Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
146 results about "Synthetic nucleic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xeno nucleic acid (XNA) is a synthetic alternative to the natural nucleic acids DNA and RNA as information-storing biopolymers that differs in the sugar backbone.
Method of sequencing a nucleic acid
InactiveUS7211390B2Improve performanceMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesPyrophosphateSynthetic nucleic acid
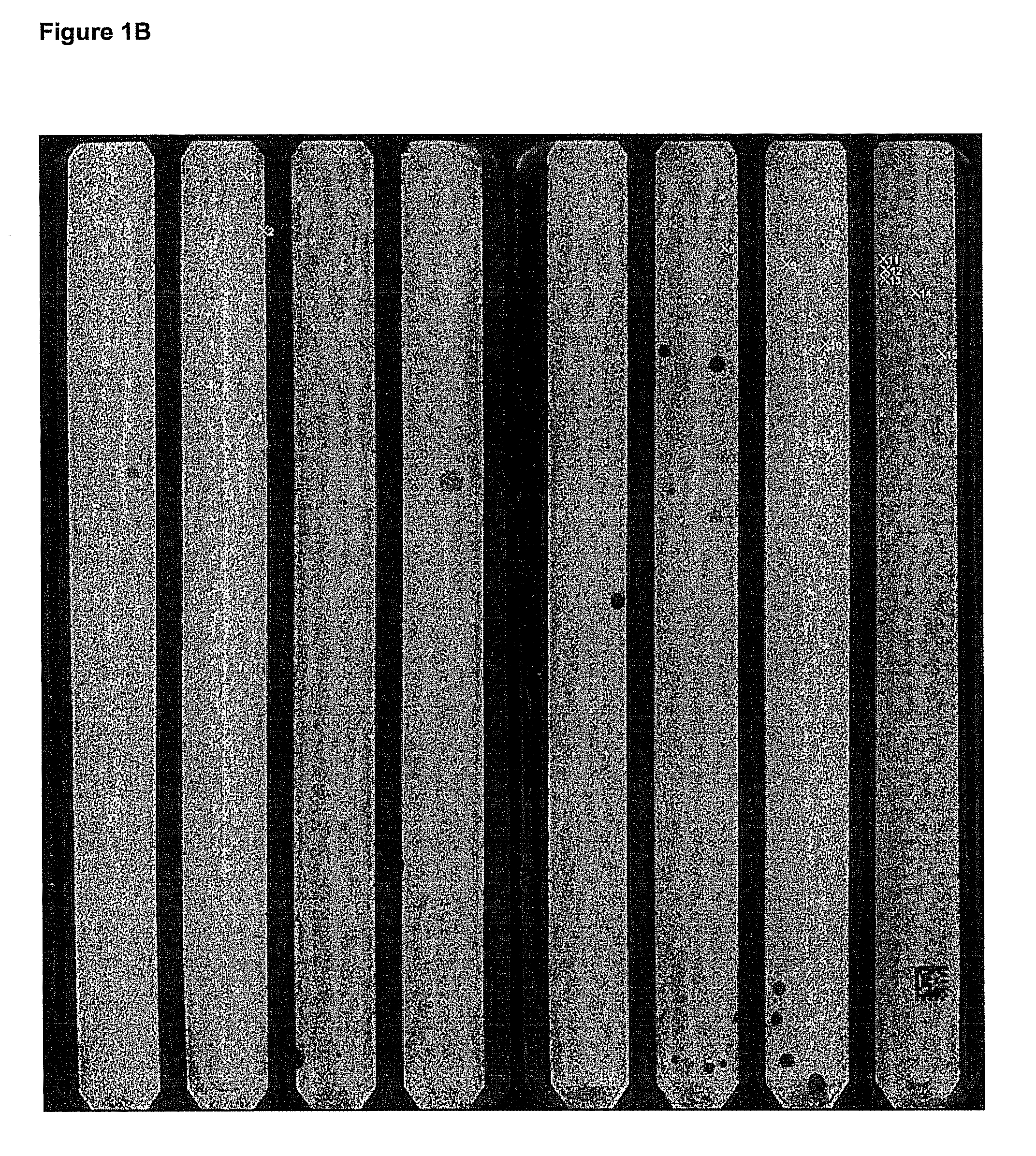
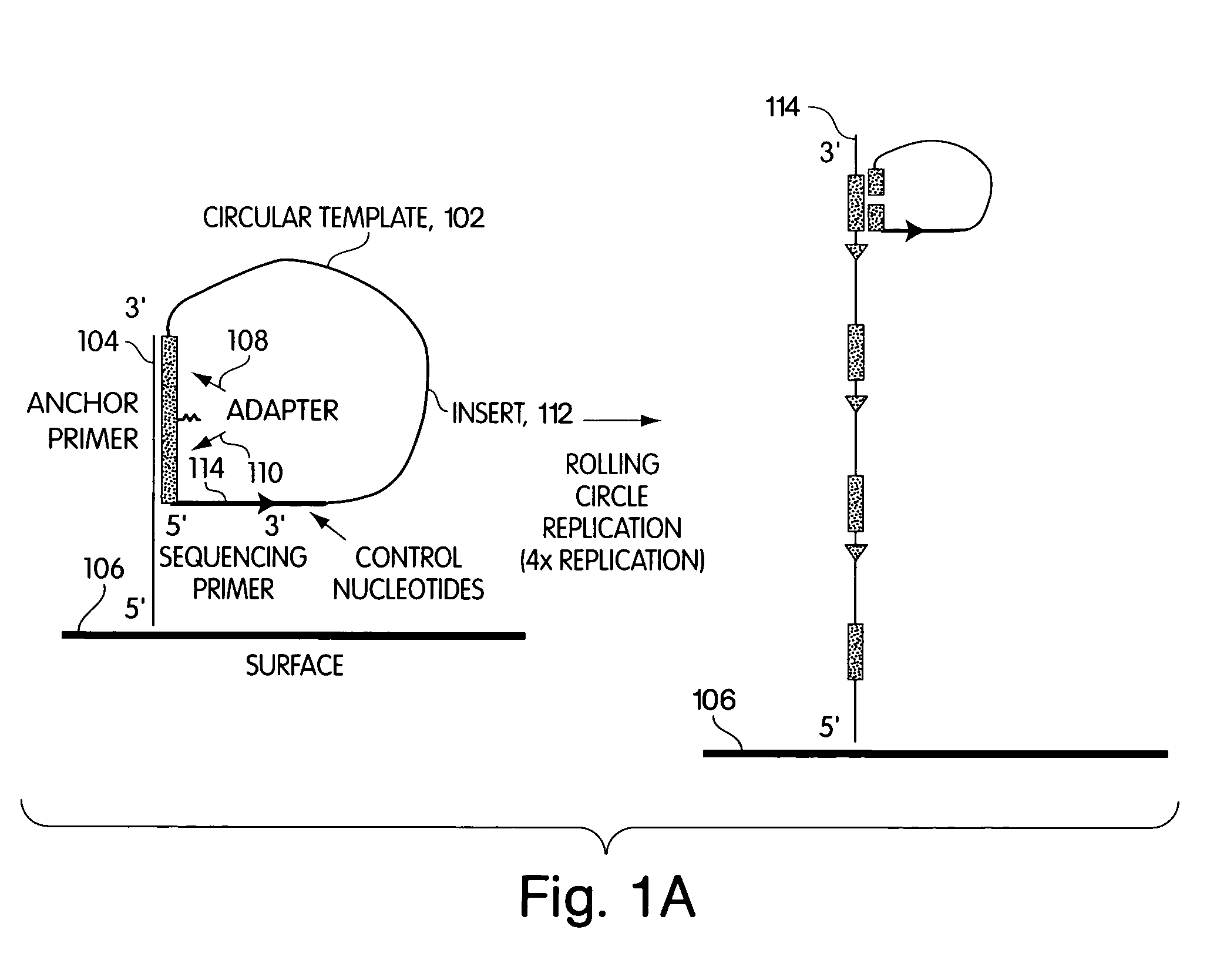
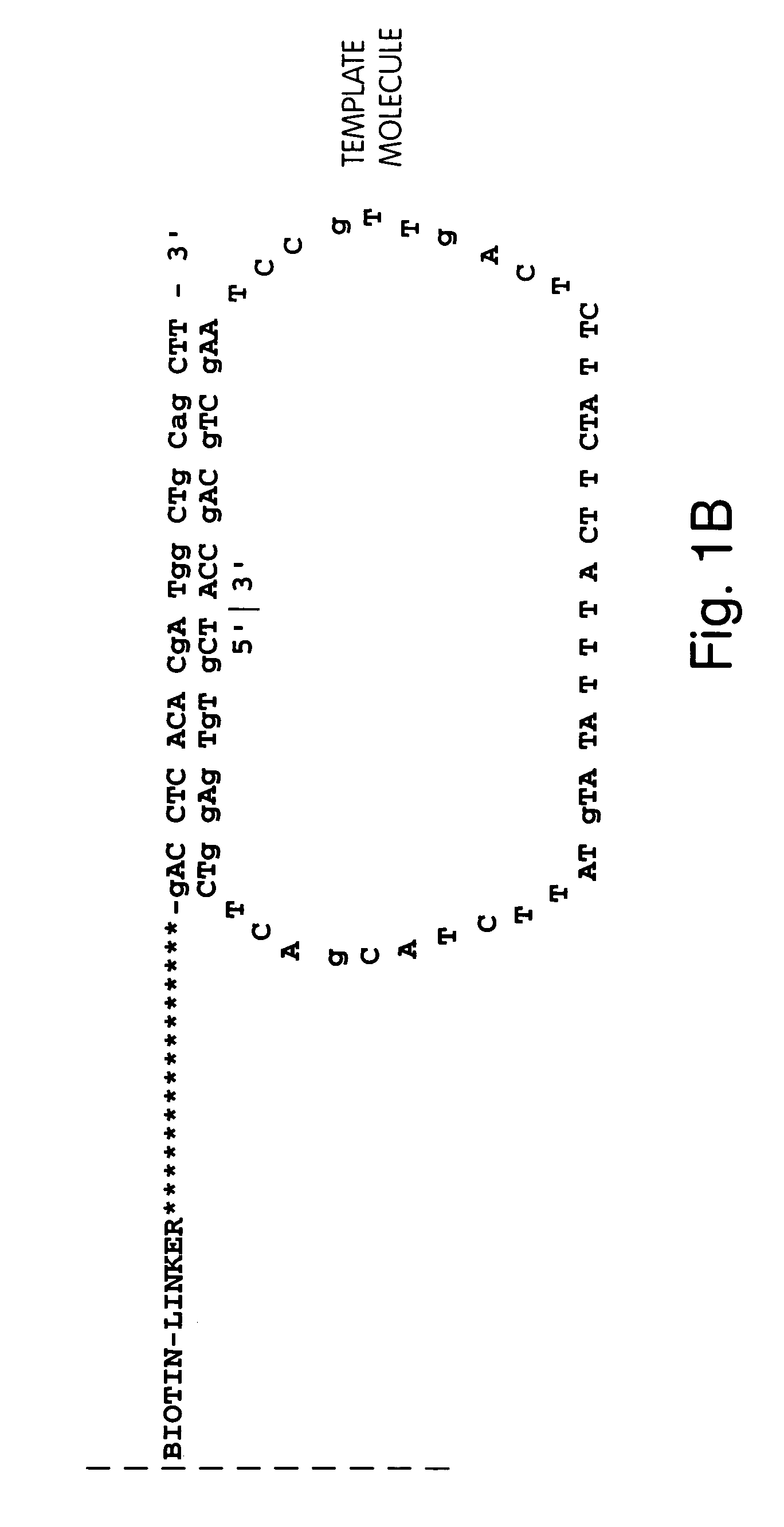
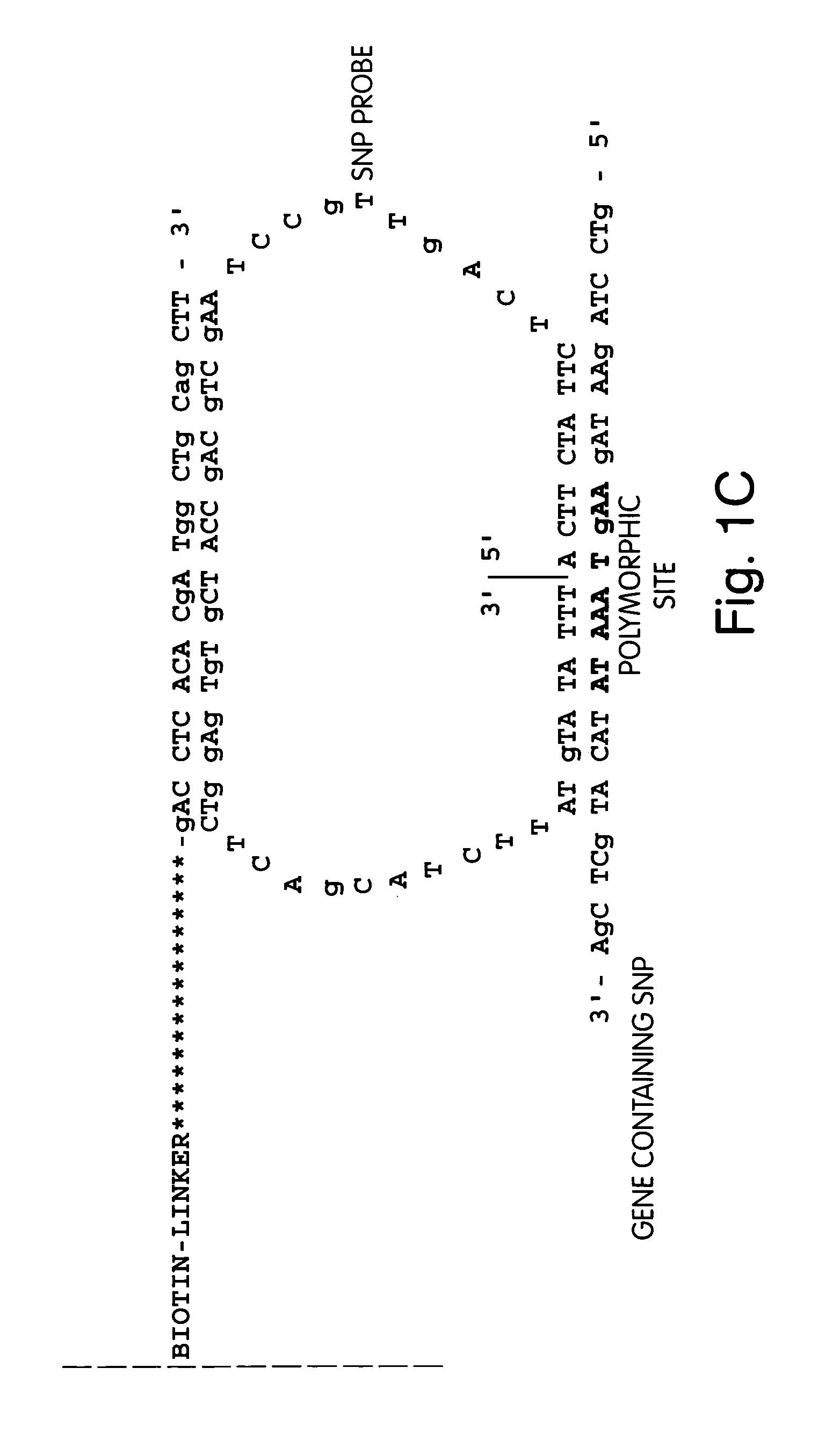
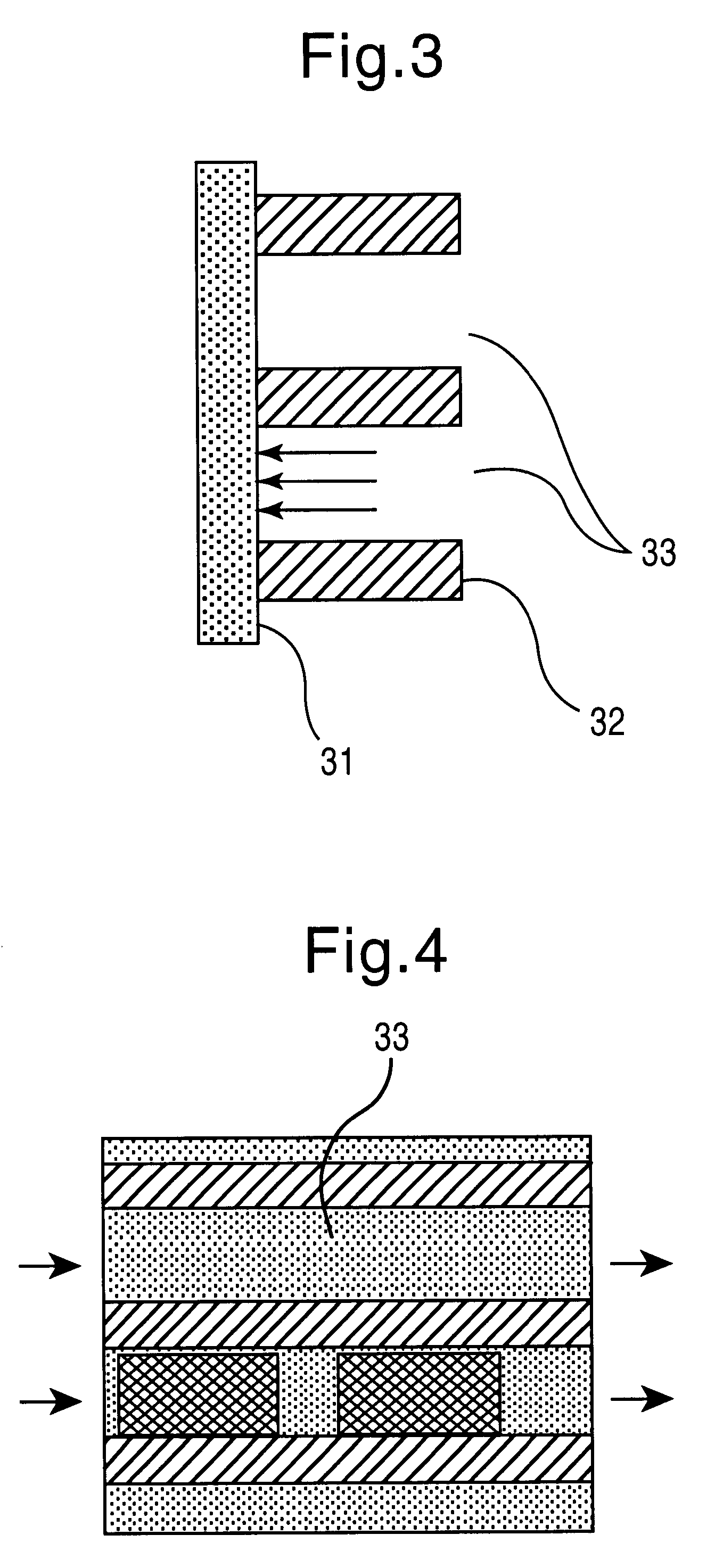
Disclosed herein are methods and apparatuses for sequencing a nucleic acid. In one aspect, the method includes annealing a population of circular nucleic acid molecules to a plurality of anchor primers linked to a solid support, and amplifying those members of the population of circular nucleic acid molecules which anneal to the target nucleic acid, and then sequencing the amplified molecules by detecting the presence of a sequence byproduct such as pyrophosphate.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
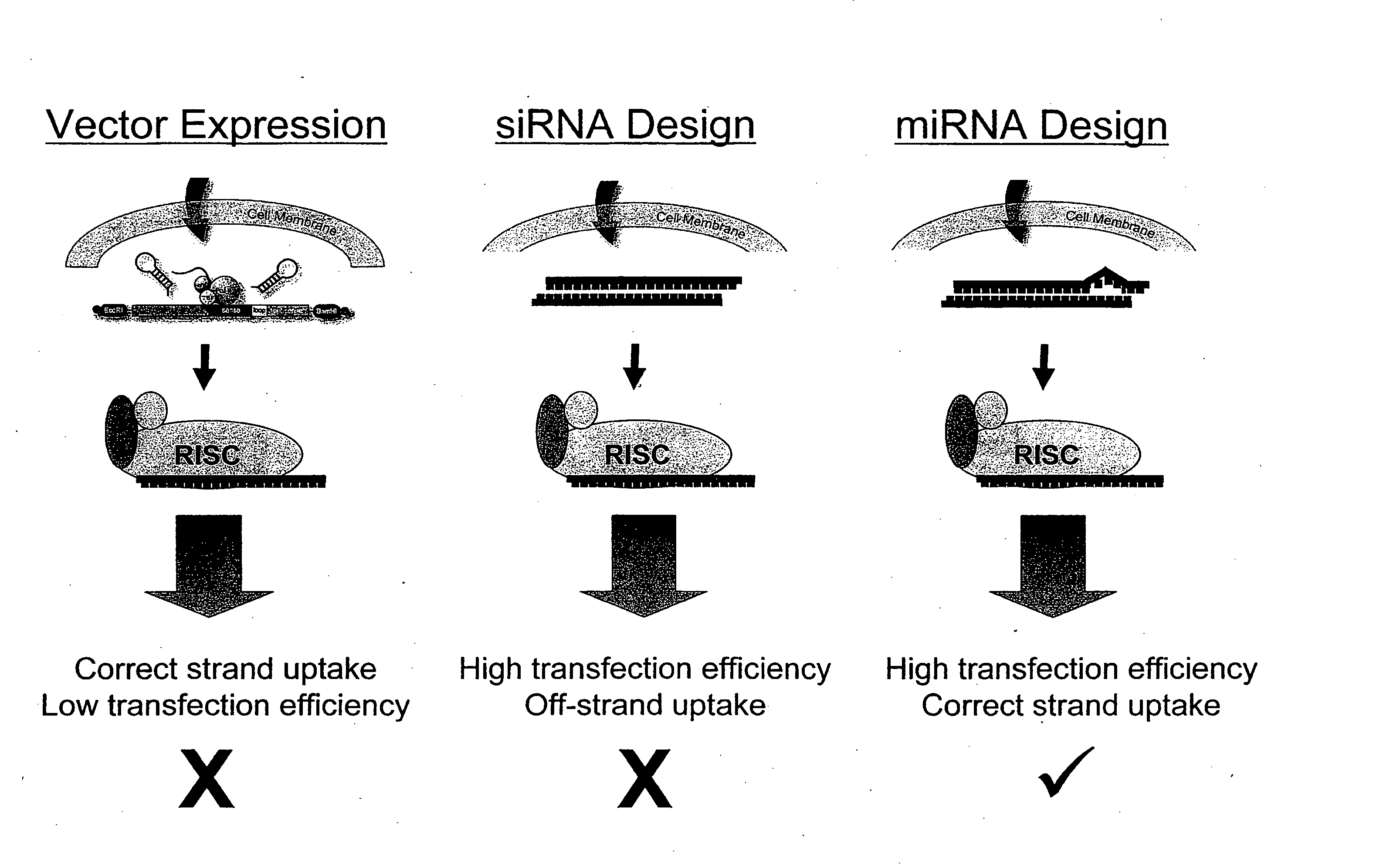
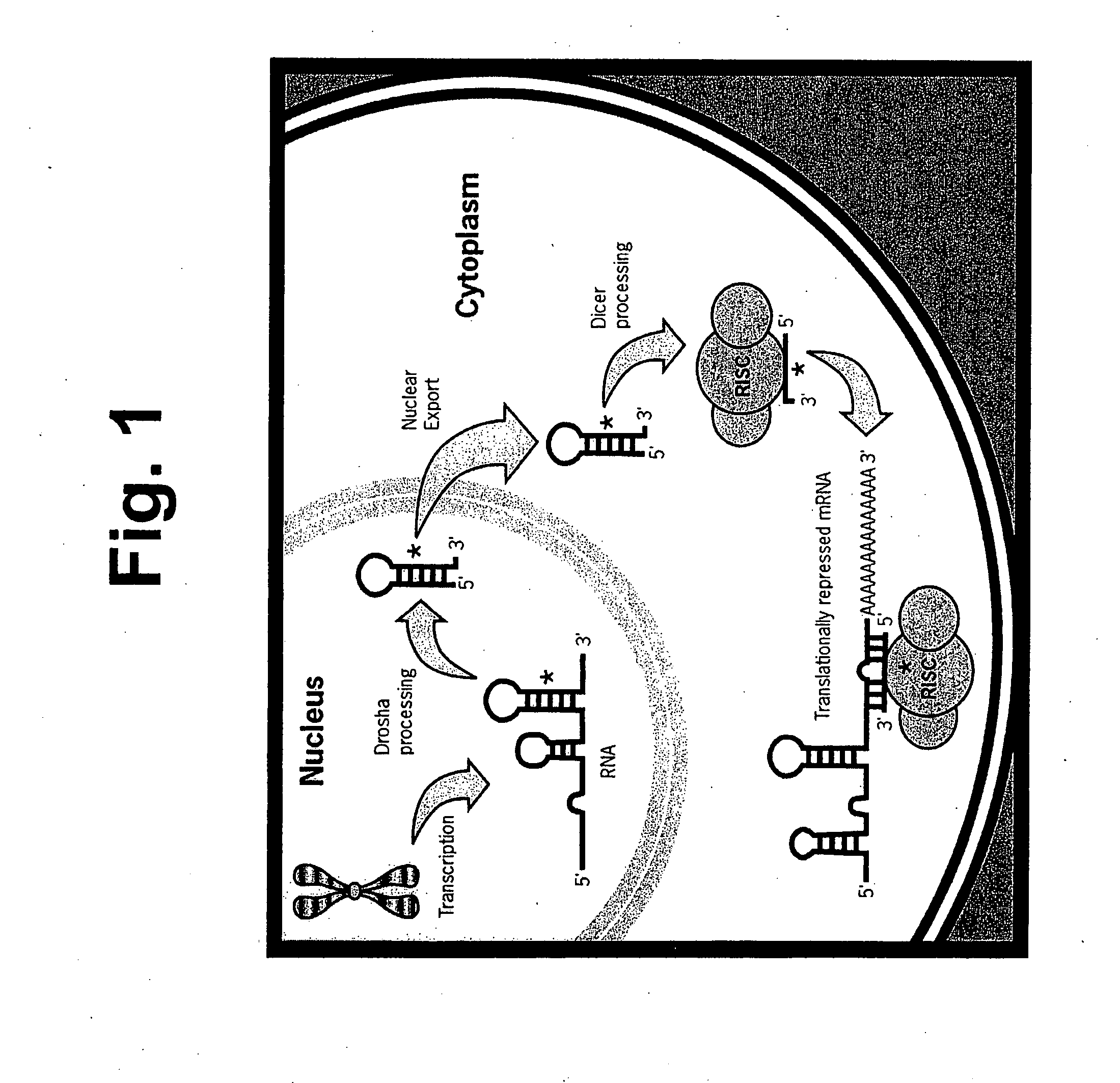
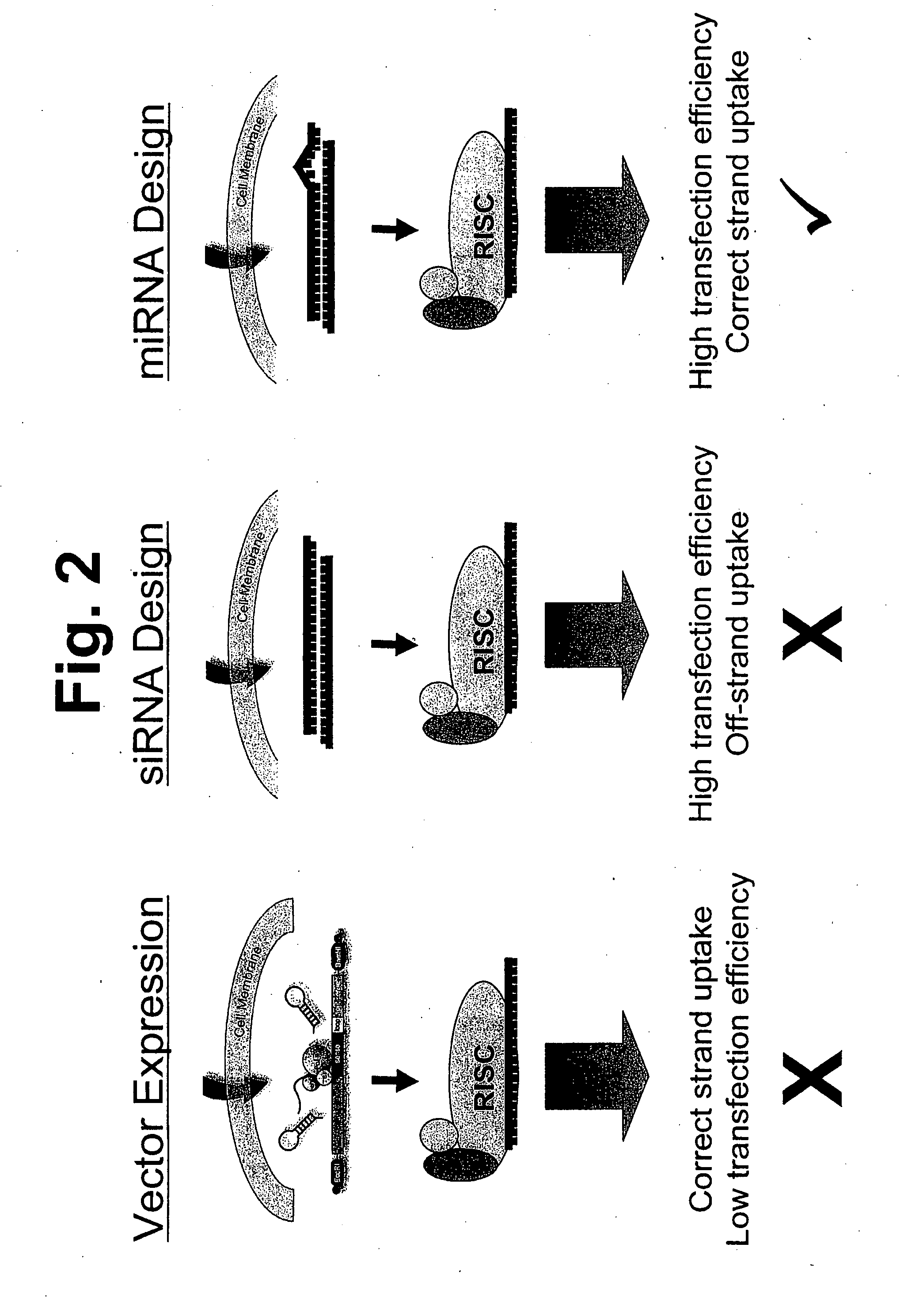
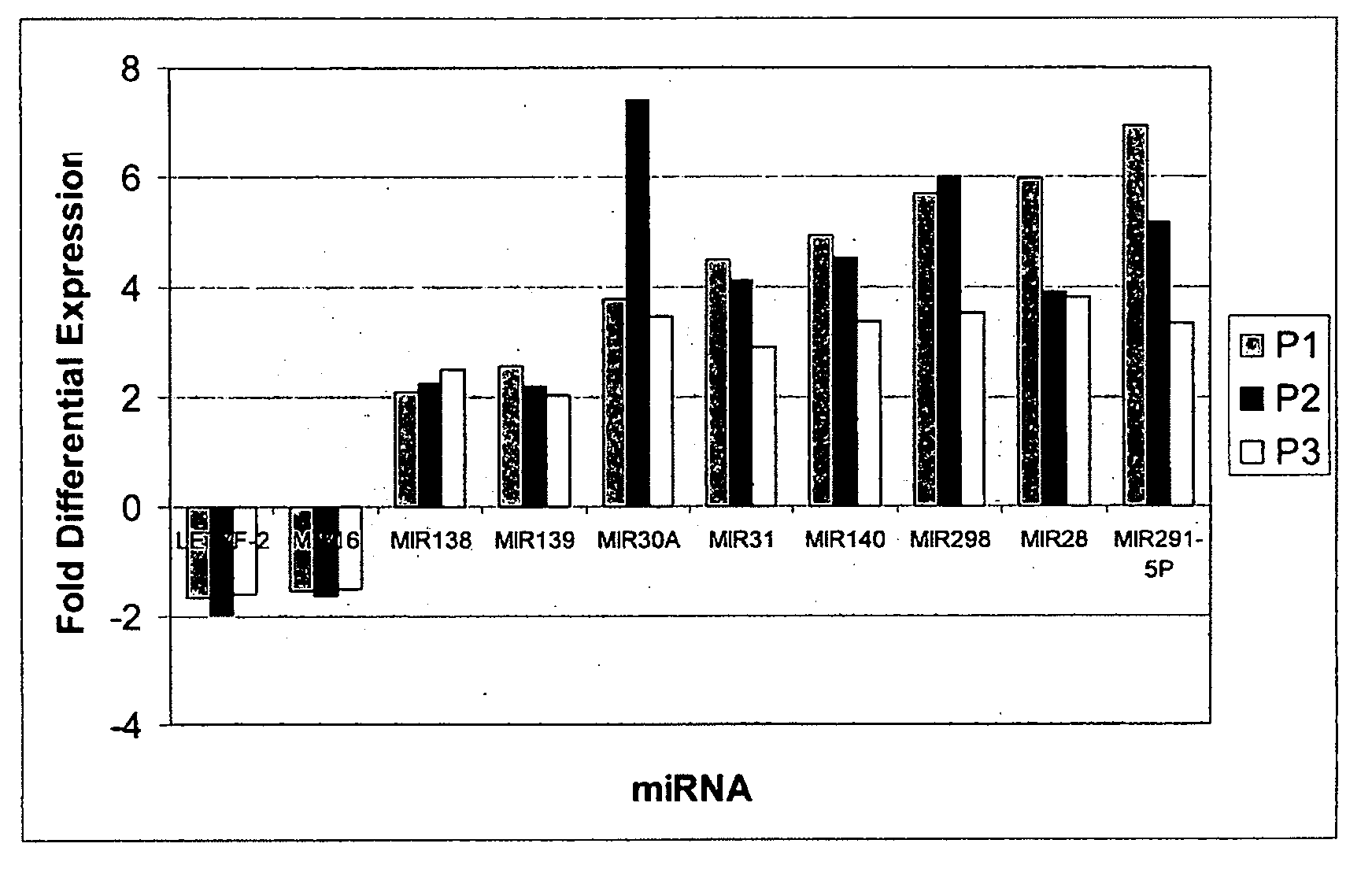
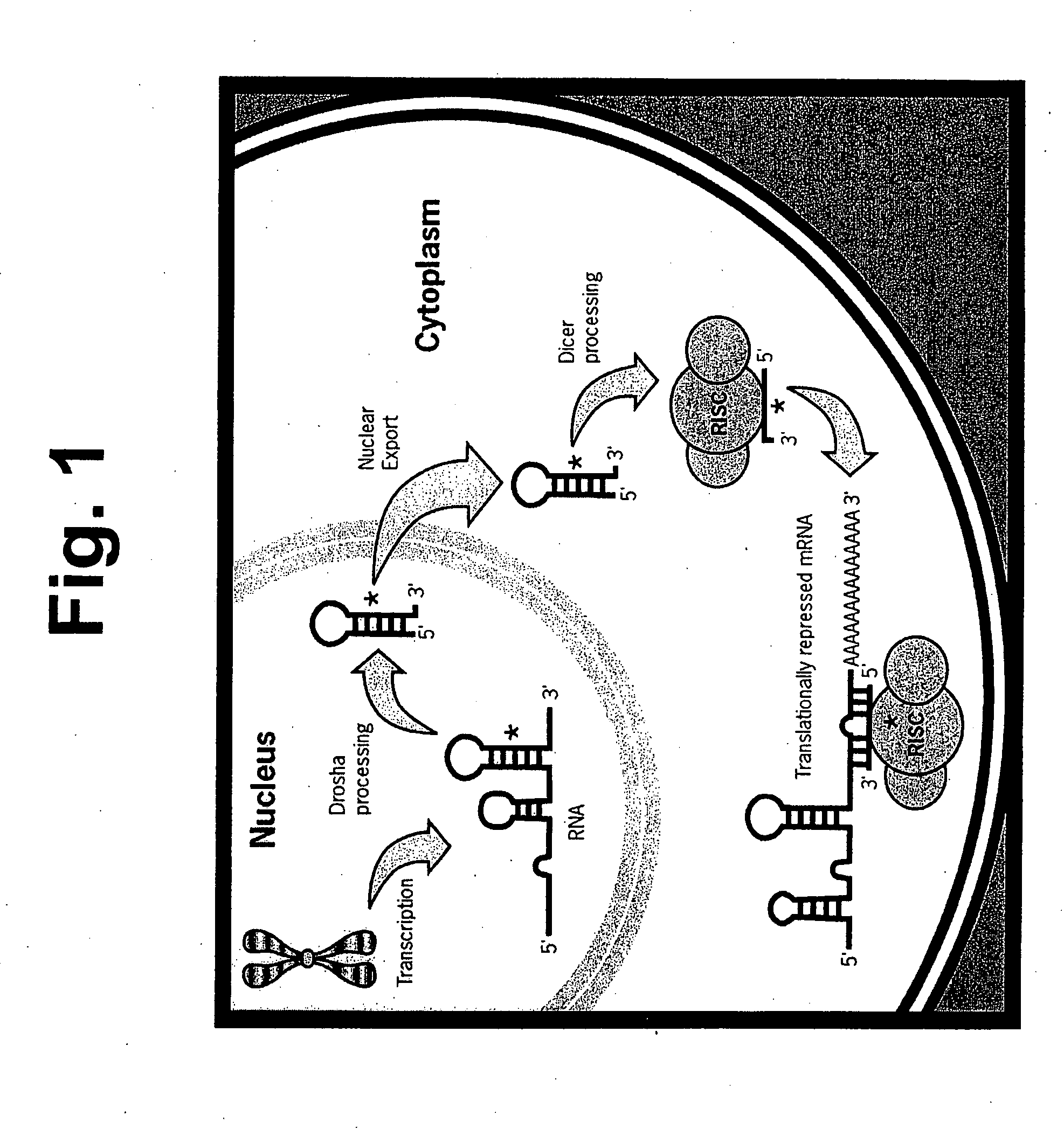
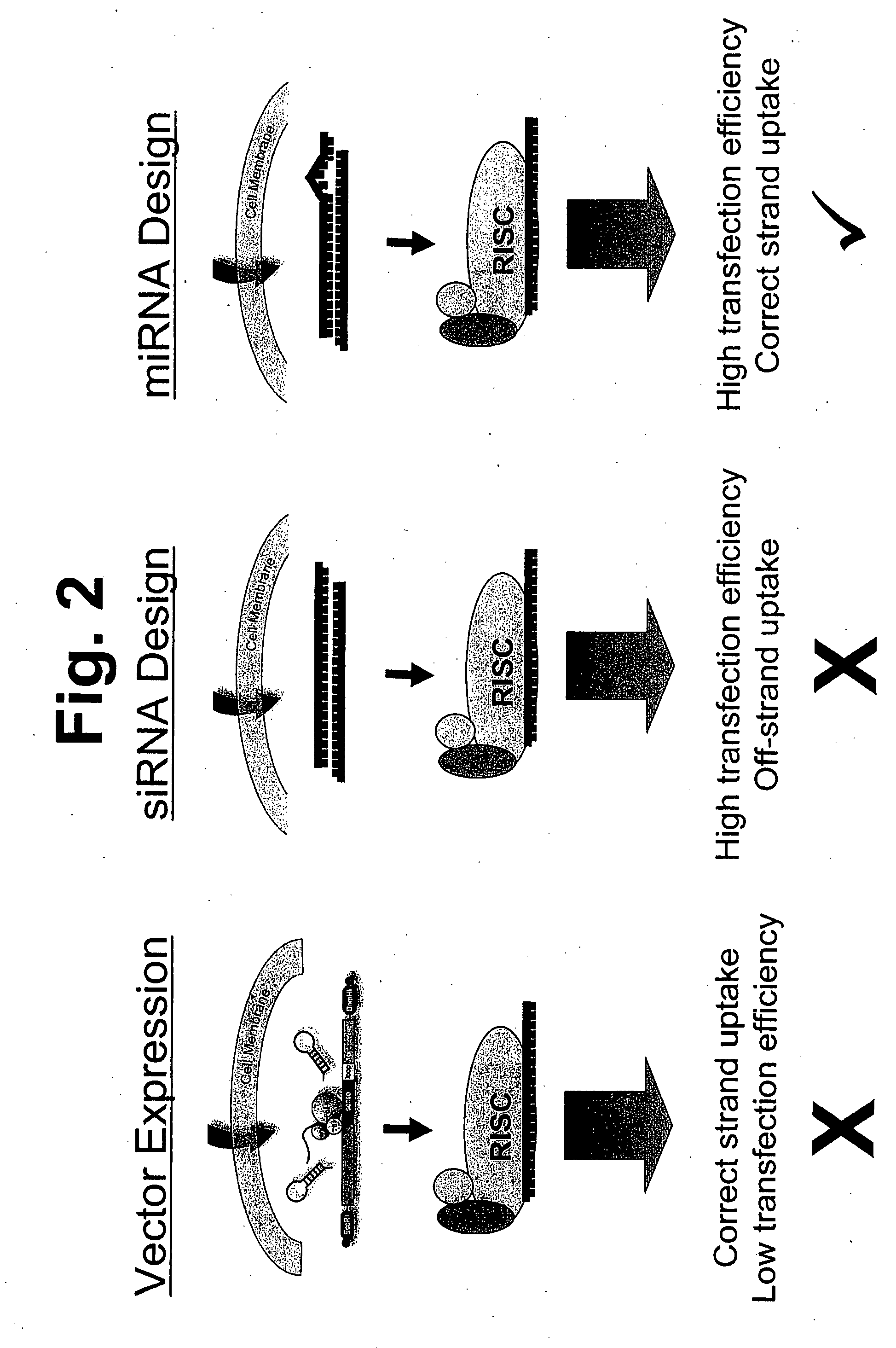
Methods and compositions involving mirna and mirna inhibitor molecules
InactiveUS20080050744A1Effective amountReduce percentageAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiologyCellular functions
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for introducing miRNA activity or function into cells using synthetic nucleic acid molecules. Moreover, the present invention concerns methods and compositions for identifying miRNAs with specific cellular functions that are relevant to therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic applications wherein synthetic miRNAs and / or miRNA inhibitors are used in library screening assays.
