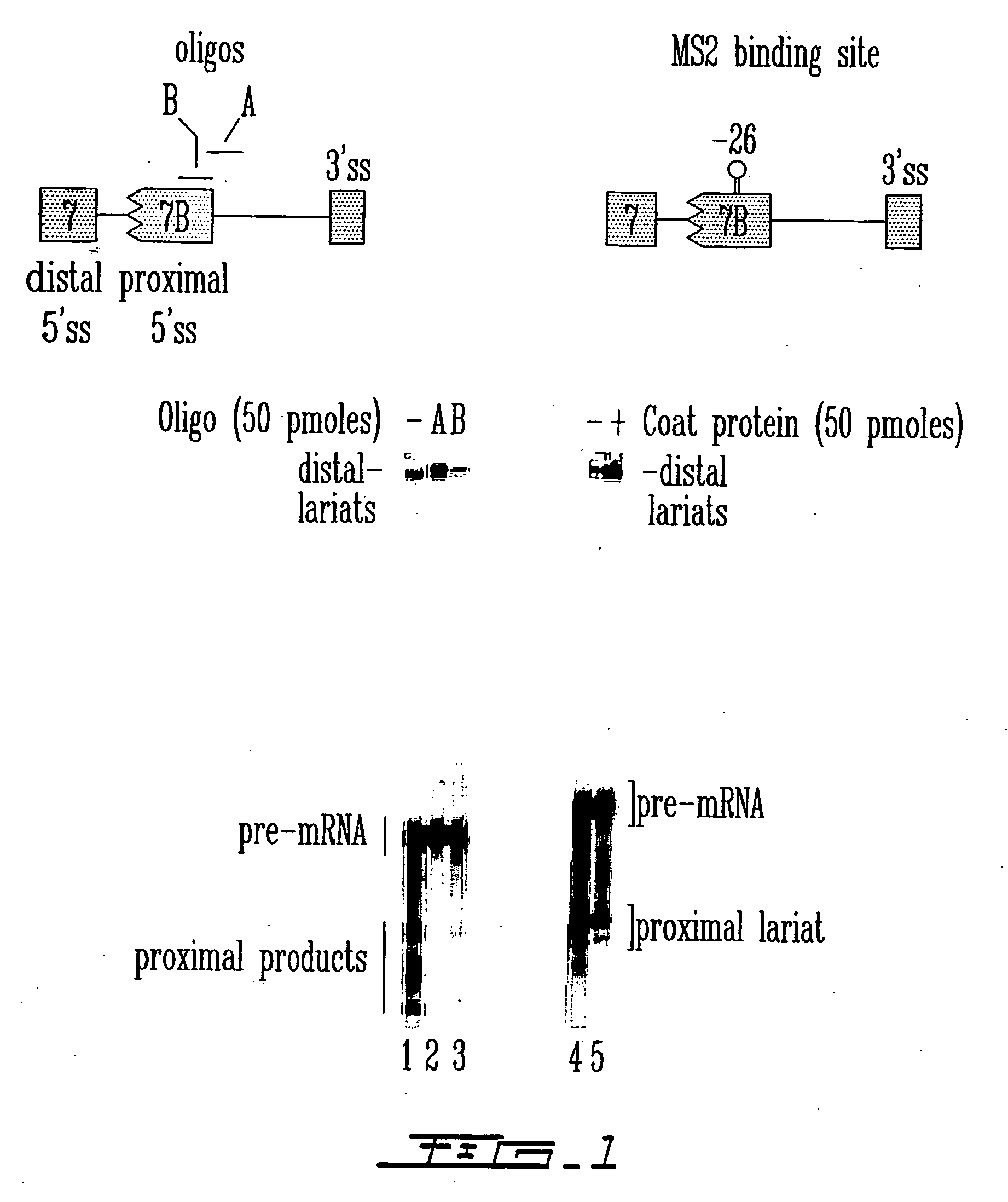
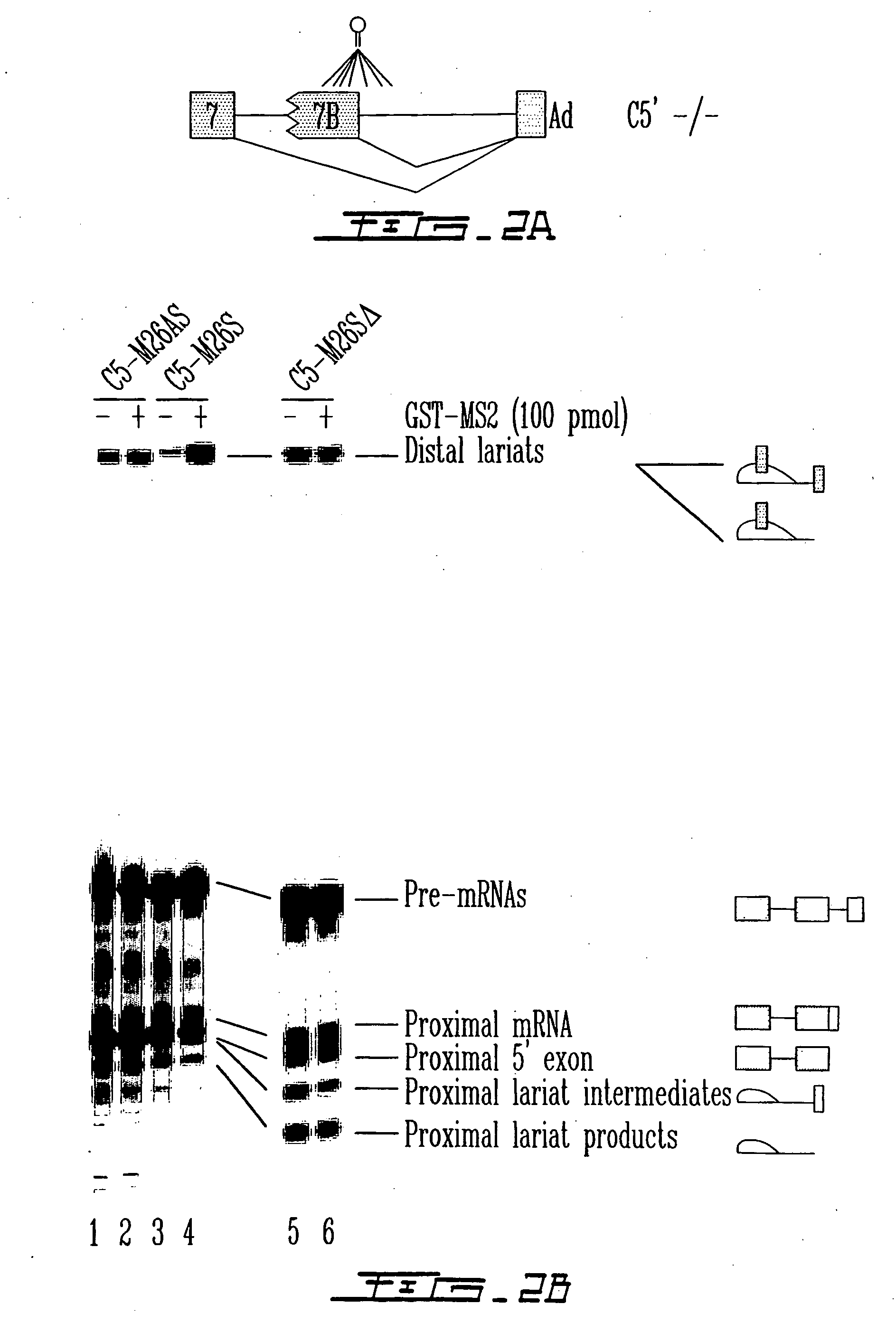
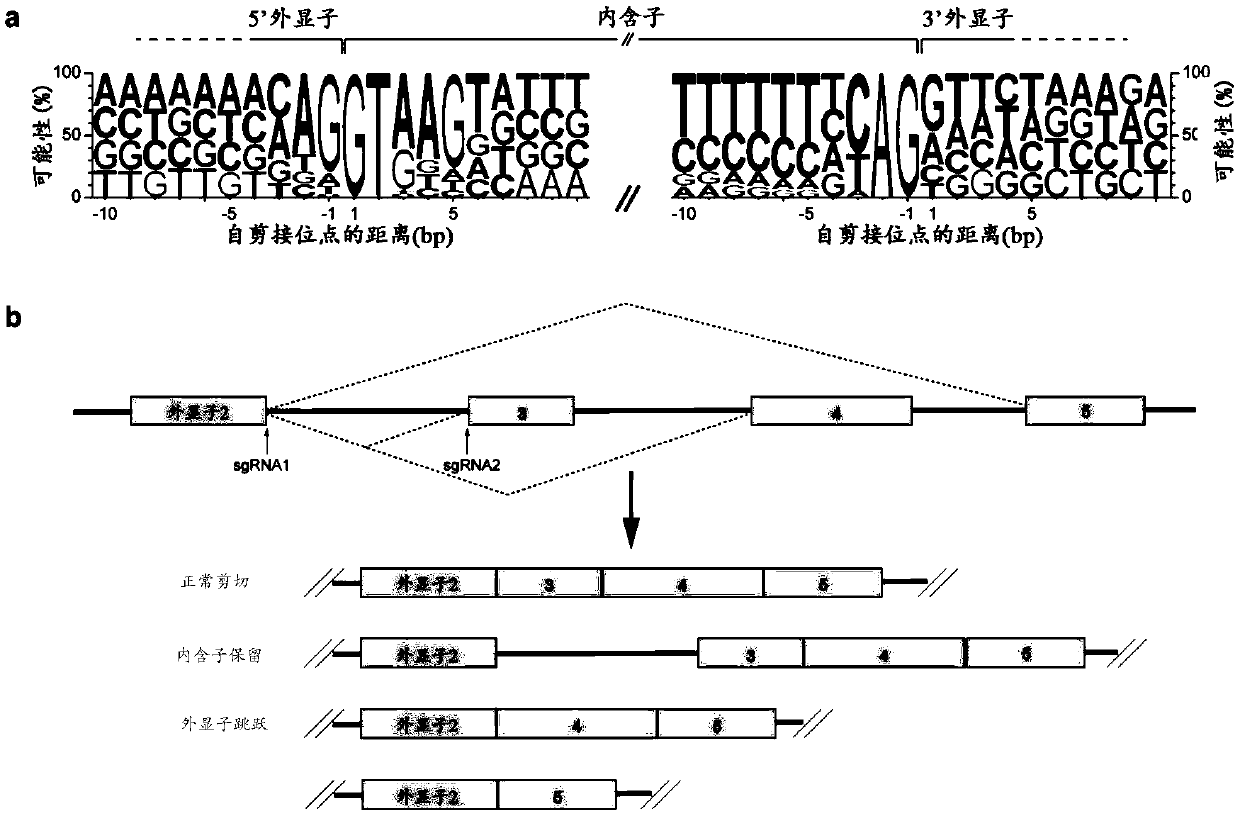
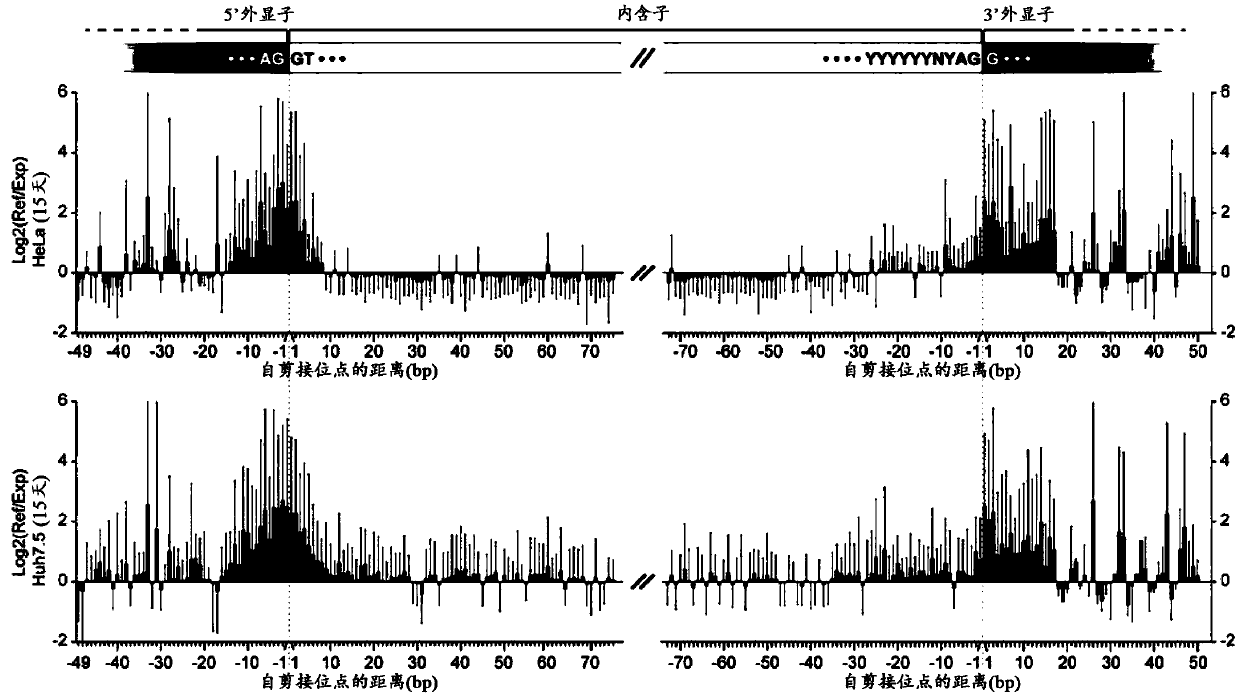
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Splice Site SNP" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
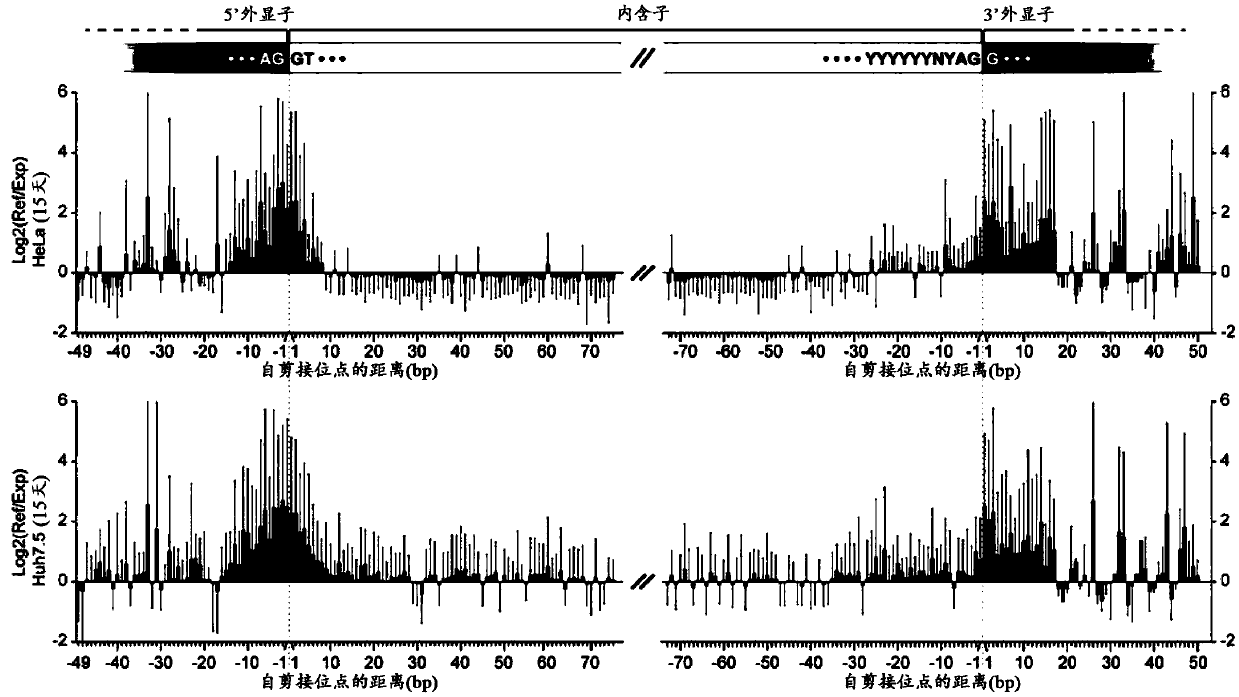
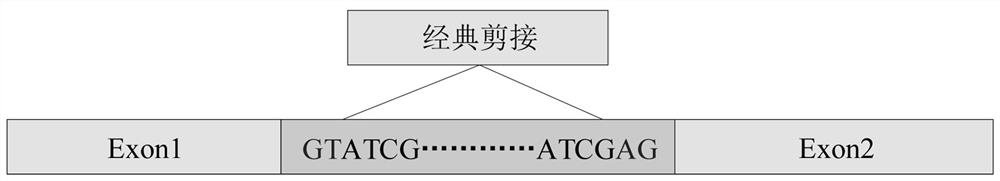
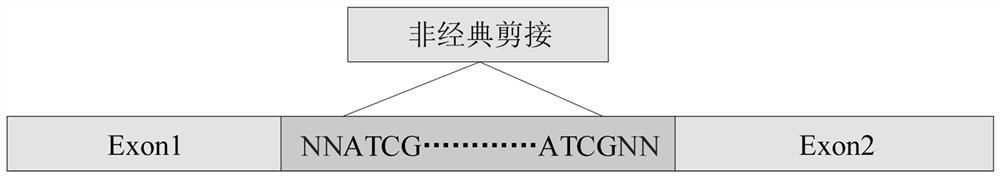
An inherited single base substitution in a sequence of eukaryotic DNA located in either an acceptor (3' or downstream) or donor (5' or upstream) splice site of a gene. Functional single nucleotide polymorphisms in these intron-exon junctions can cause incorrect RNA splicing which, in turn, alters gene expression.
Methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20050266417A1Rapid and accurate hybridizationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSplice Site SNPTarget mrna
The present invention relates to methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, deletions, or translocations; and identifying one or more target mRNA molecules differing by one or more splice site variations in a plurality of mRNA molecules. Also disclosed is a method of generating a linearly amplified representation of a whole genome. Other aspects of the present invention relate to labeled detection oligonucleotide probes and translational oligonucleotide probes as well as to methods of designing such probes.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
InactiveUS20110247090A1High expressionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideReticulum cell
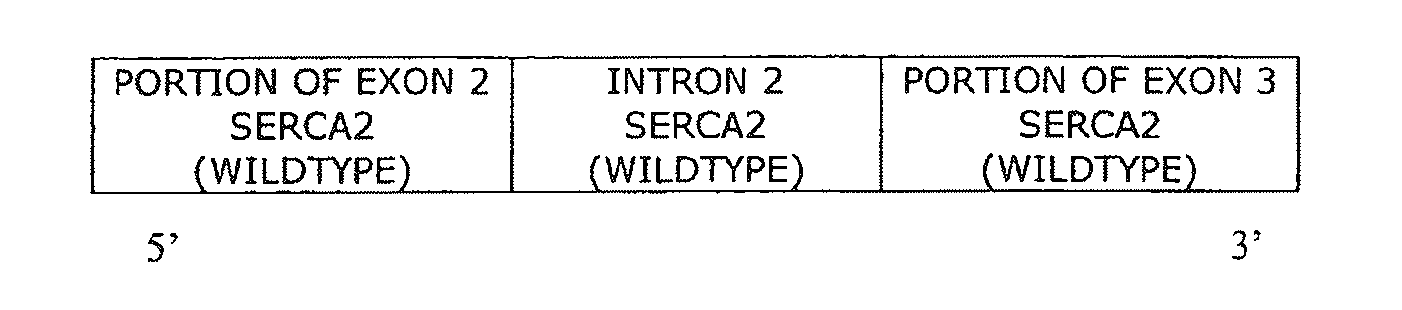
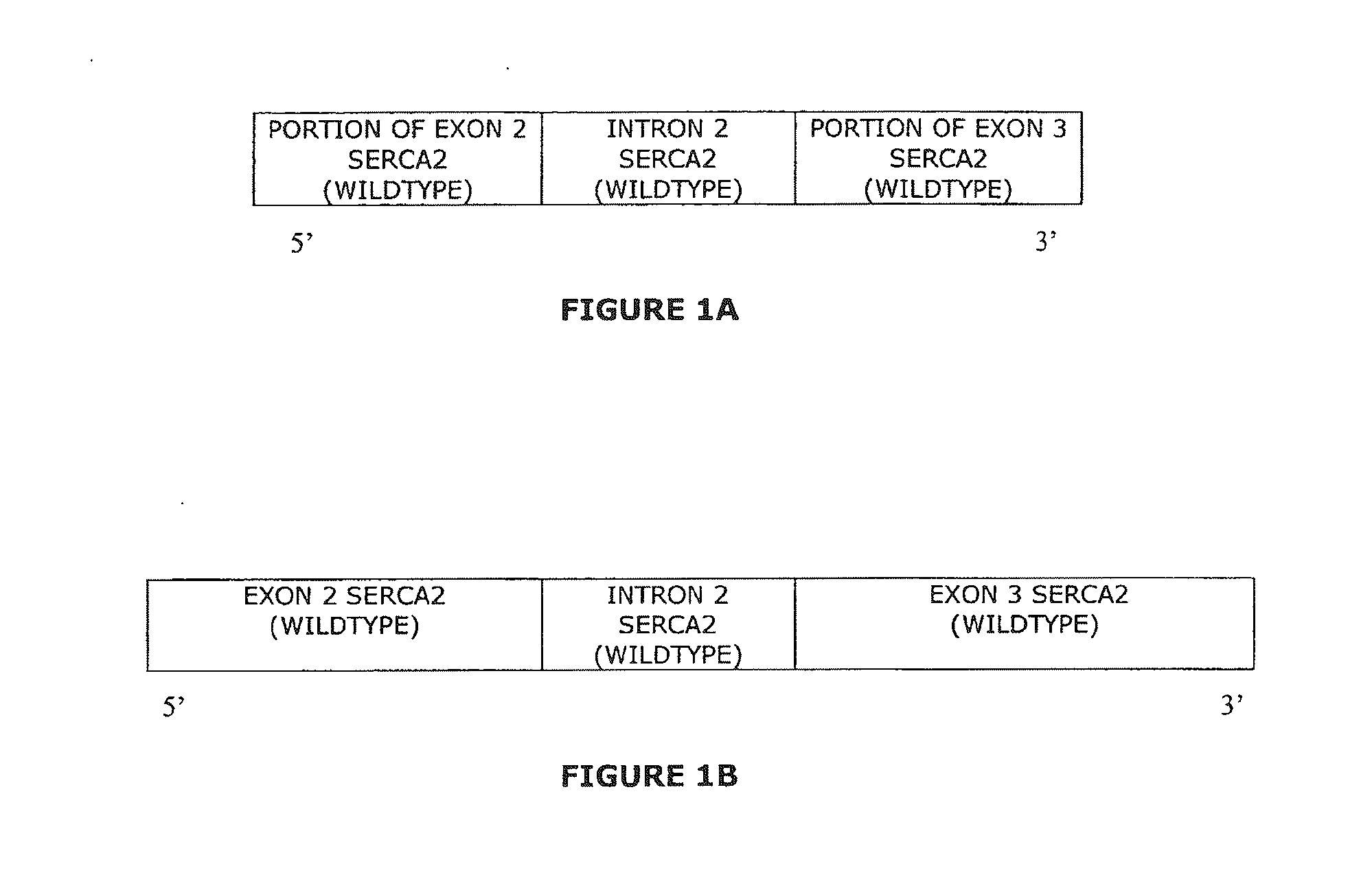
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
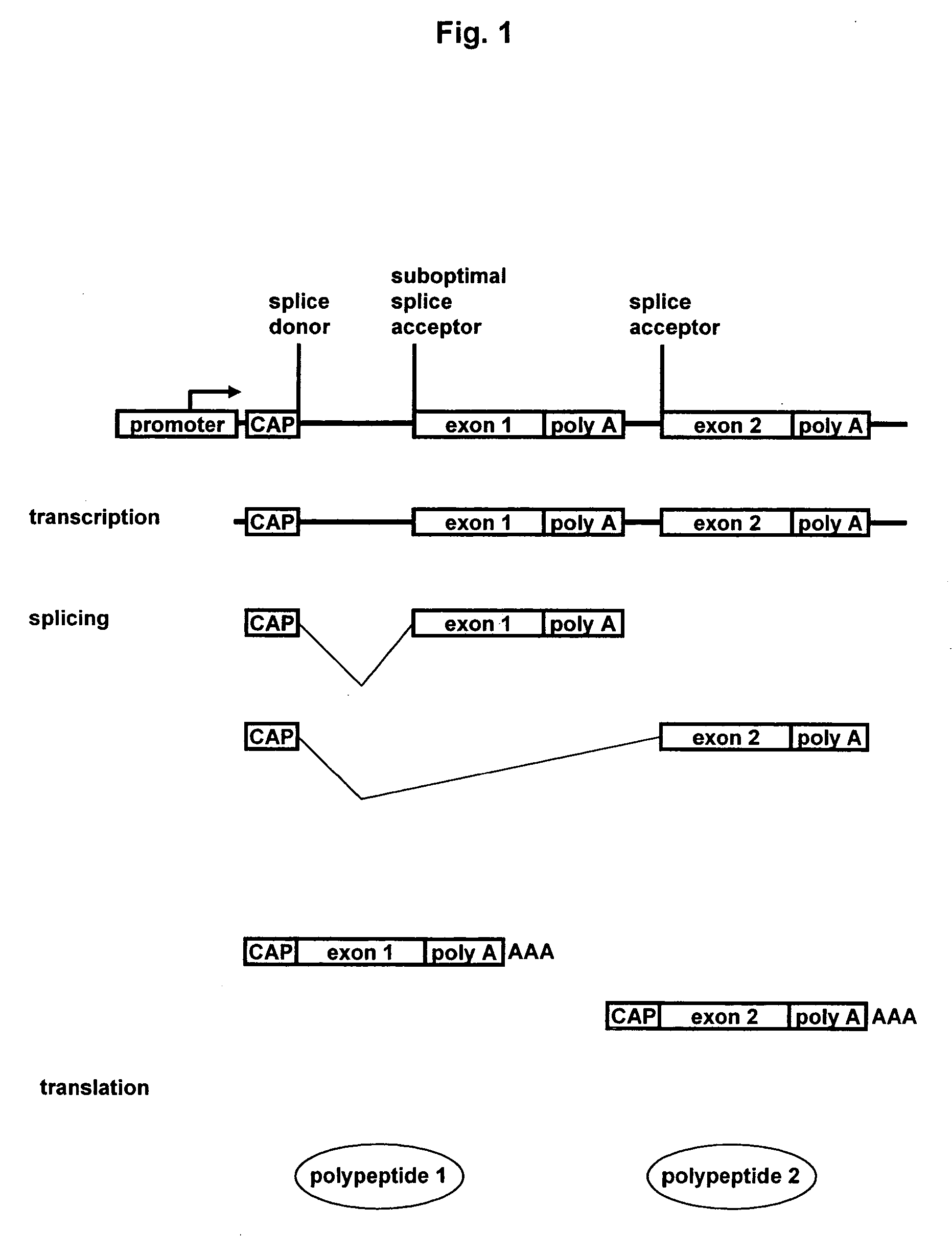
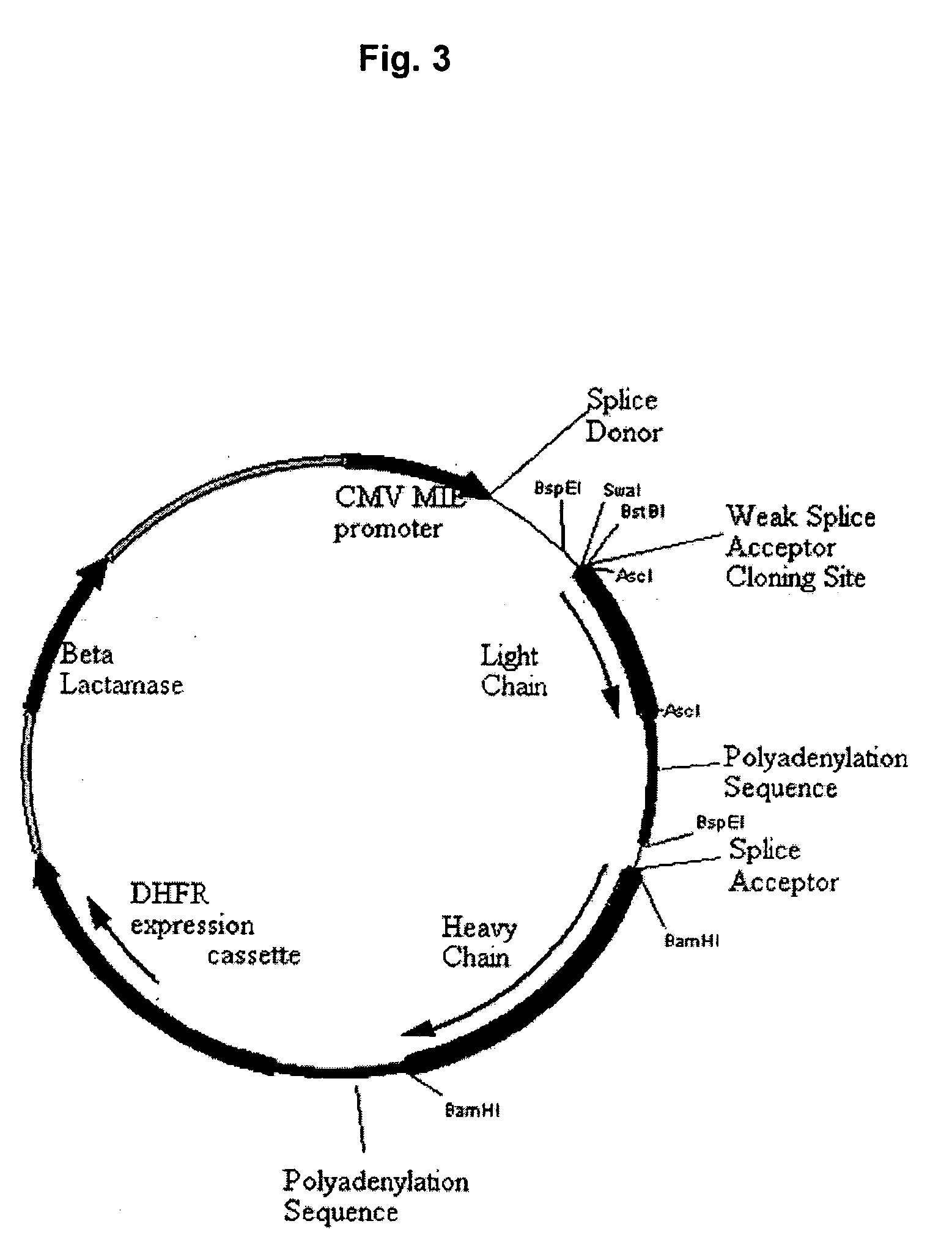
Methods and constructs for expressing polypeptide multimers in eukaryotic cells using alternative splicing
ActiveUS20050221430A1Efficient productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsGene product
The invention provides a method of producing multiple polypeptides, such as antibodies or antibody fragments, in a eukaryotic cell using a single expression vector. The expression vector is engineered to comprise two or more expression cassettes under the control of a single promoter wherein the expression cassettes have splice sites which allow for their alternative splicing and expression as two or more independent gene products at a desired ratio. Use of the vector for the efficient expression of recombinant antibodies in eukaryotic host cells is disclosed as well as the use of such antibodies in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
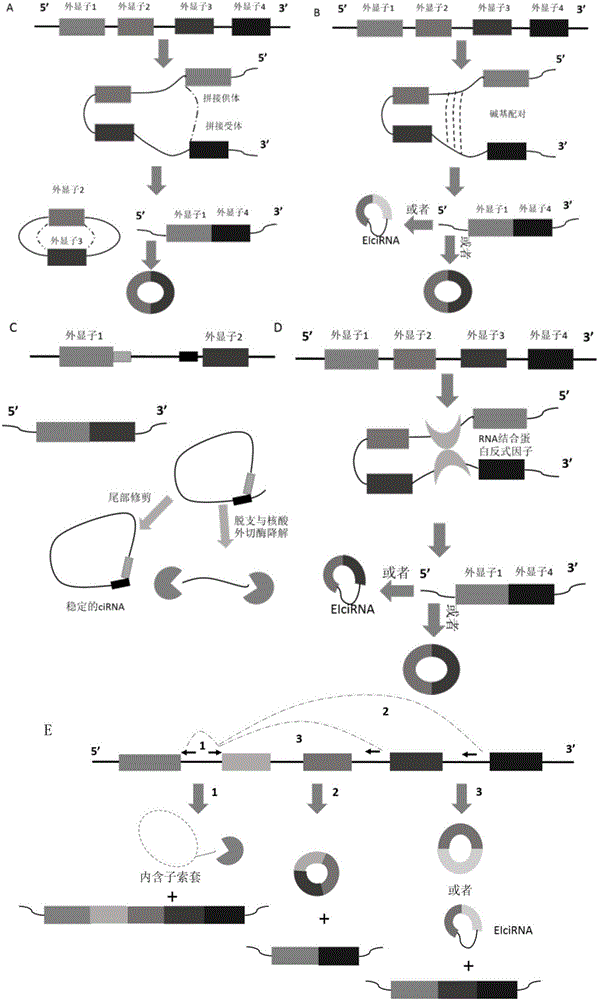
Circular RNA for translation in eukaryotic cells
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods to reprogram splice site selection in pre-messenger RNAs
InactiveUS20090186846A1Alter splice site useConvenient distanceSenses disorderNervous disorderBinding siteSplice Site SNP
The present invention relates to a method of modulating splice site selection, splicing and alternative, the method comprising the step of hybridizing an oligonucleotide-protein conjugate to a target pre-mRNA molecule in a cell or cell extract, wherein the oligonucleotide-protein conjugate comprises an oligonucleotide moiety which comprises at least two distinct sequence elements: (i) a nucleic acid sequence that is complementary to a specific region upstream of the splice site in the target pre-mRNA molecule; and (ii) an extension containing a protein binding site sequence element for covalently binding a protein; wherein the protein moiety comprises a protein capable of modulating splicing of the splice site upon binding with the protein binding site.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
