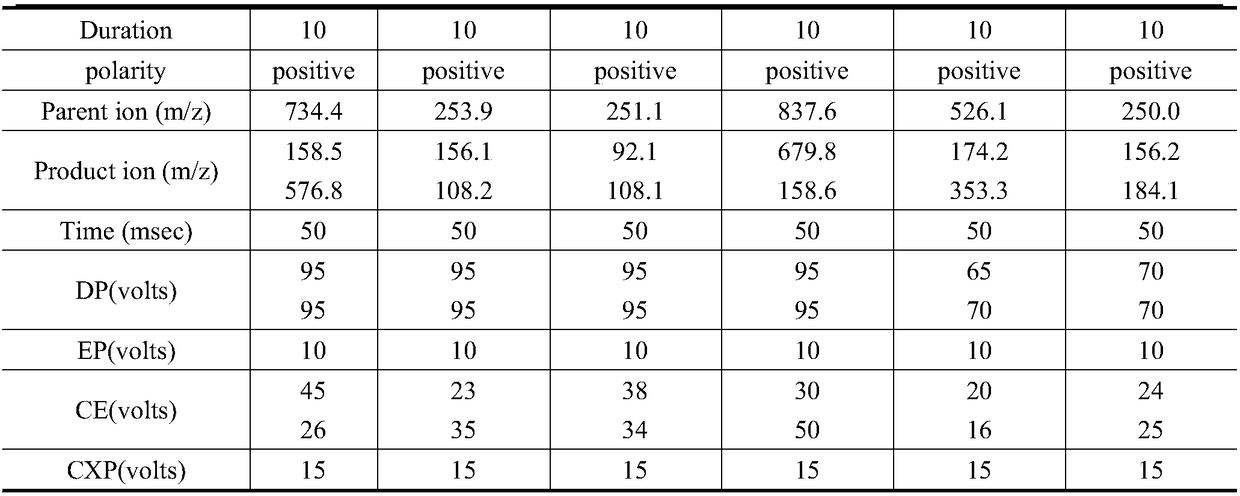
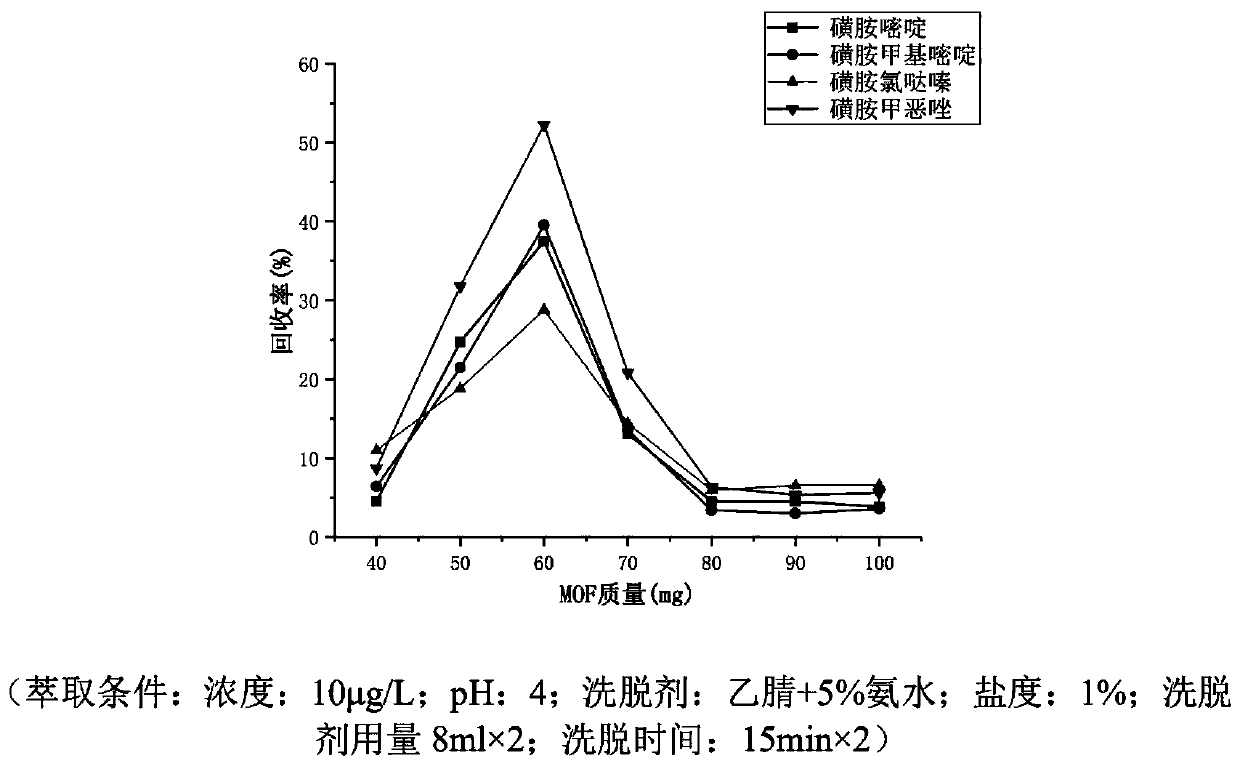
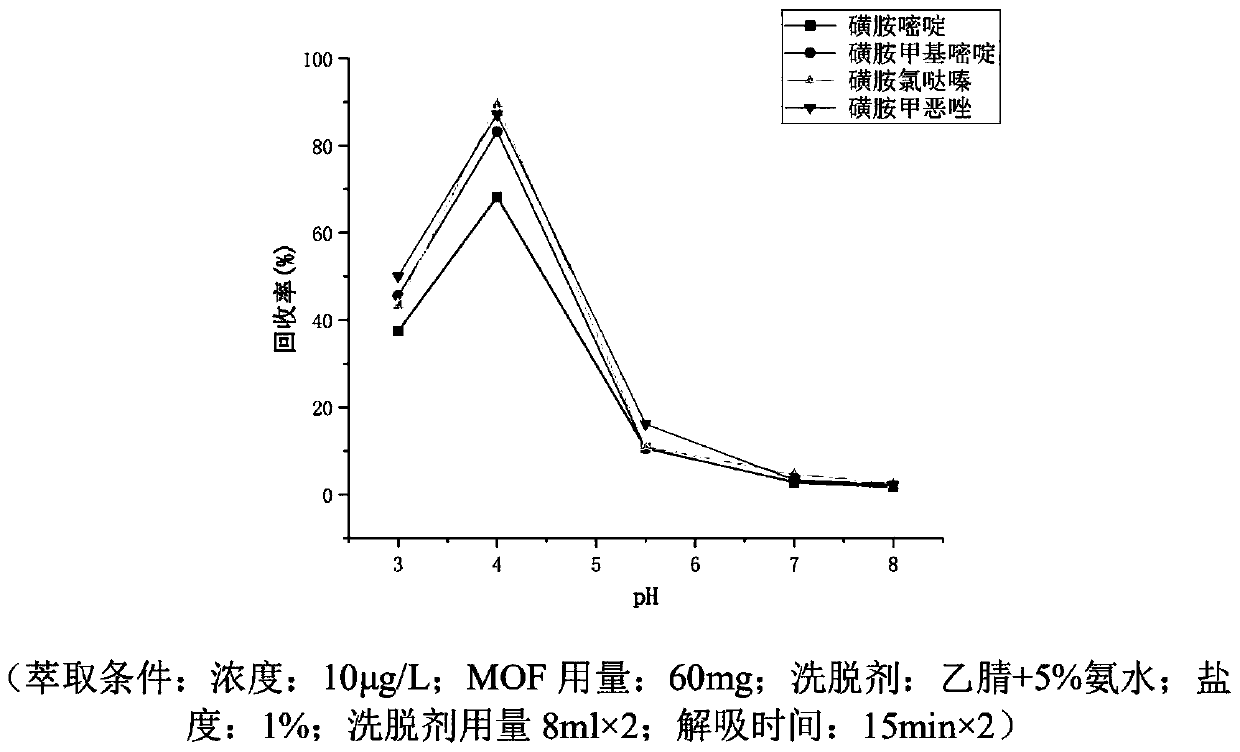
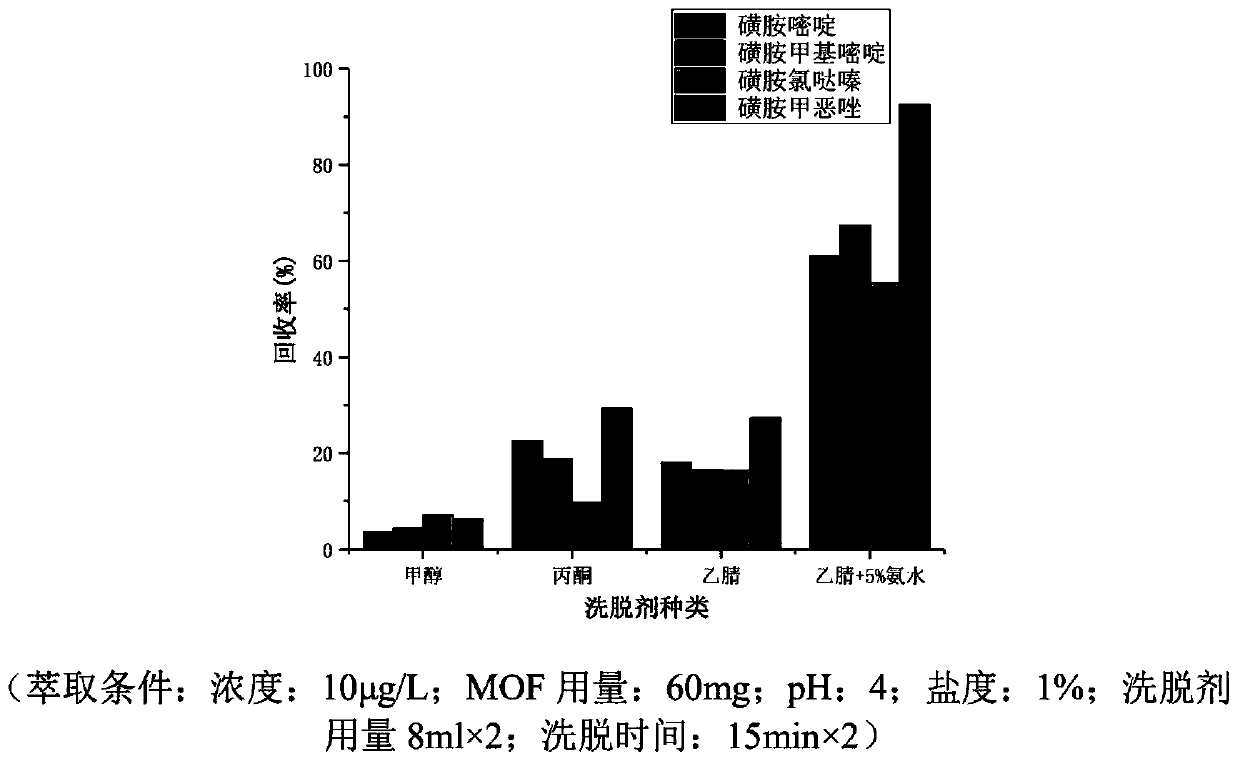
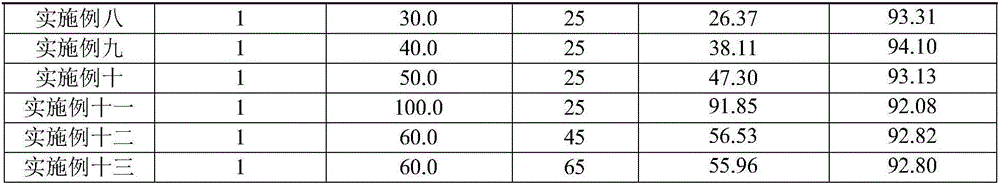
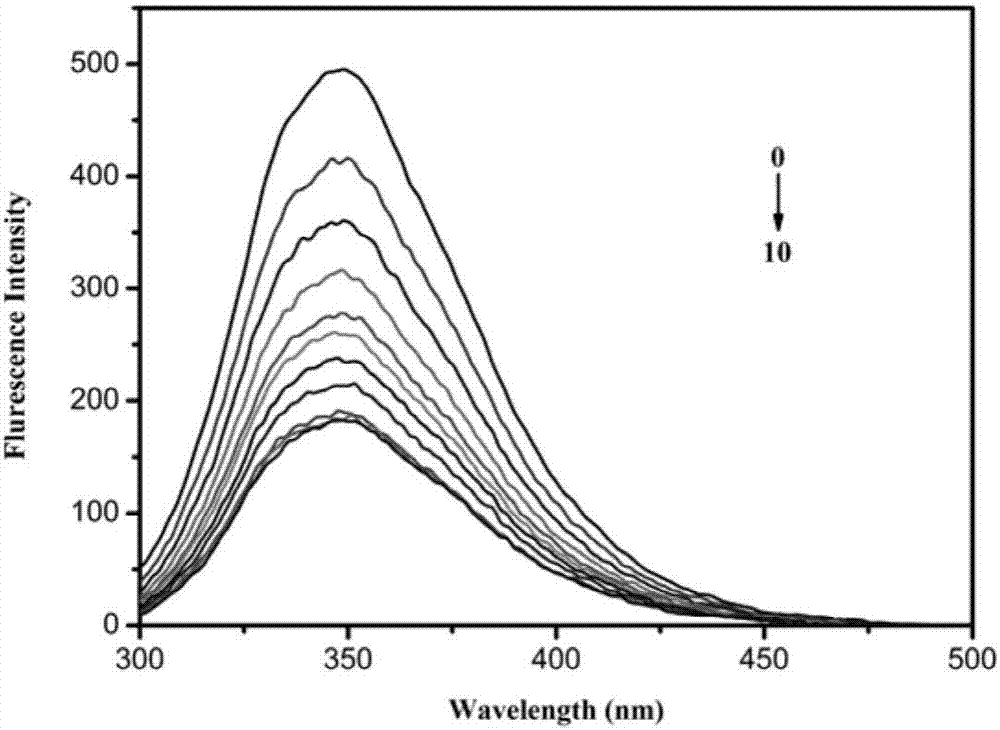
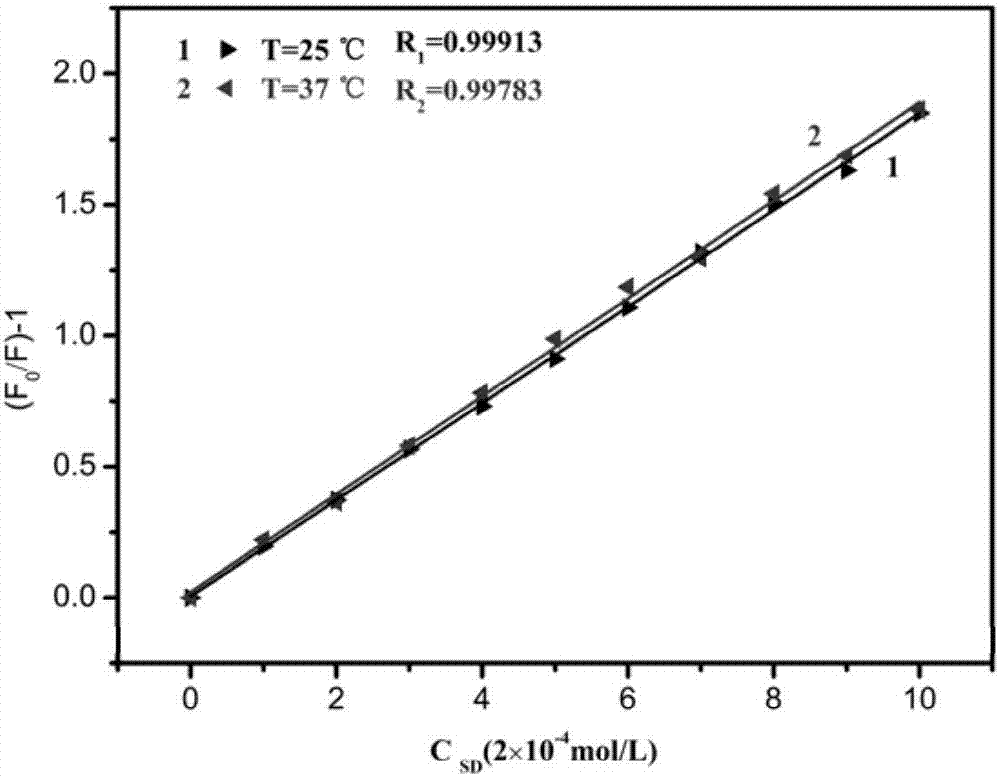
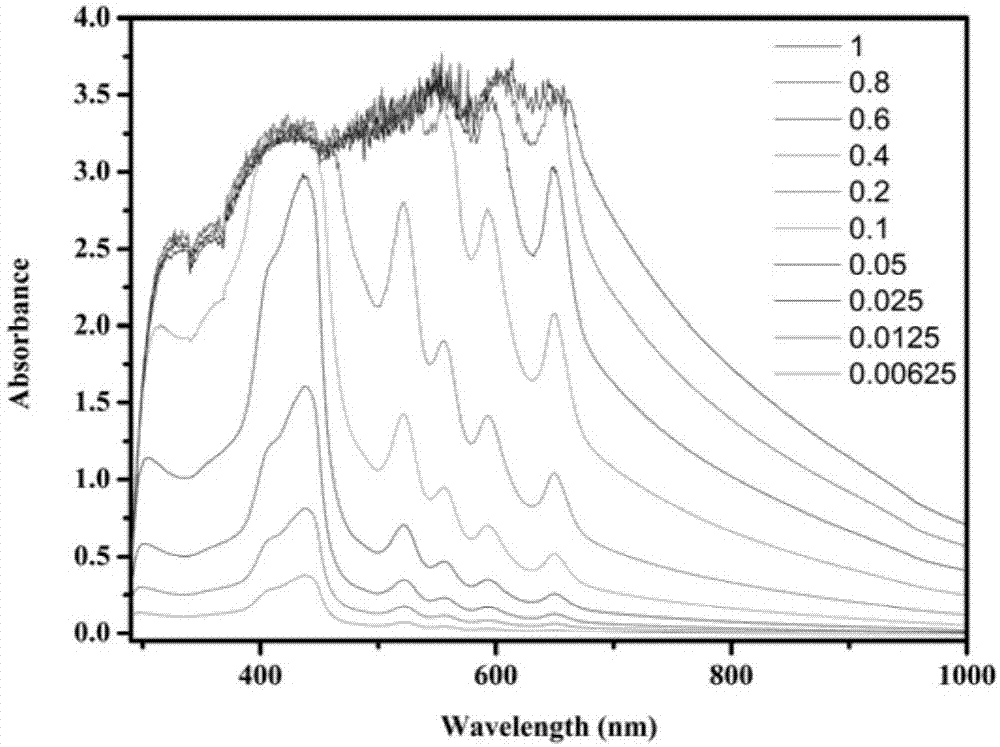
