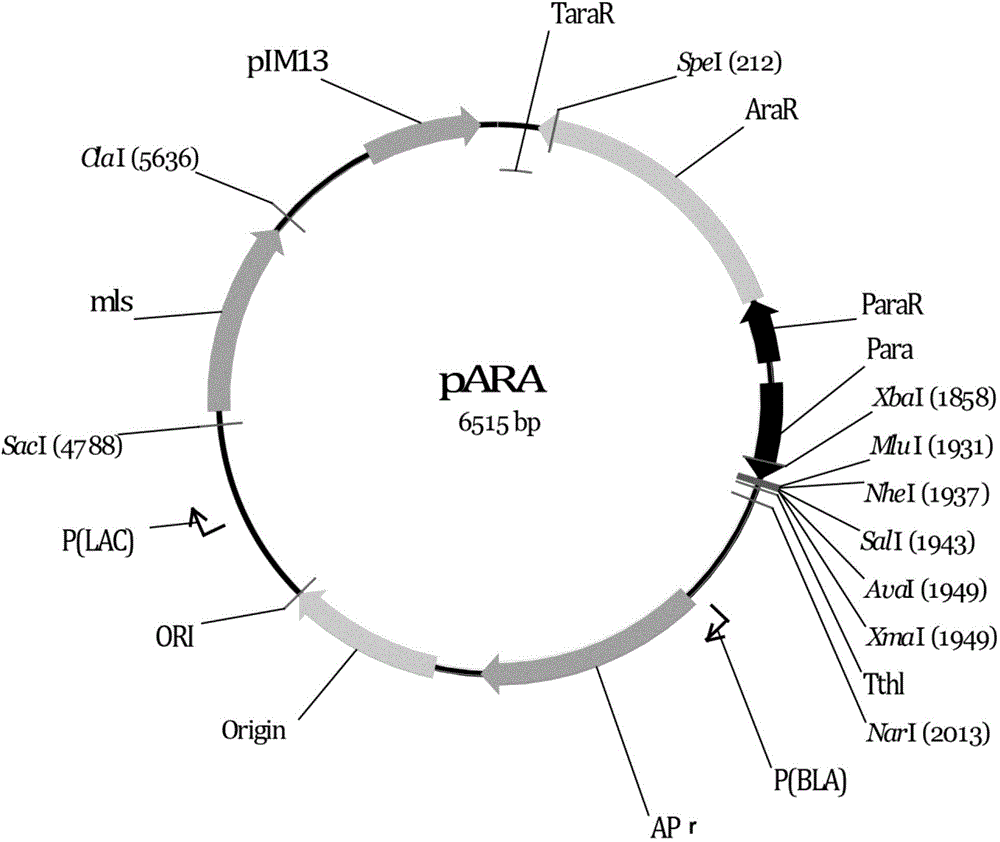
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Microbial genetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial genetics is a subject area within microbiology and genetic engineering. Microbial genetics studies microorganisms for different purposes. The microorganisms that are observed are bacteria, and archaea. Some fungi and protozoa are also subjects used to study in this field. The studies of microorganisms involve studies of genotype and expression system. Genotypes are the inherited compositions of an organism. (Austin, "Genotype," n.d.) Genetic Engineering is a field of work and study within microbial genetics. The usage of recombinant DNA technology is a process of this work. The process involves creating recombinant DNA molecules through manipulating a DNA sequence. That DNA created is then in contact with a host organism. Cloning is also an example of genetic engineering.
Genetically engineered bacteria capable of increasing yield of lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II and production method for genetically engineered bacteria
ActiveCN111979168AIncrease productionPrecise regulation of carbon fluxBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
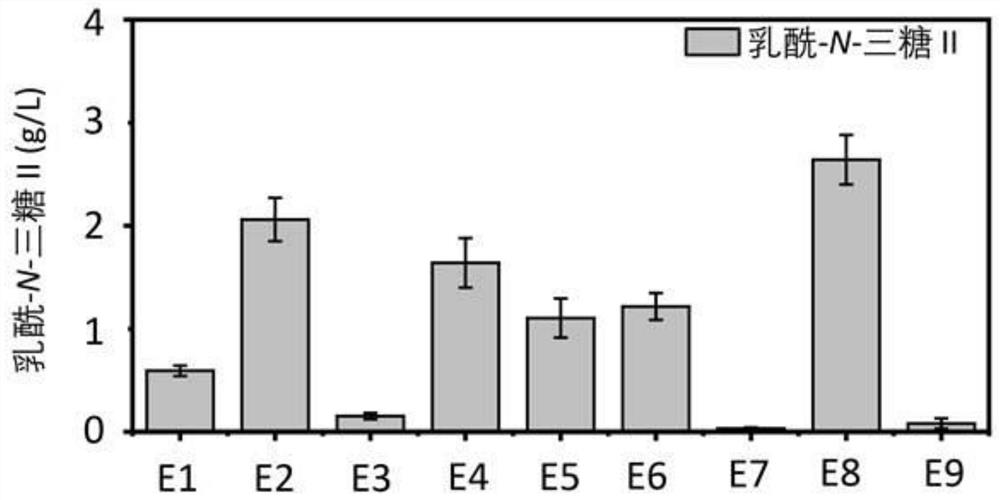
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria capable of increasing the yield of lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II and a production method, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. According to the invention, the expression of glmM, glmU, glmS and lgtA in a lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II synthetic pathway is regulated and controlled in a combined manner, so the carbon flux of a metabolic pathway is accurately regulated and controlled, and the metabolic pressure is relieved; the expression of wecB, nagB and lacZ in an escherichia coli host, namely the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide IIsynthetic pathway is knocked out, so the yield of the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II is further increased; in a flask shaking experiment, the capacity of escherichia coli for producing the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II is increased to 4.82 g / L from 0.53 g / L; in a fermentation tank with a volume of 3 L, the yield of the lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II reaches 46.2 g / L; and thus, thegenetically engineered bacteria have industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
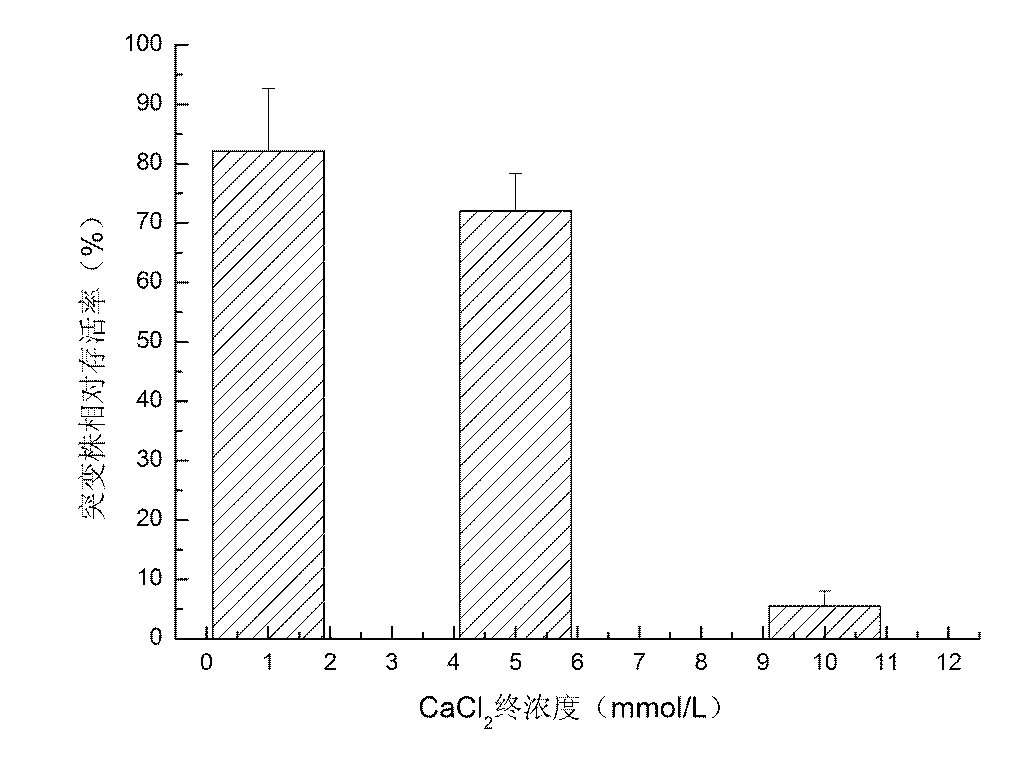
Construction method and application of a kind of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1 deletion mutant strain
InactiveCN102296033AHigh detection sensitivityLower resistanceFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyForward primer
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1 deleted mutant strain. The method is performed according to the description in the document (Yeast, 1998, 14:953-962), including designing of primers and transformation of knockout segment according to the principle of homologous recombination and gene knockout of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene. The method is a conventional method for gene knockout in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae at present. The method specifically comprises the following steps: designing primers (forward primer P1 and reverse primer P2) according to the gene sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the plasmid pFA6a-Kan MX6 by using the forward primer P1 and the reverse primer P2 to obtain a knockout segment containing forward and reverse sequences of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1 gene; and introducing the knockout segment into a Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY47421 strain cell by a lithium acetate / PEG (polyethylene glycol) transformation method, and screening to obtain the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DELTAgsh1 mutant strain YJL101C. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell DELTAgsh1 mutant strain is constructed by a microbial genetic method, and the cytotoxicity of cadmium chloride or any other heavy metal is detected by using the mutant strain, thereby enhancing the cytotoxicity detection sensitivity. The method is easy to implement and simple to operate.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Recombinant bovine tuberculosis specific antigen protein with three fused genes and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering, specifically relates to a recombinant bovine tuberculosis specific antigen protein with three fused genes and a preparation method thereof. The gene of the bovine tuberculosis specific fusion antigen protein has a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence shown as in a sequence list SEQ ID NO:1. The invention discloses a recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 / pET28a-RCE capable of expressing the bovine tuberculosis specific fusion antigen protein. The Escherichia coli is conserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with a conservation number CCTCC NO:M208244. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the three gene fused antigen protein.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Construction and application of unmarked lysobacter enzymogenes engineering strain capable of preventing plant bacteriosis
InactiveCN102943061ABroaden the range of biological controlDisease controlBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesMicrobial genetics
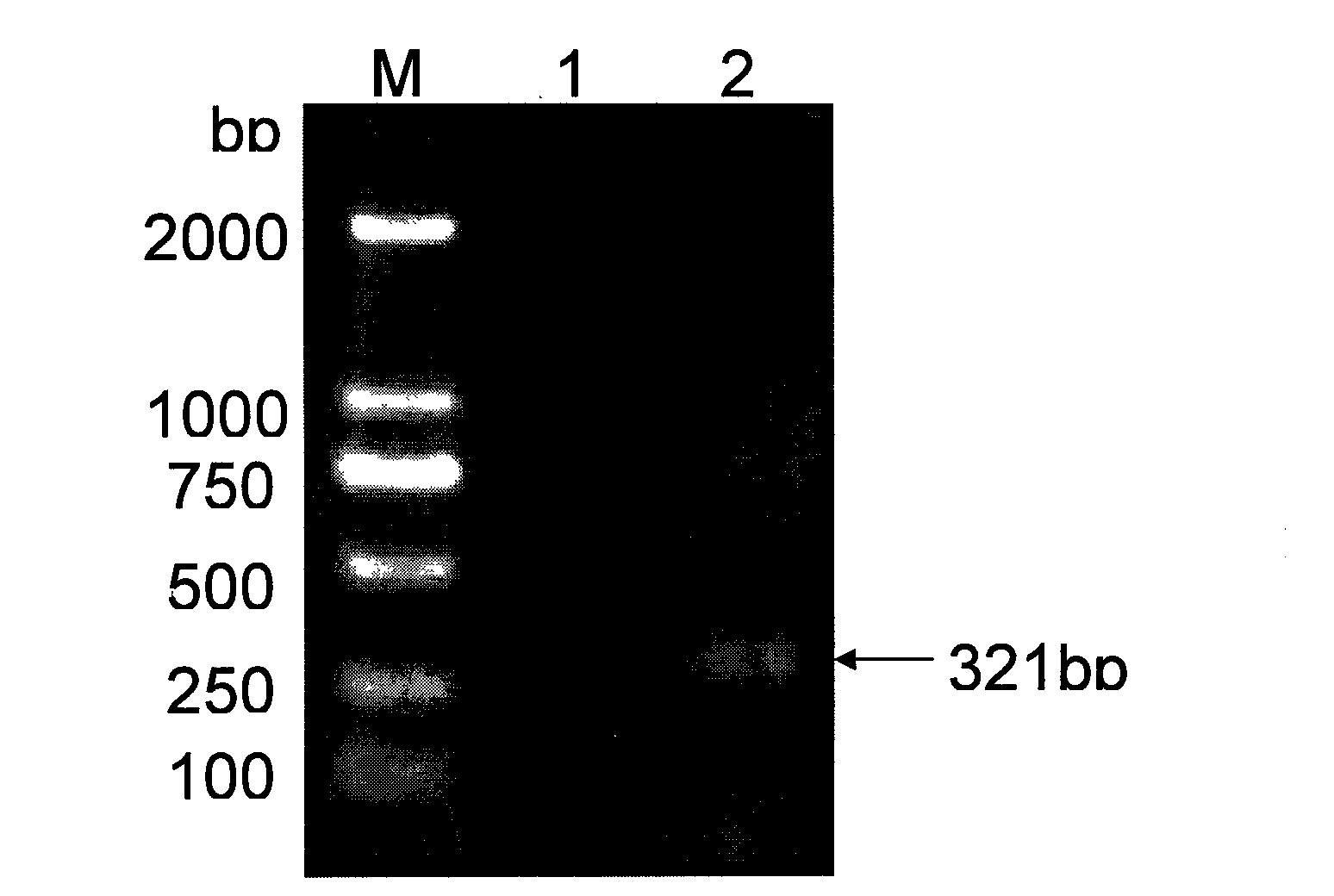
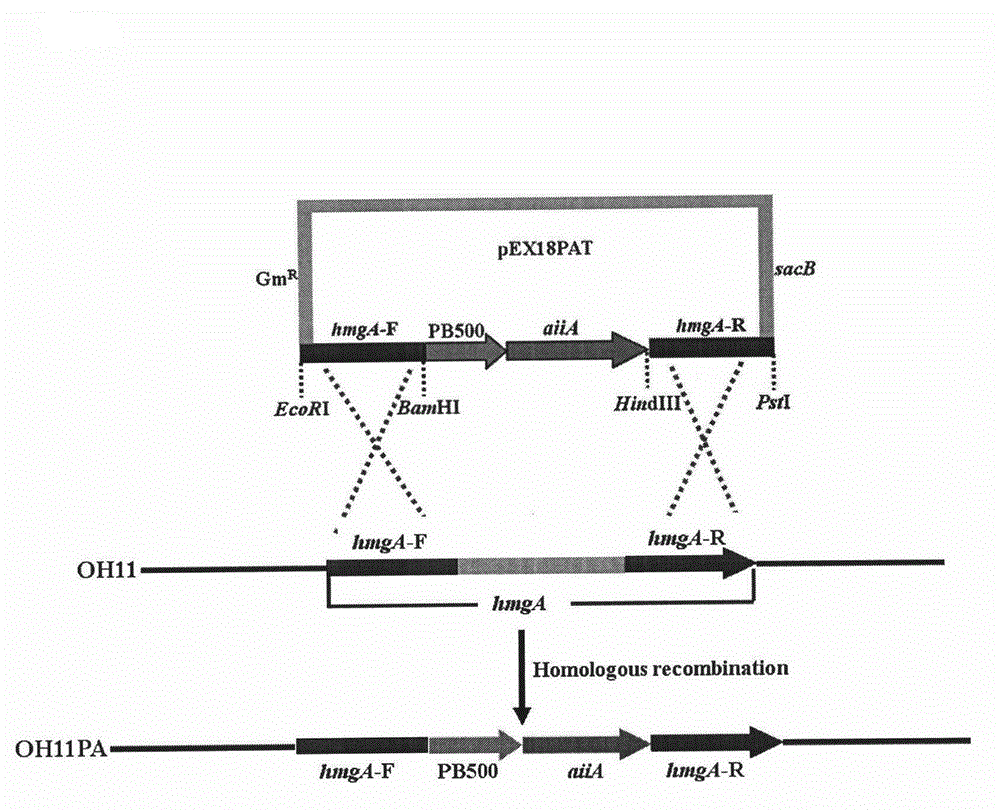
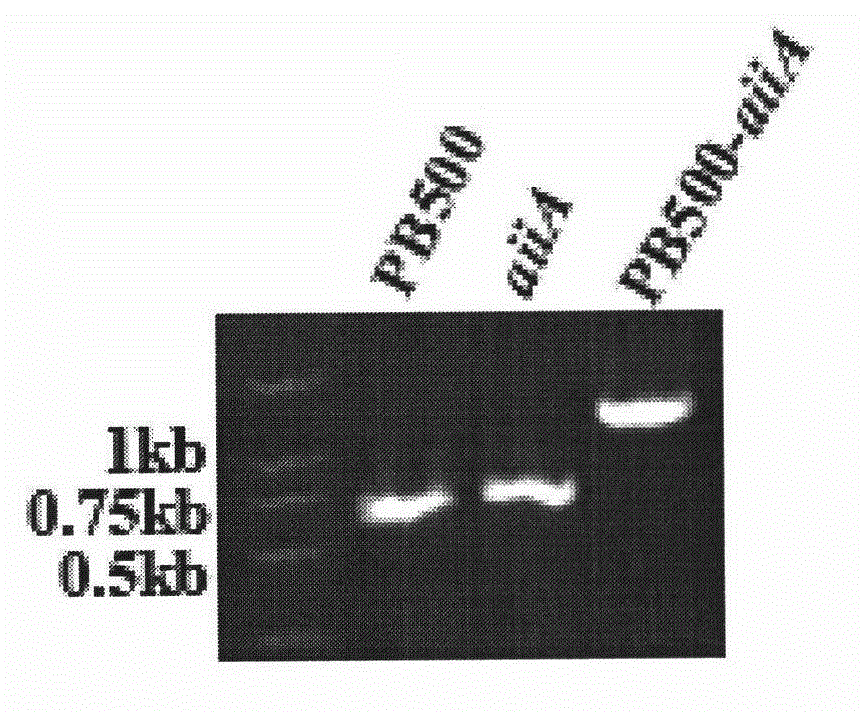
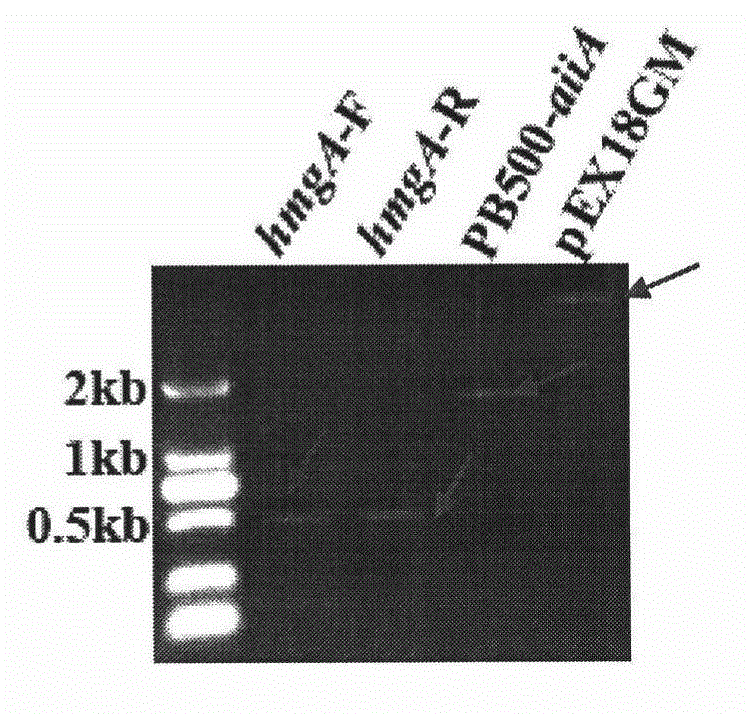
The invention relates to a construction strategy and a construction process of an unmarked lysobacter enzymogenes engineering strain capable of preventing plant bacteriosis, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. An excellent exogenous gene aiiA is directionally integrated onto a chromosome, and any marked genes are not brought into the unmarked lysobacter enzymogenes engineering strain. A quorum-sensing system for plant pathogenic bacteria can be efficiently damaged by the engineering strain, pathogenicity of the pathogenic bacteria on a host plant (Chinese cabbage) is remarkably reduced, and biological prevention of the plant bacteriosis is realized.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Efficient method of preventing growth of microbial genetic transformant after transformation
InactiveUS7145058B2Improve conversion efficiencyEliminate riskBiocideTissue cultureMicrobial GeneticMicroorganism
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Analytical method of correlation of xylanase heat resistance and N-terminal disulfide bond
InactiveCN103060424AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrobial geneticsXylanase
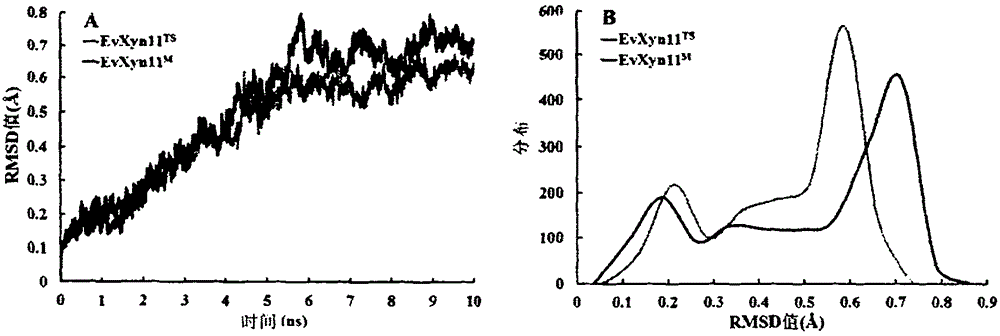
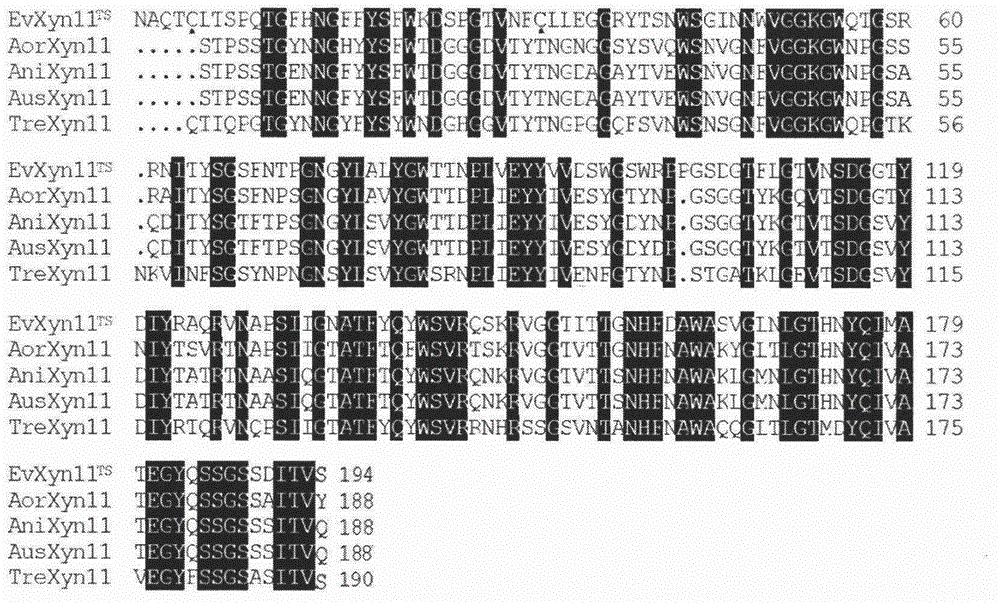