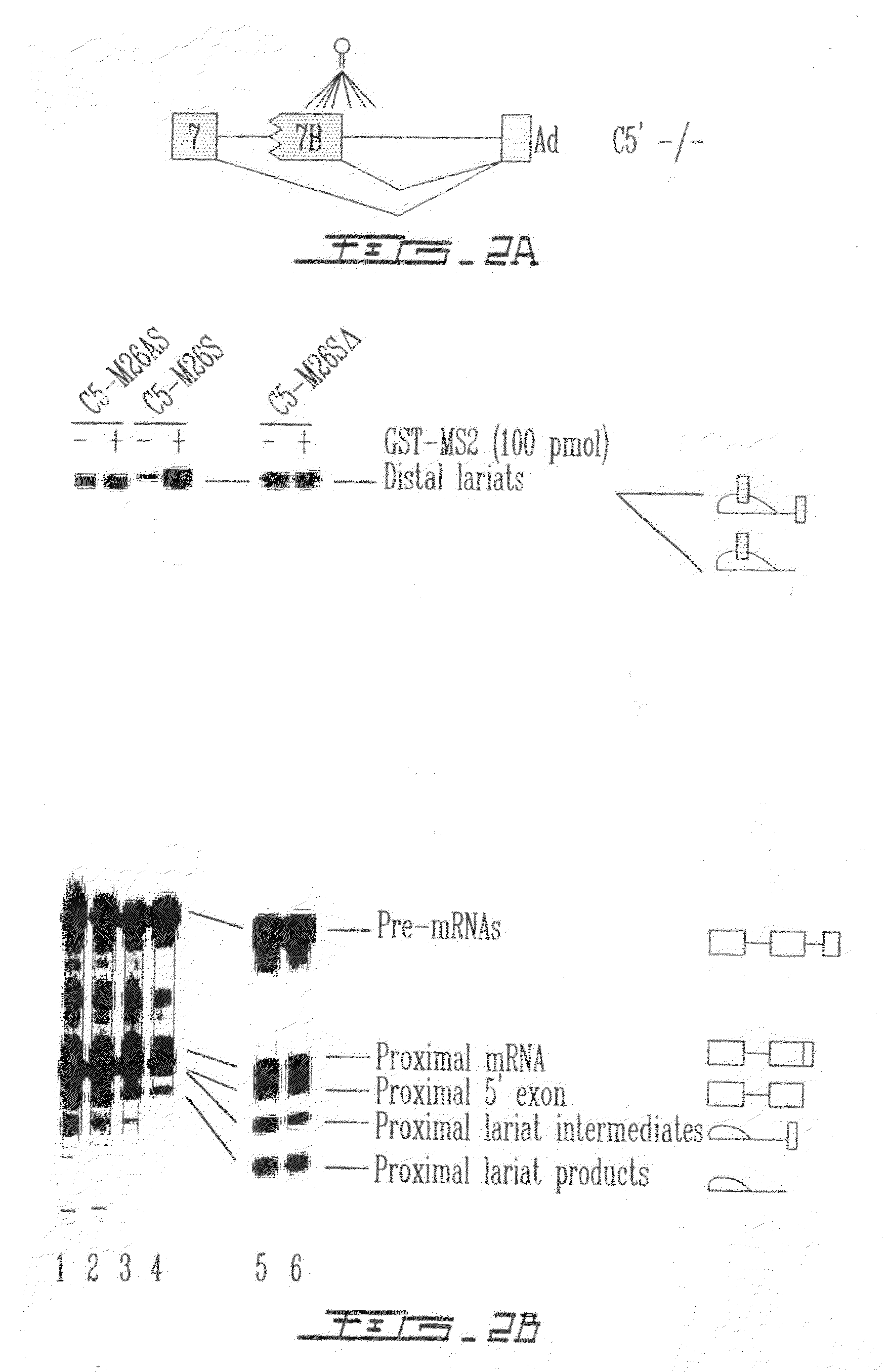
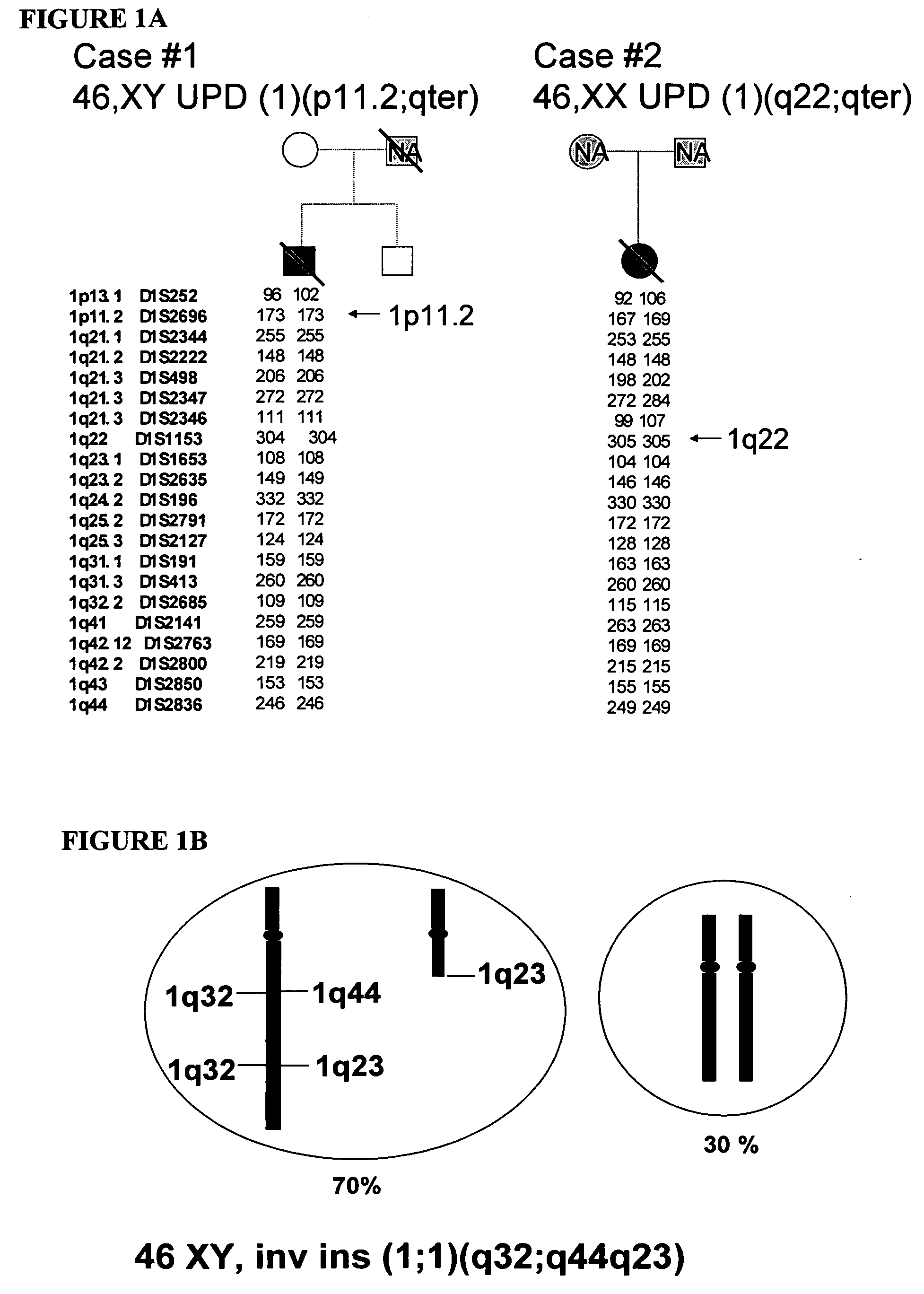
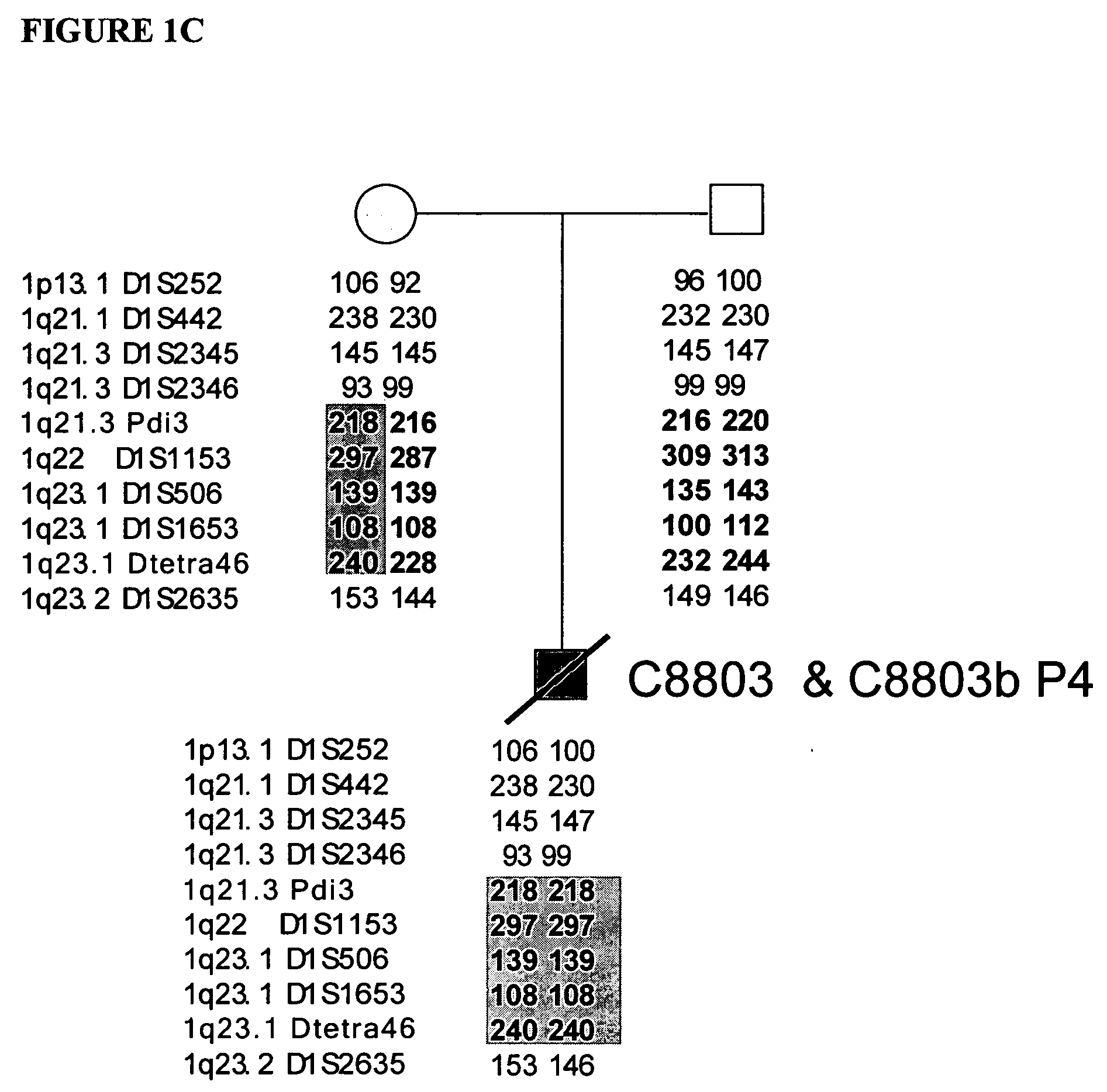
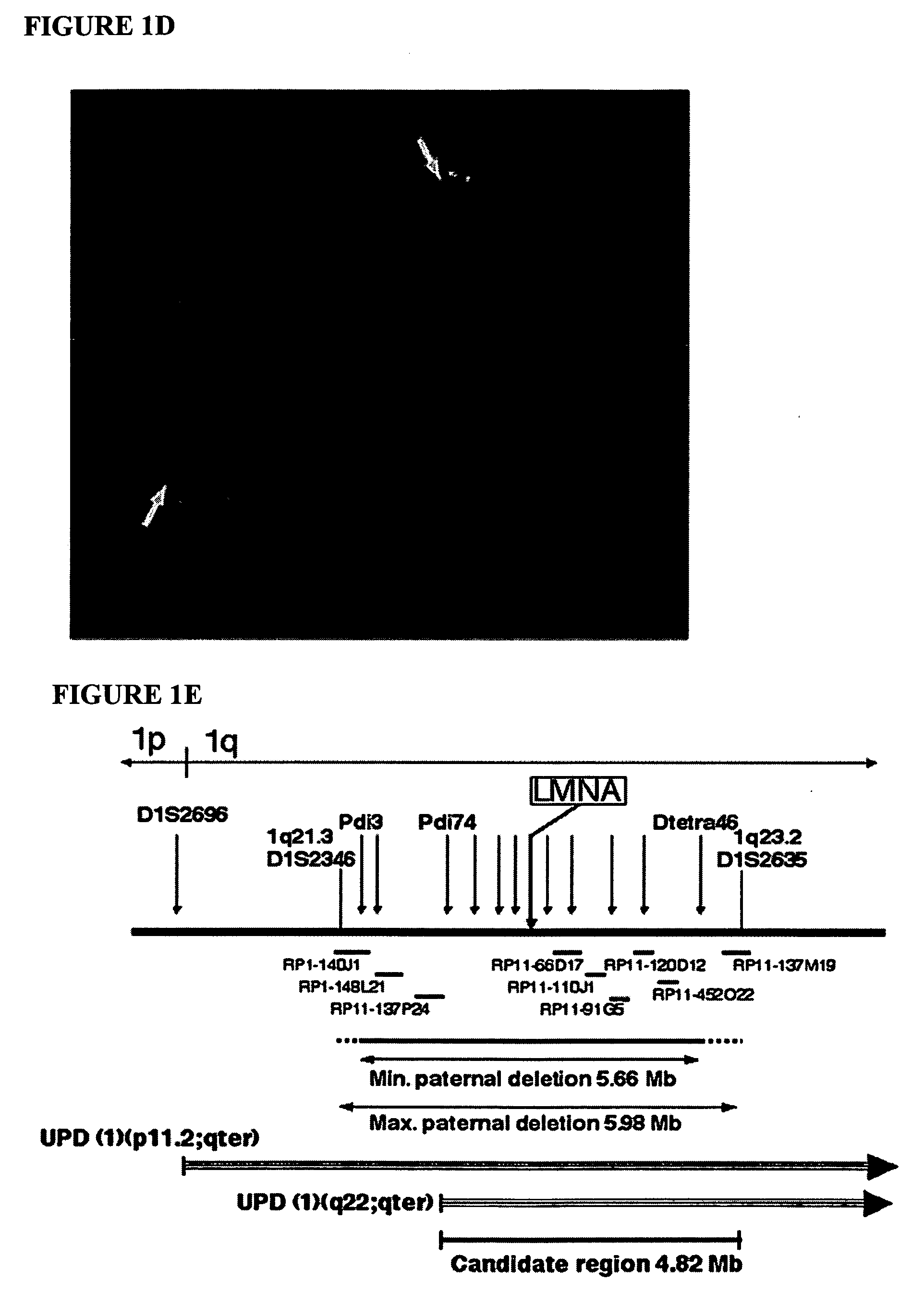
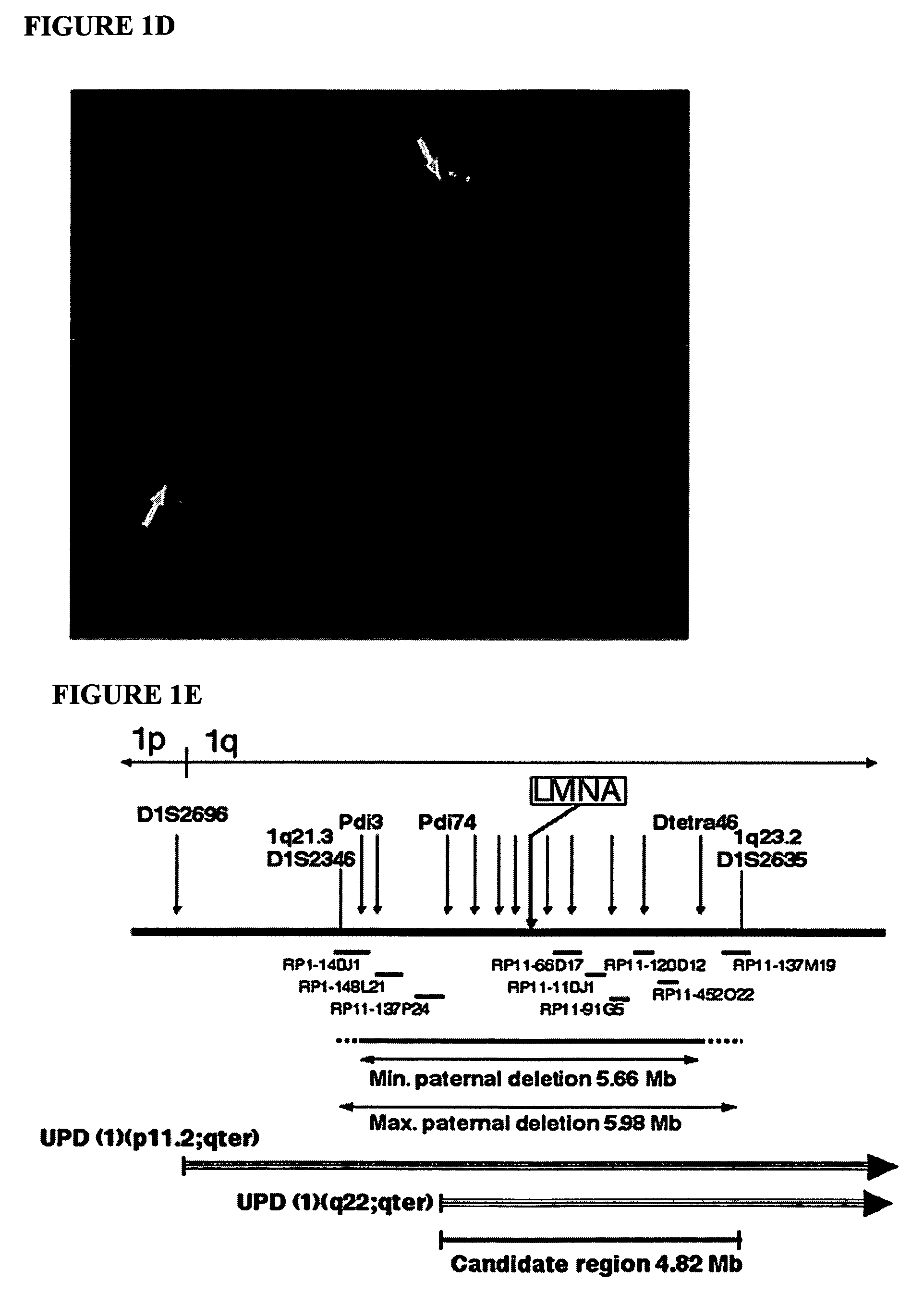
LMNA gene and its involvement in hutchinson-gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) and arteriosclerosis
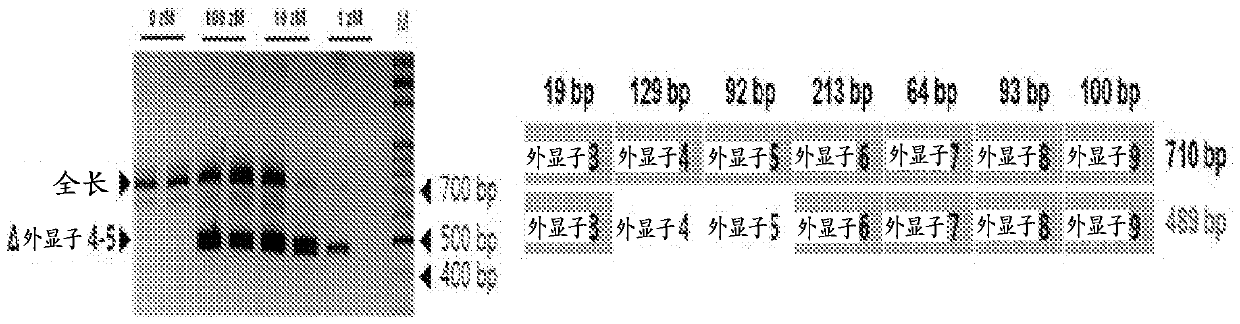
Disclosed herein are point mutations in the LMNA gene that cause HGPS. These mutations activate a cryptic splice site within the LMNA gene, which leads to deletion of part of exon 11 and generation of a mutant Lamin A protein product that is 50 amino acids shorter than the normal protein. In addition to the novel Lamin A variant protein and nucleic acids encoding this variant, methods of using these molecules in detecting biological conditions associated with a LMNA mutation in a subject (e.g., HGPS, arteriosclerosis, and other age-related diseases), methods of treating such conditions, methods of selecting treatments, methods of screening for compounds that influence Lamin A activity, and methods of influencing the expression of LMNA or LMNA variants are also described. Oligonucleotides and other compounds for use in examples of the described methods are also provided, as are protein-specific binding agents, such as antibodies, that bind specifically to at least one epitope of a Lamin A variant protein preferentially compared to wildtype Lamin A, and methods of using such antibodies in diagnosis, treatment, and screening. Also provided are kits for carrying out the methods described herein.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +2
Method of producing transcripts using cryptic splice sites
The invention is directed to a method of preparing a nucleic acid sequence with a modified splice site usage profile, which employs the use of a nucleic acid sequence comprising a cryptic splice donor site. The invention also provides a method of producing an alternate form of an RNA molecule encoded by a nucleic acid sequence, which nucleic acid sequence comprises a cryptic splice donor site, a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, and a splice acceptor site.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
Artificial riboswitch for controlling pre-mRNA splicing
ActiveUS7563601B1Efficient modulationConvenient distanceSplicing alterationSugar derivativesSplice Site SNPPrecursor mRNA
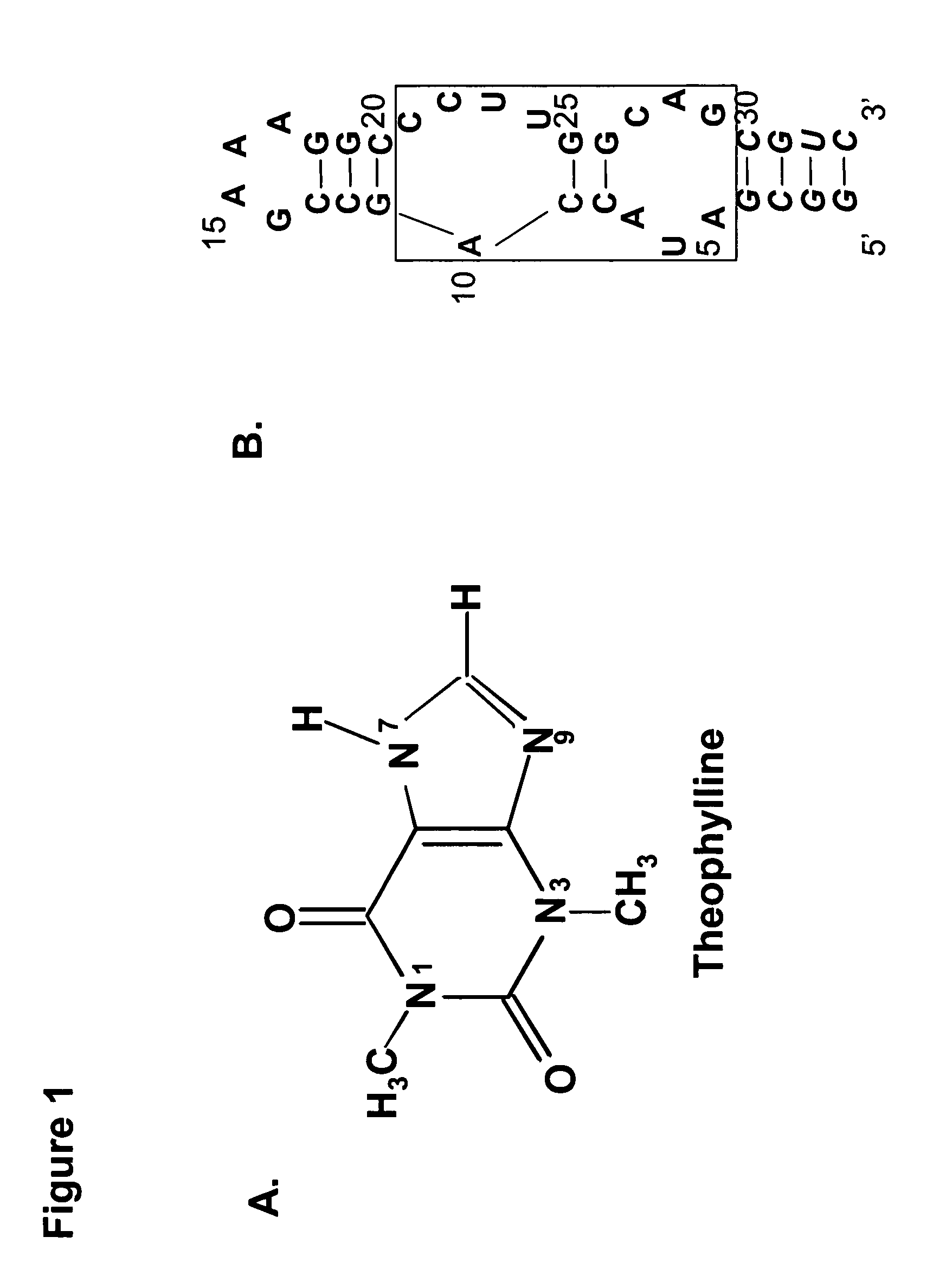
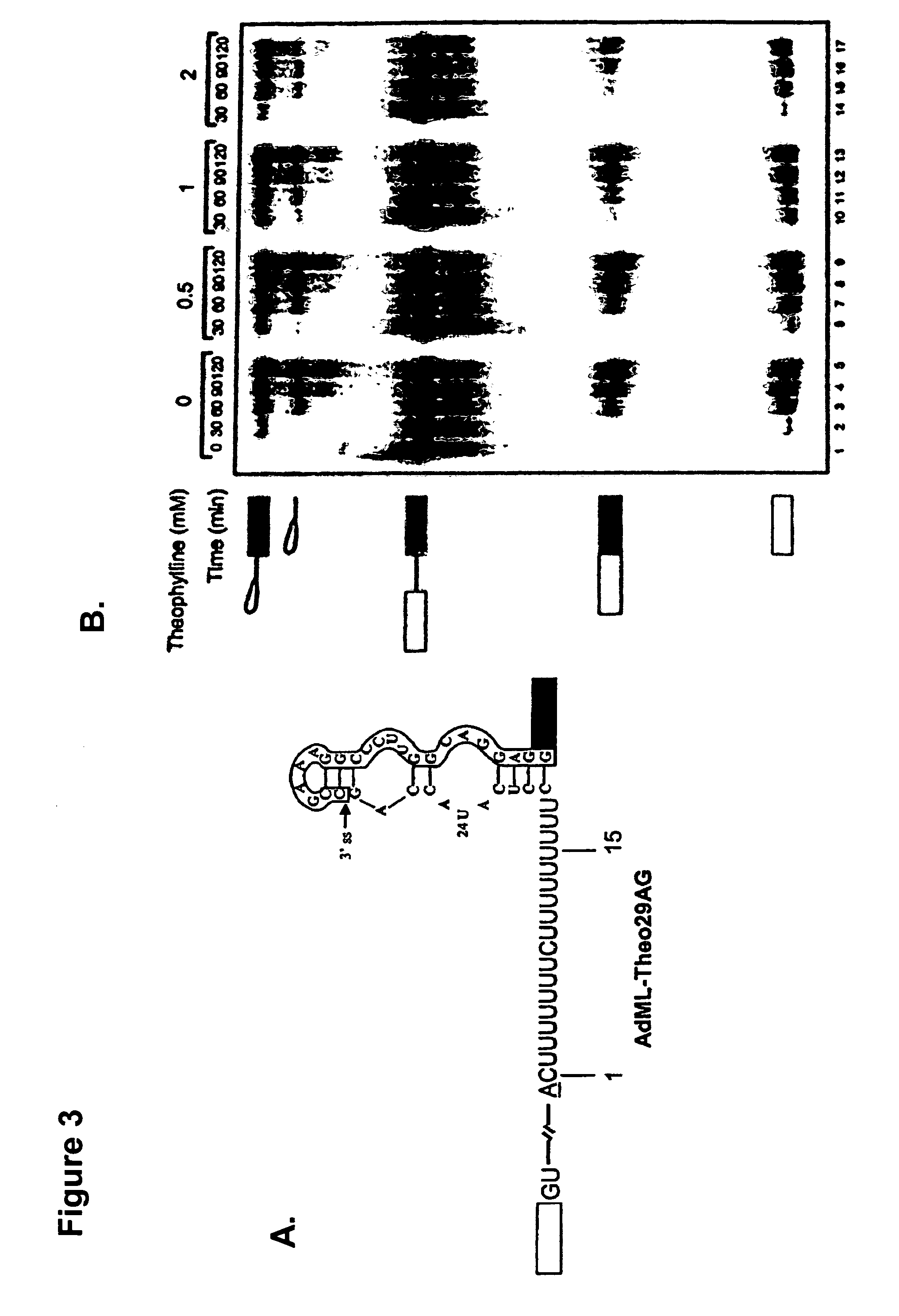
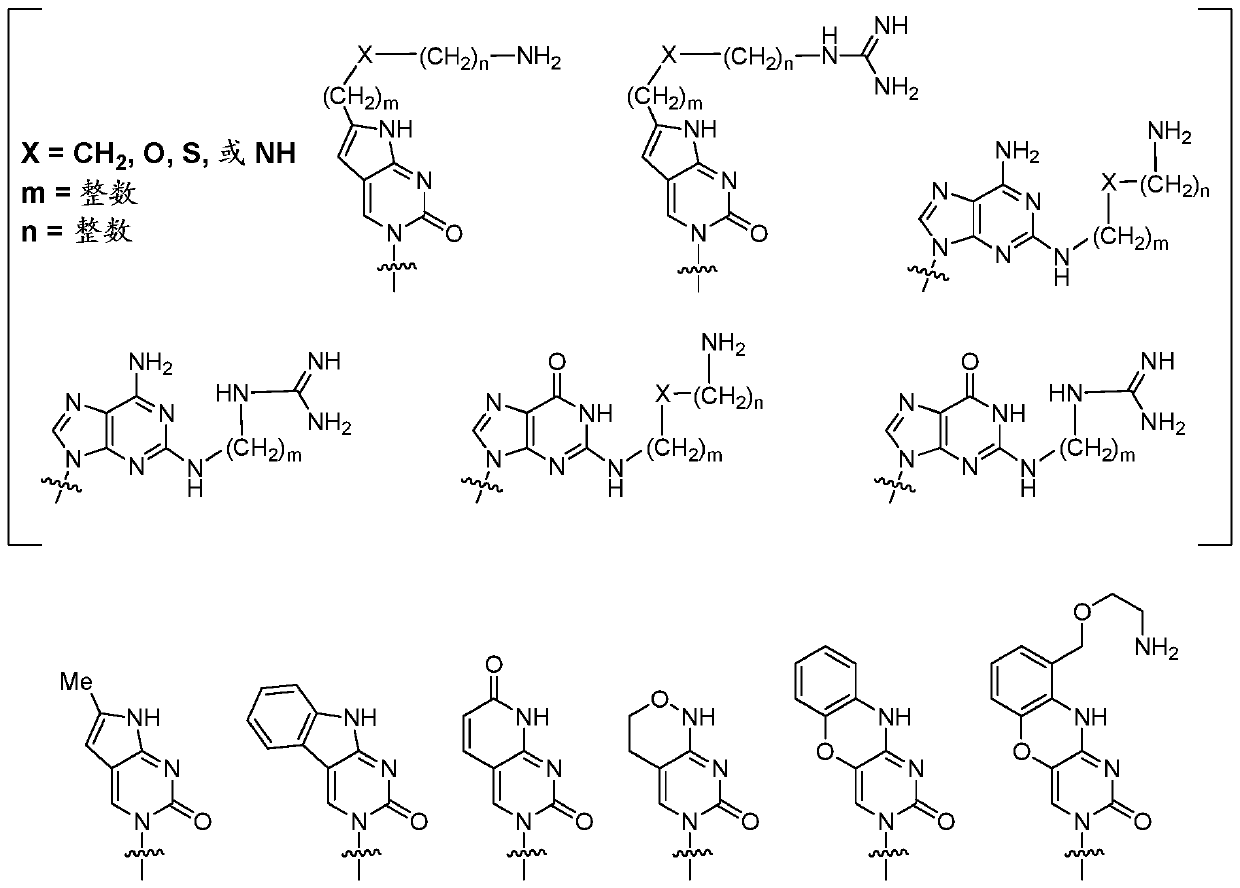
The present invention relates to riboswitches that have been engineered to regulate pre-mRNA splicing. In particular, the insertion of a high affinity theophylline binding aptamer into the 3′ splice site region, 5′ splice site region, or branchpoint sequence (BPS) of a pre-mRNA modulates RNA splicing in the presence of theophylline. Accordingly, the aspects of the present invention include, but are not limited to, theophylline-dependent riboswitches which modulate RNA splicing, methods of modulating RNA splicing using theophylline and its corresponding riboswitches, methods of improving / identifying theophylline-dependent riboswitches, methods of treating diseases associated with or caused by abnormal RNA splicing.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