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
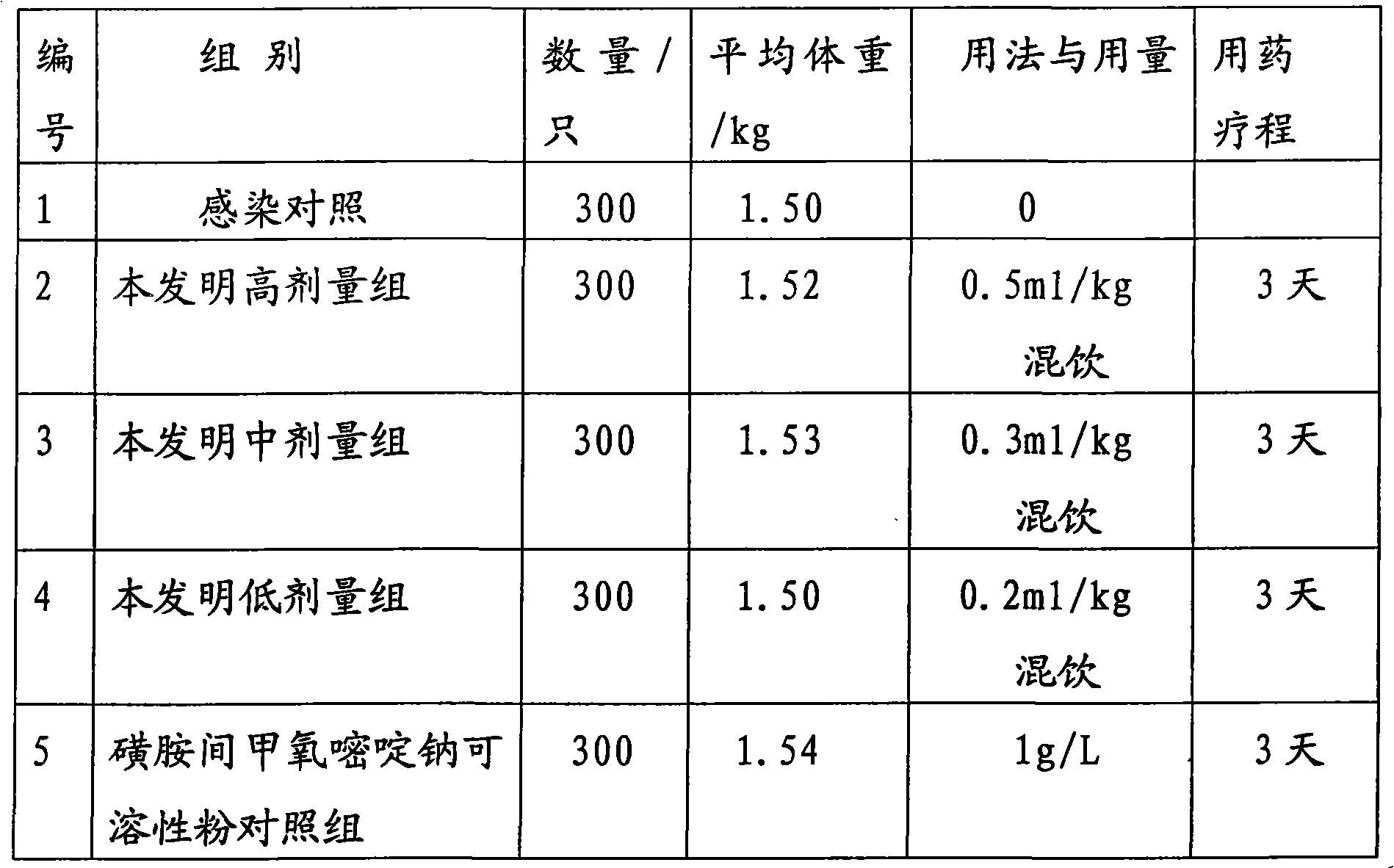
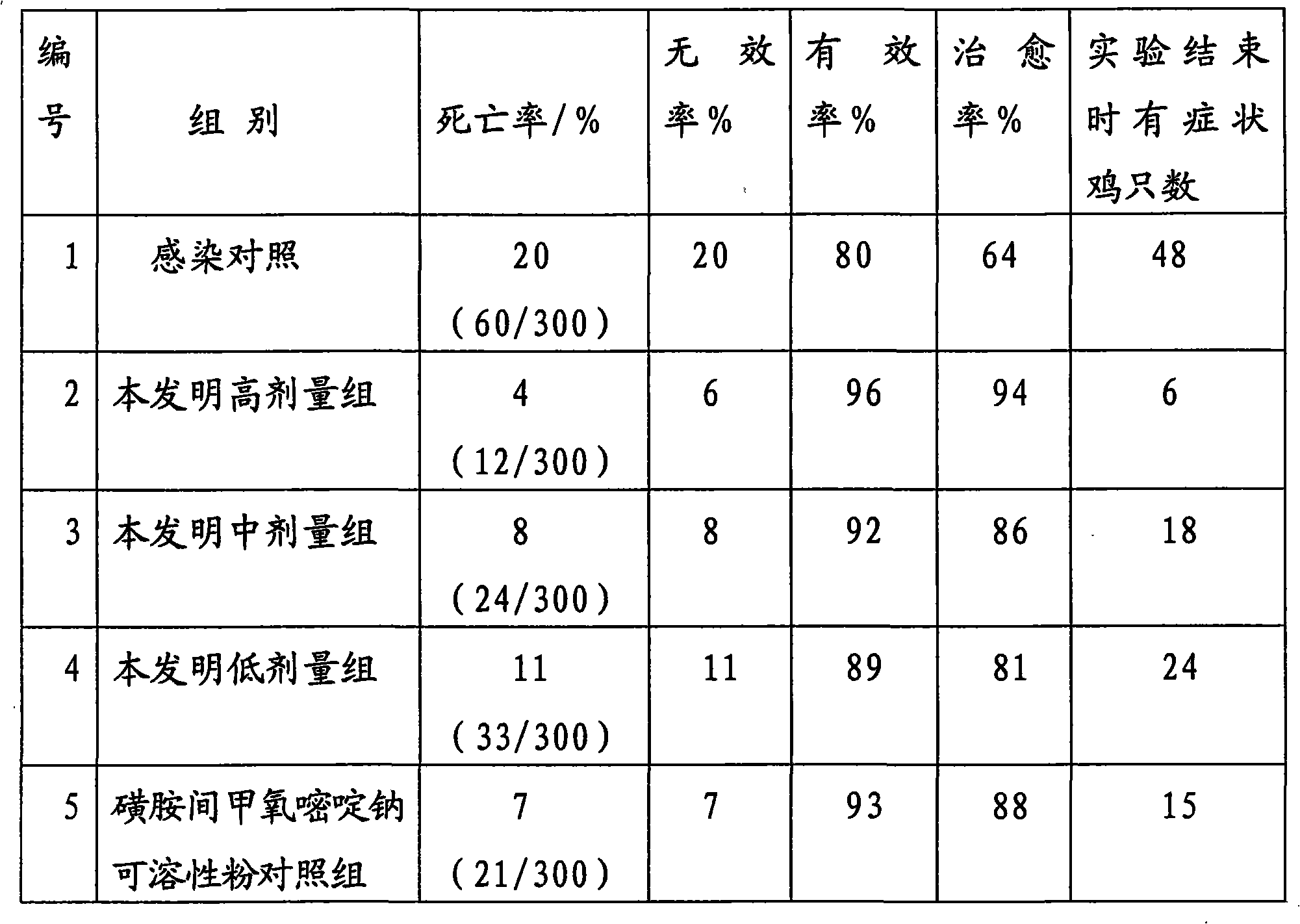
190 results about "Sulfadiazine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This medication is used to treat and prevent a wide variety of infections.
