Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
128 results about "Roxithromycin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
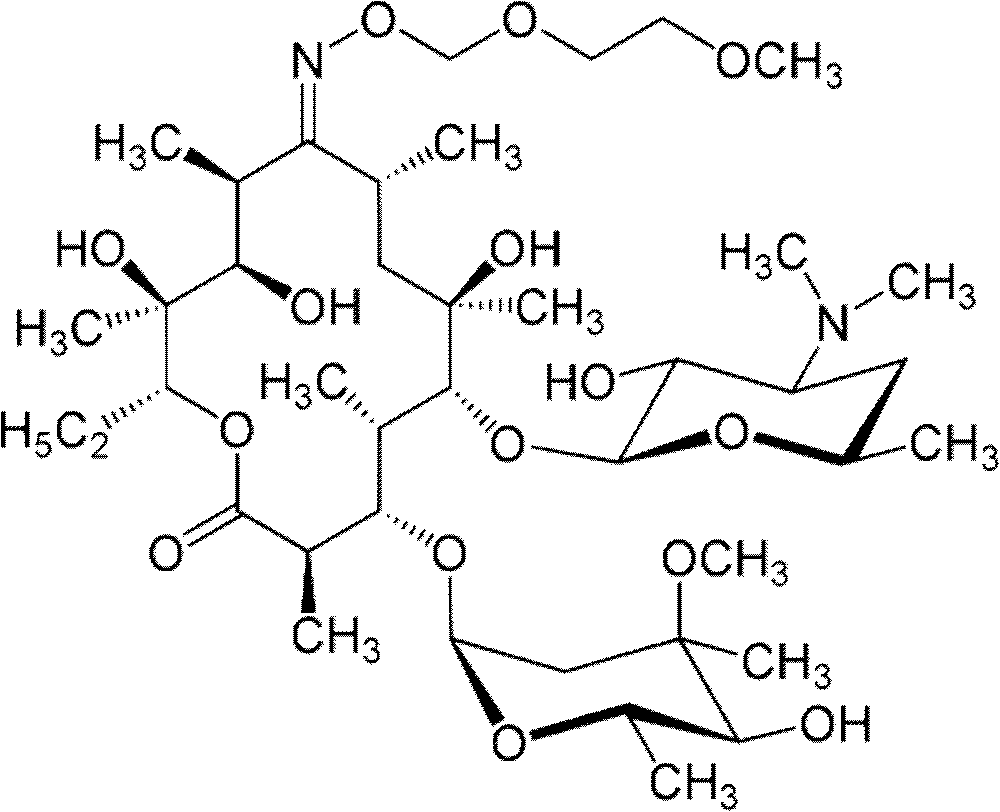
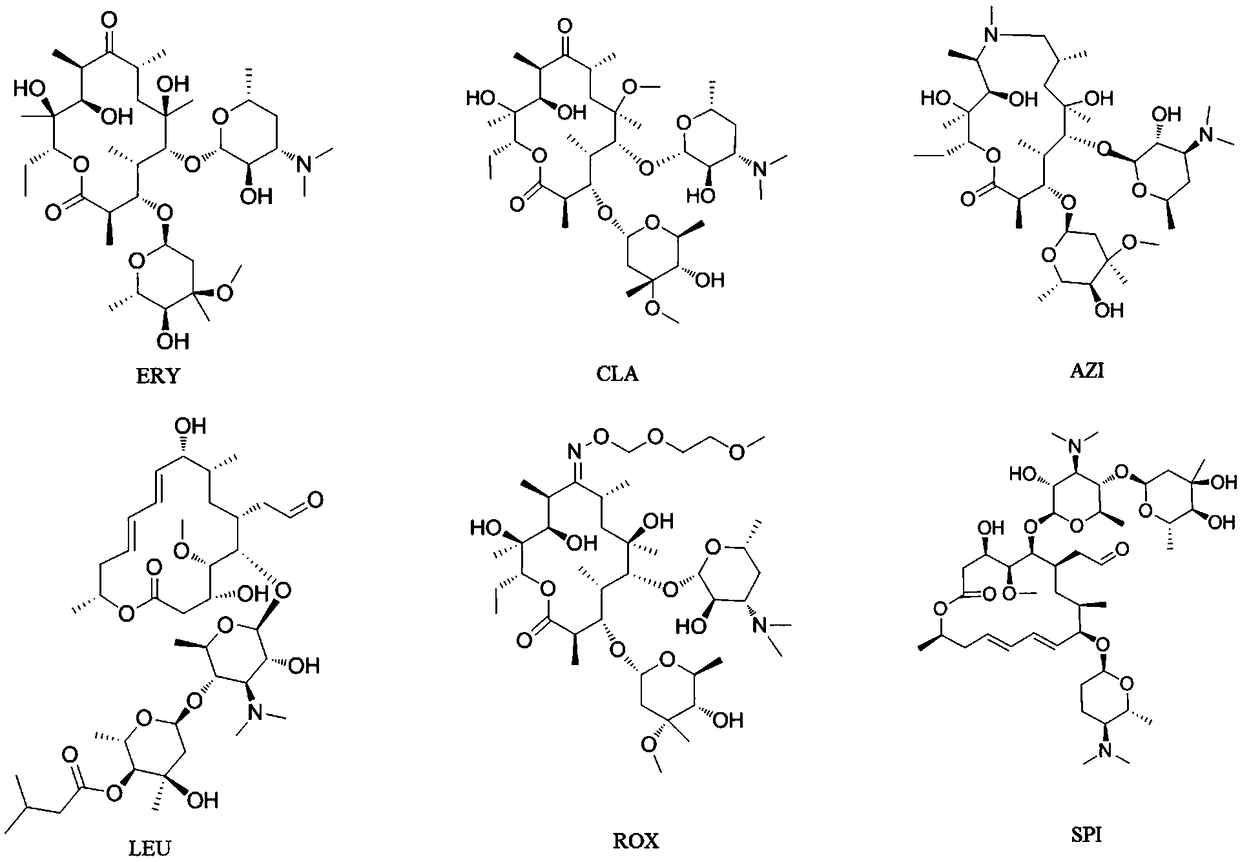
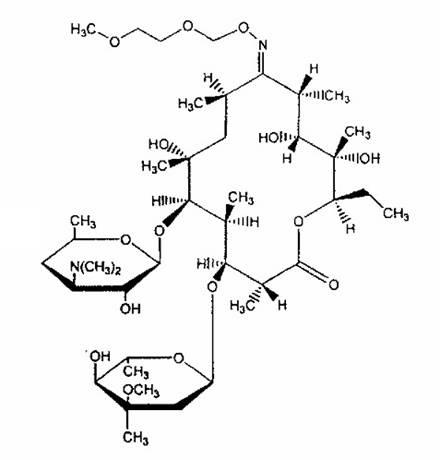
Roxithromycin is a semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic. It is used to treat respiratory tract, urinary and soft tissue infections. Roxithromycin is derived from erythromycin, containing the same 14-membered lactone ring. However, an N-oxime side chain is attached to the lactone ring. It is also currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of male-pattern hair loss.
