Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1460 results about "Solid surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
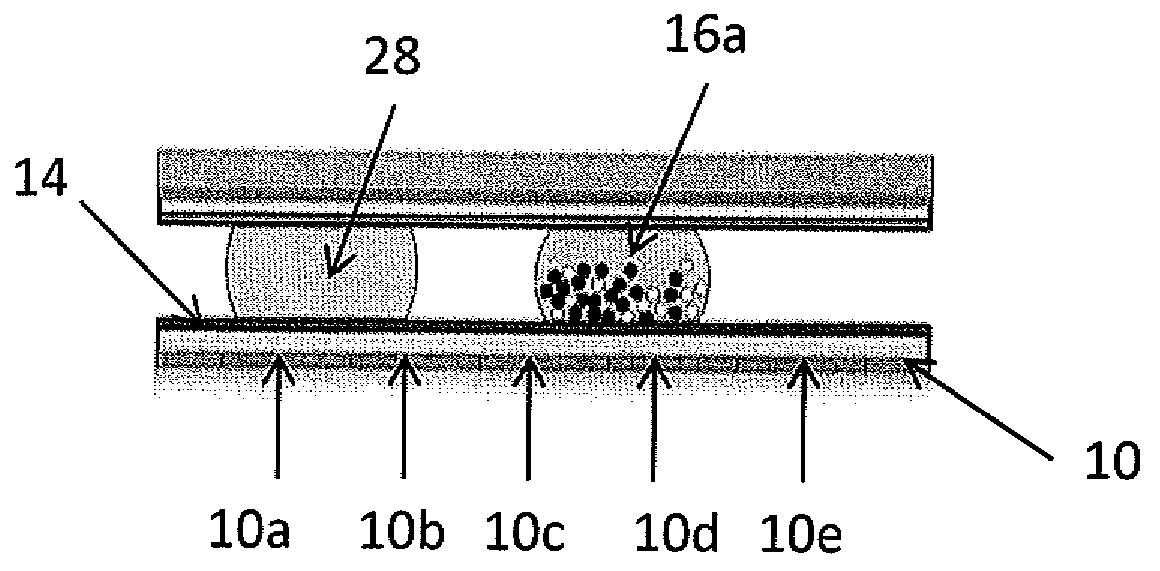
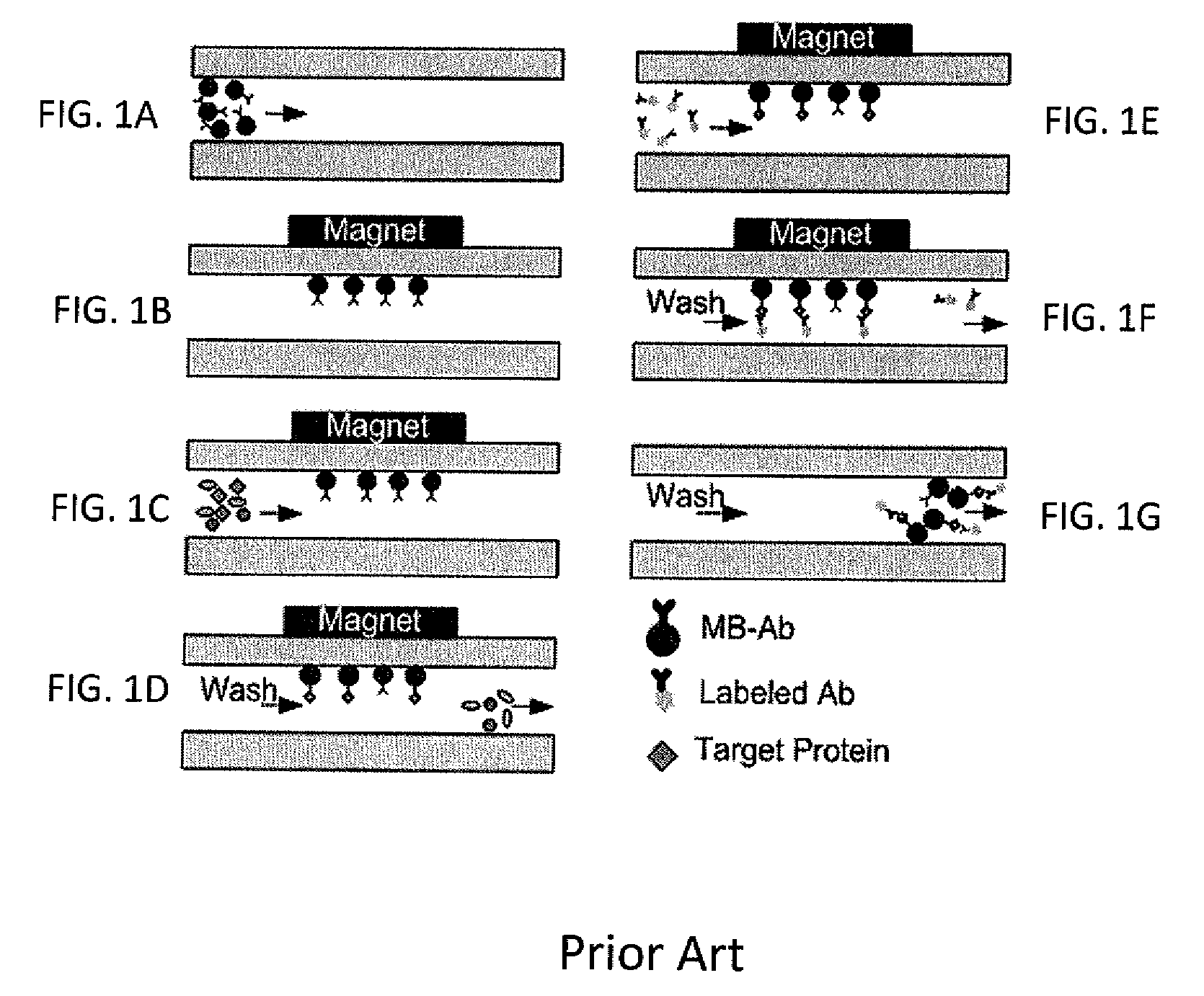
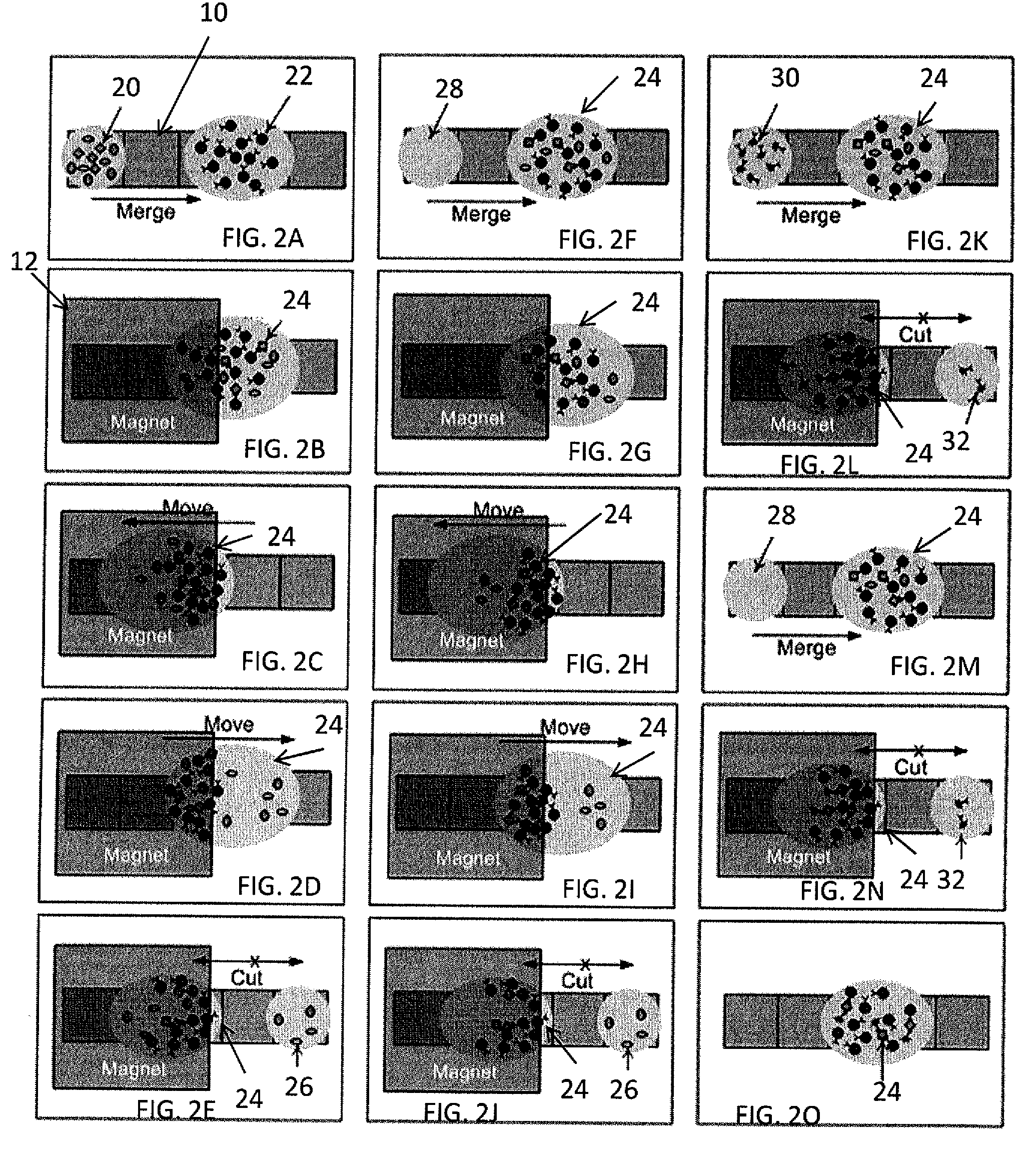
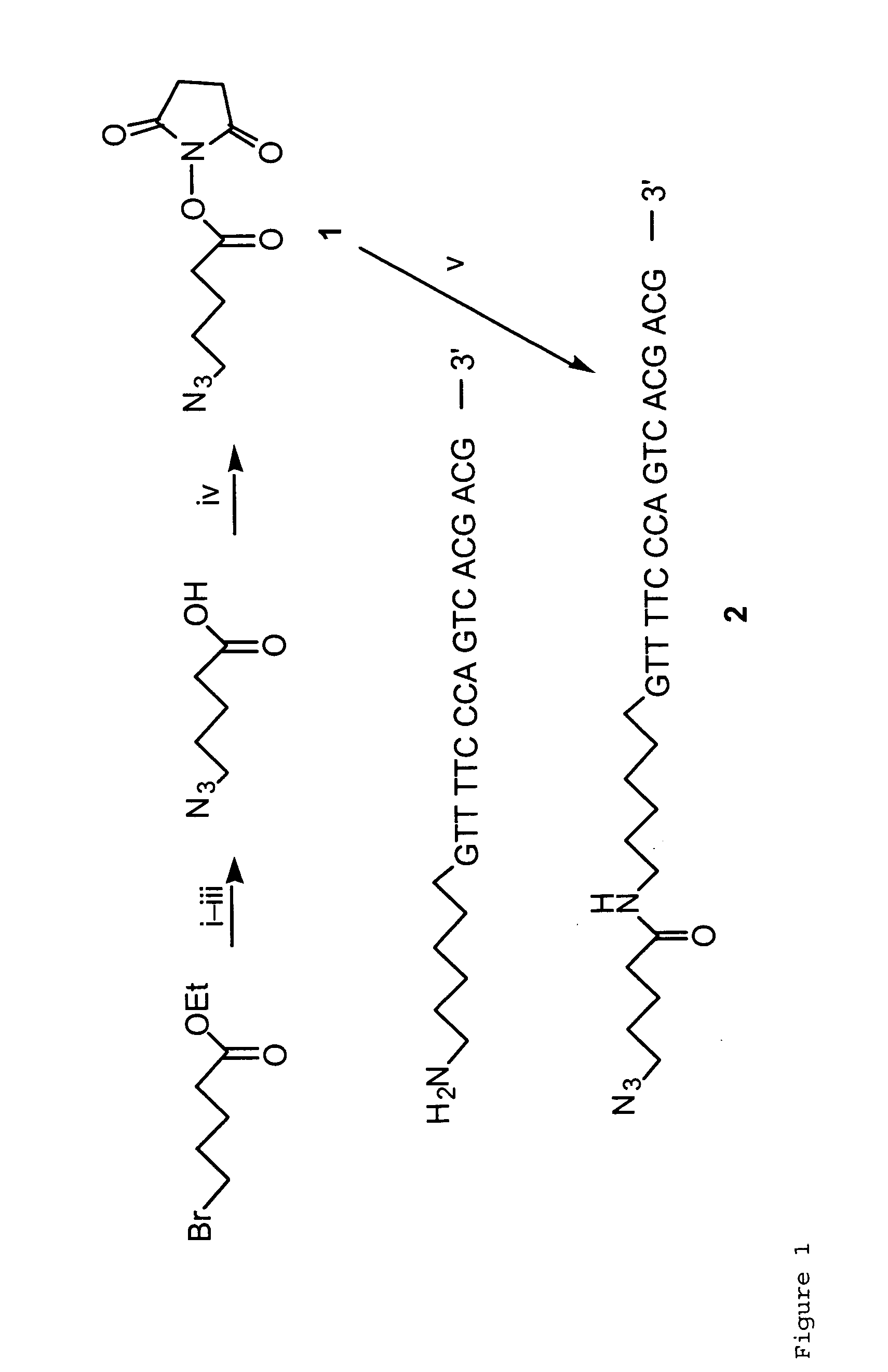
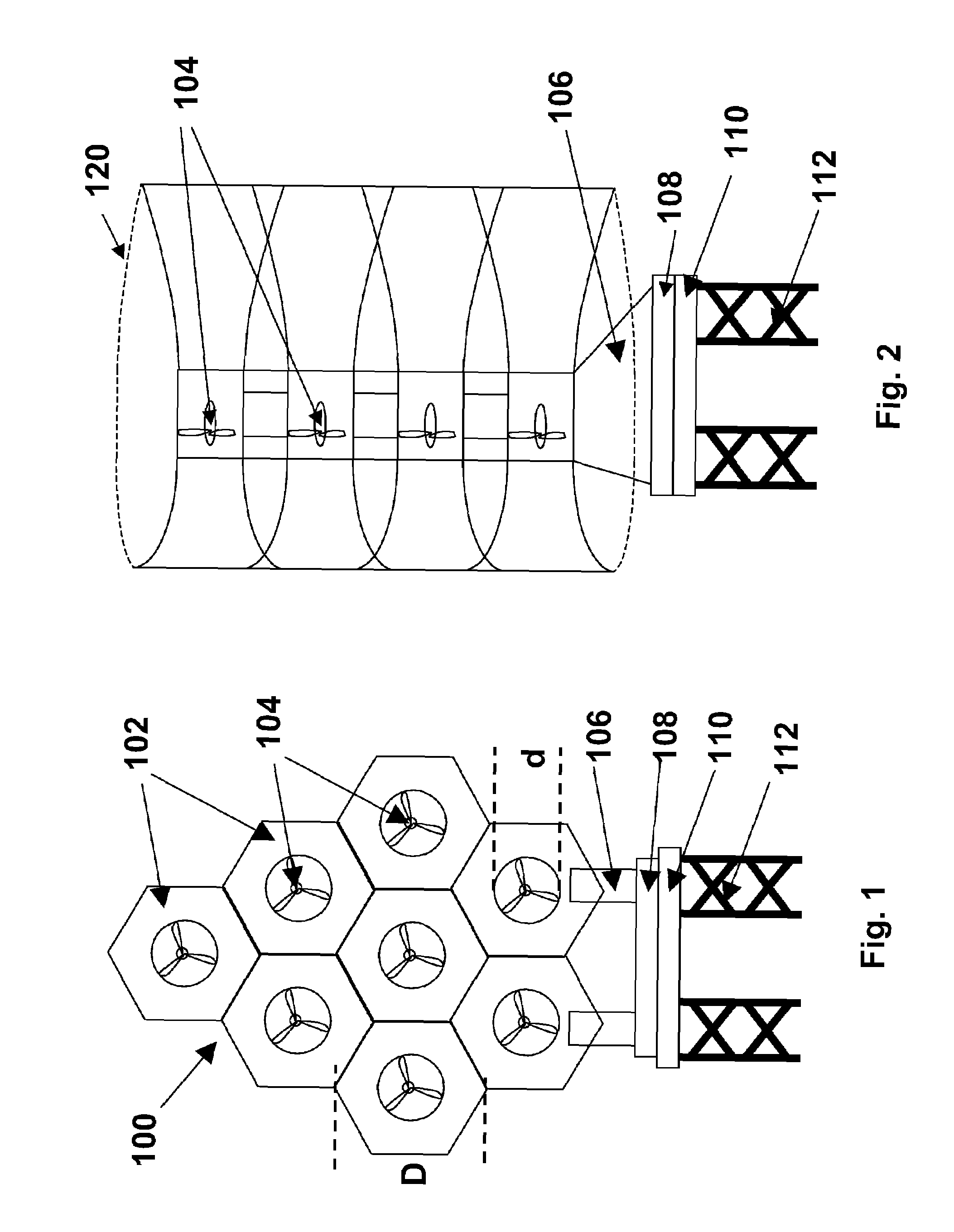
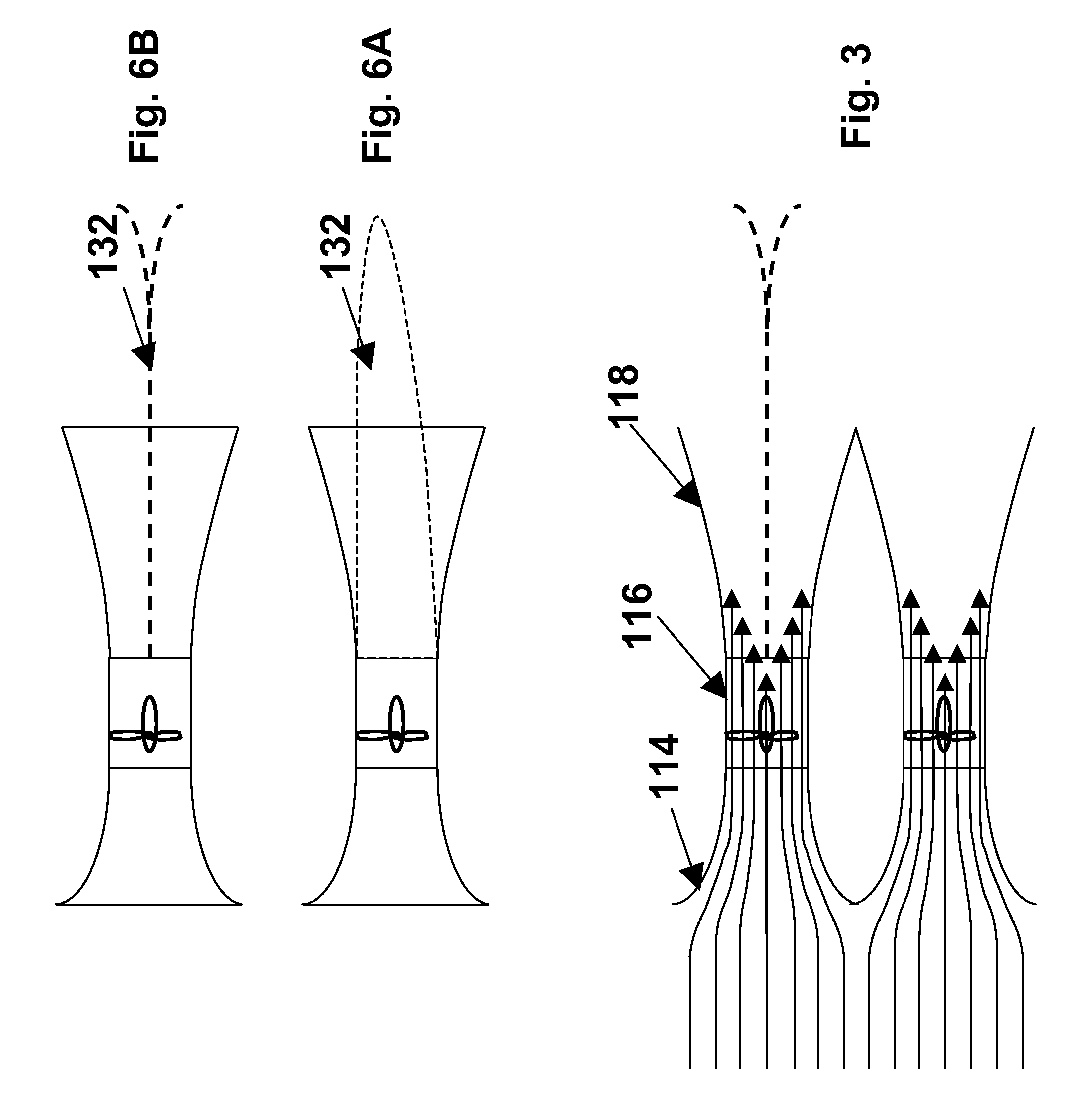
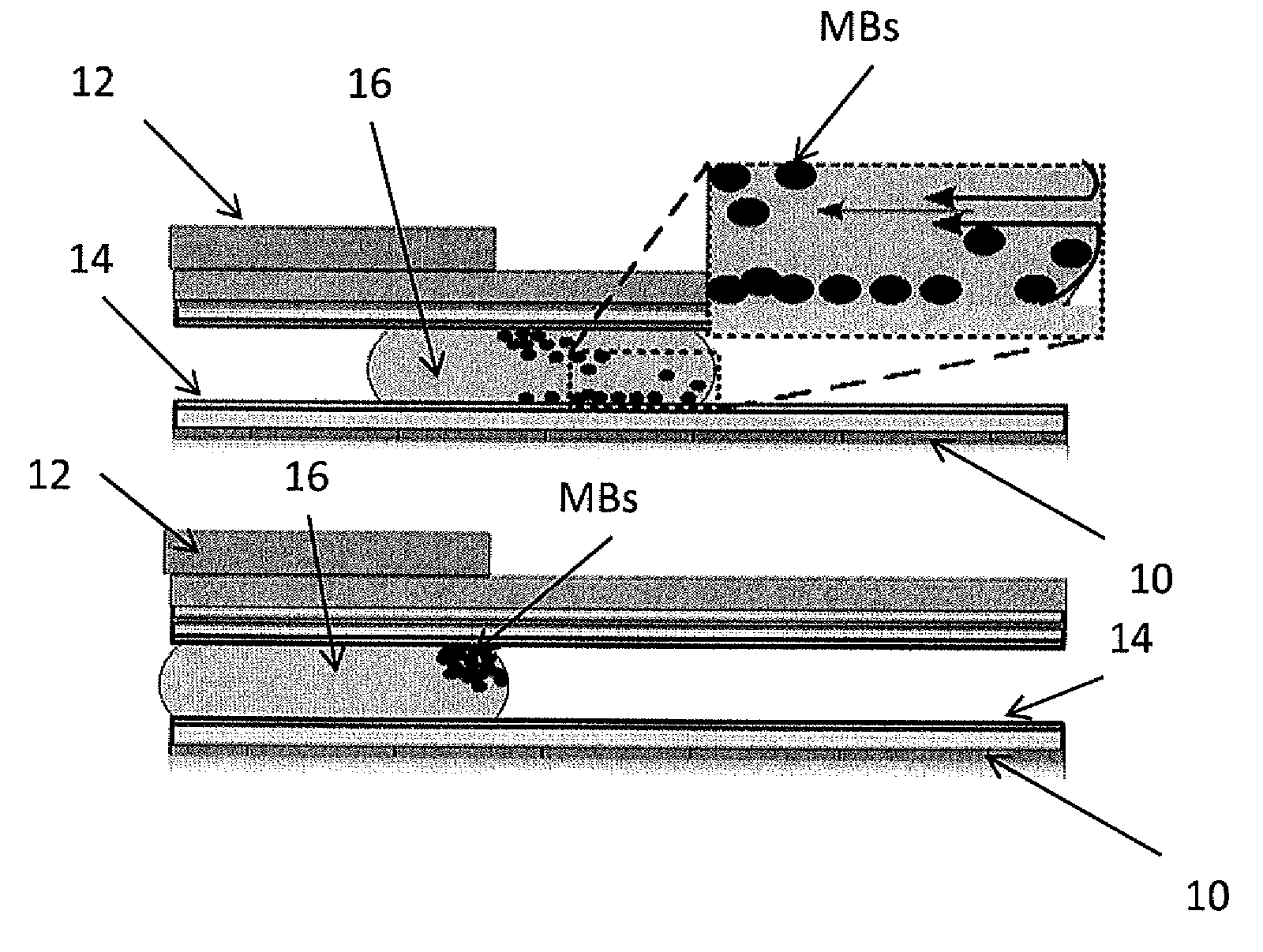
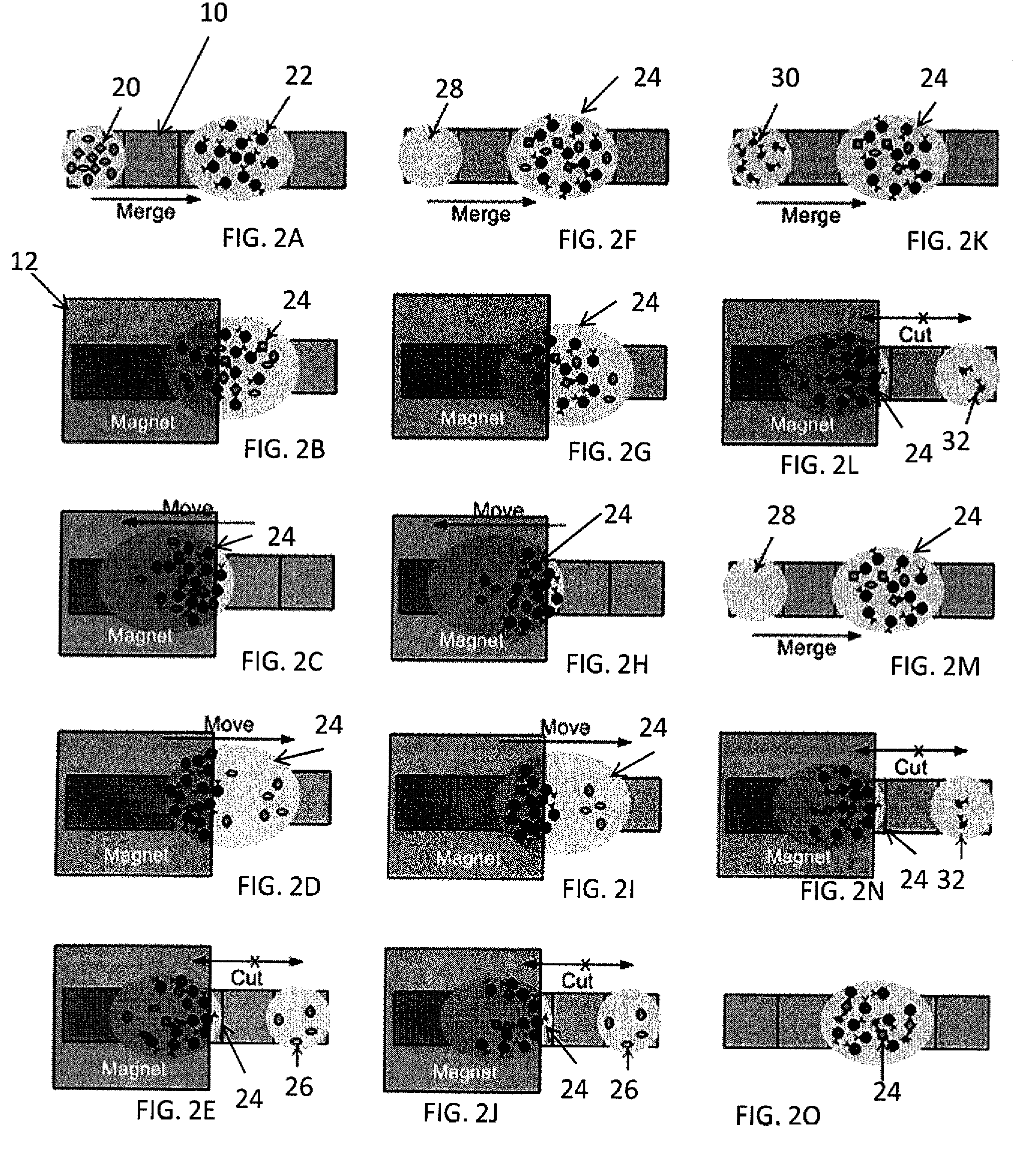
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
ActiveUS20090283407A1Increasing concentration of targetReduce concentrationElectrostatic separatorsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringDroplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
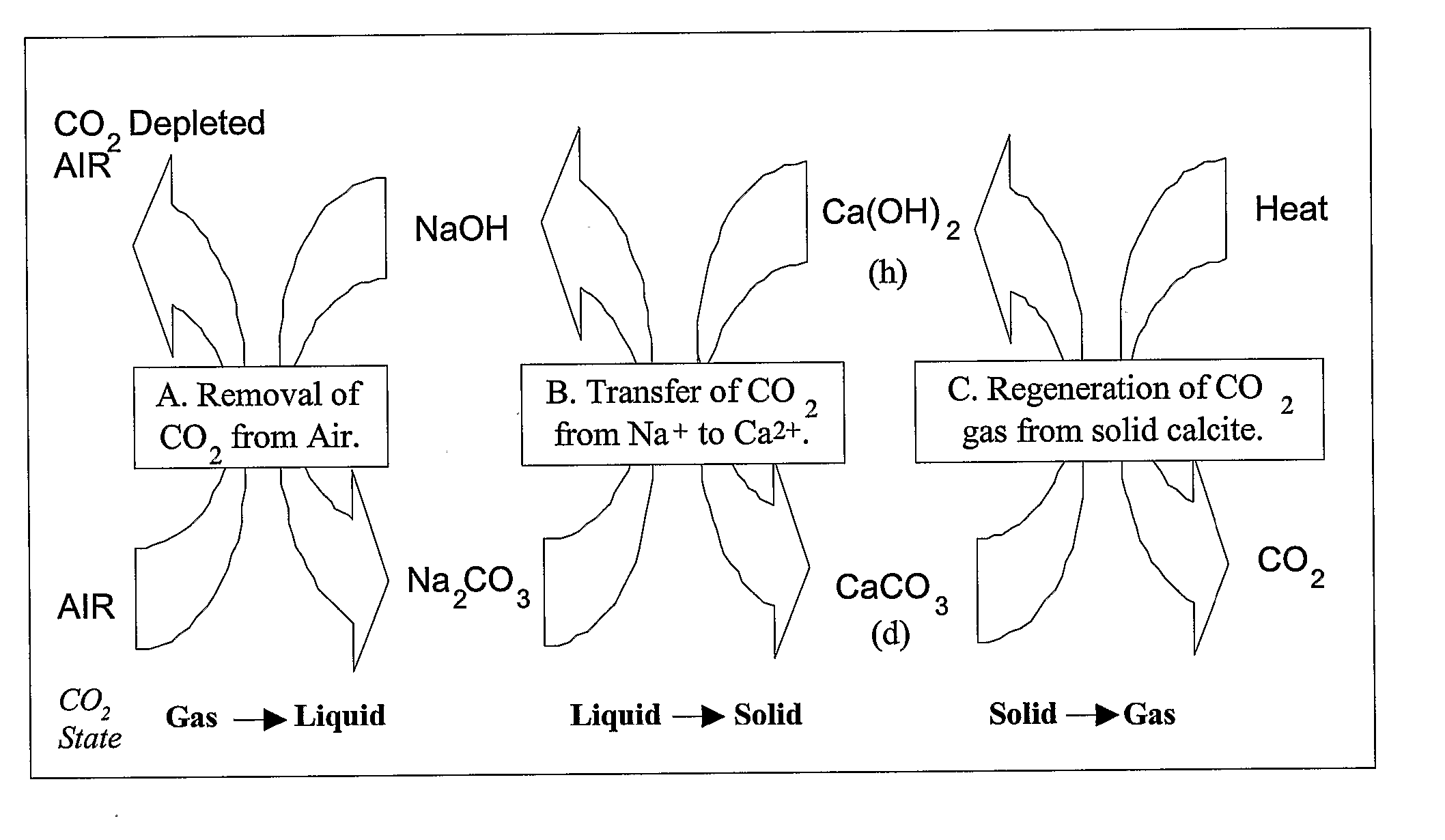
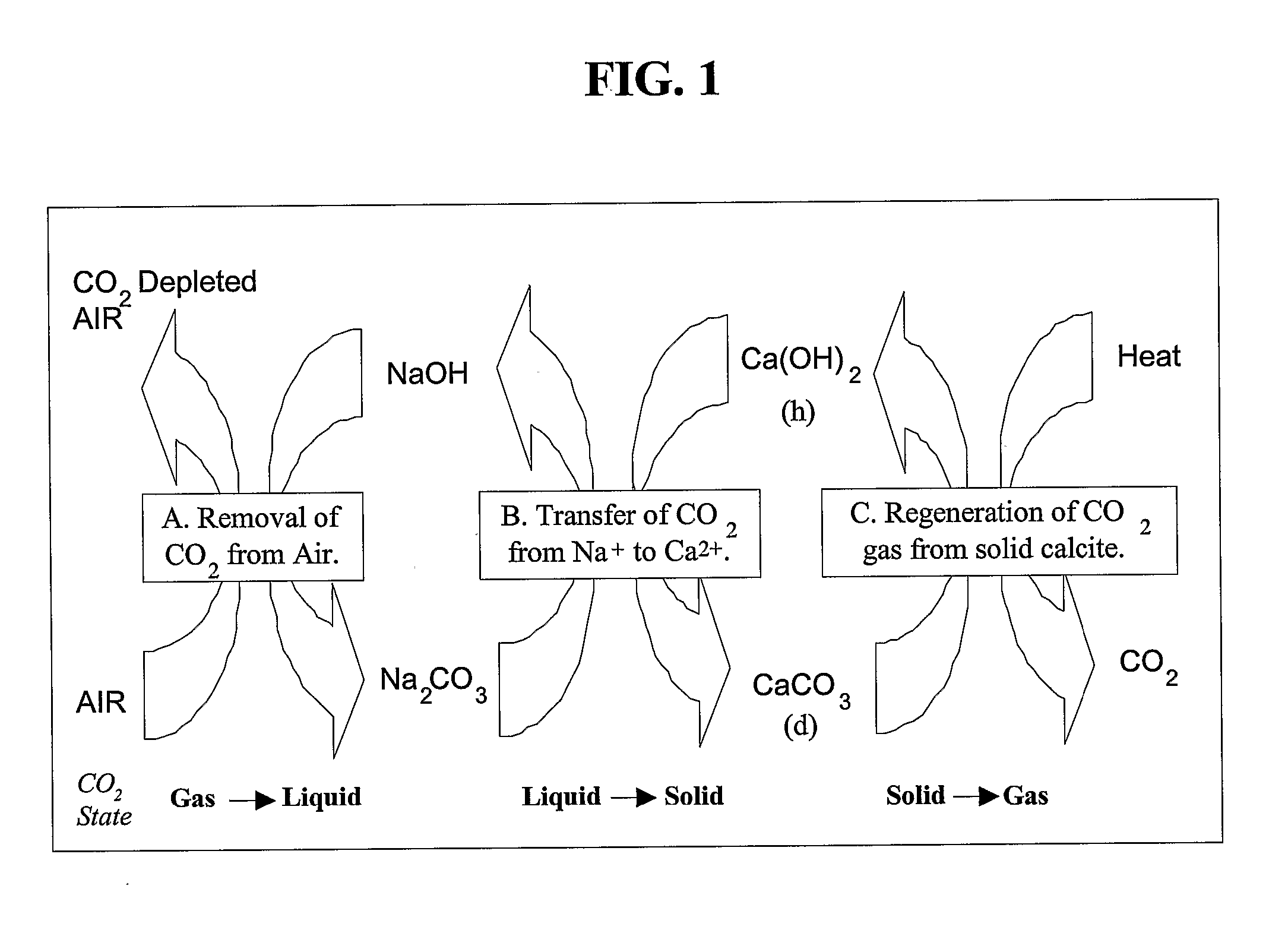
Carbon Dioxide Capture and Mitigation of Carbon Dioxide Emissions
InactiveUS20080031801A1Pressure dropCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesLiquefactionSorbentSolid surface
The present invention describes methods and systems for extracting, capturing, reducing, storing, sequestering, or disposing of carbon dioxide (CO2), particularly from the air. The CO2 extraction methods and systems involve the use of chemical processes, mineral sequestration, and solid and liquid sorbents. Methods are also described for extracting and / or capturing CO2 via condensation on solid surfaces at low temperature.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
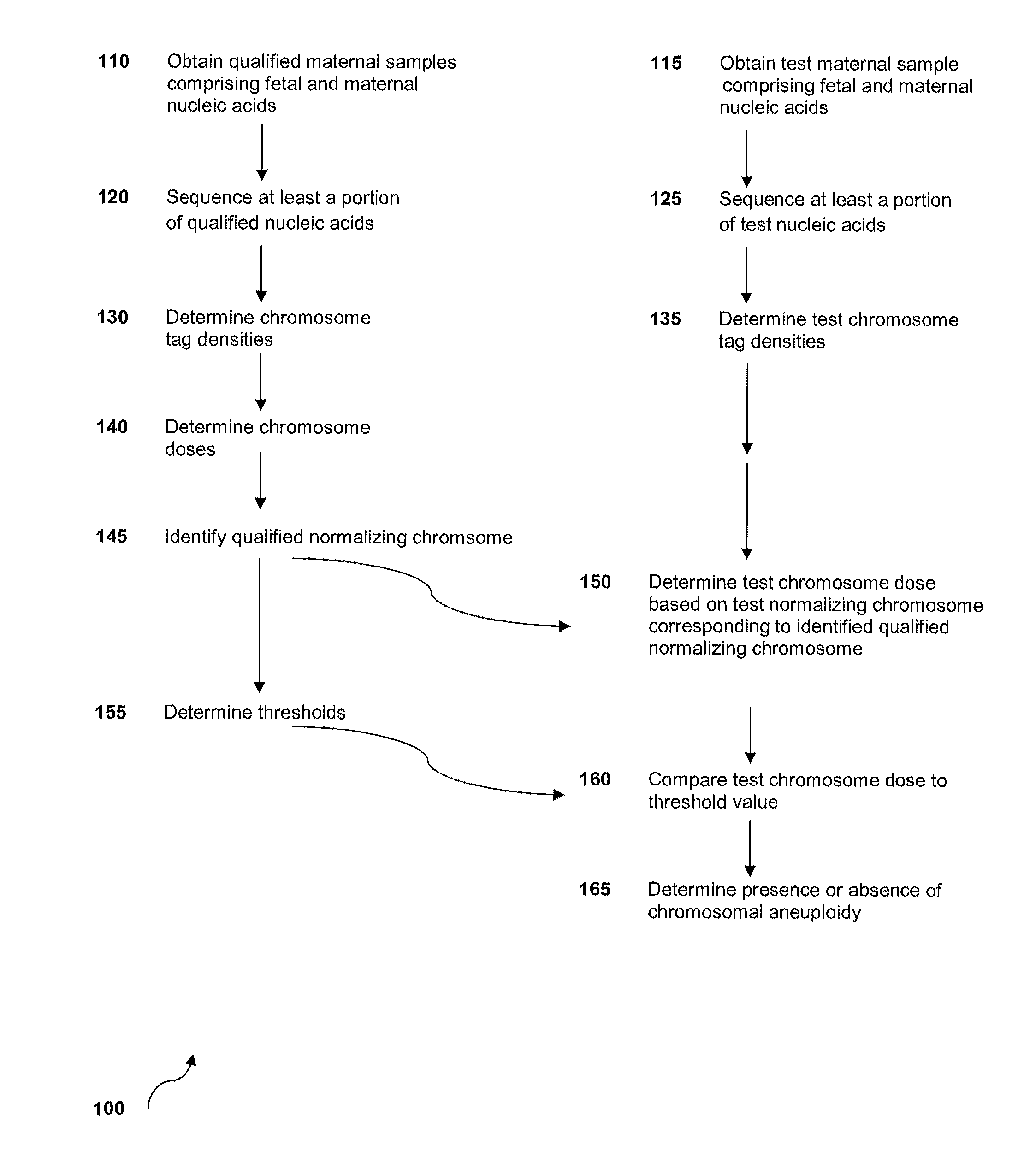
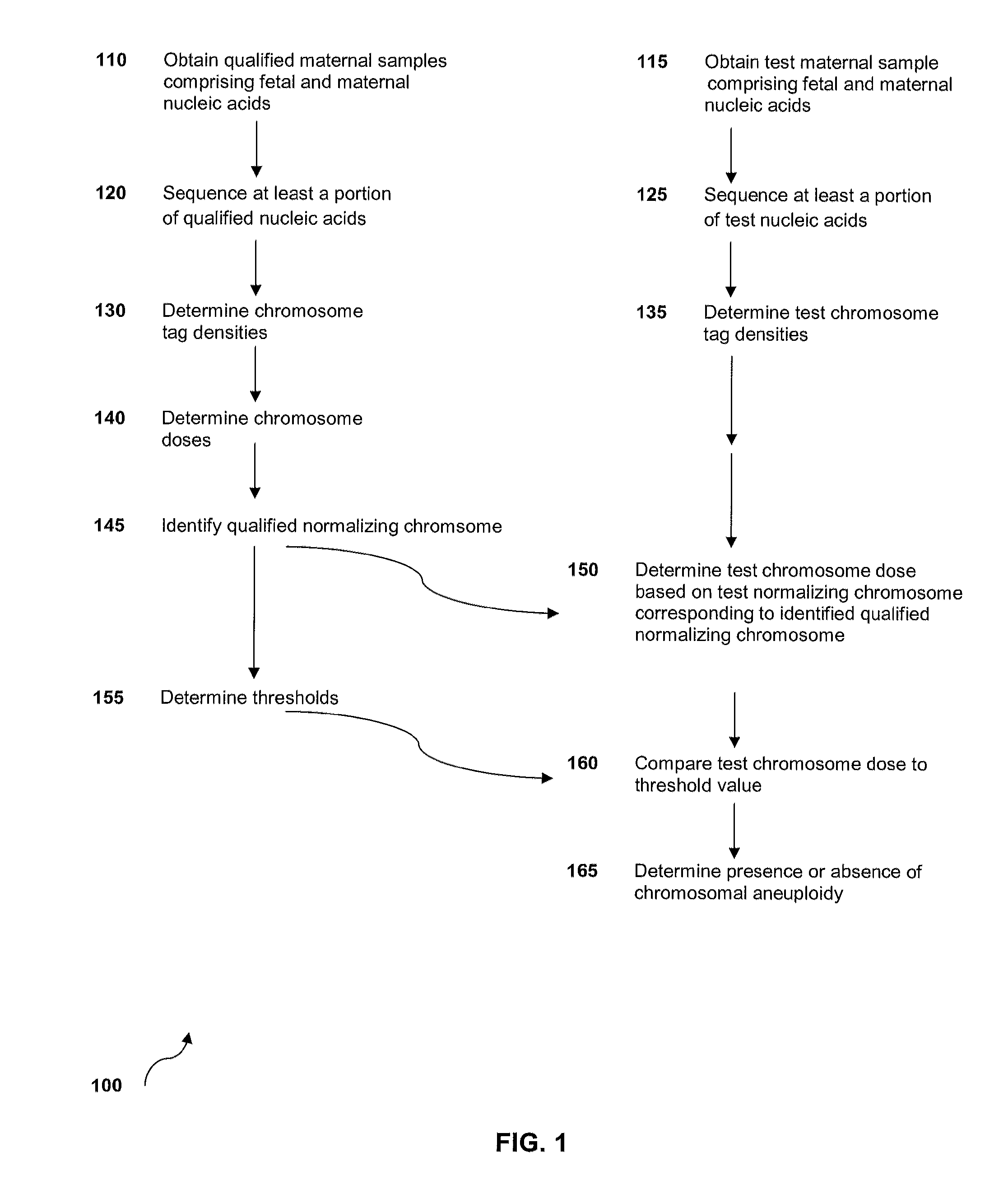
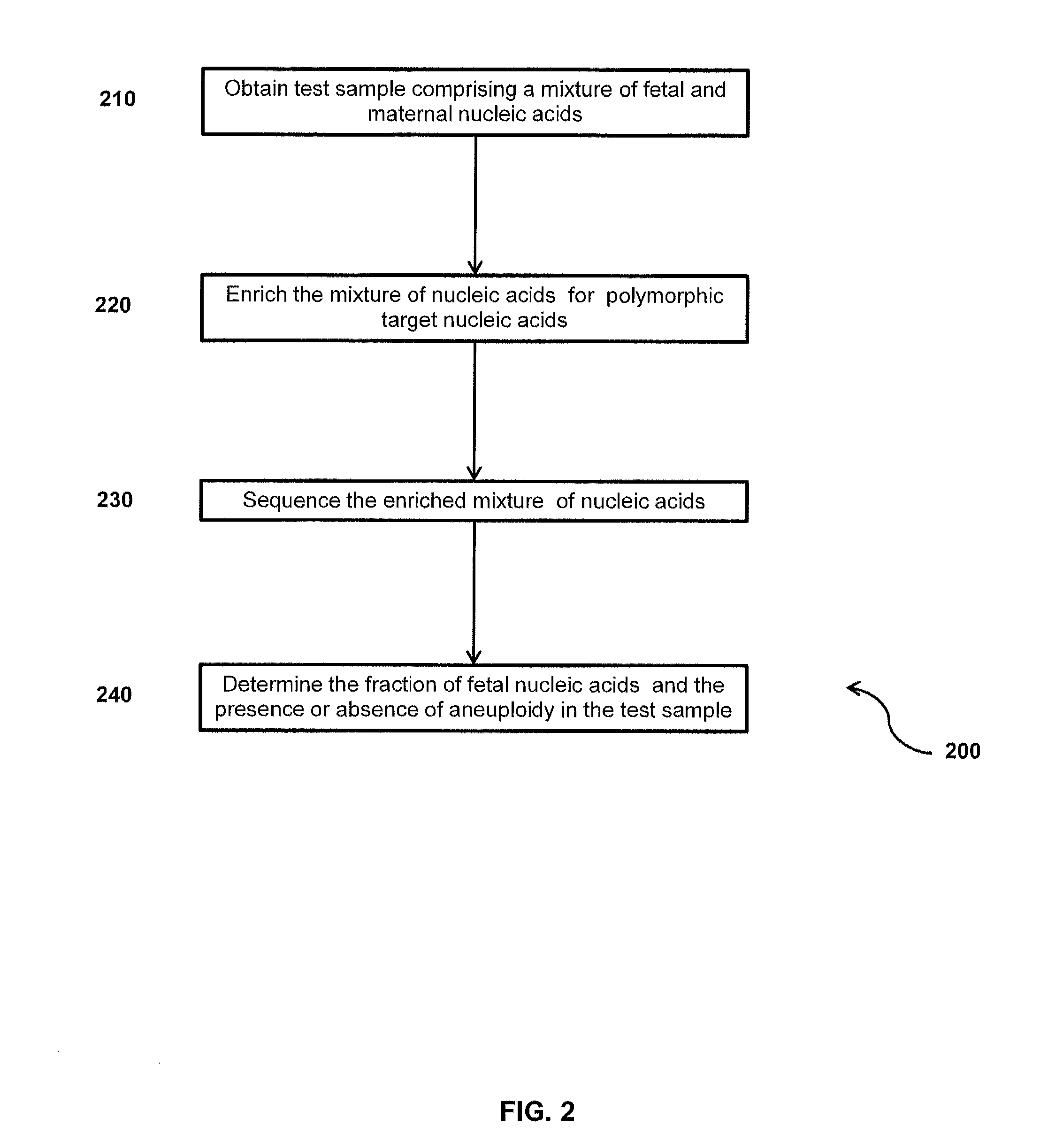
Method for sample analysis of aneuploidies in maternal samples
InactiveUS20120270739A1Decreases sequencing biasQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationPrenatal diagnosisAnalysis method
