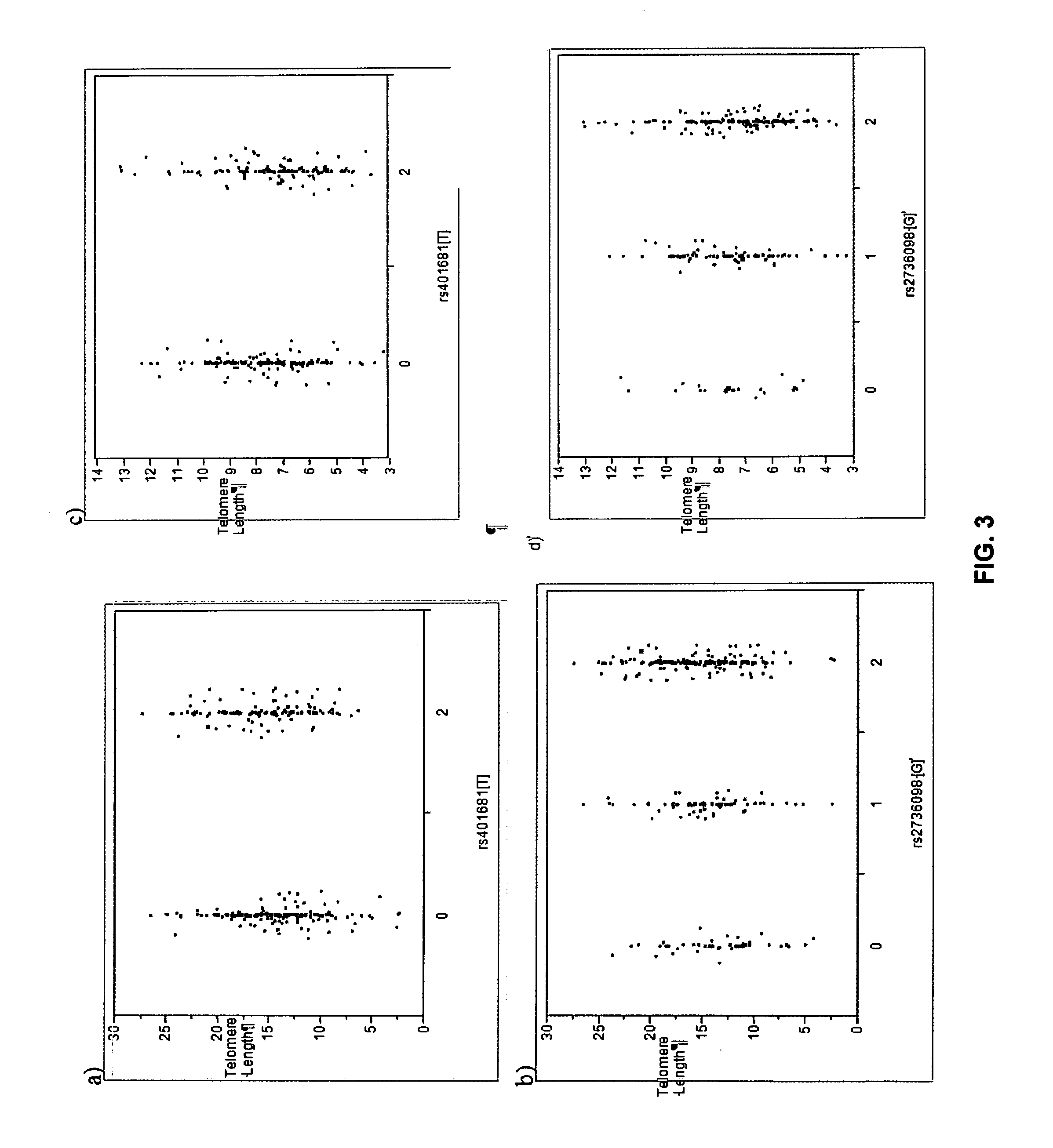
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
460 results about "Genetic variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals. There are multiple sources of genetic variation, including mutation and genetic recombination.
Methods and uses for molecular tags
ActiveUS20160026758A1Overcome limitationsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenetic analysisComputational biology
Methods and uses for molecular tags are disclosed. Molecular tags may be attached to nucleic acid molecules. The attachment of the nucleic acid molecules prior to PCR amplification and sequencing improves the accuracy of genetic analysis and detection of genetic variations and diversity. Molecular tags may also be used for detection of drug-resistant variants. Methods for using molecular tags for determining and correcting PCR errors and / or sequencing error are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method and apparatus for discovering patterns in binary or categorical data
InactiveUS20050143928A1Save time and costGood sensitivityBiostatisticsProteomicsMedical diagnosisBinary trait
The present invention relates to a computationally efficient method of finding patterns in any data that can be expressed in the form of arrays of binary features or arrays of categorical features. This includes data represented by continuous-valued attributes that can be transformed to a categorical representation, such as the discovery of patterns of genetic variability that may be causally related to diseases or traits, as well as the discovery of patterns of protein biomarkers that may be used for medical diagnostics, prognostics, and therapeutics. The invention further relates to a program storage device having instructions for controlling a computer system to perform the methods, and to a program storage device containing data structures used in the practice of the methods.
Owner:MOSER ALLAN ROBERT
Genetic Variants as Markers for Use in Urinary Bladder Cancer Risk Assessment, Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment
InactiveUS20130296175A1Easy to analyzeNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBladder cancerGenotyping
Polymorphic variants that have been found to be associated with risk of urinary bladder cancer are provided herein. Such polymorphic markers are useful for diagnostic purposes, such as in methods of determining a susceptibility, and for prognostic purposes, including methods of predicting prognosis and methods of assessing an individual for probability of a response to therapeutic 5 agents, as further described herein. Further applications utilize the polymorphic markers of the invention include screening and genotyping methods. The invention furthermore provides related kits, and computer-readable media and apparatus.
Owner:DECODE GENETICS EHF +1
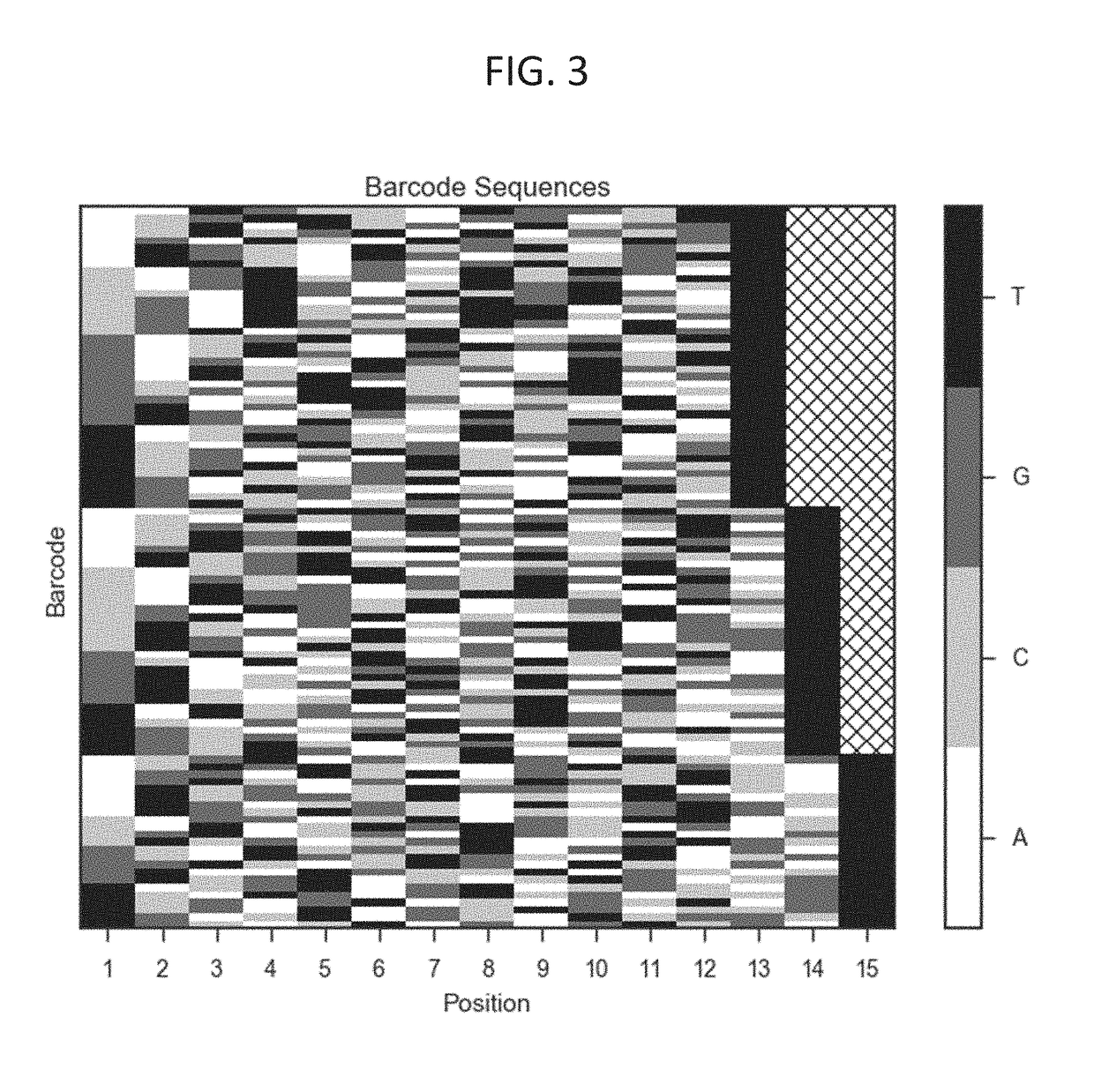
System and Methods for Detecting Genetic Variation
The invention provides methods, apparatuses, and compositions for high-throughput amplification sequencing of specific target sequences in one or more samples. In some aspects, barcode-tagged polynucleotides are sequenced simultaneously and sample sources are identified on the basis of barcode sequences. In some aspects, sequencing data are used to determine one or more genotypes at one or more loci comprising a causal genetic variant. In some aspects, systems and methods of detecting genetic variation are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD WOMENS HEALTH INC
