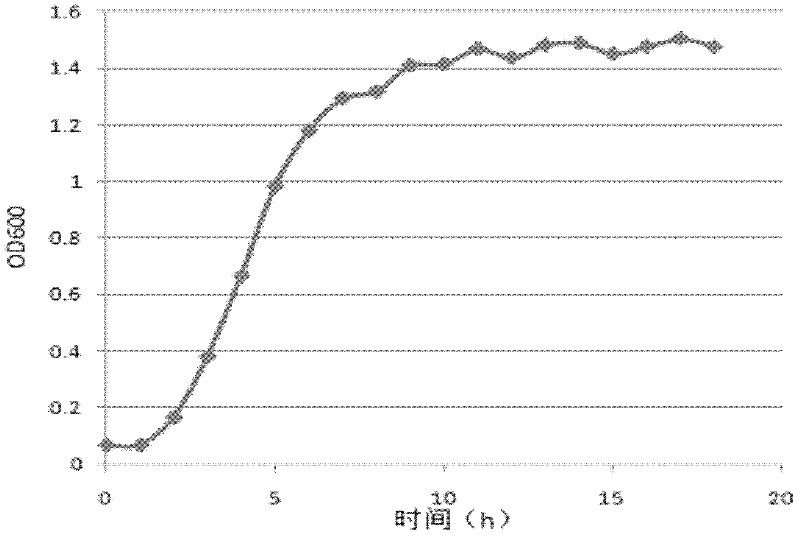
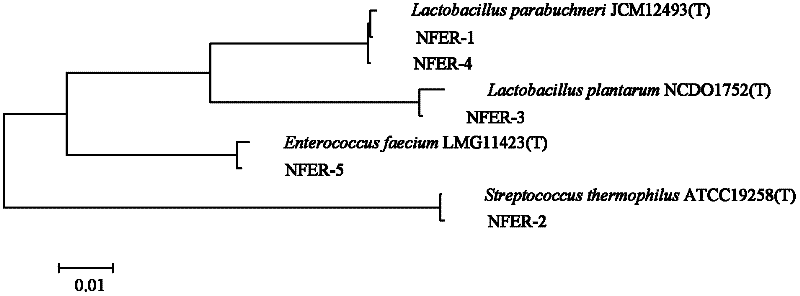
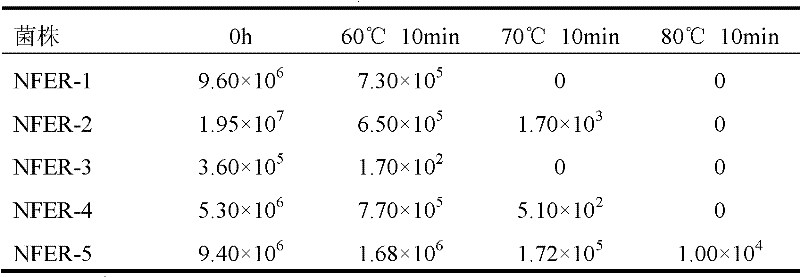
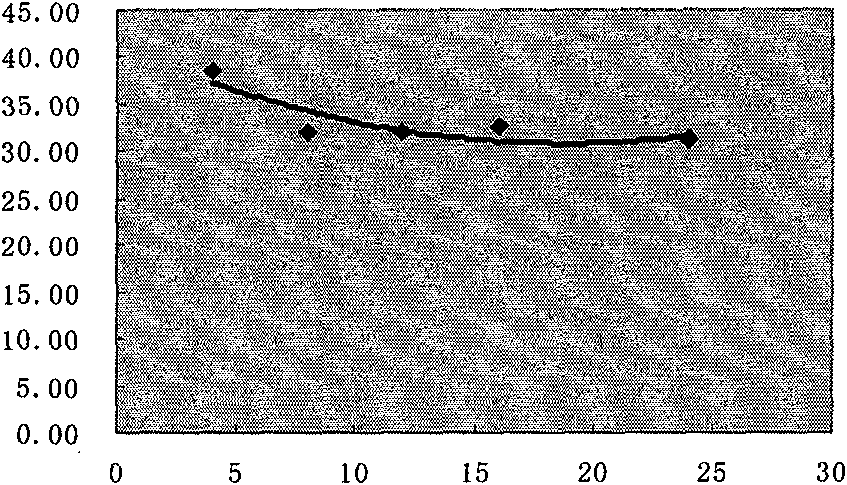
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Enterococcus avium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enterococcus avium, a species of Enterococcus, is most commonly found in birds. Rarely, it is also a cause of infection in humans, and in such cases, may be vancomycin-reistant, and is referred to as VREA. VREA cases in humans have been successfully treated with linezolid.
Enterococcus faecium and application thereof
ActiveCN102373172AStrong stress resistanceImprove anti-bacterial abilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideHigh resistanceSide effect
The invention discloses an enterococcus faecium and application thereof. An enterococcus faecium strain provided by the invention is enterococcus faecium suppressant 80, and the collection number is CGMCC No.5058. As proved by experiments, the enterococcus faecium suppressant 80 is obtained by separating, identifying and screening; and the enterococcus faecium suppressant 80 has high resistance, high bacterial resistance and probiotic characteristics, and can be taken as an additive for preparing animal feeds; and the animals include but is not limited to various animals such as pigs, cows, sheep, chicken and the like. The feeds have similar functions to antibiotic feeds, but do not have the side effects of the antibiotic feeds.