The invention provides methods for determining aneuploidy and / or fetal fraction in maternal samples comprising fetal and maternal cfDNA by massively parallel sequencing. The method comprises a novel protocol for preparing sequencing libraries that unexpectedly improves the quality of library DNA while expediting the process of analysis of samples for prenatal diagnoses. The novel protocol can be performed in solution or on a solid surface.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
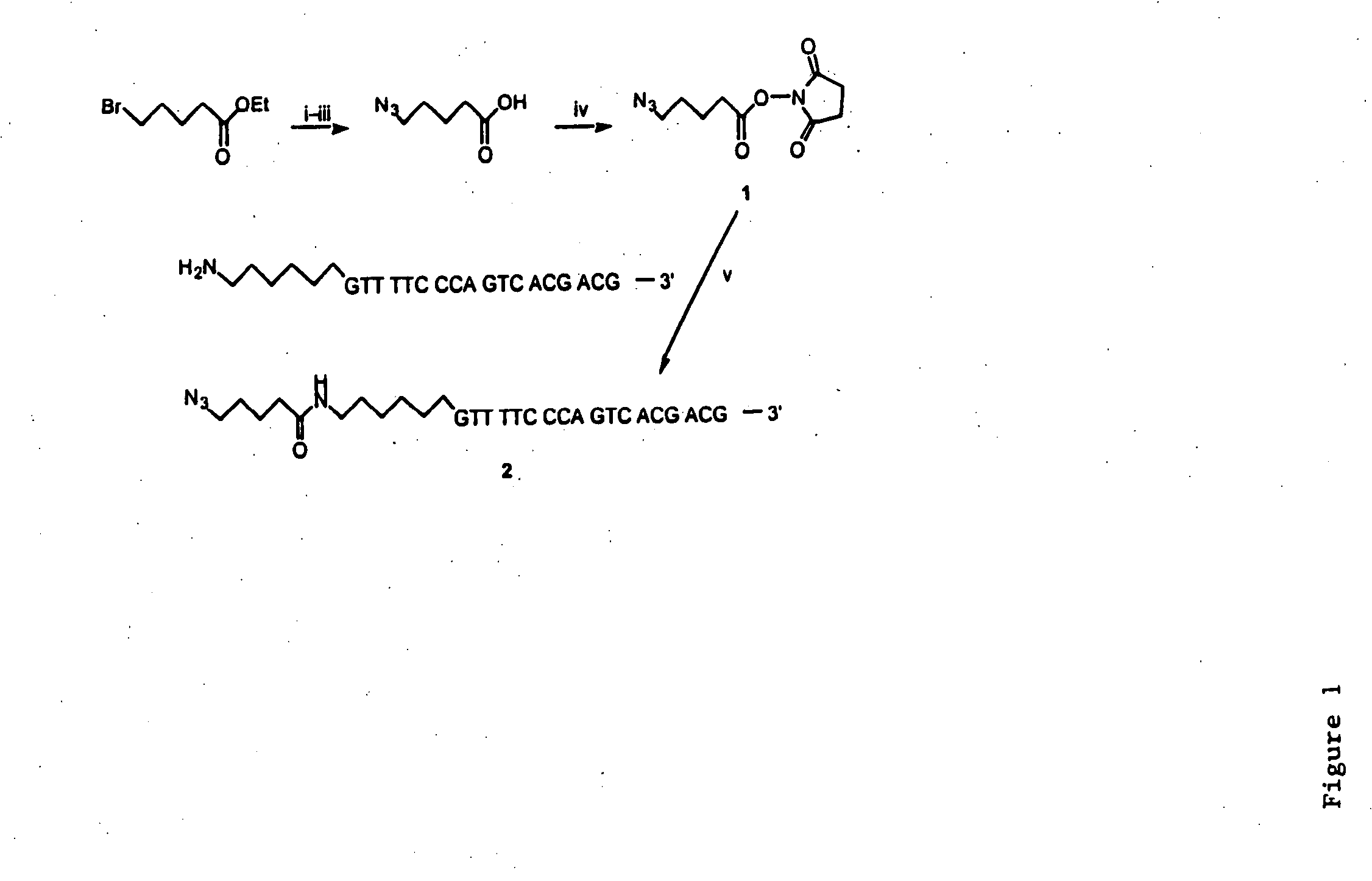
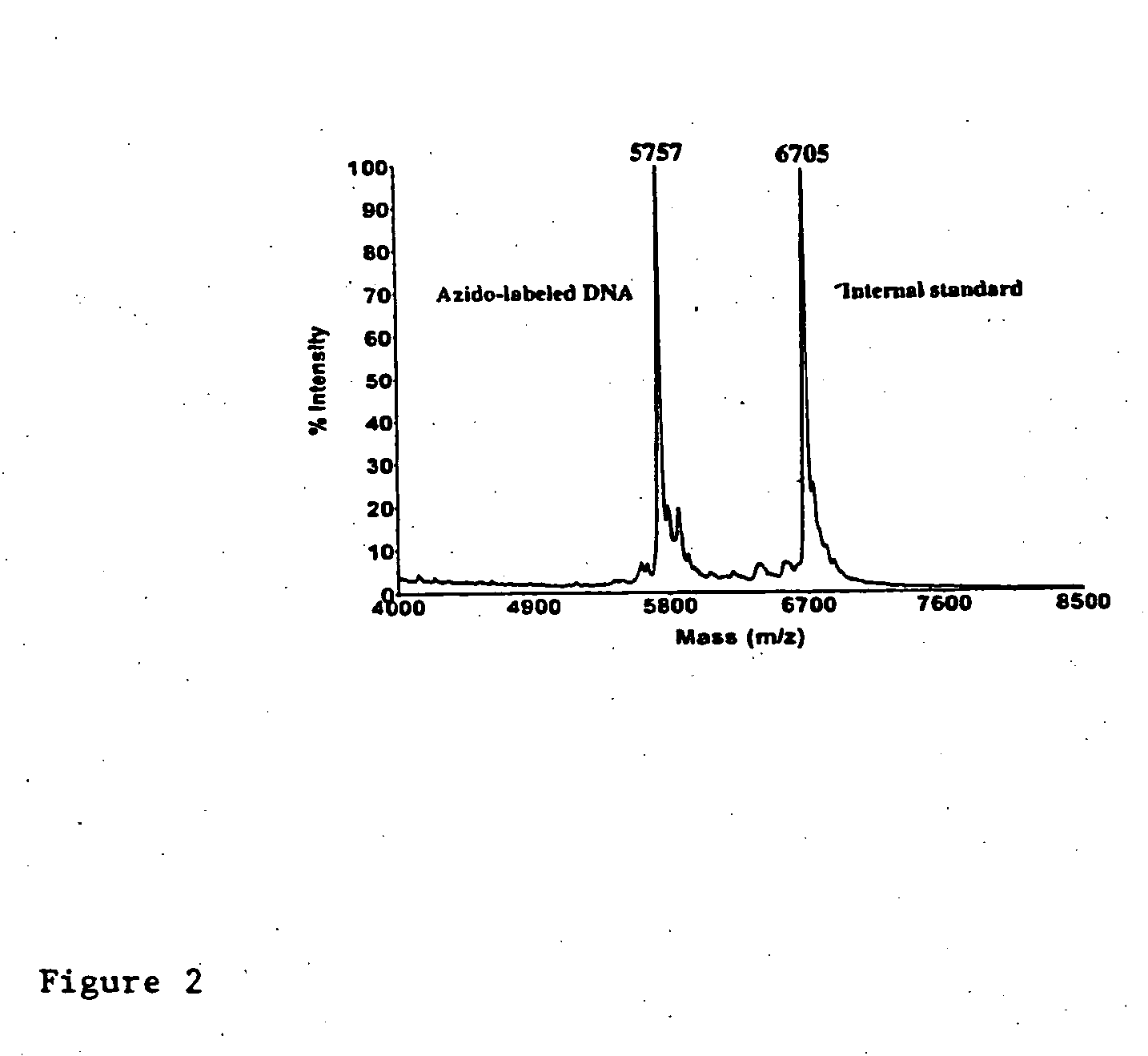
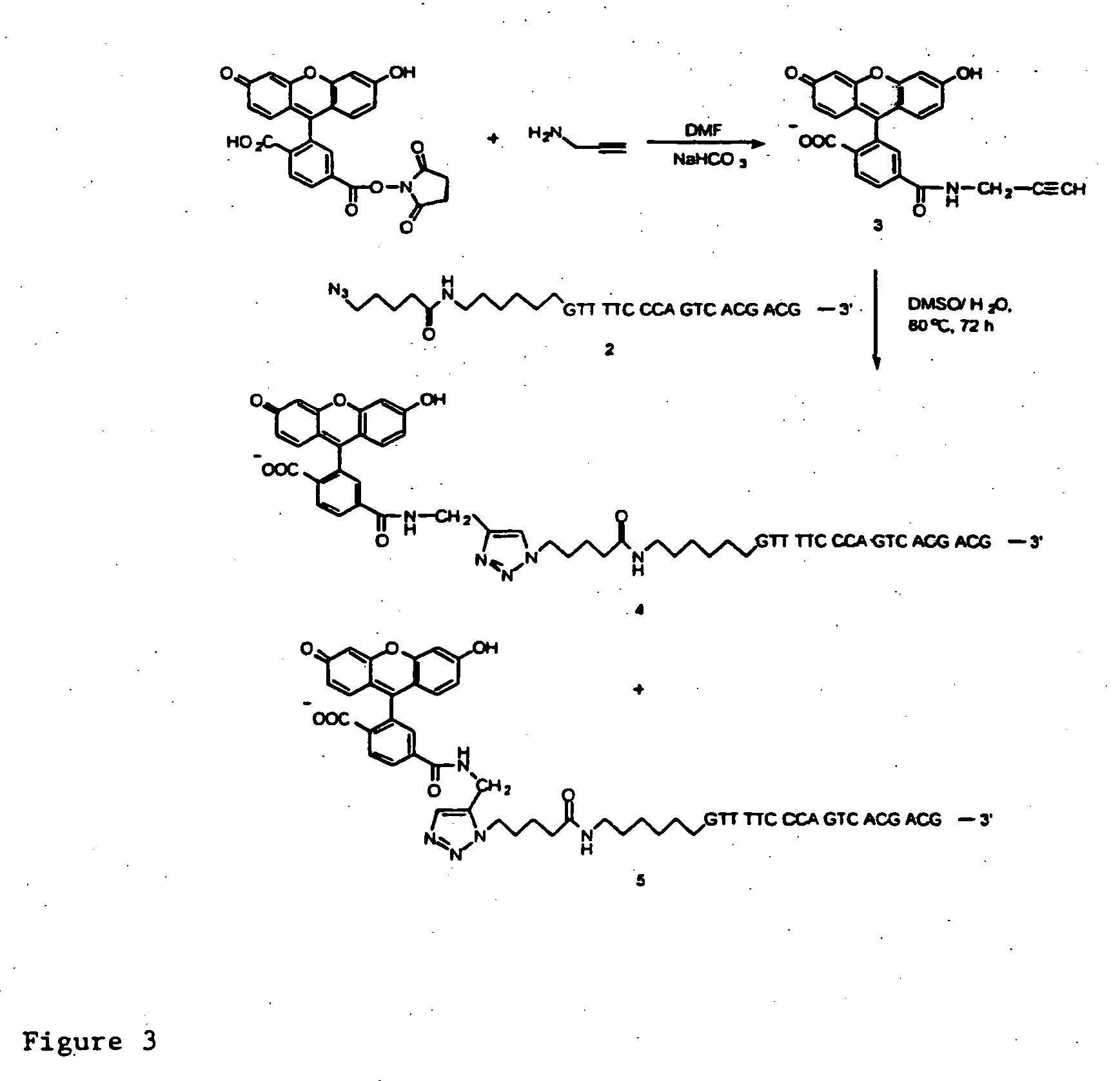
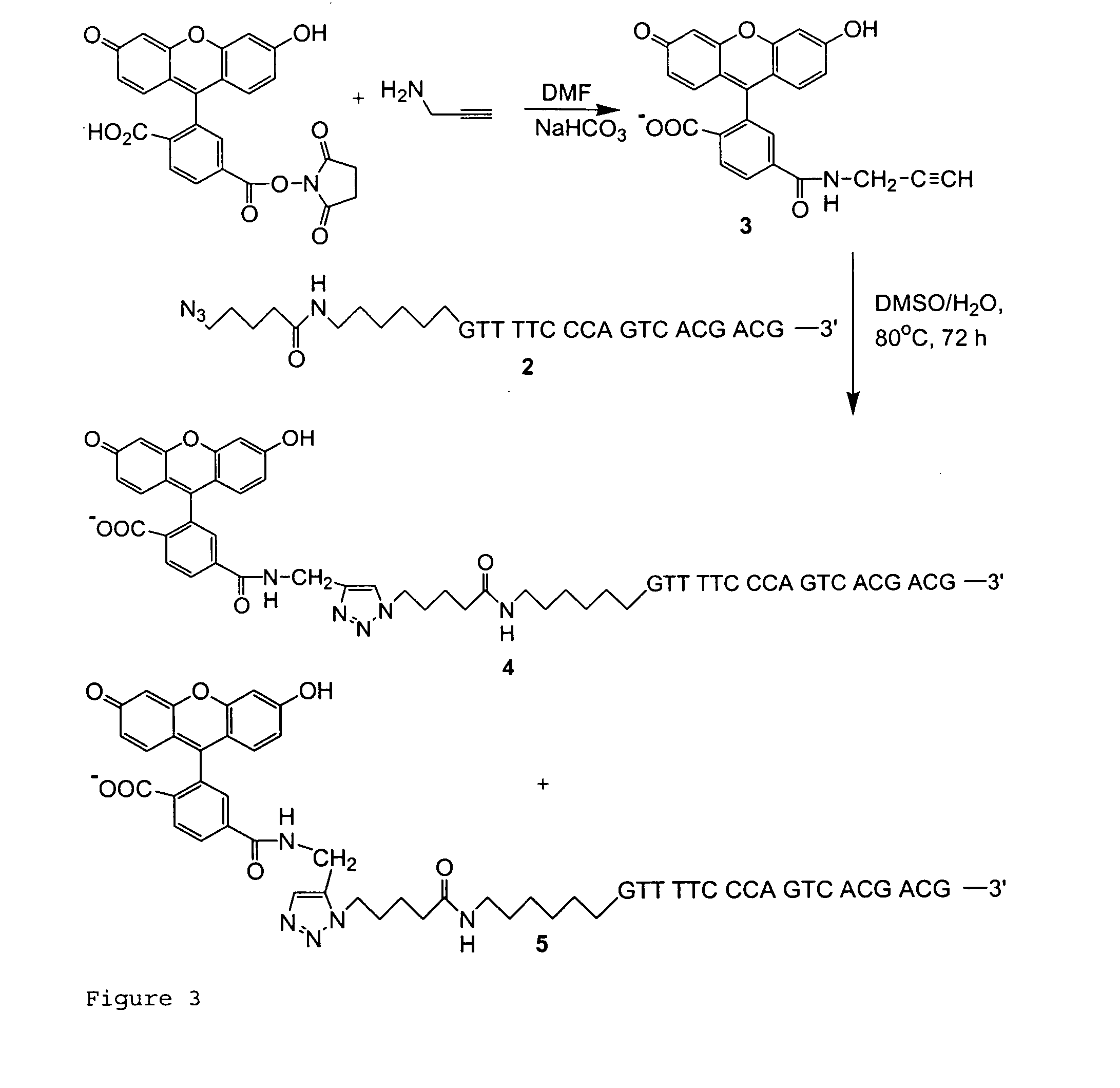
Biomolecular coupling methods using 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition chemistry
InactiveUS20050032081A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBio moleculesCycloaddition
This invention provides methods for covalently affixing a biomolecule to either a second molecule or a solid surface using 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition chemistry. This invention also provides related methods and compositions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
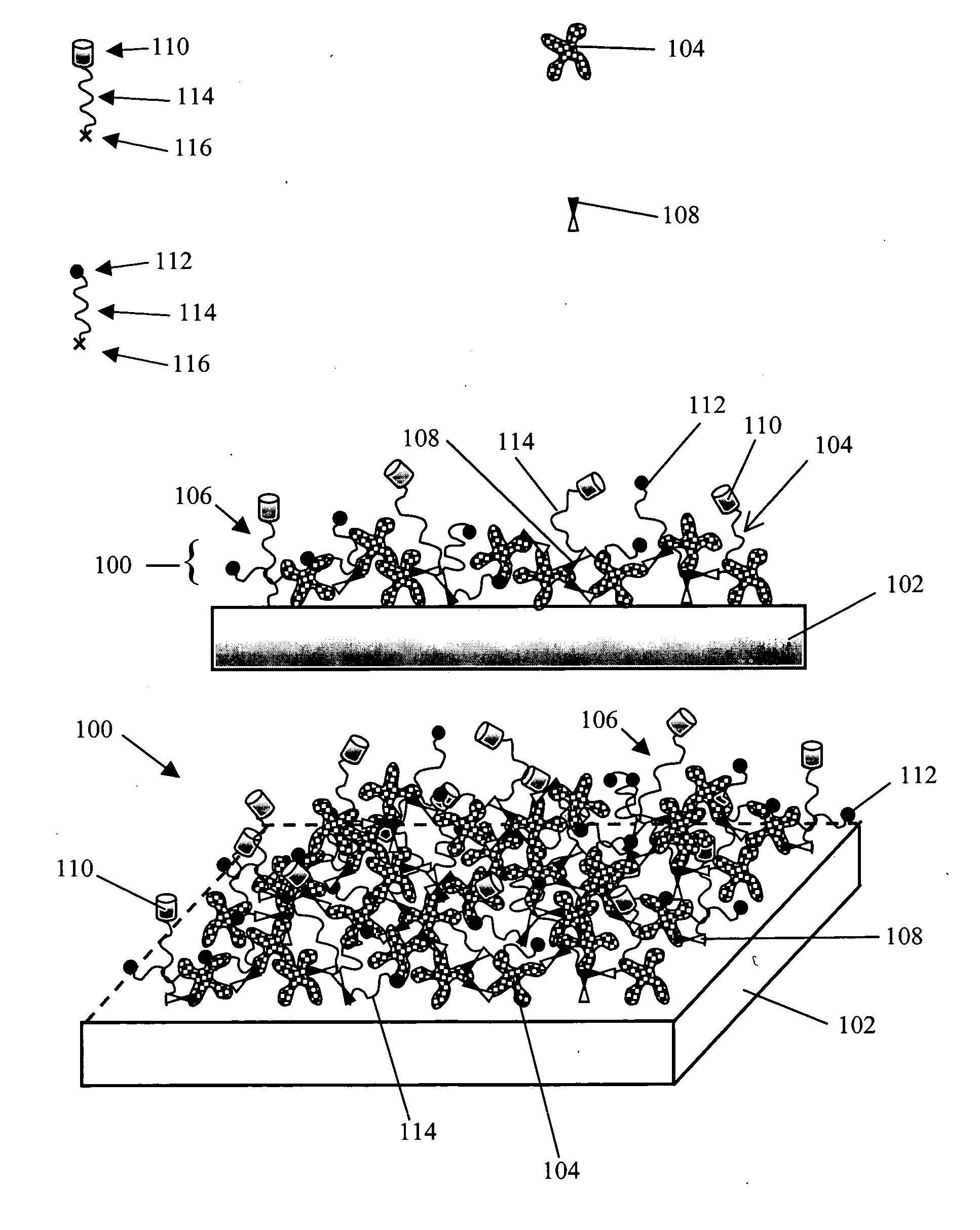
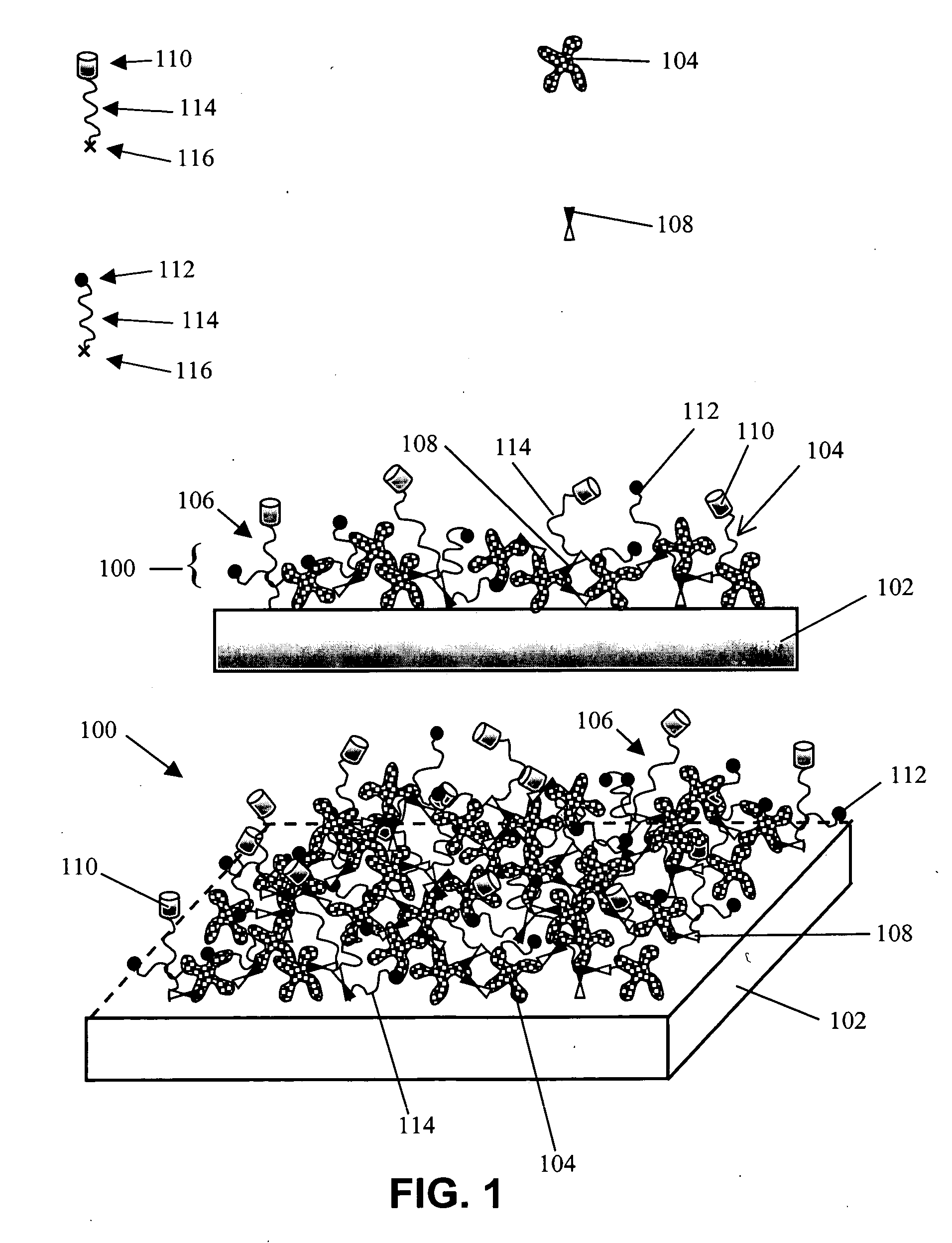
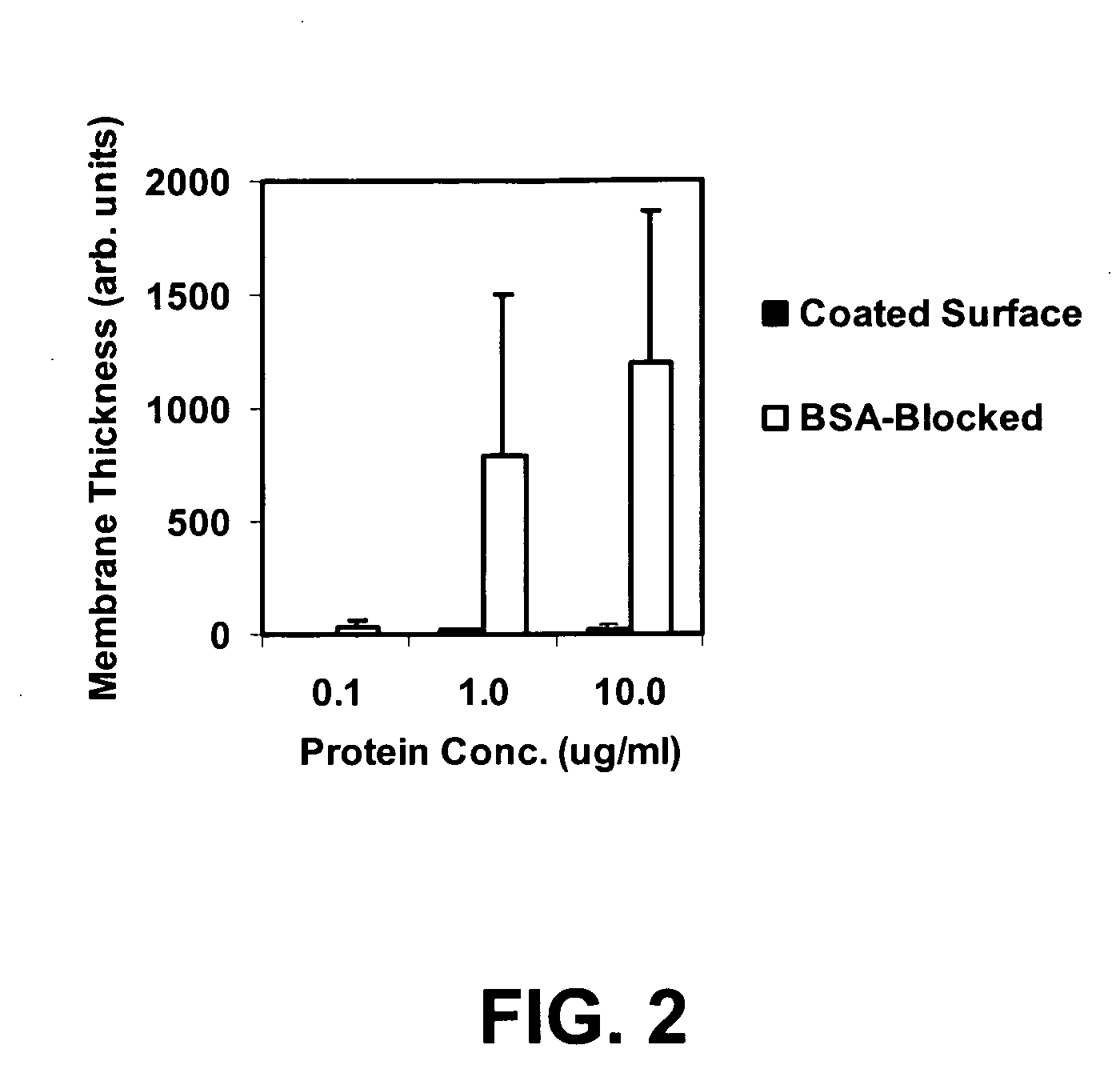
Functional surface coating
InactiveUS6844028B2Inhibit non-specific bindingImprove propertiesMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationProtein targetBound property
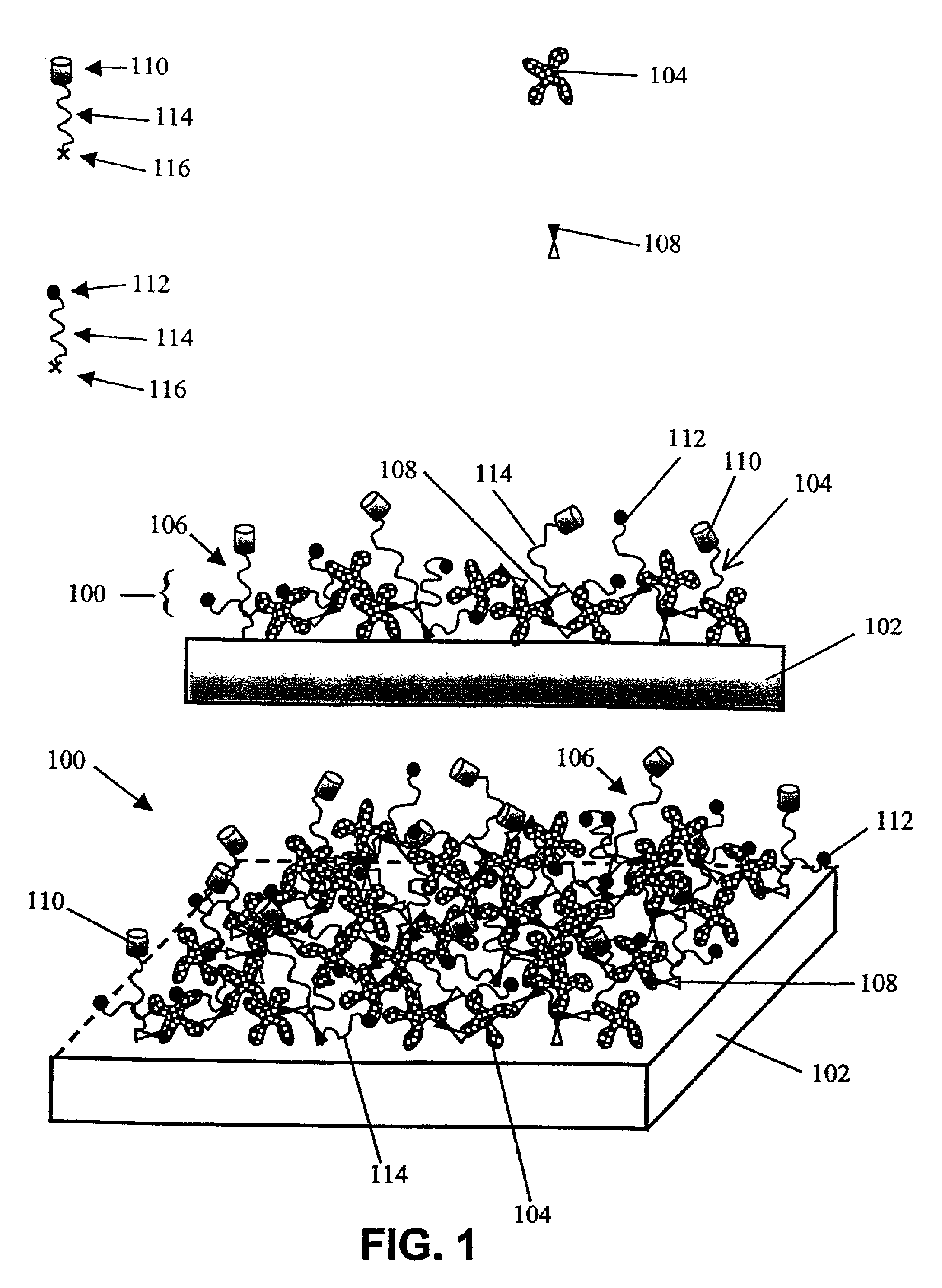
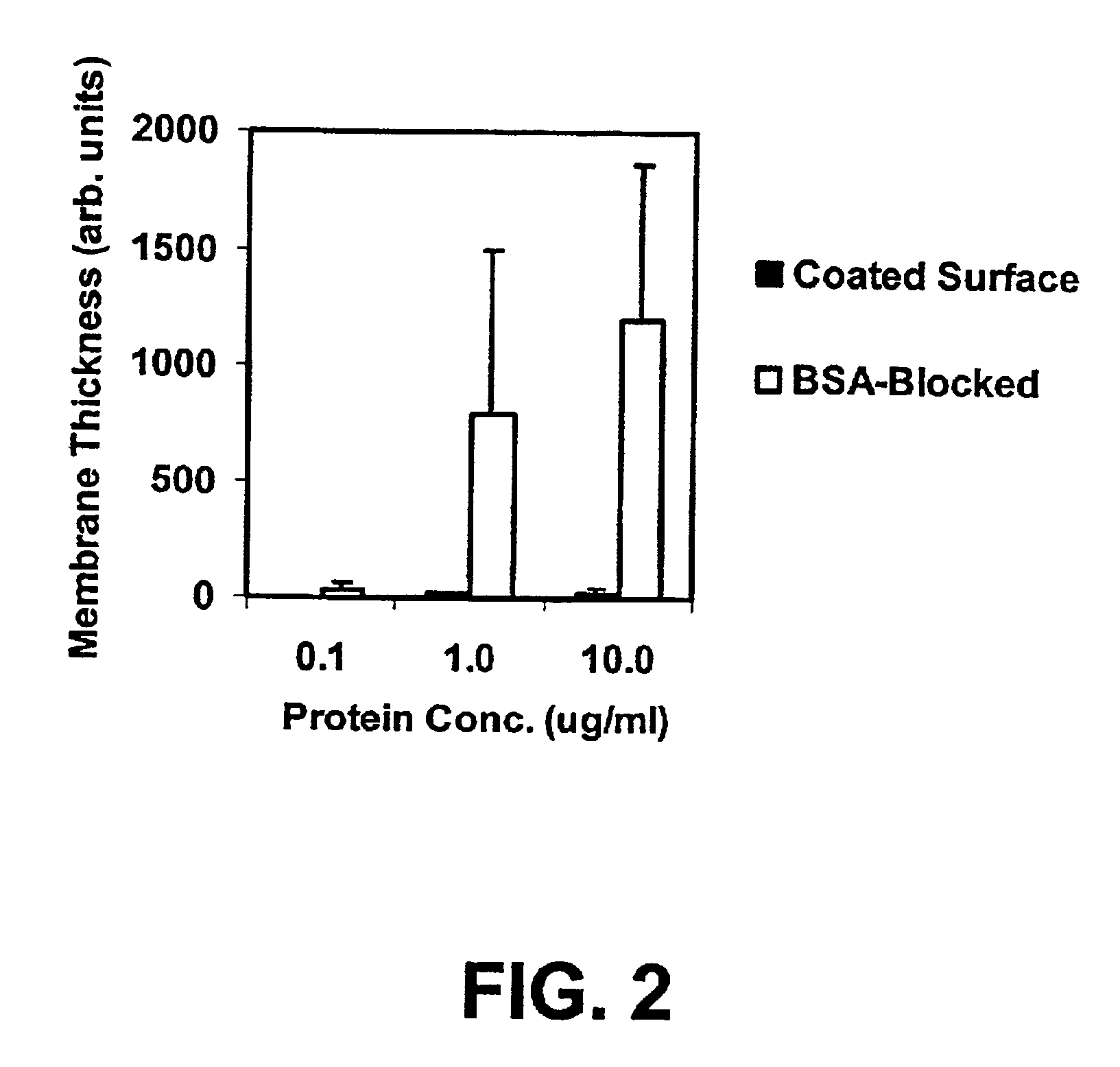
Compositions and methods of preparing functional thin films or surface coatings with low non-specific binding are described. The thin films contain specified functional groups and non-specific binding repellant components. The thin films are either covalently bound to or passively adsorbed to various solid substrates. The specified functional group provides specified activity for the thin film modified solid surfaces and non-specific binding repellant components significantly reduce the