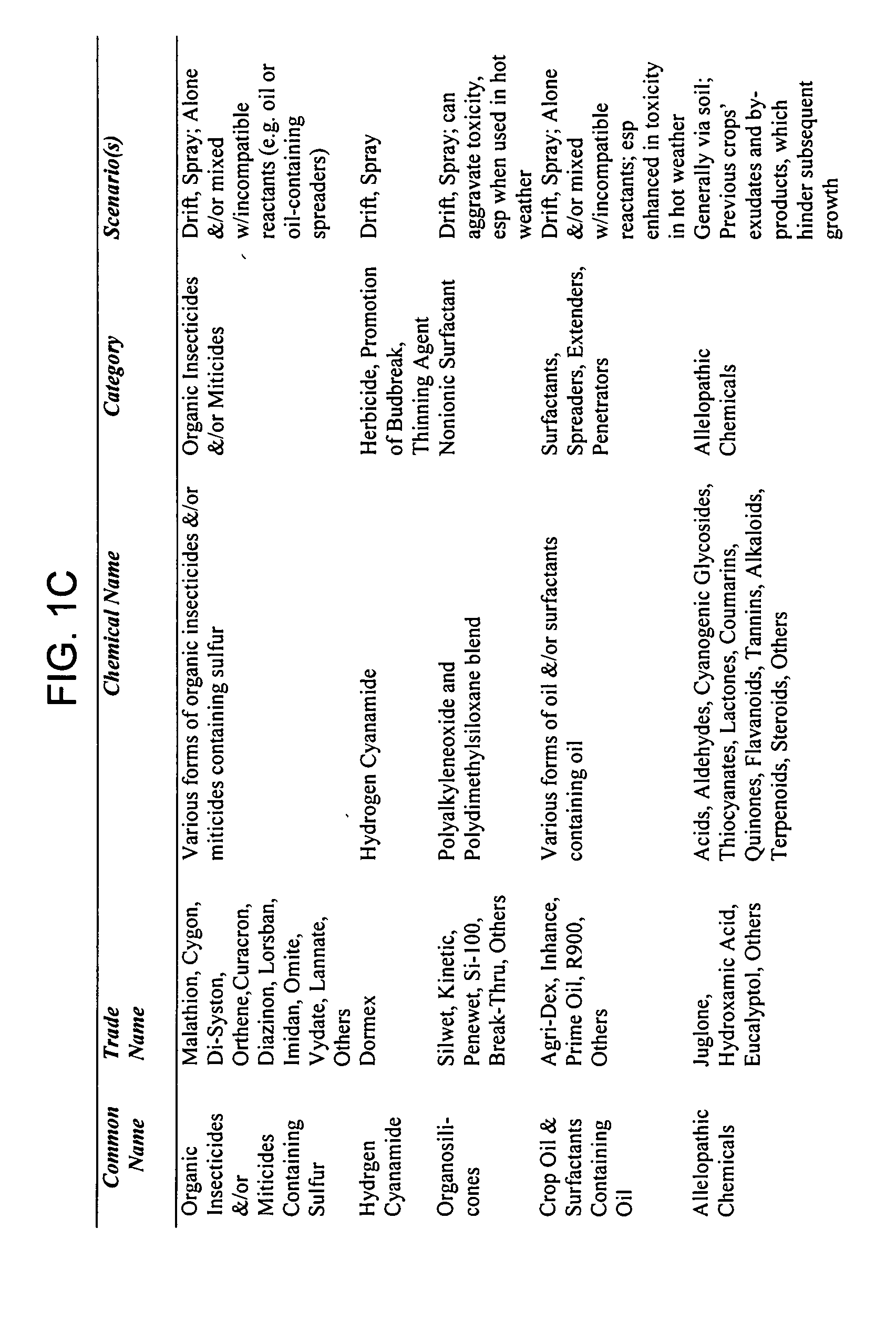
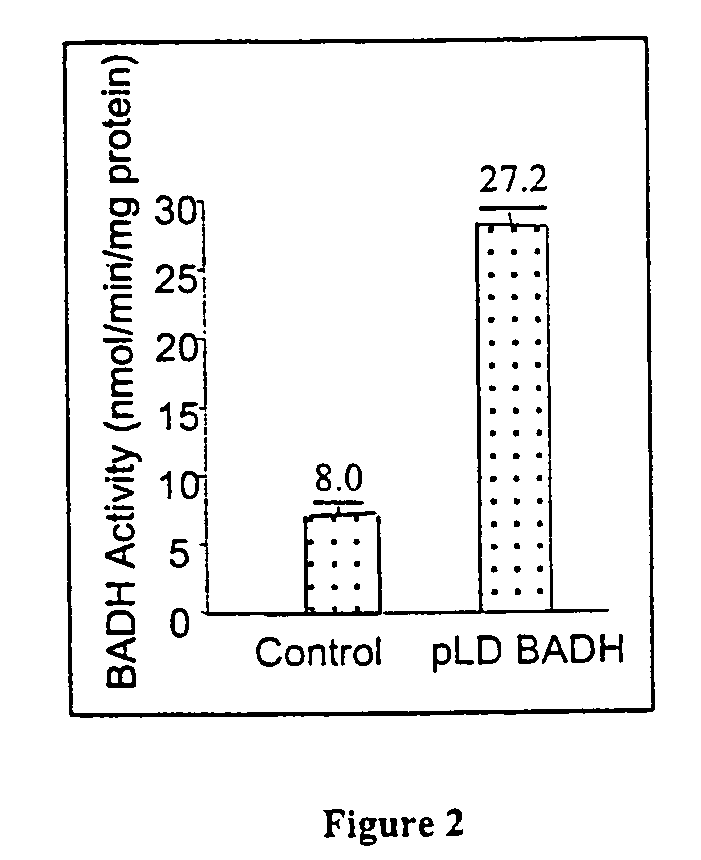
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Phytotoxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phytotoxins are substances that are poisonous or toxic to the growth of plants. Phytotoxic substances may result from human activity, as with herbicides, or they may be produced by plants, by microorganisms, or by naturally occurring chemical reactions.
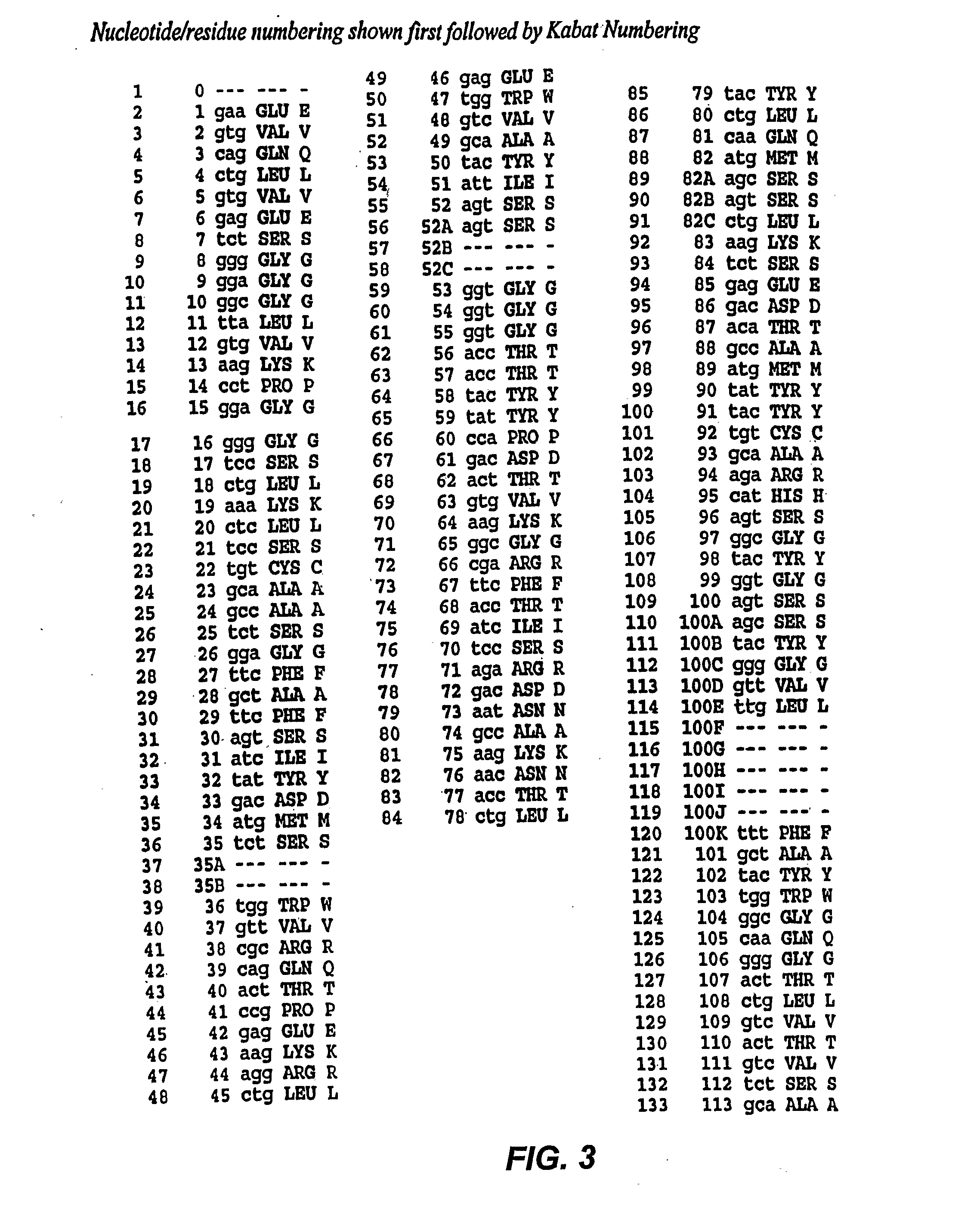
Mutated anti-cd22 antibodies and immunoconjugates
Recombinant immunotoxins are fusion proteins composed of the Fv domains of antibodies fused to bacterial or plant toxins. RFB4 (Fv)-PE38 is an immunotoxin that targets CD22 expressed on B cells and B cell malignancies. The present invention provides antibodies and antibody fragments that have improved ability to bind the CD22 antigen compared to RFB4. Immunotoxins made with the antibodies and antibody fragments of the invention have improved cytotoxicity to CD22-expressing cancer cells. Compositions that incorporate these antibodies into chimeric immunotoxin molecules that can be used in medicaments and methods for inhibiting the growth and proliferation of such cancers. Additionally, the invention provides a method of increasing the cytotoxicity of forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (“PE”) with the mutation of a single amino acid, as well as compositions of such mutated PEs, nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for using the mutated PEs.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
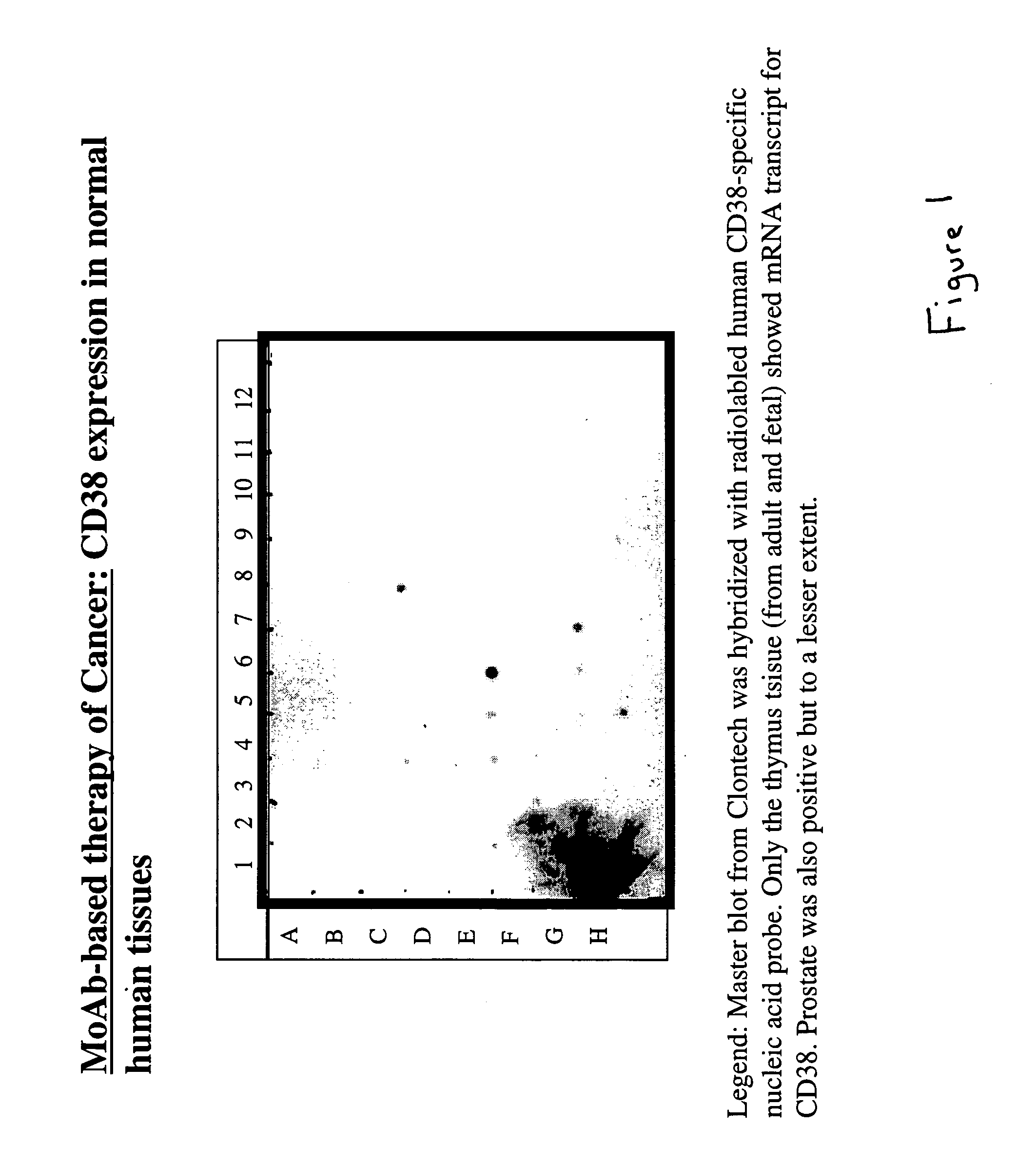
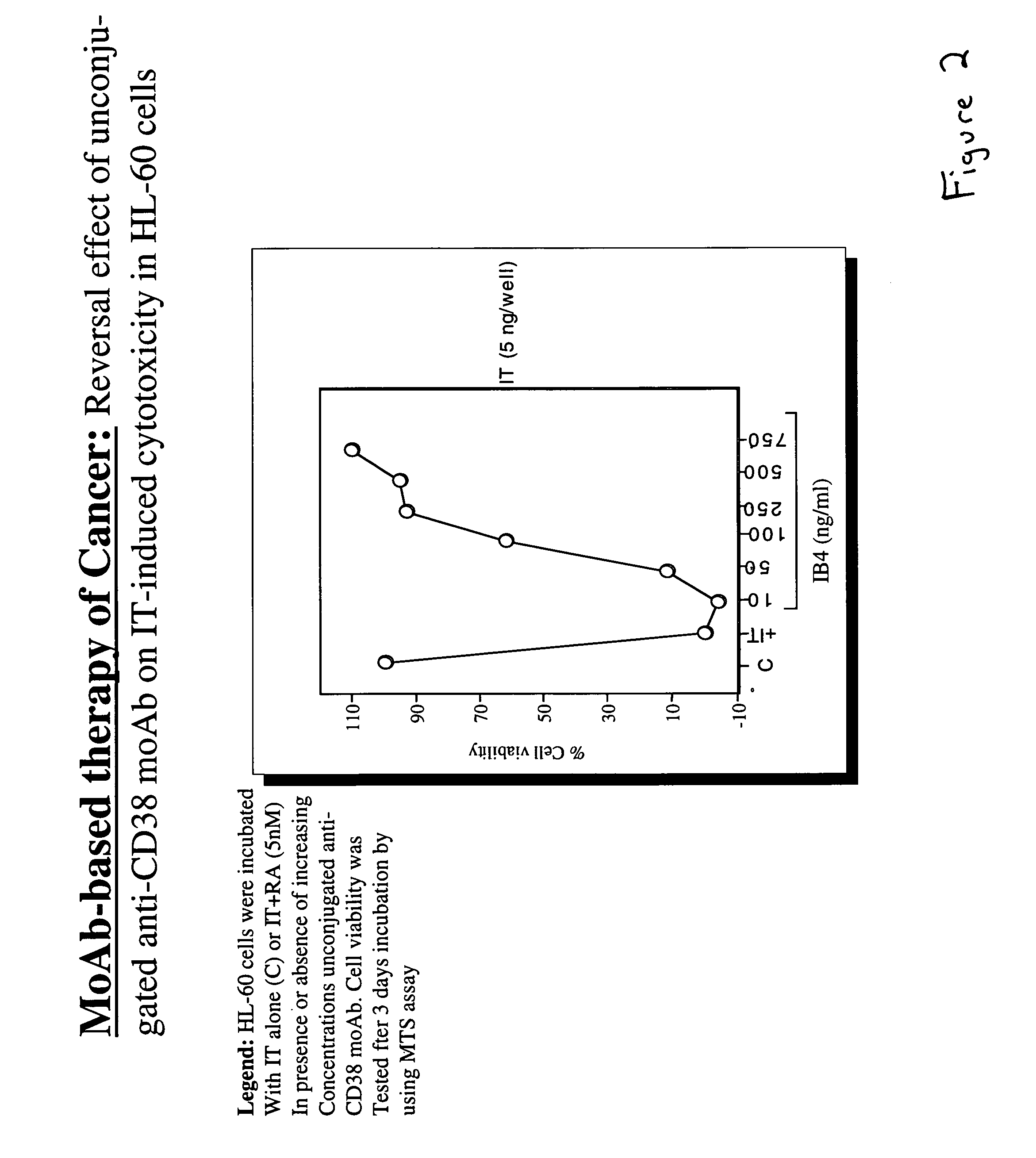
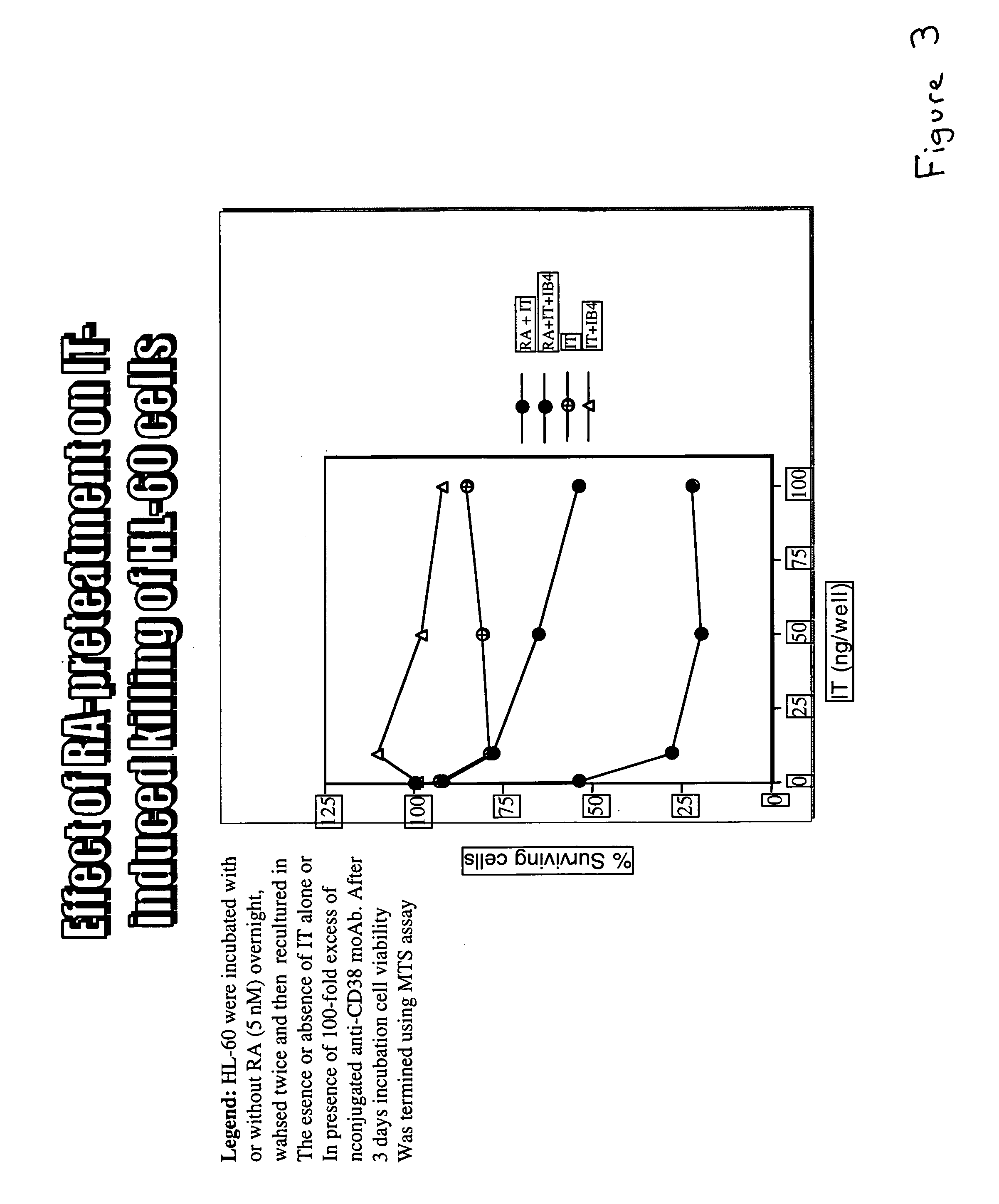
Potentiation of anti-CD38-Immunotoxin cytotoxicity
The present invention is directed to the use of agents that induce high levels of cell surface molecules to provide targets for immunotoxins directed against the same cell surface molecules. A specific example is given in which all-trans-retinoic acid (RA) is used to induce high levels of CD38 cell surface antigen expression in several myeloid and lymphoid leukemia cells. CD38 was then used as target for delivering plant toxin (gelonin) to leukemia cells. Treatment of leukemia cells with RA induced high levels of CD38 in those cells that otherwise had low CD38 expression. The RA-induced leukemia cells then became exquisitely sensitive to an immunotoxin constructed from an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody conjugated to the plant toxin gelonin.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Mutated anti-cd22 antibodies and immunoconjugates