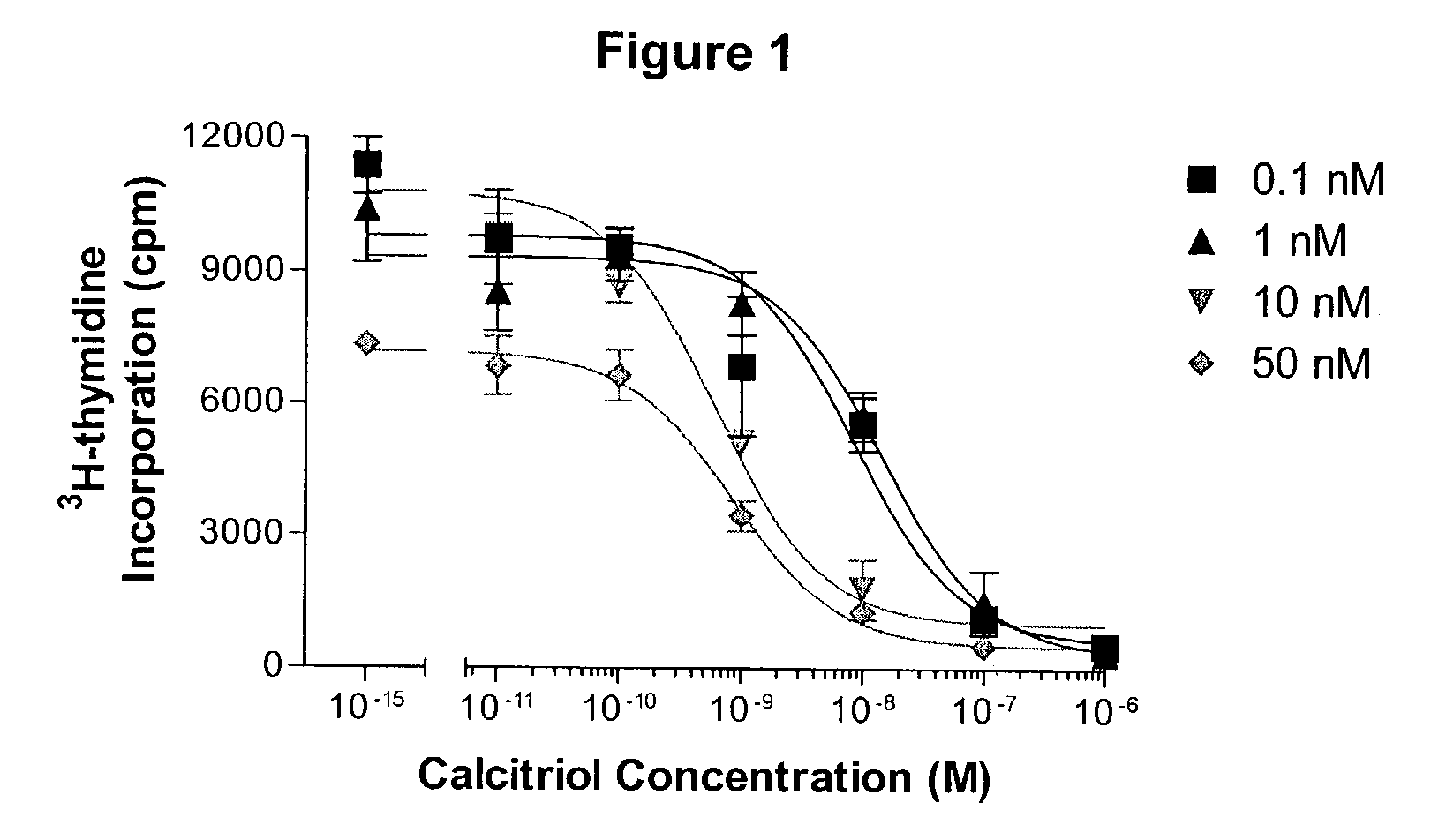
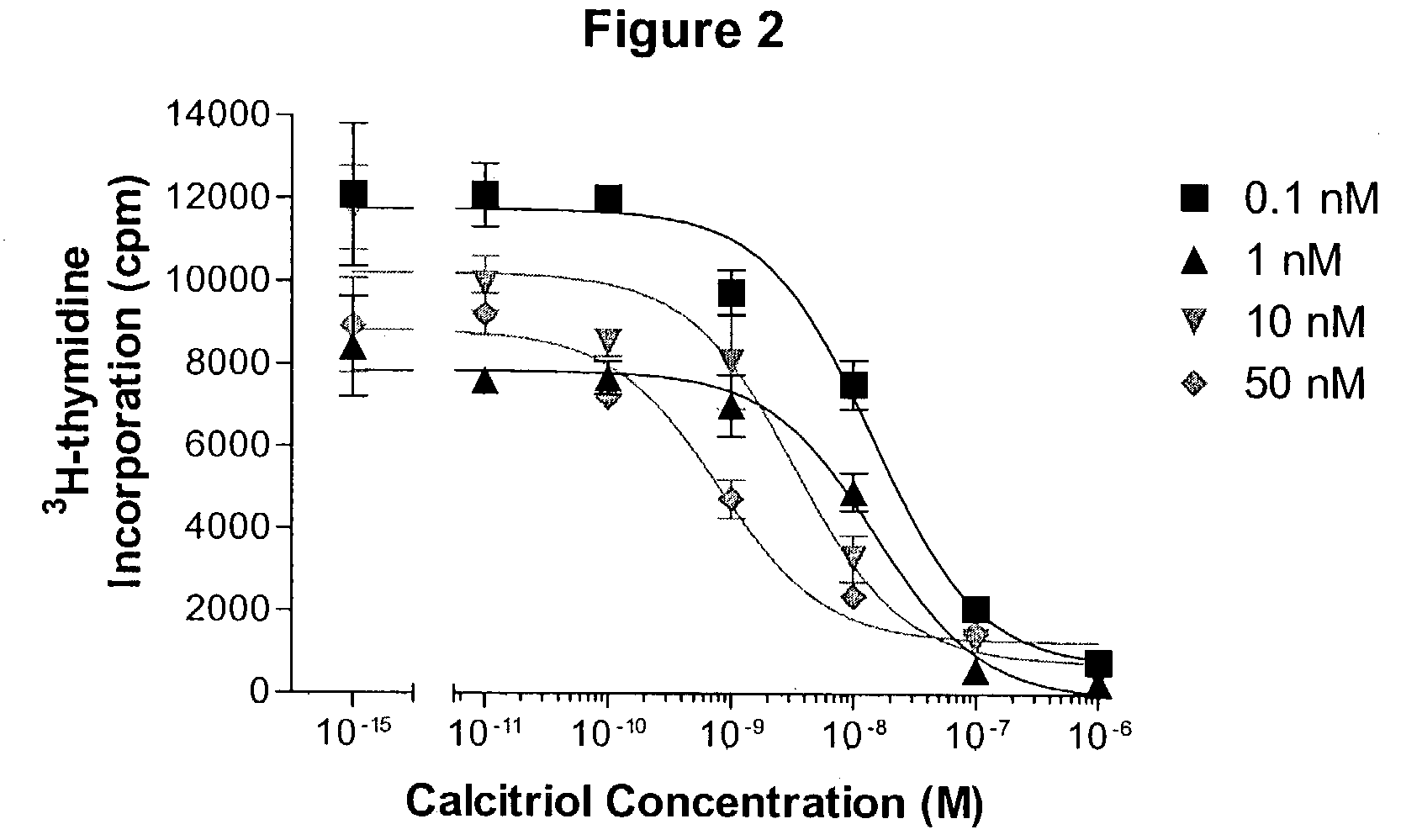
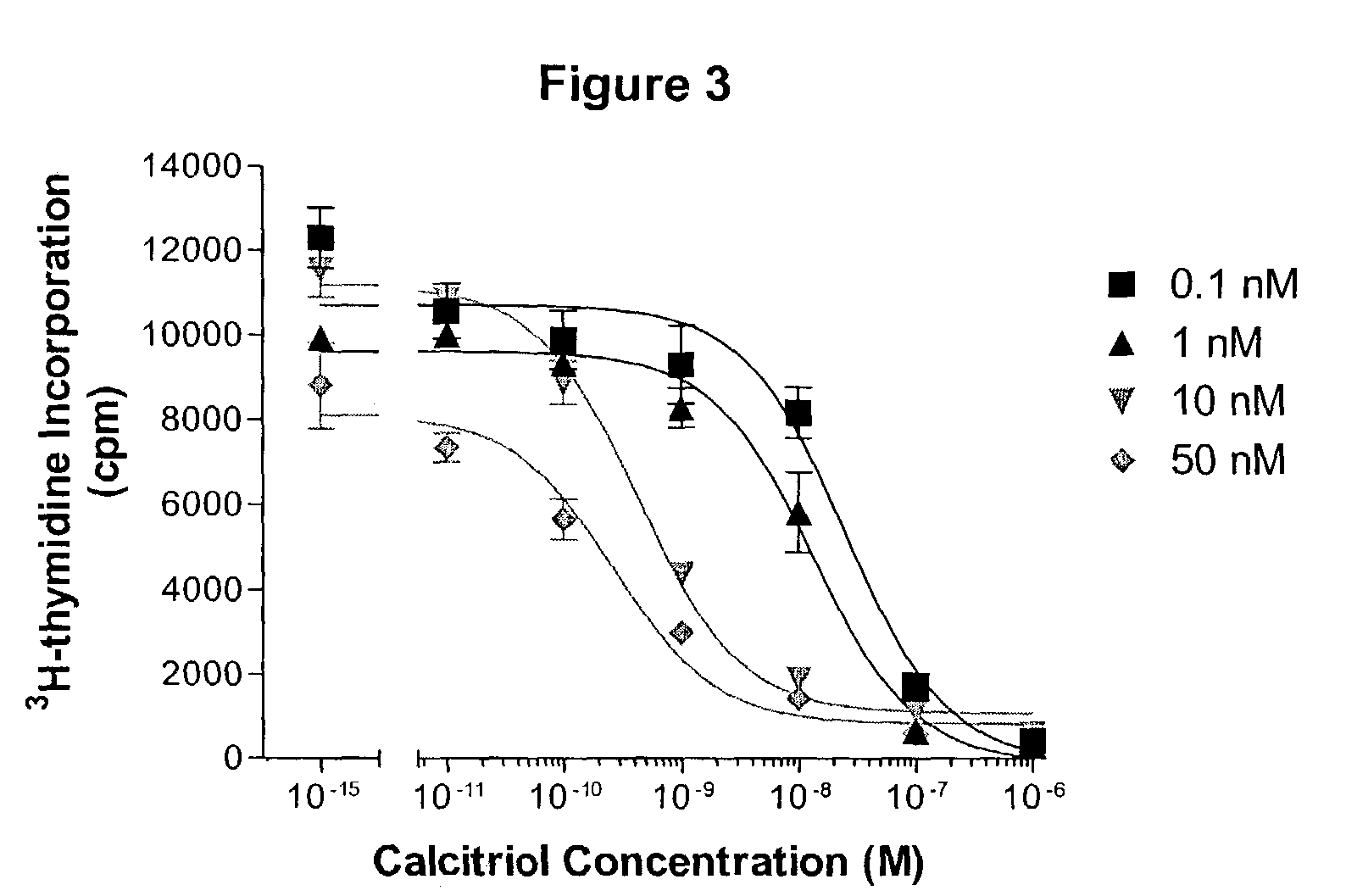
24-sulfoximine vitamin D3 compounds
The present invention provides novel sulfoximine compounds, compositions comprising these compounds and methods of using these compounds as inhibitors of CYP24. In particular, the compounds of the invention are useful for treating diseases which benefit from a modulation of the levels of 1α,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3, for example, cell-proliferative disorders.