Owner:ASURAGEN
Method for producing polymers
InactiveUS6586211B1Effective studyEfficient and rapid designMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsDouble strandPolymer
The invention relates to a method for producing polymers, in particular synthetic nucleic acid double strands of optional sequence, comprising the steps:(a) provision of a support having a surface area which contains a plurality of individual reaction areas,(b) location-resolved synthesis of nucleic acid fragments having in each case different base sequences in several of the individual reaction areas, and(c) detachment of the nucleic acid fragments from individual reaction areas.
Owner:CODEX DNA INC
Synthesis of sequence-verified nucleic acids
InactiveUS20100216648A1Efficient and cost-effective productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCombinatorial chemistrySynthetic nucleic acid
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Optimized messenger RNA
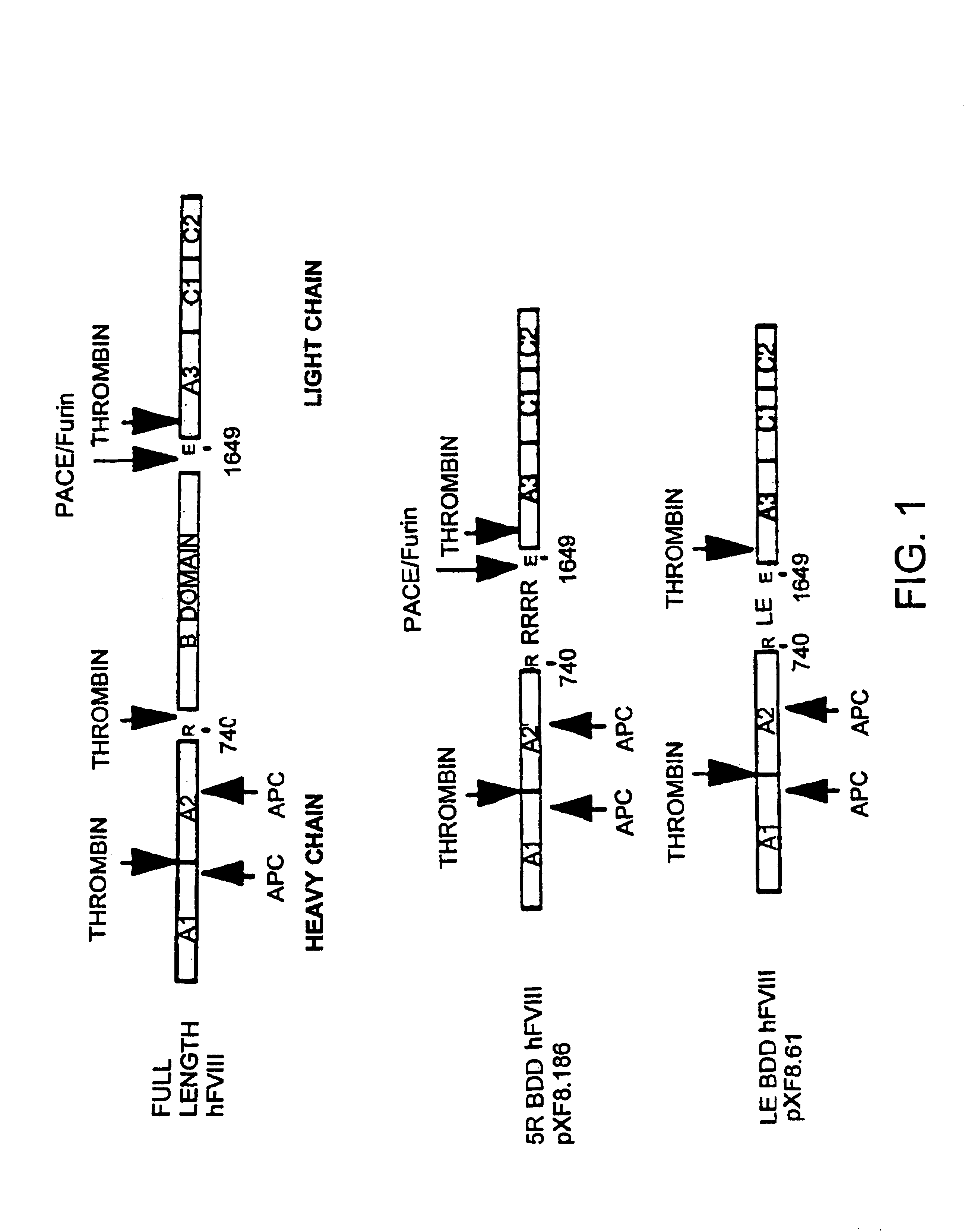
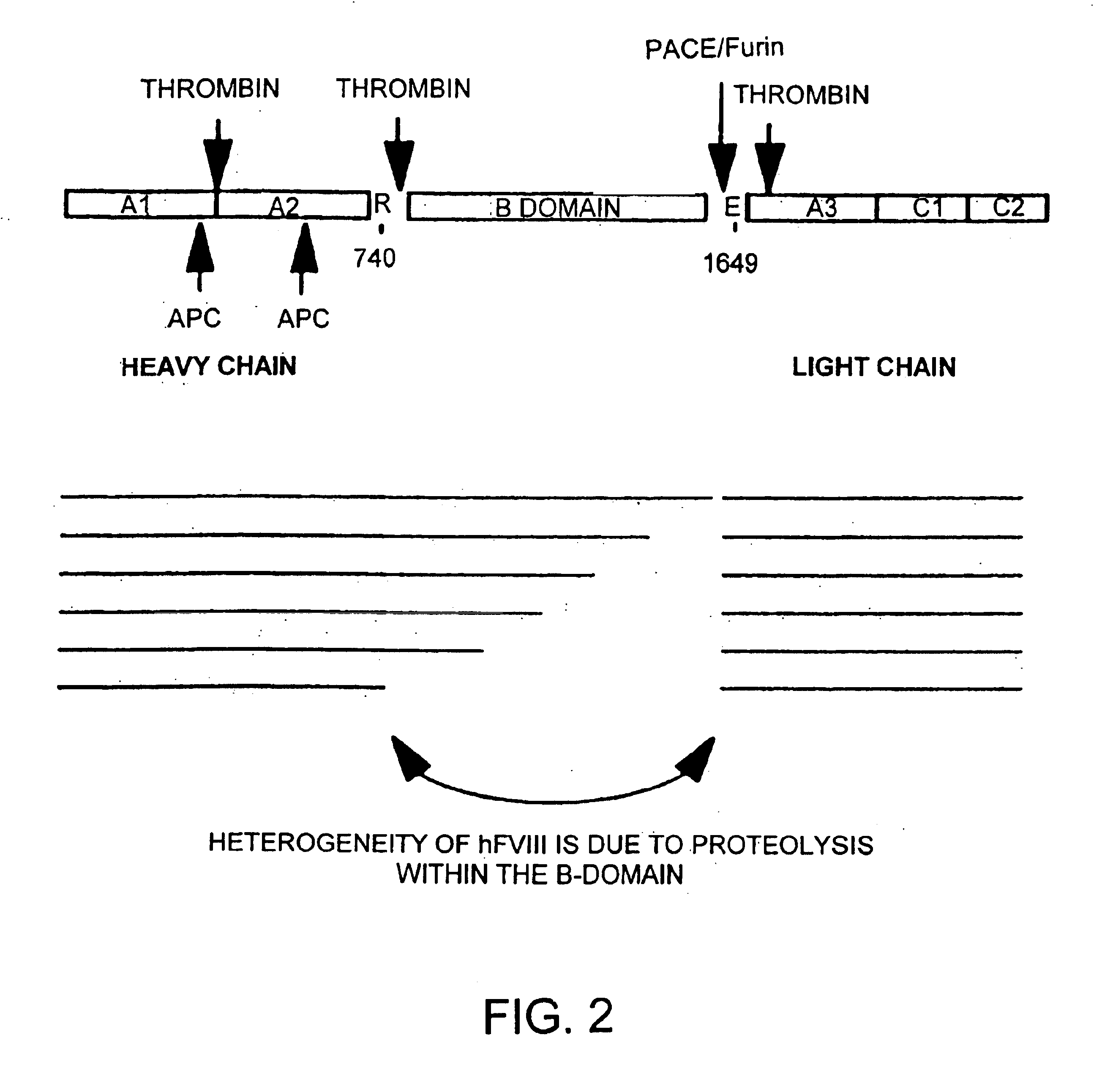
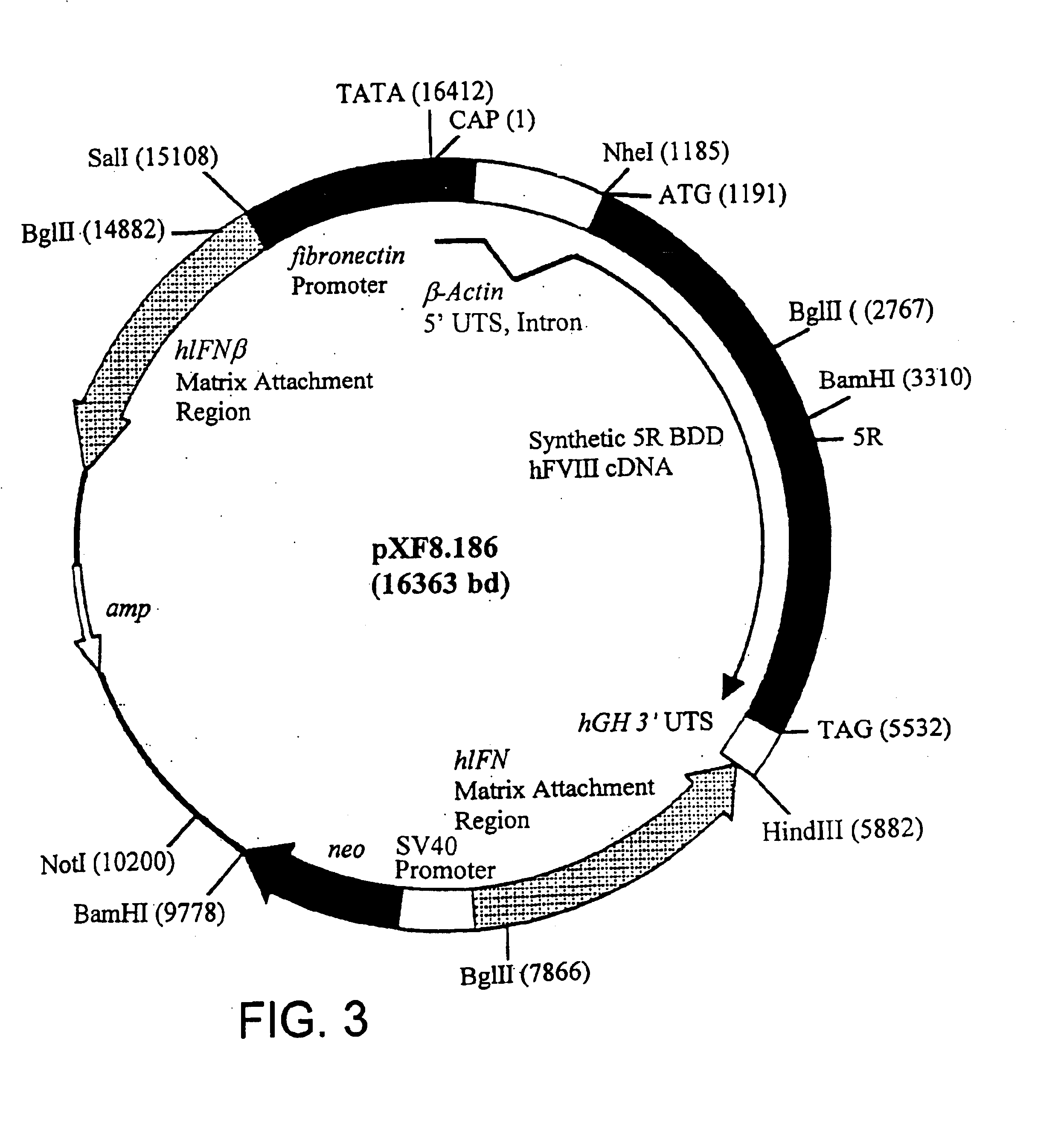
InactiveUS6924365B1Precise functionEliminates issues concerning patient complianceFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsMessenger RNANucleic acid sequence
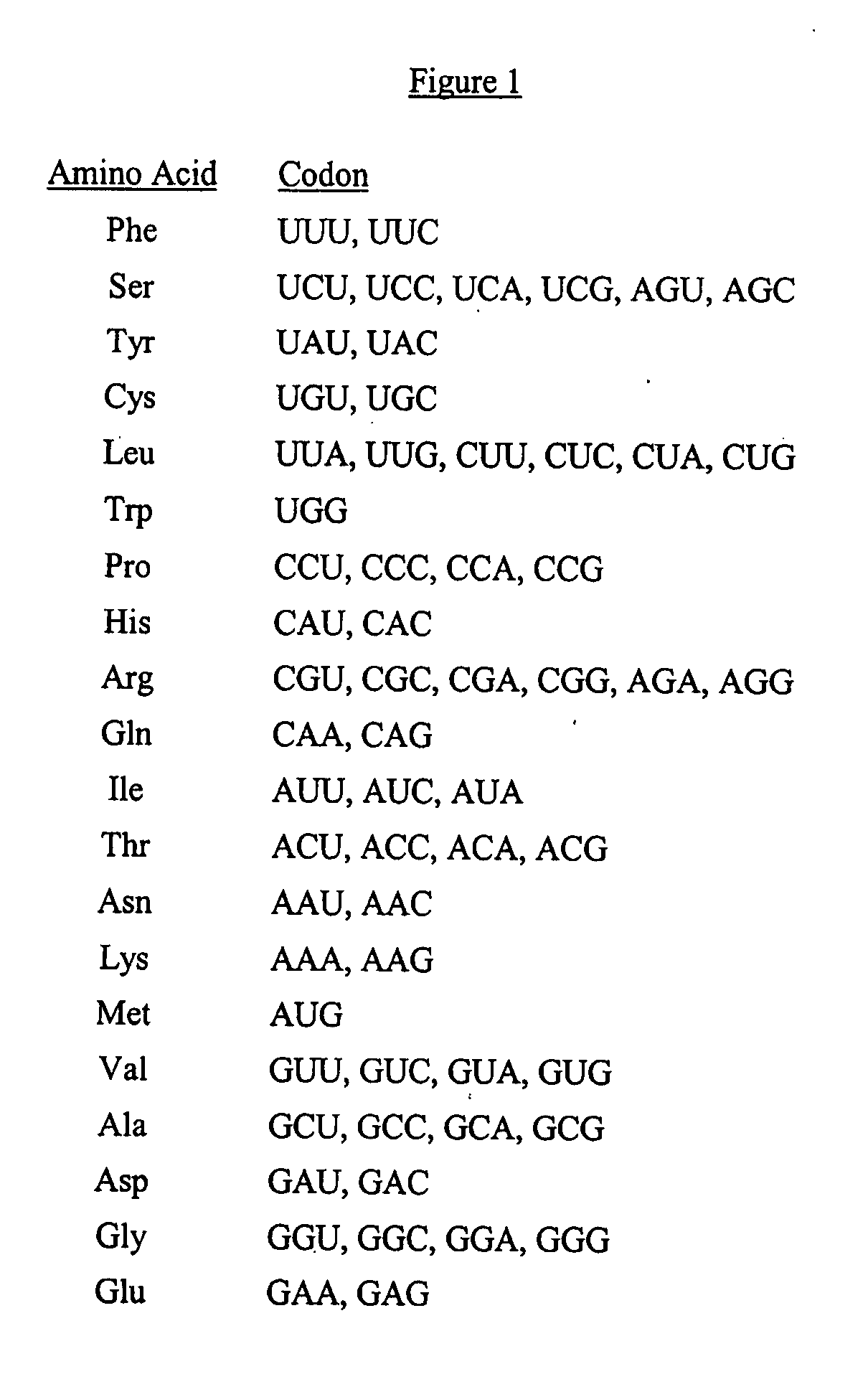
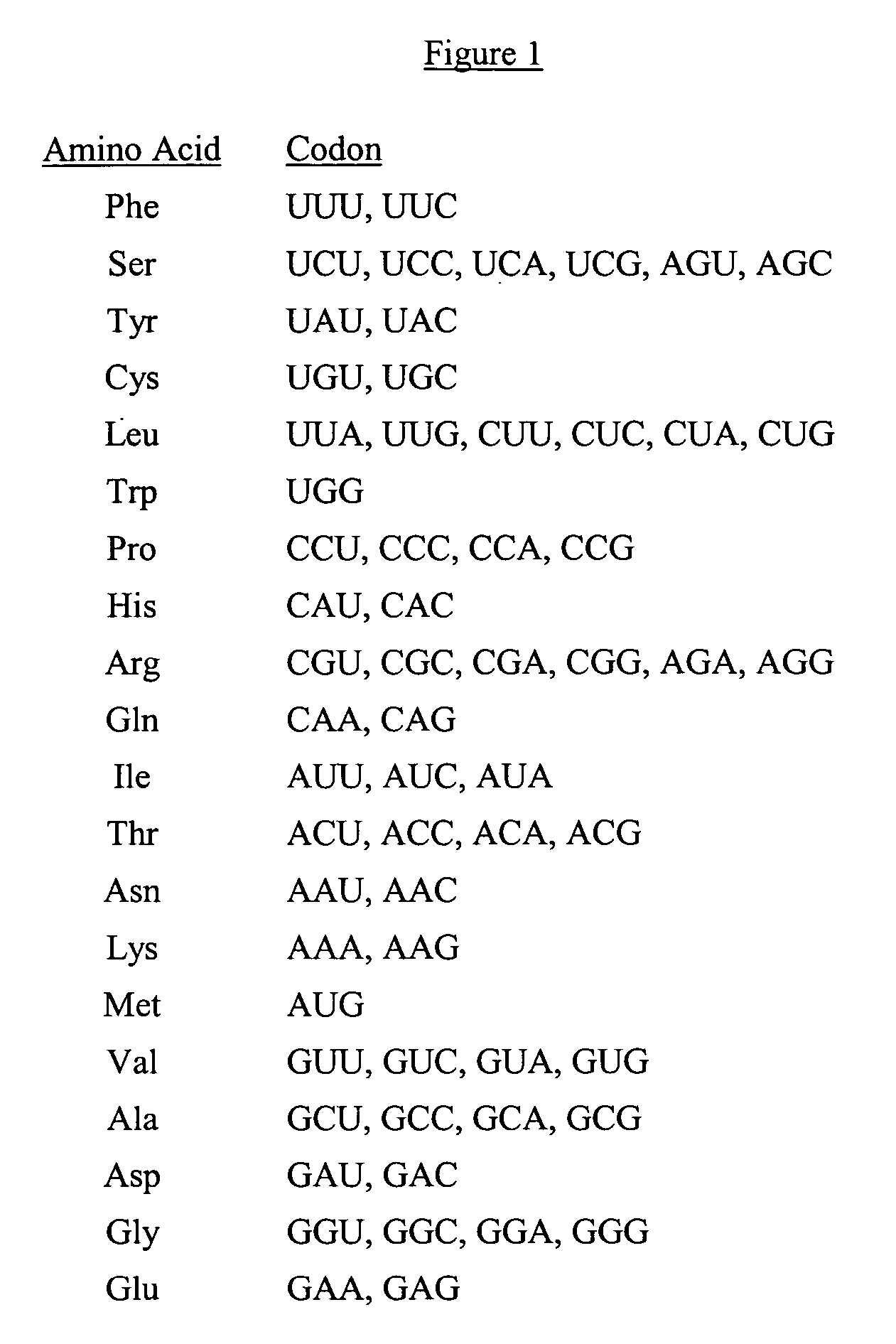
The present invention is directed to a synthetic nucleic acid sequence which encodes a protein wherein at least one non-common codon or less-common codon is replaced by a common codon. The synthetic nucleic acid sequence can include a continuous stretch of at least 90 codons all of which are common codons.
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
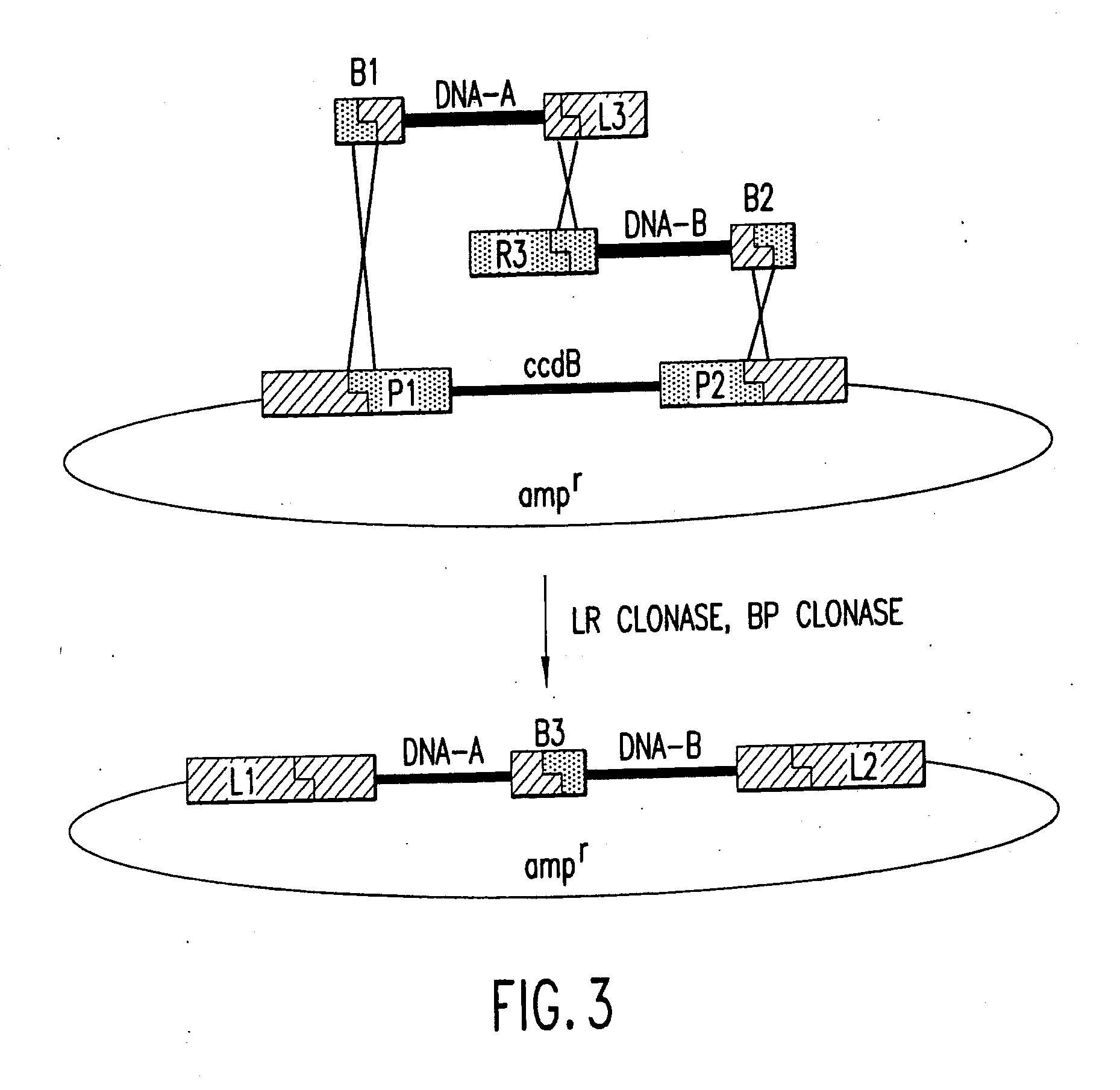
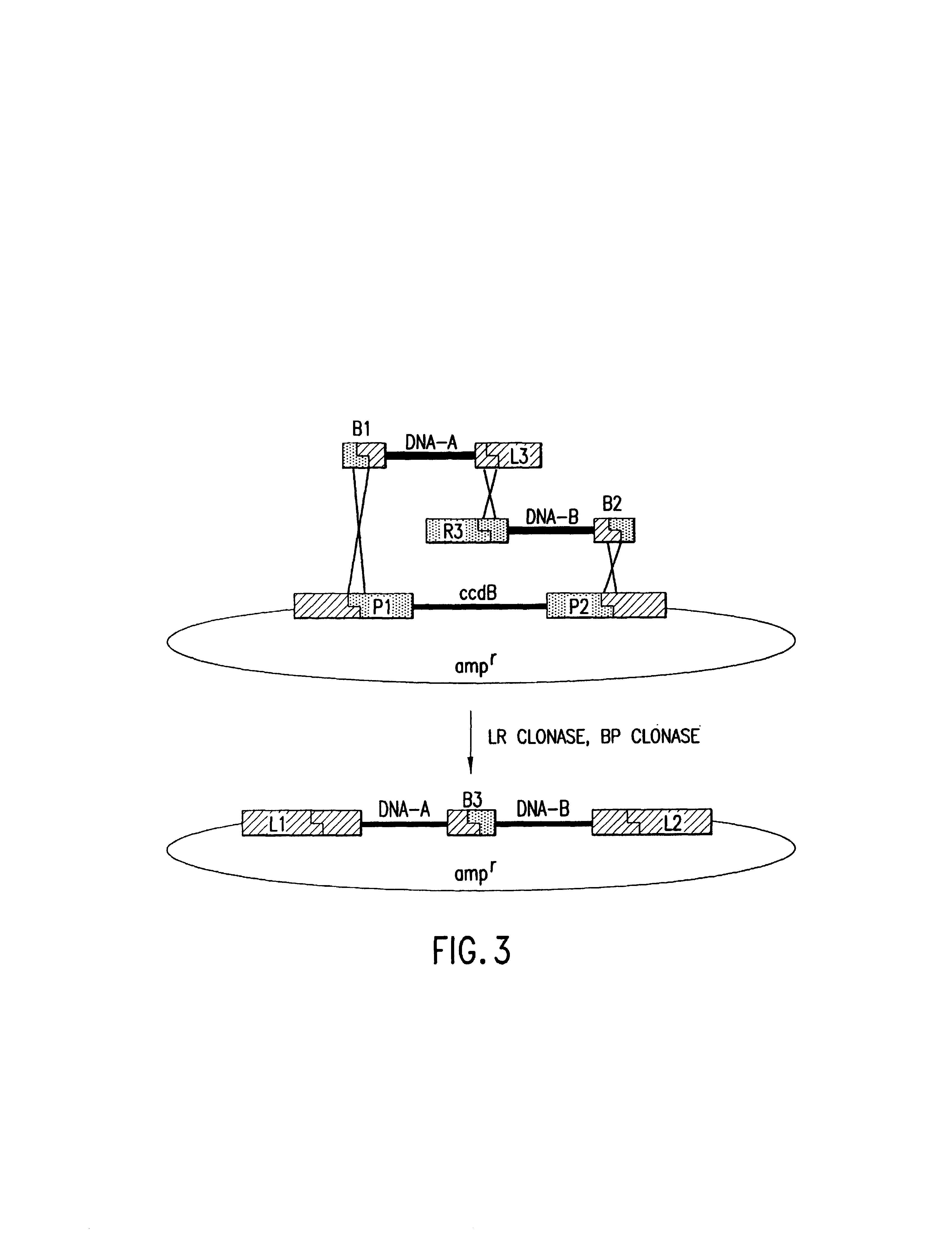
Methods and compositions for synthesis of nucleic acid molecules using multiple recognition sites