Methods and compositions for screening and treating developmental disorders
ActiveUS20140162894A1Reduce sensitivityHigh expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureGeneologiesDevelopmental disorder
This document provides methods and materials related to genetic variations of developmental disorders. For example, this document provides methods for using such genetic variations to assess susceptibility of developing Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Owner:POPULATION BIO INC +1
Mobile supplementation, extraction, and analysis of health records
ActiveUS10395772B1Validating an accuracy of the abstracted health informationMedical data miningFinanceEntity linkingHealth history
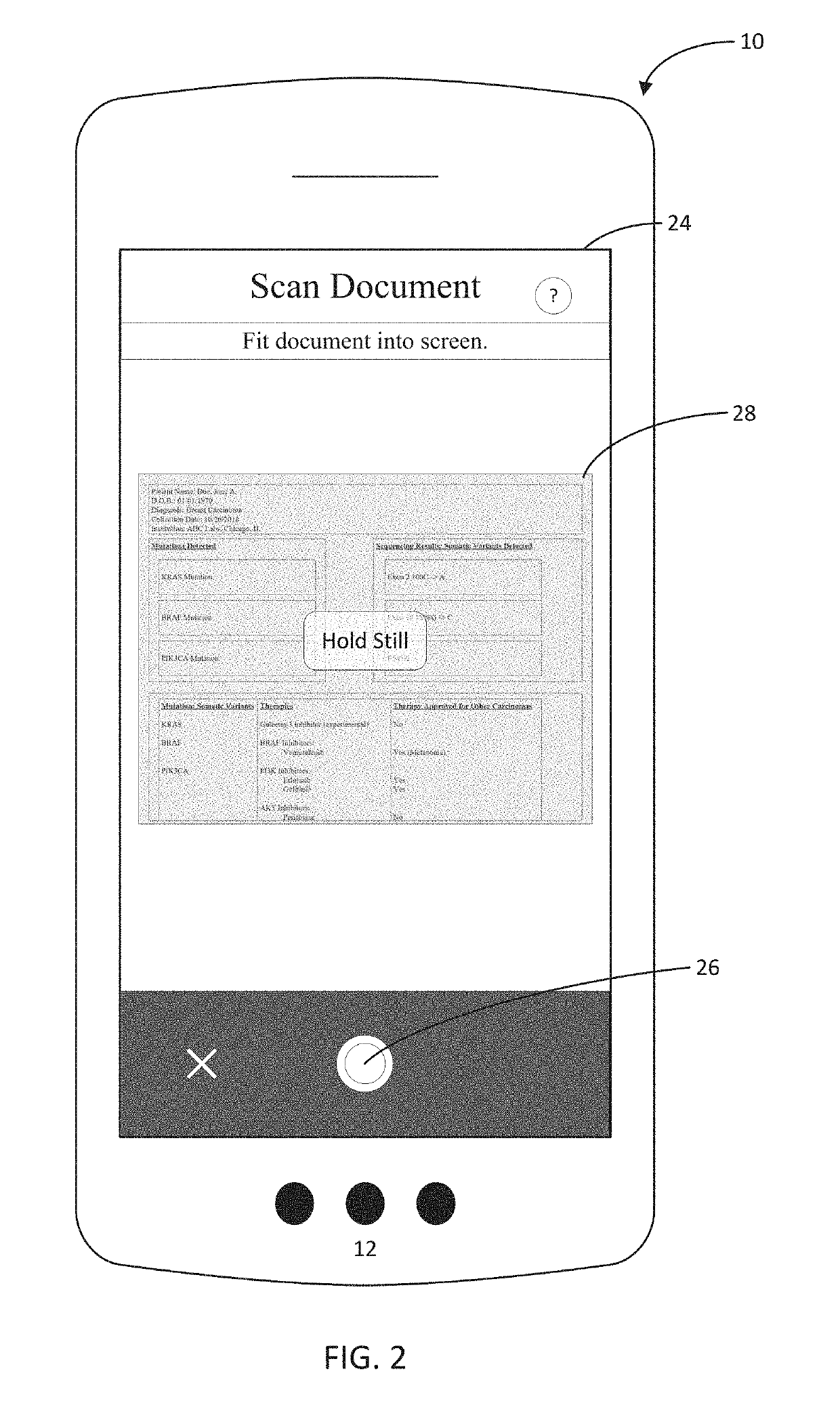
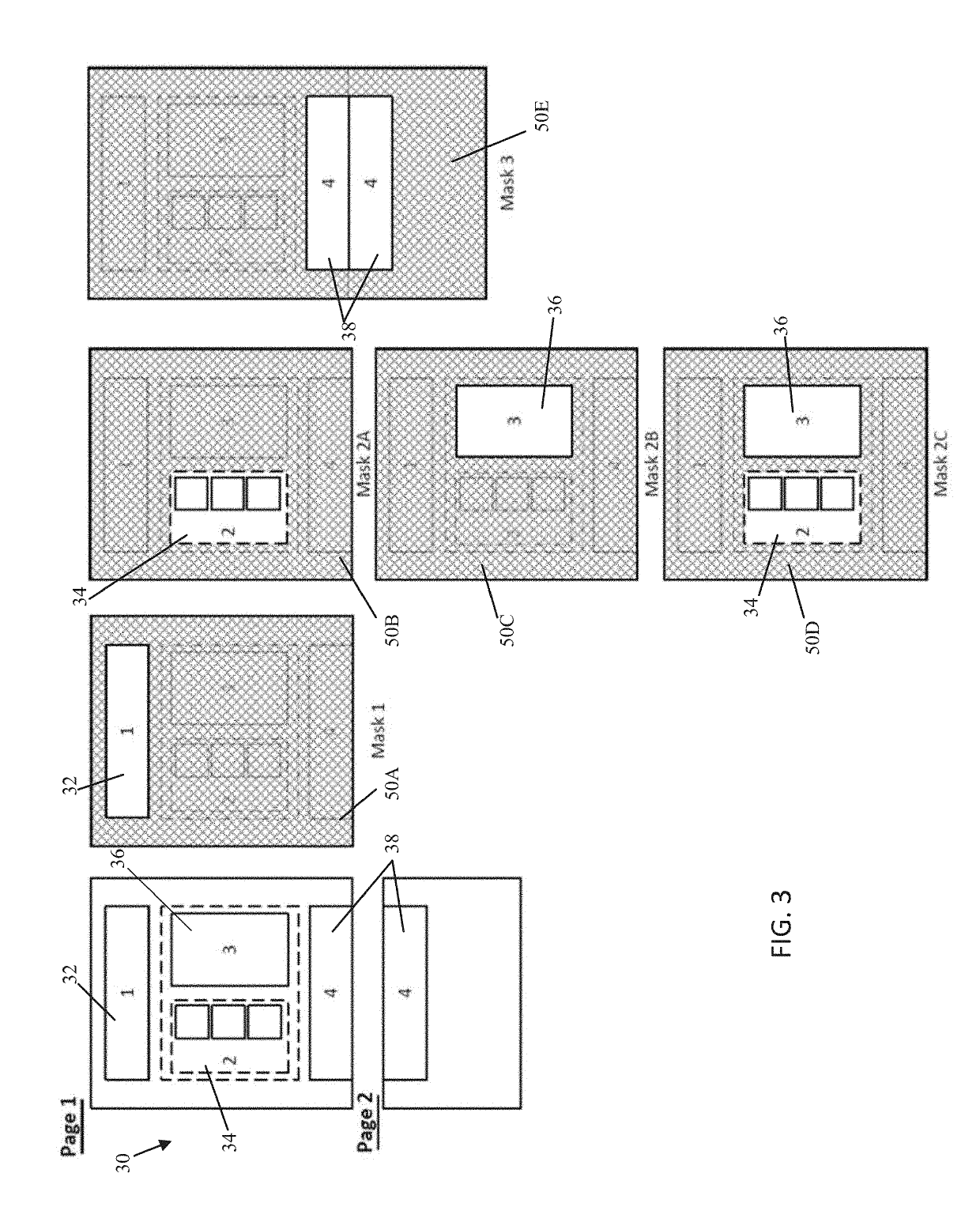
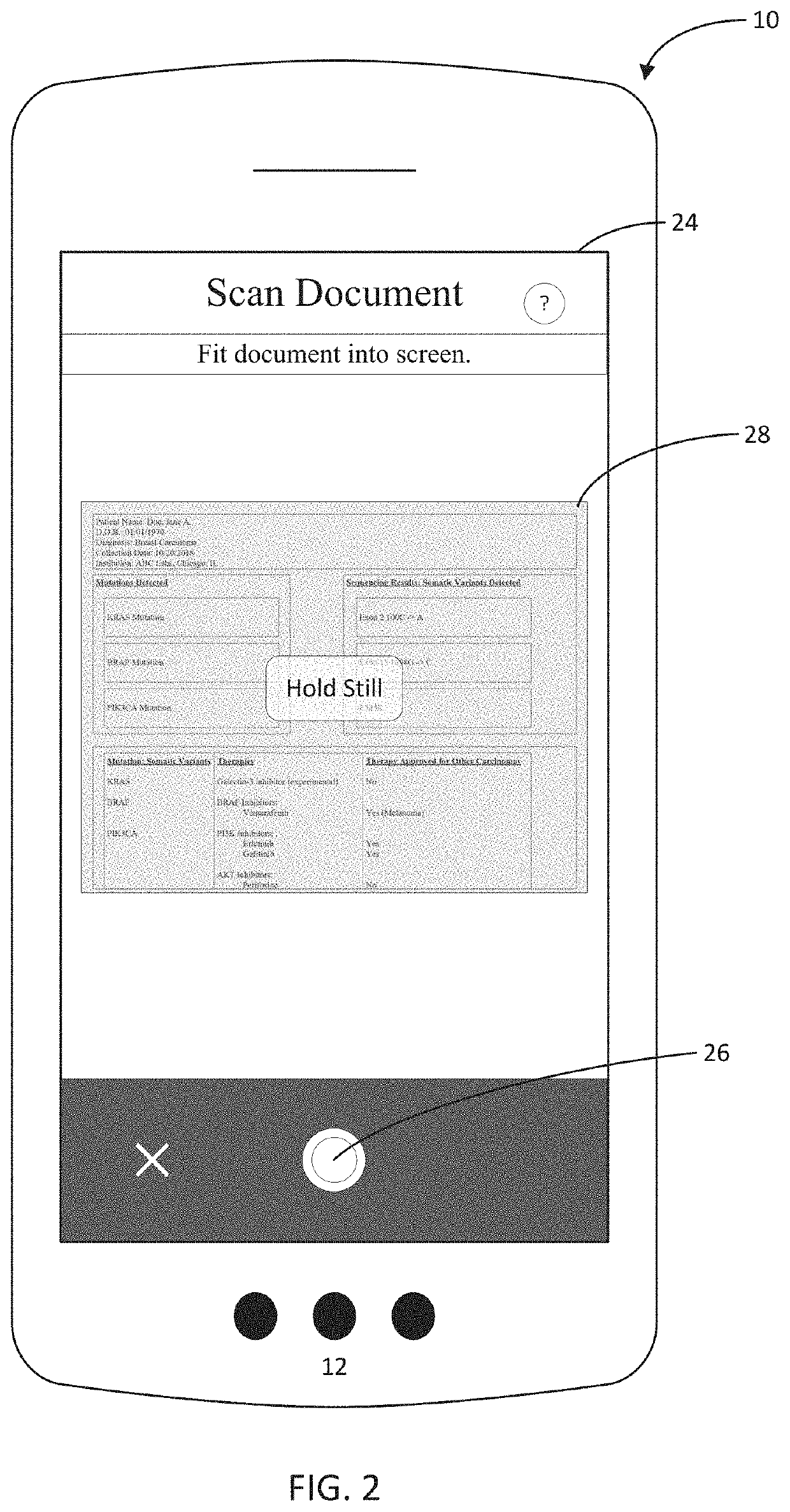
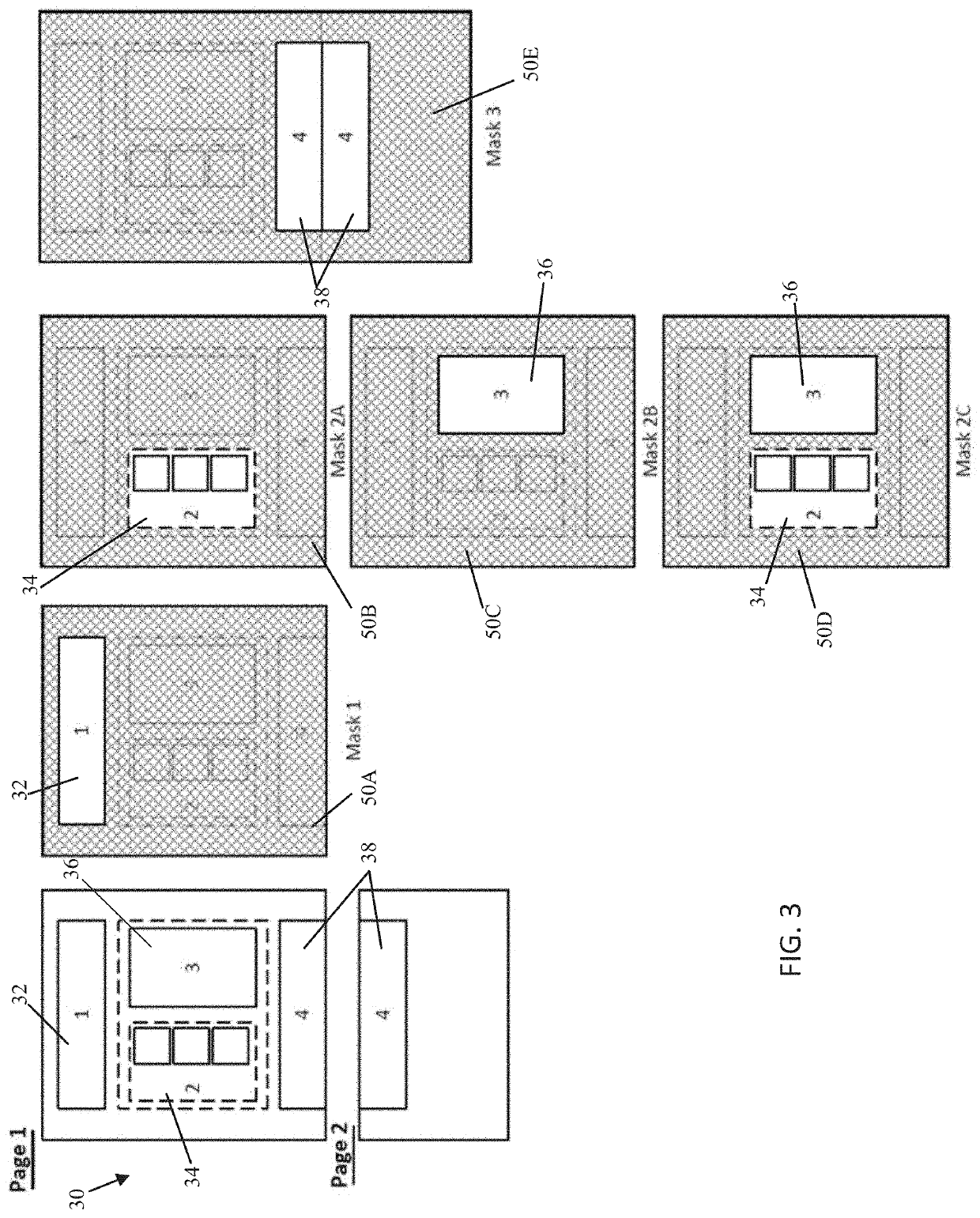
A system, method, and mobile device application are configured to capture, with a mobile device, a document such as a next generation sequencing (NGS) report that includes NGS medical information about a genetically sequenced patient. At least some of the information is extracted from the document using an entity linking engine, and the extracted information is provided into a structured data repository where it is accessible to provide information regarding the patient specifically as well as collectively as part of a cohort of patients with similar genetic variants, medical histories, or other commonalities. In one aspect, the document is matched to a template model, and the document is processed using one or more masks segregating the template model, and therefore the document, into a series of distinct subregions.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS
System for genome analysis and genetic disease diagnosis
InactiveUS20150310163A1High sensitivityIncrease the number ofProteomicsBiological testingData setGenome wide analysis
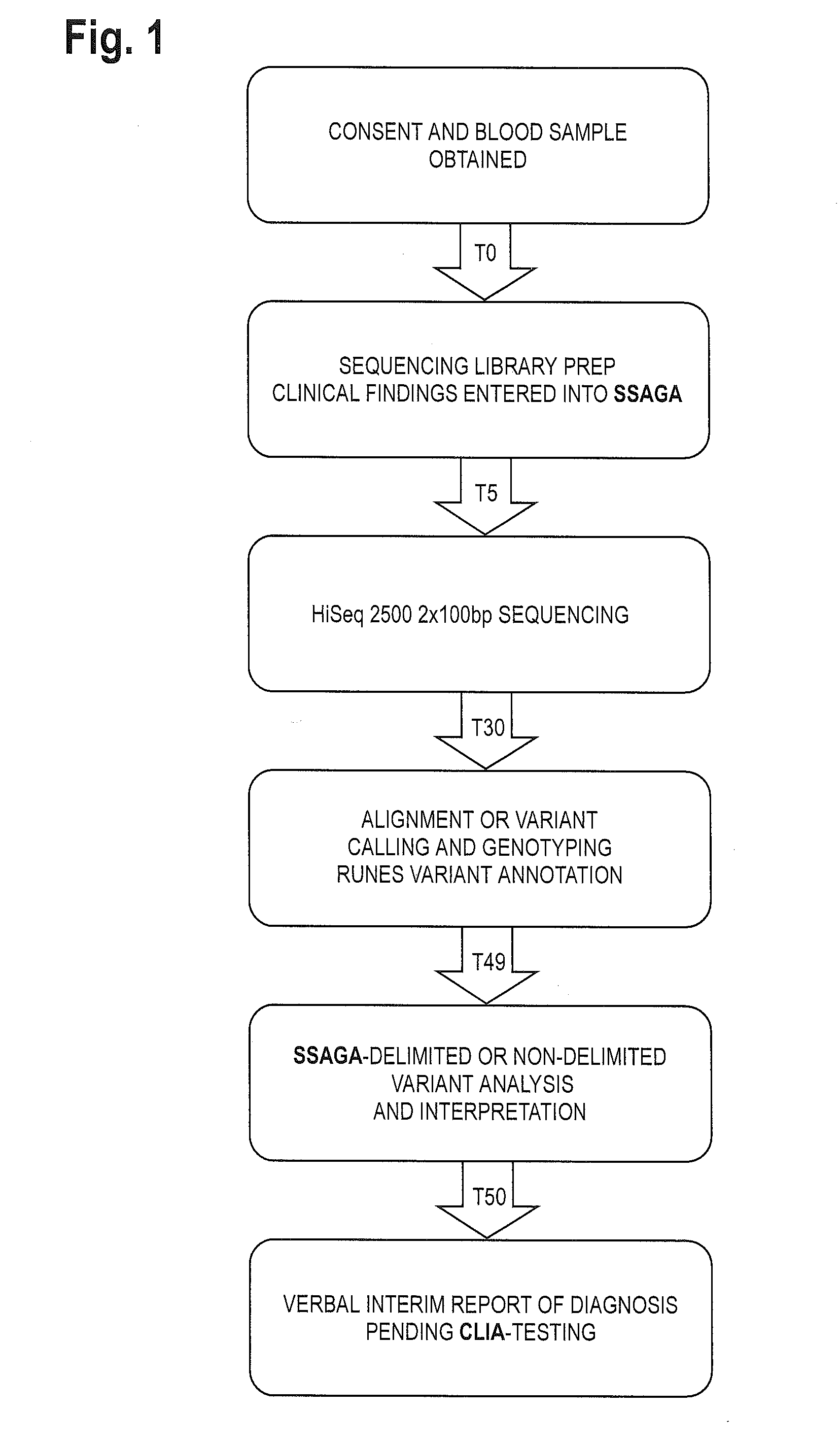
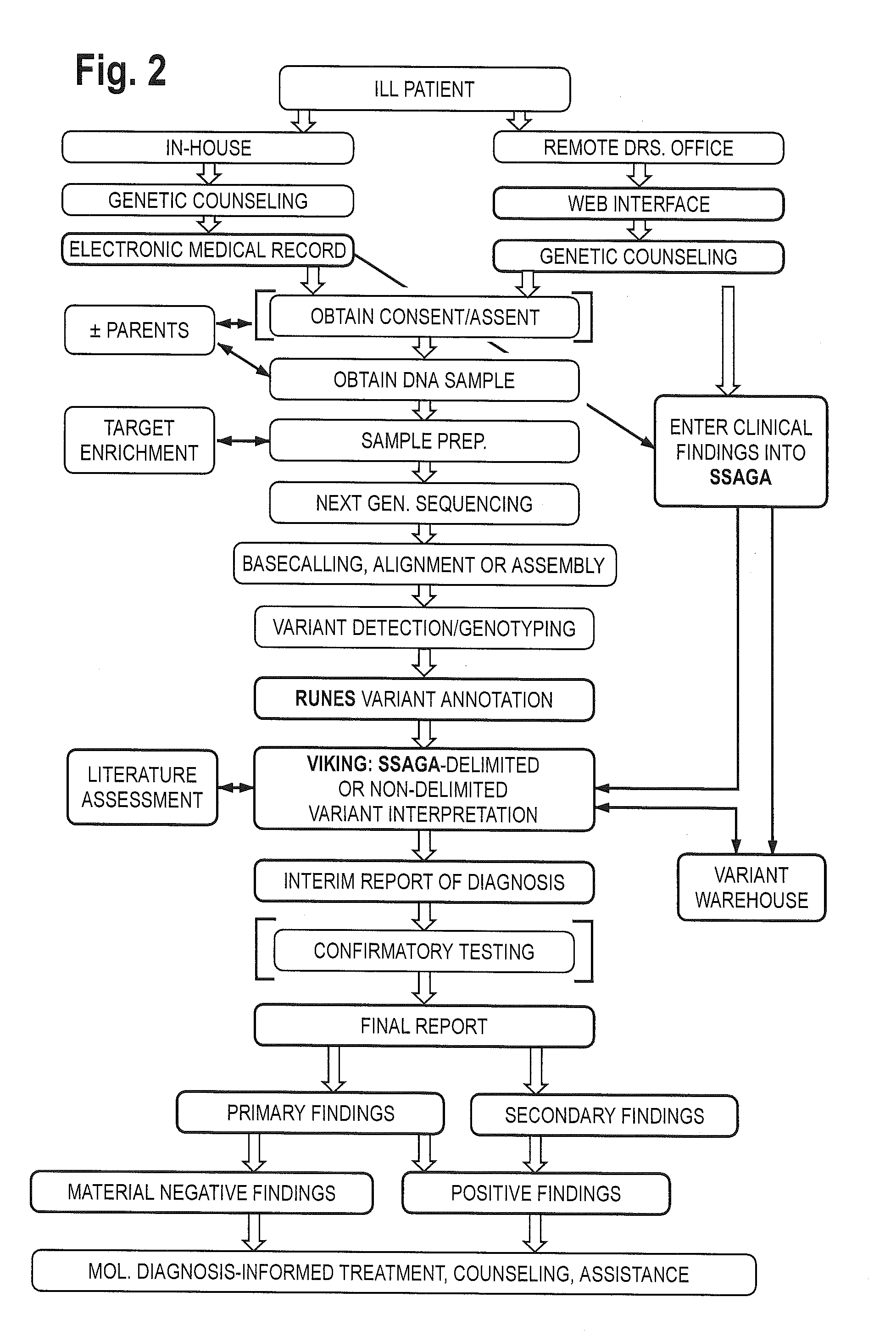
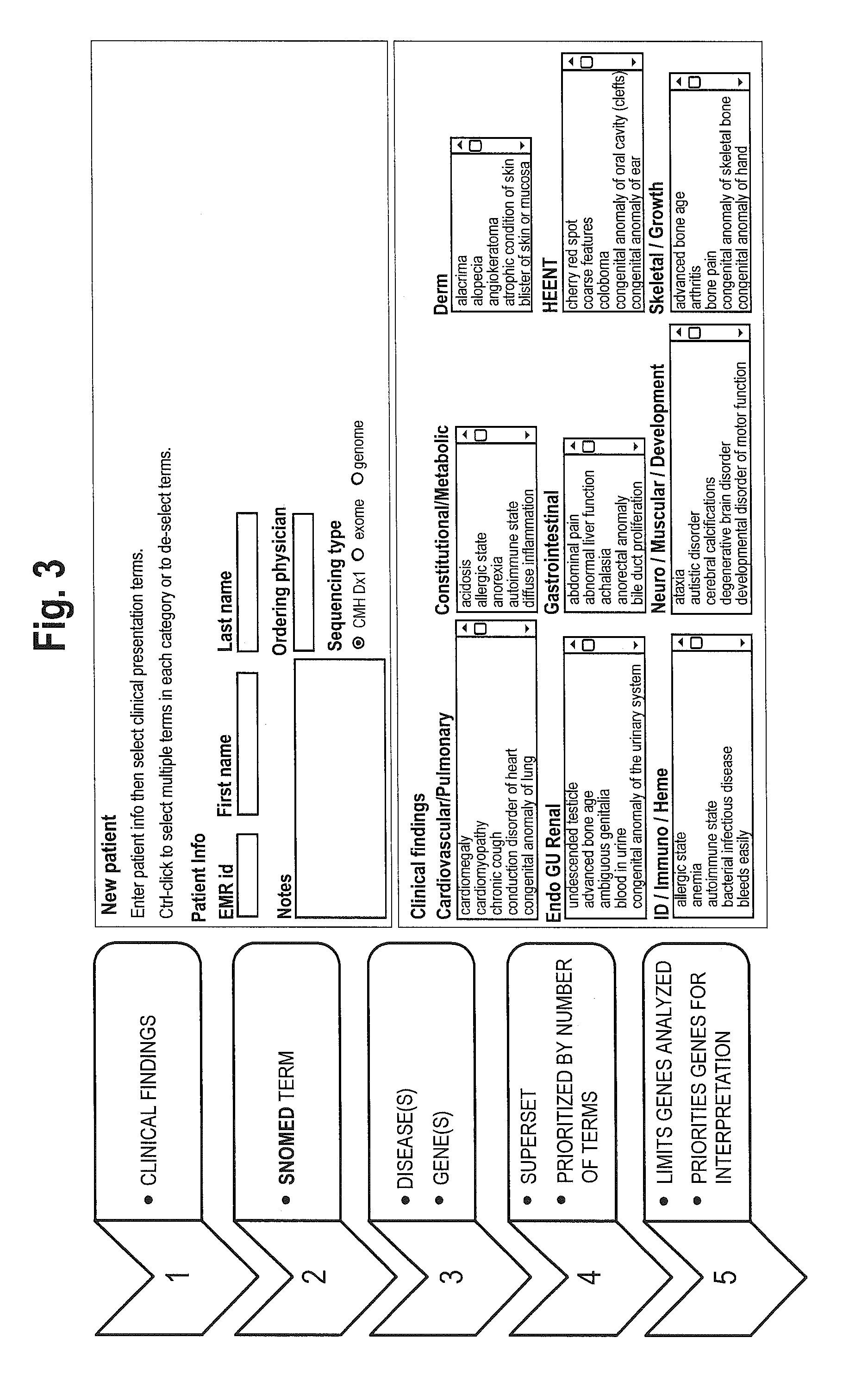
The method for genome analysis translates the clinical findings in the patient into a comprehensive test order for genes that can be causative of the patient's illness, delimits analysis of variants identified in the patient's genome to those that are “on target” for the patient's illness, and provides clinical annotation of the likely causative variants for inclusion in a variant warehouse that is updated as a result of each sample that is analyzed and that, in turn, provides a source of additional annotation for variants. The method uses a genome sequence having the steps of entering at least one clinical feature of a patient by an end-user, assigning a weighted value to the term based on the probability of the presence of the term, mapping the term to at least one disease by accessing a knowledge base containing a plurality of data sets, wherein the data sets are made up of associations between (i) clinical features and diseases, (ii) diseases and genes, (iii) genes and genetic variants, and (iv) diseases and gene variants, assigning a truth value to each of the mapped terms based on the associated data sets and the weighted value, to provide a list of results of possible diagnoses prioritized based on the truth values, with continuous adjustment of the weightings of associations in the knowledge base based on updating of each discovered diagnosis and attendant clinical features, genes and gene variants. This method can be performed in fifty hours or twenty-four hours or less.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
