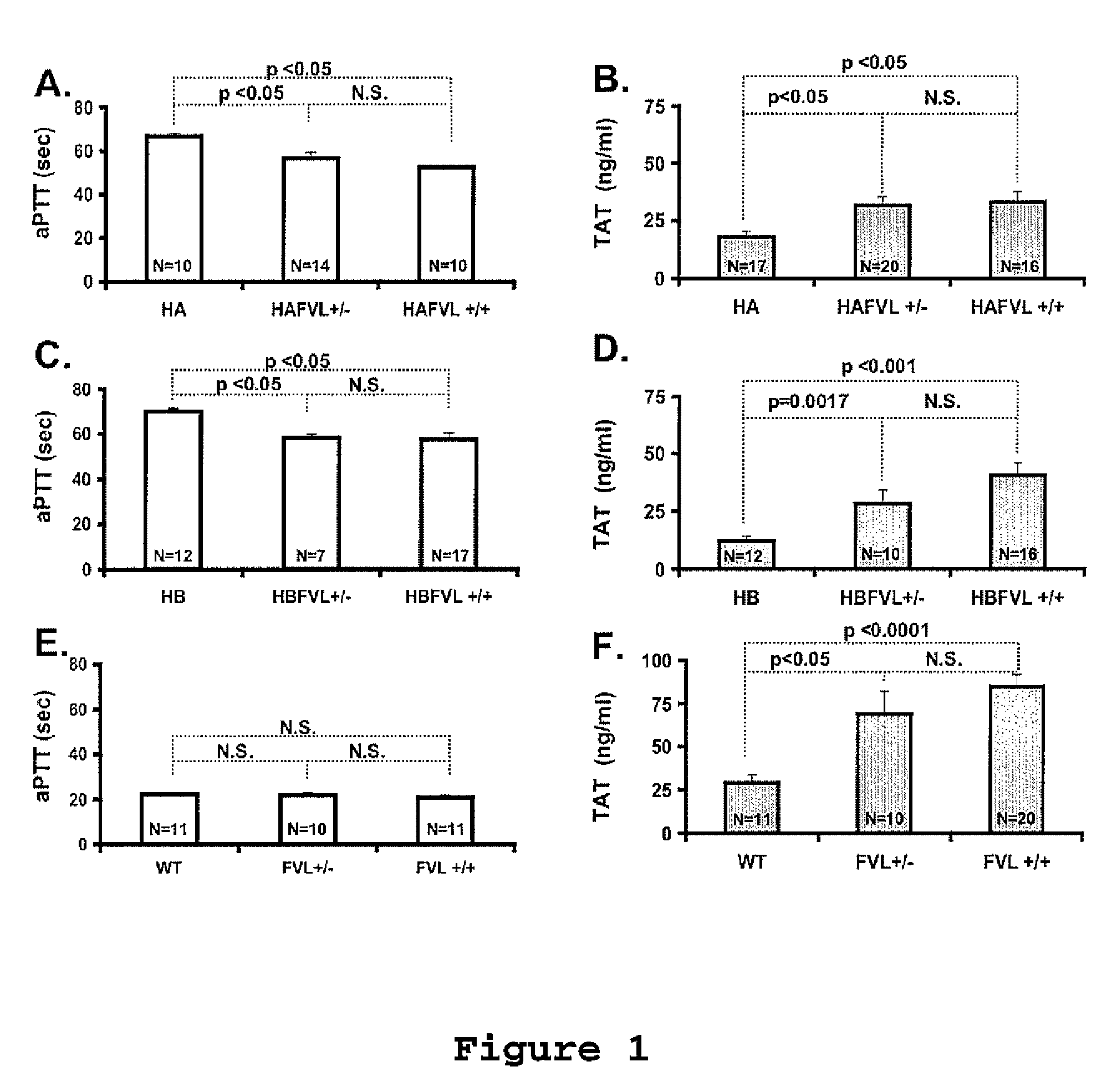
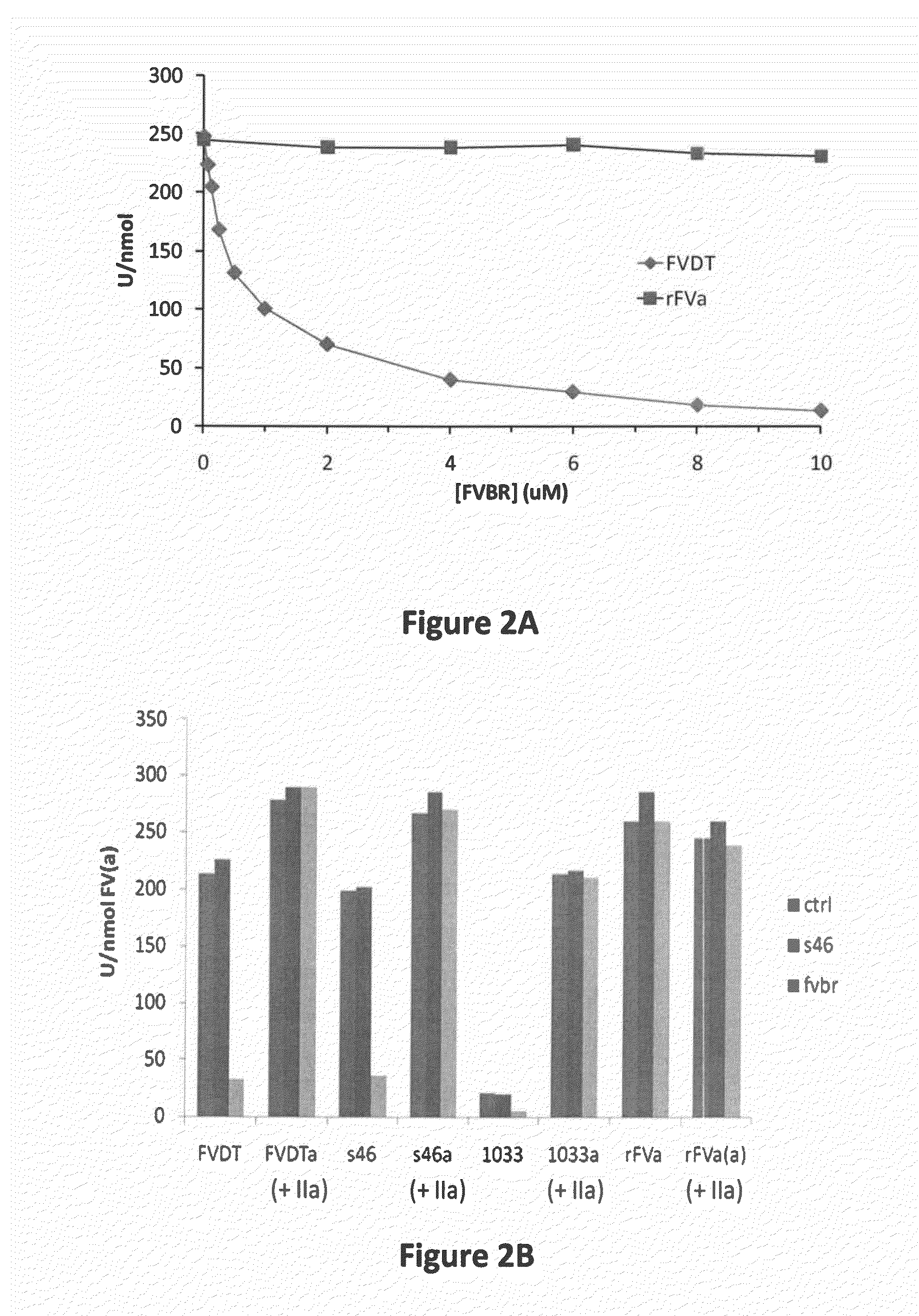
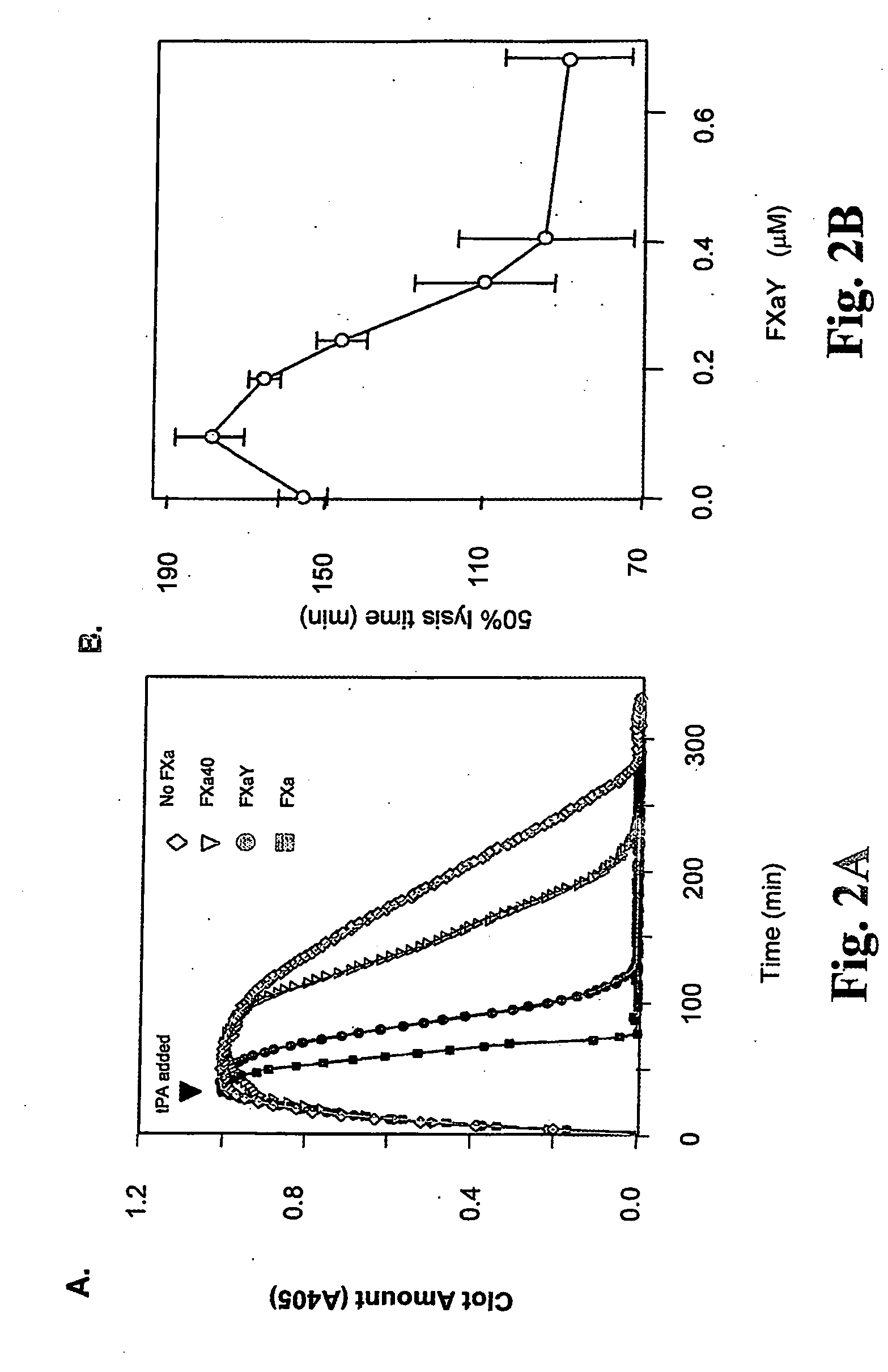
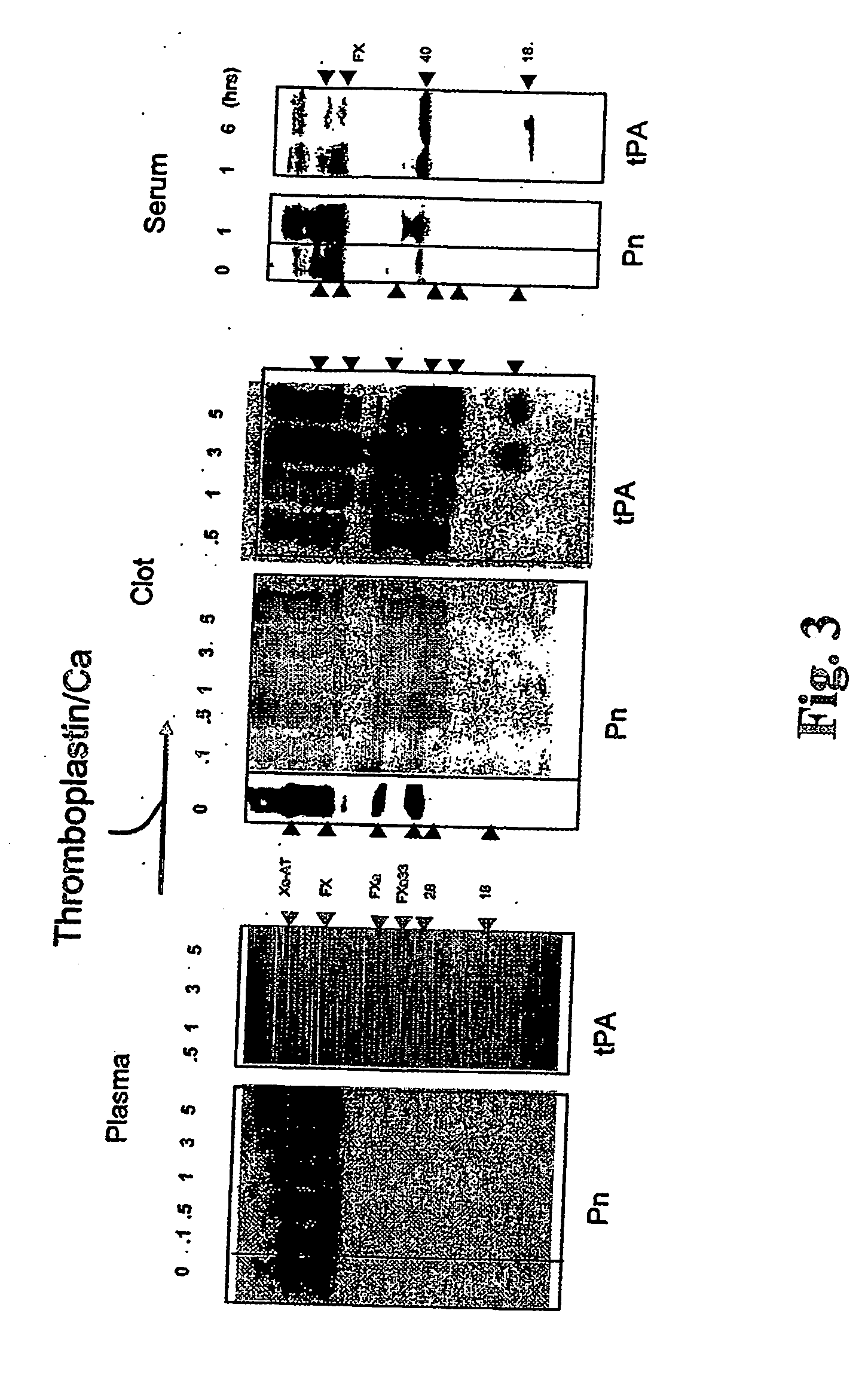
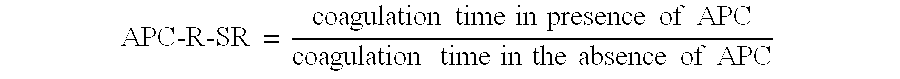Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Factor V" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
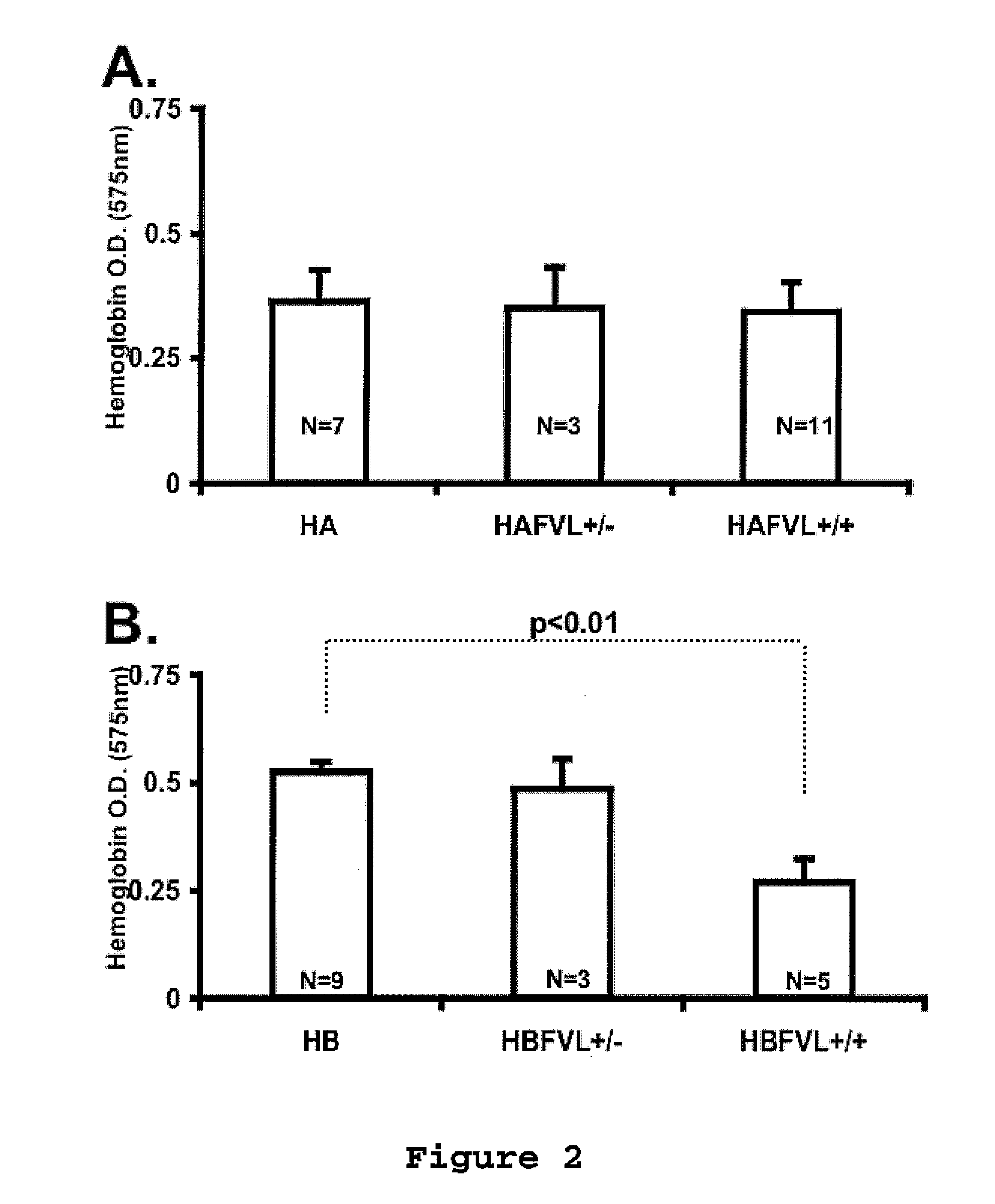
Factor V (pronounced factor five) is a protein of the coagulation system, rarely referred to as proaccelerin or labile factor. In contrast to most other coagulation factors, it is not enzymatically active but functions as a cofactor. Deficiency leads to predisposition for hemorrhage, while some mutations (most notably factor V Leiden) predispose for thrombosis.
Pharmaceutical composition comprising factor VII polypeptides and factor V polypeptides
InactiveUS7125846B2Improved and reliable and widely applicableGood coagulationPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFactor iiBleeding episodes
The present invention relates to a composition comprising factor VII or a factor VII-related polypeptide, and factor V or a factor V-related polypeptide, and the use thereof for treating bleeding episodes.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method for diagnosing an increased risk for thrombosis or a genetic defect causing thrombosis and kit for use with the same
InactiveUS6518016B1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsSugar derivativesBinding siteProtein activation
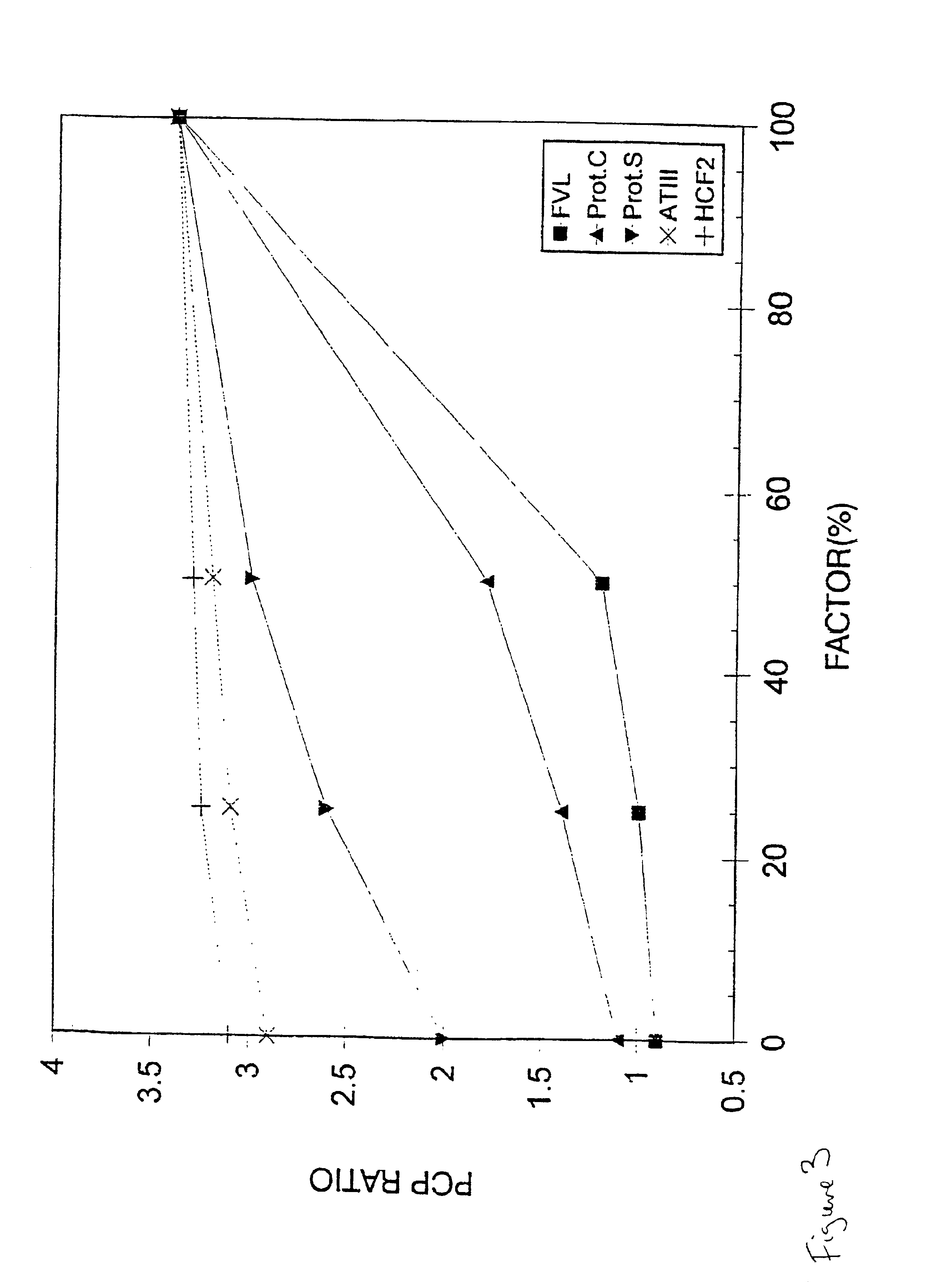
Method for screening for the presence of a genetic defect associated with thrombosis and / or poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C (APC). The method is directed at detecting one or more mutations at one or more of the cleavage and / or binding sites for APC of Factor V and / or Factor Va or at Factor VIII and / or Factor VIIIa at either nucleic acid or protein level or both.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