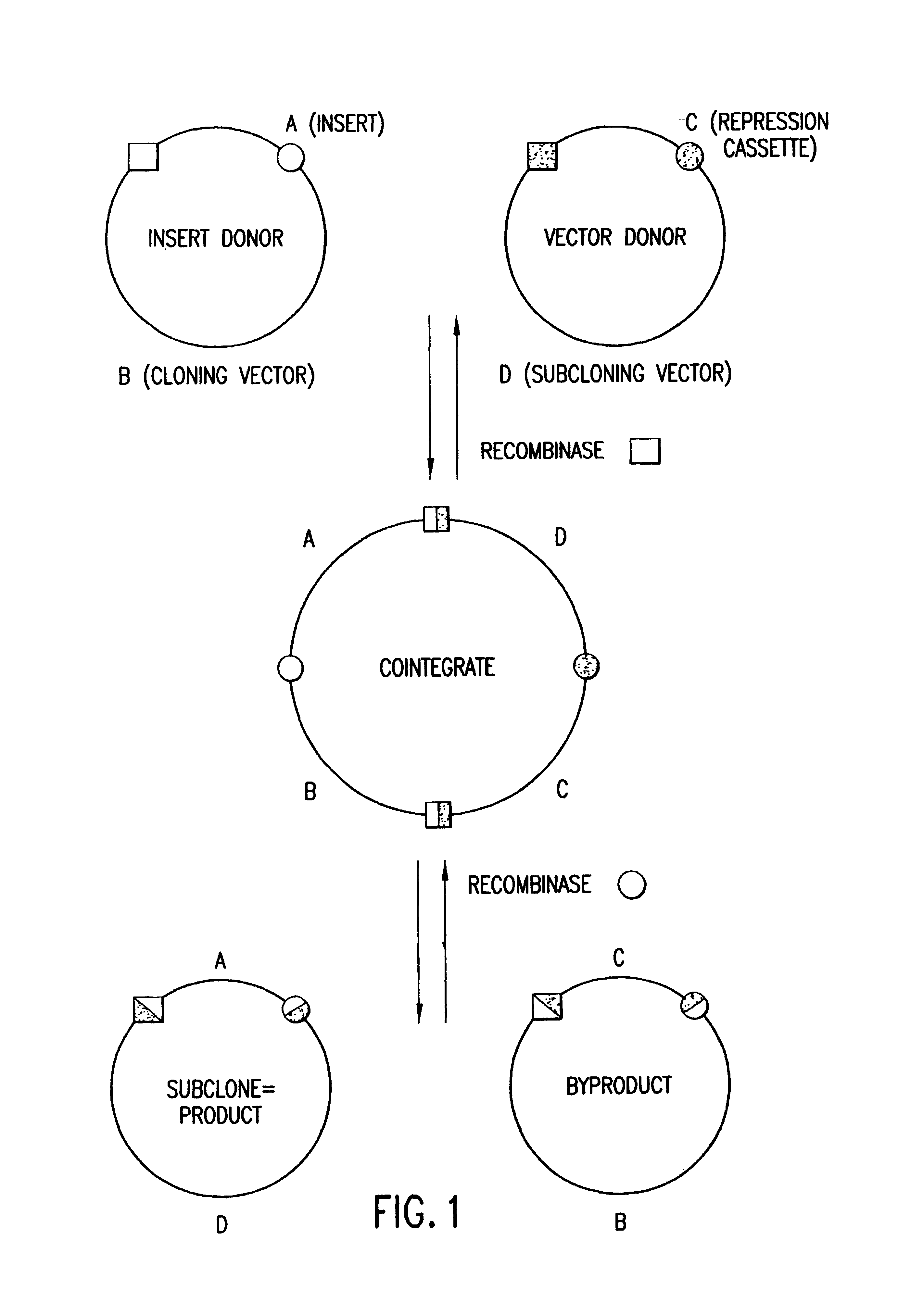
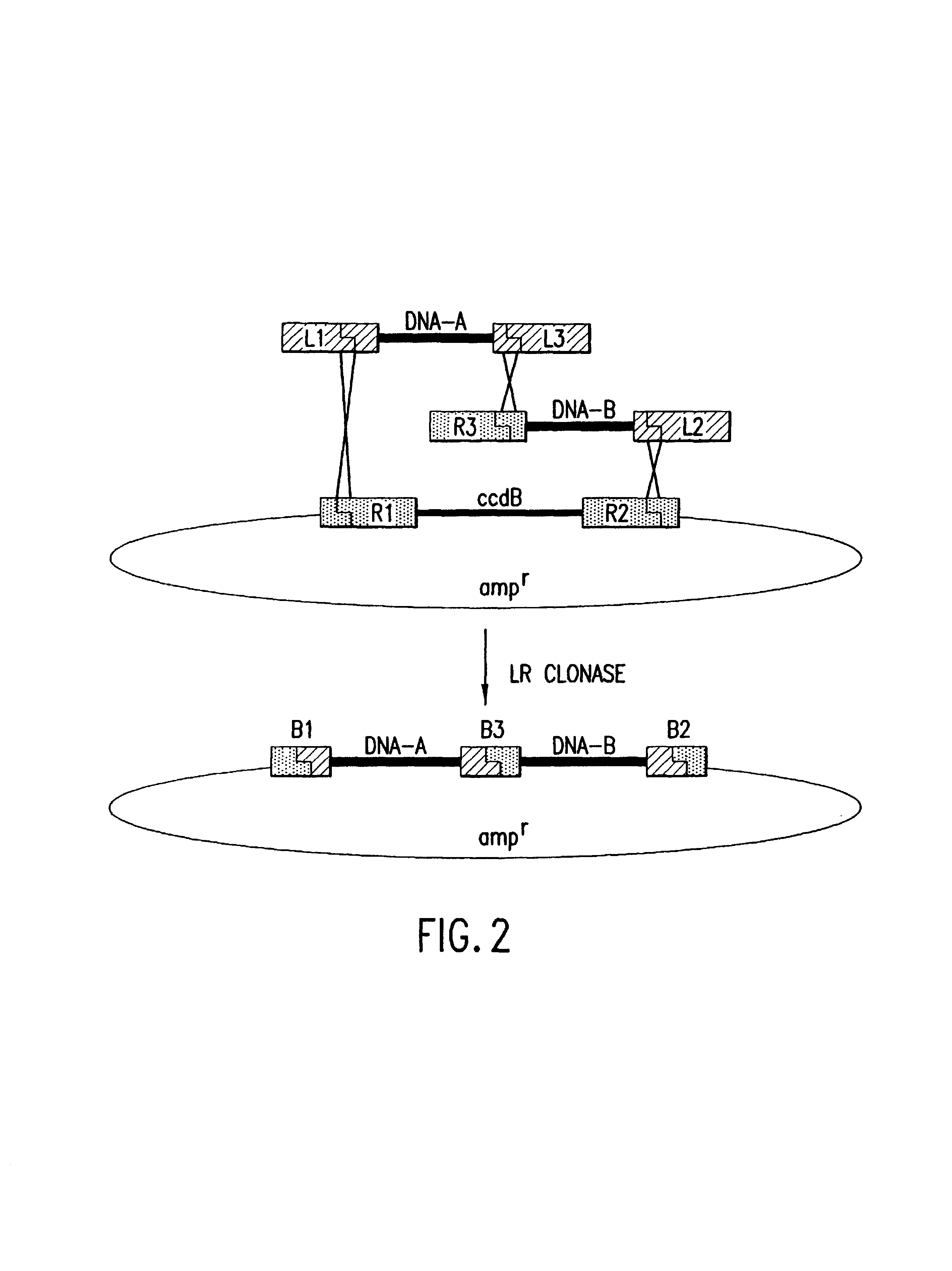
The present invention provides compositions and methods for recombinational cloning. The compositions vectors having multiple recombination sites and / or multiple topoisomerase recognition sities. The methods premit the simultaeous cloning of two or more different nucleic acid molecules. In some embodiments the molecules are fused together while in other embodiments the molecules are inserted into distinct sites in a vector. The invention also generally provides for linking or joining through recombination a number of molecules and / or compounds (e.g., chemical compounds, drugs, proteins or peptides, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.) which may be the same or different. The invention also provides host cells comprising nucleic acid molecules of the invention or prepared according to the methods of the invention, and also provides kits comprising the compositions, host cells and nucleic acid molecules of the invention, which may be used to synthesize nucleic acid molecules according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Programmable oligonucleotide synthesis
ActiveUS8173368B2Reduce yieldSynthesis is longSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligonucleotide synthesisSynthetic nucleic acid
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Iterative nucleic acid assembly using activation of vector-encoded traits
ActiveUS8053191B2Shorten the timeAssembly precisionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological activationSynthetic nucleic acid
Certain aspects of the present invention provide methods for assembling nucleic acid molecules using iterative activation of one or more vector-encoded traits to progressively assemble a longer nucleic acid insert. Aspects of the invention also provide kits, compositions, devices, and systems for assembling synthetic nucleic acids using iterative activation of one or more vector-encoded traits.