ActiveUS7982011B2Immunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesCancer cell
Recombinant immunotoxins are fusion proteins composed of the Fv domains of antibodies fused to bacterial or plant toxins. RFB4 (Fv)-PE38 is an immunotoxin that targets CD22 expressed on B cells and B cell malignancies. The present invention provides antibodies and antibody fragments that have improved ability to bind the CD22 antigen compared to RFB4. Immunotoxins made with the antibodies and antibody fragments of the invention have improved cytotoxicity to CD22-expressing cancer cells. Compositions that incorporate these antibodies into chimeric immunotoxin molecules that can be used in medicaments and methods for inhibiting the growth and proliferation of such cancers. Additionally, the invention provides a method of increasing the cytotoxicity of forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (“PE”) with the mutation of a single amino acid, as well as compositions of such mutated PEs, nucleic acids encoding them, and methods for using the mutated PEs.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods for treating a plant exposed to a phytotoxicant
Methods of treating a plant exposed to a phytotoxicant are provided. Embodiments of the subject methods include identifying a plant exposed to a phytotoxicant and applying an assimilable carbon-skeleton energy component-comprising composition to the identified plant. Embodiments of the subject compositions may include one or more of a macronutrient component, micronutrient component, vitamin / cofactor component, complexing agent and microbe. Kits for use in practicing the subject invention are also provided. The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications in which a plant is phytotoxic or at least in danger of becoming phytotoxic due to exposure or potential exposure to a phytotoxicant.
Owner:YAMASHITA THOMAS T
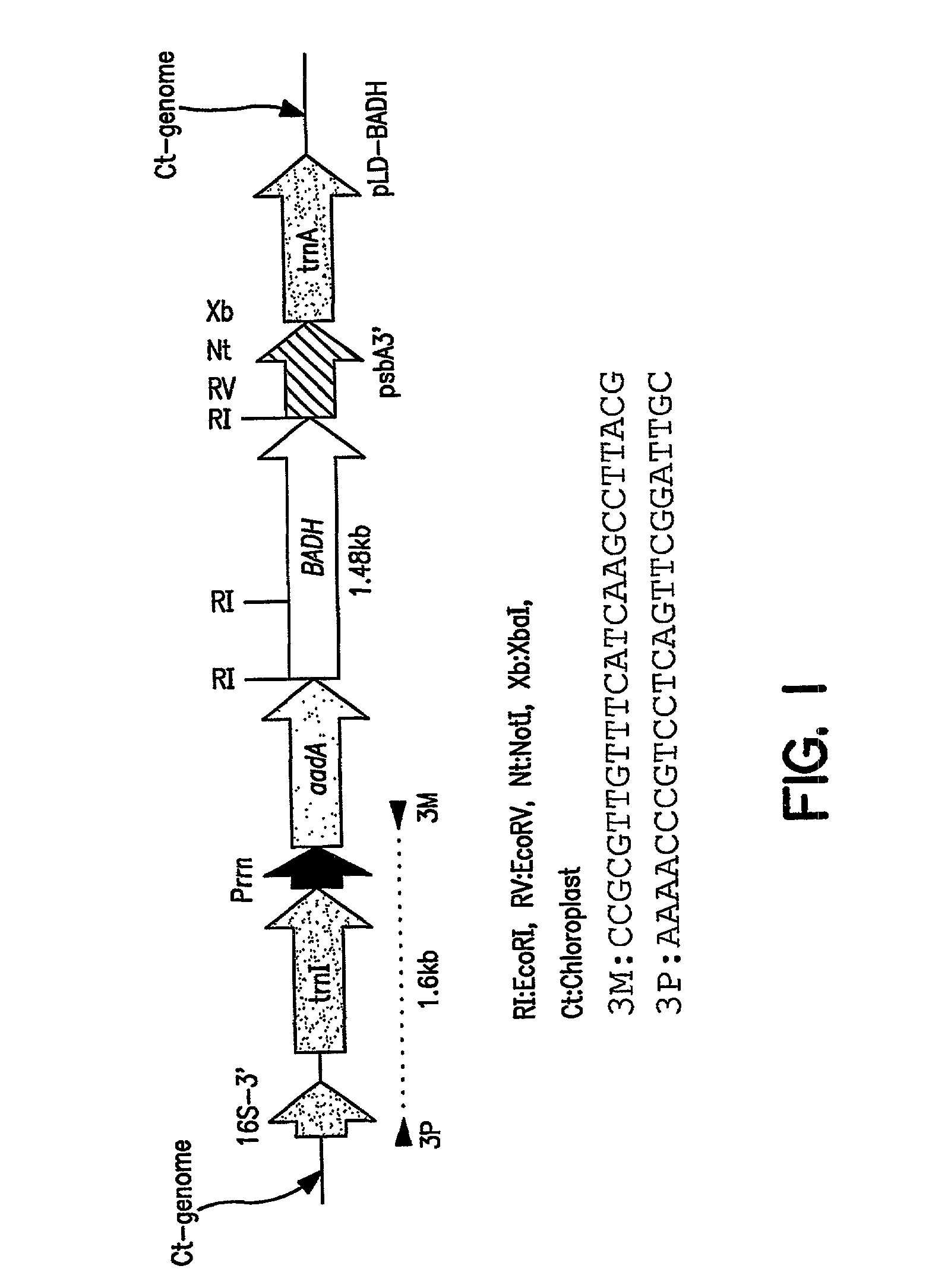
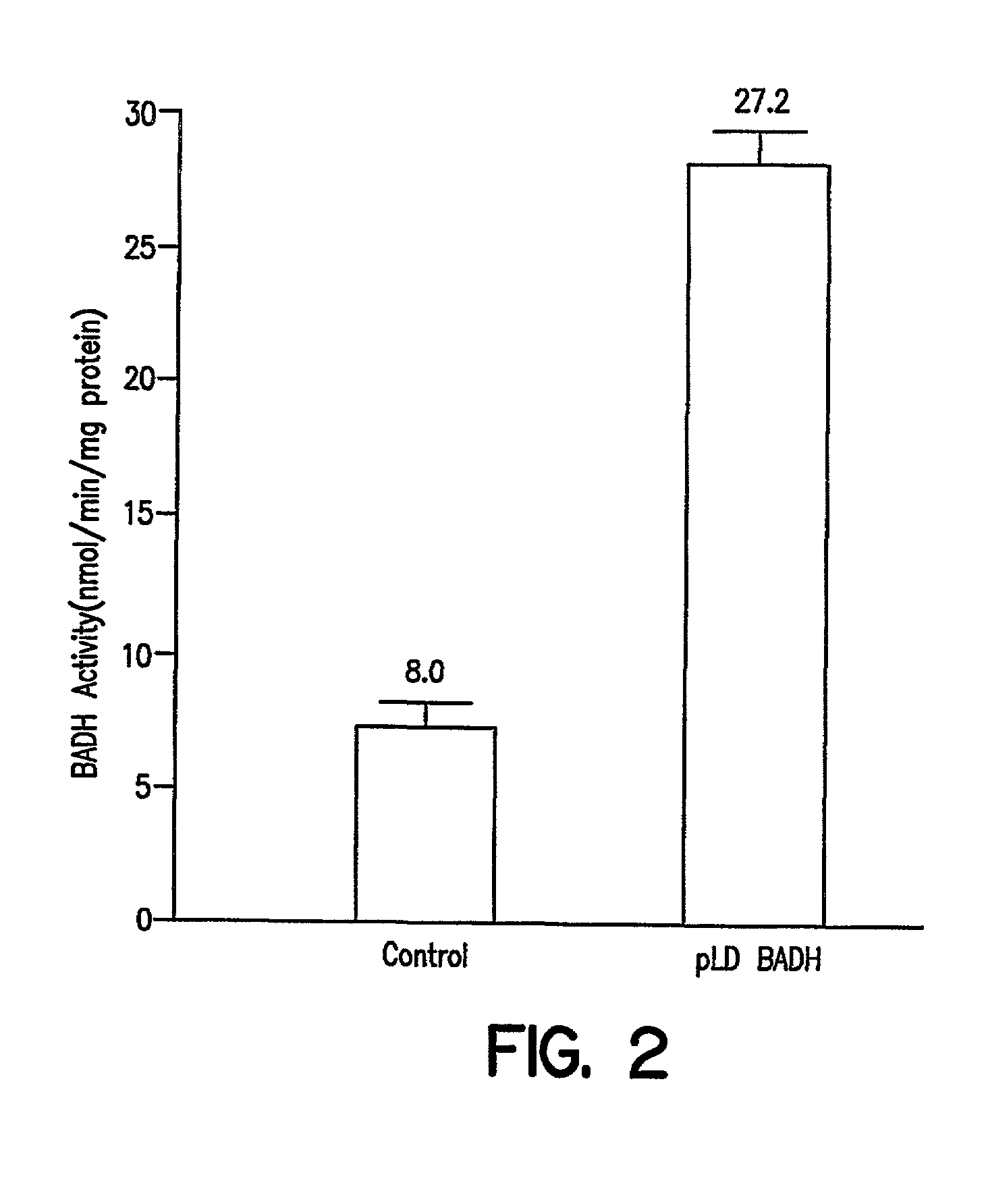
