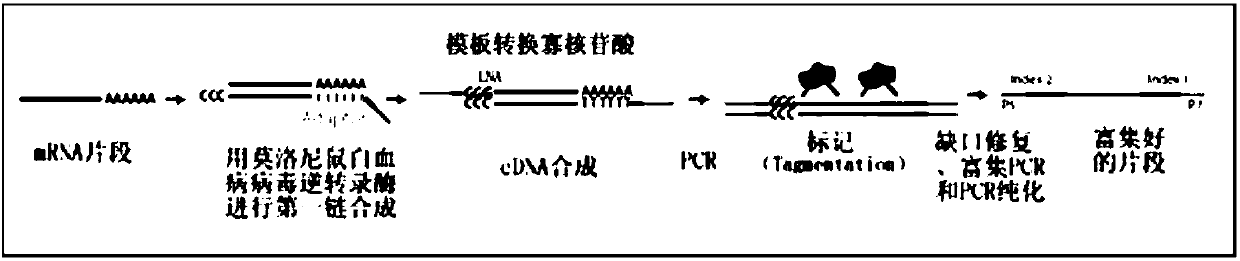
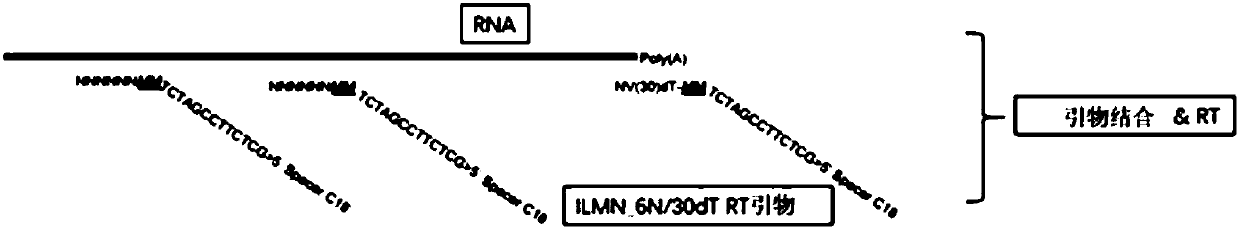
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "DNA Contamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The presence of DNA from a source foreign to the sample being analysed.
Method for making linear, covalently closed DNA constructs
InactiveUS6451563B1Bulking digestionHigh processivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructGenomic DNA
A process to obtain linear double-stranded covalently closed DNA "dumbbell" constructs from plasmids by restriction digest, subsequent ligation with hairpin oligodesoxyribonucleotides, optionally in the presence of restriction enzyme, and a final digestion with endo- and exonucleolytic enzymes that degrade all contaminating polymeric DNA molecules but the desired construct. The invention also provides a process to obtain said dumbbell constructs employing endonuclease class II enzymes. Furthermore, the invention provides a process to obtain linear, covalently closed DNA molecules, such as plasmids, free from contamination by genomic DNA, by submitting the DNA preparation to a facultative endonucleolytic degradation step and an obligatory exonucleolytic degradation step.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG +1
Method of purifying protein
InactiveUS20060142549A1Efficient removalSerum immunoglobulinsColony-stimulating factorActive proteinDNA Contamination
Problems to be Solved: The present invention provides a simpler and less expensive method for purifying physiologically active proteins, especially antibodies, which can ensure removal of impurities such as DNA contaminants and viruses, and which can minimize a loss of physiologically active proteins. Means for Solving the Problems: A method for removing impurities in a physiologically active protein-containing sample, which comprises the following steps: 1) allowing the physiologically active protein-containing sample to be converted into an aqueous solution of low conductivity at a pH below the isoelectric point of the physiologically active protein; and 2) removing the resulting particles.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method for removing DNA contaminants from a protein-containing sample
InactiveUS8420789B2Efficient removalSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsActive proteinDNA Contamination
A method is provided for purifying physiologically active proteins, especially antibodies, in order to remove impurities such as DNA contaminants and viruses with minimal loss of physiologically active proteins. The physiologically active protein is introduced into an aqueous solution of low conductivity at a pH of below the isoelectric point of the physiologically active protein to precipitate impurities as particles. The particles are removed, leaving a purified physiologically active protein.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Protein purification method
InactiveUS20130225796A1Efficient removalSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsActive proteinDNA Contamination
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
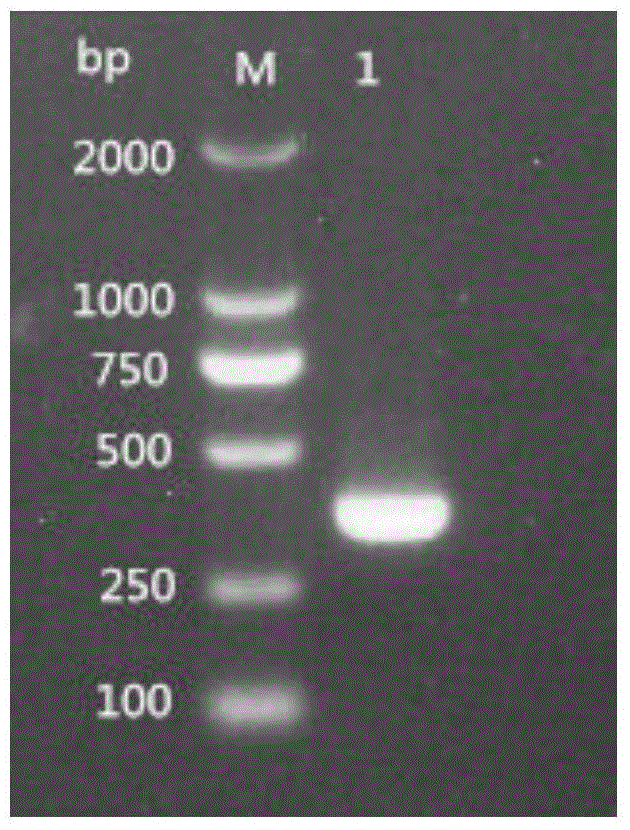
Single-cell RNA (ribonucleic acid) reverse transcription and library construction method
ActiveCN108103055AEfficient and uniform transcriptAvoid pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryTotal rna
The invention belongs to the field of transcriptome analysis and relates to a quick single-cell RNA (ribonucleic acid) reverse transcription and library construction method. According to the method, 20-500ng high-quality full-length double-chain cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) is amplified by taking 1-2000 cells or 10pg-20ng extracted eukaryote total RNA as an initial, and a high-quality cDNA library meeting downstream analysis requirements is obtained. The method effectively avoids 3' preference and genome DNA contamination in a cDNA synthesis process; an expression quantitation molecule label can assist in gene expression quantity calculation; and at the same time, the expression quantitation molecule label can also keep chain source information during complete amplification of RNA sequence information. The method can achieve a reverse transcription and amplification library construction success rate of above 95%; the cDNA library can be connected with an Illumina main stream sequencing platform; lower computer data (5M Reads) can detect gene expression of above 90%; the gene expression consistency exceeds 90%; amplification has no obvious bias; and a required sample input amount is smaller.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Multiplex PCR kit for simultaneously detecting four viruses carried by ruminants
ActiveCN104450966AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDNA ContaminationMultiplex pcrs
The invention discloses a multiplex PCR kit for simultaneously detecting four viruses carried by ruminants. The kit comprises four pairs of specific primers. The experiment proves that bluetongue, foot-and-mouth disease, peste des petits ruminants and vesicular stomatitis virus nucleic acid in clinical samples of ruminants can be simultaneously detected. The kit has the characteristics of high sensitivity, high specificity and simplicity in operation, the detection time can be saved, and the condition that DNA contamination occurs in detection is reduced.
Owner:艾军 +2
Reagents for isolation of purified RNA
ActiveUS20080057560A1Eliminate needEliminate useSugar derivativesHydrolasesOrganic solventPHENOL LIQUID
Compositions and methods to isolate intact RNA that is substantially free of DNA, termed purified RNA. RNA from any source (e.g., human, other animals, plants, viruses, etc.) may be isolated. In one embodiment, the sample is treated with phenol at a pH less than 4.0 and purified RNA is recovered from the aqueous phase. In another embodiment, RNA is precipitated from an acidified sample containing a low volume of an organic solvent. Other embodiments are disclosed. The same inventive composition may be used for several embodiments with pH adjustment. Purified RNA obtained by the inventive method may be used in assays where DNA contamination is undesirable, such as the polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:CHOMCZYNSKI PIOTR
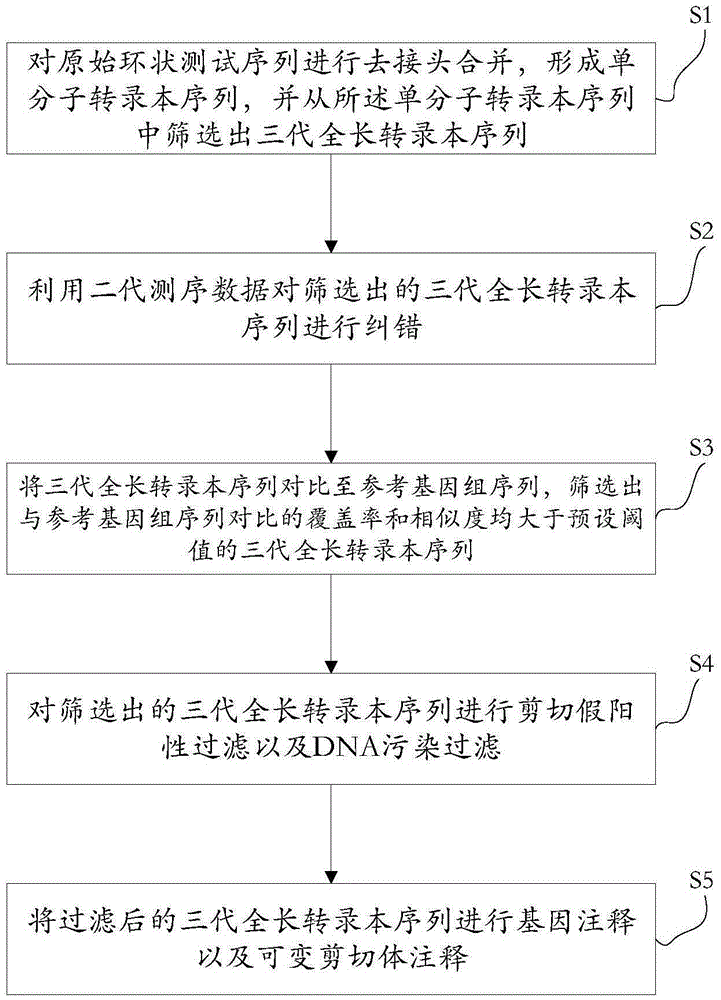
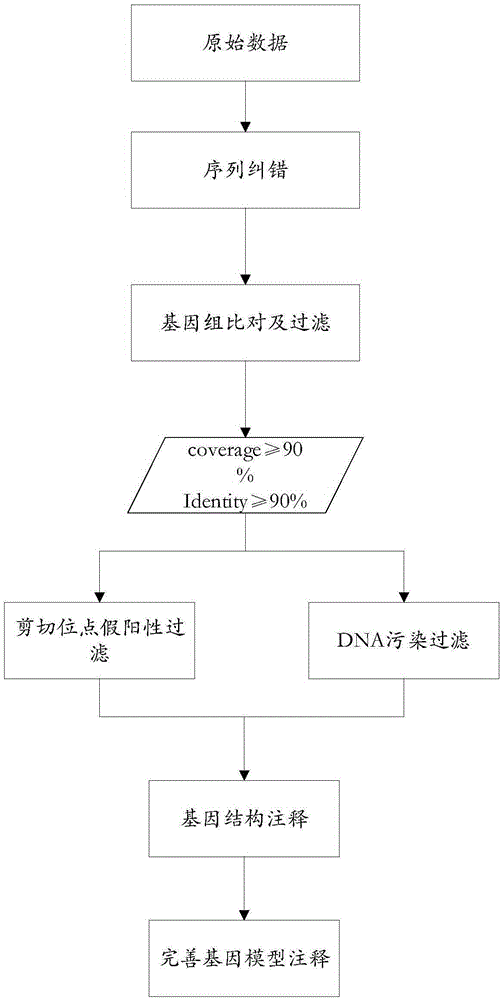
Method for detecting variable spliceosome in third generation full-length transcriptome
ActiveCN105389481AEfficient access to shear structuresPerfect commentSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genome sequenceGene model
The invention discloses a method for detecting a variable spliceosome in a third generation full-length transcriptome. The method comprises the following steps: merging original annular test sequences with joints removed to form a monomolecular transcript sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence; comparing the third generation full-length transcript sequence with a reference genome sequence, and screening a third generation full-length transcript sequence having coverage and similarity with the reference genome sequence larger than preset thresholds; carrying out splicing false positive filtration and DNA contamination filtration on the screened third generation full-length transcript sequence; and carrying out gene annotation and variable spliceosome annotation on the filtered third generation full-length transcript sequence. An overlong read length of a third generation sequencing technology mentioned in the method disclosed by the invention is large enough to cover most RNA, the third generation full-length transcript sequence can be obtained by SMRT sequencing transcriptomes without being assembled, and a splicing structure of a gene can be effectively obtained by third generation transcriptome sequencing, and more perfect gene model annotation can be constructed.