Complementation of factor xi deficeincy by factor v mutants
InactiveUS20100144620A1Restore clottingMeet growth requirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesHaemophilia CFactor XI
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Method for screening for the presence of genetic defect associated with thrombosis and/or poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C
InactiveUS6558913B1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsSugar derivativesBinding siteProtein activation
Method for screening for the presence of a genetic defect associated with thrombosis and / or poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C (APC). The method is directed at detecting one or more mutations at one or more of the cleavage and / or binding sites for APC of Factor V and / or Factor Va or at Factor VIII and / or Factor VIIIa at either nucleic acid or protein level or both.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
Stabilized proteins with engineered disulfide bonds
InactiveUS7205278B2High retention rateAvoidance of undesired activityOrganic active ingredientsFungiADAMTS ProteinsBlood plasma
The present invention relates to methods of introducing one or more cysteine residues into a polypeptide which permit the stabilization of the polypeptide by formation of at least one bond, preferably a disulfide bond, between different domains of the polypeptide. The invention also relates to polypeptides containing such introduced cysteine residue(s), nucleic acids encoding such polypeptides and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such polypeptides or nucleic acids. The invention also relates to vectors, viral particles and host cells containing such nucleic acids, and methods of using them to produce the polypeptides of the invention. Exemplified polypeptides include plasma proteins, including hepatocyte growth factor activator and plasma hyaluronin binding protein, as well as blood coagulation factors, such as Factor VIII, Factor V, Factor XII and prothrombin.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Compositions and methods for modulating hemostasis using variant forms of activated factor v
ActiveUS20090318344A1Minimal influenceModify the hemophilia phenotypeFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsCoagulation DisorderVariant form
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Stabilized Proteins with Engineered Disulfide Bonds
InactiveUS20070276128A1High retention rateAvoidance of undesired activityFactor VIIFungiCysteine thiolateBlood plasma
The present invention relates to methods of introducing one or more cysteine residues into a polypeptide which permit the stabilization of the polypeptide by formation of at least one bond, preferably a disulfide bond, between different domains of the polypeptide. The invention also relates to polypeptides containing such introduced cysteine residue(s), nucleic acids encoding such polypeptides and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such polypeptides or nucleic acids. The invention also relates to vectors, viral particles and host cells containing such nucleic acids, and methods of using them to produce the polypeptides of the invention. Exemplified polypeptides include plasma proteins, including hepatocyte growth factor activator and plasma hyaluronin binding protein, as well as blood coagulation factors, such as Factor VIII, Factor V, Factor XII and prothrombin.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for determining the coagulation potential of a plasma sample
