Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99 results about "Genome wide analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
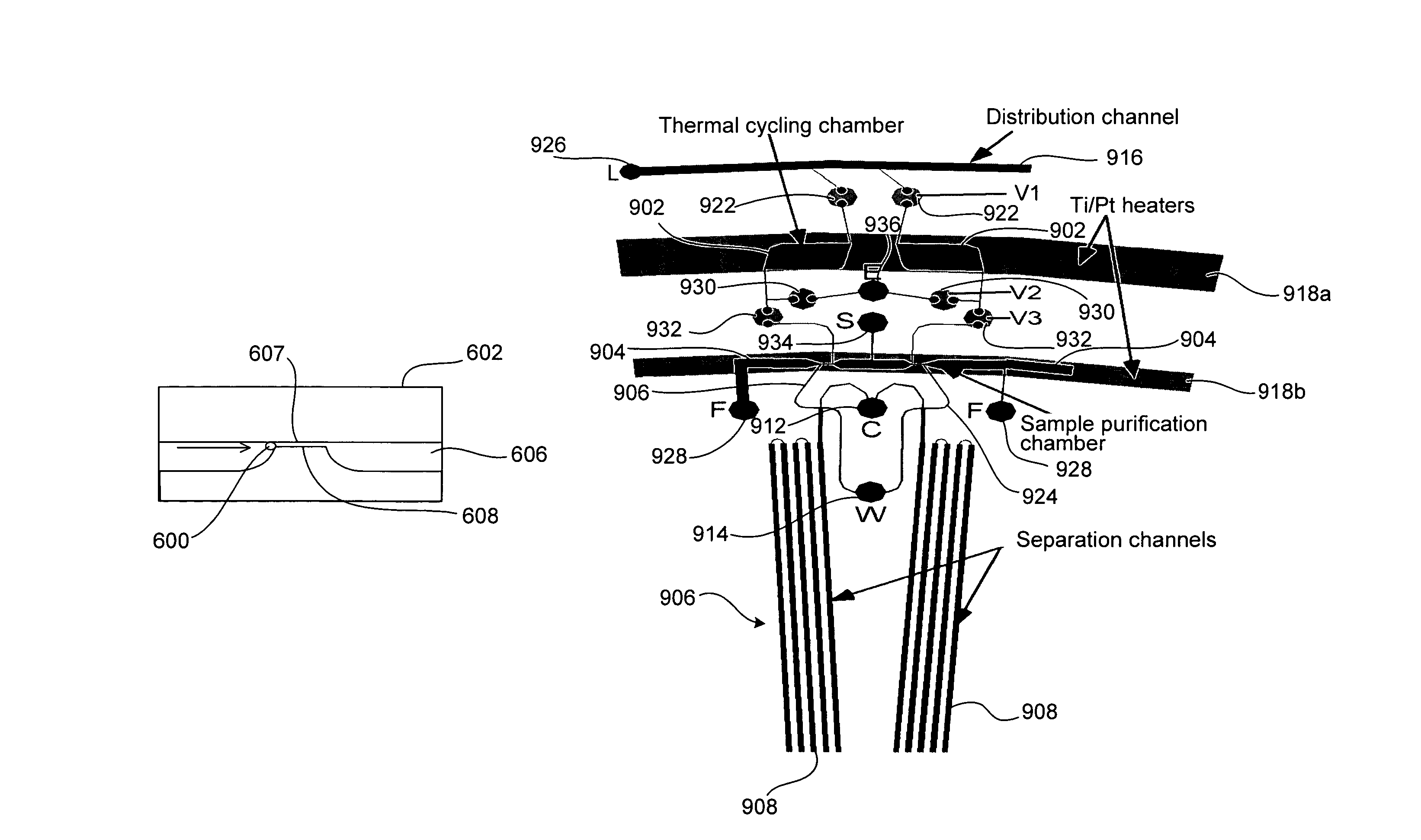
Microfabricated integrated DNA analysis system
ActiveUS7799553B2Improve automationBig spaceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsMicroreactorMicrosphere
Methods and apparatus for genome analysis are provided. A microfabricated structure including a microfluidic distribution channel is configured to distribute microreactor elements having copies of a sequencing template into a plurality of microfabricated thermal cycling chambers. A microreactor element may include a microcarrier element carrying the multiple copies of the sequencing template. The microcarrier element may comprise a microsphere. An autovalve at an exit port of a thermal cycling chamber, an optical scanner, or a timing arrangement may be used to ensure that only one microsphere will flow into one thermal cycling chamber wherein thermal cycling extension fragments are produced. The extension products are captured, purified, and concentrated in an integrated oligonucleotide gel capture chamber. A microfabricated component separation apparatus is used to analyze the purified extension fragments. The microfabricated structure may be used in a process for performing sequencing and other genetic analysis of DNA or RNA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
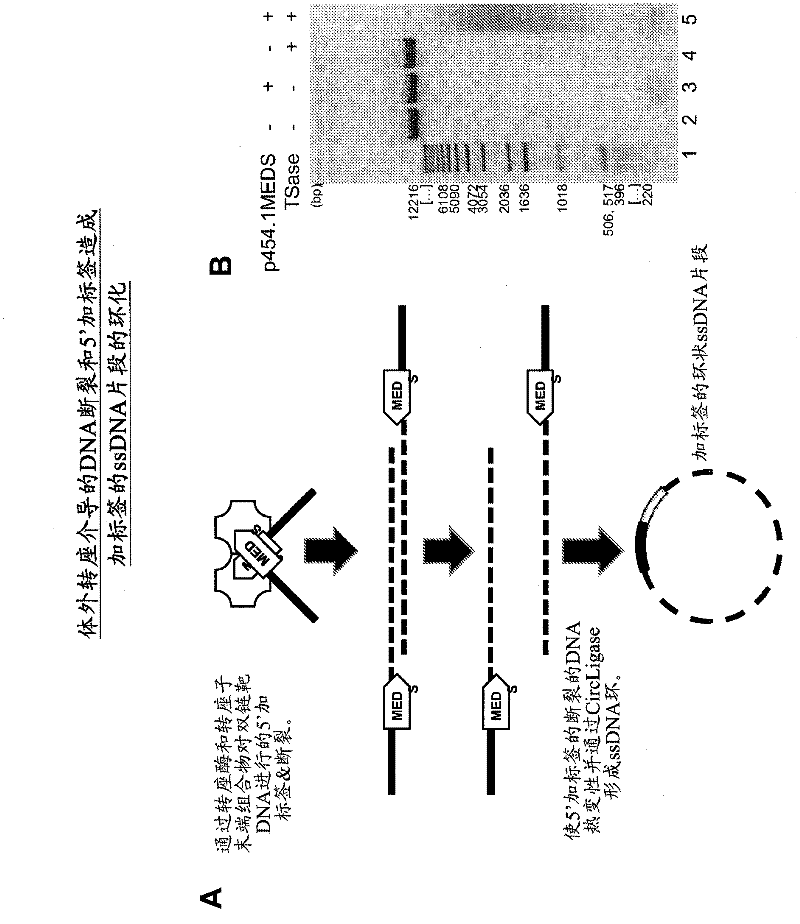
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
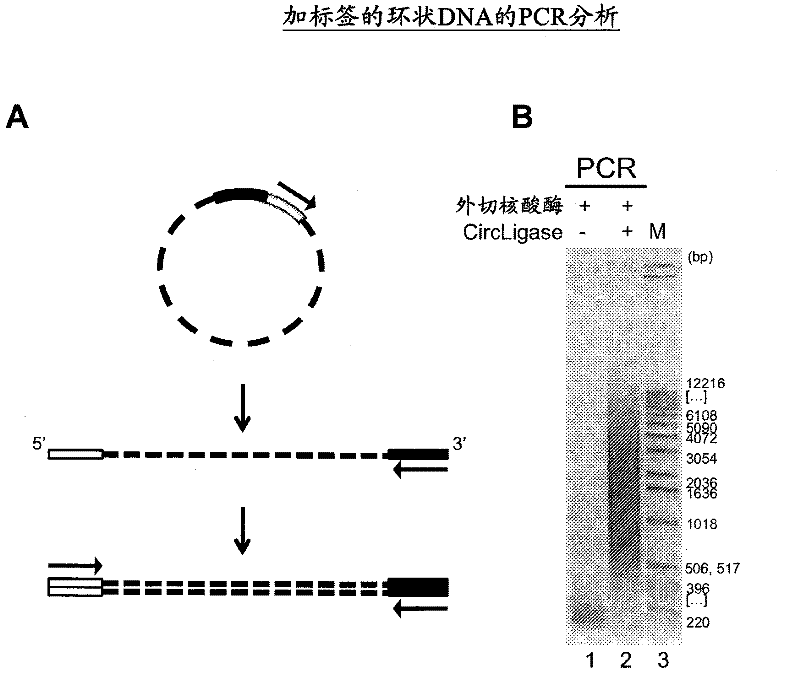
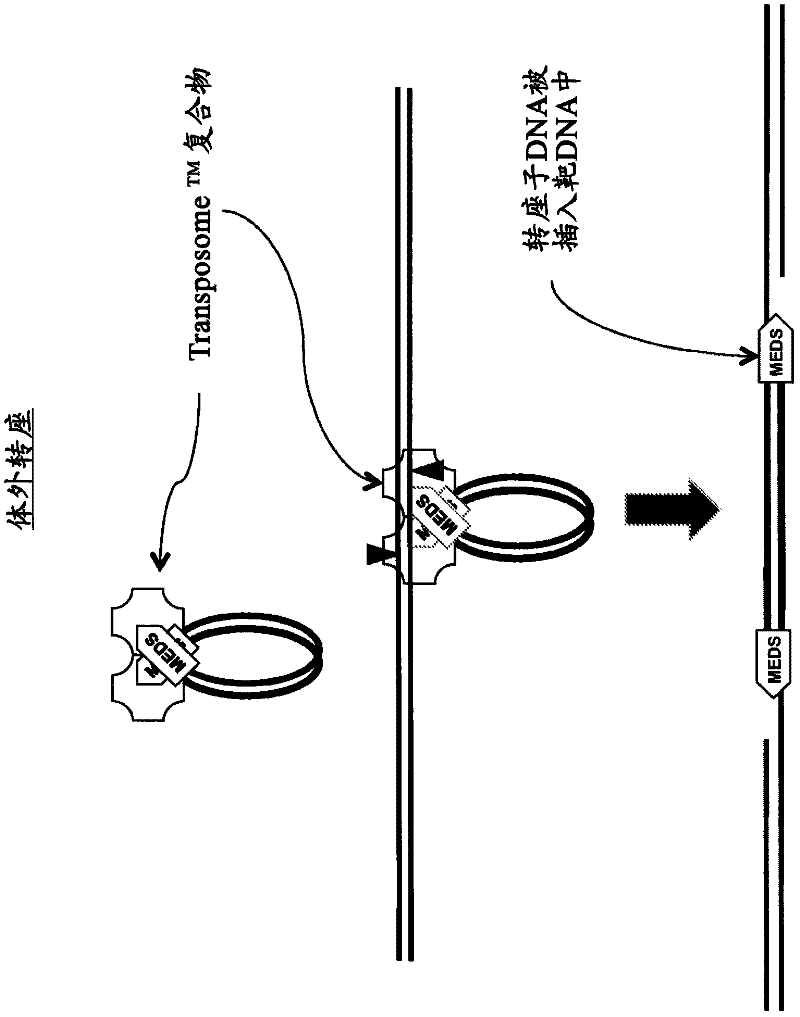
The present invention provides the use of transposases and transposon ends to generate extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, followed by the use of DNA polymerases to generate 5′- and 3′-tagged single DNA without PCR amplification reactions. Methods, compositions and kits for stranded DNA fragments, wherein the first label on the 5' end shows the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second label on the 3' end shows the same The first tab shows a sequence different from the sequence. The method can be used to generate 5' and 3' tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes including metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called "next generation sequencing") involves the process of comparative genome sequencing (CGS).
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
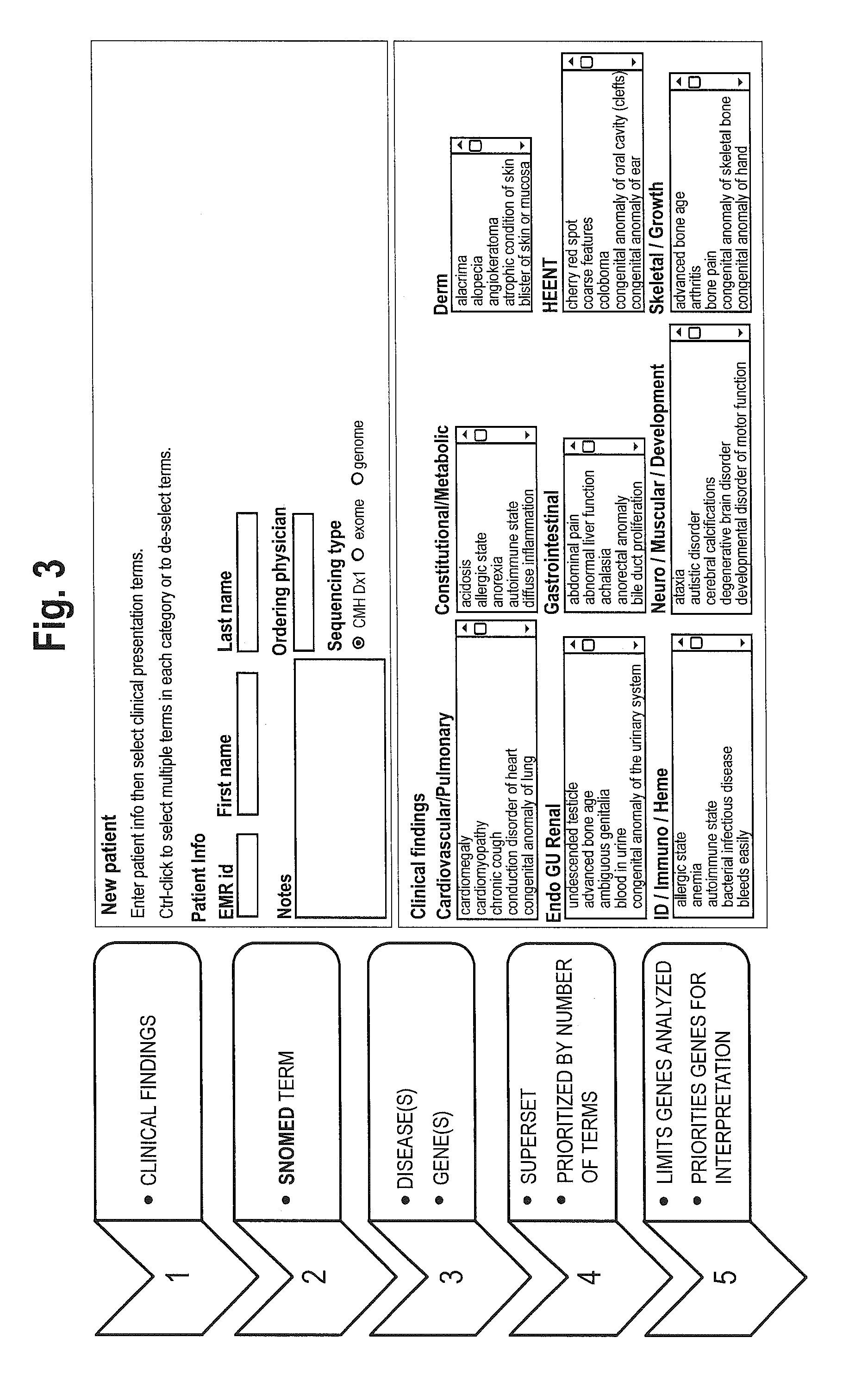
System for genome analysis and genetic disease diagnosis
InactiveUS20150310163A1High sensitivityIncrease the number ofProteomicsBiological testingData setGenome wide analysis
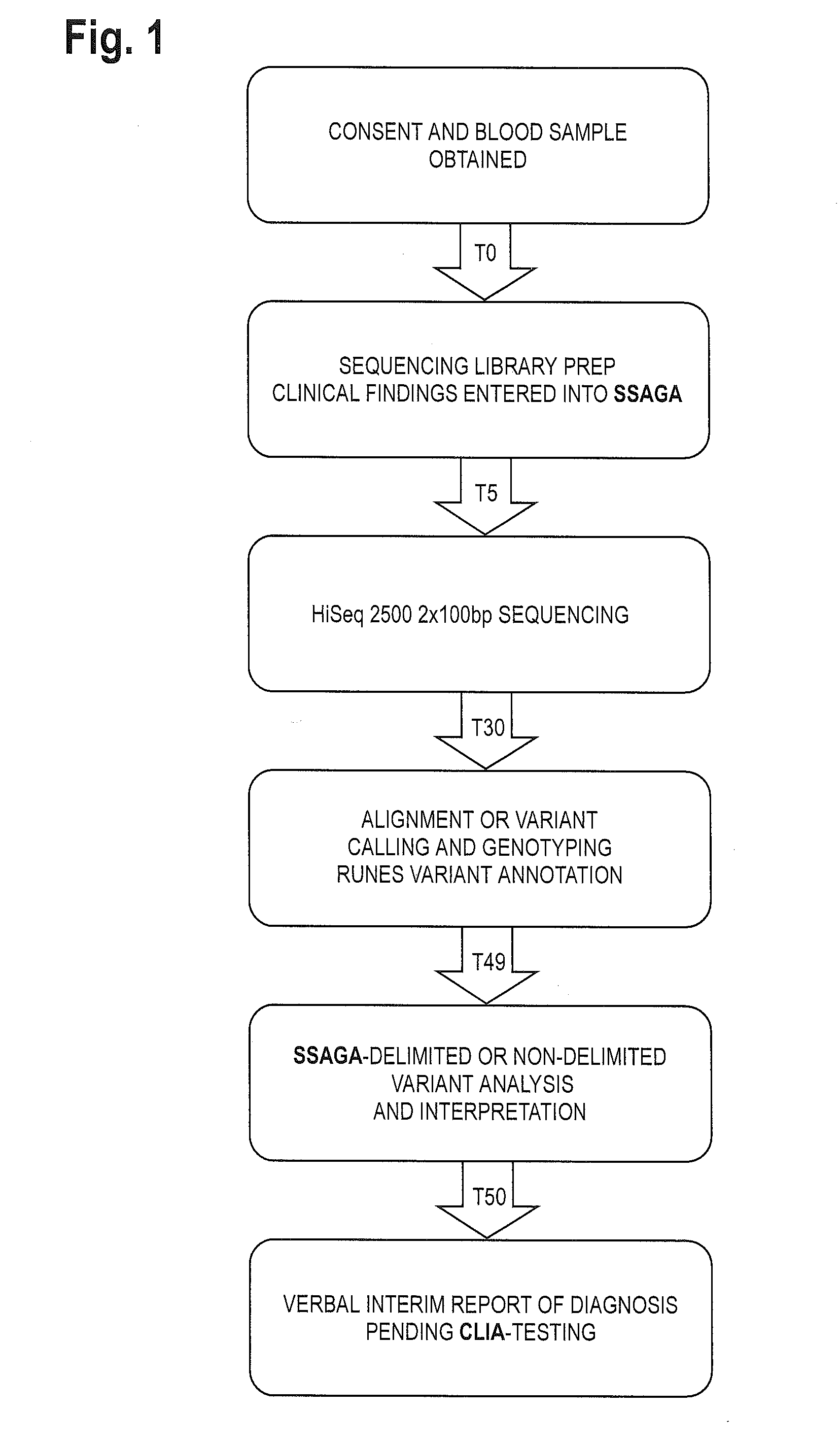
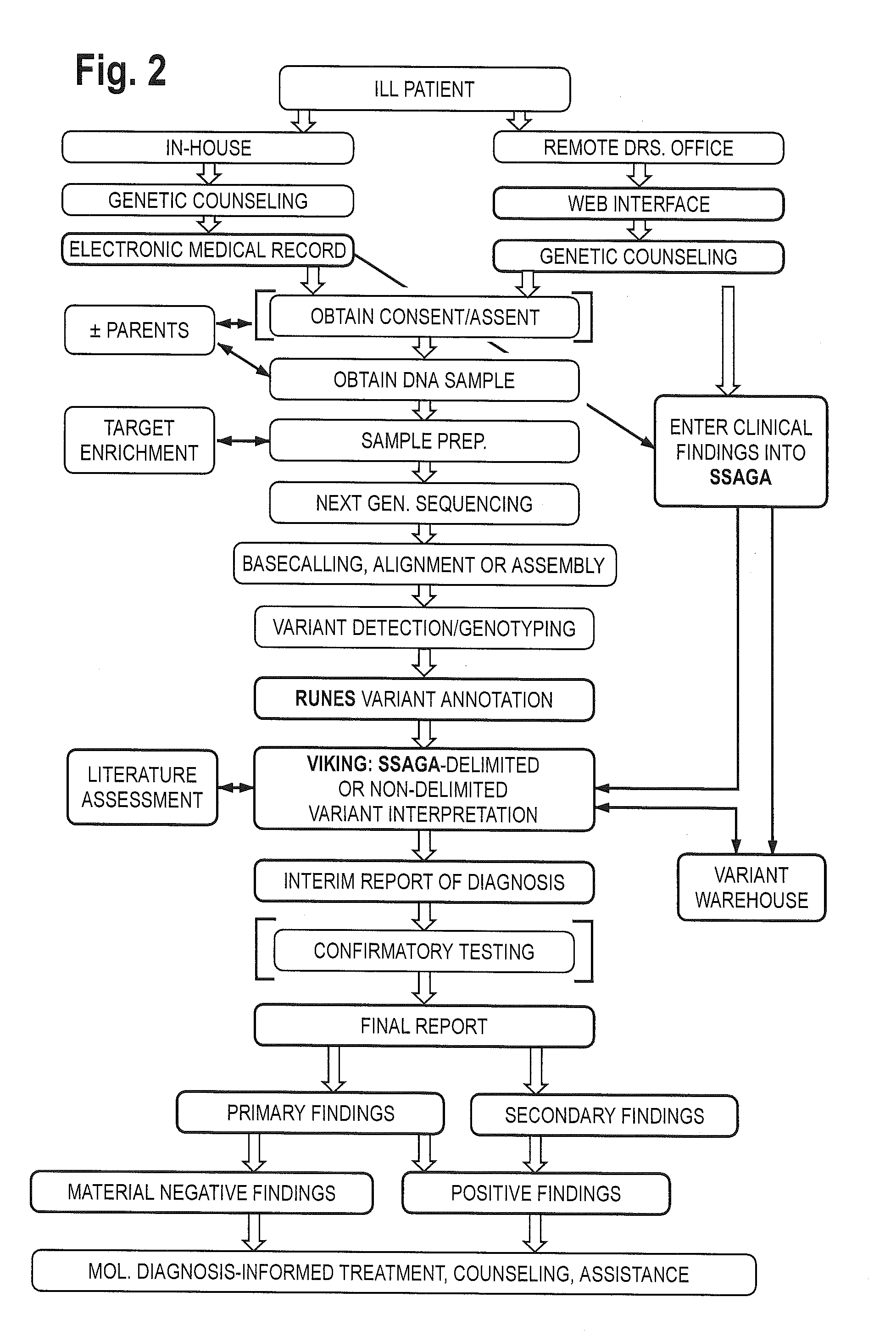