Owner:OPKO IRELAND GLOBAL HLDG LTD +1
Antimicrobial sol-gel films comprising specific metal-containing antimicrobial agents
Broadly defined sol-gel films for the coating of solid substrates, wherein such sol-gel films provide effective and durable antimicrobial properties. The utilization of such films permits relatively low-temperature production of antimicrobial substrates, such as ceramics, metals (e.g., stainless steel, brass, and the like), plastics (e.g., polyimides, polyamides, polyacrylics, and the like), glass (e.g., borosilicates, and the like), as compared with typical glazes for ceramics and the like. The inventive films comprise, as the primary antimicrobial active ingredients, certain metal-containing inorganic or organic antimicrobial compounds, such as, preferably, metal-containing ion-exchange, oxide, glass, sulfadiazine, and / or zeolite compounds (most preferably, including silver therein as the metal component). Preferably, also, the particular solid substrate to which such films are applied should exhibit substantially high melting and / or heat distortion temperatures to permit high temperature curing of the films to the solid substrate surface (in the range of 100-800° C., for example). If the solid substrate melts or distorts, the antimicrobial activity of the ultimate composite is drastically reduced. End uses for such film-coated articles include bathroom fixtures, appliances, kitchen articles and fixtures, furniture, glass, and any other surface that exhibits the high melt and / or heat distortion temperatures noted above and requires antimicrobial characteristics, including certain polymeric films. The specific method of producing such films is also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Mixed bacterial agent capable of degrading antibiotics in soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106635933AStrong stress resistanceImprove degradation rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismPenicillin
The invention discloses a mixed bacterial agent capable of degrading antibiotics in soil, belonging to the field of microbial technology. The mixed bacterial agent is prepared by mixing Bacillus subtilis J5P2 and Pseudomonas J2 according to a volume ratio of (0.1-3): 1. A preparation method for the mixed bacterial agent comprises the following steps: I, preparation of a suspension; II, colony culture: (1) preparation of a medium and (2) culture; III, separation of strains; IV, subculture and domestication: (1) domestication, (2) preparation of a LB medium, and (3) preservation; V, preparation of inoculum liquid; and VI, preparation of the mixed bacterial agent. The mixed bacterial agent provided by the invention has the characteristics of capacity of effectively degrading a plurality of residual antibiotics in soil and reducing environmental pollution, etc., and can be used for the remediation of land contaminated by antibiotics such as tetracycline, penicillin, sulfadiazines and quinolones.
Owner:HUNAN ZHONGKE AGRI
Nano carrier for tumor photo-dynamics therapy (PDT) and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108939072AGood biocompatibilityIncrease oxygen contentOrganic active ingredientsPhotodynamic therapyAbnormal tissue growthDecomposition
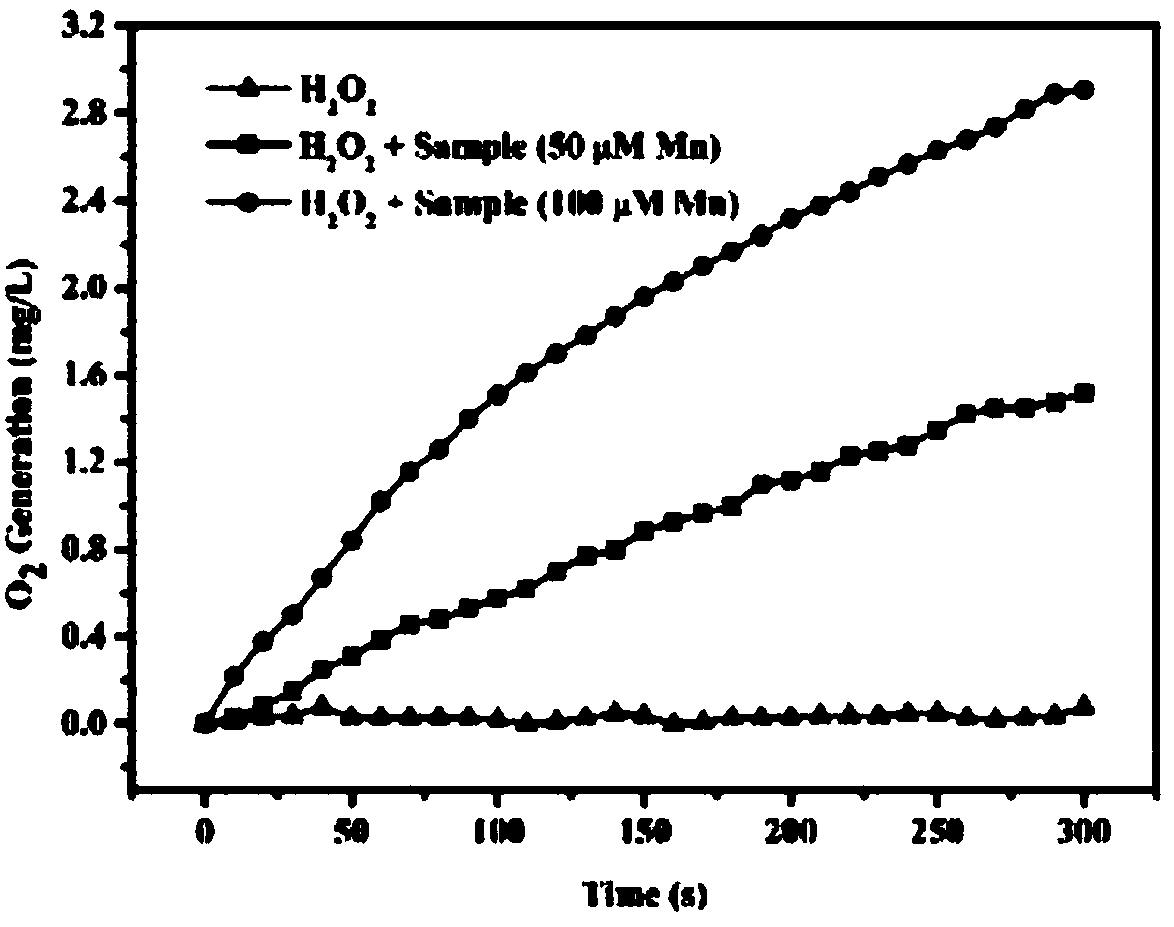
The invention provides a preparation method of a nano carrier for tumor photo-dynamics therapy (PDT). According to the preparation method, Fe<3+> salts are dissolved in DMF, then a photo-sensitizer (TCPP) is added to obtain particles (NMOFs); then the particles are dispersed in water under the assistance of ultrasonic waves; crosslinking agents (EDC and NHS) are added; after the reactions betweenBSA and sulfadiazine (SDs) finish completely, dialysis is performed to obtain particles (NMOFs@BSA / SDs); then the particles are dispersed in distilled water, then Mn<2+> salts are added, the pH is adjusted, and finally dialysis is performed to obtain a carrier (NMOFs@BSA / SDs@MnO2). Nano metal organic framework particles are taken as the basis and coated by protein (BSA) and sulfadiazine (SDs); finally the particles are in-situ mineralized to obtain required particles; SDs can specifically recognize carbonic anhydrase of tumors and is capable of actively targeting the oxygen-deficient parts oftumors; MnO2 generated in mineralization can catalyze the H2O2 decomposition to increase the oxygen content of tumors; and the PDT efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV +1
24-sulfoximine vitamin D3 compounds
InactiveUS7973024B2Extended service lifeEffectiveOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseSulfadiazine
The present invention provides novel sulfoximine compounds, compositions comprising these compounds and methods of using these compounds as inhibitors of CYP24. In particular, the compounds of the invention are useful for treating diseases which benefit from a modulation of the levels of 1α,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3, for example, cell-proliferative disorders.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
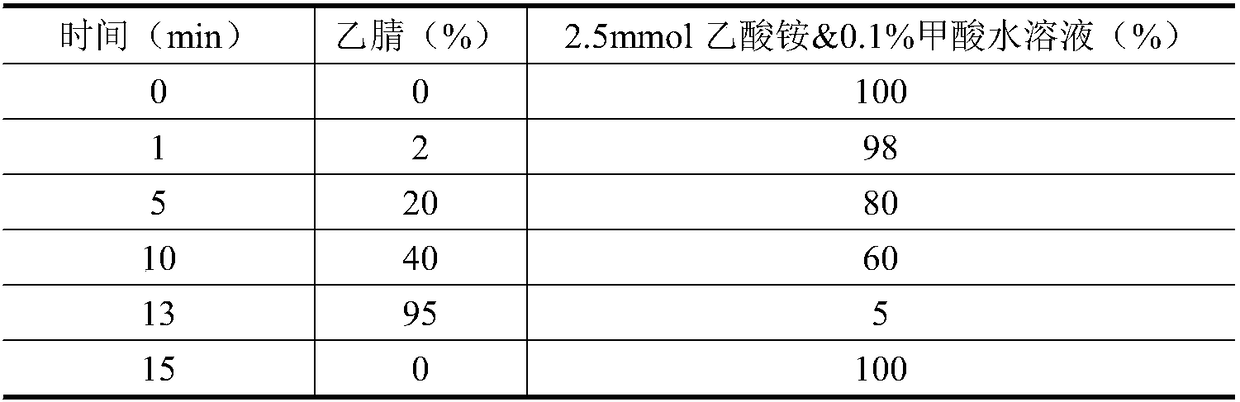
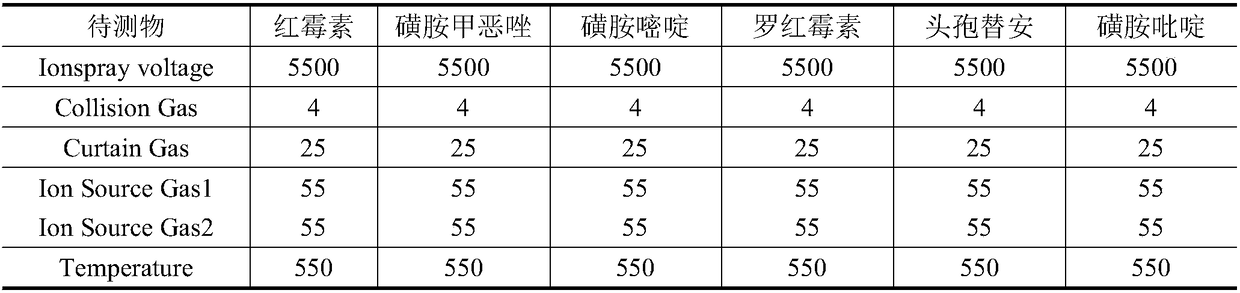
Method for determining 10 kinds of antibiotics in water environment through combination of sample pre-treatment technology and HPLC-MS
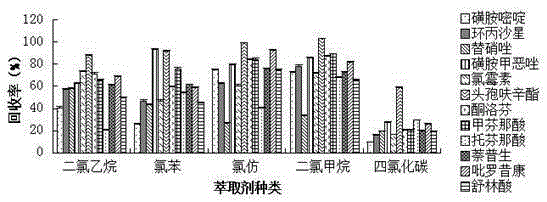
The present invention relates to a method for determining 10 kinds of antibiotics in a water environment through combination of a sample pre-treatment technology and HPLC-MS, and belongs to the field of detection of safety of trace organic contaminant residue in the water environment. The method is characterized in that a water sample is separated and enriched through combination of solid phase extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (SPE-DLLME), and then an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry instrument (UPLC-MS / MS) is adopted as a detection tool to directly determine the contents of 10 kinds of common antibiotics in the water environment (drinking water, tap water, river water, sewage treatment plant influent and effluent), wherein the 10 kinds of the common antibiotics respectively are sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, oxytetracycline, tetracycline, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, chloramphenicol, cefuroxime axetil and tinidazole. According to the present invention, the water sample pre-treatment method and the instrument detection conditions are investigated and optimized, and the optimal SPE-DLLME-UPLC-MS / MS method is established and is successfully applied for the real sample determination; and compared with the traditional method, the method of the present invention has advantages of high sensitivity, high extraction recovery rate, wide application objects, environmental protection, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Method for measuring 12 types of remaining medicine in water environment through separation and enrichment
ActiveCN105424825ASimplified processing stepsImprove extraction efficiencyComponent separationWater dischargePretreatment method
The invention relates to a method for measuring 12 types of remaining medicine in a water environment through separation and enrichment at the same time, and belongs to the field of safety detection of a trace of organic pollutant residue in the water environment. The content of 12 types of frequently-used medicine in the water environment (drinking water, faucet water, river water and water discharged into and out of sewage treatment plants) is directly measured with an ultra performance liquid-chromatography-mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS / MS) as a detection tool after a water sample is subjected to solid phase extraction combined with ultrasonic-assisted dispersion liquid-liquid micro-extraction (UA-DLLME) separation and enrichment. The 12 types of antibiotic include ketoprofen, ciprofloxacin, tinidazole, tolfenamic acid, sulfadiazine, sulindac, naproxen, sulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol, cefuroxime axetil, piroxicam and mefenamic acid. Inspection and optimization are conducted on a sample pretreatment method and instrument detection conditions of the water sample, and the optimal UA-DLLME method is established and is successfully applied to practical sample detection. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, high in extraction and recycle rate, wide in suitable object, friendly to the environment, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY +1