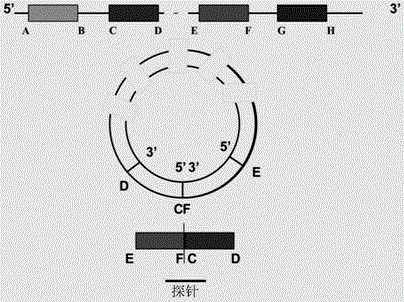
Probe, gene chip and method for detecting expression abundance of circular RNA
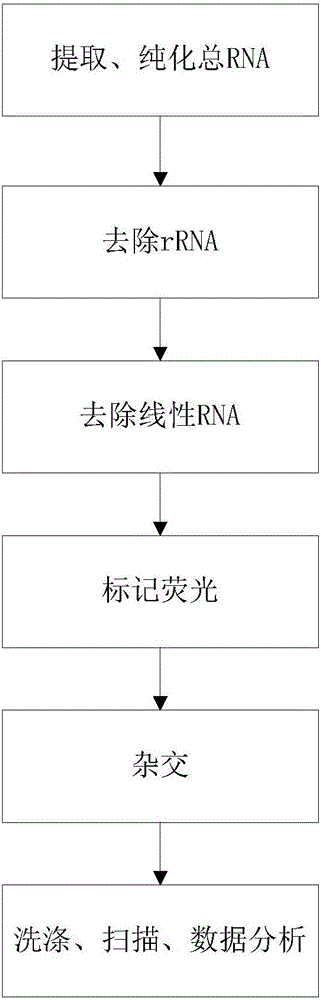
InactiveCN105803101ARapid Throughput AssayHigh-throughput detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTotal rnaLinear amplification
The invention discloses a probe for detecting expression abundance of circular RNA. The probe includes backsplicing sites at the 5' terminal of a donor exon and at the 3' terminal of an accepter exon of the circular RNA. The invention also discloses a gene chip containing the probe, and a method for detecting the expression abundance of the circular RNA by virtue of the gene chip, wherein the method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) extracting and purifying total RNA of a to-be-detected sample; 2) removing ribosome RNA; 3) enriching circular RNA; 4) conducting linear amplification to the enriched circular RNA and labeling fluorescence; 5) hybridizing a fluorescence-labeled product with a chip probe; and 6) washing and scanning the chip, and analyzing data. By designing the probe and the gene chip which are capable of achieving specific detection of the expression abundance of the circular RNA, the rapid and high-throughput detection of the expression abundance of the circular RNA can be achieved, so that shortcomings in an existing circular RNA detection technology are overcome.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
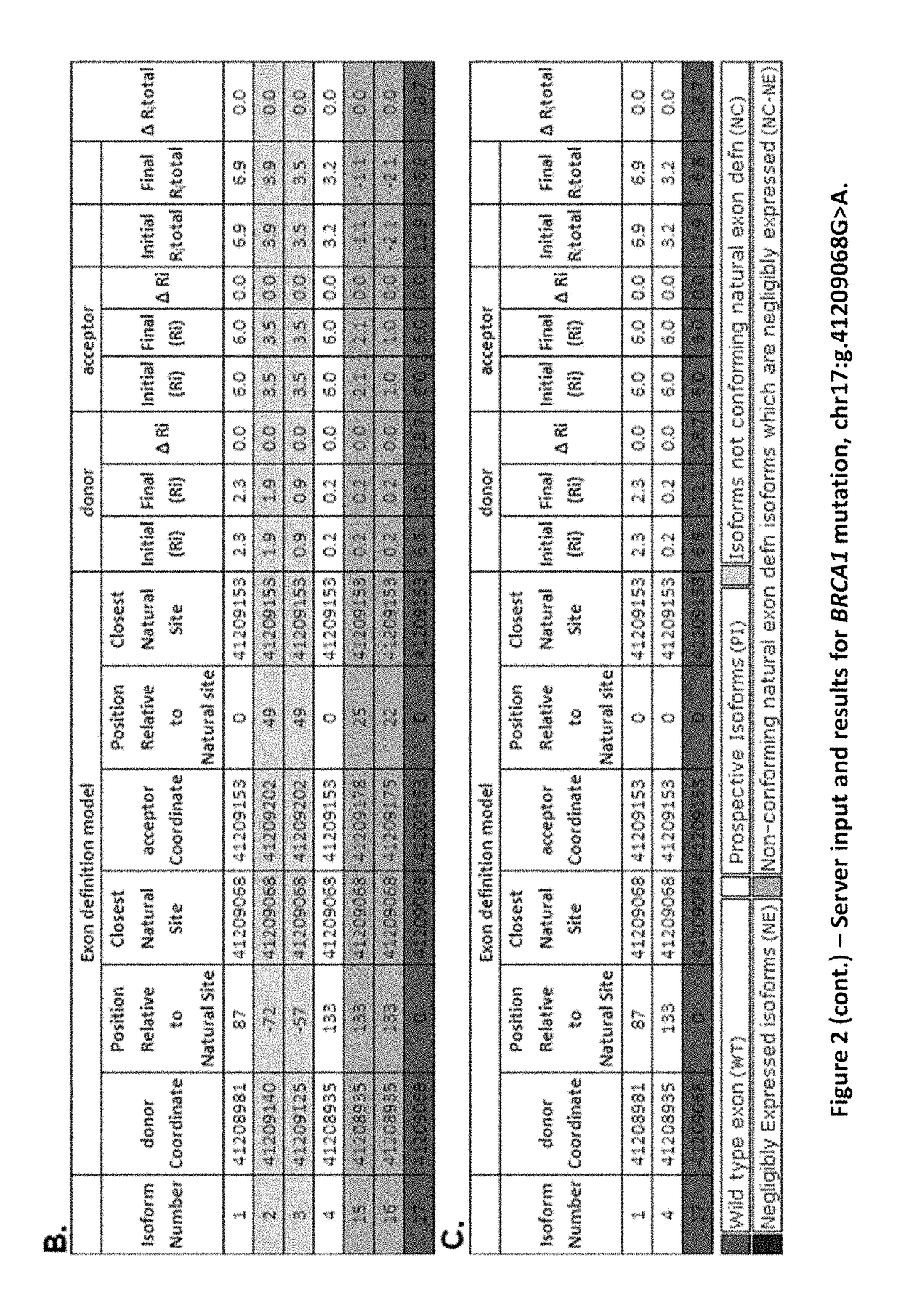
METHODS OF DETERMINING AND PREDICTING MUTATED mRNA SPLICE ISOFORMS
InactiveUS20180051326A1Assessing of changes in expression level of the geneQuantitative precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBinding siteSplice Site SNP
Mutations that affect mRNA splicing often produce multiple mRNA isoforms containing different exon structures. Definition of an exon and its inclusion in mature mRNA relies on joint recognition of both acceptor and donor splice sites. The instant methodology predicts cryptic and exon skipping isoforms in mRNA produced by splicing mutations from the combined information contents and the distribution of the splice sites and other regulatory binding sites defining these exons. In its simplest form, the total information content of an exon, Ri,total, is the sum of the information contents of its corresponding acceptor and donor splice sites, adjusted for the self-information of the exon length. Differences between Ri,total values of mutant versus normal exons that are concordant with gene expression data demonstrate alterations in the structures and relative abundance of the mRNA transcripts resulting from these mutations.