The invention provides an analytical method of correlation of xylanase heat resistance and an N-terminal disulfide bond, and belongs to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering. A result that the N-terminal disulfide bond is one of factors which affect the xylanase heat resistance is proved by adopting a scheme of combining three kinds of bioinformatics methods including the homologous comparison, the homologous modeling and the molecular dynamics simulation of a primary structure of the zymoprotein, and the result is also proved by combining an experimental means of site-specific mutagenesis and by analyzing a heat resistance mechanism of the EvXyn11TS. The research result establishes a solid foundation for the heat resistance transformation of the 11 family normal temperature high specific activity xylanase which has a similar primary structure with the EvXyn11TS.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for increasing growth speed of ganoderma lucidum mycelia and liquid fermentation biomass
InactiveCN102972211AIncreased sensitivityGood characterMutant preparationHorticultureMicrobial geneticsPeanut meal
The invention discloses a method for increasing the growth speed of ganoderma lucidum mycelia and the liquid fermentation biomass, and belongs to microbial genetics and breeding methods. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) preparing a ganoderma lucidum protoplast; (2) carrying out induced mutation on the ganoderma lucidum protoplast by nitrous acid and regenerating the protoplast; (3) inoculating peanut meal and culturing by a slant culture medium comprising maize, the peanut meal, KH2PO4, MgSO4.7H20 and VB2; (4) inoculating the peanut meal and culturing by a liquid fermentation culture medium comprising the maize, the peanut meal, peptone, glucose, yeast cream, KH2PO4 and MgSO4.7H20; and (5) obtaining active products such as biomasses and polysaccharides, triterpenoids and the like. The method has the benefits as follows: (1) a ganoderma lucidum strain with high mycelial growth speed and high biomass is obtained through induced mutation for the first time; (2) the adopted slant culture medium for the peanut meal is more favorable for quick growth of the ganoderma lucidum mycelia in comparison with a slant culture medium for potato dextrose agar; and (3) the adopted liquid fermentation culture medium for the peanut meal is more favorable for acquisition of higher biomass.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Paenibacillus polymyxa schc 33 bacterial strain, and use thereof to combat phytopathogenic fungi in fruits, vegetables or plants
InactiveUS20170303544A1High bactericidal activityProtection attackBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBiotechnology
Biofungicidal composition from a biologically pure culture of a Chilean bacterial isolate obtained from soils of the seventh region of Maule, Chile, corresponding to Paenibacillus polymyxa SCHC33, strain with the deposit number RGM2141 granted by the depository authority of the Chilean Collection of Microbial Genetic Resources (CChRGM) to be used as an environmentally friendly, biological control agent against fungal plant diseases, particularly fruits susceptible to infection by Botrytis cinerea, efficiently inhibiting conidial germination and mycelium proliferation of said phytopathogenic fungus, furthermore protects plant leaves and fruits from infection by the same fungus, and has the potential to be used in biological control of other fungi and in general of phytopathogenic microorganisms.