Owner:嘉兴菲沙基因信息有限公司
METHODs OF DETECTION AND QUANTIFICATION OF HOST CELL DNA CONTAMINATION OF PURIFIED PROTEINS
The present invention provides a novel robust, sensitive, reproducible, and accurate method of detecting and quantifying host cell genomic DNA contamination utilizing quantitative real time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR), wherein the qPCR primers are complementary to the highly repetitive host cell genomic DNA sequences, e.g., Alu-equivalent sequences. The present invention is particularly useful for determining the levels of residual genomic DNA in biological products to be administered as therapeutics, e.g., therapeutic proteins.
Owner:WYETH
RNA extraction method by using silicon film pole to adsorb RNA
InactiveCN101367857ANo pollution in the processNo contamination; extraction process can be easily automatedSugar derivativesDNA preparationSodium acetateSodium lactate
The present invention relates to a simple, effective and quick RNA extraction method for absorbing RNA by utilizing a silicon film column. The method includes the following steps: after cells are collected, denaturing solution and chloroform are added into the cells, uniformly mixed and centrifugated until the bacteria solution is divided into three layers in a tube; the top layer of liquid is extracted and transferred into the silicon film column to be centrifugated; the previous step is repeated; centrifugation is conducted again in order to ensure that no liquid exists in the silicon film column; double distilled water and eluent are added into the silicon film column; and after centrifugation, the eluent is collected into a clean centrifugal tube. The denaturing solution contains split agent, RNA extraction agent and water; wherein, the split agent is guanidinium isothiocyanate, sodium dodecyl sarcosinate or phenol; and the RNA extraction agent is sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium lactate, ascorbic acid, potassium malate, sodium oxalate or potassium tartrate. The extraction time of the method is not longer than 6 minutes, DNA pollution cannot be generated, the extraction process can be easily automated, and the purity of the extracted RNA is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
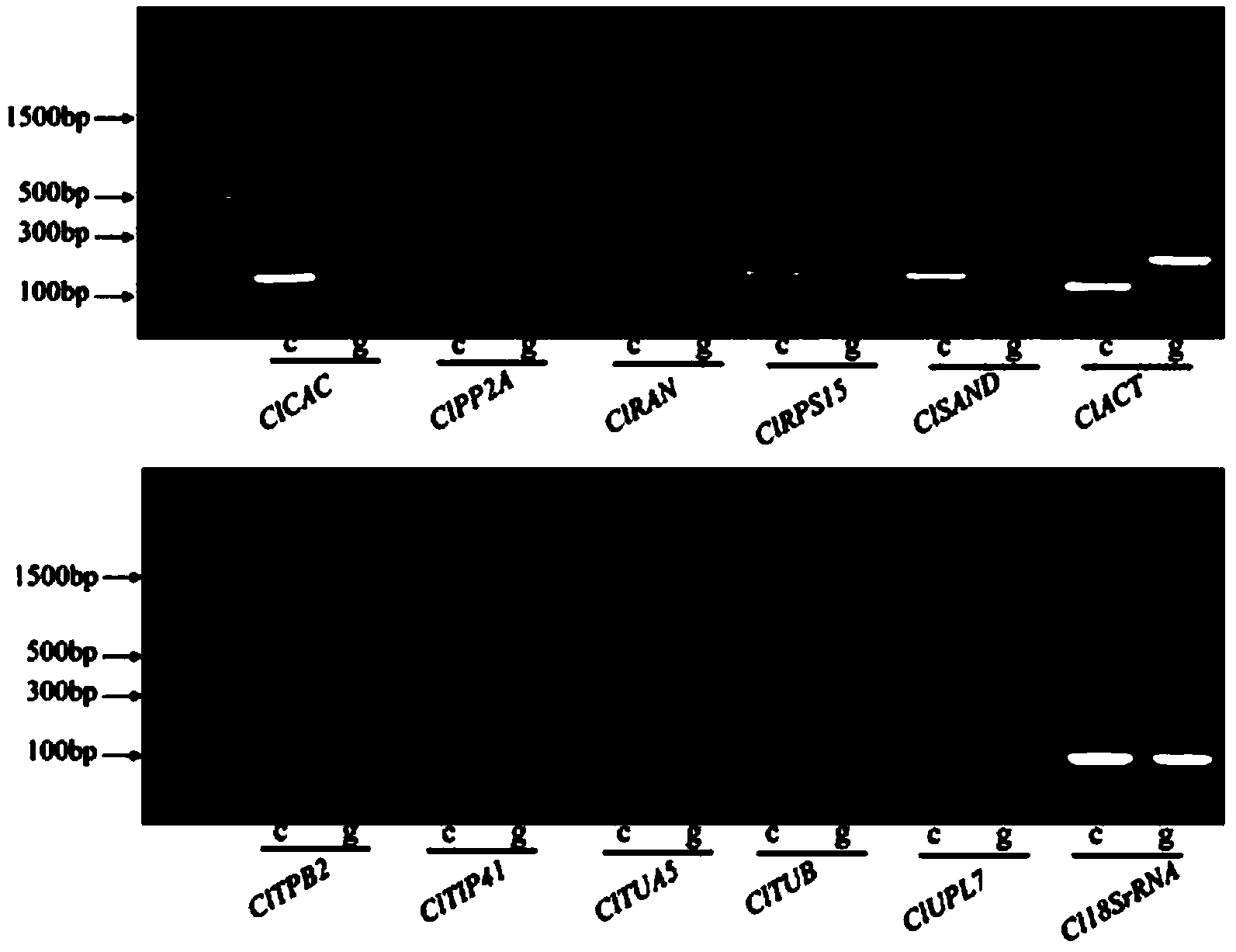
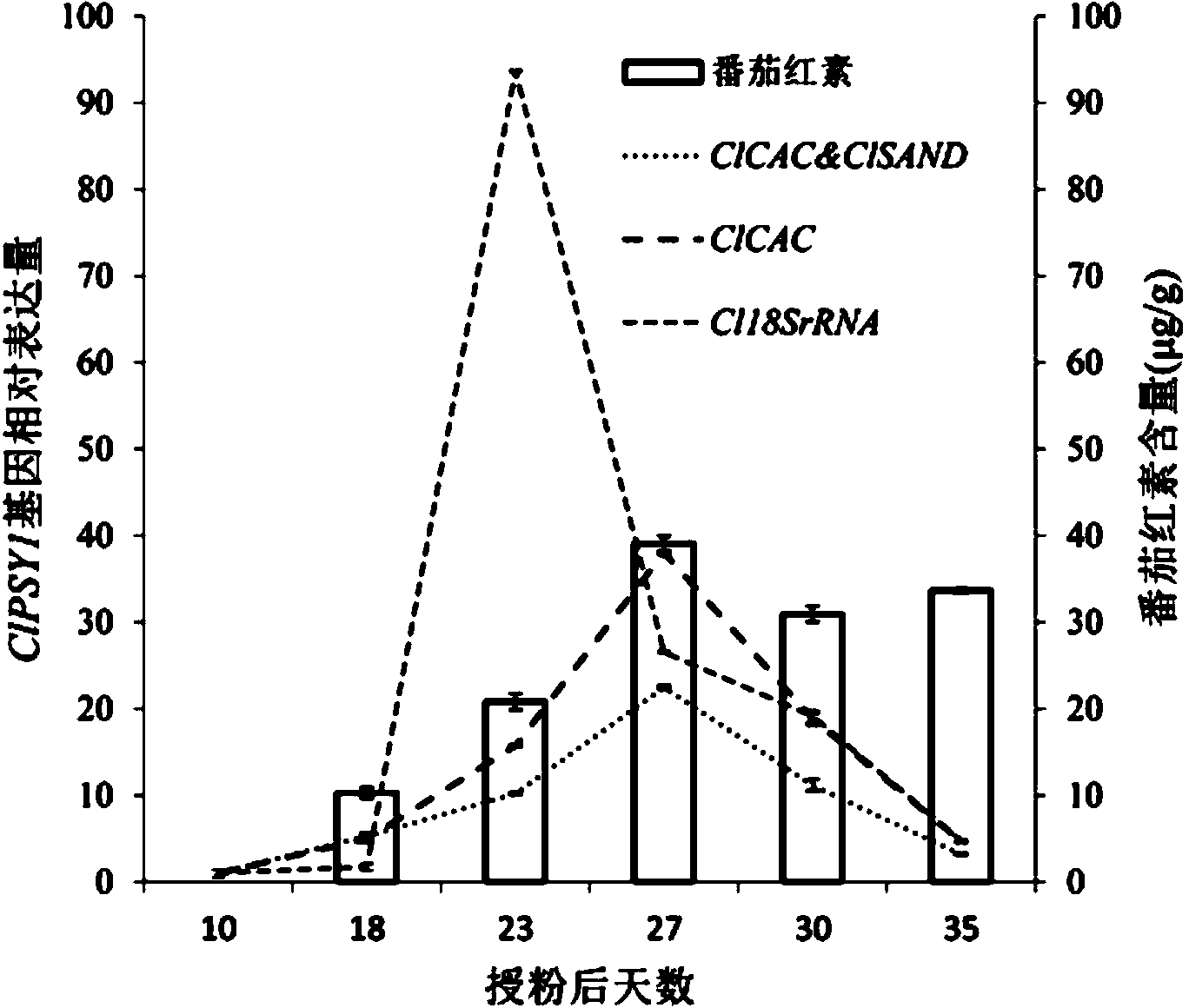
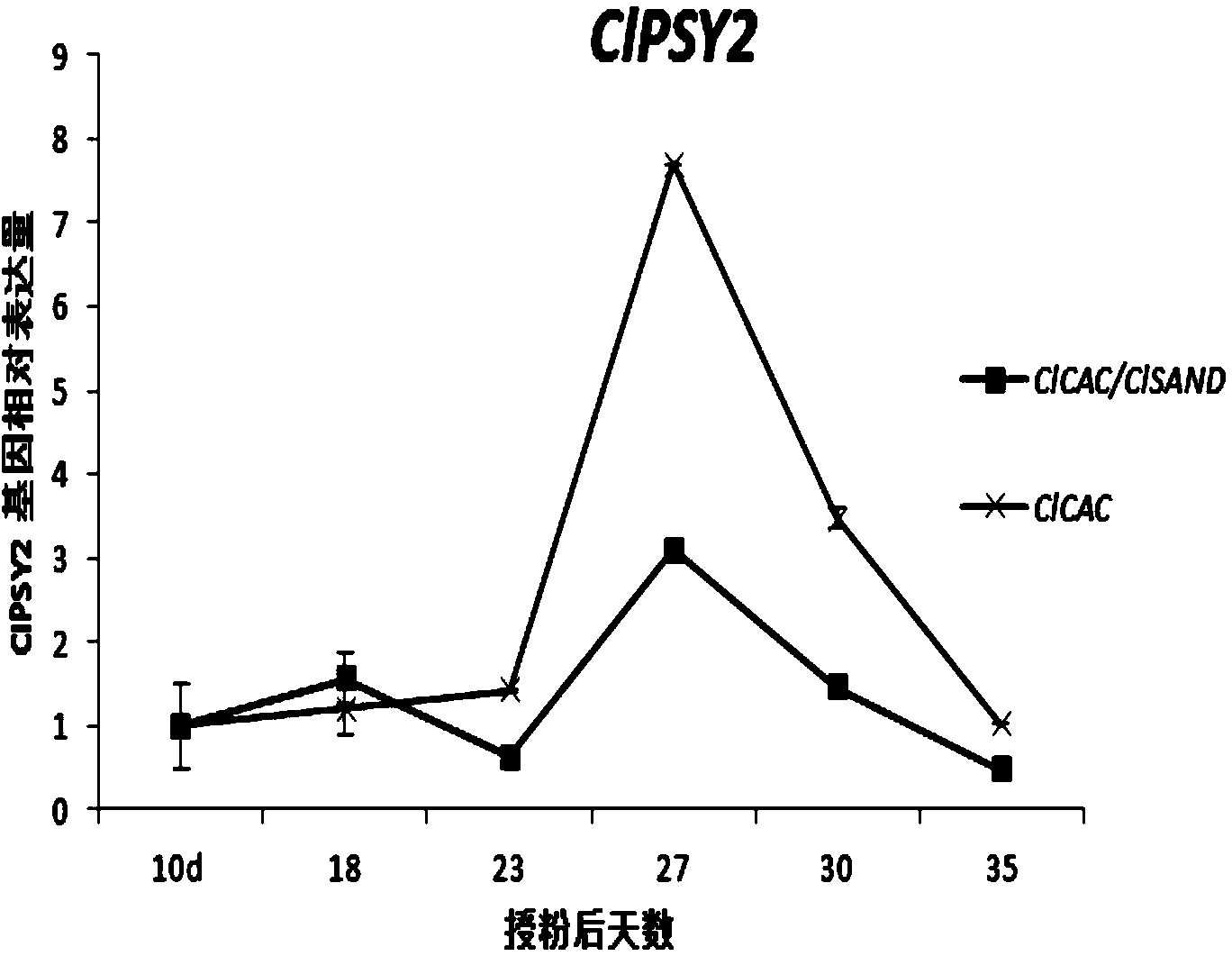
Application of ClCAC gene and ClSAND gene as reference genes in analysis of gene expression of watermelon fruits
InactiveCN104342438AProven reliabilityWide applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceGenotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis of gene expression and particularly relates to application of ClCAC gene and ClSAND gene as reference genes in analysis of gene expression of watermelon fruits. According to the invention, specific primers are designed for ClCAC gene and ClSAND gene. The specific primers cross over joint loci of two exons; no amplification product is generated when a genome DNA is used as a template; a target segment can be obtained through amplification when cDNA is used as a template; the nucleotide sequences of the primers are shown in SEQ ID No.1-4. Real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection shows that both the ClCAC gene and the ClSAND gene can be expressed stably in different development stages of watermelon fruits which are different in gene type and fruit bearing mode and thus the ClCAC gene and the ClSAND gene can be used as a reliable reference gene combination in analysis of gene expression by real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection. The reference gene combination has the advantages of good expression stability and the like and is not influenced no matter whether the genome DNA contamination exists in a cDNA sample or not.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method of isolating purified RNA with reduced DNA contaminations
ActiveUS20130225801A1Reduce amountReduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationOrganic solventWater insoluble
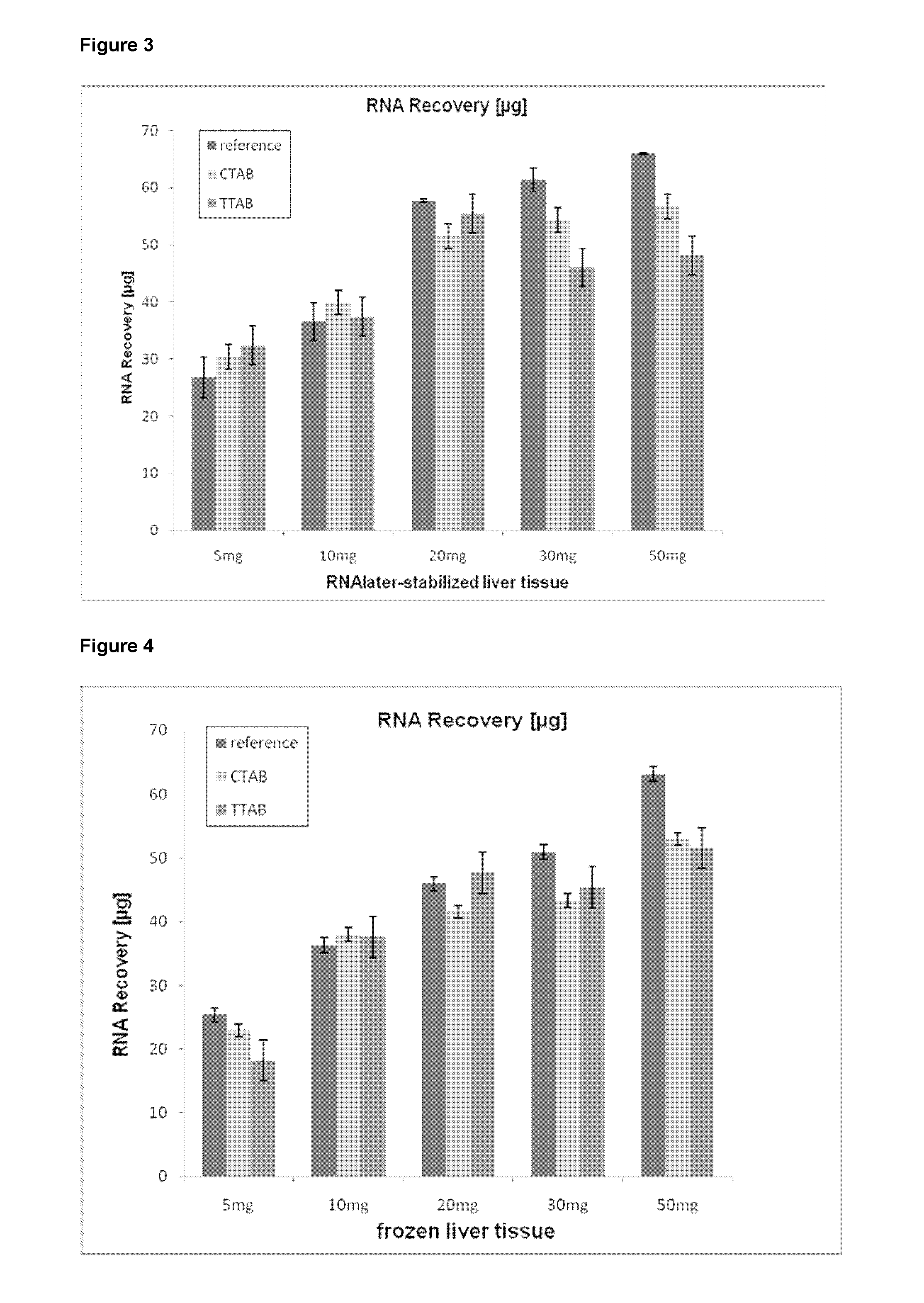
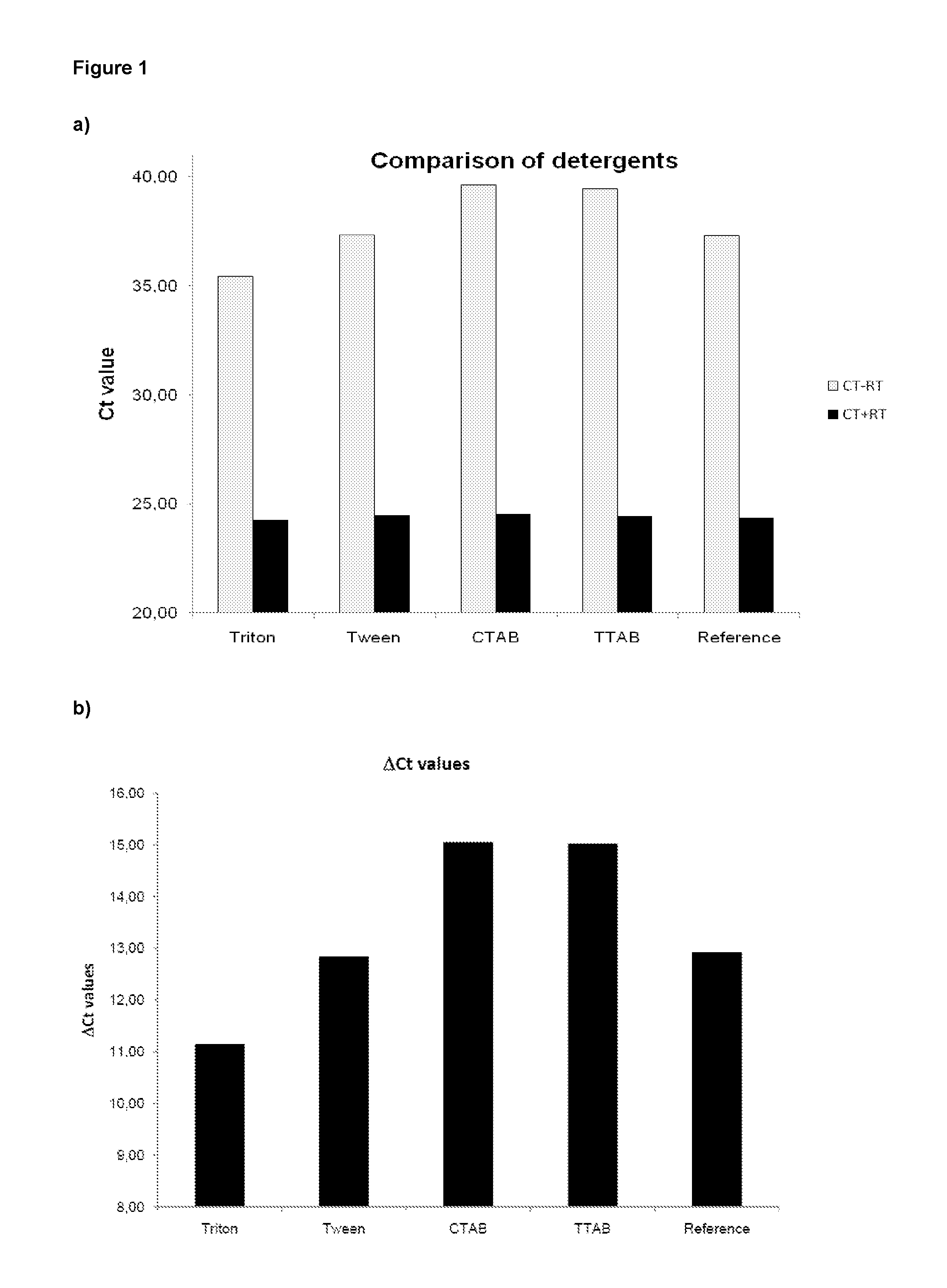
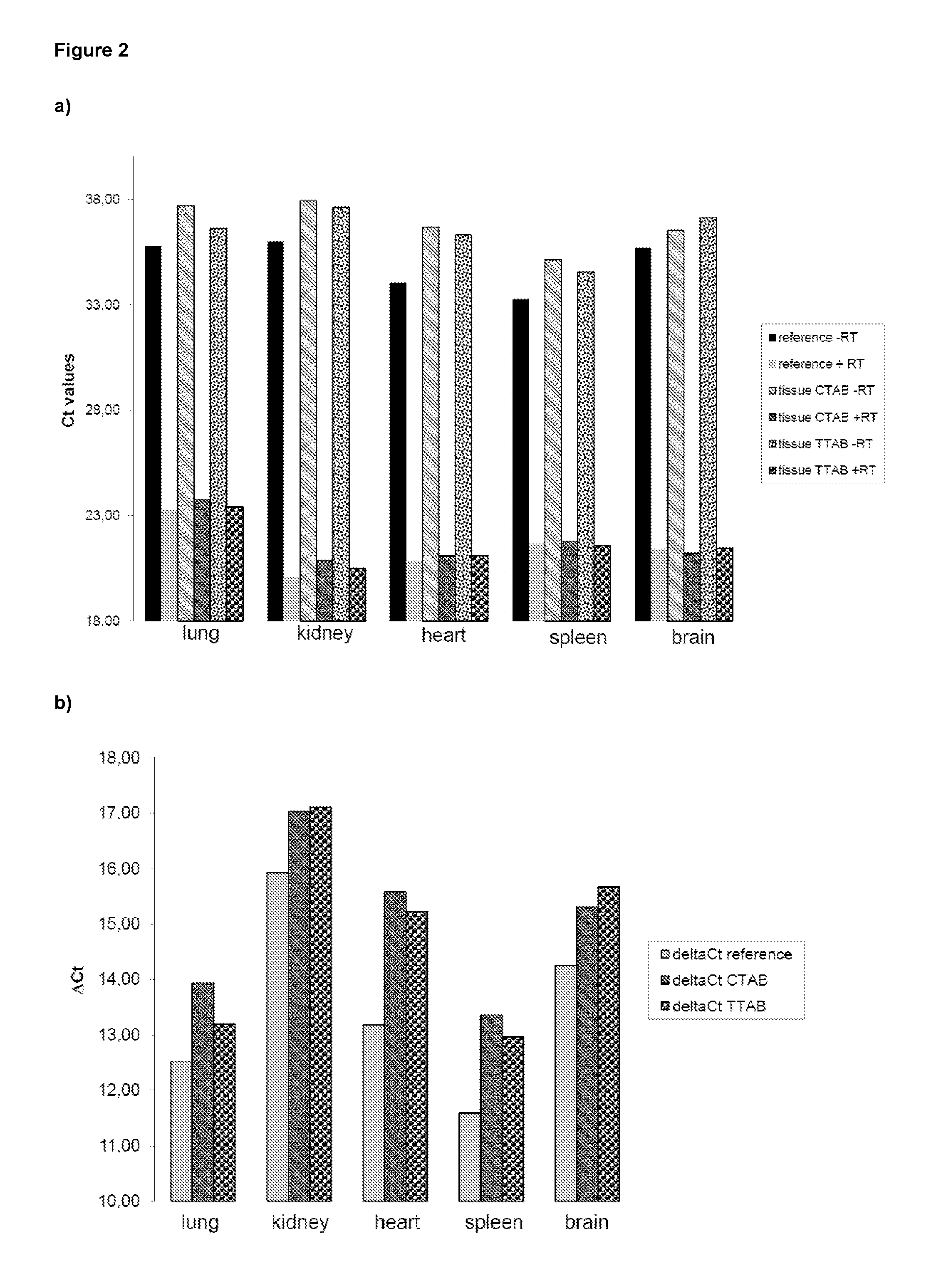
