Astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof
A technology of astaxanthin and strains, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as the accumulation of intermediate metabolites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with synthetic chromosomes producing astaxanthin
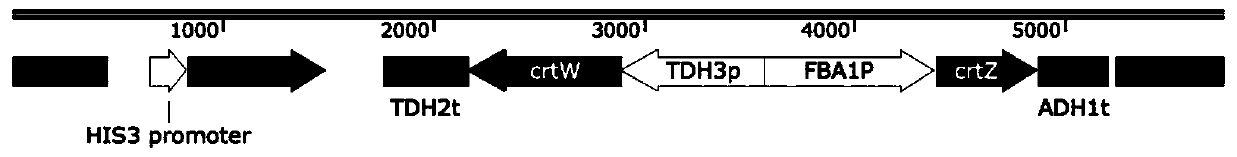
[0035] Using Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains containing synthetic chromosomes V and X as the starting strain, the specific process of constructing the astaxanthin-producing strain SyBE_SC307118 is as follows: the exogenous genes include three genes for the synthesis of lycopene and the gene for the synthesis of astaxanthin. Two genes: geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthase gene crtE, phytoene synthase gene crtYB and phytoene dehydrogenase gene crtI and β-carotene hydroxylase gene crtZ and β-carotene ketolase gene crtW, genes crtE, crtYB and crtI were integrated into synthetic chromosome V with Leu as a tag ( figure 2 ), the genes crtZ and crtW were integrated into the delta site with His as the tag ( image 3 ). Open SCRaMbLE and use the plasmid Gal-Cre-URA plasmid, transform the plasmid into the synthetic type V and X chromosome Saccharomyces cerevisi...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 plasma combined with SCRaMbLE simultaneous mutagenesis ( Figure 4 )
[0037] Experimental group (S+A): Culture the strain SyBE_SC307118 in SC-URA liquid medium overnight, insert fresh SC-URA-Gal medium at OD=1 the next day, add 1ul / 5ml estrogen, and turn on SCRaMbLE for 6h . Take 1ml of the SCRaMbLE bacterial solution in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4500 rpm for 1min, and wash with 1mLddH 2O wash twice, take 10ul to the metal sheet, and process for 20s. Put the mutagenized bacterial solution into a 1.5mL EP tube containing 1mL of normal saline; vibrate the EP tube on a vortex shaker for 1min to completely dissolve the bacterial solution attached to the metal piece in the normal saline, 4500 Centrifuge at rpm for 1 min, transfer the centrifuged bacterial liquid into fresh SC-URA medium, and incubate overnight for 16-18 hours to recover. At this time, the bacterial liquid is the mixed bacterial library on the first day, and repeat every other day f...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The astaxanthin shake flask output of embodiment 3 comparison bacterial strains
[0041] Test material: bacterial strain Test method:
[0042] Seed medium: 40 / L glucose, 6.7g / L yeast nitrogen source, 2g / L amino acid deficiency mixed powder;
[0043] Fermentation medium: 40 / L glucose, 20g / L peptone, 10g / L yeast extract powder.
[0044] The bacterial strains obtained from the experimental group (S+A), the control group (A), and the control group (S) obtained in Example 2 were respectively inoculated in 5 mL of seed culture medium, and cultivated at 30° C. and 250 rpm for 14 to 16 h to Initial cell concentration OD 600 =0.2 Transplanted in fresh 5mL seed medium, cultivated to mid-logarithmic growth under the conditions of 30°C and 250rpm, the initial cell concentration OD 600 =0.1 were inoculated in 50mL fermentation medium respectively, cultivated under the conditions of 30°C and 250rpm, and monitored the cell density (OD 600 ) and astaxanthin production ( Figure 5 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com