Owner:北京龙科方舟生物工程技术有限公司
Mink source enterococcus faecium and application thereof
Owner:SHENYANG BOYANG FEED
Screening preparation for superior enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
InactiveCN101275158AImprove moisture functionImprove oil functionSenses disorderNervous disorderMetaboliteEnterococcus avium
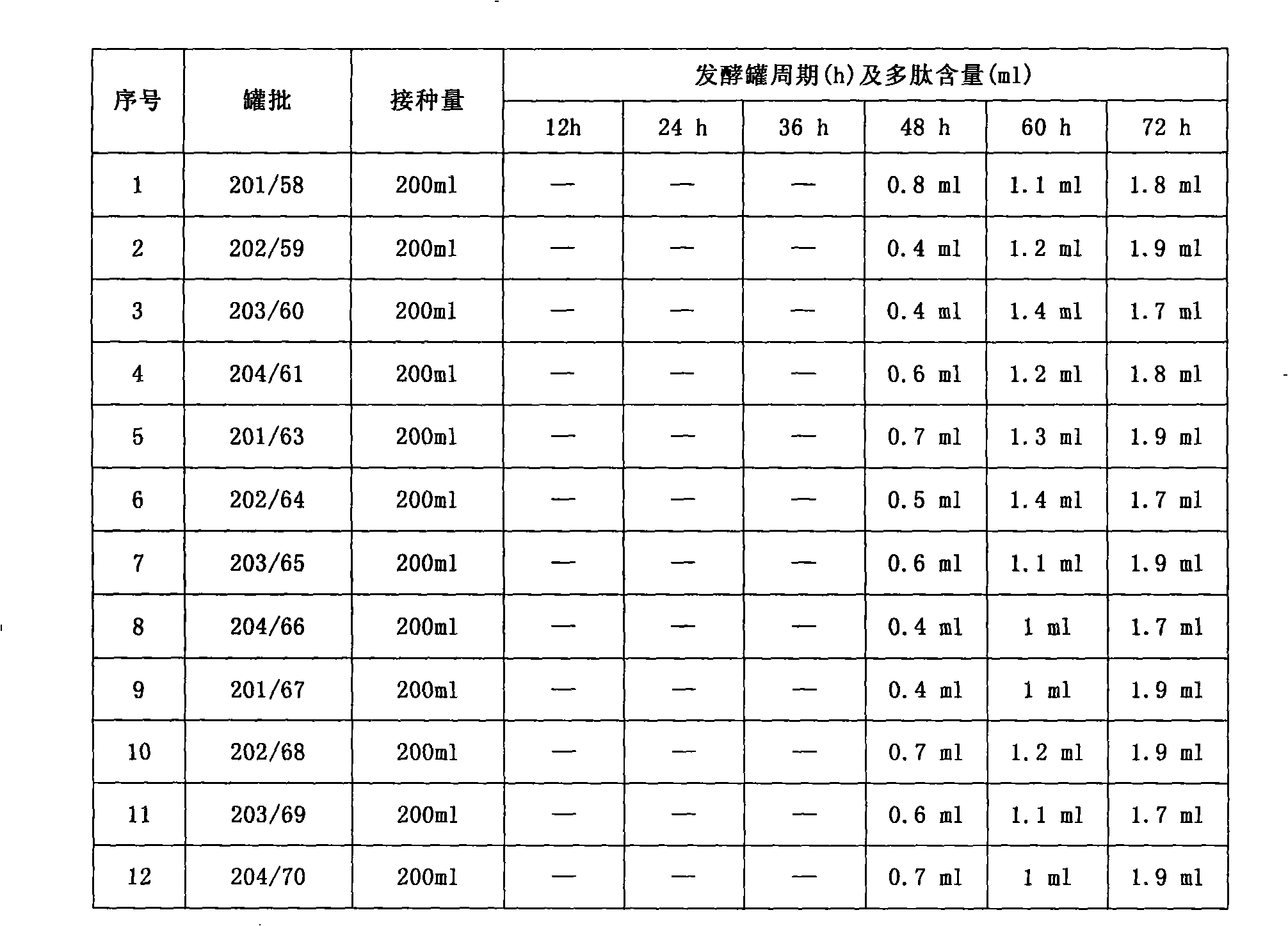
The present invention provides a screen preparing method of excellent enterococcus faecalis and its application. Enterococcus faecalis is the most common representative species in the Enterococcus, living in human intestinal, having no hazard to human, and having benefits. But Enterococcus faecali arises server infection some time, and having resistance to antibiotics. The invention repeatedly cultures and screens enterococcus faecalis, selecting out a strain which has exuberant life, quick growth speed, high fermentation unit, short fermentation cycle, high content of fermentation product, strength production adaptability as a producing strain by researching the contents of morphological characteristics, culture characteristics, physiological and biochemical response, metabolites, genetic character and protein expression, genetic stability, pilot producing index etc, forming a scale production. The broth has functions of immunity adjustment, antitumor etc.
Owner:孙卫
Novel lactic acid bacterium having high immunoglobulin-a-inducing ability
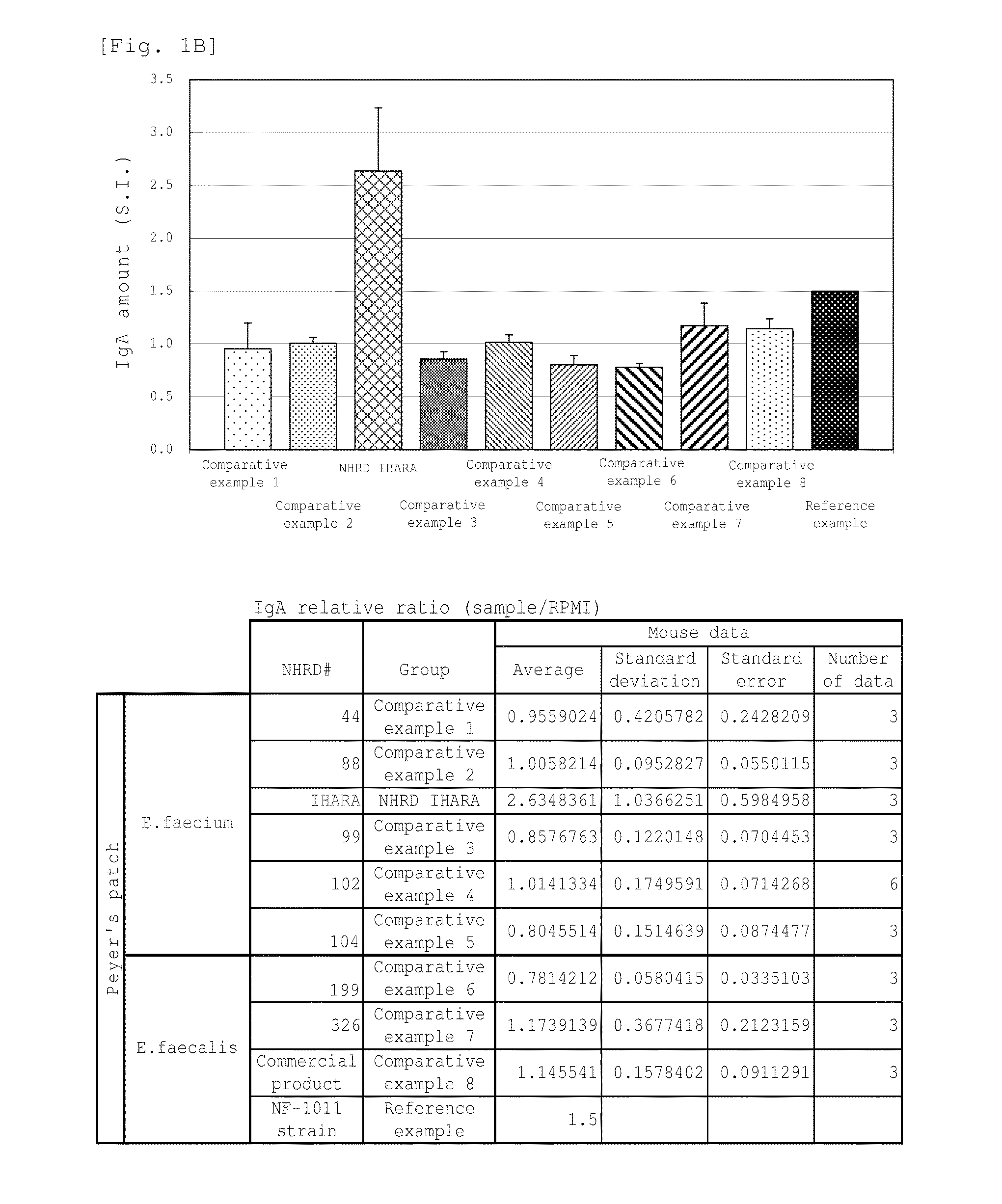
A novel lactic acid bacterium strain is found, which has a high IgA production-inducing ability and a high immunostimulating activity, and belongs to the genus Enterococcus. Thus, provided is an excellent lactic acid bacterium preparation for foods or feeds, which has a high enteric colonization rate. Specifically disclosed are: a novel lactic acid bacterium Enterococcus faecium NHRD IHARA (FERM BP-11090) which has a high IgA production-inducing ability and a high immunostimulating activity; and a lactic acid bacterium preparation for enhancing the production of immunoglobulin A, which comprises a culture of the bacterium strain, an extract of the bacterium strain, or a product of any treatment of cells of the bacterium strain.