non-specific binding to the thin film modified solid surfaces. Non-specific binding repellant components do not affect specified functional group's activity in the thin films. In these methods, specified functional groups are anchored to the solid substrates through a spacer. Surface coatings are also described having both non-specific protein binding properties combined with functional groups for specific binding activity thereby providing surface coating that specifically recognize target proteins but limit binding to non-specific protein.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method for Archiving and Clonal Expansion
InactiveUS20090203531A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationPresent methodTotal rna
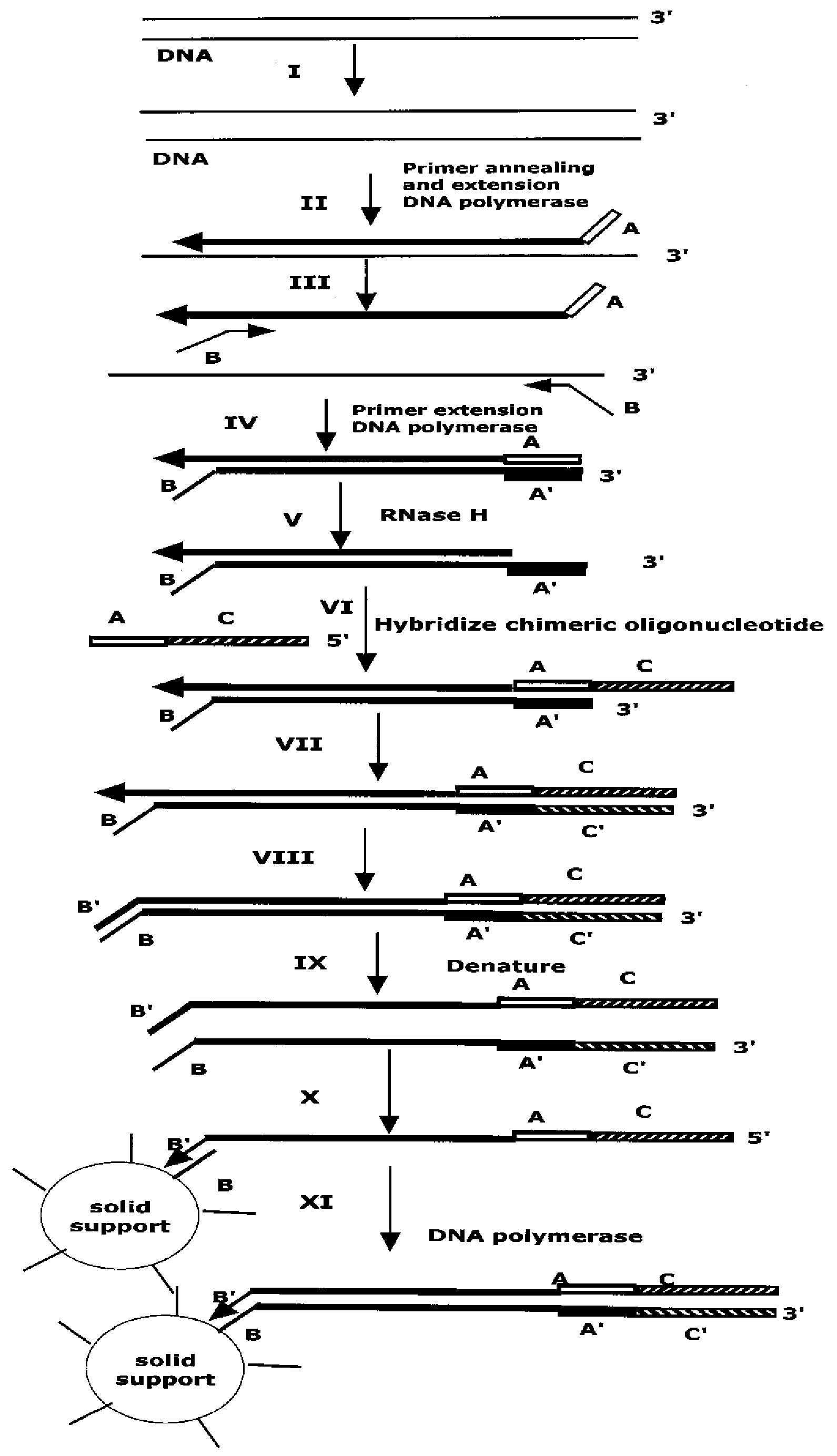
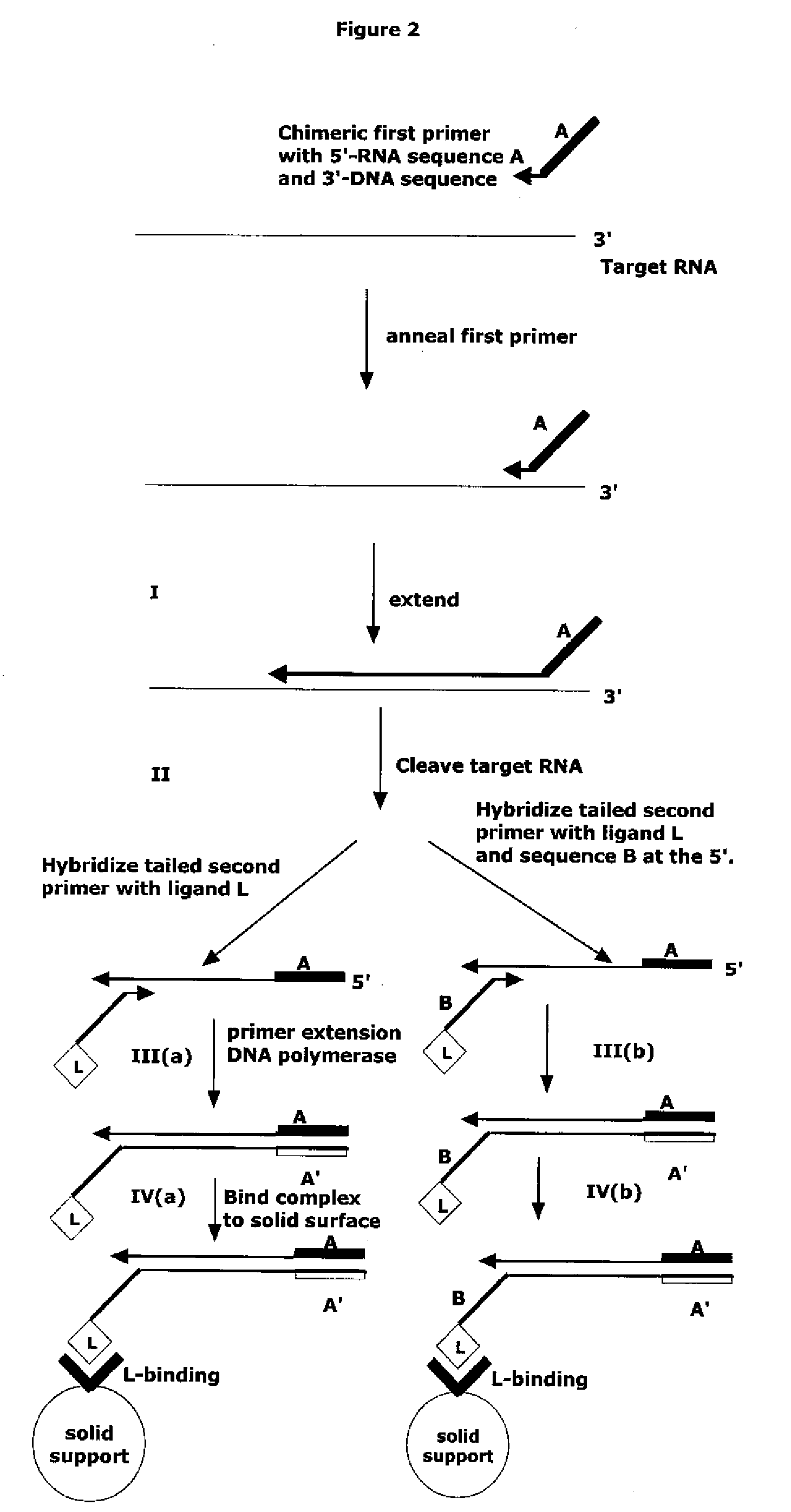
The present method provides methods, libraries, and kits related to the archiving and clonal expansion of sequences related to target polynucleotide sequences. The method allow for the attachment of polynucleotides with defined 3′ and or 5′ sequences to solid surfaces. The polynucleotides attached to the solid substrates can be stored or archived as libraries and can subsequently be retrieved for analysis, for example by clonal expansion. In some embodiments, nucleotides attached to solid surfaces can be used for sequencing of nucleotide sequences related to target RNA or target RNA. The methods are applicable to total RNA and / or total DNA analysis.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Methods and compositions for antimicrobial surfaces
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for treating solid surfaces having antimicrobial and biocidal properties. Such surfaces are capable of controlling or killing a broad spectrum of biological agents, including viruses, bacteria and other microbial agents in solids, liquids or gases that subsequently contact the treated surface.