The present invention pertains to a method of isolating RNA from a sample comprising RNA, and DNA, comprising: a) adding an acidic denaturing composition comprising a chaotropic agent and phenol to the sample; b) adding a water-insoluble organic solvent and separating the resulting phases thereby forming a multi-phase mixture comprising an aqueous phase, optionally an interphase and an organic phase, wherein the RNA is concentrated in said aqueous phase and DNA and proteins are concentrated in said organic phase and / or in said interphase; and c) isolating said RNA from said aqueous phase, wherein at least one cationic detergent is added before separating the phases. It was found that the addition of at least one cationic detergent considerably reduces the amount of DNA in the aqueous, RNA containing phase. Therefore, the present invention allows to easily isolate pure RNA which comprises considerably less DNA contaminations.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Bacteriophage genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction kit and method
ActiveCN105567678AMeet the needs of molecular experiments such as sequencingEliminate Interference ProblemsDNA preparationProtein structureDNA Contamination
The invention provides a bacteriophage genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) extraction kit and method. The kit comprises a reagent A (chloroform), a reagent B (DNase I), a reagent C (RNase A), a reagent D (precipitation buffer solution), a reagent E (pyrolysis buffer solution), a reagent F (primary pyrolysis main solution), a reagent G (secondary pyrolysis solution), a reagent H (impurity removal solution), a reagent I (DNA combination buffer solution), a reagent J (rinsing buffer solution) and a reagent K (DNA eluate). The extraction method comprises the following steps: removal of bacterium cells and fragments, degradation of bacterium nucleic acid, bacteriophage particle precipitation, bacteriophage capsid protein structure damage and hydrolysis, impurity removal, DNA liquid separation, DNA adsorption, cleaning of adsorbed DNA and elution of adsorbed DNA. The kit and method can be widely used for extracting the bacteriophage genome DNA, and has the advantages of high extraction speed, high extracted DNA yield and high purity, and the extracted DNA can not be polluted by the host bacterium genome DNA.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting ancient human remains matter DNA
InactiveCN1821265AEfficient removalIncrease template contentPeptide preparation methodsPhenol–chloroform extractionDNA Contamination
The present invention relates to method of extracting ancient human remains matter DNA. The method includes first treating skeleton sample with plasma to decompose the surface pollutant and subsequent DNA extraction. The DNA extraction includes the steps of polishing skeleton sample, hypochloric acid treatment, ultraviolet irradiation, alcohol solution washing to eliminate foreign microbe contamination, Ar / O2 (9:1) plasma treatment, grinding in liquid nitrogen to obtain powder sample; digesting and cracking sample, phenol-chloroform extraction to eliminate digested organic molecule, adsorption with silica adsorption column, and filtering in 3 KDa ultrafiltering centrifugation tube to obtain ancient human remains matter DNA. The method of the present invention can eliminate surface pollutant fast effectively, and has high ancient human remains matter DNA extracting success rate and high template content.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method suitable for rapidly extracting high quality RNA of polysaccharide polyphenol plant tissue
InactiveCN102392017AQuick extractionQuality improvementDNA preparationSecondary metaboliteDNA Contamination
The invention discloses a method suitable for rapidly extracting high quality RNA of polysaccharide polyphenol plant tissue. The method comprises the following steps: preheating a lysate at the temperature of 65 DEG C, adding plant tissue crushed by liquid nitrogen, oscillating and uniformly mixing, and then adding chloroform and isoamyl alcohol according to ratio of 24:1 for extracting; adding a deposition solution to a supernatant, centrifuging and removing the supernatant; adding a heavy suspension for heavy suspension deposition, respectively extracting by phenol water (pH<5.0) and a mixture of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol according to ratio of 24:1, centrifuging and taking the supernatant; adding anhydrous ethyl alcohol for deposition, washing sediment by 75% of ethanol, air-drying and dissolving by RNase free H2O. The present invention has the advantages that: 1, high quality RNA is successfully extracted from plant tissue containing polysaccharides, polyphenols and secondary metabolites; 2, the operation time is short; 3, no DNA pollution is generated. The main components of the lysate employed in the invention comprise CTAB, Tris-HCl, LiCl, EDTA, NaCl and PVP40; the main component of the deposition solution is LICL; the main component of the heavy suspension is NaCl.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
A Method for Parallel Assembly of Multiple Segments of DNA
InactiveCN102296059AImprove efficiencyAvoid pollutionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiological bodyExtracellular
The invention relates to a method for parallel assembly of multi-segment DNA. Choose to insert the circular or linear unit vector into the circular host or linear host to form a gene carrier, and then recover the circular or linear vector to obtain the recombined DNA genetic material. Its characteristic is that it can realize parallel and simultaneous operation of multiple pieces of DNA, thereby improving the efficiency of DNA assembly to form a new DNA structure, and preventing DNA pollution and disproportionation, ensuring the quality of assembled DNA, so that it can achieve the design purpose. The time required to assemble multiple pieces of DNA is approximately proportional to log(N). The assembly operation is carried out outside or inside the cell, so that multiple DNA molecules can be spliced in any order to form a new DNA structure. It is suitable for application in the field of genetic engineering to obtain new organisms through genetic recombination.
Owner:石振宇
Method for identifying and analyzing ancient DNA sample
The invention discloses a method for identifying and analyzing an ancient DNA sample, which comprises a method for acquiring DNA information of a to-be-tested DNA sample, wherein the method for acquiring the DNA information comprises the following steps: building a database for the to-be-tested DNA sample and performing sequencing on the to-be-tested DNA sample, so as to acquire sequencing data; filtering the sequencing data; making comparison on the filtered sequencing data, so as to obtain a comparison result, wherein the comparison result contains the DNA information of the to-be-tested DNAsample, and the comparison allows mispairing of at most four basic groups. With adoption of the method for identifying and analyzing the ancient DNA sample, the DNA information of the ancient DNA sample can be effectively acquired based on the building of the database and the sequencing of the to-be-tested ancient DNA sample; in addition, the information is accurate, is high in reliability and can be used for effectively analyzing genomes of the to-be-tested ancient DNA, such as detection of variation, identification of the ancient DNA, sex determination and assessment on modern DNA contamination rate.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Free DNA blood preservative for preventing hemolysis and applications thereof
InactiveCN109609596AImprove protectionAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCross-linkHemolysis
The invention relates to the technical field of blood sample preservation, and particularly discloses a free DNA blood preservative for preventing hemolysis and applications thereof. Each 100ml of theblood preservative comprises the following ingredients: 40.0-100.0g of imidazolidinyl urea, 4.0-20.0g of EDTA-3K, and 4.0-10.0g of glycine. The blood preservative of the invention can reduce the hemolysis phenomenon of blood cells, thereby reducing the release of genomic DNA which can be mixed with free DNA, protecting the short fragments of plasma free DNA from further degradation, preventing the free DNA from cross-linking with proteins, and providing stable environment for the free DNA. The blood preservative for the free DNA of the invention has a good protective effect on the plasma freeDNA, can prevent genomic DNA contamination, and provides high quality samples for downstream free DNA detection.