Owner:NIPPON HAM
Enterococcus faecium DT1-1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a probiotic, enterococcus faecium DT1-1 and an application thereof. The strain provided by the invention was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 22, 2018, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.16603. The enterococcus faecium DT1-1 provided by the invention has strong adhesion and good bacteriostasis, good acidresistance, gastrointestinal resistance and bile salt resistance, and can be used in feeding herbivorous animals, or preparing feed additives for herbivorous animals, or preparing feed for herbivorousanimals.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Enterococcus faecium
InactiveCN101629155AGood for healthFree from invasionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffFood additiveSynechococcus
The invention relates to enterococcus faecium Anp01 belonging to enterococcus. The enterococcus faecium Anp01 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on January 19th, 2009, and the preservation NO is M209019. The enterococcus faecium Anp01 is used as a feed additive for improving the organism immunity. The enterococcus faecium Anp01 (CCTCC M209019) belongs to normal intestinal bacteria having no toxicity and intestinal pathogenicity to human beings and animals. The feed additive prepared by using the enterococcus faecium Anp01 can not generate any toxin even under abnormal conditions, can not generate potential hazards when the immunity function of host animals is low, and is a pure natural feed additive without any external drug resistance.
Owner:邵峰 +1
Application of enterococcus faecium in preparation of L-lactic acid
ActiveCN103451244AHigh yieldImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismEnterococcus avium
The invention discloses application of enterococcus faecium in preparation of L-lactic acid, wherein the refereed bacterial strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 5, March, 2013, and has the preservation number of CGMCCNo.7274. The application method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting bacterial strains; (2) cultivating and activating in solid media; (3) cultivating seeds; (4) carrying out fermentative cultivation; (5) detecting fermentation products, and the like. The method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low cost, high yield of the target product L-lactic acid, high purity (over 98.6%), few common byproducts such as ethanol, fumaric acid, malic acid and the like, and wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG FOOD & FERMENT IND RES & DESIGN INST
Enterococcus faecium E9-10, screening and identification method thereof and application of enterococcus faecium E9-10 to degrading erythromycin and roxithromycin
ActiveCN104946557AReasonable and effective degradationImproving the Efficiency of Treating Antibiotic PollutionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementRoxithromycinMicroorganism
The invention discloses enterococcus faecium collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number being CGMCC No.10575. The enterococcus faecium has the technical effects that lactobacillus with an erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading function is screened from soil through preliminary screening and secondary screening of an antibiotic selective medium; a reasonable and effective screening method of an erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading strain is established to obtain lactobacillus meeting the needs; the safe and effective erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading strain is screened through separation, purification and screening of lactobacillus and a series of work, such as preliminary screening and secondary screening of erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading lactobacillus; when applied to control over erythromycin and roxithromycin pollution, the enterococcus faecium has the advantages of no secondary pollution, high treatment efficiency, wide range of application and low cost; the enterococcus faecium provides more choices for microbiological control over antibiotic pollution of complex environments.