Owner:SISHIELD TECH
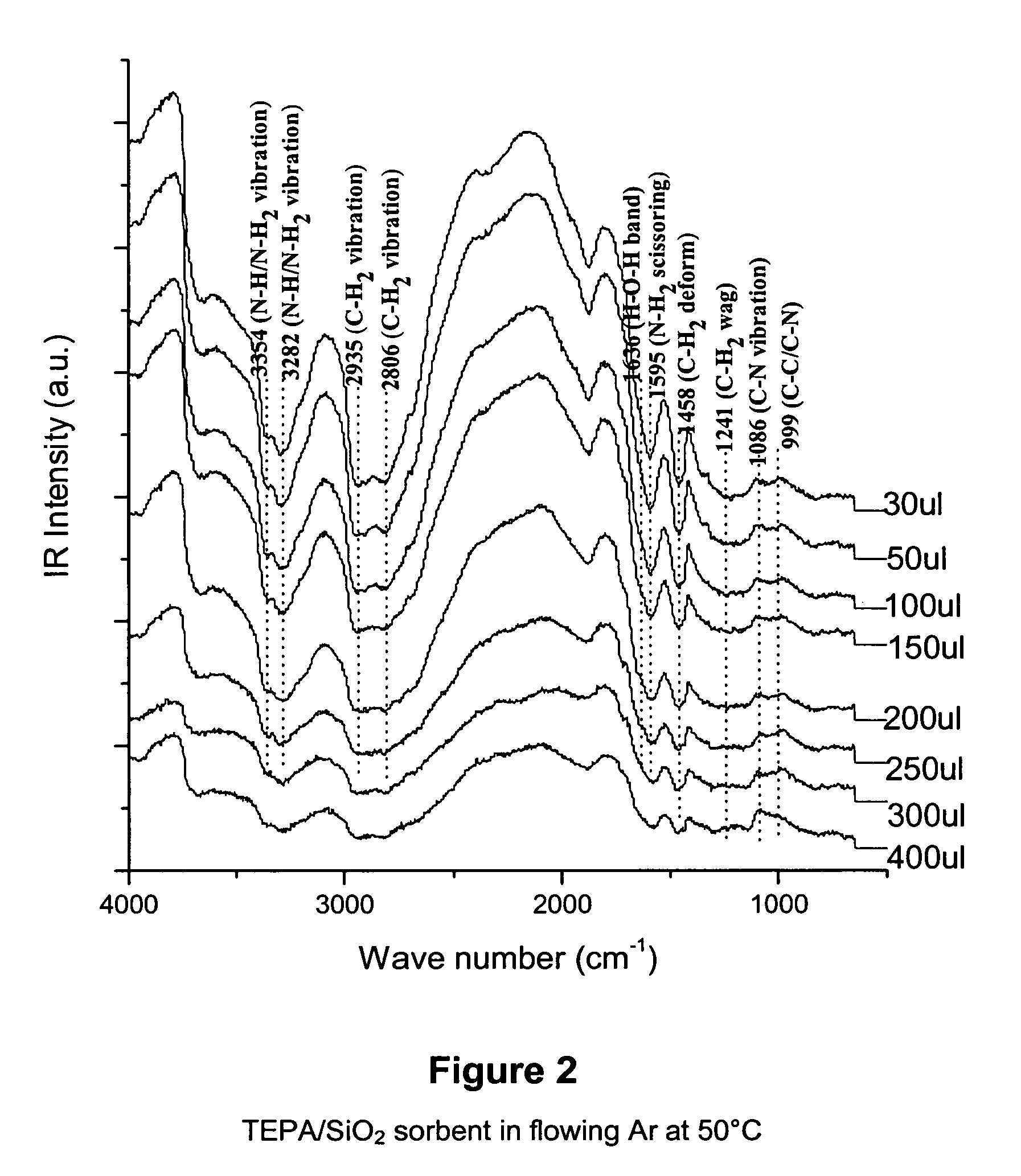
Amine absorber for carbon dioxide capture and processes for making and using the same
InactiveUS20100263534A1Lower potentialIncreasing amineGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsSulfurAbsorbent material
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
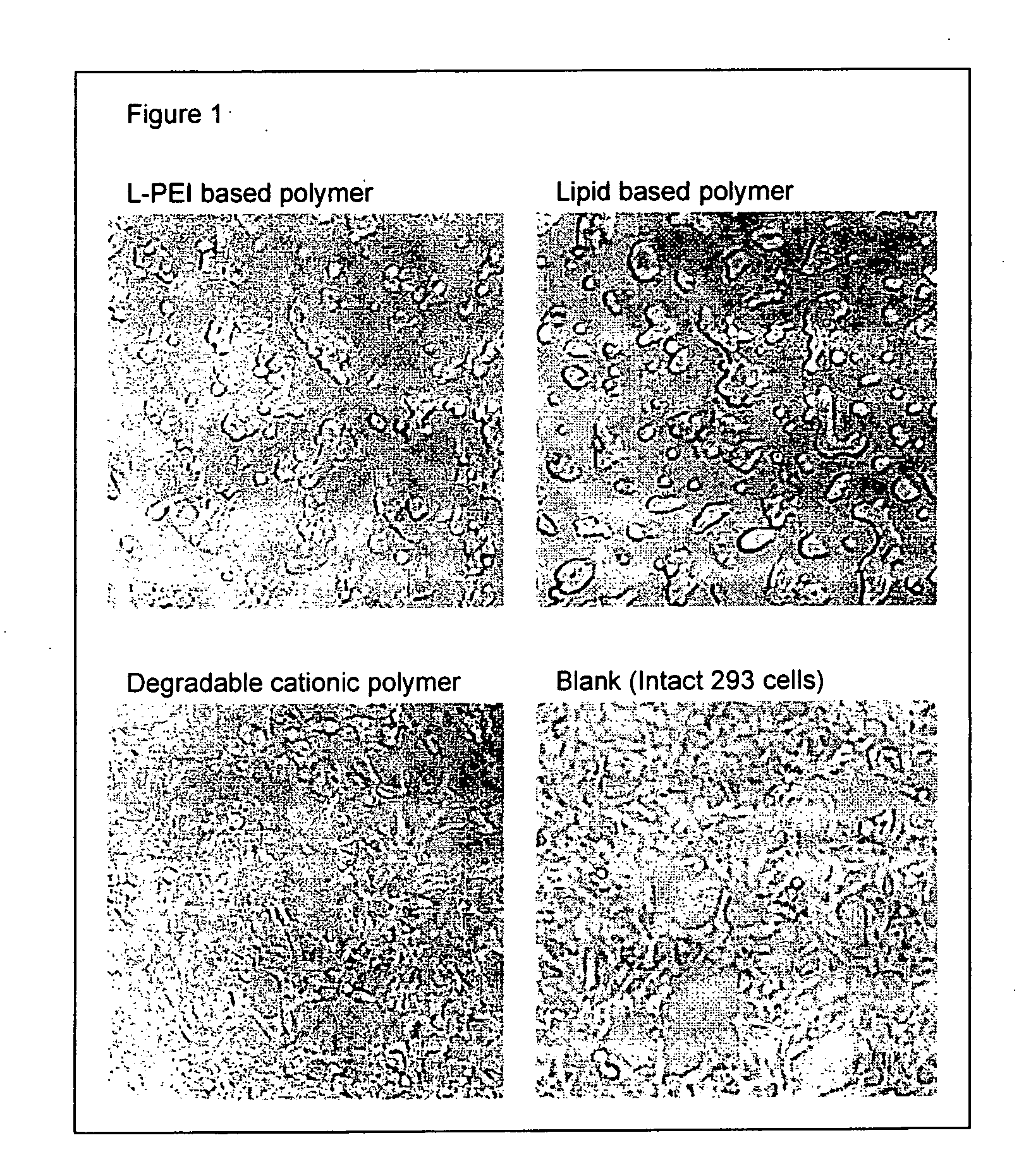
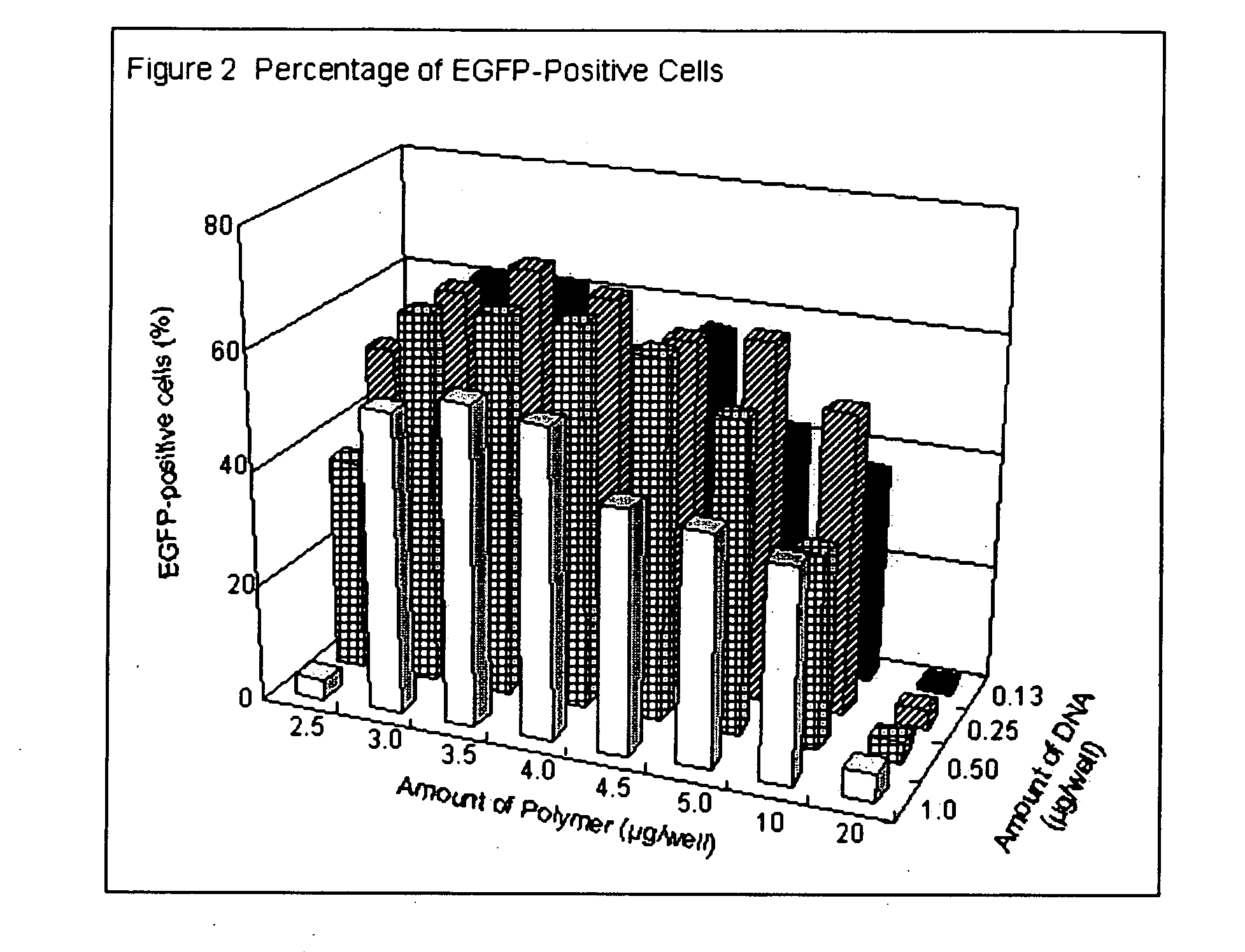
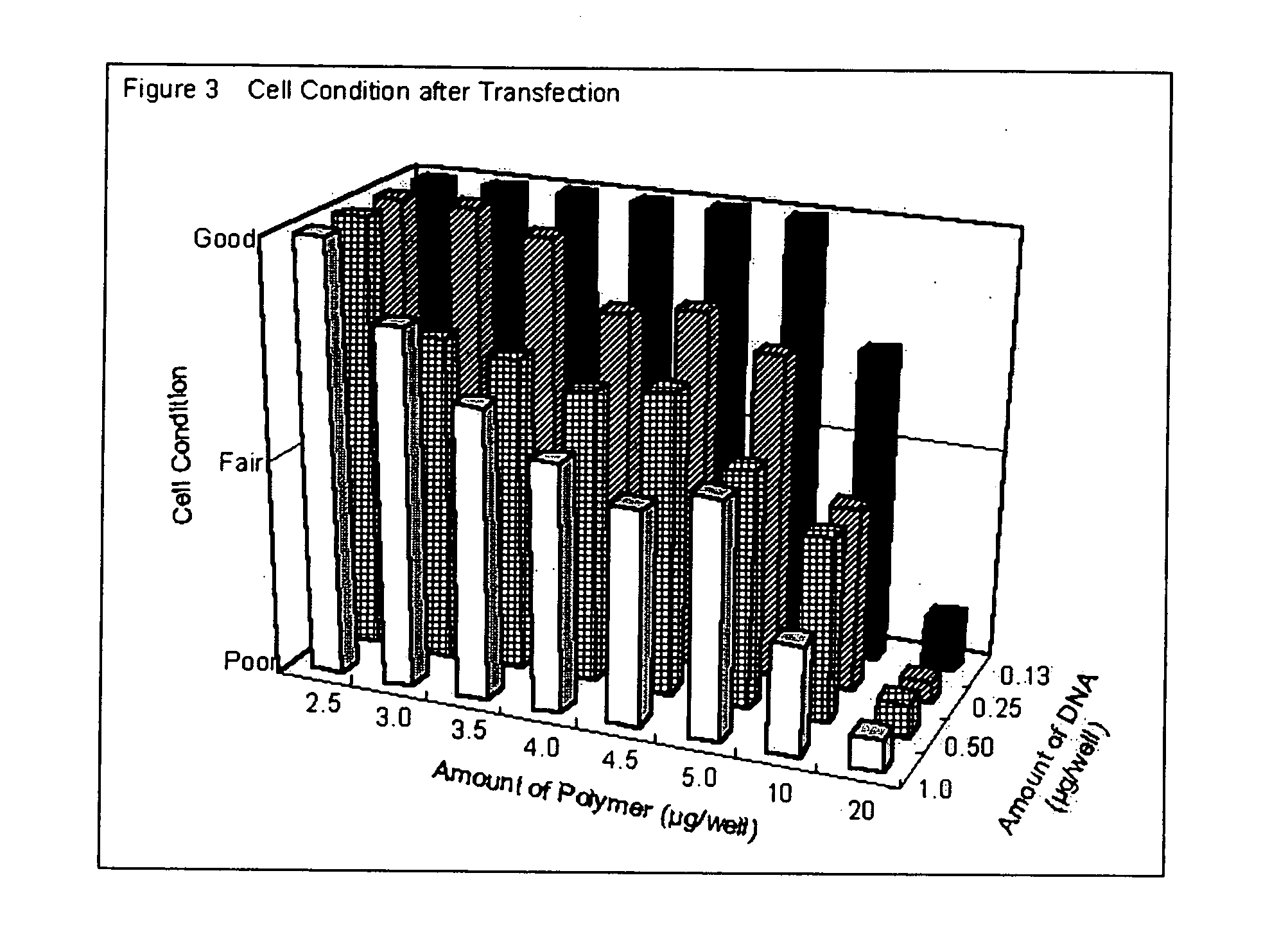
Solid surface with immobilized degradable cationic polymer for transfecting eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20060134790A1Without significant loss of transfection activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRoom temperatureTransfection
A cell transfection / culture device is disclosed which includes a solid support coated with a degradable polymer cation as a transfection reagent. The transfection / culture device is conveniently stored at room temperature until use. Cell transfection is accomplished easily by adding the nucleic acid of interest and the cells to be transfected to the transfection / culture device. Cell transfection is completed in less than one hour by using the transfection / culture device described herein.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
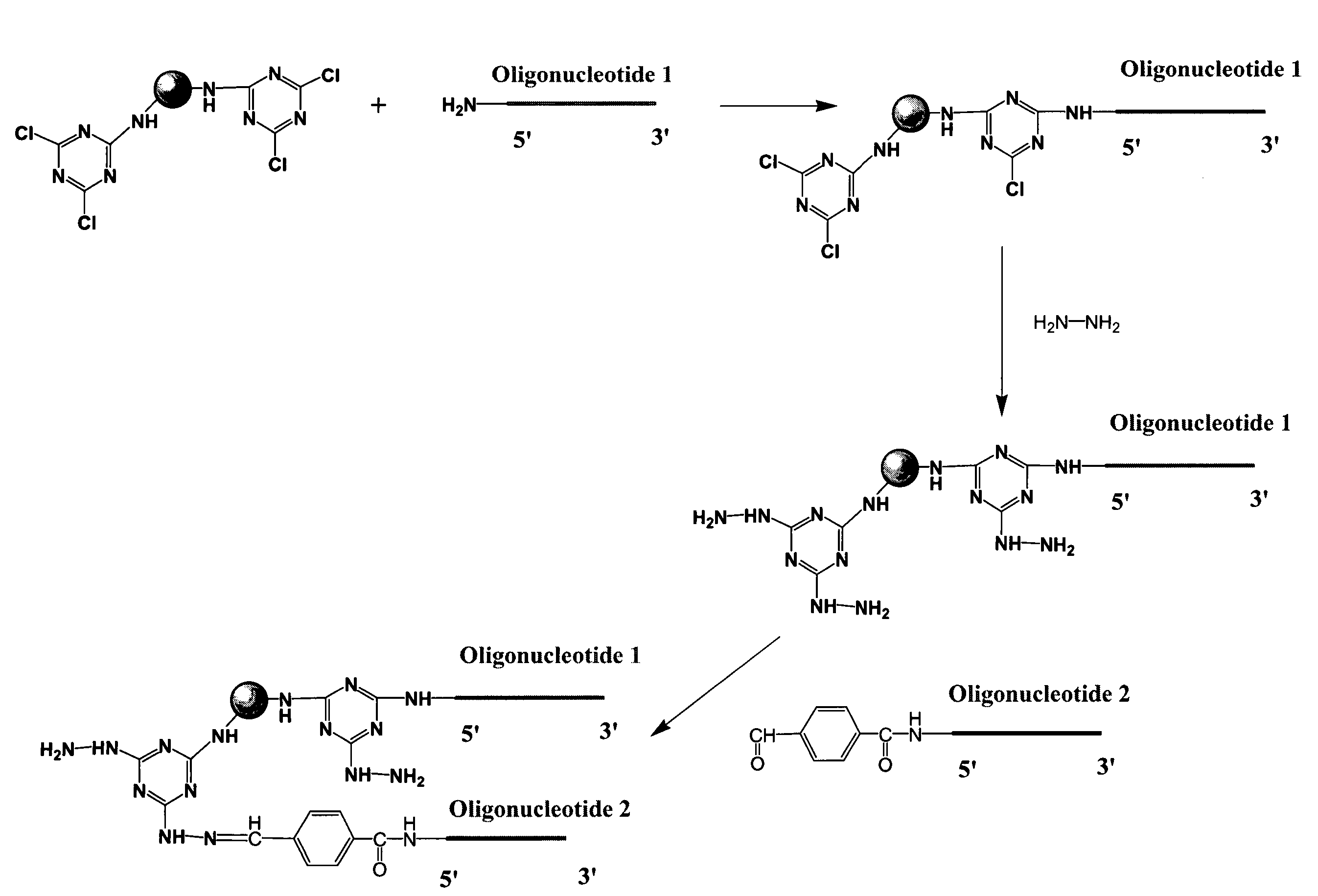
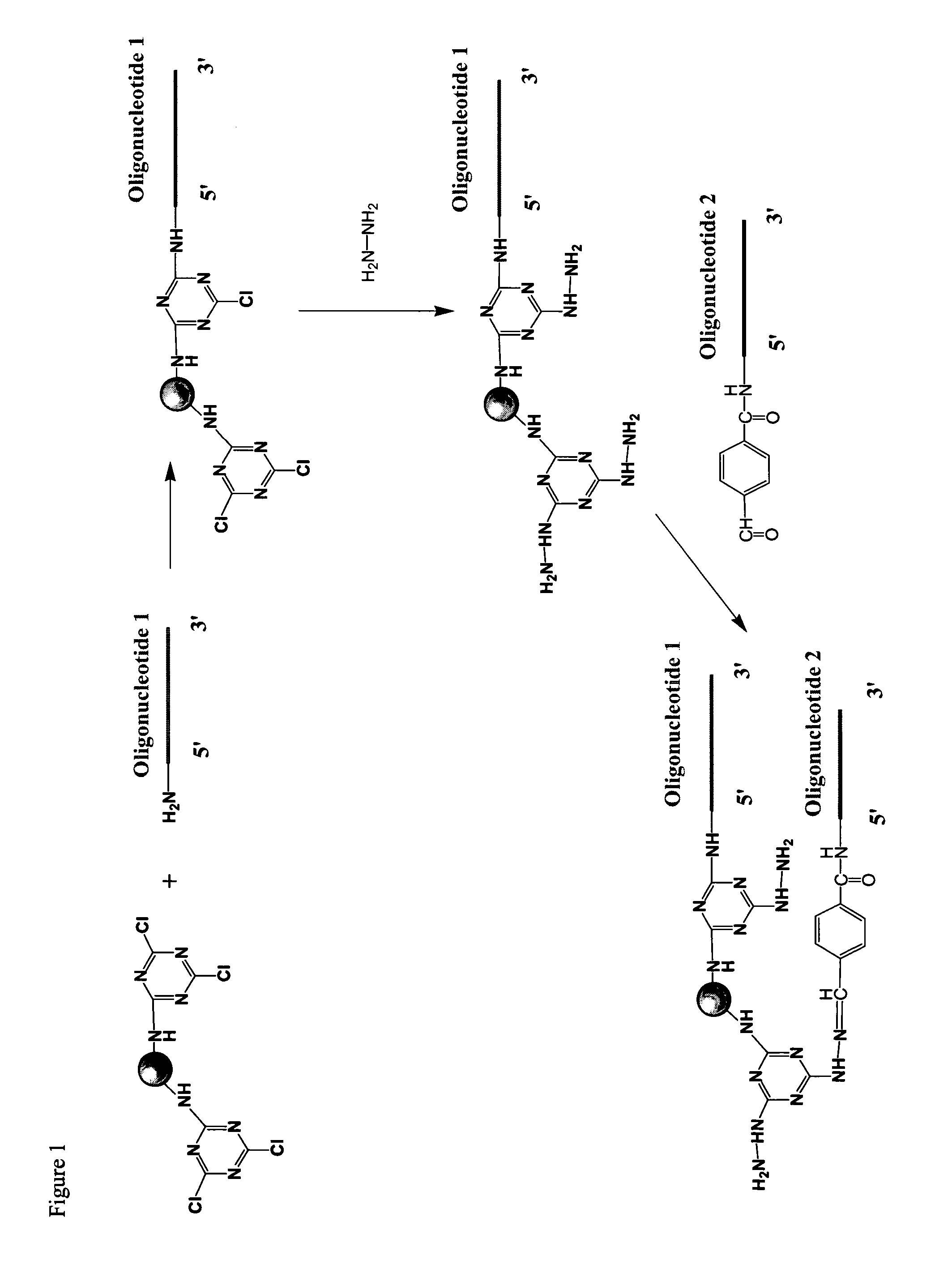
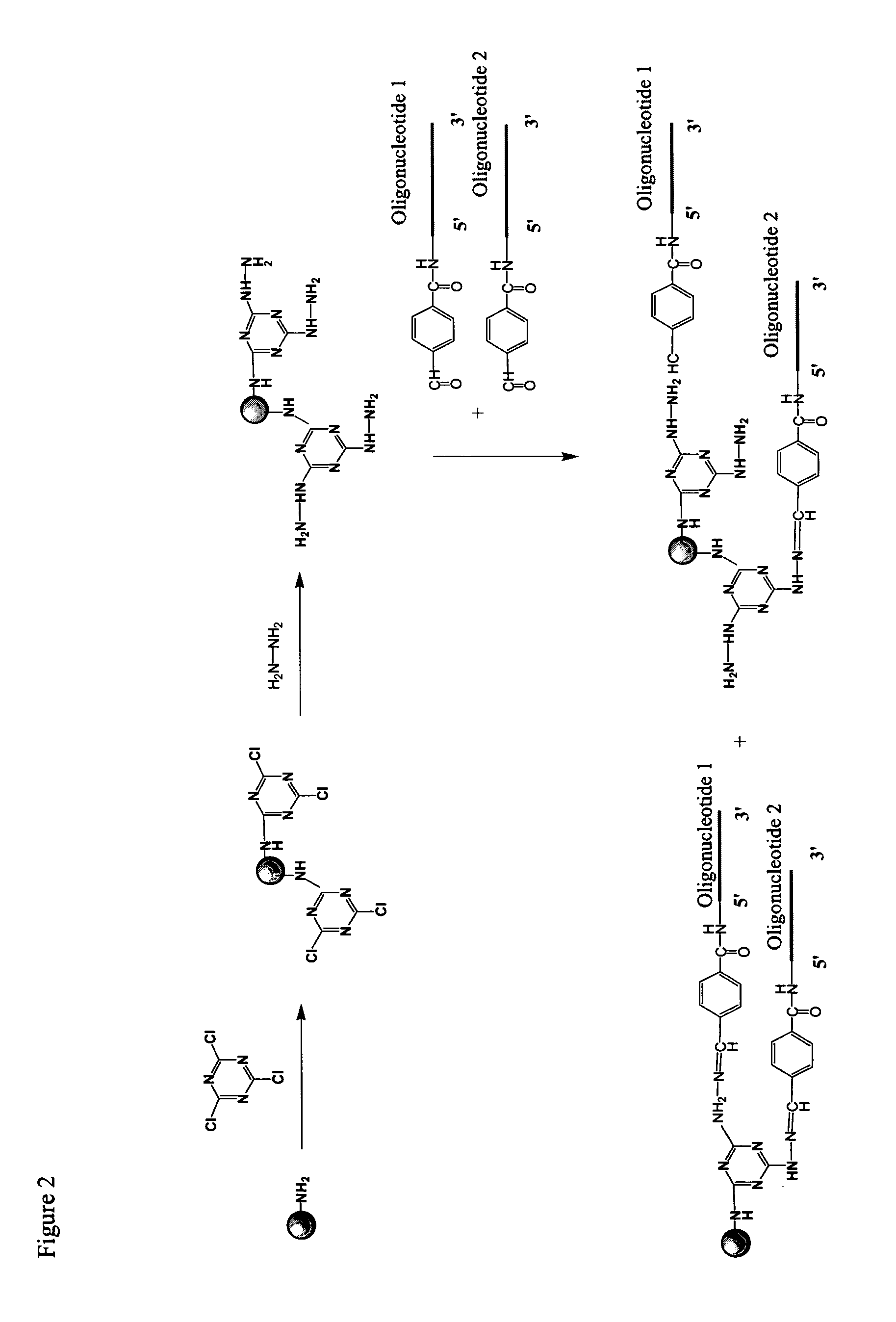
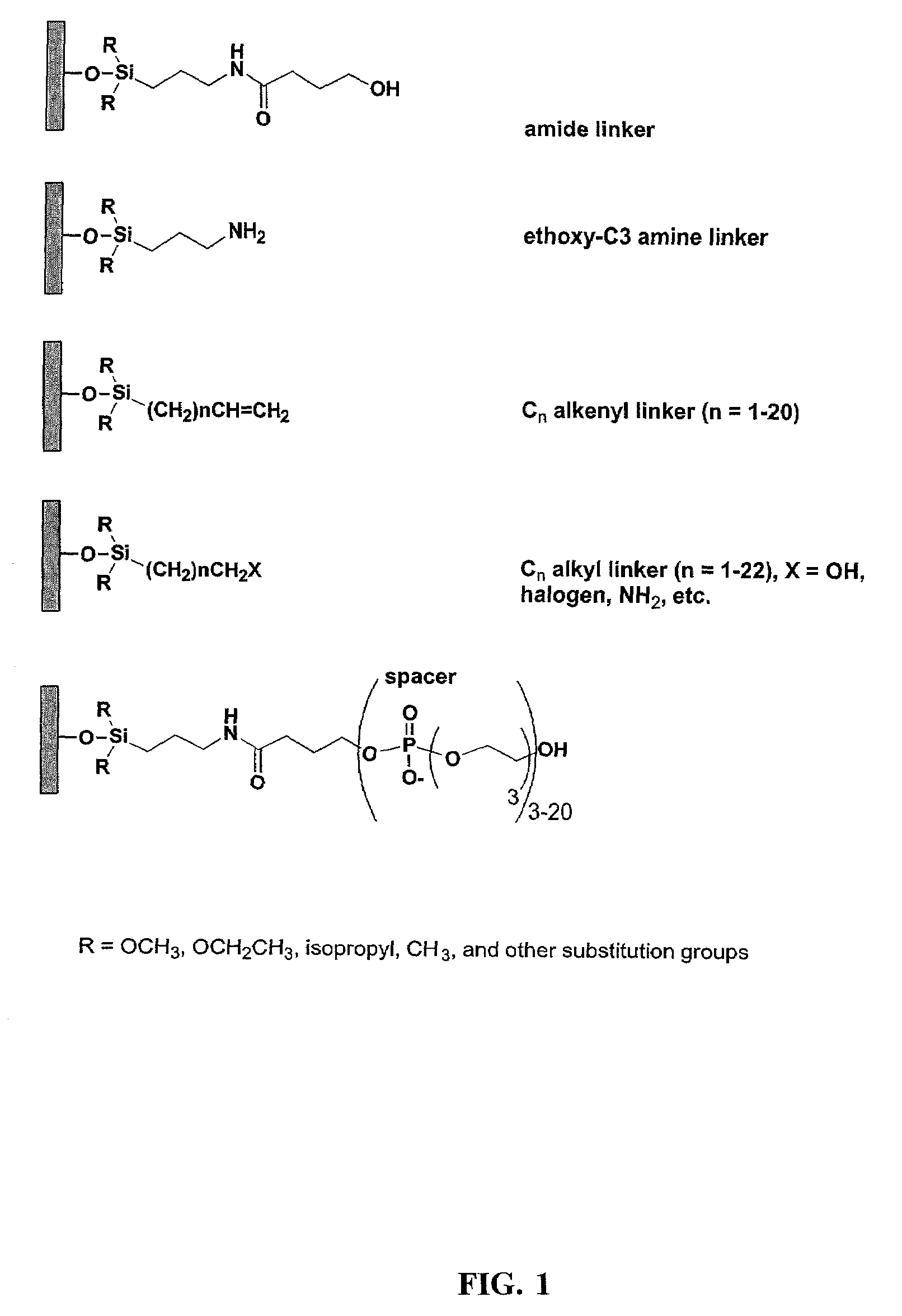
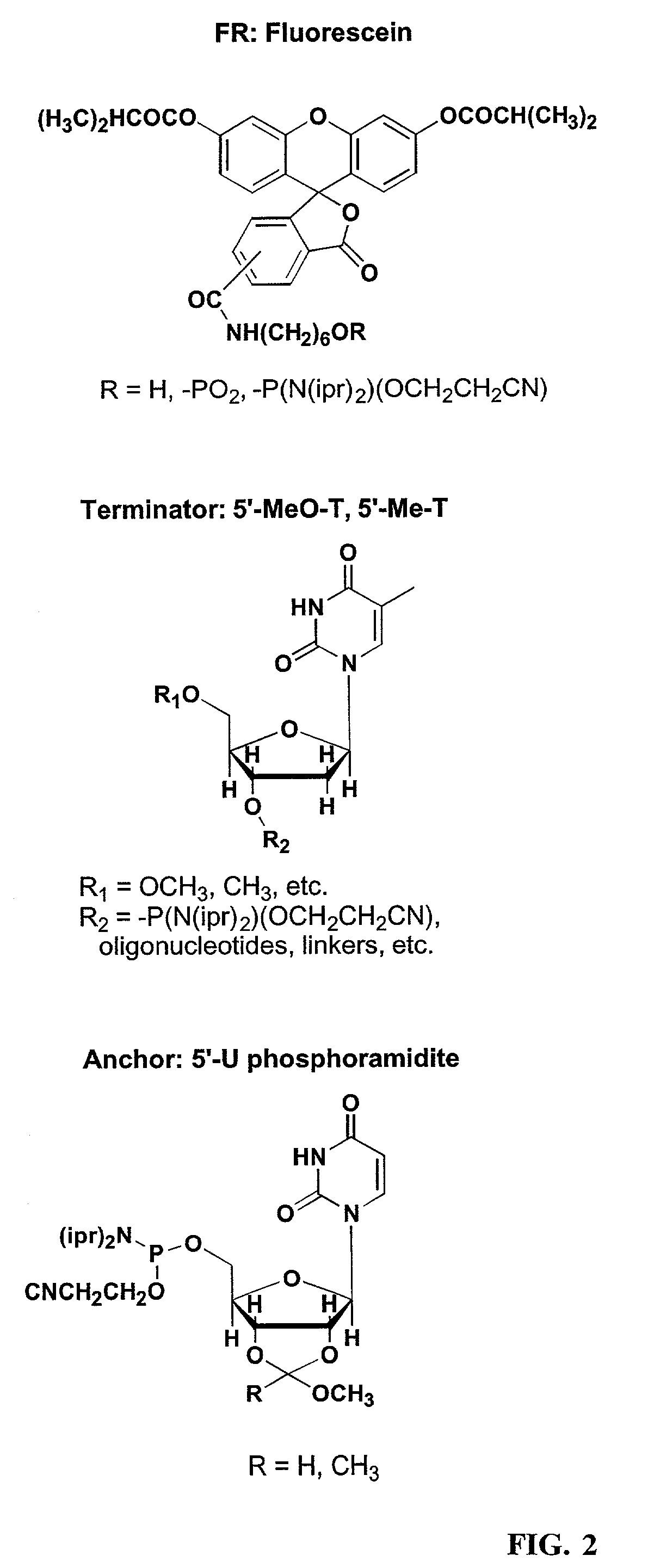
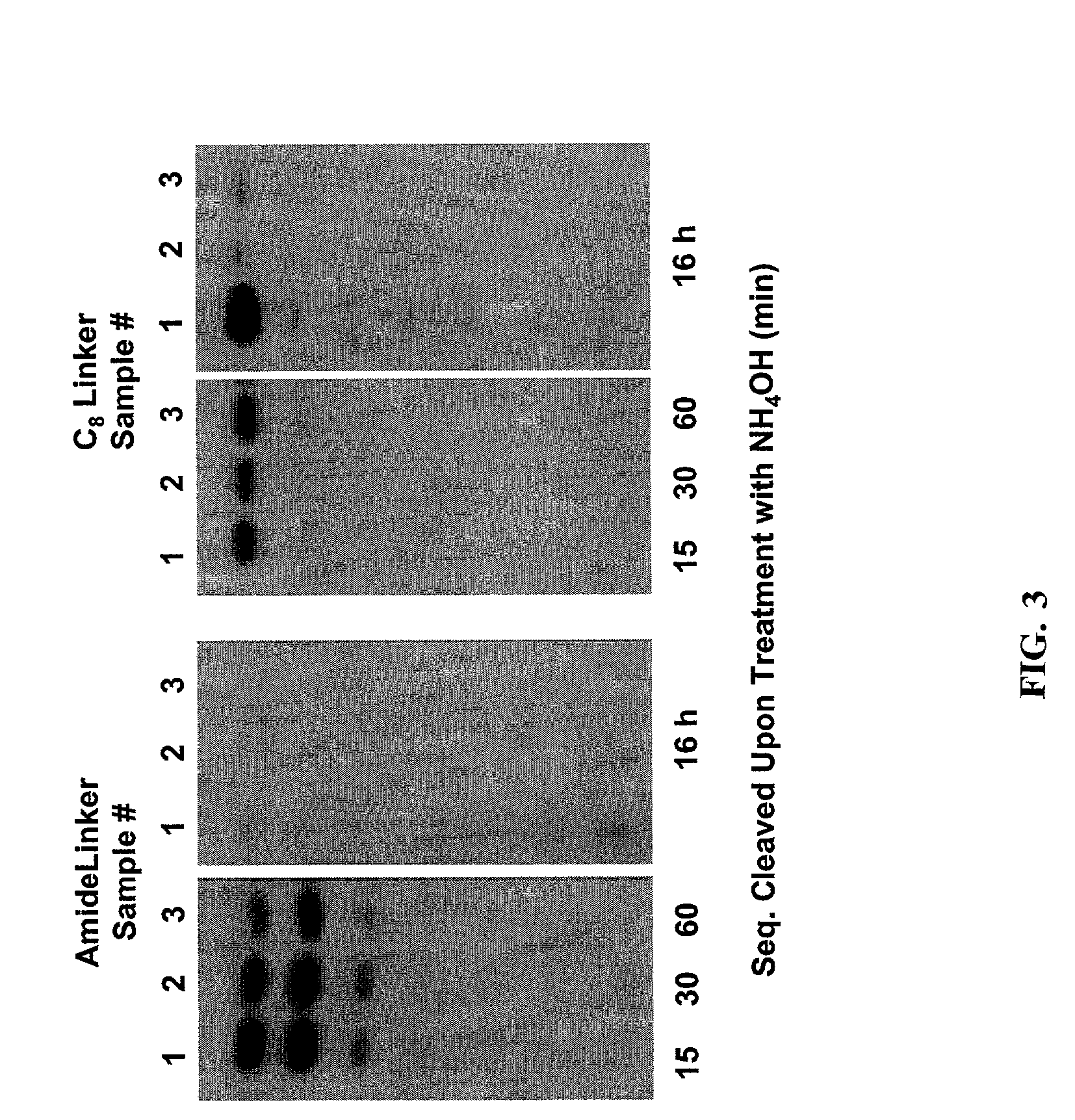
Linkers and co-coupling agents for optimization of oligonucleotide synthesis and purification on solid supports
InactiveUS7211654B2Promote hydrolysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSolid surfaceTime-Consuming
A method of modulation of synthesis capacity on and cleavage properties of synthetic oligomers from solid support is described. The method utilizes linker molecules attached to a solid surface and co-coupling agents that have similar reactivities to the coupling compounds with the surface functional groups. The preferred linker molecules provide an increased density of polymers and more resistance to cleavage from the support surface. The method is particularly useful for synthesis of oligonucleotides, oligonucleotides microarrays, peptides, and peptide microarrays. The stable linkers are also coupled to anchor molecules for synthesis of DNA oligonucleotides using on support purification, eliminating time-consuming chromatography and metal cation presence. Oligonucleotides thus obtained can be directly used for mass analysis, DNA amplification and ligation, hybridization, and many other applications.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
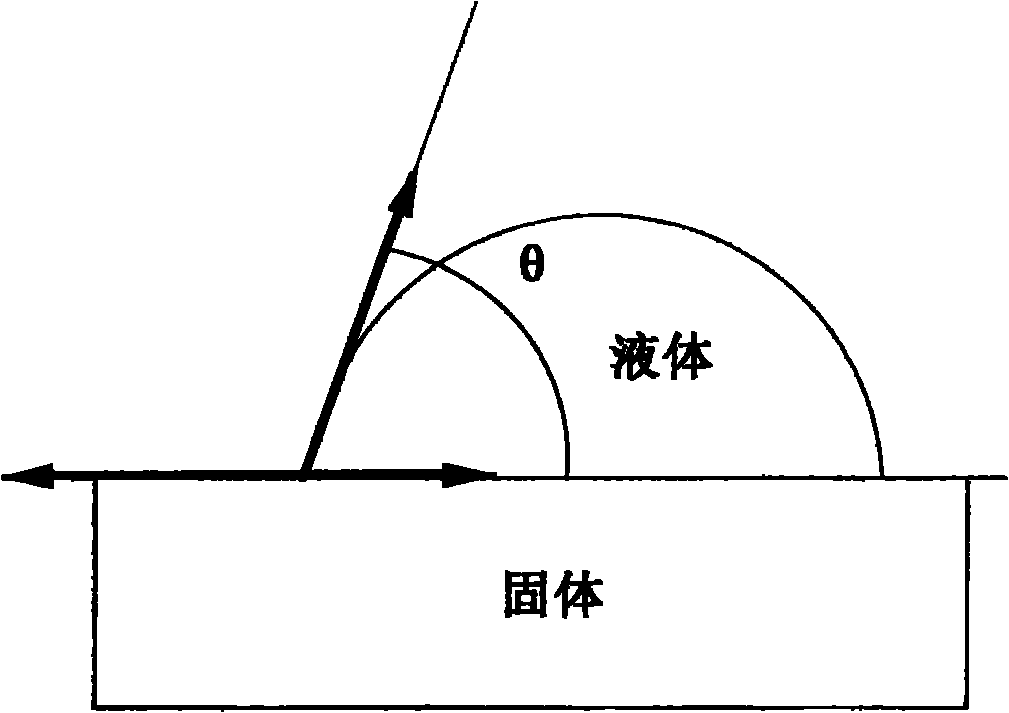
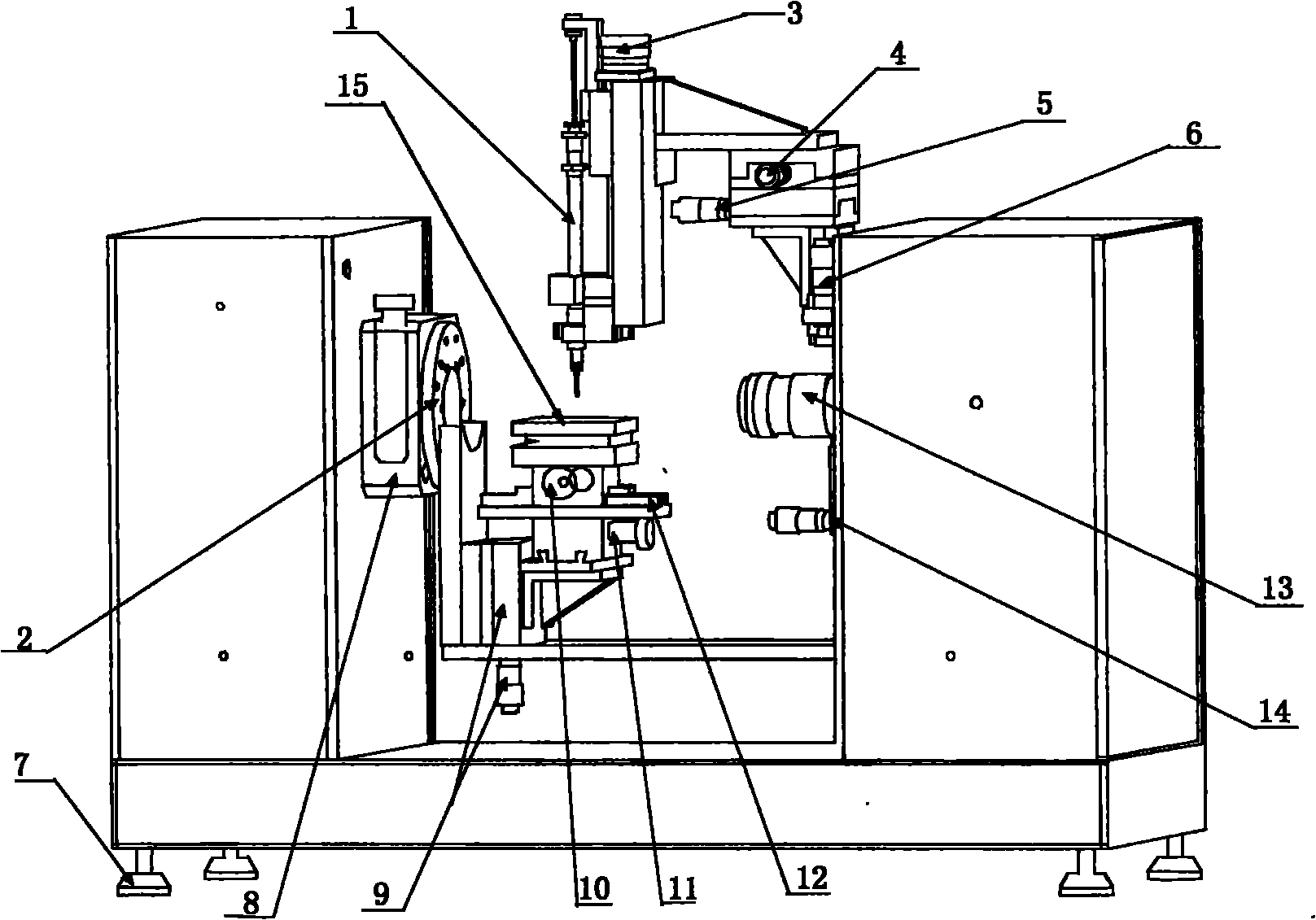
Apparatus and method for testing solid-liquid dynamic and static contact angles by actual liquid droplet method
InactiveCN101865807AHigh precisionEasy to operateSurface tension analysisPeristaltic pumpSmall droplet
The invention discloses an apparatus and a method for testing solid-liquid dynamic and static contact angles by an actual liquid droplet method. The method comprises the following steps of: during the testing, placing a solid phase sample on a sample table; controlling X, Y and Z of the sample table to move to a focusing position of a lens; sucking the liquid phase sample into a micro sample injector, injection pump or peristaltic pump; controlling the X, Y and Z of the sample injector to move to the focusing position; dripping a small droplet of the liquid and adsorbing the droplet to a needle head; moving the needle head to the surface of the solid phase sample until the liquid phase sample is adsorbed to the surface of the solid; making a software system control an optical imaging system (CCD) to capture a real-time picture and analyzing the picture by using the actual liquid droplet method; and displaying calculated solid-liquid contact angle value, solid surface free energy value and adhesion work value and managing the values by a database. The apparatus and the method can completely improve the accuracy of the analysis of the solid-liquid interfacial tension, are simple to operate, can be widely applied and have high popularization value.