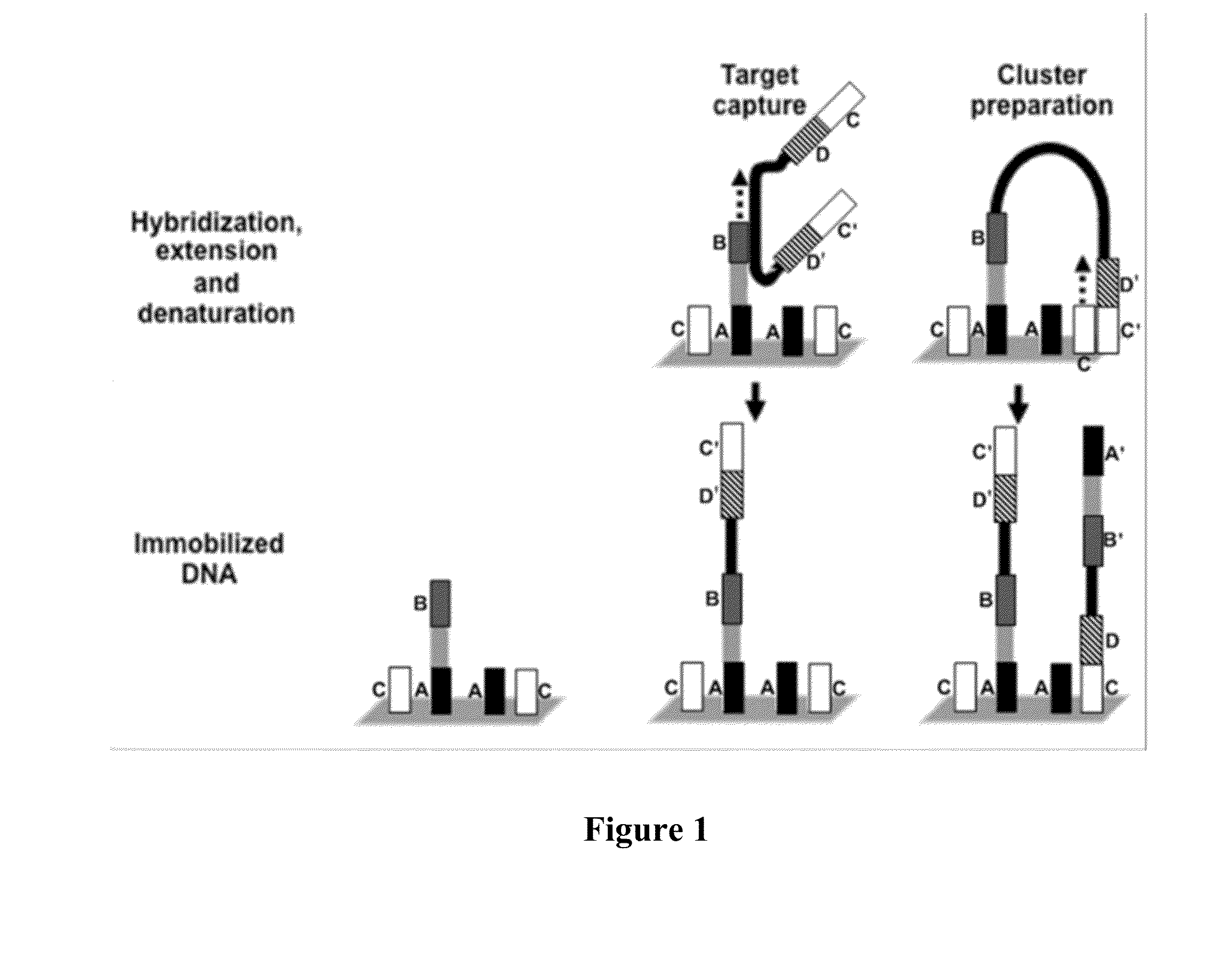
Methods of forming circular nucleic acid probes and uses thereof
InactiveUS7358047B2Enhanced interactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismNucleic Acid Probes
The present invention relates generally to a method of amplifying closed circular nucleic acid probes and, more particularly, to a method of amplifying closed circular nucleic acid probes by rolling circle amplification. The method of the present invention is useful in a range of applications involving the detection of nucleic acid sequences such as, but not limited to, the identification of genetic disorders, genetic variants or the presence of microbiological or viral agents.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Nucleic acid sequencing adapters and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170355984A1Minimize the differenceMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesVariable lengthNucleic acid sequence
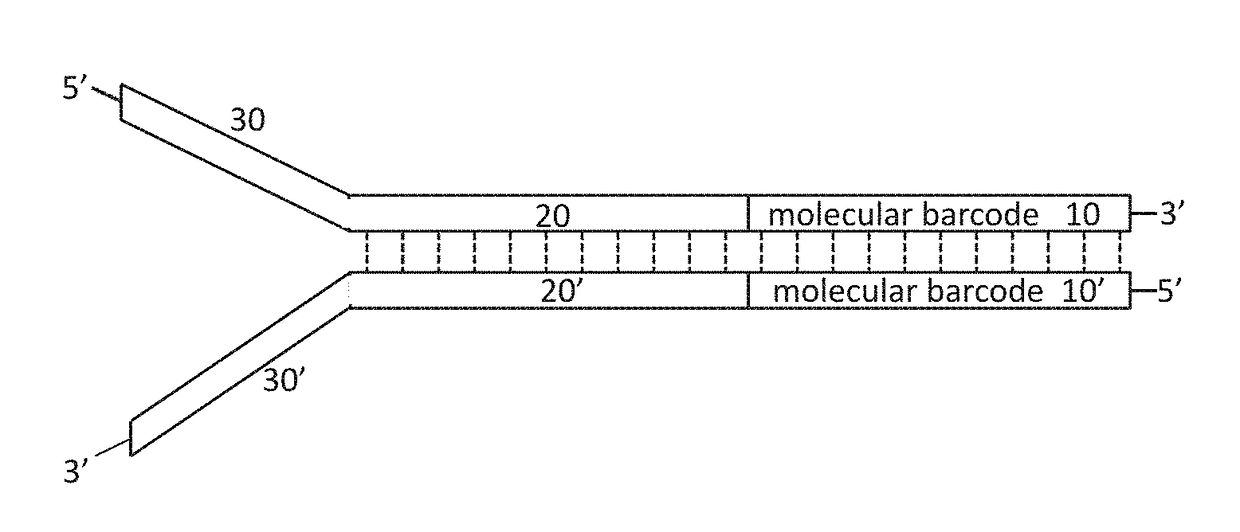
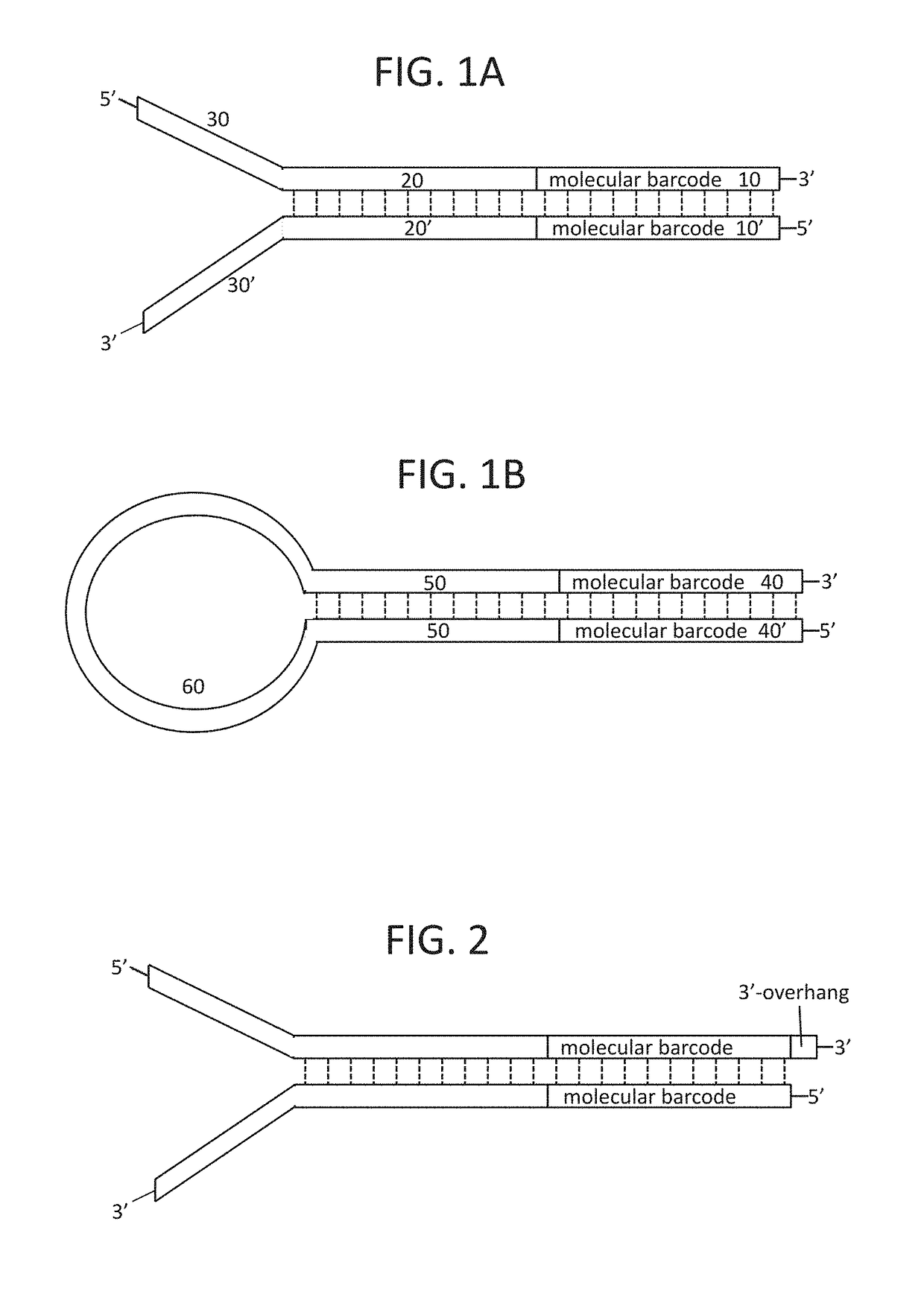
High-fidelity, high-throughput nucleic acid sequencing enables healthcare practitioners and patients to gain insight into genetic variants and potential health risks. However, previous methods of nucleic acid sequencing often introduces sequencing errors (for example, mutations that arise during the preparation of a nucleic acid library, during amplification, or sequencing). Provided herein are sequencing adapters comprising a nondegenerate or variable length molecular barcode and compositions comprising a plurality of sequencing adapters, which can be useful for sequencing nucleic acids. Further provided are methods of using the sequencing adapters, including methods of sequencing nucleic acids, methods of identifying an error in a nucleic acid sequence, and methods of determining the number of nucleic acid molecules in a library.
Owner:MYRIAD WOMENS HEALTH INC
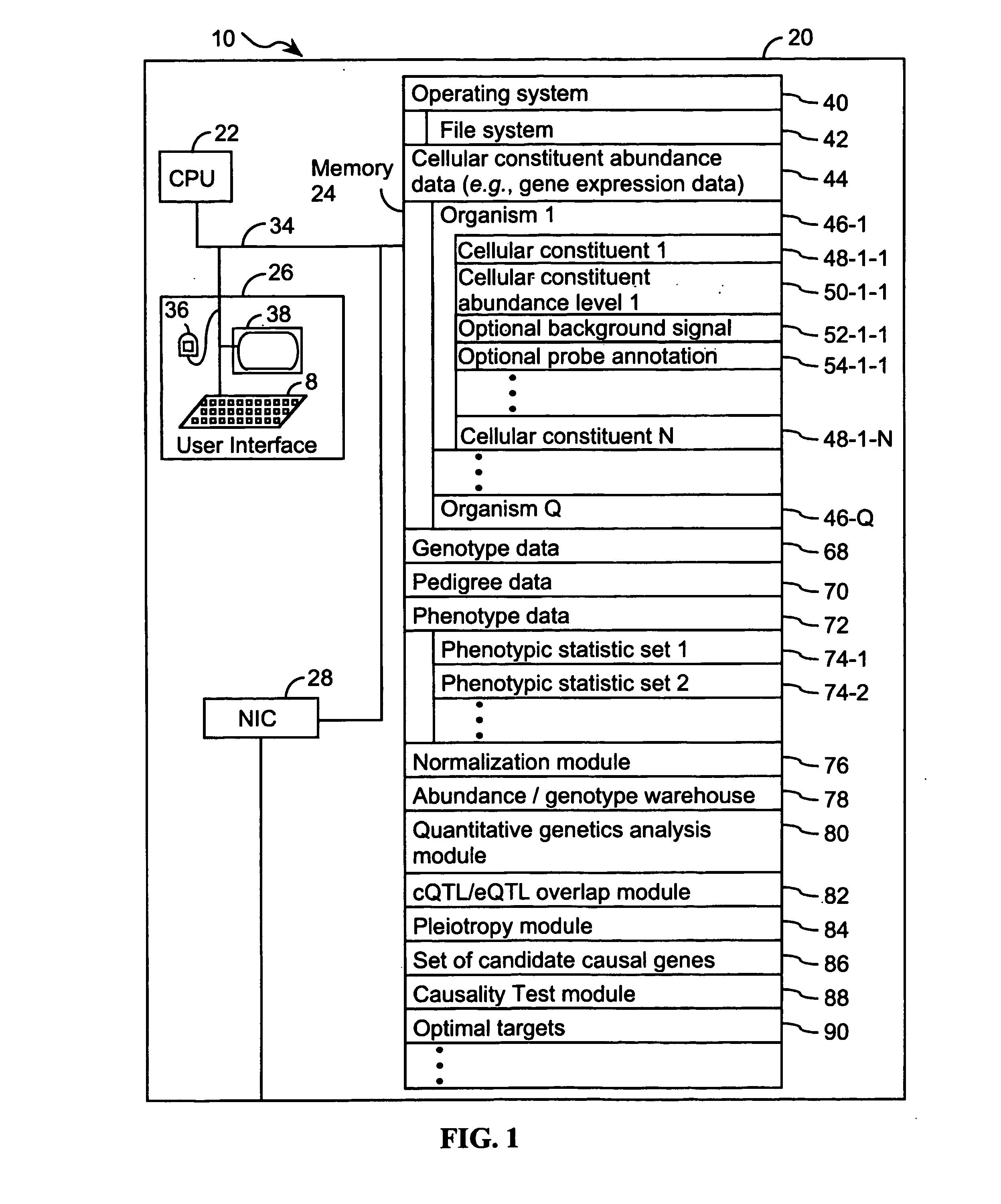
Computer systems and methods for inferring casuality from cellular constituent abundance data
InactiveUS20070038386A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCellular componentBiological body
Methods, computer program products, and systems are provided for associating a cellular constituent with a trait T exhibited by a species. A cellular constituent i that has at least one abundance quantitative trait locus (eQTL) coincident with a respective clinical quantitative trait locus (cQTL) for the trait of interest T is identified. For each eQTL, a determination is made as to whether (i) the genetic variation of the eQTL and (ii) the variation of the trait of interest T across the plurality of organisms are correlated conditional on an abundance pattern of the cellular constituent i across the plurality of organisms. When the genetic variation of (i) one of the eQTL and (ii) the variation of the trait of interest T across the plurality of organisms are uncorrelated conditional on the abundance pattern of the cellular constituent i, the cellular constituent i is considered causal for, and is therefore associated with, the trait of interest T.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
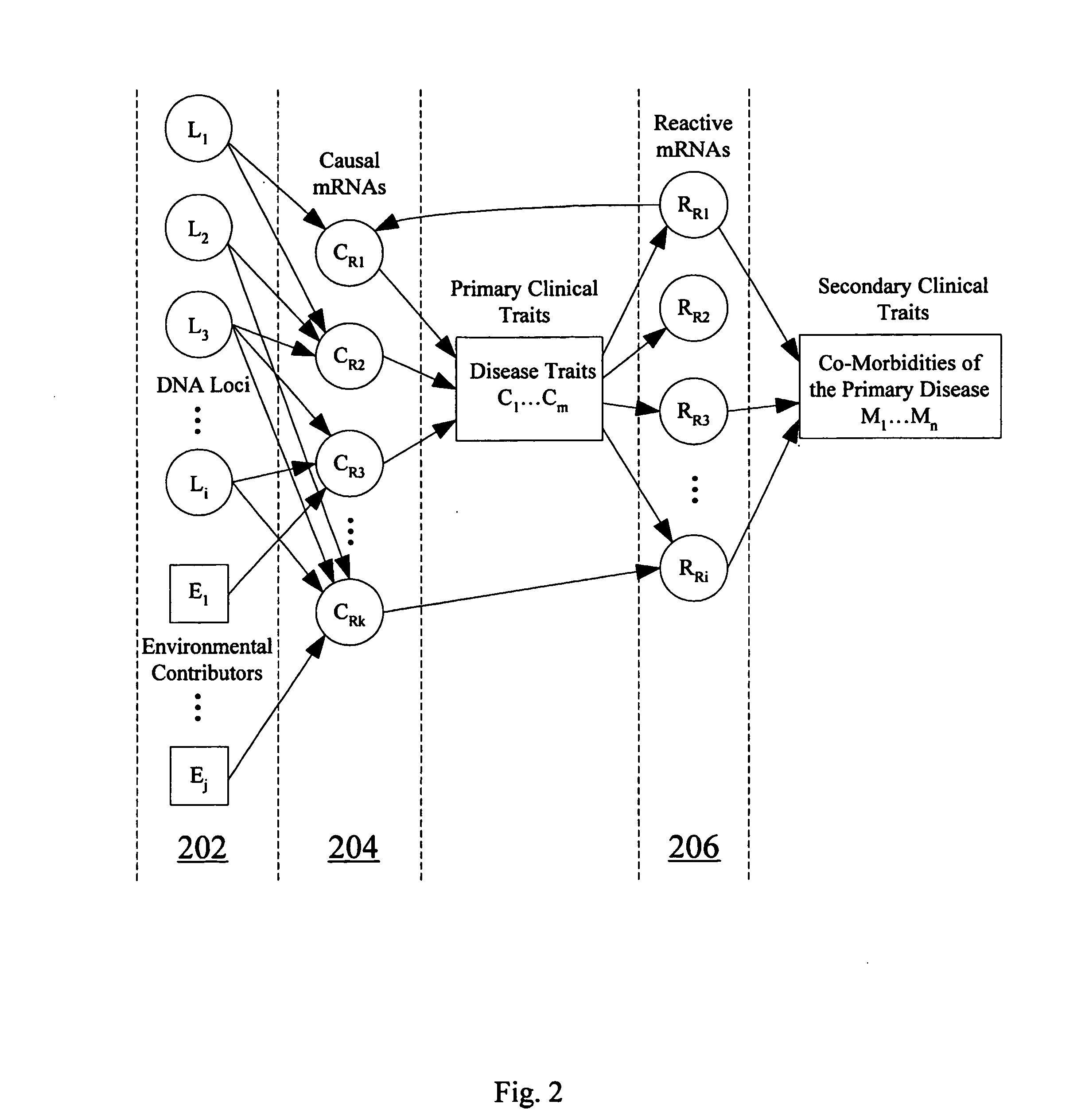
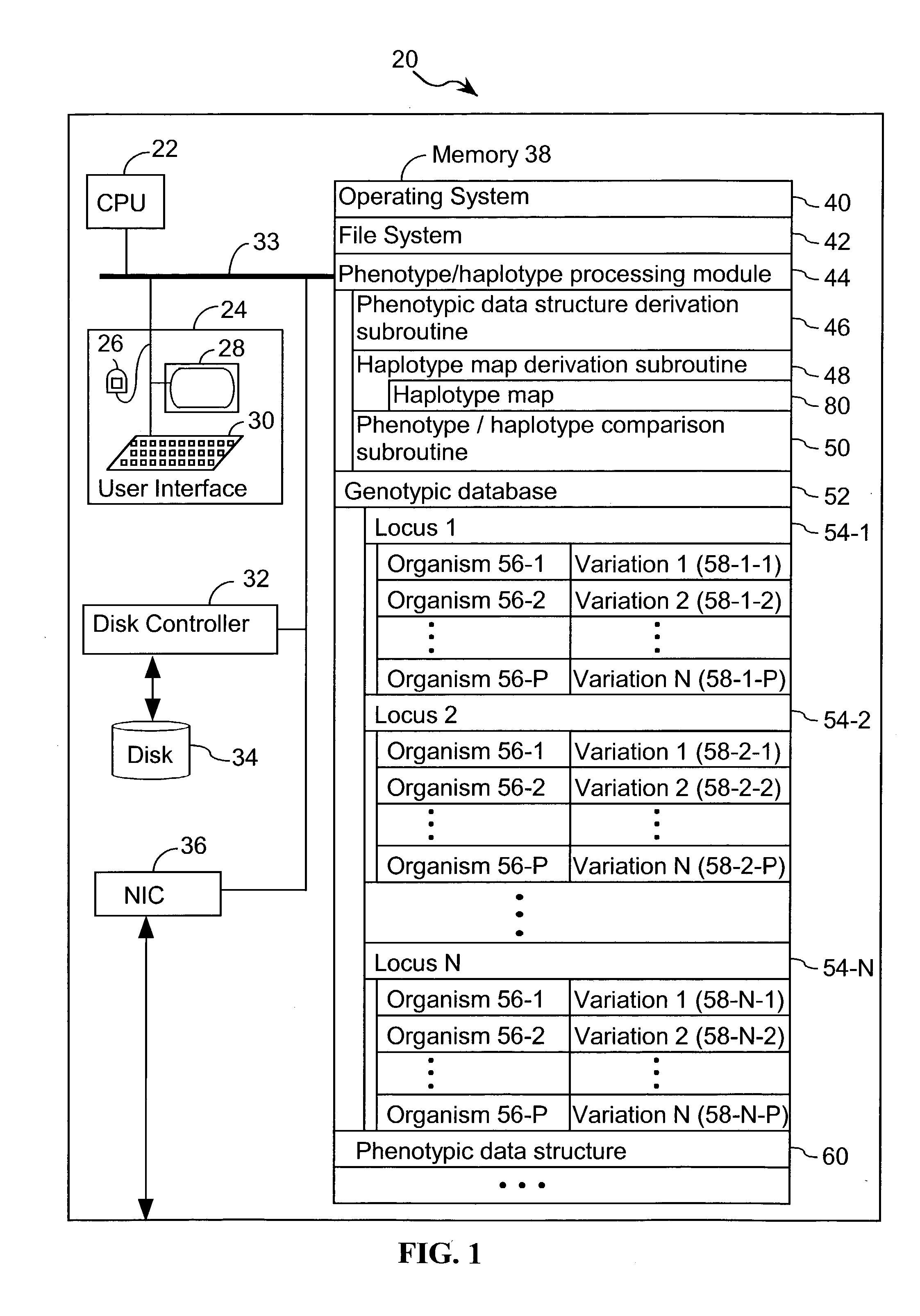
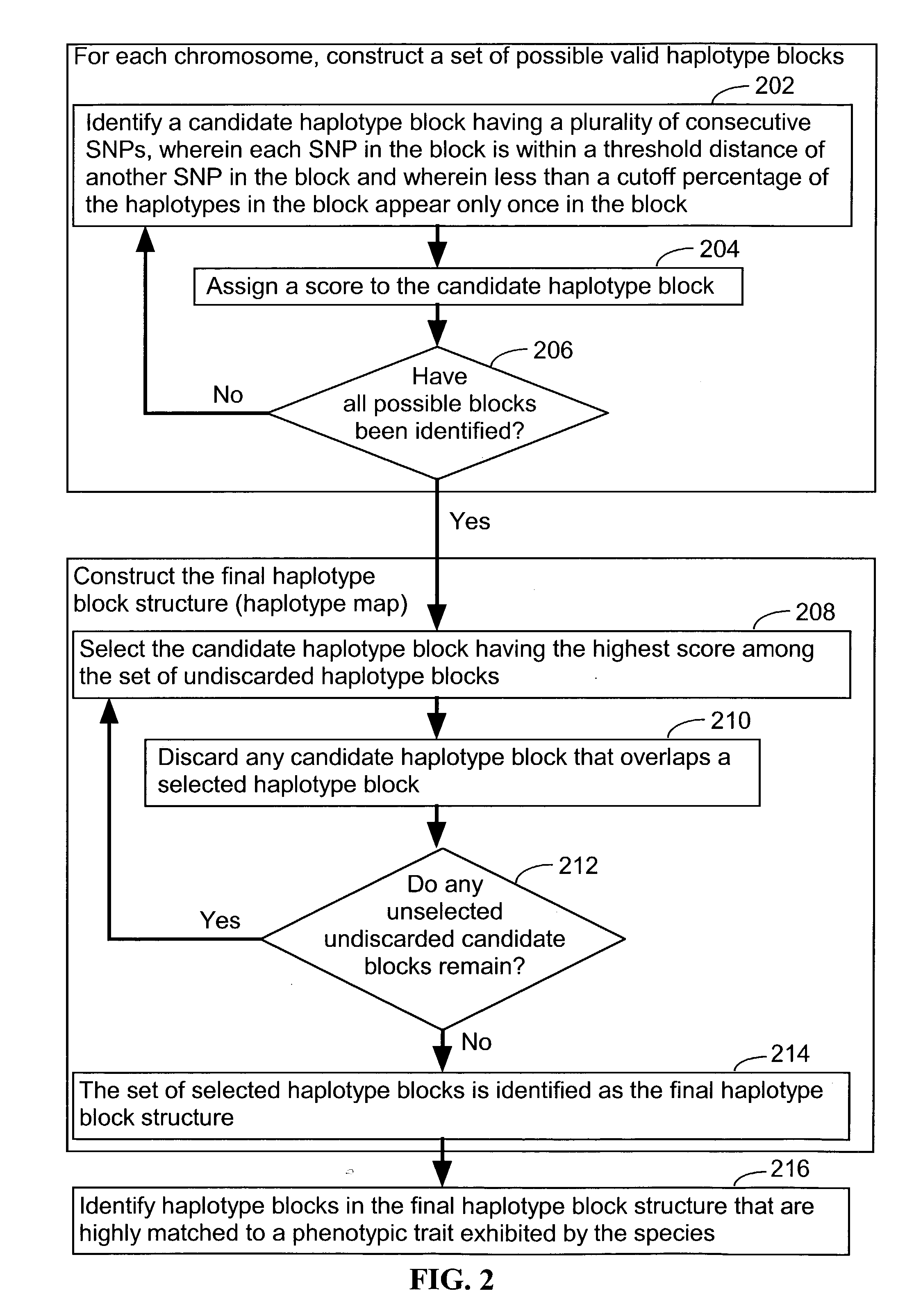