Owner:潍坊中创生物科技有限公司
Novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb and encoding gene and application thereof
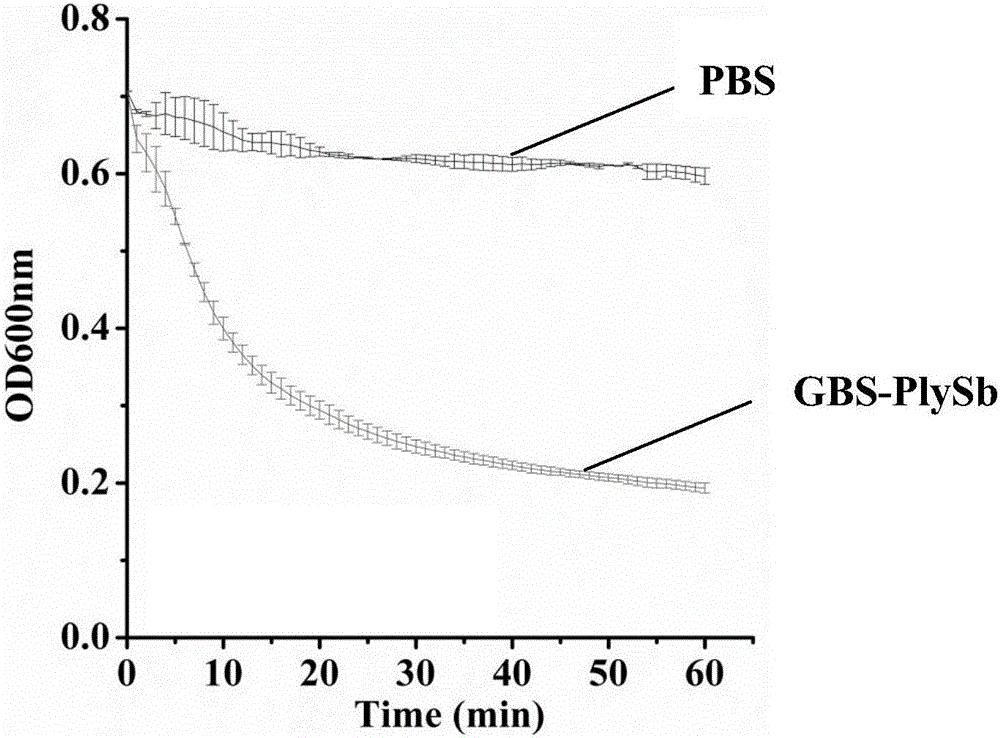
ActiveCN107177580AImprove stabilityNo apparent cytotoxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliHigh concentration
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb and an encoding gene and application thereof. The novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb has an amino acid sequence shown as in SEQ ID NO. 1; the encoding gene of the novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb has a nucleotide sequence shown as in SEQ ID NO. 2. A novel chimeric lysin is constructed by means of gene splicing and is suitable for killing various species of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, particularly various species of Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus iniae and other species; the novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb has good stability and is insensitive to high-concentration NaCl, recombinant protein GBS-PlySb is well expressible in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and a high dose of GBS-PlySb is free of significant cytotoxicity. Therefore, the novel broad-spectrum chimeric lysin BGS-PlySb is applicable independently to or as an additive to the control of various species of Streptococcus and the treatment of infections caused by these species, and has a promising application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Mediucm for detecting vana and vanb vancomycin-resistant enterocci and method of using the same
Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci detection media as well as a method of selectively detecting Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci clinically important in vancomycin resistant enterococci from testing microorganisms or specimens using the media. The media for selectively detecting Van A and Van B VRE from testing microorganisms and specimens are media where enterococci can grow where vancomycin, D-cycloserine and D-lactate are added. Preferably 32-256 mug / ml of vancomycin, 1-64 mug / ml of D-cycloserine, and 0.025-0.8 mol / l of sodium lactate are added to culture medium where enterococci can grow.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Broad Spectrum of Streptococcus Lyase and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20180104316A1High activityIncrease enzyme activityAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationEscherichia coliBacteroides
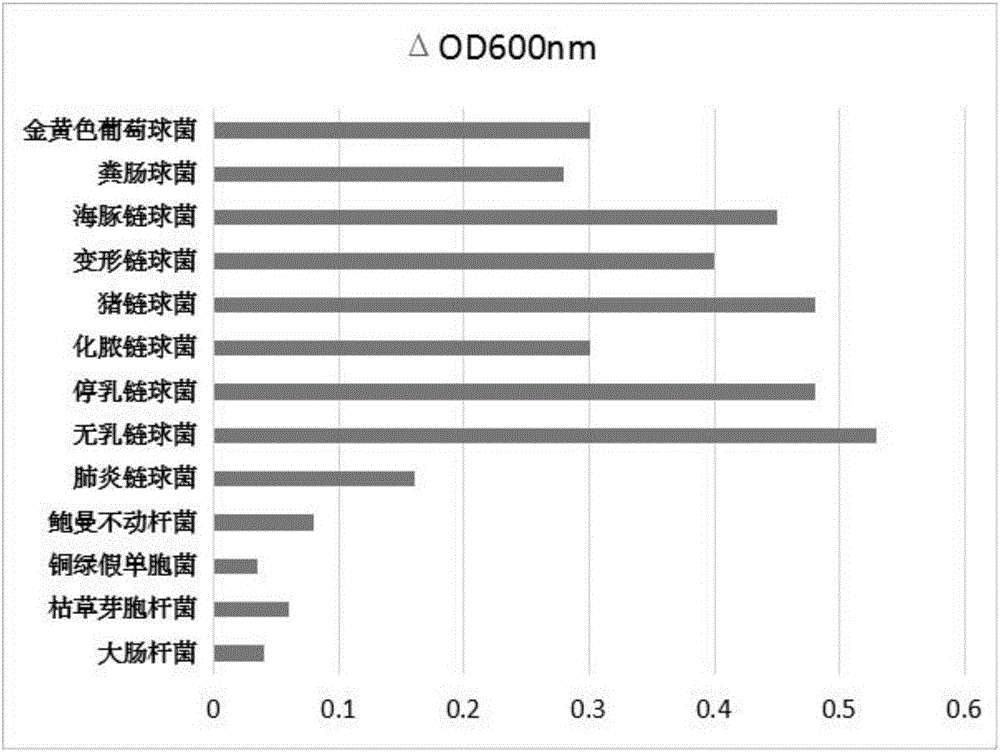
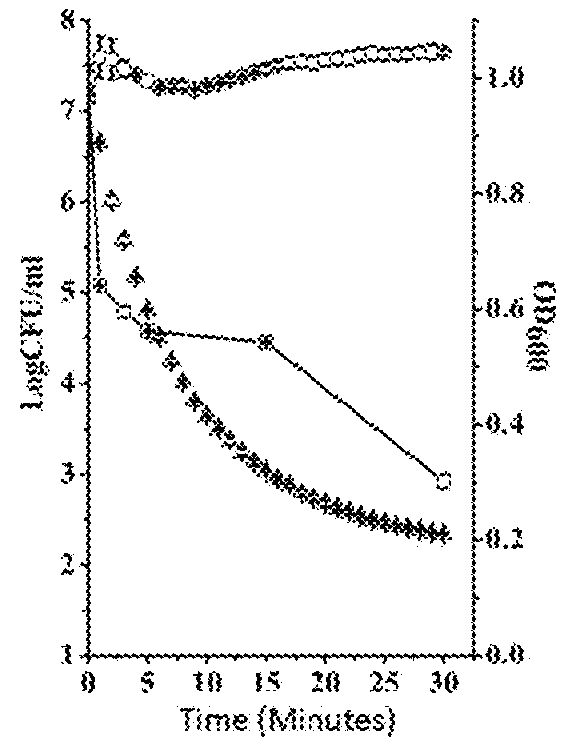
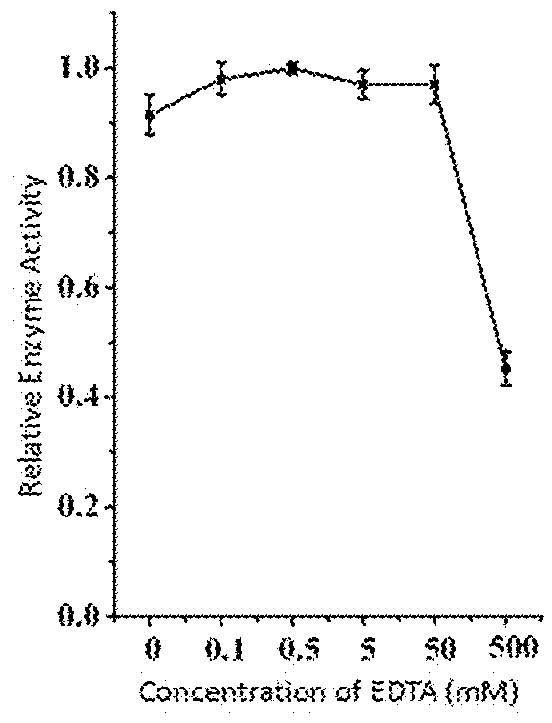
This invention discloses a lysin that can kill many species of Streptococci. A new lysin, ClyR, was constructed by the gene splicing method. The ClyR can effectively kill different species of Streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus equi, and various Enterococci and Staphylococcus aureus. ClyR shows good stability and is not sensitive to EDTA and high concentration of NaCl. Moreover, the ClyR is active in a wide range of pH and maintains high activity in pH 5-11. Recombinant protein ClyR is well expressed in E. coli stain BL21 (DE3). High doses of ClyR showed no apparent toxicity in mice. Furthermore, administration of 0.8 mg per mouse once is able to completely protect the mouse infected with lethal doses of Group B Streptococci. The ClyR can be used alone or in combination with different forms of reagents and solutions, for the control of a variety of Streptococci and for the treatment of infections caused by these bacteria. It has a broad application prospect.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
