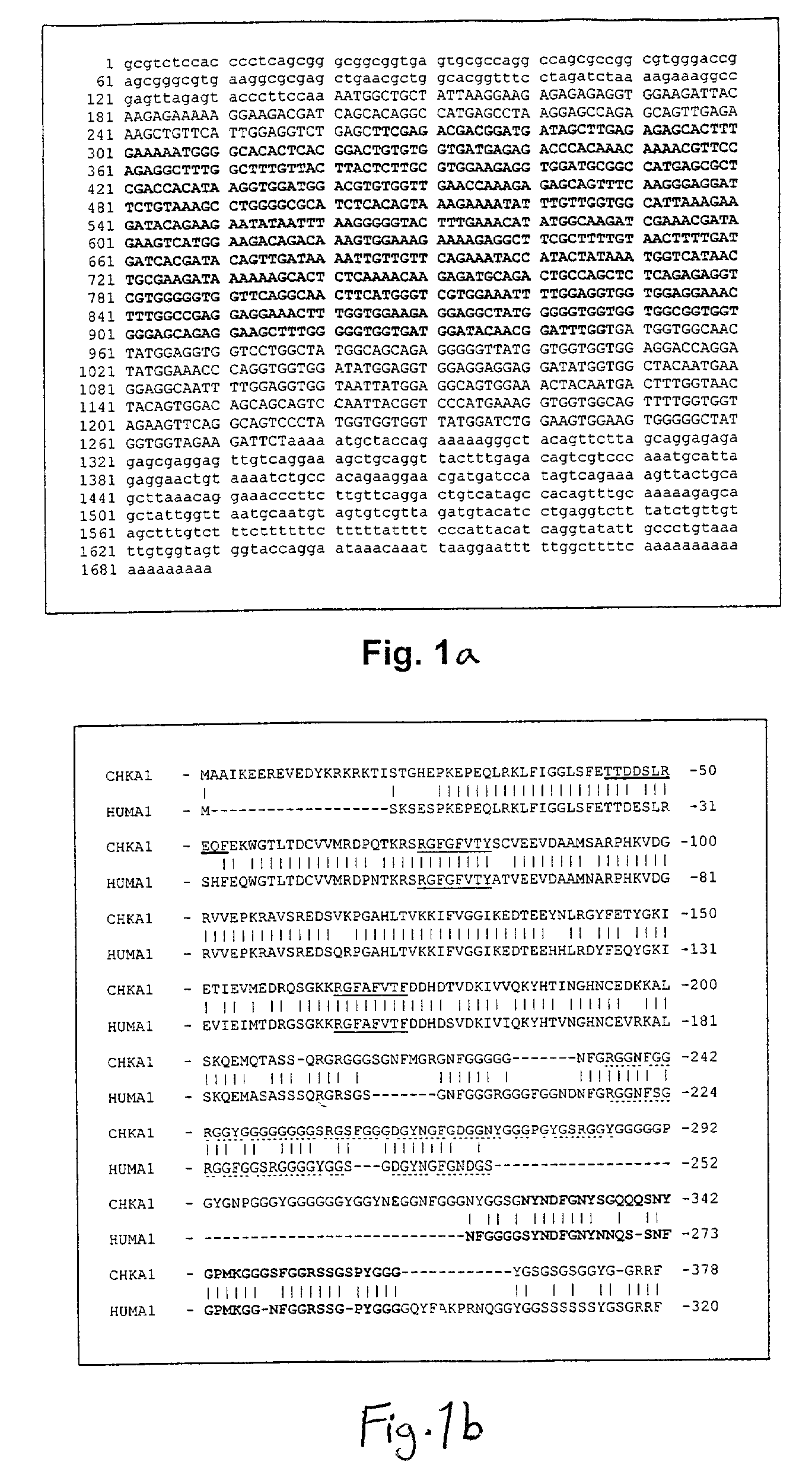
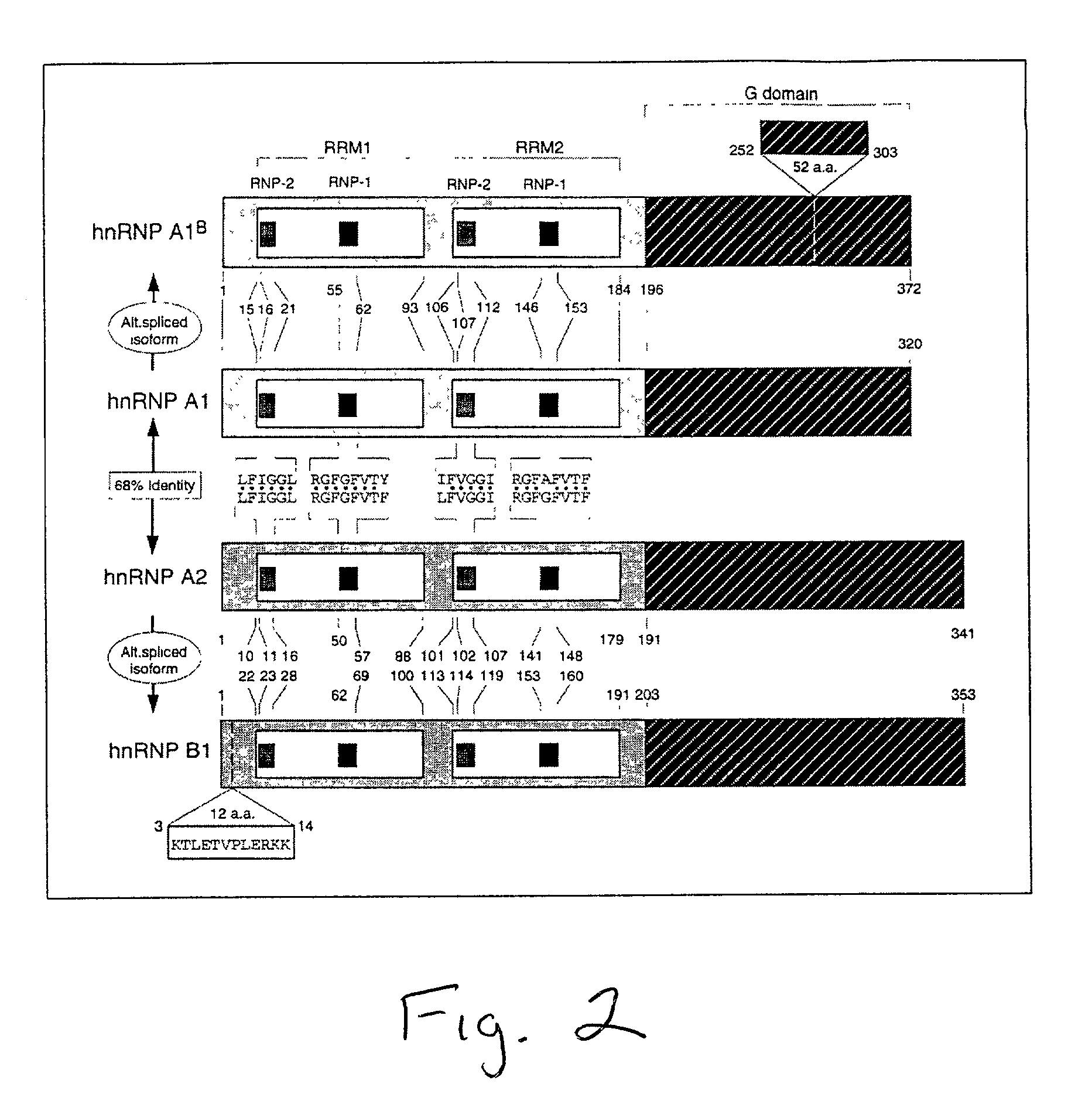
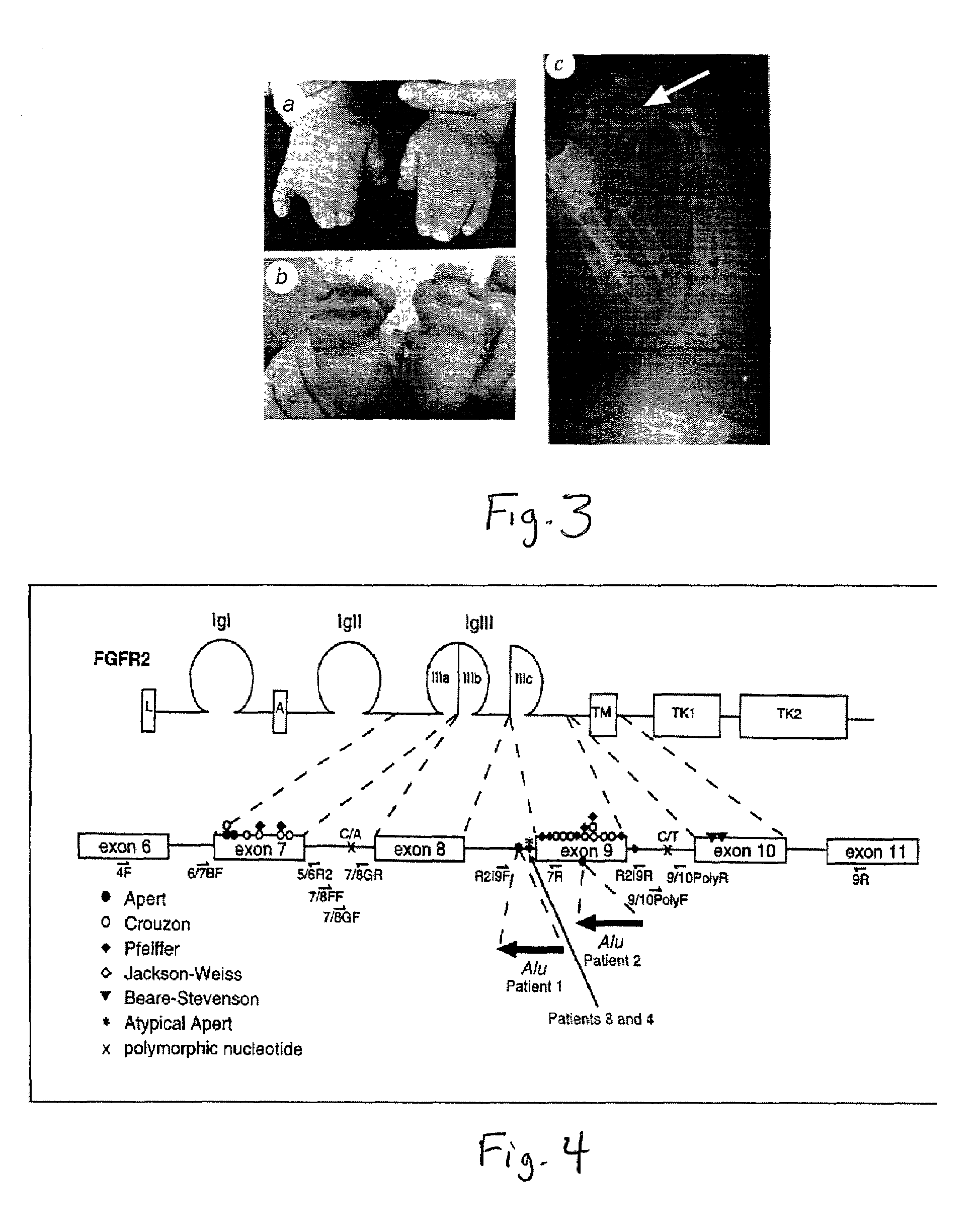
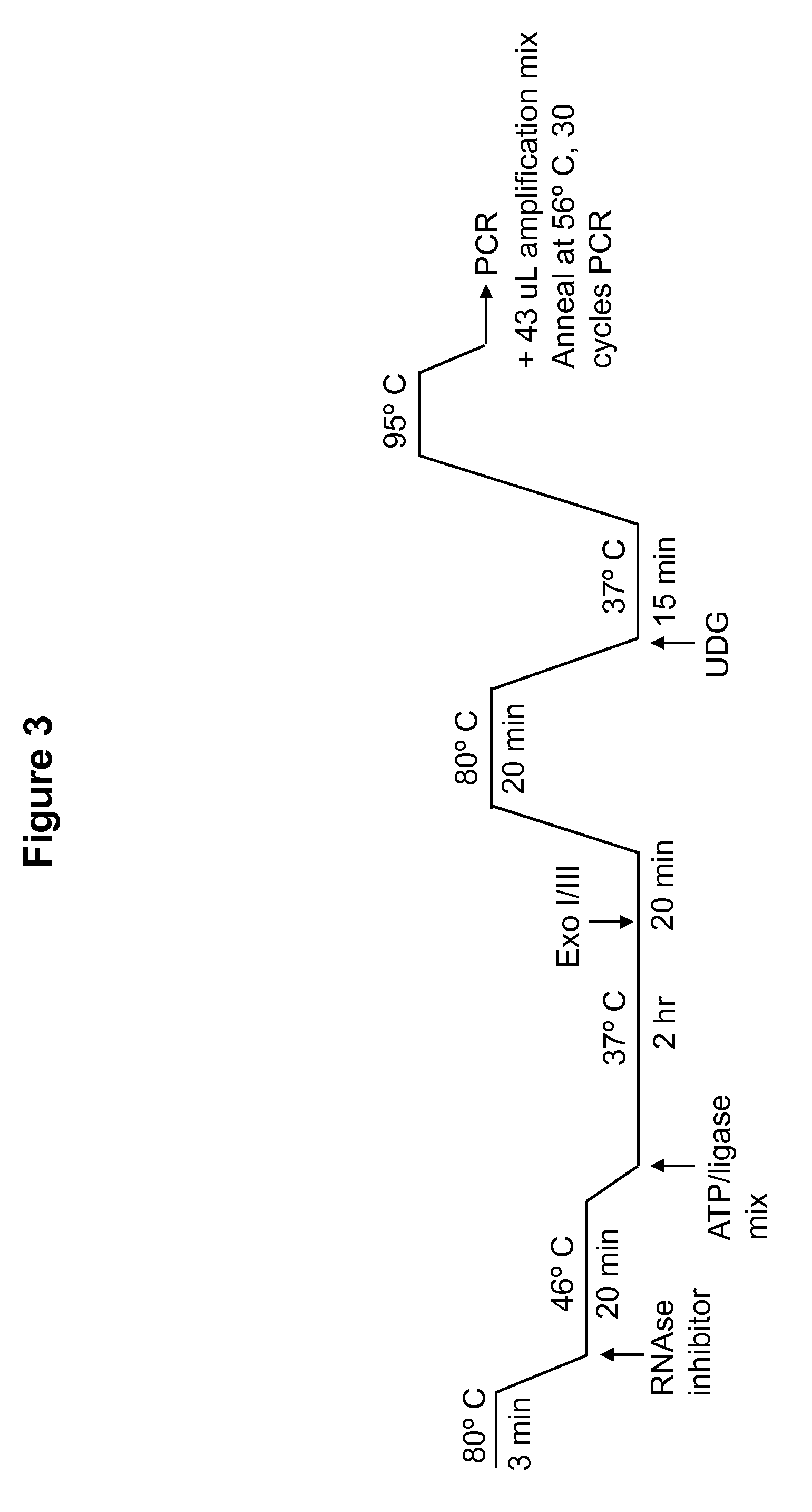
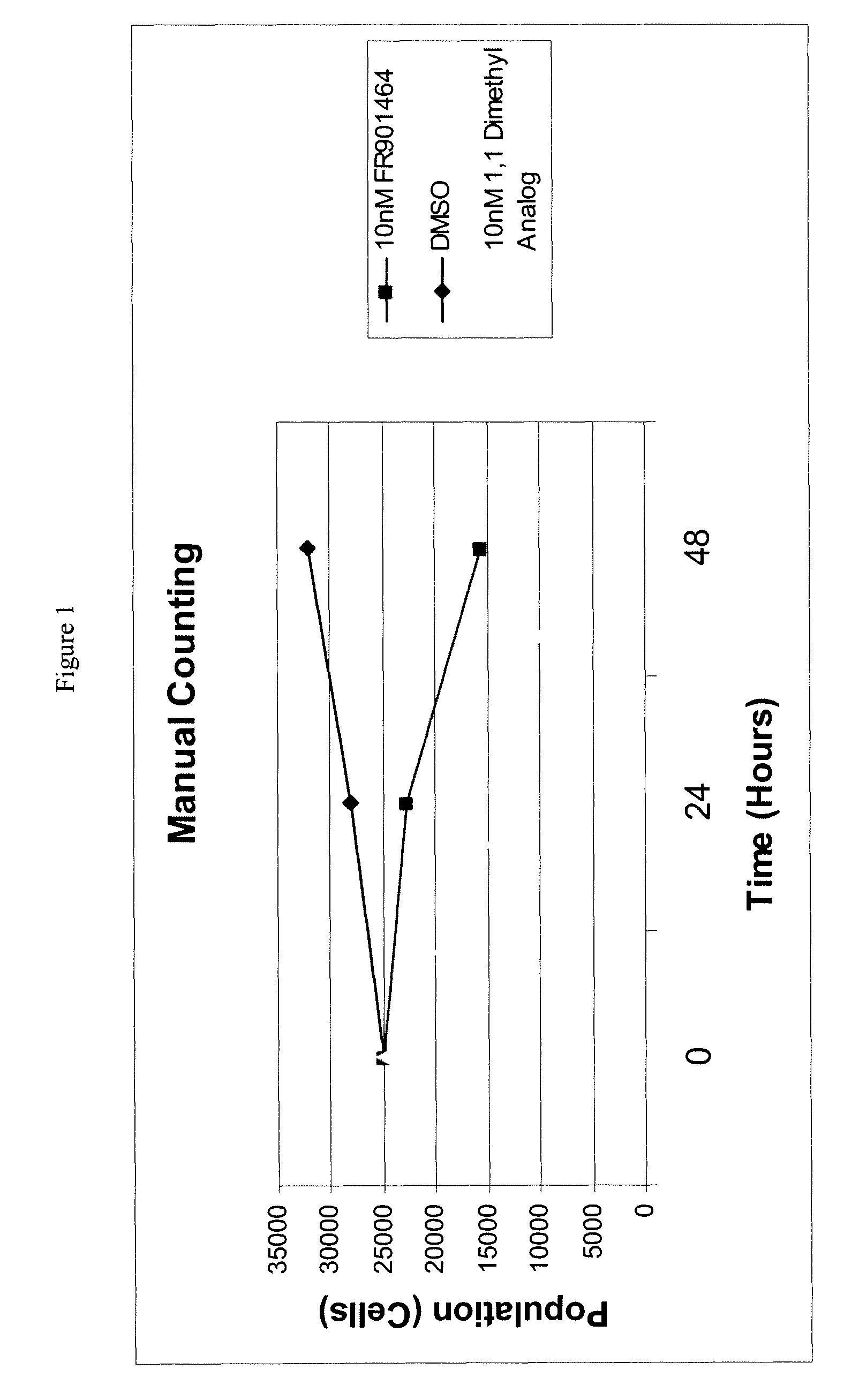
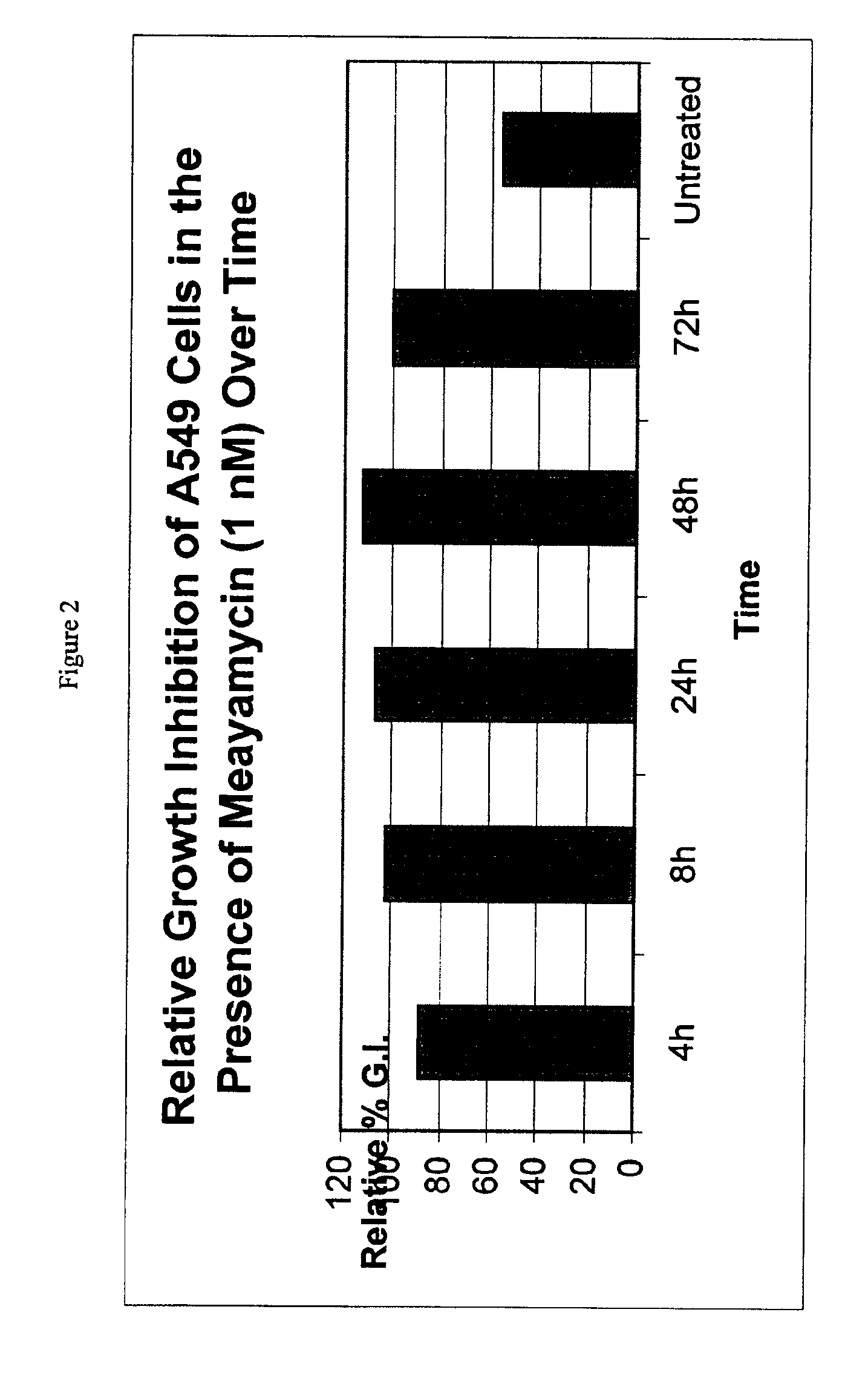