Owner:上海梭伦信息科技有限公司
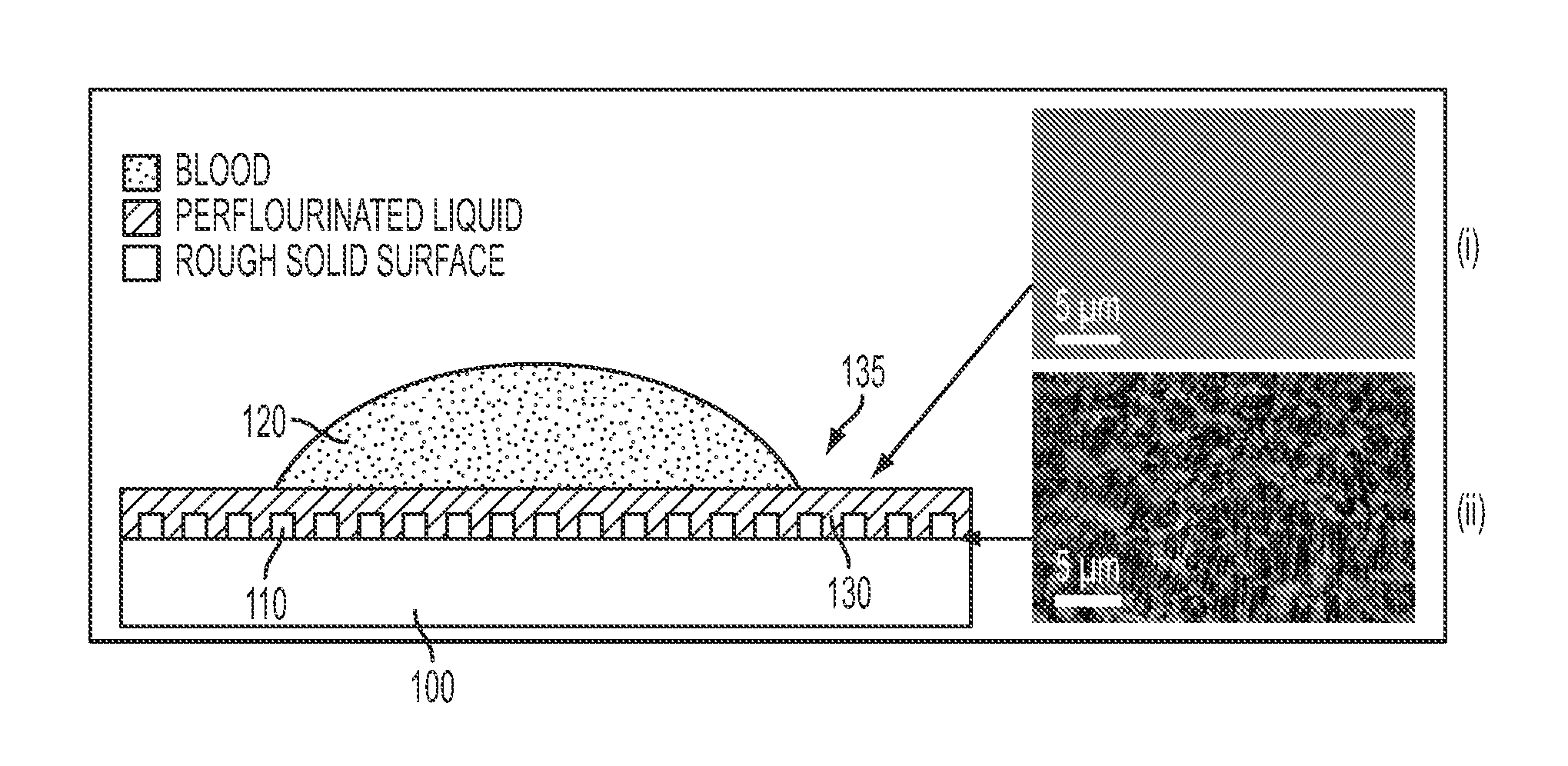
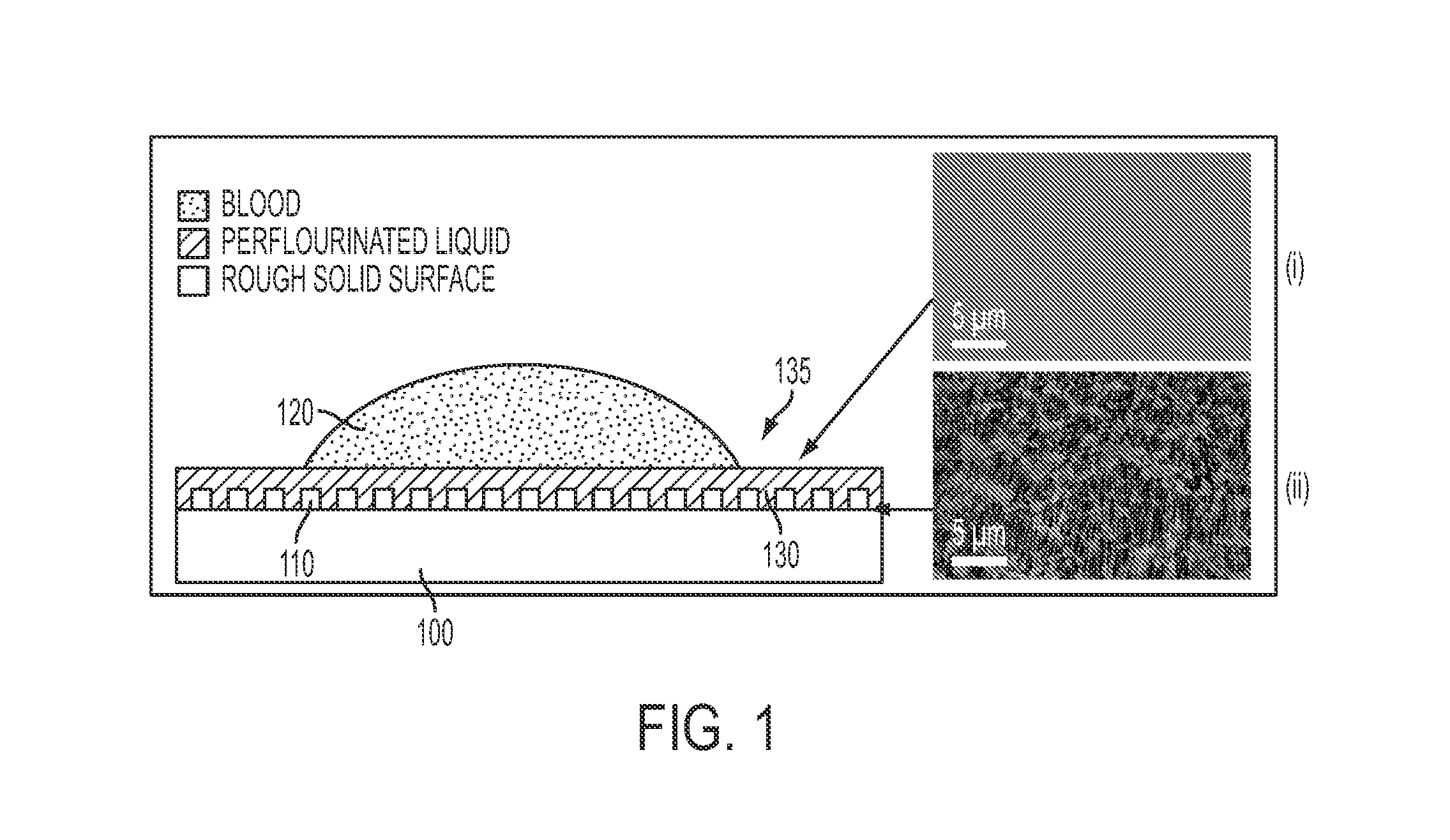
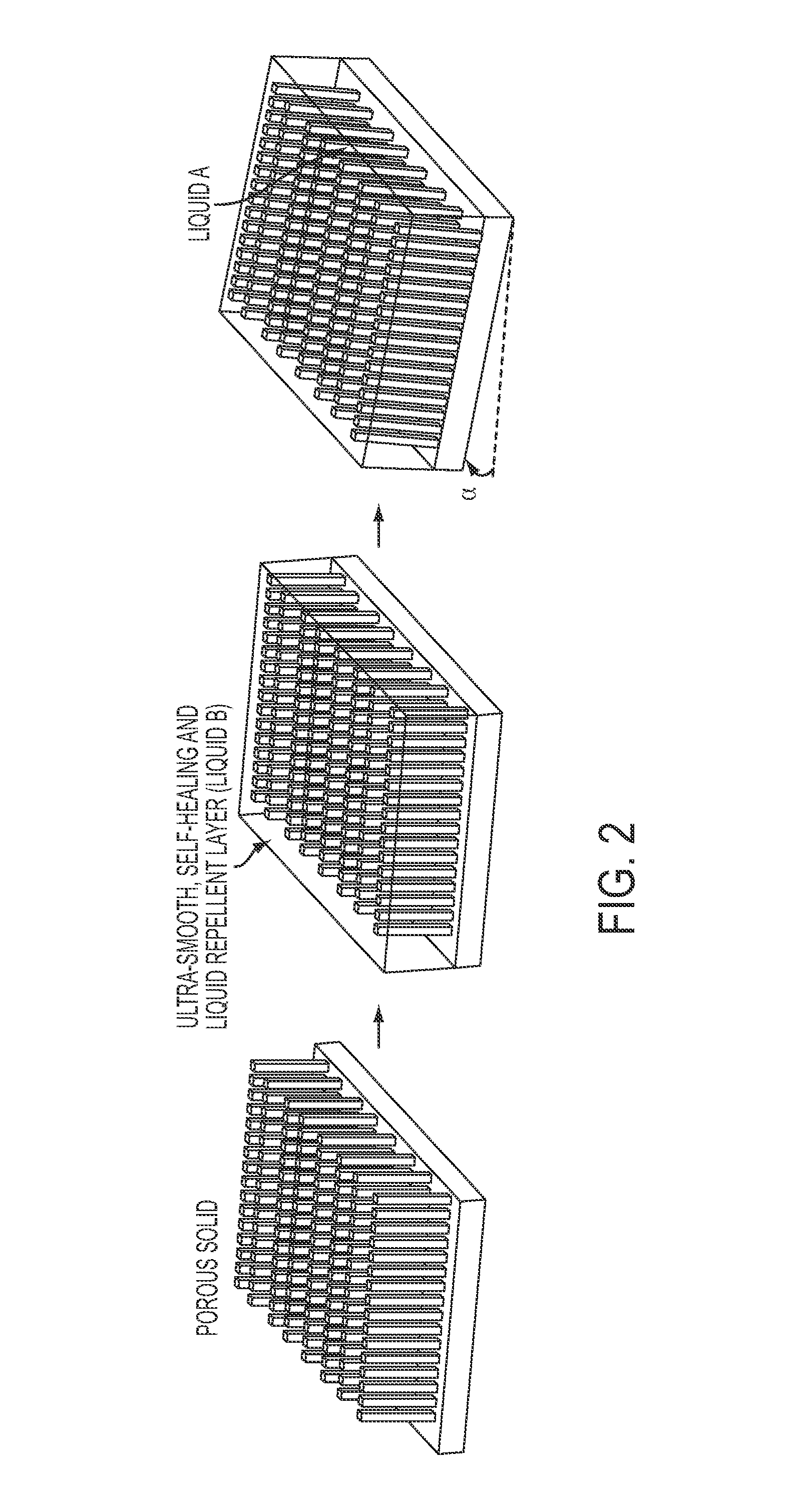
Slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces and biological applications thereof
ActiveUS20140187666A1Inhibit inflammationPrevents wound healingAntifouling/underwater paintsSurgical adhesivesSelf-healingHigh density
A self-healing, scratch resistant slippery surface that is manufactured by wicking a chemically-inert, high-density liquid coating over a roughened solid surface featuring micro and nanoscale topographies is described. Such a slippery surface shows anti-wetting properties, as well as exhibits significant reduction of adhesion of a broad range of biological materials, including particles in suspension or solution. Specifically, the slippery surfaces can be applied to medical devices and equipment to effectively repel biological materials such as blood, and prevent, reduce, or delay coagulation and surface-mediated clot formation. Moreover, the slippery surfaces can be used to prevent fouling by microorganisms such as bacteria.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Arrayed biomolecules and their use in sequencing
InactiveUS20050042649A1Reduce interferencePermit resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsVolumetric Mass DensityBiology
A device comprising an array of molecules immobilised on a solid surface is disclosed, wherein the array has a surface density which allows each molecule to be individually resolved, e.g. by optical microscopy. Therefore, the arrays of the present invention consist of single molecules that are more spatially distinct than the arrays of the prior art.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Functional surface coating
InactiveUS20050100675A1Inhibit non-specific bindingRobust attachmentPretreated surfacesBiological testingProtein targetCombinatorial chemistry
Compositions and methods of preparing functional thin films or surface coatings with low non-specific binding are described. The thin films contain specified functional groups and non-specific binding repellant components. The thin films are either covalently bound to or passively adsorbed to various solid substrates. The specified functional group provides specified activity for the thin film modified solid surfaces and non-specific binding repellant components significantly reduce the non-specific binding to the thin film modified solid surfaces. Non-specific binding repellant components do not affect specified functional group's activity in the thin films. In these methods, specified functional groups are anchored to the solid substrates through a spacer. Surface coatings are also described having both non-specific protein binding properties combined with functional groups for specific binding activity thereby providing surface coating that specifically recognize target proteins but limit binding to non-specific protein.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
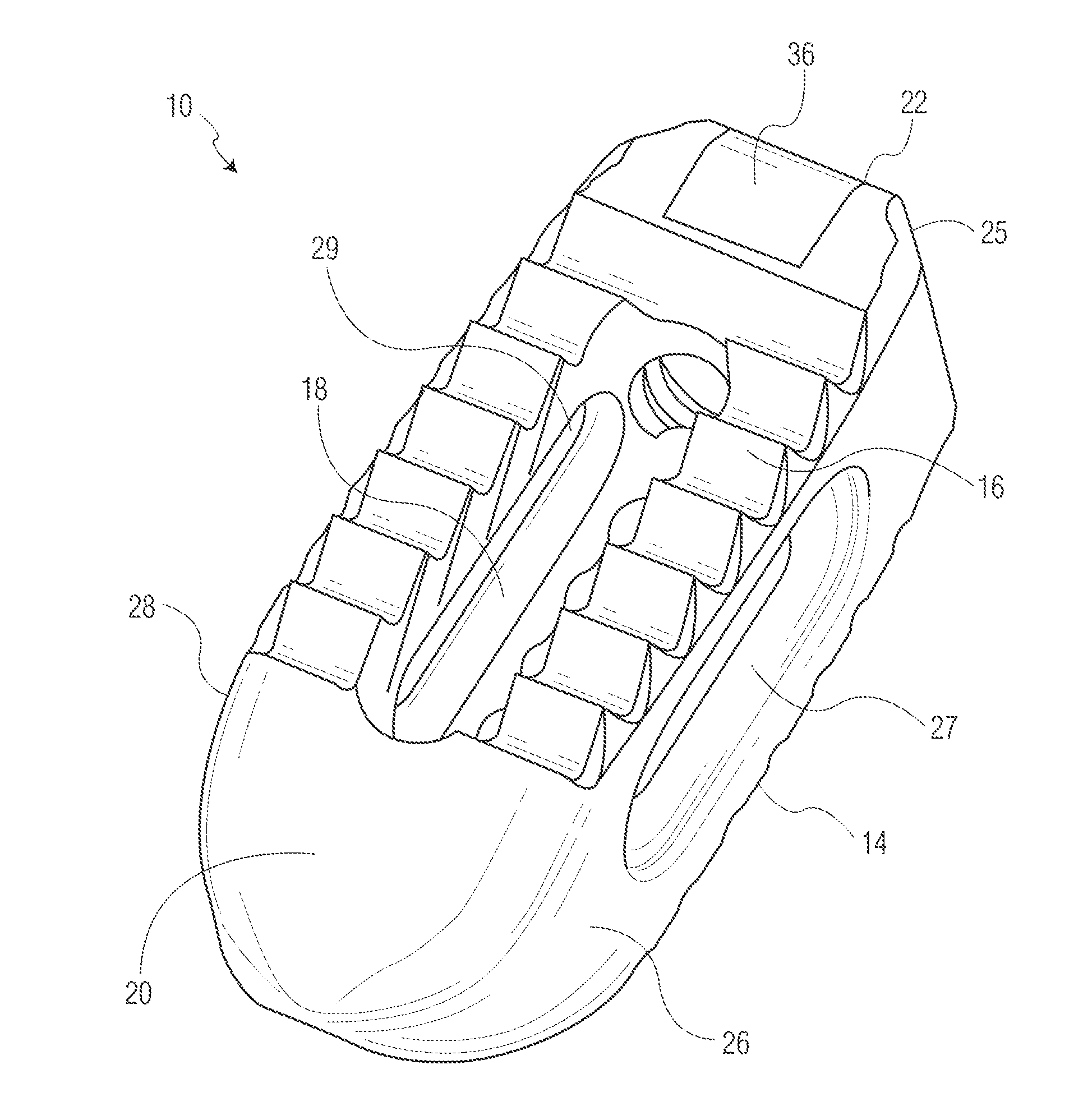
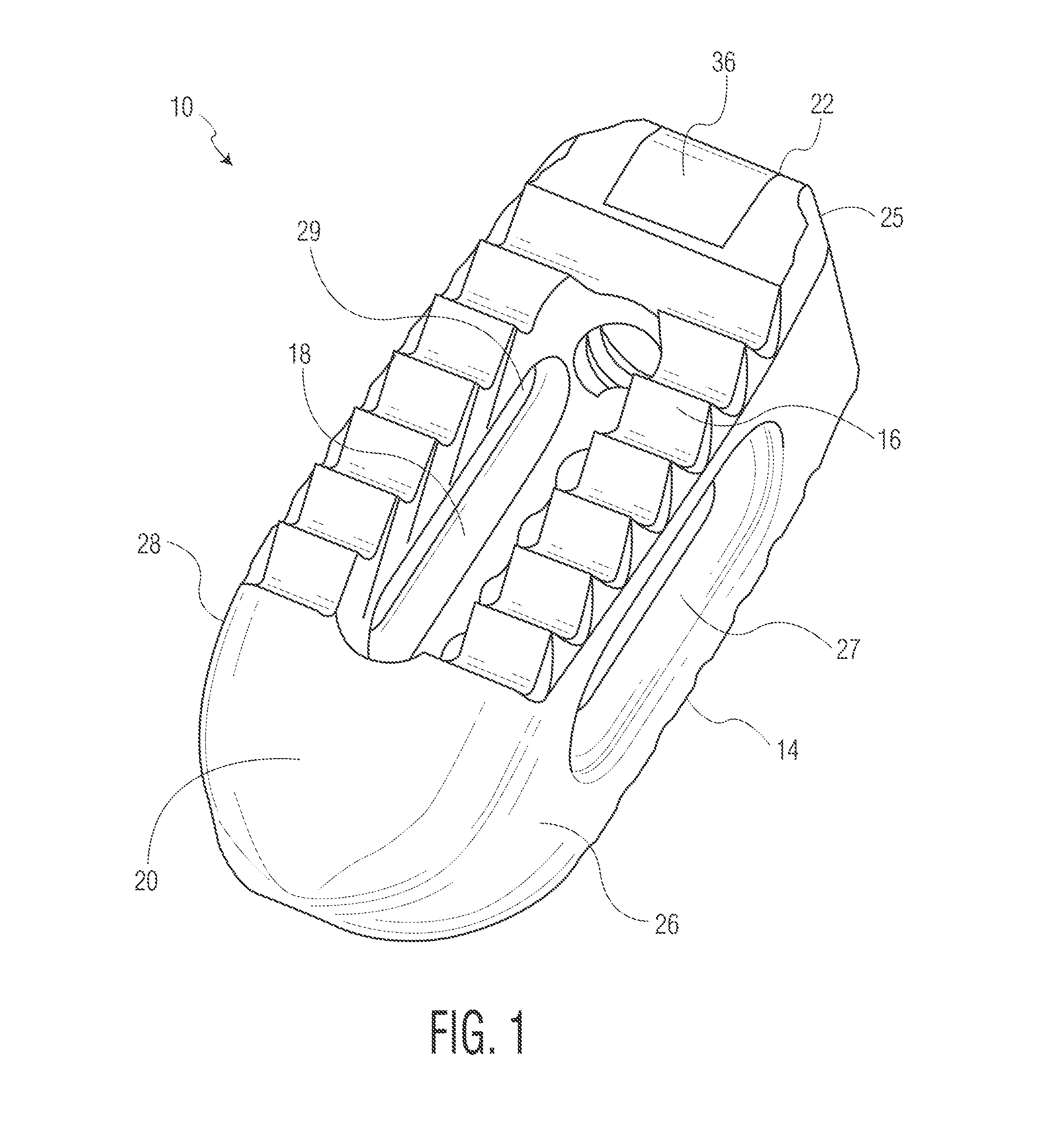
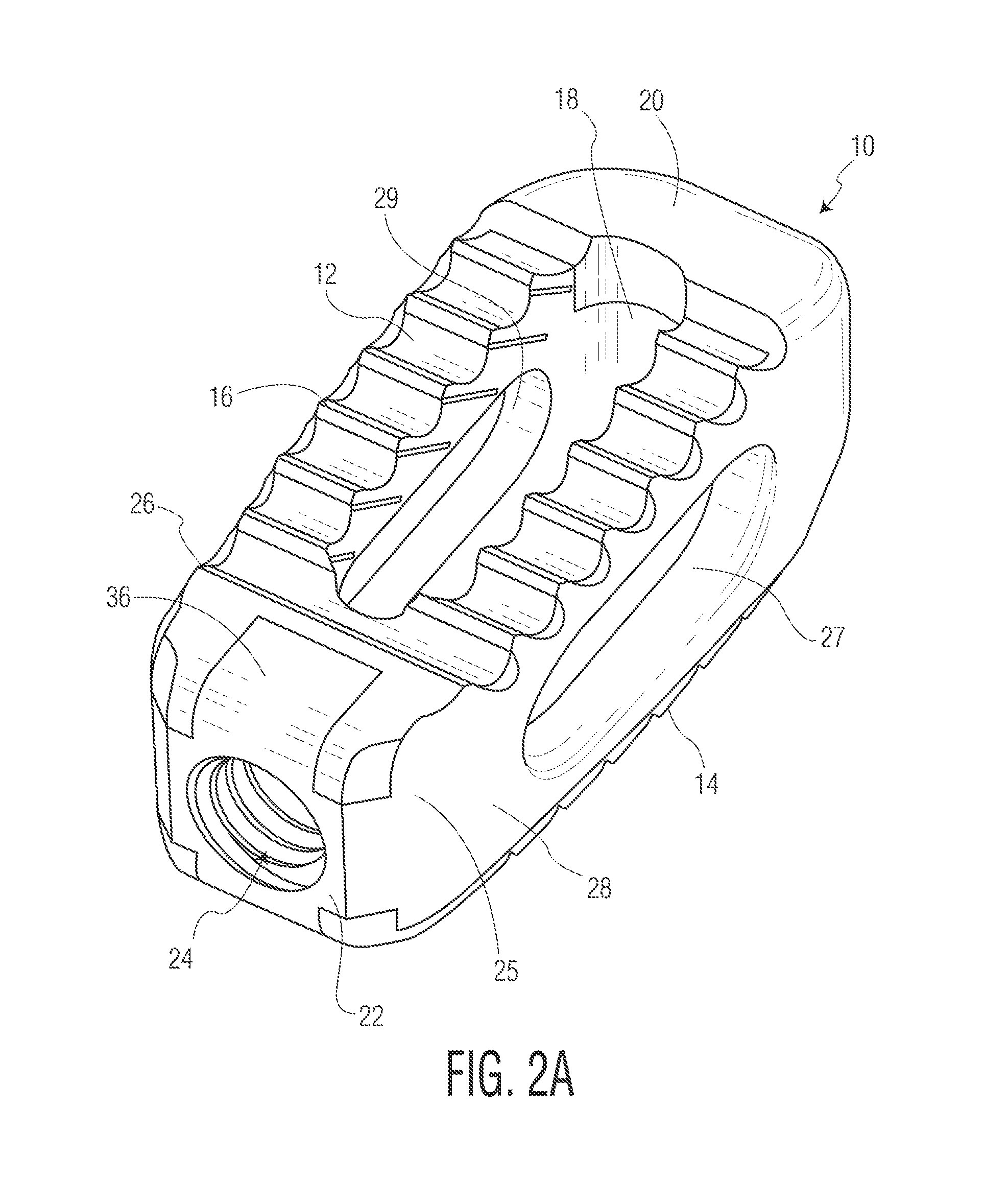
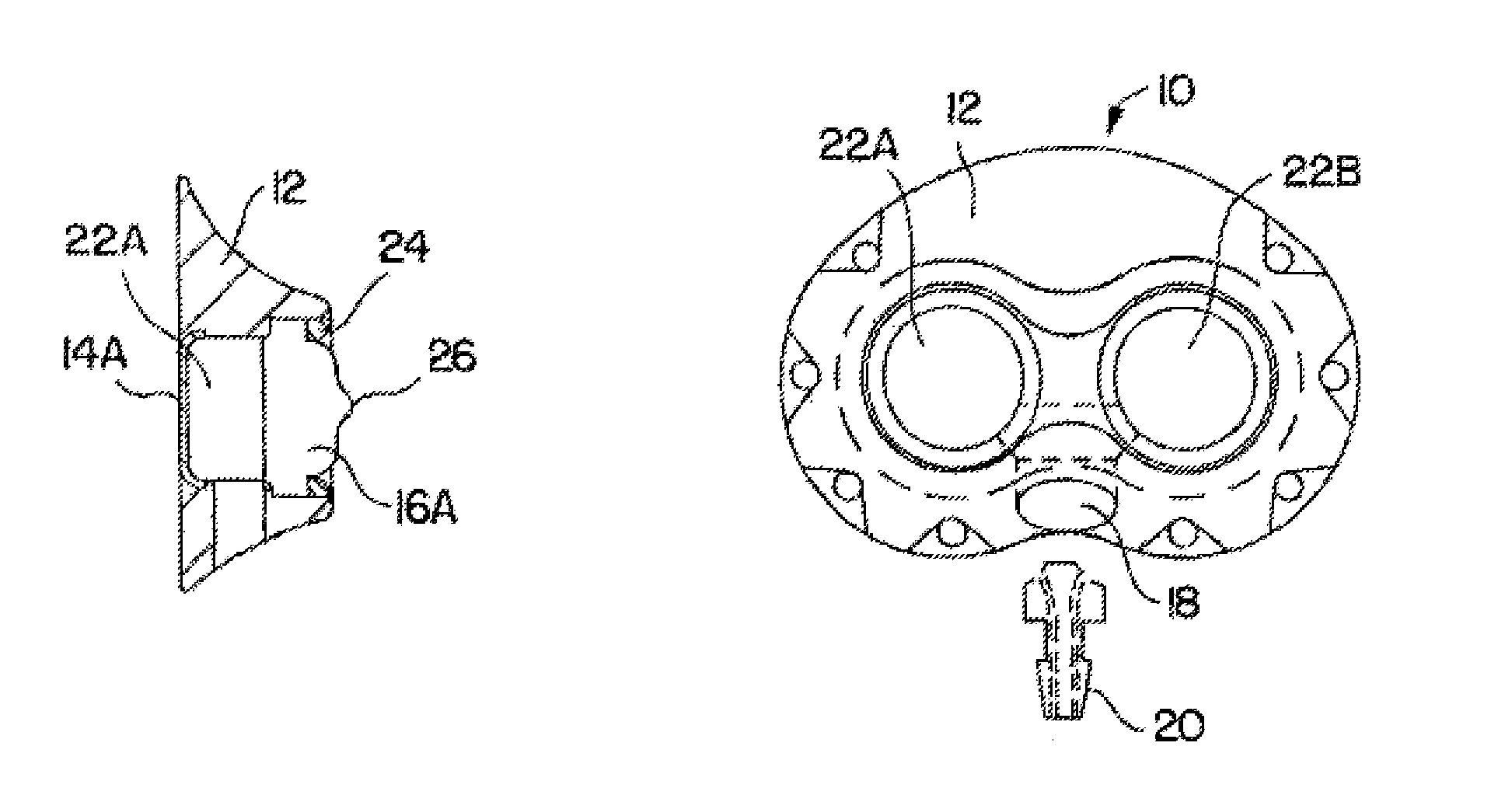
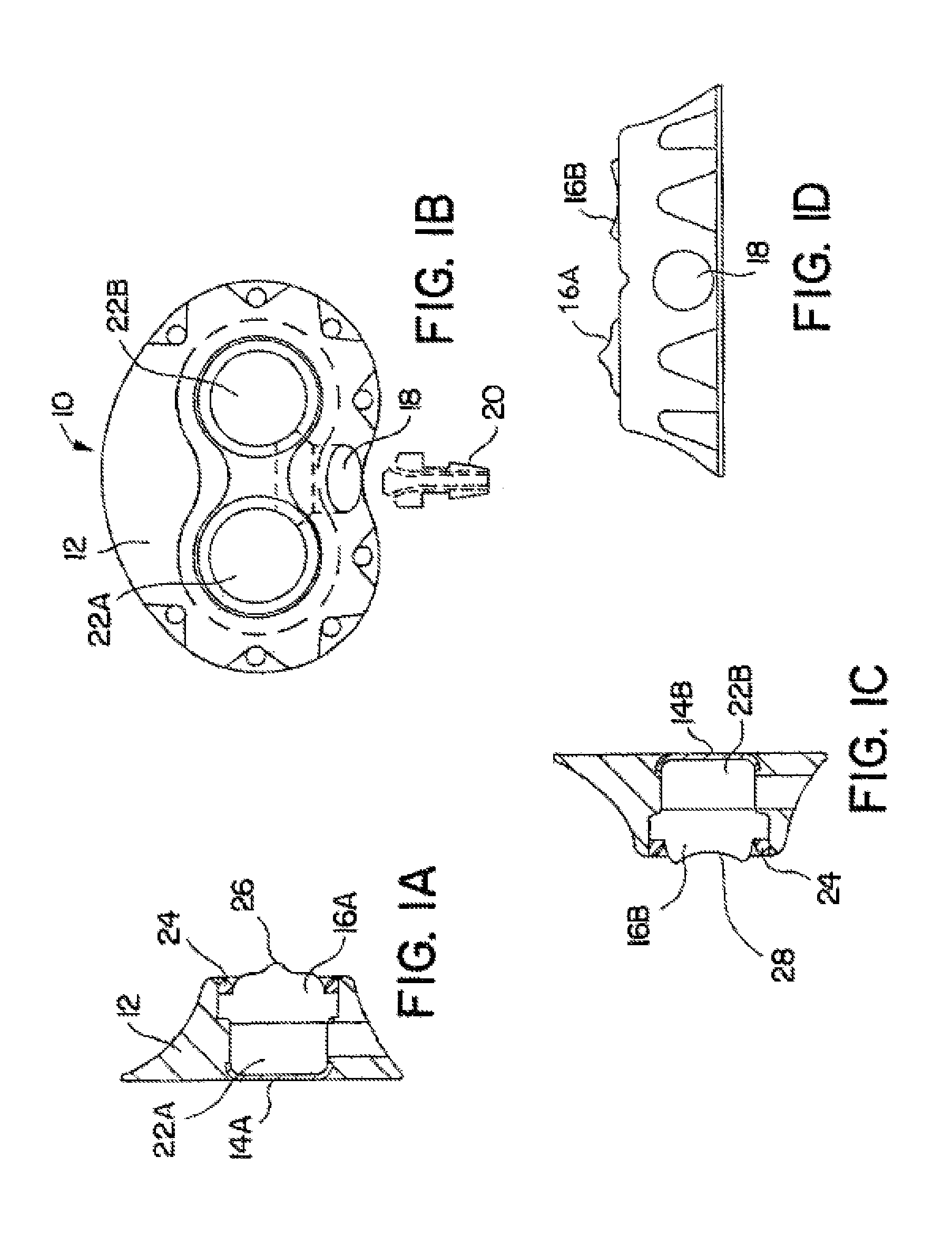
Spinal implant with porous and solid surfaces
ActiveUS20160199193A1Reduce stiffnessEasy to insertAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsSolid surfaceSpinal implant
A spinal implant including porous and solid portions is disclosed. The implant includes porous portions on upper and lower surfaces and in an interior thereof. Methods of manufacturing and implanting such implants are also disclosed.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Implantable vascular access device with ceramic needle guard insert
InactiveUS7713251B2Increase the areaReduce coagulationMedical devicesMuscle tissueVascular Access Devices
The present invention provides an improved vascular access port comprising a port base with a metallic dish insert molded (or bonded) into the bottom of the reservoir. In one embodiment, a single reservoir is provided. In another embodiment, plural reservoirs are provided. The metallic bottom of the reservoir provides a hard surface that will resist abrasion and puncture by the access needles used to infuse medication or withdraw blood. Additionally, the single and dual ports can include exit ports that are intended to better anatomically fit into the subcutaneous areas around muscle tissue.