The method for genome analysis translates the clinical findings in the patient into a comprehensive test order for genes that can be causative of the patient's illness, delimits analysis of variants identified in the patient's genome to those that are “on target” for the patient's illness, and provides clinical annotation of the likely causative variants for inclusion in a variant warehouse that is updated as a result of each sample that is analyzed and that, in turn, provides a source of additional annotation for variants. The method uses a genome sequence having the steps of entering at least one clinical feature of a patient by an end-user, assigning a weighted value to the term based on the probability of the presence of the term, mapping the term to at least one disease by accessing a knowledge base containing a plurality of data sets, wherein the data sets are made up of associations between (i) clinical features and diseases, (ii) diseases and genes, (iii) genes and genetic variants, and (iv) diseases and gene variants, assigning a truth value to each of the mapped terms based on the associated data sets and the weighted value, to provide a list of results of possible diagnoses prioritized based on the truth values, with continuous adjustment of the weightings of associations in the knowledge base based on updating of each discovered diagnosis and attendant clinical features, genes and gene variants. This method can be performed in fifty hours or twenty-four hours or less.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
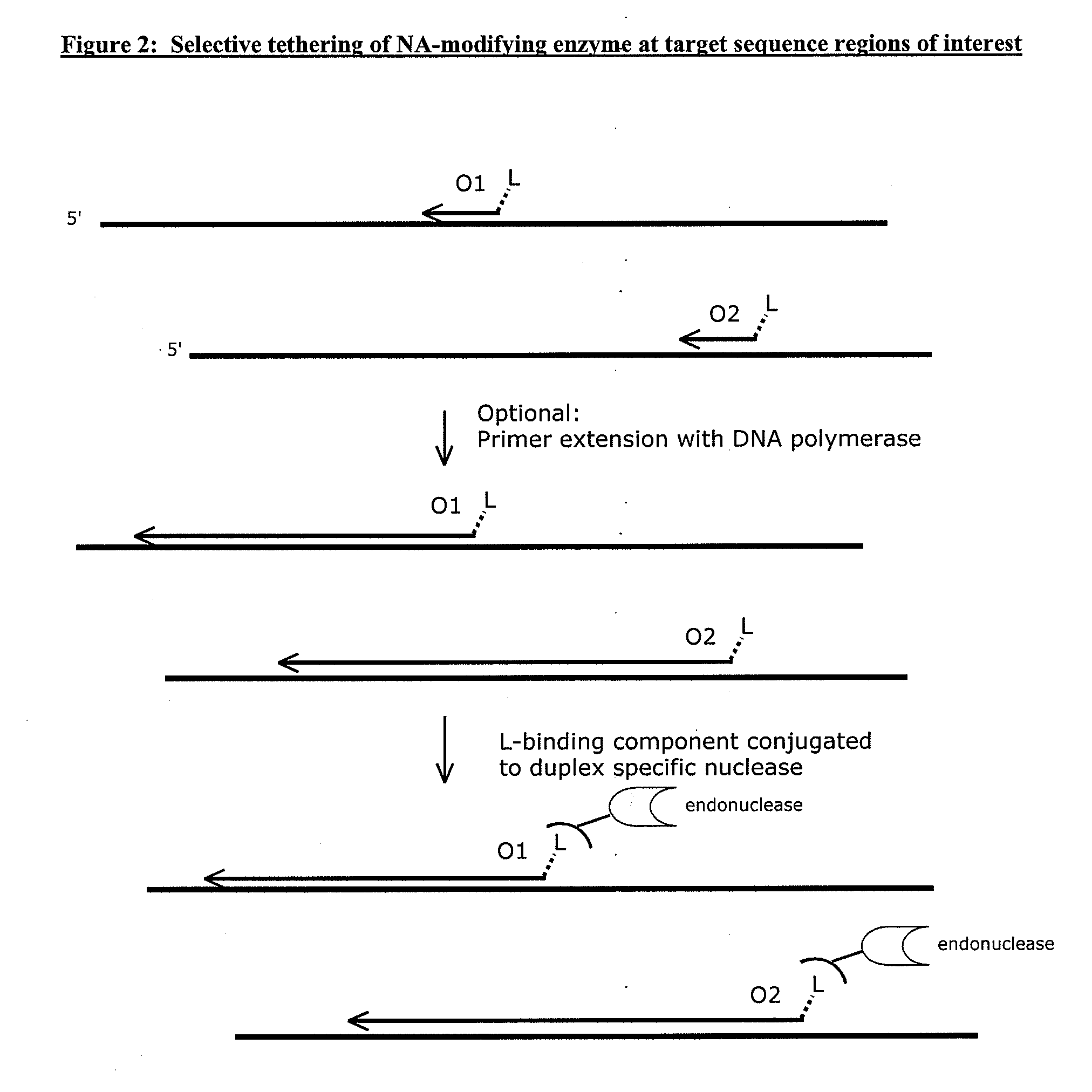
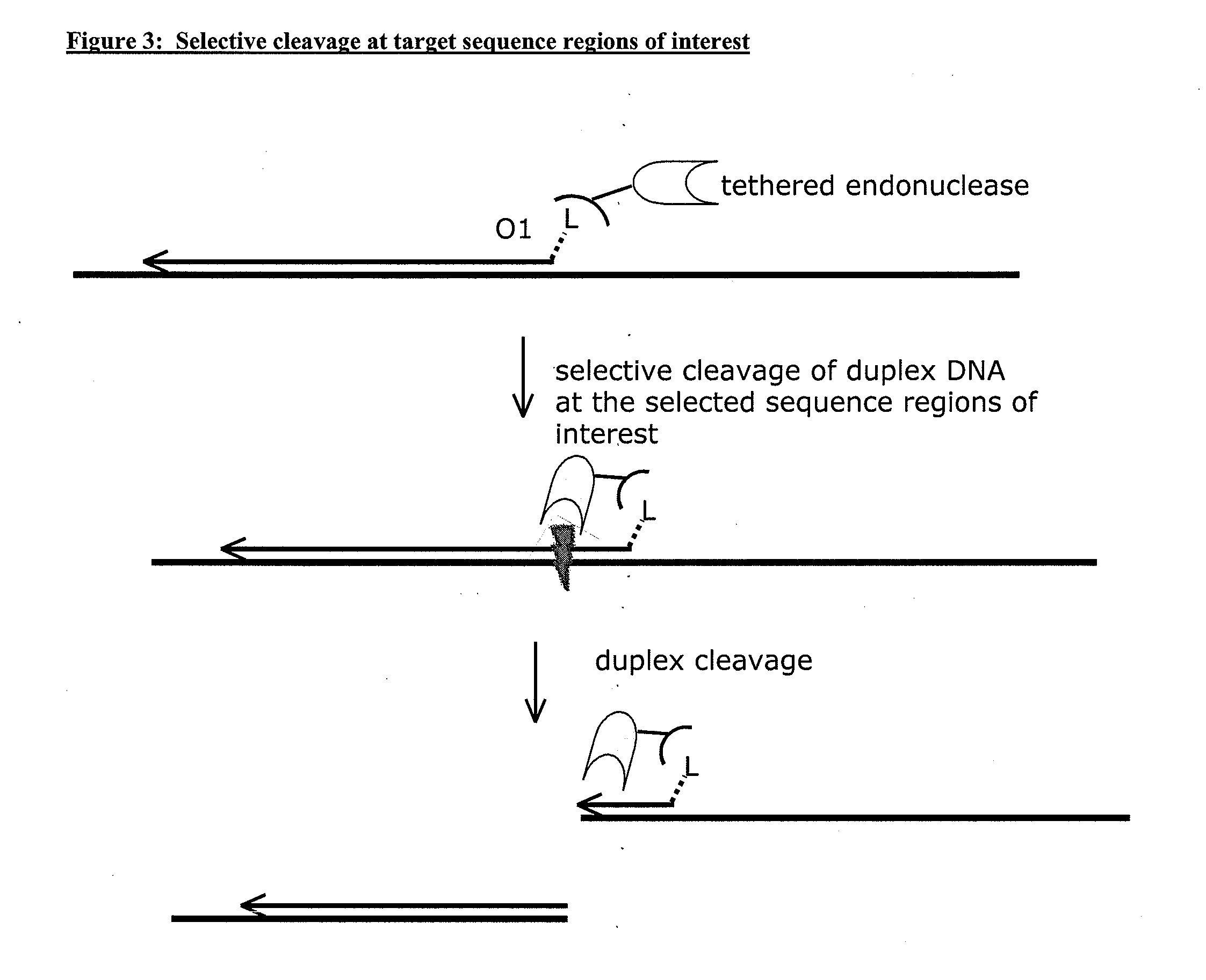
Compositions and methods for targeted nucleic acid sequence selection and amplification
InactiveUS20110105364A1Improve efficiencySuitable for automationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingGenome wide analysis
The present invention provides novel methods, compositions, and kits for the production of amplification-ready, sequence-specific, target region-specific, and strand-specific regions of interest directly from samples containing complex DNA. The methods, composition, and kits provided herein are useful for selective target generation, genome partitioning, or user-selected enrichment of desired regions of interest. The invention described herein will enable multiplexing for genome-wide analysis with increased efficiency and is amenable to automation.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
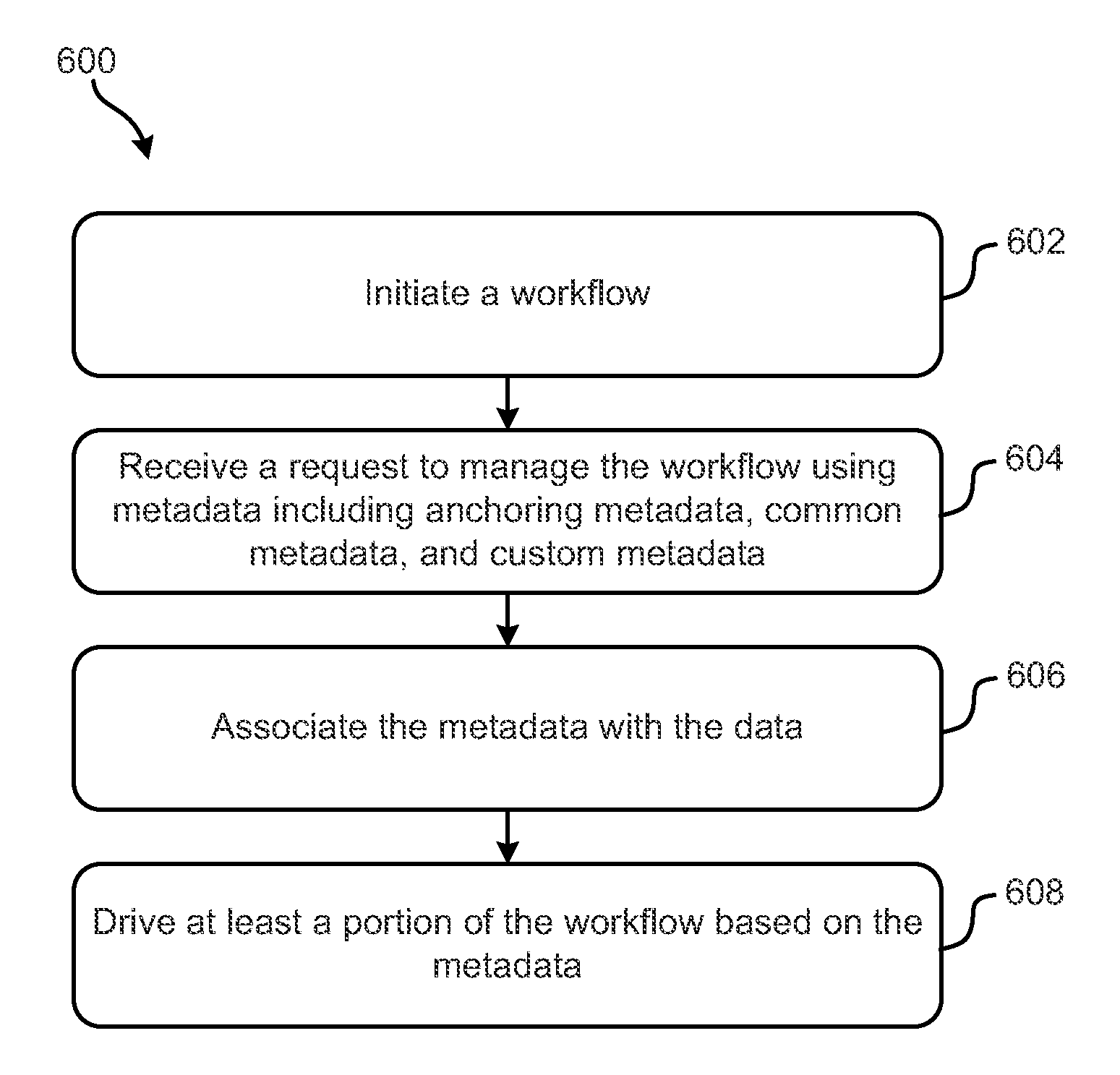
Metadata-driven workflows and integration with genomic data processing systems and techniques
ActiveUS9354922B2Metadata text retrievalDigital data processing detailsData processing systemProgram instruction
Systems, methods and computer program products configured to provide and perform metadata-based workflow management are disclosed. The inventive subject matter includes a computer readable storage medium having computer readable program instructions embodied therewith. The computer readable program instructions are configured to: initiate a workflow configured to process data; associate the data with metadata; and drive at least a portion of the workflow based on at least some of the metadata. The metadata include anchoring metadata; common metadata; and custom metadata. Inventive subject matter also encompasses a method for managing genomic data processing workflows using metadata includes: initiating a workflow; receiving a request to manage the workflow using metadata comprising: anchoring metadata, common metadata, and custom metadata, associating the metadata with the data; and driving at least a portion of the workflow based on the metadata. The workflow involves genomic analyzes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Applications of parallel genomic analysis