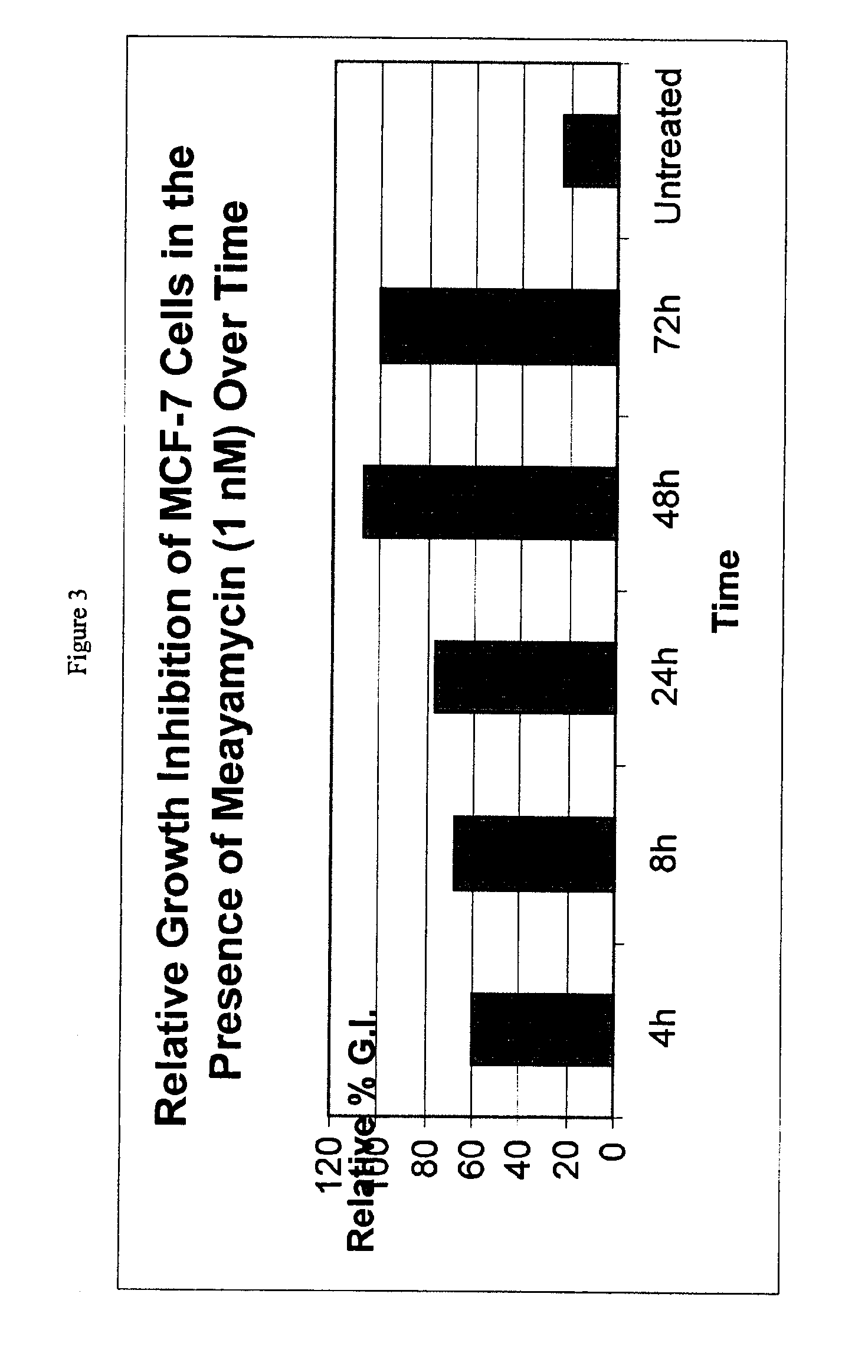
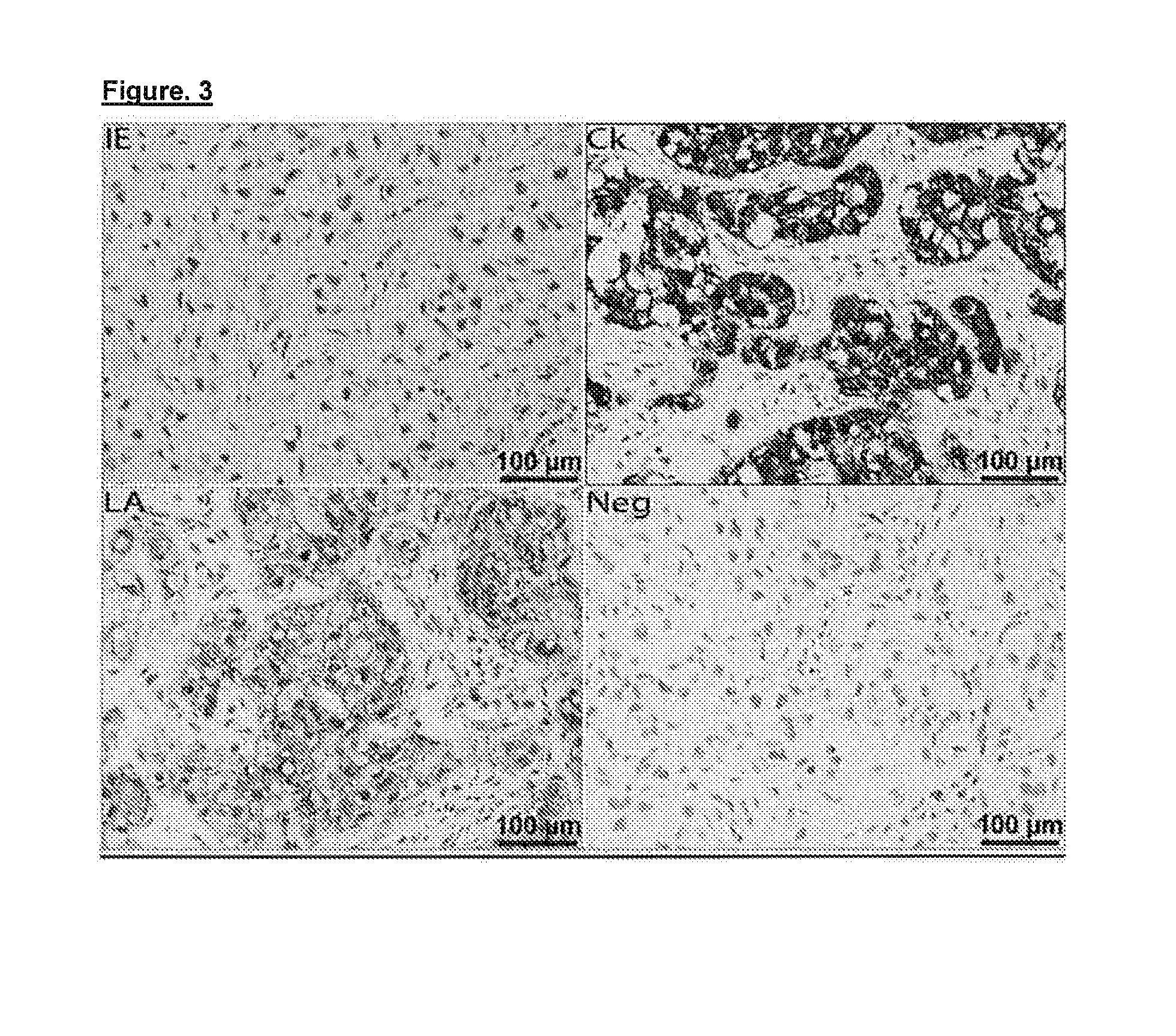
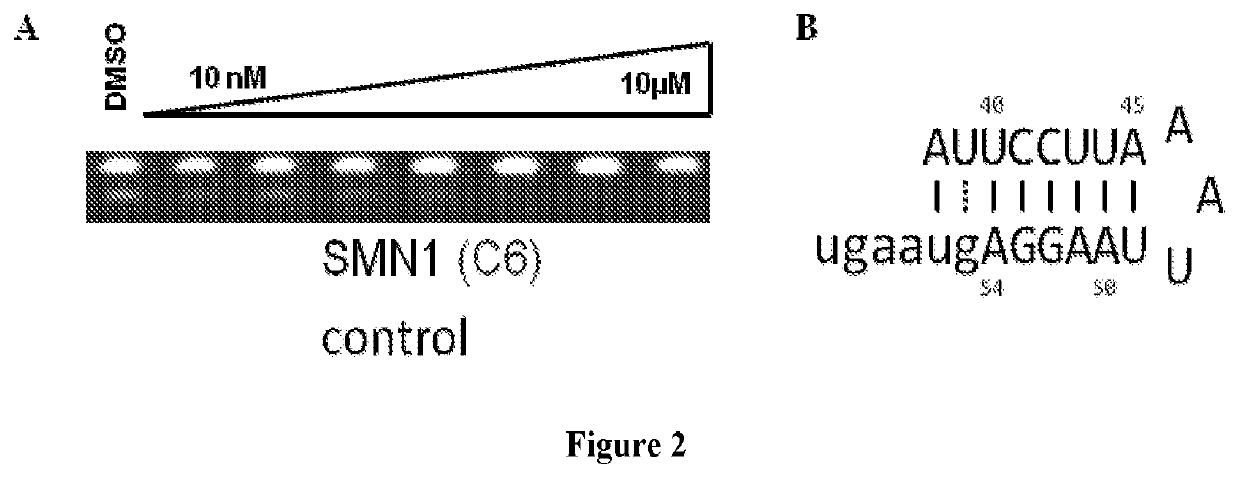
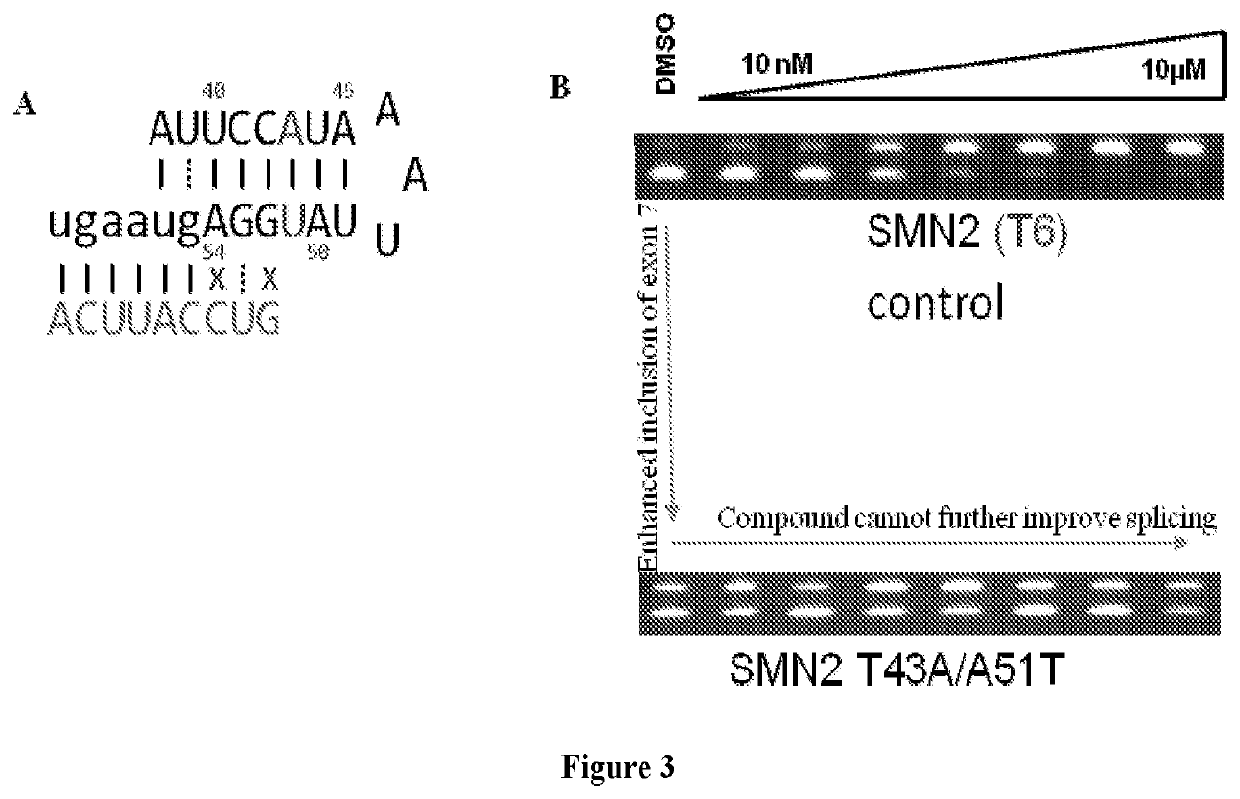
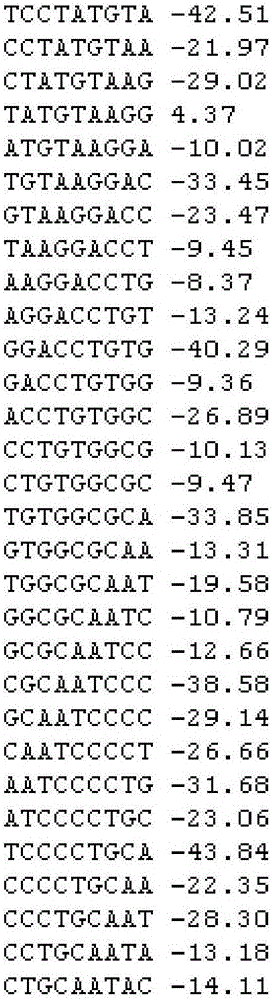Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "RNA splicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
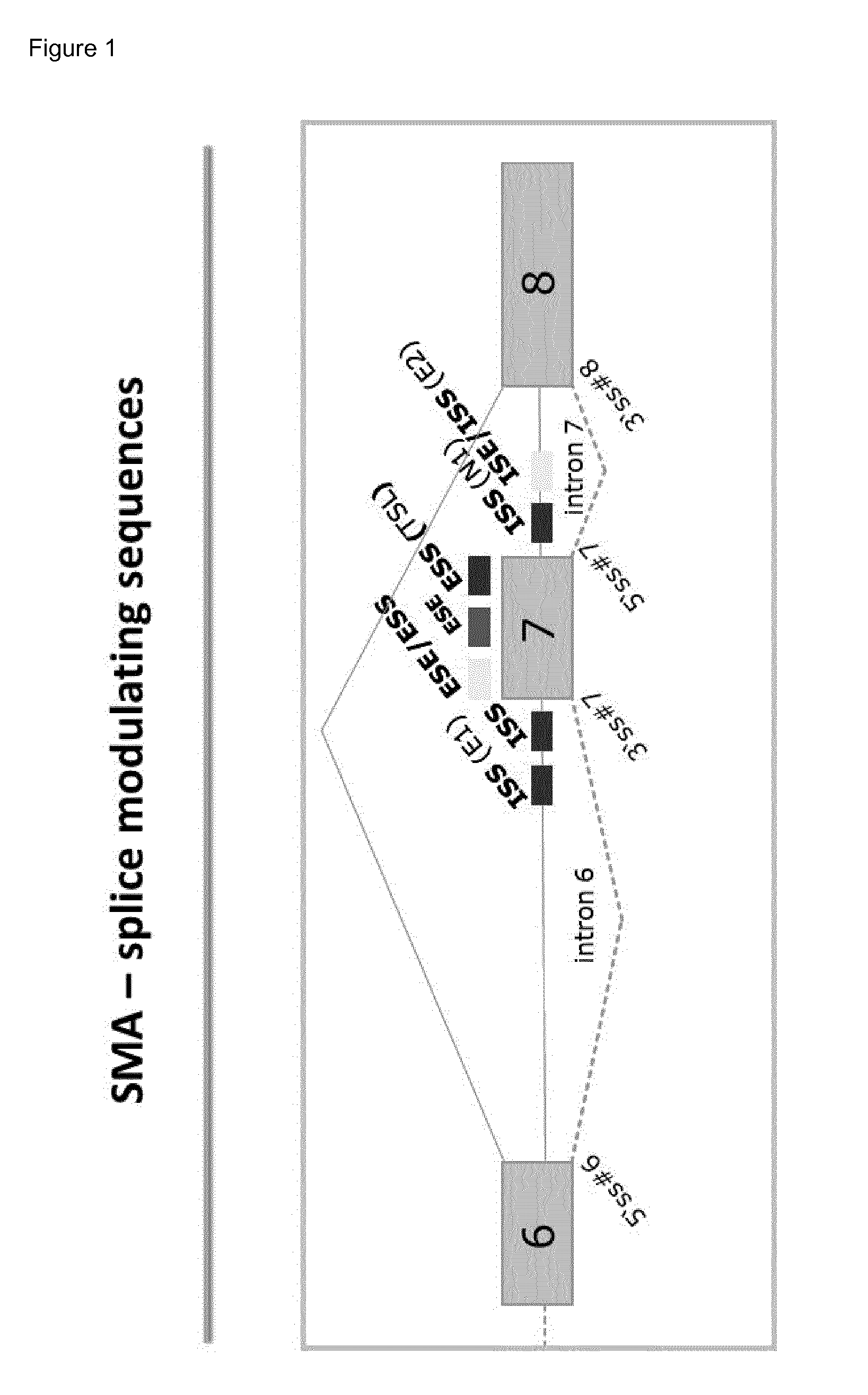
RNA splicing, in molecular biology, is a form of RNA processing in which a newly made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). During splicing, introns (Non-coding regions) are removed and exons (Coding Regions) are joined together. For nuclear-encoded genes, splicing takes place within the nucleus either during or immediately after transcription. For those eukaryotic genes that contain introns, splicing is usually required in order to create an mRNA molecule that can be translated into protein. For many eukaryotic introns, splicing is carried out in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleo proteins (snRNPs). Self-splicing introns, or ribozymes capable of catalyzing their own excision from their parent RNA molecule, also exist.