Prawn intestinal enterococcus strain as well as screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN109679869APromote growthImprove disease resistanceAntibacterial agentsBacteriaFeed conversion ratioStaphylococcus cohnii
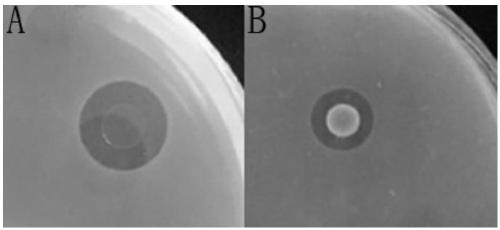
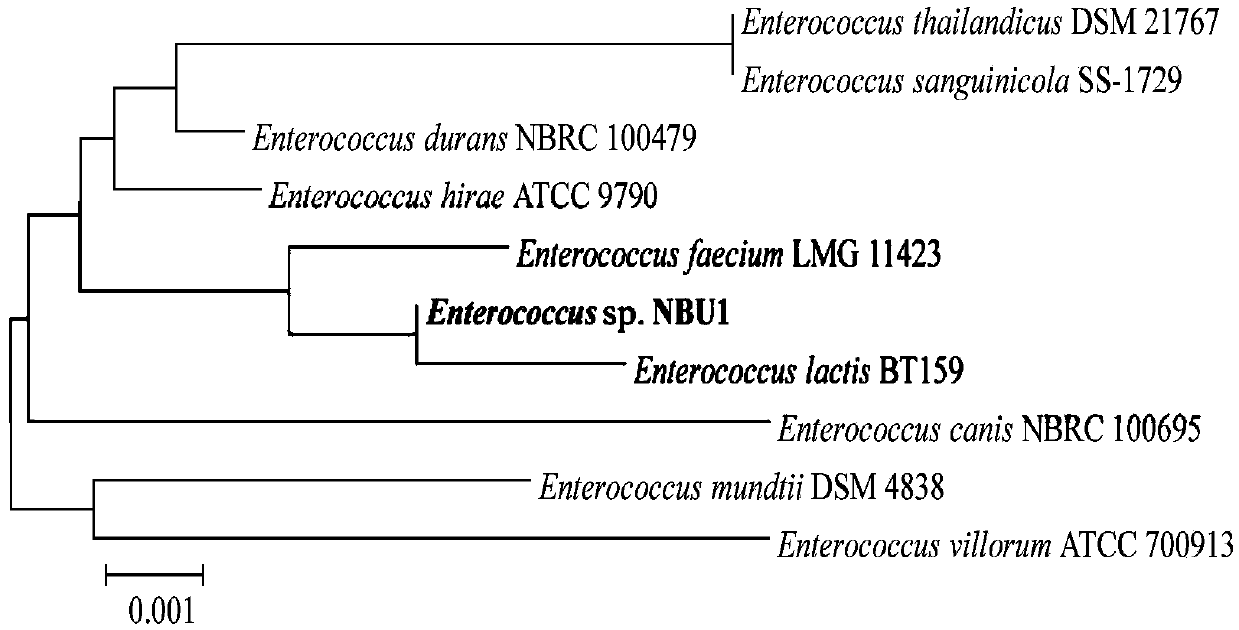
The invention discloses a prawn intestinal enterococcus strain as well as a screening method and application thereof. The prawn intestinal enterococcus strain is characterized in that the strain is NBU1 strain which is classified and named as Enterococcus sp., and was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 12, 2018, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.16735; the application of the strain in preparing a staphylococcus aureus inhibitor and / or a vibrio anguillarum inhibitor as well as preparing a probiotic additive for prawn culture has the advantagesthat better inhibitory effects on staphylococcus aureus and vibrio anguillarum are realized; the yield and the survival rate of prawns and the conversion rate of feed can be improved after the strainis fermented with the feed; in addition, the yield and the survival rate of sick prawns can be improved; the prawn intestinal enterococcus strain can be used as a high-efficiency green feed additive and an antibiotic substitute for aquatic animal cultivation.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
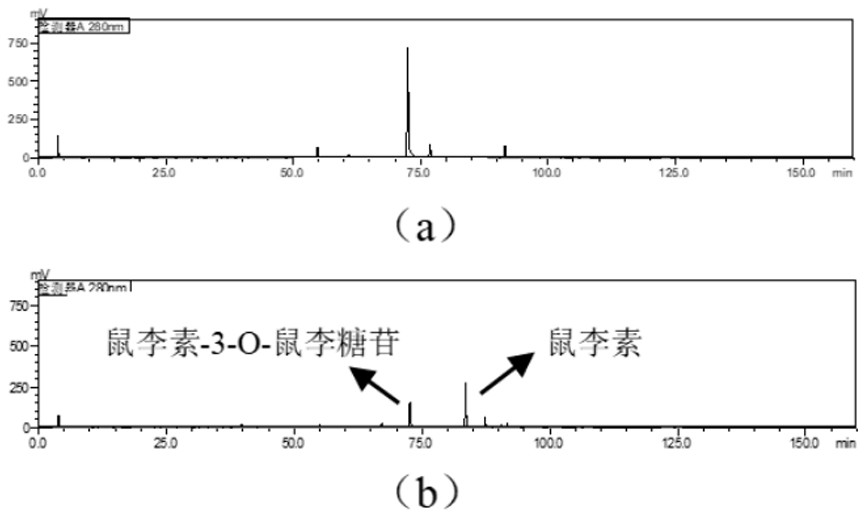
Bacterial-derived alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene, gene expression and application thereof
The invention relates to a bacterial-derived alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene, gene expression and application thereof. A bacterial strain Enterococcus avium capable of hydrolyzing rhamnetin-3-O-rhamnoside in total flavonoids of Loranthus tanakae into rhamnetin is screened out, two alpha-L-rhamnosidase genes EaRha1 and EaRha2 in bacteria are cloned and subjected to prokaryotic expression, and the target alpha-L-rhamnosidase is obtained. The enzymatic properties of the recombinant proteins EaRha1 and EaRha2 are studied to determine the hydrolysis mechanism of the two proteins on the flavonoid compounds, and a theoretical basis and a guiding effect are provided for biotransformation of the flavonoid compounds. pNPR is adopted as a substrate, the optimum pH of the recombinant protein EaRha1 is 7, the optimum temperature is 50 DEG C, and neohesperidin and naringin containing alpha-1, 2 glucosidic bonds and rutin containing alpha-1, 6 glucosidic bonds can be catalytically hydrolyzed by the recombinant protein EaRha1. Rhamnetin-3-O-rhamnoside is adopted as the substrate, the optimal pH value of the EaRha2 is 7, the optimal temperature is 60 DEG C, and the EaRha2 can hydrolyze rhamnetin-3-O-rhamnoside and quercitrin.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
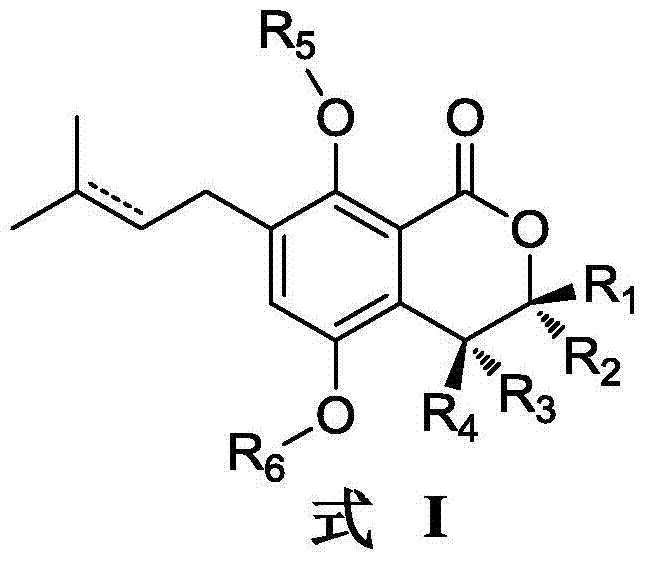
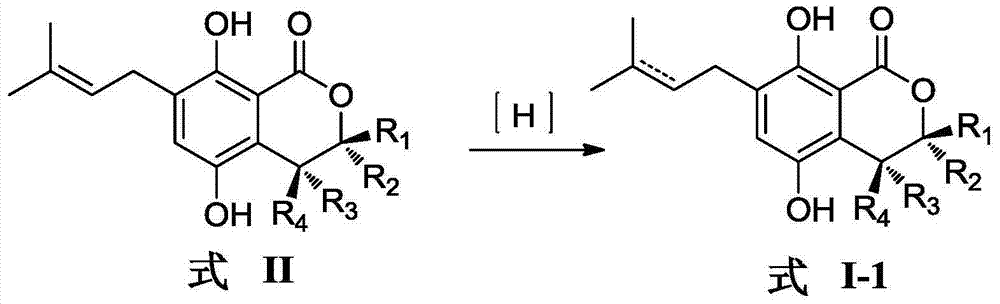
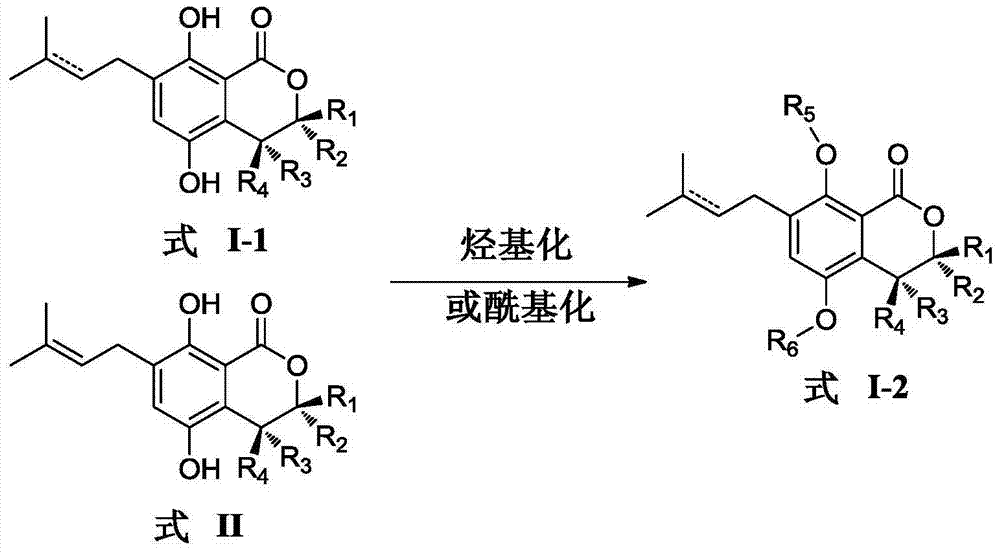
Gorgonian-originated fungus secondary metabolite derivatives and application of same as antiseptics
The invention specifically relates to gorgonian-originated fungus secondary metabolite derivatives and application of the same as antiseptics, belonging to the field of medicine. The derivatives provided by the invention exert strong inhibitory effect on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE) and certain inhibitory effect on Gram-negative bacteria; and the minimal inhibition concentrations MIC of the derivatives are all less than 12.5 mu M, which proves that the derivatives can be developed into potential antibacterial drugs.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Human binding molecules having killing activity against enterococci and staphylococcus aureus and uses thereof