Owner:苏州依科赛生物科技股份有限公司
Method for eliminating host DNA contamination for use in viral metagenomic analysis of water environment
InactiveCN108342451AQuality assuranceMeet the needs of follow-up experimentsMicrobiological testing/measurementFiltrationDigestion
The present invention discloses a method for eliminating host DNA contamination for use in viral metagenomic analysis of water environment, belongs to the field of biotechnology, and aims to solve theproblem of a small amount of host cells in a virus concentrate affect sequencing results in the viral metagenomic research of the water environment. The method for viral metagenomic analysis of the water environment is as follows: 1, filtering a water sample through gauze, removing bacteria by a filter column of a filtration system, concentrating, centrifuging, and preparing a virus particle ultra-speed-centrifuge concentrate; 2, adding DNase and RNase working solutions, performing PCR amplification, detecting whether digestion is complete, if the digestion is not complete, adding lysozyme tolyse bacterial cells, continuing digestion, and inactivating nuclease at high temperature to obtain a virus particle concentrate without host genetic material contamination; and 3, amplifying virus whole genome. The sample is treated by the lysozyme for release of DNA of the contaminated bacterial cells, then the DNA is digested by the nuclease, and the operation is simple, and the applicabilityis strong.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Method for extracting total ribonucleic acid (RNA) from bracts and inflorescences of Anthurium andraeanum
The invention discloses a method for extracting total ribonucleic acid (RNA) from bracts and inflorescences of Anthurium andraeanum. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding young and tender bracts and inflorescences of the Anthurium andraeanum by using liquid nitrogen, standing an RNA extracting solution in a water bath at the temperature of 63 to 67 DEG C for 5 to 8min, adding chloroform A in an amount which is one fifth of the volume of the RNA extracting solution, violently shaking for 15 to 20s again, standing for 5 to 8min at room temperature, centrifuging to obtain a supernatant, treating the supernatant by using chloroform and a 8M LiCl solution, and centrifuging to obtain the total RNA of the bracts and the inflorescences of the Anthurium andraeanum. By the method, the using amount of toxic and harmful medicines is furthest reduced, and the hazard of RNA extraction on human bodies is reduced; high-quality RNA which is adequate and pure and is not subjected to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contamination can be obtained; and the method is easy to operate, and a high-quality product is obtained in a short time.
Owner:FLOWERS & PLANTS RES DEV CENT ZHEJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
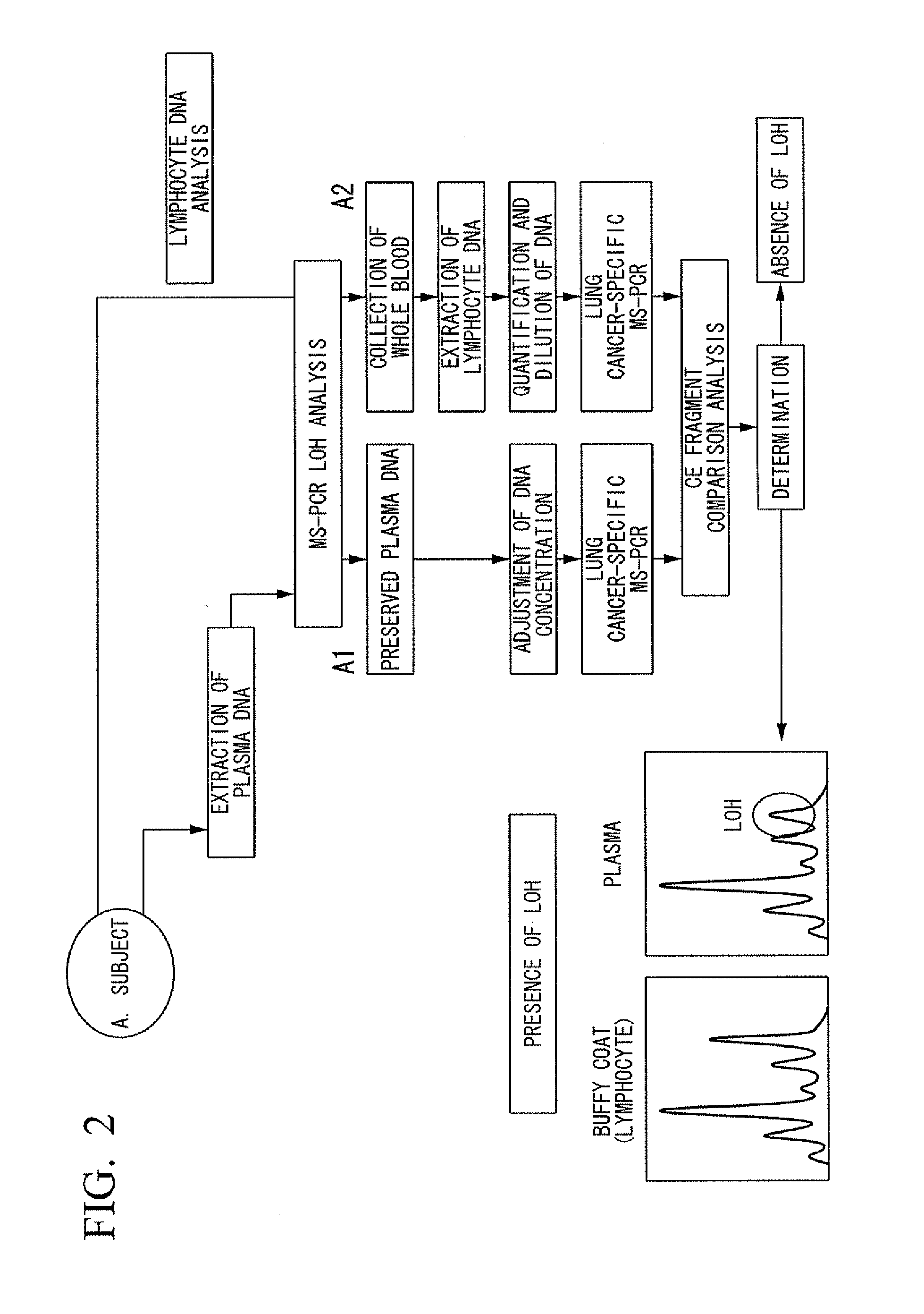
Method for diagnosis of cancer
InactiveUS20100124743A1High precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementIn-vivo testing preparationsCancer cellNormal cell
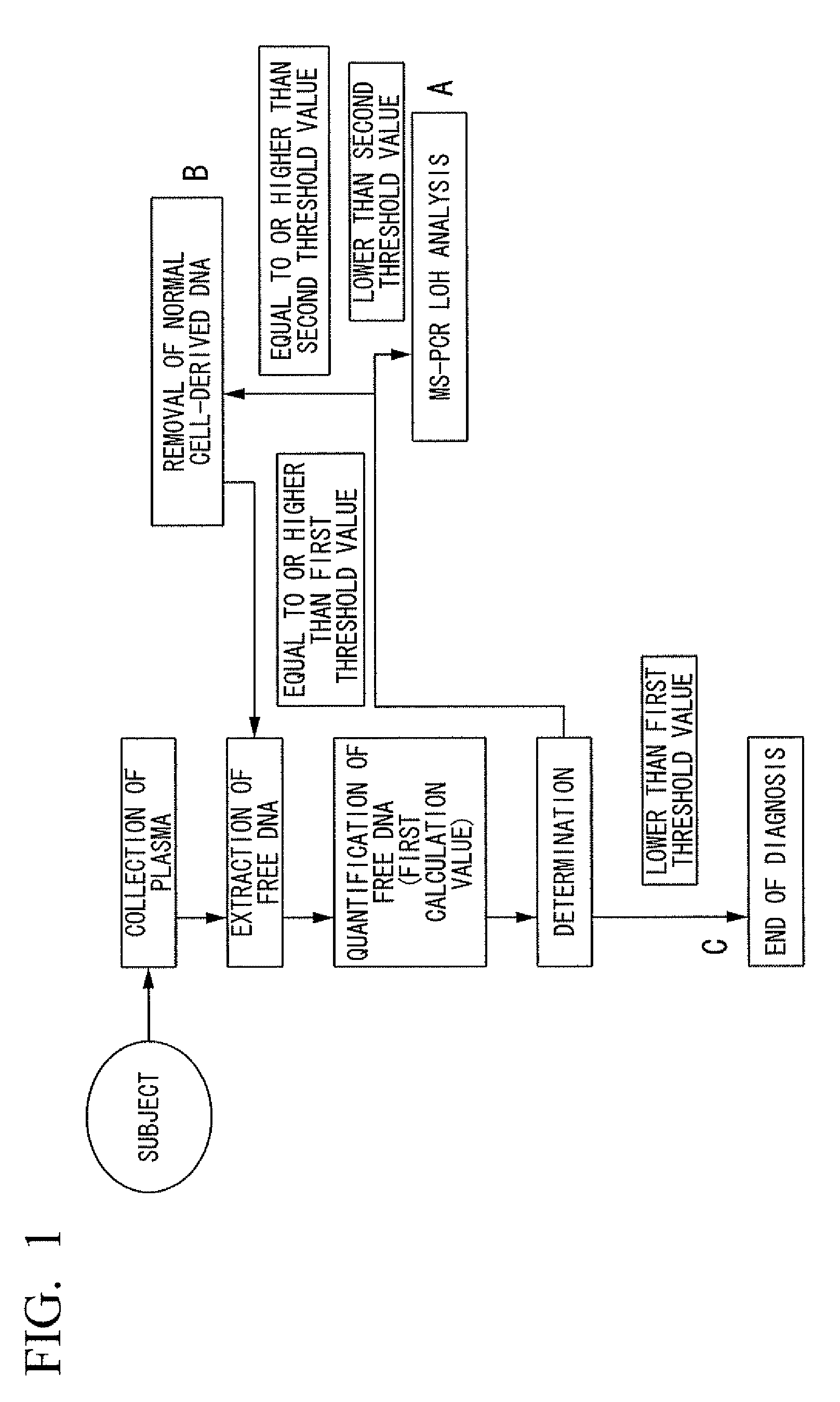
Disclosed is a method for diagnosing cancer with high accuracy through quantification of cancer cell-derived DNA, which comprises the steps of: (1) extracting free DNA from a plasma collected from a test subject; (2) quantifying the extracted free DNA and calculating the free DNA content per unit volume of the plasma to obtain a first calculation value; (3) comparing the first calculation value with a second threshold value which is equal to or higher than a first threshold value; and (4) determining that the test subject is highly unlikely affected by cancer if the first calculation value is lower than the first threshold value, determining that the test subject is likely affected by cancer if the first calculation value is equal to or higher than the first threshold value and lower than the second threshold value, or determining that the plasma used for the quantification is contaminated by normal cell-derived DNA if the first calculation value is equal to or higher than the second threshold value.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
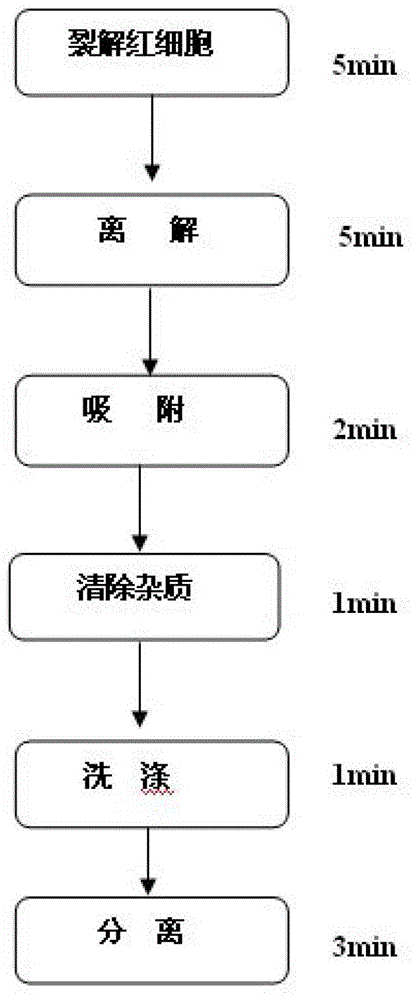
Micro-blood RNA (ribonucleic acid) quick separation method through nucleic acid adsorption
The invention discloses a micro-blood RNA (ribonucleic acid) quick separation method through nucleic acid adsorption. A nucleic acid adsorption centrifuge shield and RNA extraction reagent are used for quickly separating RNA from micro-blood, wherein the RNA extraction reagent consists of red blood cell lysis solution, dissociation solution, removing solution, washing solution and separation solution. The micro-blood RNA quick separation method through nucleic acid adsorption has the advantages that the method is simple and convenient to operate, the time is short, the sampled quantity is small, the purity of the extracted RNA is high, the RNA is not polluted by protein and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the superiority to the traditional blood RNA extraction method is shown, and application values of clinical popularization of the method for disease diagnoses and researches are further represented.