Injectable compositions for the controlled delivery of pharmacologically active compound
InactiveUS6887487B2Extend posting timeControl doseAntibacterial agentsBiocideRoxithromycinRelease time
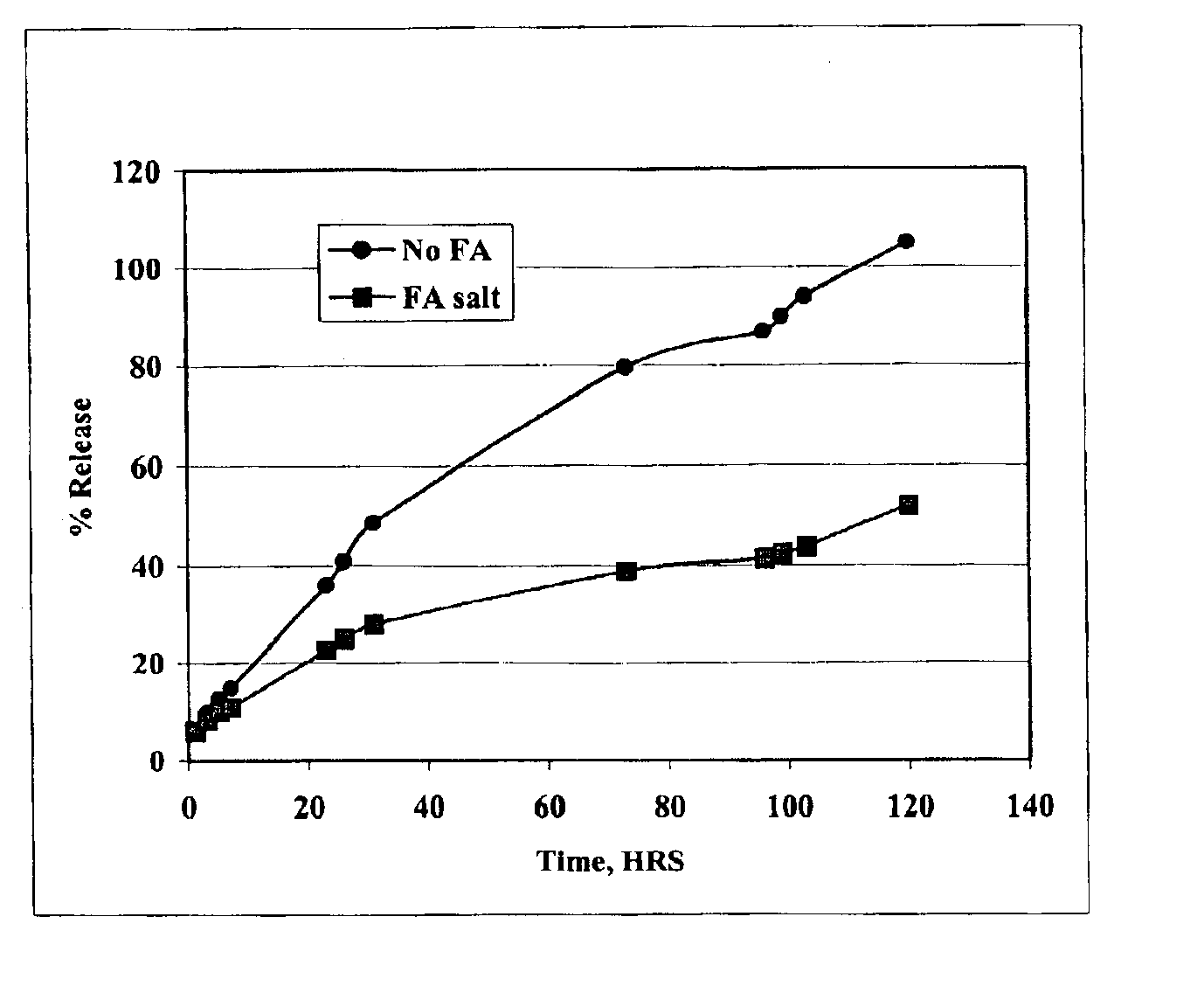
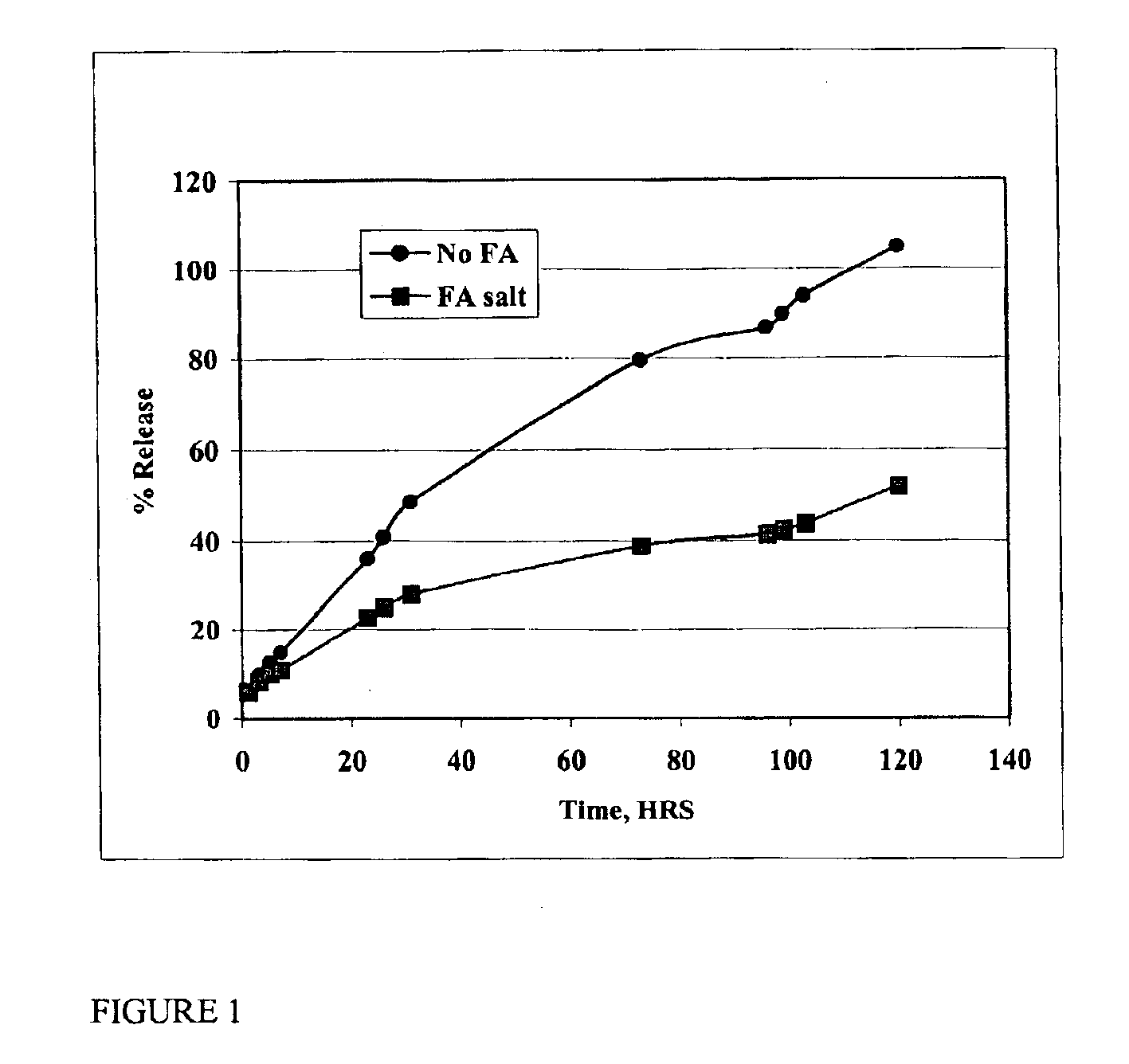
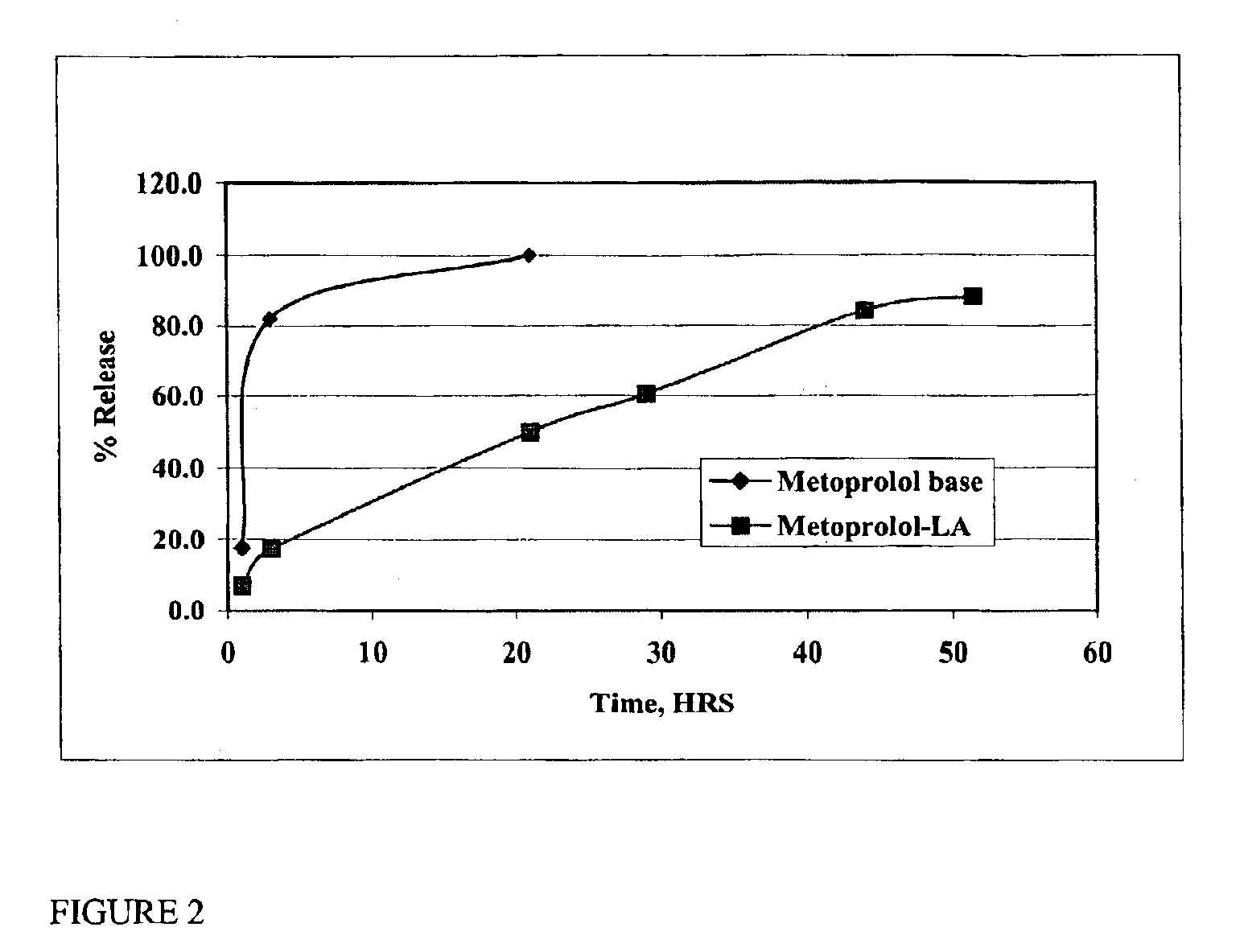
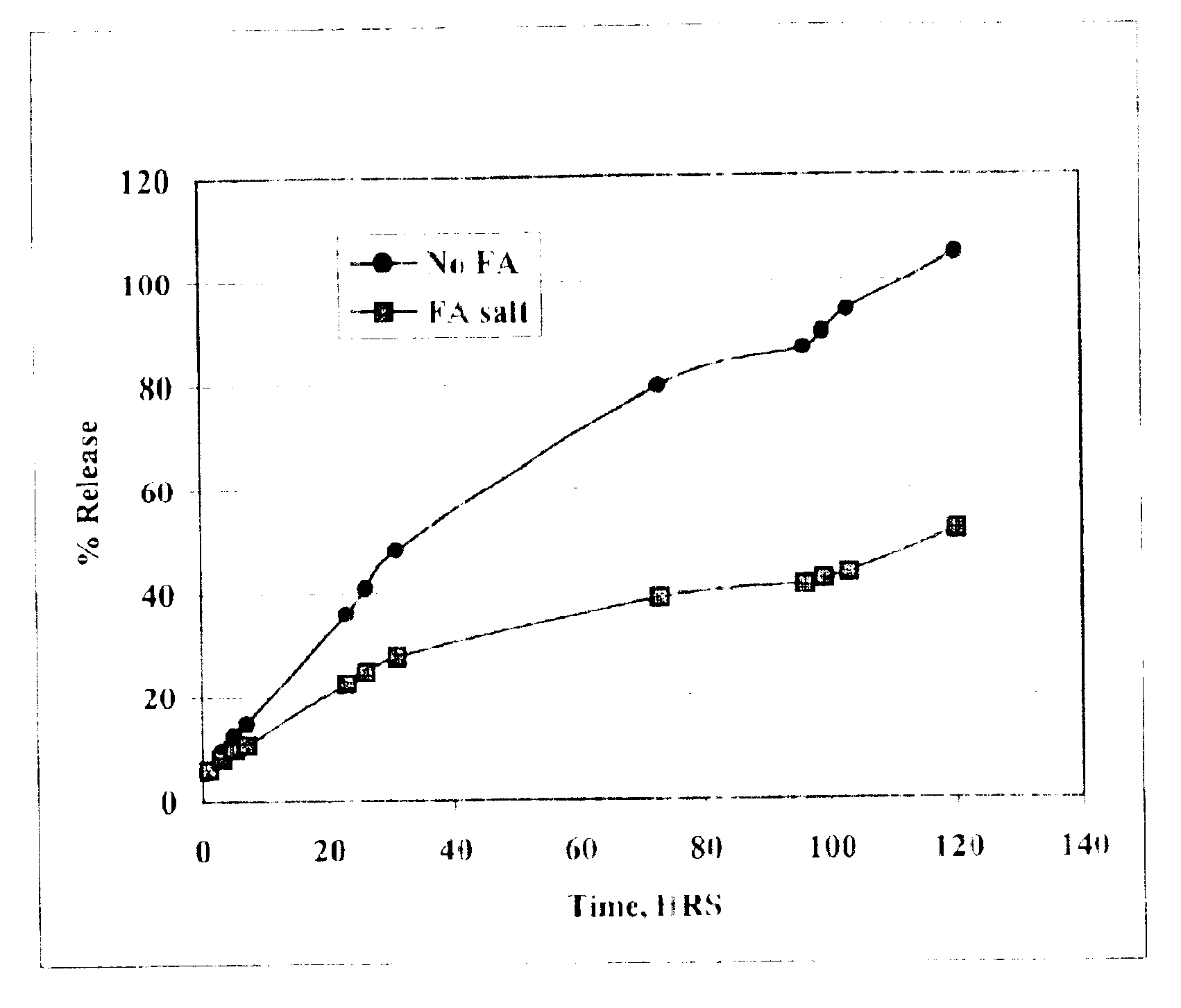
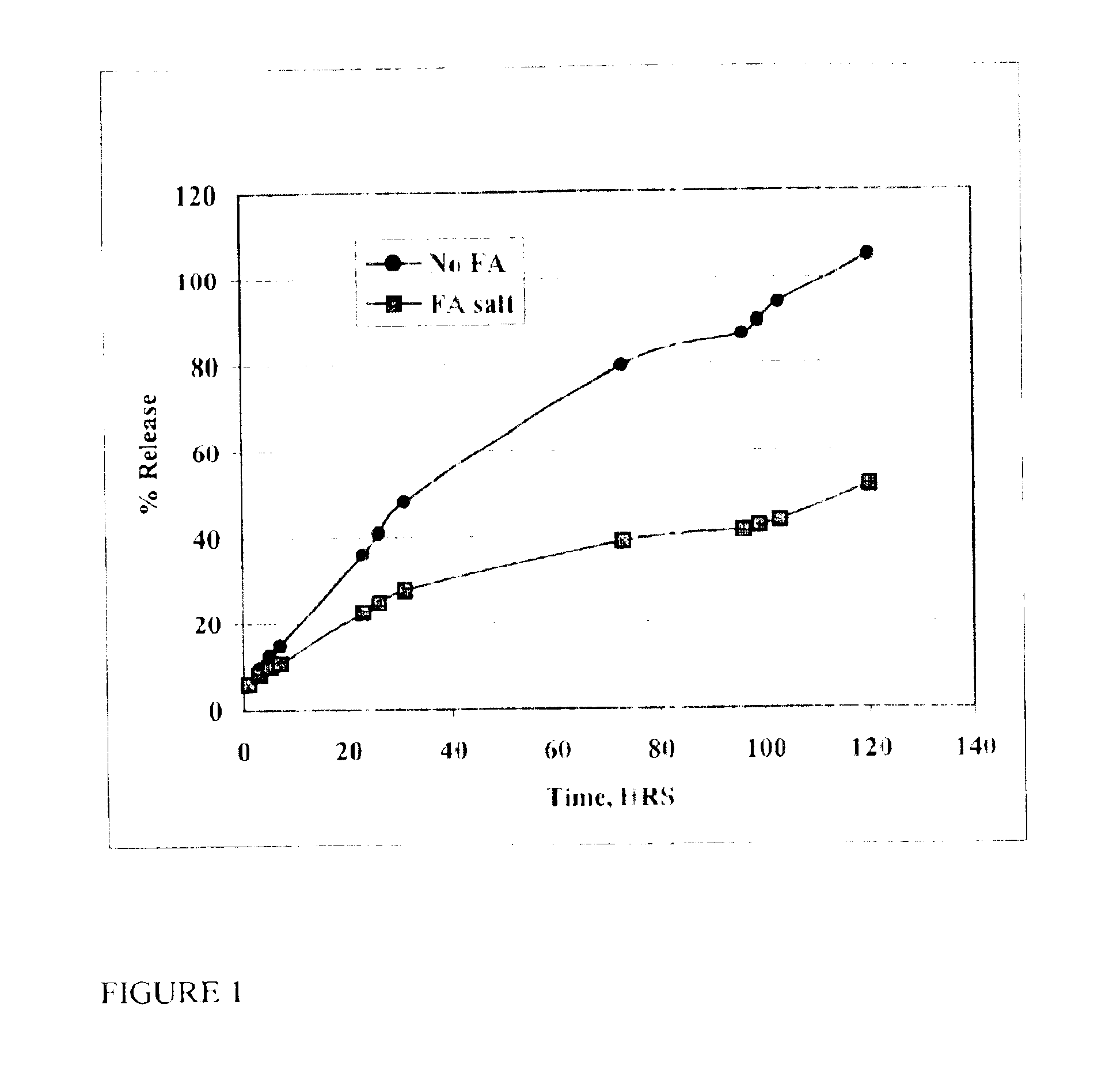
The present invention provides compositions and methods for extending the release times and lowering the toxicity of pharmacologically active compounds. The compounds comprise a salt of the pharmacologically active compound with a lipophilic counterion and a pharmaceutically acceptable water soluble solvent combined together to form an injectable composition. The lipophilic counterion may be a saturated or unsaturated C8-C22 fatty acid, and preferably may be a saturated or unsaturated C10-C18 fatty acid. When injected into a mammal, at least a portion of the composition precipitates and releases the active compound over time. Thus, the composition forms a slowly releasing drug depot of the active compound in the mammal. Therefore, the present invention enables one to provide a controlled dose administration of the active compound for a periods of up to 15 days or even longer. Many compounds can be administered according to the present invention including, but not limited to, tilmicosin, oxytetracycline, metoprolol, fluoxetine, roxithromycin, and turbinafine.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Methods for the controlled delivery of pharmacologically active compounds
InactiveUS6946137B2Low toxicitySmall investmentBiocideTetracycline active ingredientsRoxithromycinRelease time
The present invention provides compositions and methods for extending the release times and lowering the toxicity of pharmacologically active compounds. The compounds comprise a salt of the pharmacologically active compound with a lipophilic counterion and a pharmaceutically acceptable water soluble solvent combined together to form an injectable composition. The lipophilic counterion may be a saturated or unsaturated C8-C22 fatty