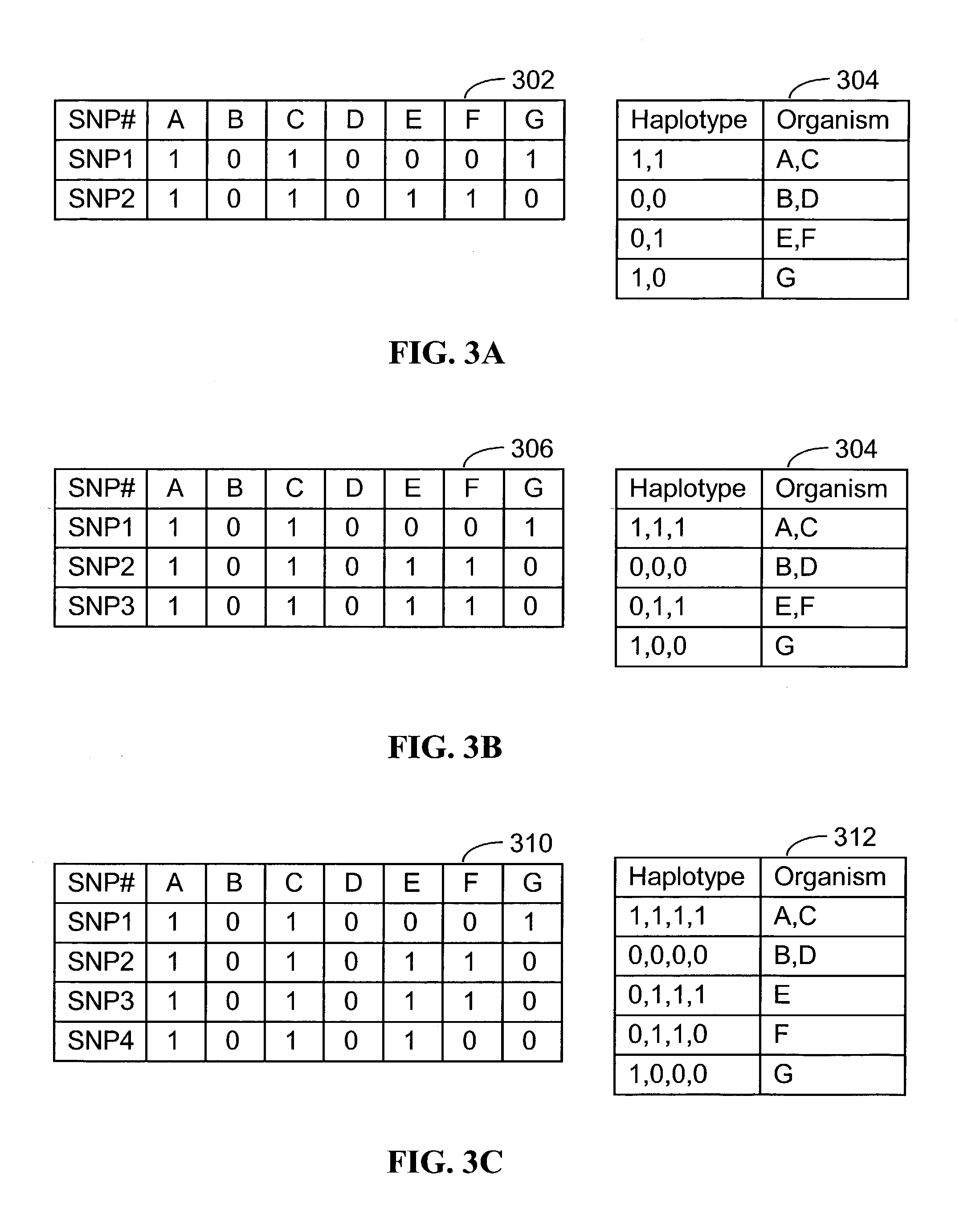
Systems and methods for predicting specific genetic loci that affect phenotypic traits
A database of genetic variations is analyzed to produce a haplotype map of the genome for strains of a single species. A computational method is used to rapidly map complex phenotypes onto the haplotype blocks within the haplotype map. The specific genetic locus regulating three different biologically important phenotypic traits in mice is identified using these systems and methods.
Owner:SANDHILL BIO CORP +1
Methods and Compositions for Diagnosing, Prognosing, and Treating Neurological Conditions
ActiveUS20140162933A1Decreased CI activityShorten the lengthCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNervous systemPhysiology
This document provides methods and materials related to genetic variations of neurological disorders. For example, this document provides methods for using such genetic variations to assess susceptibility of developing Parkinson's disease.
Owner:POPULATION BIO INC
Genetic analysis systems and methods
InactiveUS6897025B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNAGenetics
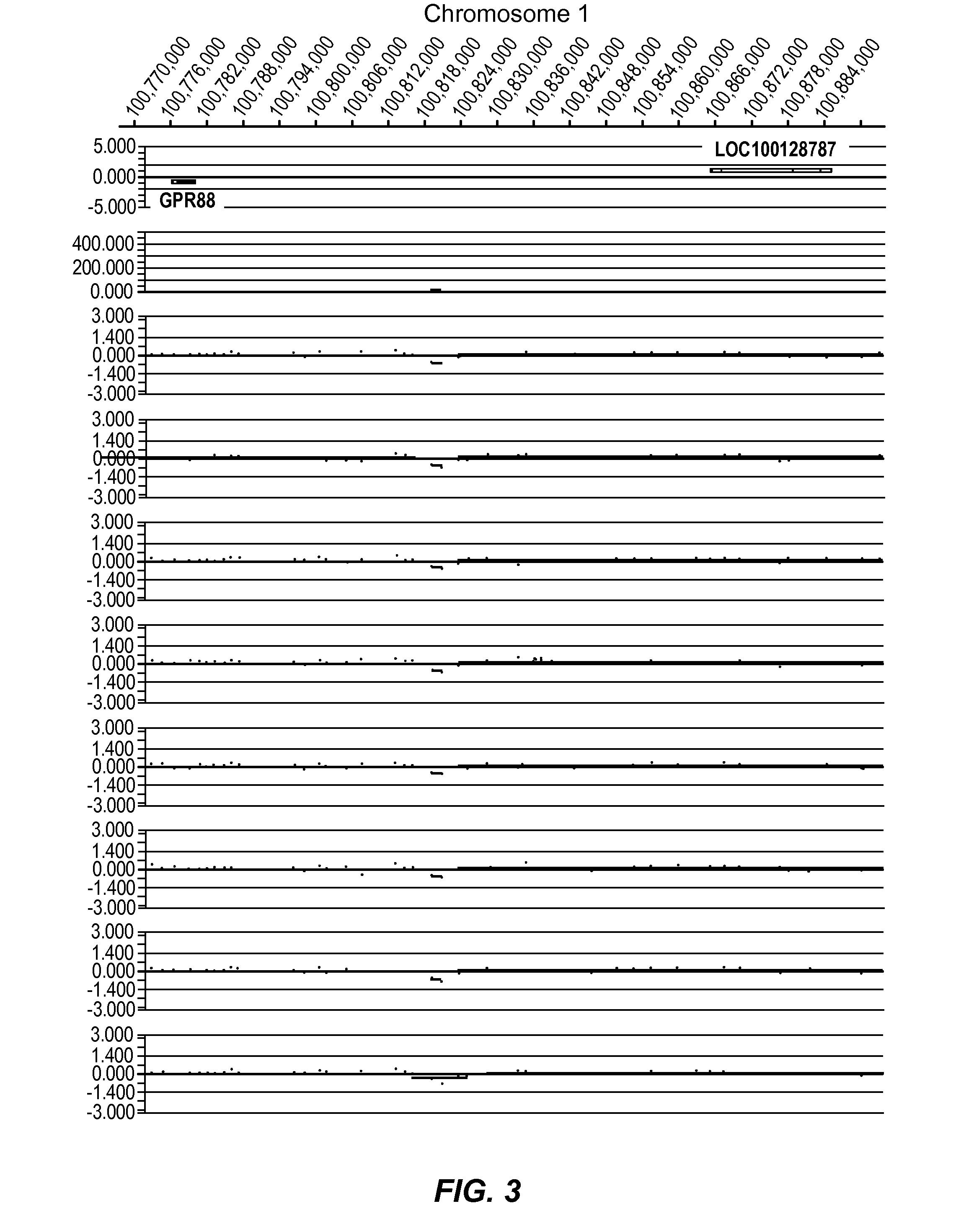
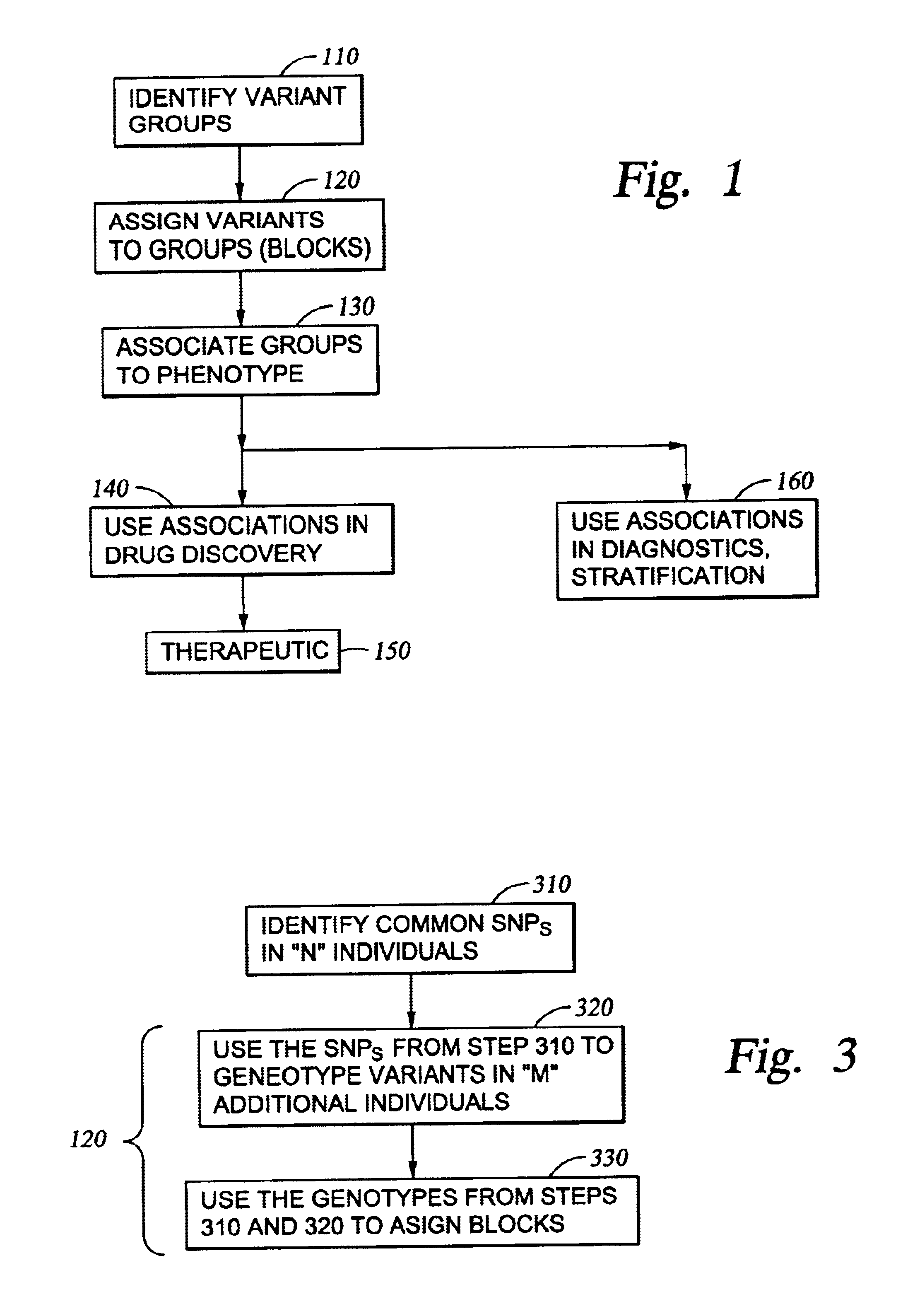
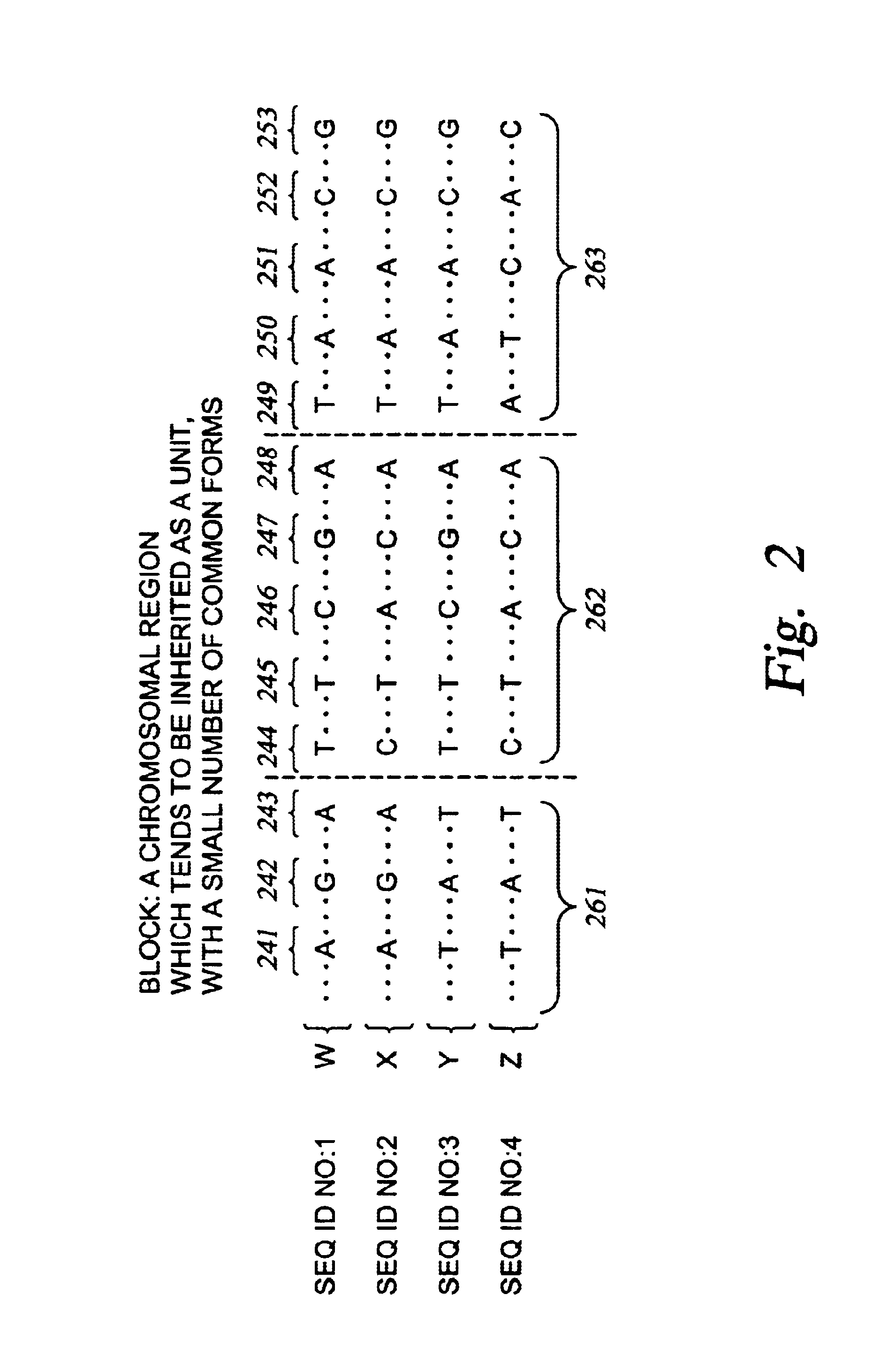
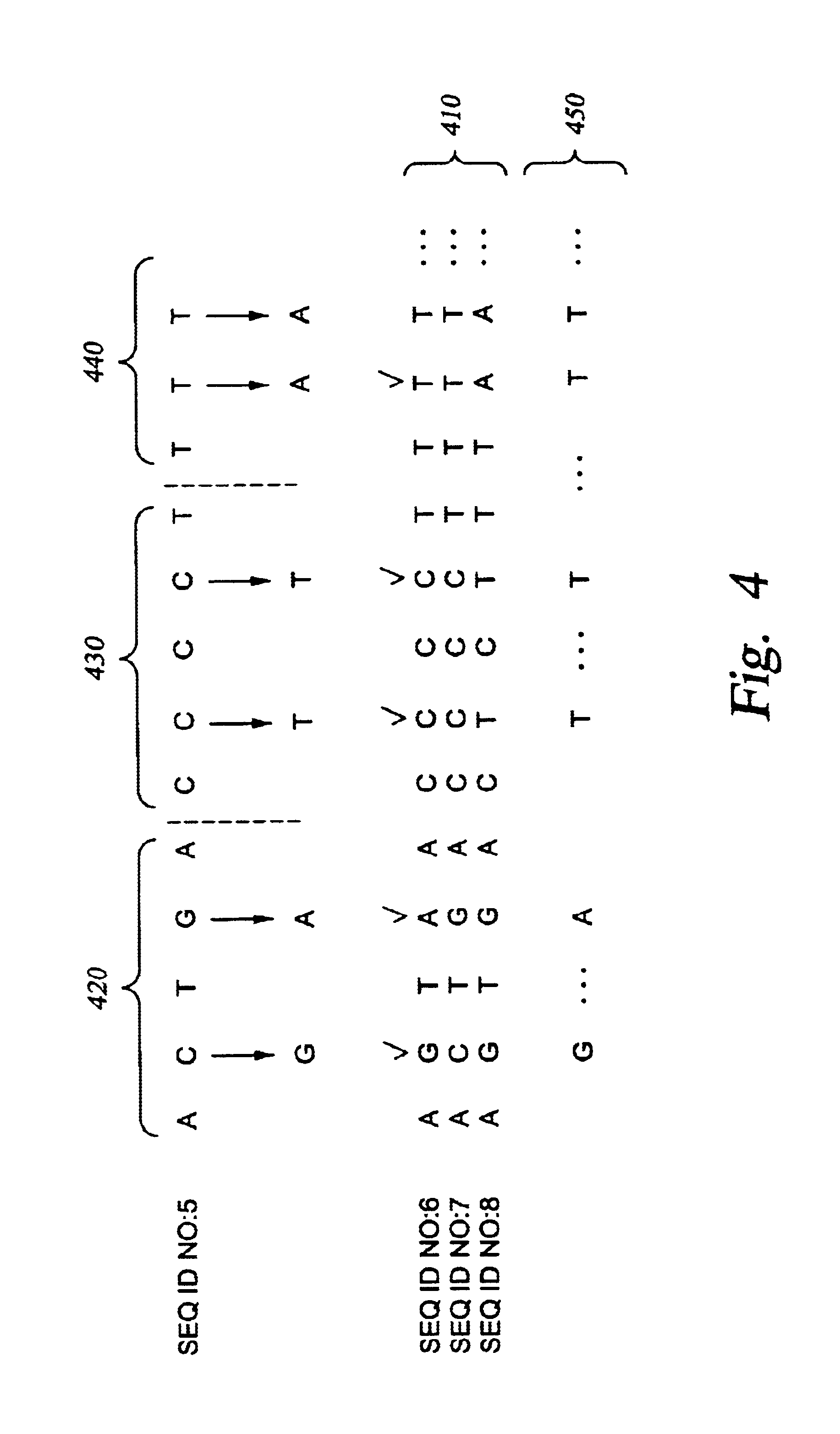
Improved systems and methods for performing genetic analyses. Full genomic DNA scans are performed on the genetic DNA from a plurality of individuals to identify genetic variants. For those variants, but not based on a full genetic DNA scan, the variants alone are scanned in additional individuals to identify blocks of the variants that tend to be inherited together.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Methods and compositions for diagnosing, prognosing, and treating neurological conditions
This document provides methods and materials related to genetic variations of neurological disorders. For example, this document provides methods for using such genetic variations to assess susceptibility of developing Parkinson's disease.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Genetic Variants Predictive of Cancer Risk
InactiveUS20110212855A1Increased susceptibilityHigh riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDiseaseGenetic variants
The invention discloses genetic variants that have been determined to be susceptibility variants of cancer. Methods of disease management, including determining increased susceptibility to cancer, methods of predicting response to therapy and methods of predicting prognosis of cancer using such variants are described. The invention further relates to kits useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:DECODE GENETICS EHF
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
InactiveUS20070037164A1Raise the possibilityDelay and reduce and preventSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFactor iiTumour necrosis factor alpha
The present disclosure describes the use of genetic variance information for genes involved in inflammatory or immunologic disease, disorder, or dysfunction. The variance information is indicative of the expected response of a patient to a method of treatment. Methods of determining relevant variance information and additional methods of using such variance information are also described.
Owner:NUVELO INC
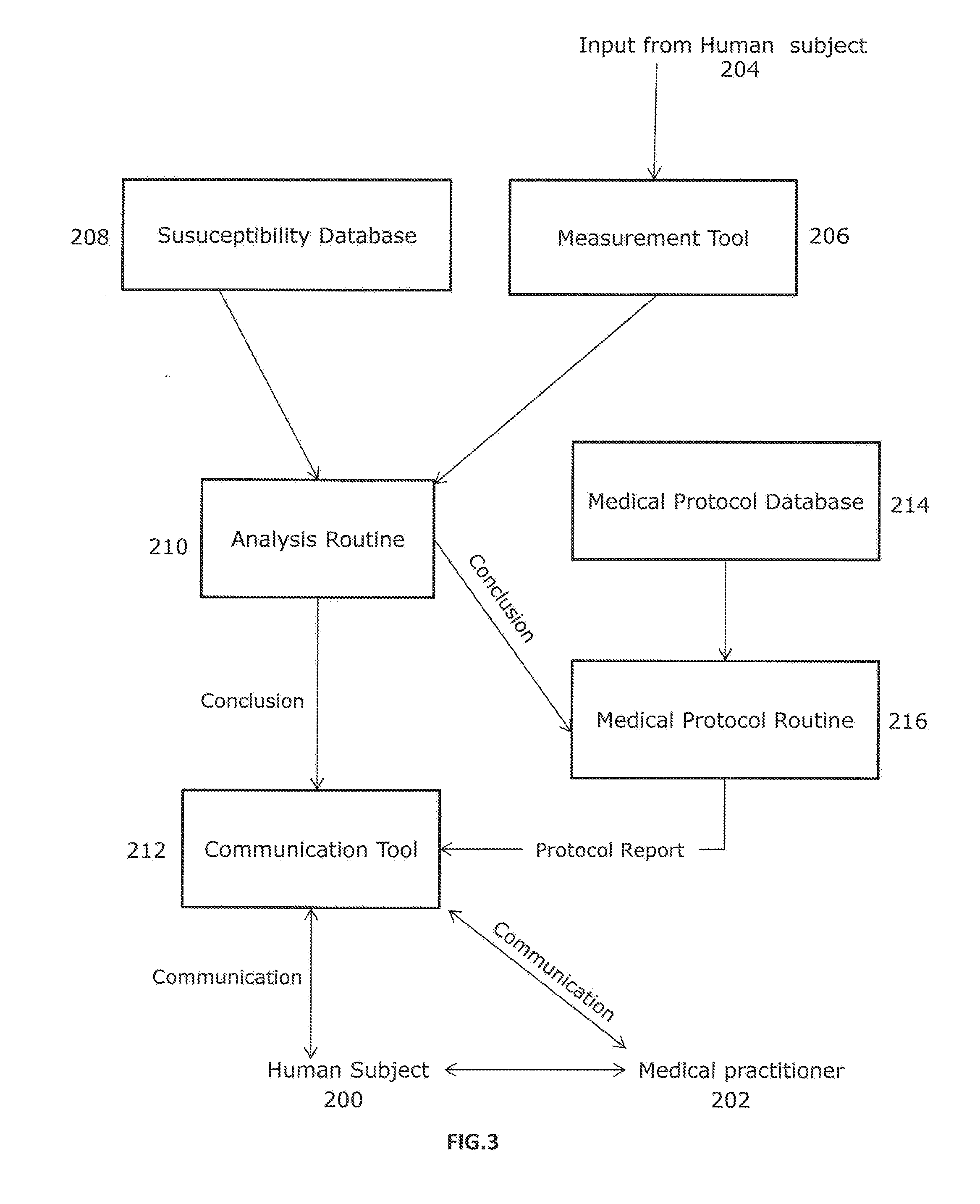
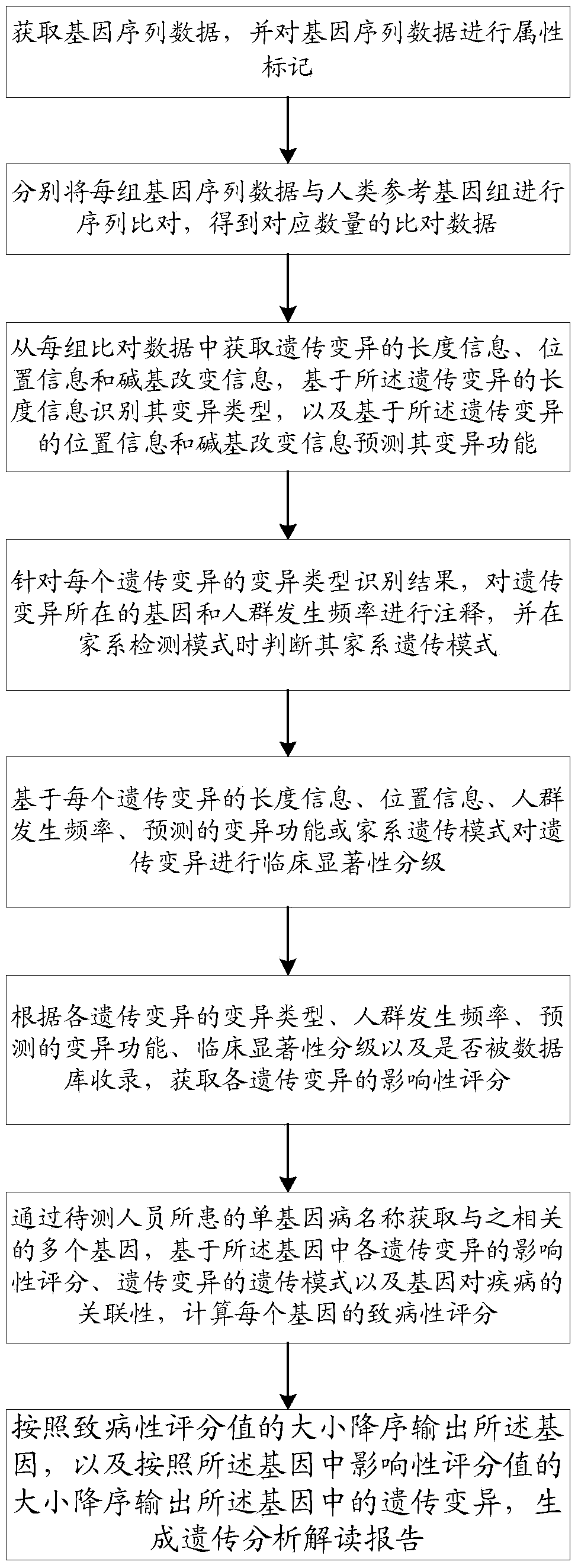
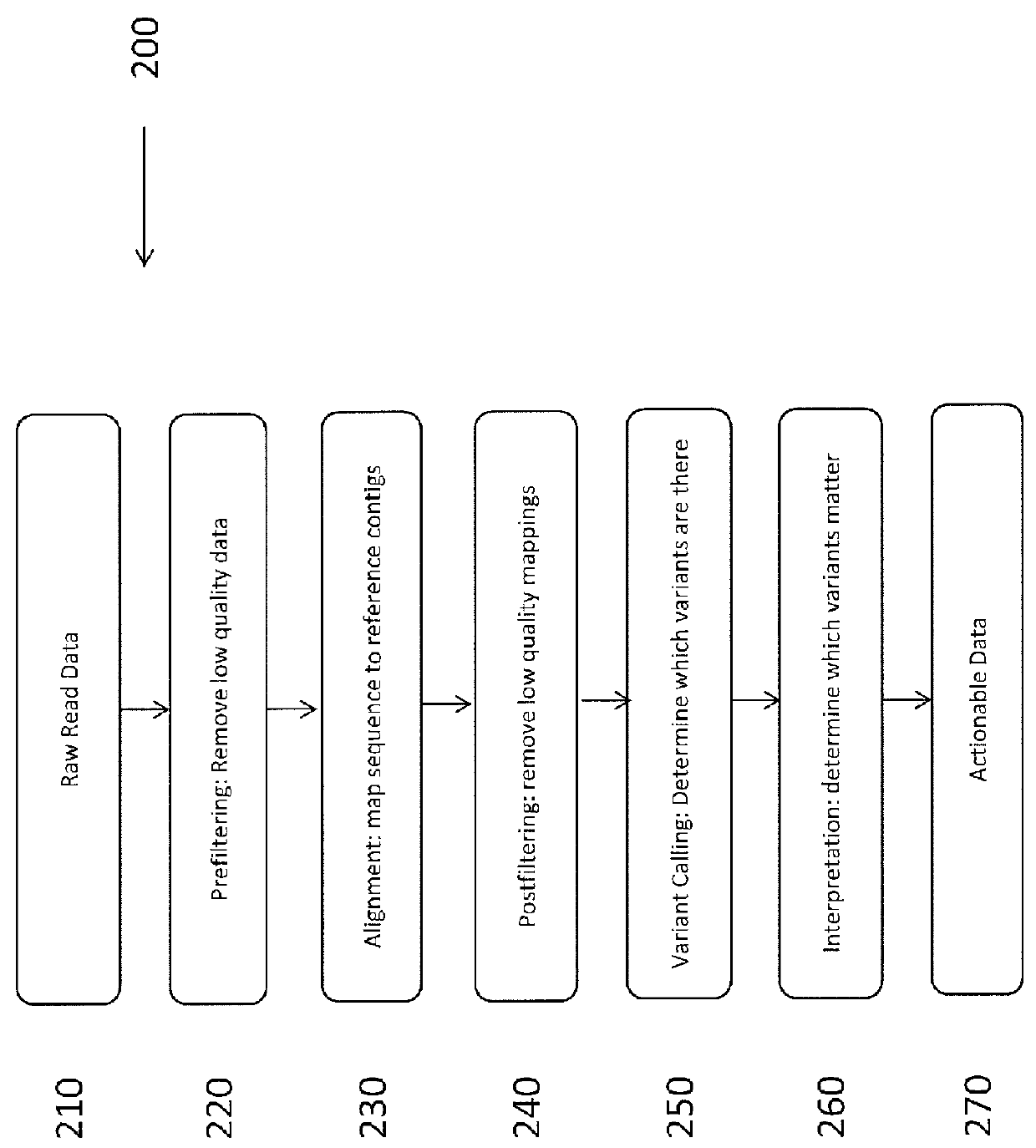