Owner:西安交通大学口腔医院
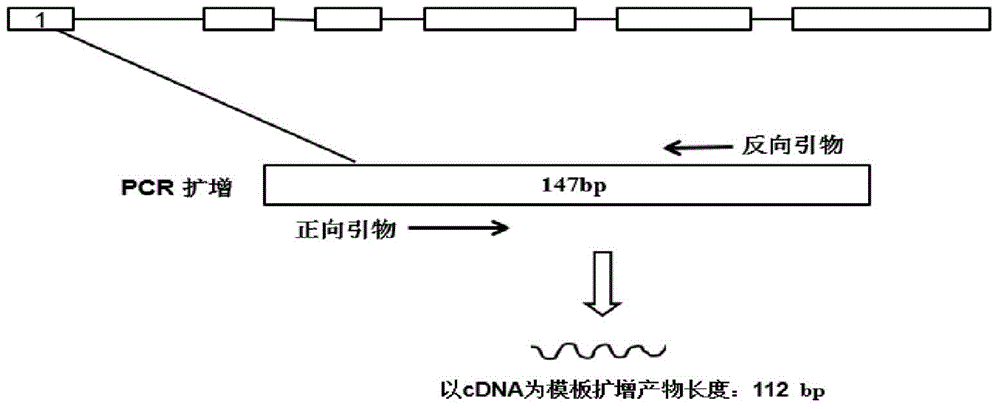
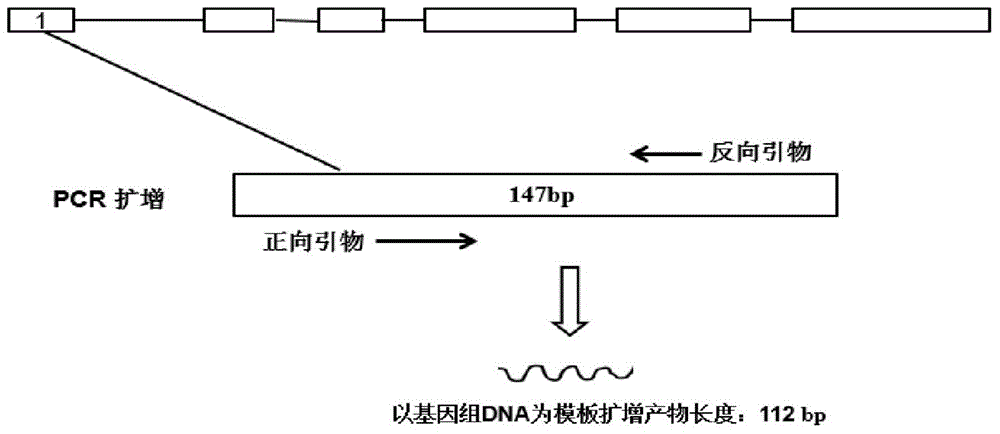
Method for detecting whether genome DNA contamination exists in cDNA sample of watermelon
InactiveCN105219861AReduce testing costsHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA ContaminationExon
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene expression analysis and discloses a method for detecting whether genome DNA contamination exists in a cDNA sample during watermelon gene expression analysis. The principle of the method is as follows: according to structure and sequence information of genes, forward and reverse primers are designed respectively on two adjacent exons, so that amplification products on a genome DNA template are larger than those on a cDNA template. According to the principle, specific primers of molecular chaperone DnaJ protein gene DNAJ widely existing in a watermelon are designed, the cDNA sample is taken as a template, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed by the aid of the primer pair, if amplification products larger than 87bp appear, the phenomenon indicates that the genome DNA contamination exists in the cDNA sample, and if only amplification products of 87bp appear, the phenomenon indicates that no genome DNA contamination exists in the cDNA sample. With the adoption of the method, the accuracy of watermelon gene expression analysis with technologies of real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR and the like can be further improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Microsatellite instability detection method
InactiveCN107475442AHigh precisionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisDNA Contamination
The invention discloses a microsatellite instability detection method, and belongs to the field of molecular diagnosis. The method used for detecting colorectal cancer microsatellite instability is invented based on multiplex fluorescent PCR technology and capillary electrophoresis technology. According to the method, a first primer pair represented by SEQ ID NO.1-2, a second primer pair represented by SEQ ID NO.3-4, a third primer pair represented by SEQ ID NO.5-6, a fourth primer pair represented by SEQ ID NO.7-8, and a fifth primer pair represented by SEQ ID NO.9-10 are used for multiplex fluorescent PCR and detection of five microsatellite points BAT-25, BAT-26, D2S123, D5S346, and D17S250. The sensitivity and the precision are higher; detection of internal reference microsatellite point Penta C is introduced to eliminate foreign DNA pollution in samples to be detected, and the credibility of obtained results is increased.
Owner:生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司
Zinc-copper superoxide dismutase SOD1 expression amount molecular detection method and primer
ActiveCN105177123AGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerDNA Contamination
The invention relates to a zinc-copper superoxide dismutase SOD1 expression amount molecular detection method and a primer used in the method. The forward primer sequence is represented by the sequence 1, and the reverse primer sequence is represented by the sequence 2. According to the provided molecular detection method, a qPCR method is adopted for the first time, the content of SOD1 is detected in the gene level; at the same time, a set of targeting primer sequences and inner reference sequences is provided; even if the RNA extracted from a sample is polluted by DNA, the difference of expression amount of SOD1 gene in different human tissues and cells can be stably, specifically, and precisely detected, moreover, the repeatability is extremely high, and solved are the problems that the commonly-used enzyme activity detection kit can be badly influenced by artificial factors, and the stability and repeatability of the kit are both very bad.