acid, and preferably may be a saturated or unsaturated C10-C18 fatty acid. The compounds precipitate in aqueous environments. When injected into a mammal, at least a portion of the composition precipitates and releases the active compound over time. Thus, the composition forms a slowly releasing drug depot of the active compound in the mammal. Therefore, the present invention enables one to provide a controlled dose administration of the active compound for a period of up to 15 days or even longer. Many compounds can be administered according to the present invention including, but not limited to, tilmicosin, oxytetracycline, metoprolol, fluoxetine, roxithromycin, and turbinafine.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Babesiidae protozoon detection primer and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit
ActiveCN103710433AHigh degree of automationEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNegative controlRoxithromycin
The invention relates to detection of a pair of babesiidae protozoon detection primer, and the upstream and downstream primer sequences are shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2. A real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for babesiidae protozoon detection comprises a Taq (thermu aquaticus) DNA polymerase mixed liquid, a ROX (roxithromycin) dye, a primer 1 with a nucleotide sequence shown as the SEQ ID No.1, a primer 2 with a nucleotide sequence shown as the SEQ ID No.2, a TaqMan probe with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.3, a negative control and a positive control. The provided real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit is convenient to use, is less in reagent use amount, greatly simplifies the operation process, reduces pollution in the operation process, is strong in detection effect specificity and is high in sensitivity.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Application of papermaking sludge based biological carbon in removal of antibiotics or heavy metals and antibiotics from water body
InactiveCN107686142ASolve pollutionImportant environmental benefitsWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryRoxithromycinAntibiotic Y
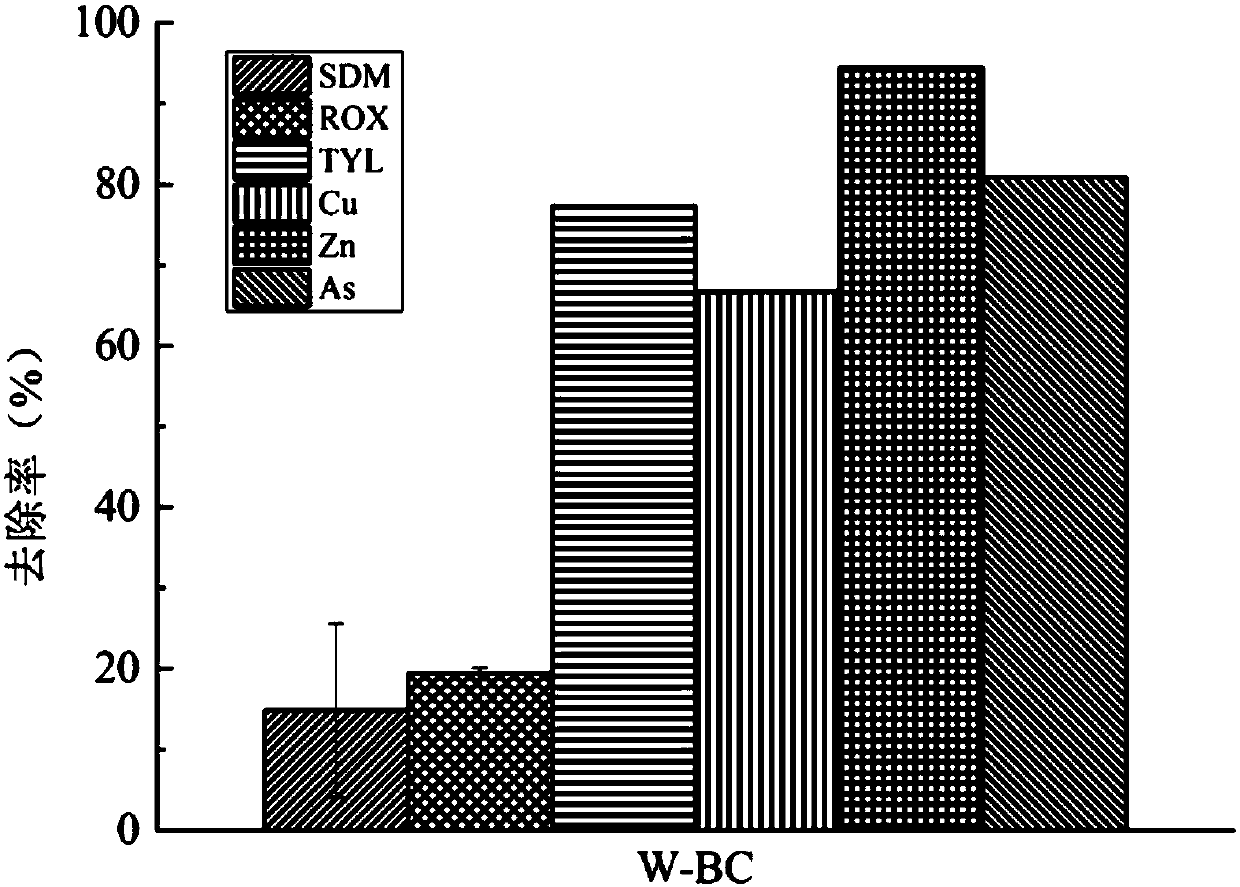
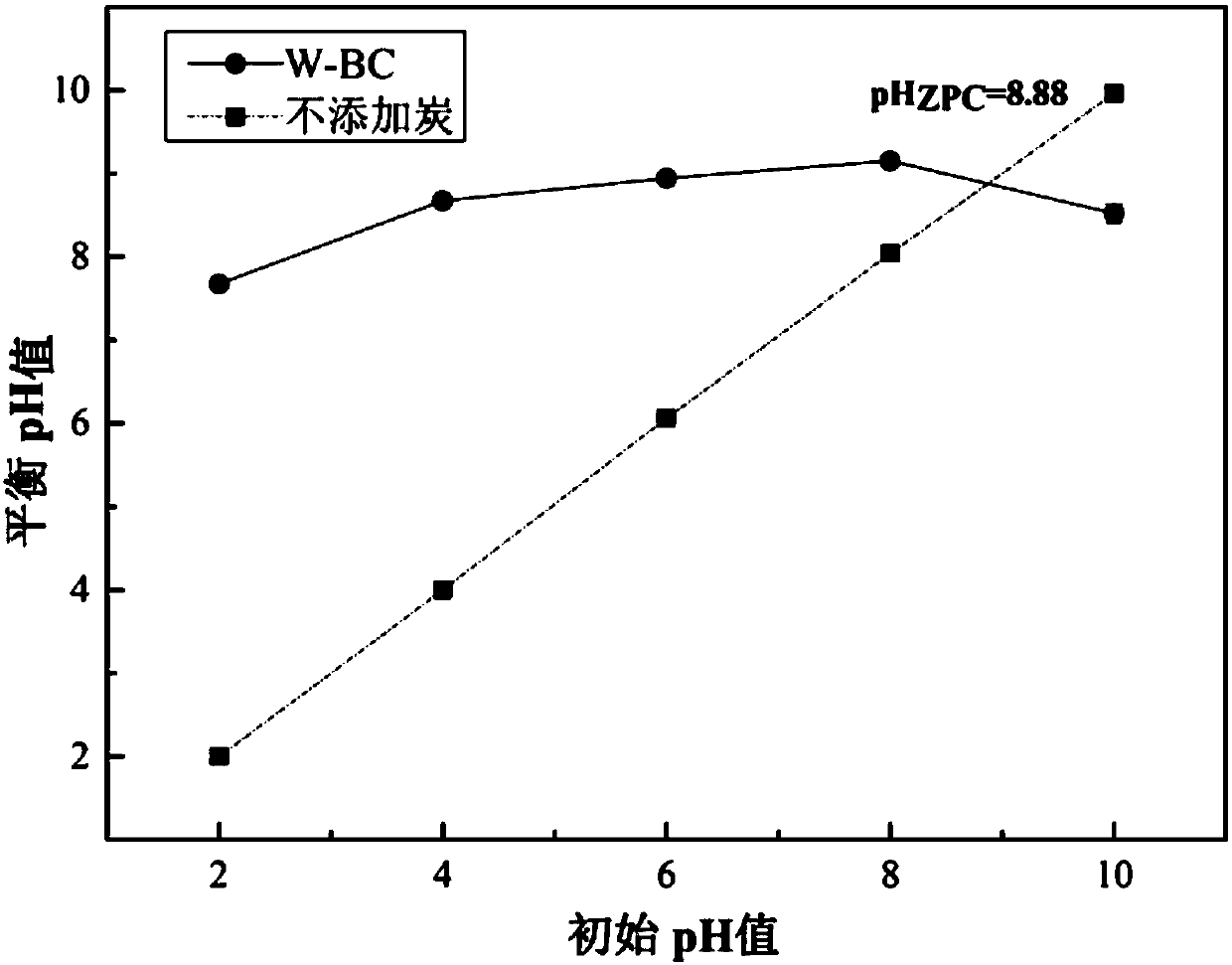
The invention discloses application of papermaking sludge based biological carbon in removal of antibiotics or heavy metals and the antibiotics from a water body and belongs to the technical field ofbiomass treatment and water treatment. The papermaking sludge based biological carbon has larger specific area and a larger pore size and can efficiently remove combined pollution of copper, zinc, arsenic, sulfadimidine, tylosin and roxithromycin. The biological carbon is simple in preparation technology, significant and stable in effect, environment-friendly and free from secondary pollution, andhas a wide application value in a heavy metal / antibiotic pollution repair aspect in the water body. Paper mill sludge difficult to treat is recycled; the environmental pollution problems of wastewater containing the heavy metals and the antibiotics are solved; and therefore, the application has important environmental and economic benefits. The biological carbon has a huge market and an application potential in waste recycling and sewage treatment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Penetrating antibiotic gel for soft tissue diseases
A penetrating antibiotic gel for treating pain, inflammation and other pathological conditions affecting musculoskeletal tissues and other soft tissues of the body. The composition includes an antibiotic compound and a mobilizing agent in an amount sufficient to enable the antimicrobial compound to penetrate into the sub-dermal soft tissues. The antimicrobial compound may be a macrolide antibiotic compound such as azithromycin, erythromycin or roxithromycin, for example, and the mobilizing agent may be an organogel compound, such as pluronic lecithin liposomal organogel (PLO). The composition may further include a penetration enhancing adjuvant, such as d-limonene, for example. The composition may be applied topically so as to penetrate into the sub-dermal soft tissues, or may injected so as to be absorbed into the soft tissues locally.