Splice choice antagonists as therapeutic agents
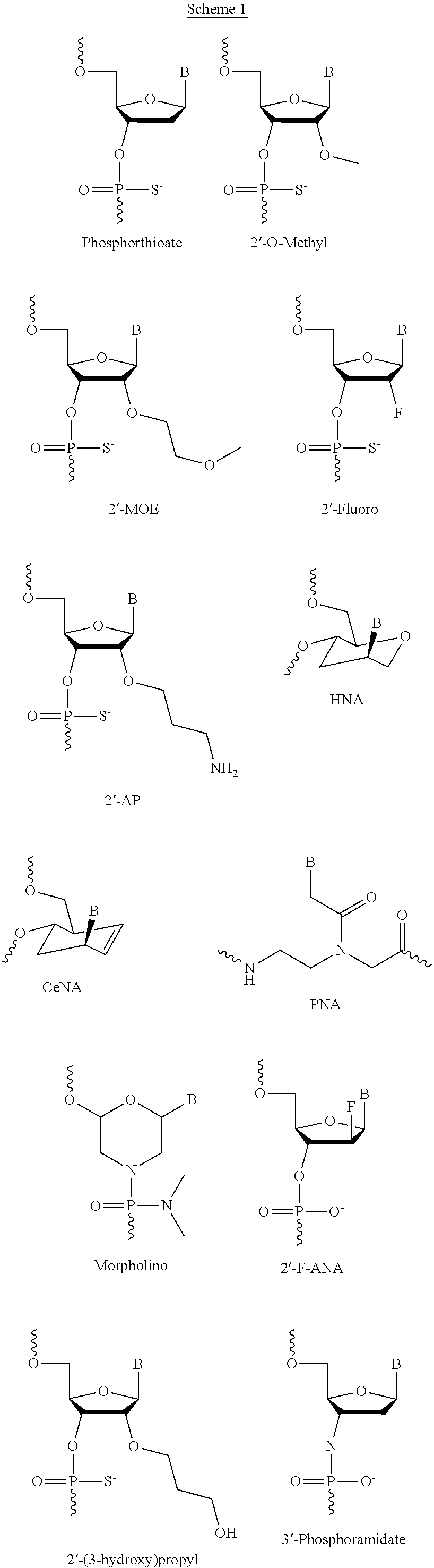
The invention relates to methods and reagents for influencing alternative RNA splicing in living cells. More particularly, the invention relates to novel means for influencing RNA splice choice in living cells using polynucleotide-based