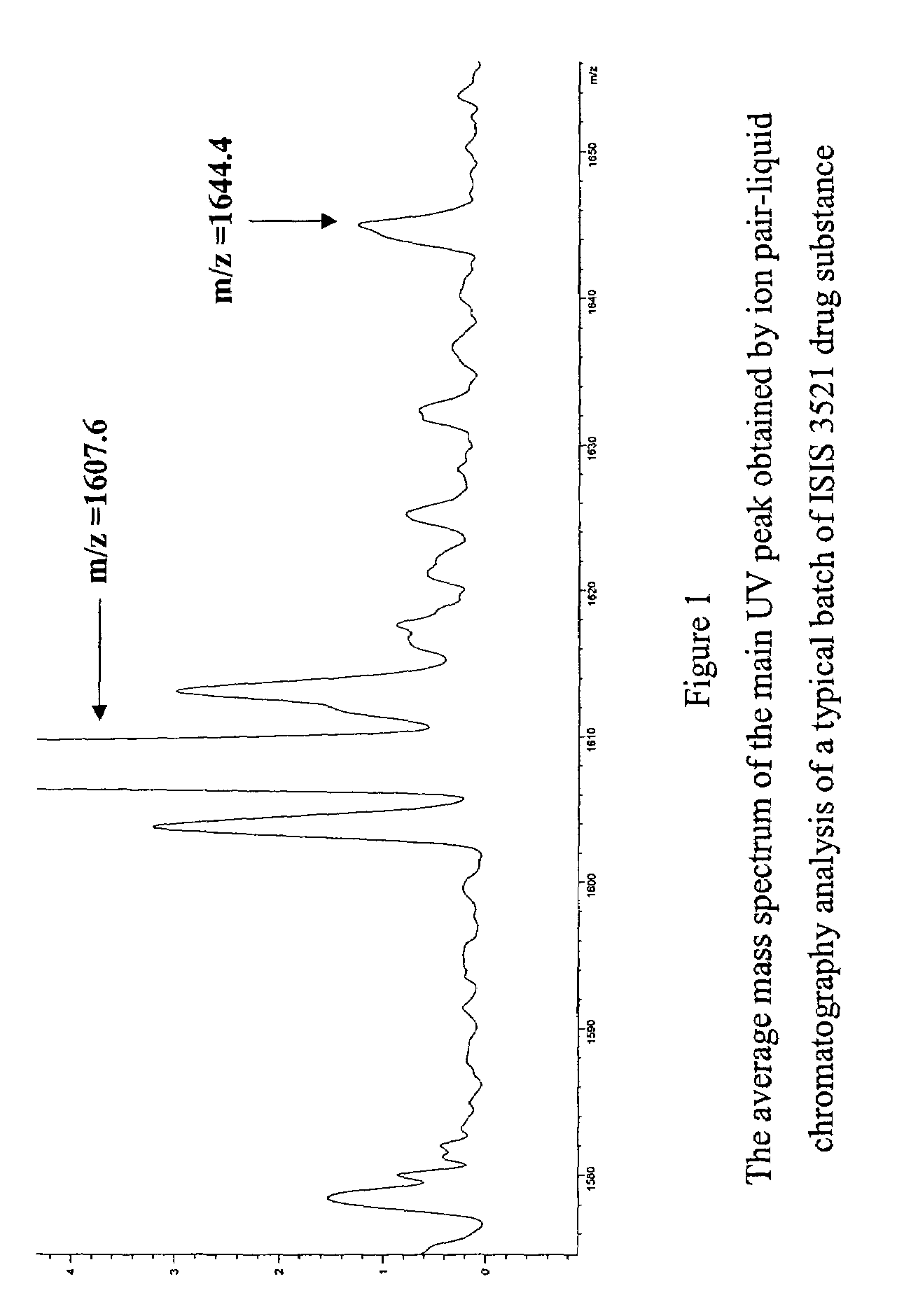
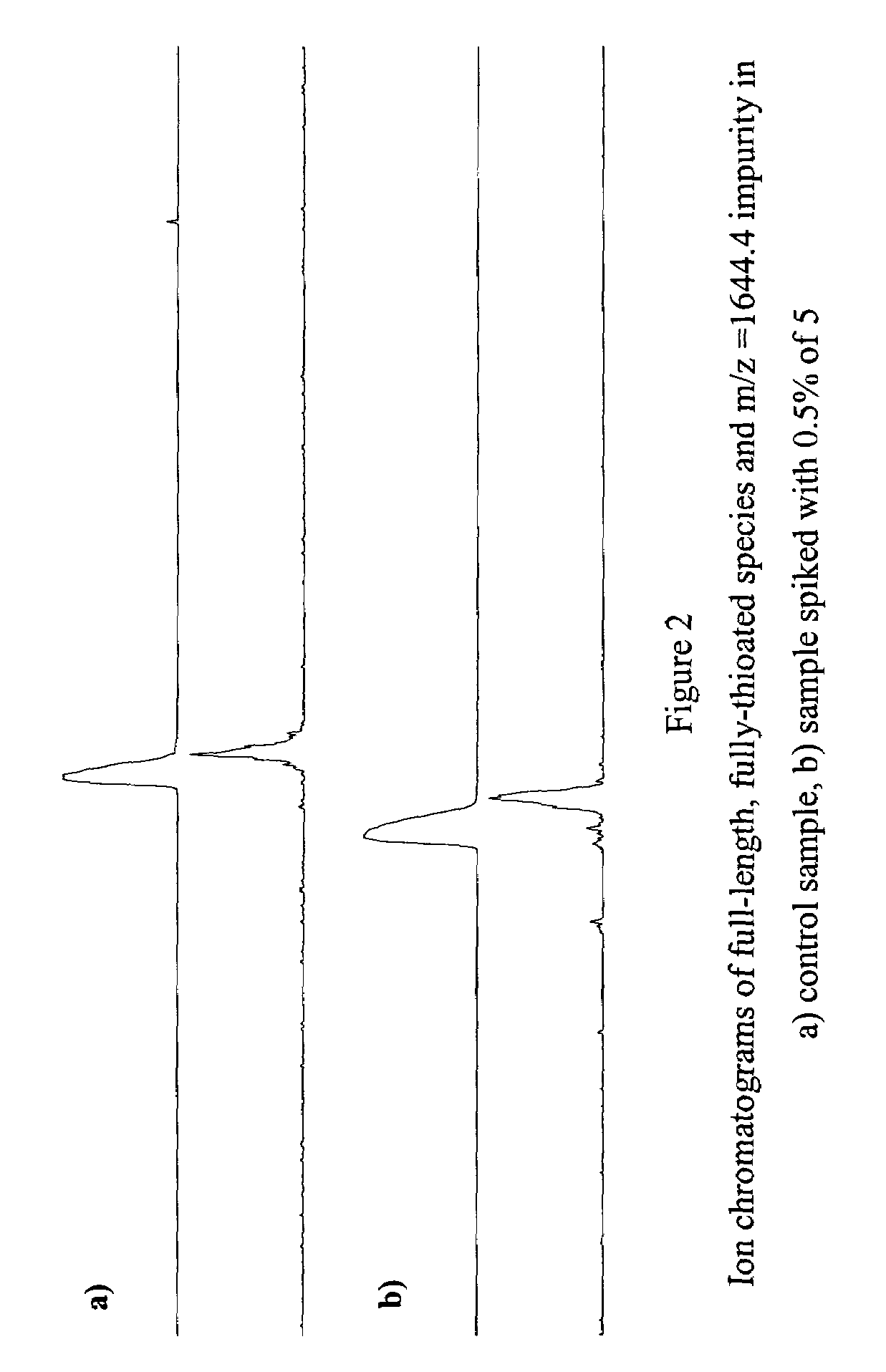
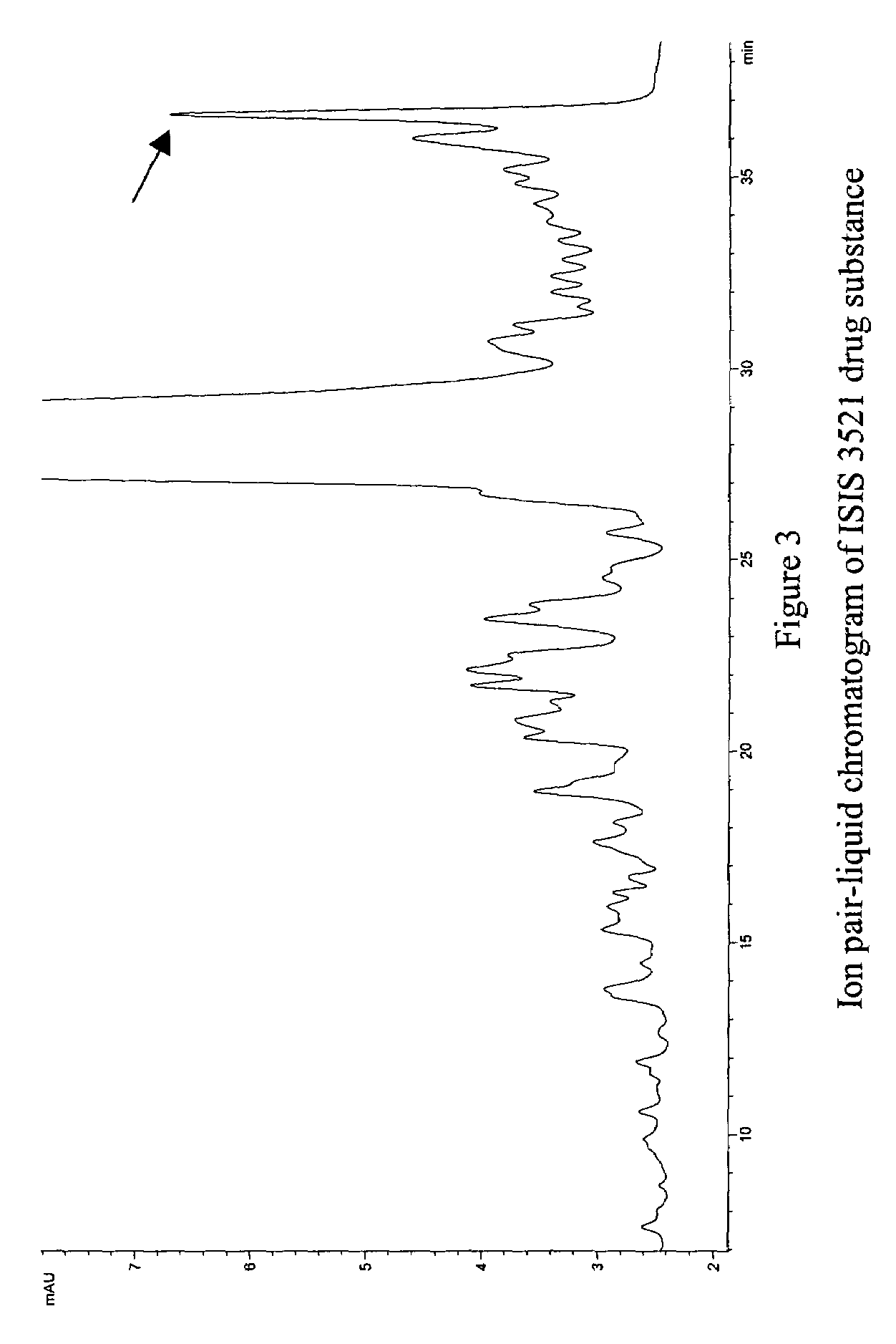
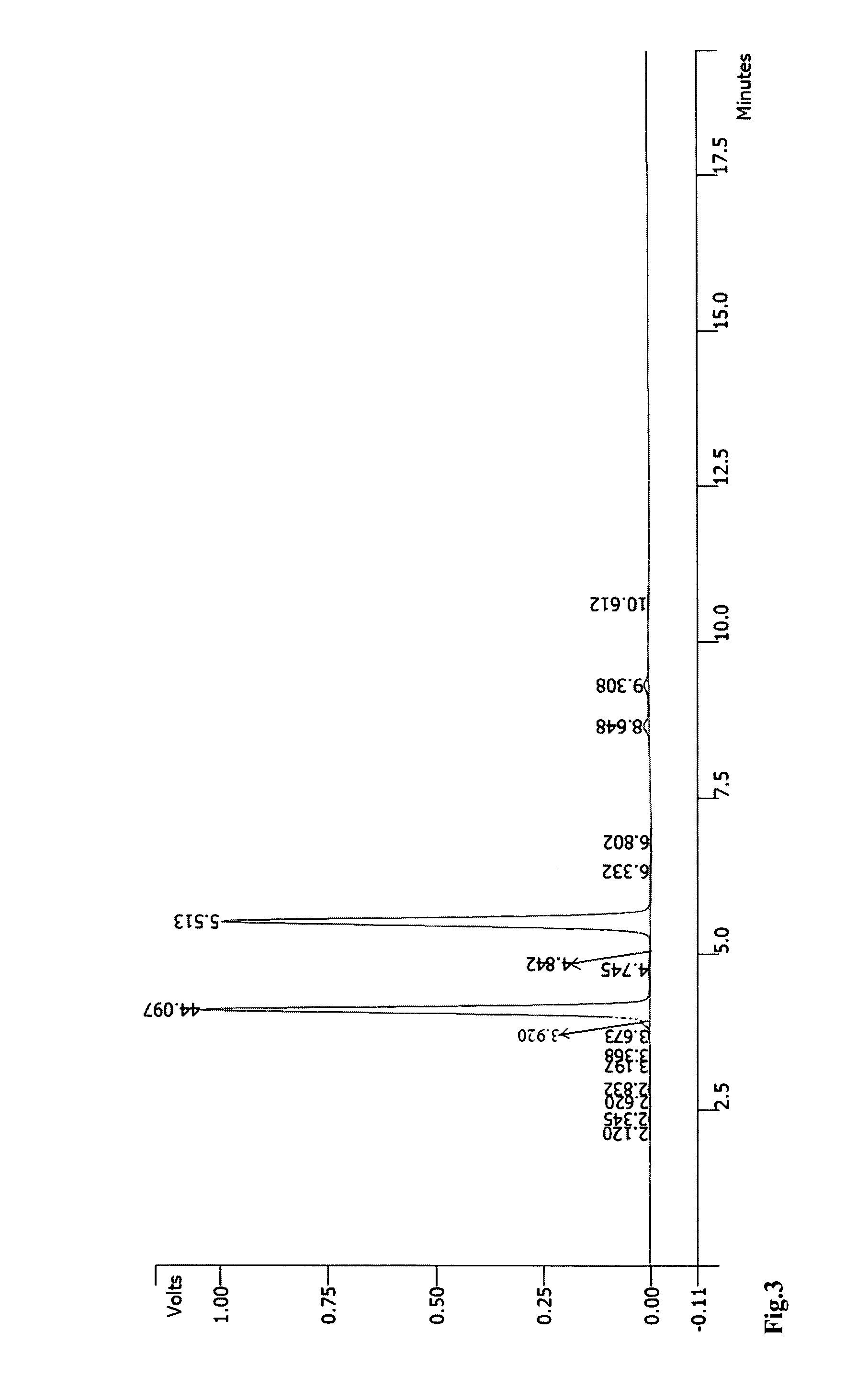
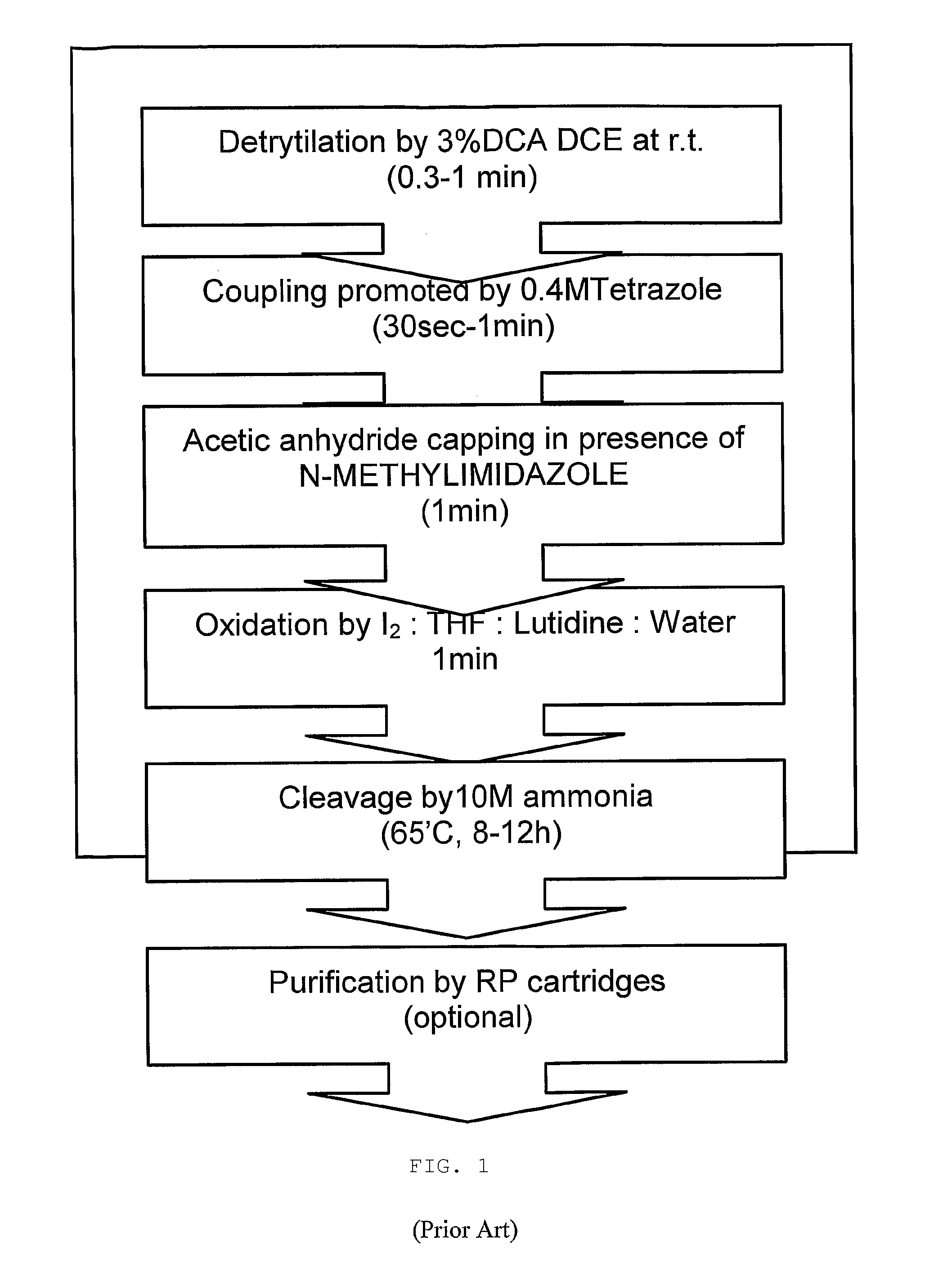
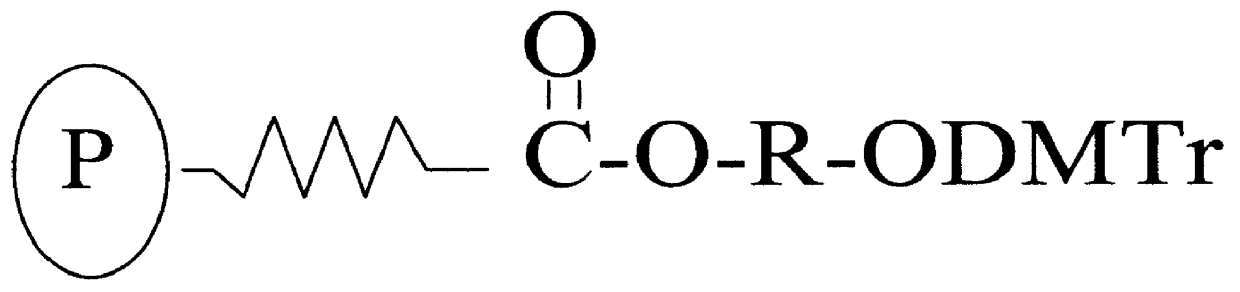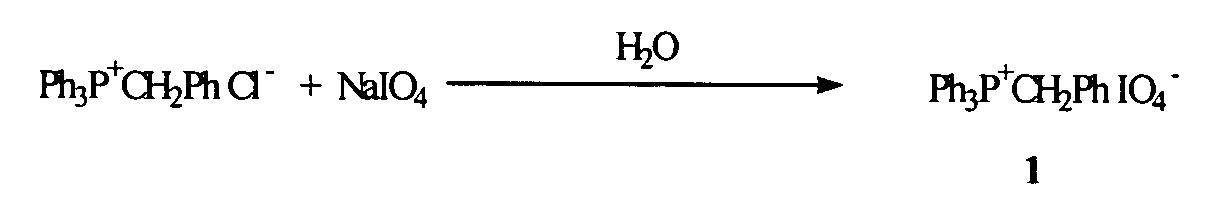Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143 results about "Oligonucleotide synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
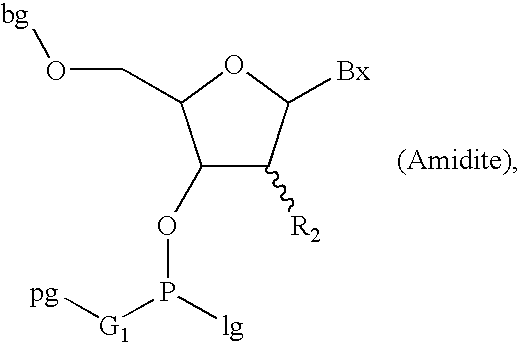
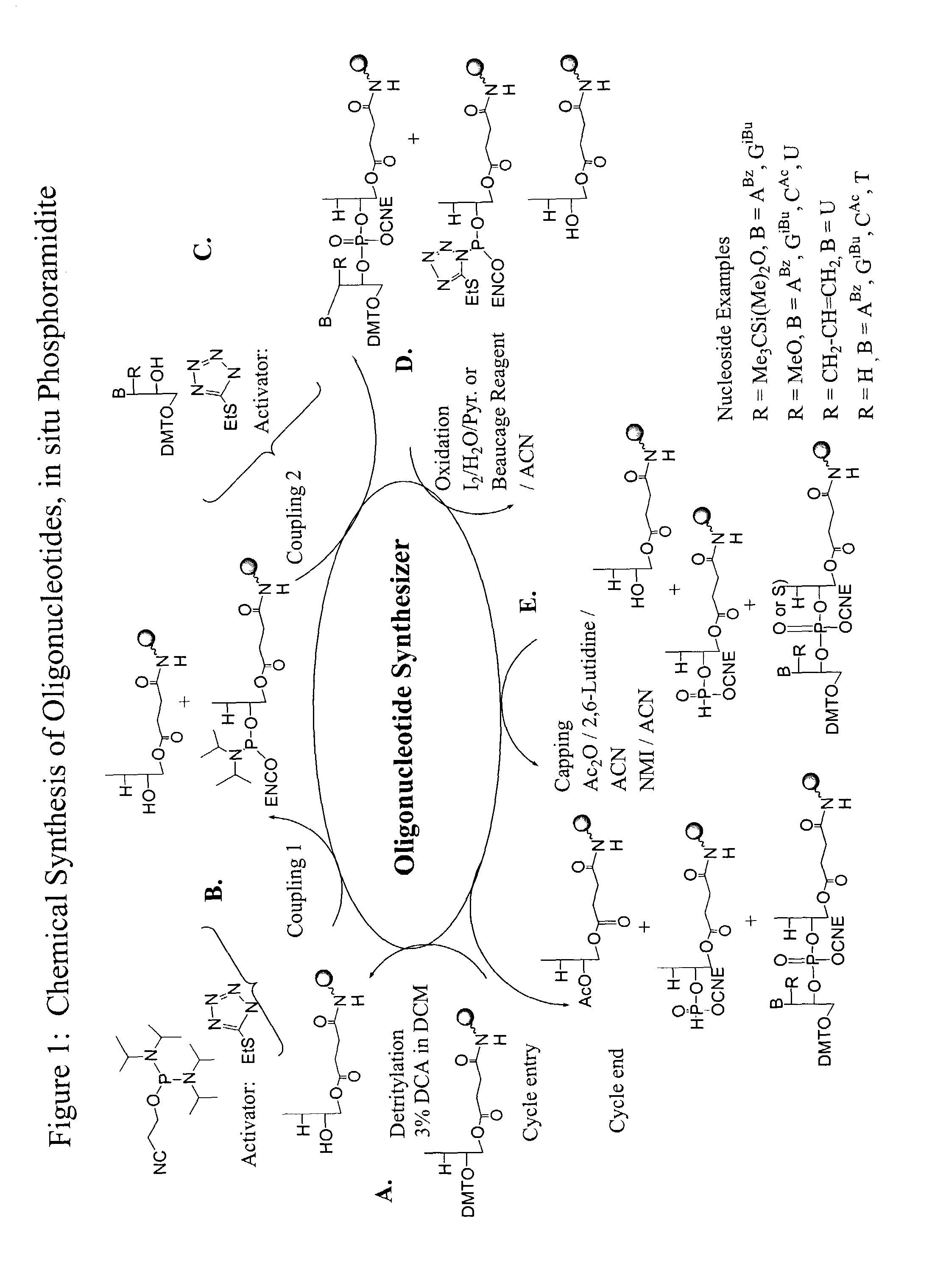
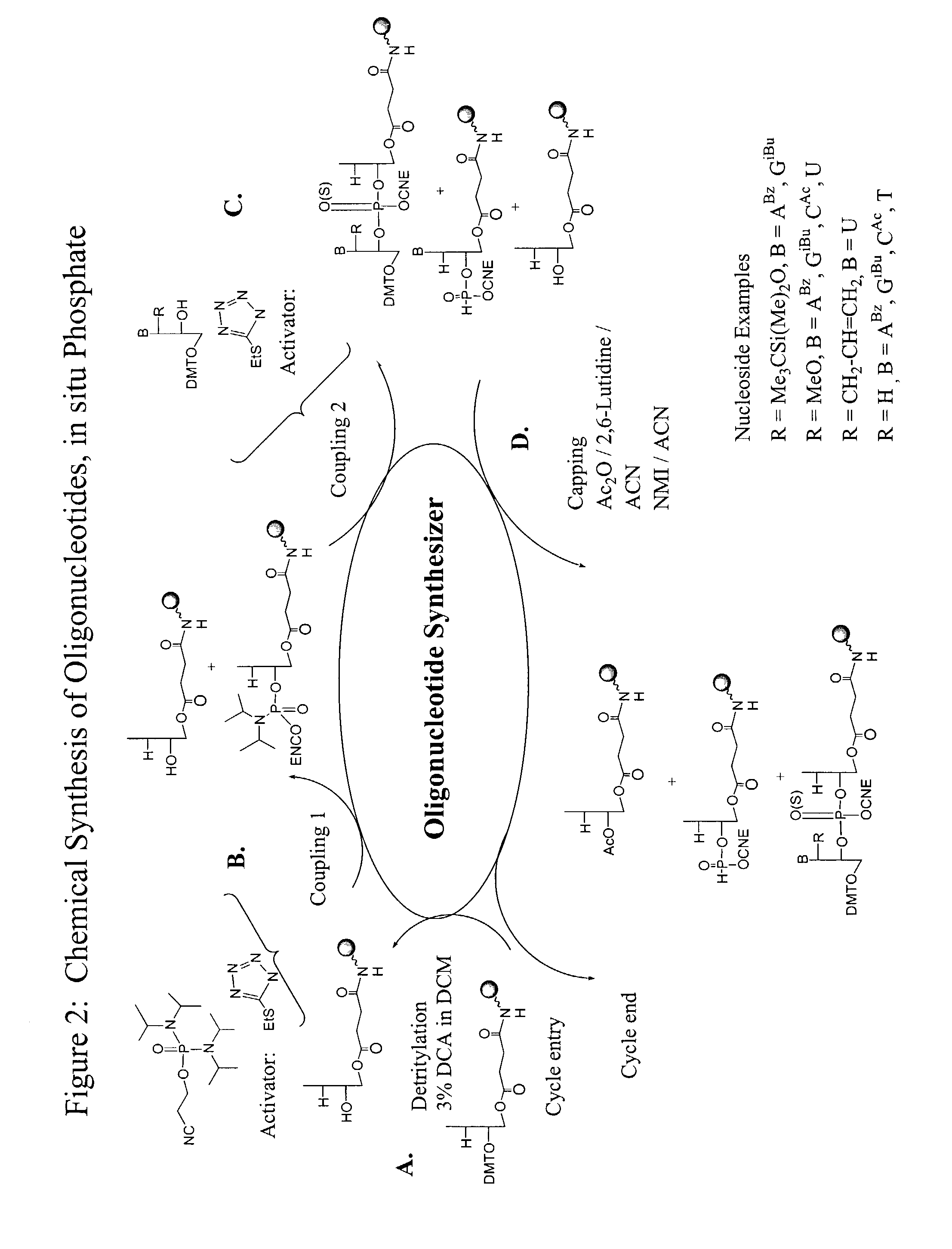
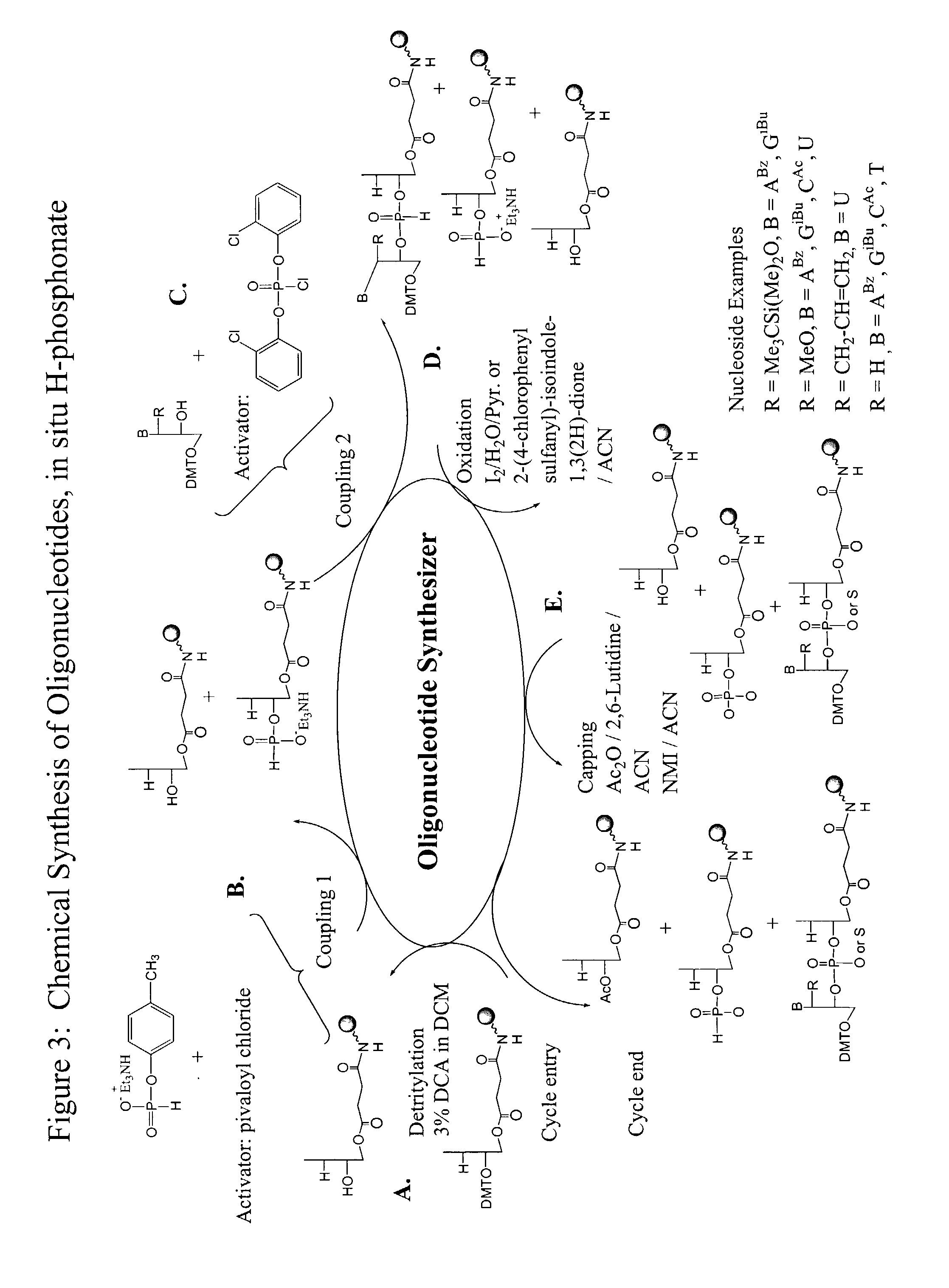
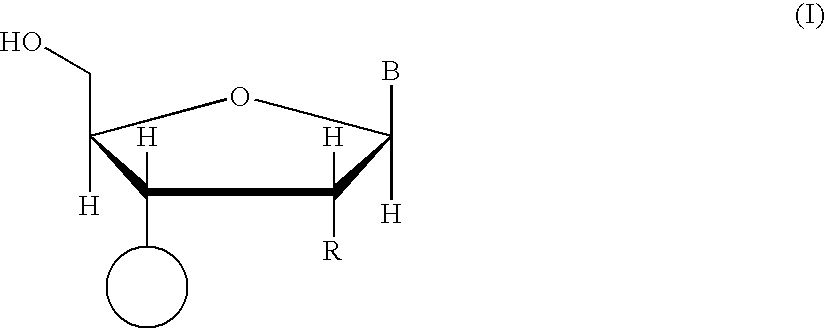
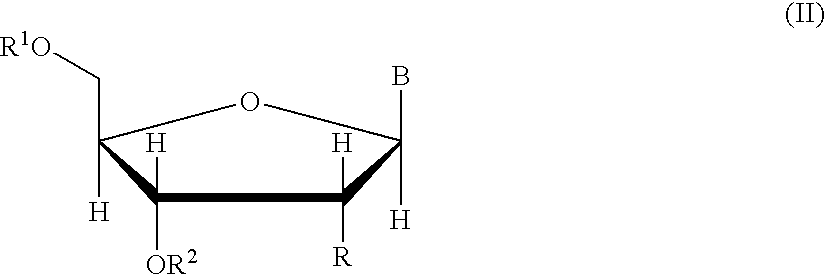
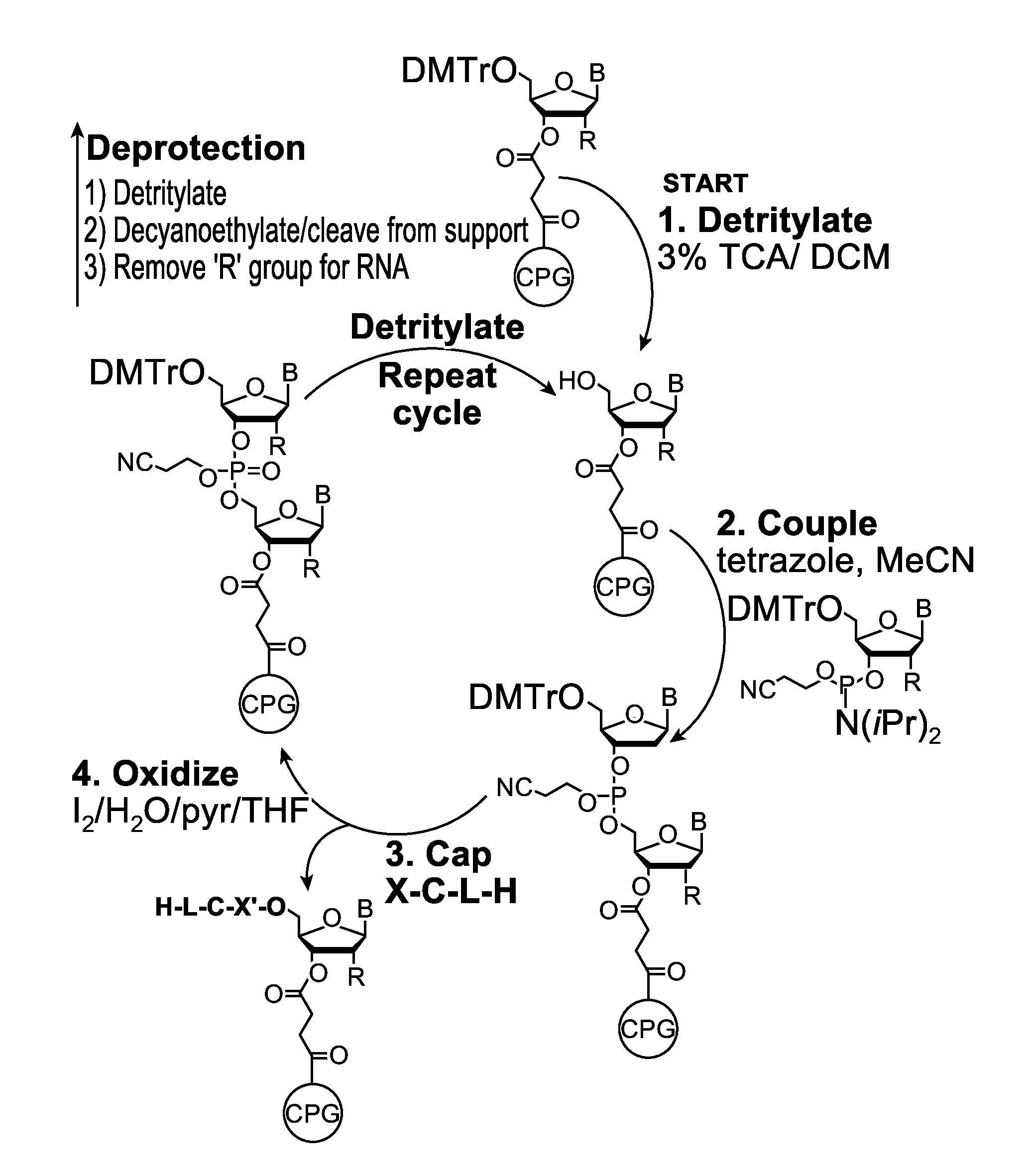
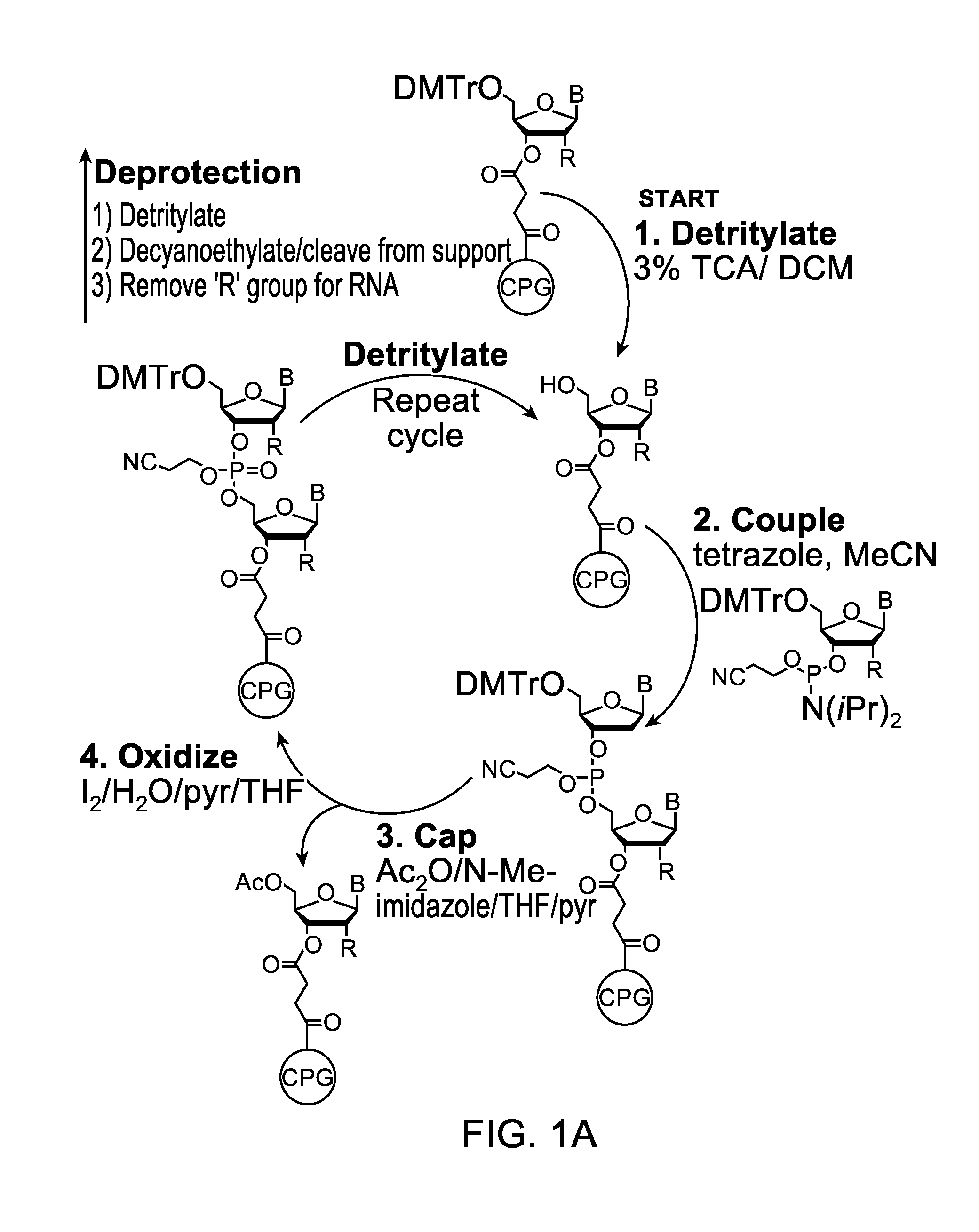
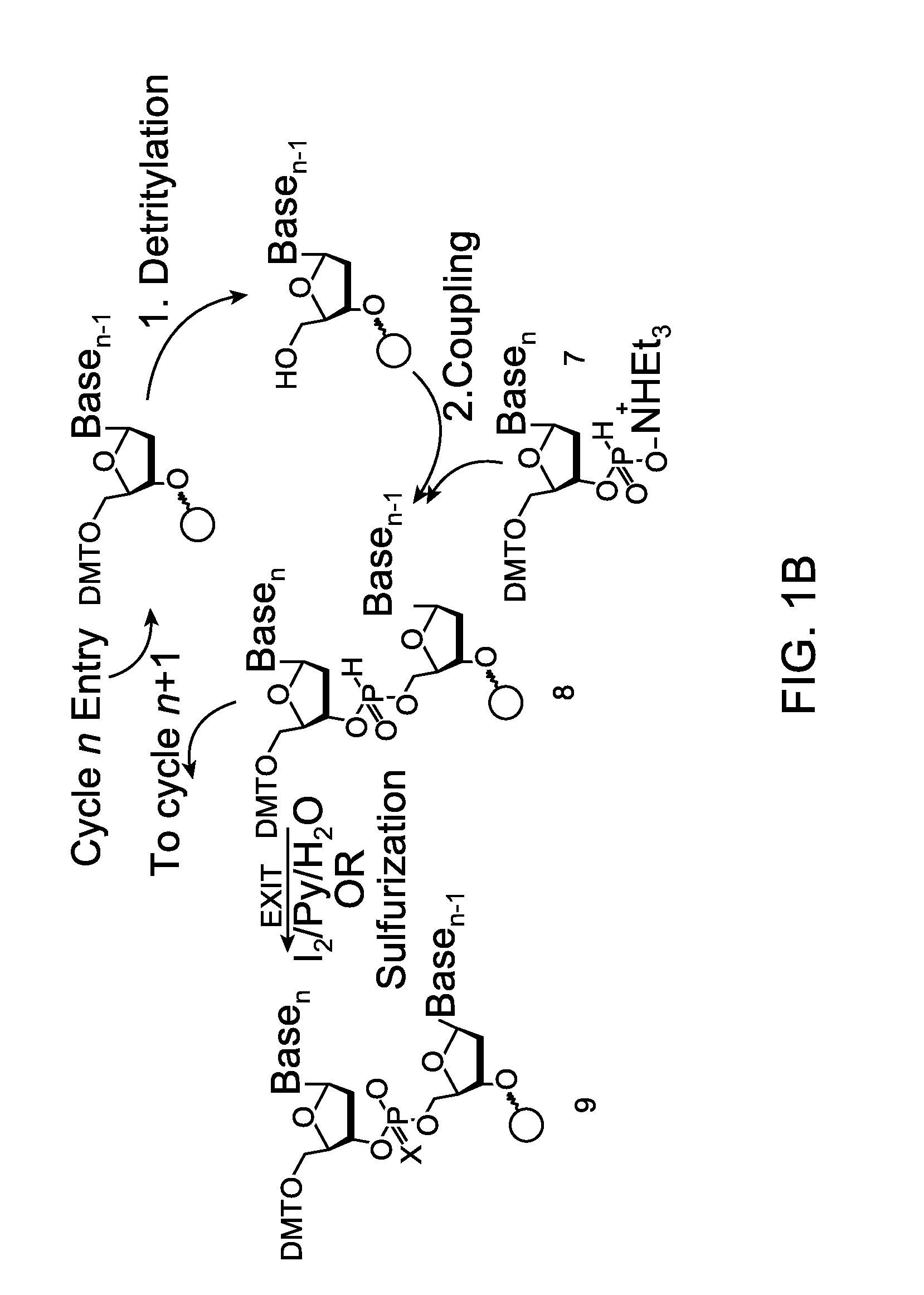
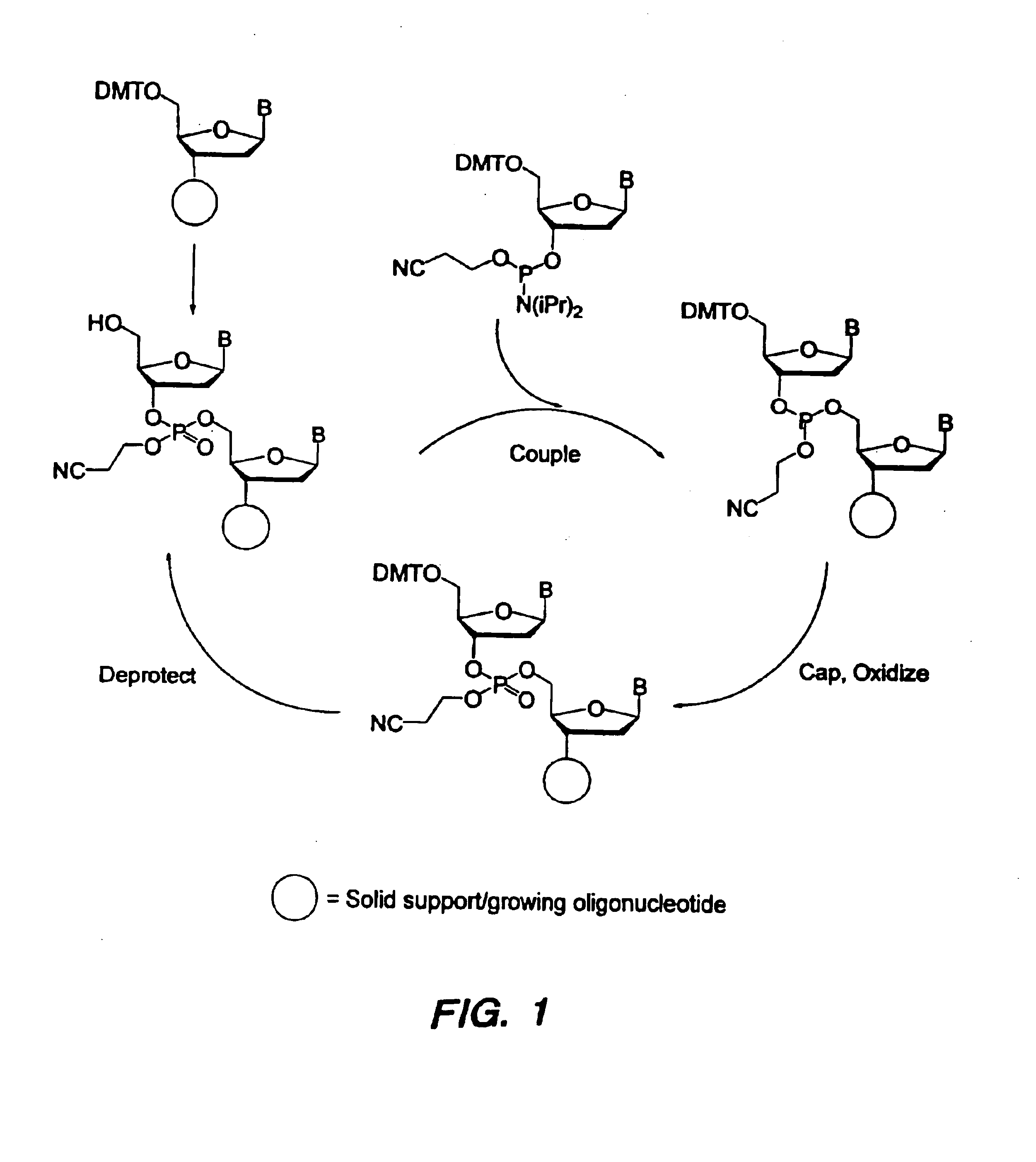
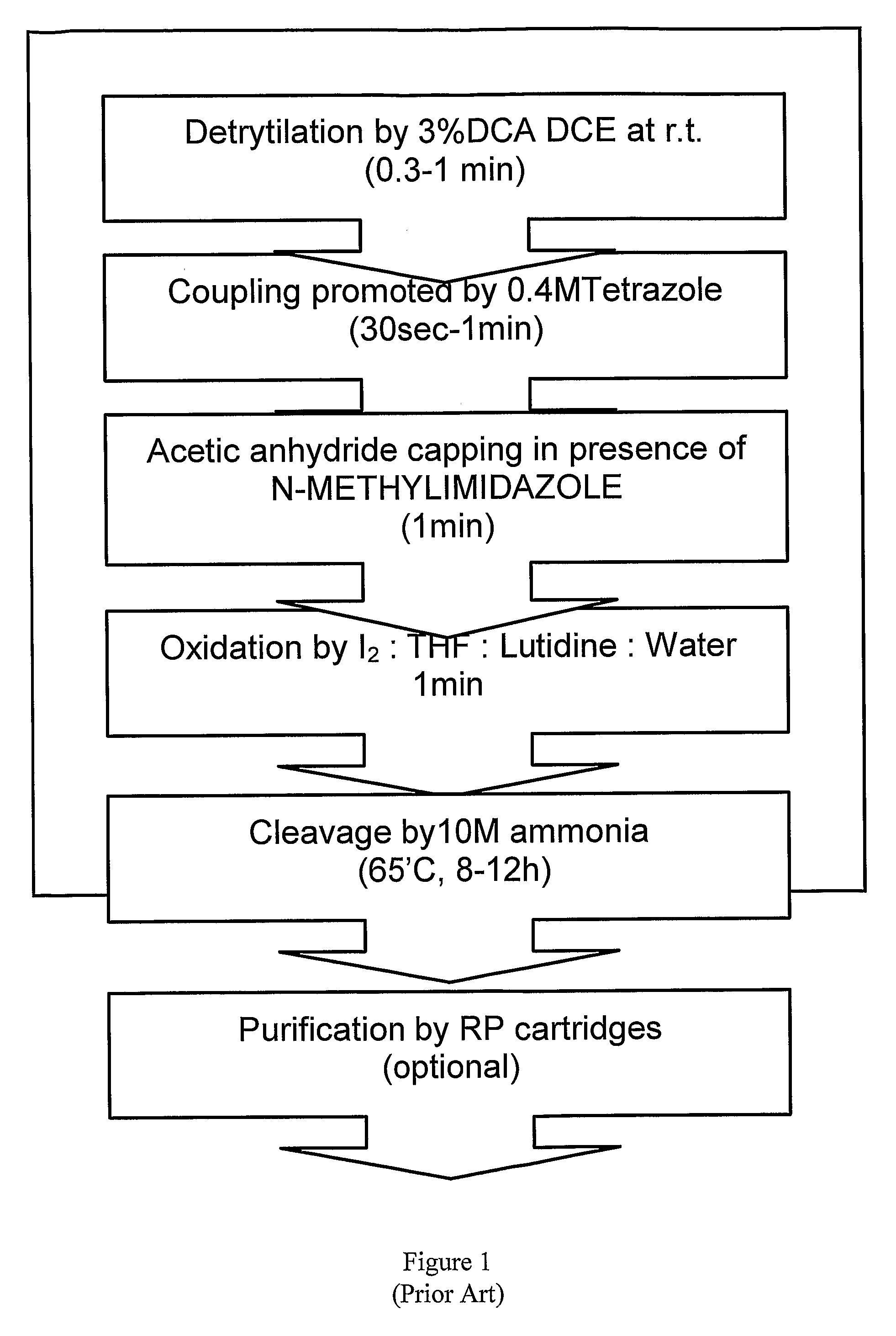
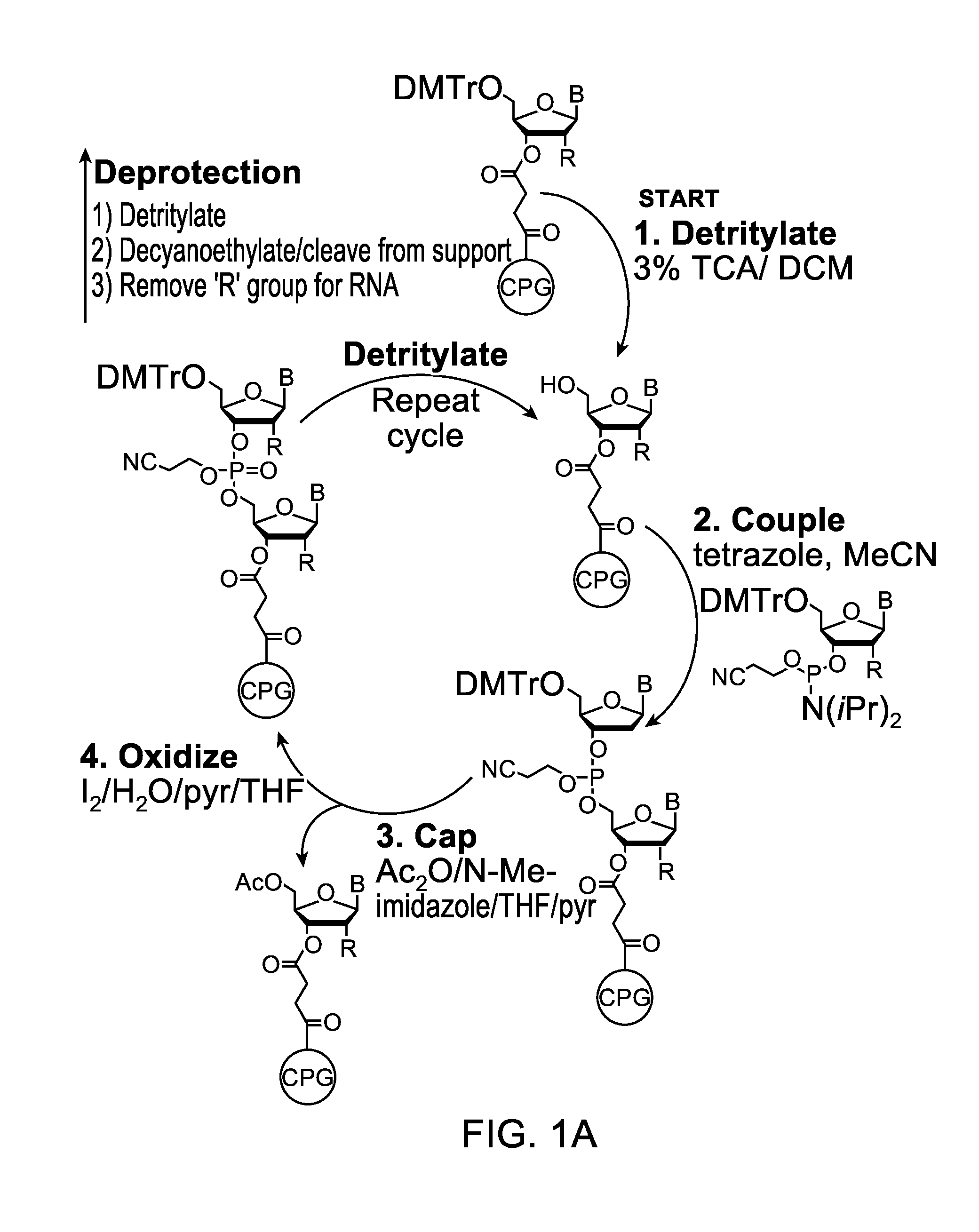
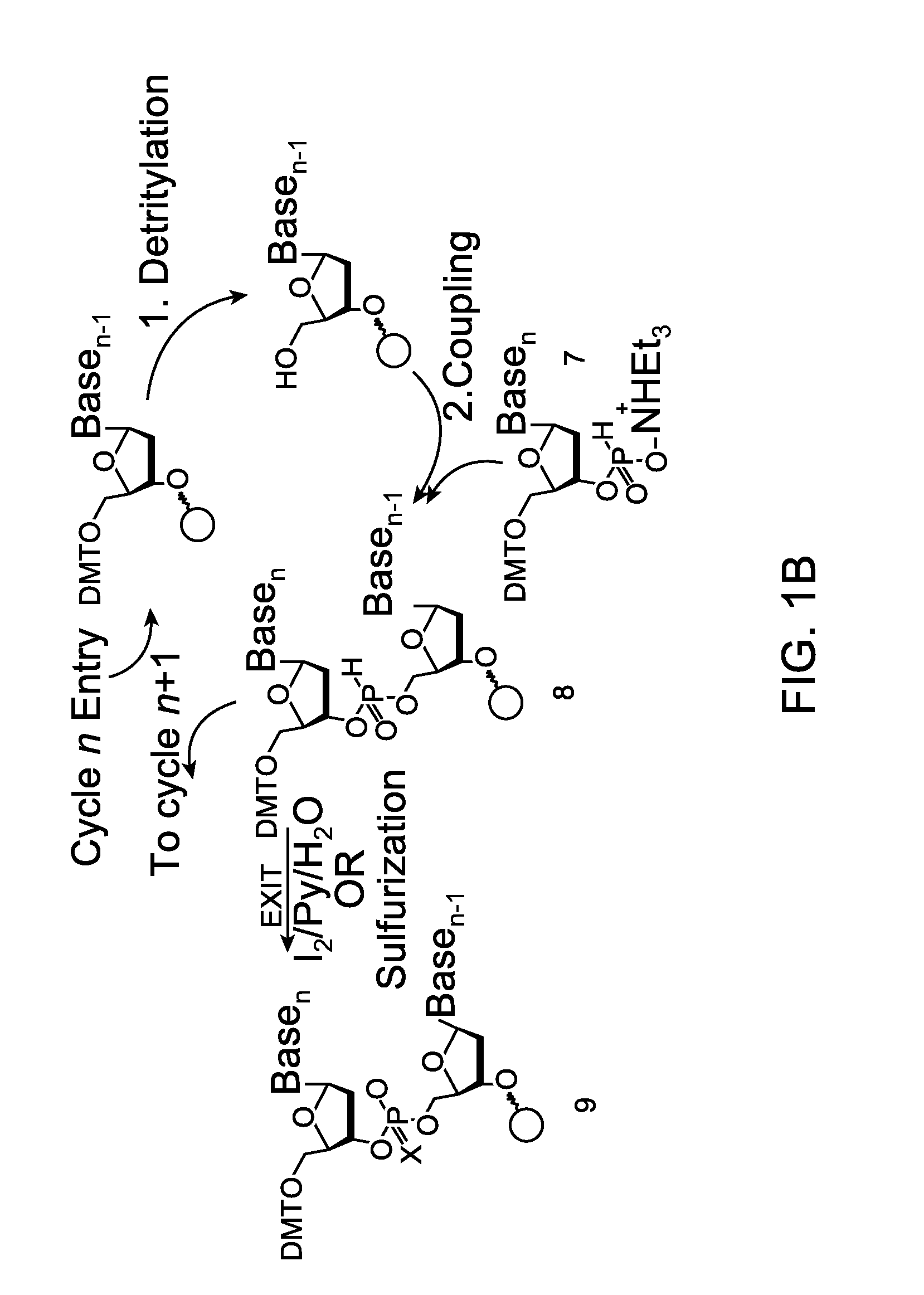
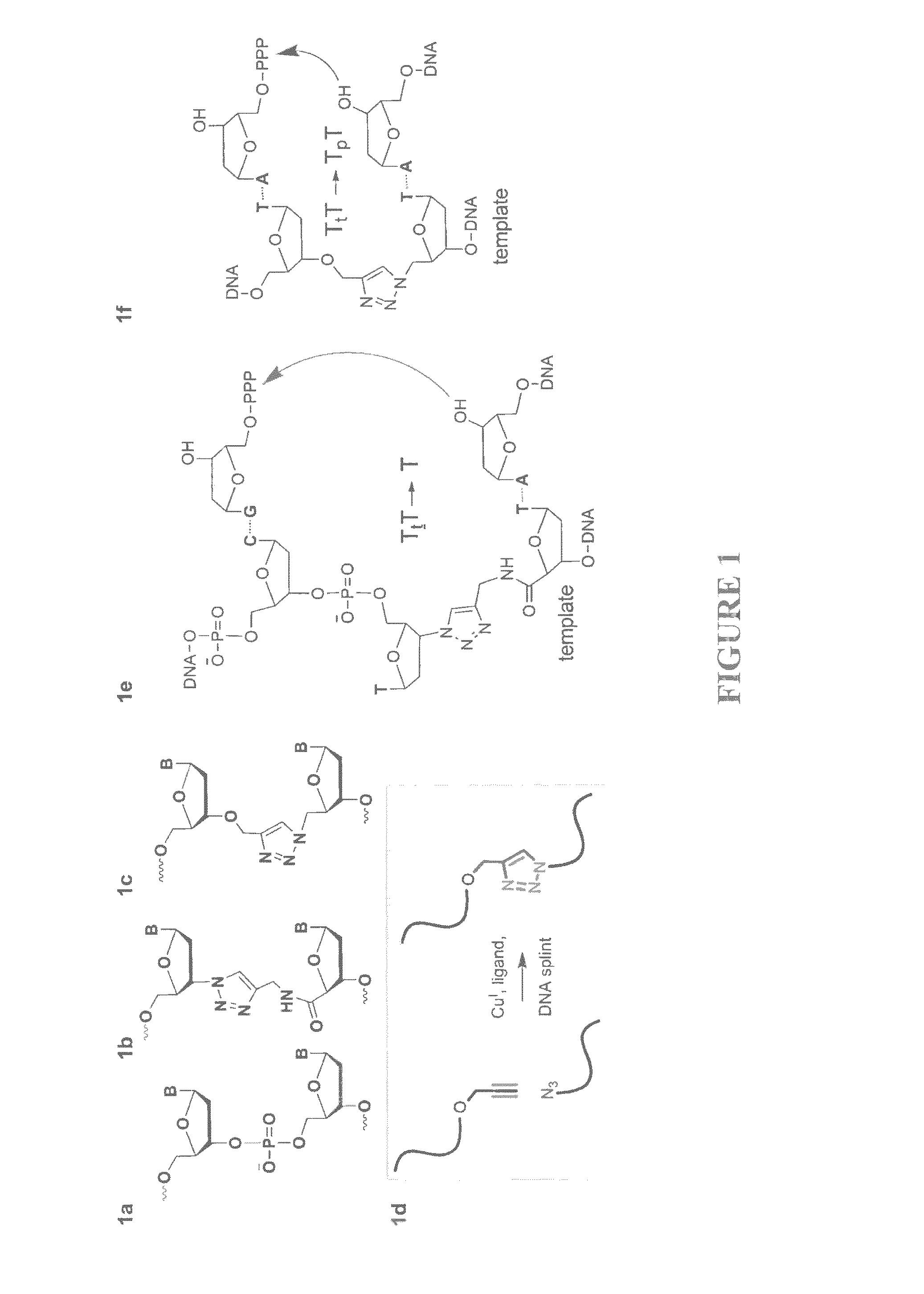
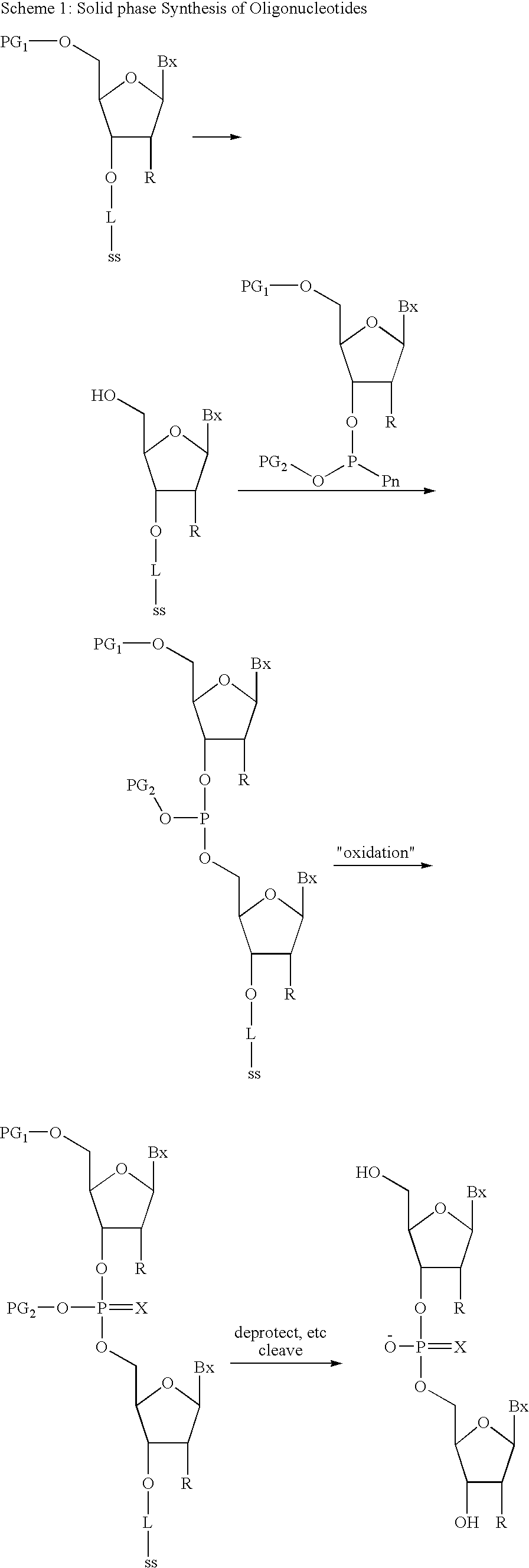
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is, most often, carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides (dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides (A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA.
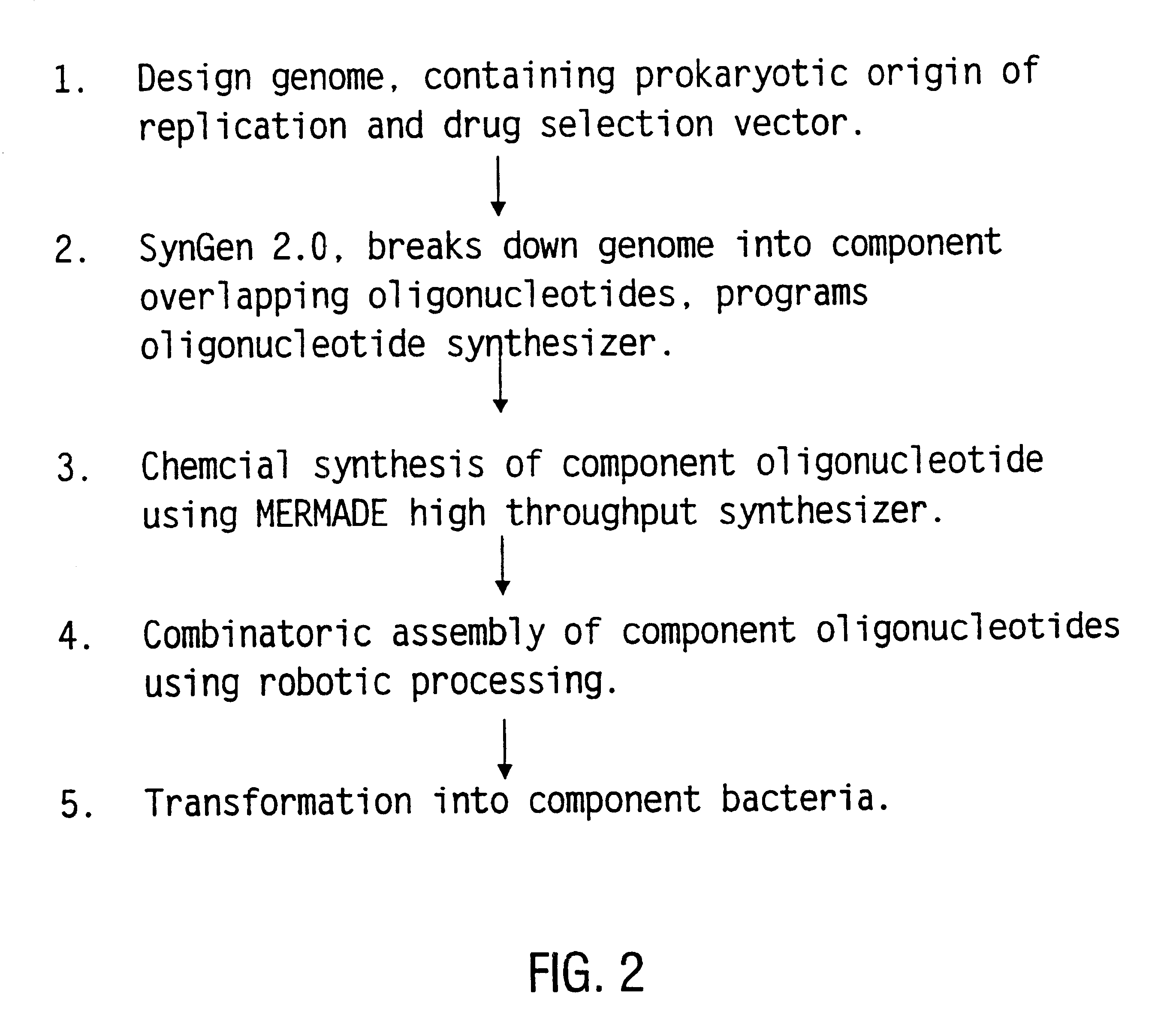
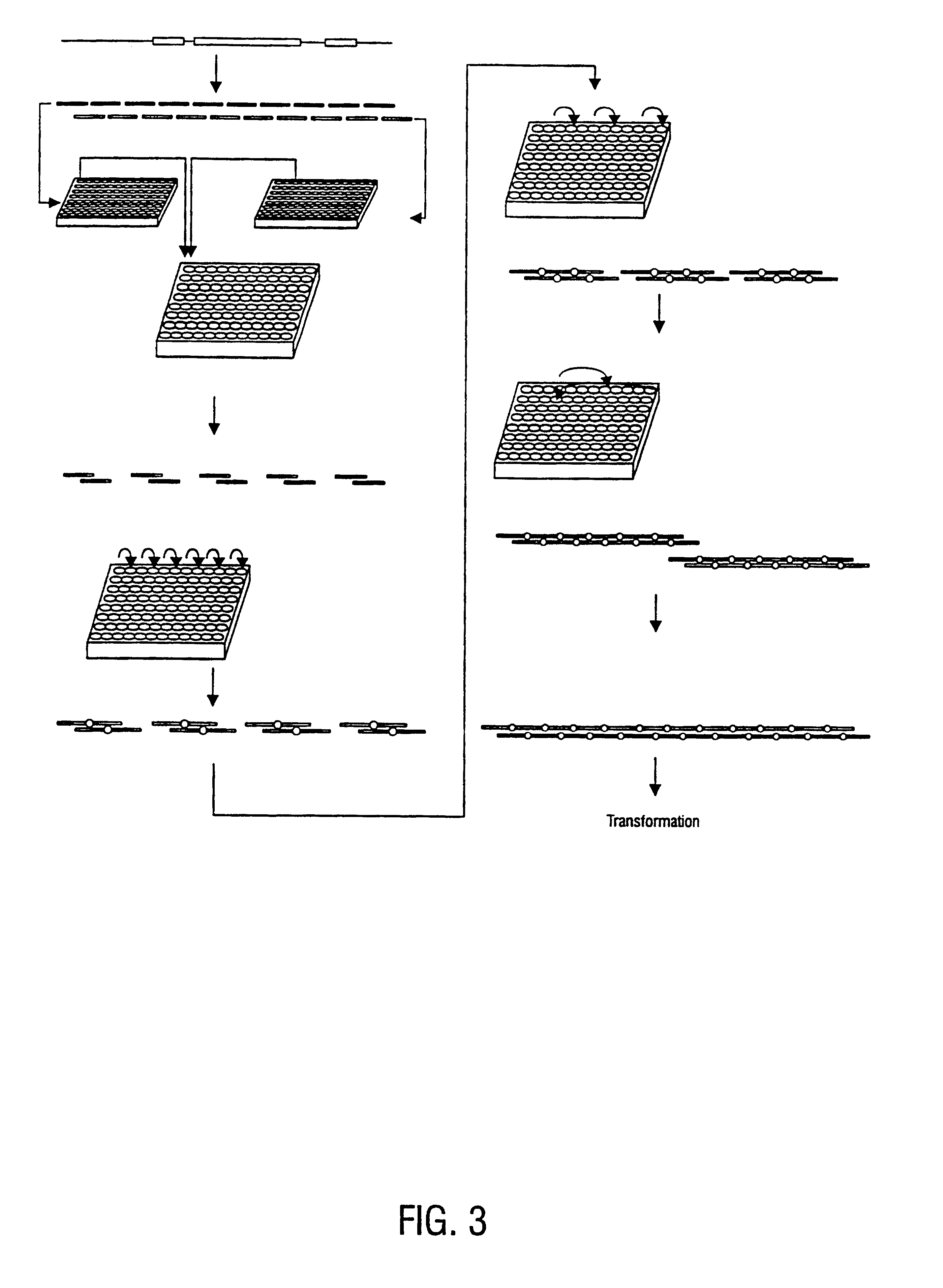
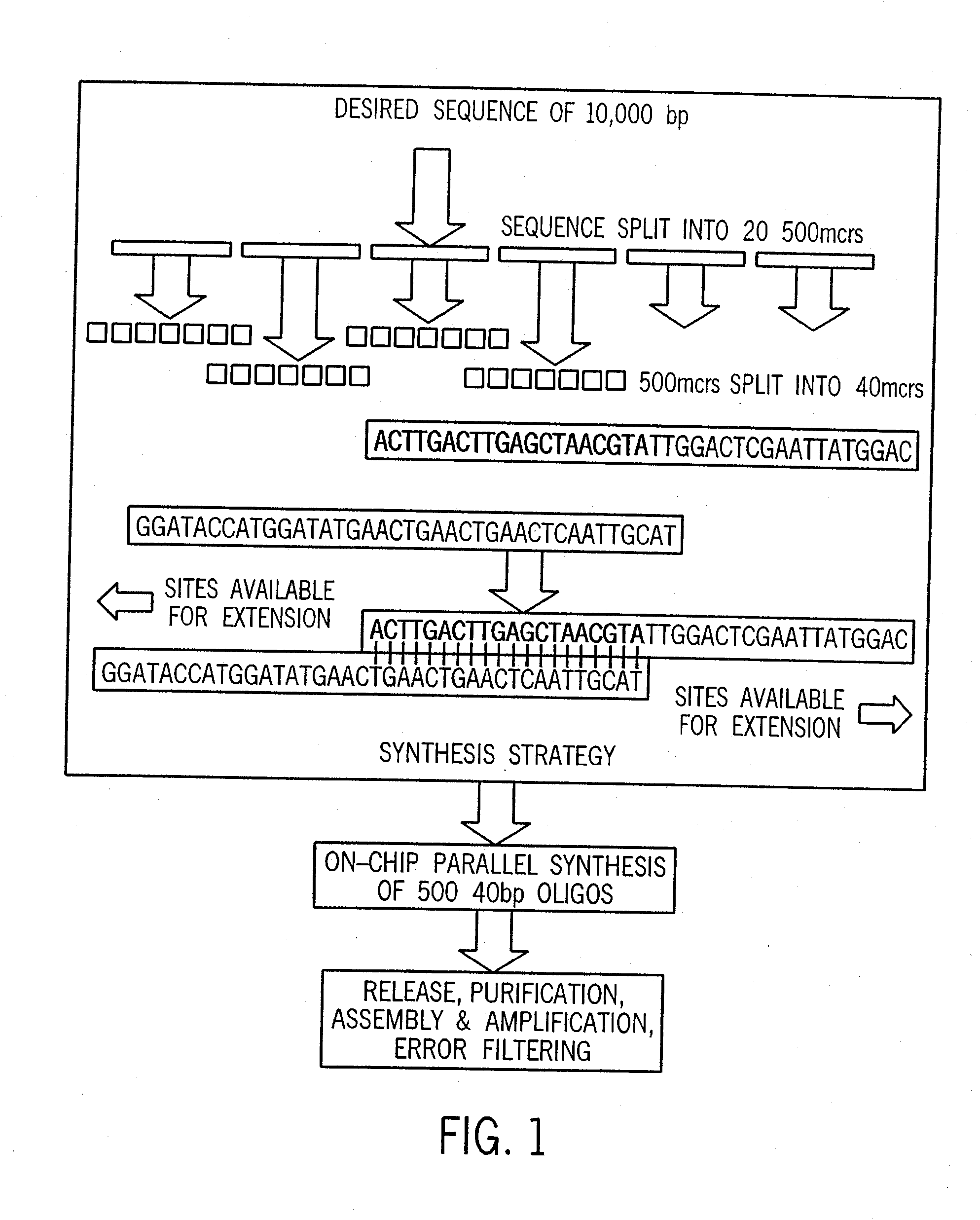
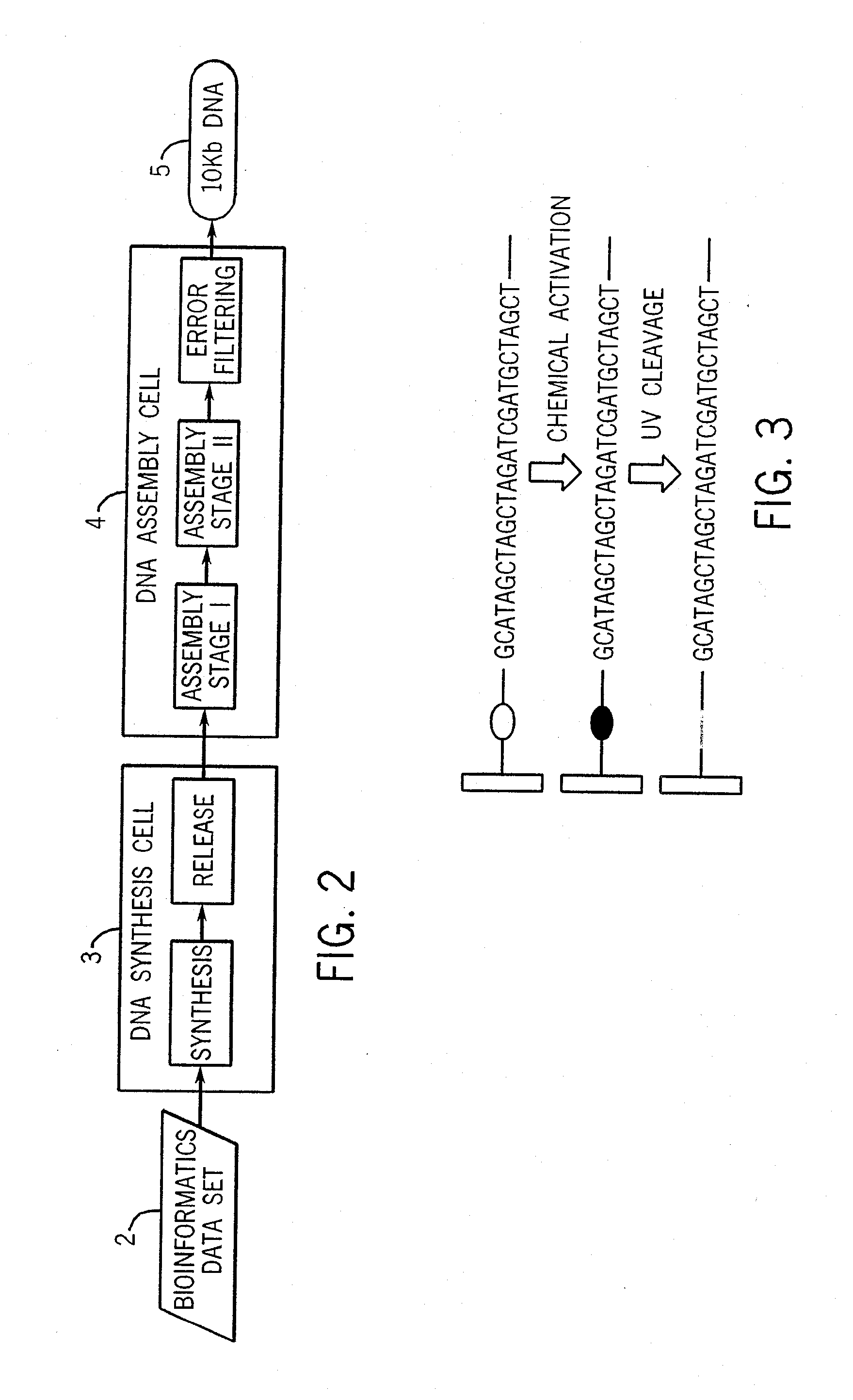
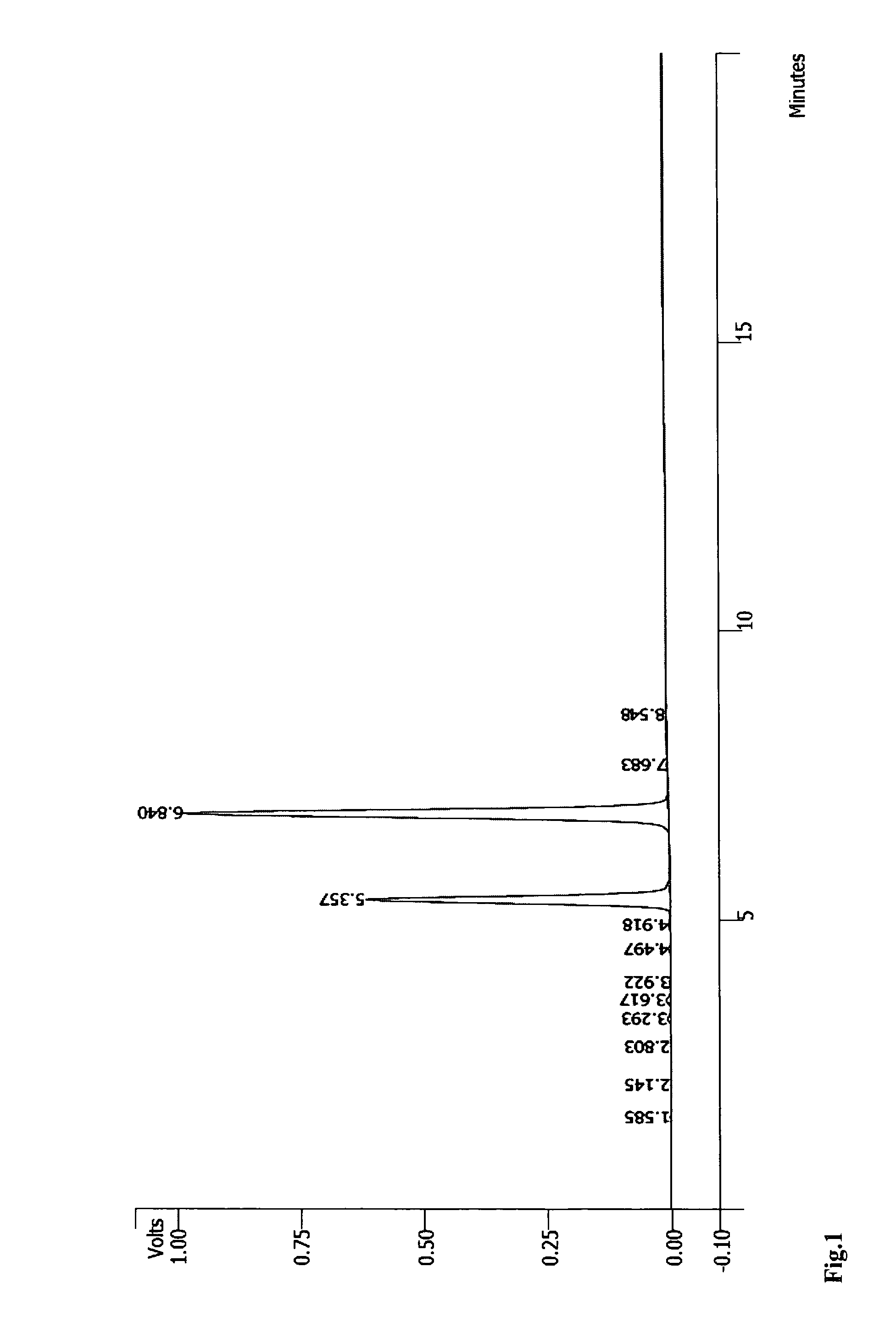
Method for the complete chemical synthesis and assembly of genes and genomes
InactiveUS6521427B1BiocideSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisHuman genome database
The present invention relates generally to the fields of oligonucleotide synthesis. More particularly, it concerns the assembly of genes and genomes of completely synthetic artificial organisms. Thus, the present invention outlines a novel approach to utilizing the results of genomic sequence information by computer directed gene synthesis based on computing on the human genome database. Specifically, the present invention contemplates and describes the chemical synthesis and resynthesis of genes defined by the genome sequence in a host vector and transfer and expression of these sequences into suitable hosts.