Owner:ALLEN DAVID M
Roxithromycin capsule and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103083278AImprove the disintegration effectHigh dissolution rateAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinDissolution
The invention discloses a roxithromycin capsule and a preparation method thereof. The roxithromycin capsule pharmaceutical composition comprises the roxithromycin, silica powder, a disintegrating agent, a filler, a lubricant, etc. The preparation technology of the roxithromycin capsule comprises a direct filling technology and a wet granulation process. The method can satisfy demands of different equipment and is beneficial for production. The prepared roxithromycin capsule is good in dissolution and small in loading difference, and is a safe, stable and effective product.
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN PHARMA RES INST CO LTD
Method for detecting antibiotic in environment sample
InactiveCN108318613AEfficient enrichmentRealize detectionComponent separationNorfloxacinSurface water
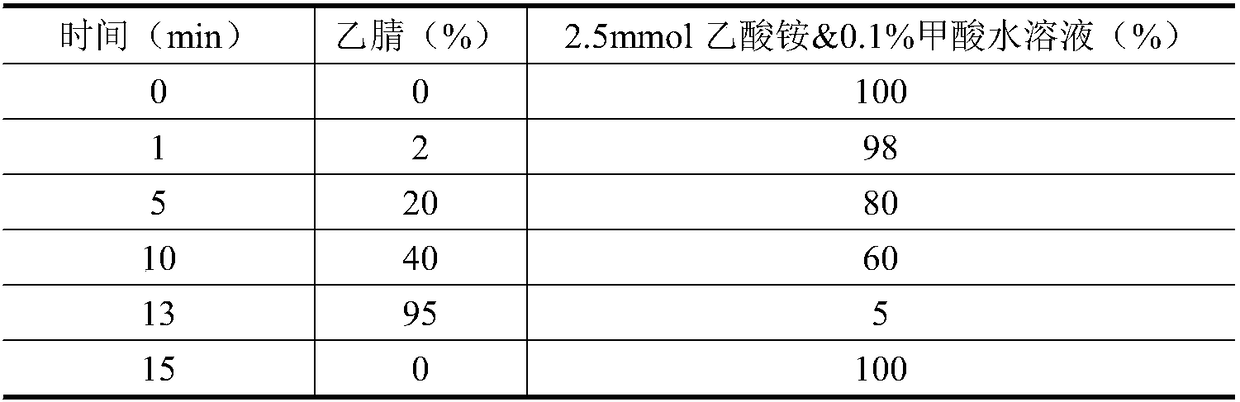
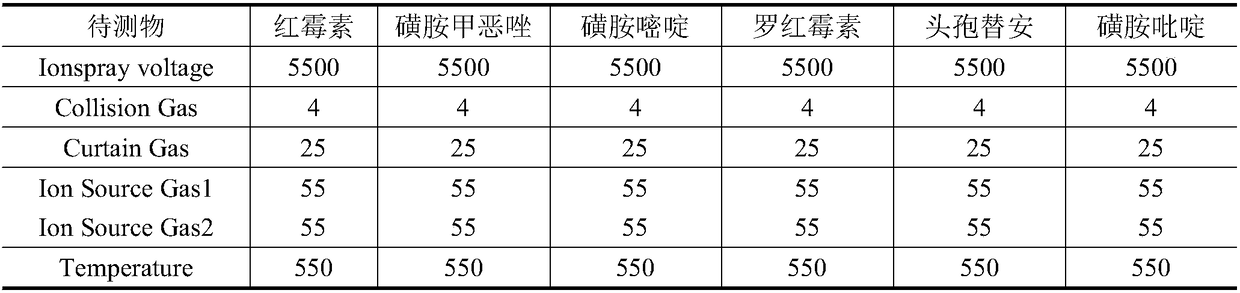
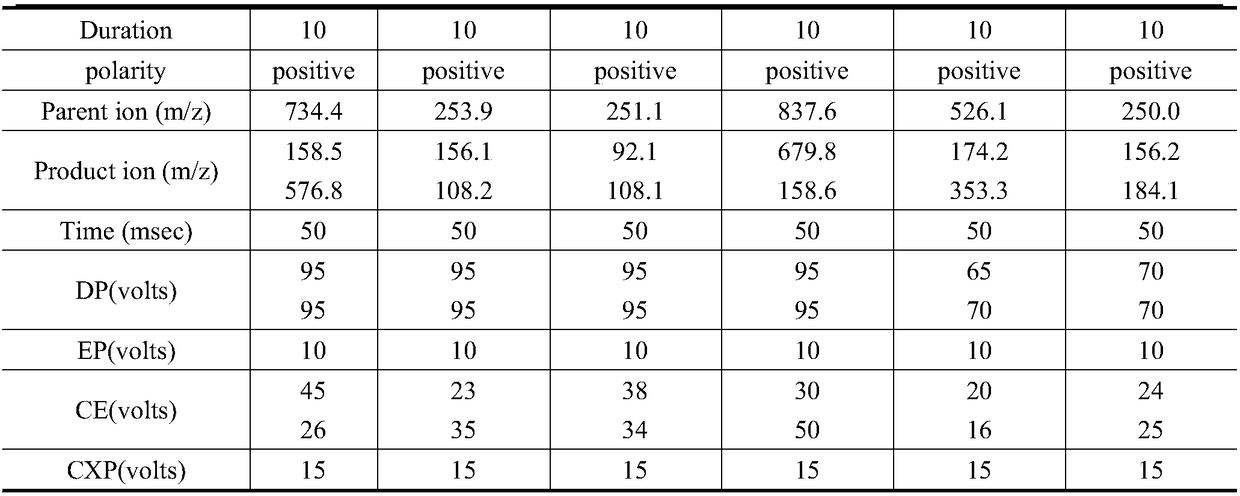
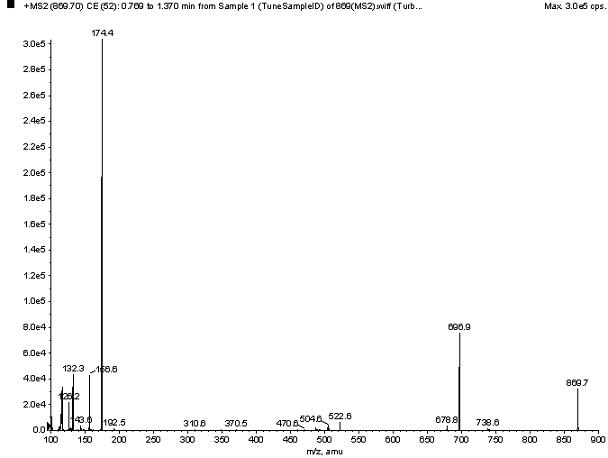
The invention relates to the technical field of environment detection and is suitable for measuring erythrocin, chloramphenicol, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, roxithromycin, cefotiam, pyridazol, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, tetracycline and doxycycline in sewage, surface water and bottom mud. After being sampled, a water sample and a mud sample are pretreated and detected through ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry, and qualitative diagnosis is conducted through the characteristic ion pair (m / z) of a target compound, a standard curve is drawn accordingto the response value and the corresponding concentration, and the external standard method is used in quantification, so that the contents of various antibiotics in the sample are obtained. The method is accurate, sensitive and simple, and is suitable for measuring the contents of 11 typical antibiotics in the sewage, the surface water and the mud at the same time.