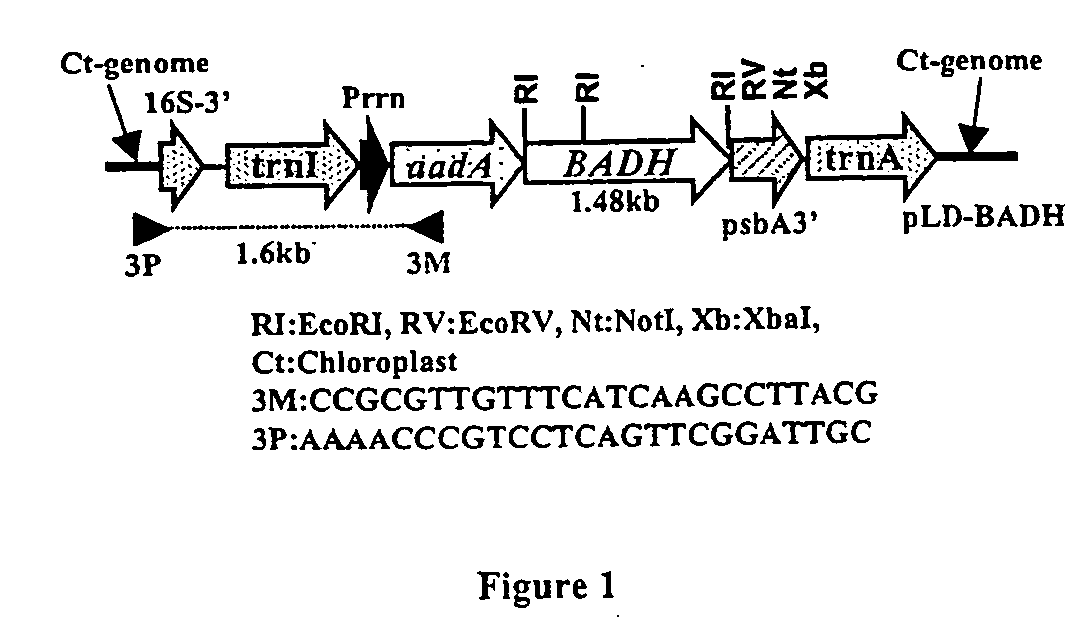
Marker free transgenic plants engineering the chloroplast genome without the use of antibiotic selection
InactiveUS20020137214A1Increased riskReduce development of resistanceOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesAntibiotic freeChloroplast
The present invention provides for a method to circumvent the problem of using antibiotic resistant selectable markers. In particular, target plants are transformed using a plastid vector which contains heterologous DNA sequences coding for a phytotoxin detoxifying enzyme or protein. The selection process involves converting an antibiotic-free phytotoxic agent by the expressed phytotoxin detoxifying enzyme or protein to yield a nontoxic compound. The invention provides for various methods to use antibiotic-free selection in chloroplast transformation.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA +1
Marker free transgenic plants: engineering the chloroplast genome without the use of antibiotic selection
InactiveUS20040231015A1Other foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesAntibiotic freeChloroplast
The present invention provides for a method to circumvent the problem of using antibiotic resistant selectable markers. In particular, target plants are transformed using a plastid vector which contains heterologous DNA sequences coding for a phytotoxin detoxifying enzyme or protein. The selection process involves converting a antibiotic-free phytotoxic agent by the expressed phytotoxin detoxifying enzyme or protein to yield a nontoxic compound. The invention provides for various methods to use antibiotic-free selection in chloroplast transformation.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
Pathogen-resistant grape plants
InactiveUS6995015B1Facilitate extraordinarily high-frequencyEnhanced embryogenic culture initiation frequencyMutant preparationAgriculturePhytotoxinPathogen
The invention features a method of producing a grape somatic embryo having resistance to a plant pathogen, the method including the steps of (a) culturing a grape somatic embryo in a first liquid culture medium that includes a plant growth regulator and a phytotoxin from a plant pathogen; (b) exchanging the first liquid culture medium for a second liquid culture medium not including the phytotoxin; (c) recovering a living grape cell or grape cell cluster from the second liquid culture, the living cell or cell cluster being resistant to the pathogen; and (d) culturing the grape cell or grape cell cluster in a third culture medium to produce a grape somatic embryo.