Owner:UNIV DE SANTIAGO DE CHILE
High efficient expression method for actinomyces-based nitrile hydratase gene in escherichia coli
ActiveCN103320458AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses a high efficient expression method for an actinomyces-based nitrile hydratase gene in escherichia coli, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering technology. The method processes high efficiency and safety. It is benefit for large scaled nitrile hydratase extraction and purification, and further theoretical research about nitrile hydratase that a large amount of soluble nitrile hydratase can be obtained in a short expression period by applications of the method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microbe-inducible gene expression control system
ActiveCN105483128AAchieve precise targetingHigh expressionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobial geneticsGene expression level
The invention aims to provide an inducible promoter, a gene induced expression control system based on the inducible promoter, and an improved microbial genetic operation tool developed based on the expression control system. L-Arabinose is used as an inducing agent. Arabinose is a carbon source common in the nature and free of inhibitory action on cell growth. The induced expression system enables gene expression level to be up-regulated up to 800 times, is better in preciseness and can be used in controlled expression of target genes in Fusiformis or other microbial cells and to optimize existing genetic modification technology and develop new tools.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Novel promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104789566AIncrease productionIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesMicrobial GeneticBiotechnology
The invention discloses a novel promoter and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. According to a method disclosed by the invention, the related promoter Pd(-35 to -10) HpaII gene is formed by series connection modification on the core area based on the promoter PHpaII; under control and transcription of the novel promoter Pd(-35 to -10) HpaII, the fibrinolytic activity of the recombinant nattokinase is up to 200.8 FU / ml. The method is efficient, safe and capable of effectively improving the expression quantity of nattokinase, and provides a theoretical basis for further study on influence of the promoter on heterologous gene expression.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Ultrasonic-mediated microbial genetic transformation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101875947ANon-destructiveLow costMicroorganism based processesOther foreign material introduction processesProbe typeMicrobial genetics
The invention relates to a low-frequency ultrasonic-mediated method for transforming microbial, which comprises the following steps: (1) culturing bacteria to a logarithmic phase in a liquid culture medium; (2) adding a substrate to be transformed into a glass bottle containing the liquid culture medium in the step 1; (3) putting the glass bottle in the step 2 into the cavity of an ultrasonic instrument; (4) starting the ultrasonic instrument, wherein the frequency is 0.1-1000KHz, the power is 0.01-1000 Watts, non-probe type contact is adopted, the whole transformation process is carried out in the solution of a bioreactor, and ultrasonic waves are continuously adjustable or intermittent; and (5) recovering cells, transferring, and coating a panel. The invention can be used for operating a single cell and a single reactor, can realize high flux, has the advantages of simple operation and voluntary control, and can realize remote control.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
GTP cyclohydrolase I gene folE and application
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Escherichia coli strains which over-produce L-threonine and processes for the production of L-threonine by fermentation
InactiveUS7220571B2Efficiently produce amino acidHigh yieldBacteriaMutant preparationBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The present invention relates to the fields of microbiology and microbial genetics. More specifically, the invention relates to novel bacterial strains and processes employing these strains for the fermentative production of amino acids such as threonine.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Travel route planning method and system based on microbial genetic algorithm
ActiveCN111369047AReduce consumptionQuick responseForecastingGenetic algorithmsAlgorithmMicrobial genetics