Owner:四川国测检测技术有限公司
Roxhthromycin soft capsule and its preparing method
InactiveCN1709273AImprove bitternessMask bitternessOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinSolubility
The present invention relates to a roxithromycin soft capsule and its preparation method. In the invented roxithromycin soft capsule its liquid medicine contains roxithromycin with effective dose and medicinal auxiliary material. Said medicinal auxiliary material includes dilutent, antioxidant, solubilizing agent, solubility promoter and pH regulator. In the liquid medicine of every standard capsule 0.01-0.25g of roxithromycin is contained. Besides, said invention also provides the concrete steps of its preparation process.
Owner:秦引林
Coated roxithromycin micro-capsule, and its prepn. method utilizing fluidized bed
InactiveCN1537539AGreat tasteNo barriers to absorptionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinMethacrylate
A coated roxithromycin microsoftgel is disclosed. Its fluidized-bed preparing method features that the solution of the copolymer of dimethylamino ethyl methylacrylate and methylacrylate in alcohol is used as the coating material to coat the roxithromycin in fluidized-bed granulator, and then is dried in hot airflow. Its advantages are no bitter taste, easy absorption in stomach and no environmental pollution.
Owner:上海丽珠制药有限公司
Pediococcus acidilactici P3-4, screening and identifying method thereof and application of pediococcus acidilactici P3-4 in degradation of erythromycin and roxithromycin
ActiveCN104911123ANo secondary pollutionImprove processing efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRoxithromycinMicroorganism
The invention discloses pediococcus acidilactici P3-4 which is preserved in a common microorganism center of the Chinese microorganism culture preservation management council. The preservation serial number of the pediococcus acidilactici P3-4 is CGMCC No.10574. A novel method for screening lactic acid bacteria is established based on the combination of the microorganism method and the chemical method, a culture medium is selected through antibiotics for primary screening and secondary screening, and a lactic acid bacterium which can degrade erythromycin and roxithromycin is screened out from soil. A reasonable and effective method for screening a strain for degrading erythromycin and roxithromycin is established, the proper required lactic acid bacterium strain is obtained, primary screening and secondary screening of the lactic acid bacterium for degrading erythromycin and roxithromycin are achieved through separation, purification and screening of lactic acid bacteria, and the safe and effective strain for degrading erythromycin and roxithromycin is obtained through screening. The pediococcus acidilactici P3-4 is used for treatment of pollution of erythromycin and roxithromycin and has the advantages that secondary pollution is avoided, treatment efficiency is high, the application range is wide, and cost is low. More options are provided for treating antibiotic pollution in complicated environments through microorganisms.
Owner:潍坊中创生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing roxithromycin dispersible tablet
ActiveCN104739792AEffective absorptionMeet the needs of takingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinPrill
The invention discloses a method for preparing a roxithromycin dispersible tablet. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pre-grinding roxithromycin, pregelatinized starch and lauryl sodium sulfate to obtain a roxithromycin pre-ground material for later use; (2) mixing the roxithromycin pre-ground material, microcrystalline cellulose and low substituted hydroxypropy cellulose, adding an ethanol aqueous solution, granulating by a wet method, drying, screening through a 20-60-mesh screen to obtain a pre-mixed granular material for later use; (3) mixing the pre-mixed granular material, silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate, and tabletting to prepare the roxithromycin dispersible tablet. According to the method, roxithromycin and partial auxiliaries are together ground, so that the hydrophilicity of a medicine is improved, the contact angle is reduced, and the bioavailability of the medicine is improved; furthermore, high-efficiency wet-process granulation and boiling drying are adopted at the same time, so that the labor intensity is reduced, the production efficiency is improved, and the prepared dispersible tablet can be quickly uniformly dispersed in water to facilitate effective absorption of a human body after the dispersible tablet is taken.
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN PHARMA CO LTD
Fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting yersinia enterocolitica
InactiveCN102329864ADetection is simple and fastSolve the cumbersome operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceRoxithromycinFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting yersinia enterocolitica, reagents in the kit comprise a front primer, a rear primer, a TaqMan probe, a fluorescence PCR premixed solution, an ROX (roxithromycin) solution, pure water and a positive standard solution, wherein the front primer, the rear primer and the TaqMan probe are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments of 20-21 bases, which are synthesized according to a specific and conserved gene nucleotide sequence of the yersinia enterocolitica and can be specifically combined with the yersinia enterocolitica. The invention further provides a method for detecting the yersinia enterocolitica, and the method comprises the following steps: performing pretreatment on samples; using the reagents of the kit for detection; and analyzing the detection result. The kit is simple, fast, sensitive, accurate and suitable for detecting a large number of samples.
Owner:南宁海关技术中心
Enterococcus faecium E9-10, screening and identification method thereof and application of enterococcus faecium E9-10 to degrading erythromycin and roxithromycin
ActiveCN104946557AReasonable and effective degradationImproving the Efficiency of Treating Antibiotic PollutionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementRoxithromycinMicroorganism
The invention discloses enterococcus faecium collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), with collection number being CGMCC No.10575. The enterococcus faecium has the technical effects that lactobacillus with an erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading function is screened from soil through preliminary screening and secondary screening of an antibiotic selective medium; a reasonable and effective screening method of an erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading strain is established to obtain lactobacillus meeting the needs; the safe and effective erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading strain is screened through separation, purification and screening of lactobacillus and a series of work, such as preliminary screening and secondary screening of erythromycin and roxithromycin degrading lactobacillus; when applied to control over erythromycin and roxithromycin pollution, the enterococcus faecium has the advantages of no secondary pollution, high treatment efficiency, wide range of application and low cost; the enterococcus faecium provides more choices for microbiological control over antibiotic pollution of complex environments.
Owner:潍坊中创生物科技有限公司
Oral disintegrating tablet using roxithromycin and ambroxol hydrochloride as active component and its preparing method and use
The invention relates to an orally disintegrating tablet comprising roxithromycin id and ambroxol hydrochloride as active ingredients and its preparation method and uses. Said invention is a medical compound resulting from mixing roxithromycin id and ambroxol hydrochloride as active ingredients and auxiliary material acceptable by pharmacology and for treatment of infection of the upper respiratory tract. Said invention provides means for covering bitter from roxithromycin id and ambroxol hydrochloride and preparation method for orally disintegrating tablets of said medical compound.