Owner:GEN9
Optimized messenger RNA
InactiveUS20080076174A1Broaden applicationEliminates issue concerning patient complianceFactor VIISugar derivativesMessenger RNAComputational biology
The present invention is directed to a synthetic nucleic acid sequence which encodes a protein wherein at least one non-common codon or less-common codon is replaced by a common codon. The synthetic nucleic acid sequence can include a continuous stretch of at least 90 codons all of which are common codons.
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
Assays for measuring nucleic acid binding proteins and enzyme activities
InactiveUS6312896B1Simple and accurate and reliable assayEfficient transferSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein insertionNucleic acid binding protein
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
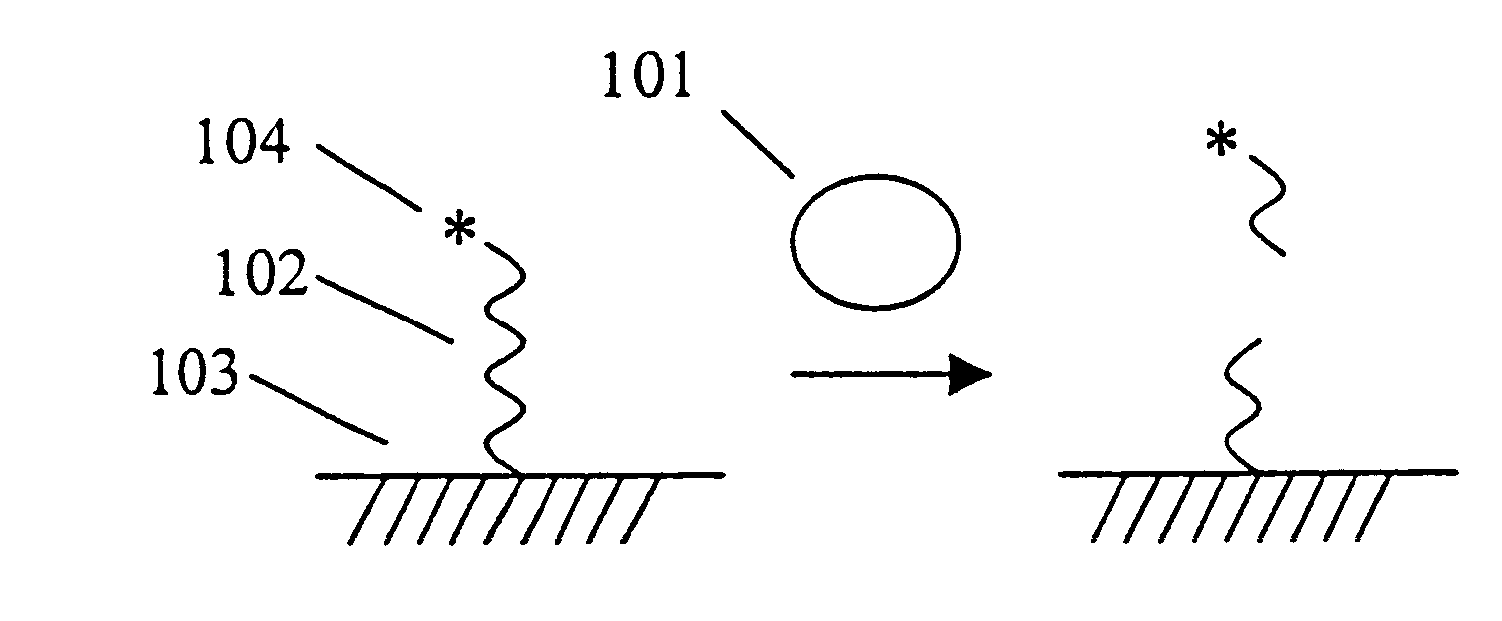
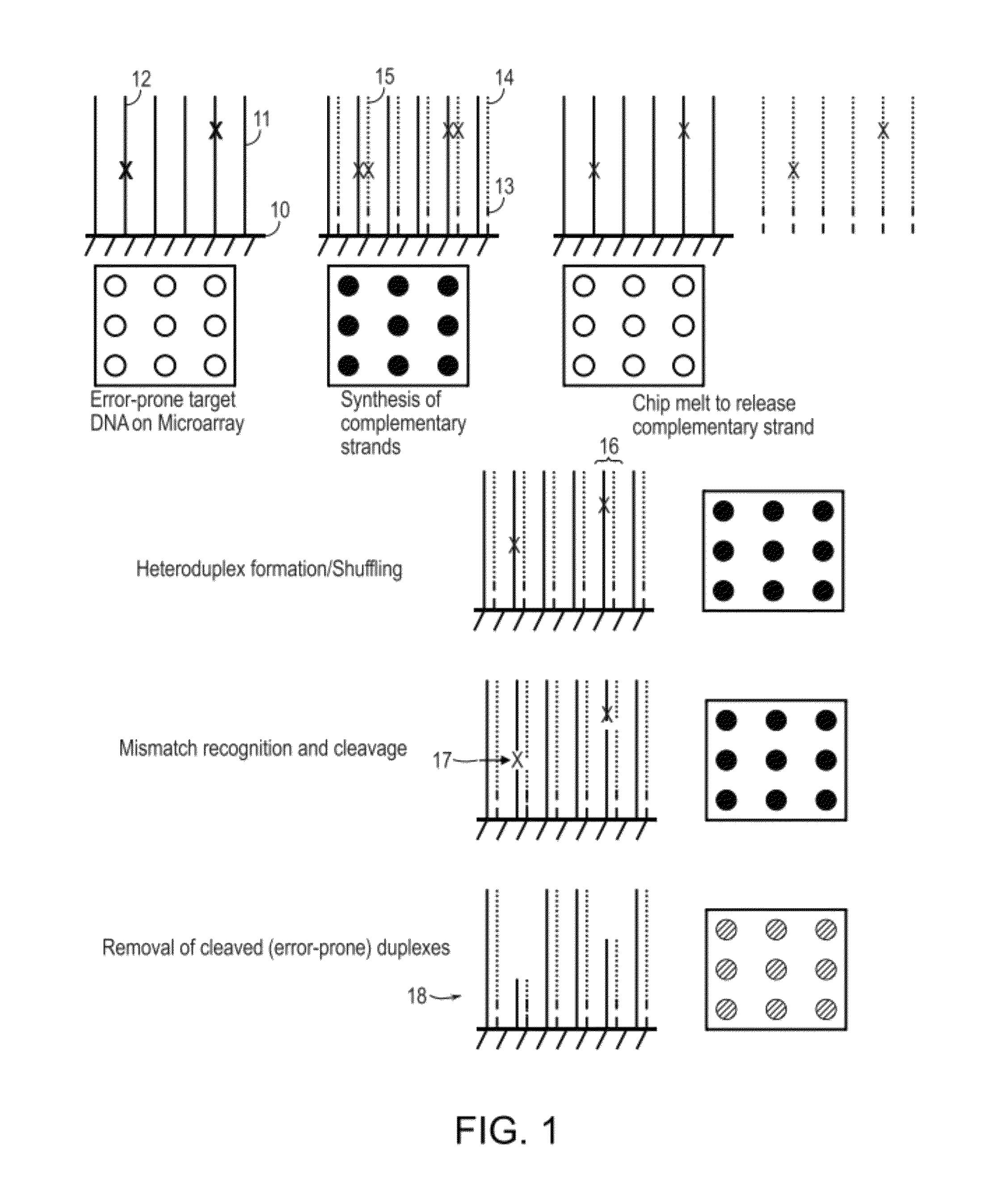
Methods and apparatuses for chip-based DNA error reduction
ActiveUS9422600B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeterologousHeteroduplex
Methods and apparatus relate to reduction of sequence errors generated during synthesis of nucleic acids on a microarray chip. The error reduction can include synthesis of complementary stands (to template strands), using a short universal primer complementary to the template strands and polymerase. Heteroduplex can be formed be melting and re-annealing complementary stands and template strands. The heteroduplexes containing a mismatch can be recognized and cleaved by a mismatch endonuclease. The mismatch-containing cleaved heteroduplexes can be removed from the microarray chip using a global buffer exchange. The error free synthetic nucleic acids generated therefrom can be used for a variety of applications, including synthesis of biofuels and value-added pharmaceutical products.
Owner:GEN9
Design, Synthesis and Assembly of Synthetic Nucleic Acids
ActiveUS20080300842A1Enhanced couplingEasy subsequent assemblyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesNucleotideOligonucleotide synthesis
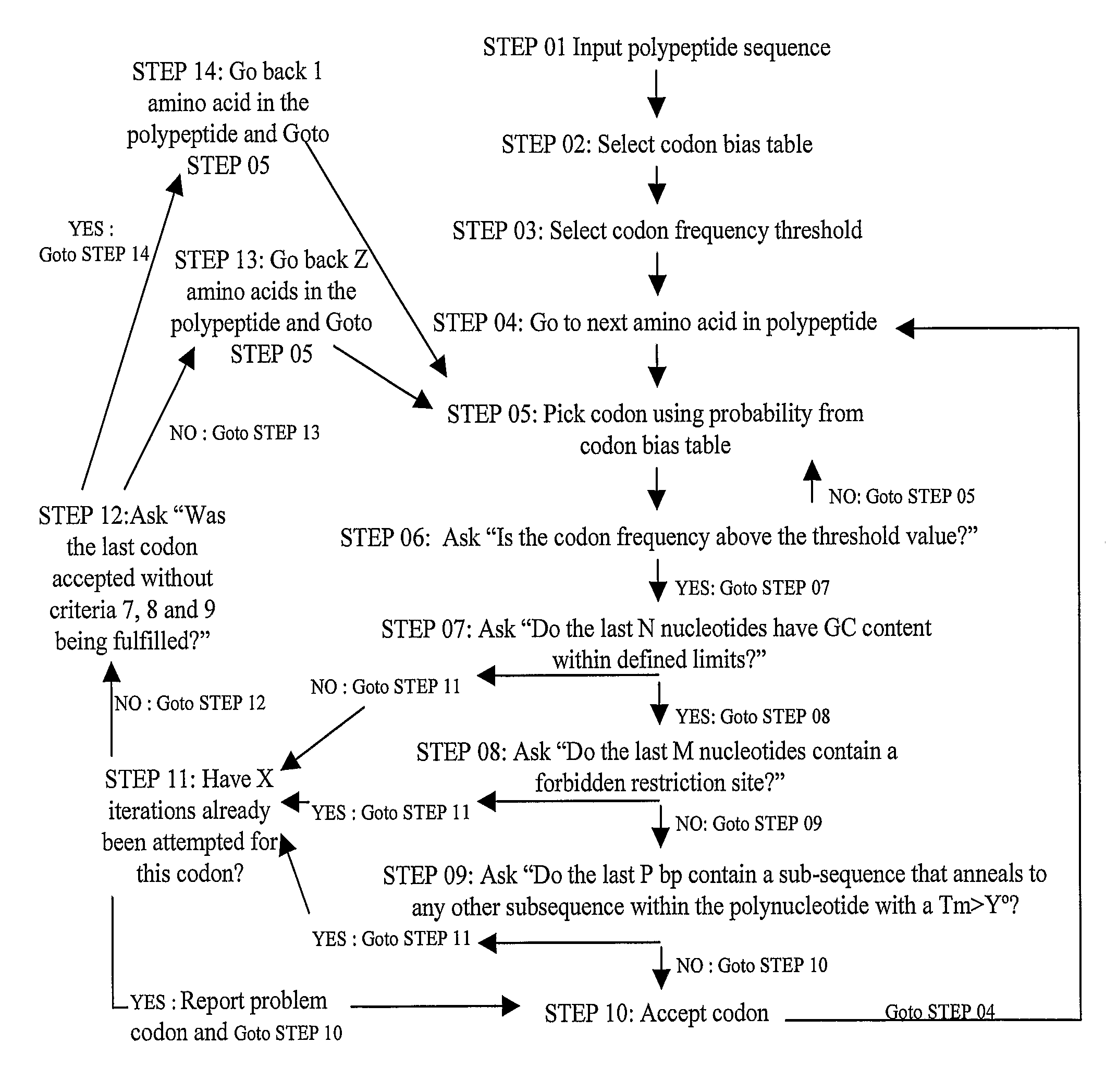
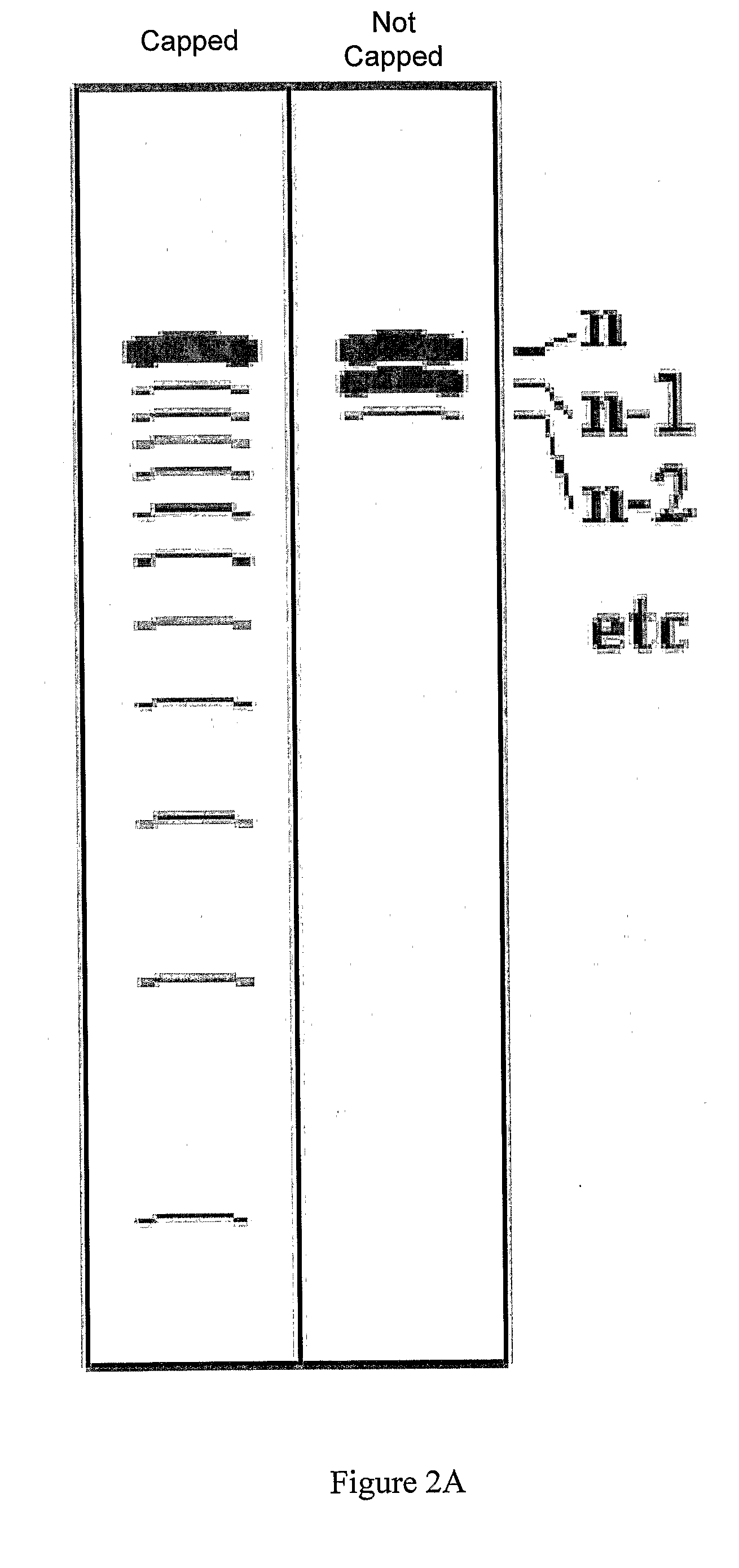
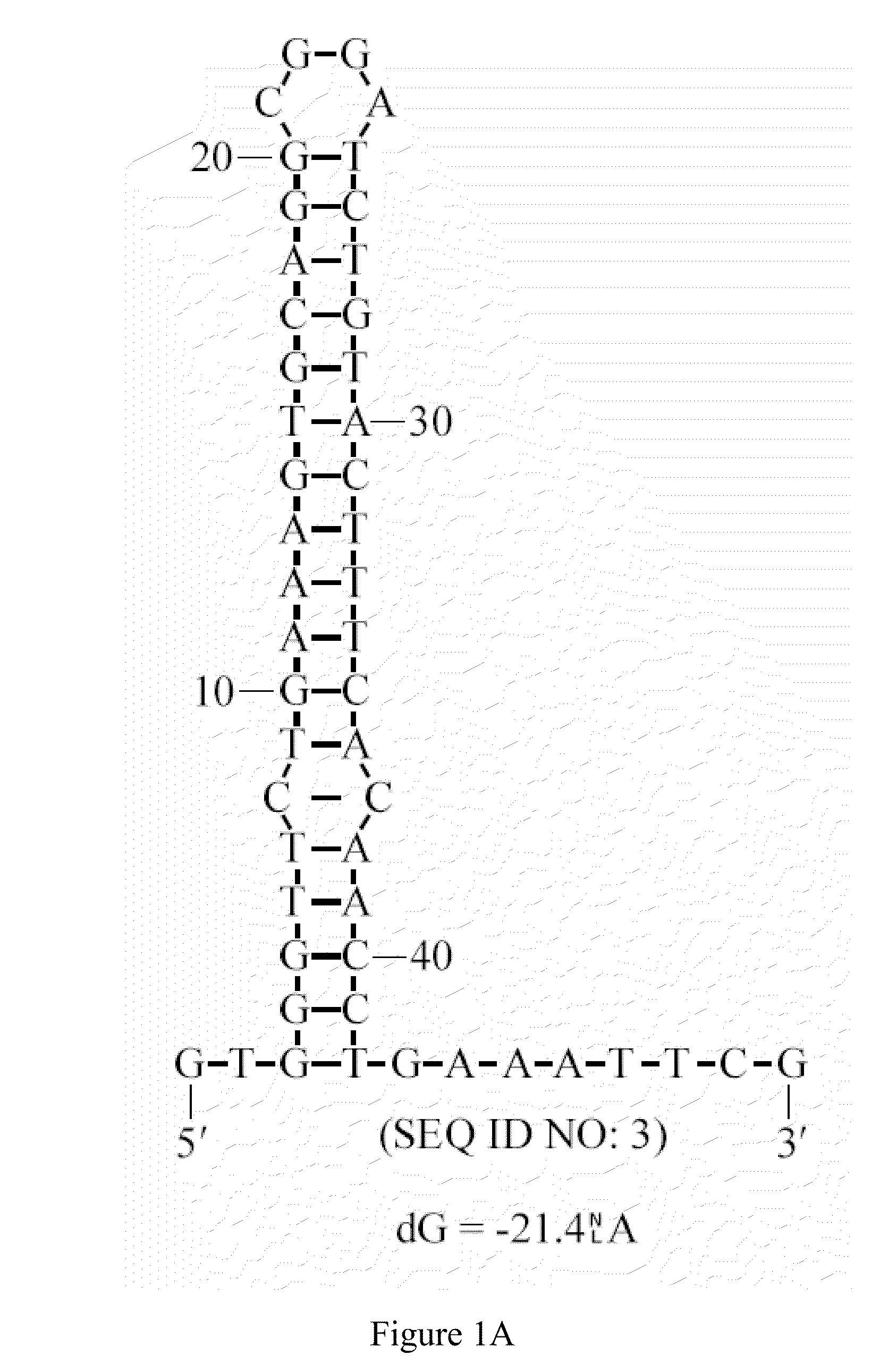
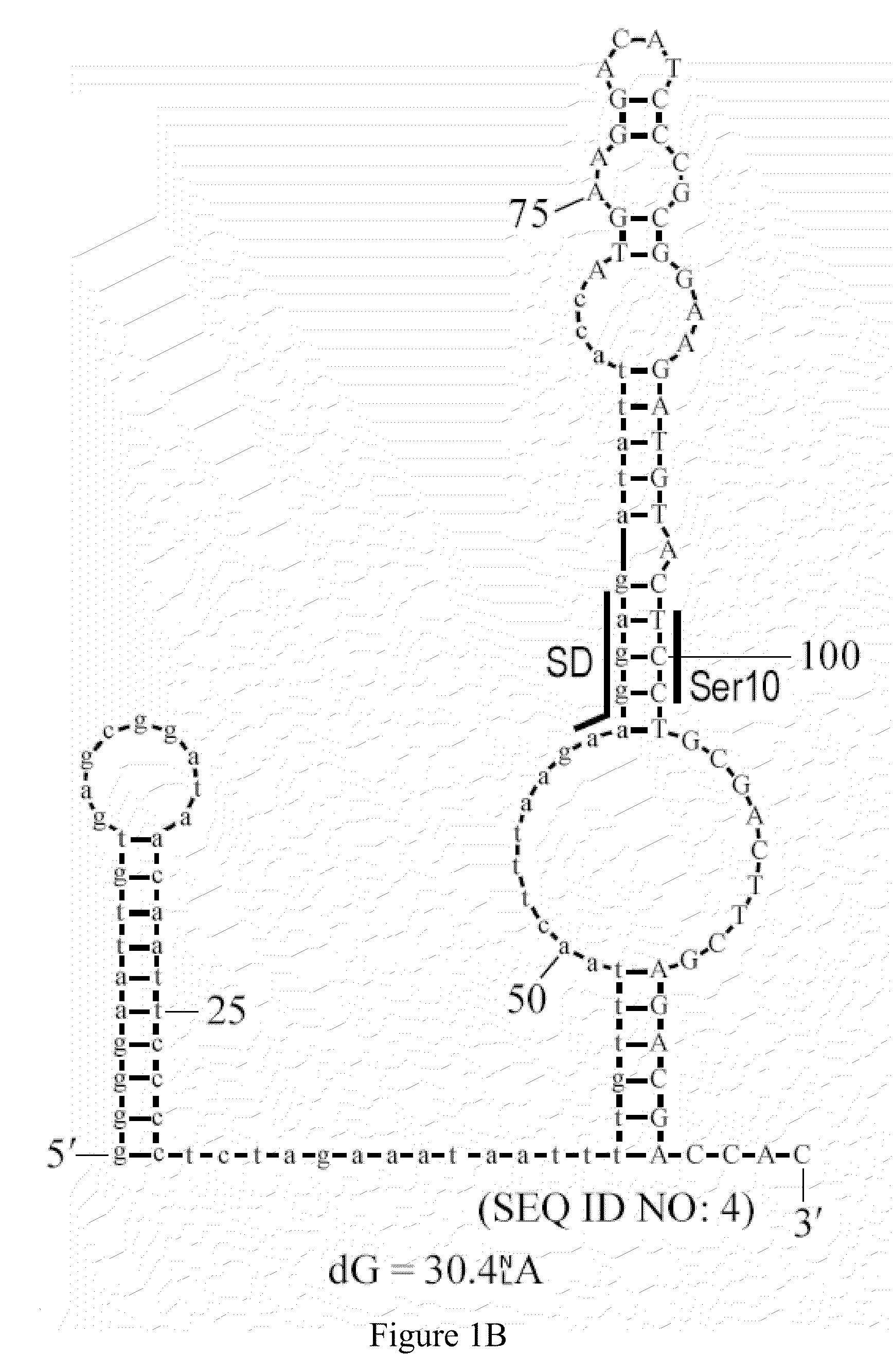
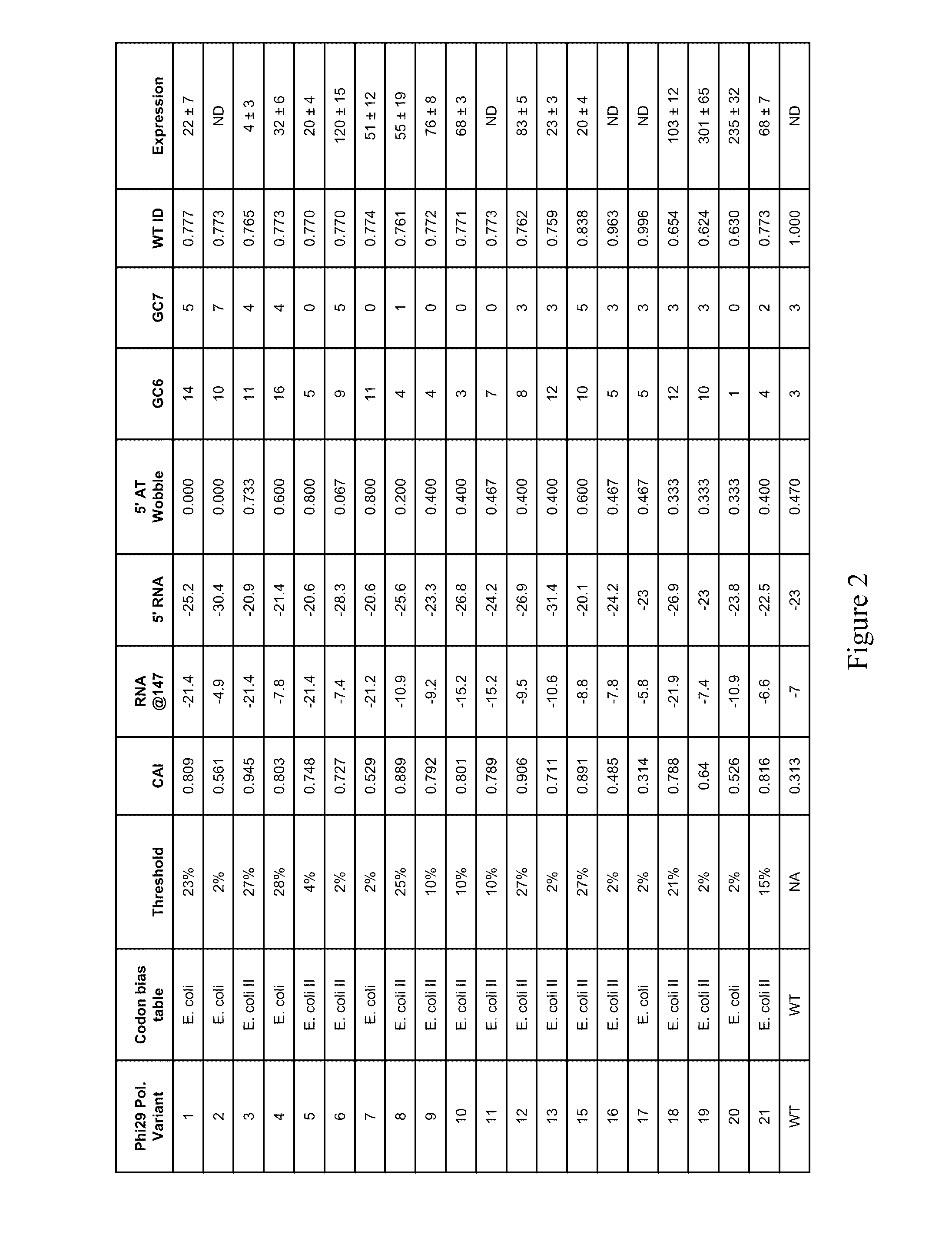
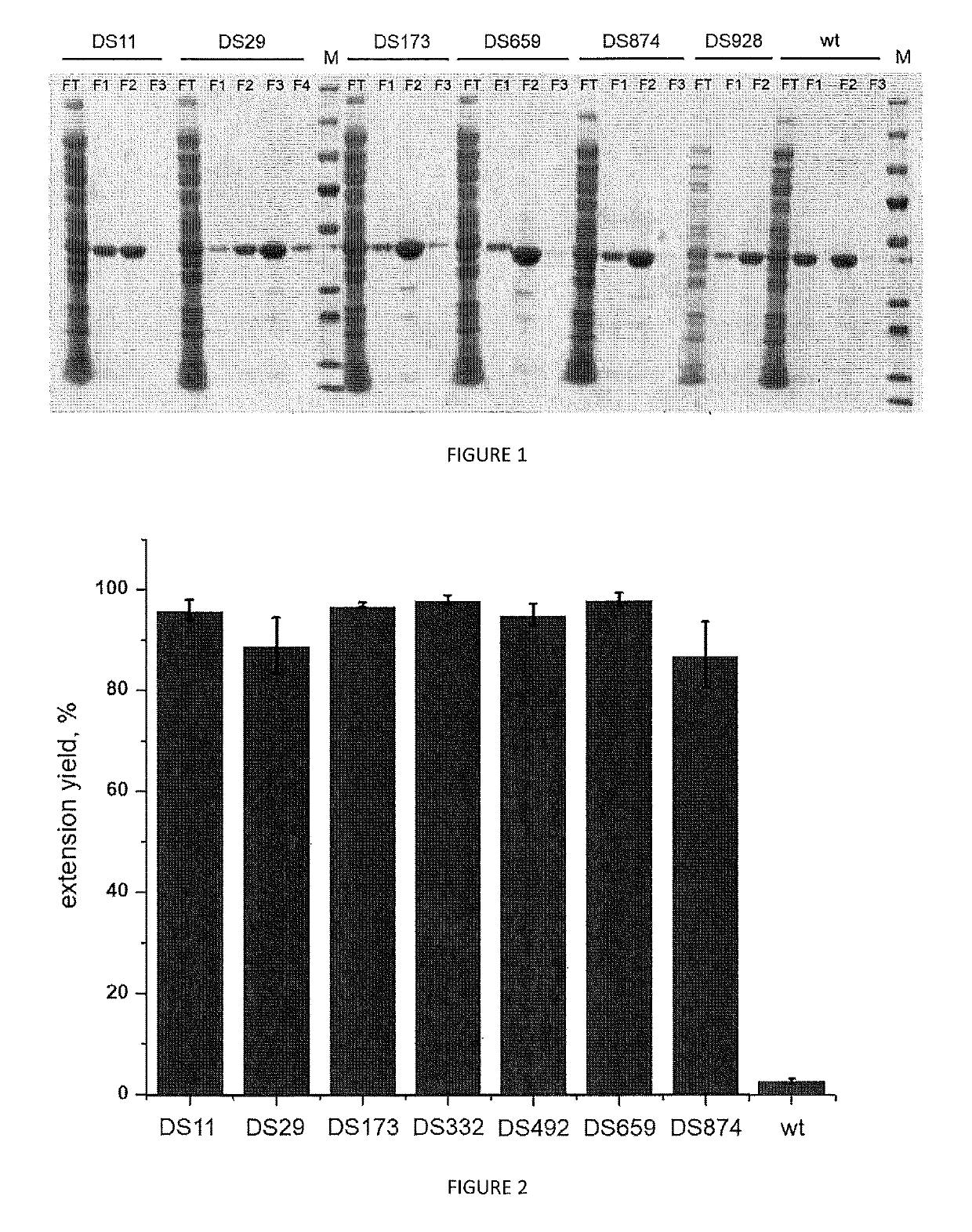
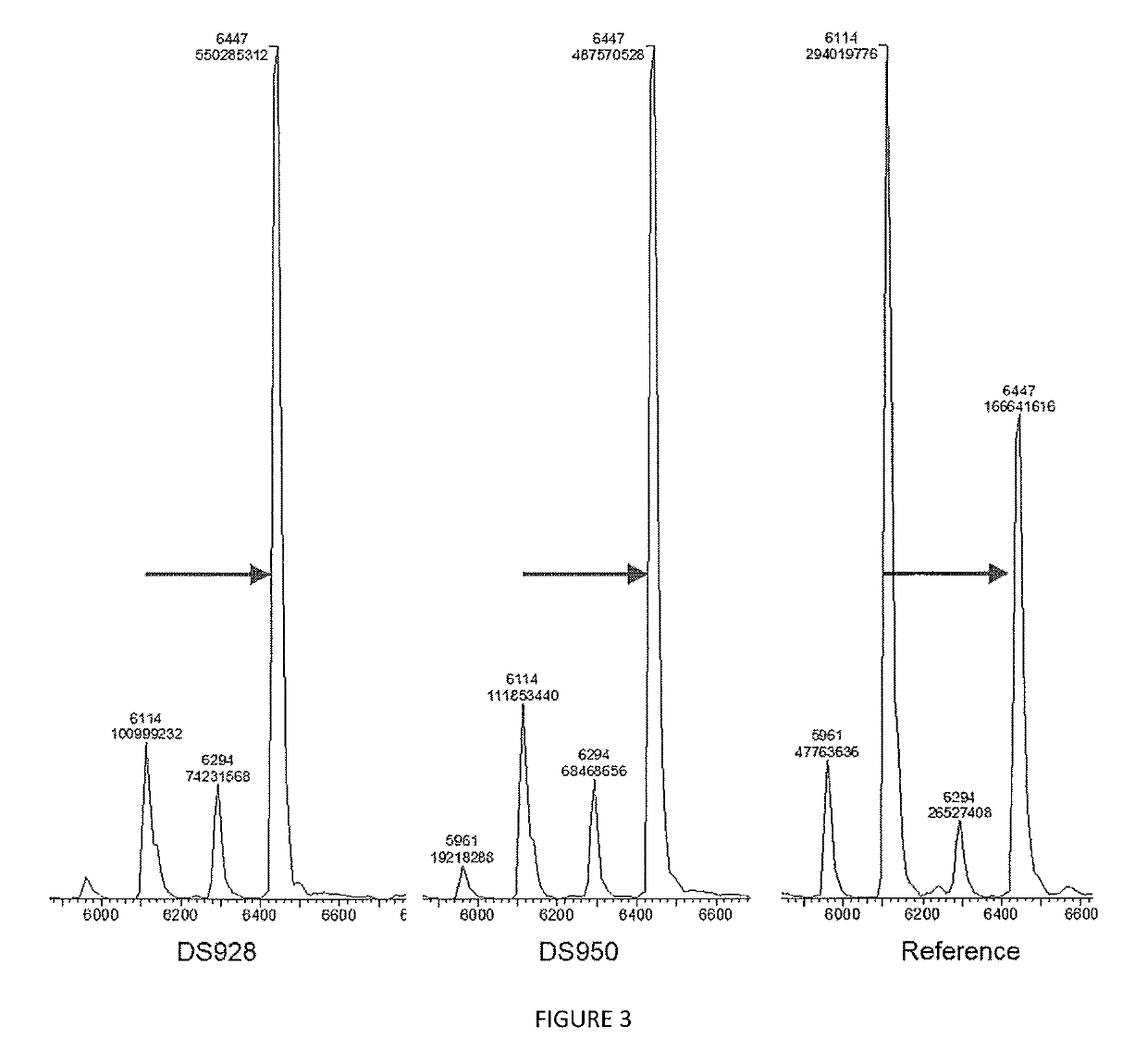
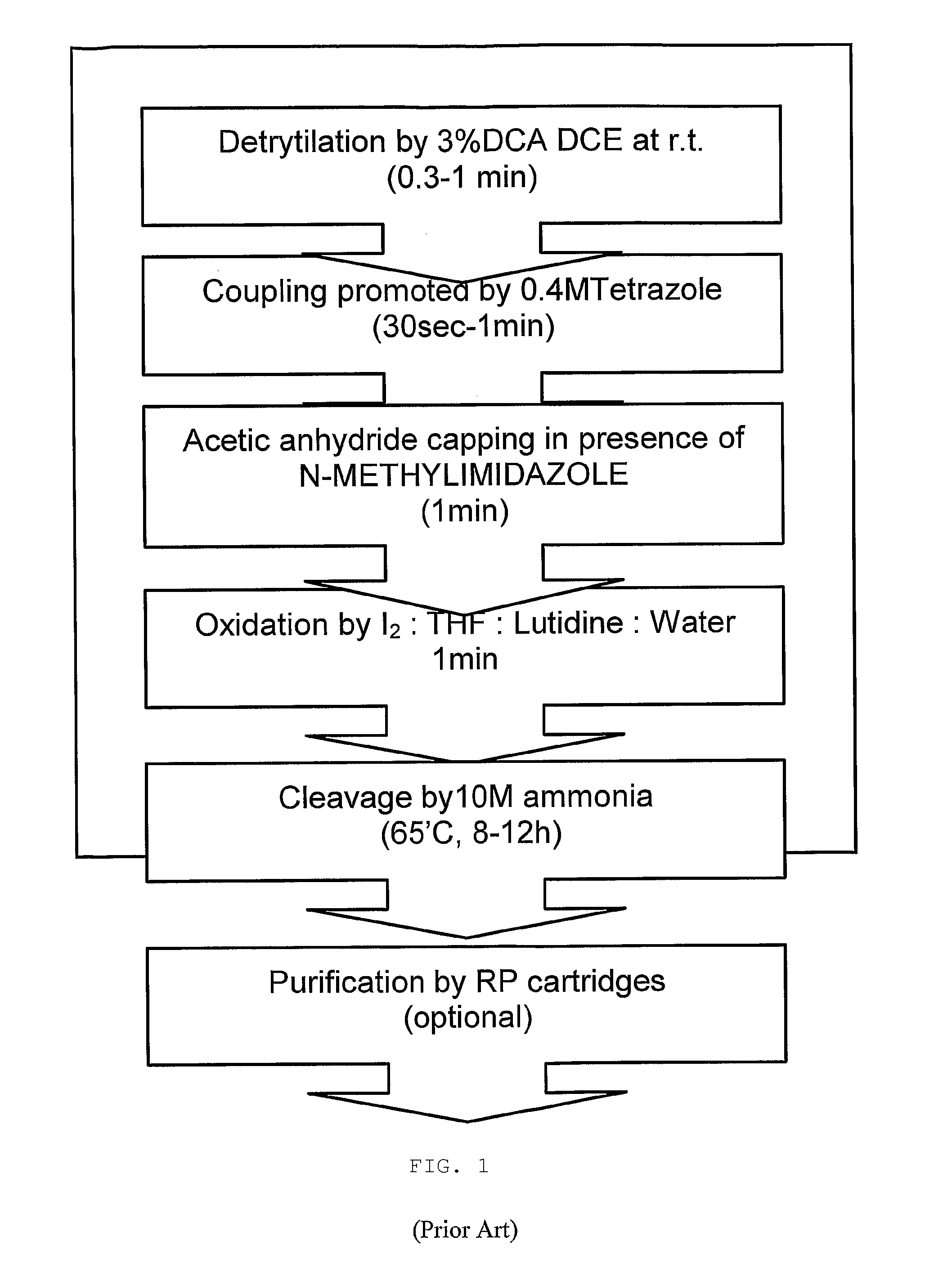