A method and system for intelligently interpreting and reporting genetic variation of monogenic diseases
ActiveCN109086571ARealize full automationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsSequence alignment
The invention discloses a method and a system for intelligently interpreting and reporting the genetic variation of a single gene disease, which can automatically analyze the genetic variation resultbased on the original sequence data of a gene of a patient, and provide a professional genetic variation analysis report, thereby improving the diagnosis and treatment efficiency of the genetic variation. The method comprises the following steps of: gene sequence data is acquired and attribute marking is performed on the gene sequence data; sequence alignment of each set of gene sequence data withhuman reference genome is performed to obtain corresponding amount of alignment data; based on the length information of genetic variation, the variation type is identified, and the variation function is predicted based on the position information and base change information of genetic variation. According to the identification results of each genetic variation type, the gene and population frequencies of genetic variation were annotated, and the family genetic pattern was judged when the family detection mode was used. The system comprises the method proposed in the technical proposal.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
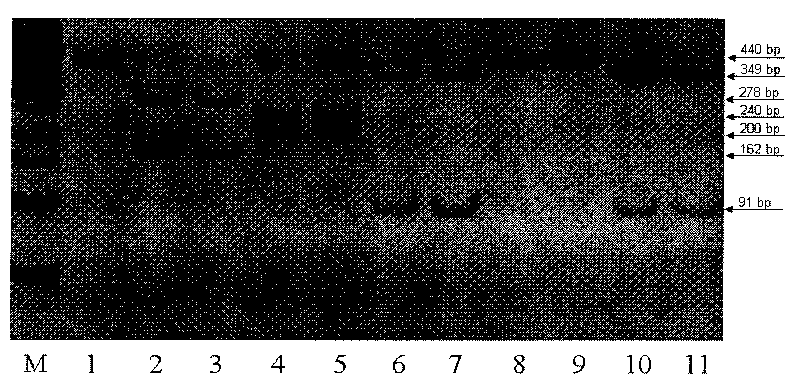
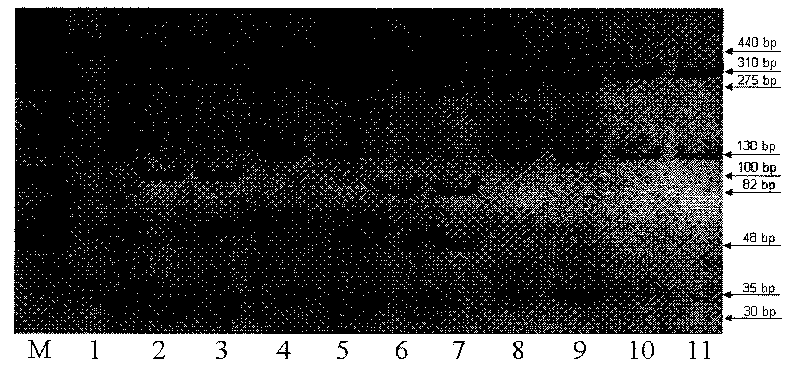
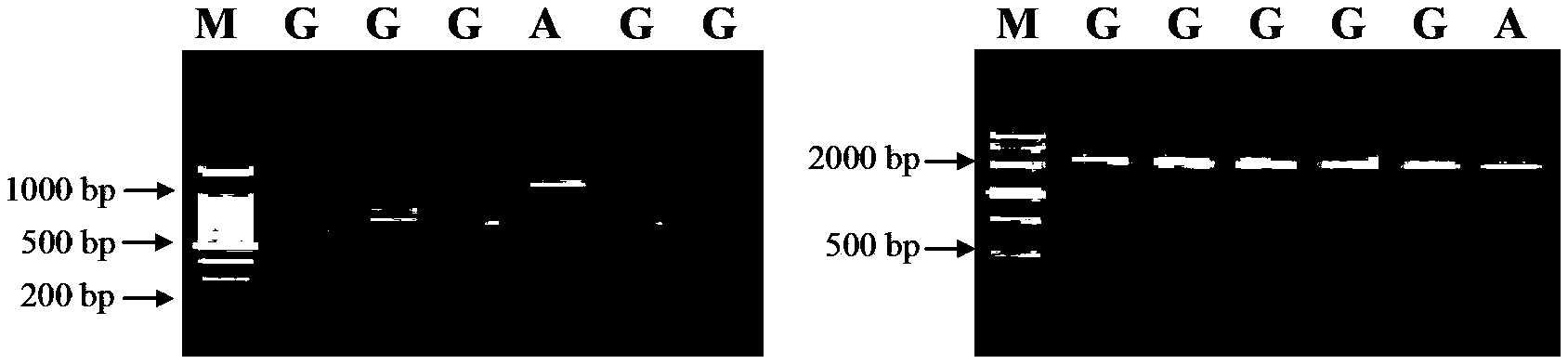
Method for quickly identifying categories of meat and dried meat products of five domestic animals
The invention relates to a method for identifying categories of meat and dried meat products of five domestic animals (namely a pig, a goat, an ox, a buffalo and a yak), which is based on genetic variation of a 440bp gene segment of a chondriosome 12S rRNA gene, adopts a PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) technique, and belongs to the field of biological high technology. The identification method of the invention comprises the following main steps: genomic DNA extraction of a sample, PCR amplification, restriction endonuclease digestion, endonuclease product detection and sample identification. The identification method of the invention has the characteristics of quickness, simpleness, economy and accuracy, which can be applied to massive detection of fresh meat and commercialized dried meat samples. The establishment of the method has important significance in the aspects of animal food inspection and quarantine, business fraud prevention and food backtracking system creation.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and compositions for screening and treating developmental disorders
ActiveUS20130316911A1Compound screeningCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAutism spectrum disorderMedicine
This document provides methods and materials related to genetic variations of developmental disorders. For example, this document provides methods for using such genetic variations to assess susceptibility of developing Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
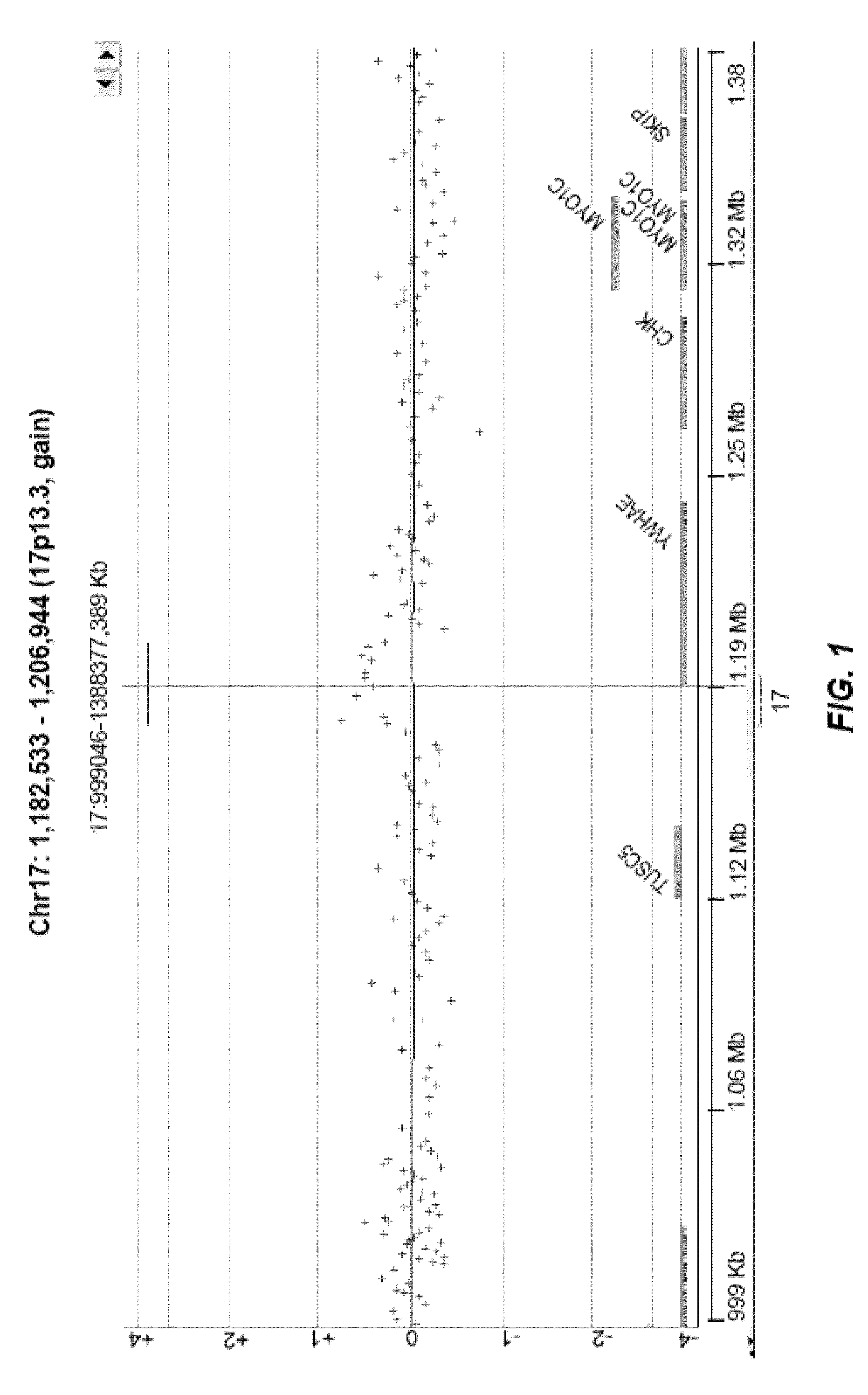
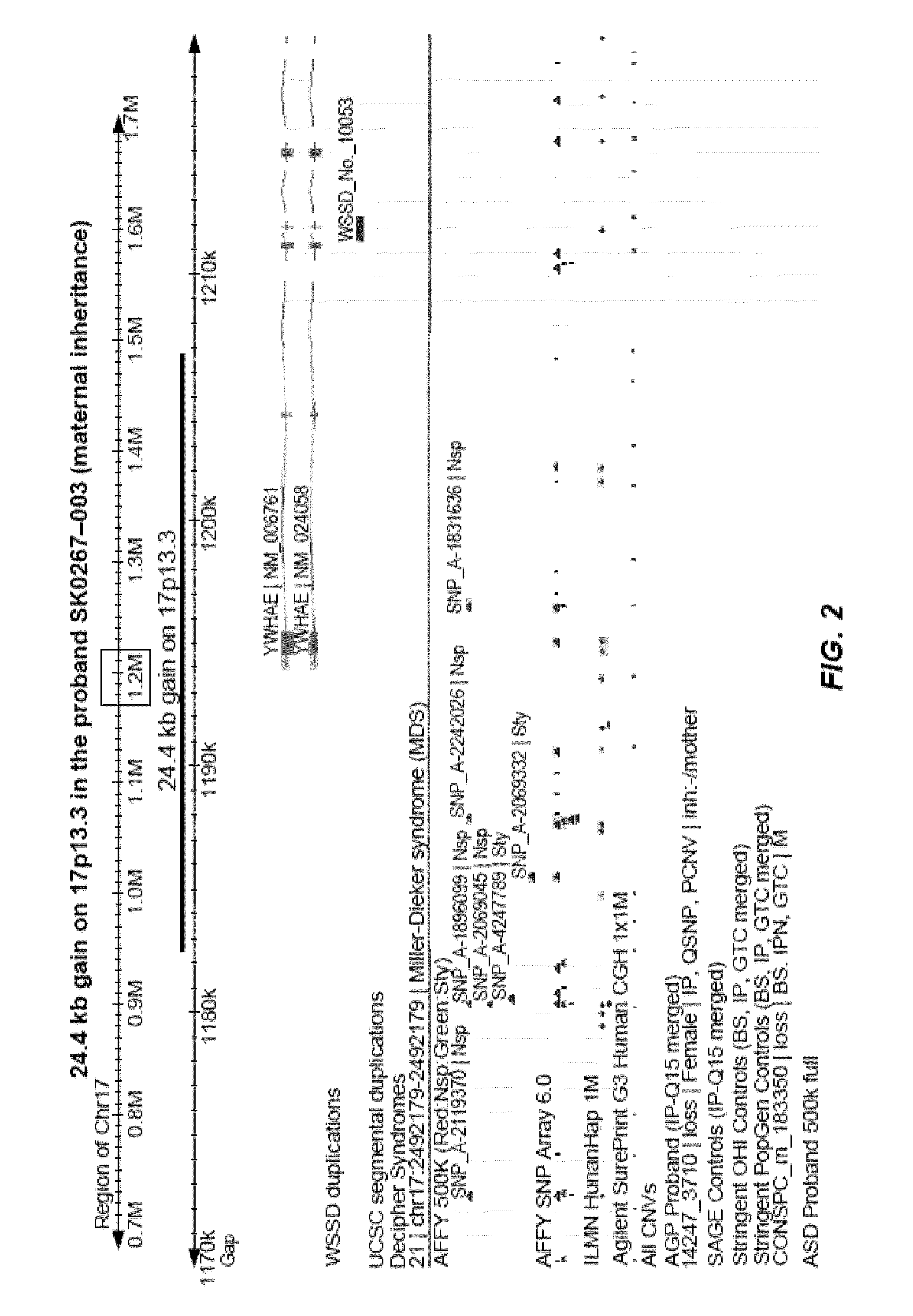
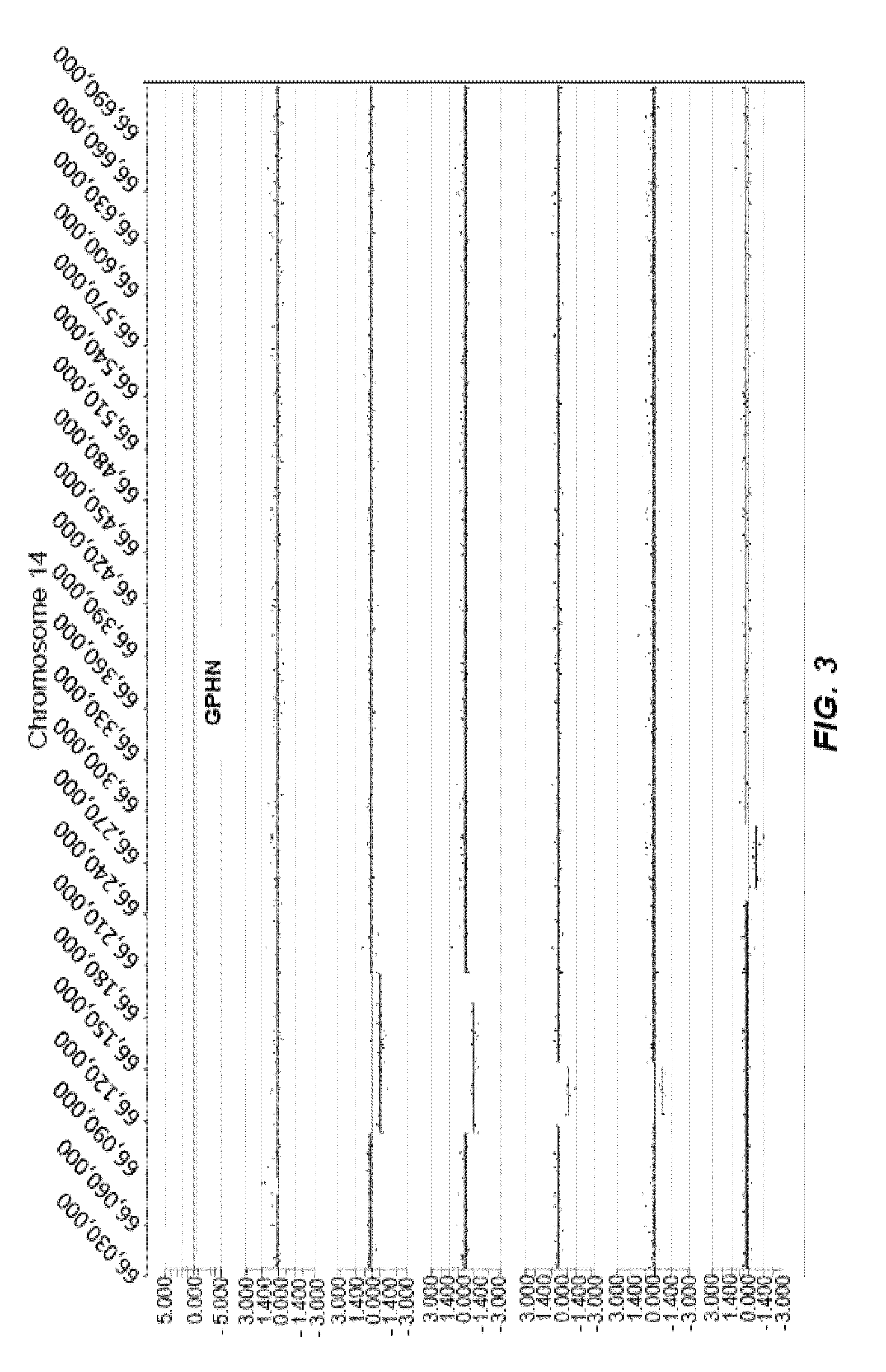
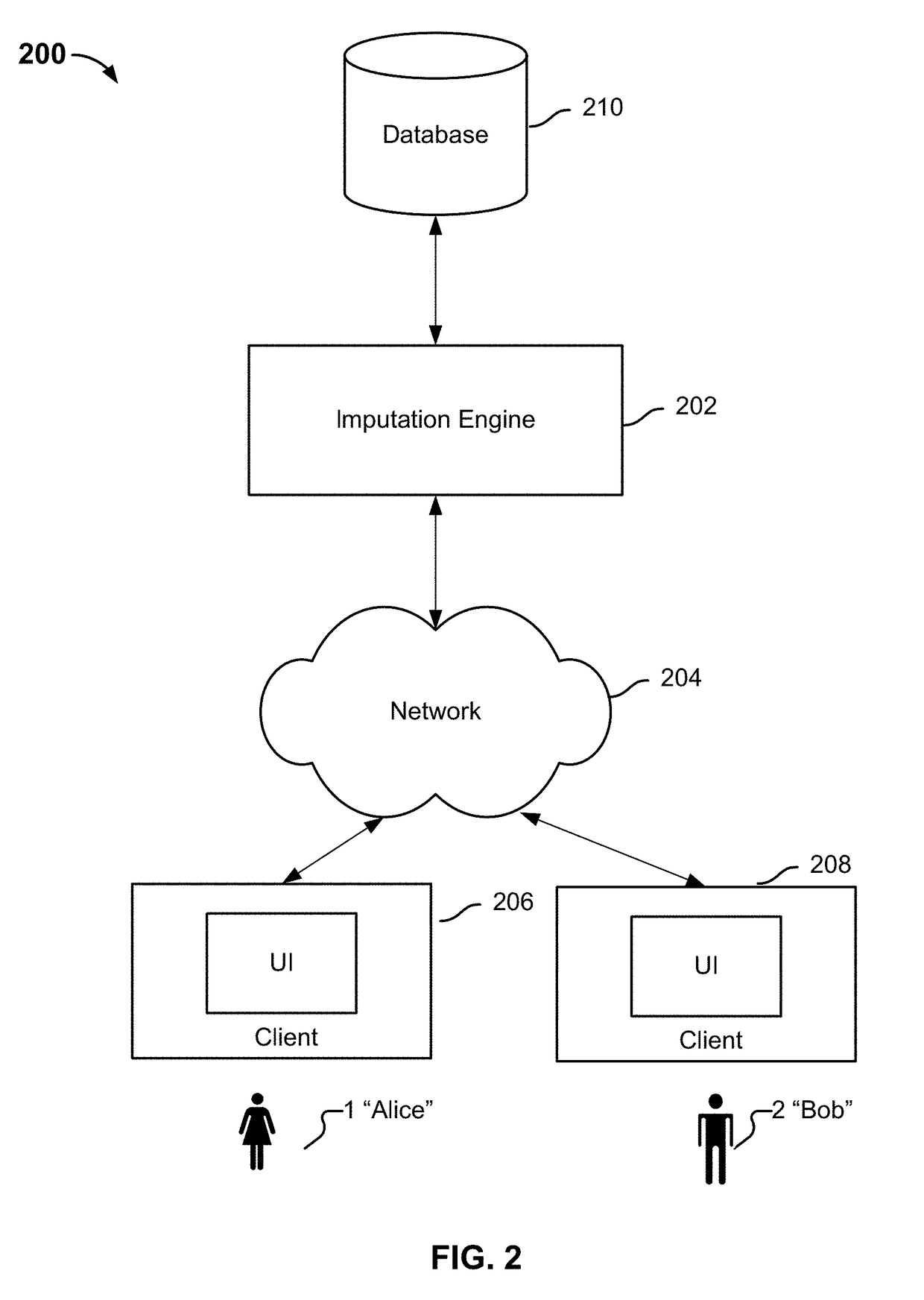
Identifying variants of interest by imputation