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US) +3
Oligonucleotide synthesis with alternative solvents
ActiveUS7276599B2Efficient synthesisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateOligonucleotide synthesis
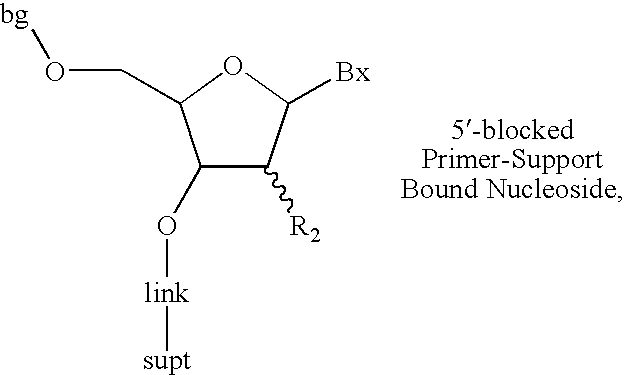
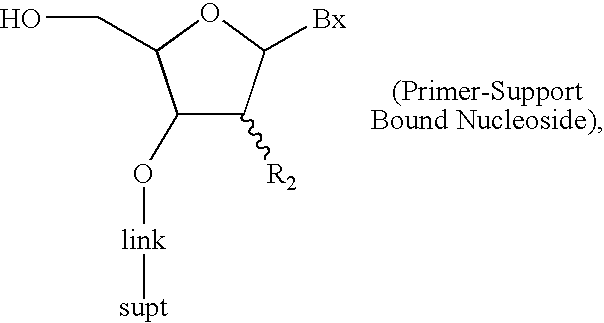
The invention provides for methods of manufacturing an oligonucleotide comprising a pentavalent phosphate triester. In particular, the method comprises providing a 5′ blocked-nucleoside, deblocking the 5′ blocked-nucleoside to form a 5′ OH-nucleoside, coupling the 5′ OH-nucleoside with a phosphoramidite to form and oligonucleotide comprising a trivalent phosphite triester; and oxidizing the oligonucleotide comprising a trivalent phosphite triester to the oligonucleotide comprising a pentavalent phosphate triester. In some embodiments, the wash between any of the steps above is with at least one solvent wash comprising a toluene.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Compounds and methods for the characterization of oligonucleotides
ActiveUS7427675B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide synthesisOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to oligonucleotide synthesis. In particular, the present invention provides methods for characterizing samples useful for making oligonucleotides.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
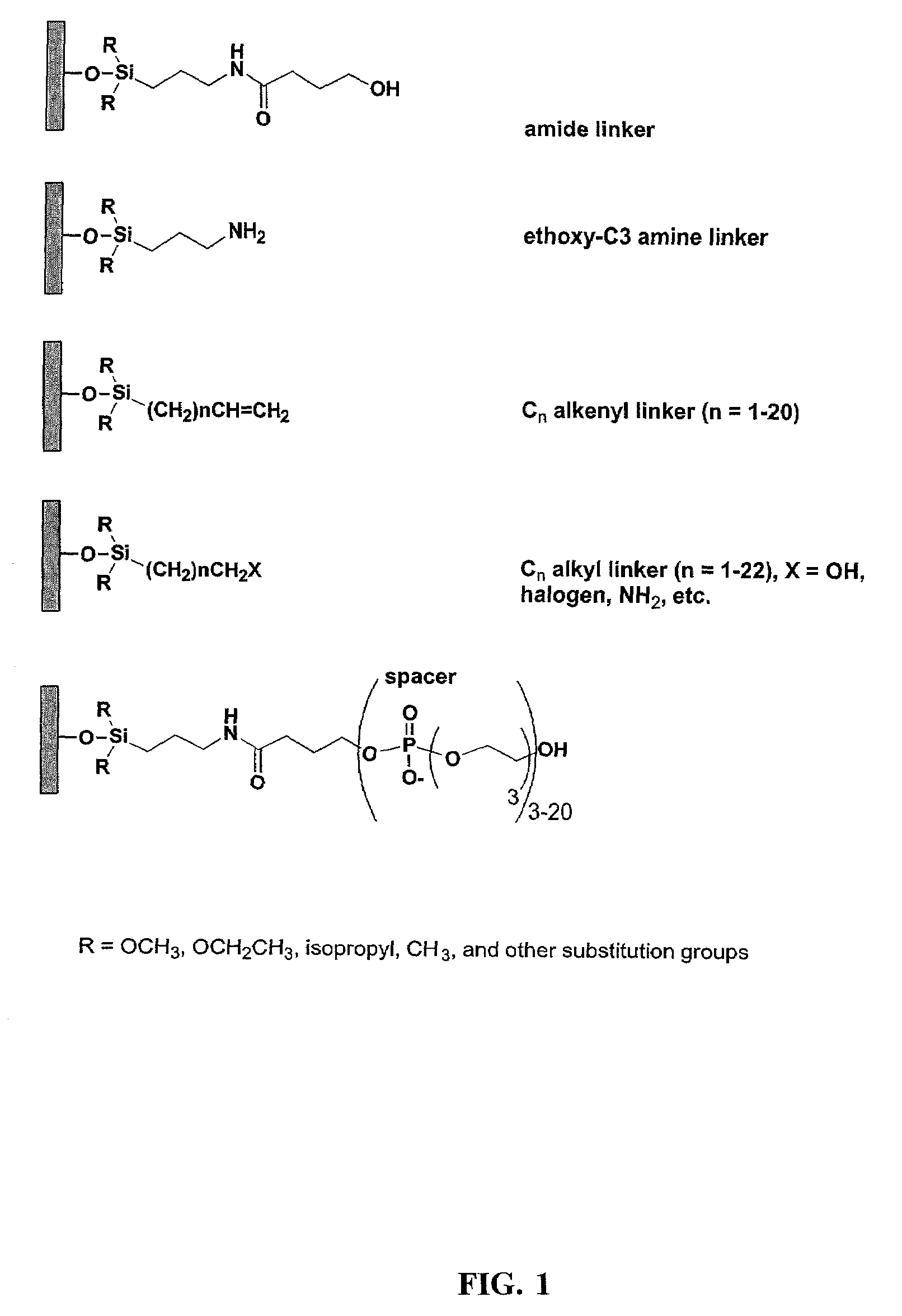
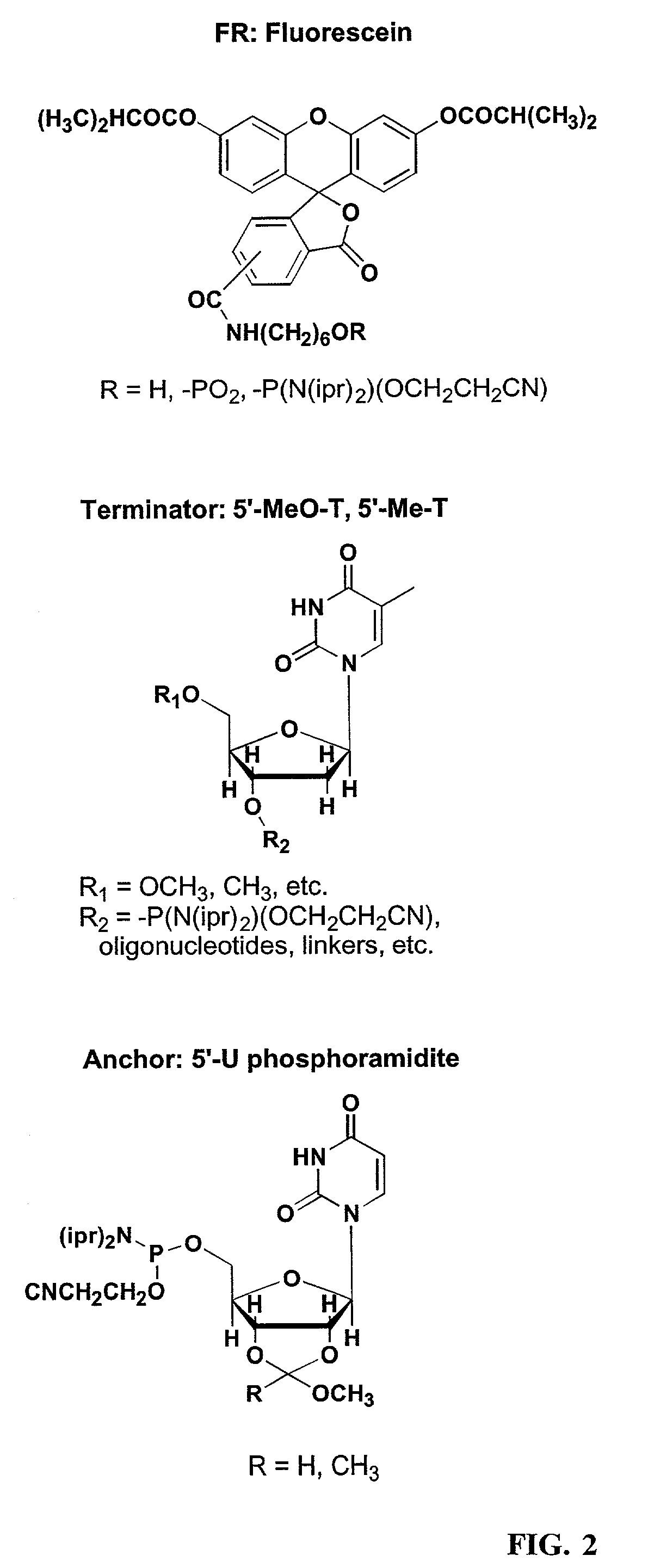
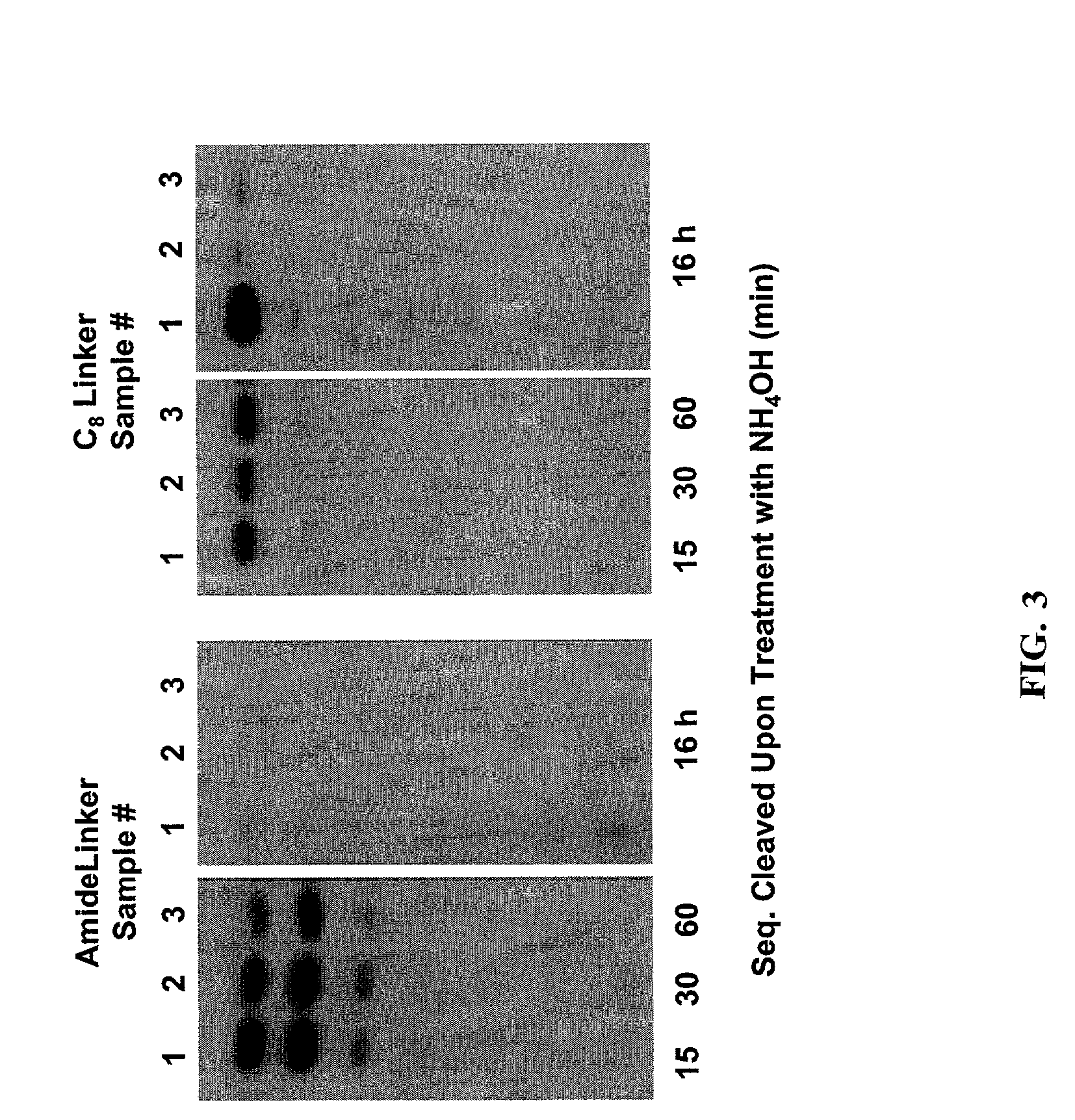
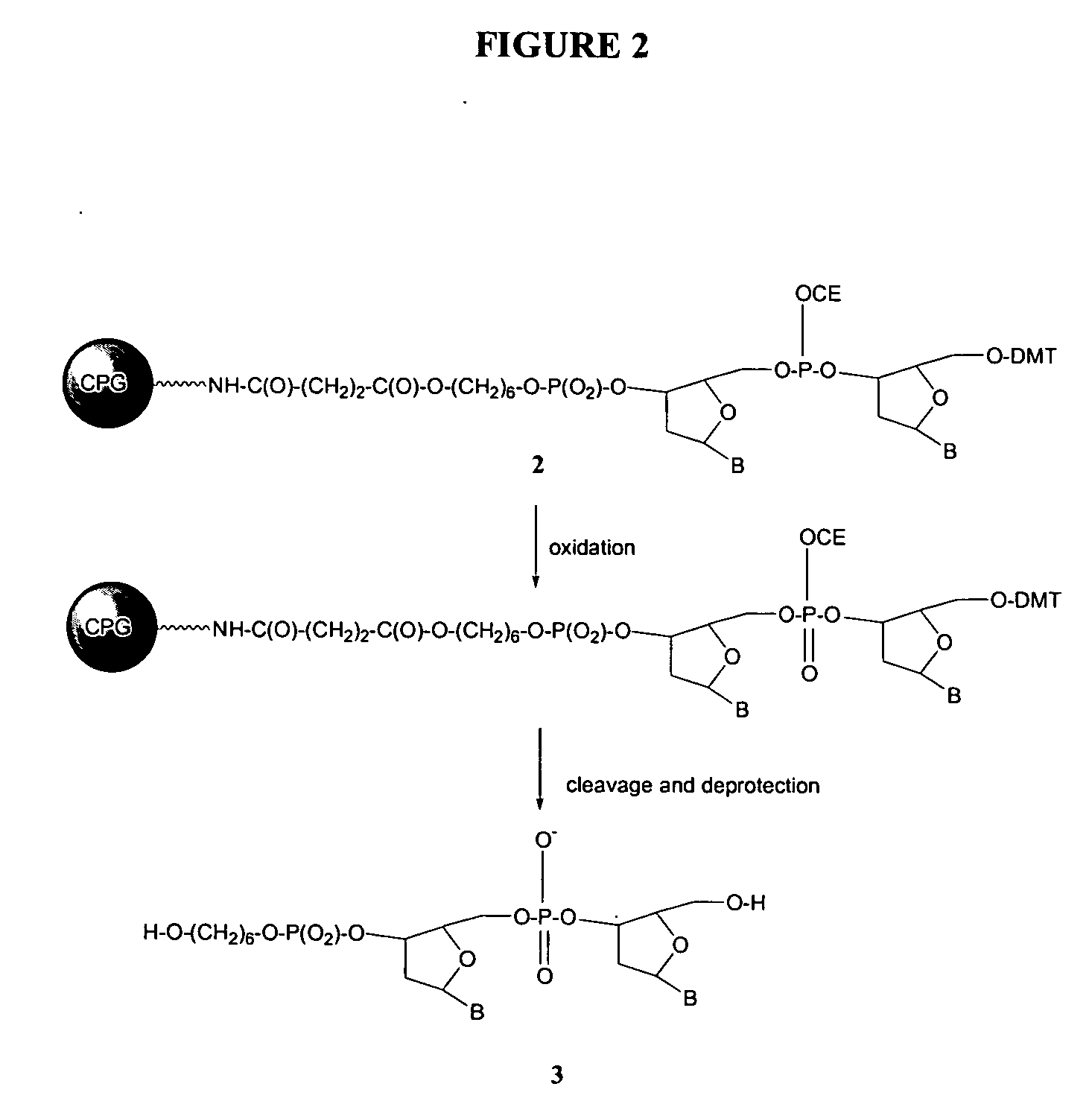
Linkers and co-coupling agents for optimization of oligonucleotide synthesis and purification on solid supports