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides with high coupling efficiency (>99.5%) are provided. Methods for purification of synthetic oligonucleotides are also provided. Instrumentation configurations for oligonucleotide synthesis are also provided. Methods of designing and synthesizing polynucleotides are also provided. Polynucleotide design is optimized for subsequent assembly from shorter oligonucleotides. Modifications of phosphoramidite chemistry to improve the subsequent assembly of polynucleotides are provided. The design process also incorporates codon biases into polynucleotides that favor expression in defined hosts. Design and assembly methods are also provided for the efficient synthesis of sets of polynucleotide variants. Software to automate the design and assembly process is also provided.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
Synthetic nucleic acids for expression of encoded proteins
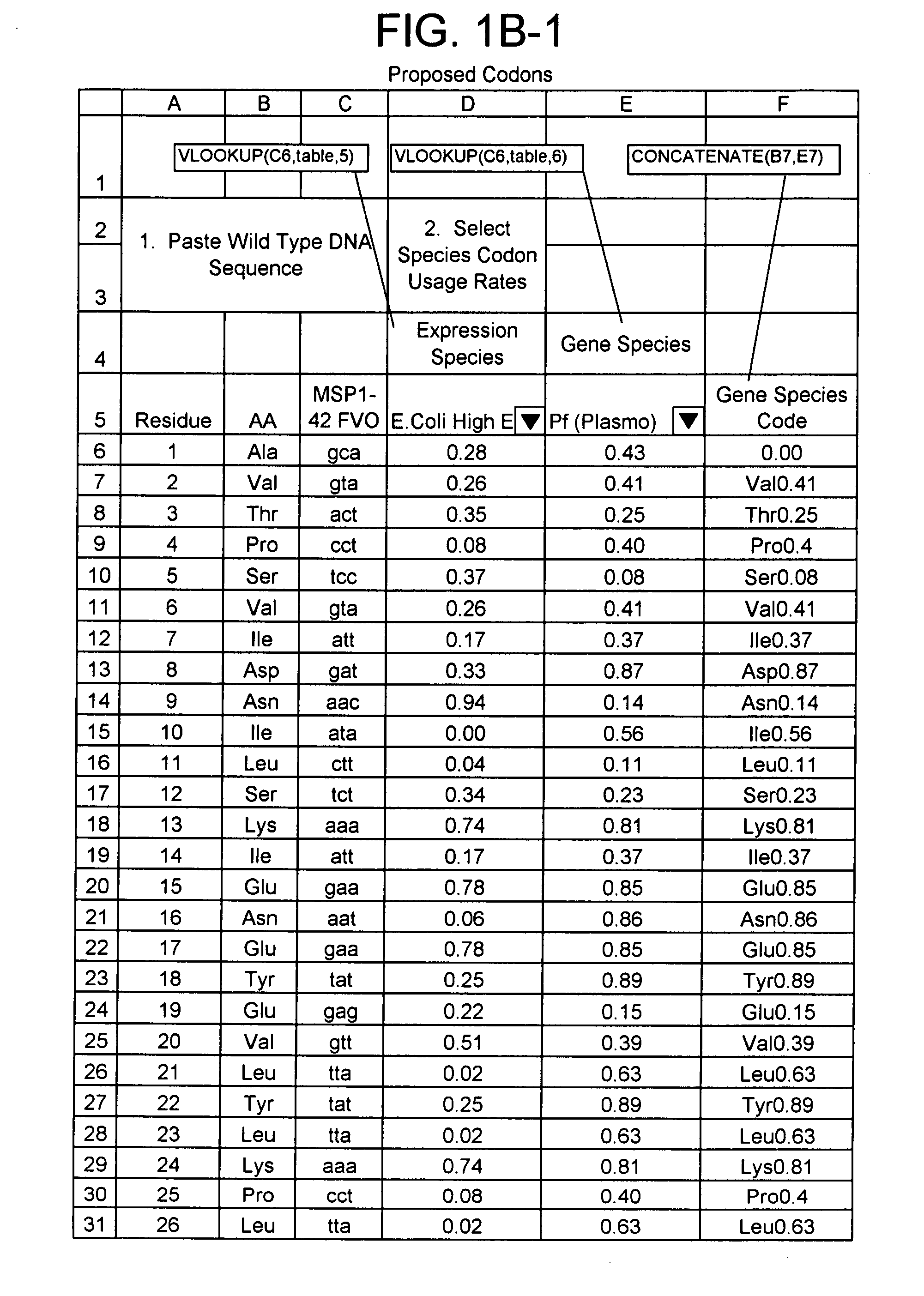
A method of designing a polynucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide sequence of a predetermined polypeptide is provided. A frequency lookup table corresponding to an expression system is obtained. The table comprises a plurality of sequence elements and a plurality of frequency ranges, each frequency range for a corresponding sequence element. Each frequency range is a range of frequencies with which a corresponding sequence element can occur in a polynucleotide. The polynucleotide sequence is defined using the frequency lookup table by determining, for each respective sequence element in the frequency lookup table, whether the respective sequence element encodes a portion of the polypeptide sequence. When the respective sequence element encodes a portion of the polypeptide sequence, the sequence element is incorporated into the polynucleotide at a frequency of occurrence that is within the frequency range specified for the respective sequence element in the lookup table. The polynucleotide sequence is then outputted.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
Method for producing polymers
The invention relates to a method for producing polymers, in particular synthetic nucleic acid double strands of optional sequence, comprising the steps: (a) provision of a support having a surface area which contains a plurality of individual reaction areas, (b) location-resolved synthesis of nucleic acid fragments having in each case different base sequences in several of the individual reaction areas, and (c) detachment of the nucleic acid fragments from individual reaction areas.
