Bacterial-derived alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene, gene expression and application thereof
A technology of rhamnosidase and rhamnoside, which is applied in the field of bioengineering and can solve the problems of high price and limited research and application of rhamnoside
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] 1. Screening and identification of α-L-rhamnosidase strains
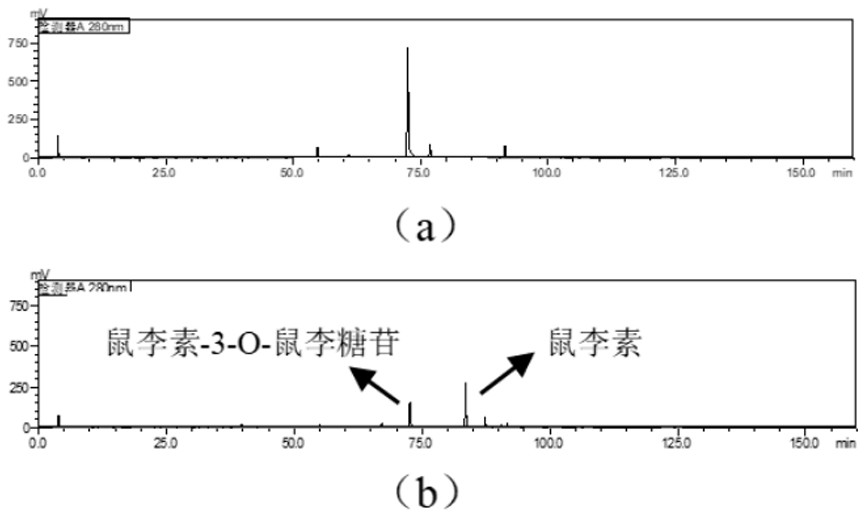
[0038] Utilizing the characteristic of α-L-rhamnosidase that can specifically cut terminal α-L-rhamnose from flavonoids and terpene-based glycosides, and using the total flavonoids of M. L-rhamnosidase bacterial strain XB. After re-validation by HPLC, it was found that the strain could stably convert rhamnoside-3-O-rhamnoside in the total flavonoids of Mulberry parasiticus into rhamnoside, and the strain was identified as Enterococcus avium by molecular biology identification ( Enterococcus avium ).
[0039] Hydrolysis of total flavonoids of Morus spp. by α-L-rhamnosidase-producing strain XB
[0040] Screening of strains
[0041] After activating the strains, cultivate them for three days, mix the bacterial liquid and the medium solution of total flavonoids of Mulberry parasitica in a sterile environment at a volume ratio of 1: 1, place them in the same environment as the bacteria and culture them, and c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com