InactiveUS7211654B2Promote hydrolysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSolid surfaceTime-Consuming
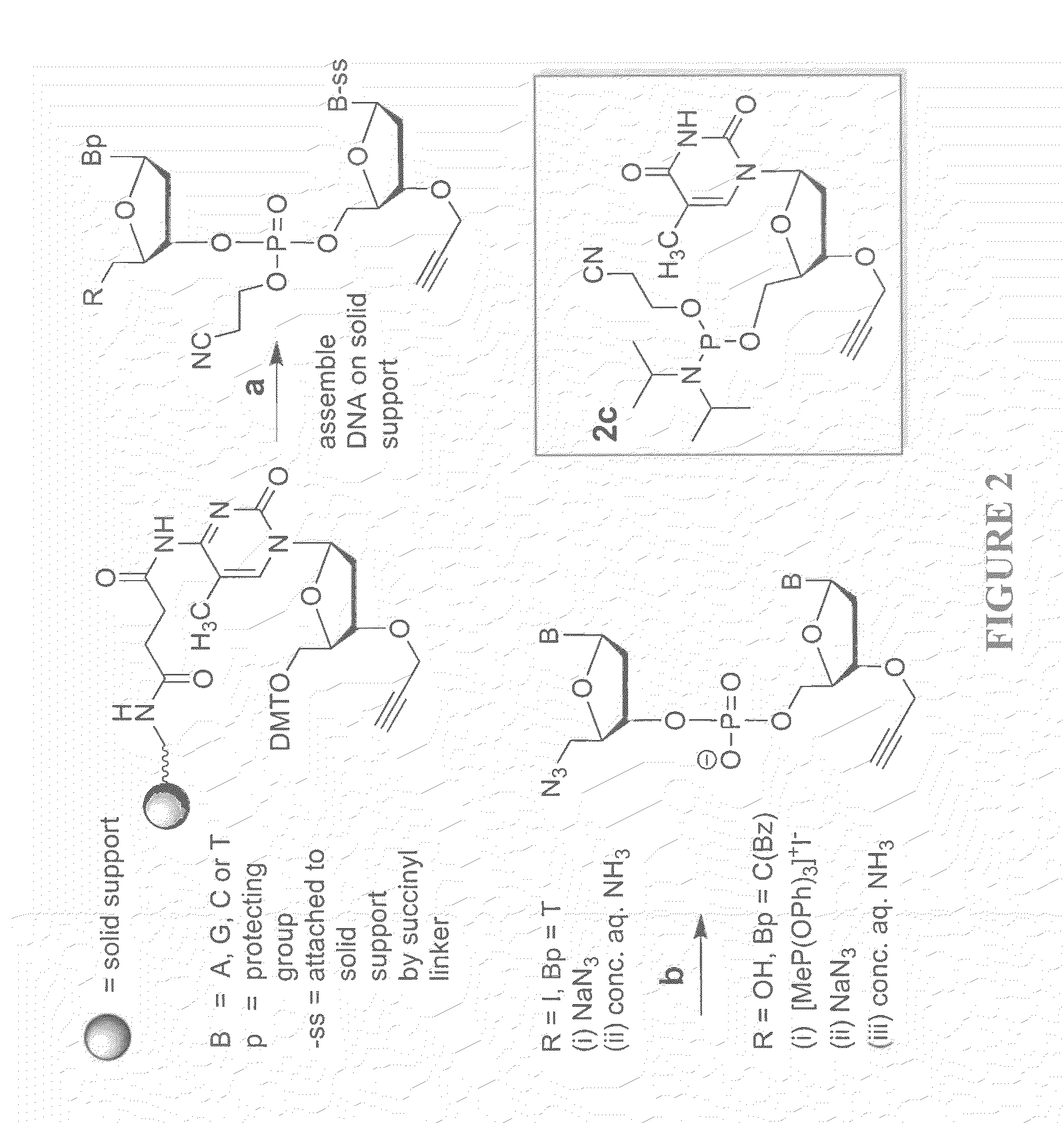
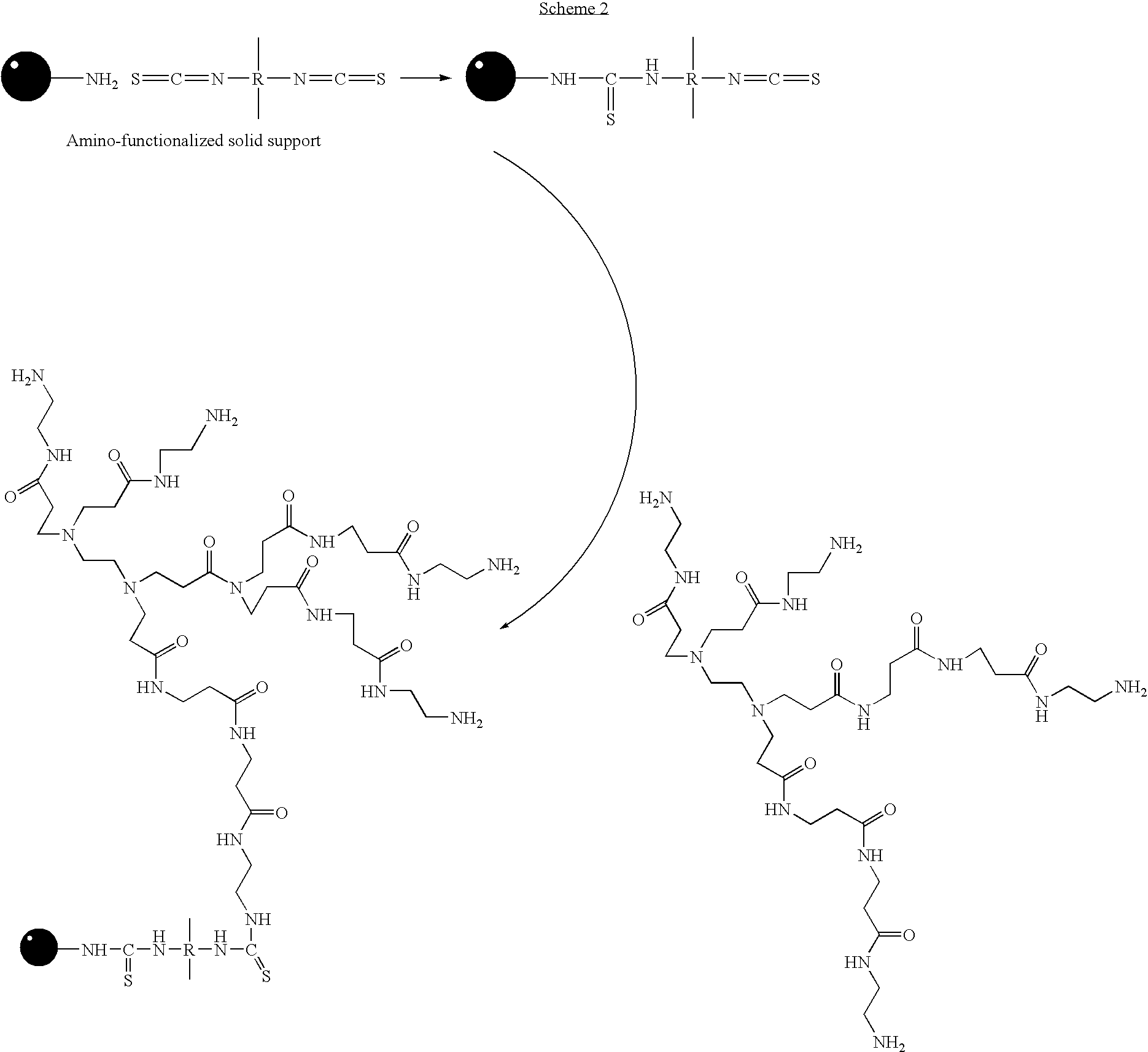
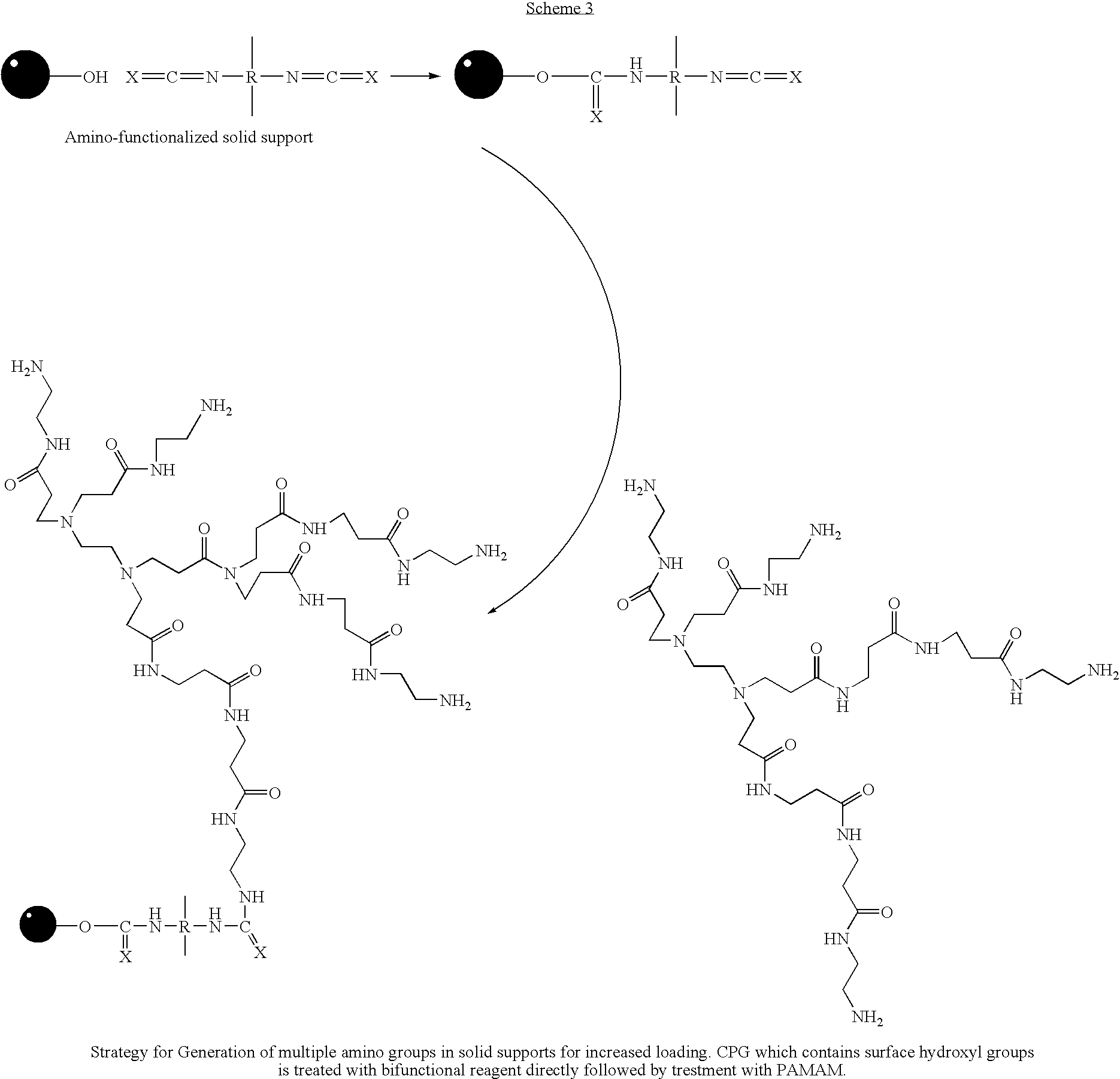
A method of modulation of synthesis capacity on and cleavage properties of synthetic oligomers from solid support is described. The method utilizes linker molecules attached to a solid surface and co-coupling agents that have similar reactivities to the coupling compounds with the surface functional groups. The preferred linker molecules provide an increased density of polymers and more resistance to cleavage from the support surface. The method is particularly useful for synthesis of oligonucleotides, oligonucleotides microarrays, peptides, and peptide microarrays. The stable linkers are also coupled to anchor molecules for synthesis of DNA oligonucleotides using on support purification, eliminating time-consuming chromatography and metal cation presence. Oligonucleotides thus obtained can be directly used for mass analysis, DNA amplification and ligation, hybridization, and many other applications.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Programmable oligonucleotide synthesis
ActiveUS8173368B2Reduce yieldSynthesis is longSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligonucleotide synthesisSynthetic nucleic acid
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Methods and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS7205399B1Avoid insufficient lengthSufficient hybridizationSugar derivativesCombinatorial chemistryOligonucleotide synthesis
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides using carbonate protecting groups and alpha-effect nucleophile deprotection