Owner:ROGAN PETER KEITH +1
LMNA gene and its involvement in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS) and arteriosclerosis
Disclosed herein are point mutations in the LMNA gene that cause HGPS. These mutations activate a cryptic splice site within the LMNA gene, which leads to deletion of part of exon 11 and generation of a mutant Lamin A protein product that is 50 amino acids shorter than the normal protein. In addition to the novel Lamin A variant protein and nucleic acids encoding this variant, methods of using these molecules in detecting biological conditions associated with a LMNA mutation in a subject (e.g., HGPS, arteriosclerosis, and other age-related diseases), methods of treating such conditions, methods of selecting treatments, methods of screening for compounds that influence Lamin A activity, and methods of influencing the expression of LMNA or LMNA variants are also described. Oligonucleotides and other compounds for use in examples of the described methods are also provided, as are protein-specific binding agents, such as antibodies, that bind specifically to at least one epitope of a Lamin A variant protein preferentially compared to wildtype Lamin A, and methods of using such antibodies in diagnosis, treatment, and screening. Also provided are kits for carrying out the methods described herein.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
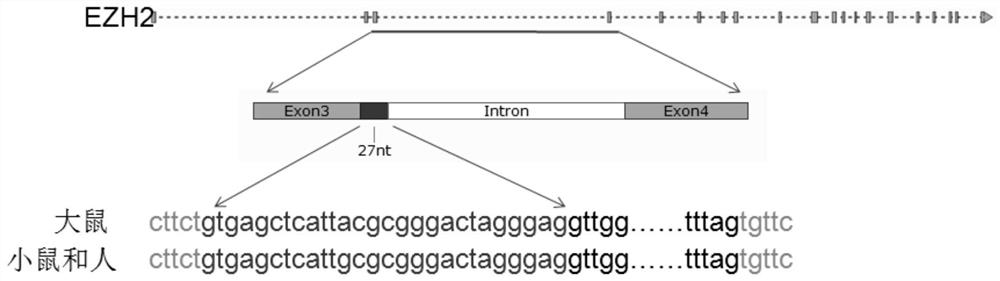
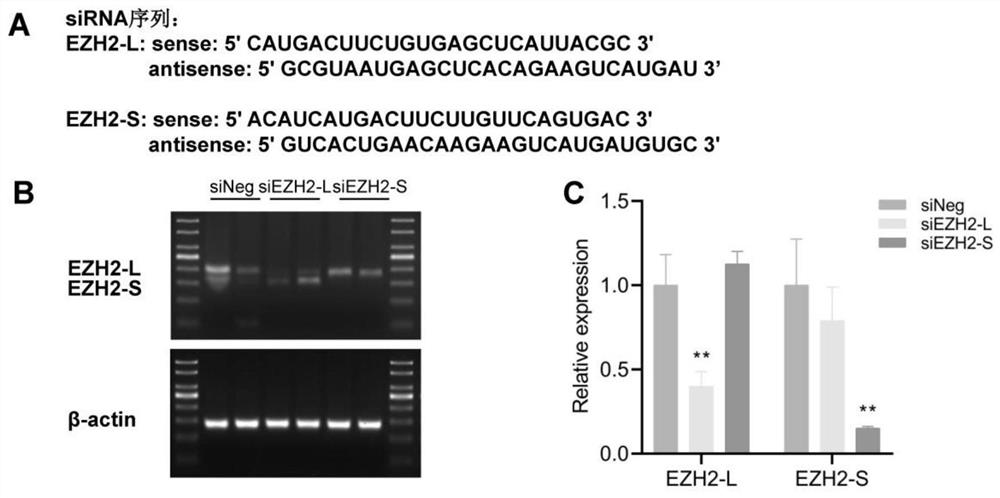
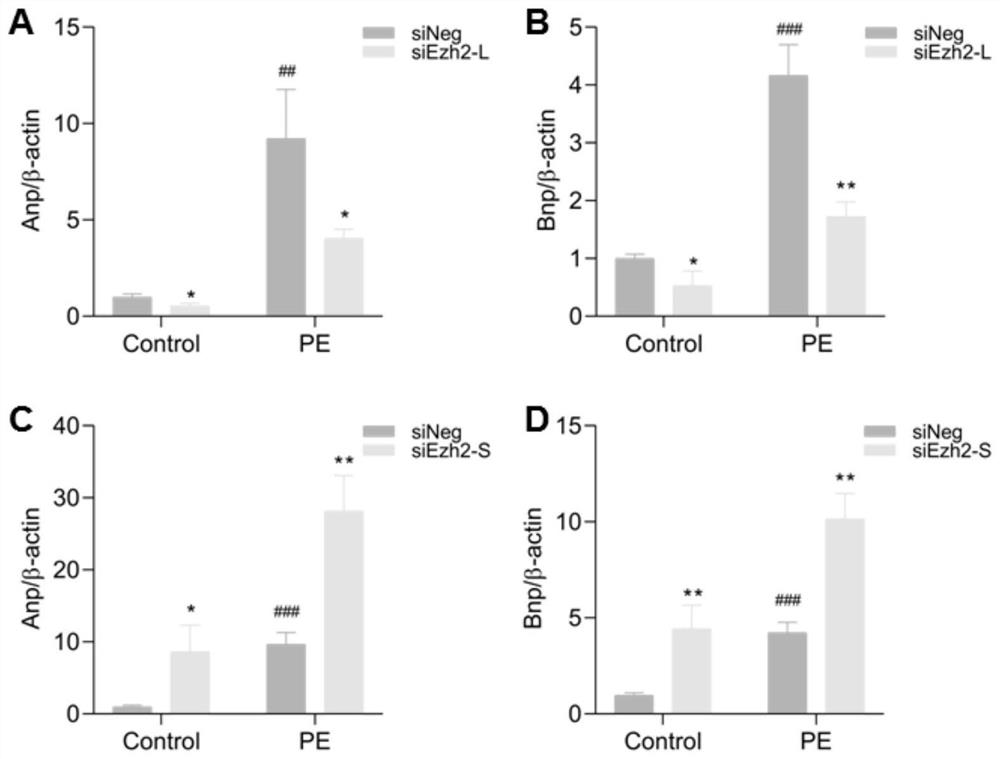
EZH2 variable spliceosome and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to an EZH2 variable splicing site and an application thereof. Specific siRNA is used for knocking down two subtypes ofEZH2-L and EZH2-S respectively, and myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure models are established at the cellular level and the animal level respectively. Results show that after the EZH2-L is knocked down, the expression level of a myocardial hypertrophy pathological gene is obviously reduced, the myocardial cell area is reduced, and the heart weight is reduced; and after the EZH2-S is knockeddown, the expression level of the myocardial hypertrophy pathological gene is remarkably increased, the myocardial cell area is increased, the heart weight is increased, and the situation prompts that the EZH2-L and the EZH2-S have the effects of promoting and inhibiting myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure respectively. In addition, after the EZH2-L is knocked down, tumor cell proliferationis inhibited, and knock-down of the EZH2-S has no influence on tumor cell proliferation. The invention provides a new target and a new strategy for research and development of medicines for treating EZH2 gene related diseases.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Alternative splicing reporter vector and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109679976AFor proper splicingVector-based foreign material introductionInteinSplice Site SNP
The invention discloses an alternative splicing reporter vector. Two sections of intron sequences intron1 and intron2 are inserted into a reporter gene sequence of a reporter gene expression vector pEGFP-C1; each of the intron1 and the intron2 has a 5' splicing site, a branch site and a 3' splicing site. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the alternative splicing reporter vector.The intron1 and the intron2 are designed and synthesized according to a splicing mechanism of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid); the intron1 and the intron2 are inserted into a reporter sequence of the reportergene expression vector respectively and are used for detecting an alternative splicing event on a cell level and a living body level; the introns containing the splicing sites are inserted so that correct splicing of post-transcriptional mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) is facilitated.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution
PendingCN109295053APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsCytosine deaminaseIntein
A method of regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution is disclosed, the method comprises expressing targeted cytidine deaminase in cellsto induce AG to AA mutation of 3' splicing site of intron of interested of gene of interested in the cells, or GT to AT mutation of 5' splicing site of the intron of interested of the gene of interested in the cells, or respective mutation of multiple C in a polypyrimidine region of the intron of interested of the gene of interested to T. The method can specifically block the exon recognition process, regulates the alternative splicing process of endogenous mRNA, induces exon skipping, activates alternative splicing sites, induces mutual exclusive exon conversion, induces intron retention andenhances exon retention.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Synthetic 5'UTRs, expression vectors, and methods for increasing transgene expression
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Methods and constructs for expressing polypeptide multimers in eukaryotic cells using alternative splicing
ActiveUS7569362B2Efficient productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsGene product
The invention provides a method of producing multiple polypeptides, such as antibodies or antibody fragments, in a eukaryotic cell using a single expression vector. The expression vector is engineered to comprise two or more expression cassettes under the control of a single promoter wherein the expression cassettes have splice sites which allow for their alternative splicing and expression as two or more independent gene products at a desired ratio. Use of the vector for the efficient expression of recombinant antibodies in eukaryotic host cells is disclosed as well as the use of such antibodies in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
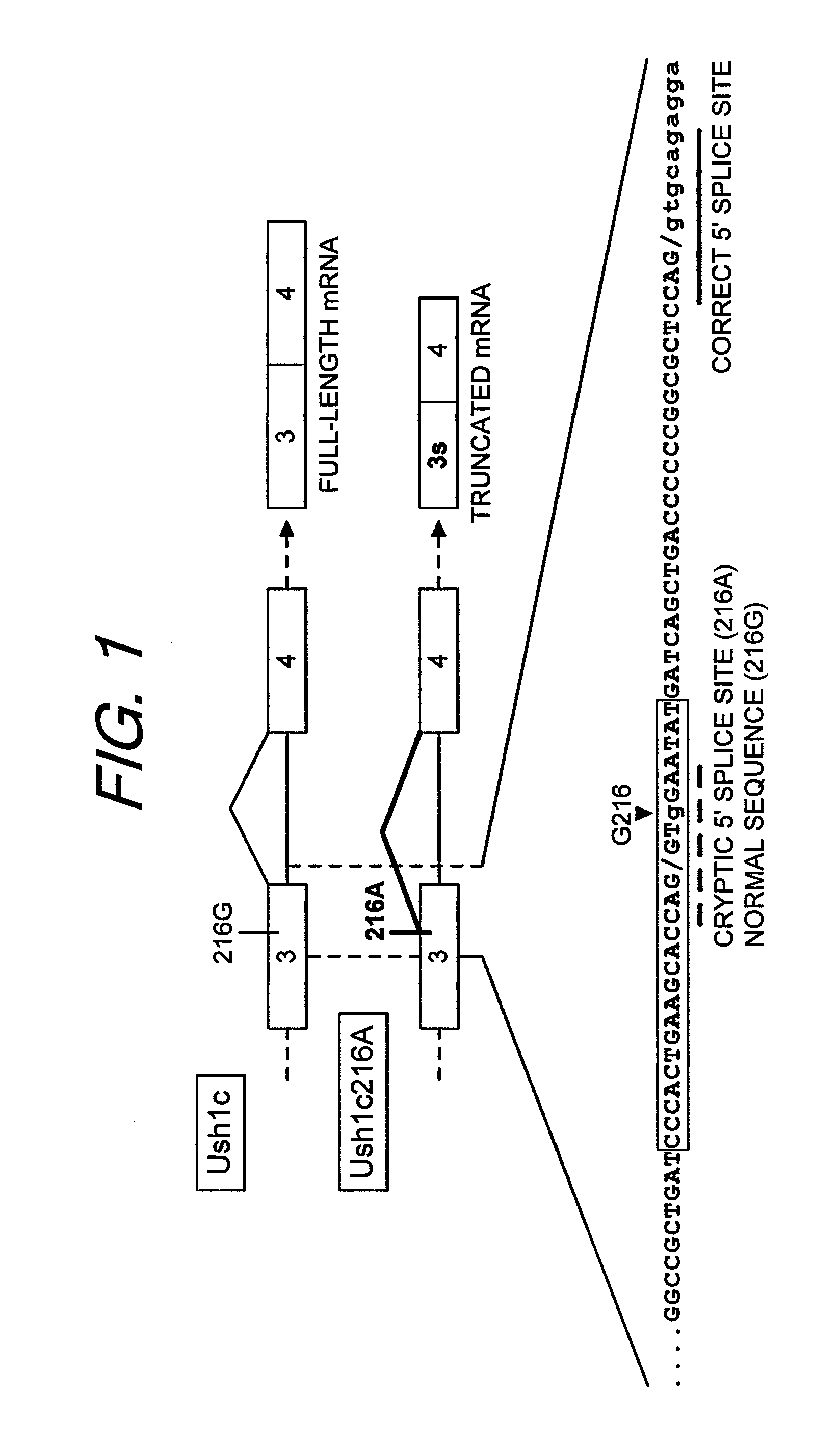
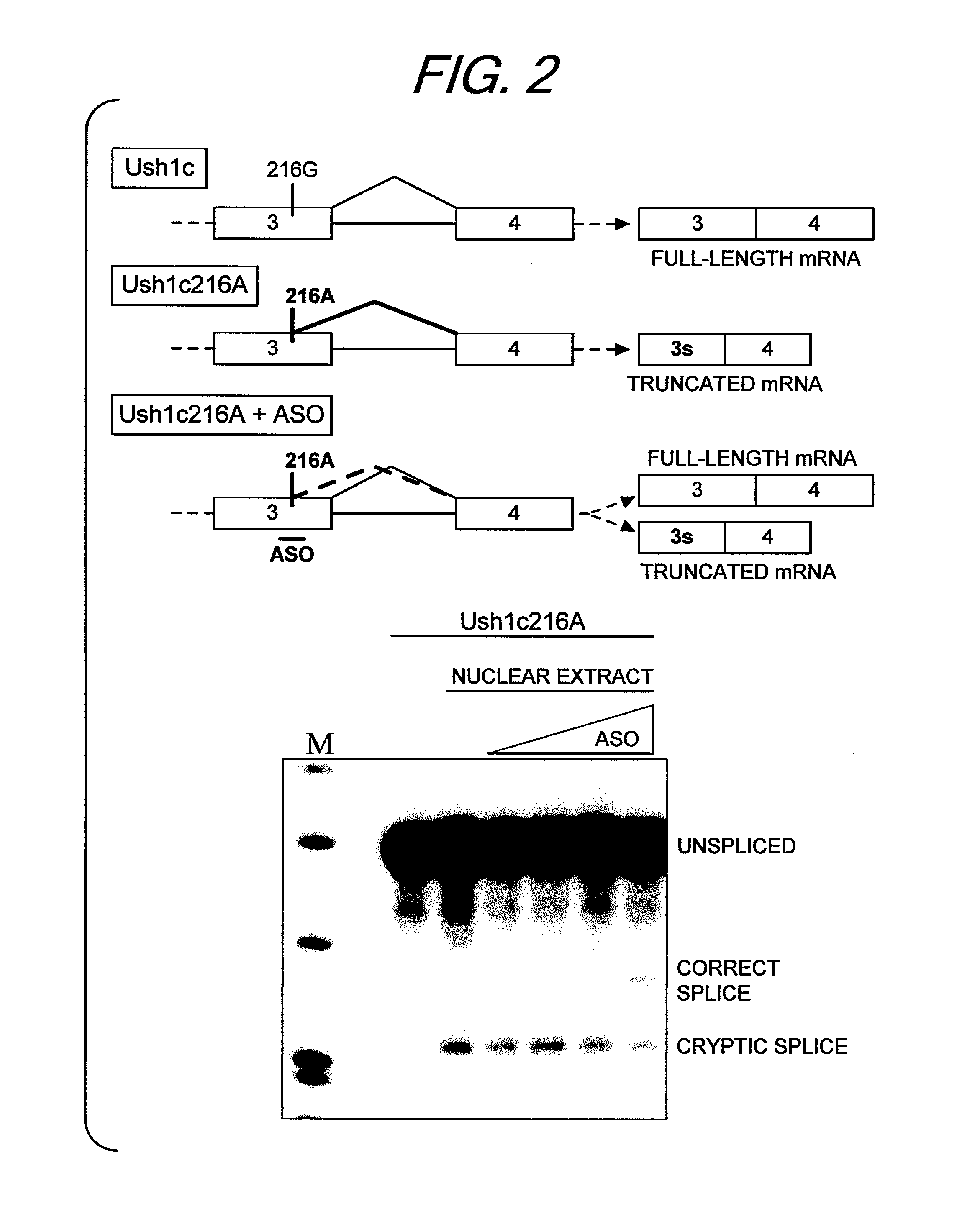
Antisense oligonucleotides that target a cryptic splice site in Ush1c as a therapeutic for Usher syndrome
The present invention provides a method for treating Usher's syndrome in a human subject including administering to the human subject an oligonucleotide having 8 to 30 linked nucleosides having a nucleobase sequence comprising a complementary region comprising at least 8 contiguous nucleobases complementary to a target region of equal length within exon 3 of an Usher RNA transcript.