Owner:BEIJING RUNDEKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Macrolide antibiotic high-selectivity solid-phase micro-extraction probe, preparation method thereof and application of probe
InactiveCN109078627AImprove adsorption capacityGood choiceComponent separationOther chemical processesRoxithromycinESI mass spectrometry
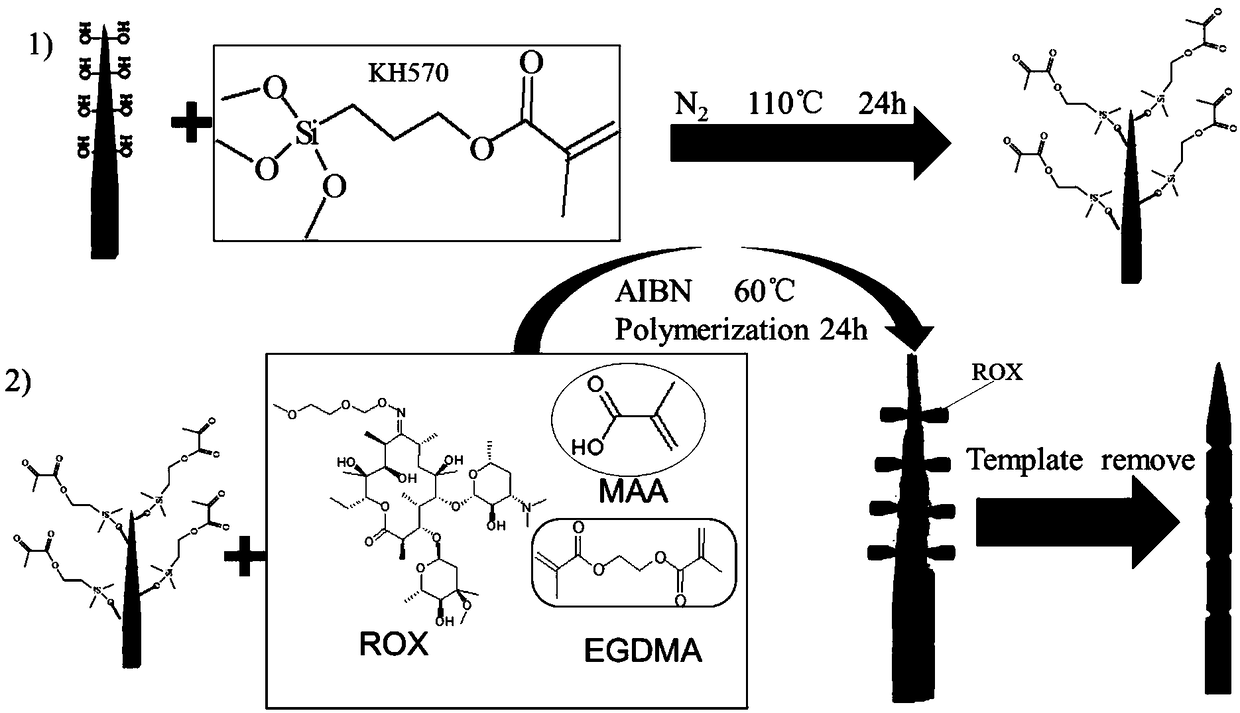
The invention discloses a macrolide antibiotic high-selectivity solid-phase micro-extraction probe, a preparation method thereof and an application of the probe. The probe takes roxithromycin as a template molecule, silanization reaction between a molecularly imprinted material and a solid substrate with hydroxyl-rich surface is implemented, and the molecularly imprinted material is bonded onto the surface of the solid substrate to prepare the solid-phase micro-extraction probe. High-selectivity and high-enrichment extraction of macrolide antibiotics in various complicated substrates can be directly implemented by the solid-phase micro-extraction probe, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis of an enriched compound in the probe can be directly implemented by the extracted solid-phase micro-extraction probe under normal pressure open conditions, and the probe has ideal sensitivity and repeatability.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ANALYSIS CHINA NAT ANALYTICAL CENT GUANGZHOU
Roxithromycin monohydrate crystal, its preparation method and composition dry suspension containing the combination of the crystal and ambroxol hydrochloride
ActiveCN102286045ACrystalline with low hygroscopicityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinSucrose
The invention relates to a roxithromycin monohydrate crystal, a preparation method thereof and a compound dry suspension containing the roxithromycin monohydrate crystal and an ambroxol hydrochloride composition. The roxithromycin monohydrate crystal provided by the invention has a molecular formula of C41H76N2O15.H2O. The preparation method comprises the steps of sample dissolving, devitrifying,smashing, water exchanging and drying. The invention also provides a composition containing the crystal, and the composition comprises 30-70 parts by weight of roxithromycin monohydrate crystals, 5-15 parts by weight of ambroxol hydrochloride, 10-30 parts by weight of xanthan gum, 10-50 parts by weight of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 2870-2920 parts by weight of cane sugar and a proper amount of banana essence. The crystal provided by the invention has low moisture absorption and good stability. The composition provided by the invention contains the roxithromycin monohydrate crystal, the suspension is in a good condition, the dissolution rate of medicaments is increased, and the bioavailability is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG LUOXIN PARMACEUTICAL GROUP STOCK CO LTD
Roxithromycin injection
InactiveCN1452975AImprove stabilityImprove solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinWater soluble
The present invention relates to Roxithromycin injection and is especially bacteria-free powder and solution of water soluble Roxithromycin salt, such as Roxithromycin hydrochloride, Roxithromycin tartrate and Roxithromycin lactobionate, for injection. The present invention also provides the preparation process of bacteria-free powder and solution of water soluble Roxithromycin salt for injection.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PUIS PHARMA FACTORY
A kind of novel roxithromycin capsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102266309AEasy to operateGood reproducibilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinSustained Release Capsule Dosage Form
The invention discloses a novel roxithromycin capsule, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 55-70% of roxithromycin, 3-6% of a binder, 15-20% of a coating material, and 6% of a plasticizer. ~8%, porogen 5~9%, glidant 0.5~1.5%. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the novel roxithromycin capsule. The roxithromycin capsule of the present invention greatly improves the disadvantages of the common oral dosage form of roxithromycin, which are frequently taken and have low bioavailability. Roxithromycin was made into pellets, and the roxithromycin pellets were made into sustained-release tablets by an improved fluidized bed coating method, and then filled into capsules to obtain roxithromycin sustained-release capsules. The operation is simple and reproducible. Well, it is easy to achieve mass production, and compared with other commercially available sustained-release capsule dosage forms, through the re-vulcanization process after fluidized coating, the coating material can exert a sustained-release effect, so as to achieve better curative effect.
Owner:江苏黄河药业股份有限公司
Oral medicine for eliminating pyloric spirillar bacilli
InactiveCN1559422ADelay drug resistanceLow costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNitroimidazoleOral medicine
An orally-applied medicine for radically treating the pylorospirobacillus contains roxithromycin, histamine H2 recepto agonist, nitroimidazole-type antibacterial agent, and proper additive.
Owner:金春华
Sustained release preparation of roxithromycin
InactiveCN1415305AGood curative effectGreat tasteAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinAdhesive
A showly-releasing roxithromycin contains roxithromycin (30-80 wt.%), slow-releasing assistant (hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, etc) (10-40 wt.%), and others (hole-forming agent, adhesive, lubricant, etc). Its advantages are long active period (24 hrs.), and low by-effect.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Oral preparation containing rokuromycin and its making method
InactiveCN1939273AQuick effectEliminate time limit for absorbing distributionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinAdditive ingredient
An orally absorbed medicine in the form of buccal lozenge, sweets, or dripping pill dissolved by saliva features that it contains roxithromycin. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:刘凤鸣
Method for purifying roxithromycin
InactiveCN102219816AGood removal effectHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationRoxithromycinContinuous use
The invention mainly discloses a method for purifying roxithromycin. The method comprises the following steps of dispersing erythromycin crude products into a mixed solvent of two lower alcohols, heating to clarify the mixed liquid obtained from the above step, cooling to make precipitates be separated from the clarified liquid obtained from the above step and stirring at a low temperature for a period of time to make the precipitates be separated from the clarified liquid fully, and filtering to obtain purified erythromycin. The method has the advantages of good impurity removal effects, high yield, continuous use feature of mother liquor, few three wastes, low cost, good adaptability for industrialization production, and favorable products with uniform granularity, good fluidity, a small number of broken crystals, and high hardness of crystals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GUOBANG PHARMA
Roxithromycin capsule and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN109248155ASimple manufacturing processExcellent qualityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinMedicine
The invention relates to a roxithromycin capsule and a preparation method of the roxithromycin capsule. The roxithromycin capsule is prepared from the following constituents in percentage by weight:50-75 % of roxithromycin, 5-25 % of corn starch, 10-30 % of low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, 0.5-6 % of a wetting agent, 0.5-3 % of a binder, and 0.5-3 % of a lubricant, wherein the binder ispolyvinylpyrrolidone; the wetting agent is selected from sodium dodecyl sulfate, Tween 80 and poloxamer; and the lubricant is selected from one or more of micropowder silica gel, magnesium stearate and talcum powder.
Owner:北京鑫开元医药科技有限公司
Roxithromycin and ambroxol hydrochloride dispersible tablets
InactiveCN101485673ASimple production processReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinCurative effect
The invention relates to a roxithromycin ambroxol dispersing tablet, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 50 to 60 percent of roxithromycin, 10 to 20 percent of ambroxol hydrochloride, 18 to 25 percent of filling agent, 10 to 15 percent of disintegrant, 0.1 to 1 percent of adhesive, and 1 to 5 percent of lubricating agent, wherein the filling agent is microcrystalline cellulose, and the disintegrant is crosslinked polyvidone. The roxithromycin ambroxol dispersing tablet has the advantages of small tablet weight, simple process, low production cost and good safety, and has better therapeutic effect when being clinically applied to upper respiratory tract infections of human bodies.
Owner:HAINAN HONZ PHARMA
Roxithromycin capsules and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN106138009AIncrease the amount of dissolutionLow costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinCellulose
The invention discloses a roxithromycin capsule and a preparation process thereof. The raw materials include roxithromycin, starch, low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, polysorbate, sodium carboxymethyl starch and silicon dioxide. The preparation process of roxithromycin capsules: (1), by weight, weigh 1500 parts of roxithromycin, 430 parts of starch, and 86 parts of low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, and then mix them uniformly; (2), by weight Add 20 parts of polysorbate; (3), add ethanol, and mix again; (4), make granules through a 18-mesh sieve; (5), dry; (6), granulate through a 18-mesh sieve; (7) 100 parts by weight of sodium starch glycolate and 42.7 parts of silicon dioxide were added, and mixed evenly; (8), packed into capsules to obtain roxithromycin capsules. The invention is convenient to take raw materials, the cost of the roxithromycin capsule is low, the process is simple, the reliability is high, and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:浙江花园药业有限公司
Gene detection reagent kit for evaluating alcohol tolerance
ActiveCN107058549AIntuitive test resultsEasy to understandMicrobiological testing/measurementRoxithromycinReference genes
The invention provides a gene detection reagent kit for evaluating alcohol tolerance. The gene detection reagent kit comprises six amplification primers for three genes including an internal reference gene GAPDH (glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase), a gene ADH1B (ethanol dehydrogenase 1B) and a gene ALDH2 (acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2) and five Taq-man probe primers. One of the Taq-man probe primers is positioned at the internal reference gene GAPDH and is used for carrying out FAM fluorescence labeling; two other Taq-man probe primers are SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) probes positioned at the gene ADH1B and are used for carrying out VIC and ROX (roxithromycin) labeling; the remaining two Taq-man probe primers are SNP probes positioned at the gene ALDH2 and are used for Cy5 and Quasar705 labeling, BHQ is used as a quenching group, and delta ct values can be computed. The gene detection reagent kit has the advantages that the alcohol tolerance of healthy persons can be evaluated by the gene detection reagent kit from the aspect of genes, and accordingly the healthy persons can know the strength and the weakness of alcohol tolerance, can drink alcohol scientifically and can carry on occasion such as party, gathering and banquet related to alcohol culture.