Owner:TIANJIN KANGTING BIOLOGICAL ENG GRP CO LTD
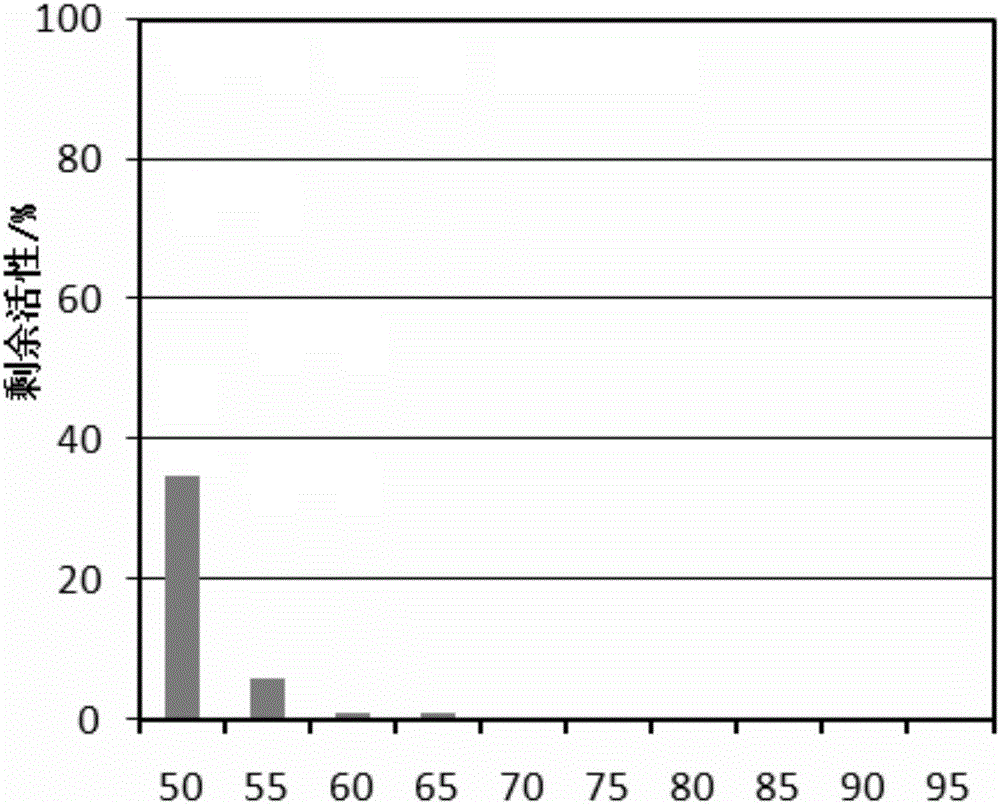
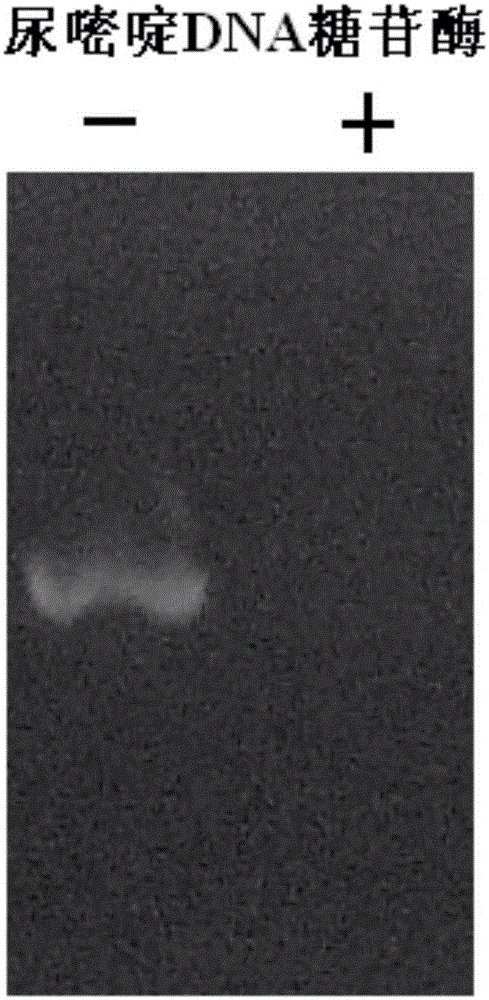
Preparation method and application of uracil DNA glycosidase
InactiveCN106754823AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorNucleic acid testHeat sensitive
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of uracil DNA glycosidase. The uracil DNA glycosidase prepared by using the method can be used for hydrolyze glucosidic bonds between uracil basic groups and deoxyriboses in DNA at the temperature of 20-37 DEG C; at the same time the glycosidase has a good heat sensitivity, when the temperature is higher than 60 DEG C, the glycosidase swiftly loses activeness, when the temperature reaches 60 DEG C for 5 minutes, the enzymatic activity loses by 99%; the prepared heat sensitive uracil DNA glycosidase can be used for preventing the sample DNA contamination in all types of nucleic acid detection reaction. The preparation method and application of uracil DNA glycosidase have the advantages being capable of both completely removing the contaminated DNA, and exerting no inhibition to the nucleic acid amplified reaction. The glycosidase can be used as a cleaning agent to the sample contamination in all types of nucleic acid amplified reaction (such as PCR), can remove the DNA contamination caused by the products of the previous amplified reaction, and increase the accuracy of nucleic acid test.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
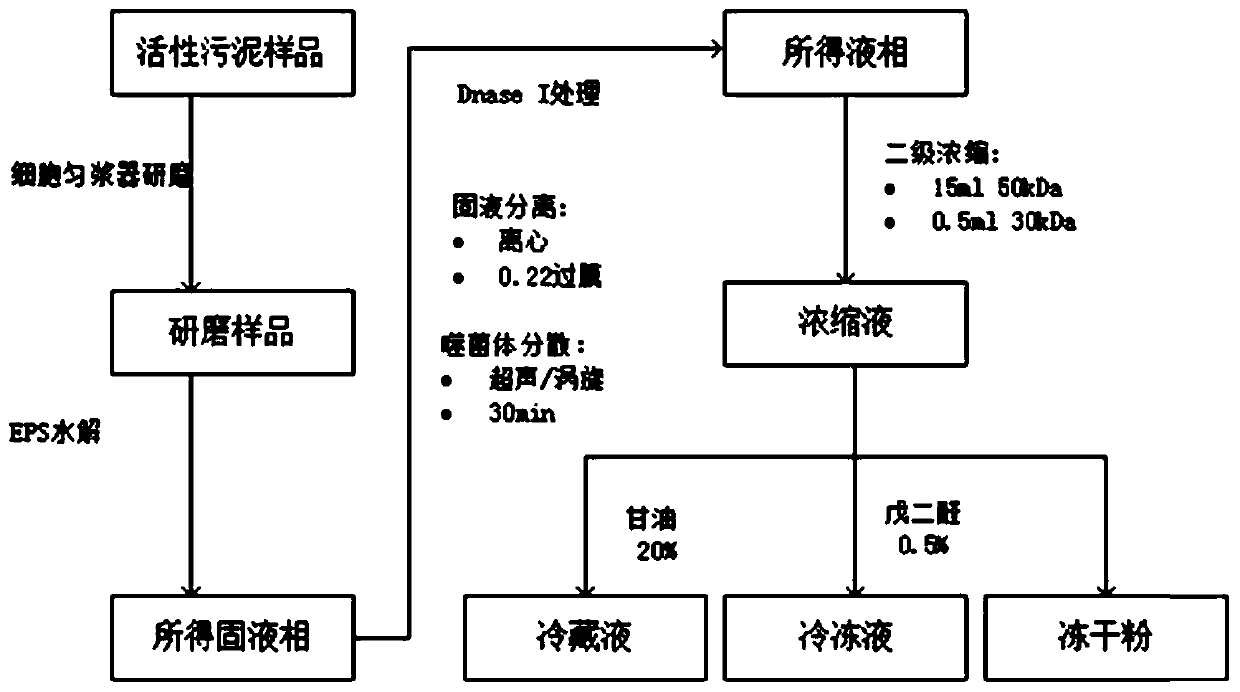
Method for extracting and enriching phage from activated sludge
ActiveCN109810951AReduce dosageShort operating timeViruses/bacteriophagesActivated sludgeUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for extracting and enriching a phage from aerobic granular sludge. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sludge grinding; (2) extracellular polymeric substancehydrolysis; (3) ultrasonic / vortex oscillation; (5) supernatant extraction; (5) secondary ultrafiltration concentration; and (6) sample preservation and fixation. The method is simple and convenient to operate, the reaction condition is mild, no toxic reagent is used, the problems that a granule sludge system is low in extraction efficiency due to EPS (extracellular polymeric substance) wrapping,and baterial cell lysis causes host DNA pollution are solved, and the method is an efficient and feasible phage extracting method. Compared with a traditional method for purifying a phage through combination of PEG and salting out, medicaments such as PEG and NaCl is not required to be used, the purifying time is shortened to about 6 h from orginal 24 h; and the obtained sample is low in salt concentration, further dialysis and desalting are not needed, and the obtained concentrated solution can be directly used for related operations such as a transmission electron microscope, DNA extraction,CsCl2 gradient centrifugation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reagent kit and method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) methylation and application
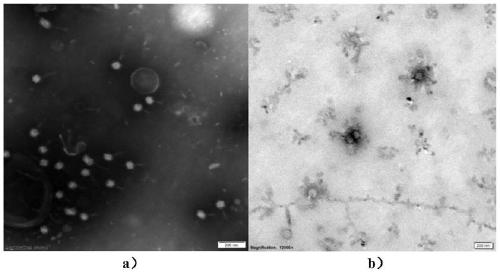
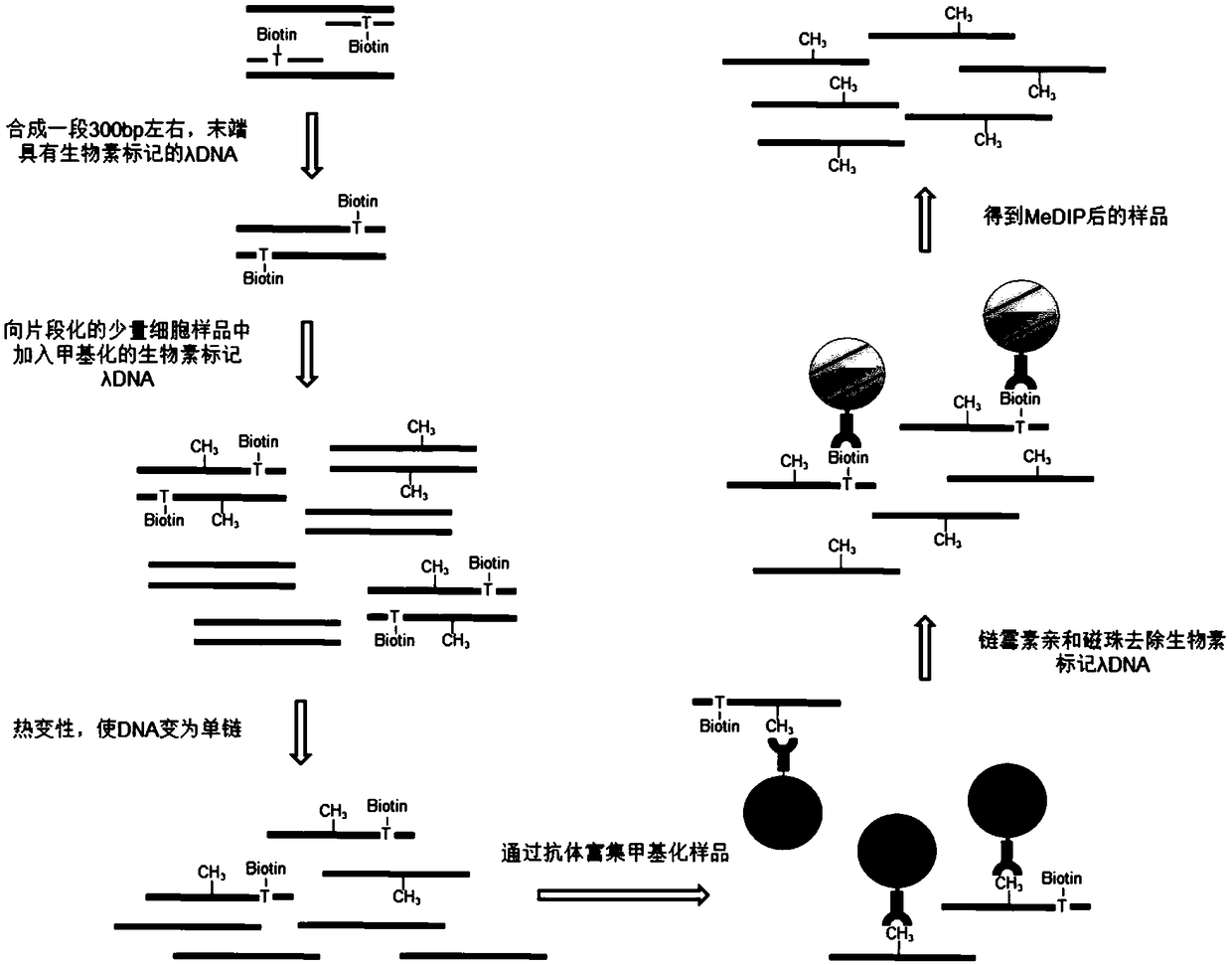
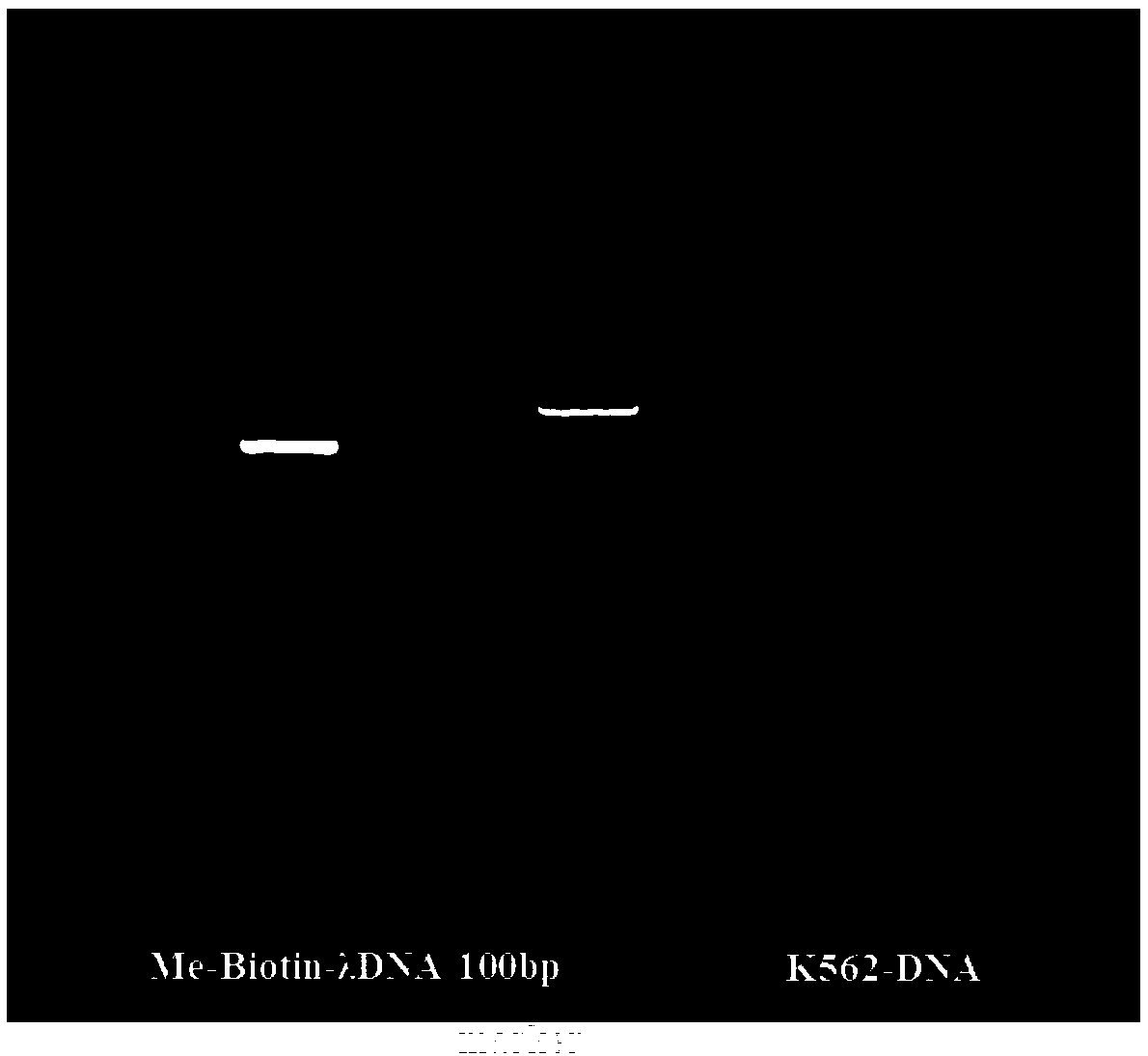
ActiveCN108796039AImprove binding efficiencyReduce lossMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationExogenous DNA