InactiveUS20030148313A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
The present invention provides parallel methods for determining nucleotide sequences of polynucleotides associated with sample tags. Applications of sequence information acquired by these methods are also provided.
Owner:STRATHMANN MICHAEL PAUL
Mapping of genomic interactions
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL SCHOOL
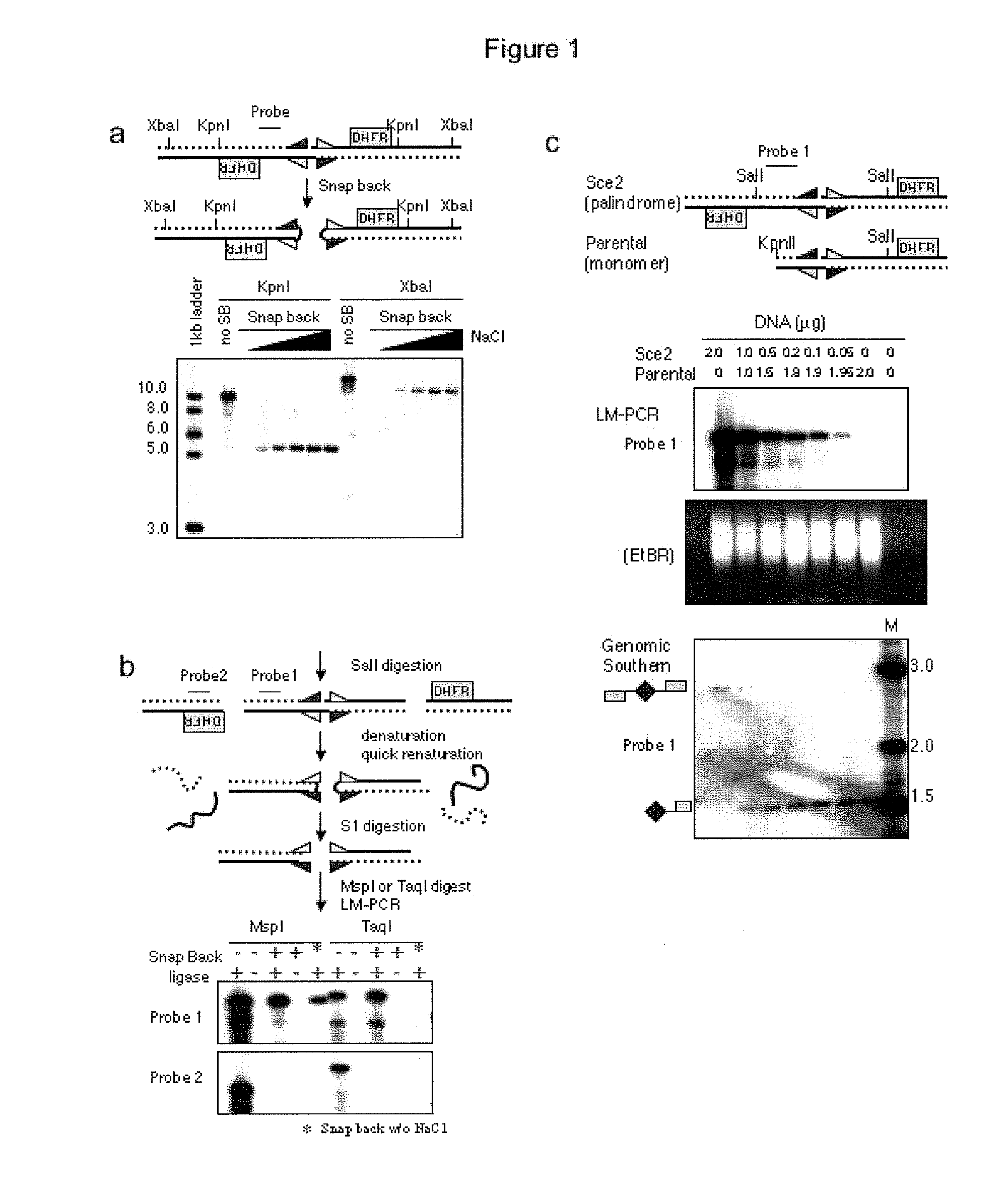
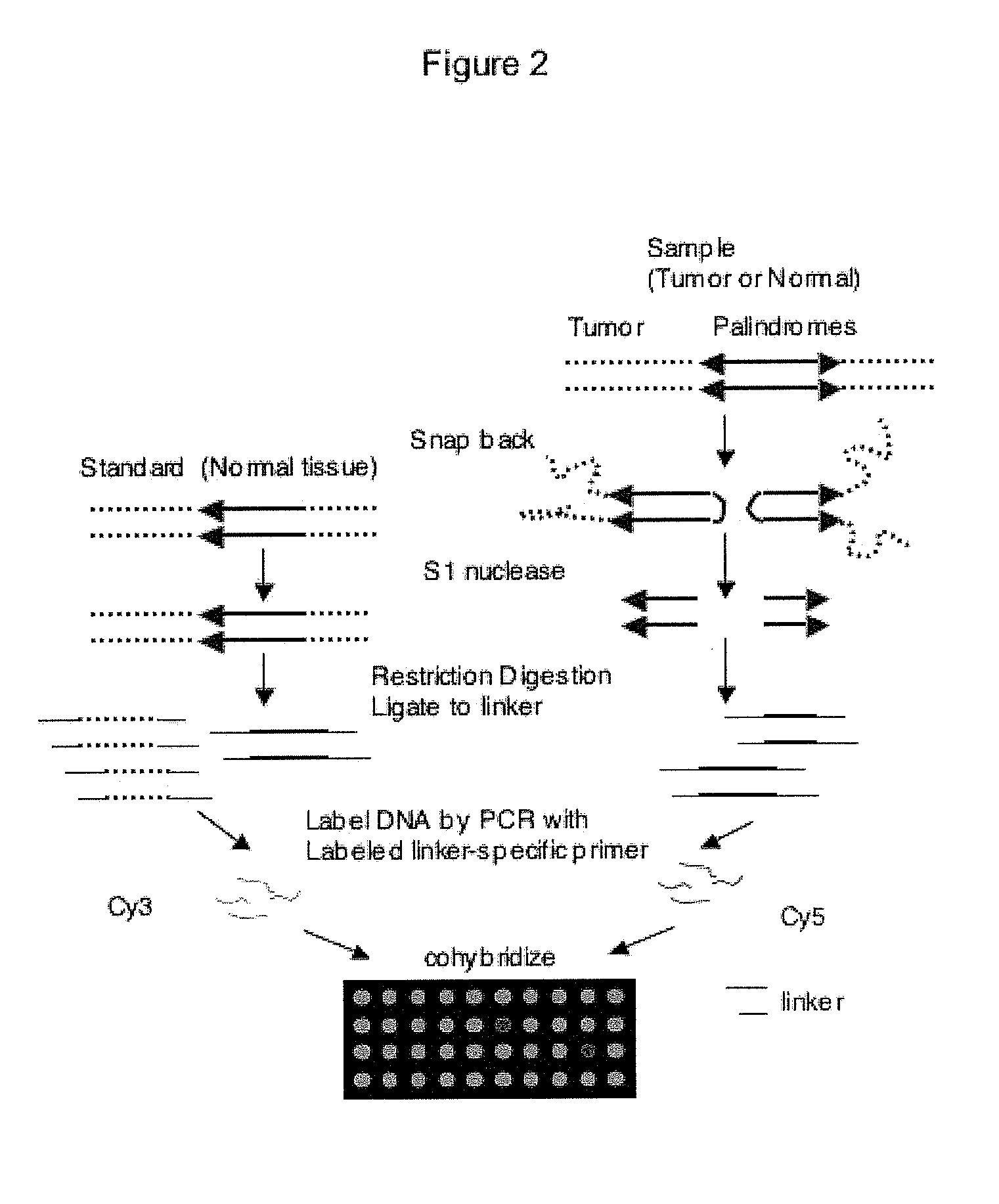
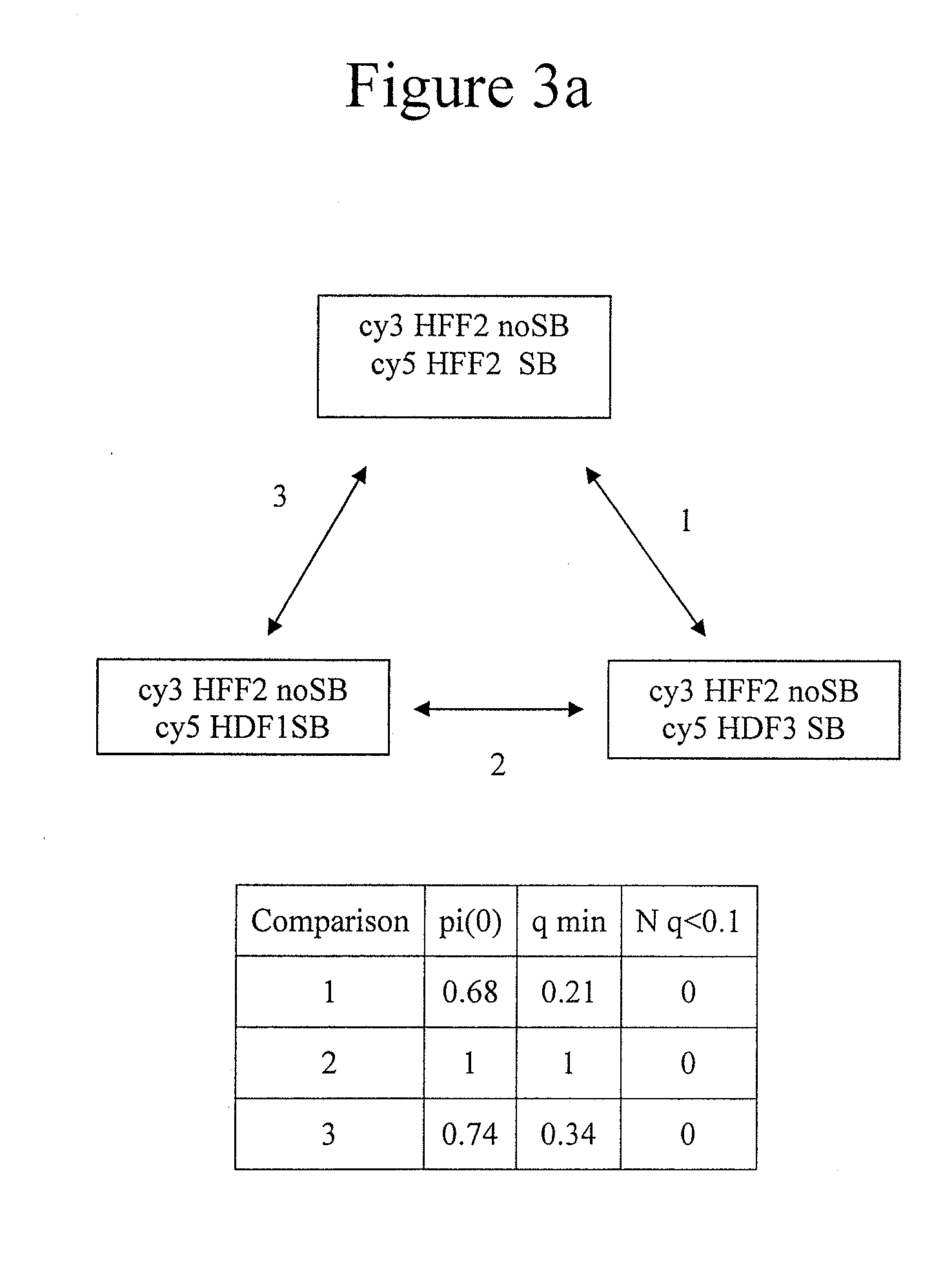
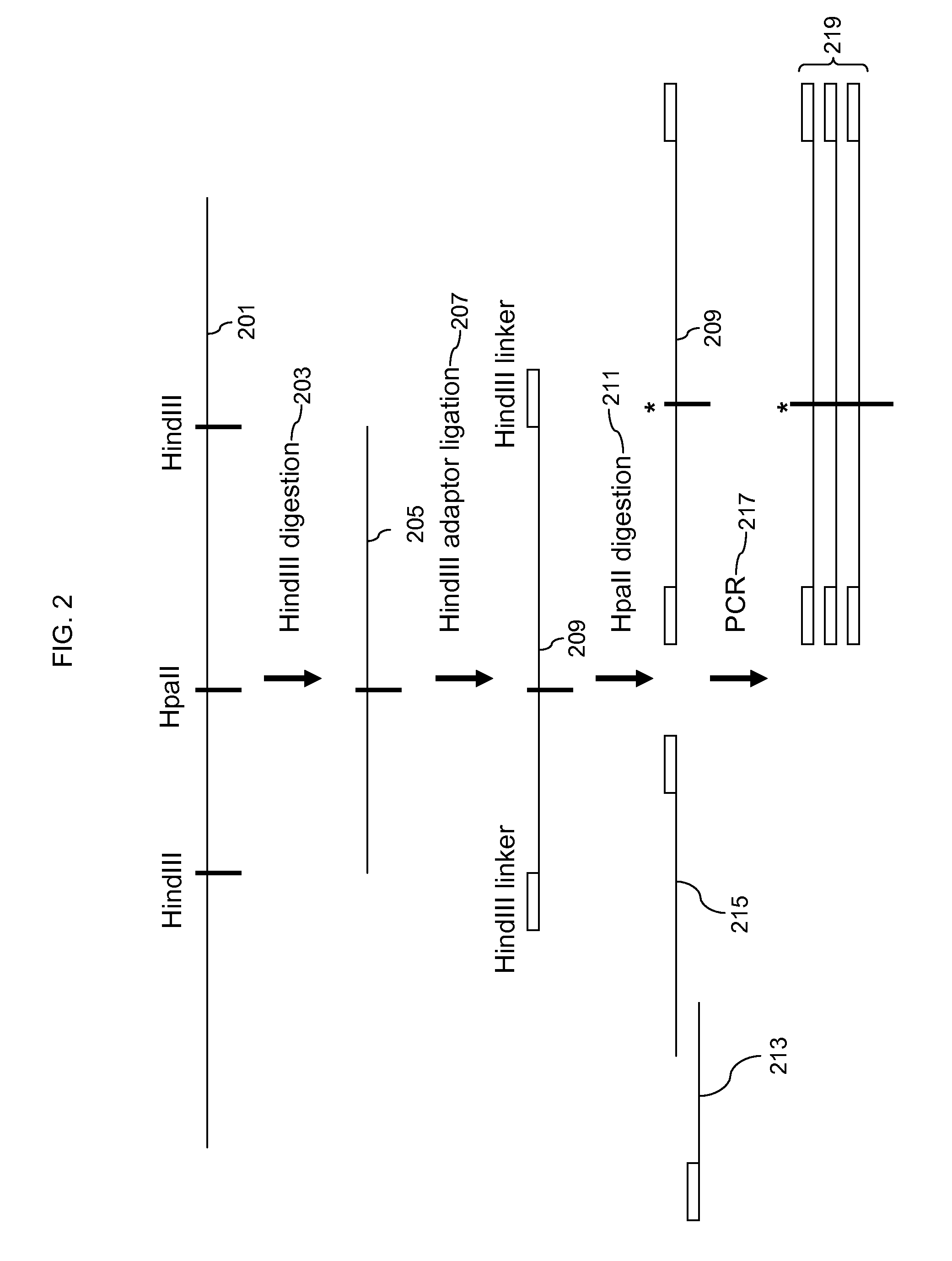
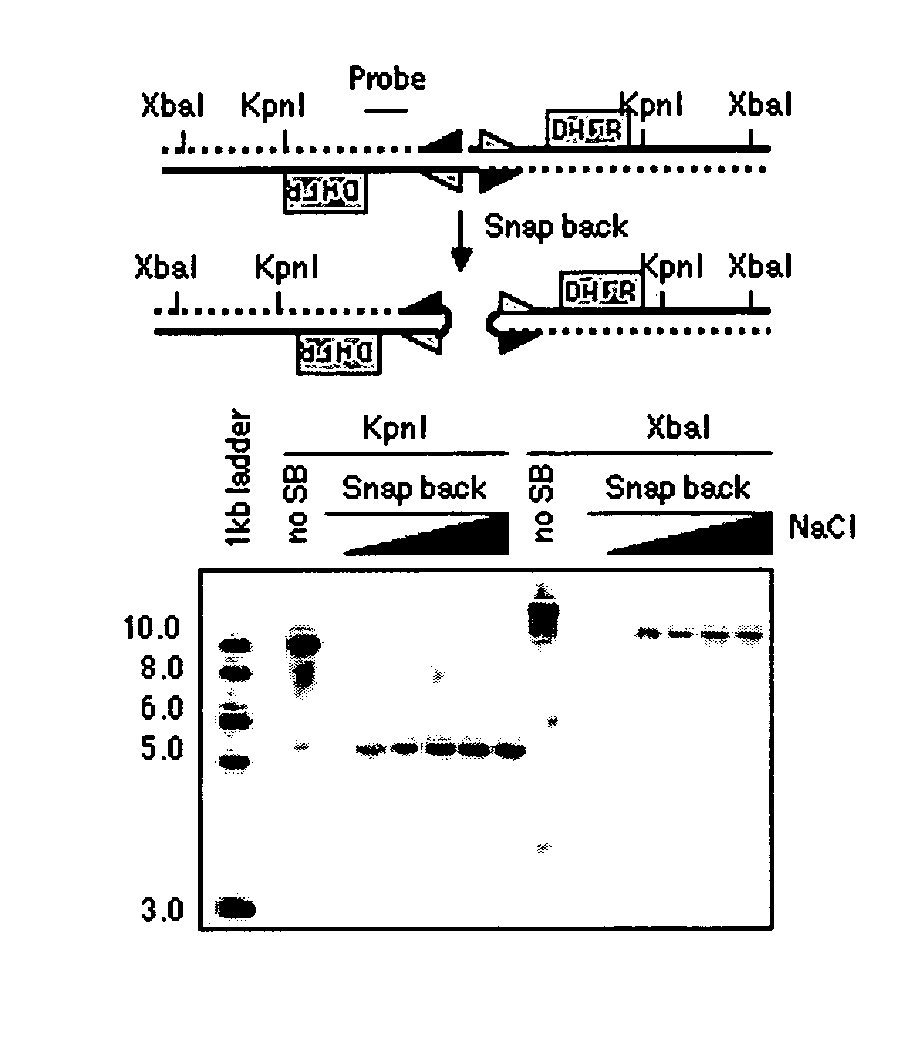
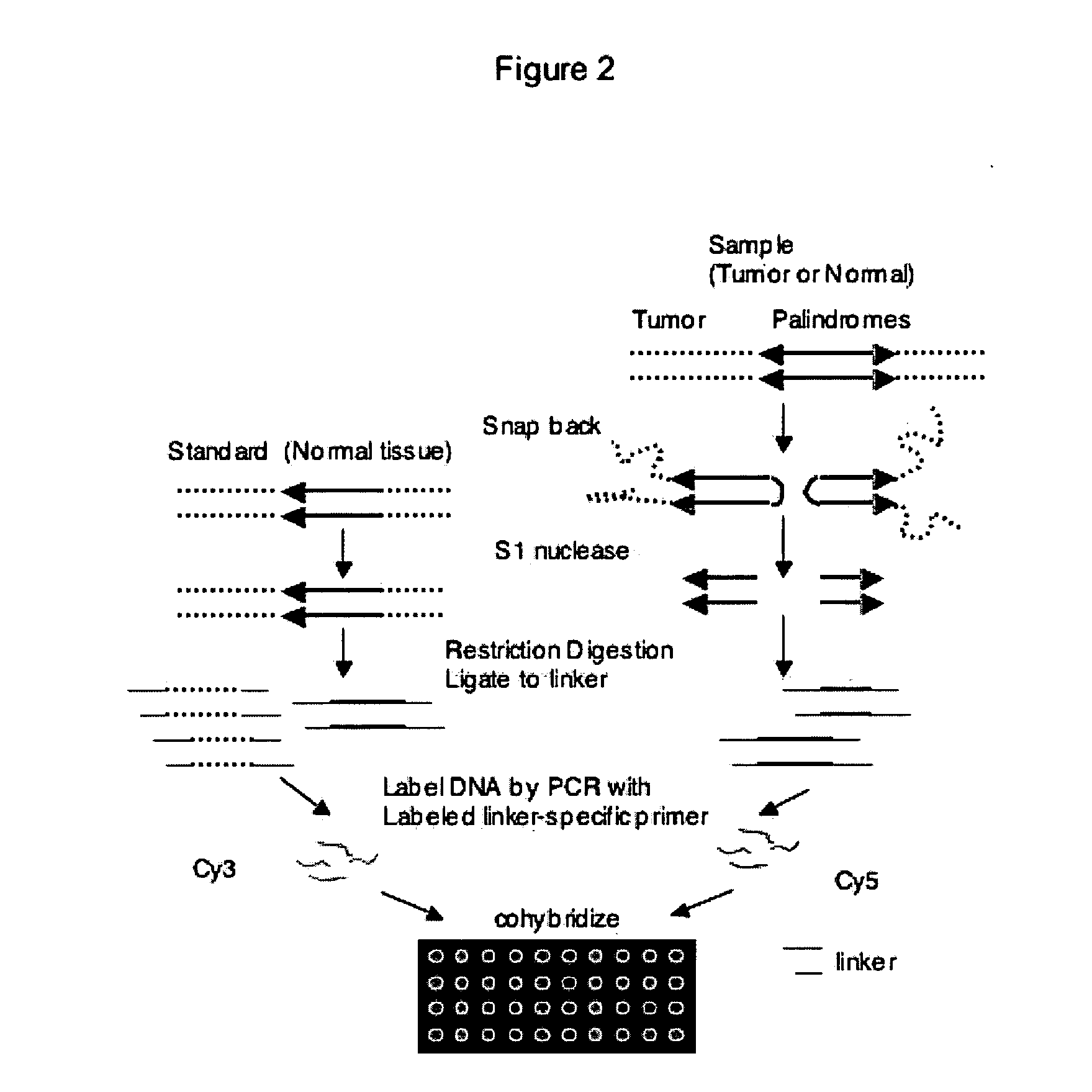
Genome-wide analysis of palindrome formation and DNA methylation
The present disclosure provides methods for detecting the genome-wide presence of methylated DNA and palindrome formation. The present disclosure also provides methods for specific enrichment of methylated DNA or DNA having a DNA palindrome. These methods have demonstrated that somatic palindromes and methylated DNA occur frequently and are widespread in human cancers. Individual tumor types have a characteristic non-random distribution of palindromes in their genome and a small subset of the palindromic loci are associate with gene amplification. The disclosed method can be used to define the plurality of genomic DNA palindromes and regions having methylated DNA associated with various tumor types and can provide methods for the classification of tumors, and the diagnosis, early detection of cancer as well as the monitoring of disease recurrence and assessment of residual disease.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
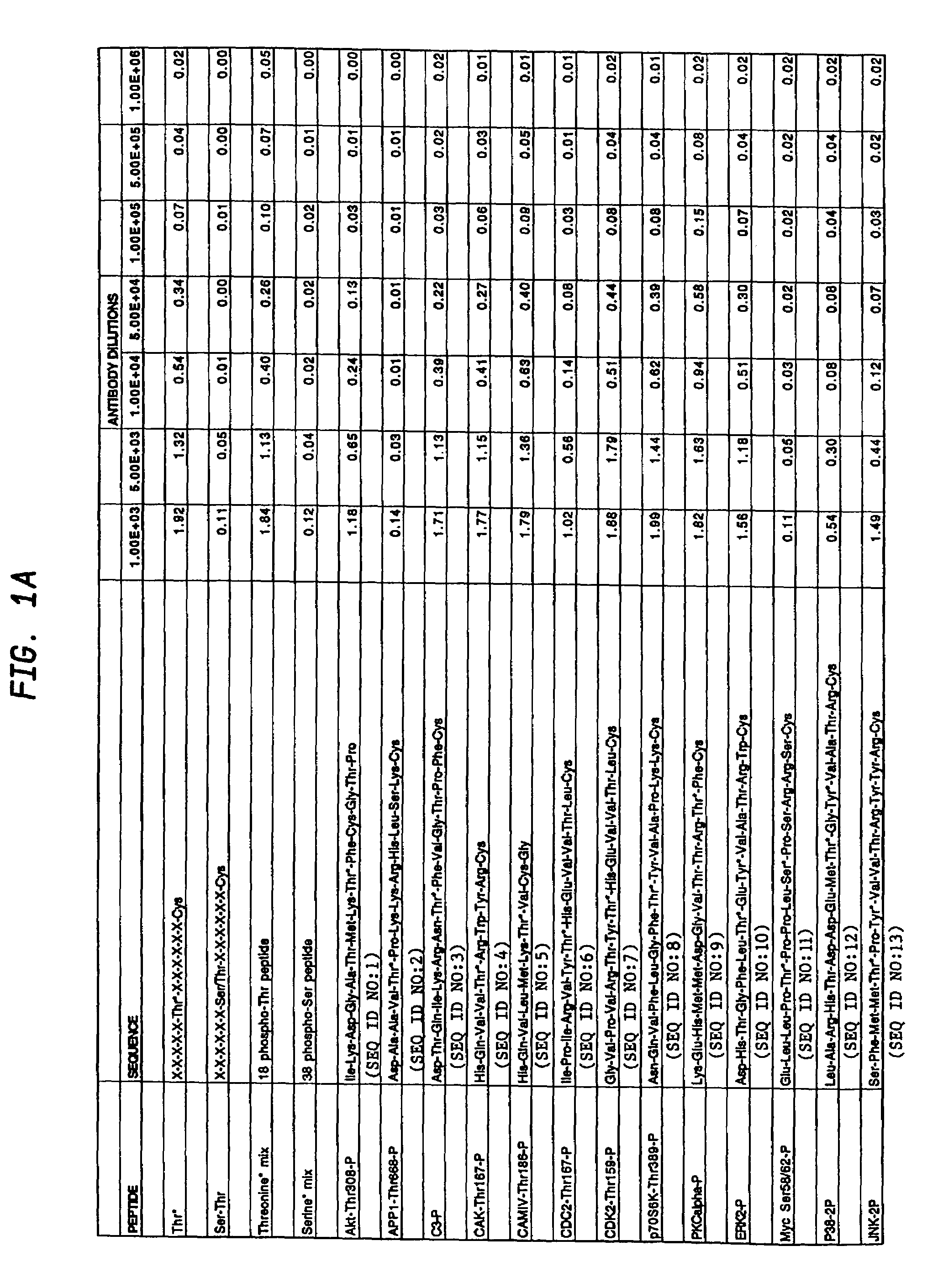
Production of motif-specific and context-independent antibodies using peptide libraries as antigens
InactiveUS7259022B2High recognitionPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningAntigenPeptide library
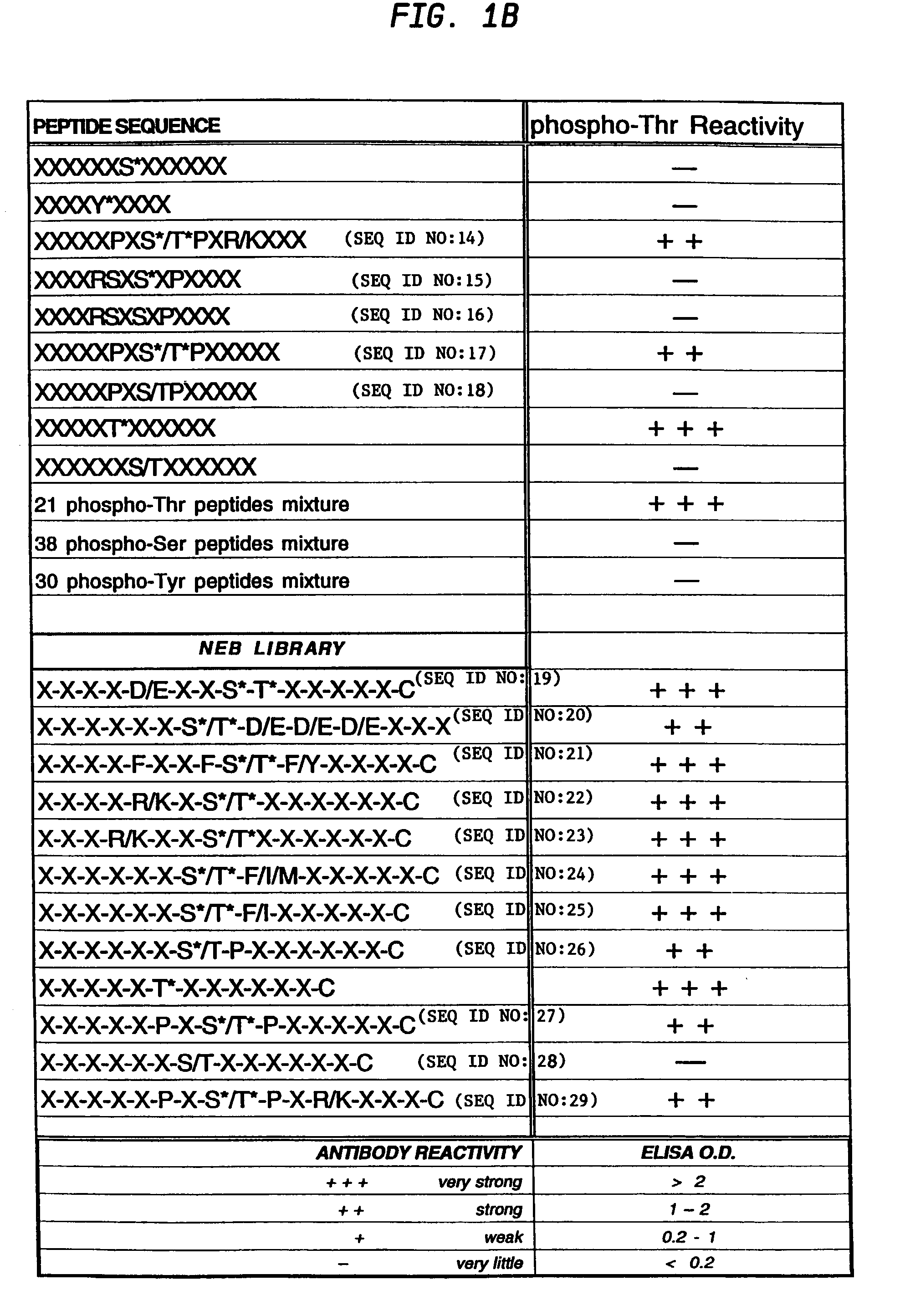
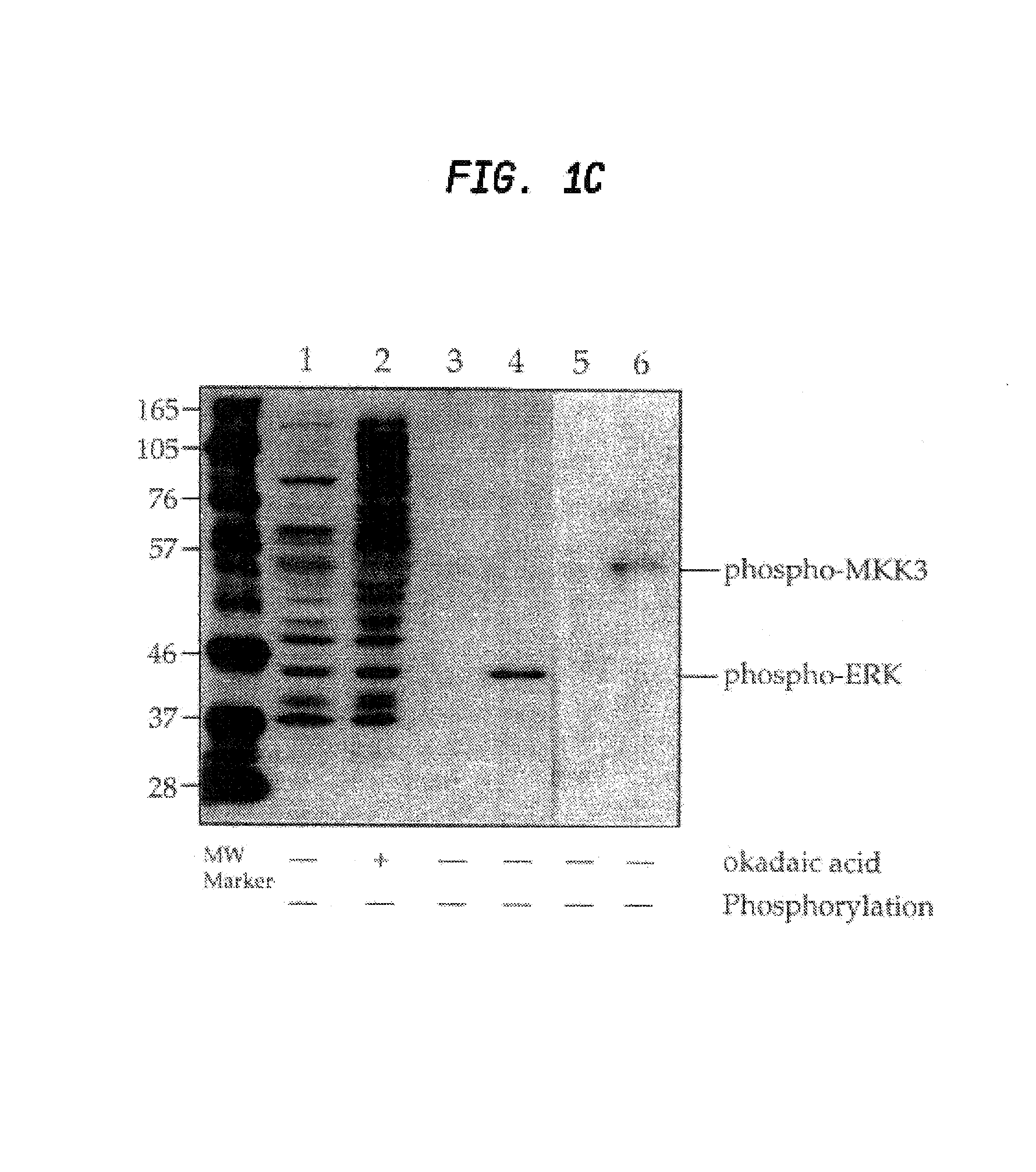
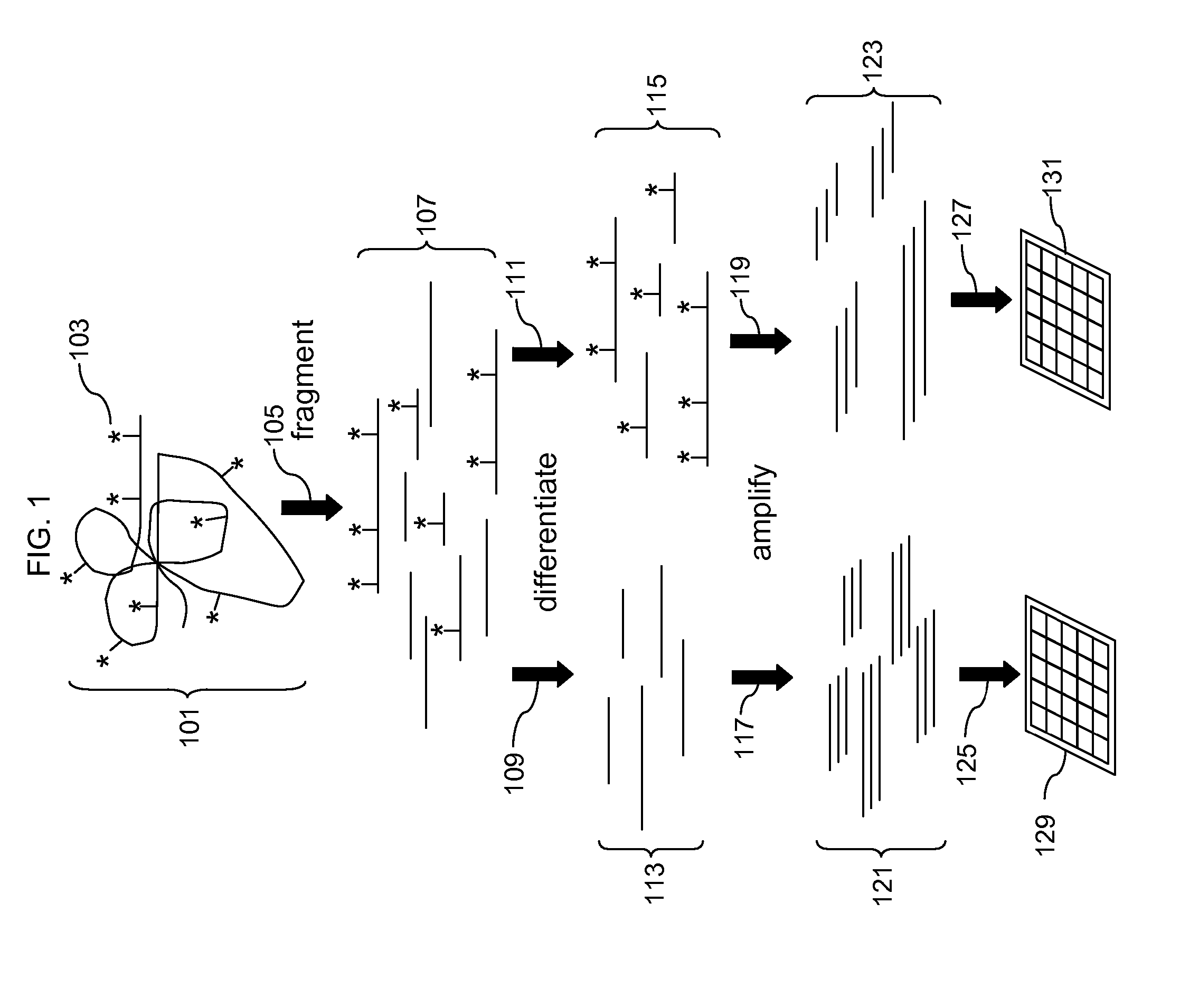
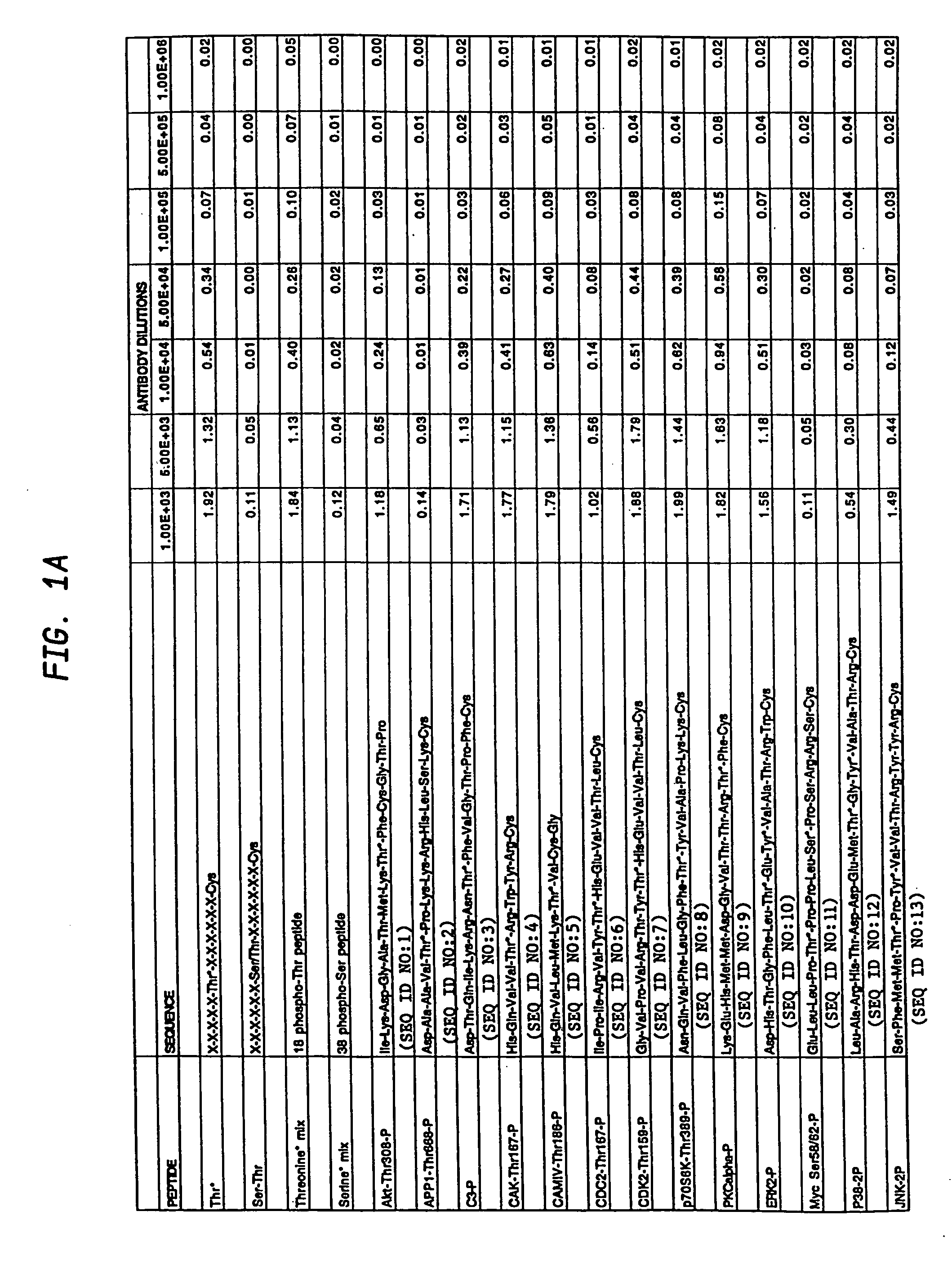
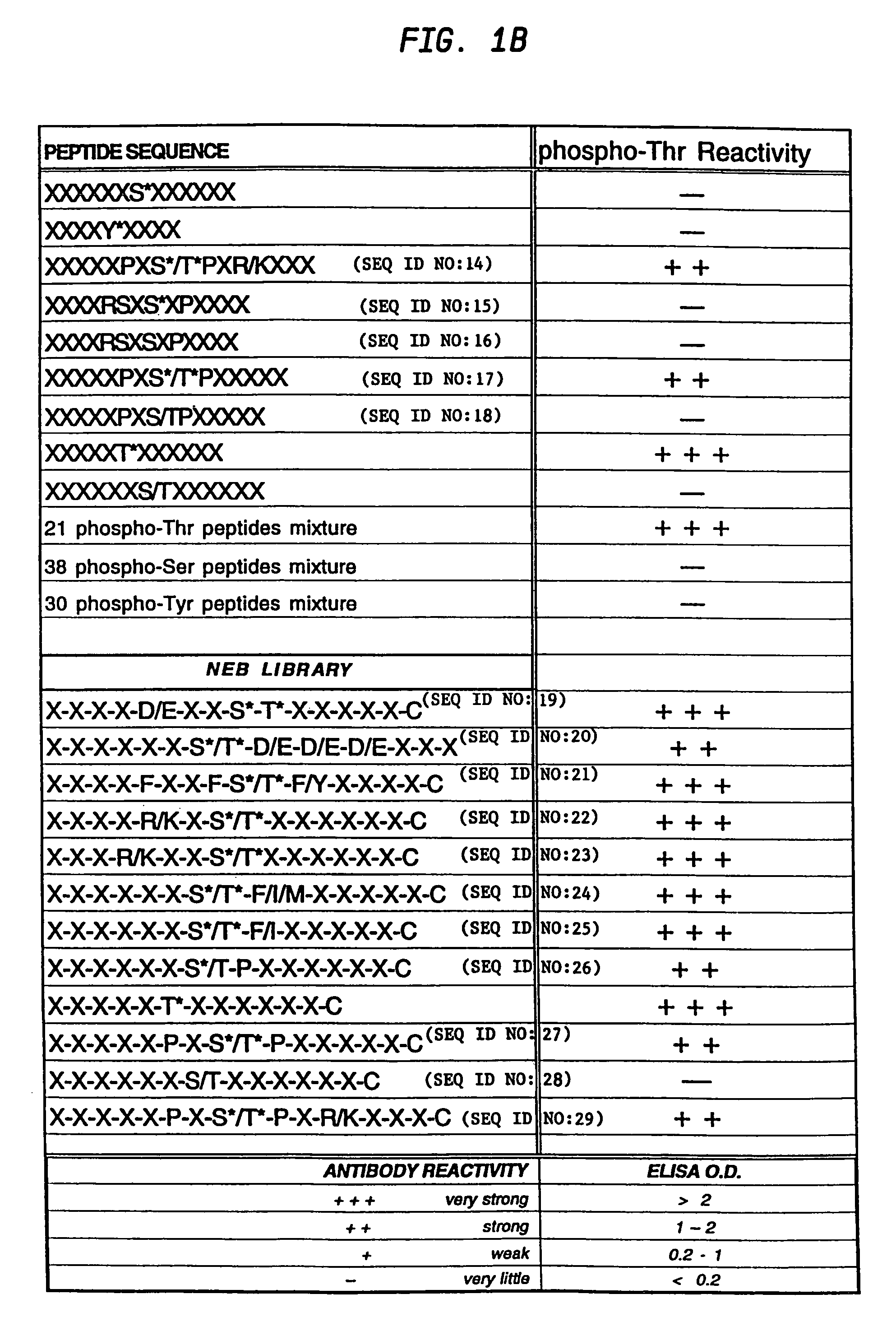
A method is provided for producing motif-specific, context-independent antibodies which recognize a plurality of peptides or proteins within a genome that contain the same motif. The method includes the step of immunizing a host with a degenerate peptide library antigen featuring (i) a fixed target motif containing one or more invariant amino acids including at least one modified amino acid, and (ii) a plurality of degenerate amino adds flanking the motif. Motif-specific, context-independent antibodies produced by the disclosed method are also provided. The method encompasses motifs consisting of a single modified amino acid, as well as short motifs comprising multiple invariant amino acids including one or more modified amino acids, such as all or part of kinase consensus substrate motifs, protein-protein binding motifs, or other cell signaling motifs. Methods of using the antibodies, e.g. for genome-wide profiling, are also provided.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