Biosensing probe kit for detecting sulfadiazine on basis of nucleotide aptamer specificity, and application thereof
ActiveCN107119054AQuick checkStable detectionMaterial analysisDNA/RNA fragmentationSulfadiazineBiotin
The invention provides a biotin-labeled sulfadiazine nucleotide aptamer. The biotin-labeled sulfadiazine nucleic acid aptamer is characterized by comprising a probe, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the probe is S-SDZ No.1. The kit and the method provided by the invention have the advantage of speediness, stability and simpleness in detection, and the prepared nucleotide aptamer is rapid in SDZ residue detection, high in sensitivity, good in repeatability and high in specificity, and has a wide application prospect in rapid detection of food safety.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compound sulfonamide suspensoid and its preparing process
ActiveCN1907264AEasy to takeDefinite curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTrimethoprimSulfadiazine
Disclosed is a compound sulfonamide turbid agent which comprises the following constituents (by weight percent): sulfadiazine 8-12, sulfamethoxazole 4-8, sulfamethoxydiazine 2-6, trimethoprim 2-6, and medicinal auxiliary materials including acid-base scale modifier, suspension auxiliary agent, acidifying agent, anti-oxidant, stabilizer and purified water.
Owner:SUZHOU KEMU ANIMAL MEDICATION
Method for detecting antibiotic in environment sample
InactiveCN108318613AEfficient enrichmentRealize detectionComponent separationNorfloxacinSurface water
The invention relates to the technical field of environment detection and is suitable for measuring erythrocin, chloramphenicol, sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, roxithromycin, cefotiam, pyridazol, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, tetracycline and doxycycline in sewage, surface water and bottom mud. After being sampled, a water sample and a mud sample are pretreated and detected through ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry, and qualitative diagnosis is conducted through the characteristic ion pair (m / z) of a target compound, a standard curve is drawn accordingto the response value and the corresponding concentration, and the external standard method is used in quantification, so that the contents of various antibiotics in the sample are obtained. The method is accurate, sensitive and simple, and is suitable for measuring the contents of 11 typical antibiotics in the sewage, the surface water and the mud at the same time.
Owner:四川国测检测技术有限公司
Method for analyzing and determining four sulfonamide antibiotics in water sample
The invention belongs to the field of antibiotic detection, and relates to a method for analyzing and determining four sulfonamide antibiotics in a water sample. A negative pressure suction filtrationmembrane solid phase extraction technology is utilized, and a metal organic framework material NH2-MIL-101(FE) membrane solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography method is adoptedto determine four antibiotics such as sulfadiazine, sulfamethazine, sulfachloropyridazine and sulfamethoxazole in an environmental water sample. The method is simple, convenient, rapid and sensitiveto operate, and has the advantages of low detection limit, accuracy and good reproducibility; and moreover, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the material preparation process is simple,the reaction conditions are mild, the application environment is friendly, and the market prospect is wide.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for removing antibiotic-sulfadiazine in water through activated carbon fiber adsorbent
InactiveCN105948158AStable removalHigh removal rateWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionFiberActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for removing antibiotic-sulfadiazine in water through activated carbon fiber adsorbent. The method comprises the steps that the activated carbon fiber adsorbent is placed into water containing antibiotic-sulfadiazine according to the certain placing amount, vibration adsorption is carried out at set temperature, the treated water is filtered after vibration adsorption is finished, activated carbon fiber adsorbing antibiotic-sulfadiazine is separated from the treated water, and therefore the antibiotic-sulfadiazine in the water is removed. The method can effectively remove antibiotic-sulfadiazine in water, and meanwhile has the advantages of being high in removal efficiency, resistant to corrosion and heat, beneficial to separation and the like. The absorbent preparation process is simple, low in cost, low in energy consumption and quite good in application prospect. The method for removing sulfadiazine through the activated carbon fiber is low in energy consumption, economic and environmentally friendly, has the certain industrial development potential and provides a new thought for removing sulfadiazine.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method of T1-MRI imaging guided photo-active therapeutic agent
ActiveCN107469079ALow costMild reaction conditionsMaterial nanotechnologyEnergy modified materialsMRI contrast agentSulfadiazine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a T1-MRI imaging guided photo-active therapeutic agent. The method comprises the following steps: preparing nano-particles having a gadolinium (manganese)-porphyrin metal organic frame structure; preparing a protein / sulfadiazine compound; mixing the nanoparticles with the compound to prepare a bovine serum albumin / sulfadiazine-gadolinium (manganese) porphyrin composite nanomaterial, and using the photo-active effect of the composite nanomaterial under the guidance of T1-MRI to prepare the photo-active therapeutic agent. The T1-MRI imaging guided photo-active therapeutic agent is a composite material having a protein / sulfadiazine-gadolinium (manganese) porphyrin metal organic frame structure, the prepared composite material has very good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, and a result of MTT test proves that the composite material can trigger the photo-active effect under the illumination of 660 nm laser, and can kill the tumor cells. The prepared composite material is a very good T1-MRI contrast agent, can be used for the screening and guided photo-active therapy of tumors, and has great potential application values in the field of treatment of tumors.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Selective coloration culture medium of clostridium perfringens
InactiveCN101659980ARapid cultivationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSulfite salt
The invention relates to a selective coloration culture medium for fast culturing and identifying clostridium perfringens. The selective coloration culture medium is characterized in that the preparation of 1000ml of the culture medium requires 12.0g-20.0g of casease hydrolysate, 6.0g-12.0g of yeast extract powder, 0.20g-0.80g of sodium sulfite, 0.005g-0.015g of polymyxin B, 0.05g-0.20g of sulfadiazine, 0.20g-0.80g of ferric citrate, 4-12 units of Y.S.N. and 10.0g-18.0g of agar powder and also requires the final addition of distilled water till the volume of 1000ml is achieved. The selective coloration culture medium has the advantages that the culturing time is obviously reduced when being compared with a conventional method and other bacteria with the same culturing characteristics are inhibited and do not grow so that the effect of fast clostridium perfringens culturing and identification can be realized.