Owner:ROSALIND FRANKLIN UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE
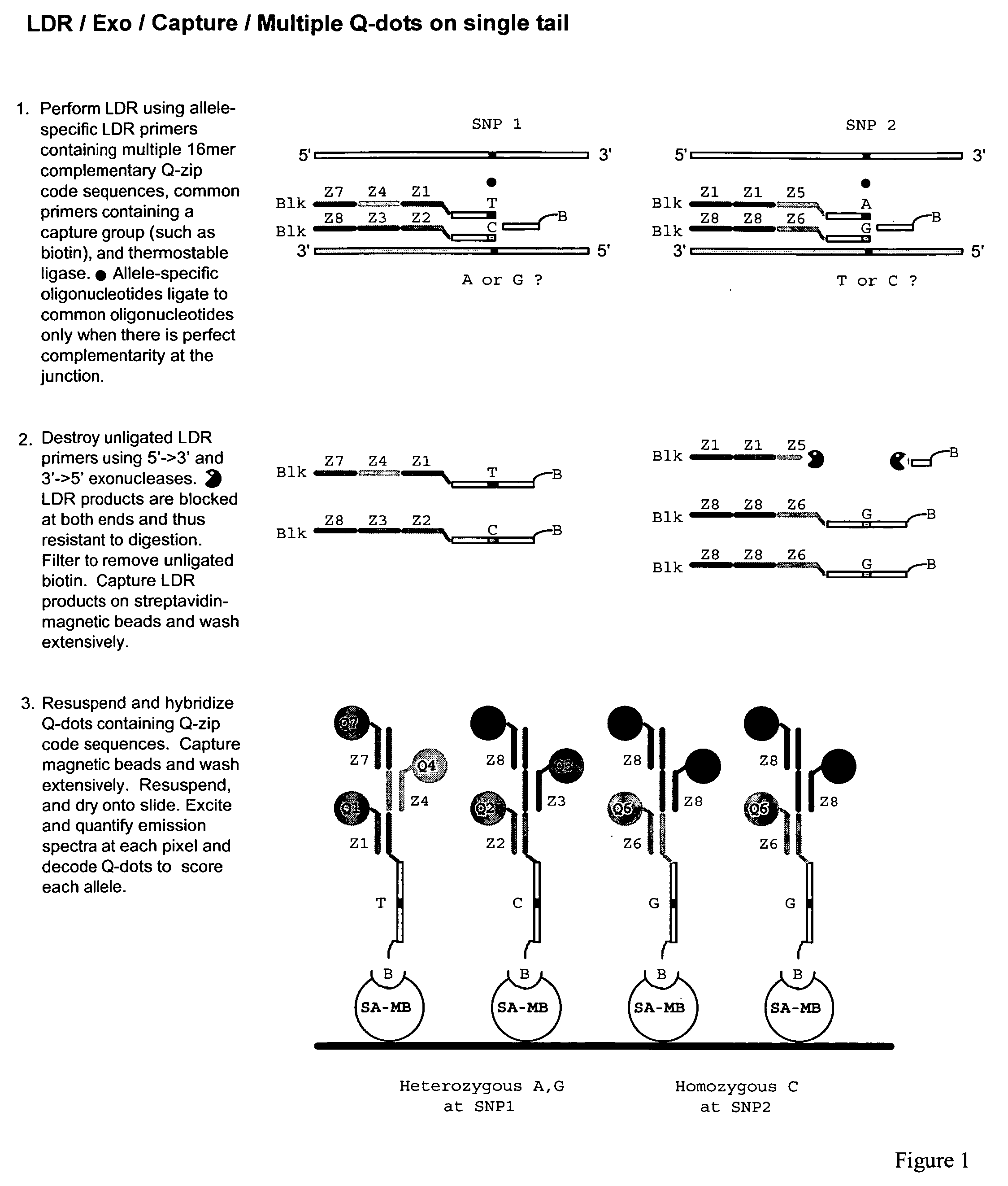
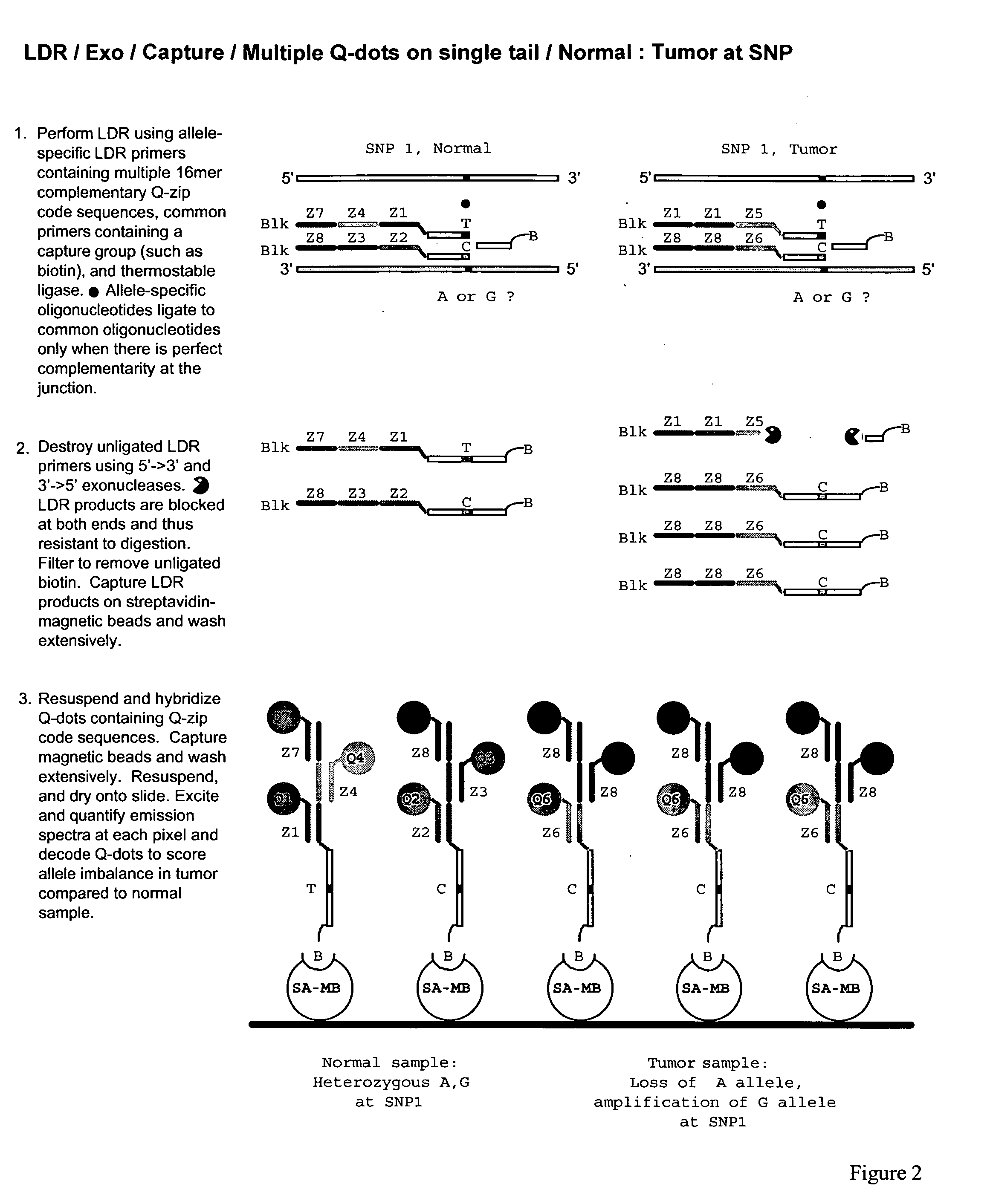
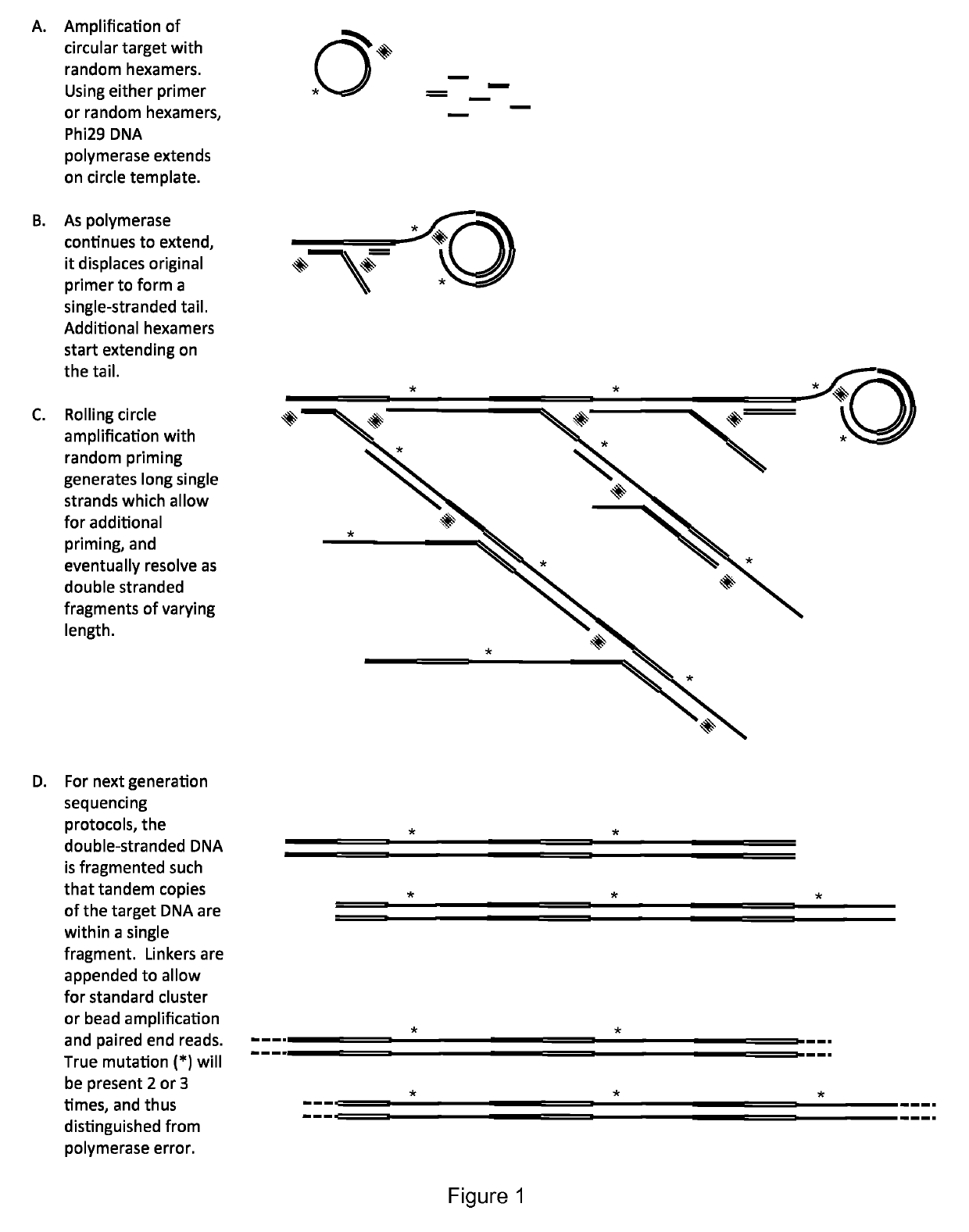
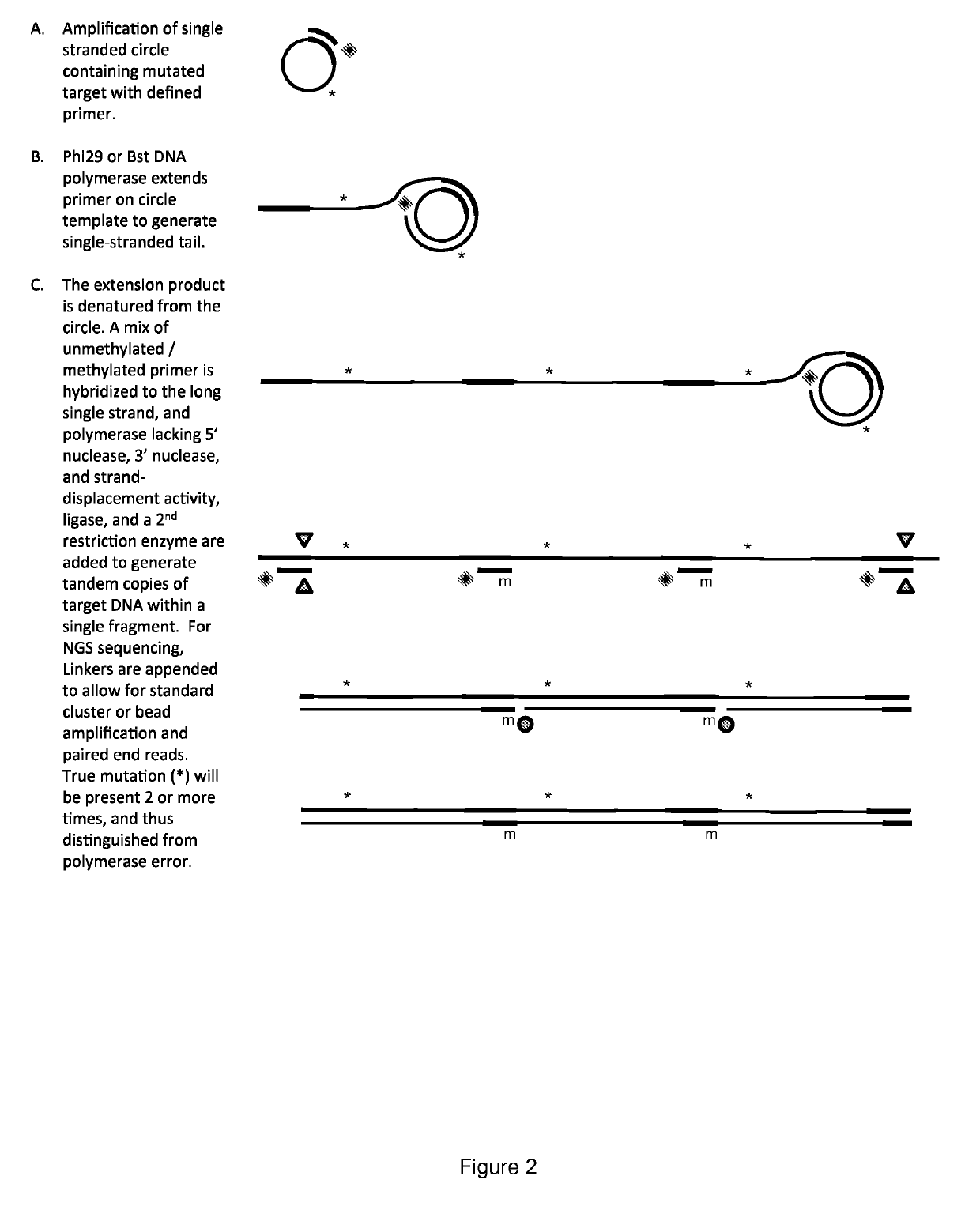
Method for identification and enumeration of nucleic acid sequence, expression, copy, or DNA methylation changes, using combined nuclease, ligase, polymerase, and sequencing reactions
The present invention relates to a method for the highly specific, targeted capture of regions of human genomes and transcriptomes from the blood, i.e. from cell free circulating DNA, exosomes, microRNA, circulating tumor cells, or total blood cells, to allow for the highly sensitive detection of mutation, expression, copy number, translocation, alternative splicing, and methylation changes using combined nuclease, ligation, polymerase, and massively parallel sequencing reactions. The method generates a collection of different circular chimeric single-stranded nucleic acid constructs, suitable for sequencing on multiple platforms. In some embodiments, each construct of the collection comprised a first single stranded segment of original genomic DNA from a host organism and a second single stranded synthetic nucleic acid segment that is linked to the first single stranded segment and comprises a nucleotide sequence that is exogenous to the host organism. These chimeric constructs are suitable for identifying and enumerating mutations, copy changes, translocations, and methylation changes. In other embodiments, input mRNA, IncRNA, or miRNA is used to generate circular DNA products that reflect the presence and copy number of specific mRNA's, IncRNA's splice-site variants, translocations, and miRNA.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Novel sequences encoding hepatitis C virus glycoproteins
InactiveUS20050266400A1Reduced activitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVectorsE2 glycoproteinGlycoprotein
The present invention concerns a modified nucleic acid molecule comprising a nucleotide sequence coding for a full length hepatitis C virus (HCV) glycoprotein selected from the group consisting of E1 glycoprotein and E1 / E2 glycoprotein heterodimer, this molecule having at least one nucleotide alteration, wherein, due to this alteration, at least one RNA splice site selected from the group consisting of RNA splice acceptor and RNA splice donor sites is eliminated from the coding sequence. The invention is also directed to methods for expressing on the surface of a cell and a pseudovirion an HCV glycoprotein, wherein the majority of the glycoprotein is full length. The invention further provides a cell and a pseudovirion expressing such glycoprotein. The invention still further provides a method for determining whether an agent inhibits HCV fusion with and entry into a target cell. The invention also provides an agent that inhibits HCV fusion with and entry into a target cell. The invention further provides methods for treating a subject afflicted with an HCV-associated disorder, for preventing an HCV infection in a subject, and for inhibiting in a subject the onset of an HCV-associated disorder.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +1
Fluorogenic probes and their use in quantitative detection of target RNA sequences
ActiveUS20180002743A1Improve stabilityQuantitatively accurateOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayFluorescence
Disclosed are compositions, reagents, methods, assays, and kits for quantitative and sensitive detection of target ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequences, particularly target RNA sequences that contain RNA spliced sites, hairpin stem-loops or other topological configurations of RNA secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure, as well as linear RNA sequences. In some embodiments, fluorogenic modified-backbone oligonucleotide probes are employed for specific sequence hybridization across the target site, followed by chemical autoligation to produce a fluorescent molecule within the ligated probes. The autoligation detection reaction is performed isothermally or through thermocycling.