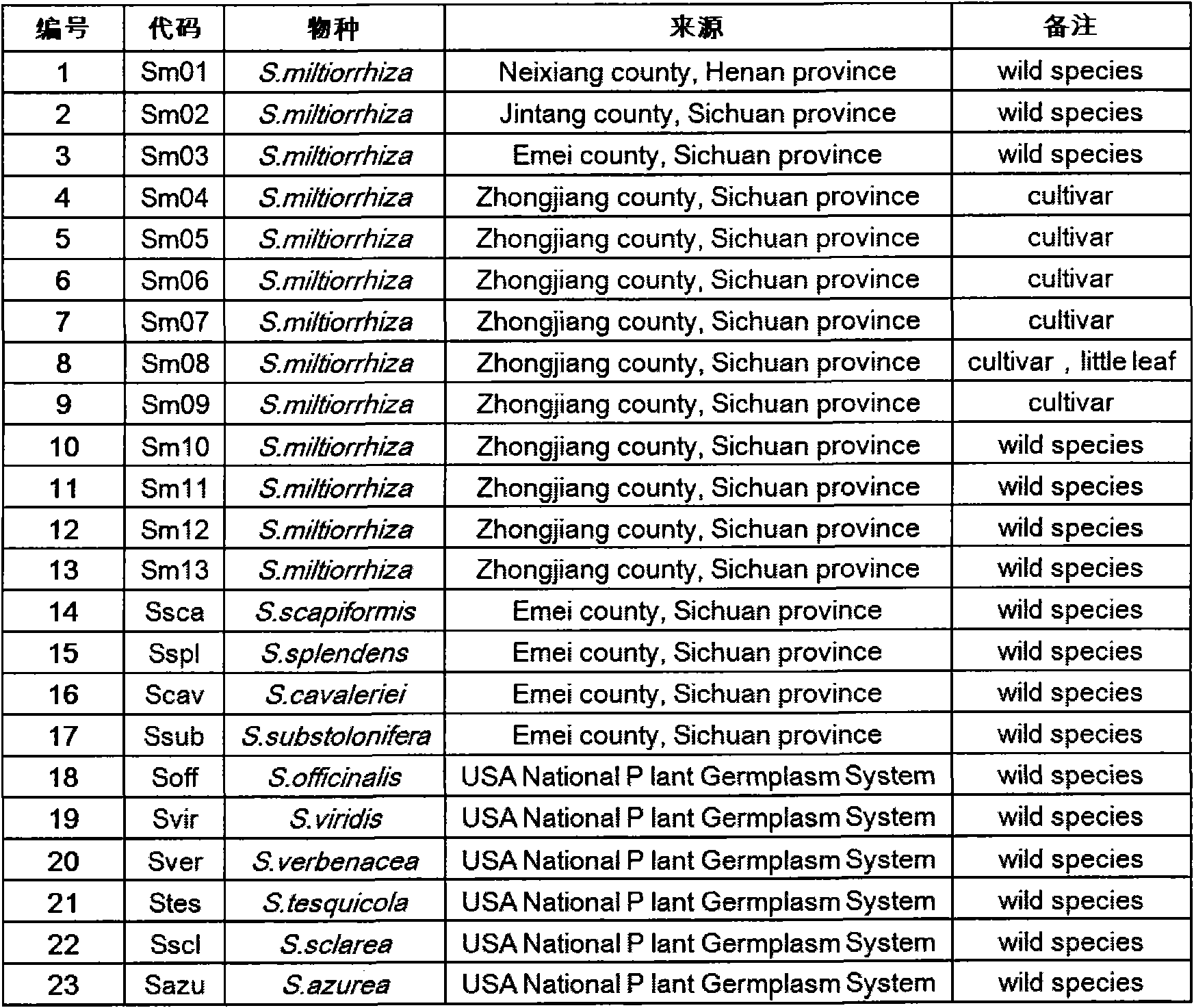
Method for preparing salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark, specific primer and application thereof
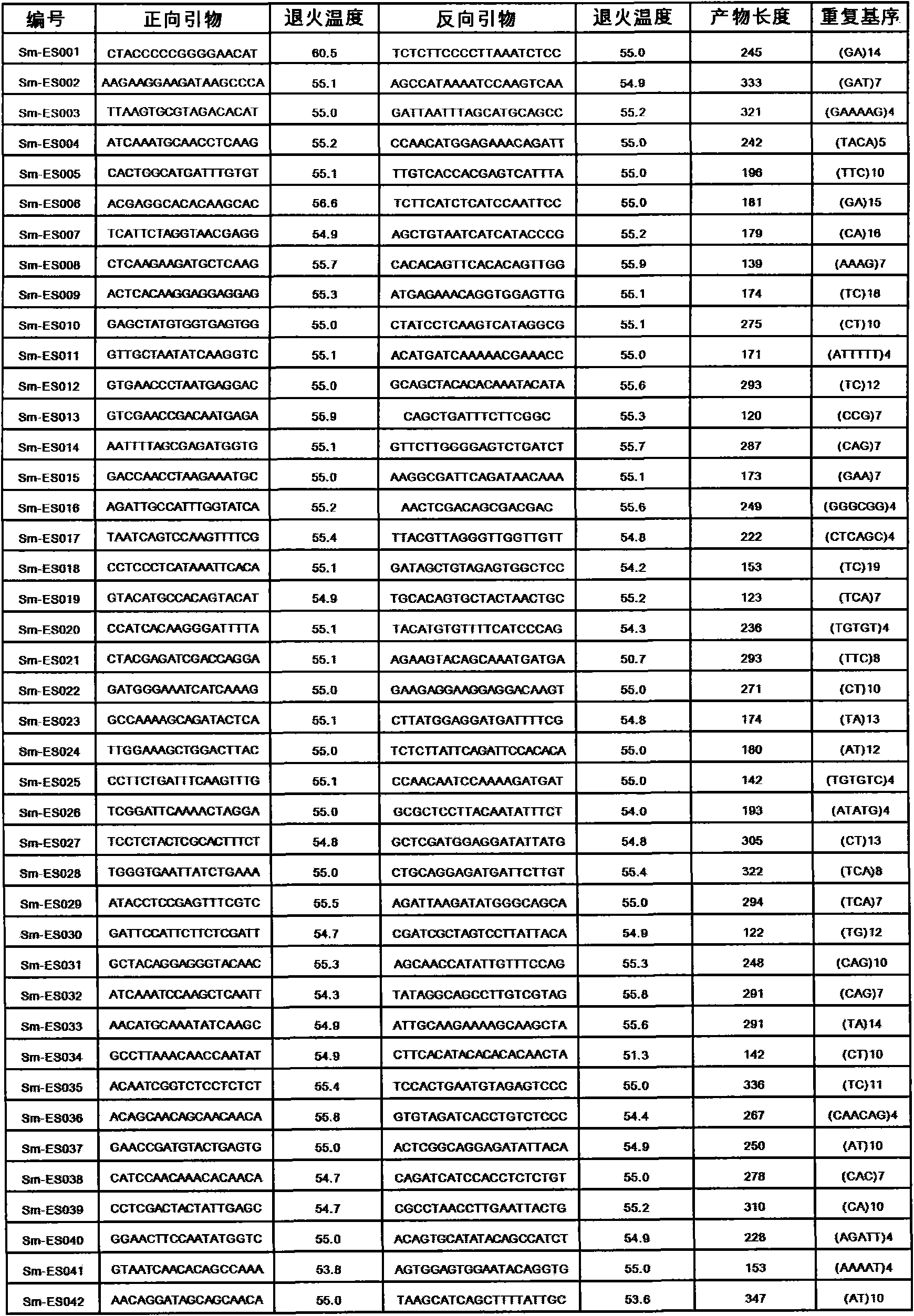
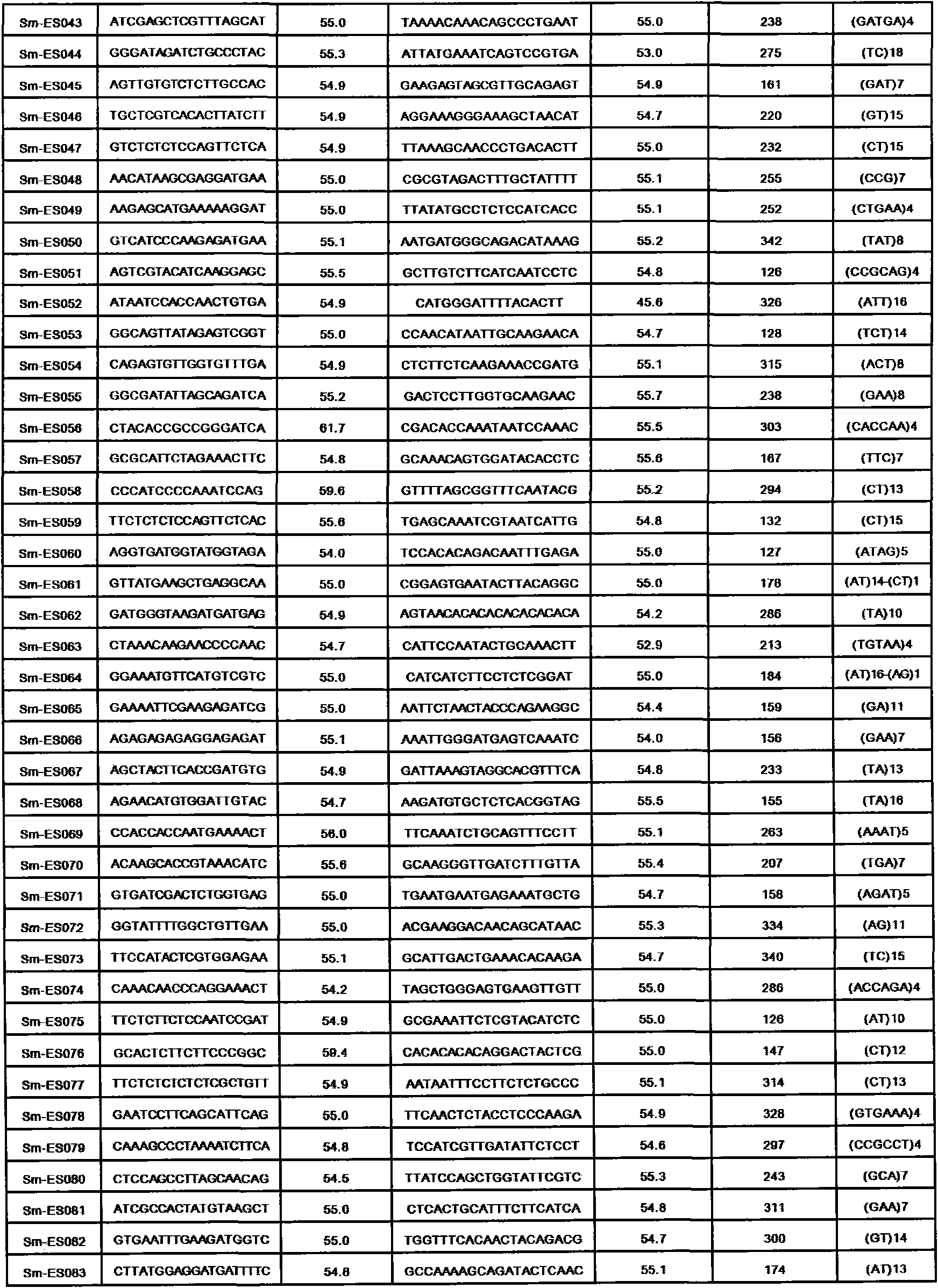
The invention discloses a method for preparing a salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark. The method mainly comprises the following steps of obtaining and pre-processing a salvia miltiorrhiza EST sequence, screening a SSR locus in the salvia miltiorrhiza EST sequence, designing and synthesizing the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR primer, screening the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR primer and the like. The method excavates the SSR locus aiming at the salvia miltiorrhiza EST and designs the PCR primer according to the flanking sequence of the SSR locus, and on the basis of this, the salvia specificEST-SSR mark system is established; and the method lays a solid foundation for genetic diversity evaluation, genetic relationship or idioplasmatic identification, genetic linkage description, molecular mark auxiliary selection, gene mapping cloning, functional genome analysis, related researches and the like of related species of the salvia miltiorrhiza and the salvia. The invention also discloses the EST-SSR locus specific primer obtained by the method for preparing the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark and the application thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
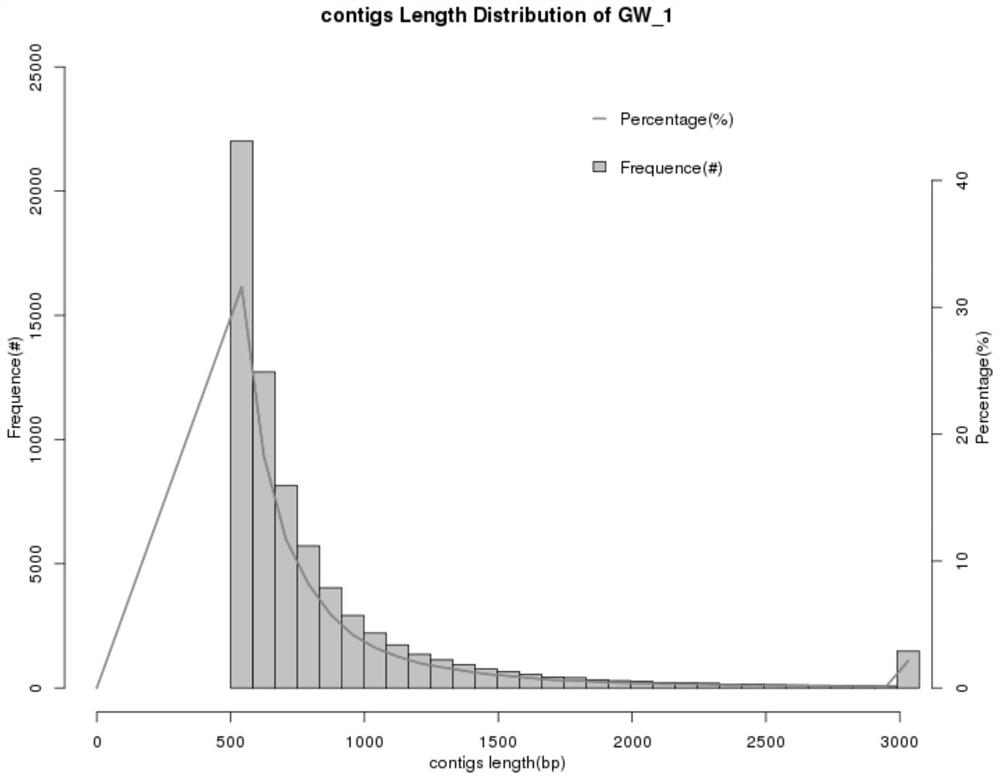
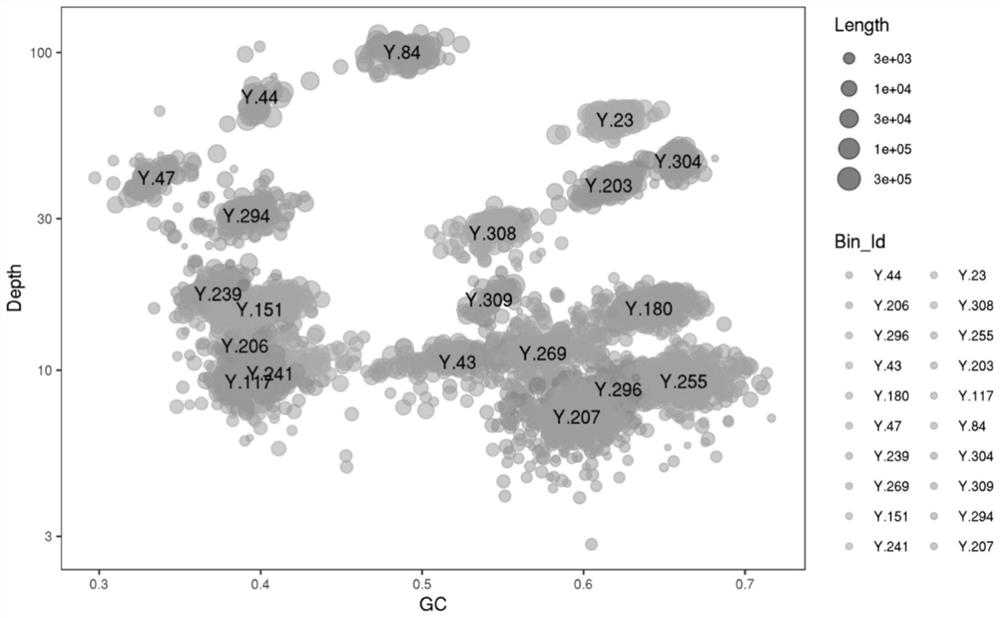
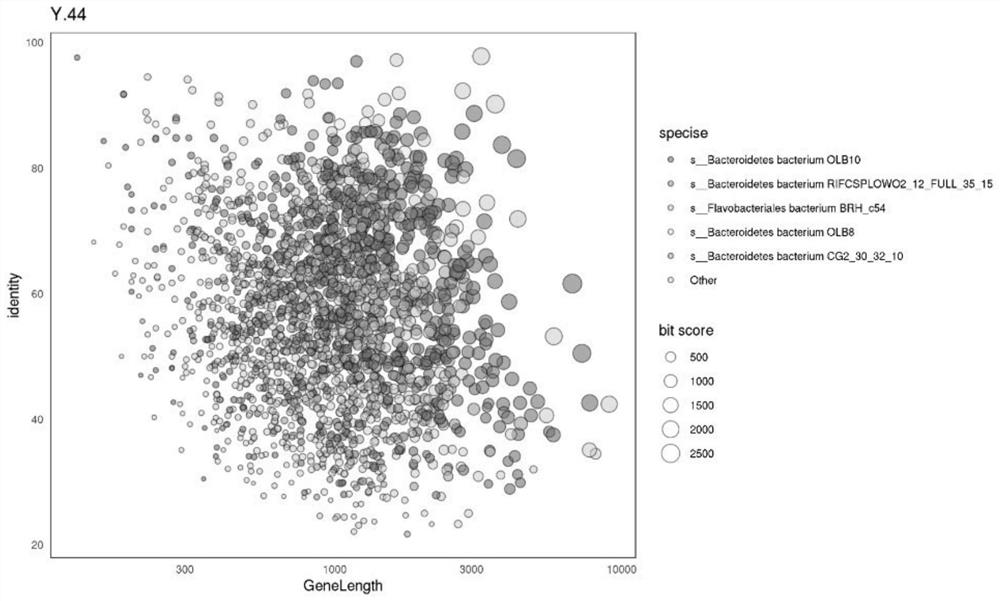
Optimized method for analyzing microbial communities through metagenome binning
ActiveCN111933218AAssembly targetedAssembly targetingSequence analysisInstrumentsMicroorganismBiocoenosis
The invention discloses an optimized method for analyzing microbial communities through metagenome binning. The method comprises the following steps of: filtering sequencing data to obtain high-quality sequencing data, selecting different assembly strategies to obtain contigs according to the source of a sample and the sequencing data volume, and analyzing gene data. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is used for simultaneously carrying out biological information analysis on the whole community and single-bacterium genome analysis independent of isolated cultureaiming at the microbial community. According to the invention, on the metagenome level, an efficient high-quality assembly algorithm which is more suitable for sample characteristics and sequencing data volume is provided, rich and comprehensive information analysis content is contained, and individuality and novelty are visualized; and the method realizes metagenome analysis qualitative change from communities to single bacteria, and the scheme comprises data correction capable of improving accuracy and comprehensive and perfect bin information summarization, is beneficial to screening valuable target bins more conveniently and efficiently, and further comprises systematically perfect mining ideas of subsequent analysis of the target bins.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENE DENOVO BIOTECH