The invention relates to a travel route planning method and system based on a microbial genetic algorithm. The method comprises the steps of constructing a scenic spot database; the user defines a playing area and an interested theme; searching scenic spot data from a scenic spot database according to the requirements of the user; defining population size, chromosome length, iteration times, crossover probability and mutation probability; encoding the scenic spot data and randomly initializing a first-generation population; calculating the fitness of each individual in the population accordingto the fitness function; screening out individuals with the best fitness; if the number of iterations is reached, decoding is carried out to generate an optimal path, planning is ended, otherwise, individuals in the current generation population are paired randomly, and individuals needing to be crossed and mutated are screened; and then a crossover event occurs at a certain probability, a mutation event occurs at a certain probability, and the step of fitness calculation is executed circularly. While reasonable route recommendation is provided, consumption of computing resources is reduced,and the response speed of recommendation results is increased.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Strain and construction method thereof, and application thereof in fermentative production of high temperature resistant xanthan
ActiveCN109385391AReduce manufacturing costBacteriaStable introduction of DNAXanthomonas campestrisBiotechnology
The invention relates to the field of microbial genetic engineering, in particular to a strain and a construction method thereof, and application thereof in fermentative production of high temperatureresistant xanthan. The genome sequence of xanthomonas campestris is changed by using a genetic engineering technology to construct a high temperature resistant xanthan engineering strain, and the xanthan synthesized from the strain can withstand high temperature without any post-fermentation treatment, so that the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Method for preparing microorganism competent cells by using constant-pressure room-temperature plasmas
ActiveCN103710335AEfficient methodSimple methodElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentElectrical/wave energy enzyme treatmentBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
The invention discloses a method for preparing microorganism competent cells by using constant-pressure room-temperature plasmas, and belongs to the application of a plasma technology in a biological technical field. According to the basic principle provided by the invention, energetic ions and charged particles in the plasmas are used for interacting with proteins and genetic materials in the microorganism cells, so as to finally cause the property change of the cells. Therefore, the cells are at a physiological status which is the most suitable for capturing and containing external DNA. The method provided by the invention uses the constant-pressure room-temperature plasmas with a liquid circulation system, and uses helium as a plasma discharging gas to take effect on the microorganism cells, so that the competent cells can be efficiently and conveniently prepared. The method is efficient, fast, safe and convenient, and can be widely used for as a novel experimental technique in fields including microbial genetics, molecular genetics and genetic engineering,.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Efficient method of preventing growth of microbial genetic transformant after transformation
InactiveUS20030186442A1Efficient and cost-effectiveGood curative effectBiocideUnknown materialsMicroorganismMicrobial Genetic
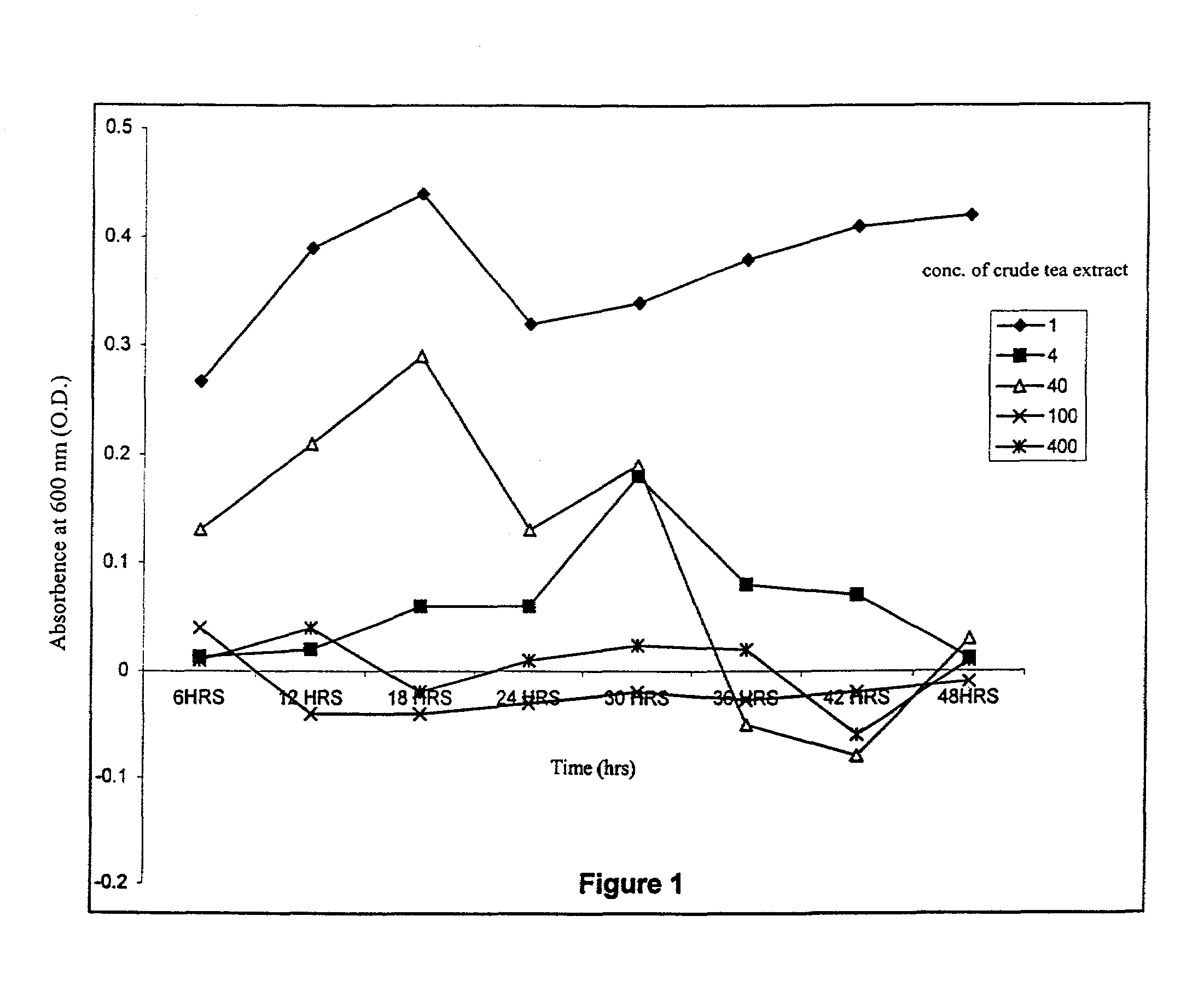
The present invention relates to an efficient and cost effective method of preventing growth of genetic transformant bacteria Agrobacterium tumefaciens after transformation in plants by using tea leaf extract as a bactericide, wherein said method leads to elimination of common problem of polyphenol oxidation during transformation and thereby helps maintain regeneration potential in explants and also helps in increased transformation efficacy
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-yield production of hydroxytyrosol and construction method thereof
ActiveCN113249240AIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHydroxytyrosolMicrobial genetics
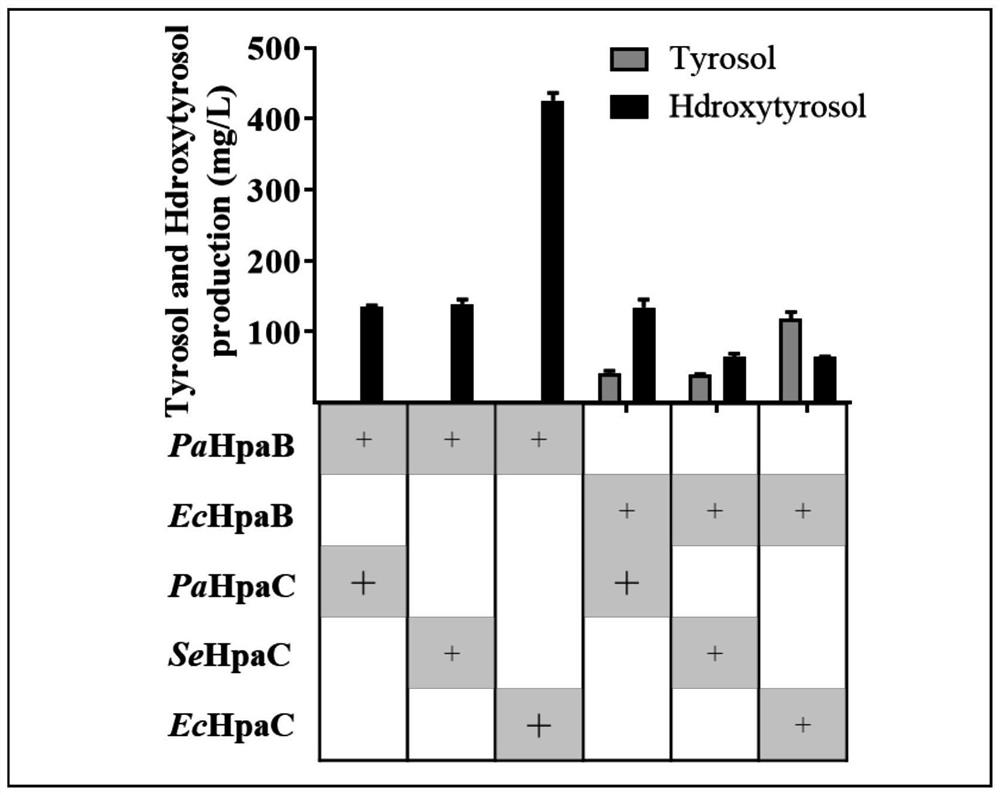
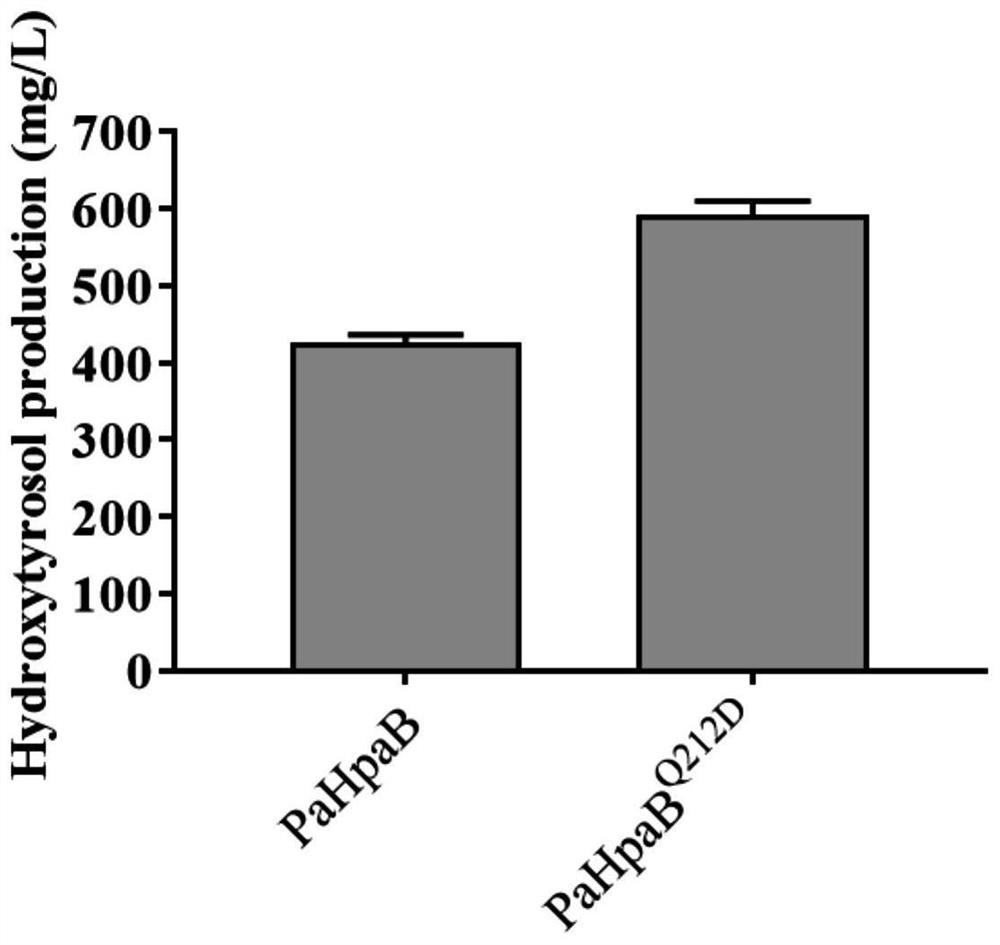
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering, and discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-yield production of hydroxytyrosol and a construction method thereof. The saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-yield production of hydroxytyrosol expresses HpaB and HpaC with specific sources on the basis of saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of synthesizing hydroxytyrosol, thereby realizing the preparation and high yield of hydroxytyrosol. The invention mainly selects 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid-3-hydroxylase derived from pseudomonas aeruginosa, and combines with riboflavin oxidoreductase with other specific sources to transfer the 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid-3-hydroxylase into saccharomyces cerevisiae chassis cells capable of producing hydroxytyrosol, thereby realizing the improvement of the yield of hydroxytyrosol; and on the basis, various modifications are further carried out, so that the yield of hydroxytyrosol of the saccharomyces cerevisiae is up to 1120mg / L, and a new way is provided for the efficient fermentation production of hydroxytyrosol by microorganisms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for enhancing worm grass fermentation biomass