ActiveCN102731651AGrowth inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsFungiStaphylococcus cohniiHeavy chain
Disclosed is a human monoclonal antibody, wherein said antibody comprises: a heavy chain CDR1 region comprising amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 296; a heavy chain CDR2 region comprising amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 297; a heavy chain CDR3 region comprising amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 298; a light chain CDR1 region comprising amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 299; a light chain CDR2 region comprising amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 300; a light chain CDR3 region comprising amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 301; characterized in that said antibody has opsonic phagocytic killing activity against at least one strain of each of at least two different Enterococcus species and against at least one strain of Staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
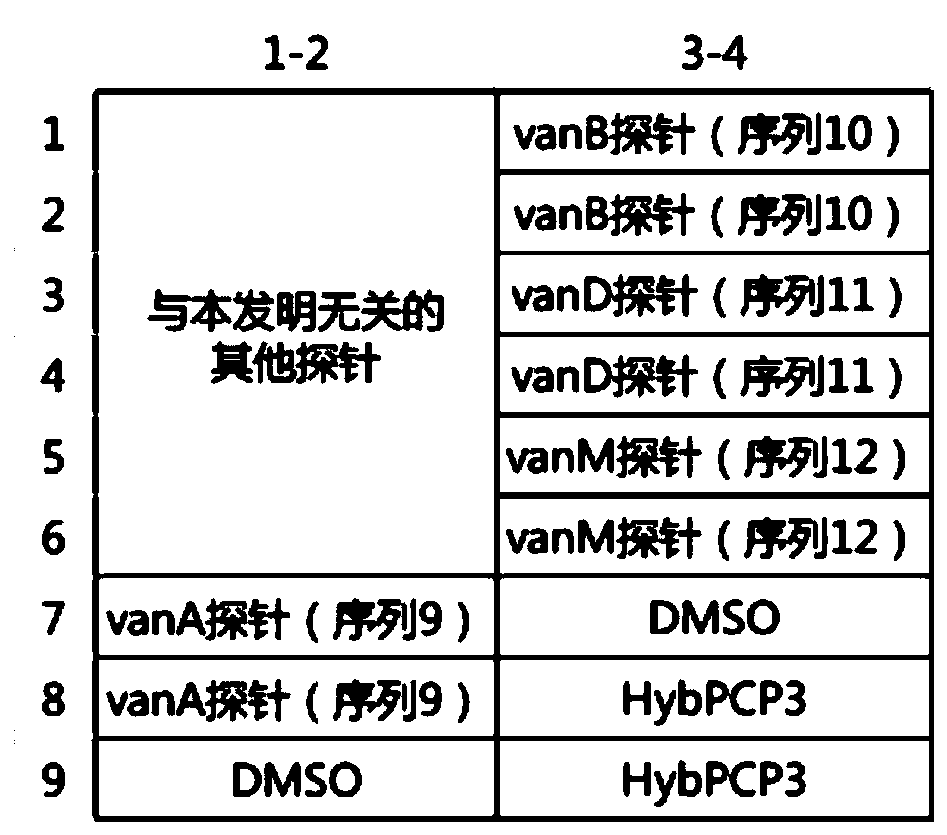
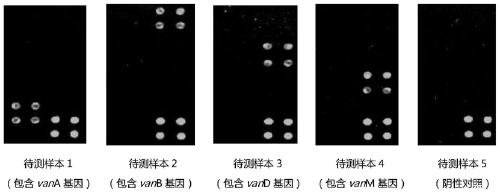
Specific primer combination and probe combination for detecting four glycopeptide drug resistance genes in enterococcus bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN110055308AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesEnterococcus avium
The invention discloses a specific primer combination and a probe combination for detecting four glycopeptide drug resistance genes vanA, vanB, vanD and vanM in enterococcus bacteria, comprising a primer combination for specific amplification of four glycopeptide drug resistance genes and further comprising specific probes for detecting the four glycopeptide drug resistance genes. A method for detecting the four glycopeptide drug resistance genes by using the specific primer and probe combinations is further provided. The combinations have high specificity and coverage, can be used not only for detecting the drug resistance genes vanA, vanB, vanD and vanM in human infected samples but also for suggesting resistance degree to vancomycin and teicoplanin, and provides a reference basis for clinical anti-infective therapy medication. At the same time, the development of glycopeptides drug resistance is monitored. The combinations can also be used for monitoring the distribution and transfer of the four glycopeptide drug resistance genes in animal and environmental samples.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Evaluation method of microorganism on influencing intestinal flora, and construction method of animal models with stable intestinal floras
InactiveCN108148918AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBifidobacterium
The invention relates to an evaluation method of a microorganism on influencing an intestinal flora, and a construction method of animal models with stable intestinal floras. The evaluation method comprises the steps of building the animal models with the stable intestinal floras; respectively feeding a sterile feed containing a microorganism to be tested and a sterile feed without the microorganism to be tested to the two groups of animal models, collecting faeces of the two groups of animal models after feeding to obtain a first faece and a second faece, determining and comparing contents ofthe intestinal floras in the first faece and the second faece; if a ratio of the logarithm sum of contents of bifidobacterium and bacterium lacticum to the logarithm sum of contents of enteric bacilli and enterococcus in the first faece is larger than a ratio of the logarithm sum of contents of bifidobacterium and bacterium lacticum to the logarithm sum of contents of enteric bacilli and enterococcus in the second faece, determining that the microorganism to be tested plays a role in promoting the intestinal flora. The evaluation method can be used for truly and accurately evaluating the influence of the microorganism on the intestinal flora.