InactiveUS6838251B1Enhanced interactionShorten clotting timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFactor XProtein activation
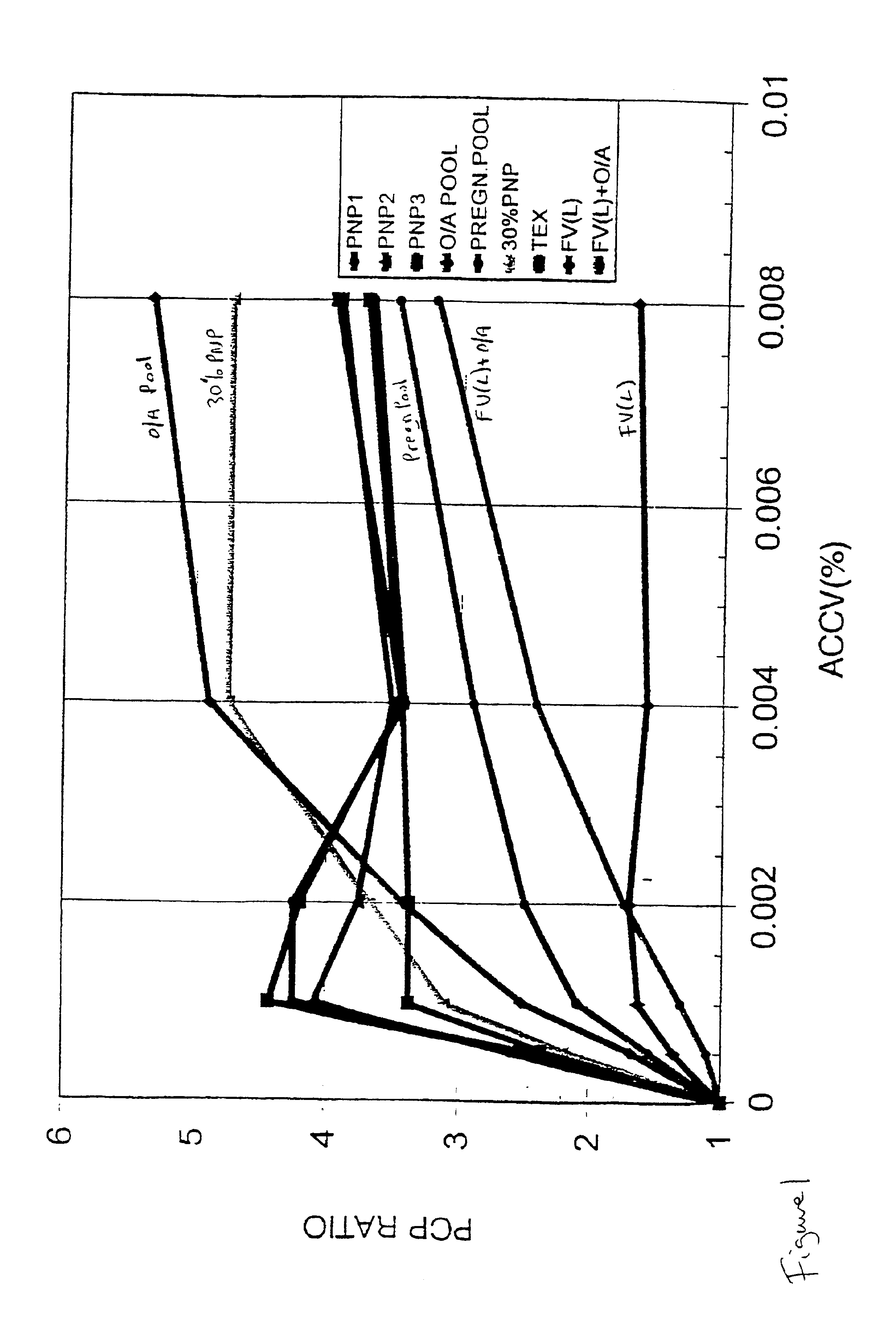
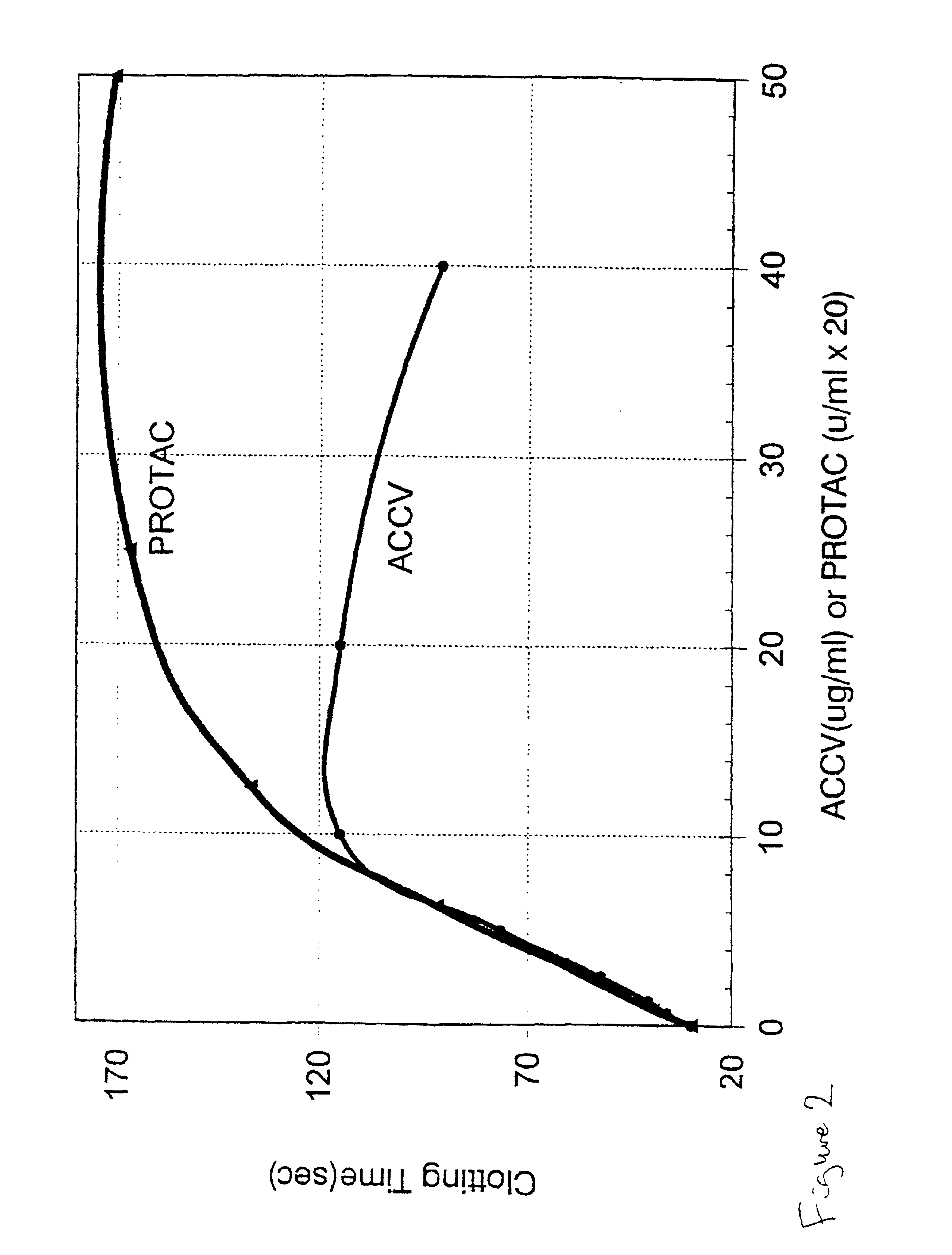
A method of determining the coagulation potential of a plasma sample be pre-incubating the plasma sample with a reagent such that endogenous protein C in the plasma is at least partially converted into activated protein C by the reagent, adding factor Xa which is progressively inactivated by antithrombin III / heparin cofactor 2 during the preincubation, adding an exogenous reagent which activates factor X to Xa or prothrombin to thrombin in a factor V-dependent manner, monitoring a reaction indicative of the rate of coagulation of the plasma sample, comparing that rate of coagulation control, or the equivalent rate determined for an individual without impaired coagulation control, or the equivalent rate determined for the plasma sample in the absence of protein C activator, and determining the coagulation potential of the plasma sample from one or other of the compairsons.
Owner:STAGO
Hematological assay
InactiveUS6994984B2Reduce the impactMinimize dependenciesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhospholipidMutant
A hematological assay is described in which the blood coagulation potential of a body fluid is assessed by reacting a sample of the body fluid with an amount of an activator reagent comprising: (a) a predetermined amount of factor Xa or a hematologically equivalent mutant thereof, and (b) a predetermined amount of factor Va, a hematologically equivalent mutant thereof or an enzyme activating endogenous factor V, (c) (optionally) phospholipids. The