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Biological pesticide having natural phytotoxin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102246826ASimple recipeSimple manufacturing methodBiocideMolluscicidesSocial benefitsSanguinarine
The invention provides a biological pesticide having natural phytotoxin and a preparation method thereof. The biological pesticide consists of barbadosnut seed extract, barbadosnut leaf extract and sanguinarine, wherein the barbadosnut seed extract is 50 to 75 percent ethanol solution extract and the barbadosnut leaf extract is 50 to 75 percent ethanol solution extract. The formula of the biological pesticide is simple and the preparation method is simple. When the pesticide is used for killing pesticides in crops, the pest killing effect is high. Meanwhile, the pesticide is also a new plant molluscicide with remarkable molluscacidal effect, and the pesticide causes little environment pollution and can create high economic and social benefit.
Owner:王乃利
Plant bactericidal agent containing diniconazole and triabendazole
The invention relates to a phytotoxin containing diniconazole and probenazole, and is characterized in that the diniconazole and the probenazole are compounded with accessory ingredient and excipient to prepare the preparations including pulvis, wettable powder, suspending agent and granular formulation; the mixture of the diniconazole and the probenazole accounts for 0.1-95% of the weight of the preparation, and the mixed weight ratio of the diniconazole and the probenazole is 1-1:100. The phytotoxin has the advantages that the diniconazole and the probenazole have remarkable synergy and continuous control effect; sterilization spectrum is expanded, the dosage of pesticide is reduced, the residual quantity of pesticide on the crops is reduced, and environmental pollution is also reduced; the phytotoxin is also safe for hunman beings and animals, and has good environmental compatibility; the plant disease is not easy to generate drug fastness.