The invention provides methods for synthesizing oligonucleotides using nucleoside monomers having carbonate protected hydroxyl groups that are deprotected with α-effect nucleophiles. The α-effect nucleophile irreversibly cleave the carbonate protecting groups while simultaneously oxidizing the internucleotide phosphite triester linkage to a phosphodiester linkage. The procedure may be carried out in aqueous solution at neutral to mildly basic pH. The method eliminates the need for separate deprotection and oxidation steps, and, since the use of acid to remove protecting groups is unnecessary, acid-induced depurination is avoided. Fluorescent or other readily detectable carbonate protecting groups can be used, enabling monitoring of individual reaction steps during oligonucleotide synthesis. The invention is particularly useful in the highly parallel, microscale synthesis of oligonucleotides.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Novel methods for the synthesis and purification of oligomers
InactiveUS20130137861A1Carbamic acid derivatives preparationSugar derivativesOligomerOligonucleotide synthesis
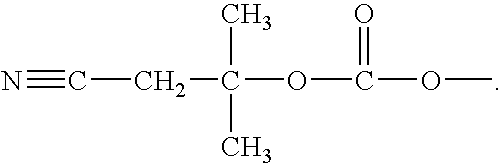
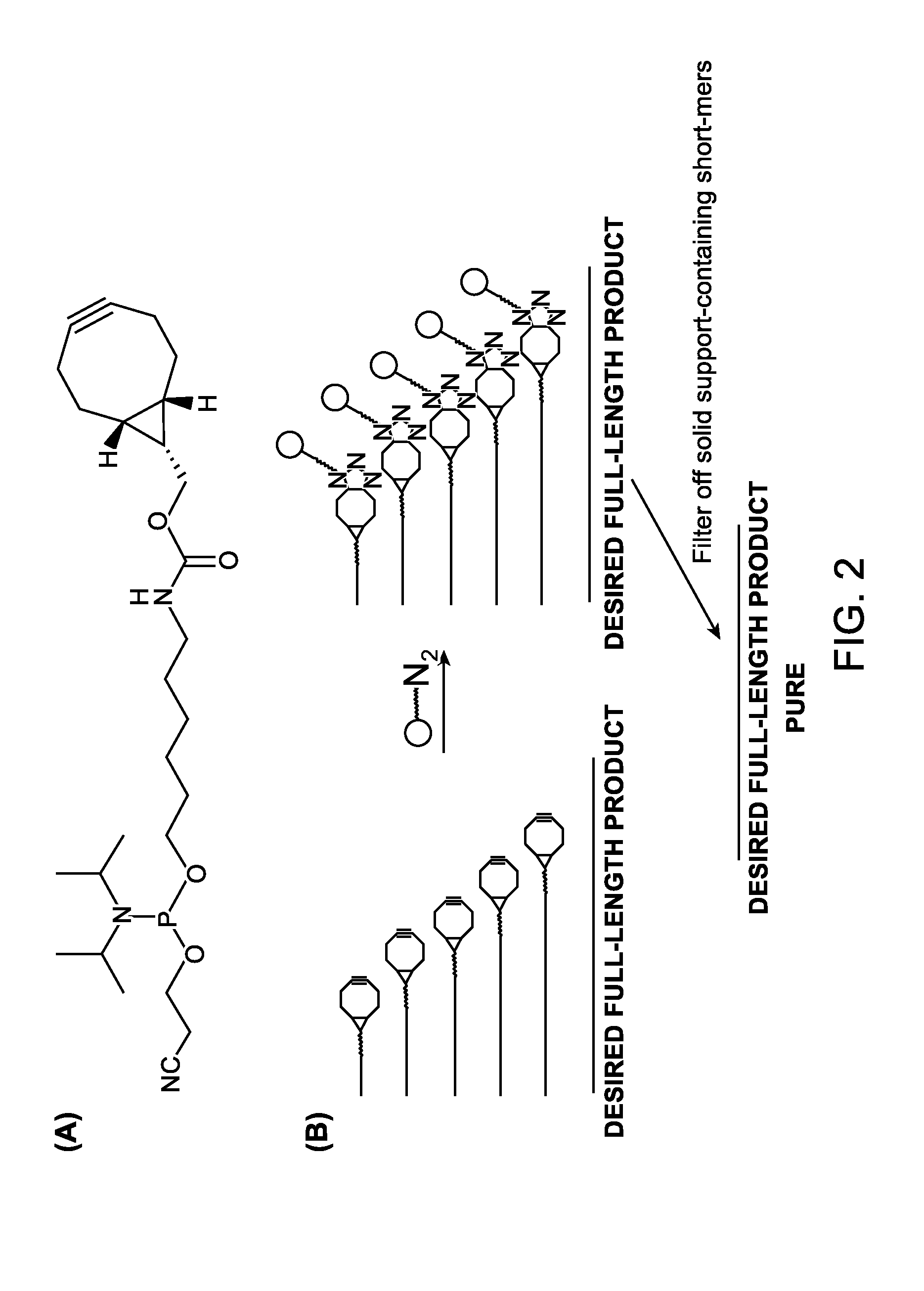
A reagent for oligonucleotide synthesis or purification, wherein the reagent has a structure of:X—C-L-H (Formula A)wherein X is a phosphoramidite group, an H-phosphonate group, an acetal group, or an isocyanate; C is a direct bond or a cleavable adaptor represented by —Ca-Cb—; L is a hydrocarbyl chain; and H is a terminal alkyne or an activated cyclooctyne. The reagent of Formula (A) can be used in the synthesis and purification of oligonucleotides.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method of synthesizing polynucleotides using ionic liquids
A method of synthesizing polynucleotides is disclosed. The method involves contacting a first nucleotide with a selected reactive group in the presence of an ionic liquid. The selected reactive group may be on a second nucleotide, a polynucleotide, or on a moiety on an insoluble substrate, for example in an oligonucleotide synthesizer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Compositions, Methods and Apparatus for Oligonucleotides Synthesis