InactiveCN104560941AIncreased radiation sensitivityGood characterFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobial geneticsAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to the technical fields of microbial genetic breeding and biological active substance production, and discloses a method for enhancing worm grass fermentation biomass. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a worm grass protoplast; (2) carrying out mutagenesis on the worm grass protoplast, and regenerating the protoplast; (3) selecting the bacterial colony, and inoculating a PDA (potato dextrose agar) culture medium; (4) inoculating a liquid fermentation culture medium; and (5) obtaining the active product containing worm grass biomass, polysaccharide, cordycepin and the like. The worm grass strain with high hypha growth speed and high biomass is obtained by mutagenesis for the first time; by using white jade snail viscera and shells as the main raw material and adding proper glucose, K2HPO4, MgSO4 and other nutrient substances, the mutagenesis worm grass strain is inoculated and subjected to submerged fermentation to produce the worm grass mycelia. The method is simple to operate, sufficiently utilizes the waste resources and enhances the worm grass fermentation biomass. The fermentation product can be used in an animal feed additive to become a green food, thereby avoiding adding antibiotics in the animal feed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for transforming Bacillus siamensis by electric shock
ActiveCN109266676ASimple genetic transformation methodEfficient Genetic Transformation MethodsVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismCompetent cell
The invention discloses a method for transforming Bacillus siamensis by electric shock, belonging to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering. The invention comprehensively optimizes factors such as preparation of competent cell, concentration of plasmid, electric shock parameter and the like during electric shock transformation of Bacillus siamensis JFL15, and establishes a simple andeffective genetic transformation method of Bacillus siamensis for the first time. The genetic transformation method of Bacillus siamensis of the invention is simple in operation, high in conversion rate, stable in effect, and can be used for the knockout of CRISPR -cas9 gene and the large plasmid () 11kbp for homologous recombination knockout vector with high efficiency, not only laid a good foundation for genetic modification of Bacillus siamensis, and has an important significance for accelerating its application in industrial production, but also provided an important reference for genetictransformation of other Bacillus spp.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
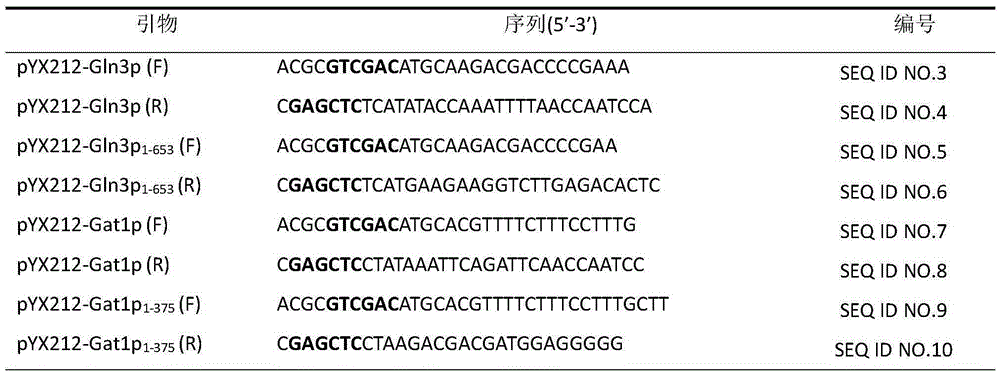
Method with function of reducing accumulation of ethyl carbamate in rice wine fermentation
InactiveCN105273918AMeet production requirementsReduce contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
The invention belongs to the field of microbial genetics and molecular biology and discloses a method with a function of reducing accumulation of ethyl carbamate in rice wine fermentation. Genetically engineered bacteria modified by nitrogen catabolite repression regulation factors are adopted for rice wine fermentation, and engineered saccharomyces cerevisiae eliminates nuclear localization regulatory sequences of the regulation factors Gln3p and Gat1p and mutates phosphorylation sites of the nuclear localization sequences. In a simulated rice wine fermentation system, compared with rice wine with wild strains for fermentation, rice wine fermented with the genetically engineered bacteria has the advantages that contents of carbamide and ethyl carbamate in the rice wine are decreased by 63% and 72% respectively, the content of the ethyl carbamate in the rice wine is decreased to about 55.53 microgram / L, and contents of major nutrient substances and characteristic flavor substances are less in difference. Therefore, the method has a huge potential of application to rice wine production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Black box adversarial sample generation method based on microbial genetic algorithm
ActiveCN111797975AReduce the number of queriesShorten the timeNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsMicrobial GeneticMicroorganism
The invention relates to a black box adversarial sample generation method based on a microbial genetic algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence safety. The method mainly solves the problem of excessive number of times of query required for successfully attacking a neural network model to generate an adversarial sample under the condition of a black box, combines twotypical methods in black box attacks, namely migration attacks and output-based attacks, and solves the discretization problem by using a simple microbial genetic algorithm.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Construction method and application of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1 deleted mutant strain