reagent may be dry (e.g. lyophilised) or in an aqueous solution preferably buffered to a pH from 6 to 10 (preferably 7 to 8), if desired incubating, if necessary inducing coagulation by the addition of one or more coagulation accelerants such as calcium chloride, and establishing a value indicative of the coagulation potential, e.g. by measuring the time to clotting on an optical coagulometer or through use of a chromogenic substrate. It is preferred to use at (b) factor V activator from purified Russell's Viper venom (RVV-V). An activator reagent is also described containing the components mentioned above preferably in one or more buffer solutions or in dried, e.g. lyophilised form.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Coagulation proteins, coagulation-anticoagulation protein complexes, derivatives thereof and their uses
InactiveUS20070025979A1Enhance dissolving said blood clotHigh dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsFibrinogenSide effectFactor X
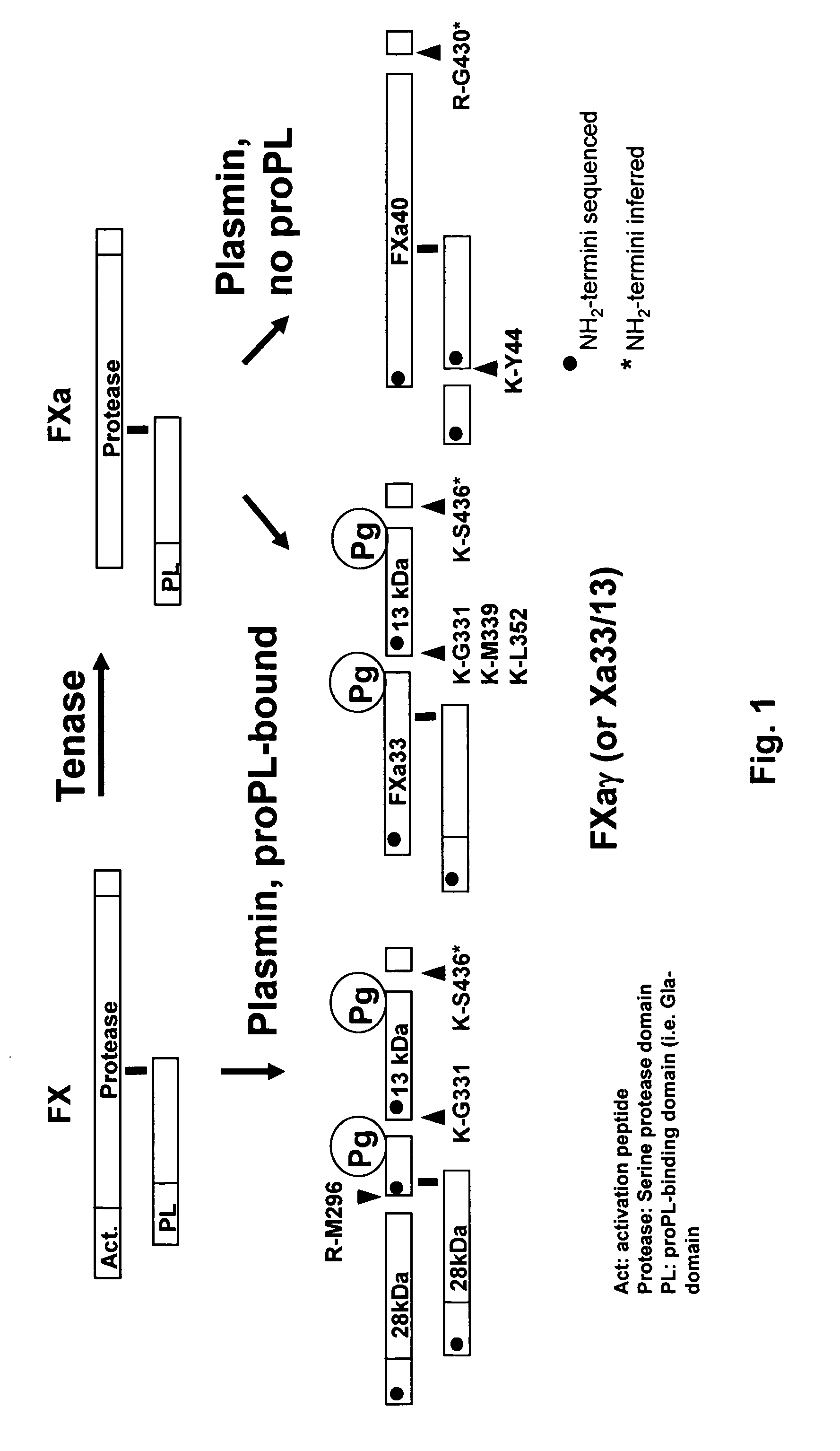
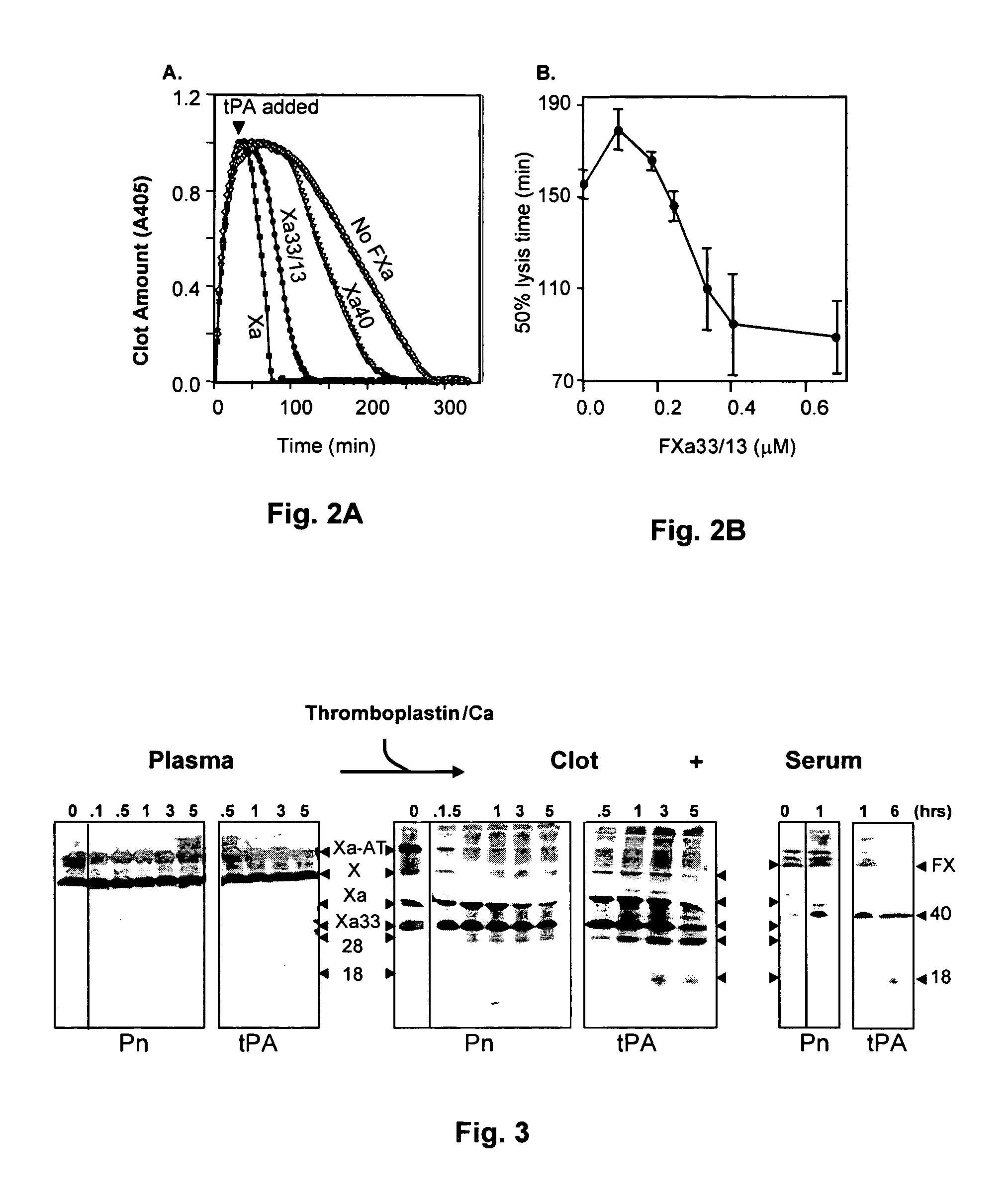
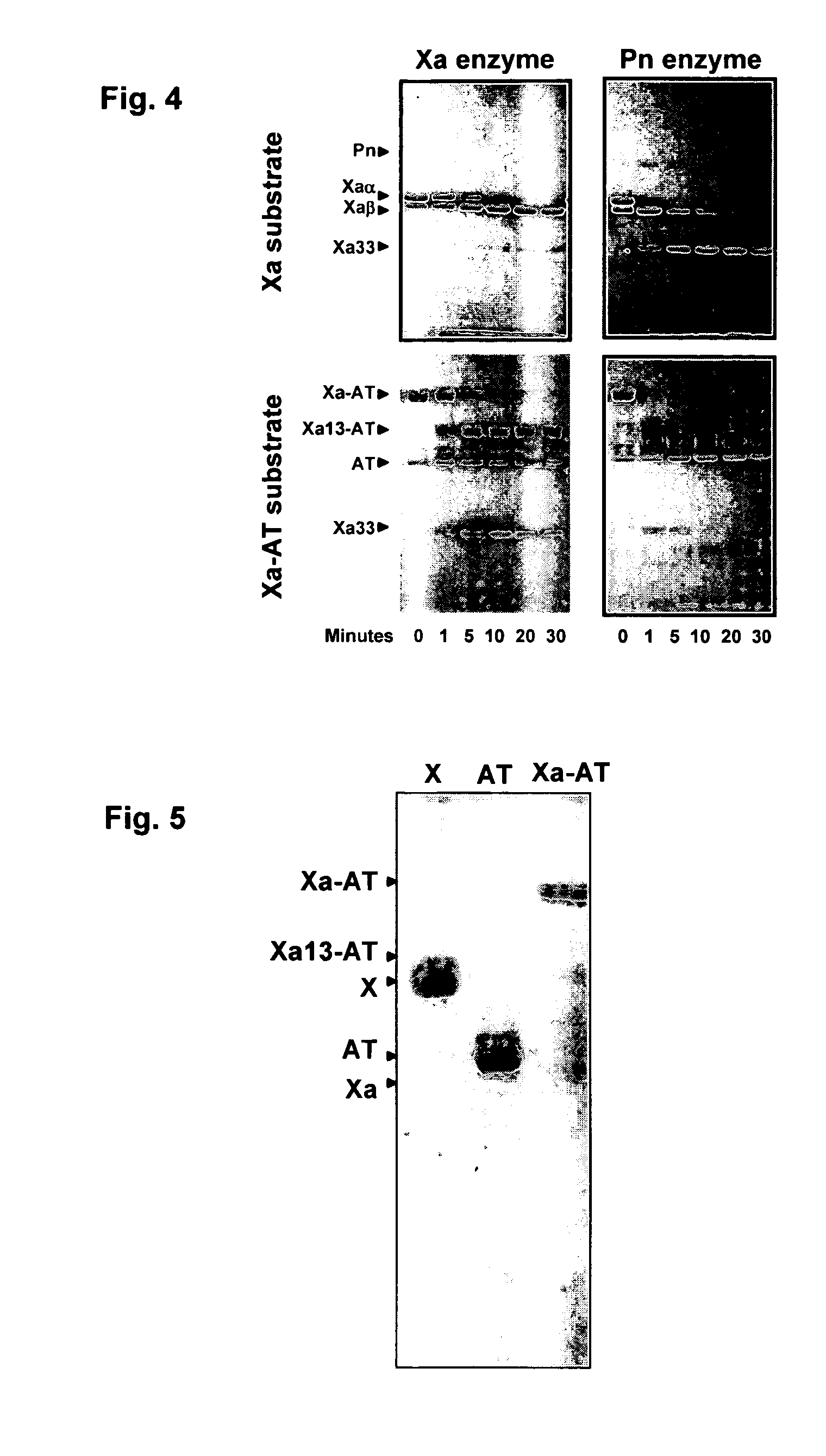
The present invention relates to the use of coagulation proteins and complexes thereof with anticoagulation proteins for the lysis of blood clots or other applications affected by accelerated plasmin production. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for accelerating the dissolution of a blood clot through the administration of at least one coagulation protein, with or without being in complex with a serpin, comprising a basic C-terminal amino acid, wherein the coagulation protein may be a derivative of Factor X or Factor V or a combination thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and prophylaxis of blood clots are also provided, wherein, the methods and products