Analytical method of correlation of xylanase heat resistance and N-terminal disulfide bond
A technology of xylanase and disulfide bond, which is applied in the fields of microbial genetic engineering, bioinformatics and genetic engineering, and can solve the problems that natural enzymes are difficult to reach.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
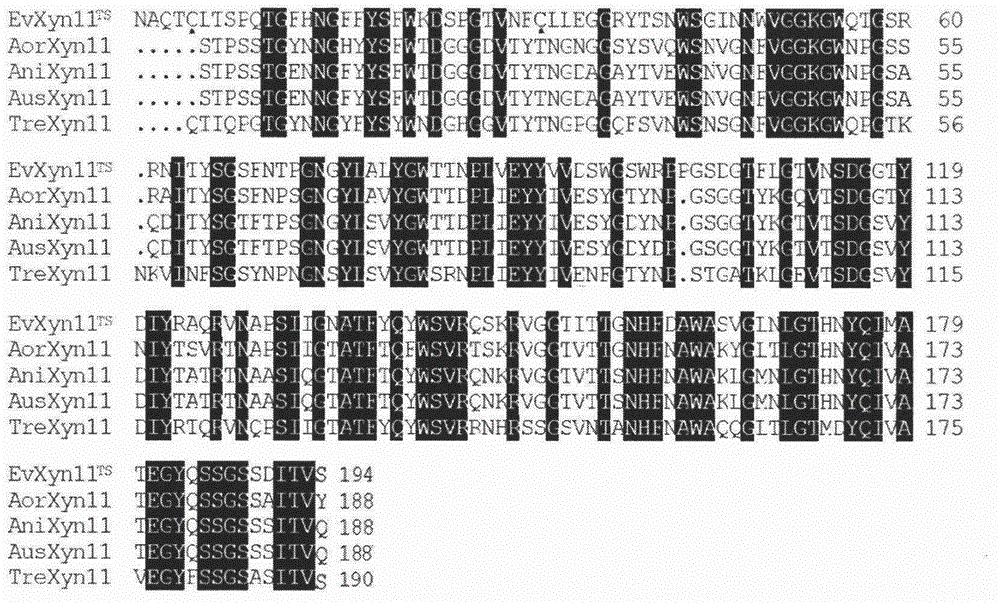
[0019] Example 1 Homologous Alignment of the Primary Structure of Xylanase: The Heat-resistant EvXyn11 TS The sequence was homologously compared with other xylanase sequences of the 11 family, and it was found that it was derived from Aspergillus oryzae (Aor), Aspergillus niger (Ani), Aspergillus usamii (Aus) and Li Trichoderma reesei (Tre) has the highest homology of xylanases, which are 64.4%, 62.4%, 62.4% and 54.9%, respectively. Thermostable xylanase EvXyn11 expressed in E.coli TS The optimum temperature of xylanase is 75°C, and all enzyme activities are retained after treatment at 80°C for 15 minutes; while the optimum temperature of other xylanases is 50°C-55°C, and they are stable at 45°C-50°C. The multiple sequence homology alignment of the primary structures of these enzymes was performed using the Clustal W online program, and the results are shown in figure 1 . Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that their homology in the N-terminal region is relatively low, an...
Embodiment 2
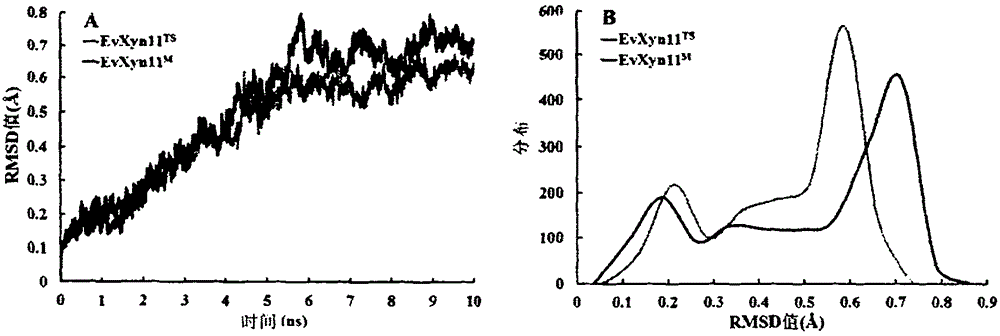
[0020] Example 2 Homology Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Taking Thermotolerant EvXyn11 TSThe crystal structure (PDB: 2VUL) was used as a spatial structure modeling template, and the mutant enzyme EvXyn11 was analyzed using the SWISS-MODEL online program (http: / / swiss-model.expasy.org / on-line) M Perform homology modeling. Using the GROMACS 4.0 package (http: / / www.gromacs.org / ) at high temperature for EvXyn11 TS and EvXyn11 M The structure was simulated by Molecular dynamics (MD), and the MD simulation system was set as: temperature 500K, force field GROMOS 96, solute molecules were wrapped by 1.5nm SPC / E water molecule layer. Before the MD simulation, two energy optimizations were performed on the constrained and unconstrained solute molecular systems, that is, the steepest descent method was used to optimize 800 steps, and the conjugate gradient method was used to optimize 1200 steps. The MD simulation is carried out in two steps: first, the bound solute molec...
Embodiment 3
[0021] Example 3 Recombinant plasmid pUCm-T-Syxyn11 M Construction of: Designing the xylanase EvXyn11 TS Cys5 in the amino acid sequence was mutated to Thr5 to remove its N-terminal disulfide bond. According to the artificially synthesized Syxyn11 nucleotide sequence (GenBankaccession no. JX459567), design a pair of PCR mutation primers, respectively CMT-F: 5'- GAATTC AACGCTCAAACT CTTACCTCTCCCAC-3' (the underlined part is the EcoR I restriction site, and the boxed part is the mutant codon) and CMT-R: 5'- GCGGCCGC TTAACTAACAGTAATGTCAGA-3' (the underlined part is the Not I restriction site, and the italic part is the stop codon), synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Company. The PCR conditions are: 94°C, pre-denaturation for 2 minutes; 30 cycles (94°C for 30s, 50°C for 30s, 72°C for 40s); 72°C, full extension for 10 minutes. Using plasmid pUCm-T-Syxyn11 as template, CMT-F and CMT-R as primers, PCR amplified mutant enzyme coding gene Syxyn11 M . The PCR product was analyzed by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com