The invention discloses a reagent kit for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) methylation. The reagent kit at least comprises biotin-labeled methylated lambda-DNA and streptomycin-enveloped magneticbeads. The invention further discloses application of the reagent kit to detecting methylation of a few DNA samples and a method for detecting the DNA methylation and application of the method. The low sample amount can reach 1 ng. According to the technical scheme, the reagent kit, the application and the method have the advantages that the lowermost initial sample amount required for detectingthe DNA methylation can be obviously lowered, specific reagent kits and experimental equipment can be omitted, accordingly, the cost can be saved, and the reagent kit and the method are high in universality; exogenous DNA pollution can be prevented when methylated DNA is enriched, influence of exogenous DNA information can be prevented if processes for detecting the DNA methylation by means of library construction and high-throughput sequencing are adopted, accordingly, the reagent kit and the method are favorable for further reducing the sequencing cost, and the quality of data can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
RT-PCR method integrated with restriction endonuclease removal of DNA pollution
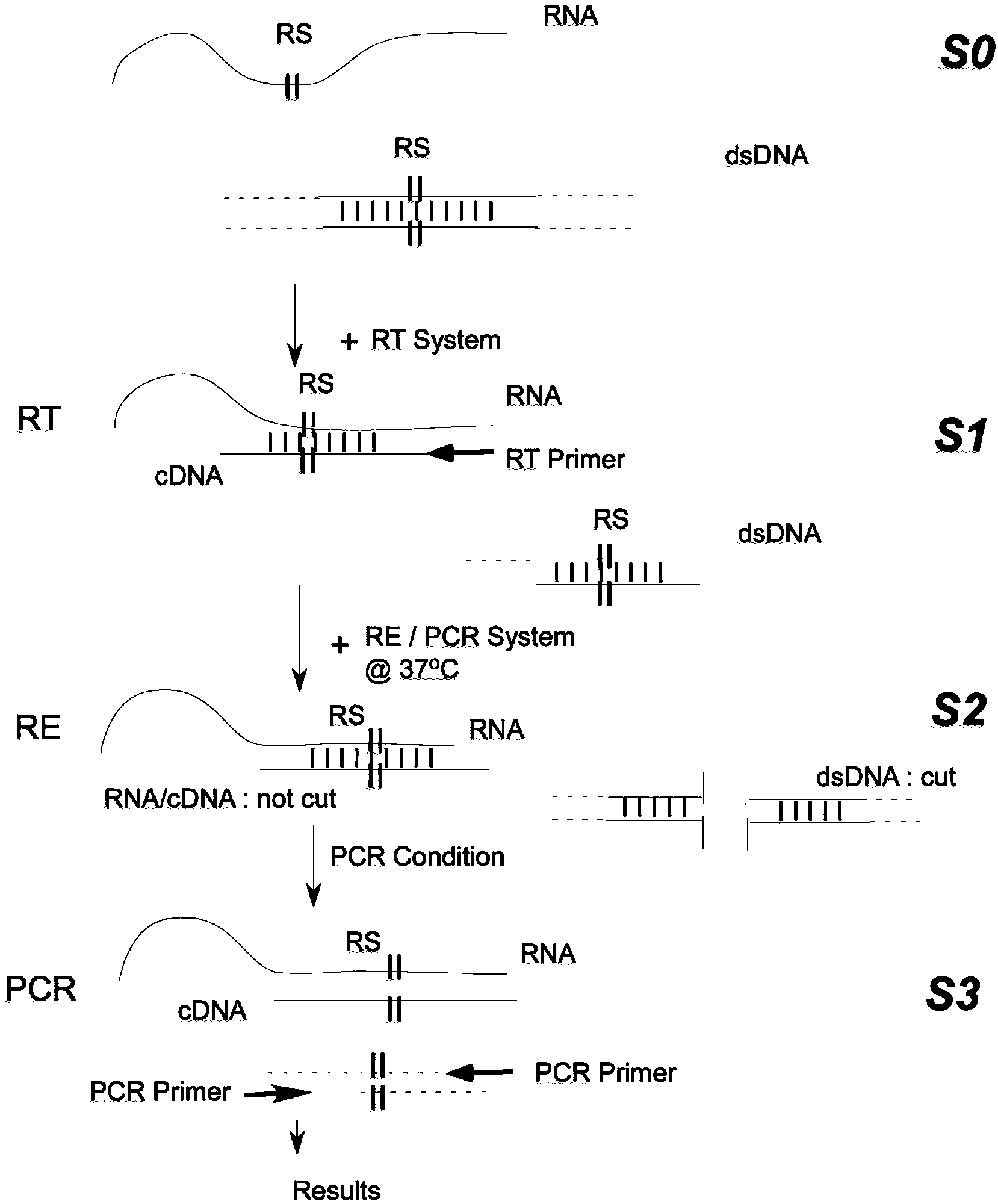
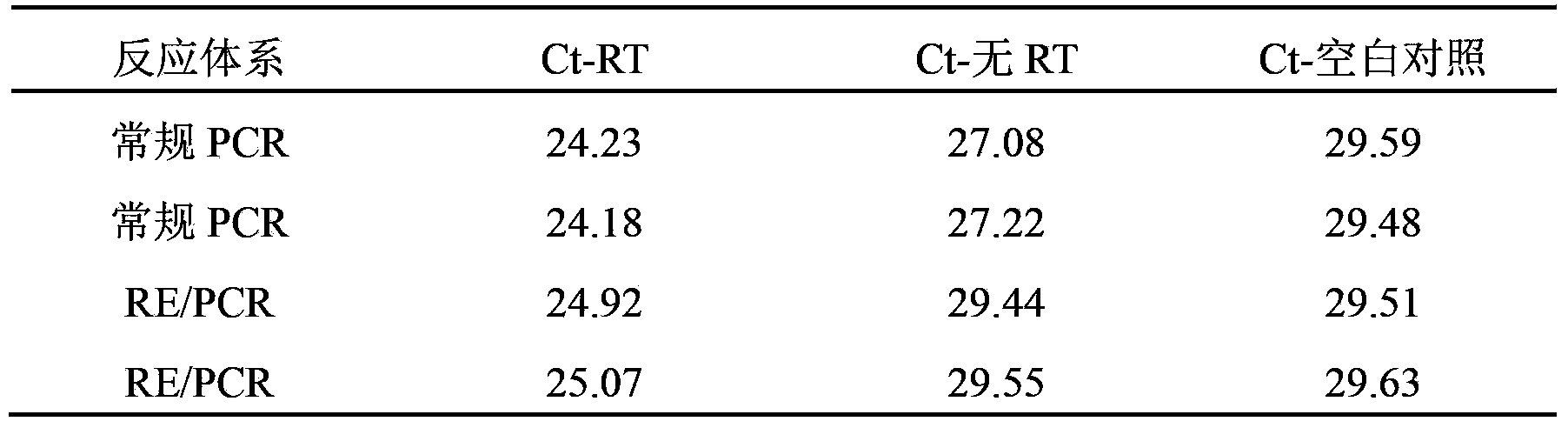
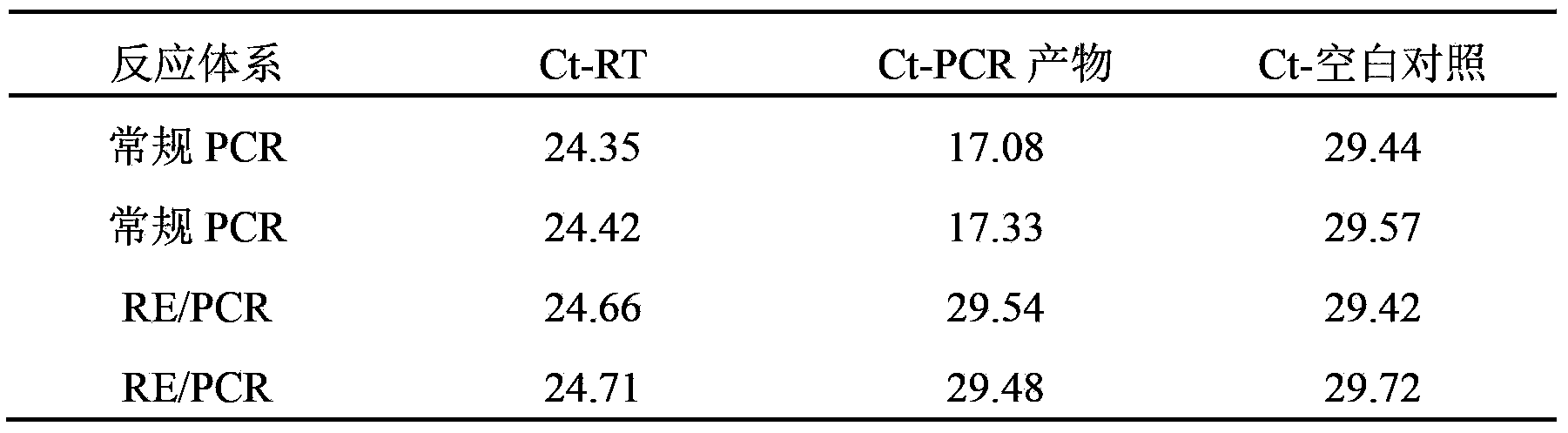
ActiveCN103382502AAmplification efficiency is not affectedAvoid cross-contamination interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexEnzyme digestion
The invention provides a RT-PCR method integrated with restriction endonuclease removal of DNA pollution. According to the method, sequence of a restriction endonuclease recognition site on target RNA is selected as a RT-PCR amplification region. After reverse transcription, enzyme digestion reaction and PCR reaction are integrated in a system and are successively and continuously carried out. cDNA sequence and target RNA form RNA / DNA heteroduplex which will not be cut, trace amounts of genome DNA or cross-contaminated PCR amplification products are all double-stranded DNA which will be cut, and restriction endonuclease is inactivated during the PCR pre-denaturation process. Thus, cross contamination and interference of trace amounts of genome DNA or amplification products are avoided, and PCR amplification efficiency of cDNA will not be influenced. By the adoption of the method, DNase enzyme treatment is not required during the RNA sample preparation process, and cross contamination of PCR products is also greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JFK BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method of isolating purified RNA with reduced DNA contaminations
ActiveUS9487550B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce amountSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationOrganic solventCationic detergent
The present invention pertains to a method of isolating RNA from a sample comprising RNA, and DNA, comprising: a) adding an acidic denaturing composition comprising a chaotropic agent and phenol to the sample; b) adding a water-insoluble organic solvent and separating the resulting phases thereby forming a multi-phase mixture comprising an aqueous phase, optionally an interphase and an organic phase, wherein the RNA is concentrated in said aqueous phase and DNA and proteins are concentrated in said organic phase and / or in said interphase; and c) isolating said RNA from said aqueous phase, wherein at least one cationic detergent is added before separating the phases. It was found that the addition of at least one cationic detergent considerably reduces the amount of DNA in the aqueous, RNA containing phase. Therefore, the present invention allows to easily isolate pure RNA which comprises considerably less DNA contaminations.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com