Owner:CODEX DNA INC
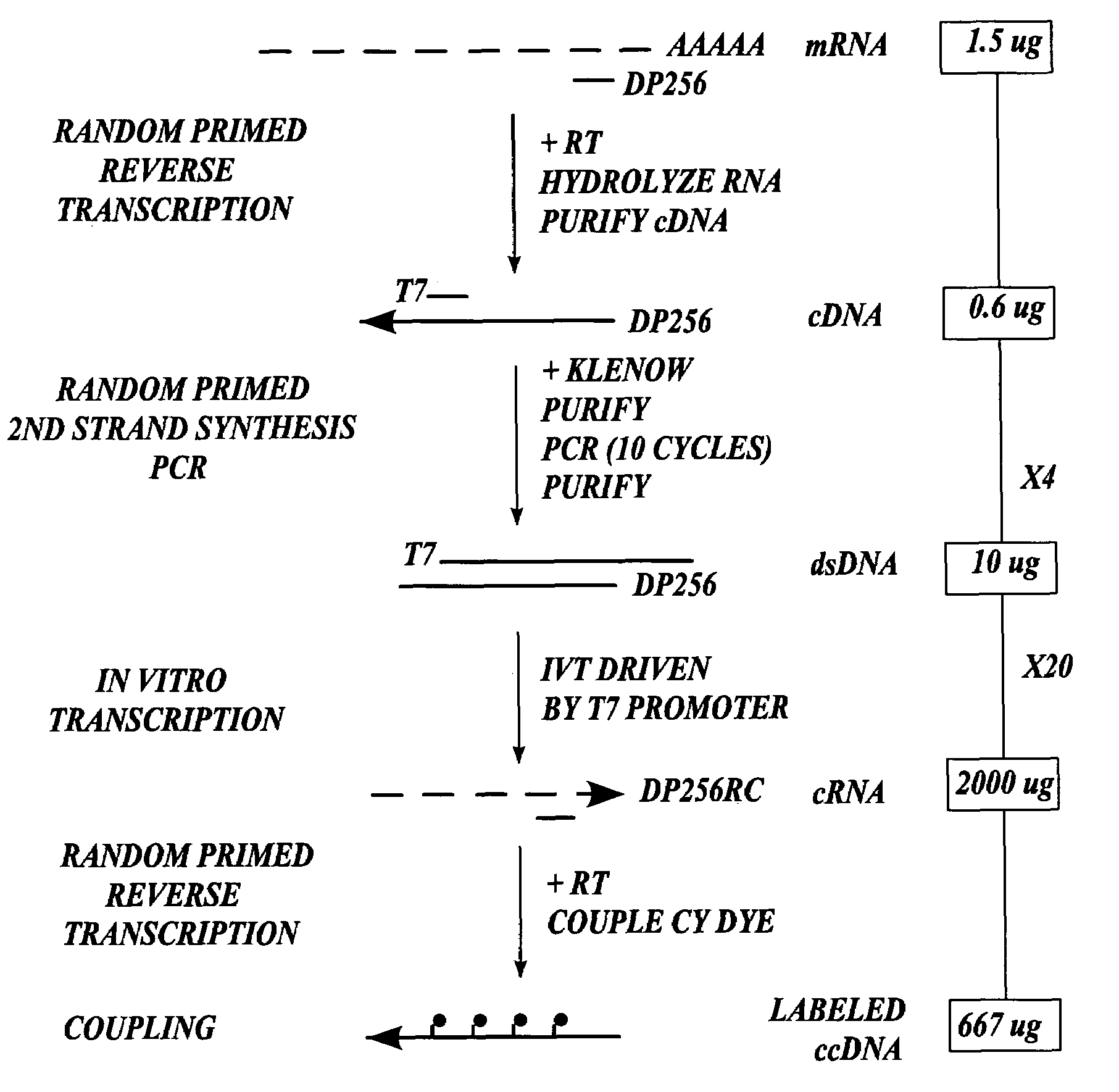
Methods for preparing nucleic acid samples useful for screening dna arrays
InactiveUS7432084B2High sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationEnzymatic synthesisImmobilized Nucleic Acids
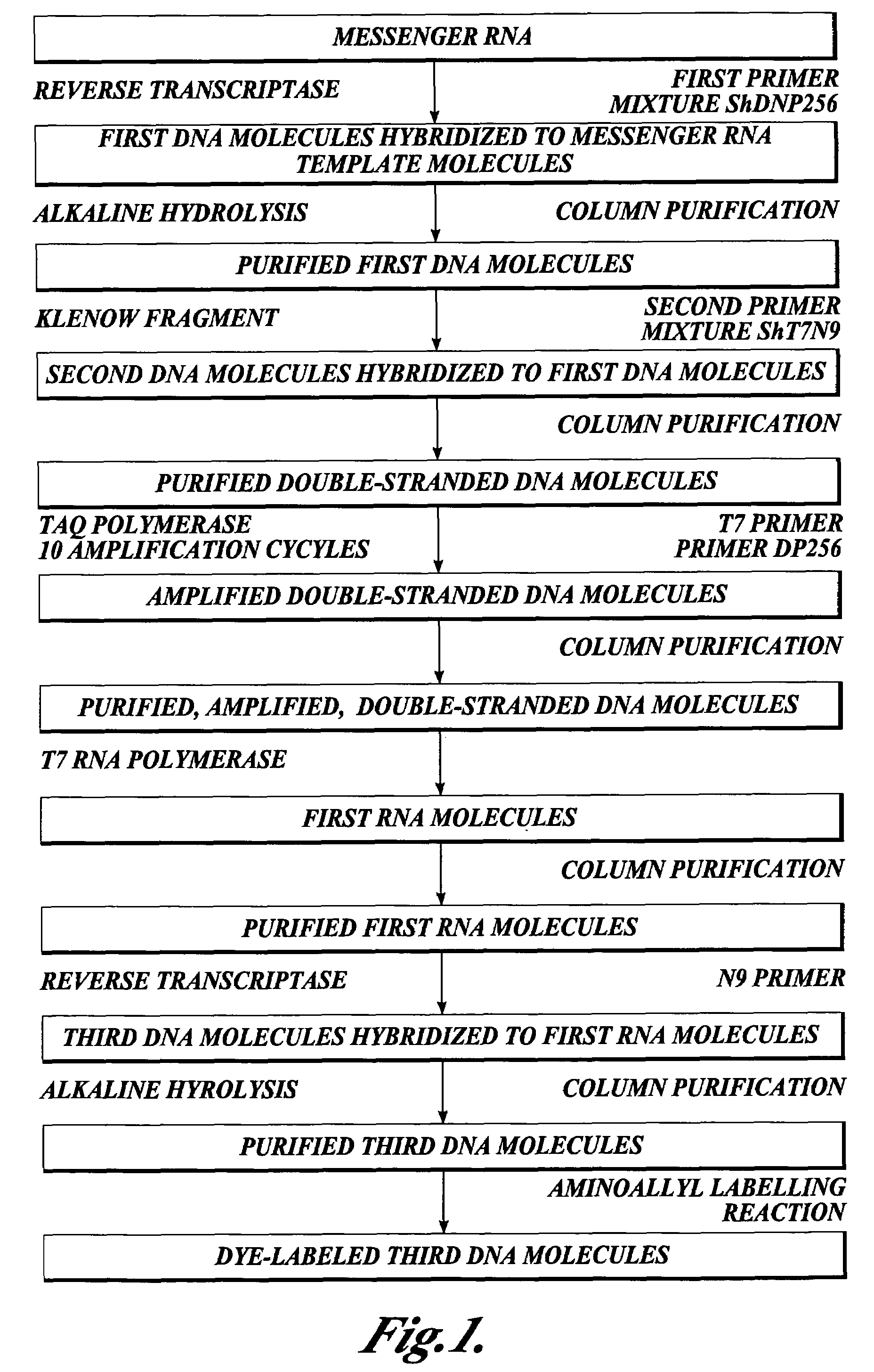
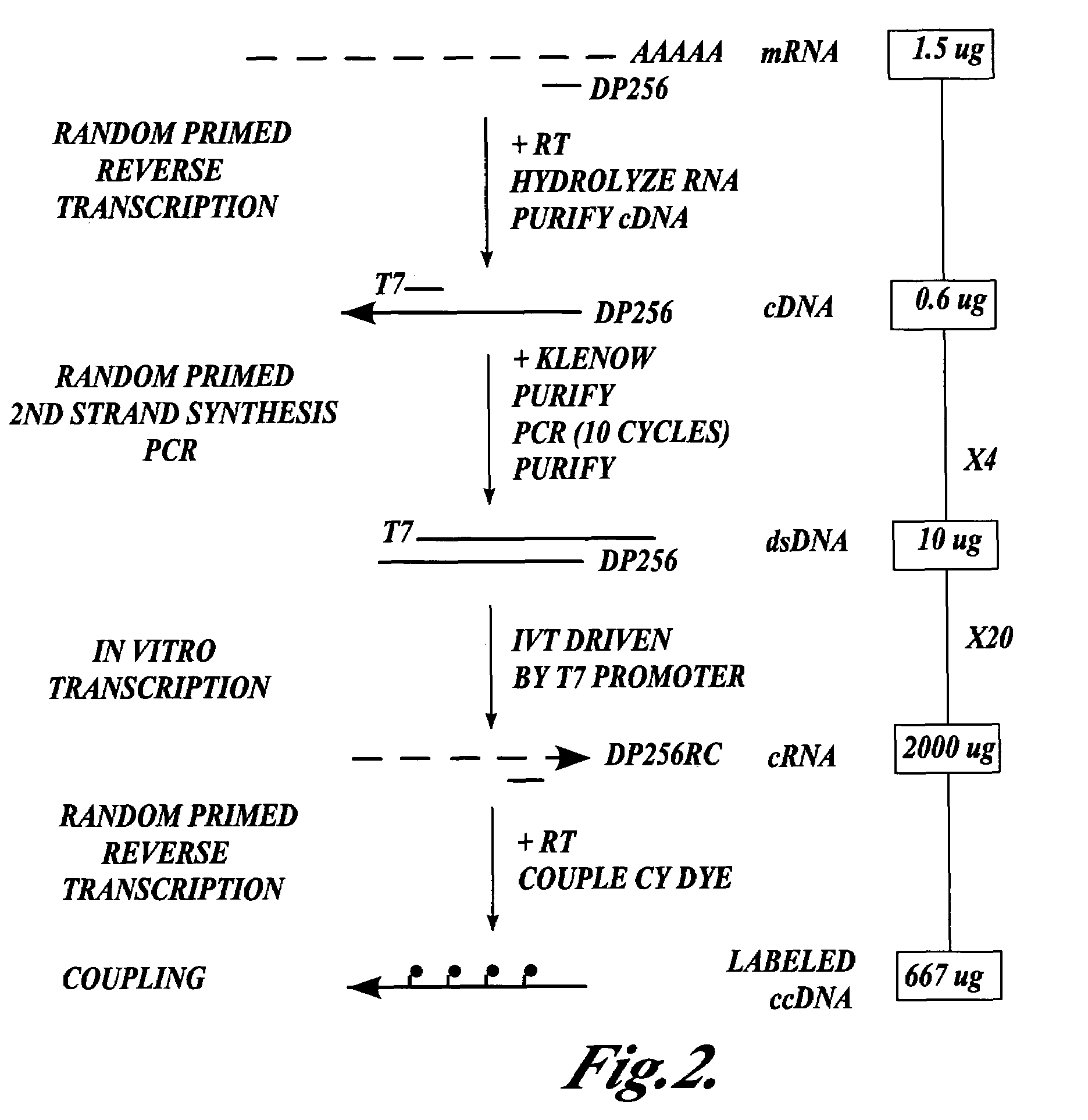
In one aspect the present invention provides methods of synthesizing a preparation of nucleic acid molecules, the methods comprising the steps of: (a) utilizing an RNA template to enzymatically synthesize a first DNA molecule that is complementary to at least 50 contiguous bases of the RNA template; (b) utilizing the first DNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a second DNA molecule, thereby forming a double-stranded DNA molecule wherein the first DNA molecule is hybridized to the second DNA molecule; (c) utilizing the first or second DNA molecule of the double-stranded DNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a first RNA molecule that is complementary to either the first DNA molecule or to the second DNA molecule; and (d) utilizing the first RNA molecule as a template to enzymatically synthesize a third DNA molecule that is complementary to the first RNA molecule. In another aspect, the present invention provides processed DNA samples prepared by a method of the invention for synthesizing a preparation of nucleic acid molecules. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods for hybridizing a processed DNA sample to a population of immobilized nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods and compositions for synthesis of nucleic acid molecules using multiple recognition sites
The present invention provides compositions and methods for recombinational cloning. The compositions include vectors having multiple recombination sites and / or multiple topoisomerase recognition sites. The methods permit the simultaneous cloning of two or more different nucleic acid molecules. In some embodiments the molecules are fused together while in other embodiments the molecules are inserted into distinct sites in a vector. The invention also generally provides for linking or joining through recombination a number of molecules and / or compounds (e.g., chemical compounds, drugs, proteins or peptides, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.) which may be the same or different. The invention also provides host cells comprising nucleic acid molecules of the invention or prepared according to the methods of the invention, and also provides kits comprising the compositions, host cells and nucleic acid molecules of the invention, which may be used to synthesize nucleic acid molecules according to the methods of the invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Synthetic nucleic acid molecule compositions and methods of preparation
InactiveUS20080090291A1Decreasing frequency of recombinationIncrease the differenceFungiBacteriaSynthetic nucleic acidChemistry
A method to prepare synthetic nucleic acid molecules having reduced inappropriate or unintended transcriptional characteristics when expressed in a particular host cell.
Owner:PROMEGA
Synthetic nucleic acid molecule compositions and methods of preparation
ActiveUS20080070299A1Increase the number ofReduce in quantitySugar derivativesBacteriaSynthetic nucleic acidChemistry
A method to prepare synthetic nucleic acid molecules having reduced inappropriate or unintended transcriptional characteristics when expressed in a particular host cell.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Method of designing synthetic nucleic acid sequences for optimal protein expression in a host cell
InactiveUS20080076161A1Accelerate the accumulation processImprove solubilityBacteriaDepsipeptidesWild typeNucleic acid sequencing
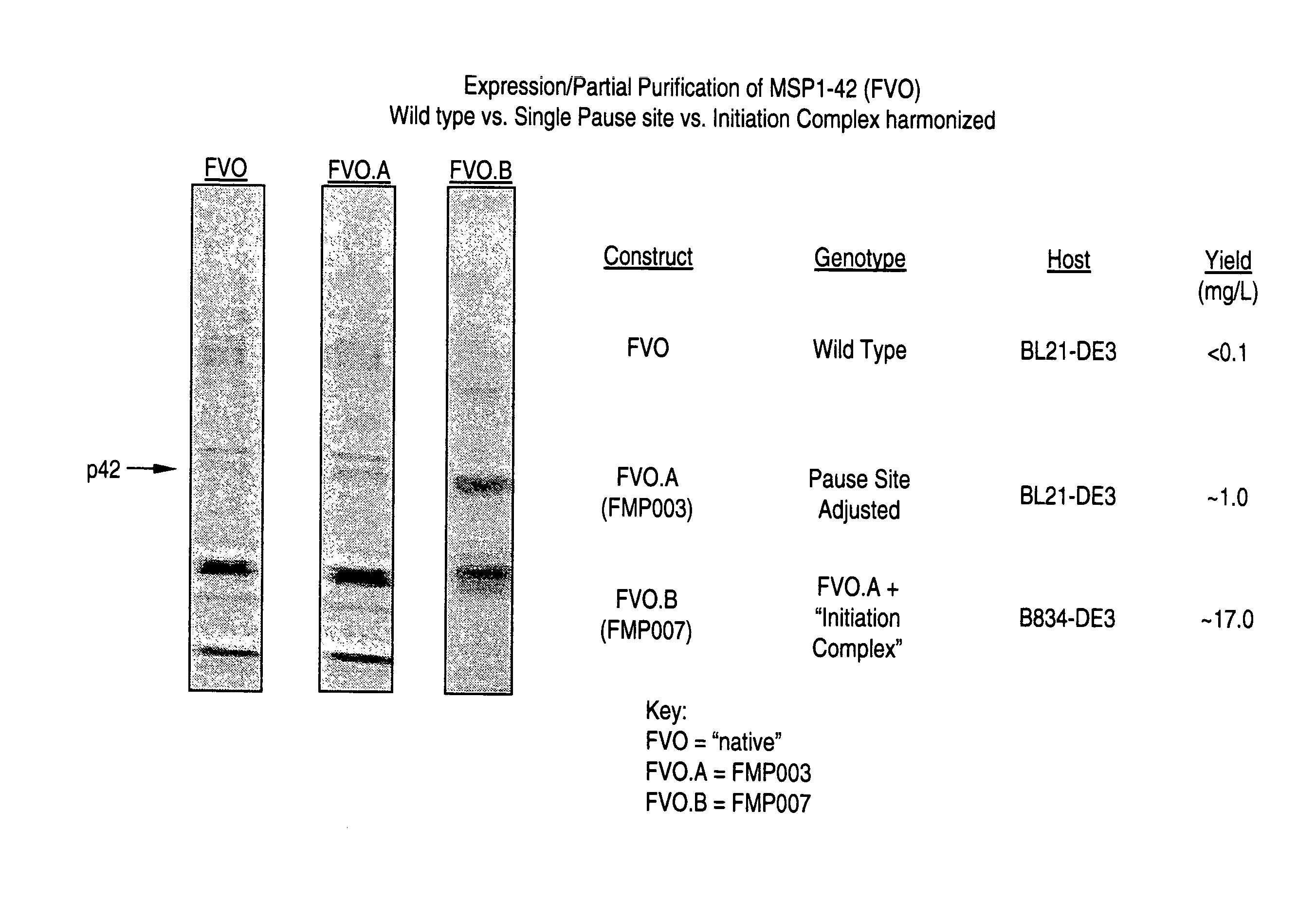
The present invention provides a method for modifying a wild type nucleic acid sequence encoding a polypeptide to enhance expression and accumulation of the polypeptide in the host cell by harmonizing synonymous codon usage frequency between the foreign DNA and the host cell DNA. This can be done by substituting codons in the foreign coding sequence with codons of similar usage frequency from the host DNA / RNA which code for the same amino acid. The present invention also provides novel synthetic nucleic acid sequences prepared by the method of the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Synthetic nucleic acid molecule compositions and methods of preparation
ActiveUS20060068395A1Improve the level ofIncrease the number ofSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSynthetic nucleic acidChemistry
A method to prepare synthetic nucleic acid molecules having reduced inappropriate or unintended transcriptional characteristics when expressed in a particular host cell.
Owner:PROMEGA
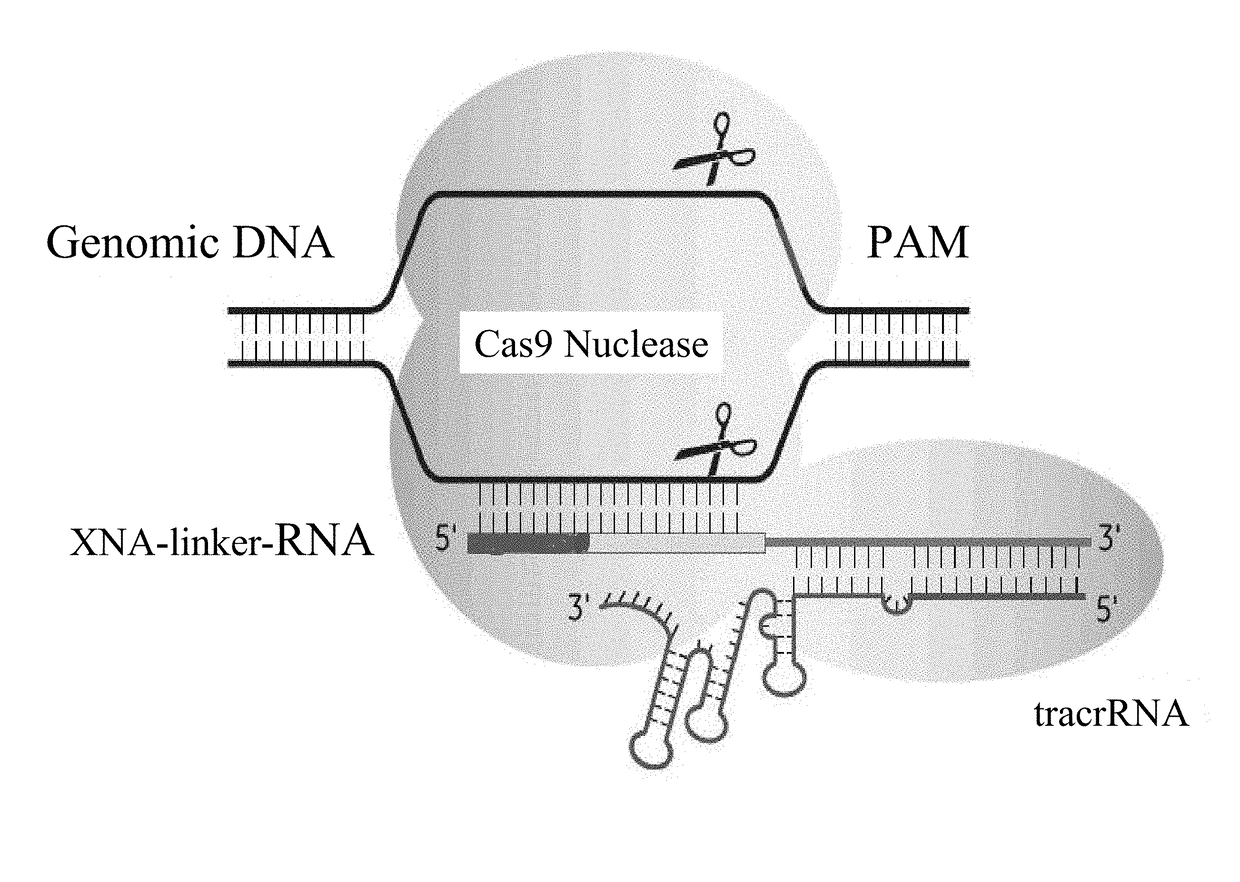
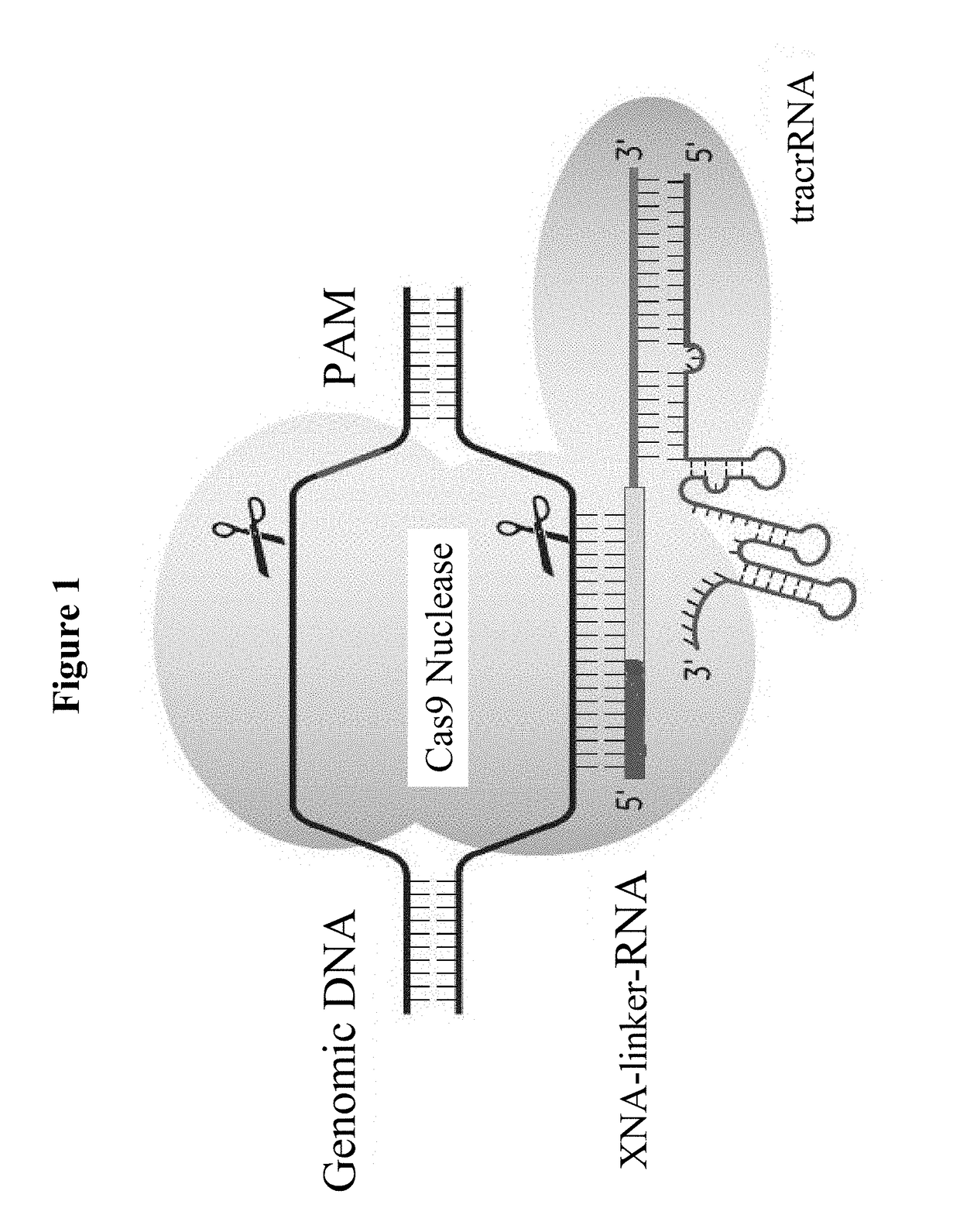
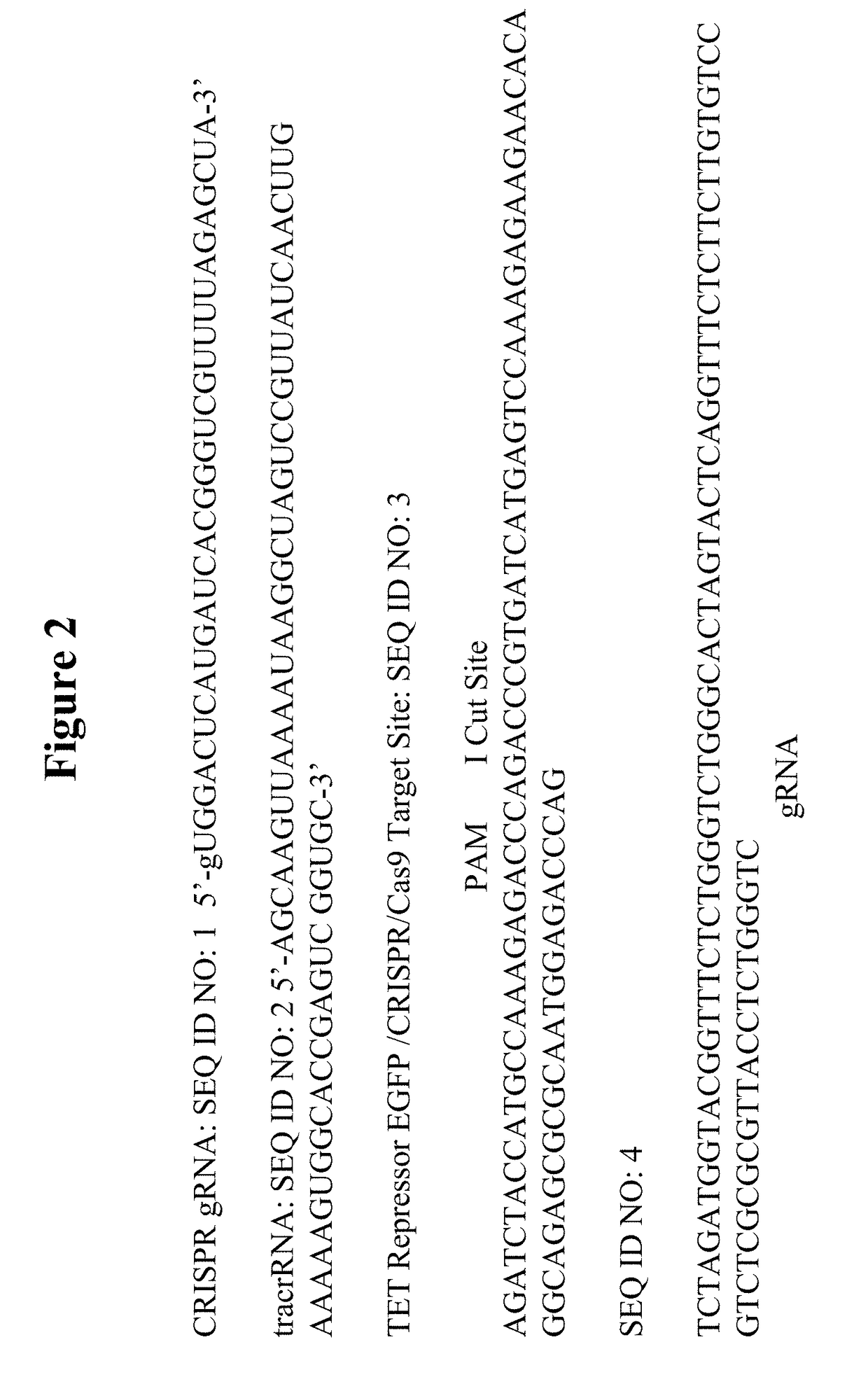
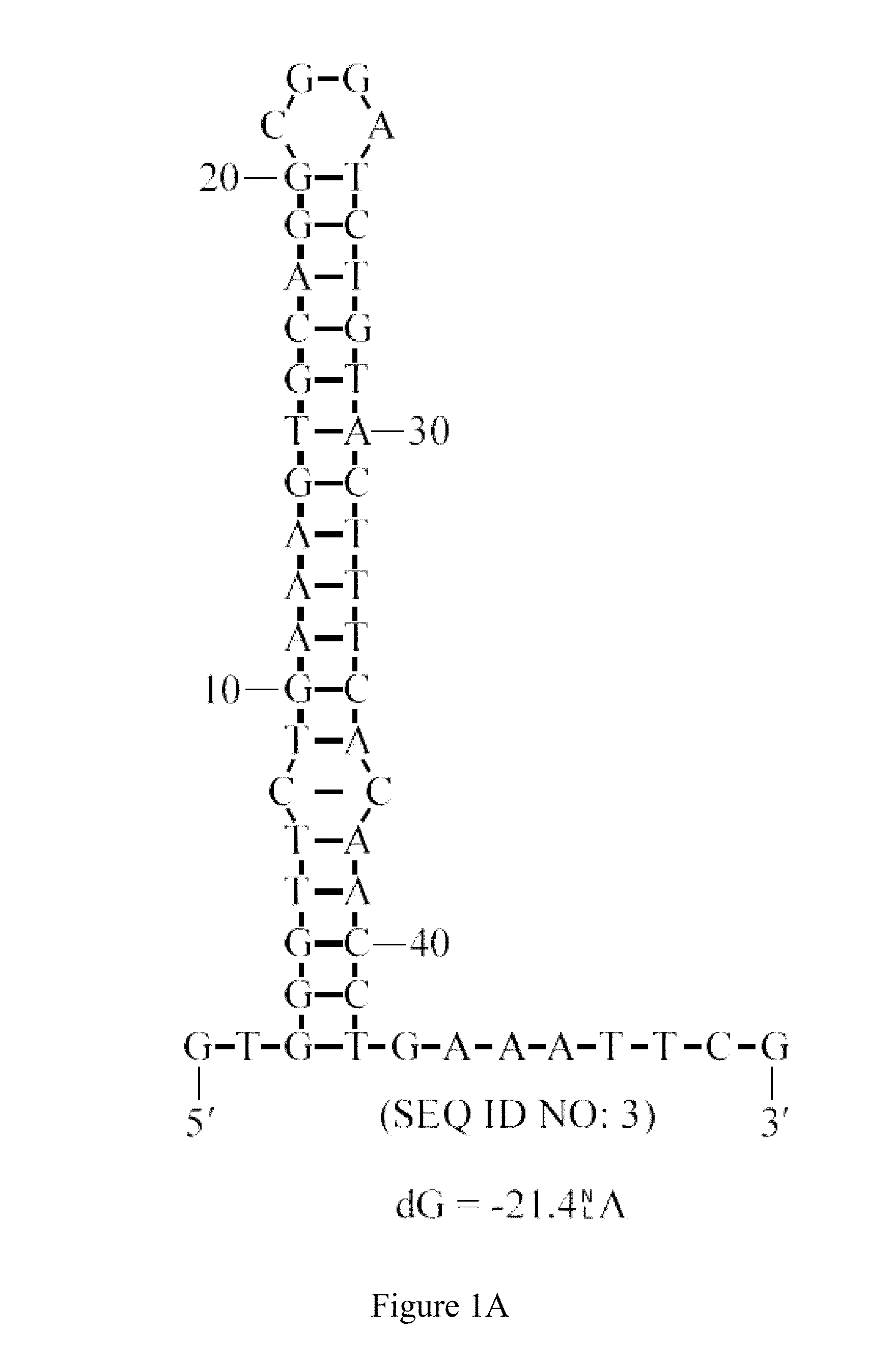
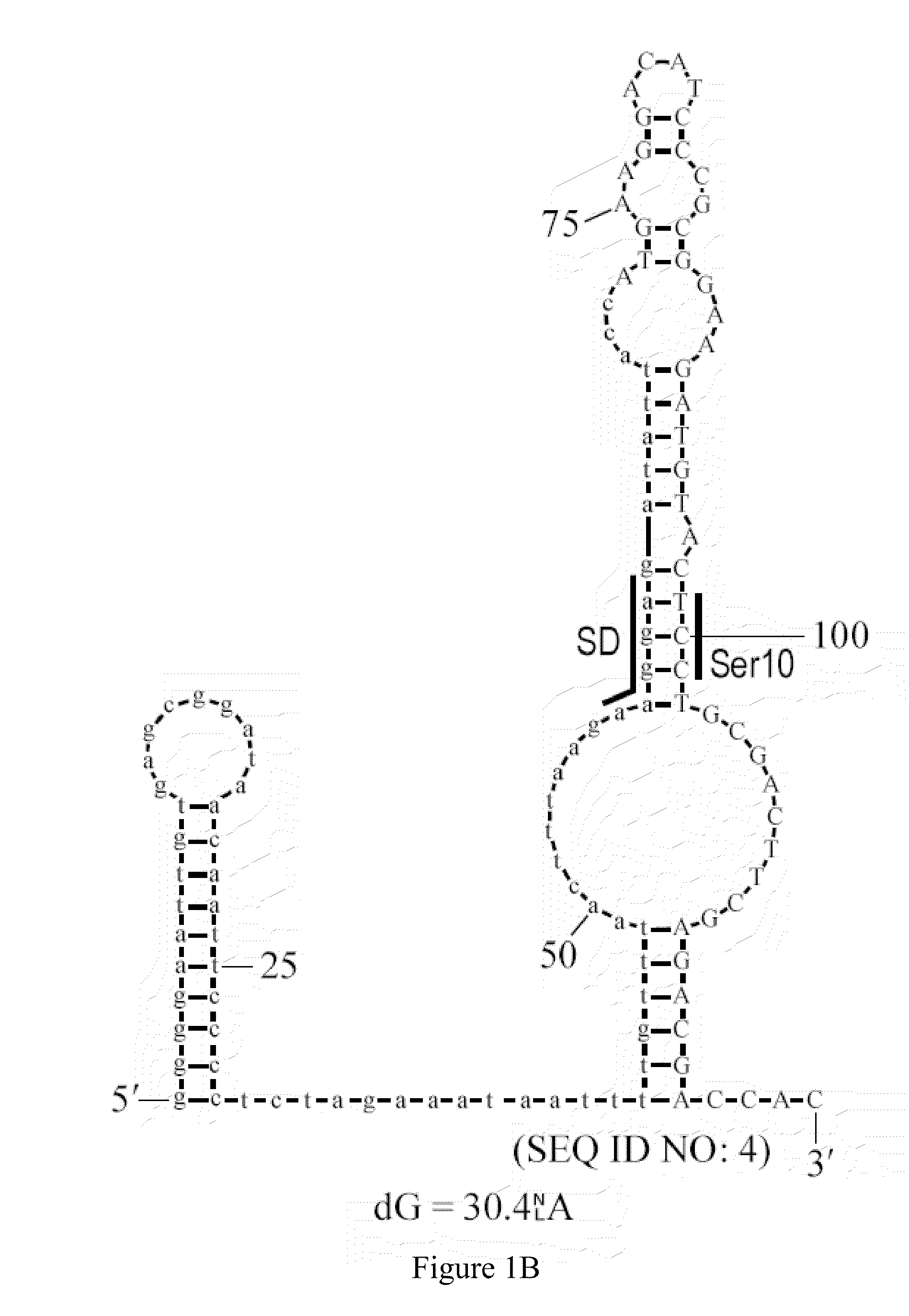
SPECIFIC SYNTHETIC CHIMERIC XENONUCLEIC ACID GUIDE RNA; s(XNA-gRNA) FOR ENHANCING CRISPR MEDIATED GENOME EDITING EFFICIENCY
ActiveUS20180066258A1Enhancing crispr mediated genome editing efficiencyImprove editing efficiencySugar derivativesStable introduction of DNADiseasePrimary cell
The invention provides specific synthetic chimeric xenonucleic acid guide RNA; s(XNA-gRNA) for enhancing crispr mediated genome editing efficiency. The invention also provides methods and compositions for inducing CRISPR / Cas-based gene editing / regulation (e.g., genome editing or gene expression) of a target nucleic acid (e.g., target DNA or target RNA) in a cell. The methods include using single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that have been chemically modified with xeno nucleic acids which enhance gene regulation of the target nucleic acid in a primary cell for use in ex vivo therapy or in a cell in a subject for use in in vivo therapy. Additionally, provided herein are methods for preventing or treating a genetic disease in a subject by administering a sufficient amount of a sgRNA that has been chemically modified with xeno nucleic acids to correct a mutation in a target gene associated with the genetic disease.