Owner:PRIMO MEDICAL GRP INC
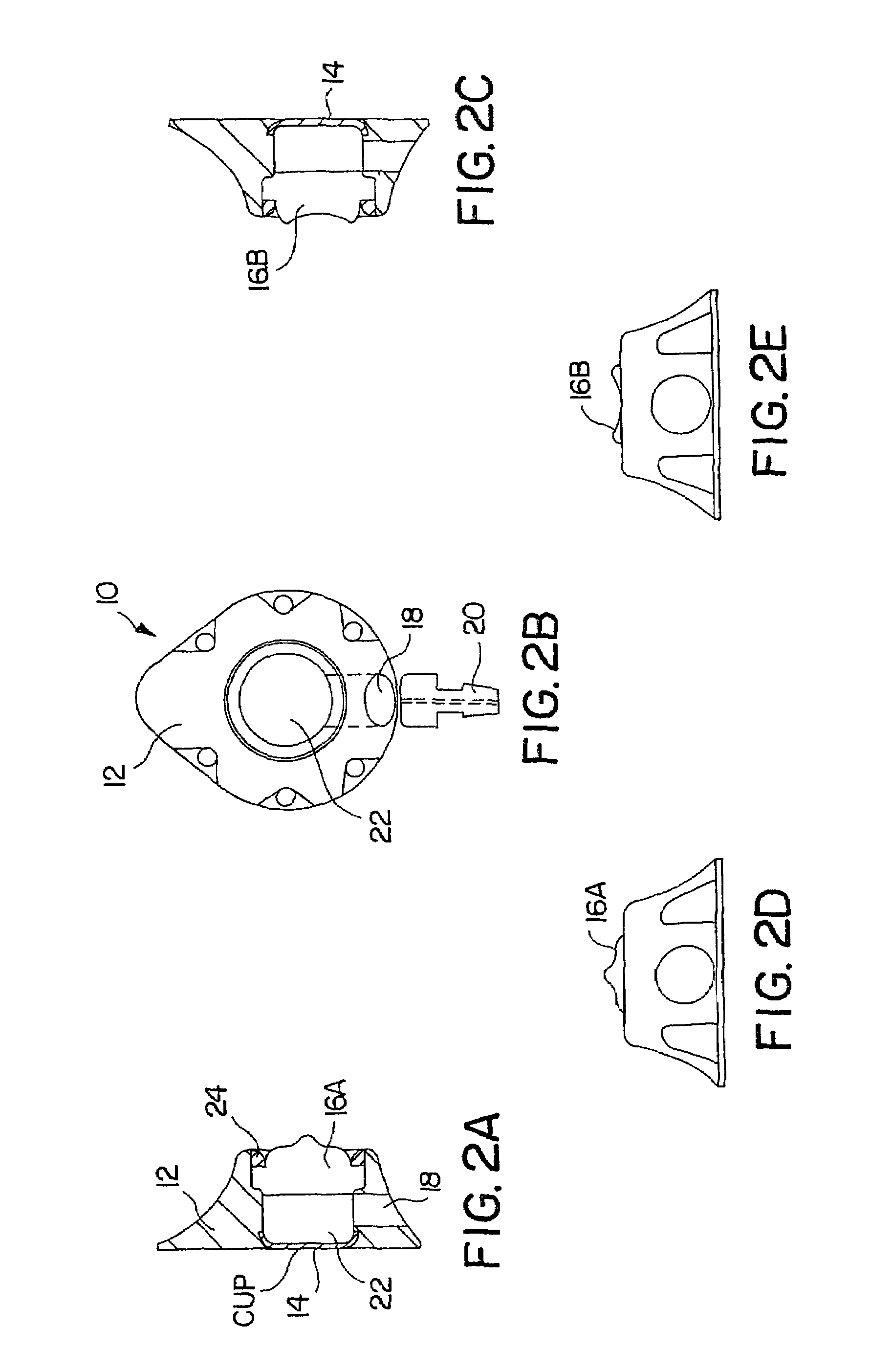
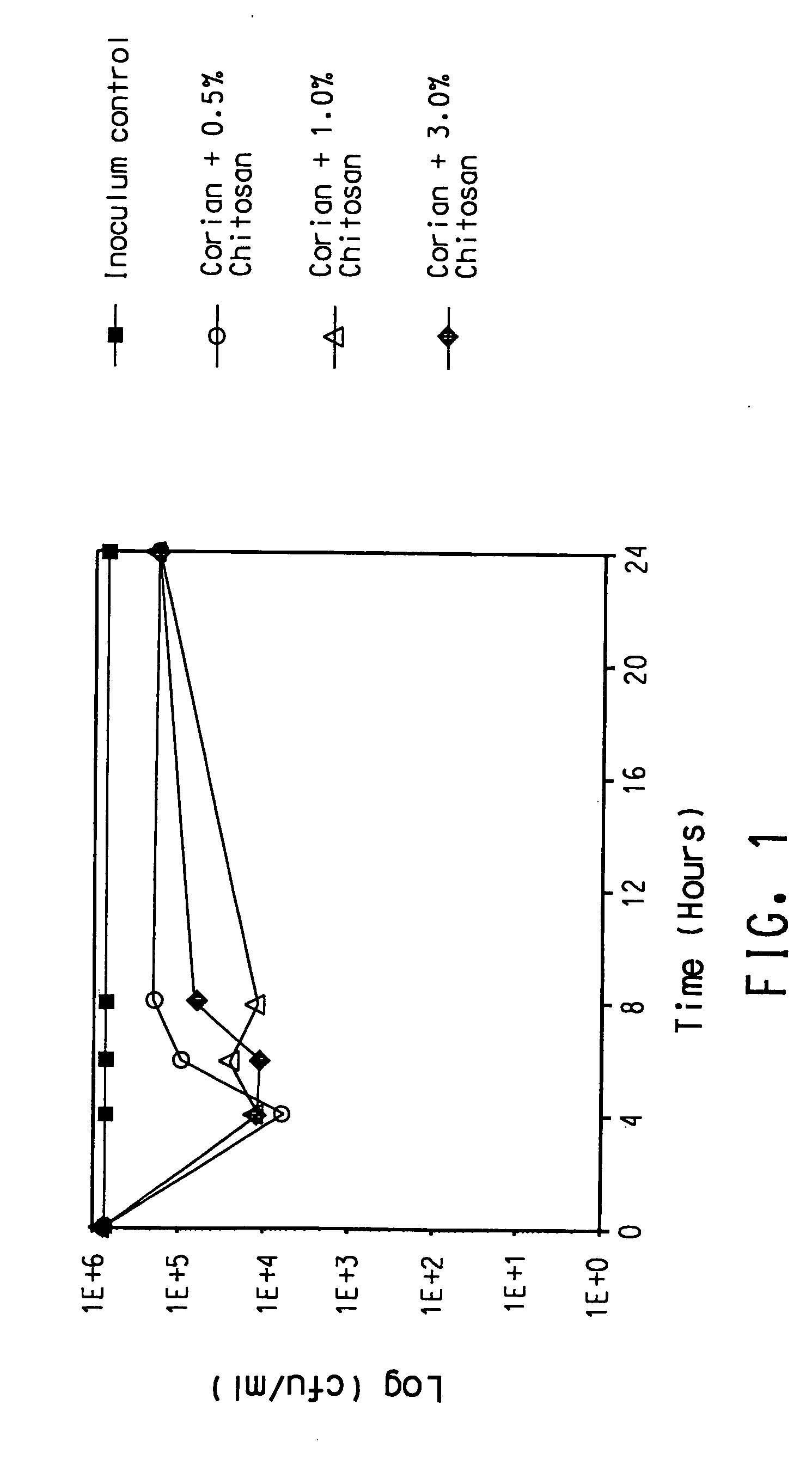
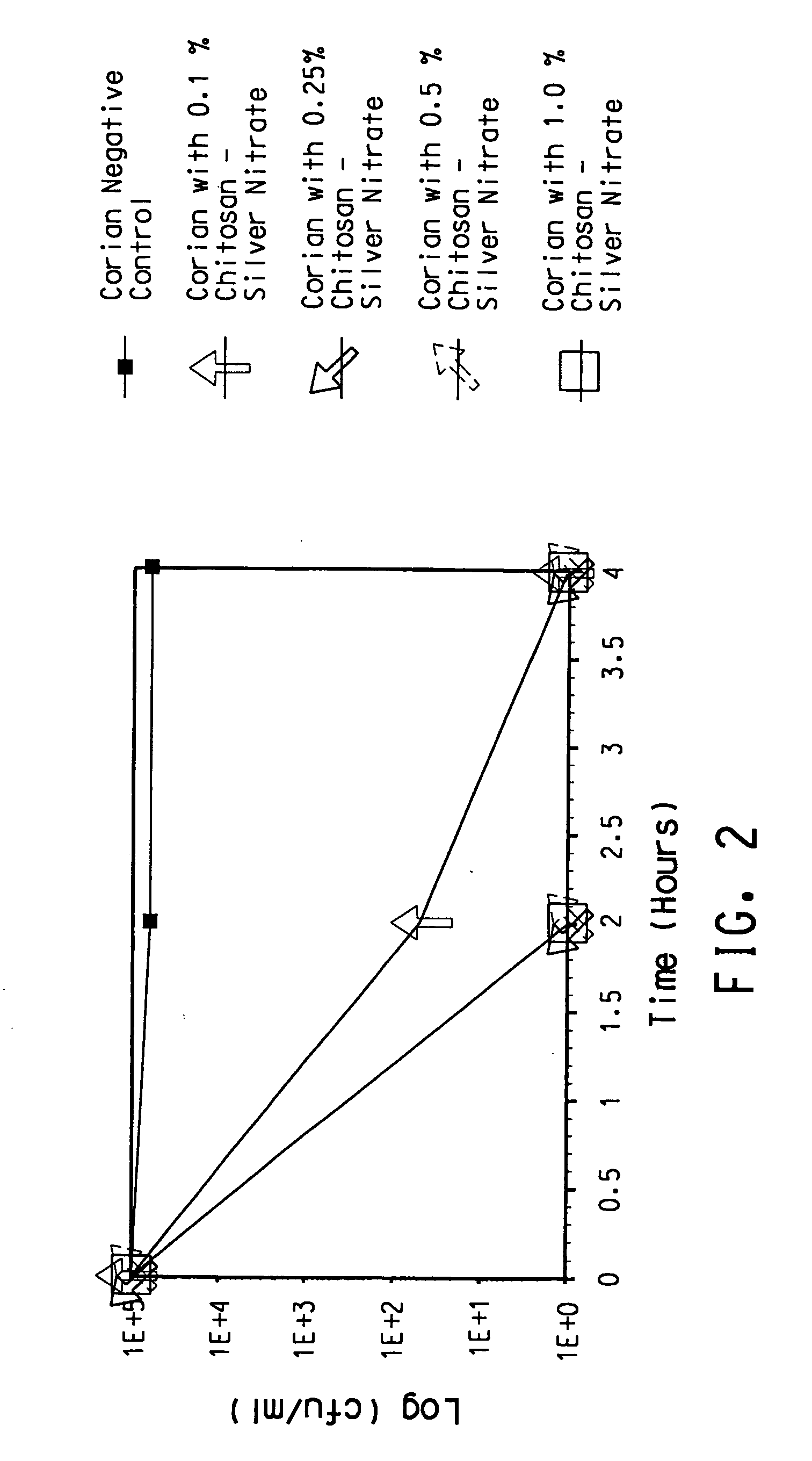
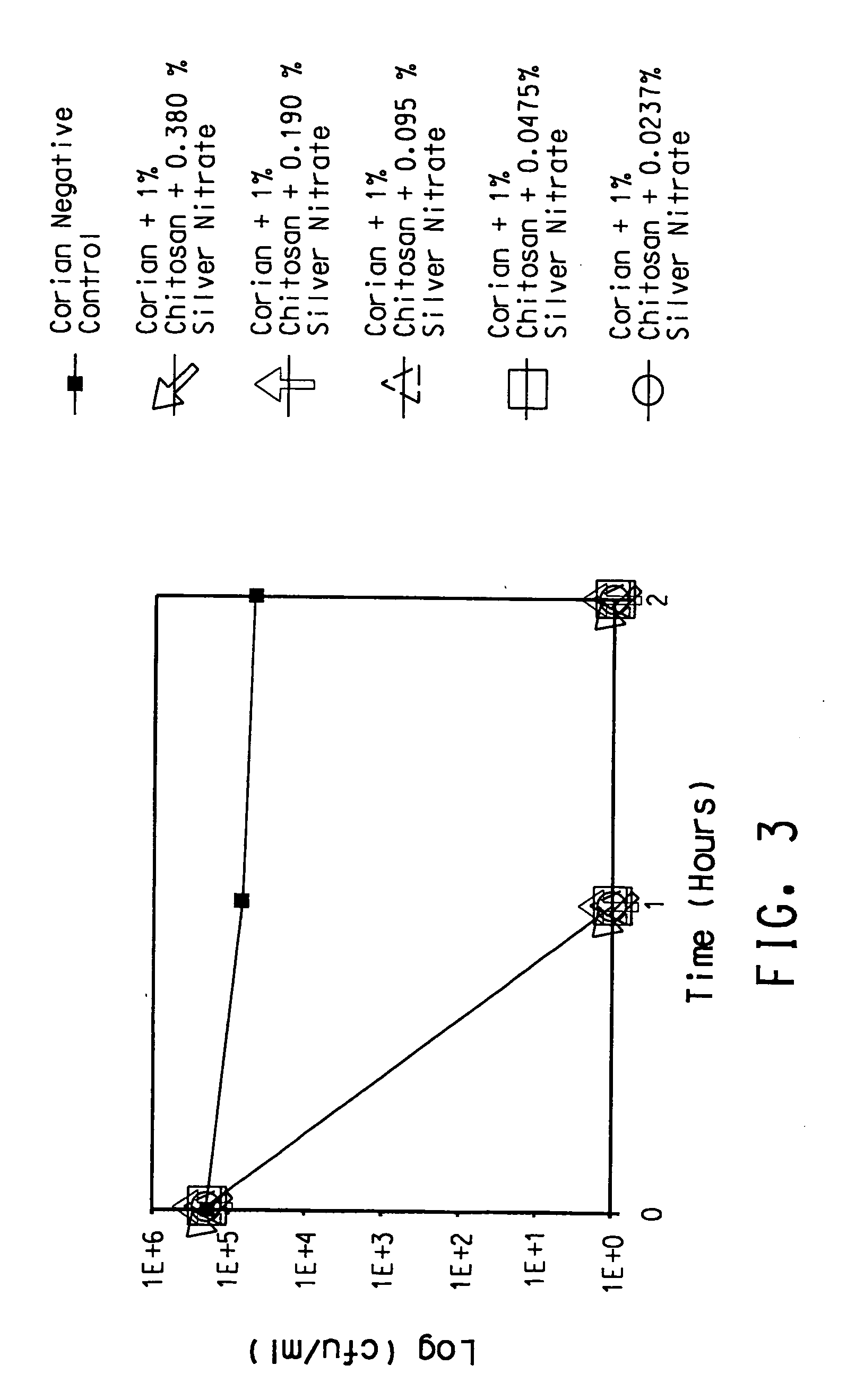
Antimicrobial solid surface materials containing chitosan-metal complexes
A solid surface material with an antimicrobial agent in a thermoset and / or thermoplastic resin matrix where the antimicrobial agent comprises a chitosan-metal complex.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Biomolecular coupling methods using 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition chemistry
InactiveUS20090240030A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCouplingCycloaddition
This invention provides methods for covalently affixing a biomolecule to either a second molecule or a solid surface using 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition chemistry. This invention also provides related methods and compositions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
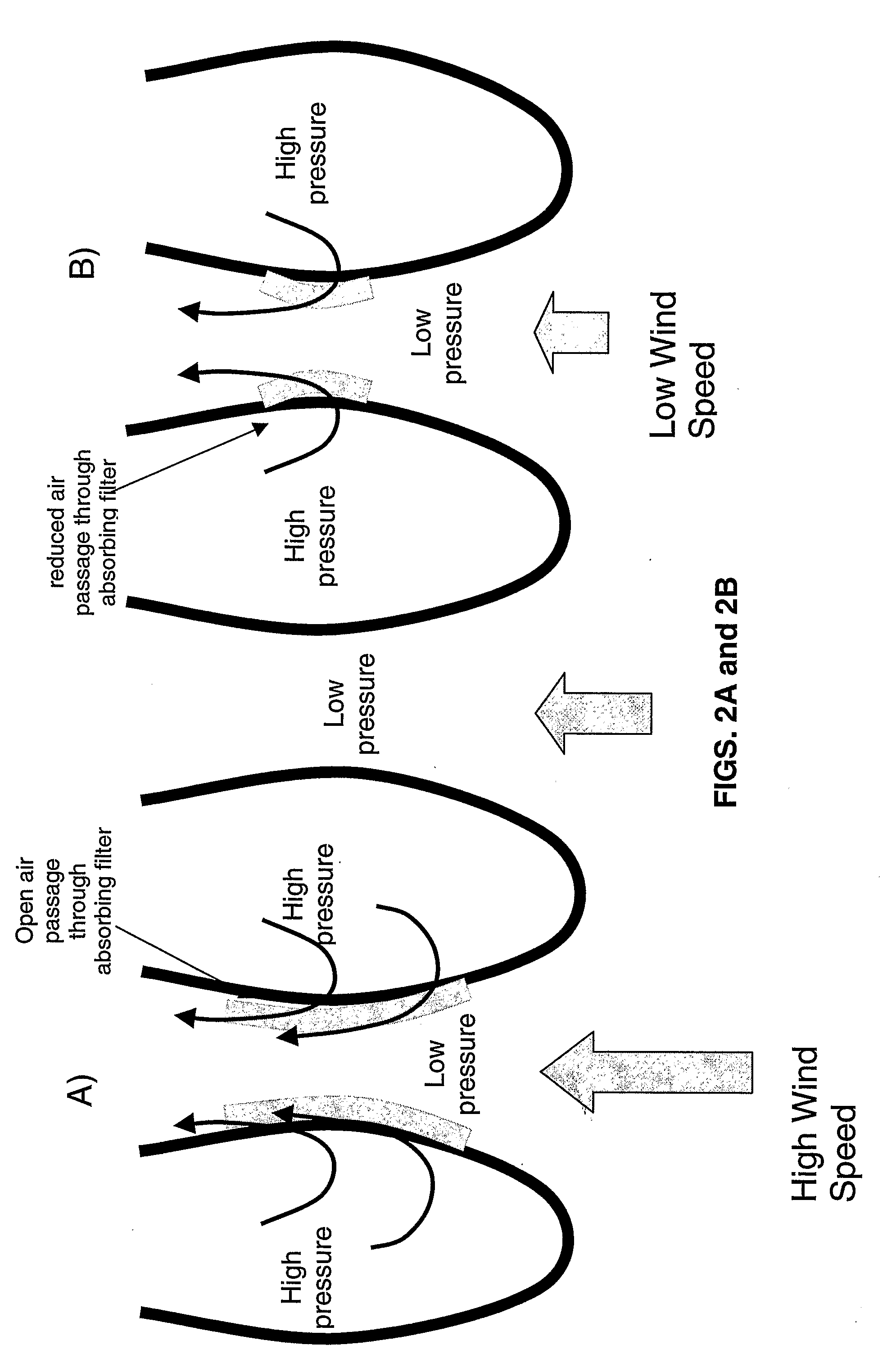
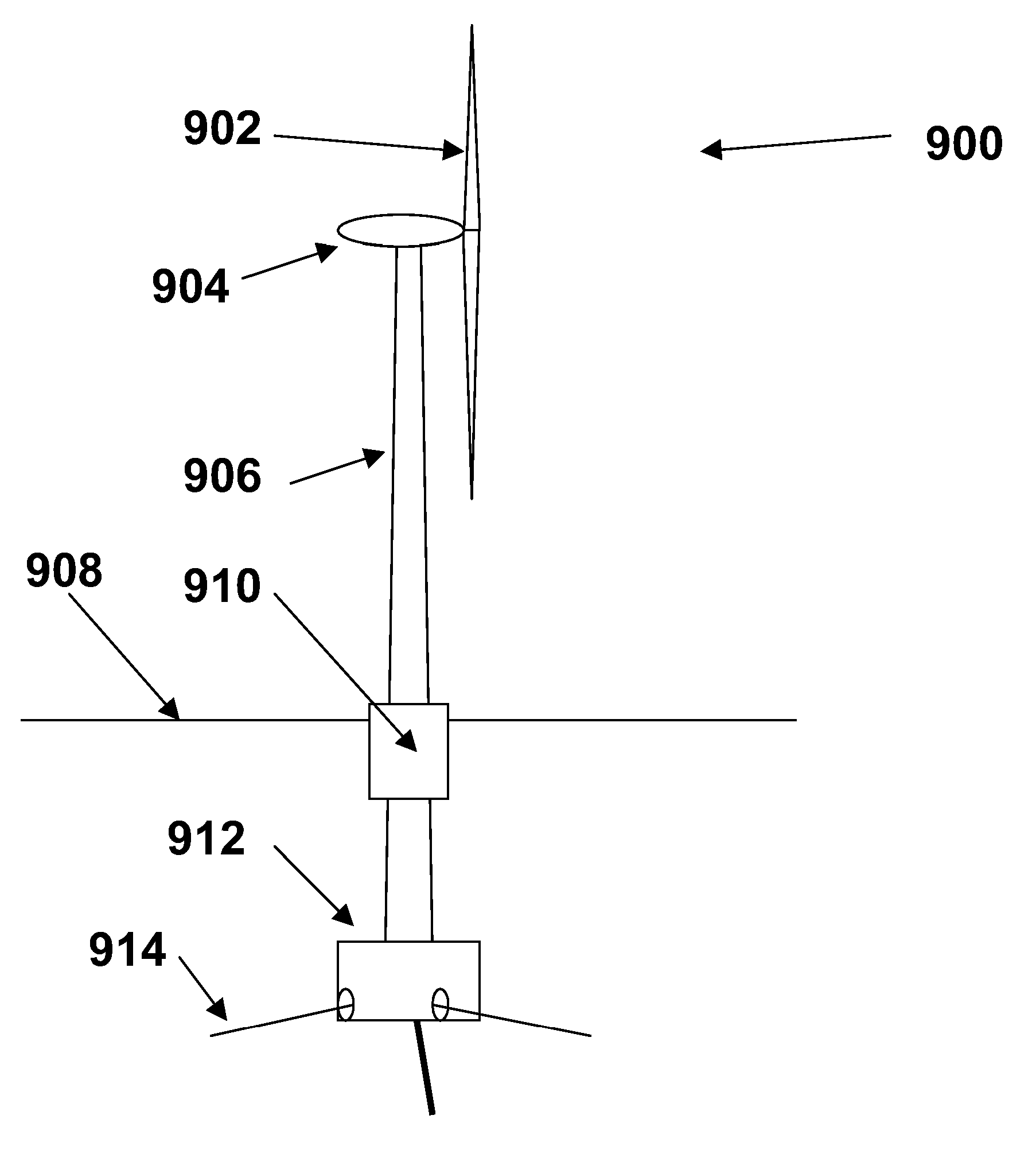
Power generation assemblies, and apparatus for use therewith
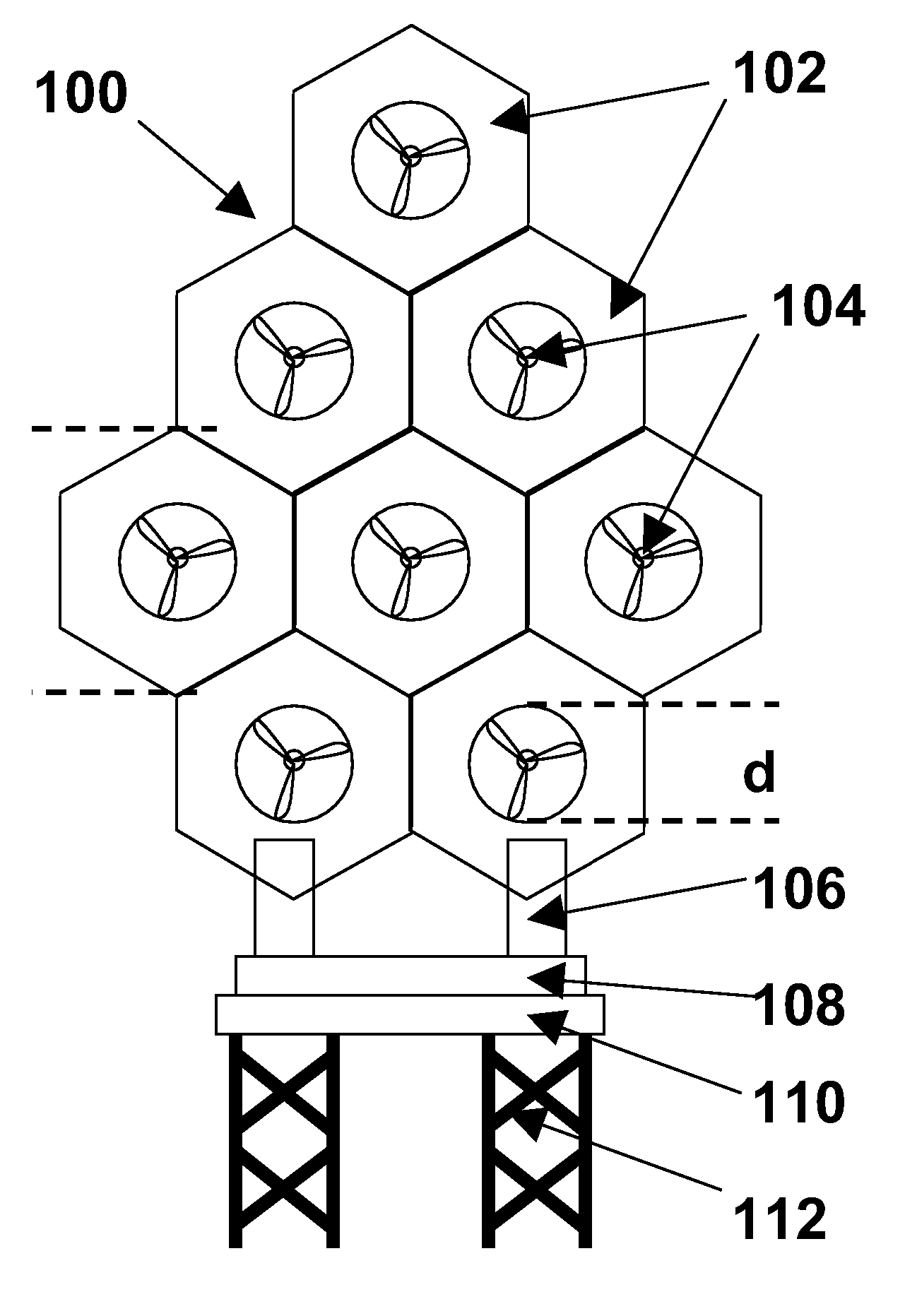
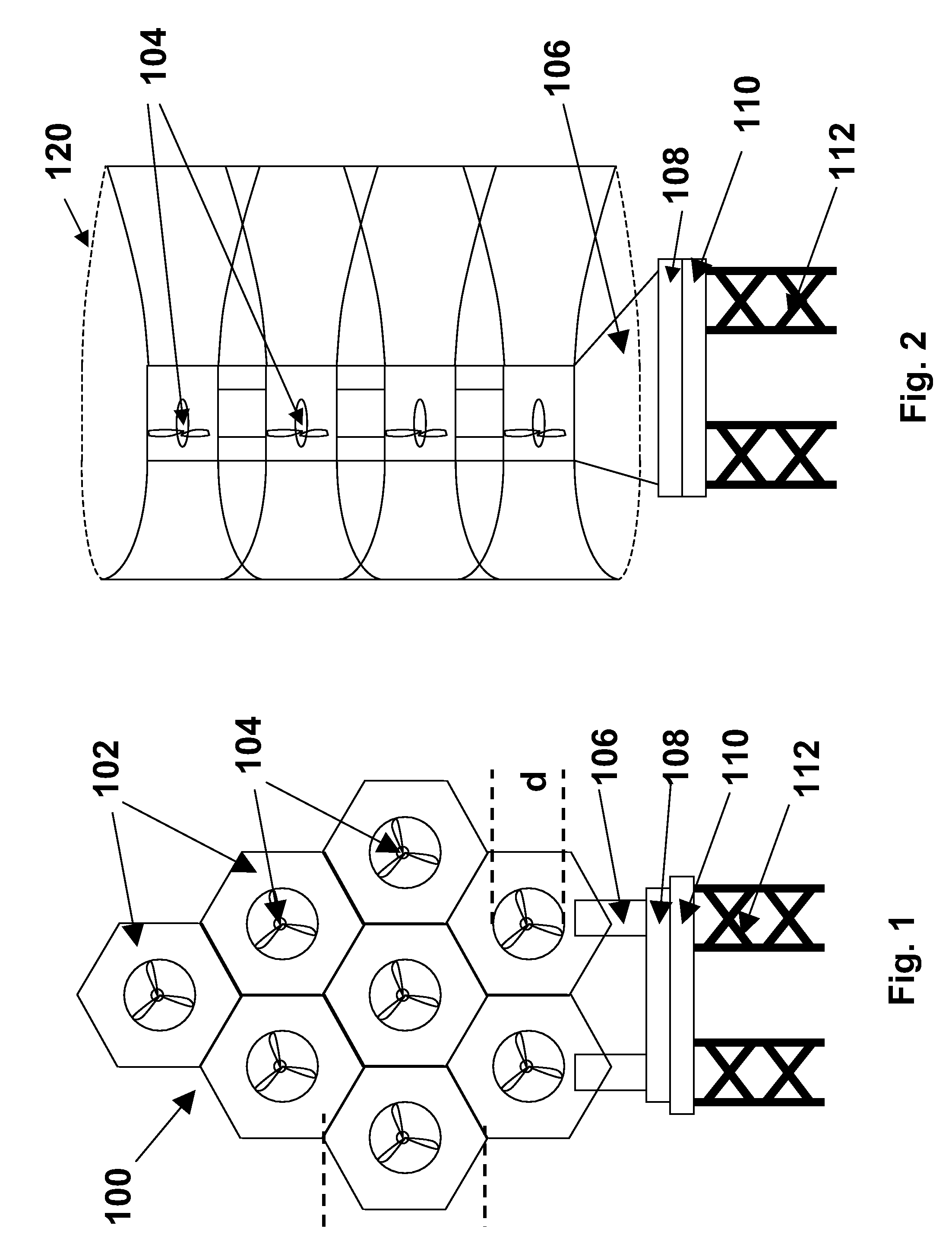
ActiveUS7293960B2Increase hydrodynamic massExtended maintenance periodPropellersWind motor controlIsoetes triquetraMarine engineering
A floating power generation assembly comprises at least three floating units (900) floating on a body of water, and at least three anchors (916) secured to a solid surface beneath the body of water, each of the floating units (900) being provided with a power generator, the floating units (900) being arranged substantially at the vertices of at least one equilateral triangle. Ship borne apparatus for deploying the floating units of such a power generation assembly and a novel multiple wind turbine assembly are also described.