InactiveCN102296033BHigh detection sensitivityLower resistanceFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerAgricultural science
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1 deleted mutant strain. The method is performed according to the description in the document (Yeast, 1998, 14:953-962), including designing of primers and transformation of knockout segment according to the principle of homologous recombination and gene knockout of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene. The method is a conventional method for gene knockout in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae at present. The method specifically comprises the following steps: designing primers (forward primer P1 and reverse primer P2) according to the gene sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the plasmid pFA6a-Kan MX6 by using the forward primer P1 and the reverse primer P2 to obtain a knockout segment containing forward and reverse sequences of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gsh1 gene; and introducing the knockout segment into a Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY47421 strain cell by a lithium acetate / PEG (polyethylene glycol) transformation method, and screening to obtain the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DELTAgsh1 mutant strain YJL101C. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell DELTAgsh1 mutant strain is constructed by a microbial genetic method, and the cytotoxicity of cadmium chloride or any other heavy metal is detected by using the mutant strain, thereby enhancing the cytotoxicity detection sensitivity. The method is easy to implement and simple to operate.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
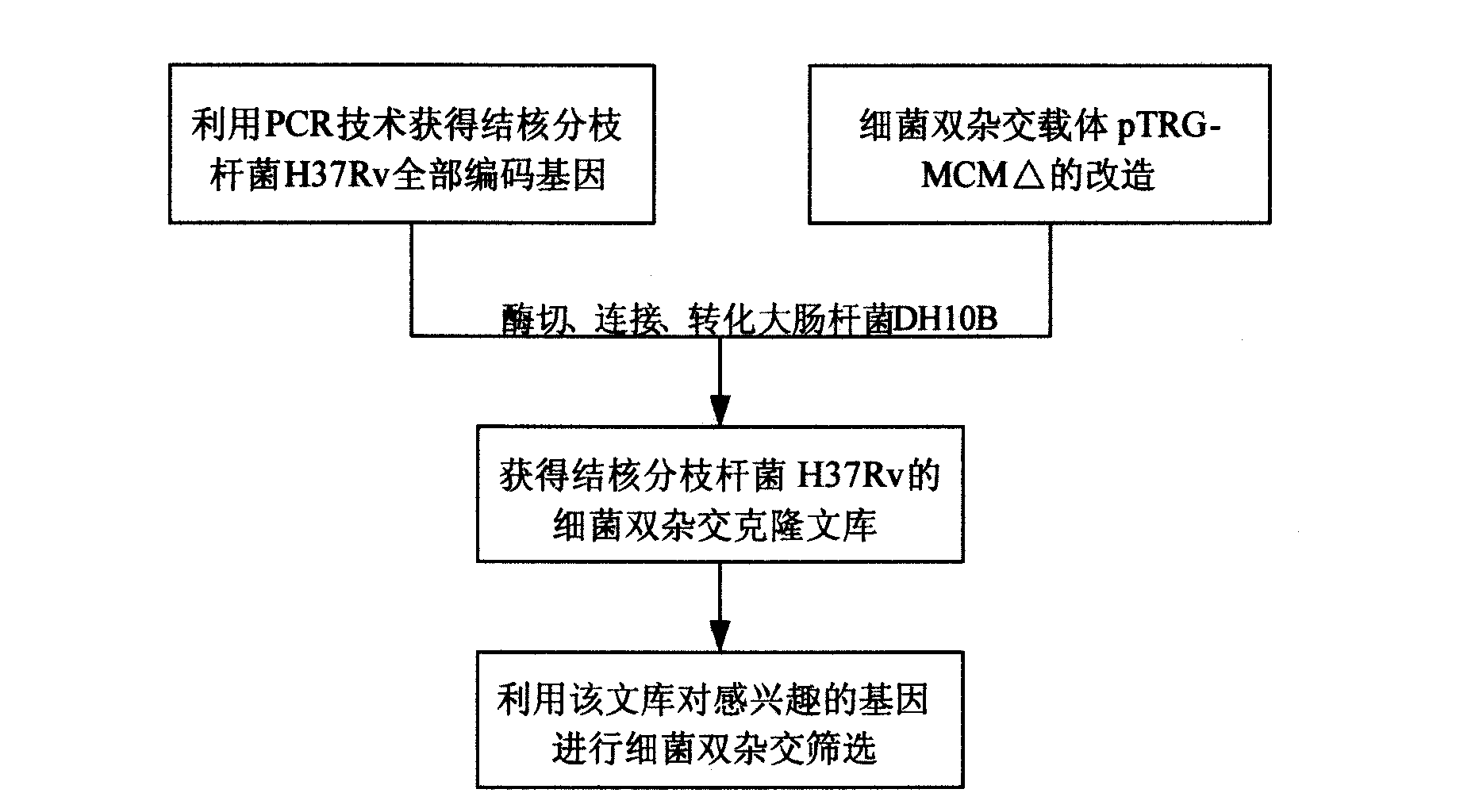
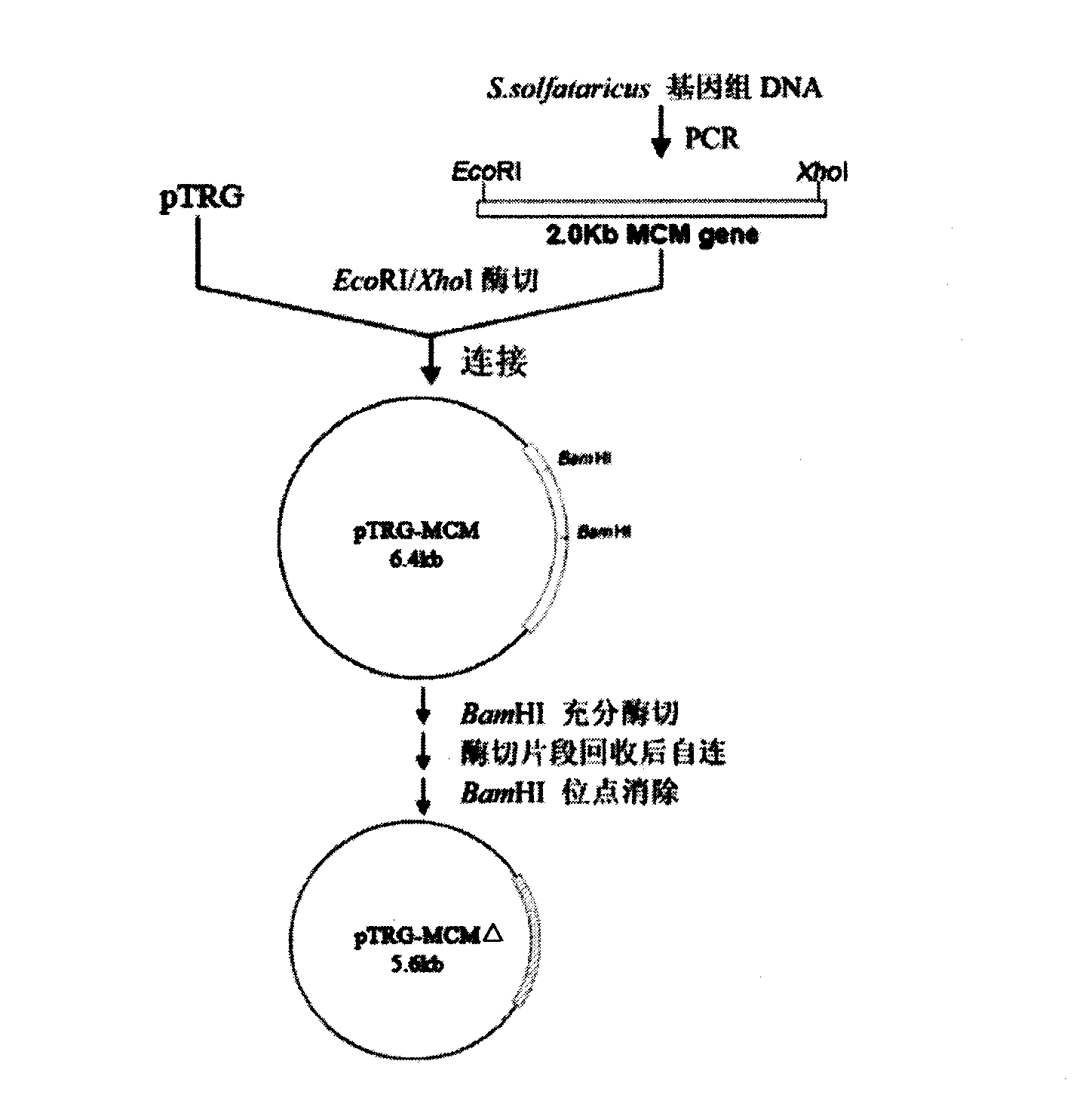
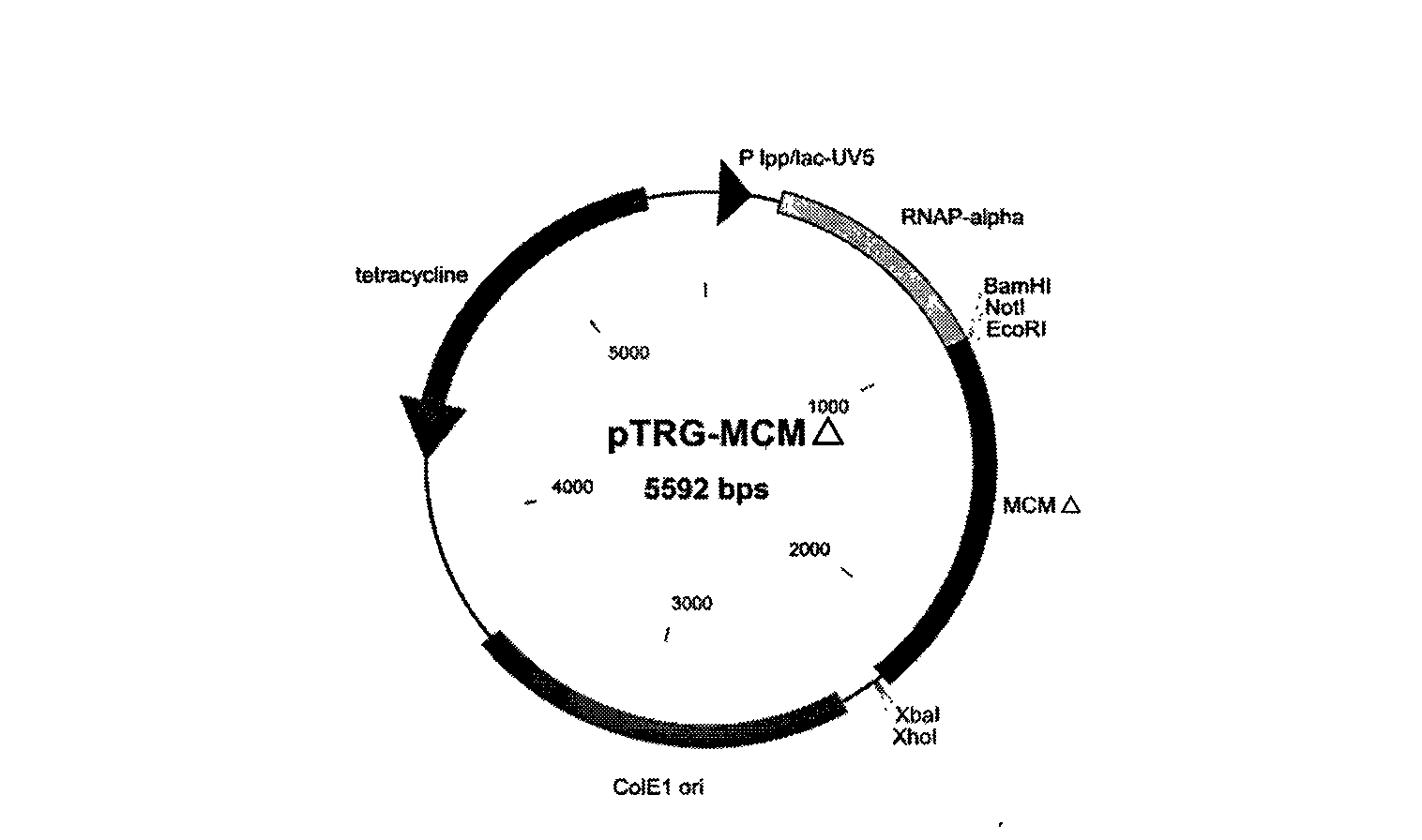
Construction method of complete mycobacterium tuberculosis genome ORF clone library and application thereof
InactiveCN101538581AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliMicrobial Genetic
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering, specifically relates to a construction method of a complete mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome ORF bacterial two-hybrid clone library and application thereof. The construction method is characterized by comprising the following steps: preparing a bacterial two-hybrid carrier pTRG-MCM delta suitable for constructing the complete mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome ORF clone library; obtaining all encoded genes of the mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv by a PCR reaction; accurately cloning all encoded genes of the mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv into the constructed bacterial two-hybrid carrier pTRG-MCM delta; and transforming Escherichia coli DH10B to obtain the complete mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv genome ORF bacterial two-hybrid clone library.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A method for preparing microbial competent cells using atmospheric pressure room temperature plasma
ActiveCN103710335BEfficient methodSimple methodElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentElectrical/wave energy enzyme treatmentMicrobial geneticsPlasma technology
The invention discloses a method for preparing microorganism competent cells by using constant-pressure room-temperature plasmas, and belongs to the application of a plasma technology in a biological technical field. According to the basic principle provided by the invention, energetic ions and charged particles in the plasmas are used for interacting with proteins and genetic materials in the microorganism cells, so as to finally cause the property change of the cells. Therefore, the cells are at a physiological status which is the most suitable for capturing and containing external DNA. The method provided by the invention uses the constant-pressure room-temperature plasmas with a liquid circulation system, and uses helium as a plasma discharging gas to take effect on the microorganism cells, so that the competent cells can be efficiently and conveniently prepared. The method is efficient, fast, safe and convenient, and can be widely used for as a novel experimental technique in fields including microbial genetics, molecular genetics and genetic engineering,.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method and device for genetic transformation of cell
InactiveCN101948825ADoes not damage the structureRealize synchronous controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobial geneticsPlant cell