Analysis of methylation using nucleic acid arrays
ActiveUS7901882B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenome wide analysisBioinformatics
Arrays for genome-wide analysis of methylation are disclosed. In a preferred aspect arrays comprising a plurality of probes complementary to a plurality of identified CpG islands in the human, mouse and rat genome are disclosed. The arrays may be used to detect methylation within CpG islands in samples from human, mouse and rat genomes.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Production of motif-specific and context-independent antibodies using peptide libraries as antigens
A method is provided for producing motif-specific, context-independent antibodies that recognize a plurality of peptides or proteins within a genome that contain the same post-translationally modified motif. The method includes the step of immunizing a host with a degenerate peptide library antigen featuring (i) a fixed target motif containing one or more invariant amino acids including at least one modified amino acid, and (ii) a plurality of degenerate amino acids flanking the motif. Motif-specific, context-independent antibodies produced by the disclosed method are also provided. The method encompasses motifs consisting of a single modified amino acid, as well as short motifs comprising multiple invariant amino acids including one or more modified amino acids, such as all or part of kinase consensus substrate motifs, protein-protein binding motifs, or other cell signaling motifs. Methods of using the antibodies, e.g. for genome-wide profiling, are also provided.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Methods for decentralized genome storage, distribution, marketing and analysis
PendingUS20200073560A1Easy to optimizeEasy to understandInput/output to record carriersData stream serial/continuous modificationData packBio molecules
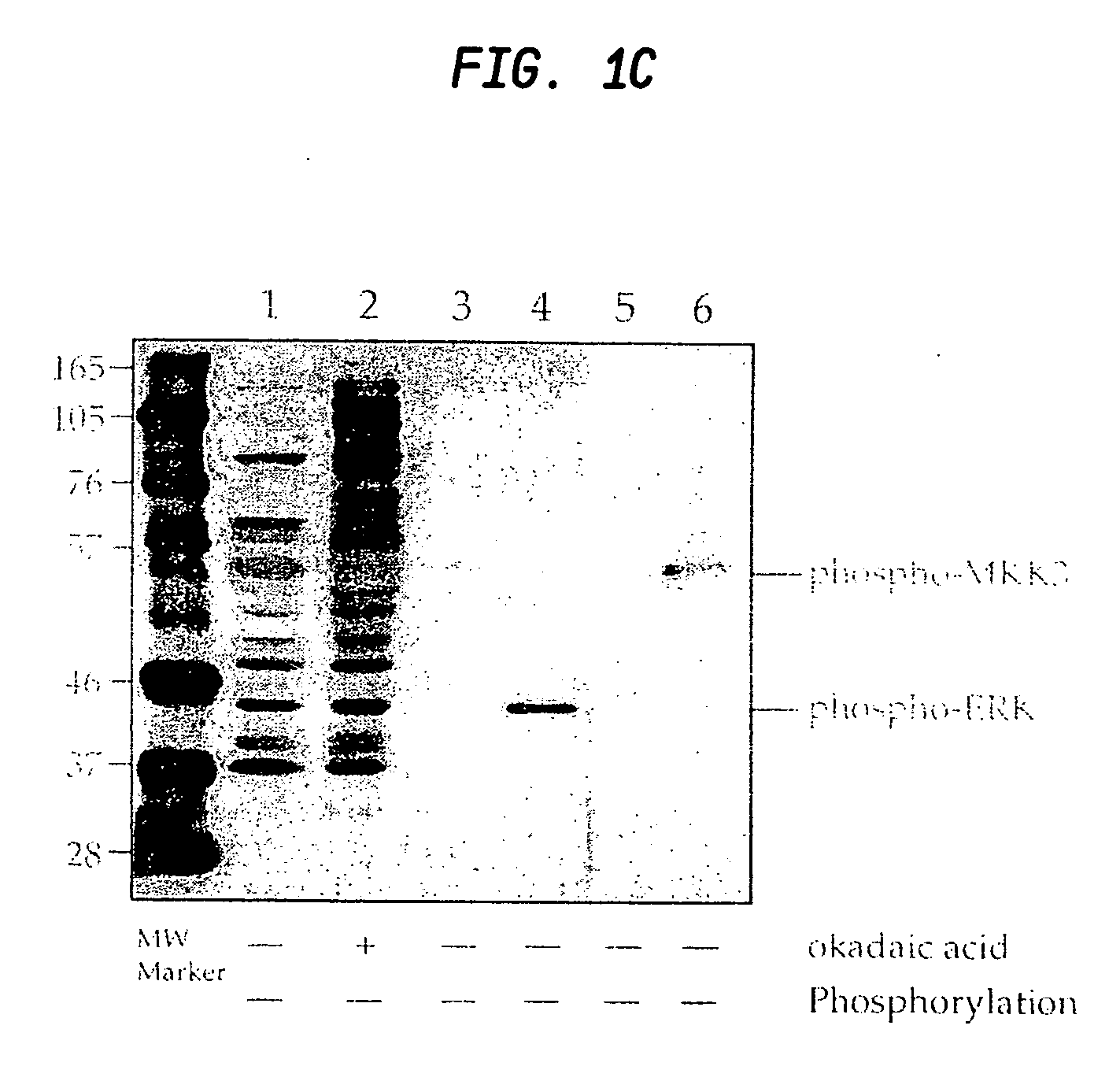
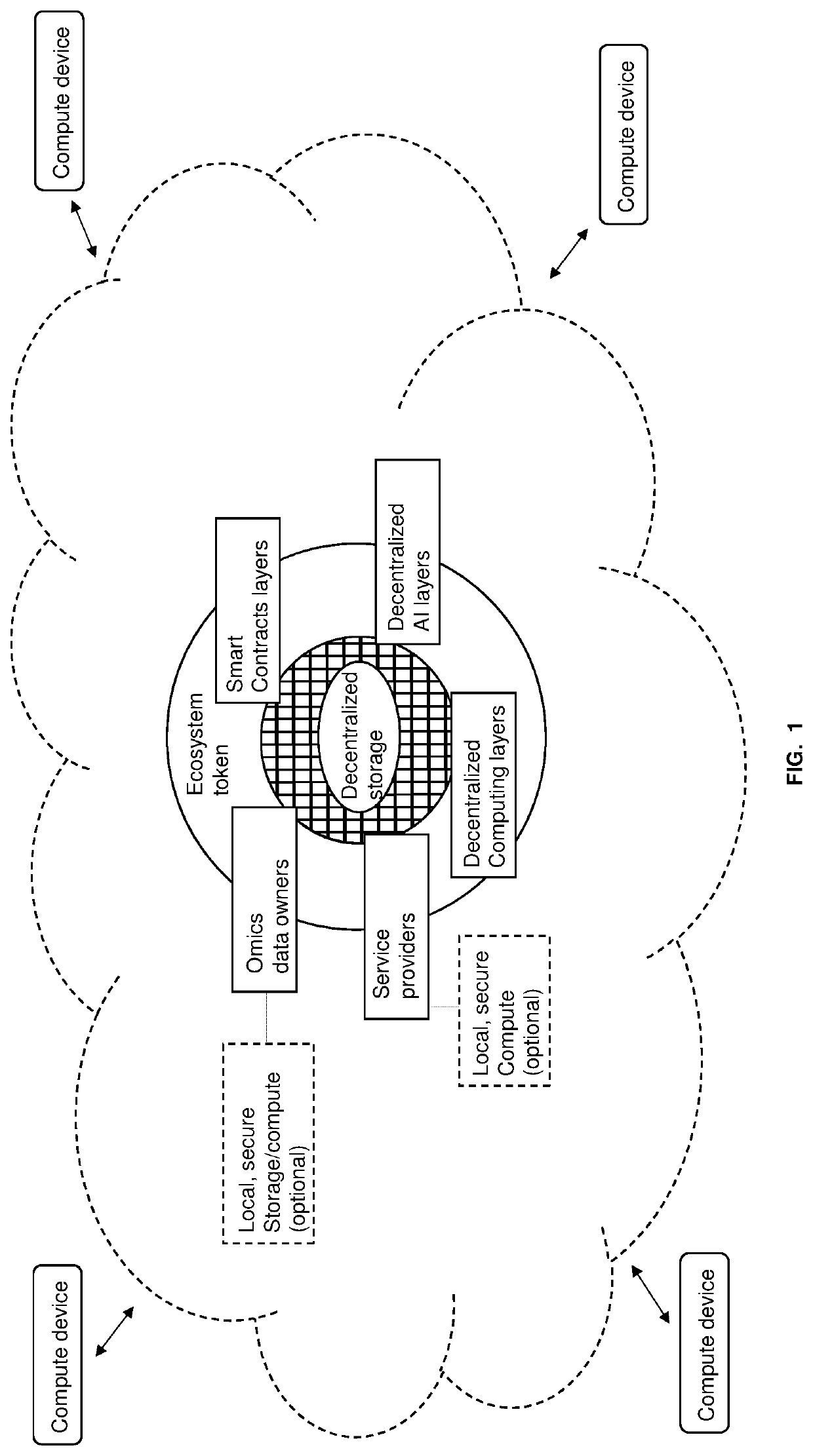
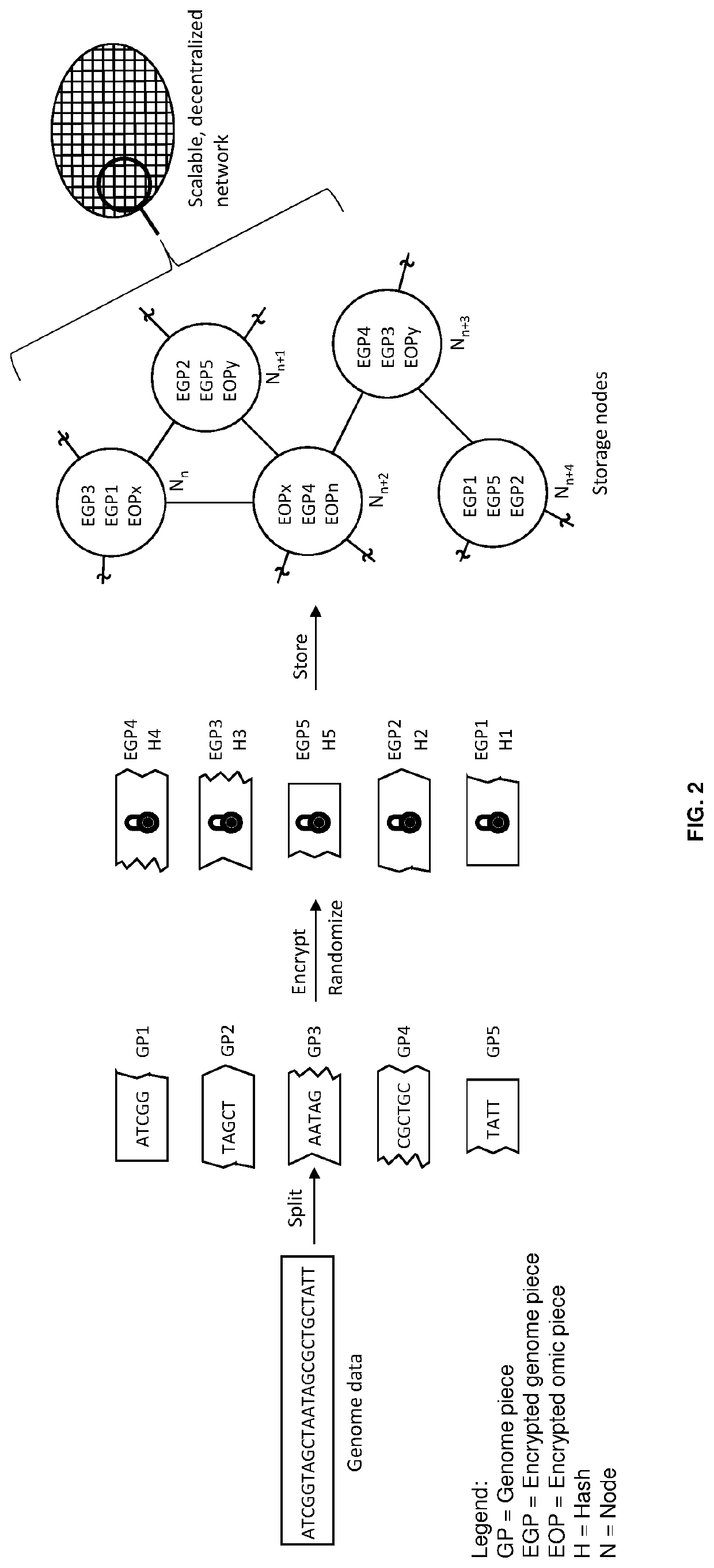
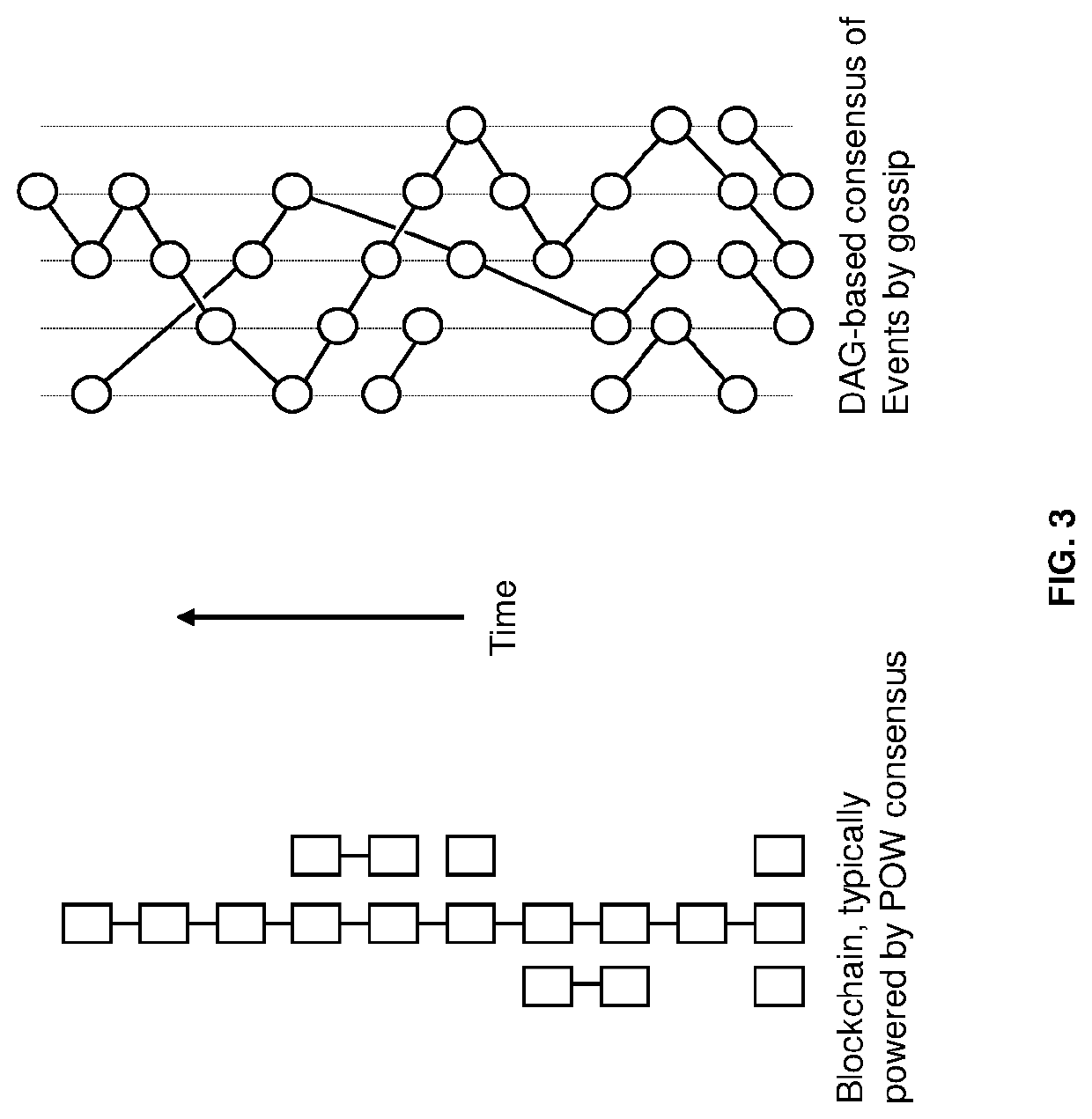
Techniques for storing omics data that indicates long sequences of elements associated with a particular biological molecule include receiving digital omics data comprising over two kilobytes. The digital omics data is split into multiple partitions. The maximum partition size is much less than then a number of elements in a typical instance of the particular biological molecule. Each partition is encrypted. Each encrypted partition is inserted into a corresponding data packet that includes an owner field that uniquely indicates an owner of the omics data. Each data packet is uploaded into a non-centralized, peer-to-peer distributed storage network. Thus, genome data is encrypted and stored in a distributed, scalable, fully decentralized, fast, and highly secure network. The network further provides for decentralized computing, trustless validation of the genomes by way of oracles and trustless genome analysis by third party providers through smart contracts.