ActiveUS20160122755A1Reduce error rateImprove fidelityNucleotide librariesLibrary member identificationOligonucleotide synthesisBioinformatics
Owner:GEN9
Oligonucleotide ligation
ActiveUS20130046084A1Efficient methodImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSynthesis methodsAlkyne
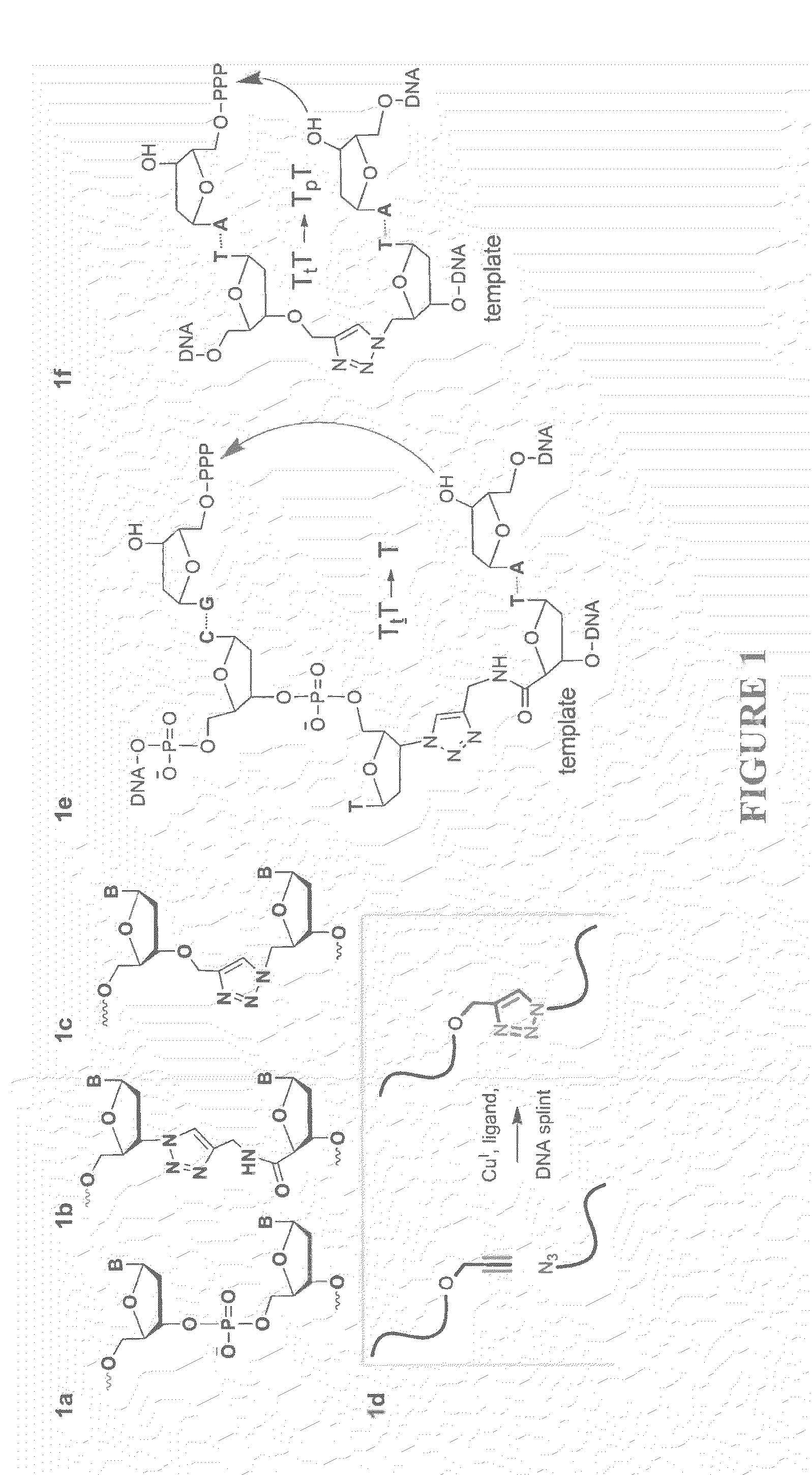
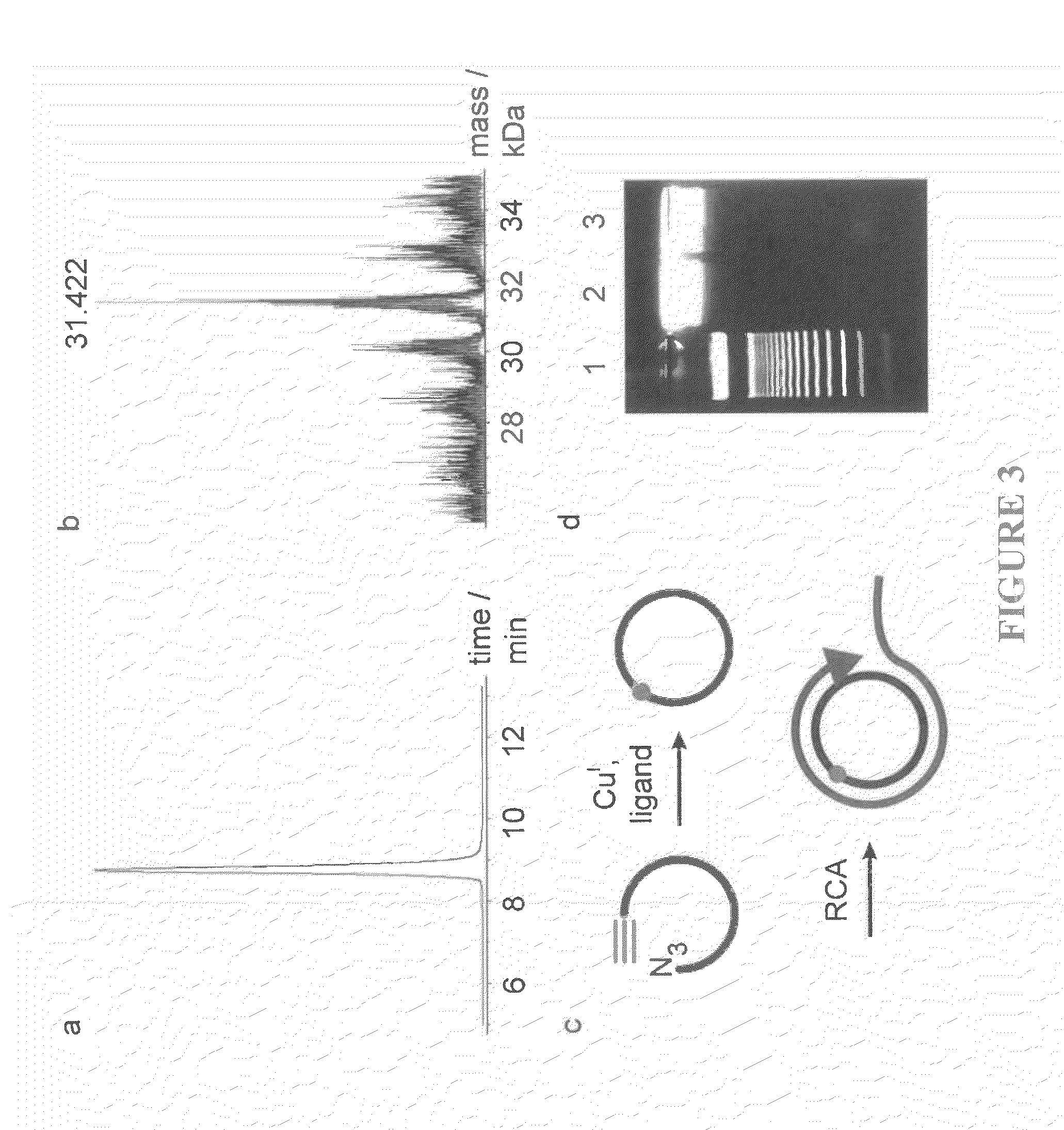
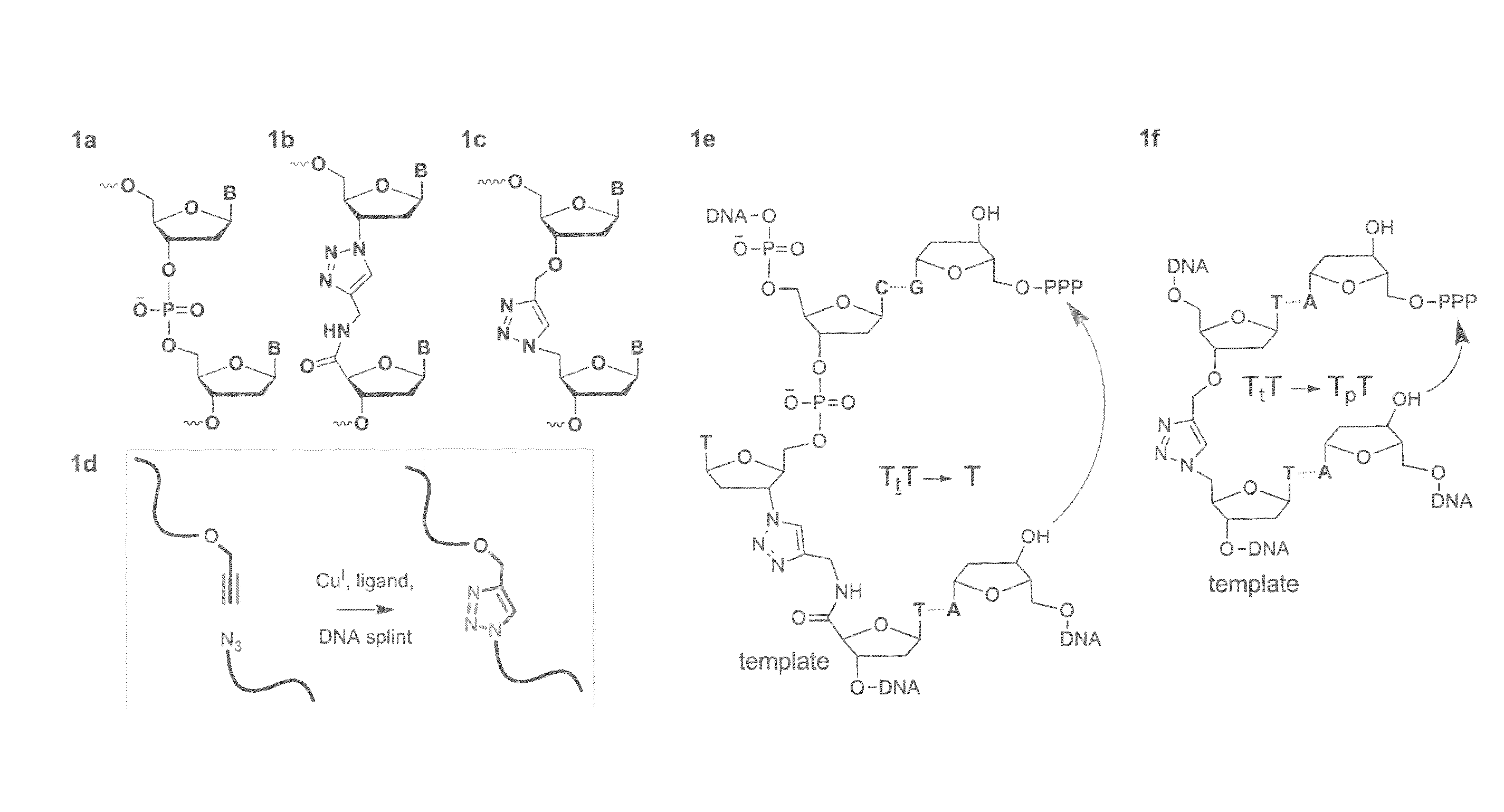
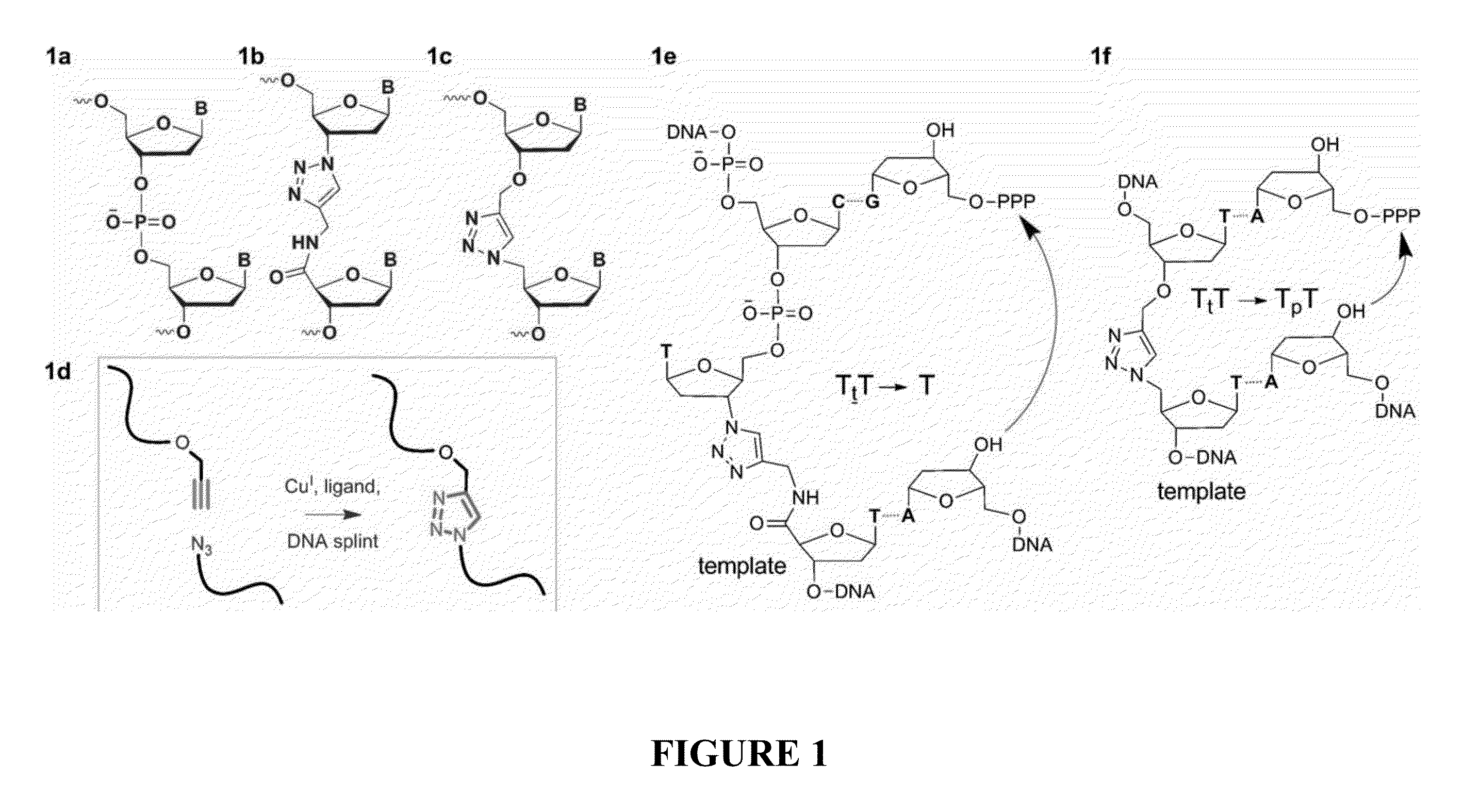
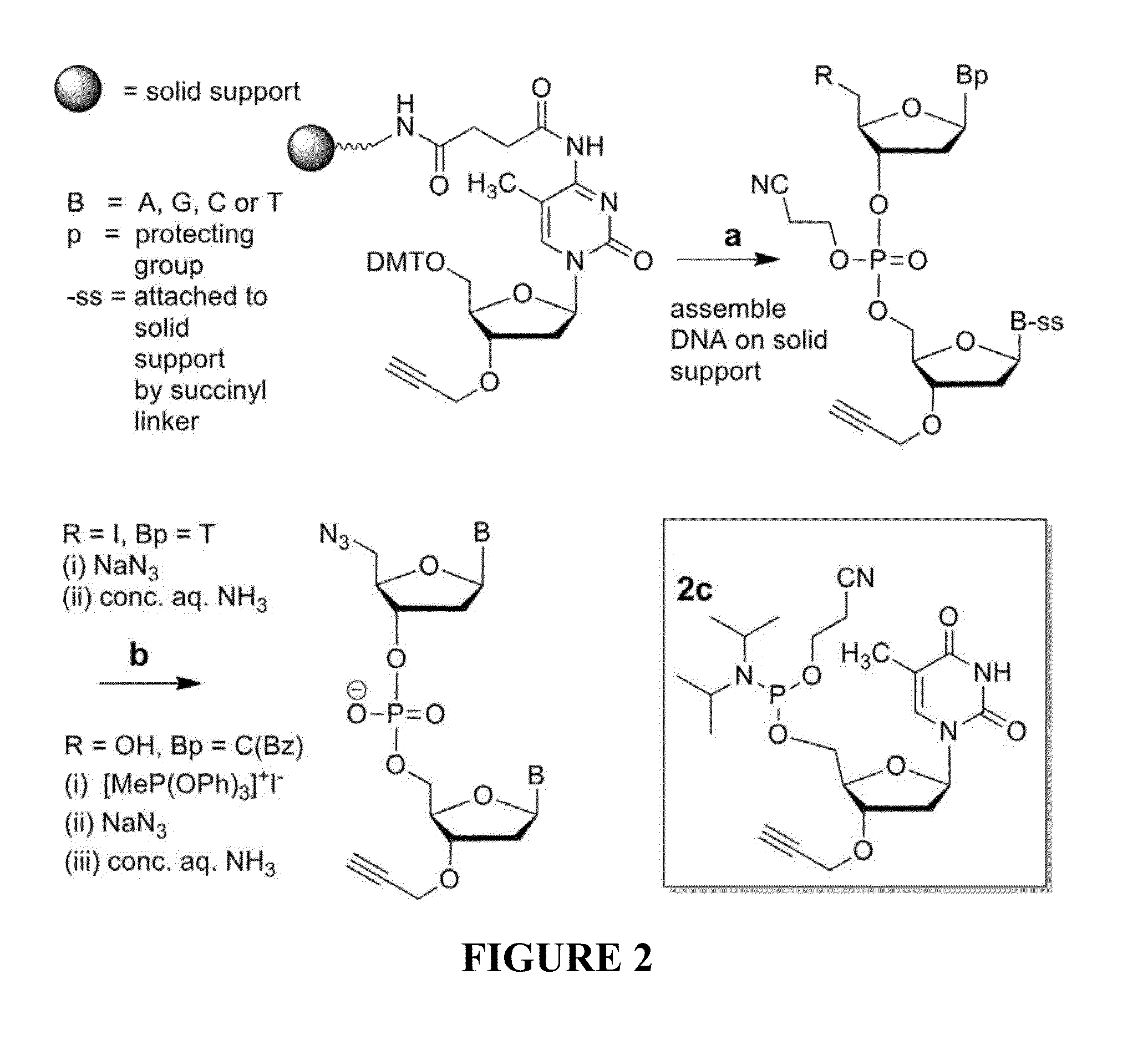
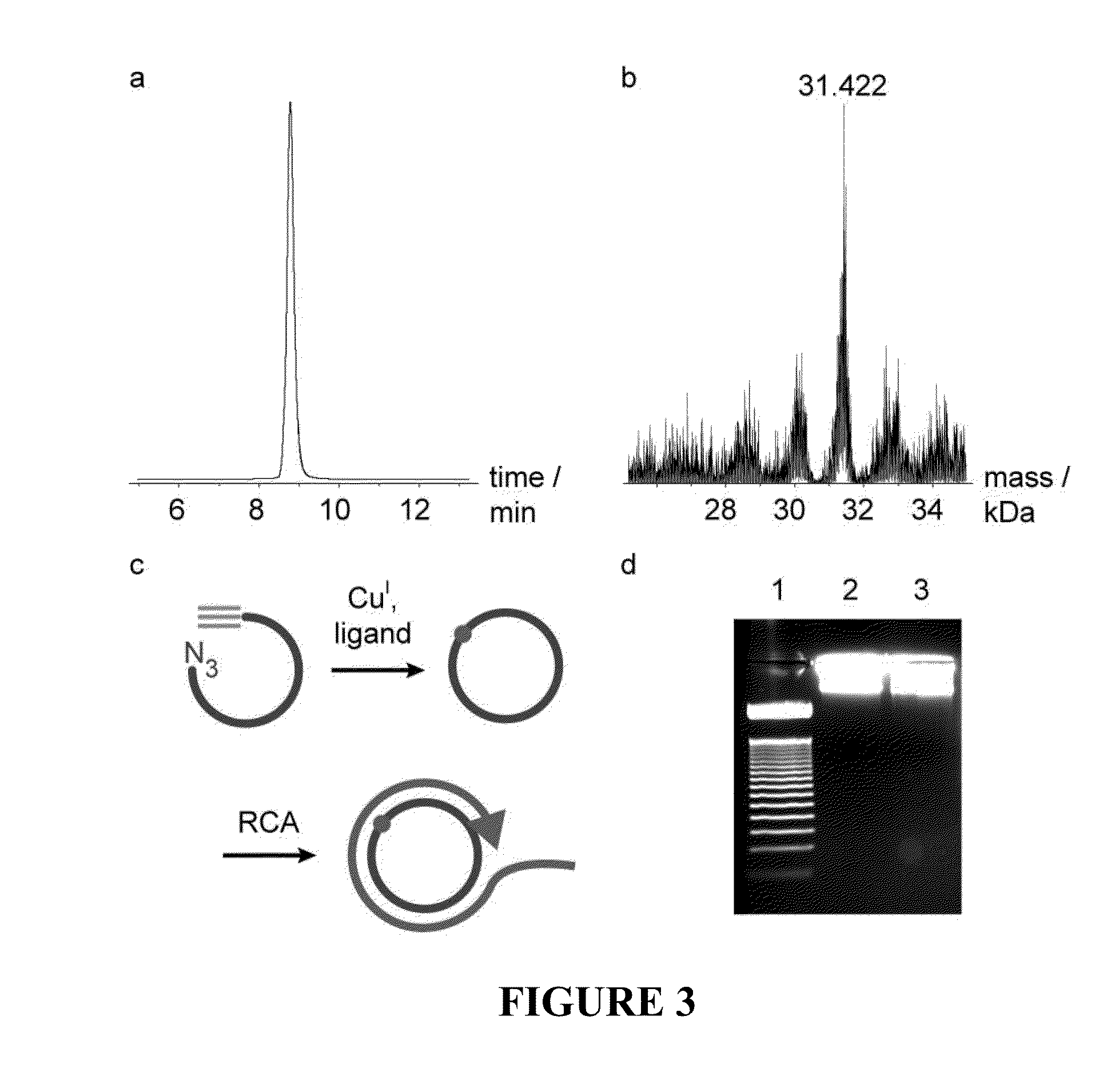
Oligonucleotide chemistry is central to the advancement of core technologies such as DNA sequencing, forensic and genetic analysis and has impacted greatly on the discipline of molecular biology. Oligonucleotides and their analogues are essential tools in these areas. They are often produced by automated solid-phase phosphoramidite synthesis but it is difficult to synthesize long DNA and RNA sequences by this method. Methods are proposed for ligating oligonucleotides together, in particular the use of an azide-alkyne coupling reaction to ligate the backbones of oligonucleotides together to form longer oligonucleotides that can be synthesized using current phosphoramidite synthesis methods.
Owner:ATDBIO LTD
Design, Synthesis and Assembly of Synthetic Nucleic Acids
ActiveUS20080300842A1Enhanced couplingEasy subsequent assemblyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesNucleotideOligonucleotide synthesis
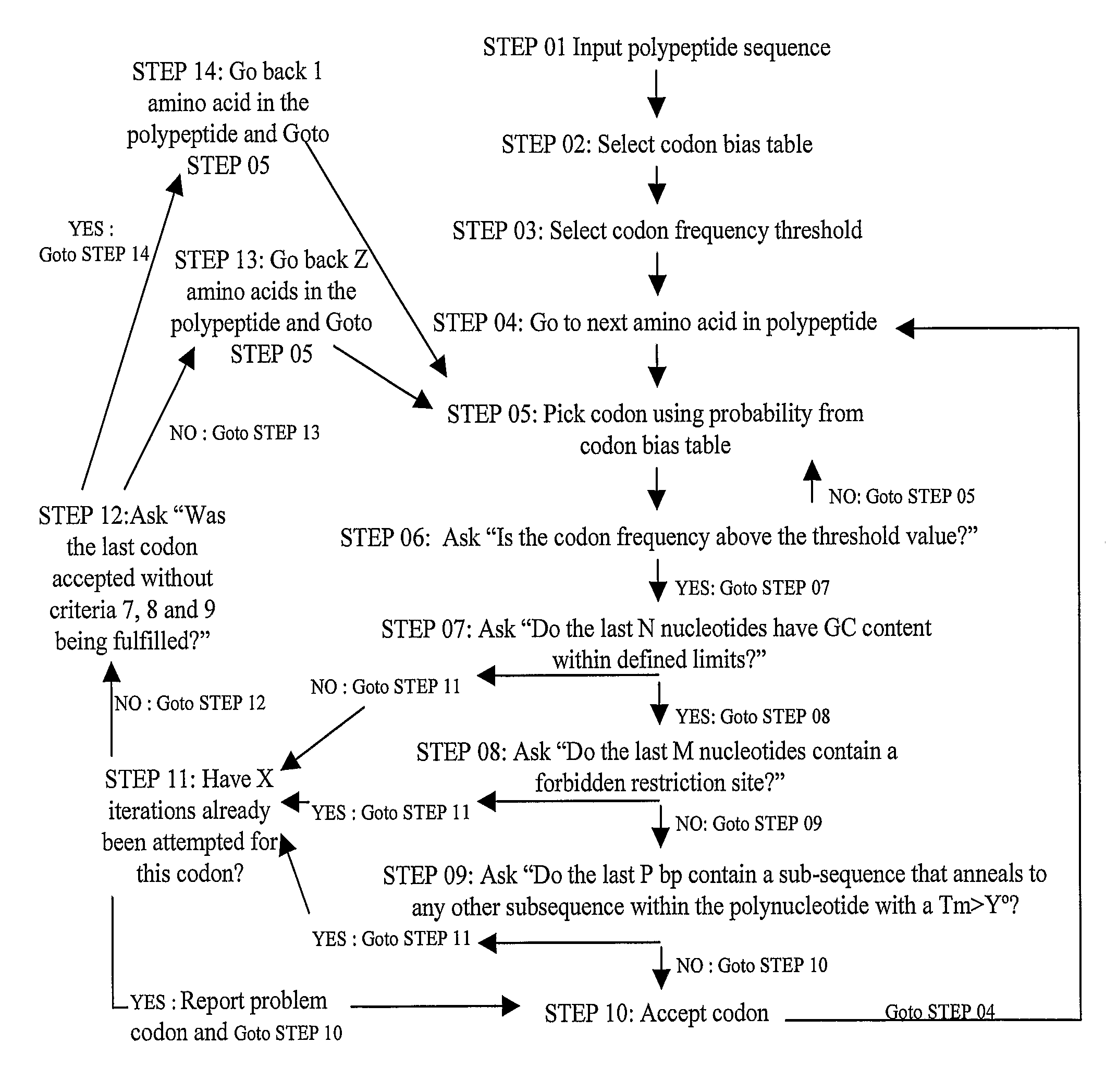
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides with high coupling efficiency (>99.5%) are provided. Methods for purification of synthetic oligonucleotides are also provided. Instrumentation configurations for oligonucleotide synthesis are also provided. Methods of designing and synthesizing polynucleotides are also provided. Polynucleotide design is optimized for subsequent assembly from shorter oligonucleotides. Modifications of phosphoramidite chemistry to improve the subsequent assembly of polynucleotides are