Owner:张少武
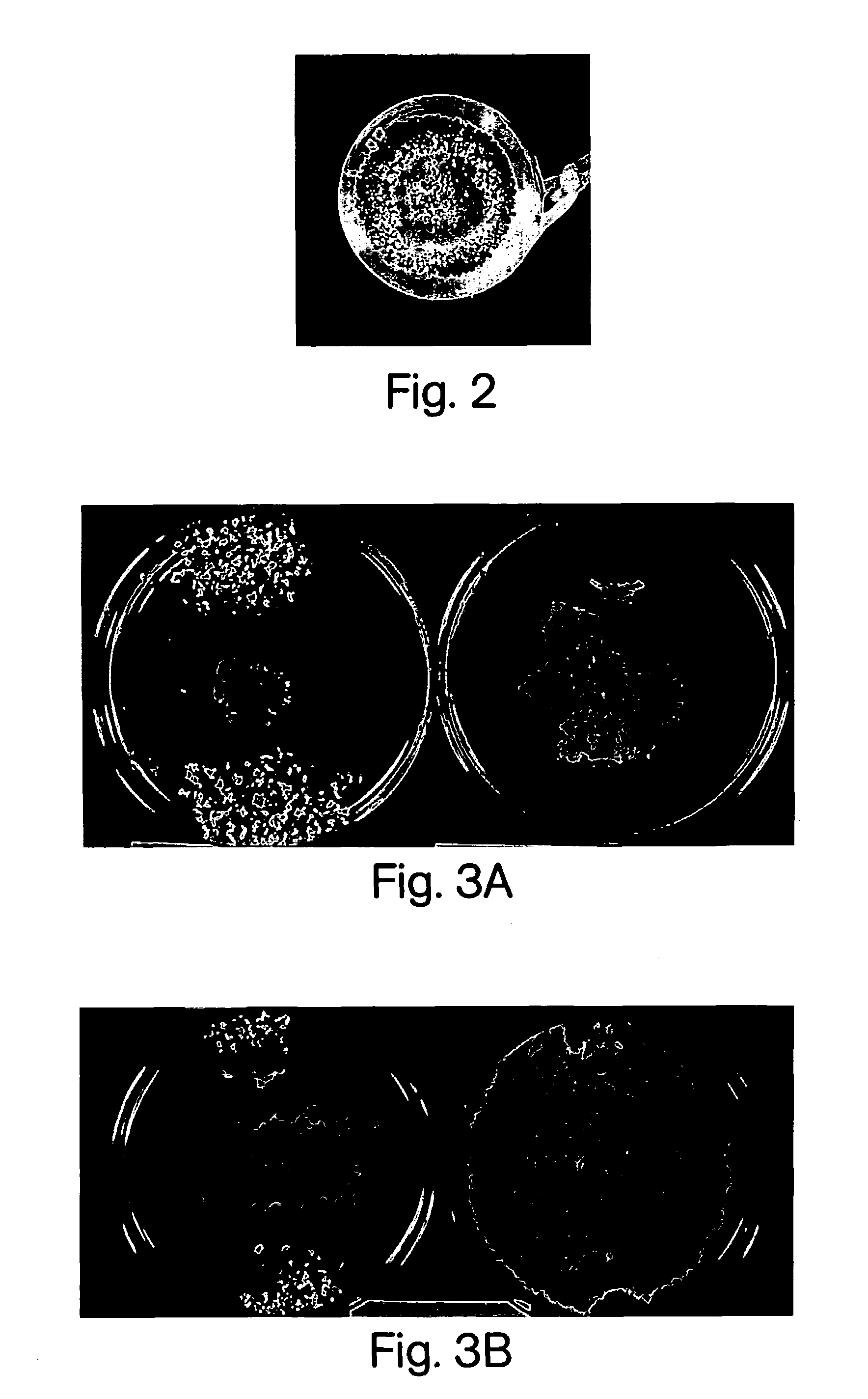
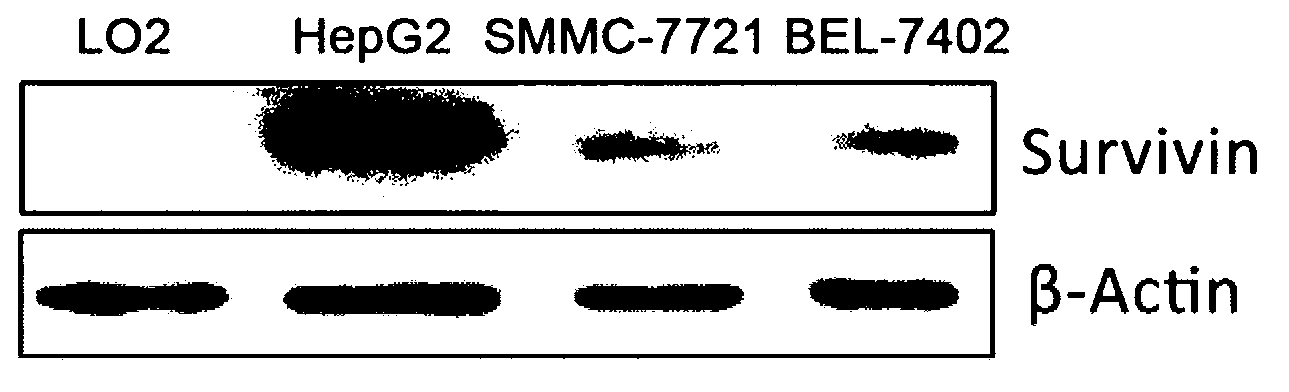
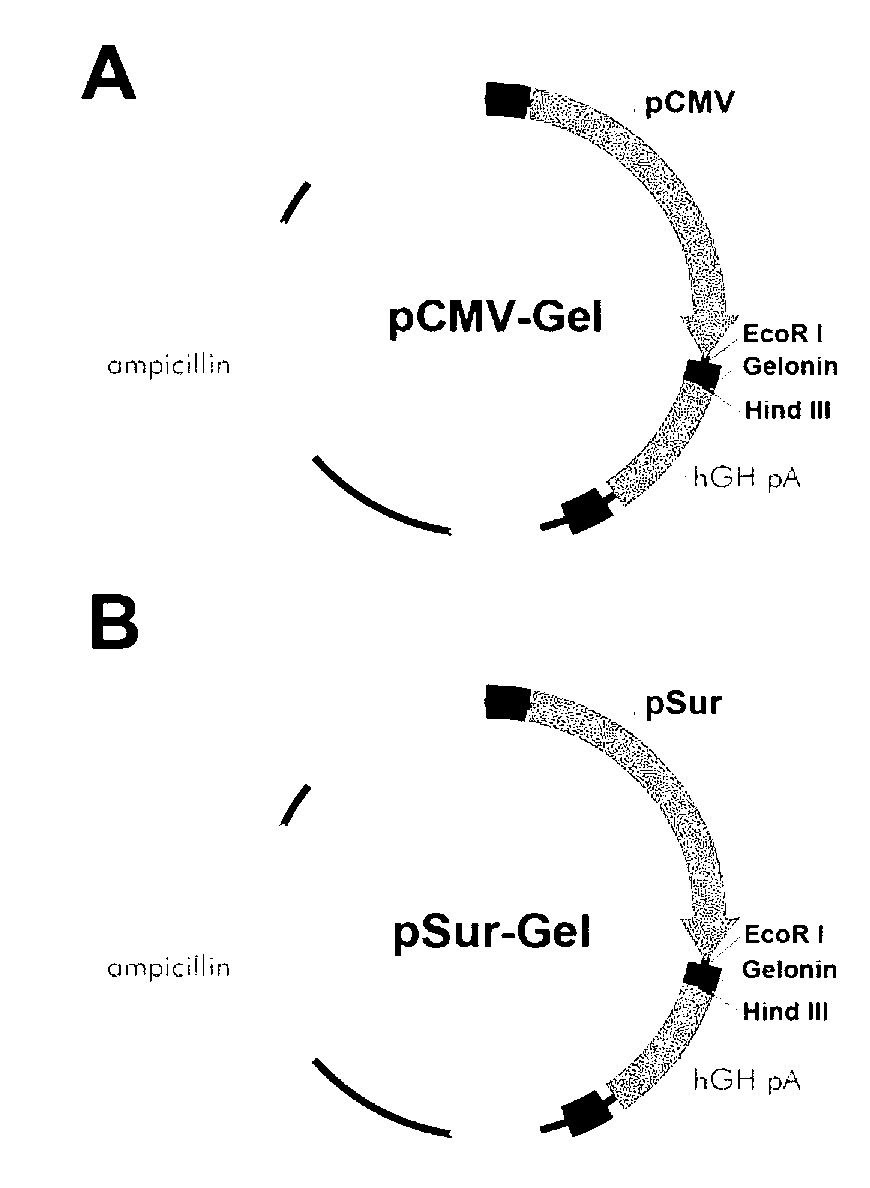
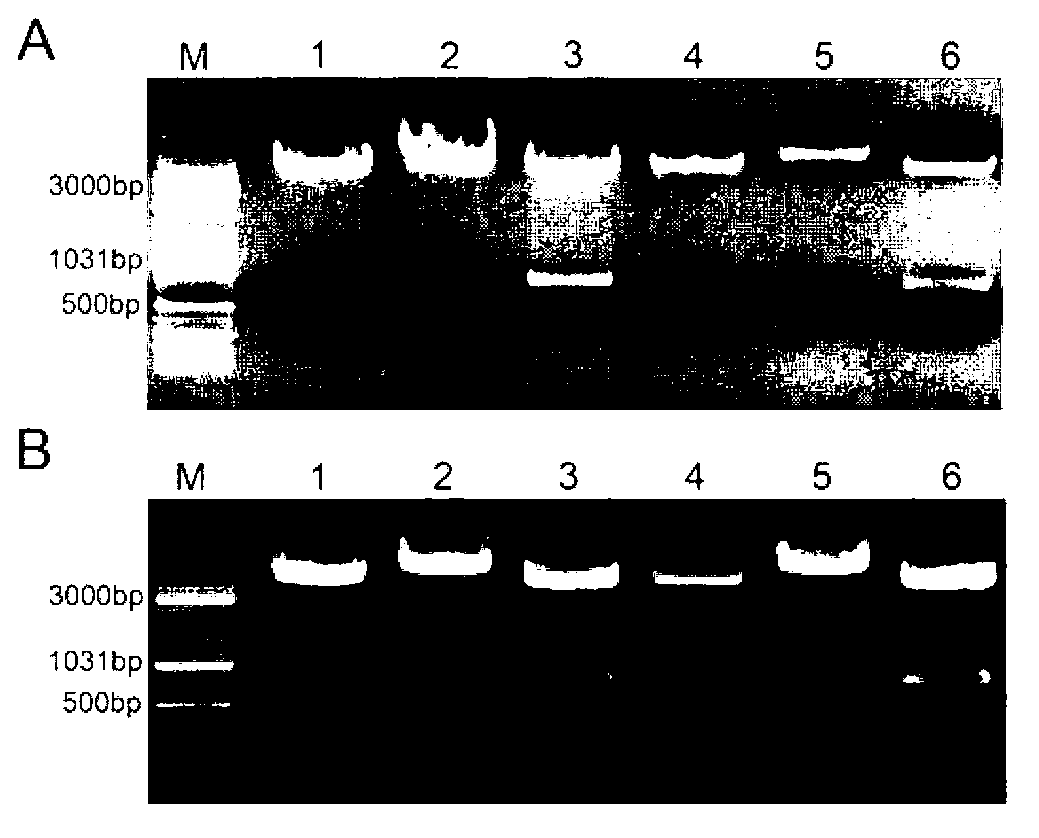
Survivin promoter mediated recombinant vector for expressing Gelonin phytotoxin genes and usage thereof
InactiveCN103290029AInhibition of value addedGrowth inhibitionGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemGeloninClinical tests
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and in particular relates to a survivin promoter mediated recombinant vector for expressing Gelonin phytotoxin genes and usage of the recombinant vector, aiming to a method for searching safe and effective phytotoxin to treat liver cancer. The technical scheme of the invention is that a survivin promoter is operatively connected with a gene expression frame formed by the Gelonin phytotoxin genes. The invention also provides the survivin promoter mediated recombinant vector for expressing the Gelonin phytotoxin genes. A new method is provided for survivin promoter mediated phytotoxin target gene treatment, and a safe and effective cancer treatment new strategy is provided for a clinical test; and therefore, the recombinant vector has high application value and wide application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Successive planting resistant agent
ActiveCN1907035APromote germinationIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMetabolitePhytotoxin
The invention discloses an anti-stubble agent, which comprises the following parts: insect nematology, insect body, insect metabolite and disaccharide or oligosaccharide. The invention can supplement soil nutrition, which reduces nematology quantity effectively.