of the present invention advantageously accelerate clot dissolution while potentially minimizing the adverse side-effects, such as hemorrhaging, seen with other clot dissolving agents. The present invention also provides a method for detecting a fibrinolytic potential in a subject.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Method evolved for recognition of thrombophilia (MERT)
Methods for predicting an individual's genetic risk for developing venous thrombosis in diverse ethnic populations is disclosed, as are arrays and kits which can be used to practice the method. The method includes screening for mutations, polymorphisms, or both, in at least eight venous thrombosis-related molecules, such as antithrombin III, protein C, protein S, fibrinogen, factor V, prothrombin (factor II), methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) molecules which are associated with venous thrombosis.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Dry heat processing stabilizer for prothrombin complex or factor v a IX preparation
InactiveCN100482272CLittle loss of activityAvoid damagePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsZymogenArginine
The invention relates to a stabilizing agent for preventing blood clotting factor reactive loss for prothrombin composite or blood clotting factor IX preparation during virus animatum eradication by dry heat, wherein the stabilizing agent is sucrose or / and arginine or its salt, it also can contain one or more of the conventional glycine, NaCl, citric acid trisodium and hamocura.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINXING MEDICINE
Method for diagnosis of thrombotic disorders
InactiveUS6867045B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisReference sampleTest sample
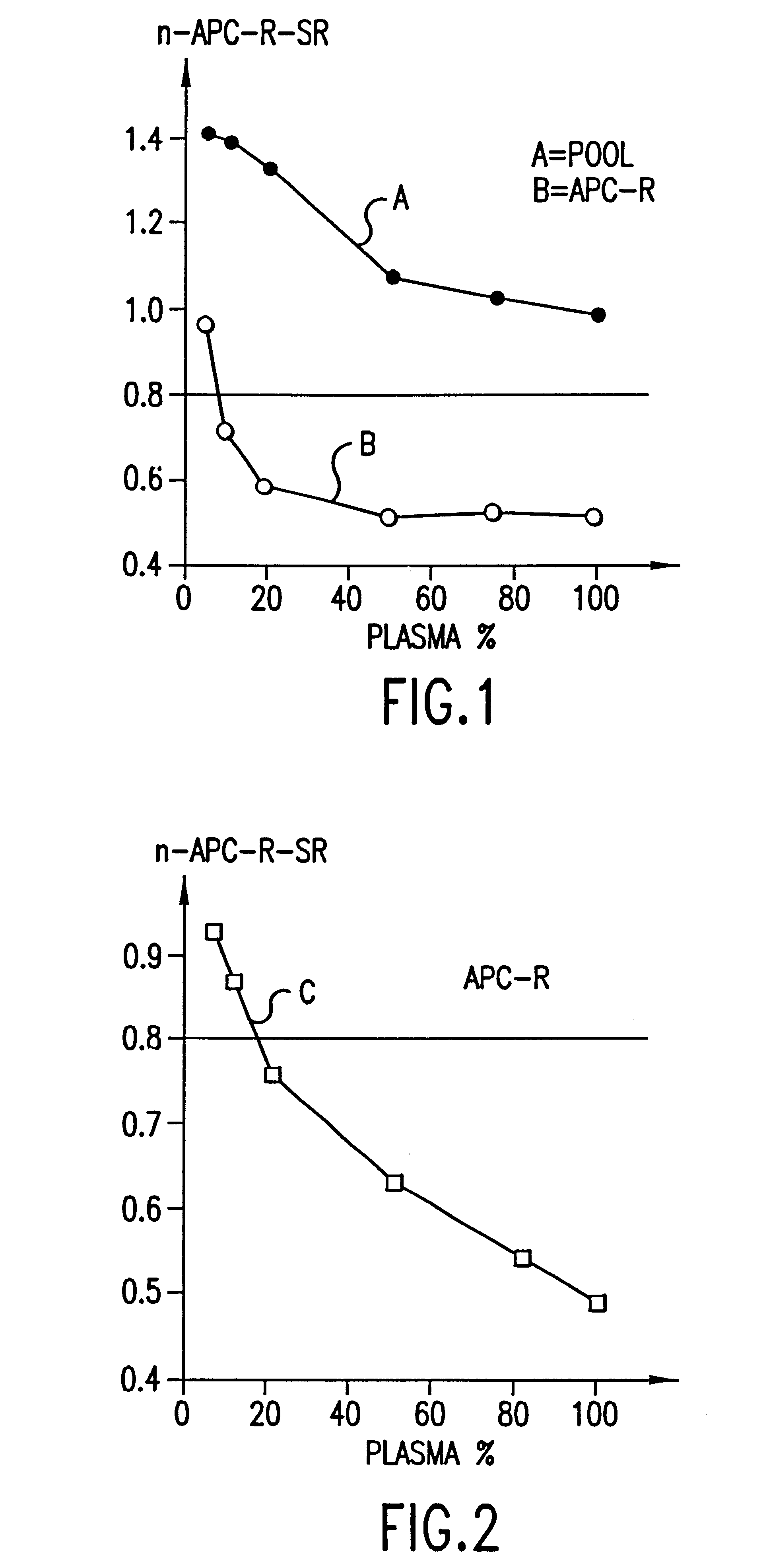