Owner:GENETIC INTELLIGENCE INC
Method and kit for characterizing microorganisms
ActiveUS20140249036A1Shorten the timeQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationForward primerMicroorganism
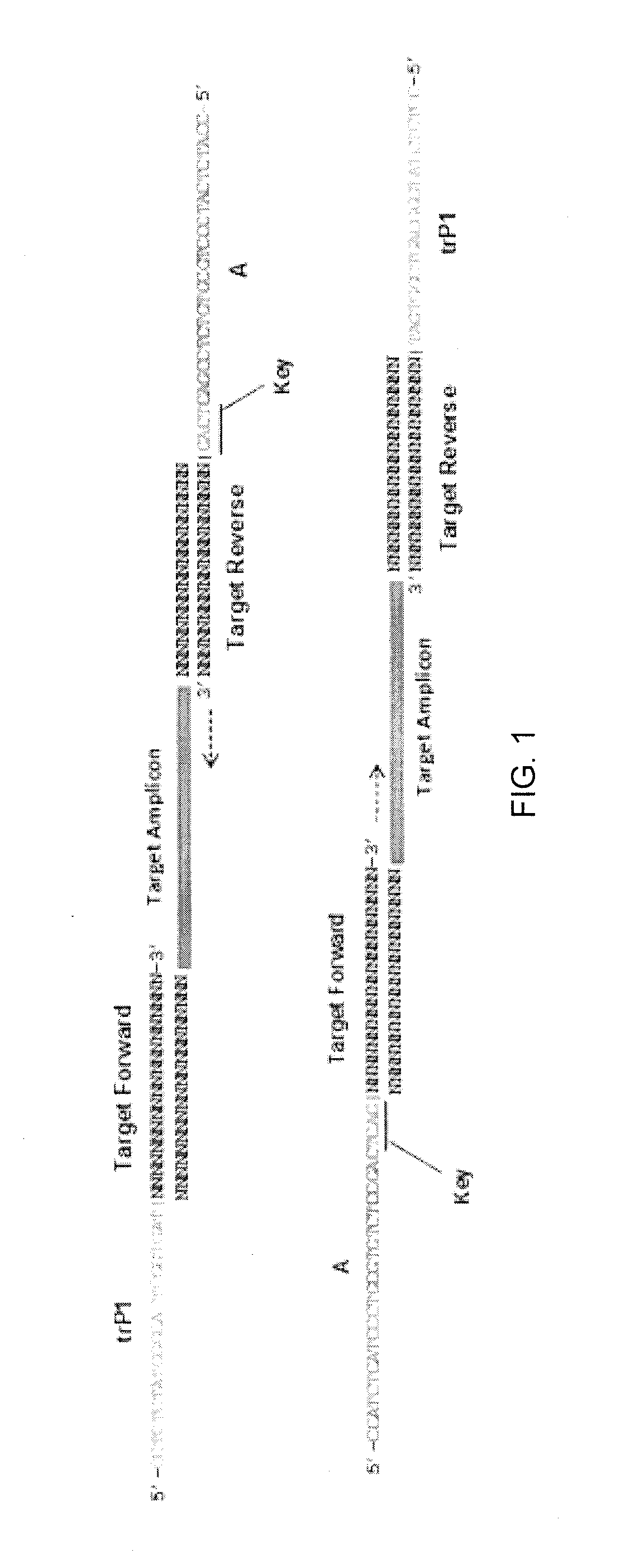
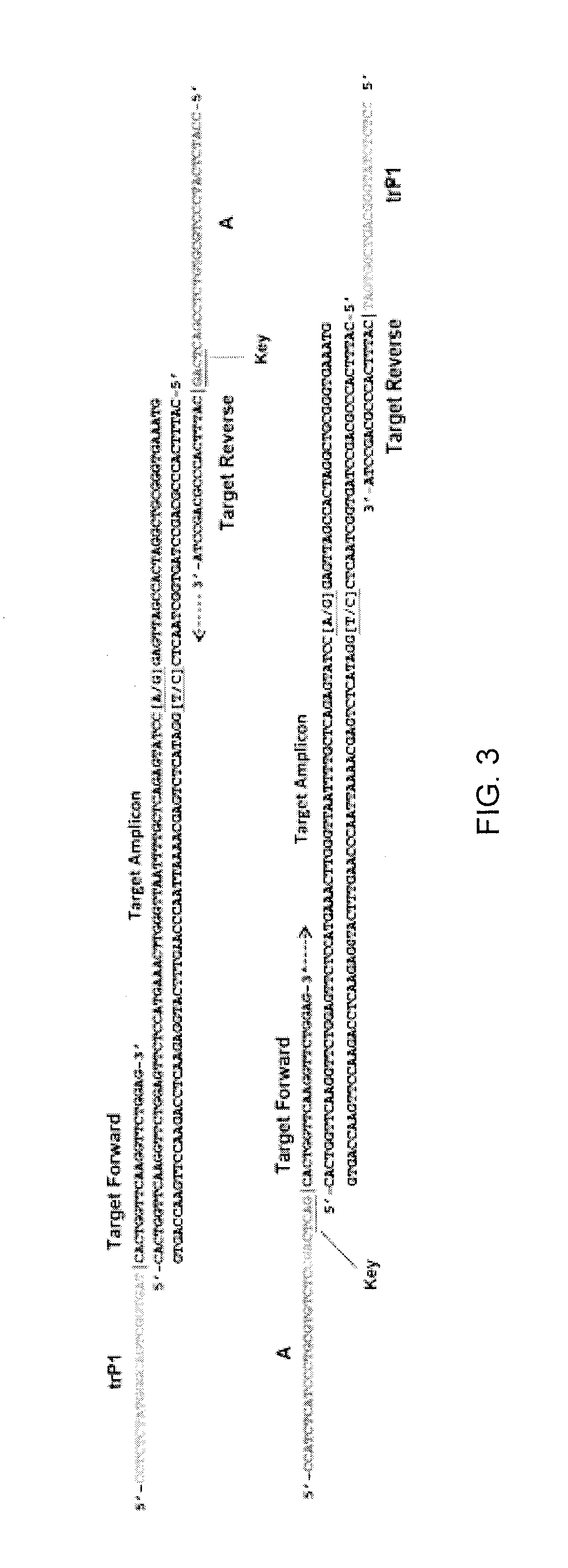
The present disclosure provides methods of characterizing one or more microorganisms and kits for characterizing at least one microorganism. Exemplary methods include preparing an amplicon library, sequencing a characteristic gene sequence to obtain a gene sequence, and characterizing the one or more microorganisms based on the gene sequence using a computer-based genomic analysis of the gene sequence. Exemplary kits include at least one forward primer including an adapter sequence and a priming sequence, for a target sequence, and at least one reverse primer.
Owner:FRY LAB
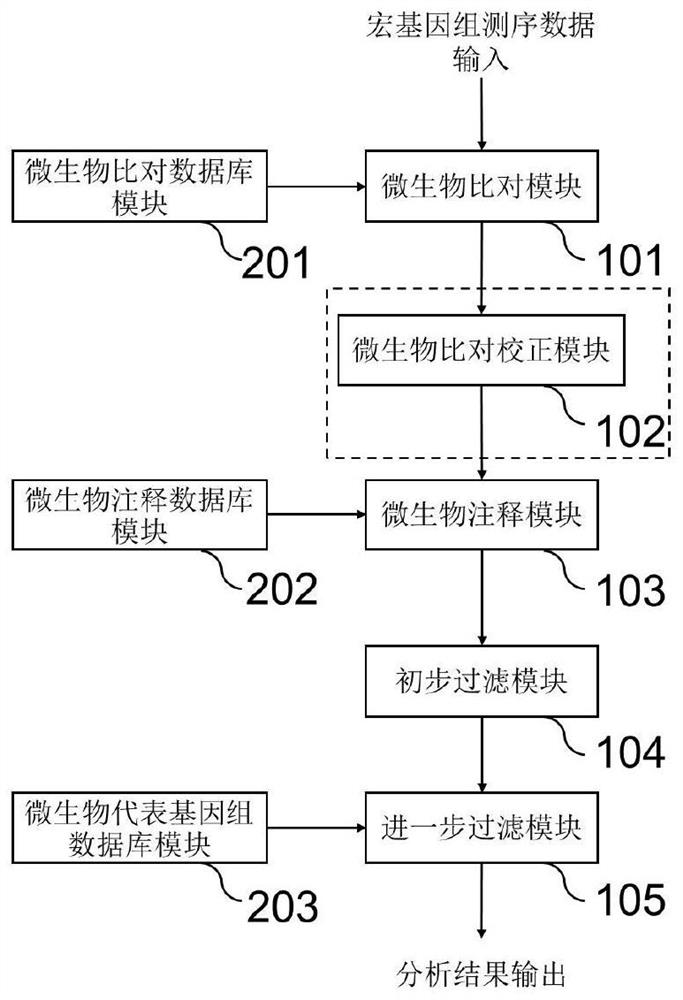
Method and system for detecting microorganisms and drug-resistant genes in sample
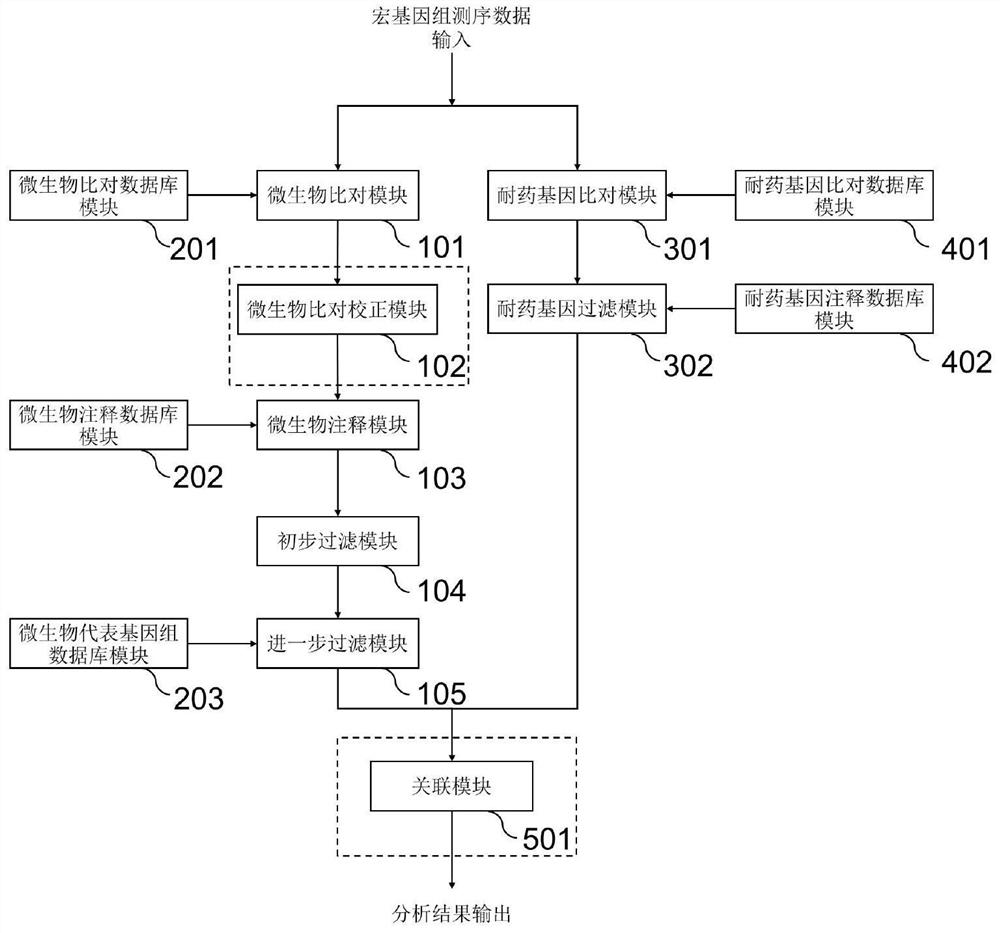
ActiveCN112530519AAccurate identificationAccurate detectionProteomicsGenomicsGenomic sequencingPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a method for detecting microorganisms in a sample, which belongs to the technical field of metagenome analysis and comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring metagenome sequencing data of the sample; and S2, performing species analysis on the metagenome sequencing data. The method further comprises a step of carrying out drug resistance gene analysis on the metagene sequencing data of the sample. The invention also discloses a system for detecting microorganisms and drug-resistant genes in a sample. On the basis of a comprehensive and accurate database and an intelligent analysis and screening algorithm, pathogenic microorganisms and drug-resistant genes are effectively identified by utilizing a metagenome sequencing method, false positive is effectively reduced,bacteria suspected to correspond to the detected drug-resistant genes can be prompted, and better technical support is provided for accurate diagnosis and treatment of infection; in addition, according to the method and the system, potential new pathogenic microorganisms can be accurately analyzed, and technical support is provided for early warning of new infectious diseases.
Owner:广东美格基因科技有限公司
Integrated Analyses of Breast and Colorectal Cancers
InactiveUS20100136560A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCellular pathwaysIntracellular signalling
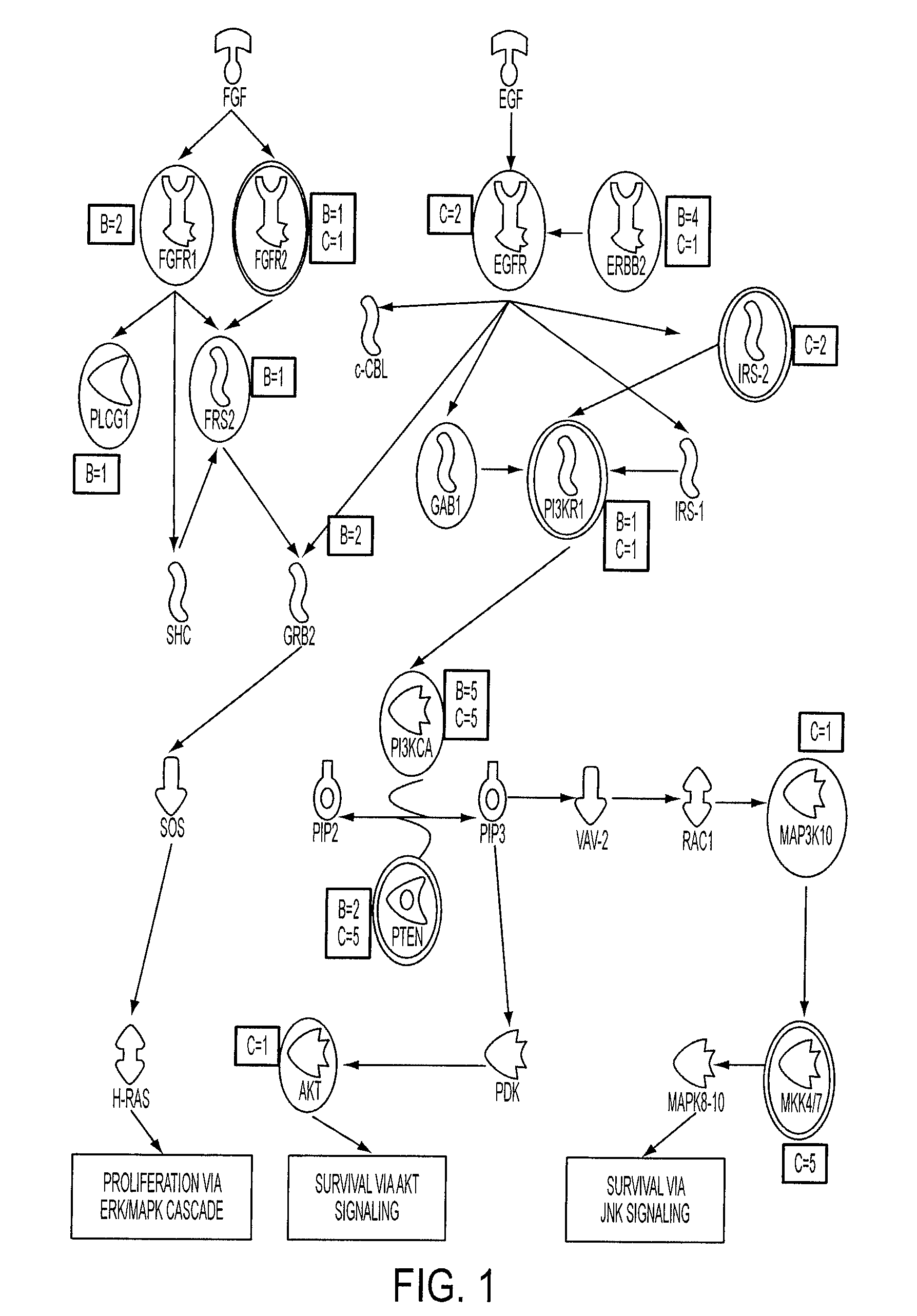
Genome-wide analysis of copy number changes in breast and colorectal tumors used approaches that can reliably detect homozygous deletions and amplifications. The number of genes altered by major copy number changes—deletion of all copies or amplification of at least twelve copies per cell—averaged thirteen per tumor. These data were integrated with previous mutation analyses of the Reference Sequence genes in these same tumor types to identify genes and cellular pathways affected by both copy number changes and point alterations. Pathways enriched for genetic alterations include those controlling cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, DNA topological change, and cell cycle control. These analyses provide an integrated view of copy number and sequencing alterations on a genome-wide scale and identify genes and pathways that are useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for producing optically active alpha-hydroxy amides
InactiveUS20080261286A1High optical purityOxidoreductasesRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliOpen reading frame
An objective of the present invention is to provide efficient methods for producing (R)-2-chloromandelamide with high optical purity. Another objective of the present invention is to provide novel methods for producing α-ketoamide reductases that reduce 2-chlorobenzoyl formamide to (R)-2-chloromandelamide with high optical purity, using NADPH as the coenzyme.An enzyme exhibiting high stereoselectivity was purified from a number of Saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymes with 2-chlorobenzoyl formamide-reducing activity, and the biochemical properties of the purified enzyme were analyzed. The analysis of a partial internal amino acid sequence of the purified enzyme revealed that the enzyme may be encoded by the putative open reading frame (ORF) YDL124w reported in the genome analysis. YDL124w was cloned and expressed in E. coli, and was subsequently shown to encode the α-ketoamide reductase. It was found that these resulting transformants facilitated the production of (R)-2-chloromandelamide from 2-chlorobenzoyl formamide.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
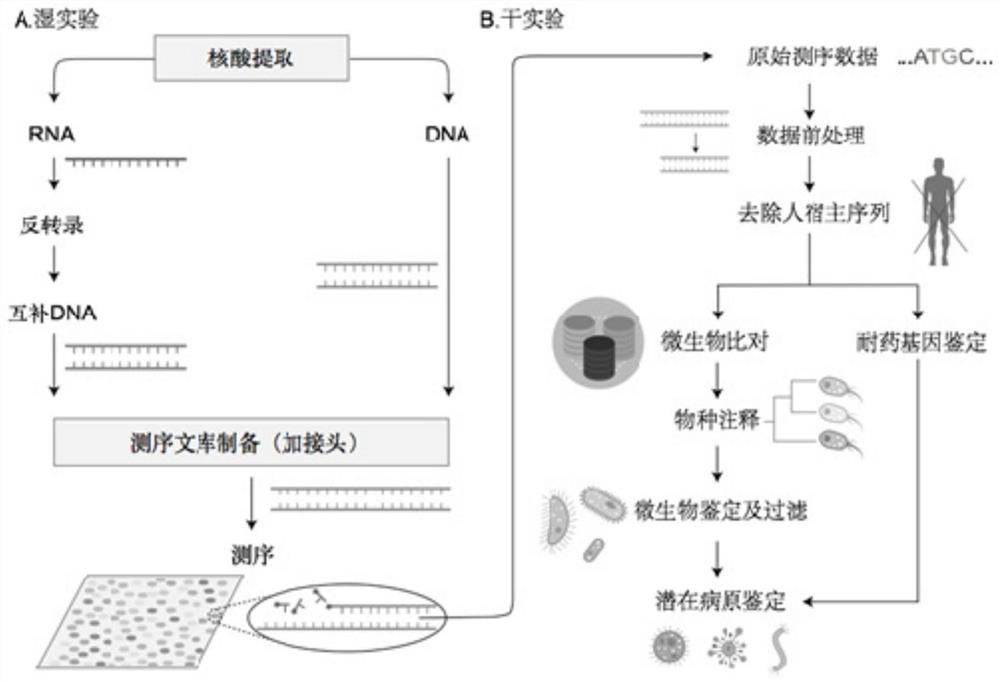
Method for identifying and analyzing ancient DNA sample
The invention discloses a method for identifying and analyzing an ancient DNA sample, which comprises a method for acquiring DNA information of a to-be-tested DNA sample, wherein the method for acquiring the DNA information comprises the following steps: building a database for the to-be-tested DNA sample and performing sequencing on the to-be-tested DNA sample, so as to acquire sequencing data; filtering the sequencing data; making comparison on the filtered sequencing data, so as to obtain a comparison result, wherein the comparison result contains the DNA information of the to-be-tested DNAsample, and the comparison allows mispairing of at most four basic groups. With adoption of the method for identifying and analyzing the ancient DNA sample, the DNA information of the ancient DNA sample can be effectively acquired based on the building of the database and the sequencing of the to-be-tested ancient DNA sample; in addition, the information is accurate, is high in reliability and can be used for effectively analyzing genomes of the to-be-tested ancient DNA, such as detection of variation, identification of the ancient DNA, sex determination and assessment on modern DNA contamination rate.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
String matching in hardware using the fm-index
InactiveUS20120233185A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData packAlgorithm
String matching is a ubiquitous problem that arises in a wide range of applications in computer science, e.g., packet routing, intrusion detection, web querying, and genome analysis. Due to its importance, dozens of algorithms and several data structures have been developed over the years. A recent breakthrough in this field is the FM-index, a data structure that synergistically combines the Burrows-Wheeler transform and the suffix array. In software, the FM-index allows searching (exact and approximate) in times comparable to the fastest known indices for large texts (suffix trees and suffix arrays), but has the additional advantage to be much more space-efficient than those indices. This disclosure discusses an FPGA-based hardware implementation of the FM-index for exact and approximate pattern matching.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System for animal health diagnosis
Selecting the nutrition for an animal or animal group comprises performing a diagnostic test to obtain first data. A data base that comprises first data relating a genomic analysis of a bodily fluid or tissue sample from an animal to a physiological condition and optionally the genotype of the animal is accessed. A data base that comprises second data relating to effects of nutrition on genomic analysis is accessed. The first and second data are processed with input data defining the physiological condition and optionally the genotype of the animal or animal group to derive the nutrition for an animal or animal group.