Owner:刘奇志
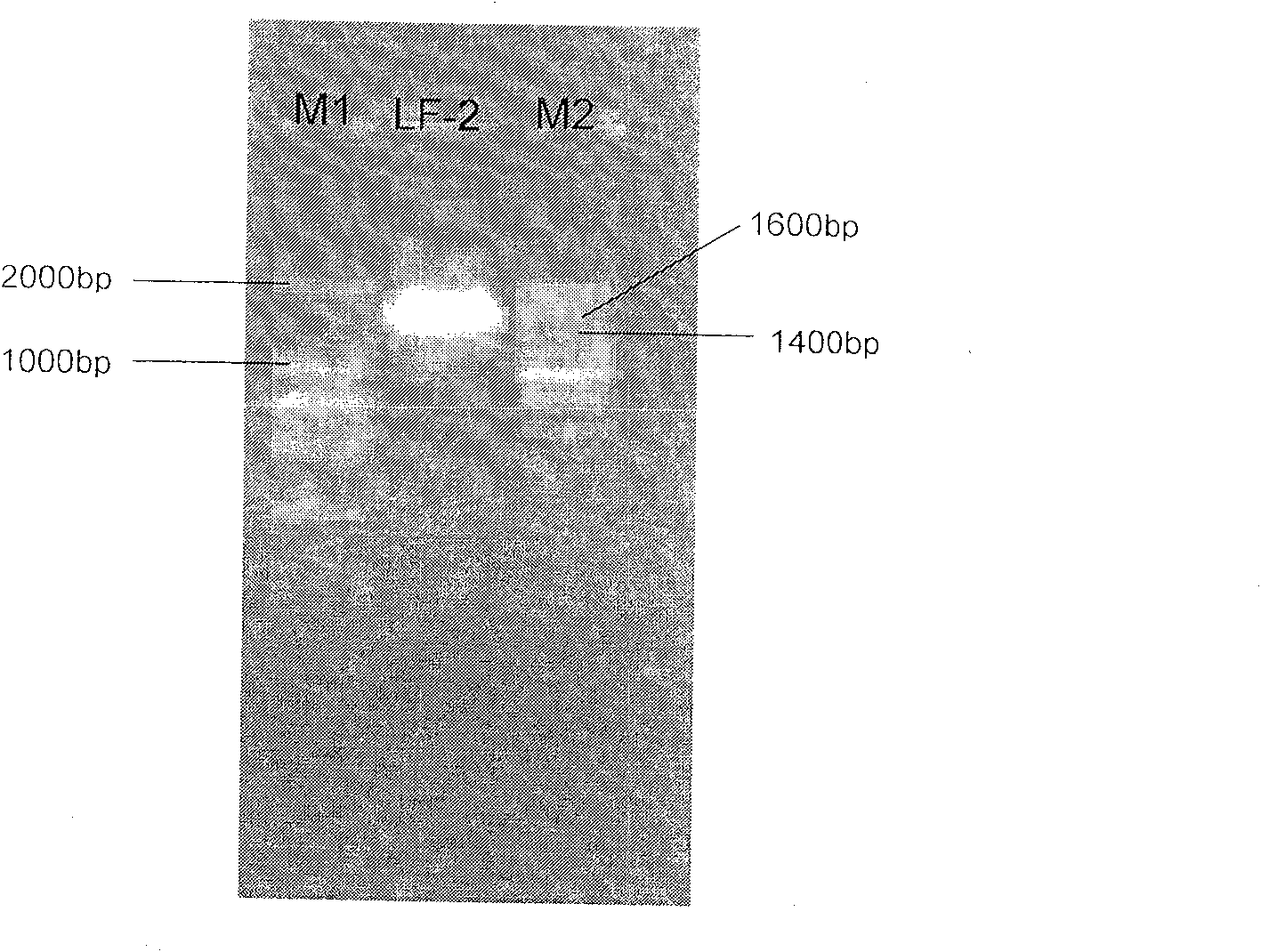
New campylobacterium LF-3 and its application
InactiveCN101067122AAvoid poisoningBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAbove groundPhytotoxin
The present invention discloses one kind of new Bacillus flexus LF-3 in the preservation number of CCTCC M 206128. The Bacillus flexus LF-3 can degrades phytotoxin effectively, and eliminate toxicity of the alkaloid 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethyl piperidone (TMPD) extracted and separated from the above-ground parts of Oxytropis glacialis as one kind of poisonous grassland weed. The present invention is significant in eliminating the poisoning of Oxytropis glacialis and the biological control and ecological research of Oxytropis glacialis.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Herbicide comprising phytotoxins of Lasiodiplodia theobromae (LT) fungus, a process of producing the herbicide and a method of using the same
InactiveUS6277786B1Sure easyInhibitionBiocideAnimal repellantsLasiodiplodia theobromaeBotryodiplodia theobromae
The invention relates to describe host-specific extracellular phytotoxins produced by Lasiodiplodia theobromae (LT, also Botryodiplodia theobromae) that has a broad range as a pre-emergent and / or post-emergent bioherbicide, this isolate has been deposited in Microbial Type Culture Collection, Chandigarh, India and given an accession number MTCC 3068, a method using LT-toxin has been developed for controlling certain herbs including Parthenium hysterophorus, duckweeds, jimsonweed, black nightshade, prickly sida and Euphorbia hirta, these phytotoxins can be used partially pure, as a cell-and spore-free filtrate, a crude filtrate, or a crude suspension of the culture and optionally along with other additives.
Owner:NAGARJUNA HLDG PRIVATE +1
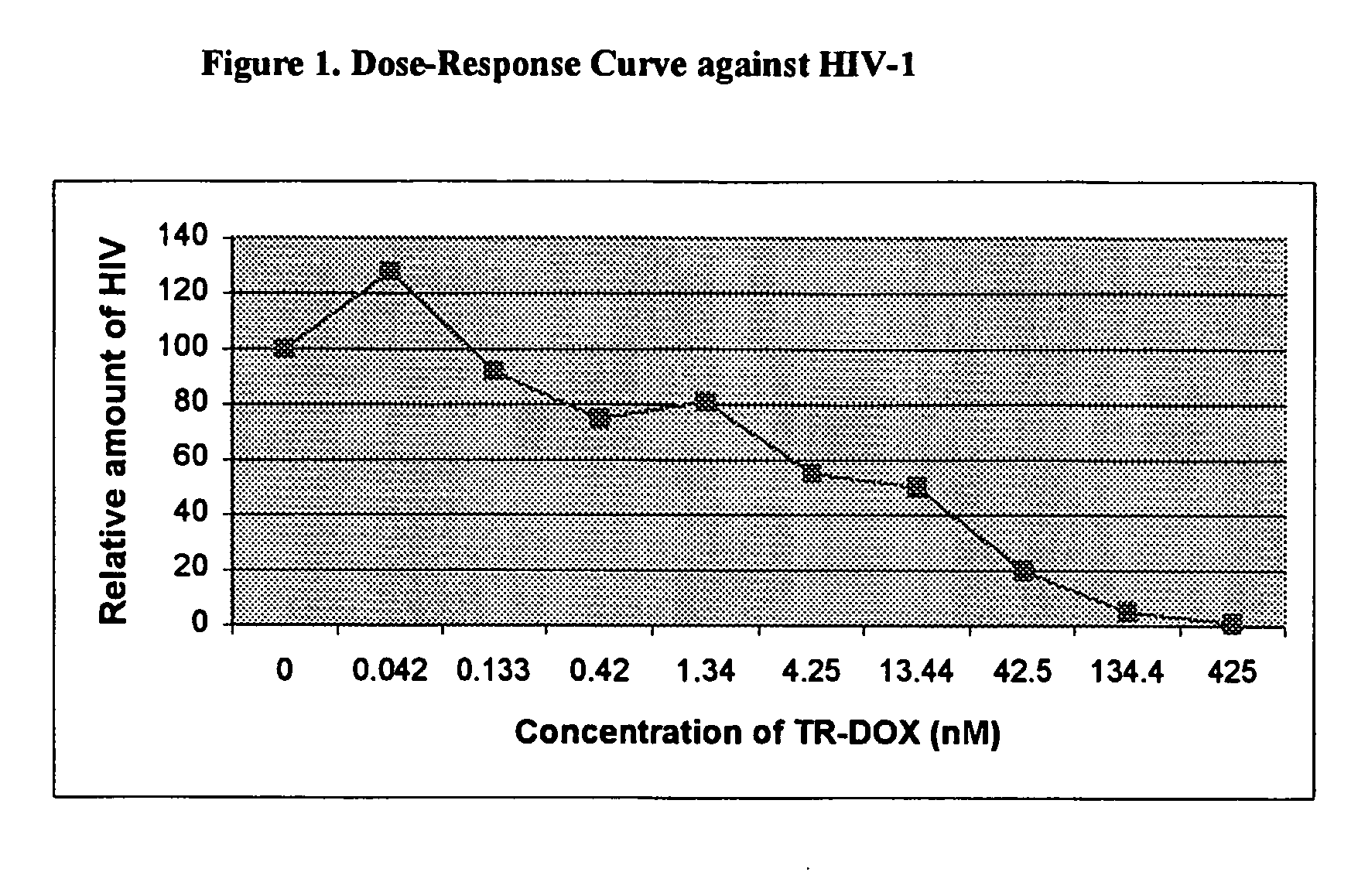
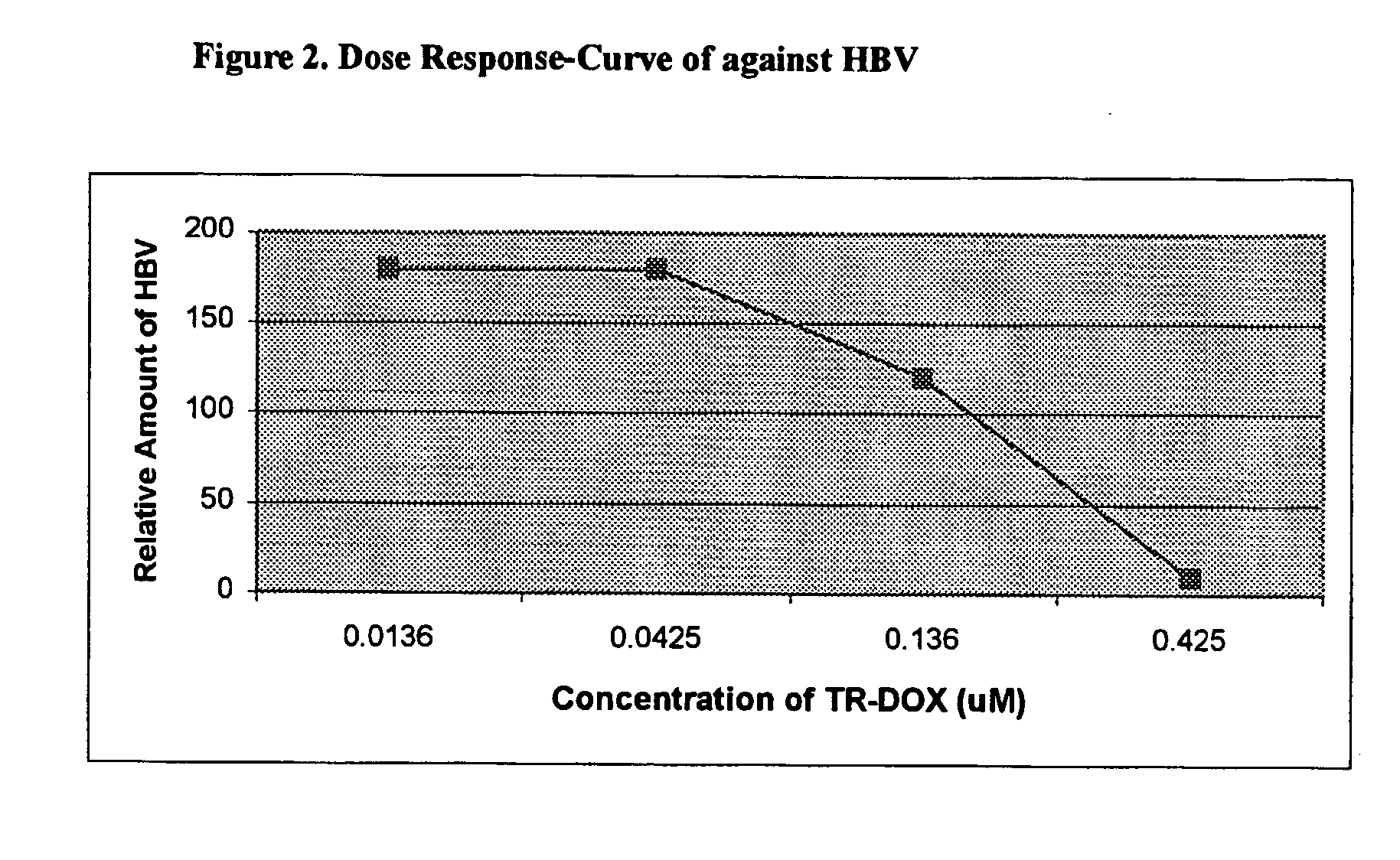
Targeted delivery of drugs for the treatment of viral infections
InactiveUS20040152071A1Antibacterial agentsBiocideAlkylating antineoplastic agentCytotoxic antibiotics
Conjugates of transferrin or transcobalamin with anti-viral agents are useful in the treatment of viral infections. Suitable anti-viral agents include apoptosis inducing compounds, compounds which inhibit the replication of the virus, a cytotoxic antibiotic, an alkylating agent, a plant toxin, and a bacterial mutant toxin. Transferrin or transcobalamin is preferably coupled to the anti-viral agent by means of glutaraldehyde.
Owner:FAULK PHARMA INC
Pathogen-resistant grape plants
InactiveUS20060035377A1Promote formationIncrease frequencyOther foreign material introduction processesAgricultureGrowth plantPhytotoxin
Owner:SUBRAMANIAN JAYASANKAR +2
Triticum aestivum Mevalonate kinase gene TaMVK, and separation cloning and enzymatic activity determination method thereof
The invention which belongs to the molecular biological field relates to a technology of key enzymatic gene Triticum aestivum Mevalonate kinase gene TaMVK separation cloning, enzymatic protein prokaryotic expression, enzymatic protein separation purifying, and in vitro detection of the enzymatic activity, wherein the TaMVK is obtained from a Triticum aestivum species Zea mays, and can be synthesized with isoprenoid substances of Triticum aestivum chlorophyll, carotenoid, cytokinin, abscisic acid, gibberellin, dolichol, terpenoids, coenzyme Q, sterol, phytotoxin and the like. An important technological reserve is provided for further constructing an eukaryotic gene expression vector of the Mevalonate kinase gene, converting corresponding crops, especially plants which depend on secondary metabolism to obtain important business values, and discussing relationships of the overexpression of the Mevalonate kinase gene in acceptor plants with important agronomic properties of secondary metabolic products, the grain size, the grain weight, and the like, thereby improving the crop output, dissecting structures of the intron, the exon and the promoter of the Mevalonate kinase gene, researching functions of the promoter, and developing a relevant molecular mark.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Process for producing herbicides from a fungus alternaria alteranata f.sp. lantanae
A process for producing herbicides from a fungus Alternaria alteranata f.sp. lantanae deposited as a pure culture as ITCC-4896, comprising culturing the fungus in a liquid broth; subjecting the broth to the step of filtration to separate the broth containing phytotoxins from mycelium; extracting the phytotoxins from said broth to obtain the phytotoxins; and subjecting the phytotoxins to chemical characterization.