Owner:深圳市百澳飞生物技术有限公司
Enterococcus faecium, high-density fermentation culture method thereof, and microecological preparation prepared by adopting enterococcus faecium
ActiveCN108641979ASignificant probioticSignificant stress resistanceBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffSynechococcusLactobacillus
The invention provides enterococcus faecium, a high-density fermentation method of enterococcus faecium, and a microecological preparation prepared by adopting enterococcus faecium, belonging to the technical field of culturing of lactic acid bacteria. An enterococcus faecium strain with the obvious probiotic property and stress resistance is screened and taken as a feed additive, and the enterococcus faecium strain can effectively replace part of antibiotics. The enterococcus faecium provided by the technical scheme is E13-5, and is assigned with the preservation number of CCTCC M2017191. Theenterococcus faecium provided by the invention can be used as the safe and efficient novel feed additive for replacing part of the antibiotics, and thus the demands of the modern feed industry and livestock breeding industry are satisfied.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH INC +1
Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
InactiveUS7988958B2Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesEnterococcus avium
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the levels of colonization by at least one target bacteria in animals, especially poultry.
Owner:STATE RES CENT FOR APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECH MINIST OF HEALTH & SOCIAL DEV RF AS REPRESENTED BY THE DIRECTOR OF THE STATE RES CENT FOR APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECH MINIST OF HEALTH & SOCIAL DE +1
Preparation method of beverage containing sporogenous lactic bacterium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a beverage containing sporogenous lactic bacterium. Endo-sporogenous lactic bacterium such as bacillus coagulans or enterococcus are used as main ingredients, the sporogenous lactic bacterium are screened and cultured and are positioned in aqueous solution in a dormant state, the dormant lactic bacterium are mixed with sterilized aqueous solution to prepare lactic bacterium water beverage, and then the lactic bacterium water beverage is canned in a packaging container. According to the preparation method of the beverage, the calories of the lactic bacterium beverage is reduced, the storage life of the lactic bacterium beverage is prolonged, the lactic bacterium can be utilized effectively, the manufacture cost is reduced, the lactic bacterium cannot be damaged before reaching the intestinal tract and thus the beverage is beneficial to the health of human body.
Owner:QINGDAO ANBEIKANG BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Lactic acid bacterium having high immunoglobulin-A-inducing ability
A novel lactic acid bacterium strain is found, which has a high IgA production-inducing ability and a high immunostimulating activity, and belongs to the genus Enterococcus. Thus, provided is an excellent lactic acid bacterium preparation for foods or feeds, which has a high enteric colonization rate. Specifically disclosed are: a novel lactic acid bacterium Enterococcus faecium NHRD IHARA (FERM BP-11090) which has a high IgA production-inducing ability and a high immunostimulating activity; and a lactic acid bacterium preparation for enhancing the production of immunoglobulin A, which comprises a culture of the bacterium strain, an extract of the bacterium strain, or a product of any treatment of cells of the bacterium strain.
Owner:NIPPON HAM
Method of producing lactic bacteria and killed lactic bacterial cells belonging to the enterococcus
A method of culturing is provided which keeps physiology activity of bacterial cell belonging to the Enterococcus genus and also a method of producing killed bacterial cells belonging to the Enterococcus genus. <??>In the method of culturing bacterial cells belonging to the Enterococcus genus, the method cultures bacterial cells belonging to the Enterococcus genus in an aerobic manner under the culturing conditions of (i) pH: 5.5 to 7.5, (ii) stirring method: 5 to 40 times per minute, (iii) temperature conditions: 30 to 40 DEG C, and (iv) culturing time: 6 to 24 hours, and extracts viable bacteria from culture solution.