Owner:JAN BIOTECH INC
Methods to reprogram splice site selection in pre-messenger rnas
InactiveUS20060058253A1Alter splice site useSenses disorderNervous disorderMessenger RNABinding site
The present invention relates to a method of modulating splice site selection, splicing and alternative, the method comprising the step of hybridizing an oligonucleotide-protein conjugate to a target pre-mRNA molecule in a cell or cell extract, wherein the oligonucleotide-protein conjugate comprises an oligonucleotide moiety which comprises at least two distinct sequence elements: (i) a nucleic acid sequence that is complementary to a specific region upstream of the splice site in the target pre-mRNA molecule; and (ii) an extension containing a protein binding site sequence element for covalently binding a protein; wherein the protein moiety comprises a protein capable of modulating splicing of the splice site upon binding with the protein binding site.
Owner:UNIV DE SHERBROOKE
Method for predicting splicing sites with paired two ends
PendingCN114566215AImprove convenienceImprove predictive performanceBiostatisticsProteomicsData setSample sequence
The invention discloses a double-end paired splicing site prediction method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a double-end paired splicing site sample sequence as a reference data set and an independent data set; coding the base sequence through a plurality of feature extraction modes based on the sequence, physicochemical properties and the like; combining a plurality of features as a multi-channel multi-dimensional vector representation; training a convolutional neural network model; and finally, evaluating. The prediction method can be combined with multiple feature representation modes of the sample to help the convolutional neural network to fully learn the intrinsic mode of the sample, and the accuracy of predicting the splicing sites with the paired two ends is improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
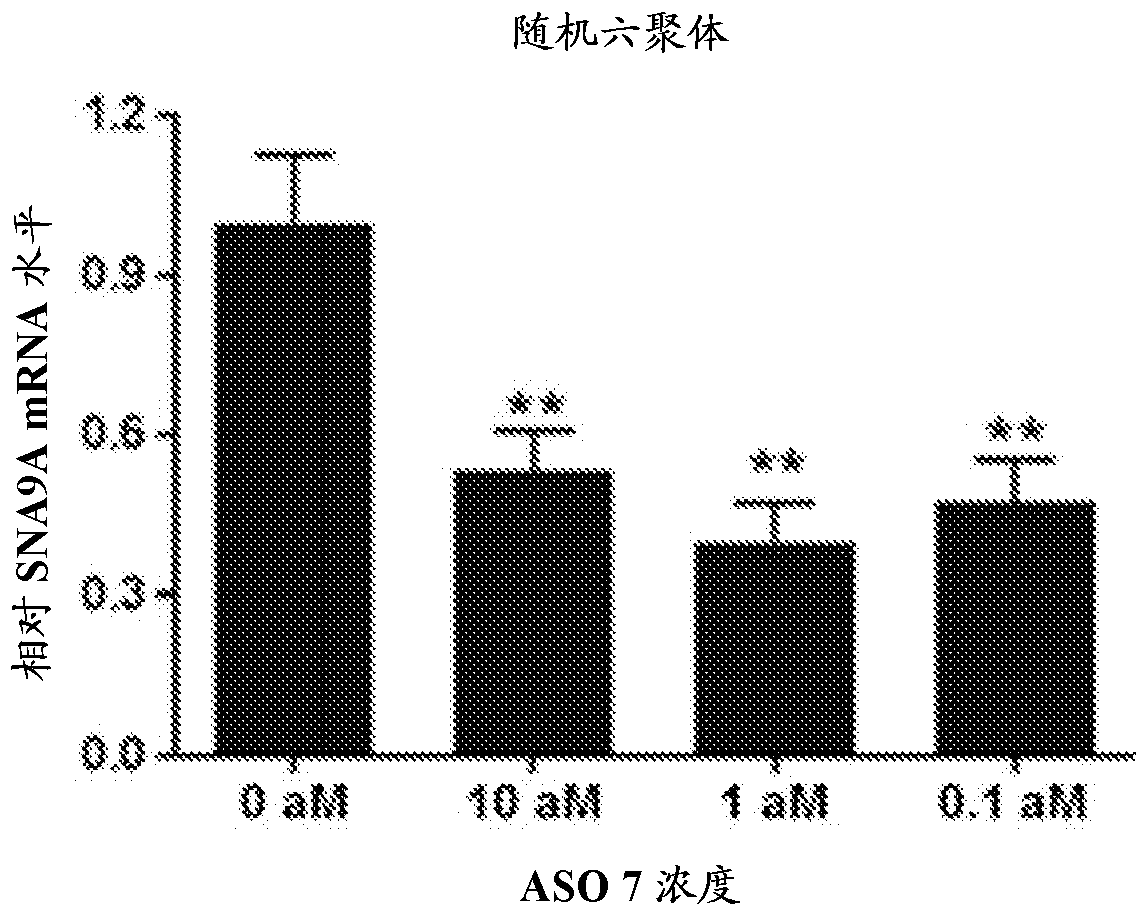
Scn9a antisense pain killer
The current invention provides peptide nucleic acid derivatives targeting the 3' splice site of exon 4 in the human SCN9A pre-mRNA. The peptide nucleic acid derivatives potently induce SCN9A mRNA splice variant(s) lacking the SCN9A exon 4 in cells, and are useful to safely treat pains or conditions involving Nav1.7 activity.
Owner:OLIPASS CORP
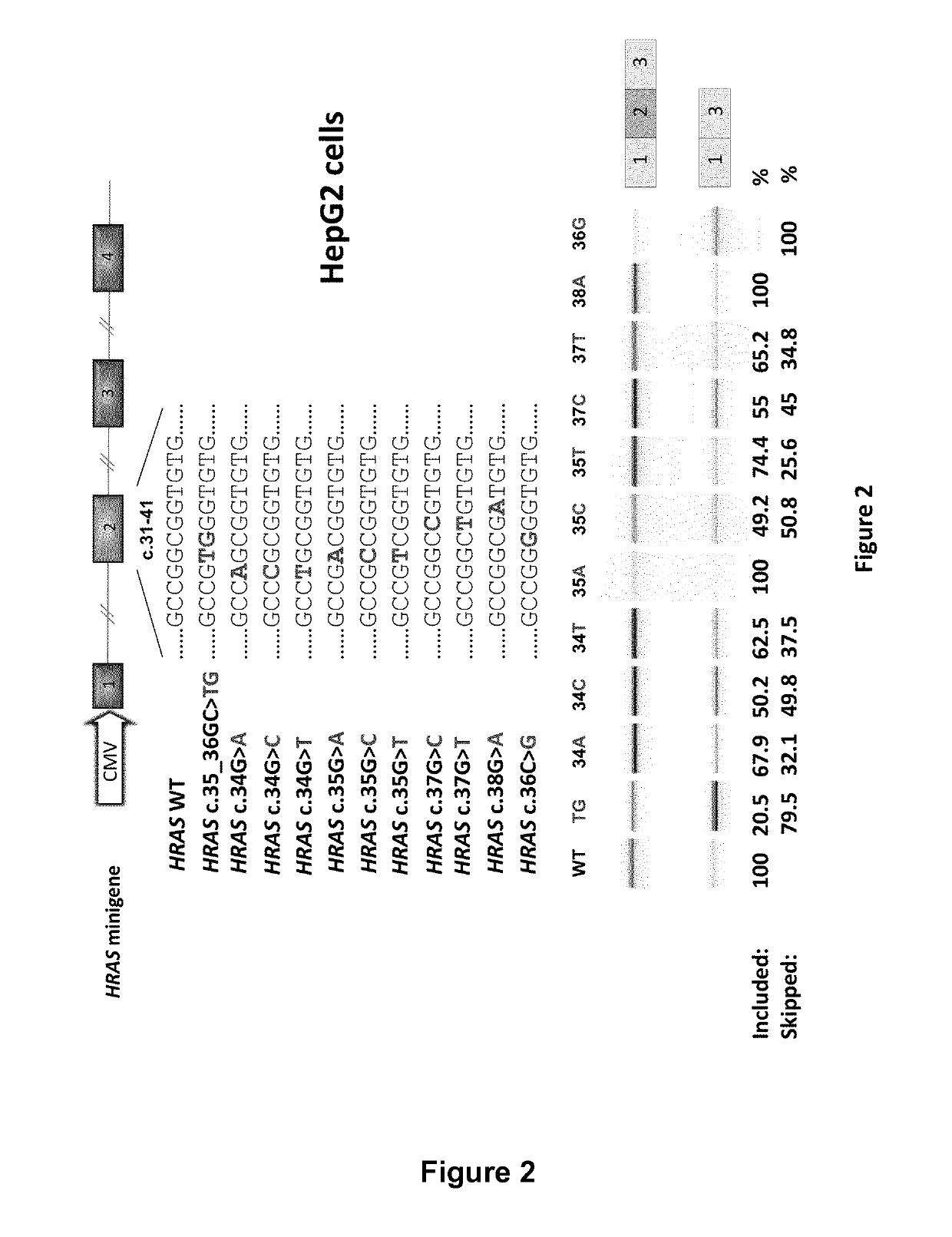
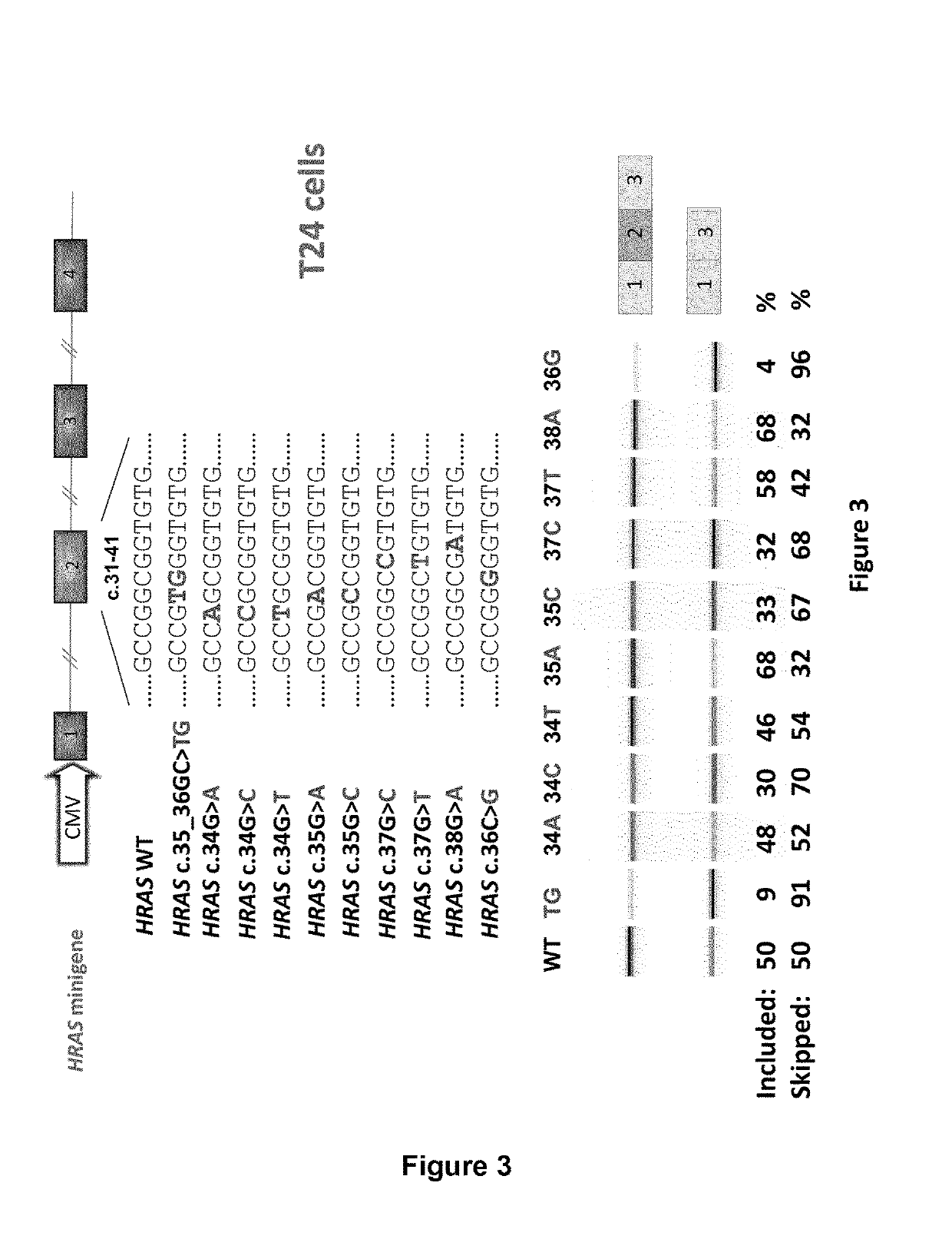
RAS exon 2 skipping for cancer treatment
ActiveUS10266828B2Reduced growth and proliferation and deathReduced growth and proliferationSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseaseActivating mutation
There is provided SSOs targeting the region of HRAS, KRAS, and HRAS exon 2 that harbors the activating mutations and which harbors ESE activity. Moreover, there is provided SSOs targeting the 3′- and 5′-splice sites. The SSOs targeting the 5′ splice site sequence of HRAS exon 2, the 3′ splice site sequence of KRAS exon 2 and the 3′ splice site sequence of NRAS exon 2, as well as SSOs that targets ESEs in a conserved part of exon 2 in the HRAS, KRAS and NRAS exon 2 sequences can induce complete or nearly complete exon 2 skipping in cancer cell lines. This results in growth and proliferation inhibition and concomitantly in death of cancer cells. Therefore this invention is directed towards treatment of cancerous diseases and other conditions where RAS signaling is involved.