Processing genetic information comprises: receiving an input that includes information pertaining to a specific genetic variant; and identifying, in a database comprising genotype information of a plurality of candidate individuals, a matching individual imputed to have the specific genetic variant. The genotype information of the matching individual corresponding to the specific genetic variant is not directly assayed.
Owner:23ANDME
Systems and methods for identifying polymorphisms
InactiveUS20150356243A1Convenient treatmentGood estimateHealth-index calculationProteomicsDiseasePhenotypic trait
Owner:MULTIMODAL IMAGING SERVICES CORP +1
Method And System For Phasing Individual Genomes In The Context Of Clinical Interpretation
ActiveUS20130085728A1Improve accuracyIncrease sample sizeDrug and medicationsAnalogue computers for chemical processesData setMendelian inheritance
The present disclosure presents a unified system to phase a personal genome for downstream clinical interpretation. In an embodiment, an initial phasing is generated using public datasets, such as haplotypes from the 1000 Genomes Project, and a phasing toolkit. A local perturbation algorithm is applied to improve long range phasing. If available, a Mendelian inheritance pipeline is applied to identify phasing of novel and rare variants. These datasets are merged, followed by correction by any experimental data. This allows for full clinical interpretation of the role of a group of variants in a gene, whether inherited or de novo variants.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Mobile supplementation, extraction, and analysis of health records
ActiveUS20200126663A1Validating an accuracy of the abstracted health informationMedical data miningFinanceEntity linkingMobile device
A system, method, and mobile device application are configured to capture, with a mobile device, a document such as a next generation sequencing (NGS) report that includes NGS medical information about a genetically sequenced patient. At least some of the information is extracted from the document using an entity linking engine, and the extracted information is provided into a structured data repository where it is accessible to provide information regarding the patient specifically as well as collectively as part of a cohort of patients with similar genetic variants, medical histories, or other commonalities. In one aspect, the document is matched to a template model, and the document is processed using one or more masks segregating the template model, and therefore the document, into a series of distinct subregions.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS
Identifying Possible Disease-Causing Genetic Variants by Machine Learning Classification
The techniques described herein relate identification of disease-causing genetic variant by machine learning classification. The techniques may include receiving a training dataset of predetermined variants associated with disease. A hyperplane is identified having a maximum margin between points of the dataset. Patient input data is received including an observed variant of a gene. Features of the observed variant are selected, and a score is determined The score is determined using Support Vector Machine algorithms based on an observation of a novel non-linear relationship with the selected features of the observed variant. The observed variant may be classified based on the score indicating a distance of the observed variant from the identified hyperplane.