Owner:OCEAN WIND TECH
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
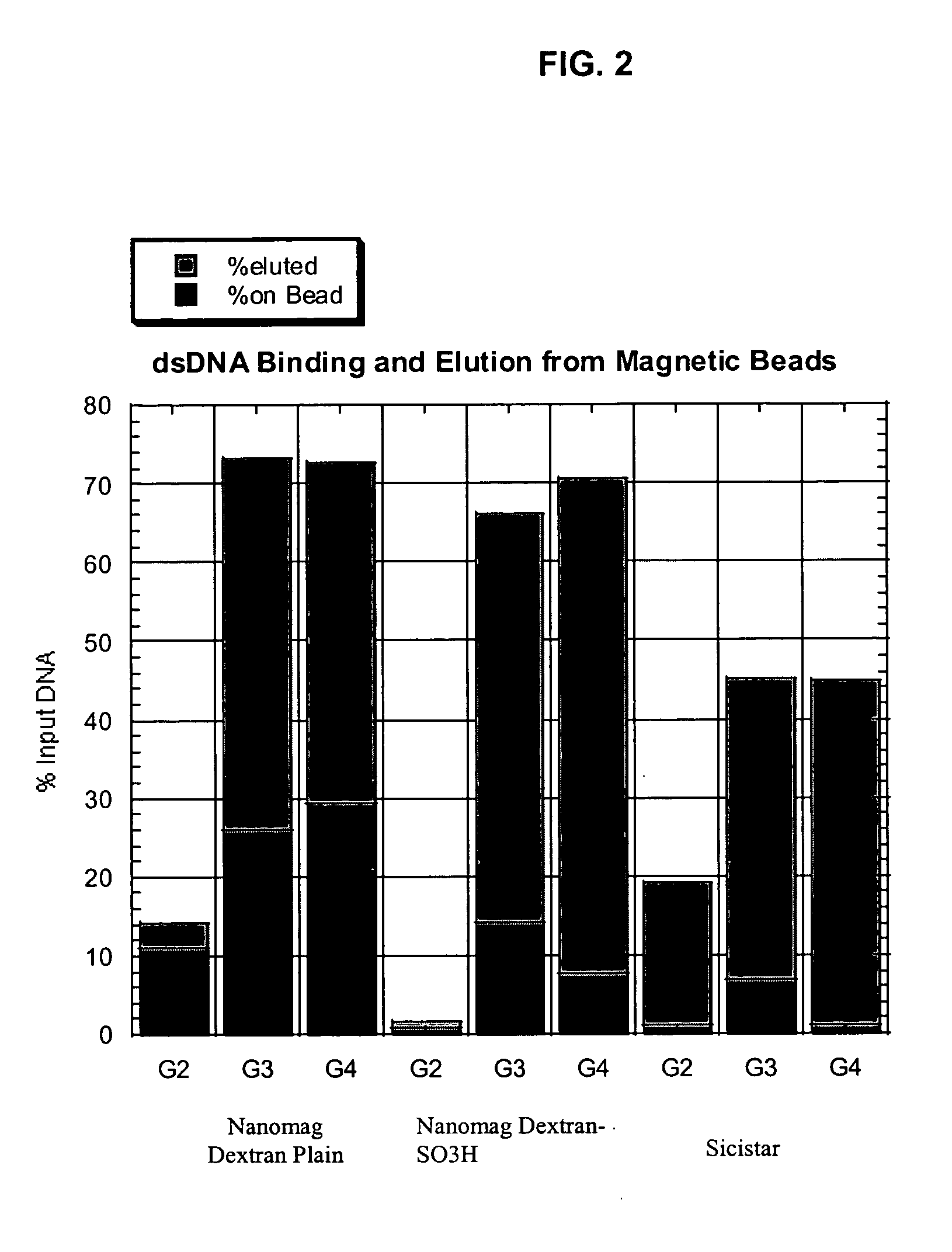
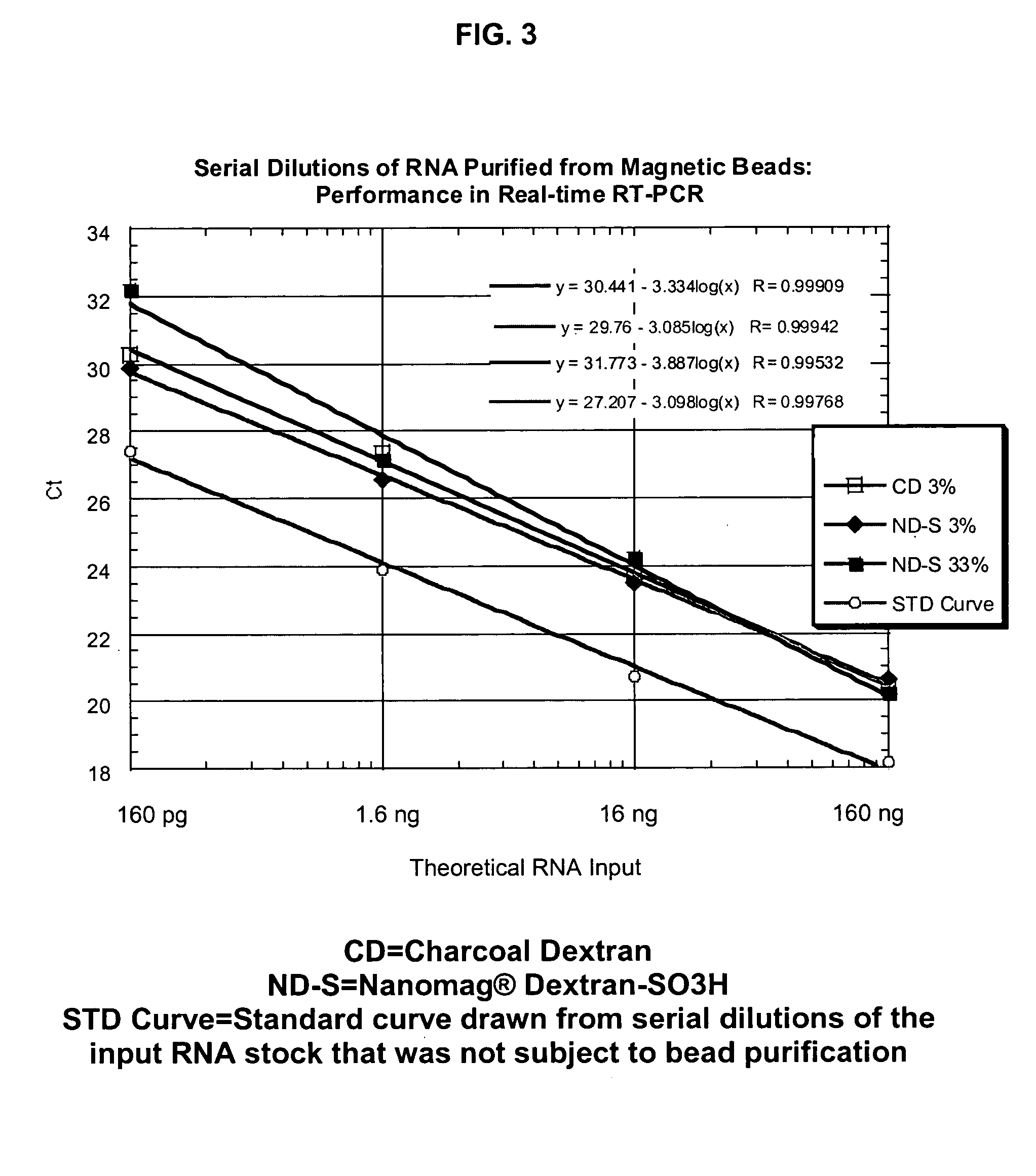
Modified surfaces as solid supports for nucleic acid purification
ActiveUS20050208510A1Faster throughputEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideMicroparticle
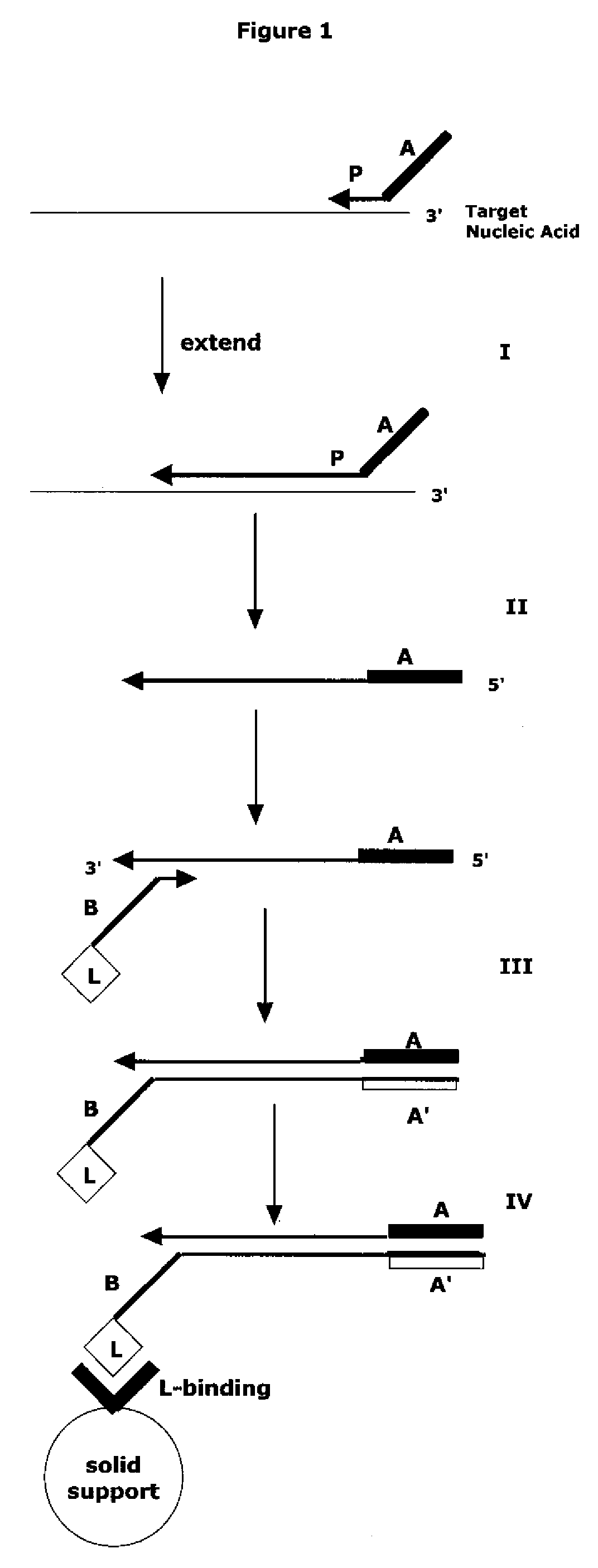
The invention relates to methods of separating polynucleotides, such as DNA, RNA and PNA, from solutions containing polynucleotides by reversibly binding the polynucleotides to a solid surface, such as a magnetic microparticle.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods of reversibly binding a biotin compound to a support
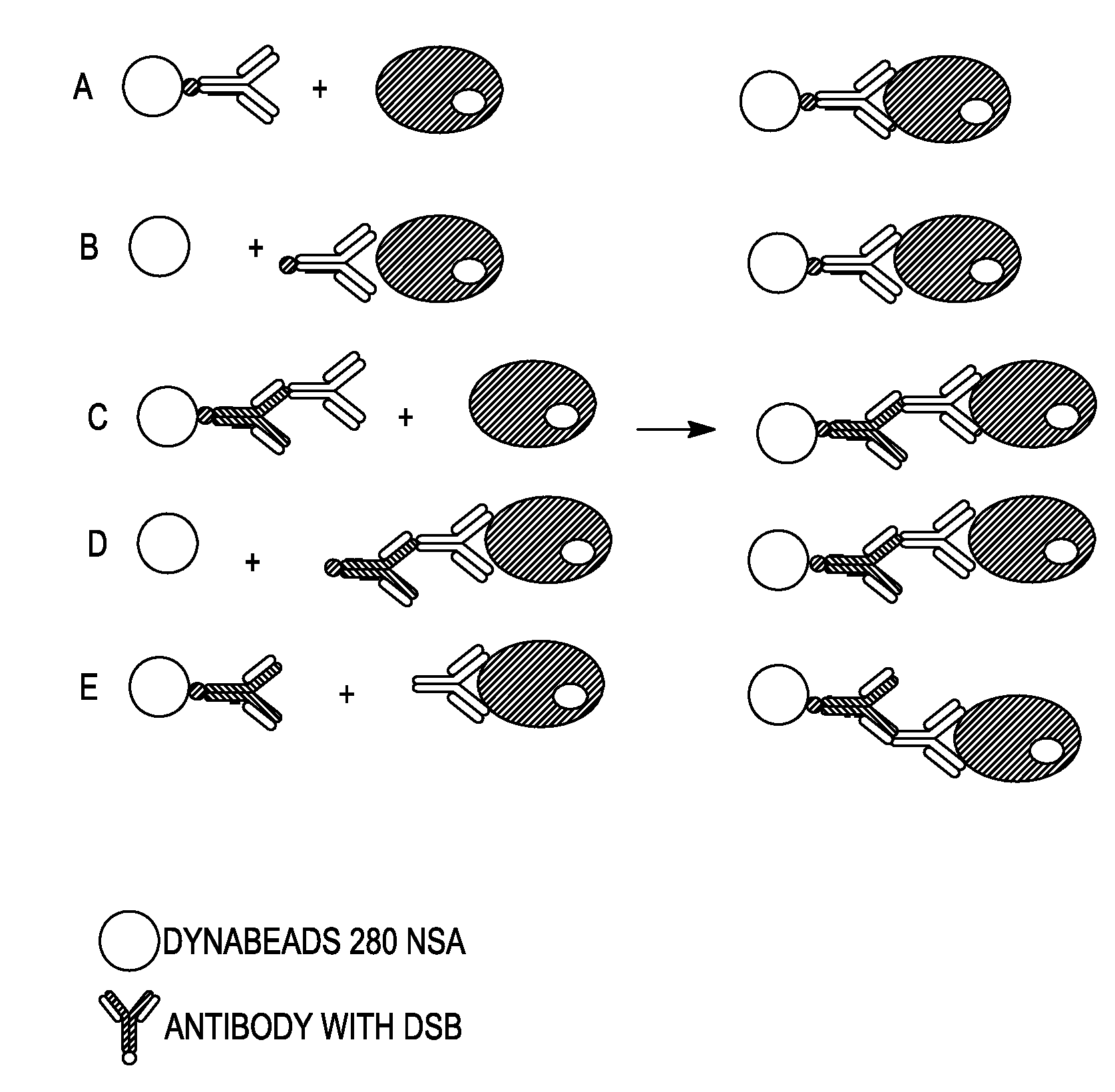
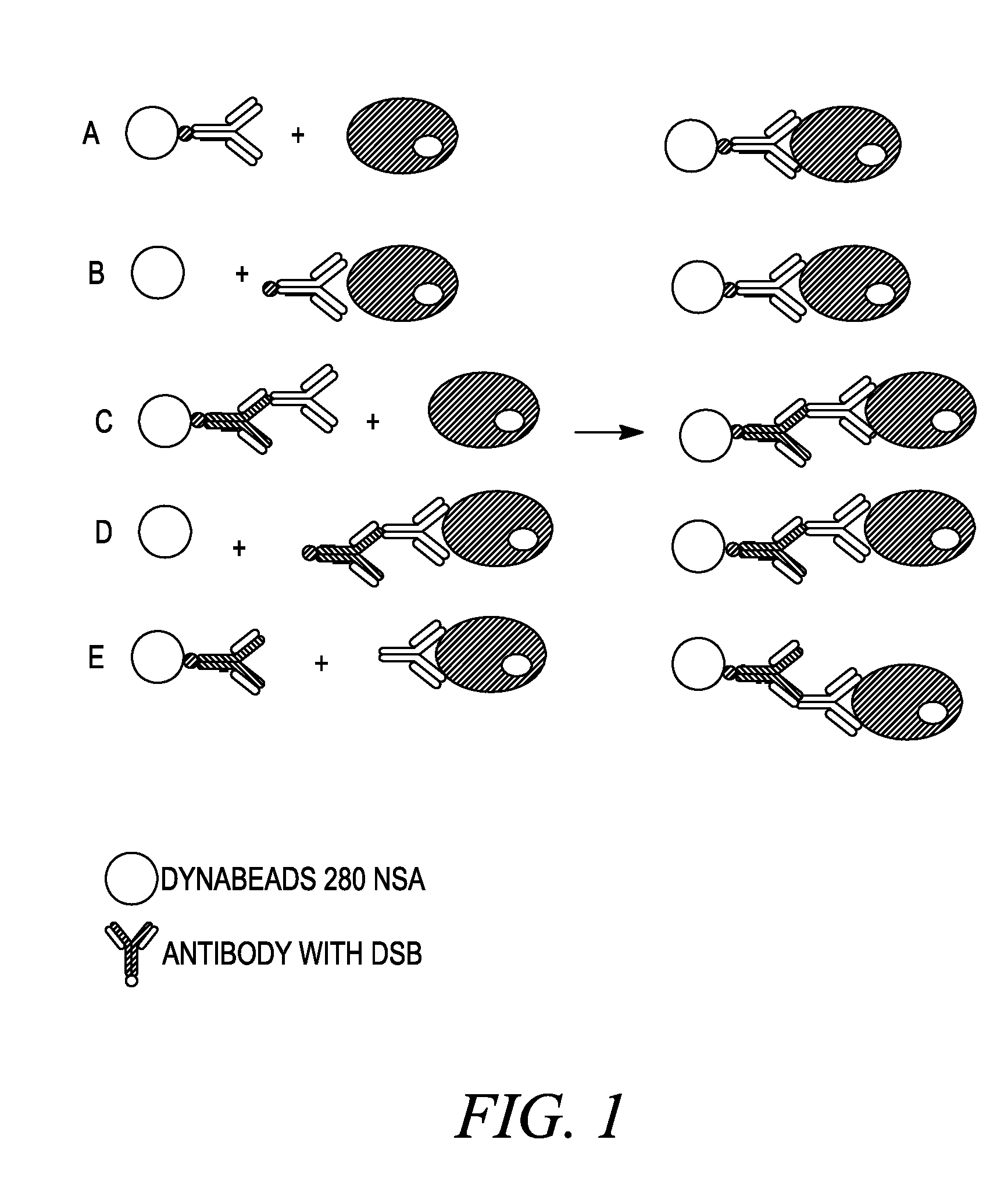
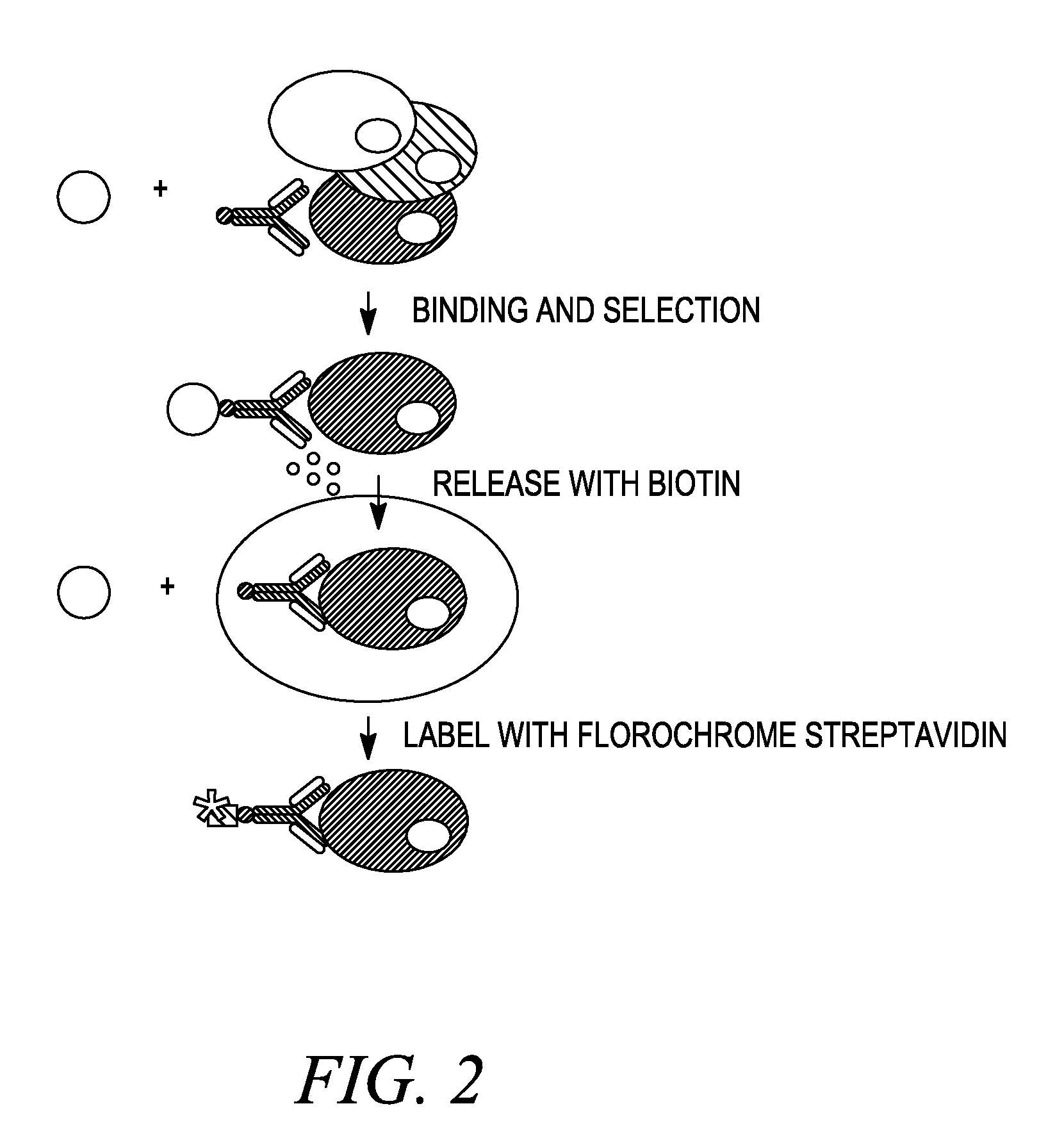
InactiveUS20080255004A1Strong interactionAvoid lengthBiomass after-treatmentElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentBiotin-streptavidin complexProtein target
Methods of reversal of the binding between a biotin compound and a biotin-binding compound are disclosed. A method of reversibly releasing a biotinylated moiety from a streptavidin (or avidin) coated support is shown as an example. The strong interaction between streptavidin or avidin-biotin is made much weaker by using a combination of modified streptavidin or avidin and modified biotin like desthiobiotin or a derivative thereof like DSB-X Biotin. A protein, such as an antibody may be biotinylated with the modified biotin. When this protein is isolated by binding the modified biotin to the modified streptavidin or avidin bound to an solid surface, it may be released under very gently and very rapid conditions by addition of free biotin. In contrast to proteins obtained by the prior art release methods the protein obtained using the previously available release methods, the proteins obtained using the methods disclosed herein will maintain their native conformation. Uses of the methods in various procedures including cell detachment procedures and techniques of detection, identification, determination, purification, separation and / or isolation of target proteins or nucleic acid molecules are also described.
Owner:LIFE TECH AS
Power generation assemblies, and apparatus for use therewith
ActiveUS20060171798A1Increase hydrodynamic massExtended maintenance periodPropellersWind motor controlIsoetes triquetraEngineering
A floating power generation assembly comprises at least three floating units (900) floating on a body of water, and at least three anchors (916) secured to a solid surface beneath the body of water, each of the floating units (900) being provided with power generation means, the floating units (900) being arranged substantially at the vertices of at least one equilateral triangle. The invention also provides ship-borne apparatus for deploying the floating units of such a power generation assembly and a novel multiple wind turbine assembly.
Owner:OCEAN WIND TECH
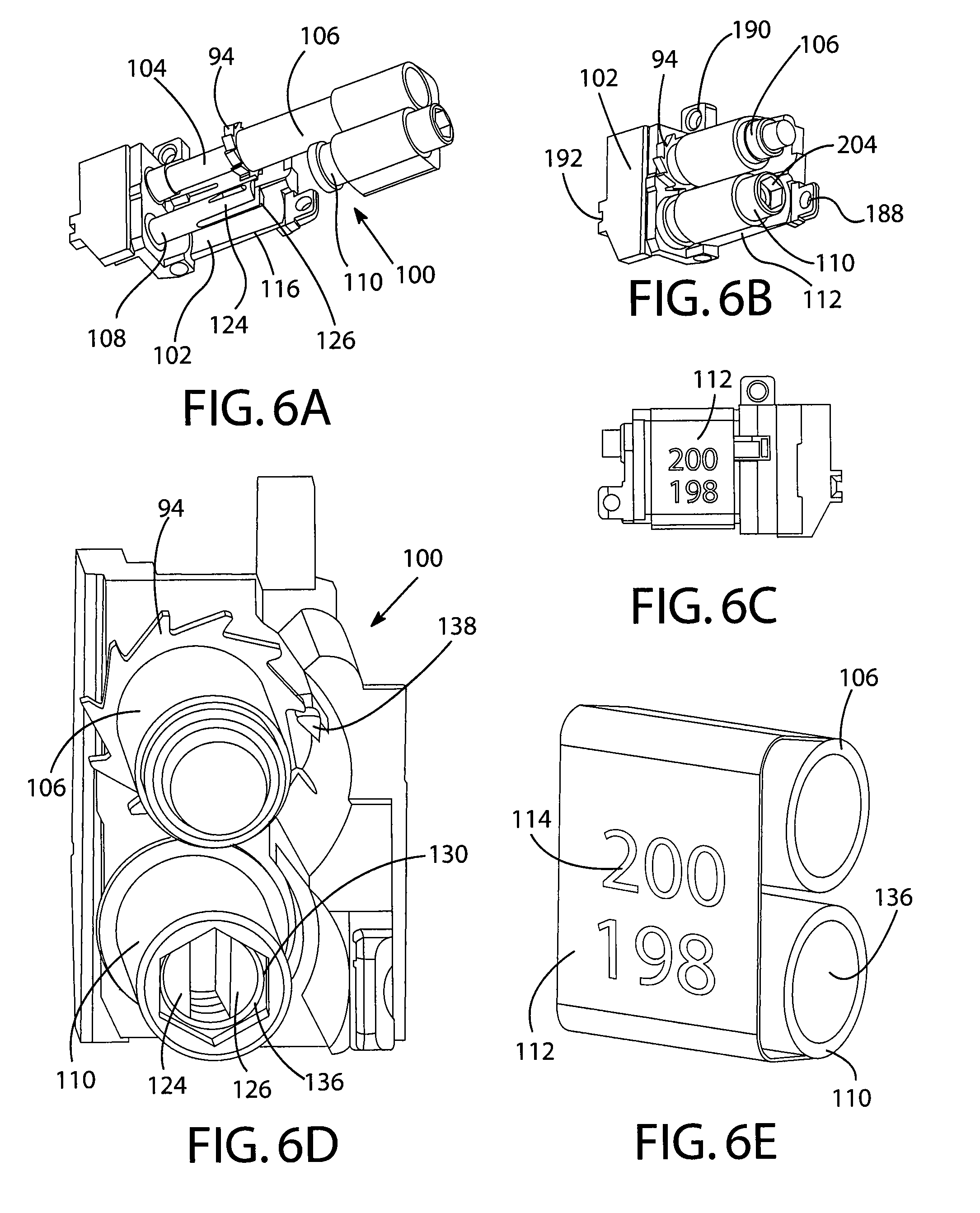
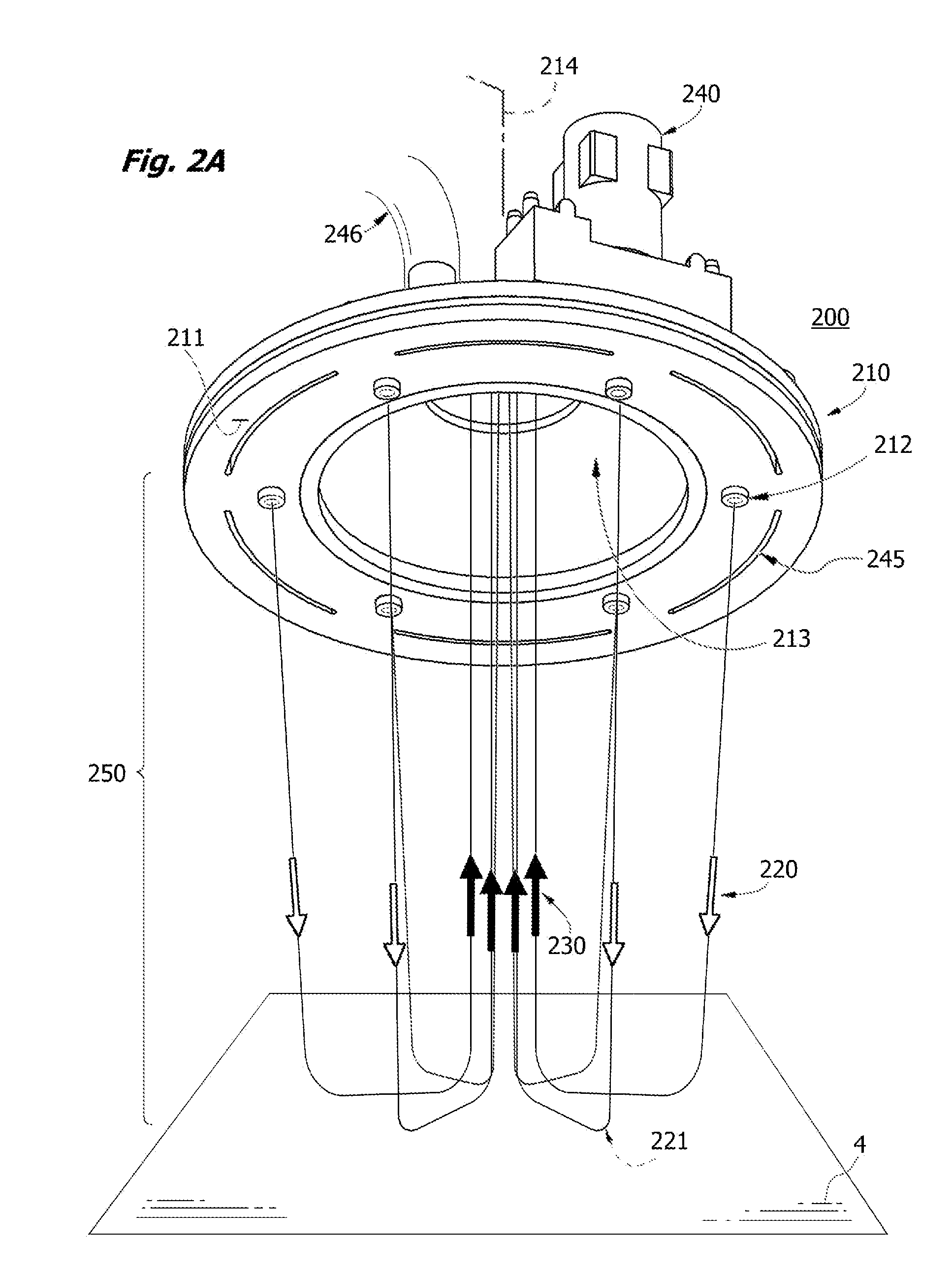
Dose counters for inhalers, inhalers and methods of assembly thereof
ActiveUS20110283997A1Prevent unwanted motionReliable countingMedical devicesLiquid transferring devicesBobbinEngineering
A manually operated metered dose inhaler includes a dose counter chamber including a dose display tape driven by a ratchet wheel which is driven in turn by an actuator pawl actuated by movement of a canister, the tape unwinding from a stock bobbin during use of the inhaler, a rotation regulator being provided for the stock bobbin and including a wavelike engagement surface with concavities which engage against control elements in the form of protrusions on resilient forks of a split pin thereby permitting incremental unwinding of the stock bobbin yet resisting excessive rotation if the inhaler is dropped onto a hard surface.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IRELAND +2
Particle Interrogation Devices and Methods
InactiveUS20110186436A1Reduce elutriative lossImprove sampling efficiencyOptical radiation measurementSludge treatmentParticle trappingEngineering
Devices, apparatus and methods are disclosed for non-contact pneumatic sampling and sampling of surfaces, persons, articles of clothing, buildings, furnishings, vehicles, baggage, packages, mail, and the like, for contaminating aerosols indicative of a hazard or a benefit, where the contaminating aerosols are chemical, radiological, biological, toxic, or infectious in character. In a first device, a central orifice for pulling a suction gas stream is surrounded by a peripheral array of convergingly-directed gas jets, forming a virtual sampling chamber. The gas jets are configured to deliver millisecond pneumatic pulses that erode particles from solid surfaces at a distance. In another aspect of the invention, a suction gas stream is split using an air-to-air concentrator so that a particle-enriched gas flow is directed to a particle trap and any particles immobilized in the particle trap (including any adsorbed vapors associated with the particles) are selectively analyzed to detect trace residues associated with explosives.