provided. The design process also incorporates codon biases into polynucleotides that favor expression in defined hosts. Design and assembly methods are also provided for the efficient synthesis of sets of polynucleotide variants. Software to automate the design and assembly process is also provided.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
Methods for the synthesis and purification of oligomers
InactiveUS8889851B2Carbamic acid derivatives preparationSugar derivativesPurification methodsOligomer
A reagent for oligonucleotide synthesis or purification, wherein the reagent has a structure of:X—C—L—H (Formula A)wherein X is a phosphoramidite group, an H-phosphonate group, an acetal group, or an isocyanate; C is a direct bond or a cleavable adaptor represented by —Ca—Cb—; L is a hydrocarbyl chain; and H is a terminal alkyne or an activated cyclooctyne. The reagent of Formula (A) can be used in the synthesis and purification of oligonucleotides.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS7045319B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligoribonucleotidesProtein target
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Oligonucleotide ligation
ActiveUS8846883B2Improve thermal stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthesis methodsAlkyne
Oligonucleotide chemistry is central to the advancement of core technologies such as DNA sequencing, forensic and genetic analysis and has impacted greatly on the discipline of molecular biology. Oligonucleotides and their analogues are essential tools in these areas. They are often produced by automated solid-phase phosphoramidite synthesis but it is difficult to synthesize long DNA and RNA sequences by this method. Methods are proposed for ligating oligonucleotides together, in particular the use of an azide-alkyne coupling reaction to ligate the backbones of oligonucleotides together to form longer oligonucleotides that can be synthesized using current phosphoramidite synthesis methods.