The present invention provides an in vitro method useful for the diagnosis of a thrombotic disorder in a subject, having or at risk of having the disorder. Specifically, the disorder exemplified herein is associated with APC resistant Factor V and Va. The clotting time of a test sample is analyzed in the presence and absence of APC and compared with a standard reference sample in order to diagnose the subject.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Process for determining a resistance to activated protein C
InactiveUS6251619B1Reduce in quantityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPrairie rattlesnakeFactor X
A process for determining a resistance to activated protein C of a test specimen of human plasma following the steps of: (1) mixing together (a) the test specimen of human plasma, (b) a reactant deficient in factor V which supplies at least most of the coagulation factors other than factor V, and (c) the venom of Crotalus viridis helleri which specifically activates factor X to Xa, and incubating the mixture of (a), (b) and (c) for at least one minute at a temperature of between 10 and 45° C.; (2) introducing into the incubated mixture(i) Ca2+ or (ii) Ca2++exogenic activated protein C; and (3) determining the coagulation time (i) in the absence of activated protein C and (ii) in the presence of activated protein C. Steps (1) to (3) are repeated, but replacing, in step (1), the test specimen with a normal plasma as control and correlating resistance to activated protein C by comparing the determinations made in steps for the test specimen and for the normal plasma. The initiation of coagulation is caused by activating factor X to Xa using the venom of Crotalus viridis helleri in the presence of (i) Ca2+ or (ii) Ca2++ exogenic activated protein C.