Owner:DIACARTA LTD
Synthetic nucleic acids for expression of encoded proteins
ActiveUS8126653B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesNucleotidePolynucleotide
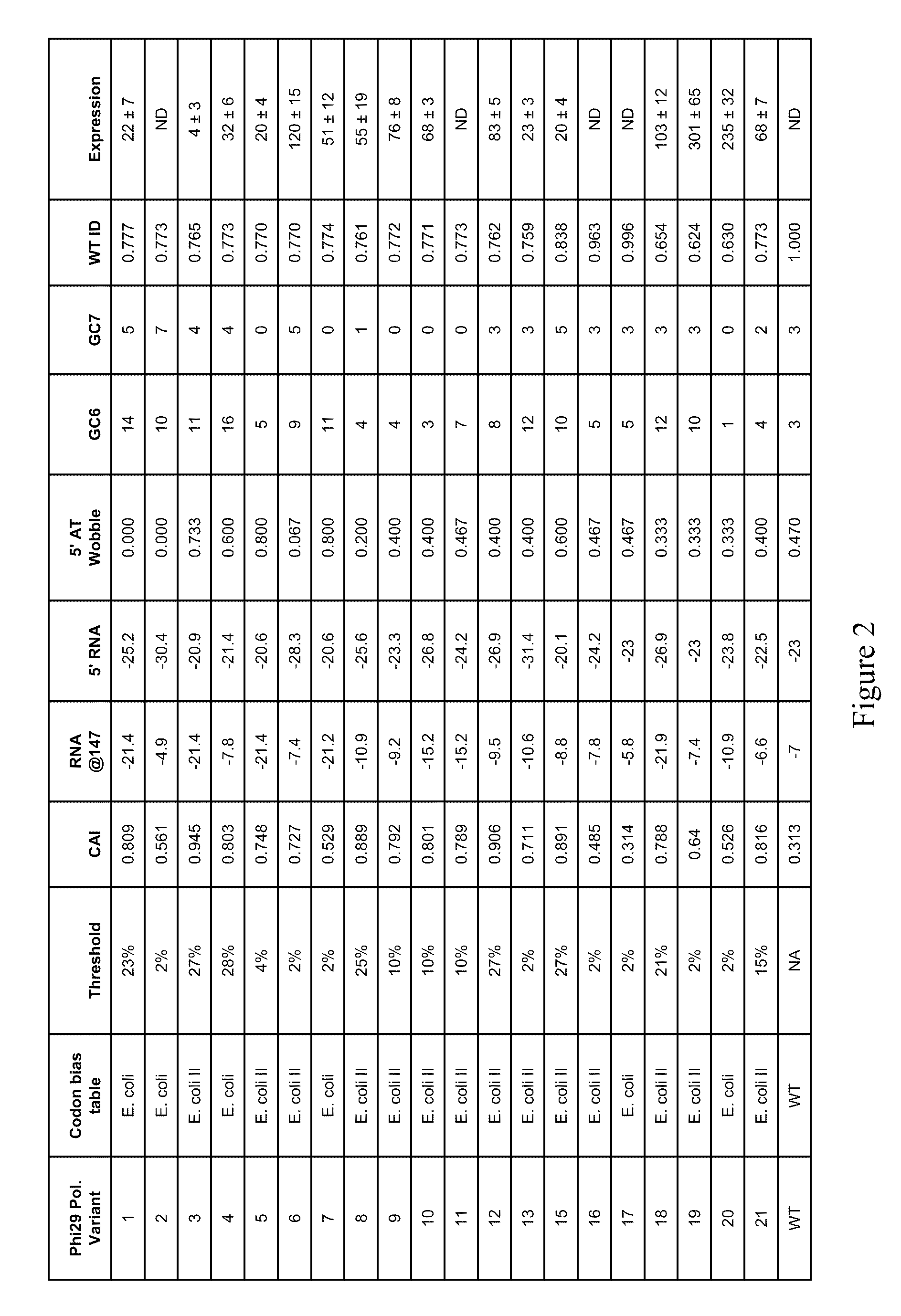
A method of determining a property that affects expression of polynucleotides in an expression system. A plurality of polynucleotides, each encoding a polypeptide sequence, is constructed. An amino acid is encoded a plurality of times in both a first and second polynucleotide in the plurality. The amino acid is encodable by a plurality of synonymous codons including a first codon. The first codon is in the first polynucleotide at a first frequency relative to other synonymous codons, and is in the second polynucleotide at a second frequency relative to other synonymous codons. The first and second frequencies are different. Each polynucleotide is individually expressed in the expression system to measure an expression property value of the polynucleotides, thereby determining a property that affects expression of polynucleotides. The property is an effect that a frequency of use of one or more codons has on expression of polynucleotides in the expression system.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
Variants of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and uses thereof
ActiveUS10435676B2Improve abilitiesLow costImmobilised enzymesTransferasesNucleotideAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to a variant of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) which (i) comprises the amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID Nº 2 or a functionally equivalent sequence, with at least an amino acid substitution at position corresponding to residue C302 or functionally equivalent residue, wherein the position is numbered by reference to the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID Nº 1, (ii) is able to synthesize a nucleic acid fragment without template and (iii) is able to incorporate a modified nucleotide into the nucleic fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +2
Design, synthesis and assembly of synthetic nucleic acids
InactiveUS20130196864A1Peptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide synthesisPolynucleotide
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides with high coupling efficiency (>99.5%) are provided. Methods for purification of synthetic oligonucleotides are also provided. Instrumentation configurations for oligonucleotide synthesis are also provided. Methods of designing and synthesizing polynucleotides are also provided. Polynucleotide design is optimized for subsequent assembly from shorter oligonucleotides. Modifications of phosphoramidite chemistry to improve the subsequent assembly of polynucleotides are provided. The design process also incorporates codon biases into polynucleotides that favor expression in defined hosts. Design and assembly methods are also provided for the efficient synthesis of sets of polynucleotide variants. Software to automate the design and assembly process is also provided.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
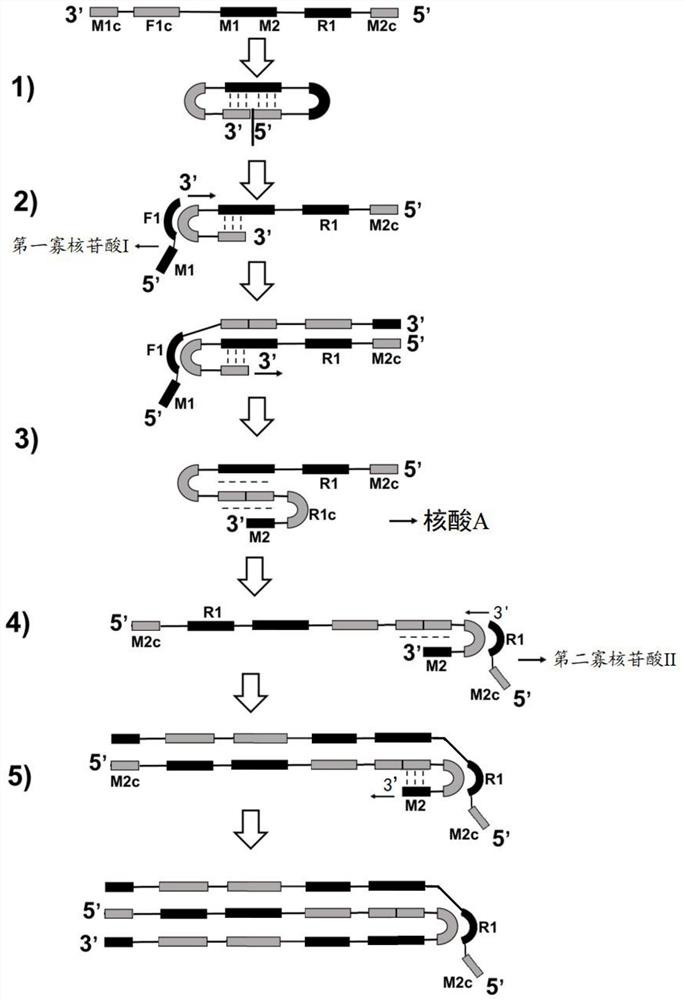
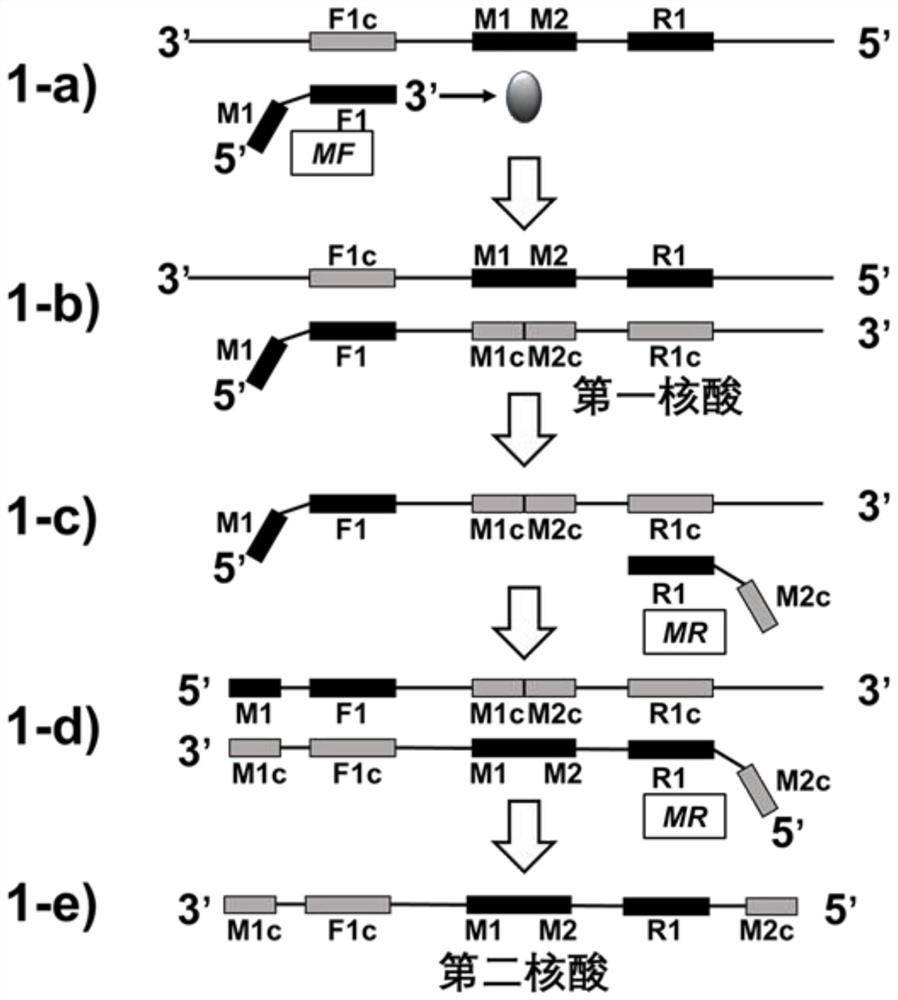
Method for synthesizing nucleic acid under constant temperature condition, kit and application
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing nucleic acid under a constant temperature condition, a kit and application. The method comprises the steps that a nucleic acid is provided, the nucleic acid is sequentially composed of an M1c region, an F1c region, an M region, an R1 region and an M2c region in the 3'to 5 'direction, the M region comprises an M1 region and an M2 region, and annealing of the M2c region at the 5'end and the M1c region at the 3' end of the nucleic acid and the M region on the same chain can form a closed ring structure; a first oligonucleotide I and a second oligonucleotide II of a primer are respectively annealed with an F1c region and an R1c region of the nucleic acid, and the nucleic acid is used as a template to react so that a nucleic acid chain continuously extends. According to the nucleic acid synthesis method disclosed by the invention, the length of the core primer is about 30bp and is shortened by 10bp compared with the core primer which is about 40bp and is used by LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) and CAMP (Cyclic Amplified Polymorphism), so that about 1 / 4 of primer cost can be saved, and meanwhile, the reaction rate of nucleic acid synthesis is also improved.