Owner:PIERIANDX INC
Molecular marker related with wheat thousand grain weight and applications thereof
InactiveCN104342484AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGrain weight
The invention discloses a molecular marker related with wheat thousand grain weight and applications thereof. Through the heritable variation analysis on 6-SFT gene of a wheat natural variation group, people find that the 6-SFT gene has two SNPs corresponding to the 1371st and 2450th positions in the tail ends from 1 to 5' in the sequence one. Three haplotypes exist in the two SNP, namely haplotype A (G,G) haplotype B (G,A), and haplotype C (A,G). Through correlation analysis, the wheat thousand grain weights of the three homozygous haplotypes are accord with a relationship as follows: the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype C > the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype B > the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype C. The invention also provided a CAPS label for detecting the two SNPs. Experiments have proved that the wheat with a higher thousand grain weight can be found through detecting the two SNPs. A novel method is provided for the wheat breeding assisted by a molecular labeling technology, and the provided molecular maker has an important meaning for the breeding and researches of wheat species with a high yield.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
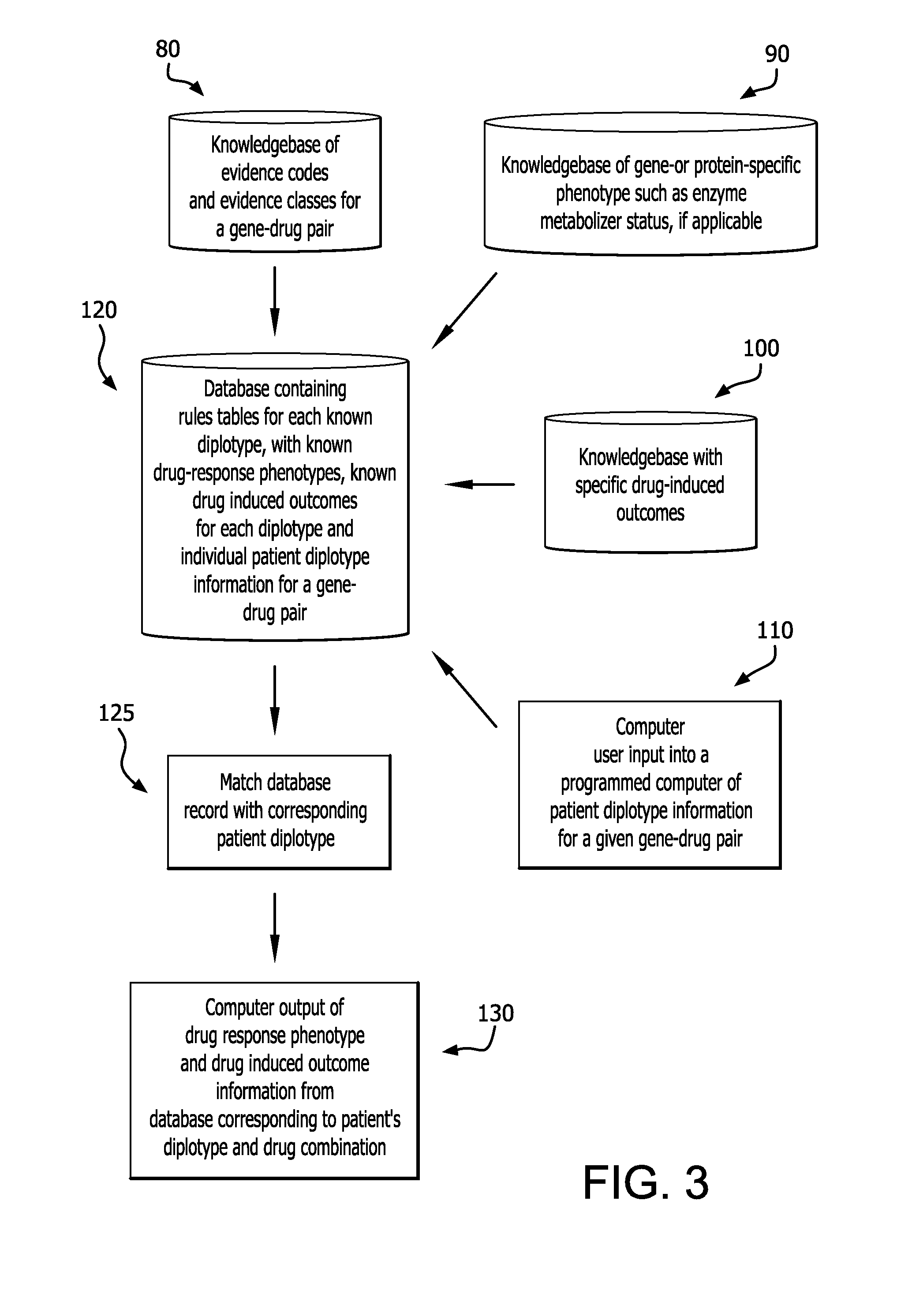
Method for translating genetic information for use in pharmacogenomic molecular diagnostics and personalized medicine research
A gene-drug specific system for classifying individual genetic variants based on strength-of-evidence of clinical utility from published scientific and clinical data that support their effect on modifying drug response and behavior. This allows categorization of the genetic variants into evidence classes that have a wide range of uses such as pharmacogenomic molecular diagnostics and personalized medicine research designed to guide the clinical implementation of PGx. Furthermore, this information can be combined with a knowledgebase of drug-response phenotypes, a knowlegebase of specific drug-induced outcomes and individual patient diplotype information for a gene-drug combination into a programmed computer to output corresponding patient-specific predicted drug responses.
Owner:CORIELL INST FOR MEDICAL RES
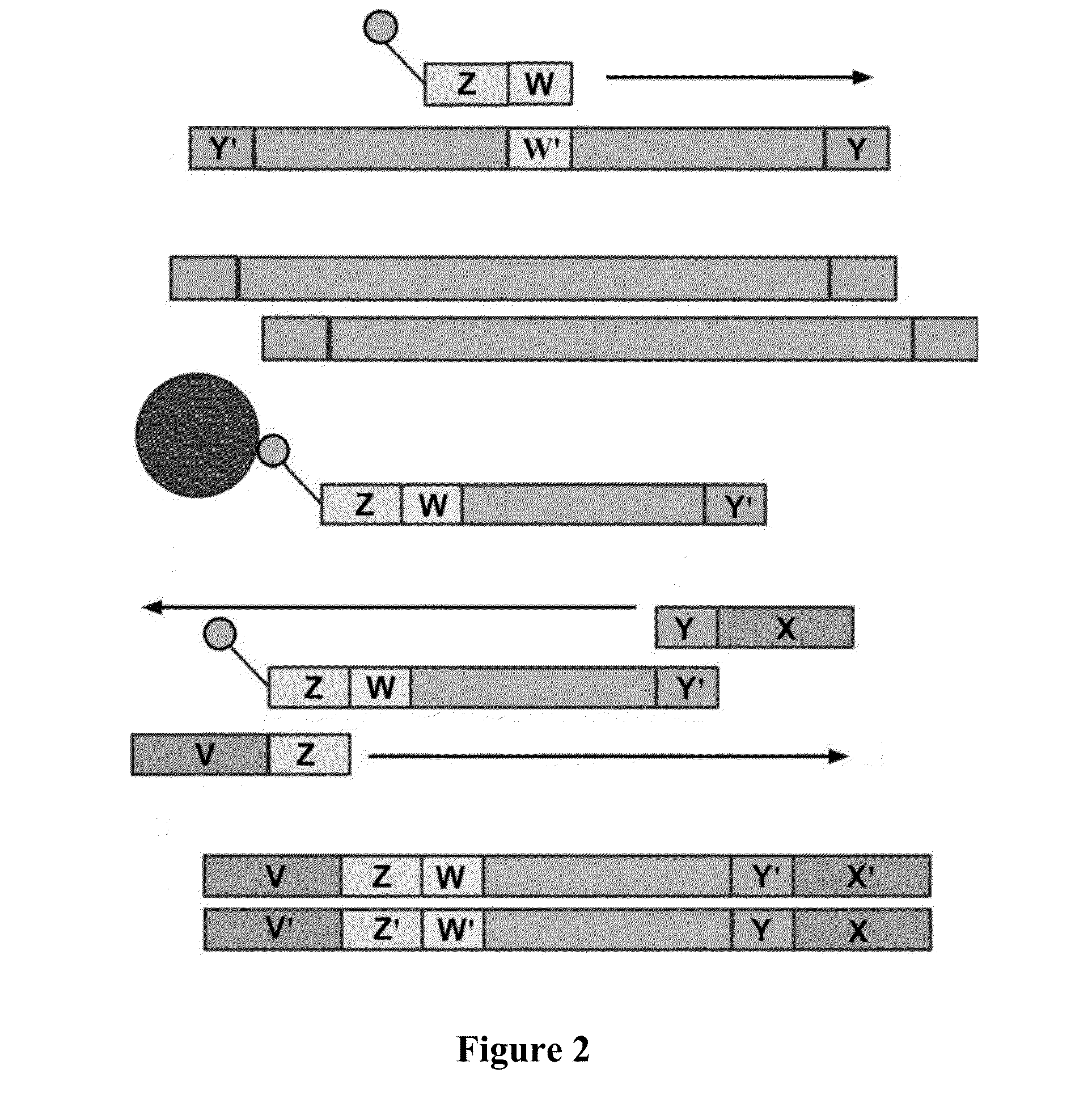
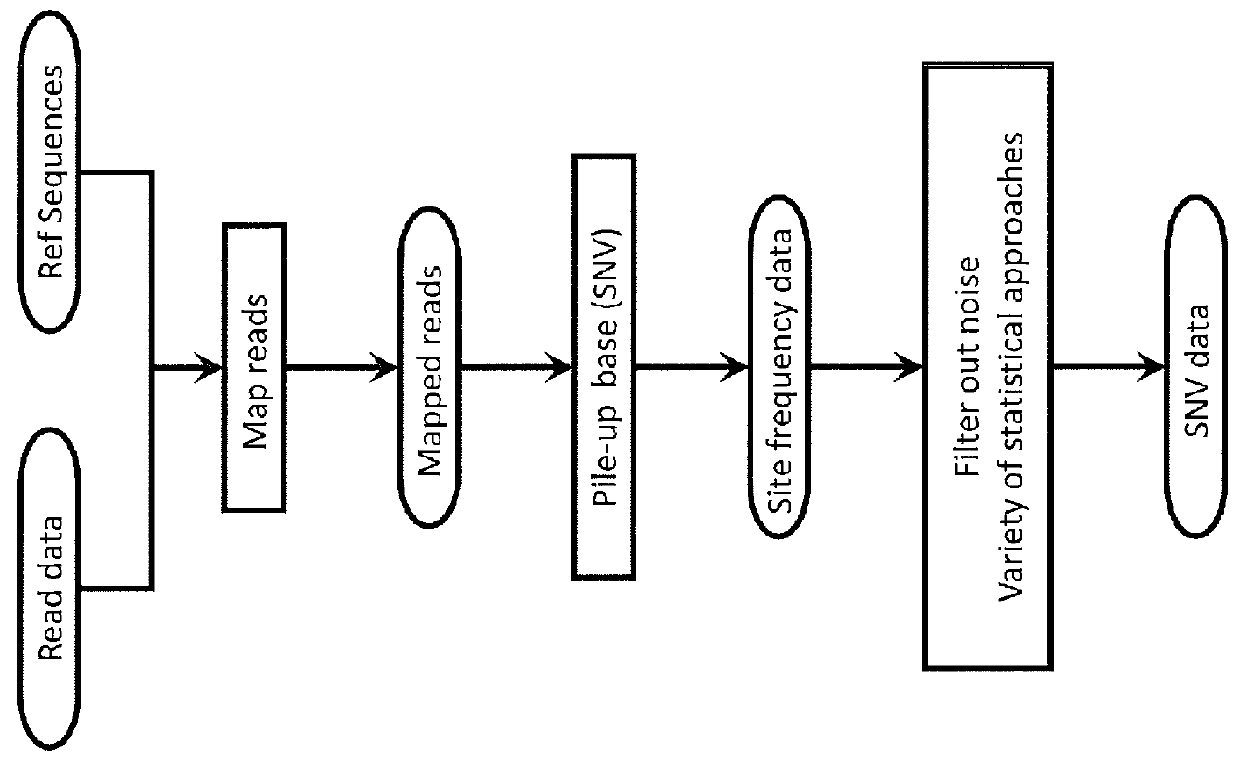
System and Method for Detecting Population Variation from Nucleic Acid Sequencing Data
InactiveUS20160034638A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsPopulation variationNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a method of identifying genetic variants within a population of sequences. The method includes the steps of aligning a set of sequence data reads to reference sequences, dividing reference sequences into multiple tracks of overlapping regions of analysis (ROAs), partitioning each read into a ROA, identifying a plurality of sequence patterns in the reads, setting a sequence pattern frequency threshold value, eliminating any sequence pattern that has a value below the frequency threshold value forming a plurality of dictionaries from the sequence patterns having a value above the frequency threshold value, and cross-validating sequence patterns via partial sequence assembly. The method may optionally include amending the reference sequences used in iterative re-alignment of sequence data.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Systems and methods for scalable unsupervised multisource analysis
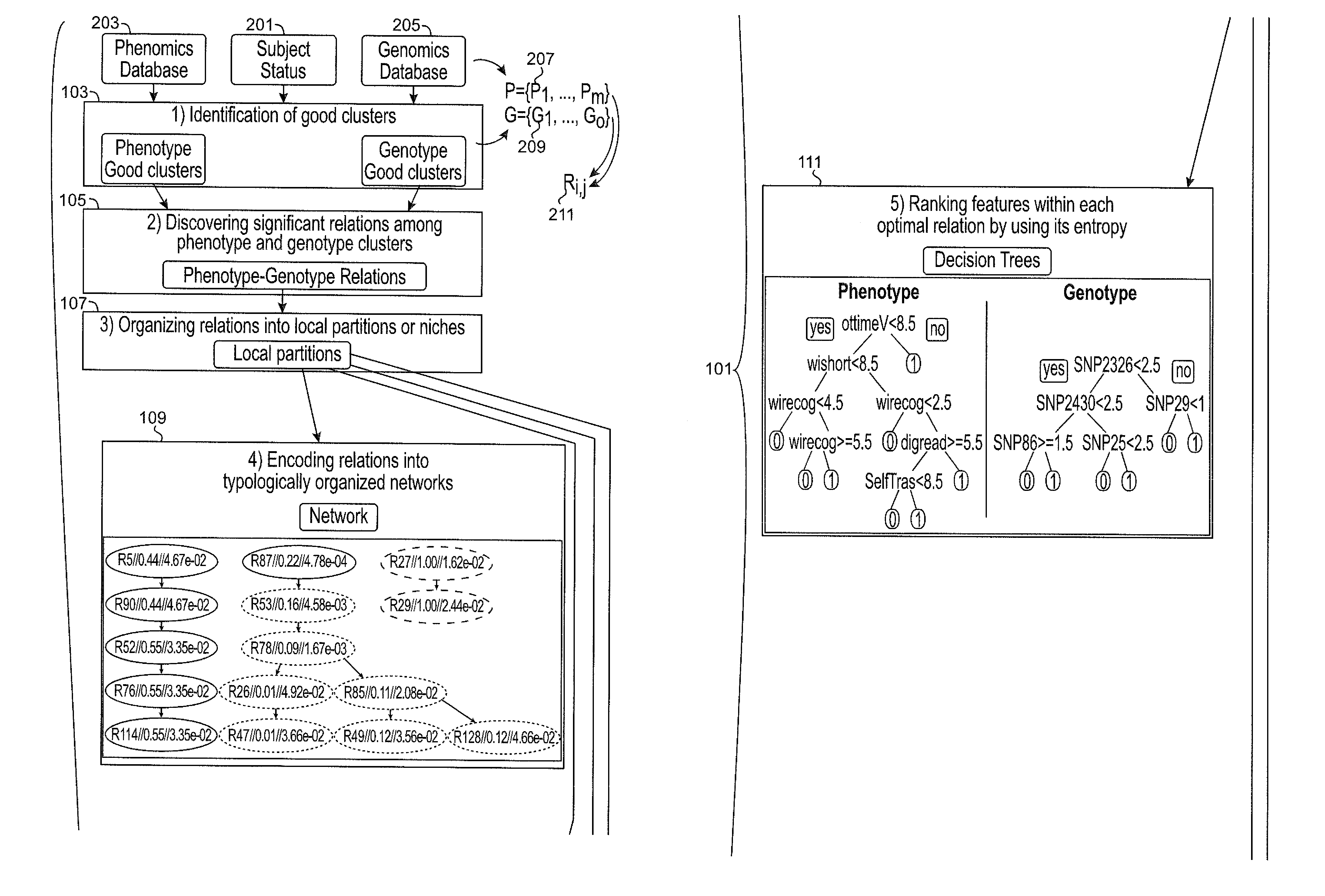
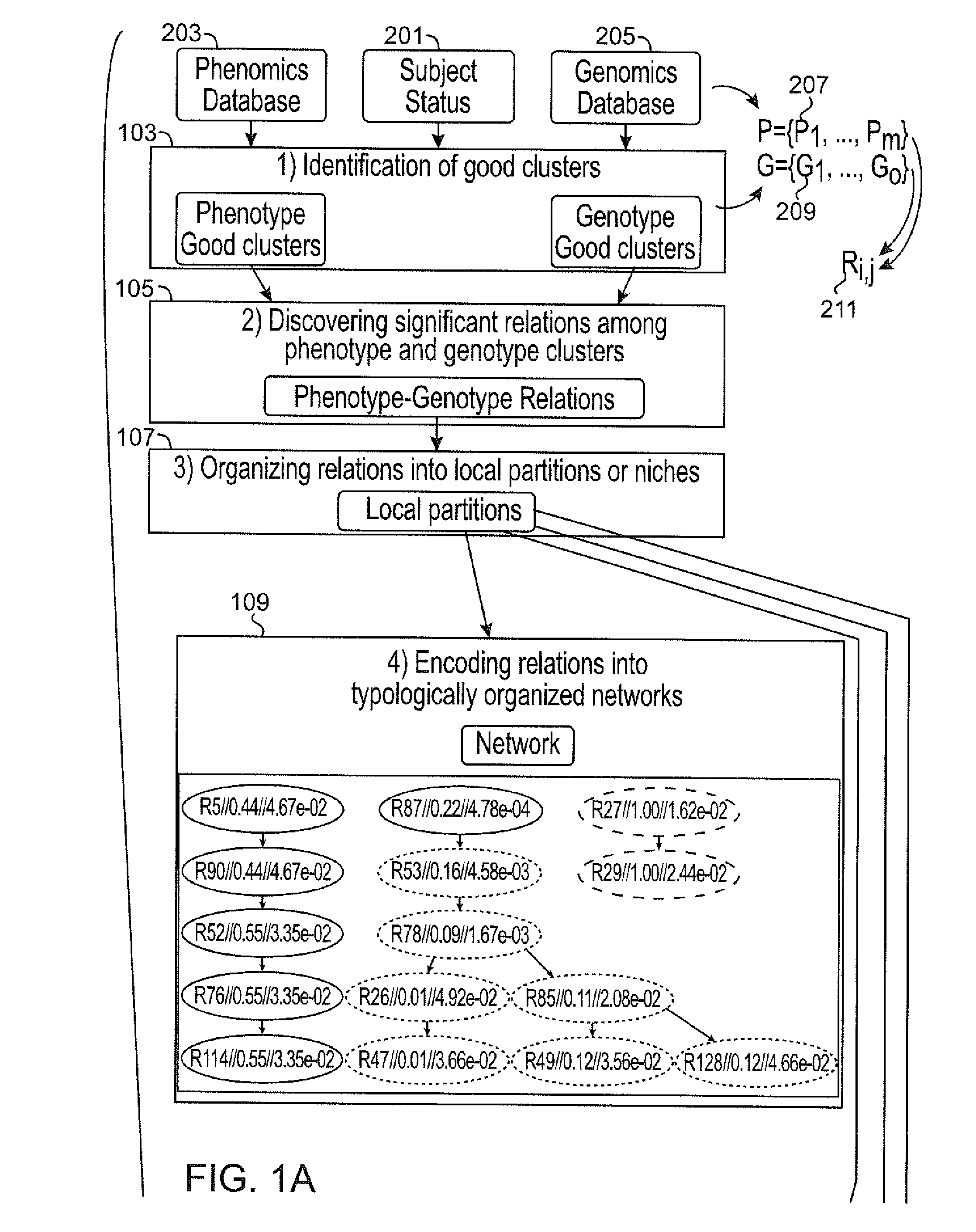
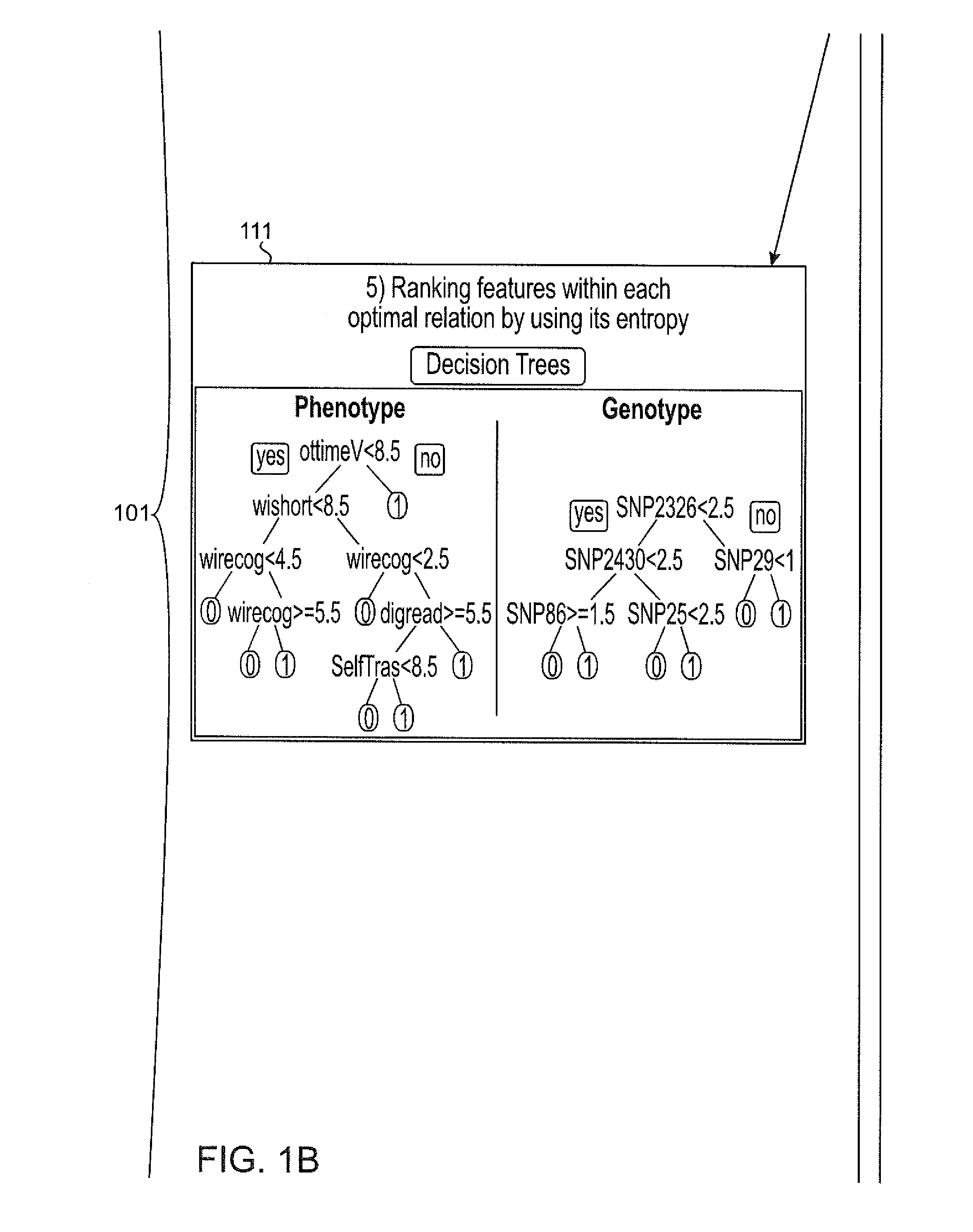
Systems and methods for identifying genetic variations in a disease and diagnosing a patient with a mental illness, or a generic variant of same. The systems and methods use genomics and phenomics in a computer-implemented methods to identify biclusters in phenomic and genomic data, discover relationships among the biclusters, organize the relations into partitions, rank the predictive utility of features, and map the disease risk function. This can in turn be used to diagnose a patient in a person-centered fashion.