Owner:ATDBIO LTD
Method and system for the generation of large double stranded DNA fragments
InactiveUS20070196834A1Synthesis fastMinimal operator interventionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide synthesisDouble stranded
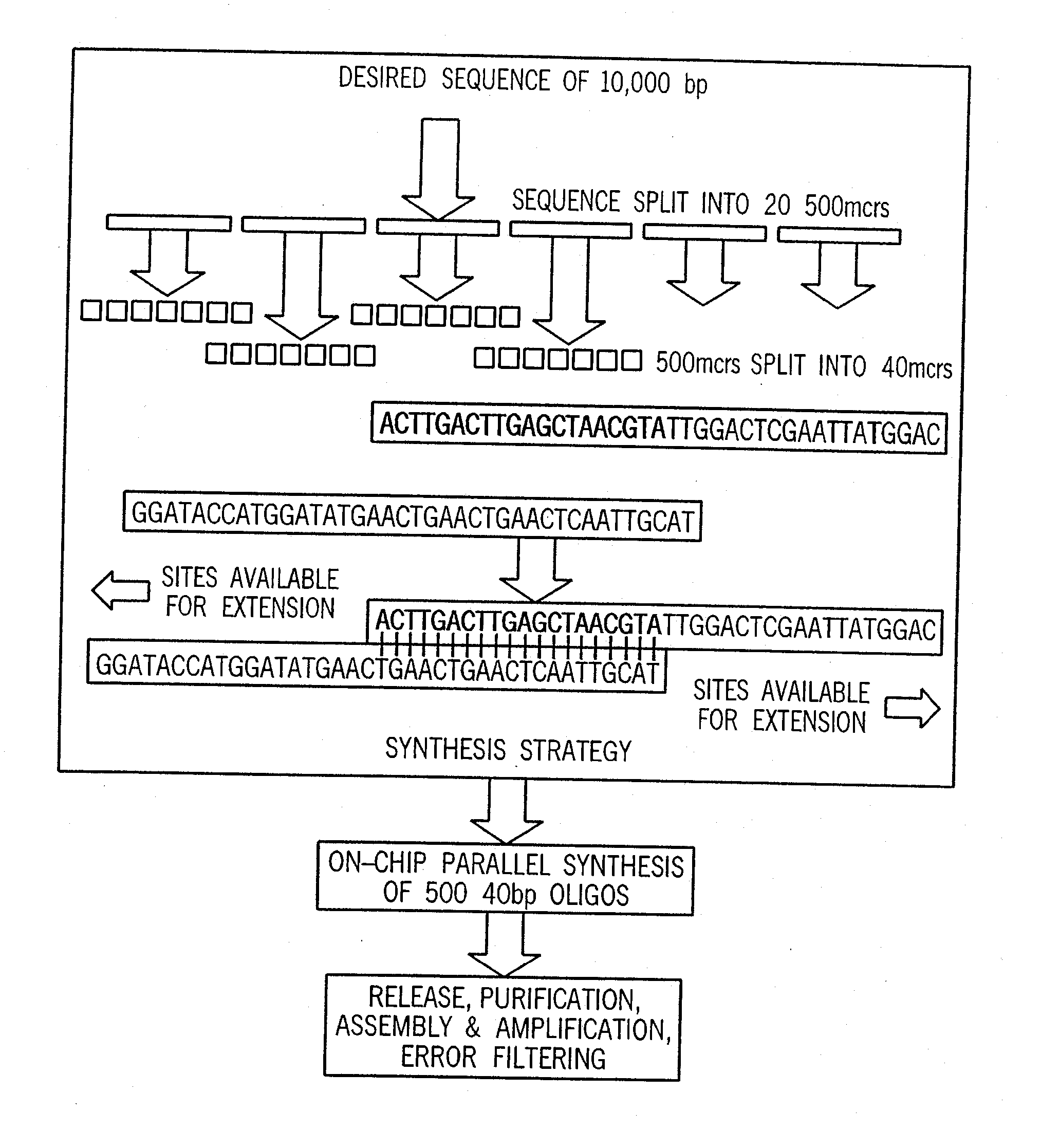
Synthesis of long chain molecules such as DNA is carried out rapidly and efficiently to produce relatively large quantities of the desired product. The synthesis of an entire gene or multiple genes formed of many hundreds or thousands of base pairs can be accomplished rapidly and, if desired, in a fully automated process requiring minimal operator intervention, and in a matter of hours, a day or a few days rather than many days or weeks. Production of a desired gene or set of genes having a specified base pair sequence is initiated by analyzing the specified target sequence and determining an optimal set of subsequences of base pairs that can be assembled to form the desired final target sequence. The set of oligonucleotides are then synthesized utilizing automated oligonucleotide synthesis techniques. The synthesized oligonucleotides are subsequently selectively released from the substrate and used in a sequential assembly process.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Universal support for the synthesis of oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6090934AHindered rotationPromote rapid formationSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationOligonucleotide synthesisAcid labile
A universal polymer support containing an organic aliphatic molecule of structure having at least a pair of cis-hydroxyl groups where one of the hydroxyl groups is attached to the polymer support through a covalent linkage and the other hydroxyl group is protected by an acid labile group.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
Design, synthesis and assembly of synthetic nucleic acids
InactiveUS20130196864A1Peptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide synthesisPolynucleotide
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides with high coupling efficiency (>99.5%) are provided. Methods for purification of synthetic oligonucleotides are also provided. Instrumentation configurations for oligonucleotide synthesis are also provided. Methods of designing and synthesizing polynucleotides are also provided. Polynucleotide design is optimized for subsequent assembly from shorter oligonucleotides. Modifications of phosphoramidite chemistry to improve the subsequent assembly of polynucleotides are provided. The design process also incorporates codon biases into polynucleotides that favor expression in defined hosts. Design and assembly methods are also provided for the efficient synthesis of sets of polynucleotide variants. Software to automate the design and assembly process is also provided.
Owner:DNA TWOPOINTO
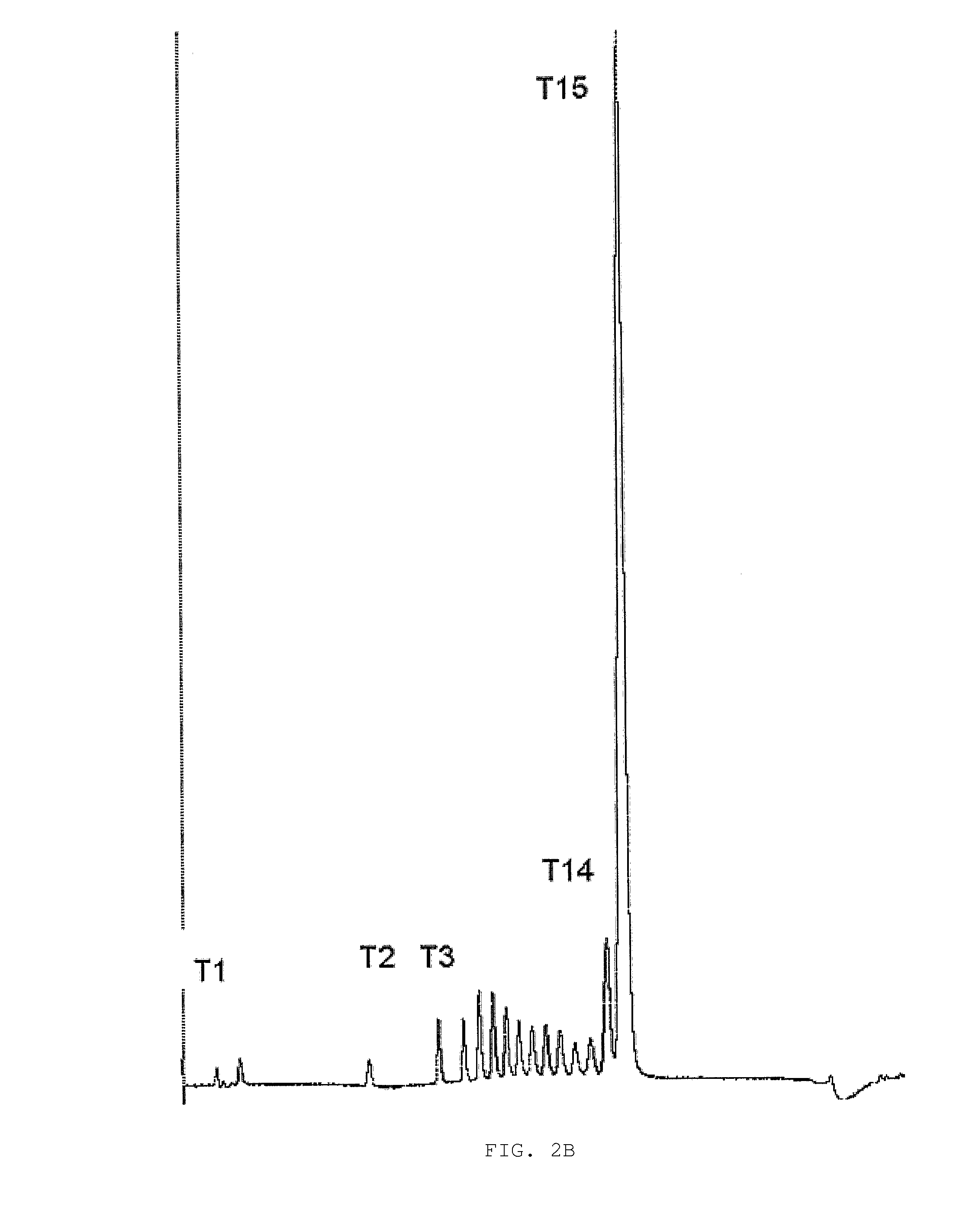
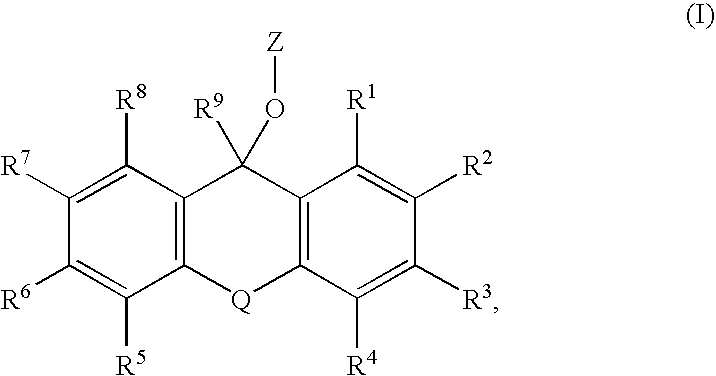
Substituted Pixyl Protecting Groups for Oligonucleotide Synthesis
InactiveUS20070276139A1Sugar derivativesPhosphorus organic compoundsOligonucleotide synthesisCombinatorial chemistry
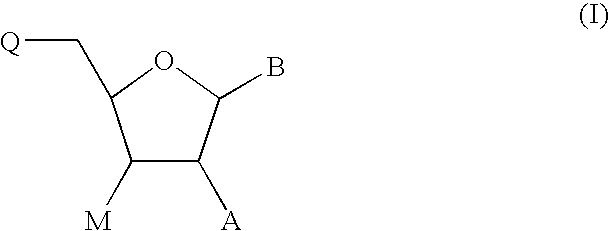
The present invention describes an improved hydroxyl protecting group of formula (1), wherein R2 and R7 are specified substituents and Q is O, S, NR10 or N(C═O)R10.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Processes and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis and purification
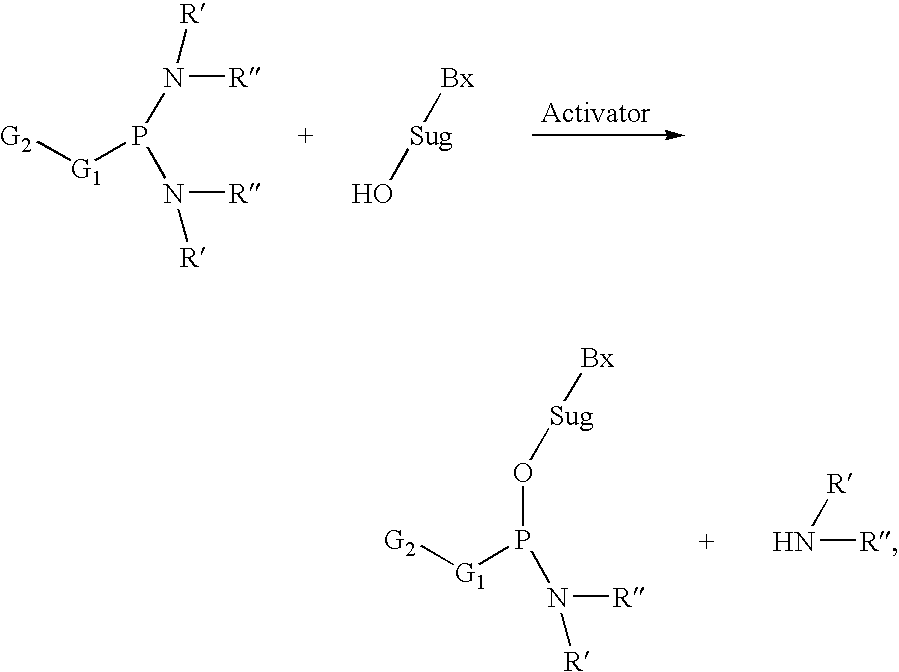
The present invention relates to processes and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis and purification. One aspect of the present invention relates to compounds useful for activating phosphoramidites in oligonucleotide synthesis. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing oligonucleotides via the phosphoramidite method using an activator of the invention. Another aspect of the present invention relates to sulfur-transfer agents. In a preferred embodiment, the sulfur-transfer agent is a 3-amino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-5-one. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a phosphorothioate by treating a phosphite with a sulfur-transfer reagent of the invention. In a preferred embodiment, the sulfur-transfer agent is a 3-amino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-5-one. Another aspect of the present invention relates to compounds that scavenge acrylonitrile produced during the deprotection of phosphate groups bearing ethylnitrile protecting groups. In a preferred embodiment, the acrylonitrile scavenger is a polymer-bound thiol. Another aspect of the present invention relates to agents used to oxidize a phosphite to a phosphate. In a preferred embodiment, the oxidizing agent is sodium chlorite, chloroamine, or pyridine-N-oxide. Another aspect of the present invention relates to methods of purifying an oligonucleotide by annealing a first single-stranded oligonucleotide and second single-stranded oligonucleotide to form a double-stranded oligonucleotide; and subjecting the double-stranded oligonucleotide to chromatographic purification. In a preferred embodiment, the chromatographic purification is high-performance liquid chromatography.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Oligonucleotide ligation
InactiveUS20130046083A1Inhibition formationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSynthesis methodsAlkyne
Oligonucleotide chemistry is central to the advancement of core technologies such as DNA sequencing, forensic and genetic analysis and has impacted greatly on the discipline of molecular biology. Oligonucleotides and their analogues are essential tools in these areas. They are often produced by automated solid-phase phosphoramidite synthesis but it is difficult to synthesize long DNA and RNA sequences by this method. Methods are proposed for ligating oligonucleotides together, in particular the use of an azide-alkyne coupling reaction to ligate the backbones of oligonucleotides together to form longer oligonucleotides than can be synthesized using current phosphoramidite synthesis methods.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
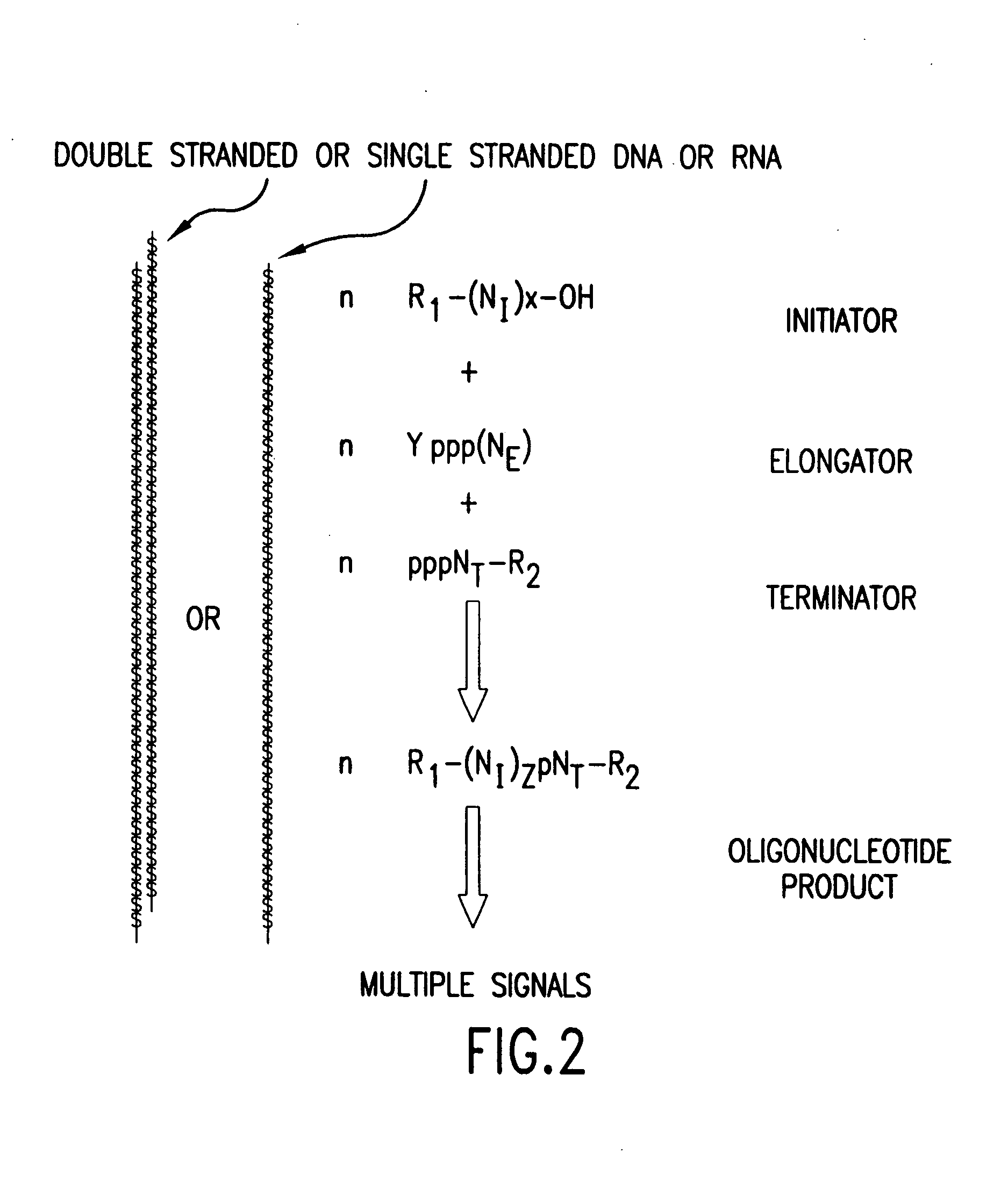
Compositions, methods and detection technologies for reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050214796A1MicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementDendrimerOligoribonucleotides
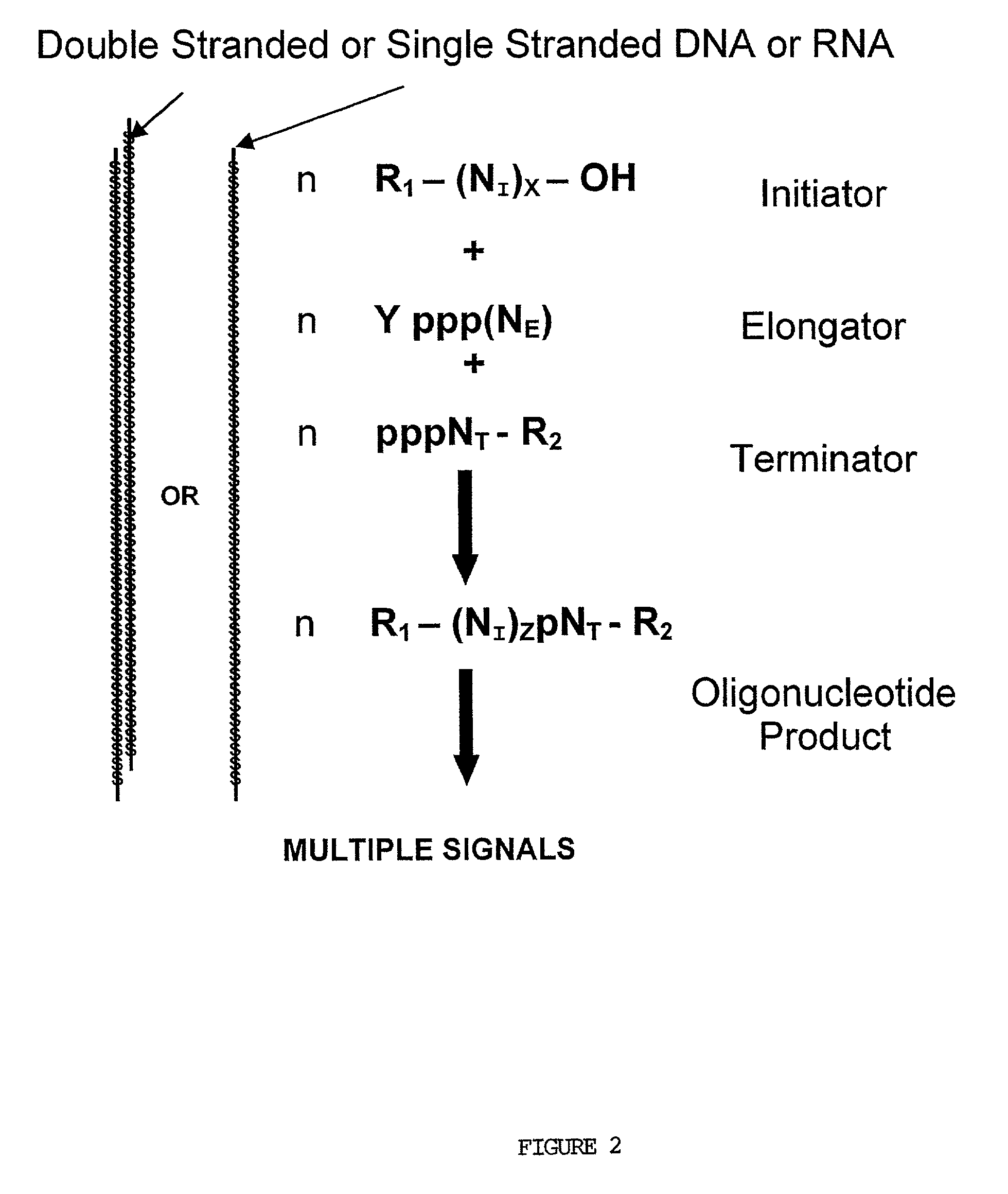
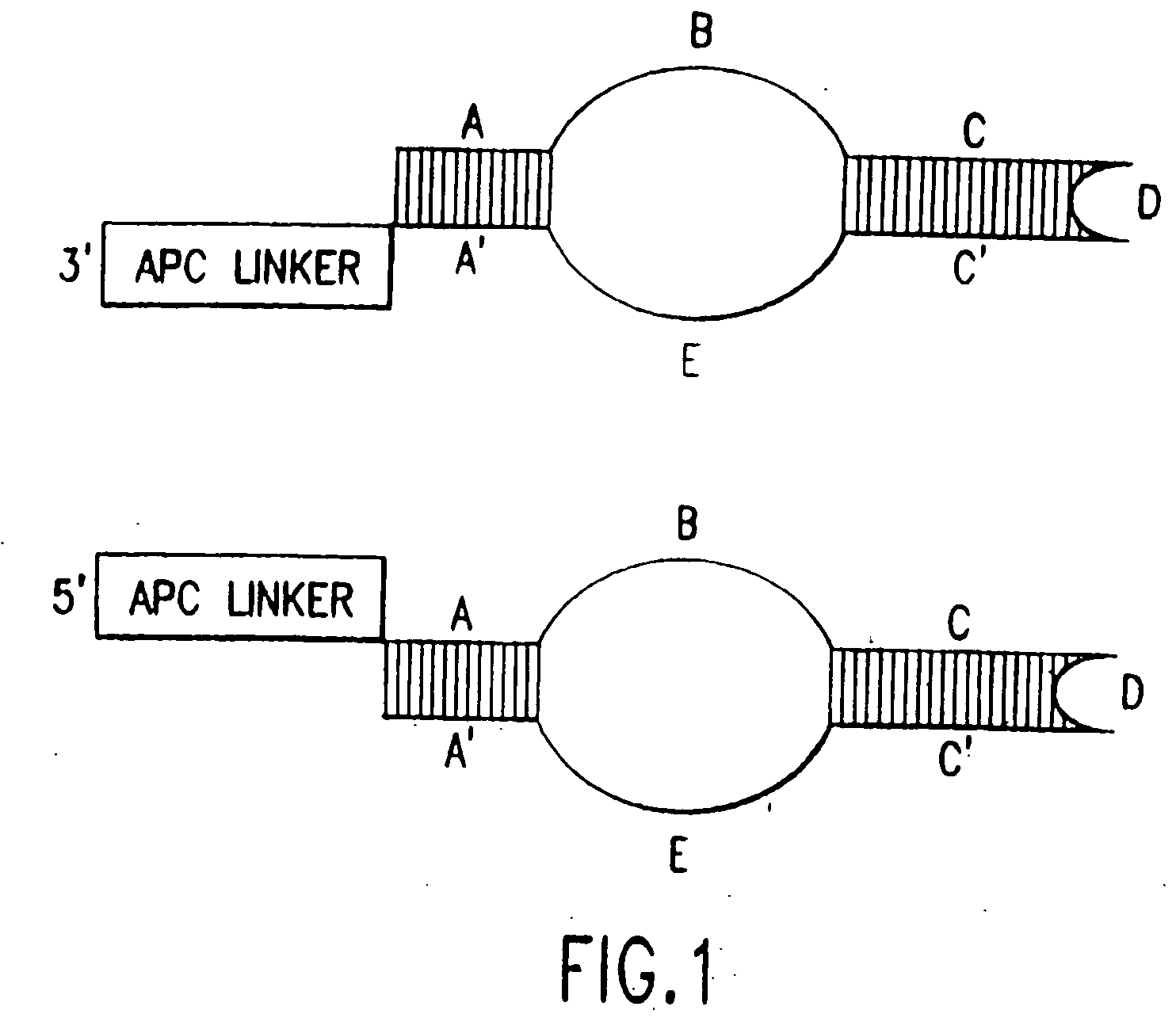
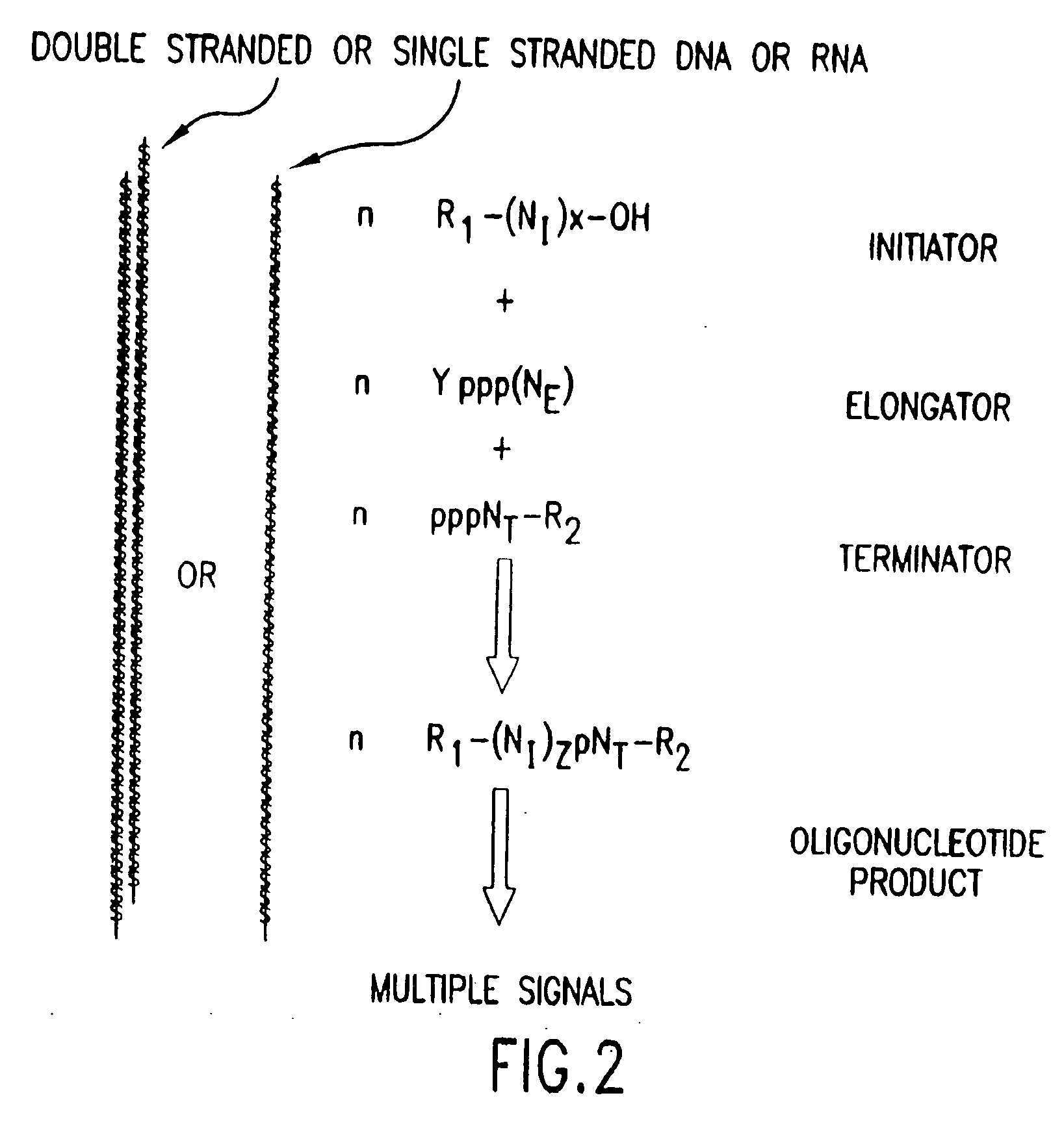
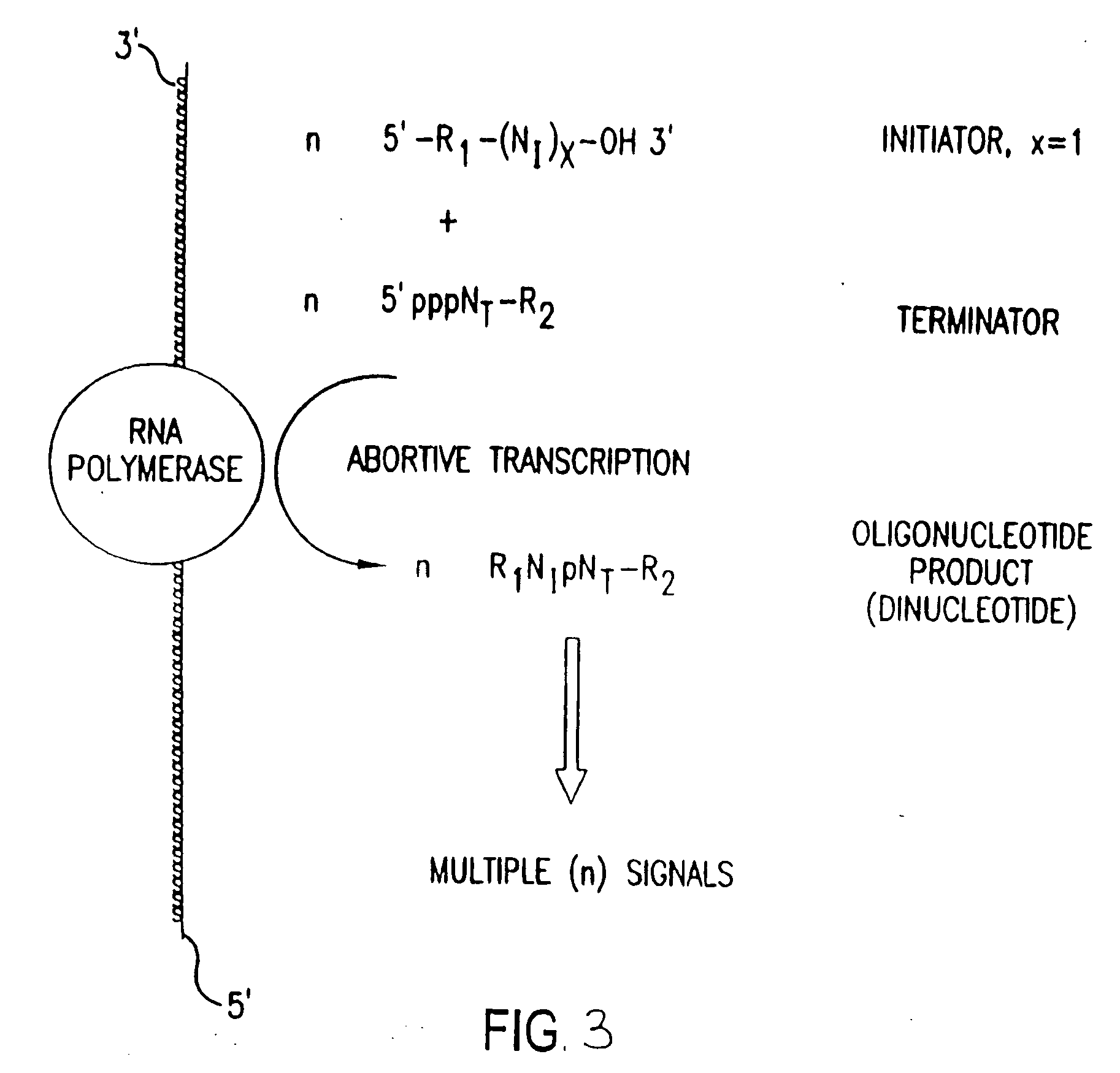
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a molecule of interest by generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a polynucleotide sequence and detecting said products. The invention also provides for methods of multiplex abortive transcription. In a further aspect, the invention provides for the use of dendrimers containing abortive promoter cassettes. In one aspect, the invention provides for abortive promoter cassettes suitable for use in the present invention. In one aspect the products of abortive transcription are detected with the use of mass spectrometry. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting a target protein, DNA or RNA by generating multiple detectable RNA oligoribonucleotides by abortive transcription that are detected, including by mass spectrometry.