Owner:NAT RES DEV CORP
Methods for Treating a Plant Exposed to a Phytotoxicant
Methods of treating a plant exposed to a phytotoxicant are provided. Embodiments of the subject methods include identifying a plant exposed to a phytotoxicant and applying an assimilable carbon-skeleton energy component-comprising composition to the identified plant. Embodiments of the subject compositions may include one or more of a macronutrient component, micronutrient component, vitamin / cofactor component, complexing agent and microbe. Kits for use in practicing the subject invention are also provided. The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications in which a plant is phytotoxic or at least in danger of becoming phytotoxic due to exposure or potential exposure to a phytotoxicant.
Owner:YAMASHITA THOMAS T
Formulations for imparting traceability and/or trackability to one or more chemicals
The invention relates to chemical formulations that can be used to render such chemicals easier to identify upon application to a surface. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to formulations designed to render herbicides, fungicides, pesticides, insecticides and / or phytotoxins easier to identify upon application to one or more types of vegetation. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to formulations designed to render water-soluble herbicides, fungicides, pesticides, insecticides and / or phytotoxins easier to identify upon application to one or more types of vegetation.
Owner:CRIMALDI JOSEPH JAMES
Triticum aestivum mevalonate kinase (TaMVK) gene as well as isolation colonizing and enzyme activity measuring method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to technologies for isolation colonizing of a triticum aestivum mevalonate kinase (TaMVK) gene as a key enzyme gene which is obtained from Jinan 13 as a wheat variety and participates in isoprene-like substances such as wheat chlorophyll, carotenoid, cytokinin, abscisic acid, gibberellin, dolichol, terpenoid, coenzyme Q, sterol, phytotoxin and the like as well as prokaryotic expression of enzyme protein, separated purification of the enzyme protein and detection in vitro on the enzyme activity of the TaMVK gene. The invention provides important technical storage for further constructing a eukaryotic gene expression vector of the TaMVK gene and converting the eukaryotic gene expression vector into a corresponding crop, particularly obtaining plants with important commercial value by means of secondary metabolism, discussing the relationships between the overexpression of the TaMVK gene in a receptor plant and important economical characters such as a secondary metabolite, the seed size, the grain weight and the like, further improving the yield of the crops, analyzing the structures of an introne, an exon and a promoter of the TaMVK gene, researching the functions of the promoter and developing a relevant molecular marker.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel acid-producing Klebsiella bacterium LF-1 and uses thereof
The invention discloses Klebsiella oxytoca LF-1, which was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 20, 2006, and its preservation numbers are respectively CCTCC NO: M 206126; the Klebsiella oxytoca Bacteria LF-1 can effectively degrade phytotoxins, especially the toxicity of the toxic alkaloid 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidone (TMPD) extracted and separated from the above-ground parts of Oxytropis glaciens, which is of great importance to the thorough Solve the poisonous damage of Oxytropis glacier, and play a positive role in the biological control of grassland poisonous weeds and the research of grassland ecology.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Formulations for imparting traceability and/or trackability to one or more chemicals
The invention relates to chemical formulations that can be used to render such chemicals easier to identify upon application to a surface. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to formulations designed to render herbicides, fungicides, pesticides, insecticides and / or phytotoxins easier to identify upon application to one or more types of vegetation. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to formulations designed to render water-soluble herbicides, fungicides, pesticides, insecticides and / or phytotoxins easier to identify upon application to one or more types of vegetation.