The invention discloses a method for genetic transformation of a cell. An ultrasonic transformation device is utilized, and the following parameters are set for the ultrasonic transformation device: 1) the ultrasonic transmitting frequency is 0.1 to 1,000 KHz; and 2) the ultrasonic output power is 0.01 to 1,000Watt / cm<2>; and under the conditions, a biomacromolecule to be transformed is transformed into microbial cells, microalgae cells and animal and plant cells. The invention also provides the ultrasonic transformation device for implementing the method. The method and the device can be used for microbial genetic transformation, mass and energy transfer among cells and regular transformation of nucleic acid, protein, polysaccharide and medicament in a bioreactor.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
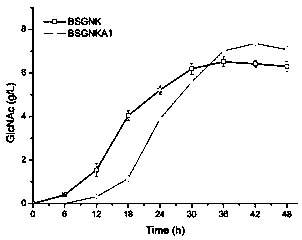
Recombinant bacillus subtilis and application
InactiveCN108486025AEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial GeneticMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of recombinant microbial genetic engineering, particularly relates to a construction method of a recombinant bacillus subtilis strain, and further relatesto application of the recombinant bacillus subtilis strain, in particular to the application thereof to synthesis of acety-lglucosamine. The construction method of a recombinant bacillus subtilis comprises the steps as follows: using bacillus subtilis BSGNK-PxylA-glmS-P43-GNA1 as a starting strain, knocking out KHG / KDPG aldolase gene kdgA, and obtaining the recombinant bacillus subtilis strain. The recombinant bacillus subtilis, provided by the invention, can efficiently utilize glucose to synthesize the acety-lglucosamine, and the fermentation yield of shake flask can reach 7.34 g / L, which is11.84% higher than that before the knockout, thereby laying a foundation for further transforming the bacillus subtilis to produce glucosamine through metabolic engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNDE BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Construction method and application of high-yield lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide microorganism
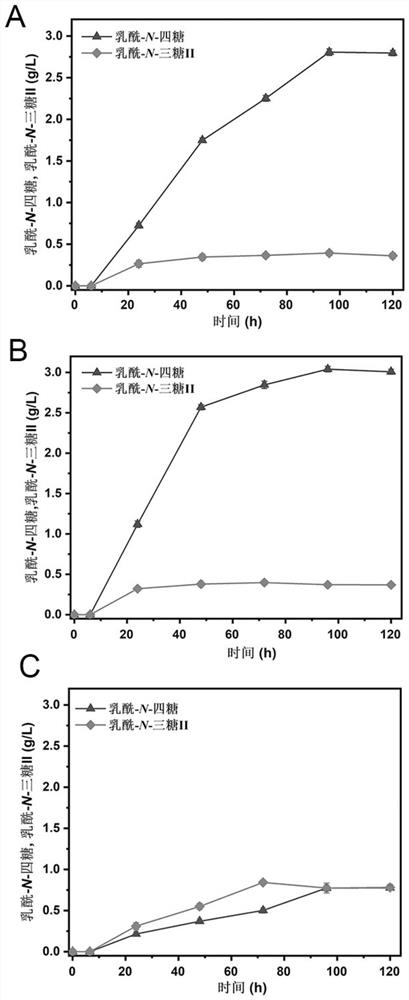
PendingCN113652385AEfficient productionIncrease supplyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a high-yield lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide microorganism, and belongs to the field of microbial genetic engineering. According to the method, a strain which is constructed in an early stage and is used for efficiently producing a precursor substance lactoyl-N-trisaccharide II is used as an original strain, and a key gene for synthesizing lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide is over-expressed, so that the strain has the synthesis capability of producing lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide. An efficient beta-1, 3-galactosyl transferase gene is screened, the coexpression beta-1, 3-galactosyl transferase gene and a UDP-glucose 4 epimerase gene (galE) which is a key gene for strengthening a UDP-galactose pathway are reasonably designed on a carrier pCDFDuet-1, so that the synthesis of the lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide is improved, and in a shake flask experiment, the yield of the lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide is increased, and the yield of the lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide is increased. In a bottle shaking experiment, the capacity of producing the lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide by the escherichia coli is 3.04 g / L, the yield of the lactoyl-N-tetrasaccharide in a 3L fermentation tank reaches 25.49 g / L, and the construction method has an industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
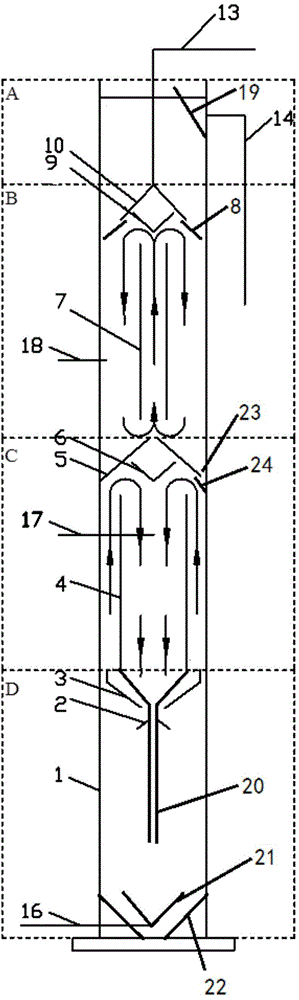
Biological fluidized bed reactor
ActiveCN104787878APromote circulationPromote genetic evolutionWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMicrobial GeneticFluidized bed
The invention discloses a biological fluidized bed reactor. The biological fluidized bed reactor comprises a barrel body, wherein a solid-liquid separation zone, a second internal circulation zone, a first internal circulation zone and a complete mixing zone are sequentially arranged inside the barrel body; a mud collecting plate is arranged at the bottom of the complete mixing zone; a water inlet pipe is arranged above the mud collecting plate; the water inlet pipe extends upwards from the bottom of the complete mixing zone to form a plurality of water inlet branch pipes; a first gas guide plate and a first mud guide plate are further arranged at the top of the complete mixing zone; the water inlet branch pipes can be in mutual basin matching with the inverted conical structures of a nozzle 20 and the mud collecting plate 22, so that the biomass carrier after sufficient reaction can be intensively mixed with eutrophic sewage to be treated, the microorganism can be enabled to fully proliferate, and the treatment capacity can be enhanced. The biological fluidized bed reactor disclosed by the invention brings convenience for circulation of the biomass carrier, so as to promote microbial genetic evolution in the reactor and enhance the treatment capacity.
Owner:陆继来
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com