Owner:国科宁波生命与健康产业研究院
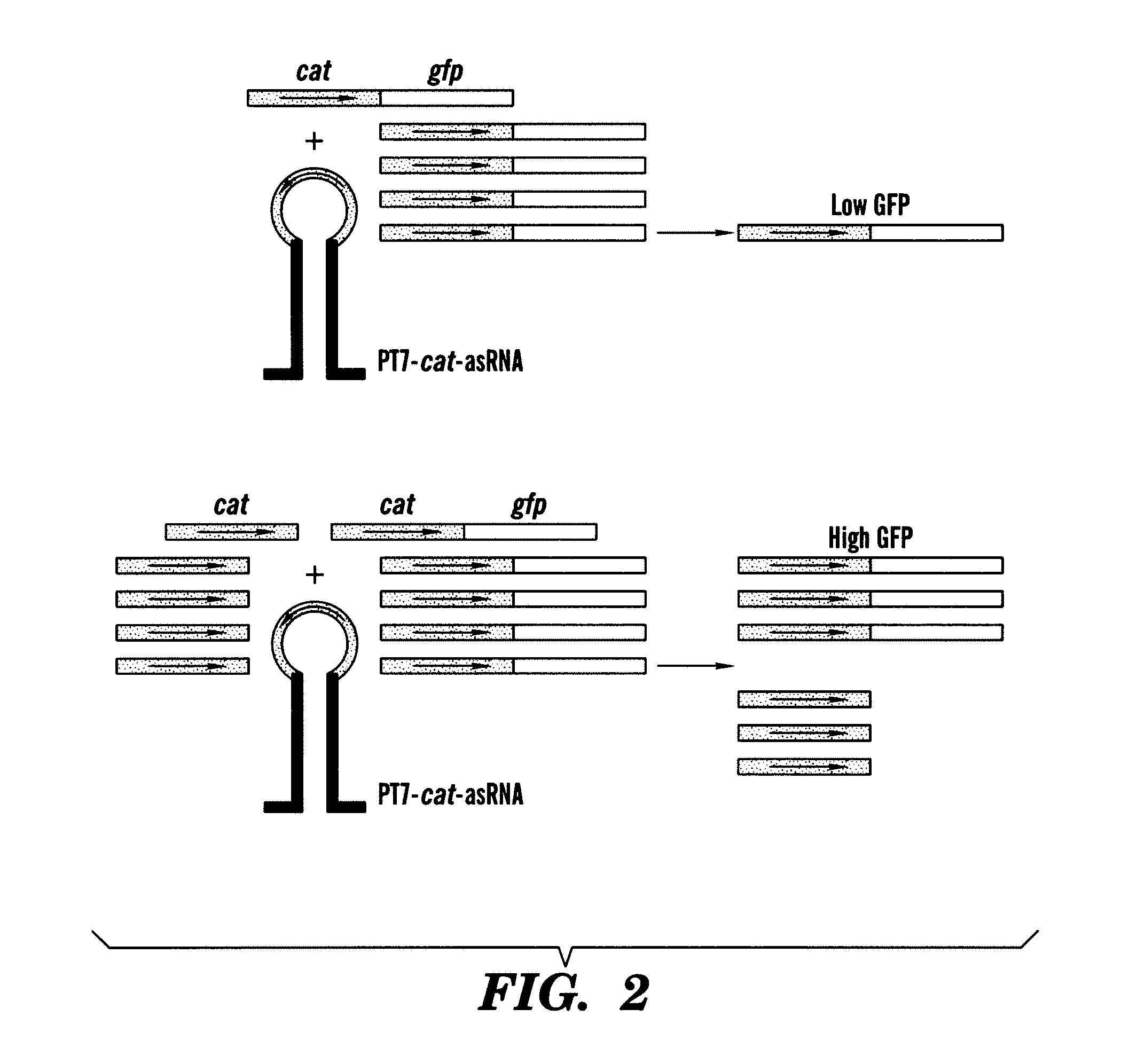
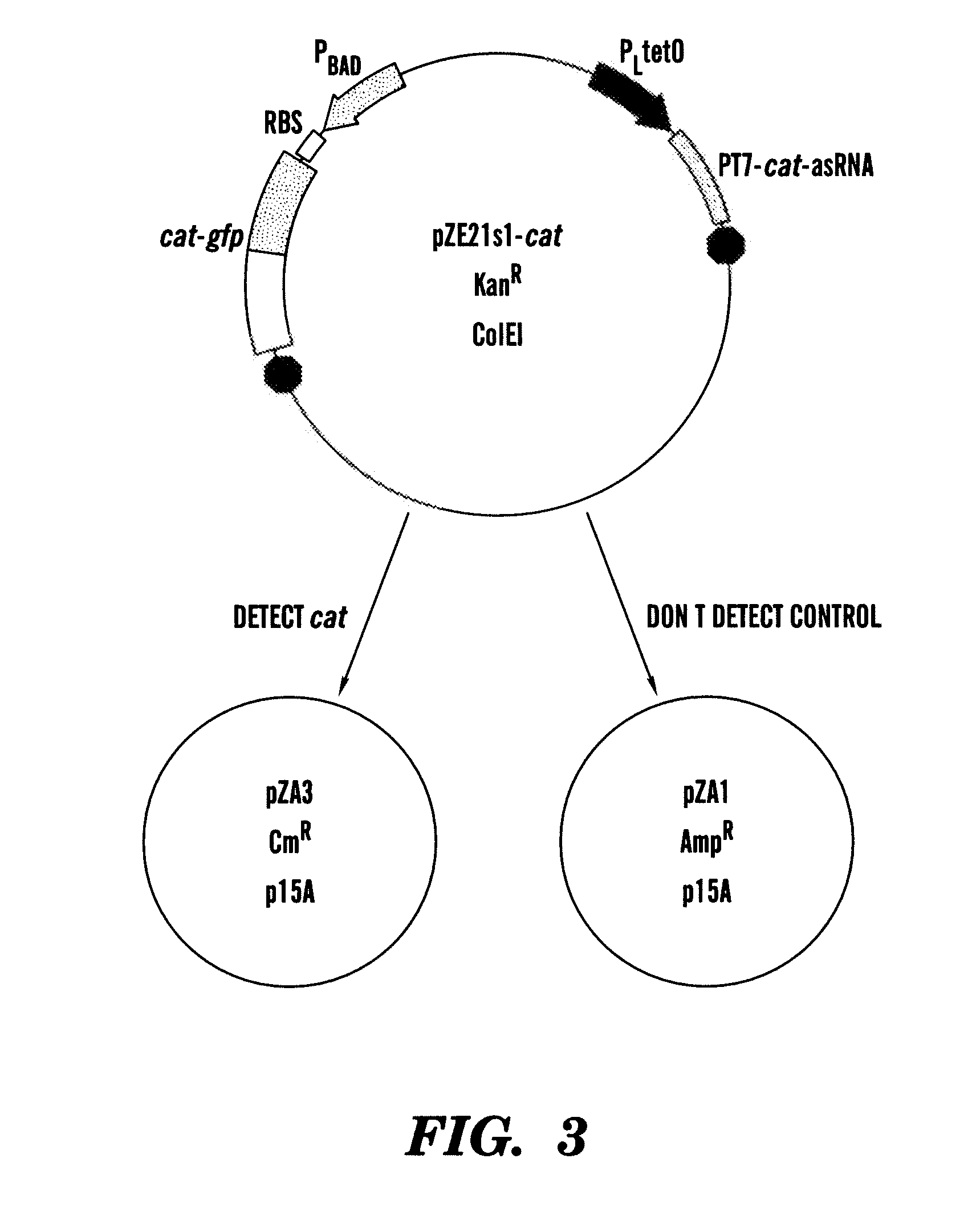
In vivo gene sensors
Described are methods and compositions for the detection of target genes. The inventors have developed a synthetic nucleic acid sensor-effector gene circuit. In cells without a target gene, the circuit suppresses e.g., effector production, but in the presence of the target gene the suppression is subject to competition, such that the synthetic sensor is de-repressed and permits expression of the effector gene. The methods and compositions described further permit the selective expression of an effector gene in those cells expressing the target gene. In this manner, cells expressing a target gene can be selectively targeted for treatment or elimination. In certain aspects, the methods and compositions described permit the selective expression of an agent such as a therapeutic gene product, in a specifically targeted population of cells in an organism.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
Methods for detecting nucleic acids in a sample
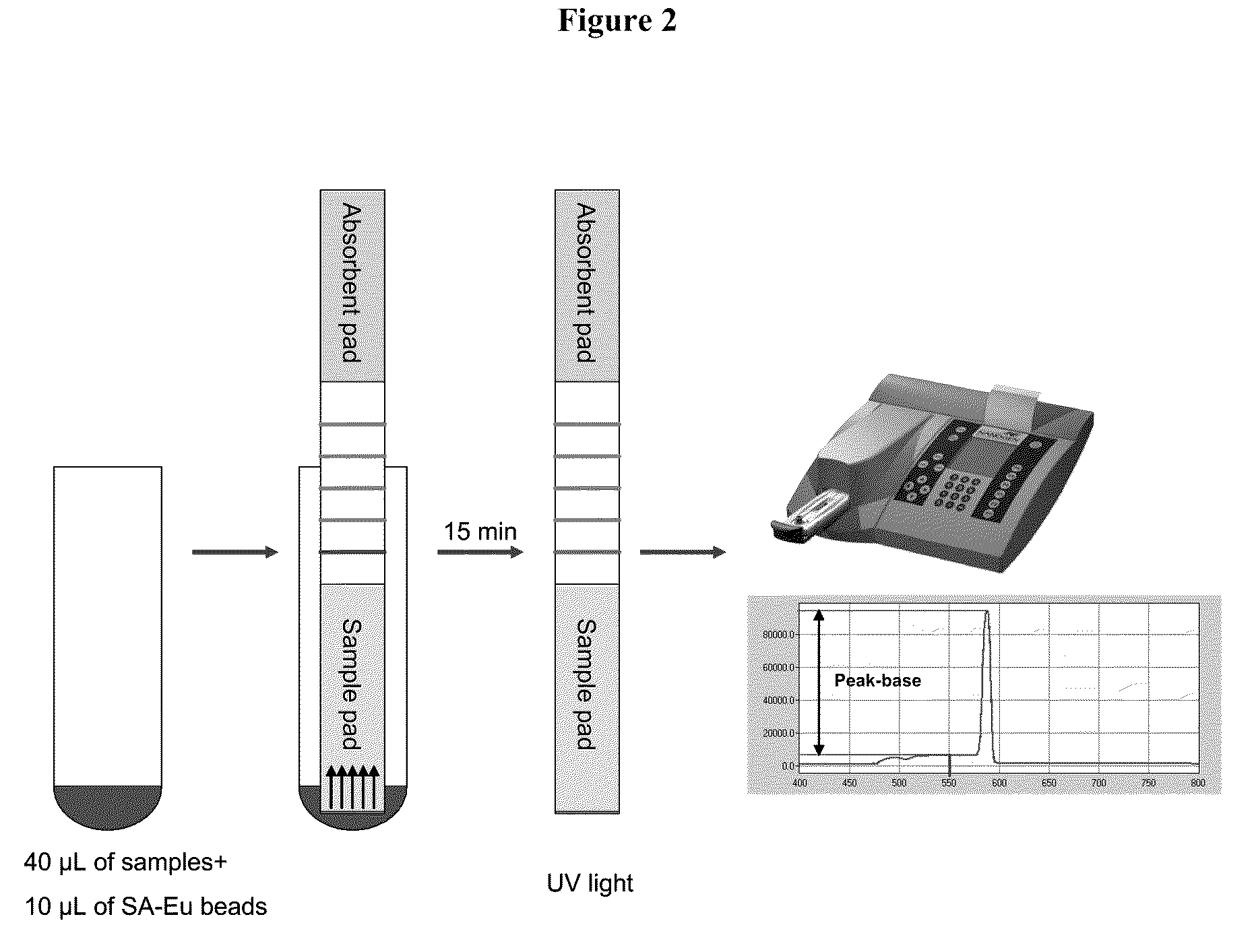
InactiveUS20100167294A1Simple working processFinish quicklyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle strandProtein antigen
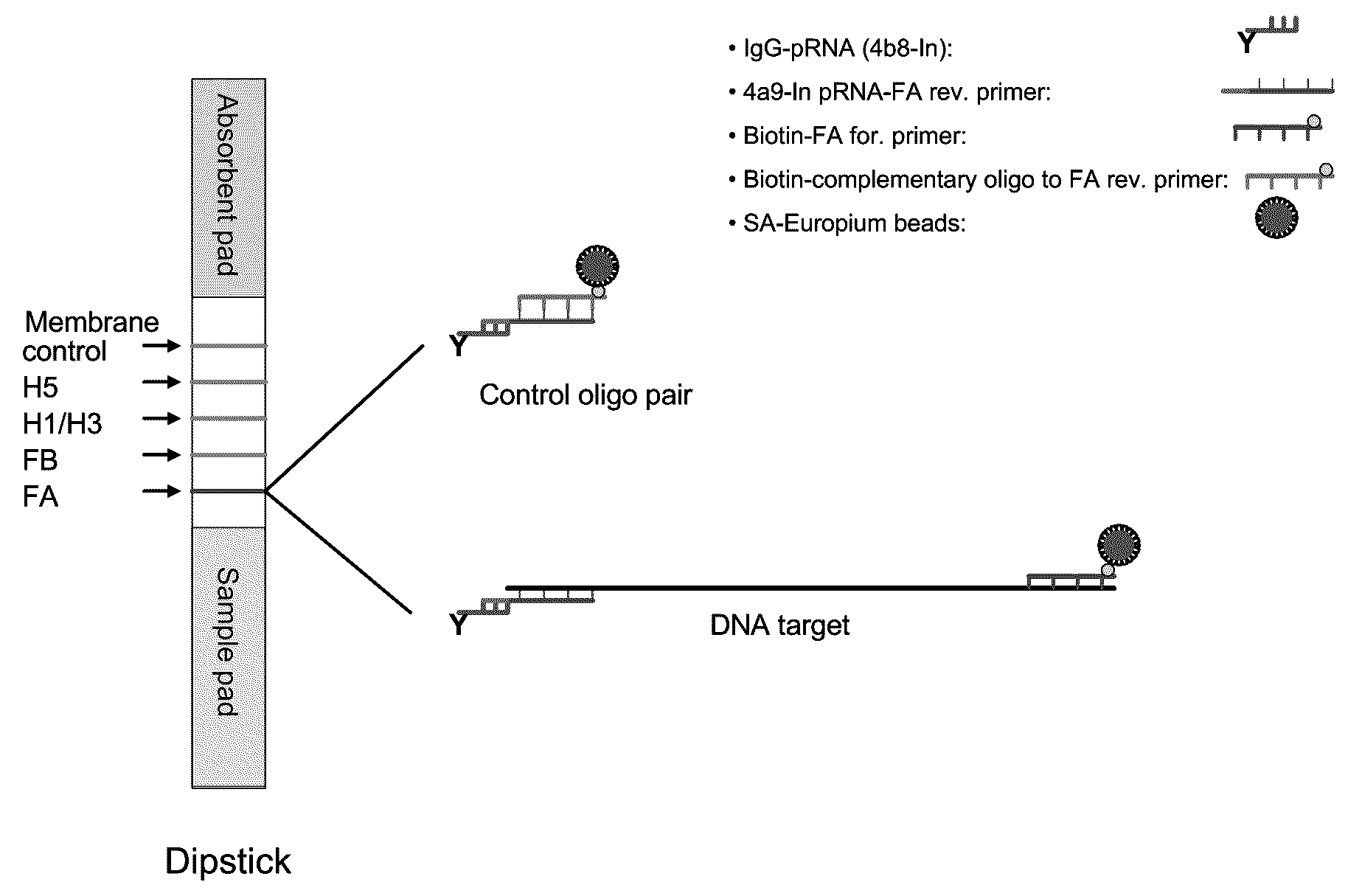
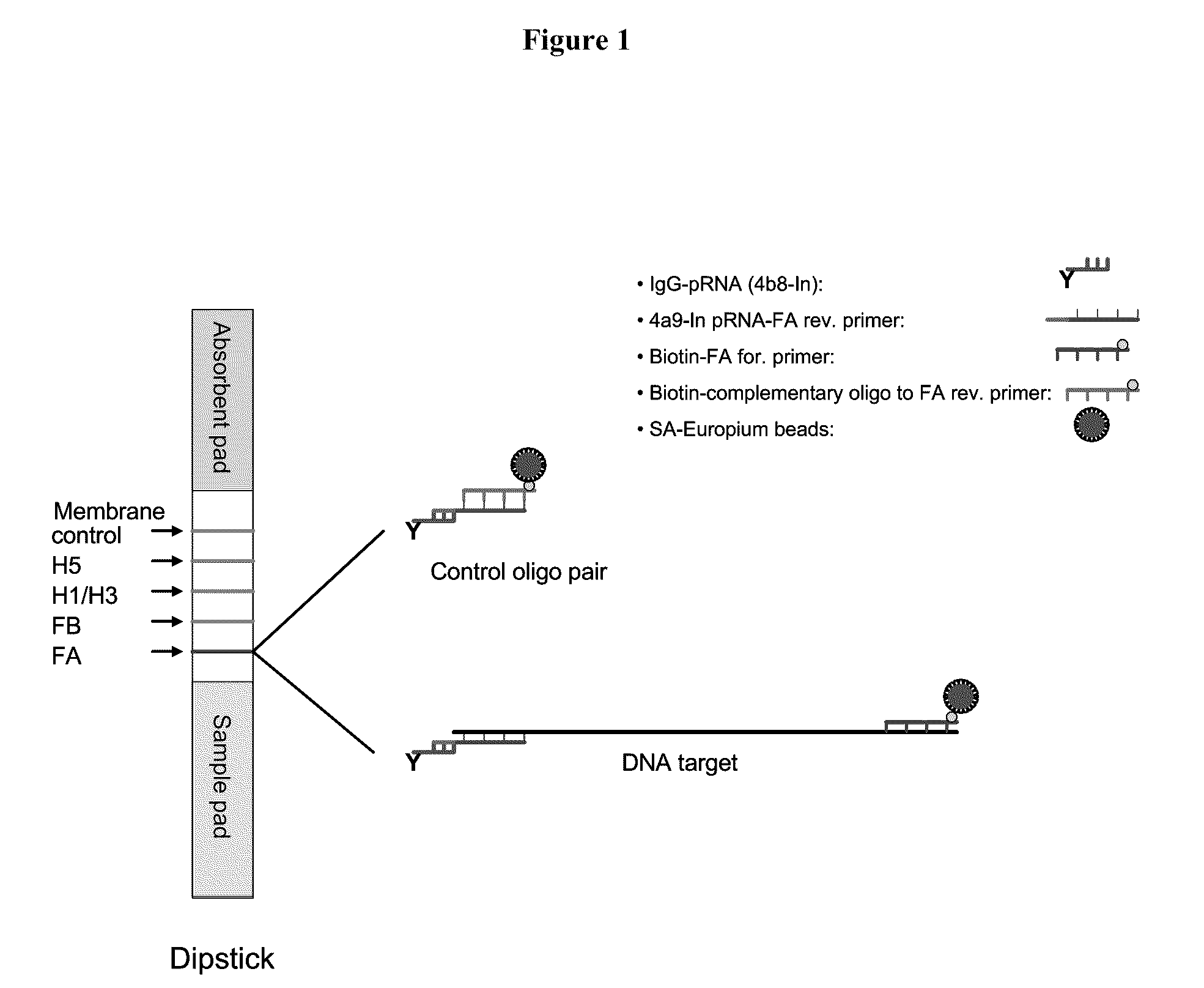
Systems and methods are provided for immobilizing nucleic acid amplicons and protein antigens on a test device. Amplicons comprising a synthetic binding unit and a detectable label are generated and immobilized at predetermined locations on a test device by specific binding interactions between the synthetic binding unit and a synthetic capture unit located at the predetermined locations. The synthetic binding unit may include a unique design such that during amplification, a region of the synthetic binding unit is not subject to the amplification reaction, and thus the amplicon remains single stranded and available for binding to the synthetic capture unit during the capture process. In certain embodiments, the synthetic binding unit and a synthetic capture unit include synthetic nucleic acid analogs that do not interact with native nucleic acids or enzymes that act thereon. In one embodiment the synthetic binding unit and synthetic capture unit comprises puranosyl RNA (pRNA).
Owner:NEXUS DX
Programmable Oligonucleotide Synthesis
ActiveUS20100015668A1Reduce yieldSynthesis is longSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligonucleotide synthesisNucleotide synthesis
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
DNA-templated combinatorial library device and method for use
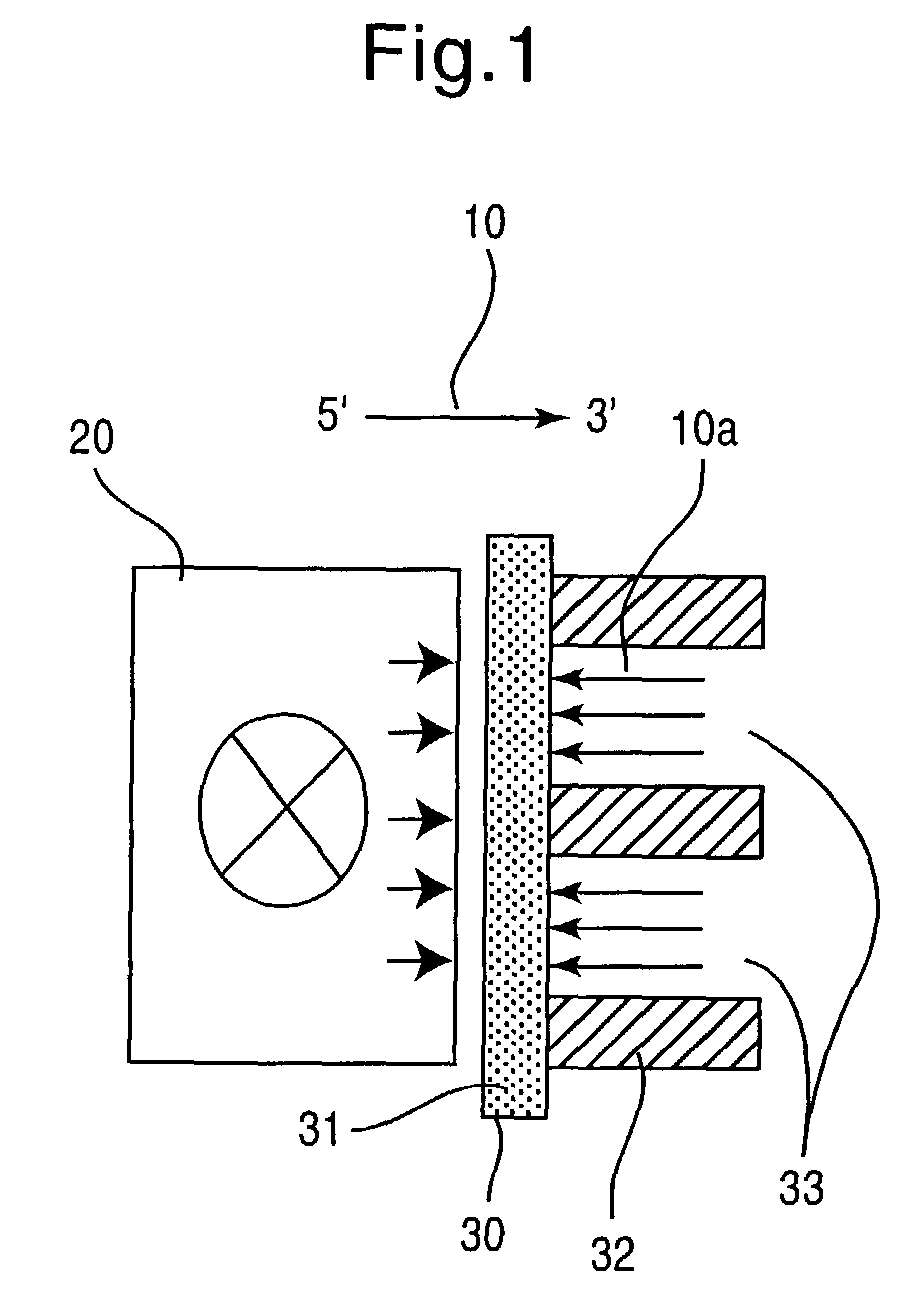
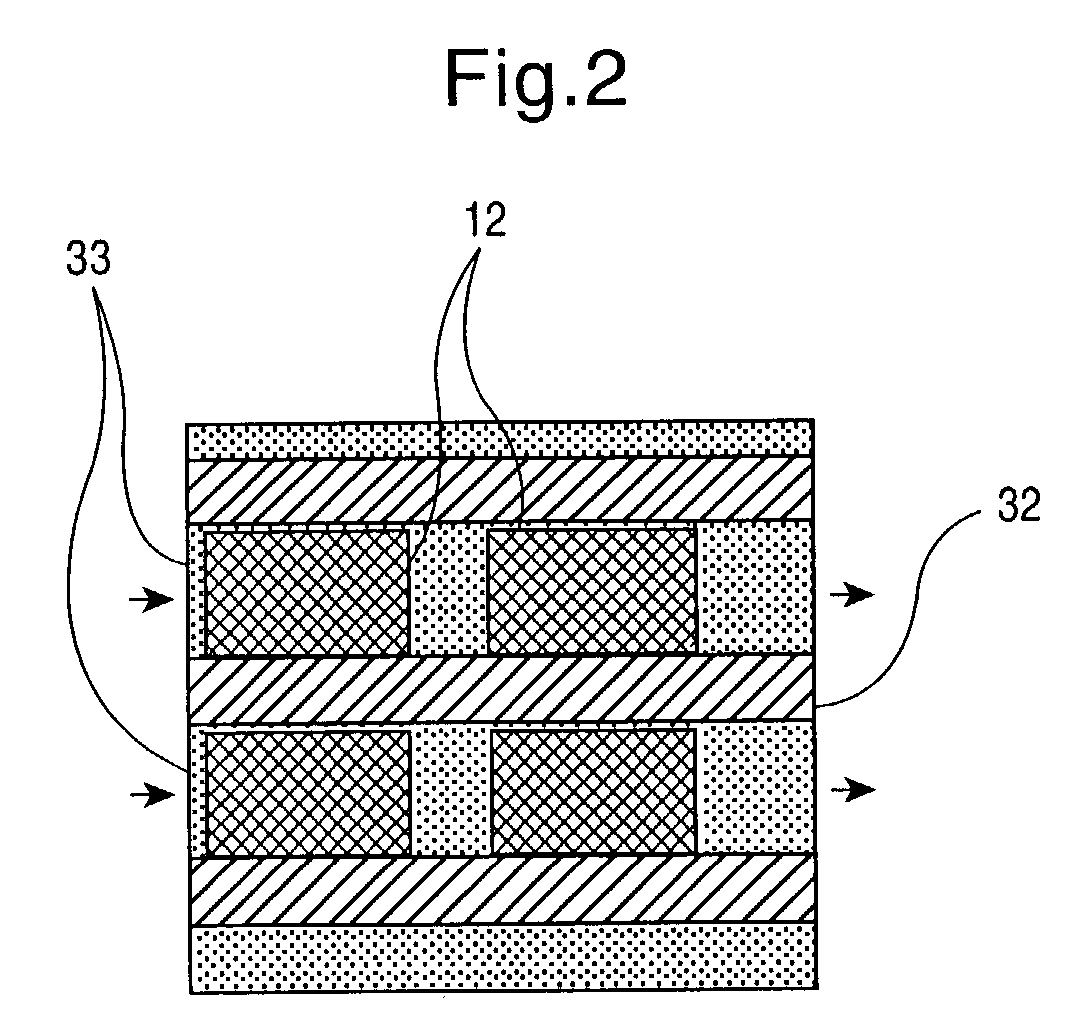
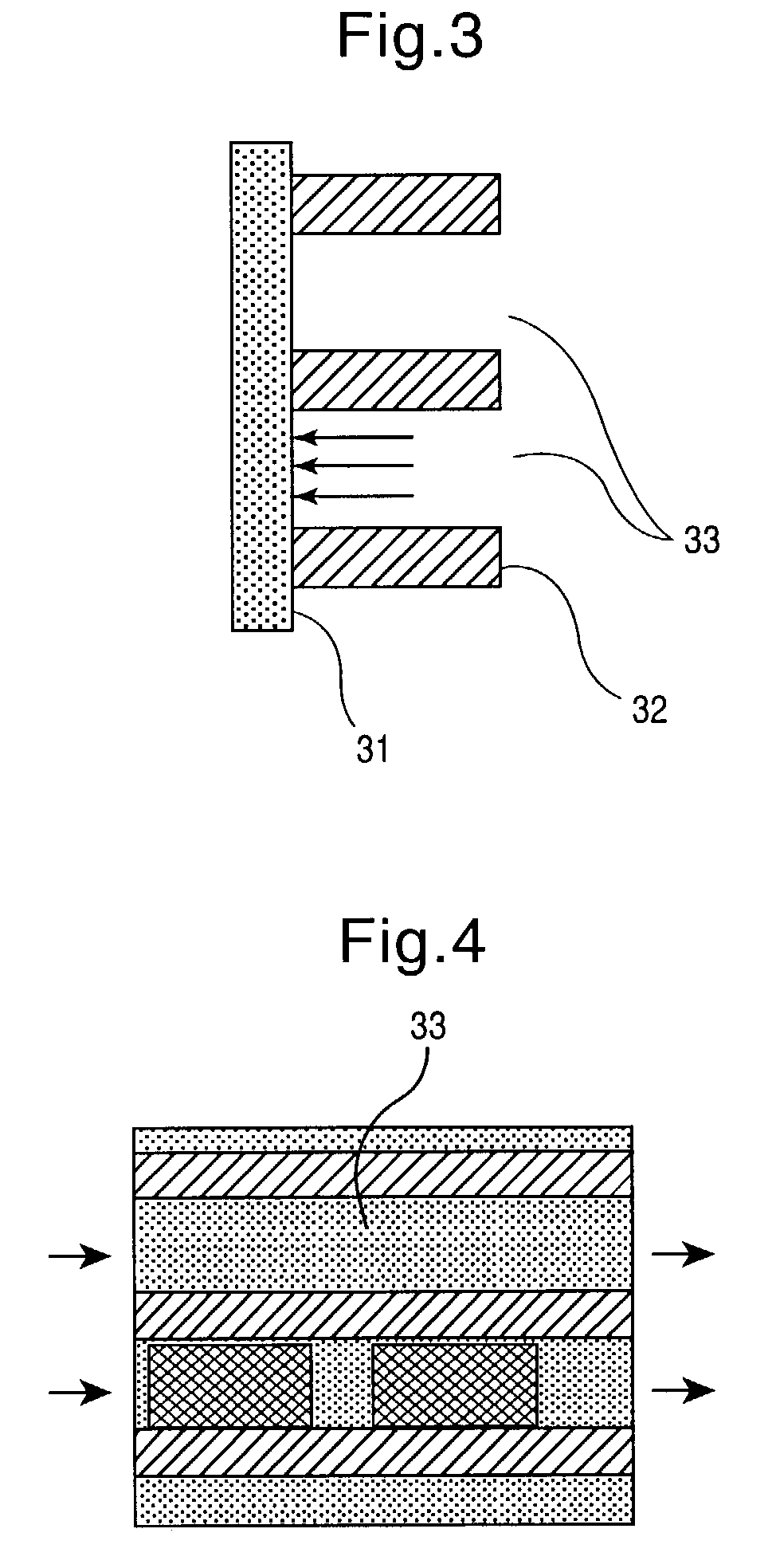
InactiveUS20060099626A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompound (substance)Chemical library
The present invention provides a device and method for synthesizing nucleic acid-templated combinatorial chemical libraries. The device includes a splitting filter having an array of immobilized capture nucleic acids and a chemical coupling filter having an array of non-specific binding features, wherein the plates are positioned to provide for alignment between the capture sites of the first filter and the non-specific binding features of the second filter plate. The molecules bound to the splitting filter can be transferred to the chemical coupling filter and then reacted with site-specific reagents to chemically modify the bound molecules.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com