Owner:ZWIR JORGE S
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS20060127940A1Rapid and specific and sensitive hybridization detectionEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
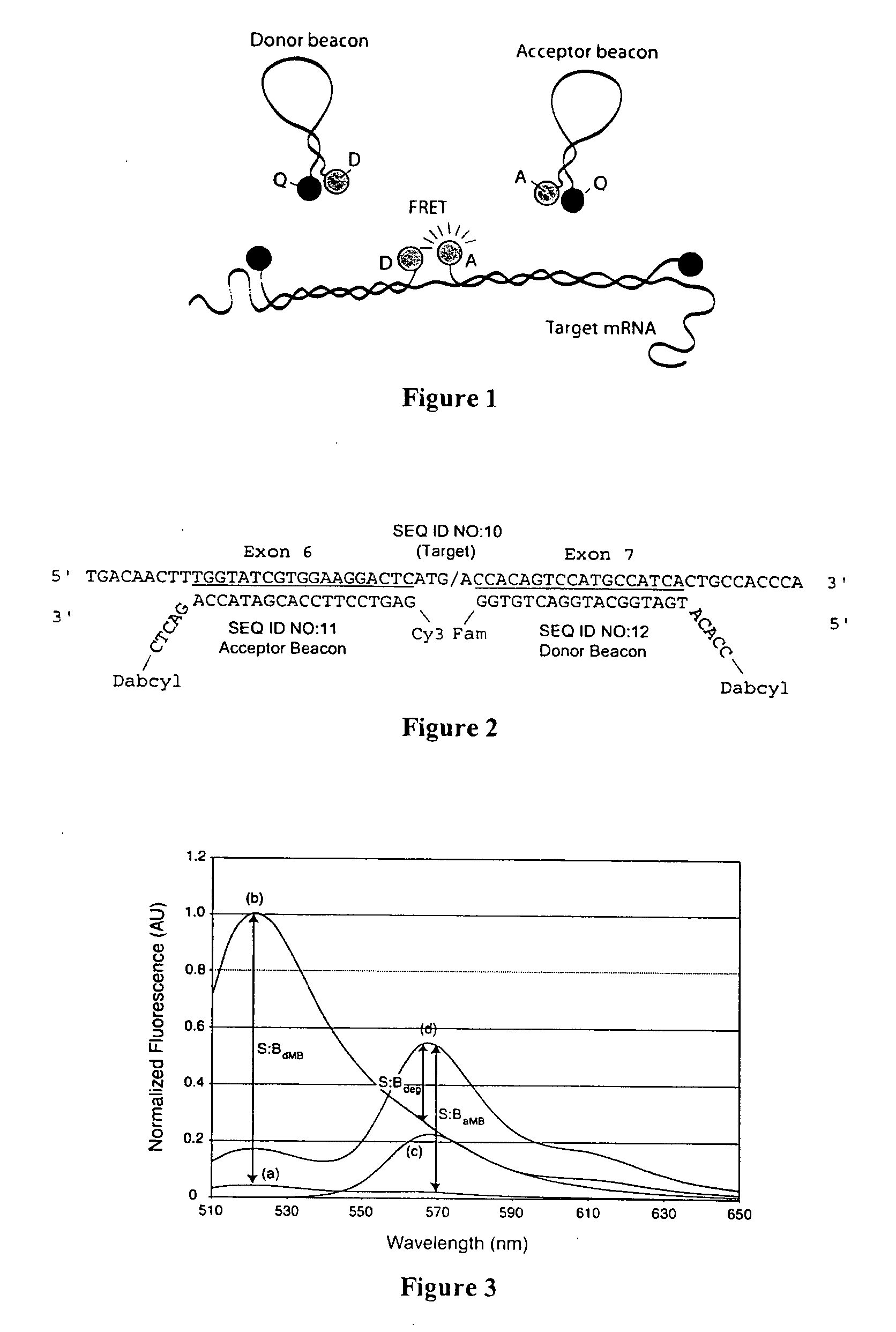
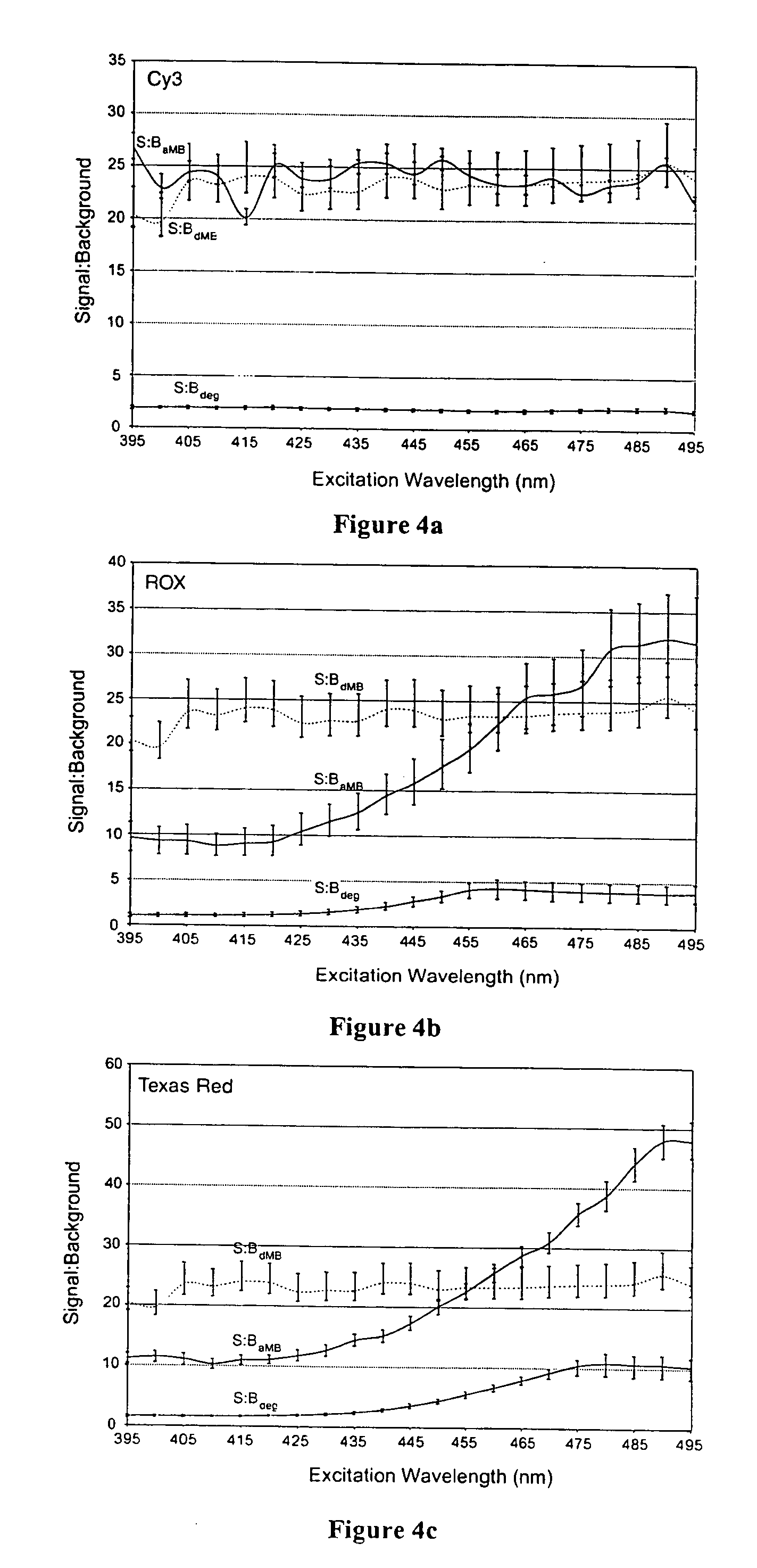
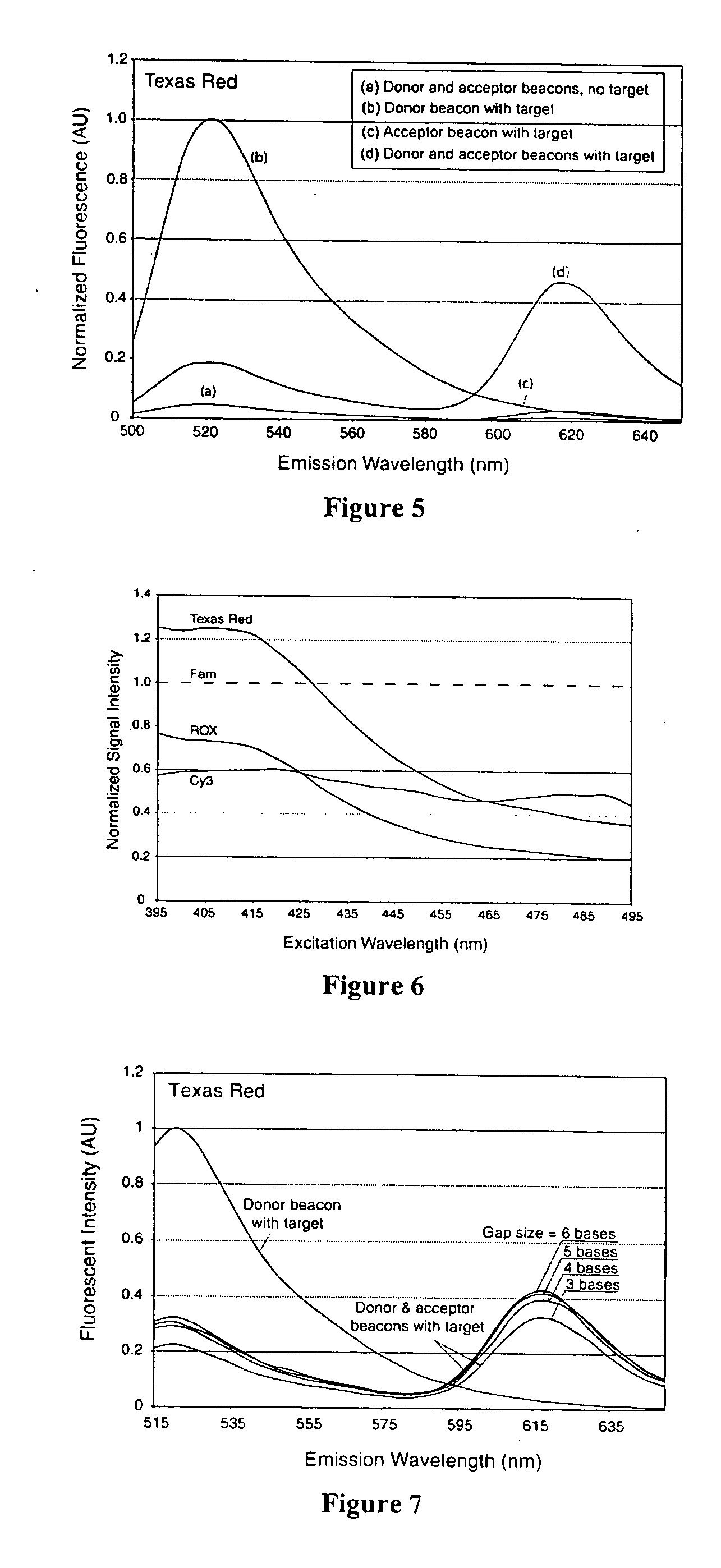
Dual nucleic acid probes with resonance energy transfer moieties are provided. In particular, fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties are provided on hairpin stem-loop molecular beacon probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid, e.g. mRNA, to generate an observable interaction. The invention also provides lanthanide chelate luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties on linear and stem-loop probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid to generate an observable interaction. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific and sensitive hybridization determination in vivo. The probes are used in methods of detection of nucleic acid target hybridization for the identification and quantification of tissue and cell-specific gene expression levels, including response to external stimuli, such as drug candidates, and genetic variations associated with disease, such as cancer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
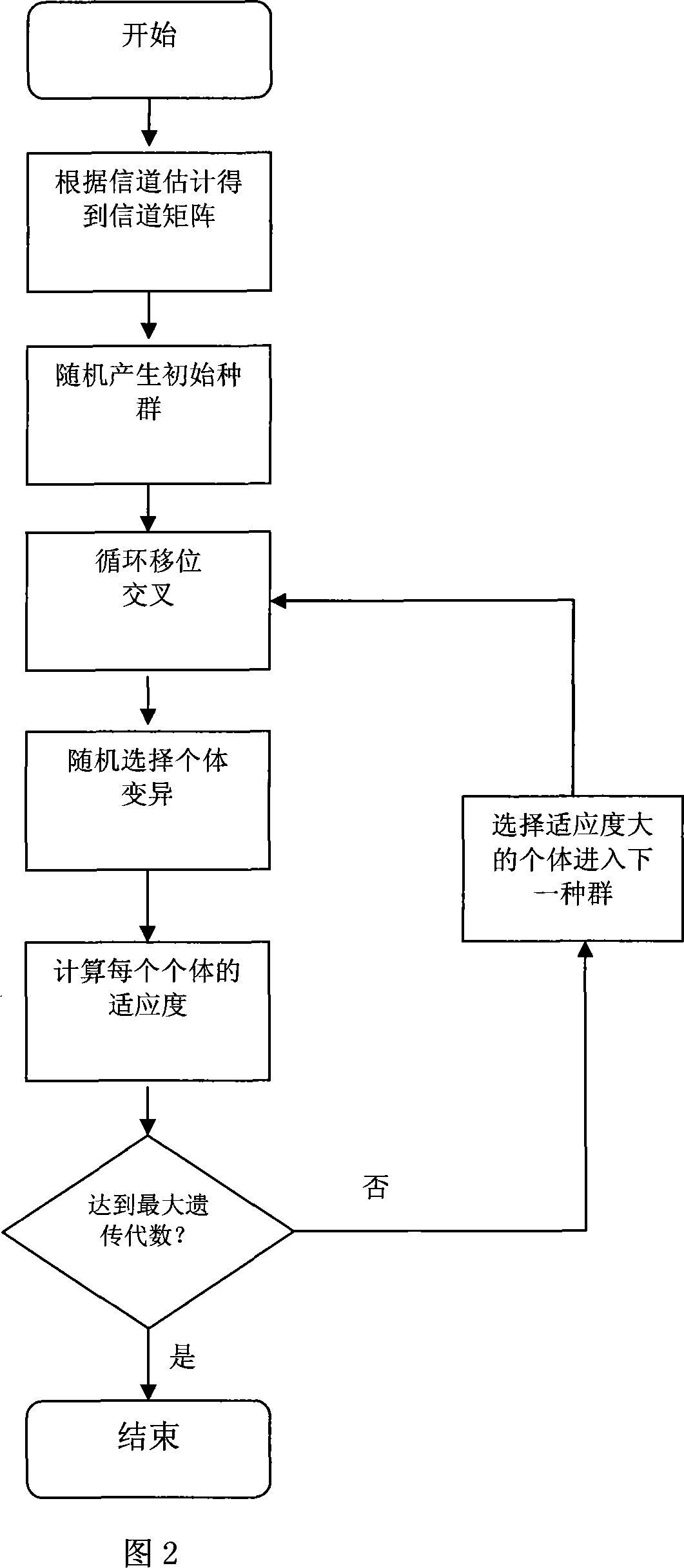
OFDM sub-carrier allocation method based on generic algorithm
InactiveCN101146079AImprove performanceIncrease the speed of genetic evolutionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksWireless transmissionCarrier signal
The invention provides an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system subcarrier allocation method based on SGA in wireless transmission technology field. Firstly, the invention obtains channel status information of each user on different subcarriers, according to channel estimation; and then, transfers SGA for optimum subcarrier allocation; wherein the SGA adopts integer coding and cyclic shift scissor to improve search capability; after fitness function computation of species group with generic variation each time, continues to judge whether the algorithm should stop, according to the termination condition and obtains the subcarrier allocation proposal. Compared with prior art, the invention improves system performance greatly and the advanced SGA in the invention has faster velocity of convergence, compared with the traditional SGA.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com