Owner:SYDDANSK UNIV
Acetyl-coa carboxylase2 antisense oligonucleotides
The present invention provides the peptide nucleic acid derivative which targets 5' splice site of the human ACC2 pre-mRNA "exon 12". The peptide nucleic acid derivatives in the present invention strongly induce splice variants of the human ACC2 mRNA in cell and are very useful to treat conditions or disorders of skin aging associated with the human ACC2 protein.
Owner:OLIPASS CORP
Natural Cryptic Exon Removal by Pairs of Antisense Oligonucleotides
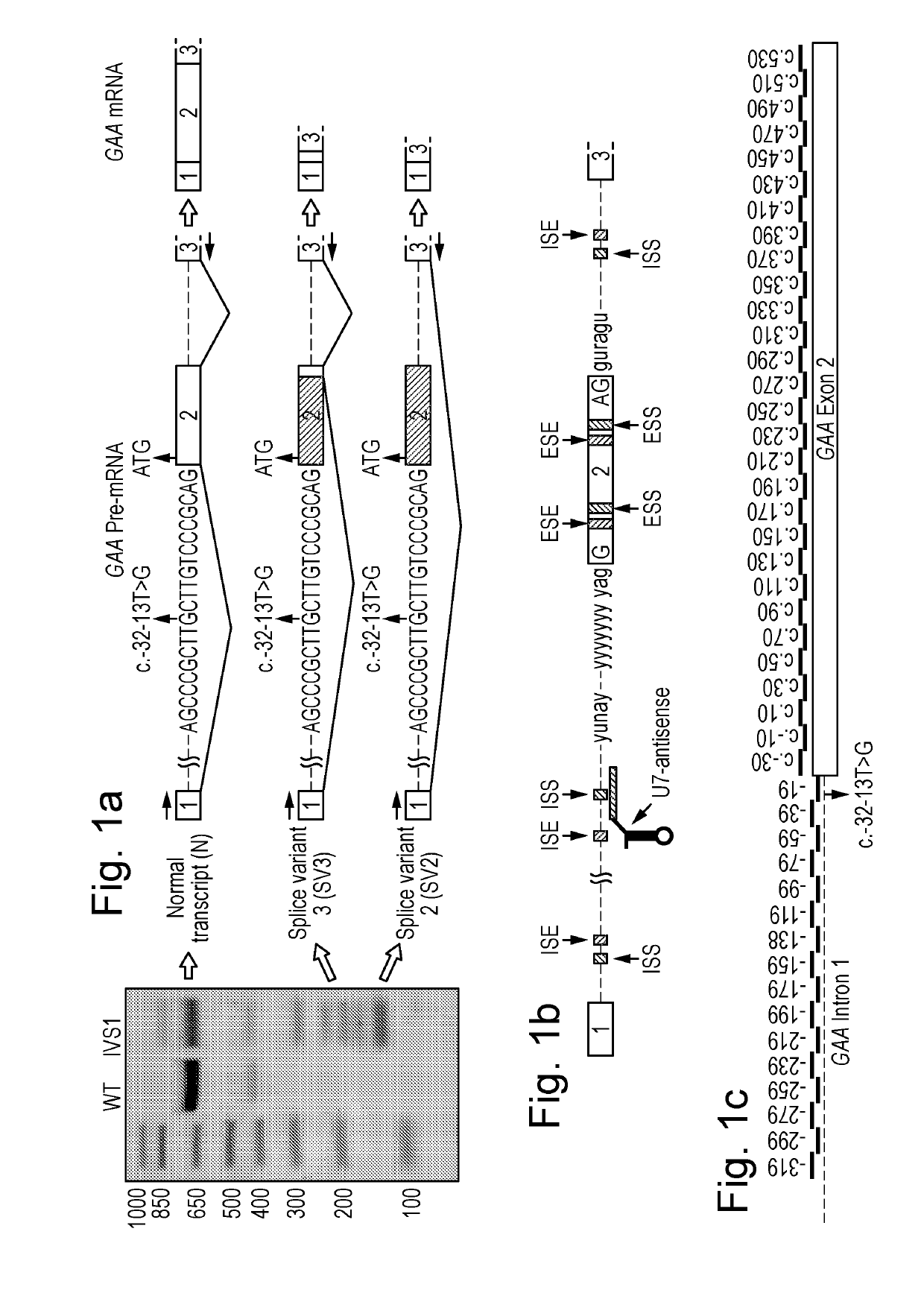
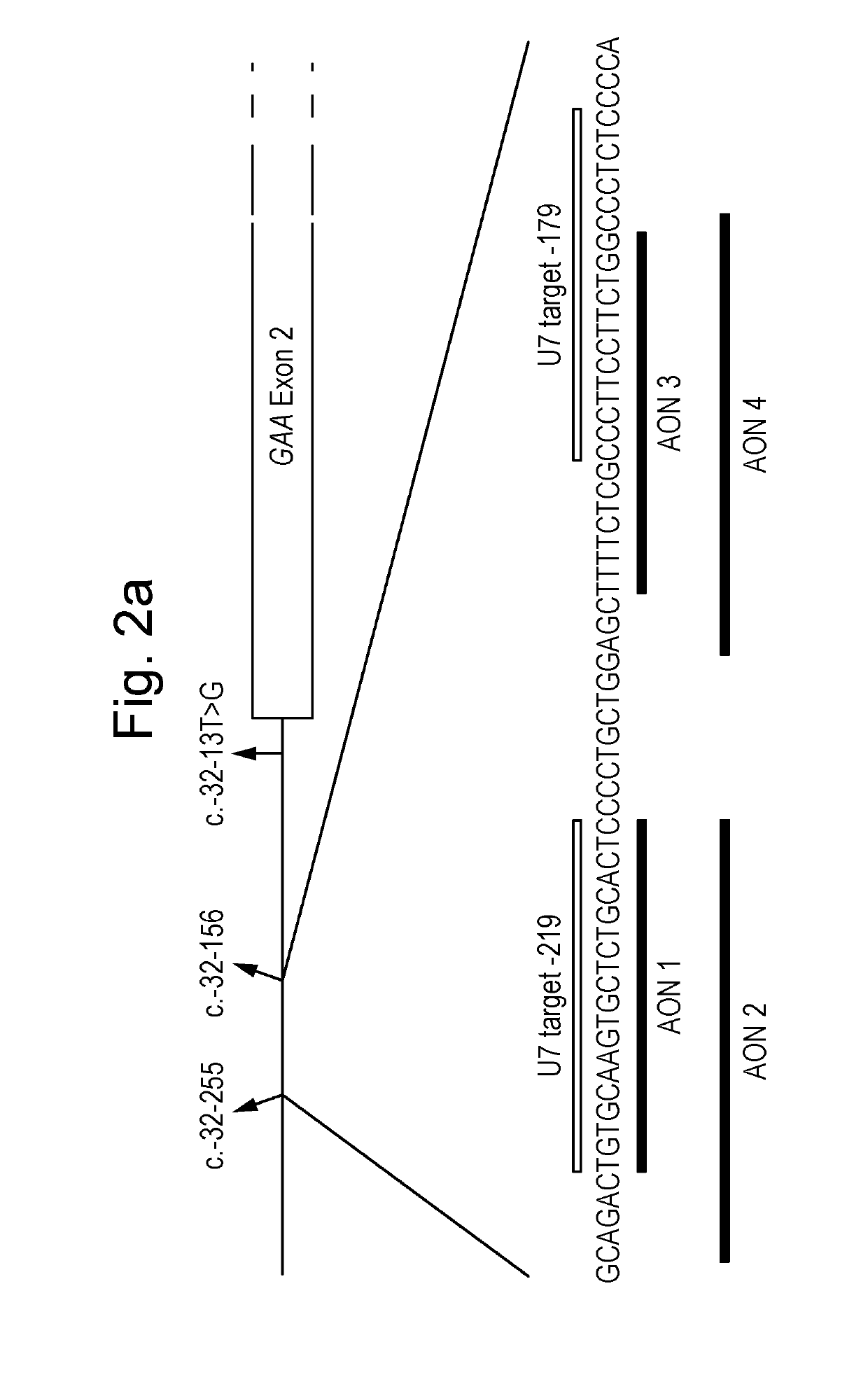
ActiveUS20190194661A1Restores enzyme activityEffective recoveryOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationSplice Site SNPGenetics
The invention relates to a method for repairing aberrant splicing in Pompe patients that carry the IVS1 variant, wherein such aberrant splicing is caused by the expression of a natural pseudo exon present in GAA intron 1, comprising blocking of either the natural cryptic 3′ splice site or the natural cryptic 5′ splice site of said natural pseudo exon with an antisense oligomeric compound (AON). Further, the invention comprises an antisense oligomeric compound targeting SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 180, preferably selected from the sequences of SEQ ID NO: 91-179, sequences that are complementary to said sequences or sequences that have an identity of 80% with said sequences or the complementary sequences and a second AON from the sequences of SEQ ID NO: 346-508, sequences that are complementary to said sequences or sequences that have an identity of 80% with said sequences or the complementary sequences.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Third-generation sequencing RNA-seq comparison method based on WFA algorithm
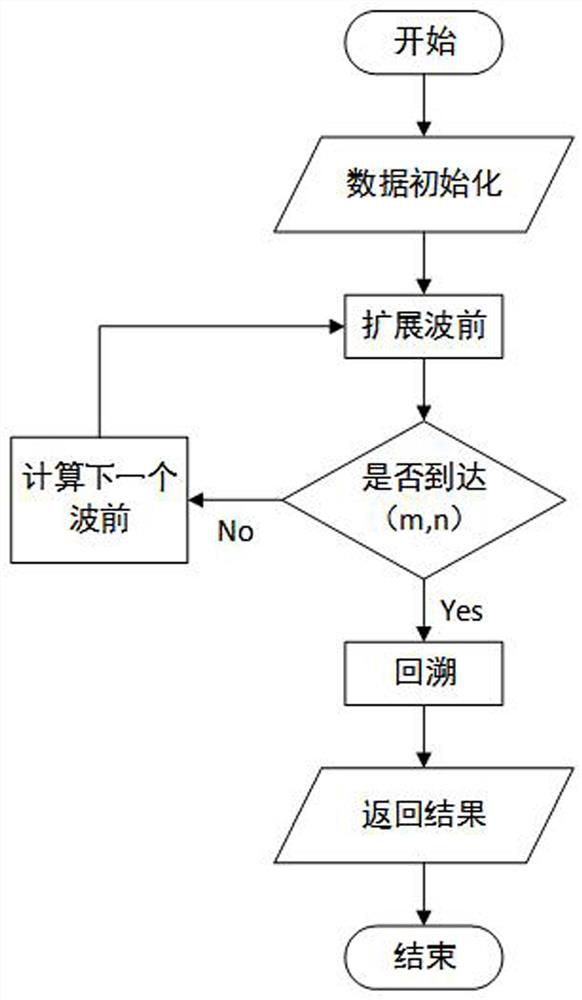
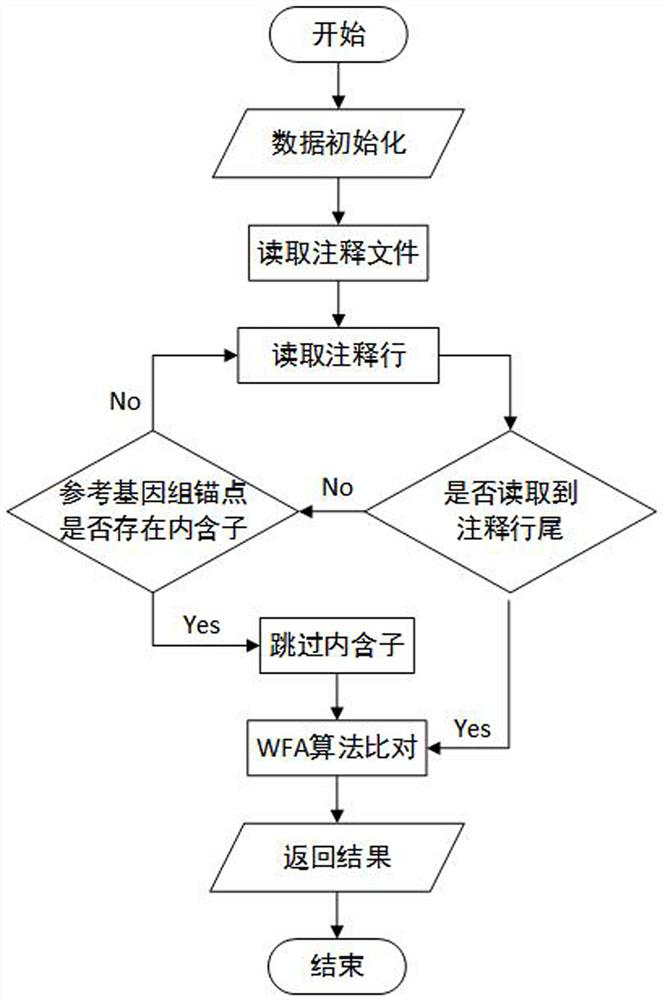
PendingCN114550820AAccurate identificationImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsGraph mappingRegion selection
The invention discloses a third-generation sequencing RNA-seq comparison method based on a WFA algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a data set containing a target sequence and a query sequence; then indexing the reference genome; carrying out region selection and graph mapping; searching the longest common subsequence LCSk of the k-length substring, and then carrying out anchor point filtering and anchor point comparison; and introducing an annotation file to obtain a comparison result, and finally evaluating the comparison result. Experiments prove that the method provided by the invention effectively improves the accuracy of sequence alignment, especially the accuracy of splicing site alignment, and reduces the alignment time to a certain extent.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
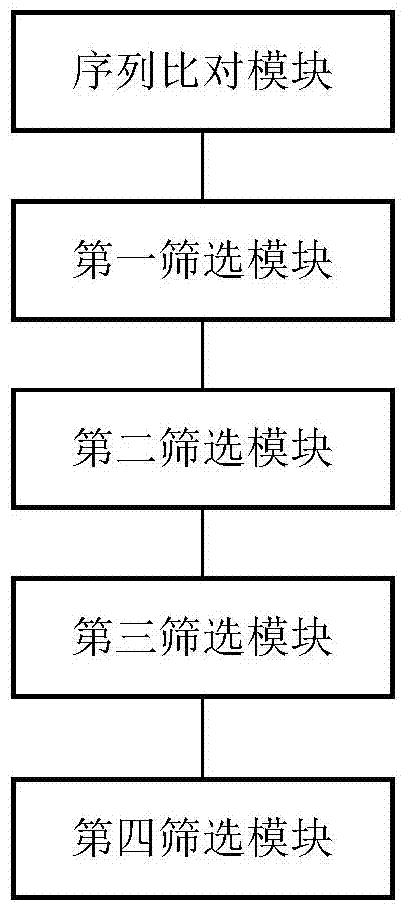
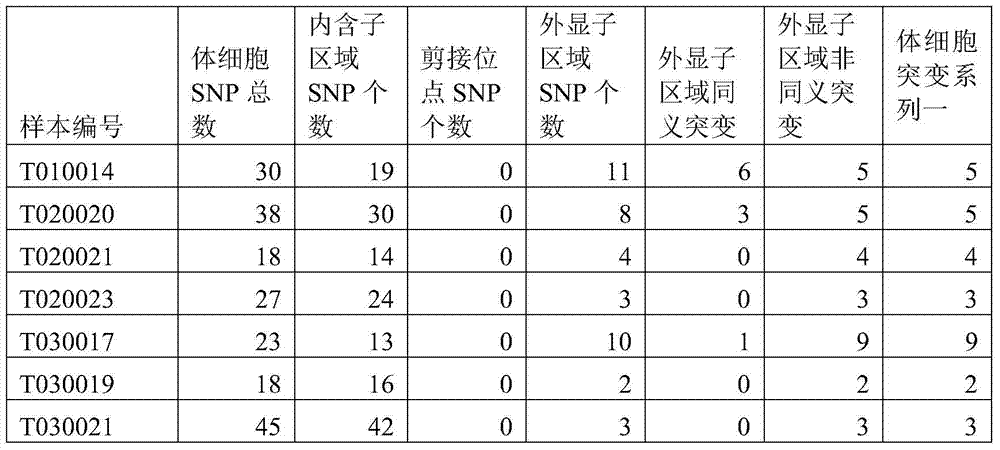
Method and device for detecting somatic single nucleotide mutation
ActiveCN104462869BRealize detectionSimple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle nucleotide mutationMutation frequency
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting somatic cell SNP. The method comprises the steps of S1, comparing DNA sequencing data of somatic cells with reference genome data to obtain data of all SNP loci; S2, screening out SNP loci which occur on splicing loci and SNP loci which occur on exons and cause nonsynonymous mutation of amino acid to obtain a first SNP locus set; S3, removing SNP loci with the thousand-people mutation frequency higher than 5% in the first SNP locus set to obtain a second SNP locus set; S4, screening out SNP loci which are resources of somatic cell mutation from the second SNP locus set to obtain a third SNP locus set; S5, screening out SNP loci with the frequency of supporting sequences lower than 75% from the third SNP locus set to obtain SNP loci containing somatic cell SNP. By means of the method, somatic cell mutation can be detected through simple samples, and therefore the cost is lowered.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com