Owner:HEMOPET
Methods for comparative metagenomic analysis
PendingUS20210249102A1BiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionSequence analysisGenome sequence analysis
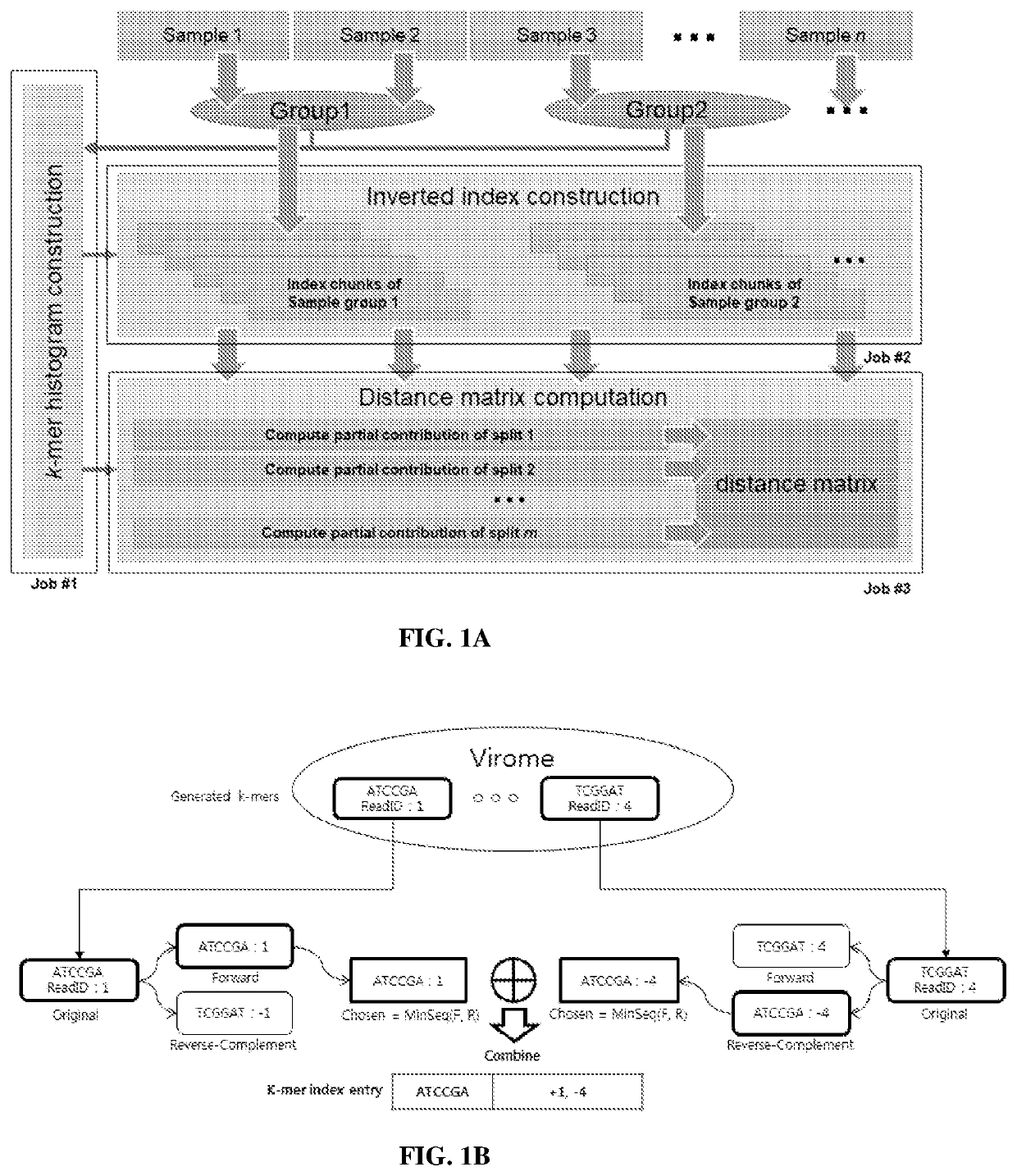
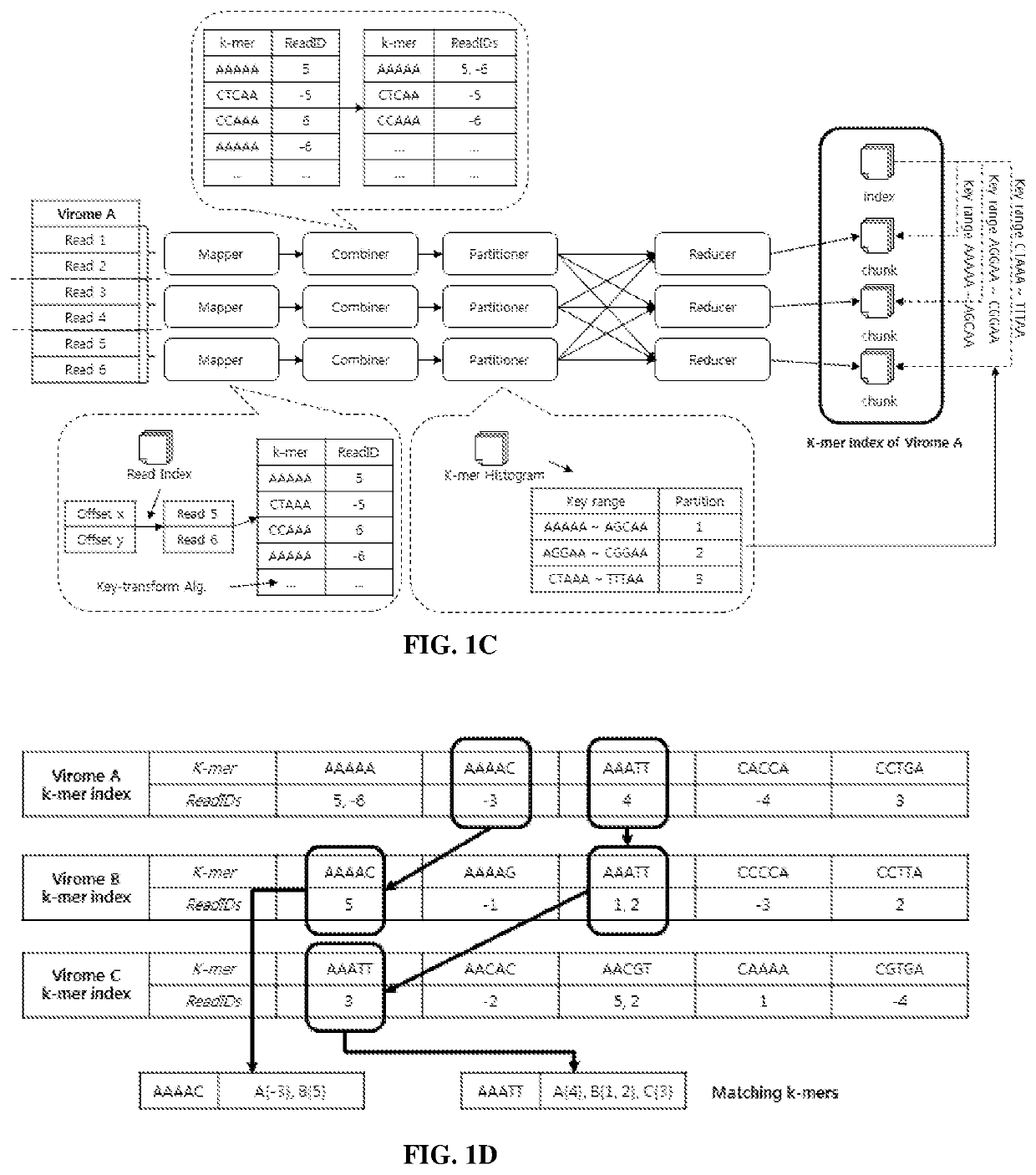
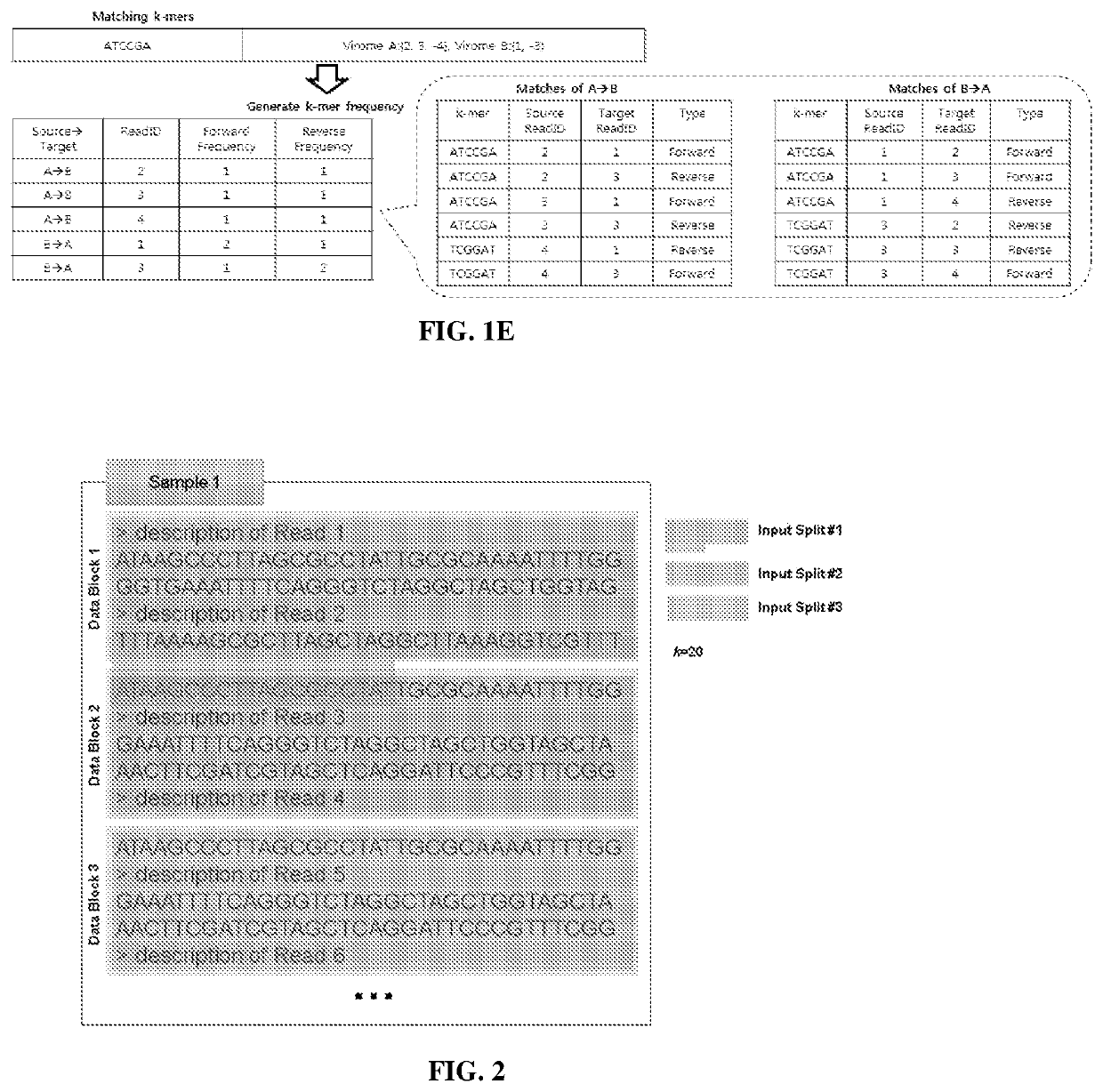
Systems and methods for metagenomic analysis are provided. A method of metagenome sequence analysis of two or more samples can include (i) counting the abundance of each k-mer deconstructed from sequencing reads of nucleic acids in each sample, and (ii) using a vector space model to compute the genetic distance between each of the two or more samples according to the abundance of the k-mers. In some embodiments, counting includes (a) constructing a k-mer histogram containing the distribution of k-mers for each sample, and (b) dividing k-mers into partitions having approximately an equal number of k-mers based on the histogram, preparing an inverted index of the k-mers in each partition, and assigning a weight to each k-mer according to its abundance. Method of developing diagnostic and prognostic information using the methods of sequence analysis are also provided.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
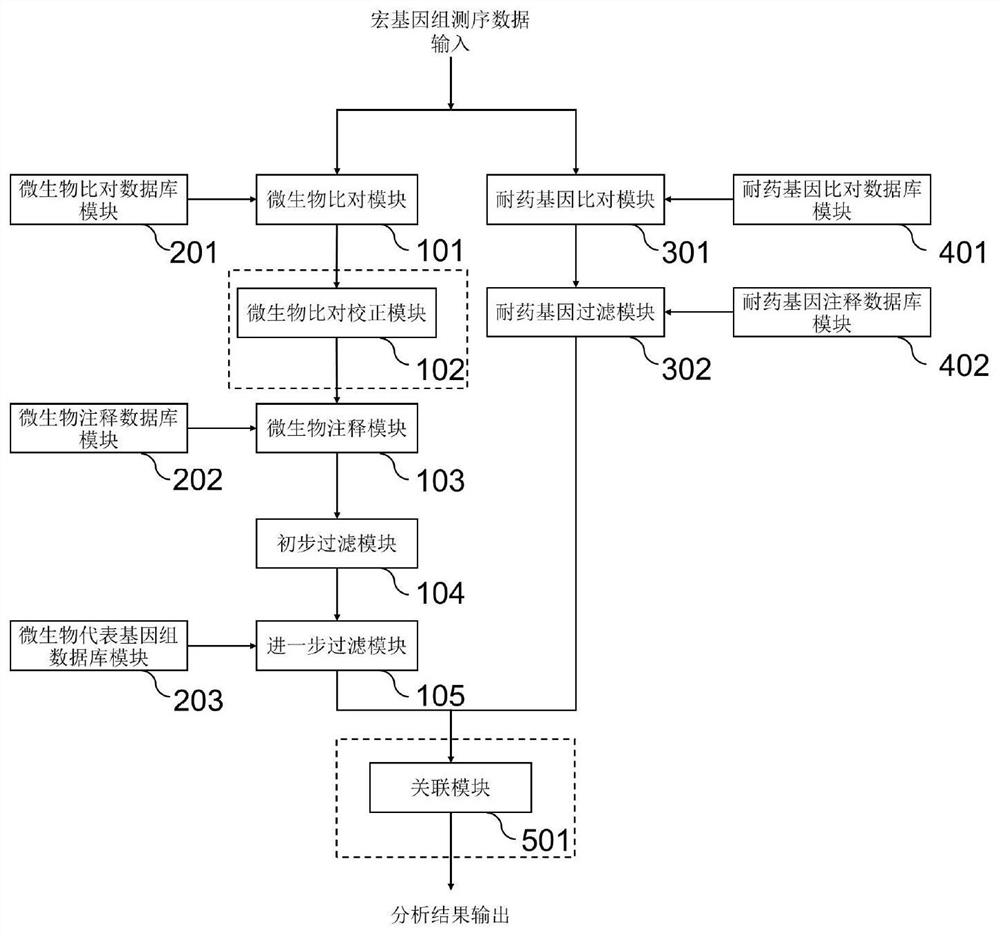
Microorganism contrast result correction method and system based on metagenome sequencing
PendingCN113689912AAccurate identificationAccurate detectionProteomicsGenomicsGenomic sequencingPathogenic microorganism
The invention discloses a method for detecting microorganisms in a sample, and belongs to the technical field of metagenome analysis. The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining metagenome sequencing data of a sample; and S2, performing species analysis on the metagenome sequencing data. The method further comprises a step of performing drug resistance gene analysis on the metagenome sequencing data of the sample. The invention also discloses a system for detecting microorganisms and drug-resistant genes in a sample. Based on a comprehensive and accurate database and an intelligent analysis and screening algorithm, pathogenic microorganisms and drug-resistant genes are effectively identified by utilizing a metagenome sequencing method, false positives are effectively reduced, bacteria suspected to correspond to the detected drug-resistant genes can be prompted, better technical support is provided for accurate diagnosis and treatment of infection, in addition, according to the method and the system, potential new pathogenic microorganisms can be accurately analyzed, and technical support is provided for early warning of new infectious diseases.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIGE GENE TECH CO LTD
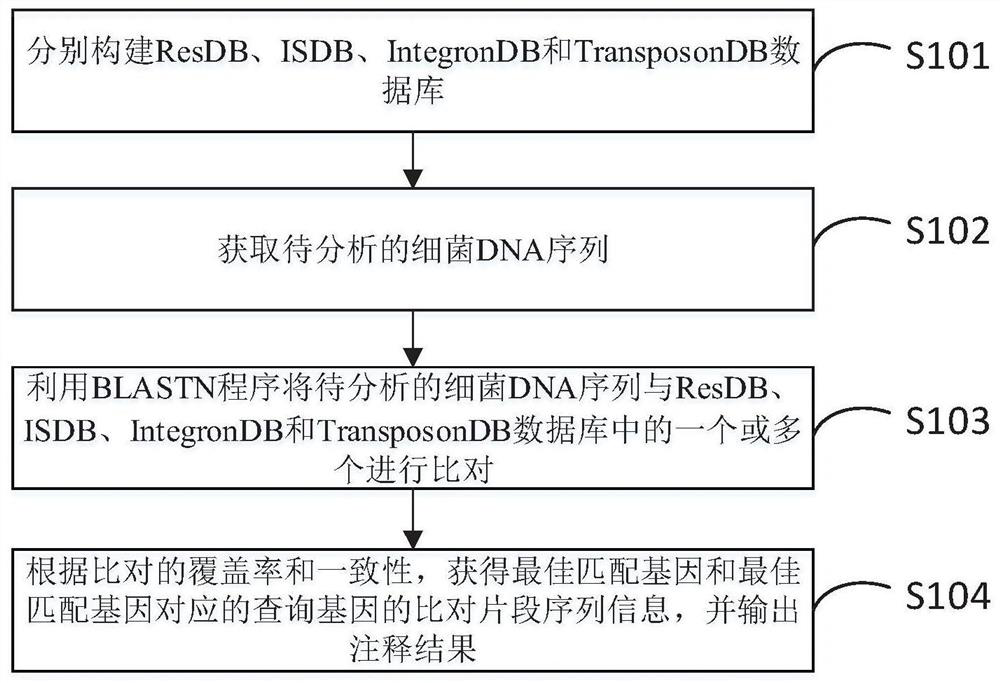
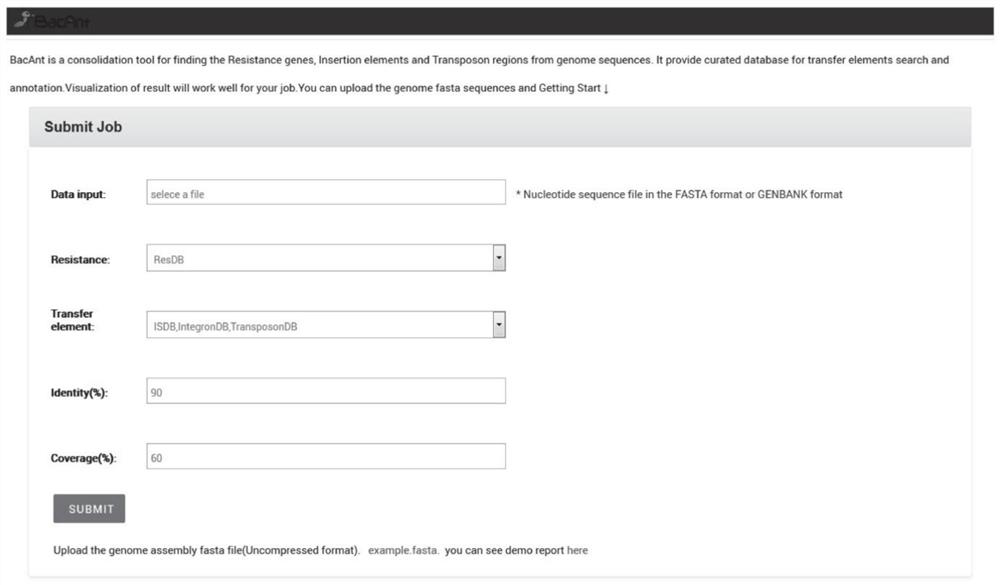
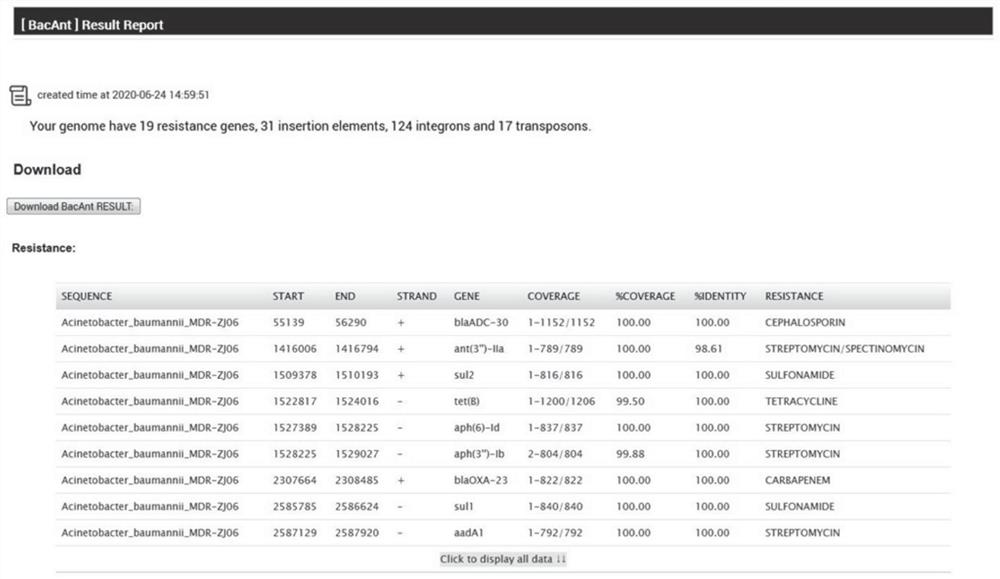
Rapid annotation method and device for a bacterial DNA sequence
PendingCN112017729ASimplify and optimize the analysis processQuick analysisProteomicsGenomicsGenome wide analysisOptimal matching
The invention discloses a rapid annotation method and device for a bacterial DNA sequence. The method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing a ResDB database, an ISDB database, an IntegronDB database and a TranssposonDB database; obtaining a bacteria DNA sequence to be analyzed; comparing the bacteria DNA sequence to be analyzed with one or more of a ResDB database, an ISDB database, an IntegronDB database and a TranssposonDB database by using a BLASTN program; and according to the coverage rate and consistency of comparison, obtaining comparison fragment sequence informationof the optimal matching gene and the query gene corresponding to the optimal matching gene, and outputting an annotation result. The method is helpful for simplifying and optimizing the current genome analysis process and accelerating the subsequent genome analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for genome-wide analysis of palindrome formation and uses thereof
The present invention provides a method for rapidly detecting the genome-wide presence of palindrome formation. The method has demonstrated that somatic palindromes occur frequently and are widespread in human cancers. Individual tumor types have a characteristic non-random distribution of palindromes in their genome and a small subset of the palindromic loci are associate with gene amplification. The disclosed method can be used to define the plurality of genomic DNA palindromes associated with various tumor types and can provide methods for the classification of tumors, and the diagnosis, early detection of cancer as well as the monitoring of disease recurrence and assessment of residual disease.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
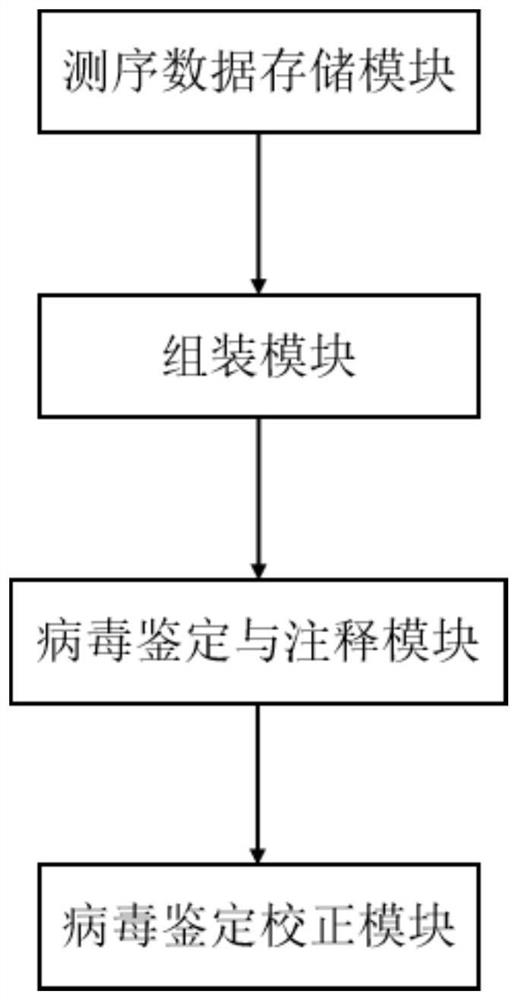
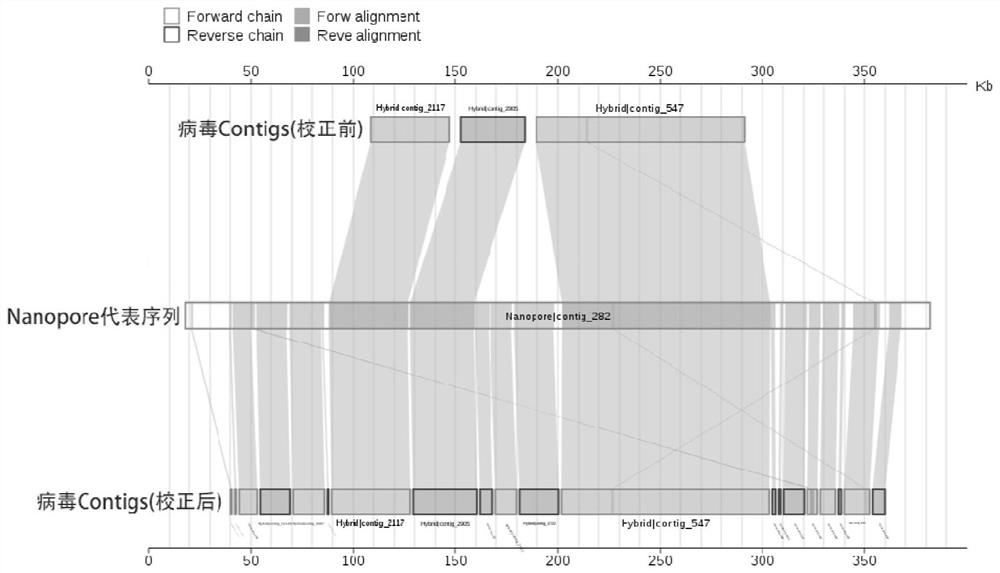
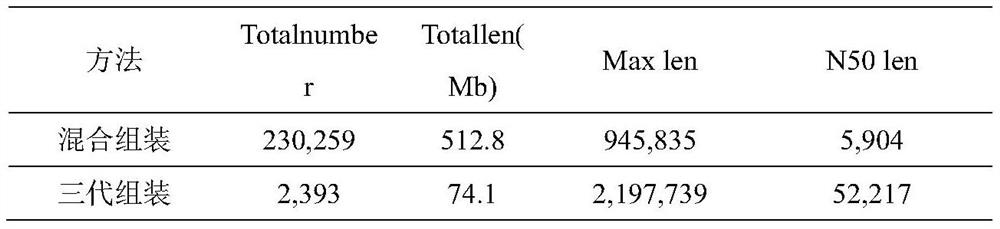
Method and system for detecting macro virus group in sample
ActiveCN114121160AImprove identification sensitivityImprove accuracySequence analysisInstrumentsData setContig
The invention discloses a method for detecting a macro virus group in a sample, and belongs to the technical field of metagenome analys.The method comprises the steps that second-generation sequencing data and third-generation sequencing data of a to-be-detected sample are mutually corrected and mixed and assembled to obtain mixed and assembled contigs, and the third-generation sequencing data are independently assembled to obtain Nanopore contigs; further, the mixed assembly contigs and the Nano-virus contigs are respectively subjected to comparison and annotation, so that candidate virus contigs, non-virus contigs and Nano-virus contigs are obtained, and the candidate virus contigs, the non-virus contigs and the Nano-virus contigs are subjected to comparison and annotation; and finally, carrying out clustering analysis on the three data sets, carrying out further comprehensive analysis according to a clustering result, supplementing missing virus sequences, and correcting a species annotation result to obtain a more sensitive, accurate and comprehensive virus identification result.