Owner:TIANJIN KANGTING BIOLOGICAL ENG GRP CO LTD
Derivatives of erythromycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin or azithromycin with antibiotic and mucolytic activity
InactiveUS20010031736A1Improved pharmacological profileGood effectBiocideSugar derivativesRoxithromycinAzithromycin
A pharmaceutical with an enhanced pharmaceutical profile comprises a mucolytic and an antibiotic in which the mucolytic is present in an amount of greater than one molar equivalent of the antibiotic. The antibiotic may be selected from Erythromycin, Roxithromycin, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Dirithromycin; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts or esters thereof. The mucolytic is a mucolytically active thiol, especially N-acetylcysteine, mercaptoethanesulfonic acid, tiopronin or methylcysteine. The adducts can be isolated via a simple and efficient process.
Owner:RUSSINSKY
Application of macrolide antibiotics in blocking influenza virus infection
InactiveCN109833326AGood ability to inhibit influenza virusAvoid infectionAntiviralsAmine active ingredientsRoxithromycinAzithromycin
The invention relates to an application of macrolide antibiotics in blocking influenza virus infection, specifically, the invention discloses the application of macrolide antibiotics including azithromycin, erythromycin, roxithromycin, medimycin or acetylspiramycin or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for blocking influenza virus infection, and the application of the macrolide antibiotics in preparation of a medicinefor treating or preventing influenza virus infection. The experiments confirm that the aforementioned macrolide antibiotics have the ability to resist influenza virus infection and are capable of performing prophylactic treatment of influenza virus infection. At the same time, the invention also validates the action mechanism of azithromycin for treatment of influenza. Therefore, the aforementioned macrolide antibiotics or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a composition comprising the aforementioned macrolide antibiotics can be prepared as the medicinefor treating or preventing the influenza virus infection.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF SYST MEDICINE
Detection method of residual amount of a plurality of macrolide veterinary drugs in casings
InactiveCN102313787AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionHigh recovery rateComponent separationRoxithromycinRelative standard deviation
The invention relates to the fields of analytical chemistry and food safety, and provides a detection method of the residual amount of a plurality of macrolide veterinary drugs in casings. The detection method comprises the following steps of: extracting a sample with methanol or acetonitrile; purifying the obtained extracting solution by a C18 or Oasis HLB (hydrophilic-lipophilic balance) solid-phase extraction column, taking an acetonitrile-methanoic acid aqueous solution with the concentration of 0.15% as a mobile phase, and performing gradient elution by adopting a ZORBAX Eclipse C8 analytical column; and performing electro-spraying, separating by a cationic scanning mode and detecting the residual amount of seven types of macrolide veterinary drugs. The detection lower limit of the seven types of macrolide veterinary drugs is 20 mu g / kg. The recovery rates of spiramycin, tilmicosin, oleandomycin, tylosin, erythrocin, roxithromycin and josamycin are respectively 71.4-78.8, 75.7-85.6, 81.1-85.8, 78.9-83.0, 87.1-89.6, 83.7-85.4 and 75.6-81.8; and the indoor relative standard deviations for the recovery rates of the spiramycin, the tilmicosin, the oleandomycin, the tylosin, the erythrocin, the roxithromycin and the josamycin are respectively 7.7-11.1, 8.0-15.7, 10.5-16.4, 8.1-12.5, 10.5-12.4, 10.6-14.4 and 7.8-18.0. The detection limit, the recovery rate, the precision and the like meet the related requirements at home and abroad.
Owner:林维宣
Novel method for separating/enriching trace roxithromycin in environment
InactiveCN101699255AEasy to handleHigh enrichment factorPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceRoxithromycinFluorophotometry
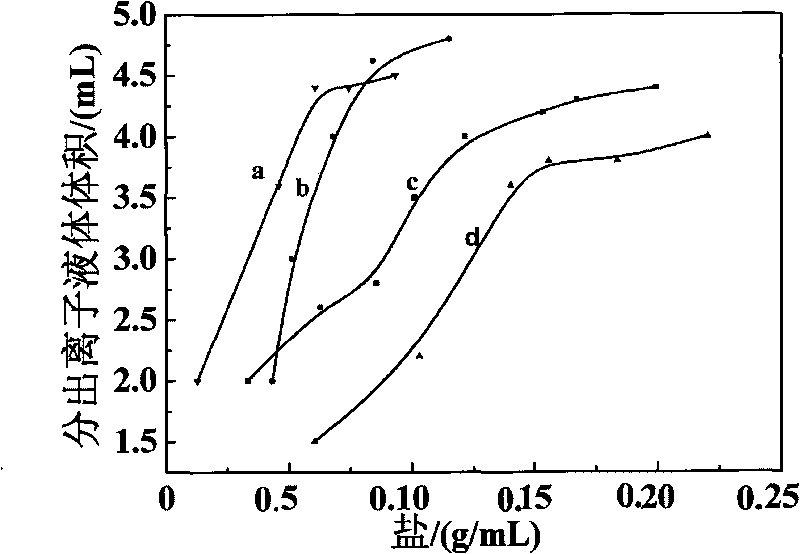
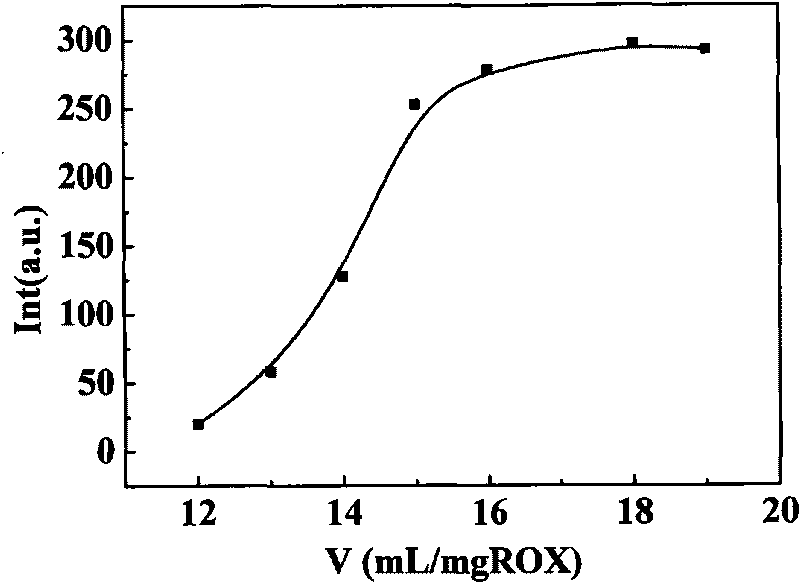
The invention provides a novel method for separating / enriching trace roxithromycin in environment. The method comprises the following steps: adding 0.4mg.mL<-1> researched roxithromycin test solution in a mouth polished colorimetric tube, wherein the volume of the roxithromycin test solution accounts for 1 / 50 of total volume of total solution in sublation; adding solid salt to adjust the ionic strength of the solution, shaking the solution to ensure that the solution can be sufficiently dissolved, and adjusting pH to be between 10.8 and 11.8, wherein the salt is solid salt of Na2CO3, (NH4)2SO4, NaH2PO4, MgSO4, Na2SO3 and NaOH; transferring the solution into a sublation column, adding the sublation solvent ionic liquid [Bmim]BF4 into the sublation column, and bringing to total volume by adding water, wherein the volume of the ionic liquid [Bmim]BF4 accounts for 1 / 25 of total volume of total solution in sublation, and the sublation flow rate of N2 is between 5 and 25mL.min<-1>; floating for 5 to 60 minutes, standing for 1 minute after aeration is stopped; taking out upper enriched [Bmim]BF4 phase by a burette when no air bubble exists; adding a certain amount of 75 percent sulphuric acid and 12 to 19 mL / mg of ROX into the sublation column to perform a color development reaction at room temperature for 0 to 70 minutes; analyzing and determining the content of the solution by using a molecule fluorescence photometry in 350nm excitation wavelength and 508nm emission wavelength. The method optimizes the best condition of sublation, and carries out separation / enrichment analysis on the trace roxithromycin in an actual environmental water sample by combining the molecule fluorescence photometry under an optimized testing condition.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com