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Oligonucleotide synthesis method using highly dispersible liquid-phase support
ActiveUS9284344B2High yieldProduce simply and efficientlySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSynthesis methodsSolvent
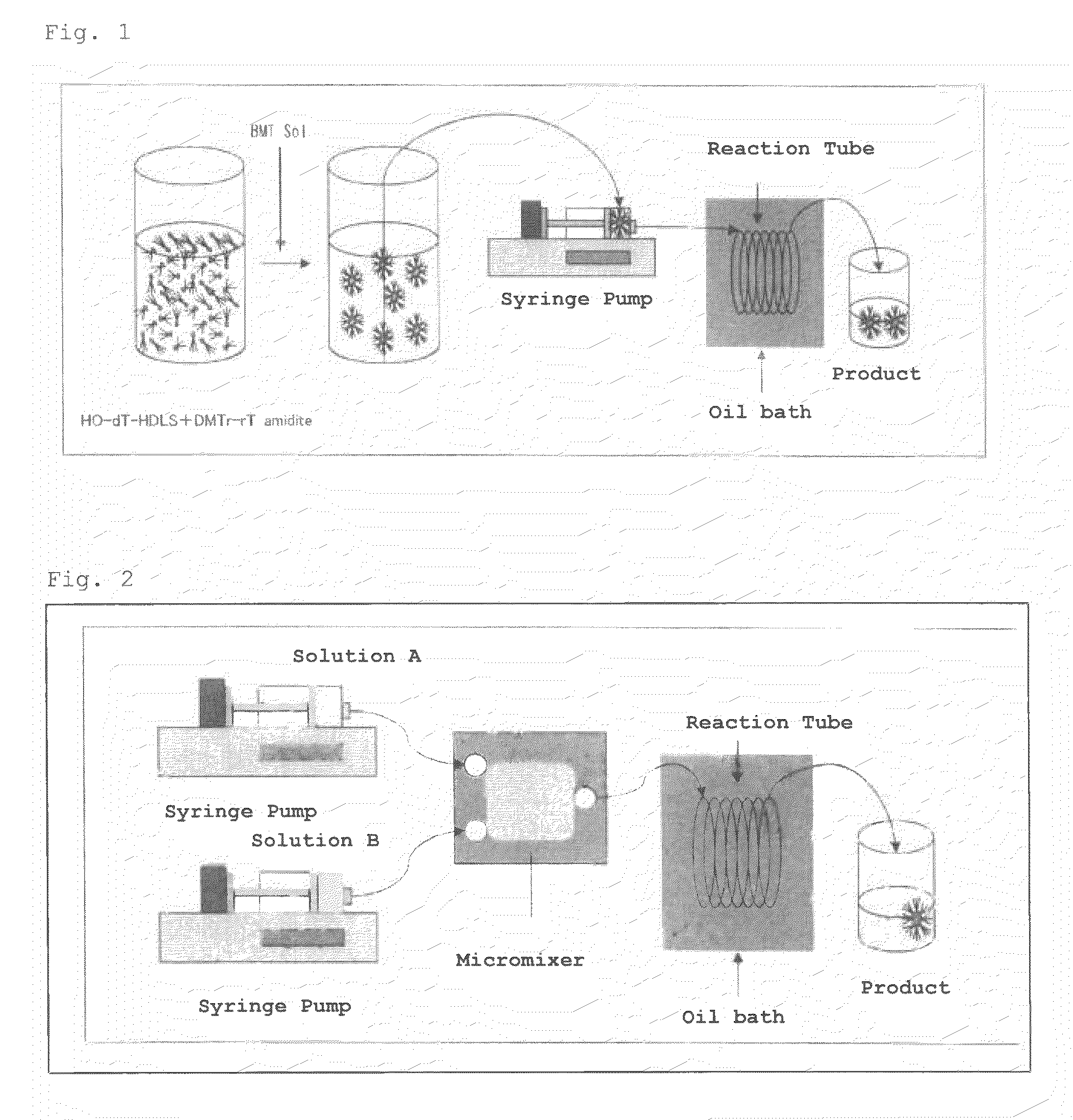
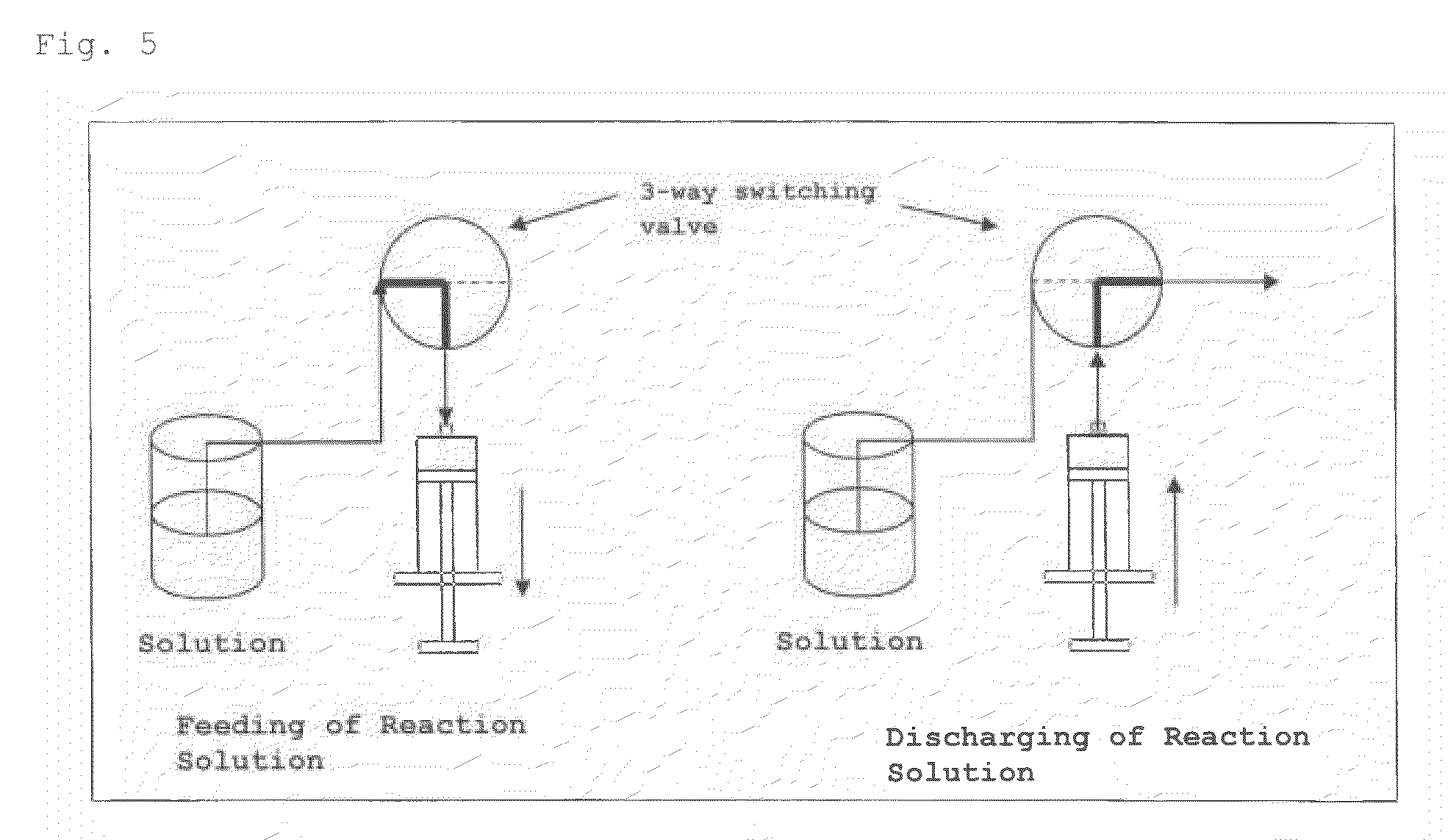
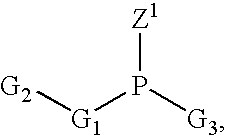
A nucleic acid synthesis method enabling a reaction in a fluid (flow) with a highly dispersible liquid-phase support to improve coupling efficiency is provided.The method for synthesizing an oligonucleotide comprising: sequentially condensing and oxidizing a nucleoside phosphoramidite compound in the presence of an acid / azole complex compound using a starting raw material, i.e., hydrophobic group-bonded nucleoside represented by Formula (1):where R1: an alkylene group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, R2: an alkylene group having 1 to 22 carbon atoms, R3 and R4 each independently represent an alkyl group having 1 to 22 carbon atoms or the like, R5: a single bond or an alkylene group having 1 to 22 carbon atoms, R6: each independently an alkyl group having 6 to 30 carbon atoms, n represents an integer of 2 to 6, X represents a hydrogen atom, hydroxyl group, or the like, Y: a protecting group deprotectable under an acidic condition, and Z: an adenyl group, a guanyl group, or the like having a polar group optionally protected by a protecting group,wherein a condensation reaction is performed by preliminarily dissolving the hydrophobic group-bonded nucleoside or hydrophobic group-bonded oligonucleotide and the nucleoside phosphoramidite compound in a non-polar solvent, and contacting the resulting solution with the acid / azole complex compound or a solution containing the complex compound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Process of purifying phosphoramidites
A process of purifying phosphoramidite precursors useful in inter alia synthesis of oligonucleotides comprises dissolving a crude phosphoramidite in a polar phase, adding a basic compound to the polar phase, adding a portion of water to the polar phase, contacting the polar phase with a first apolar phase to extract impurity into the apolar phase, separating the first apolar phase from the polar phase, adding a second aliquot of water to the polar phase, and contacting the polar phase with a second apolar phase, whereby the phosphoramidite partitions into the second apolar phase.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Methods and processes for attaching compounds to matrices
InactiveUS20050239112A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical MoietyEngineering
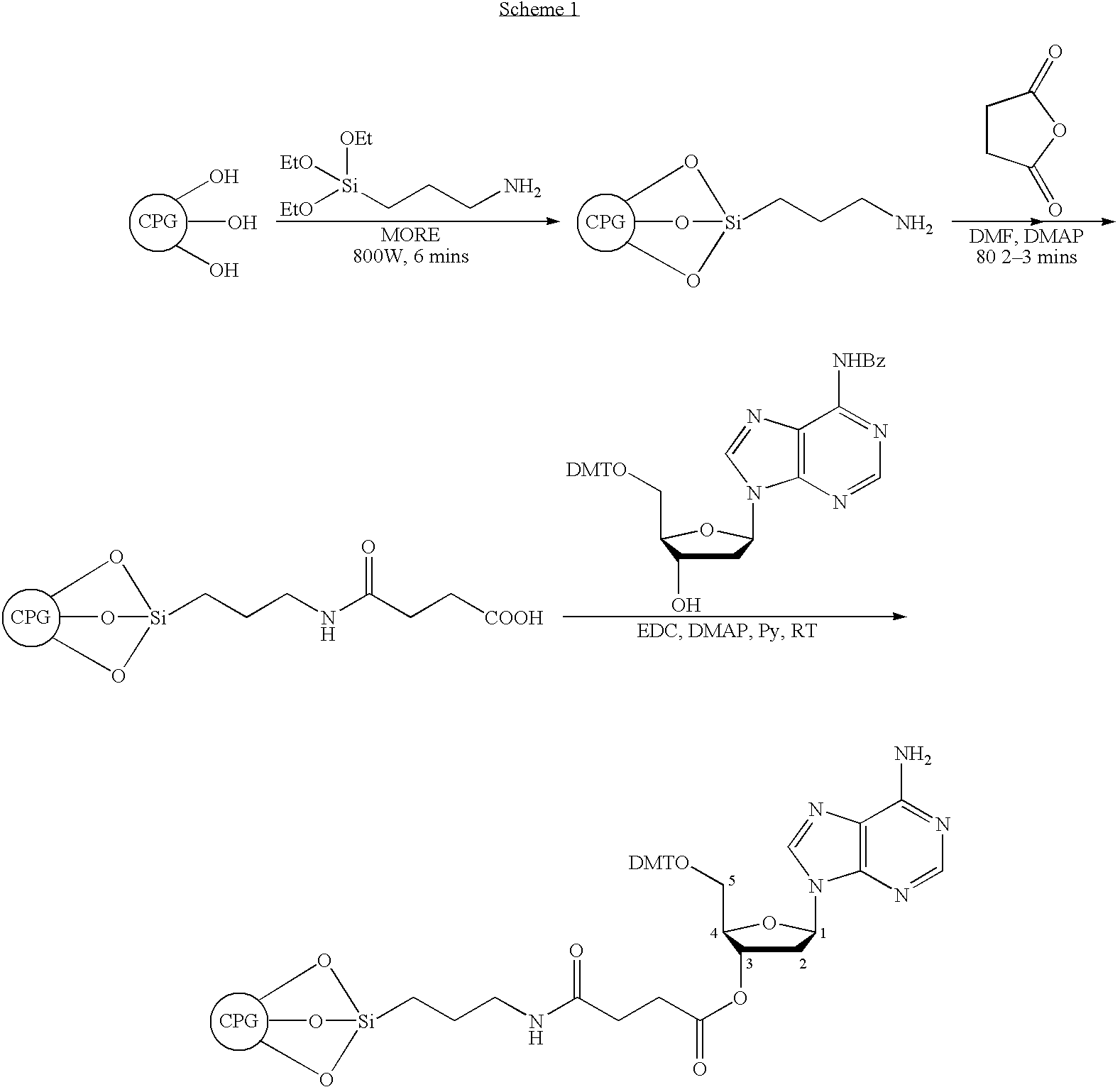
The present invention describes extremely rapid and efficient methods for the attachment of chemical moieties to matrices by the use of microwave technology. The methods of the invention can be applied in a variety of ways for the preparation of different types of matrices for a variety of applications including but not limited to the functionalization of various solid supports, and matrices in the form of powder, beads, sheets, and other suitable surfaces for use in applications including but not limited to oligonucleotide synthesis, peptide synthesis, environmental clean up (removal of toxic materials), immunoassays, affinity chromatography, combinatorial chemistry, microarrays, proteomics and medical diagnostics.
Owner:SPRING BANK
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050064414A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligoribonucleotidesProtein target
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a target molecule by generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a defined polynucleotide sequence. The methods generally comprise using a nucleoside, a mononucleotide, and oligonucleotide, or a polynucleotide, or analog thereof, to initiate synthesis of an oligonucleotide product that is substantially complementary to a target site on the defined polynucleotide sequence; optionally using nucleotides or nucleotide anologs as oligonucleotide chain elongators; using a chain terminator to terminate the polymerization reaction; and detecting multiple oligonucleotide products that have been synthesized by the polymerase. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting a target protein, DNA or RNA by generating multiple detectable RNA oligoribonucleotides by abortive transcription.
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Programmable Oligonucleotide Synthesis
ActiveUS20100015668A1Reduce yieldSynthesis is longSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligonucleotide synthesisNucleotide synthesis
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
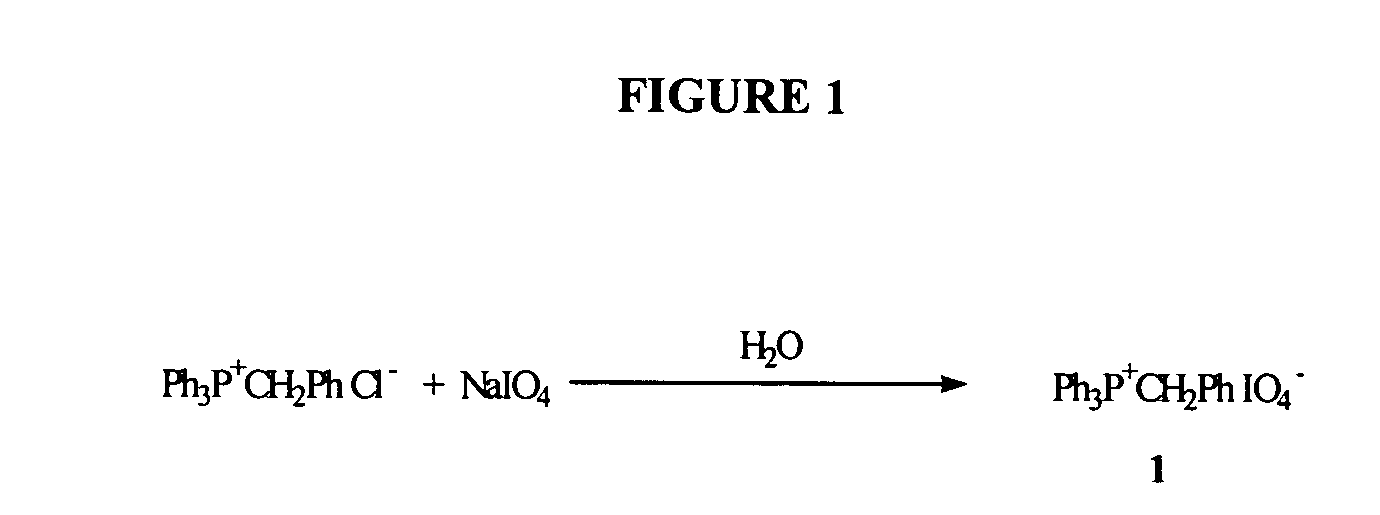
Oligonucleotide synthesis using periodate salts
The present invention relates generally to nucleic acid chemistry and to the chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides. More particularly, the invention relates to improved methods for synthesizing oligonucleotides wherein periodate salts are used (e.g., in organic solvents) as an oxidation reagent in oligonucleotide synthesis (e.g., for automated phosphoramidite synthesis of oligonucleotides). The invention finds utility in the fields of biochemistry, molecular biology, and pharmacology, and in medical diagnostic and screening technologies.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20060204964A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LOligonucleotide synthesis
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a target molecule by the use of nucleotide analogs containing moieties that enable detection. Such analogs may be incorporated into nucleic acids. In one embodiment, nucleotide analogs are used in a process generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a defined polynucleotide sequence. The methods generally comprise using a nucleoside, a mononucleotide, an oligonucleotide, or a polynucleotide, or analog thereof, to initiate synthesis of an oligonucleotide product that is substantially complementary to a target site on the defined polynucleotide sequence; optionally using nucleotides or nucleotide analogs as oligonucleotide chain elongators or chain terminators to terminate the polymerization reaction; and detecting multiple oligonucleotide products that have been synthesized by the polymerase.
Owner:HANNA MICHELLE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com