Owner:河合 康雄
Antibacterial macrolactin a that bacillus polyfermenticus kjs-2 produced in
InactiveUS20100087516A1Broad spectrum of antibiotic activityExcessive activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismEnterococcus avium
The present invention relates to uses of Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2 (KCCM 10769P), which is a new bacillus strain, as an antibiotic. Macrolactin A of the present invention, which is produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, shows a broad spectrum of antibiotic activity against a variety of microorganisms and fungi, and is proved to be very efficient for the inhibition of particularly vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) that are multidrug-resistant bacteria. The antibiotic Macrolactin A produced by Bacillus polyfermenticus KJS-2, can be used as an excellent antibiotic against vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), and thus the present invention is a very useful invention for medical industry.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Method for identifying clinic infected pig enterococcus by MALDI-TOFMS technology
InactiveCN107219293ARapid identificationStrong acquired drug resistanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiologyBacilli
The invention relates to the field of bacteria detection, and particularly discloses a method for identifying clinic infected pig enterococcus by an MALDI-TOFMS technology. The method has the technical scheme that the method for identifying the clinic infected pig enterococcus by the MALDI-TOFMS technology is characterized by comprising the following steps that 1, a formic acid extraction method is used for sample processing and sample application; 2, the sample treated in the first step is subjected to mass spectrometry by using an MALDI Biotyper high-flux microbiological identification system; a mass spectrum is obtained; 3, BioTyper software is used for analyzing the obtained mass spectrum to obtain the standard atlas of the enterococcus mass spectrum diagram; 4, the enterococcus to be detected is cultured and purified through brain heart infusion agar; the treatment in the first step and the second step is performed; 5, the enterococcus mass spectrum diagram to be detected is subjected to clustering analysis. The method disclosed by the method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient; the speed is high; the accuracy is high.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & ECONOMY
Enterococcus faecium strain and application thereof in alkekengi bean curd processing
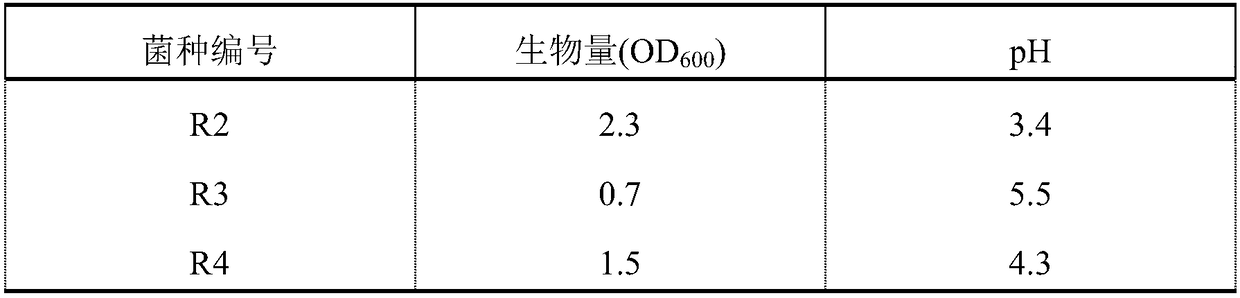
ActiveCN108239616ASimple cultivation conditionsFast acid productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetic acidEnterococcus avium
The invention relates to an enterococcus faecium strain. The 16S rDNA gene sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The strain is R2, the classification and naming of which is enterococcus faecium, the preservation number of which is CGMCC No.14944. The invention also relates to an application of the R2 in alkekengi bean curd processing. The application comprises the following steps: sterilization byyellow serofluid; inoculating R2 to the sterilized yellow serofluid; leaving the mixture to stand to ferment, wherein the pH value of the yellow serofluid reaches a preset value to obtain the alkekengi; adding the alkekengi into boiled soybean milk to obtain uncongealed beancurds, and carrying out follow-up treatment on the uncongealed beancurds to obtain alkekengi bean curds. The enterococcus faecium strain is simple in culture condition, high in acid-yielding speed, and good in stability; the alkekengi bean curds are produced by means of the strain, so that the content of polluting pathogenic bacterium and infectious microbes can be reduced effectively, and in the fermenting process, nutrients are not supplemented, and meanwhile, after fermentation, a proper acidity can be achieved without supplementing acetic acid, so that the production cost is lowered effectively.
Owner:HUAINAN NORMAL UNIV
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the level of colonization of at least one target bacteria in animals, particularly poultry.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI (US) +1
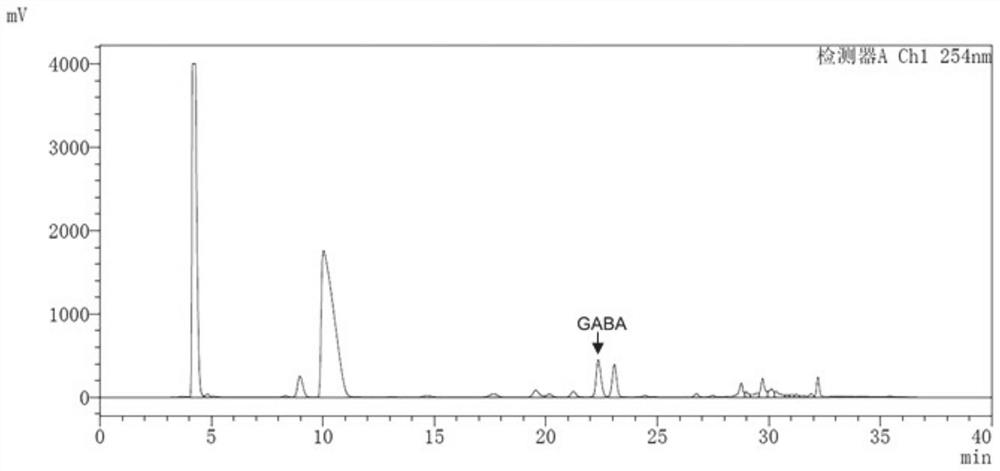
Human-derived enterococcus avialis capable of producing gamma-aminobutyric acid and application of human-derived enterococcus avialis
The invention discloses human-derived enterococcus avialis capable of generating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The human-derived enterococcus avialis strain is named as Enterococcusavium MRS4-2, theenterococcus avialis strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 30, 2020, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.20990. The invention also discloses an application of the enterococcus avialis to production of the gamma-aminobutyric acid by using a culture medium added with glutamic acid or glutamate or an MRS culture medium added with soybean mealenzymatic hydrolysate. Experiments show that the GABA generated by the enterococcus avium has an adjusting effect on intestinal flora, which indicates that the GABA has a probiotic effect in the aspects of maintaining intestinal flora balance, adjusting body health and the like, and besides, the fact that the enterococcus avium has application potential in development of intestinal health micro-ecological products and probiotic fermentation products is also confirmed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Recombinant Enterococcus faecium vaccine strain labeled with eGFP and having resistance to porcine transmissible gastroenteritis and porcine epidemic diarrhea, and application thereof
InactiveCN107828706ATimely confrontationThe immunization route saves time and effortSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaDiseaseEnterococcus avium
The invention discloses a recombinant Enterococcus faecium vaccine strain labeled with eGFP and having resistance to porcine transmissible gastroenteritis and porcine epidemic diarrhea, and an application thereof. The vaccine strain adopts Enterococcus faecium isolated from a porcine intestinal colon segment as a vaccine antigen delivery live vector, and contains an eGFP-labeled constitutive-expression TGEV S protein D antigen site and PEDV S protein neutralizing epitope region ps420 Protein recombinant expression vector. A bivalent oral vaccine having resistance to the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis and porcine epidemic diarrhea, prepared from the recombinant Enterococcus faecium vaccine strain, can achieve the purpose of preventing two-disease through one-time immunization, and has the advantages of environmental protection, high efficiency, safety and good probiotics.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Broad spectrum of Streptococcus lyase and use thereof
ActiveUS9993532B2Increase enzyme activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationEscherichia coliBacteroides
This invention discloses a lysin that can kill many species of Streptococci. A new lysin, ClyR, was constructed by the gene splicing method. The ClyR can effectively kill different species of Streptococci, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus uberis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus equi, and various Enterococci and Staphylococcus aureus. ClyR shows good stability and is not sensitive to EDTA and high concentration of NaCl. Moreover, the ClyR is active in a wide range of pH and maintains high activity in pH 5-11. Recombinant protein ClyR is well expressed in E. coli stain BL21 (DE3). High doses of ClyR showed no apparent toxicity in mice. Furthermore, administration of 0.8 mg per mouse once is able to completely protect the mouse infected with lethal doses of Group B Streptococci. The ClyR can be used alone or in combination with different forms of reagents and solutions, for the control of a variety of Streptococci and for the treatment of infections caused by these bacteria. It has a broad application prospect.
Owner:PHAGELUX INC
Novel enterococcus and streptococcus strains and bacteriocins
Novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus bacteriocins produced by novel Enterococcus and Streptococcus strains are used for at least reducing the levels of colonization by at least one target bacteria in animals, especially poultry.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI (US) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com