Owner:CHENGDU RICH SCI IND
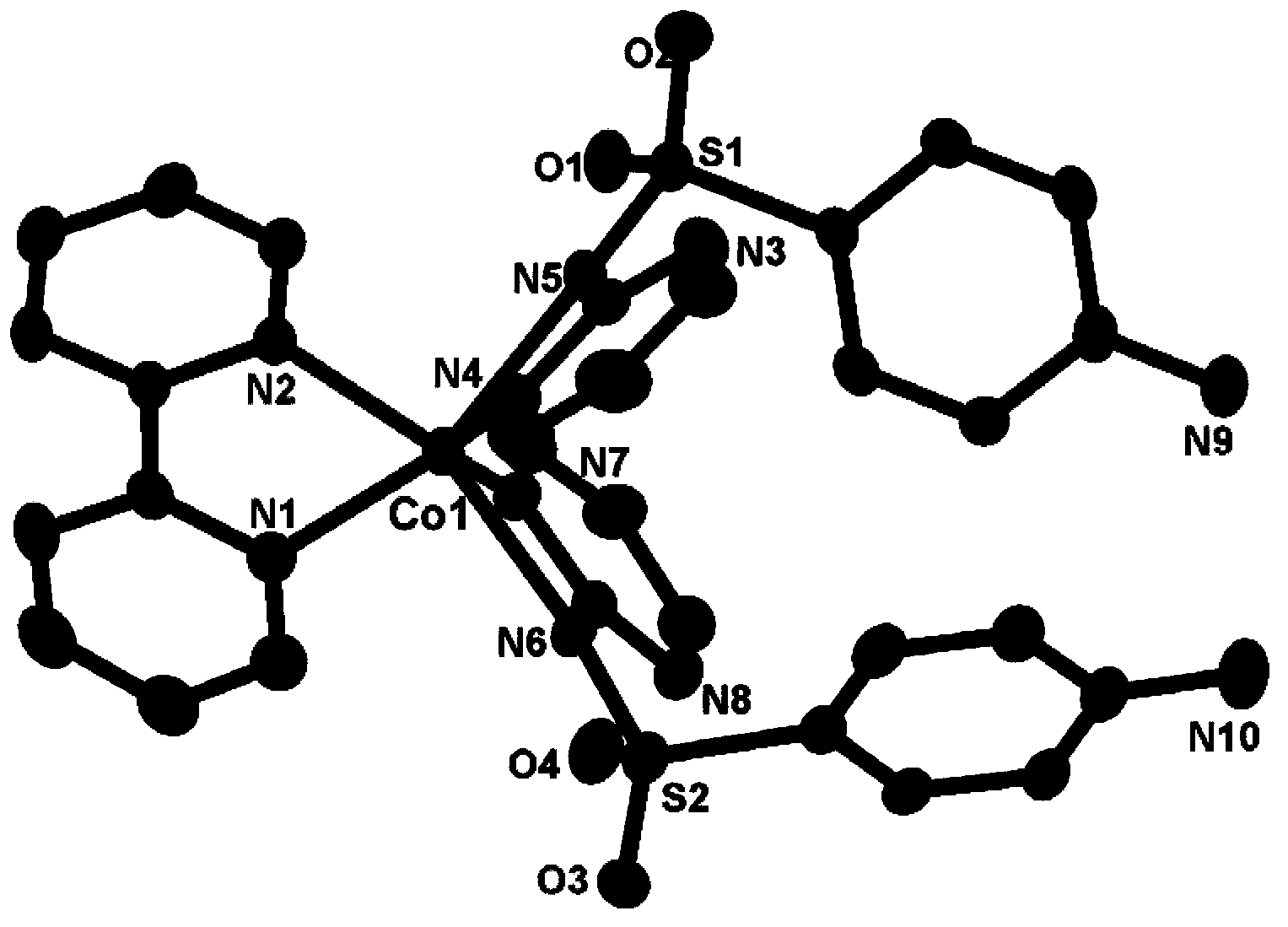
Cobalt complex with electrochemical catalytic activity
InactiveCN103435659AHigh electrochemical catalytic activityAccurate spatial structureCobalt organic compoundsElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
The invention discloses a cobalt complex with electrochemical catalytic activity and a preparation method thereof. The cobalt chemical combined electro-catalysis material is a cobalt complex with a certain spatial structure, the molecular formula of the cobalt complex is C3OH26CoN10O4S2. The preparation method of the cobalt complex chemical combined electro-catalysis material comprises the following steps: enabling sulfadiazine with conjugate big Phi bond, 2, 2'-dipyridyl and cobalt ions with electro-catalysis activity to be subjected to chemical reaction, so as to obtain the novel cobalt complex containing sulfadiazine and dipyridyl. According to the invention, the cobalt complex has electro-catalysis activity, accurate spatial structure and molecular formula; cobalt atoms can form a stable coordination bond with a ligand by using the empty d electronic orbit of the atoms, so as to facilitate electron to be transmitted, and further facilitate the proceeding of the electrochemical reaction; the prepared cobalt complex has good electro-catalysis activity, and has wide application prospects as an electro-catalysis active material.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Quinolone and sulpha compound extraction method from animal sample and special immuno affinity absorbent
InactiveCN101455958AHigh selectivityEasy to handleOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesSulfamonomethoxineSulfadiazine
The invention discloses a method and special immune affinity adsorbent for extracting quinolone compound and / or sulfonamide compound. The immune affinity adsorbent consists of a solid-phase carrier and Norfloxacin monoclonal antibody and / or sulfamethoxazole monoclonal antibody coupled with the carrier, wherein the Norfloxacin monoclonal antibody and the sulfamethoxazole monoclonal antibody are obtained by taking Norfloxacin hapten, sulfamethoxazole hapten and carrier protein conjugate as immunogen; the quinolone compound is at least one of the following 13 types of compounds: Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Pefloxacin, Ofloxacin, Enoxacin, Marbofloxacin, Lomefloxacin, Danofloxacin, Enrofloxacin, Sarafloxacin, Difloxacin, Oxolinic acid and Flumequine; and the sulfonamide compound is at least one of the following 6 types of compounds: sulfapyridine, sulfathiazole, sulphapyridine, sulfamethizole, sulfamonomethoxine and sulfamethoxazole.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Compound sulfadiazine injection and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101991587AGood curative effectExpanded antimicrobial spectrumAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseTreatment effect
The invention discloses a compound sulfadiazine injection and a preparation method thereof. The compound injection comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-12 parts of sulfamonomethoxine sodium, 1-5 parts of trimethoprim (TMP), 0.1-0.3 part of anhydrous sodium sulfite, 0.01-0.05 part of disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate, 8-10 parts of sulfamethoxazole, 20-50 parts of propylene glycol, 1-5 parts of ethanolamine and 45-79 parts of injection water. Compared with the single sulfamonomethoxine sodium, the compound preparation prepared from the sulfamonomethoxine sodium, the sulfamethoxazole and the TMP expands an antibacterial spectrum, enhances the curative effect of the injection and enlarges the clinical application range; and the compound preparation can be applied to treating infection caused by bacteria as well as fever, high fever and dyspnea caused by toxoplasma, and the preparation has better treatment effect on diseases such as appetite decrease and even anorexia, diarrhea and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN BIJIA PHARMA CO LTD
Oral liquid preventing and curing gallinaceous leucocyto zoonosis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101879171APrograms that omit the use of mixing materialsImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical product form changeCarboxymethyl celluloseALUMINUM STEARATES
The invention provides an oral liquid preventing and curing gallinaceous leucocyto zoonosis and a preparation method thereof. The oral liquid comprises sulfadiazine, TMP, aluminum stearate, alcohol, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, and Tween -80. The concrete preparation method comprises the following steps that: (1) the aluminum stearate is porphyrized, to which the alcohol is added, (2) the sulfadiazine and the TMP are added to the solution of the step (1), (3) distilled water is taken and stirred evenly, (4) the Tween -80 is added and stirred evenly, (5) the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is taken and is mixed into paste with the distilled water and the paste is added to the solution of the step (4) to be mixed well, and (6) anhydrous sodium sulfate is added and dissolved, the distilled water is added and stirred evenly, the pH value is adjusted to 9.5 to 11.5 with 0.5 percent of sodium hydroxide water solution and the product is obtained. The oral liquid adopts the suspension technology. The slightly soluble sulfadiazine and TMP are made into suspension liquid. The procedure of stirring feed is left out. The use is convenient and the efficacy is obvious.
Owner:天津市万格尔生物工程有限公司
Method for degrading sulfadiazine in water by activating persulfate with coagulated sludge
InactiveCN109179626ARealize resource utilizationSimple manufacturing methodWater contaminantsSludge treatment by pyrolysisSulfadiazineSludge