Owner:DIAGNOSTICA STAGO SA
Method for diagnosis of thrombotic disorders
InactiveUS20050260696A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisReference sampleTest sample
The present invention provides an in vitro method useful for the diagnosis of a thrombotic disorder in a subject, having or at risk of having the disorder. Specifically, the disorder exemplified herein is associated with APC resistant Factor V and Va. The clotting time of a test sample is analyzed in the presence and absence of APC and compared with a standard reference sample in order to diagnose the subject.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST & RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of Inactivating Blood Coagulation Factor and Blood Coagulation Factor-Inactivated Sample
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Lipid nanodiscs and nanorods as modulators of clotting factor function in vivo
InactiveUS20160367677A1High expressionStable and firmPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLipid formationFactor X
The present invention includes composition and methods of using a lipid nanodisk or nanotube composition comprising a lipid composition of phosphatidylserine and galactosylceramide and a membrane-bound Factor VIII protein, a membrane-bound Factor IX protein, a membrane-bound Factor VIII-Factor IX protein complex, or a membrane-bound Factor V-Factor X protein complex in or about the lipid nanodisks or nanotubes.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Haemophilus culture medium and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104120094AEffectively cededFull of nutritionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHaemophilusHaemophilus influenzae
The invention provides a haemophilus culture medium and a preparation method thereof. The haemophilus culture medium comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.3-3% of Columbia agar, 0.001-0.003% of X factor, 0.001-0.003% of Y factor and 0.0005-0.002% of bacitracin disk antibacterial agent, and the culture medium is prepared by heating and mixing the components; the culture medium is rich in nutrition, the consistency of culture capacity is high, the growth of bacteria is easily observed, by maintaining the normal activity of the factor V and factor X under specific conditions, Haemophilus influenzae grows stably, the culture medium has strong anti-bacterial capability, the haemophilus can be effectively separated, the cost is greatly reduced, the direct cost is equivalent to only about 30% of that of foreign modified chocolate agar; and the preparation method is simple and suitable for the requirement on large-scale industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN CHUANHE MEDICAL TECH
Factor VóÄa inhibitor
The present invention relates to novel inhibitors of Factors VIIa, IXa, Xa, XIa, in particular Factor VIIa, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these inhibitors, and methods for using these inhibitors for treating or preventing thromboembolic disorders, cancer or rheumatoid arthritis. Processes for preparing these inhibitors are also disclosed.
Owner:ファーマサイクリックス リミティド ライアビリティ カンパニー
Methods for treating a hemostasis related disorder using activated forms of Factor V
ActiveUS8236764B2Modify the hemophilia phenotypeMinimal influenceFactor VIISugar derivativesDiseaseCoagulation Disorder
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Pharmaceutical composition comprising factor vii polypeptides and factor v polypeptides
InactiveCN1596125AShorten the setting timePeptide/protein ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyFactor iiBleeding episodes
The present invention relates to a composition comprising factor VII or a factor VII-related polypeptide, and factor V or a factor V-related polypeptide, and the use thereof for treating bleeding episodes, such as for reducing clotting time, enhancing haemostasis or increasing the clot strength.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Therapeutics for trauma induced factor v consumptive coagulopathy
InactiveUS20120065137A1Reduces severity and propensityHigh strengthPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesConsumptive CoagulopathyFactor V
A process of treating trauma induced factor V consumptive coagulopathy is presented whereby a subject is administered a preparation of isolated factor V or a variant thereof. Administration of factor V surprisingly improves clot times and reduces the severity and propensity of bleeding events.
Owner:JENNY RICHARD +1
Compositions and Methods for Modulating Hemostasis Using Variant Forms of Activated Factor V
ActiveUS20120288895A1Modify the hemophilia phenotypeMinimal influenceFactor VIIFungiCoagulation DisorderBiochemistry
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
FACTOR V/Va-TARGETING APTAMER COMPOSITONS AND METHODS OF USING THE SAME
ActiveUS20170355992A1Prevent thrombosisActivity regulationDNA/RNA fragmentationCancer researchFactor V
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Compositions and Methods for Modulating Thrombin Generation
ActiveUS20140221291A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsThrombin generationPeptide
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Use of coagulation proteins to lyse clots
InactiveUS20060275277A1Enhance dissolving said blood clotHigh dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectLysis
The present invention relates to the use of coagulation proteins for the lysis of blood clots. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for accelerating the dissolution of a blood clot through the administration of at least one coagulation protein comprising a basic C-terminal amino acid, wherein the coagulation protein may be a derivative of Factor X or Factor V or a combination thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and prophylaxis of blood clots are also provided, wherein, the methods and products of the present invention advantageously accelerate clot dissolution while potentially minimizing the adverse side-effects, such as hemorrhaging, seen with other clot dissolving agents. The present invention also provides a method for detecting a fibrinolytic potential in a subject.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Cell growth regulating factor V and its prepn process
InactiveCN1506075AEnhance immune functionGood effectOrganic active ingredientsBird material medical ingredientsHistiocyteDuodenal mucous membrane
The present invention is one kind of natural cell growth regulating factor V and its preparation process. The preparation process includes screening Gram-positive coccus or bacillus and Gram-negative coccus or bacillus, freeze preserving coccus or bacillus strain, conventional culture of the coccus or bacillus strain at 4-38 deg.c, once filtering to eliminate harmful bacteria while leaving beneficial thallus segment, extracting natural gene, adding alanine into the natural gene, safety test, preparing into solution or powder, and sealing. The cell growth regulating factor V has the functions of stimulating and strengthening immunity, strengthening TC, repairing and reforming necrotic, degenerative, atrophic, fibrillated and calcified pancreatic histiocyte, regenerating capillary vessel, so that it can repair and reform gastric and duodenal mucous membrane tissues.
Owner:谢旭明
Chocolate agar plate and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of culture media, in particular to a chocolate agar plate, which is more comprehensive in nutrition and capable of effectively promoting growth of corresponding bacteria and increasing the separation rate of the corresponding bacteria. According to a preparation method of the chocolate agar plate, after a culture solution is subjected to high-temperature sterilization, a mixed solution is subjected to heating hemolysis, so that a factor V and a factor X in red blood cells are released. During heating, the substance is heated for a short time at a relatively high temperature to promote rapid rupture of cell walls, and then is continuously heated at a slightly low temperature, so that other nutrient substances are prevented from being destroyed byhigh temperature while substances in red blood cells are fully released. The preparation method is simple to operate, has low requirements on equipment, can effectively improve the product quality, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:中秀科技股份有限公司
Compositions and methods for modulating thrombin generation
ActiveUS9321826B2Peptide/protein ingredientsFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingThrombin generationPeptide
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com