Owner:ENERTECHNIX
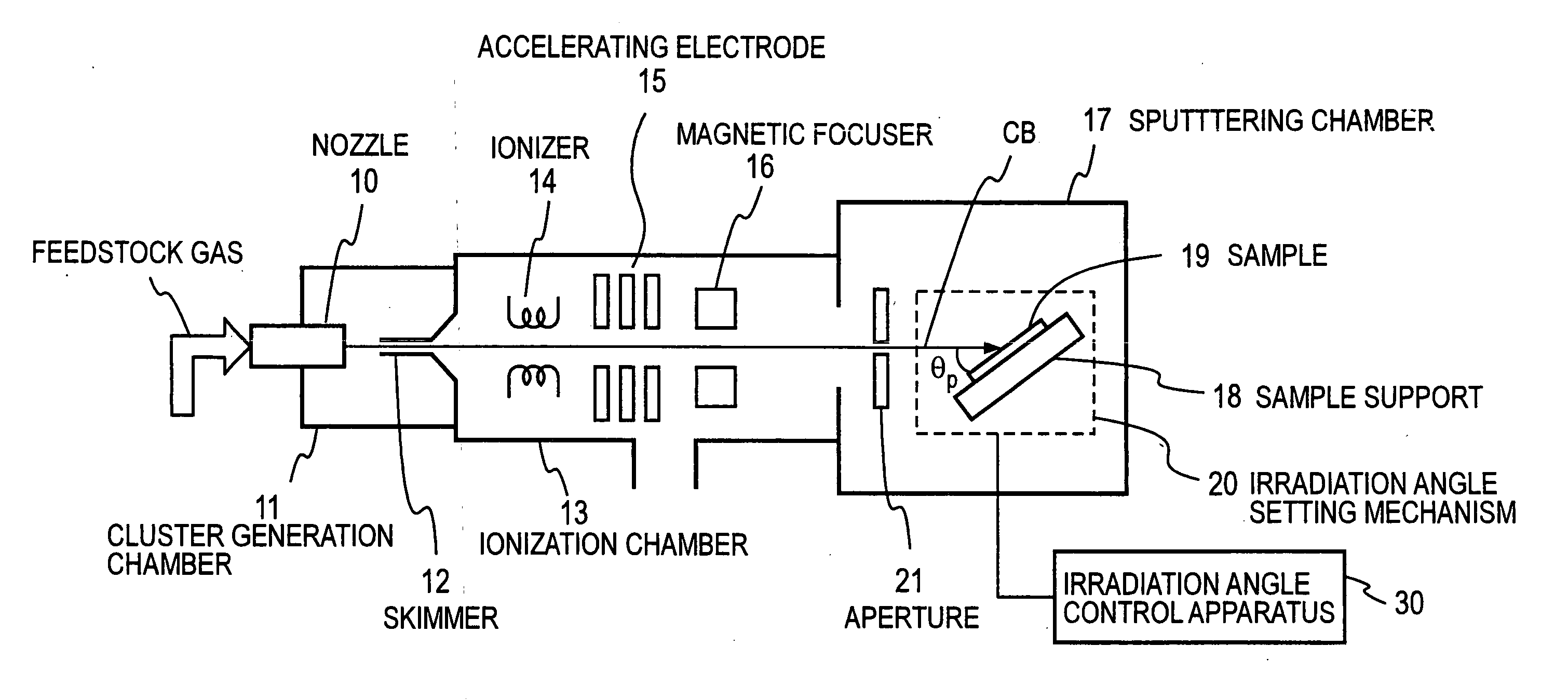
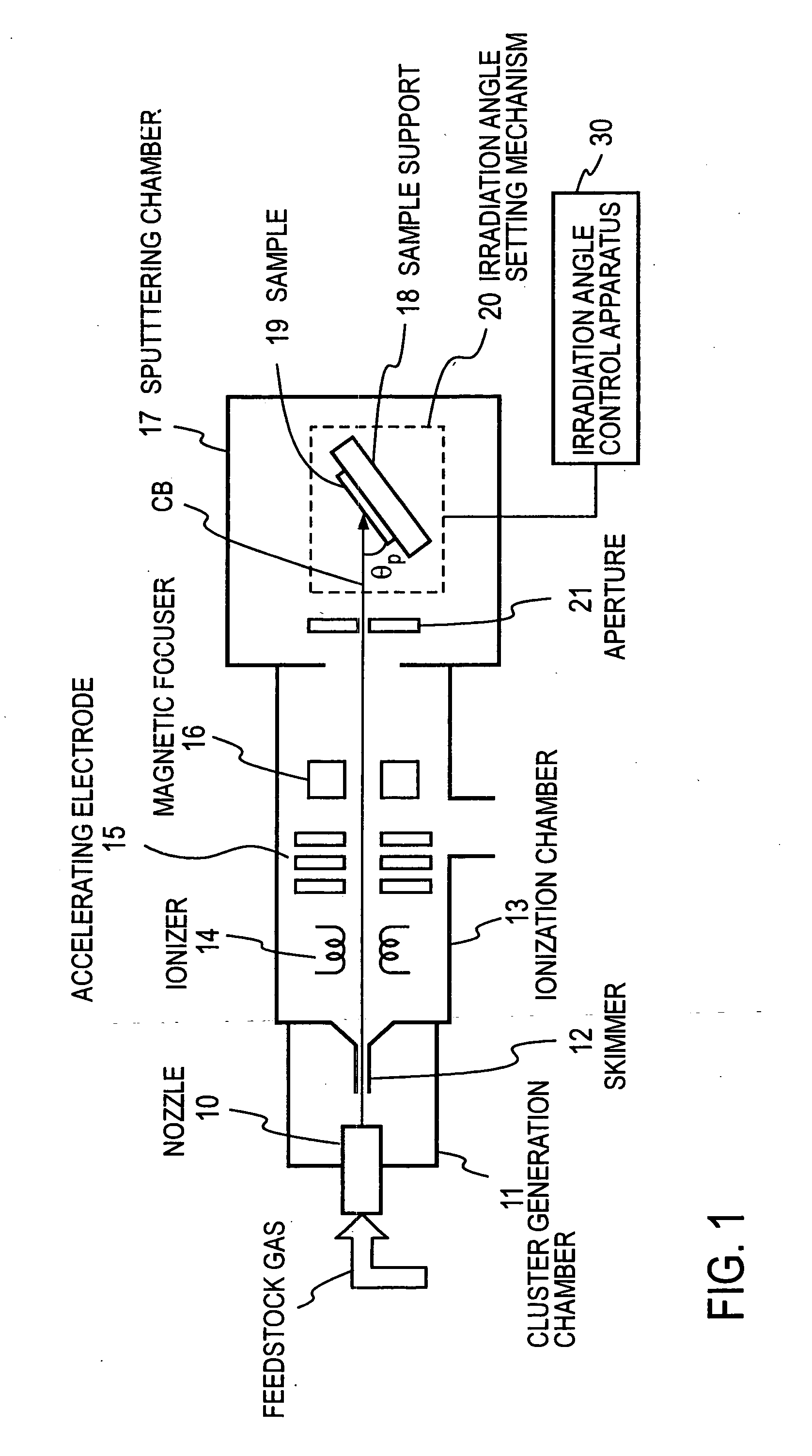
Method and device for flattening surface of solid
ActiveUS20060278611A1Small surface roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsGas cluster ion beamIrradiation
In a method of irradiating a gas cluster ion beam on a solid surface and smoothing the solid surface, the angle formed between the solid surface and the gas cluster ion beam is chosen to be between 1° and an angle less than 30°. In case the solid surface is relatively rough, the processing efficiency is raised by first irradiating a beam at an irradiation angle θ chosen to be something like 90° as a first step, and subsequently at an irradiation angle θ chosen to be 1° to less than 30° as a second step. Alternatively, the set of the aforementioned first step and second step is repeated several times.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Particle Interrogation Devices and Methods
InactiveUS20110203931A1Efficient suctionReduce lossesOptical radiation measurementSludge treatmentParticle trappingEngineering
Devices, apparatus and methods are disclosed for non-contact pneumatic sampling and sampling of surfaces, persons, articles of clothing, buildings, furnishings, vehicles, baggage, packages, mail, and the like, for contaminating aerosols or vapors indicative of a hazard or a benefit, where the contaminating aerosols or vapors are chemical, radiological, biological, toxic, or infectious in character. In a first device, a central orifice for pulling a suction gas stream is surrounded by a peripheral array of convergingly-directed gas jets, forming a virtual sampling chamber. The gas jets are configured to deliver millisecond pneumatic pulses that erode particles and vapors from solid surfaces at a distance. In another aspect of the invention, a suction gas stream is split using an air-to-air concentrator so that a particle-enriched gas flow is directed to a particle trap and particles immobilized therein are selectively analyzed for explosives and explosives related materials under optimized conditions for analyzing particle-associated constituents and a bulk flow is directed to a vapor trap and free vapors immobilized therein are selectively analyzed for explosives and explosives related materials under optimized conditions for analyzing free vapors. Detection signals from the particle channel and the vapor channel are compared or integrated to detect trace residues associated with explosives.
Owner:ENERTECHNIX
Method to consolidate solid materials during subterranean treatment operations
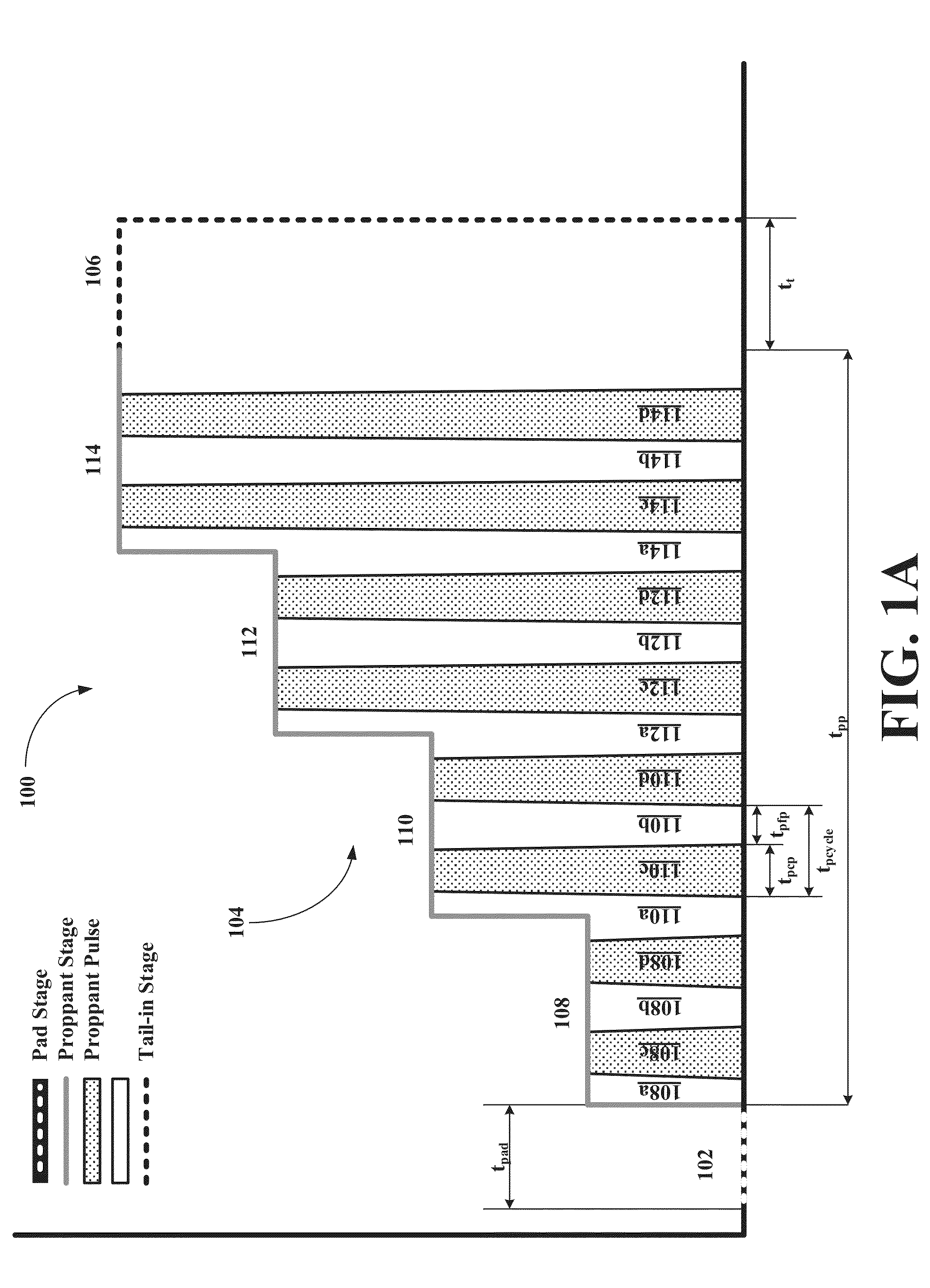
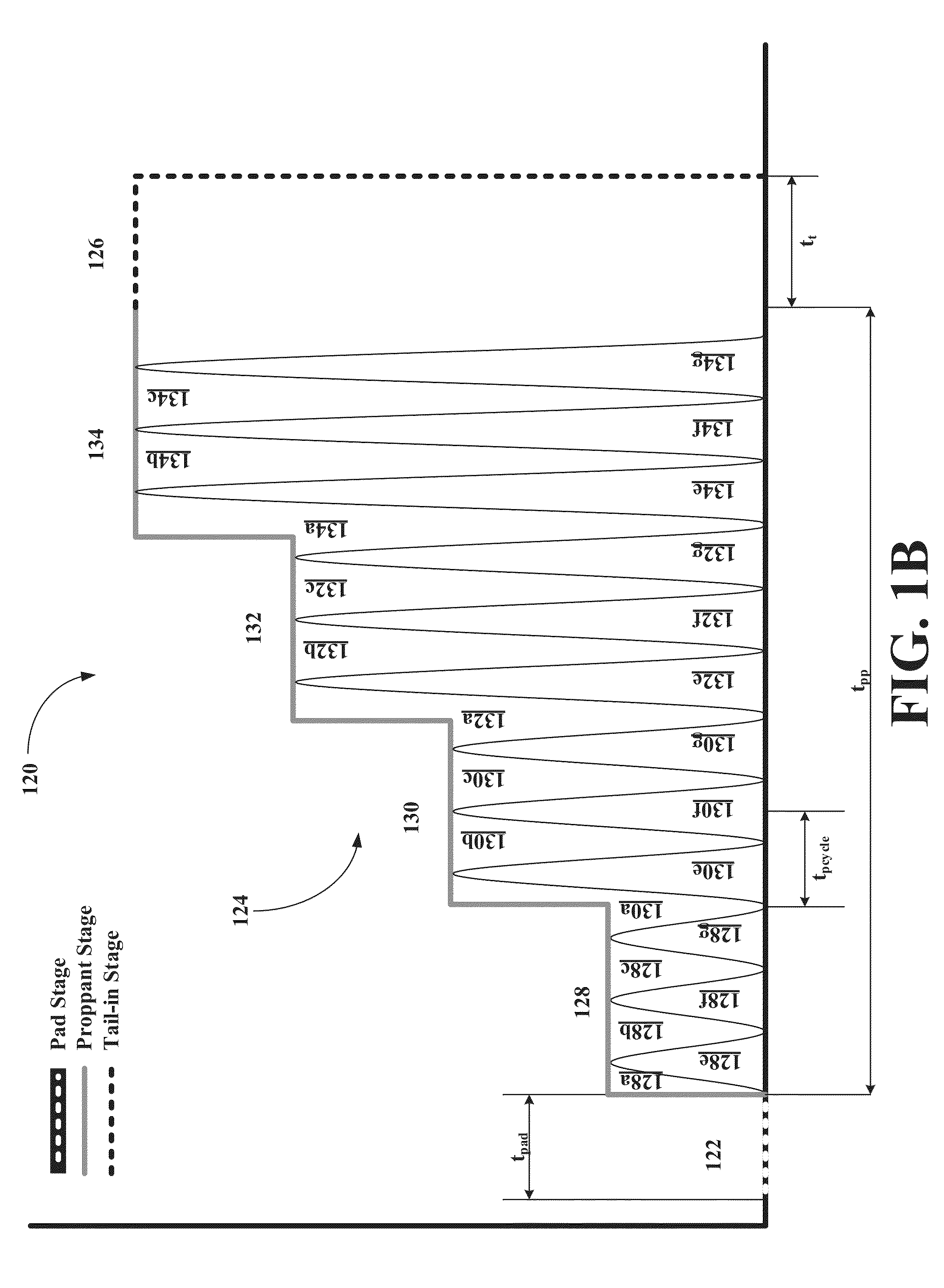
ActiveUS20150068747A1Delayed consolidationAltered propertyScale removal and water softeningFluid removalSolid surfaceChemistry
Compositions include (1) aggregating compositions capable of forming deformable partial or complete coatings on formation surfaces, formation particle surfaces, downhole fluid solid surfaces, and / or proppant surfaces, where the coatings increase aggregation and / or agglomeration propensities of the particles and surfaces to form particles clusters or pillars having deformable coatings, and (2) aggregation stabilizing and / or strengthening compositions capable of altering properties of the coated clusters or pillars to form consolidated, stabilized, and / or strengthened clusters or pillars. Methods for stabilizing aggregated particle clusters or pillars include (1) treating the particles with an aggregating composition to form aggregated clusters or pillars and (2) treating the aggregated particle clusters or pillars with a stabilizing or strengthening composition to form consolidated, stabilized, and / or strengthened clusters or pillars.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
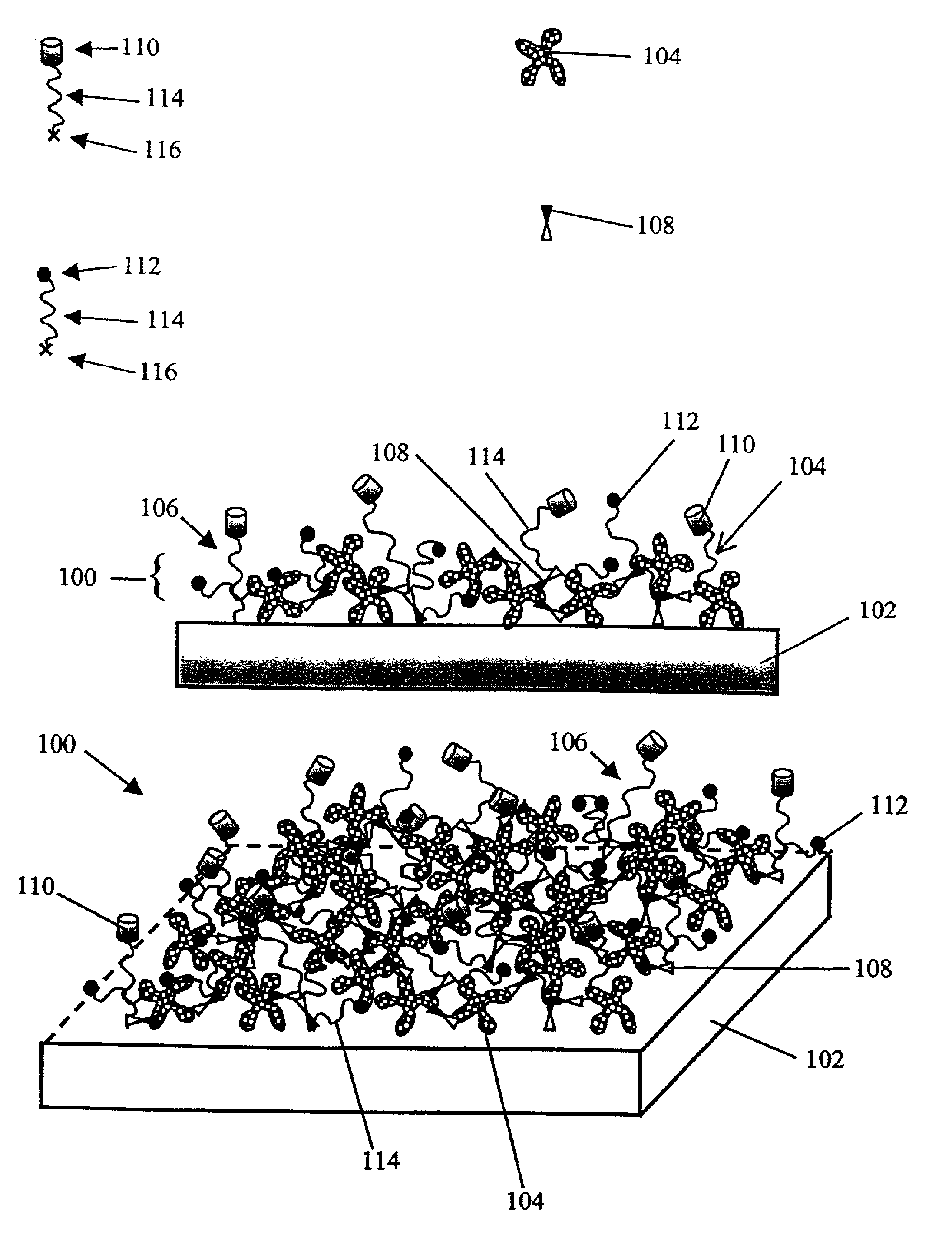
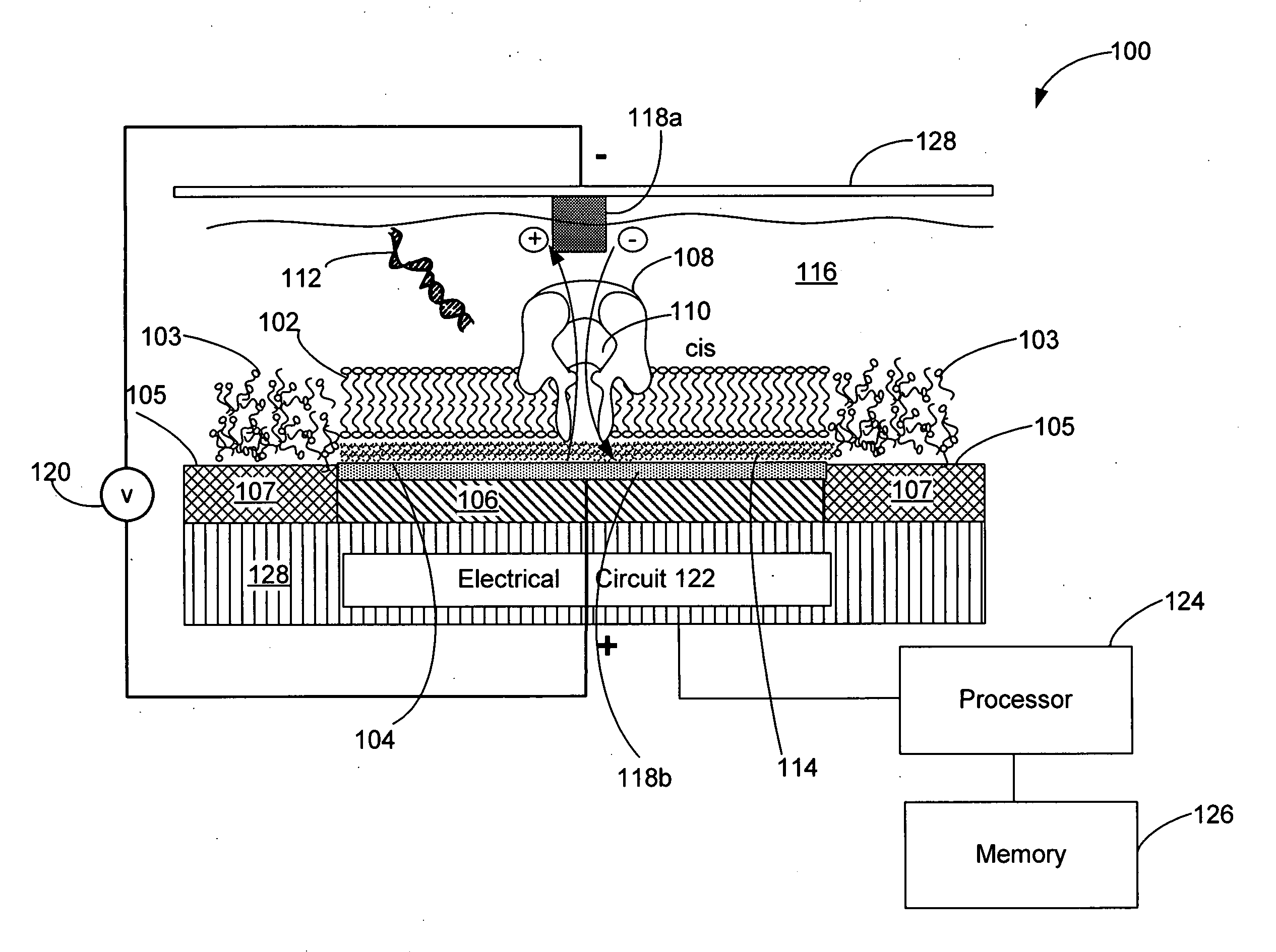
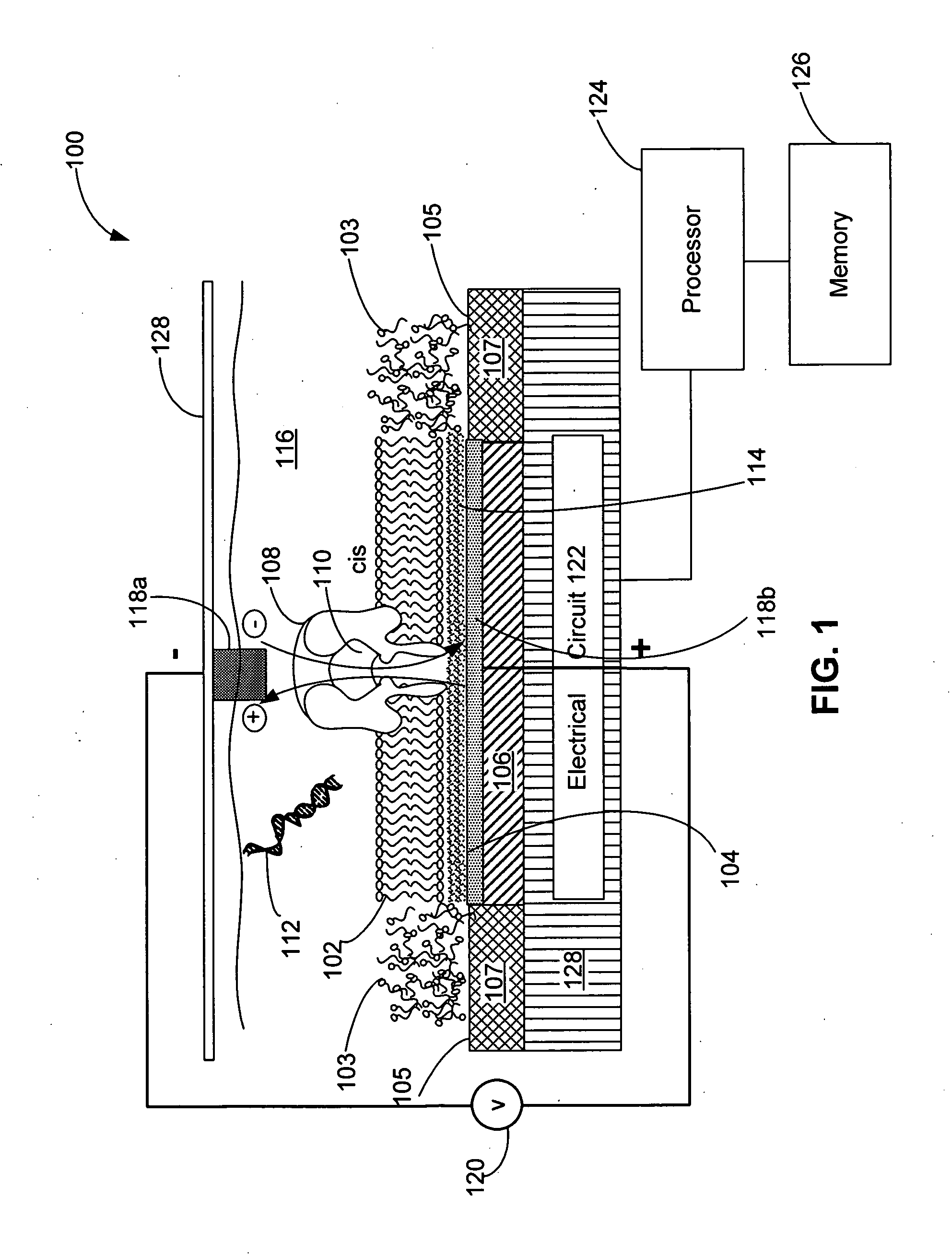
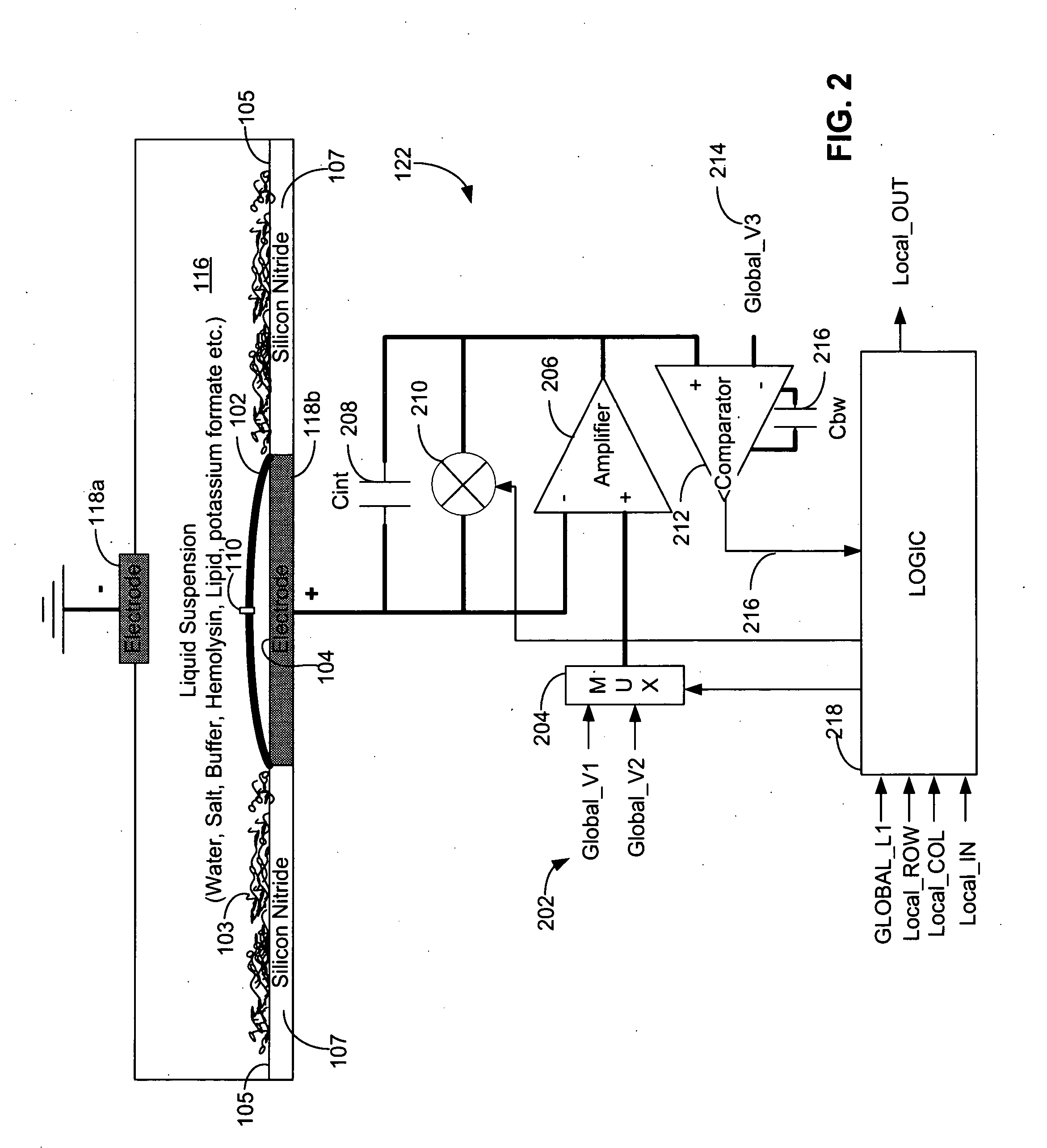
Systems and methods for assembling a lipid bilayer on a substantially planar solid surface
InactiveUS20120052188A1Microbiological testing/measurementPretreated surfacesLipid bilayerSolid surface
Techniques for assembling a lipid bilayer on a substantially planar solid surface are described herein. In one example, a lipid material such as a lipid suspension is deposited on a substantially planar solid surface, a bubble filled with fast diffusing gas molecules is formed on the solid surface, and the gas molecules are allowed to diffuse out of the bubble to form a lipid bilayer on the solid surface.
Owner:GENIA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com