Owner:广东美格基因科技有限公司
Production of motif-specific and context-independent antibodies using peptide libraries as antigens
A method is provided for producing motif-specific, context-independent antibodies that recognize a plurality of peptides or proteins within a genome that contain the same post-translationally modified motif. The method includes the step of immunizing a host with a degenerate peptide library antigen featuring (i) a fixed target motif containing one or more invariant amino acids including at least one modified amino acid, and (ii) a plurality of degenerate amino acids flanking the motif. Motif-specific, context-independent antibodies produced by the disclosed method are also provided. The method encompasses motifs consisting of a single modified amino acid, as well as short motifs comprising multiple invariant amino acids including one or more modified amino acids, such as all or part of kinase consensus substrate motifs, protein-protein binding motifs, or other cell signaling motifs. Methods of using the antibodies, e.g. for genome-wide profiling, are also provided.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
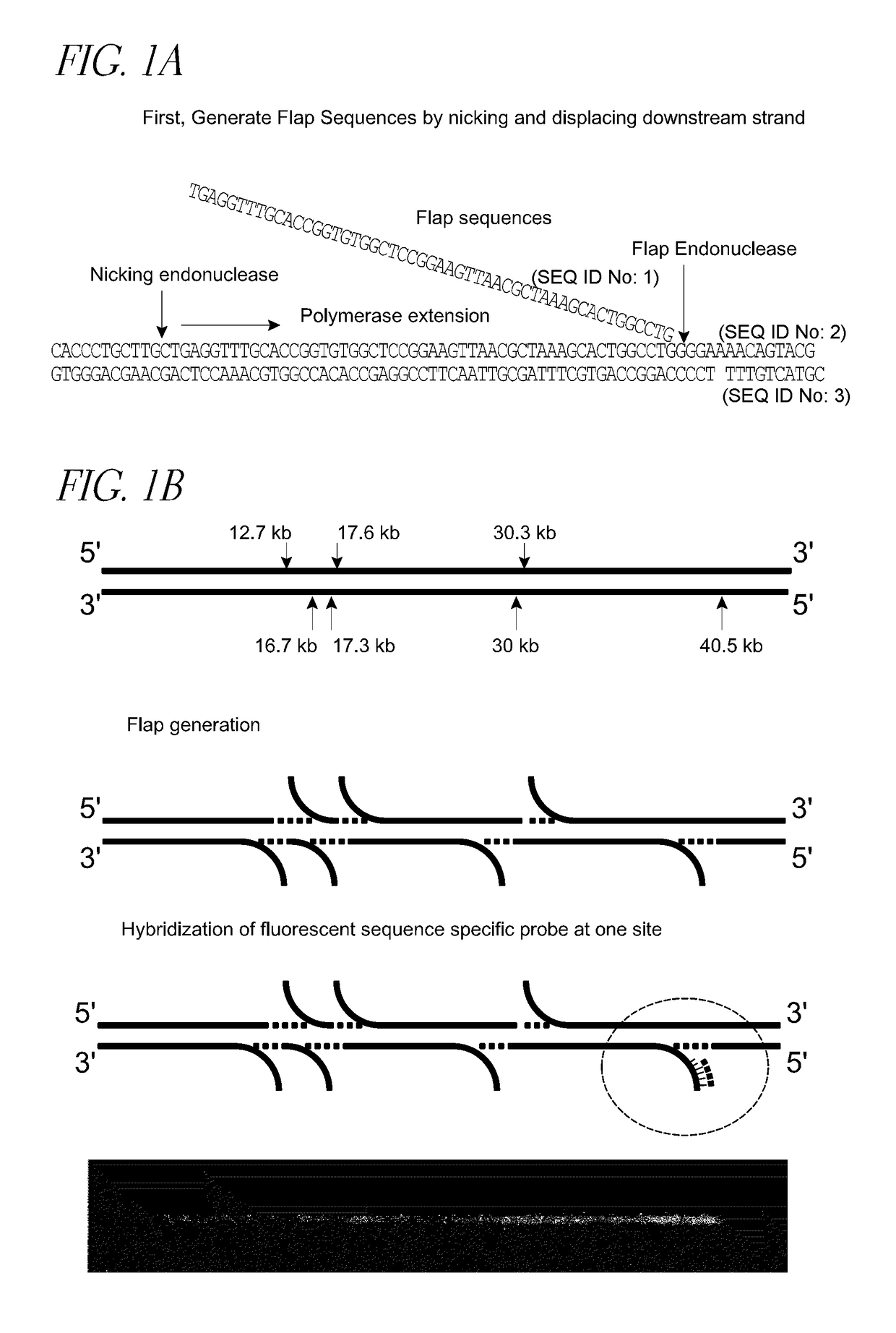
Methods and devices for single-molecule whole genome analysis
Provided are methods and devices for single-molecule genomic analysis. In one embodiment, the methods entail processing a double-stranded nucleic acid and characterizing said nucleic acid. These methods are useful in, e.g. determining structural variations and copy number variations between individuals.
Owner:BIONANO GENOMICS
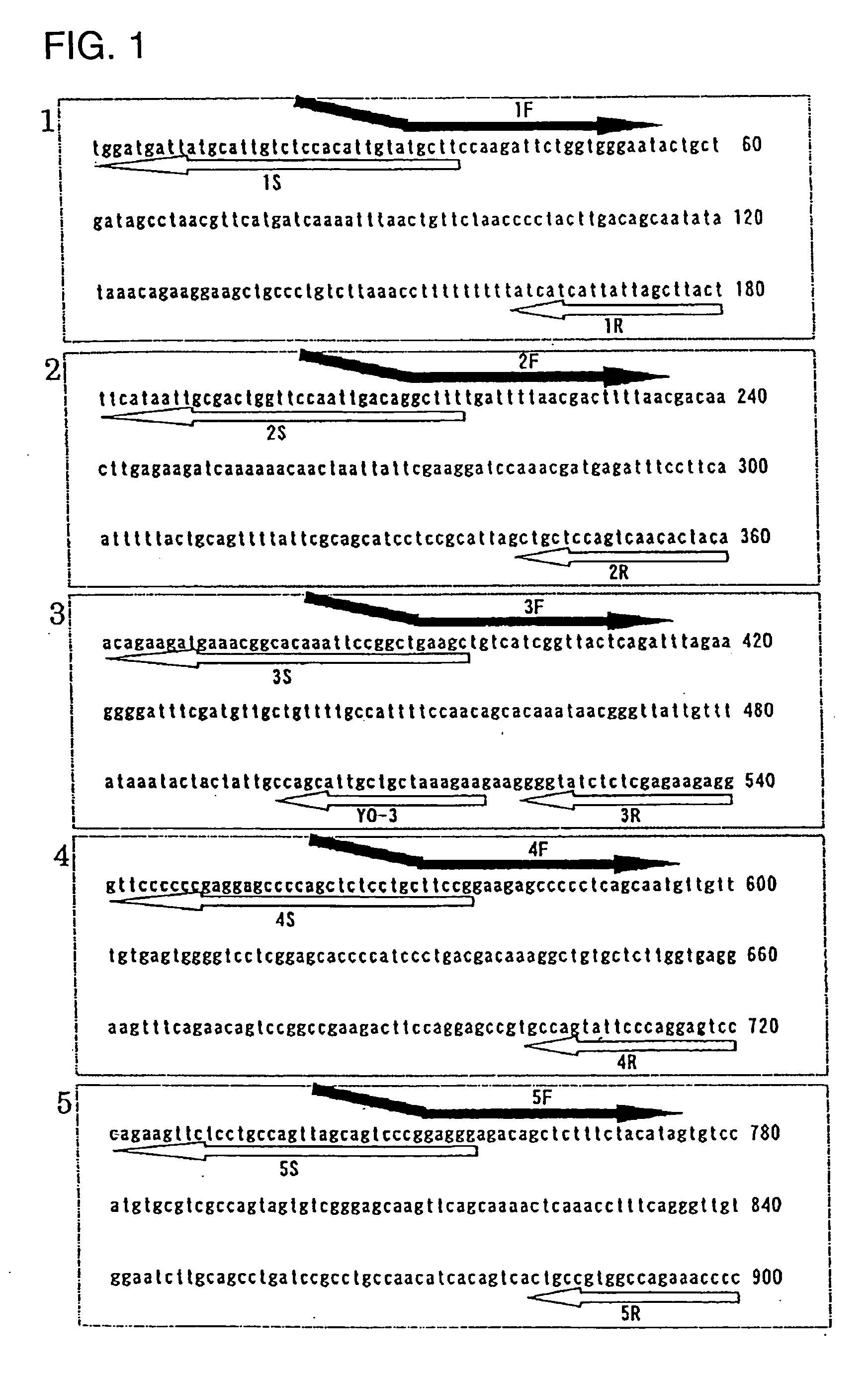
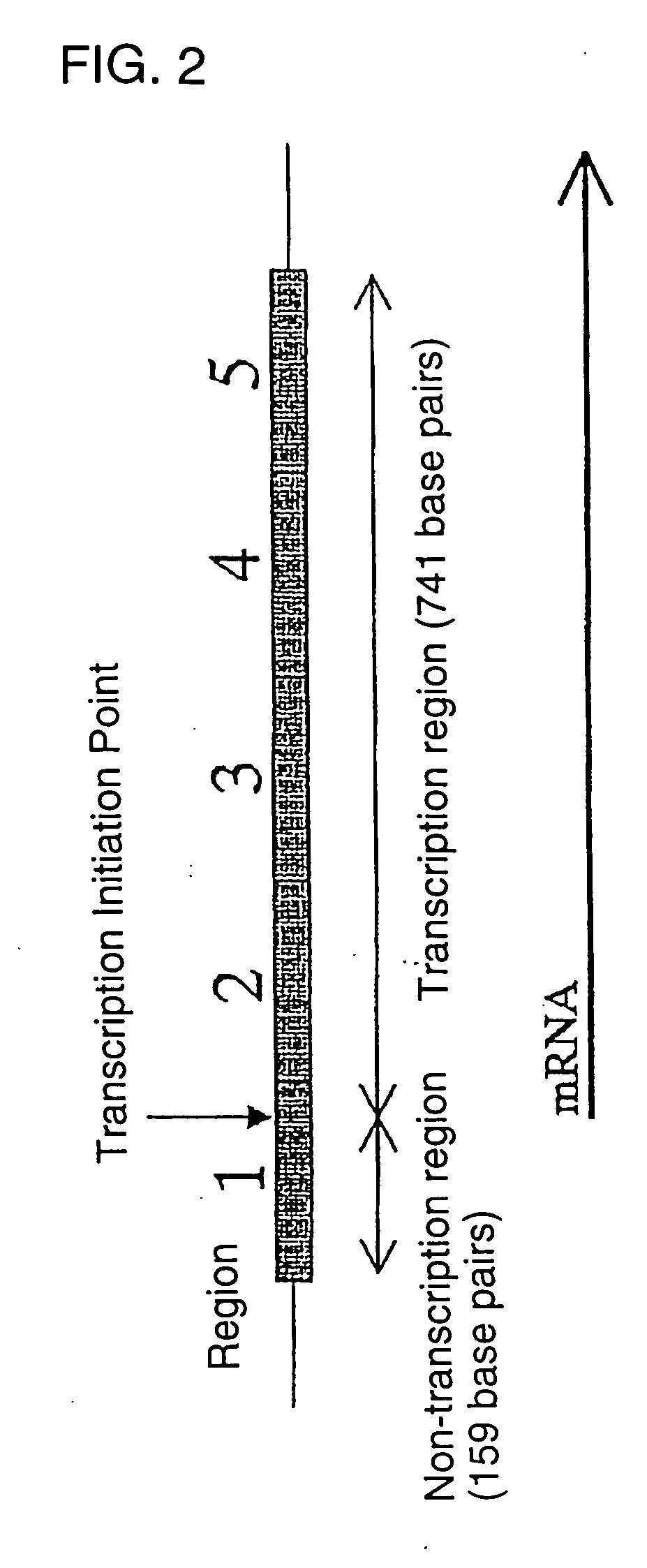
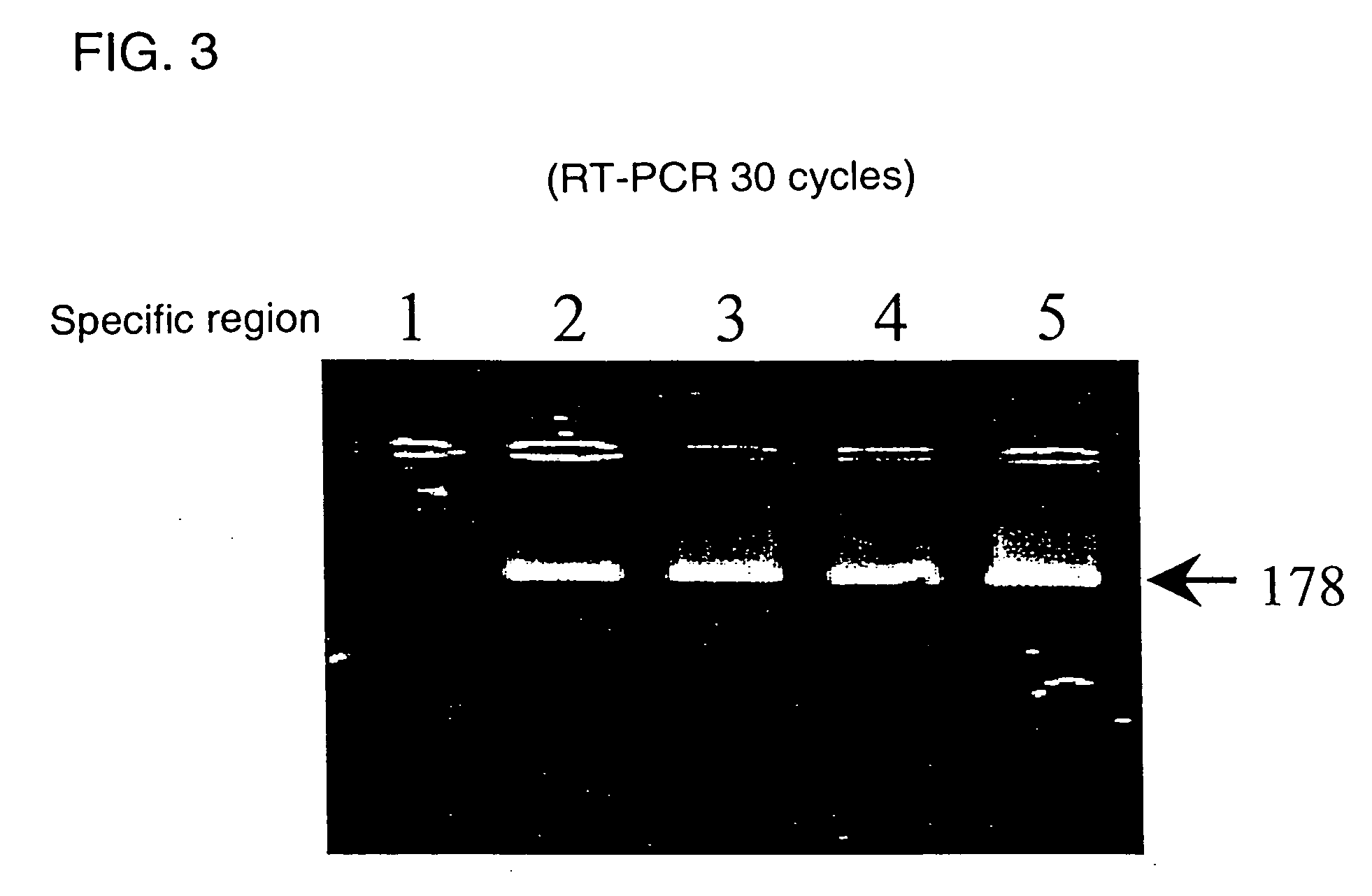
Novel genome analyzing method
InactiveUS20050064486A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
A novel transcriptome analyzing method and to provide a gene found by this method and a protein encoded by the gene. A method for determining whether or not a continued arbitrary DNA sequence existing in the genome of an arbitrary biological species, in which the nucleotide sequence is already known but its possibility of being a gene expression region is unclear (specific region), is the specific region, which comprises detecting whether or not a nucleotide sequence that corresponds to the nucleotide sequence of the region is present in the RNA of the biological species, and a method for determining the gene expression region in an arbitrary region on a genome or the entire genome, which comprises repeatedly carrying out the above method.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
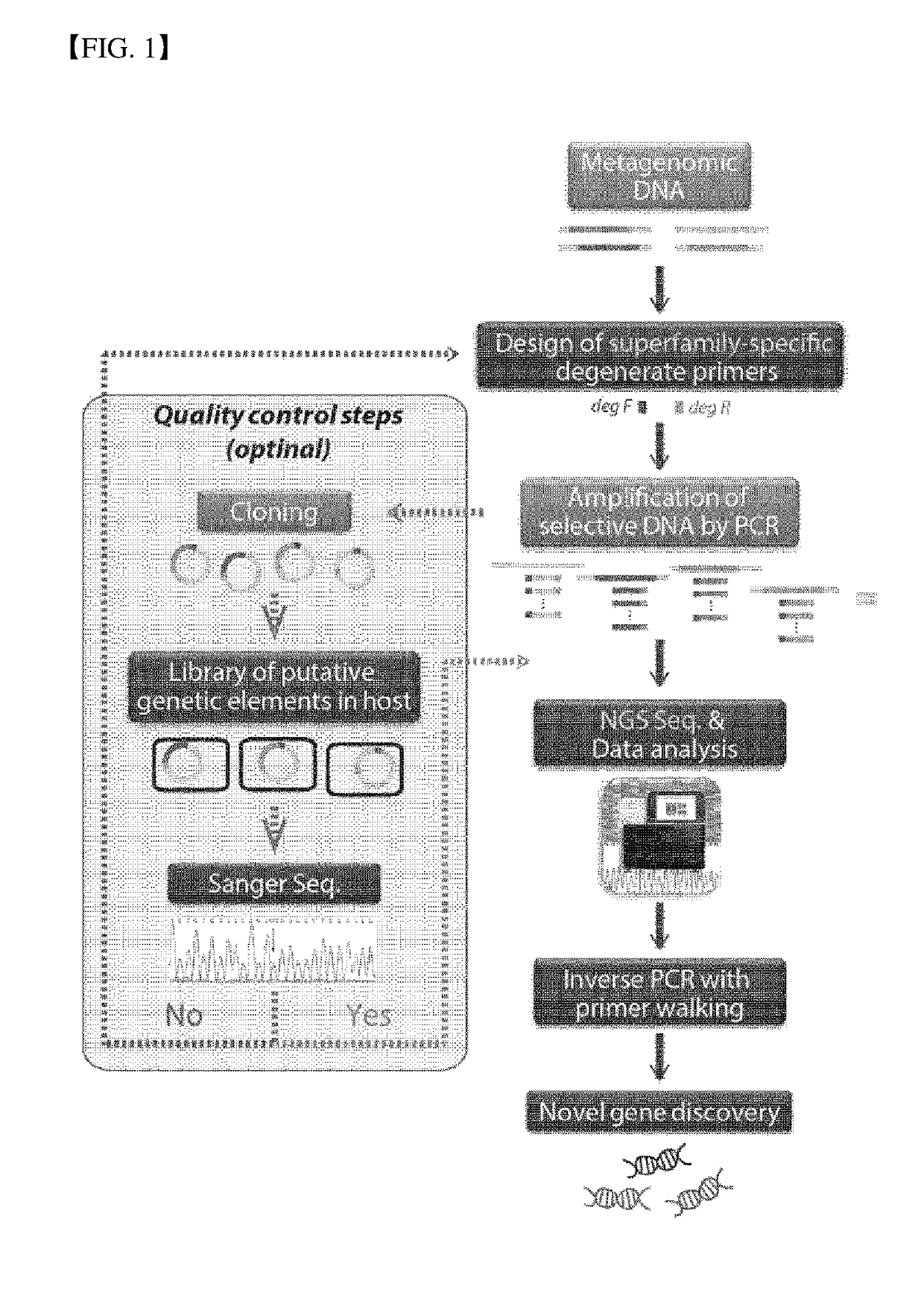
Method for Exploring Useful Genetic Resources Through Bulk Metagenome Analysis and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20180230528A1Quick fixQuickly absenceMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation analysisResource information
The present invention relates to a degenerate primer for analysis of a massive amount of metagenomic information and a method and a kit for analyzing metagenomic information using the same. The method for the metagenomic information analysis and the primer set used for the method according to the present invention can be applied for quickly determining the utility value of a massive amount of metagenome samples. In particular, the superfamily-specific degenerate primer of the present invention is used to quickly detect the presence or absence of the genetic information of the target peptides in the metagenome by a simple method, thereby collecting a large amount of useful peptide resource information from various metagenome samples at high speed. Further, the present invention may be used for screening new peptide genes by designing and producing superfamily-specific degenerate primers of new target peptides based on the method of the present invention. In addition, the method of the present invention can be applied not only to enzymes but also to studies related to polypeptides, oligopeptides, antibiotic resistance genes, antimicrobial peptides, antifungal peptides, oligopeptides, markers, or single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
Owner:LEE IN OK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com