The invention relates to a method for degrading sulfadiazine in water by activating persulfate with coagulated sludge. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a persulfate activator: carrying out natural air-drying, crushing, drying, crushing and sieving on the coagulated sludge; taking the crushed sludge, adding the crushed sludge into a tubular furnace, pyrolyzing the sludge in anitrogen atmosphere, and cooling the obtained pyrolysis product to obtain a black carbonized material; and 2, acting persulfate with the prepared carbonized material to treat sulfadiazine wastewater:adding carbonized material to the sulfadiazine wastewater, carrying out a reaction on a shaking table at room temperature, adding the persulfate, and continuing the reaction under the above conditions, wherein a detection result shows that the method has a high removal rate. The method has the advantages of realization of recycling of wastes by using the coagulated sludge as a main raw material, simple and easy preparation process, low cost, and great application prospect in the removal of antibiotics and other refractory organic pollutants.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of molecularly imprinted polymer of sulfadiazine for controlled catalytic degradation
InactiveCN102786643APromote regenerationSelective catalytic degradation controllableOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSulfadiazineMicrosphere
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a molecularly imprinted polymer of sulfadiazine for controlled catalytic degradation, belonging to the technical field of material preparation and pollution control of water environments. The molecularly imprinted polymer of sulfadiazine for controlled catalytic degradation is prepared according to the steps of preparation of a substrate material of a molecularly imprinted controlled catalytic material by loading catalytic inorganic nanoparticles on a surface of a silica nanosphere, and coating of a layer of imprinted polymer on the surface of the silica nanospher by a controlled polymerization technology. When observed through a transmission electron microscope, the catalytic material has a uniform microstructure and good dispersibility. The catalytic degradation capability of the catalyst is evaluated by a static catalytic degradation experiment. Experimental results show that the catalyst has certain selective catalytic degradation capability for sulfadiazine and good regeneration performance and can be used in certain potential applications.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Process for preparing rapidly responsive pH sensitive hydrogel
The present invention is the preparation process of fast responding pH sensitive hydrogel, and belongs to the field of polymer material preparing technology. The preparation process of the hydrogel includes the following steps: dissolving sulfadiazine in alkali aqua and acetone solution, dripping acrylyl chloride to react, filtering the product, washing to eliminate unreacted monomer and impurity and drying to obtain sulfadiazine monomer; mixing N-vinylpyrrolidone, sulfadiazine monomer, 1N, N-methylene diacrylamide, azodiisobutyronitrile and dimethyl sulfoxide to form mixed solution and react in water bath at 30-100 deg.c for 2-24 hr to obtain hydrogel; soaking and washing with deionized water to eliminating unreacted monomer, cross-linking agent and solvent impurity, and drying to obtain the pH sensitive hydrogel. The prepared pH sensitive hydrogel is especially sensitive in pH 6.8-7.2, and is expected to prepare medicine release controlling supplementary material.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
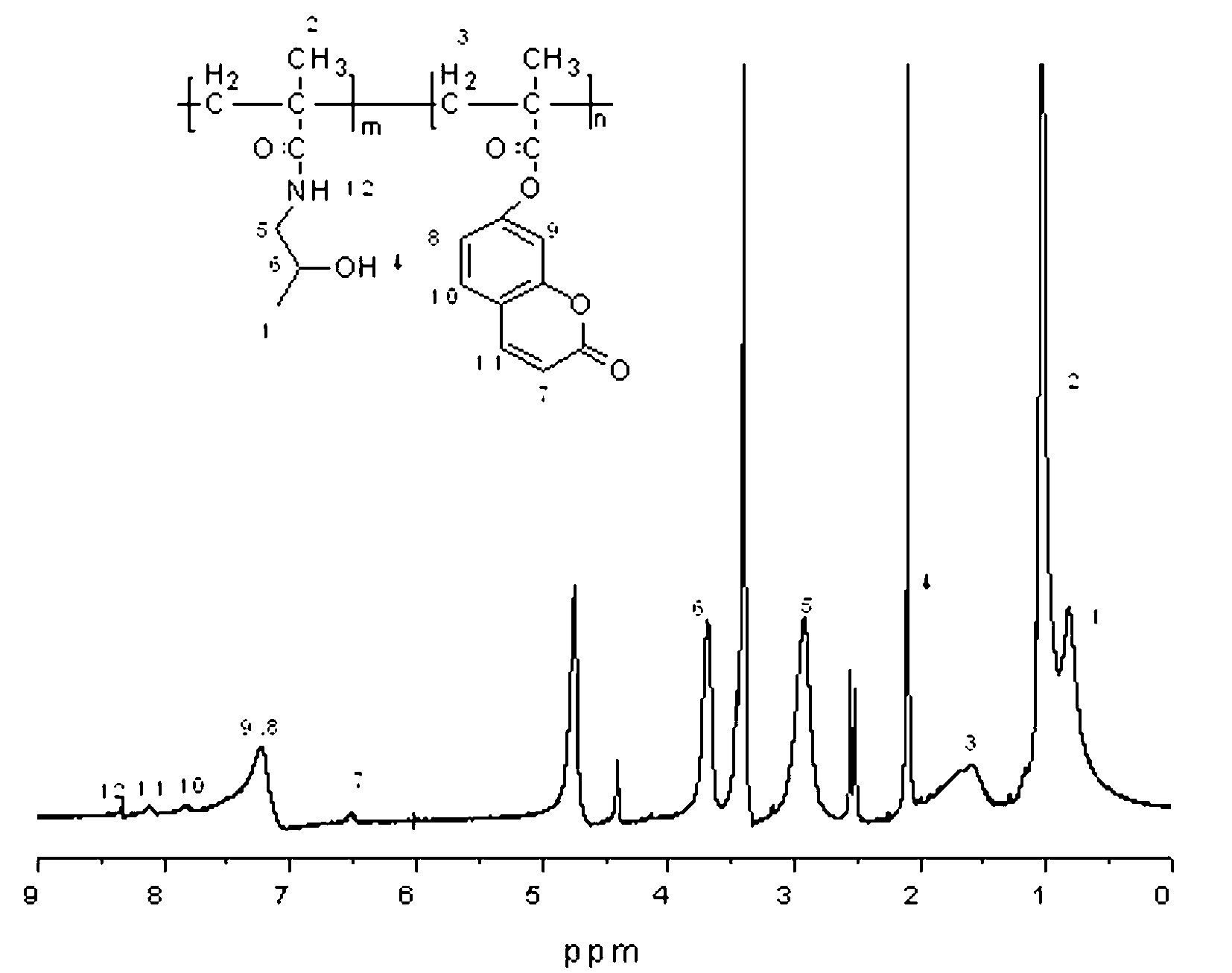
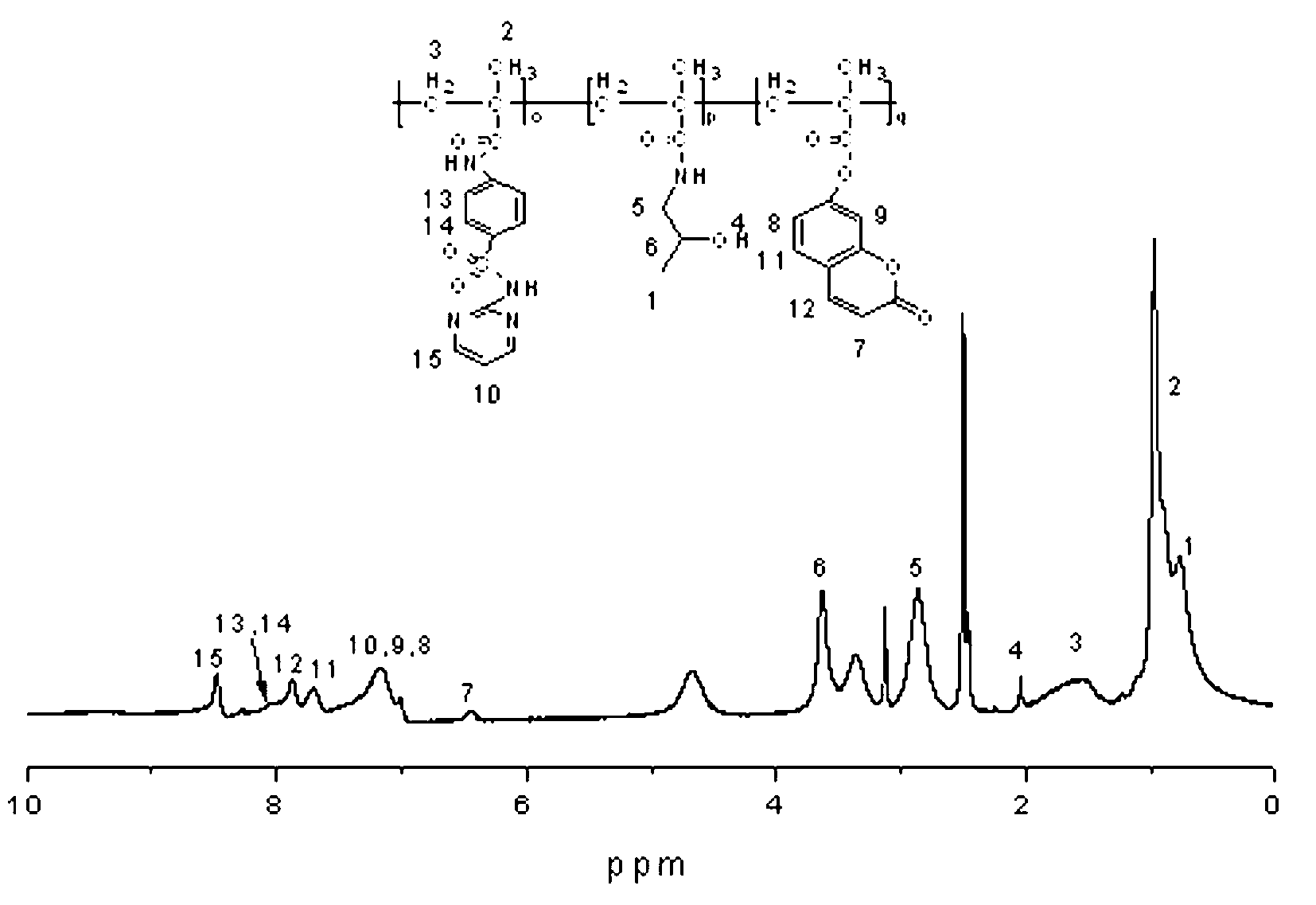
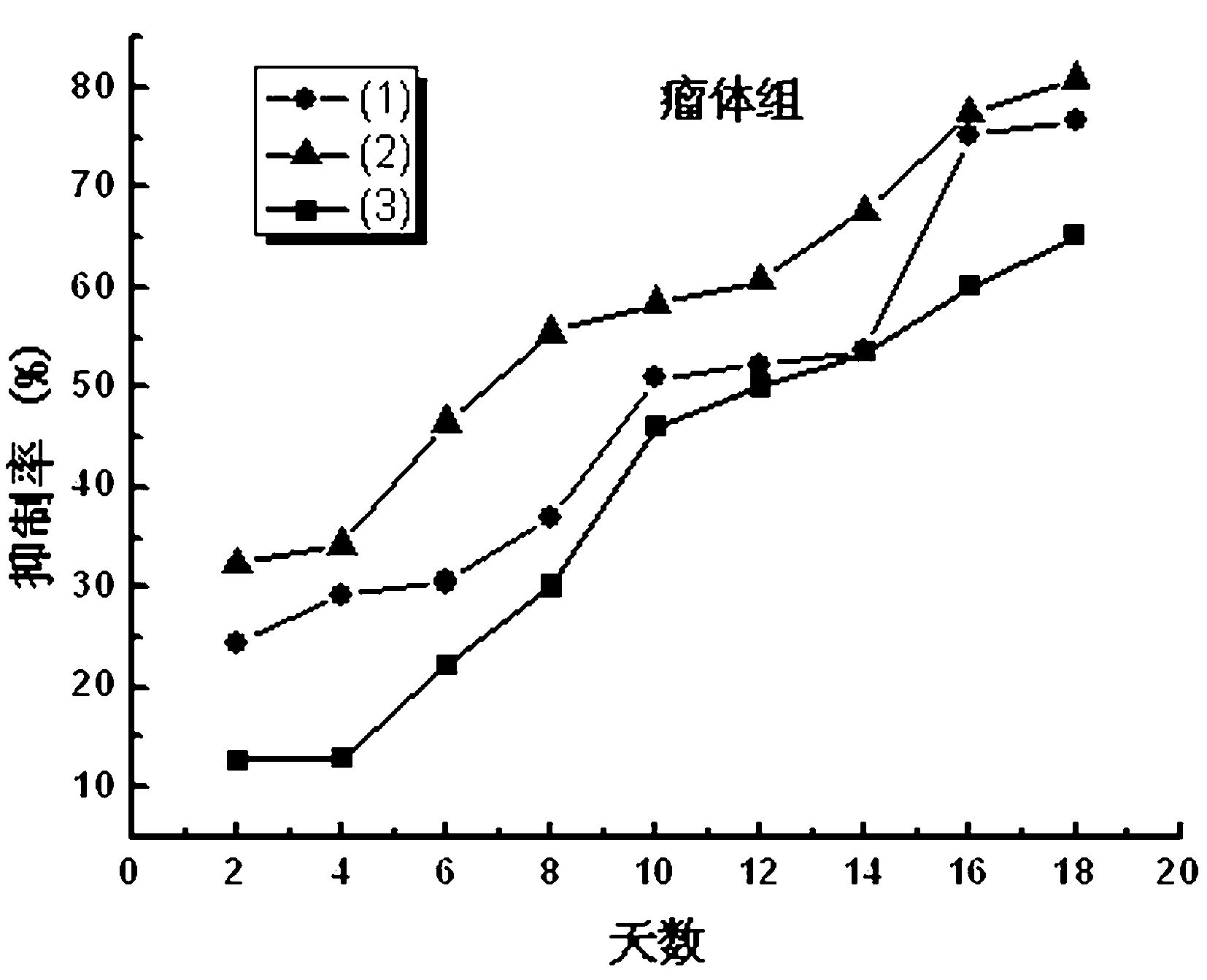
Coumarin macromolecule polymer with anti-tumor activity and preparation method of coumarin macromolecule polymer
InactiveCN103012671AHas antitumor activitySmall toxicityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetTumor targeting
The invention provides a coumarin macromolecule polymer with anti-tumor activity. 7-hydroxycoumarin or 7-hydroxycoumarin and sulfadiazine is or are connected to N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide through a polymerization mode to form a macromolecule copolymer with good biological compatibility. The macromolecule copolymer is used for connecting the 7-hydroxycoumarin with anti-tumor activity and the sulfadiazine to a tumor targeted drug carrier N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide to ensure that the anti-tumor activity is overlapped, further the inhibition of the macromolecule polymer to tumors is promoted, and the standing time of anti-tumor drugs in tumors is greatly prolonged; and meanwhile, by adopting the macromolecule carrier HPMA (hydroxypropyl methacrylate), the toxicity of the anti-cancer drugs is reduced, and the hurt to normal tissues is decreased. The coumarin macromolecule polymer can be used for preventing and treating cancers such as gastric cancer, colon cancer, hepatoma and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Strip dyeing method for corn fibers
The invention relates to a strip dyeing method for corn fibers. The method comprises the following processes of: 1, dyeing, namely filling the corn fiber strips into a dye vat, rotating the dye vat, adding polyol ester liquid into the dye vat, rotating the dye vat, adding a carrier, namely polyolefin elastomer (POE) liquid, into the dye vat, rotating the dye vat, adding univadine diiodofluorescein (DIF) into the dye vat, rotating the dye vat, adding univadine DPS into the dye vat, rotating the dye vat for minutes, adding a disperse dye, namely Terasil sulfadiazine (SD), into the dye vat, rotating the dye vat, starting to raise the temperature to 70+ / -2 DEG C at the temperature rise speed of 1.5 to 2 DEG C per minute, raising the temperature to 90+ / -2 DEG C by keeping the temperature rise speed at 1 DEG C per minute, keeping the temperature for 10 seconds, raising the temperature to 110+ / -2 DEG C at the temperature rise speed of 1 DEG C per minute, keeping the temperature for 20 to 30 minutes, lowering the temperature to 50+ / -2 DEG C at the temperature descent speed of 2 DEG C per minute, and discharging the liquid; and 2, performing post treatment, namely adding the dyed corn fiber into the dye vat, adding soaping liquid 209, sodium bicarbonate and sodium hydrosulfite into the dye vat, raising the temperature to between 60 and 65 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 15 to 20 minutes, and discharging the liquid. The homochromatism, the dyeing uniformity and the stability of dyeing are improved by the method; the dyeing effect is good; and the color fastness is good. The injury to the fibers in the dyeing process is low.