Owner:CRIMALDI JOSEPH JAMES
High-affinity aptamers specifically binding to lactoxins 1 and 4 and their applications
ActiveCN105505939BImprove stabilityHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsGonyautoxinPhytotoxin
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and provides an aptamer capable of being specifically combined with gonyautoxin 1 (GTX1) and gonyautoxin 4 (GRX4). The general formula is 5'-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATG-N40-CCTATGCGTGCTACCGTGAA-3', wherein N represents any one of bases A, T, C and G, and N40 represents a random sequence with the length of 40bp. The high-affinity aptamer capable of being specifically combined with GTX1 and GTX4 is obtained by screening on the basis of graphene oxide SELEX technology. The single-chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) adapter can be used for separation and enrichment of trace amounts of GTX1 and GRX4 in the sample, analysis detection of GTX1 and GRX4, preparation of neutral or antagonistic GTX1 and GRX4 drugs, and removal of toxins in a water body.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Process for producing herbicides from a fungus Alternaria alteranata f.sp. lantanae
A process for producing herbicides from a fungus Alternaria alteranata f.sp. lantanae deposited as a pure culture as MTCC 5432 and ITCC-4896, comprising culturing the fungus in a liquid broth; subjecting the broth to the step of filtration to separate the broth containing phytotoxins from mycelium; extracting the phytotoxins from said broth to obtain the phytotoxins; and subjecting the phytotoxins to chemical characterization.
Owner:NAT RES DEV CORP
PD-L1 targeting immunotoxin as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113912733AStrong specificityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEngineered geneticMutant
The invention relates to PD-L1 targeting immunotoxin as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The immunotoxin comprises a carrier and toxic molecules. The carrier is an antibody or other polypeptides capable of being combined with PD-L1 molecules; the toxic molecules are bacterial toxins, plant toxins and human-derived toxic molecules, and mutants of these toxins. The immunotoxin is formed by coupling the toxic molecule with a carrier capable of being combined with a tumor cell PD-L1 through a chemical cross-linking method, or the immunotoxin is expressed by fusing genes of the toxic molecule and the carrier through a gene engineering method, and the immunotoxin can be used for treating tumors. According to the invention, the chemical coupling immunotoxin D-CUS245C based on the cucurmosin mutant CUS245C and the PD-L1 monoclonal antibody Durvamab is successfully prepared; the immunotoxin has a remarkable targeted killing effect on PD-L1 overexpressed tumor cells, and the maximum targeted therapeutic index can reach 1,100,000 or above. Therefore, the PD-L1 targeting immunotoxin has a wide anti-tumor application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Successive planting resistant agent
ActiveCN100479663CPromote germinationIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMetabolitePhytotoxin
The invention discloses an anti-stubble agent, which comprises the following parts: insect nematology, insect body, insect metabolite and disaccharide or oligosaccharide. The invention can supplement soil nutrition, which reduces nematology quantity effectively.
Owner:刘奇志
Agricultural compositions and methods related thereto
PendingUS20220174960A1Improve abilitiesCalcareous fertilisersPlant growth regulatorsActive agentPhytotoxin
The invention relates to compositions for use in agriculture and horticulture, wherein the compositions comprise one or more carbohydrates and one or more active agents selected from the group comprising one or more phytotoxins, one or more nutrients, and one or more organic molecules. Methods of preparing and using the compositions are also provided, for example in the control of unwanted plants, to promote the growth of one or more desired plants, and / or to minimise environmental impacts stemming from the widespread use of large quantities and concentrations of agricultural chemicals.
Owner:FORD STEPHEN REYNOLD +4
Preparation method and application of pittosporum tobira fruit extract
InactiveCN106977359AEfficient extractionStrong aromaOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsFiltrationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a preparation method of pittosporum tobira fruit extract. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) weighing pittosporum tobira fruits, and mixing the weighed pittosporum tobira fruits with 95% ethanol; (2) performing reflux extraction and suction filtration at a high temperature, collecting an extraction liquid, extracting the filter residues for three times, and combining the extraction liquid; and (3) concentrating the extraction liquid in the step (2) in vacuum at a reduced pressure and drying the same to constant weight to obtain the pittosporum tobira fruit extract. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple and reasonable in design, and can effectively extract active ingredients of the pittosporum tobira fruits. In important raw materials such as medicines, food and cosmetics, more than half of the compounds are sesquiterpenoids which almost have relatively strong fragrance and biological activity, have many important biological functions and physiological activity and further have activities such as bacteria resistance, virus resistance, cytokine, immunosuppression, tumor resistance, phytotoxin, insect hormone and insect anti-feedant and etc.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH +1
Staphylococcus pasteuri LF-2 and application thereof
InactiveCN100560712CBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsMicroorganismStaphylococcus pasteuri
A Staphylococcus pasteuri LF-2 is stored in CCTCC and the preservative number is M206127. It could degrade vegetable toxin and TMPD toxicity effectively and be used for grassland poisonous weeds biological control and ecological research.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
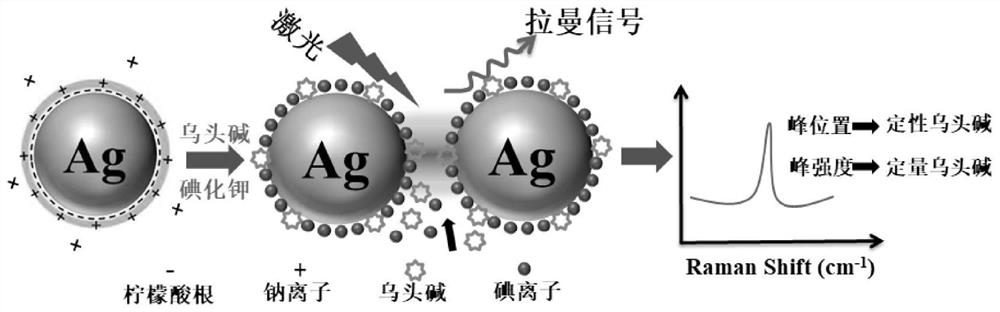
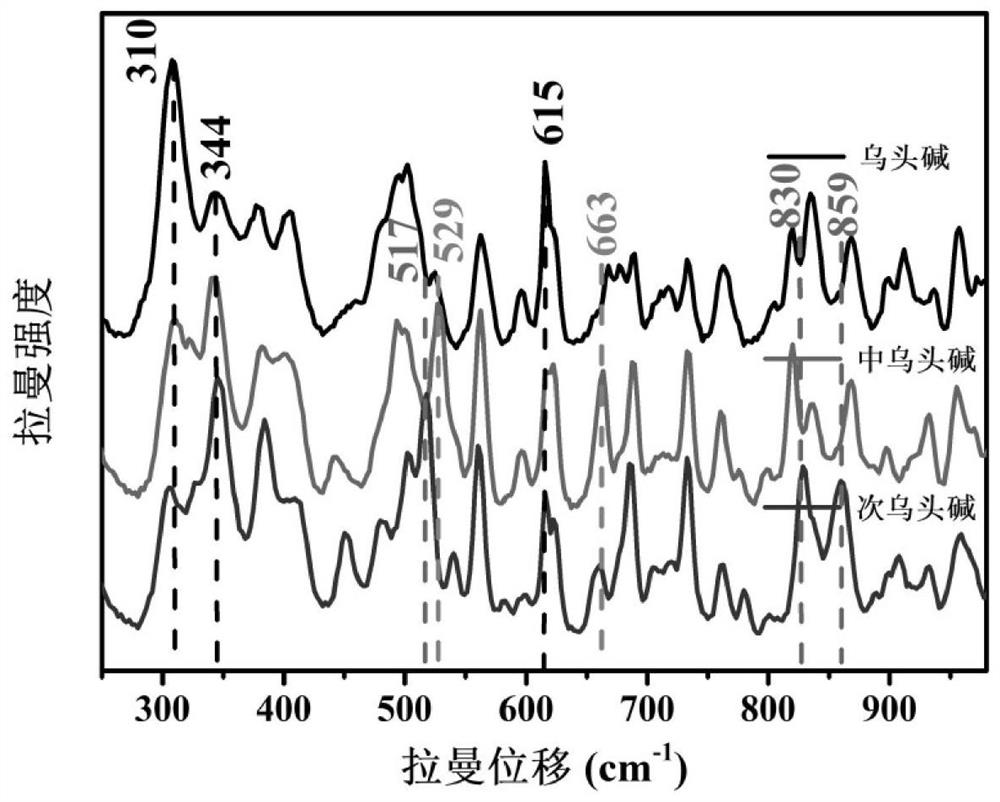
Qualitative and quantitative detection method of aconitine phytotoxin
ActiveCN112304919AQualitative Analysis of TypesRealize total quantitative analysisPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringInorganic saltsChemical physics
The invention discloses a qualitative and quantitative detection method of aconitine phytotoxin. The method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing standard solutions with different concentrations of aconitine, aconitine, aconitine and mixed aconitine with silver nanoparticle sol respectively, and adding an inorganic salt solution to obtain a standard to-be-detected solution; (2) detecting the standard to-be-detected solution by using a Raman spectrometer, and recording the position and intensity of a characteristic peak; and (3) obtaining a to-be-detected sample solution from a to-be-detected sample according to the same method as step (1), detecting the to-be-detected sample solution by using the Raman spectrometer, recording the position and intensity of the characteristic peak, and carrying out qualitative and quantitative analysis on the variety of aconitine phytotoxins in the to-be-detected sample according to step (2). The method has the advantages of being simple and rapid in detection process, rapid in response, low in detection cost, high in detection sensitivity and the like, and can meet the actual requirements of plant toxin field detection.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com