Owner:HEILAN HOME
Sulfadiazine salt high-molecular hydrogel dressing and its preparation method
InactiveCN1970092AIncrease moisture contentIncrease elastic strengthOrganic active ingredientsAbsorbent padsPotassium persulfateSulfadiazine
The invention discloses a making method of macromolecular aquagel dressing of sulfanilamide pyrimidine salt, which comprises the following steps: dissolving N, N'-methylene diacrylamide into acrylic acid completely; dripping sodium hydroxide solution into acrylic acid; adding polyvinyl alcohol solution and chitose acetic acid solution; stirring evenly to obtain solution A; dispersing sulfanilamide pyrimidine salt powder into glycerin to obtain solution B; blending potassium persulfate solution and residual water completely to obtain solution C; dripping solution A in the solution B; stirring evenly; adding solution C; pouring into mould; heating to obtain the product to treat burn.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Simple method for screening sulfadiazing (SD) degradating bacterial for treating SD-contxined sewage
InactiveCN1657607AHigh COD concentrationGood antibacterial effectTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaSulfadiazineScreening method
A simple method for screening the sulfadiazine (SD) degradating bacteria used to effectively treat the SD contained sewage by aerobic deep-well method includes such steps as using the selective culture medium for primarary screening, using the complete culture medium for rejuvenation, and using the selective culture medium for verification.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spray film forming preparation for burn and scald injury
InactiveCN104352437AGood for recoveryAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteriostatic agentPlasticizer
The invention discloses a spray film forming preparation for burn and scald injury. The preparation contains sulfadiazine, a biocompatible macromolecular film forming component with at least 2% by weight of polyvinyl alcohol and hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), a plasticizer, an anti-sticking agent and a bacteriostatic agent which are combined. According to the spray film forming preparation, sulfadiazine, the film forming component, the anti-sticking agent and the plasticizer are mixed to form suspension, the suspension is sprayed to the burned skin, and a film is formed.
Owner:南京泽恒医药技术开发有限公司
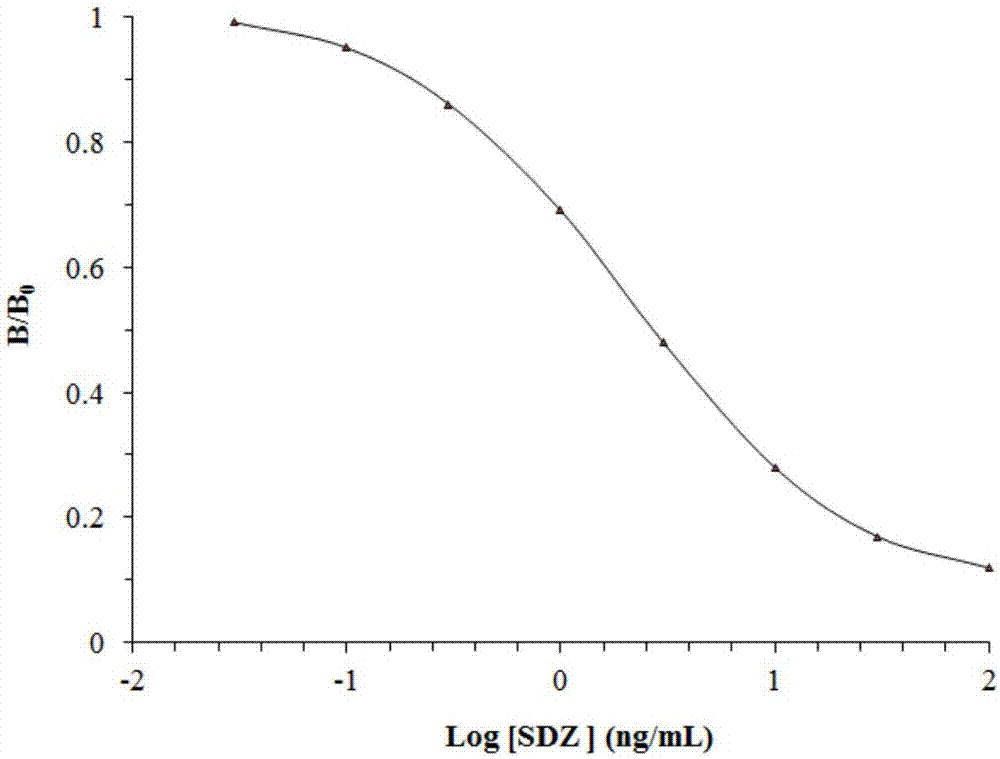
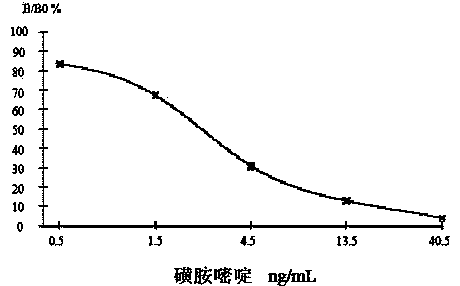
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting sulfadiazine and detection method thereof
The invention discloses an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting sulfadiazine and a detection method thereof. The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting sulfadiazine includes a sulfadiazine specific antibody, and a coating sulfadiazine-carrier protein conjugate and an enzyme-labeled second antibody, or a coating second antibody and an enzyme-labeled sulfadiazine. The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting sulfadiazine can simultaneously detect large quantities of samples; the main reagents are all provided in a working liquid form, and the detection method is simple and is easy to implement; and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit has the characteristics of high specificity, high sensitivity, high precision, high accuracy and the like, and can play an important role in detection of the residual amount of sulfadiazine in animal foodstuffs and fodders.
Owner:JIANGSU WISE SCI & TECH DEV
Quick-acting scarless burn and scald ointment
InactiveCN101869655AEasy to makeLow costHydroxy compound active ingredientsAerosol deliverySulfadiazineMedicine
The invention provides quick-acting scarless burn and scald ointment. The ointment comprises the following components in weight proportion: the ratio of rheum officinale: tendril-leaved fritillary bulb: compound sulfamethoxazole: sulfadiazine: gentamicin: borneol: bark oil: Vaseline: cefradine is (15-25):(8-12):(10-20):(0-12):(2-6):(3-8):(5-7):(85-125):(0-1). The drugs are weighed and mixed in specified amount, are grinded and mixed to prepare the ointment. The burn and scald ointment can treat various burn and scald wounds, has short course of treatment, and scars cannot be left after healing.
Owner:刘福民
Method for simultaneously screening multiples categories of drug residues in fish by using ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole rod time-of-flight mass spectrometry
InactiveCN109917047AHigh recovery rateImprove solubilityComponent separationPretreatment methodSudan III
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously screening multiples categories of drug residues in fish by using ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole rod time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The multiples categories of drugs screened simultaneously comprise enrofloxacin, danofloxacin, tetracycline, oxytetracycline , chlortetracycline, doxycycline, chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, florfenicol, sulfamethoxazole, sulfamethoxazole, sulfathiazole, sulfadiazine, sulfadoxine, sulfisoxazole, sulfaphenirazole, sulfacetamide, sulfamethazine, azithromycin, tilmicosin, medimycin, roxithromycin, acetylspiramycin, doramectin, sudan I, sudan II, sudan III, sudan IV and rhodamine B. By optimizing the parameters of a d-SPE pretreatment method, all target drugs can obtain good recovery rates.29 kinds of target drugs are simultaneously screened by an optimized chromatographic mass spectrometry condition, thereby achieving simultaneous screening of common multiples categories of drug residues in fish. The method has a good application prospect in the field of fish food.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
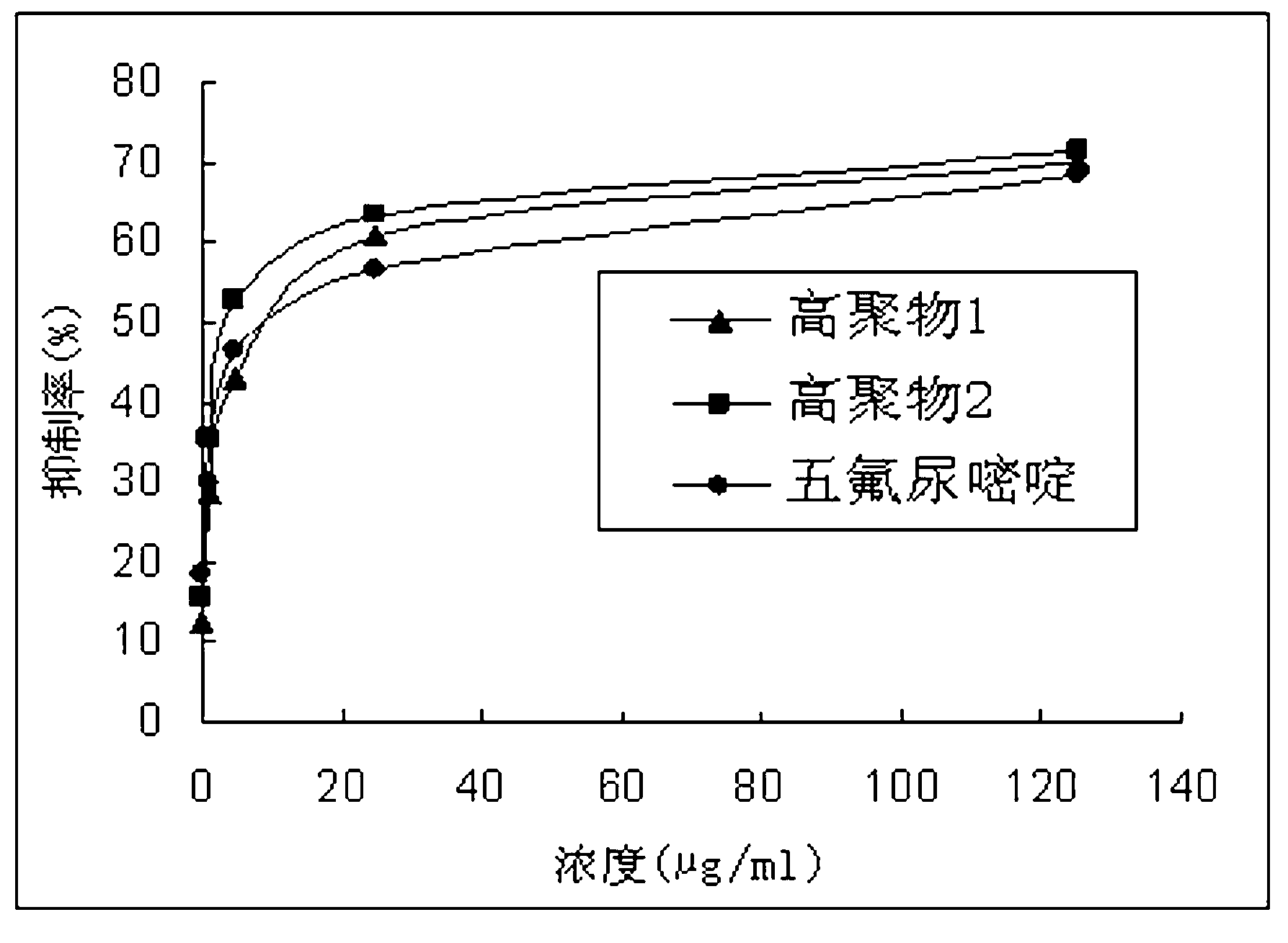
5-fluorouracil copolymer with anti-tumor activity and preparation method of 5-fluorouracil copolymer
InactiveCN103012672AGood biosolubilityLow toxicityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetTumor targeting
The invention provides a 5-fluorouracil copolymer with anti-tumor activity. 5-fluorouracil or 5-fluorouracil and sulfadiazine is or are connected to N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide through a polymerization mode to form a macromolecule copolymer with good biological compatibility. The macromolecule copolymer is used for connecting the 5-fluorouracil with anti-tumor activity and the sulfadiazine to a tumor targeted drug carrier N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide to ensure that the anti-tumor activity is overlapped, further the inhibition of the macromolecule polymer to tumors is promoted, and the standing time of anti-tumor drugs in tumors is greatly prolonged; and meanwhile, by adopting the macromolecule carrier HPMA (hydroxypropyl methacrylate), the toxicity of the anti-cancer drugs is reduced, the hurt to normal tissues is decreased, and a new idea is provided for preparing novel anti-tumor drugs.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com