reagents that compete for binding sites in nucleotide binding proteins, and novel methods for using these reagents as therapeutics.
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
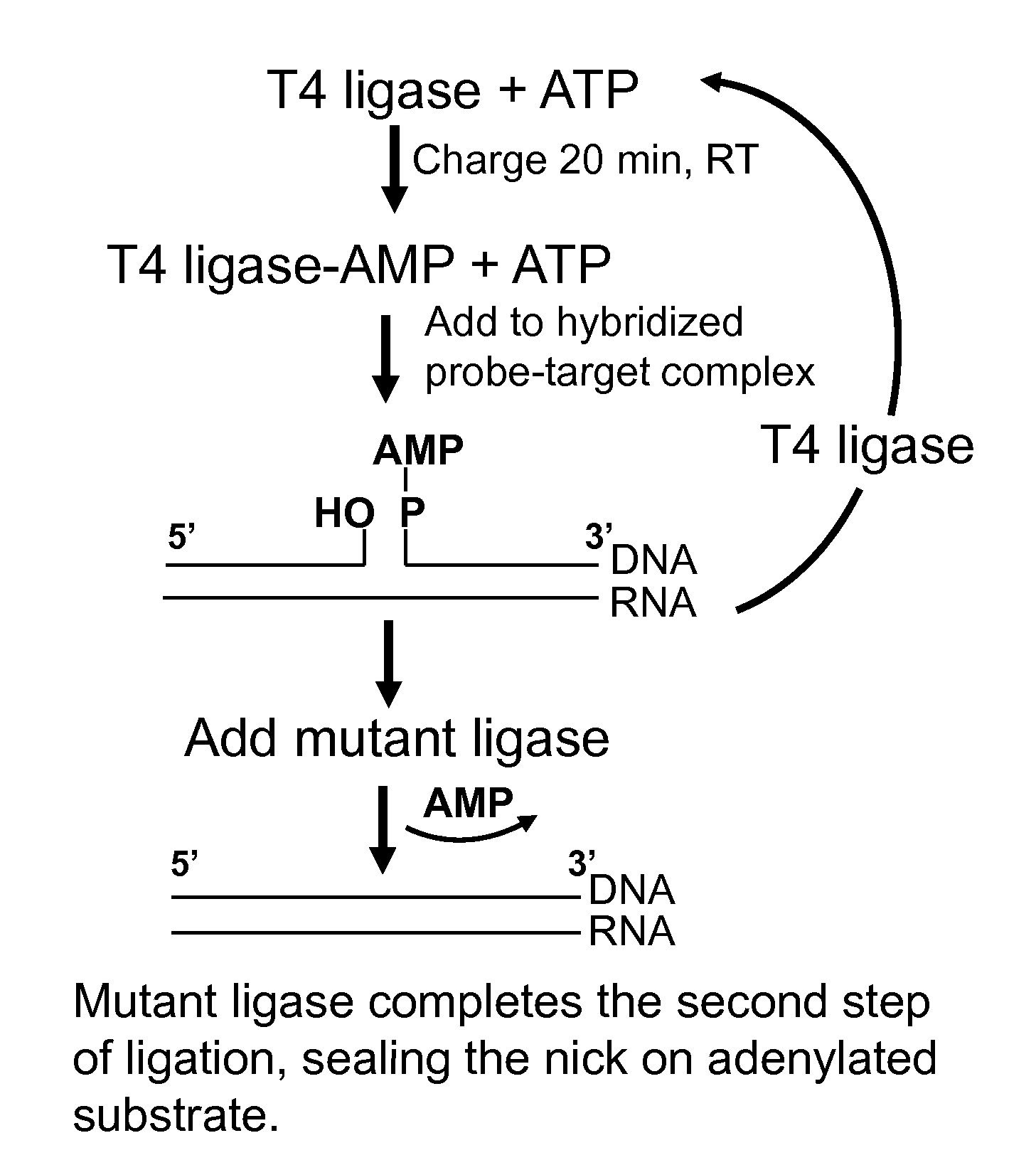
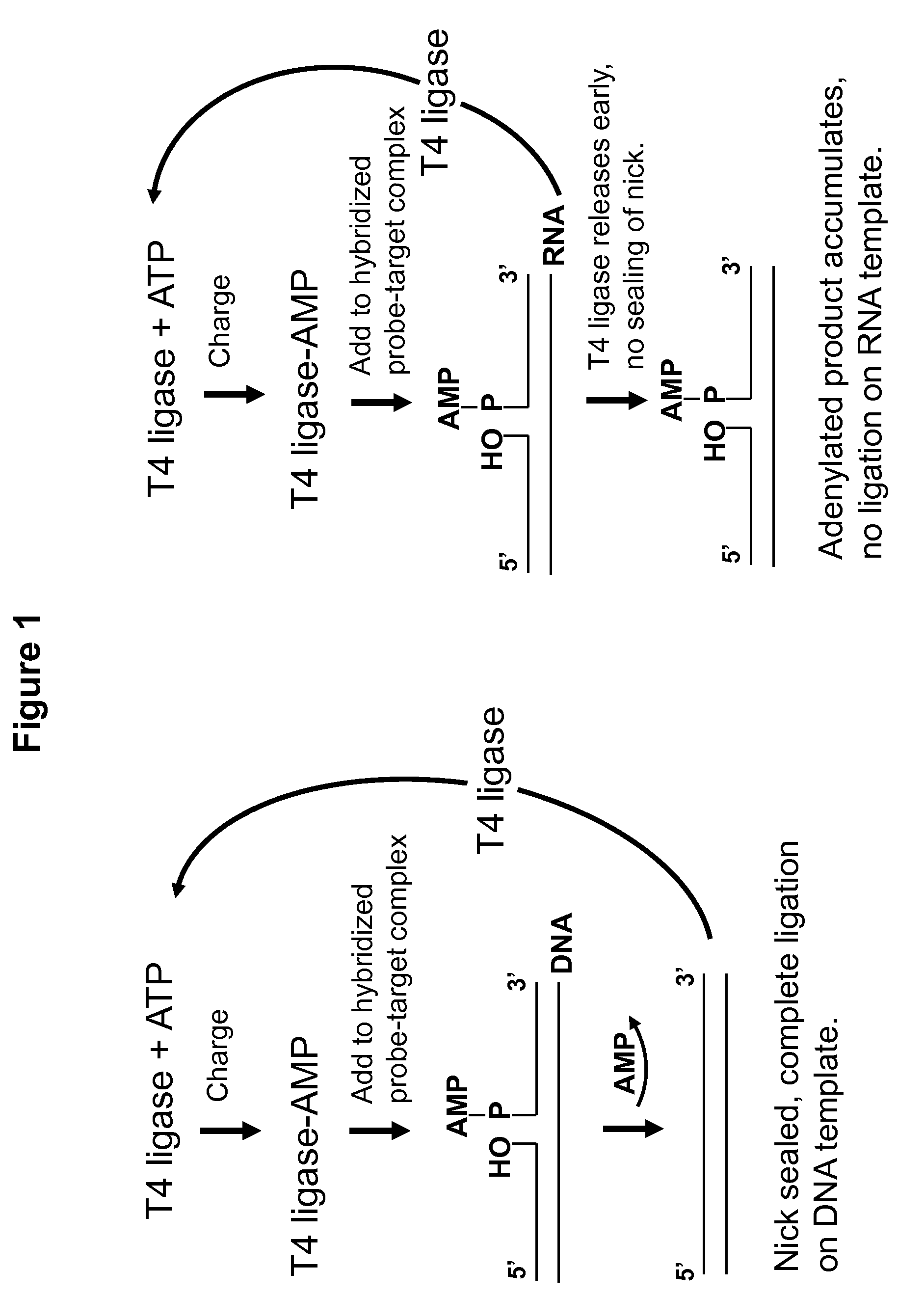
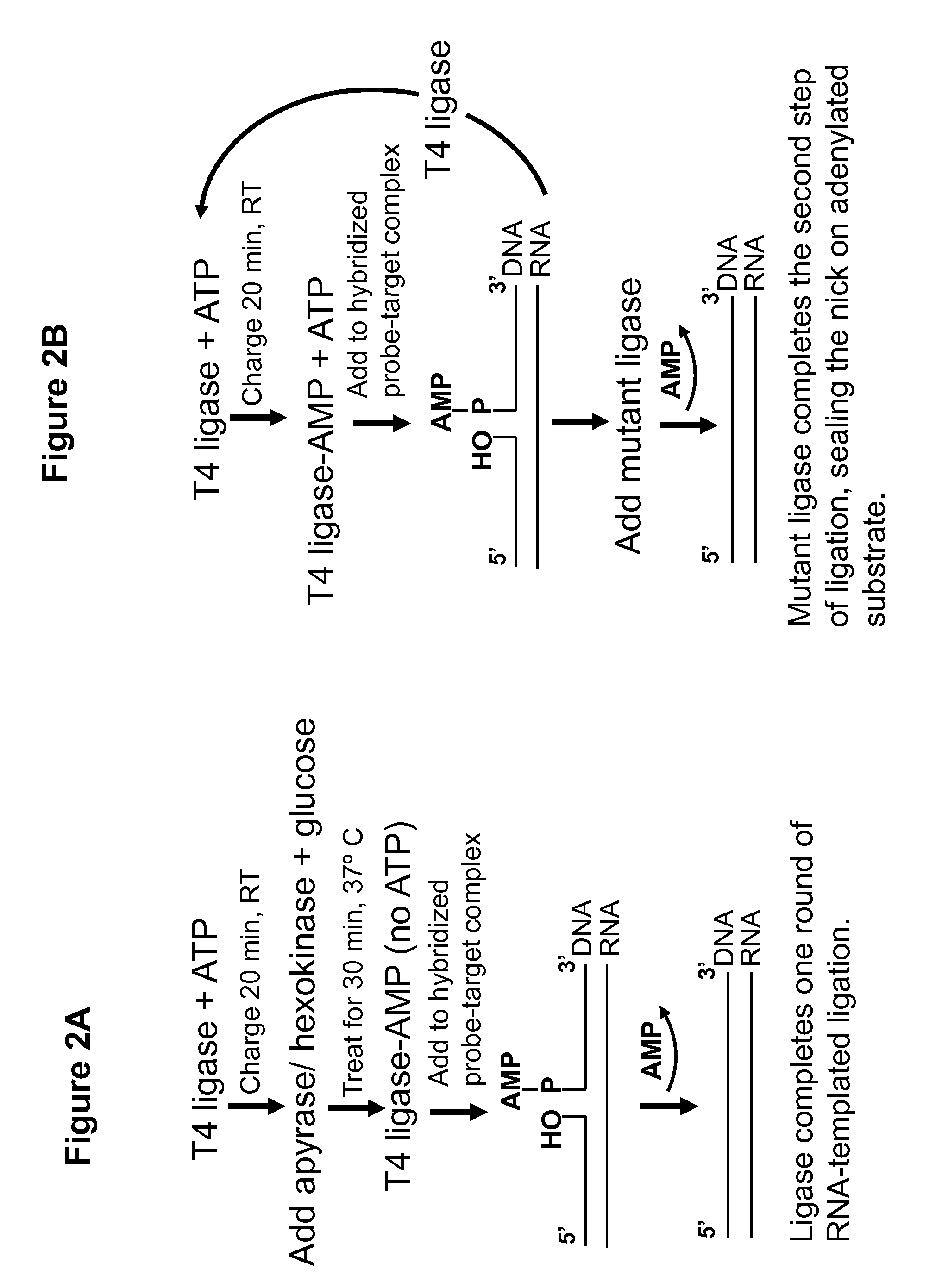
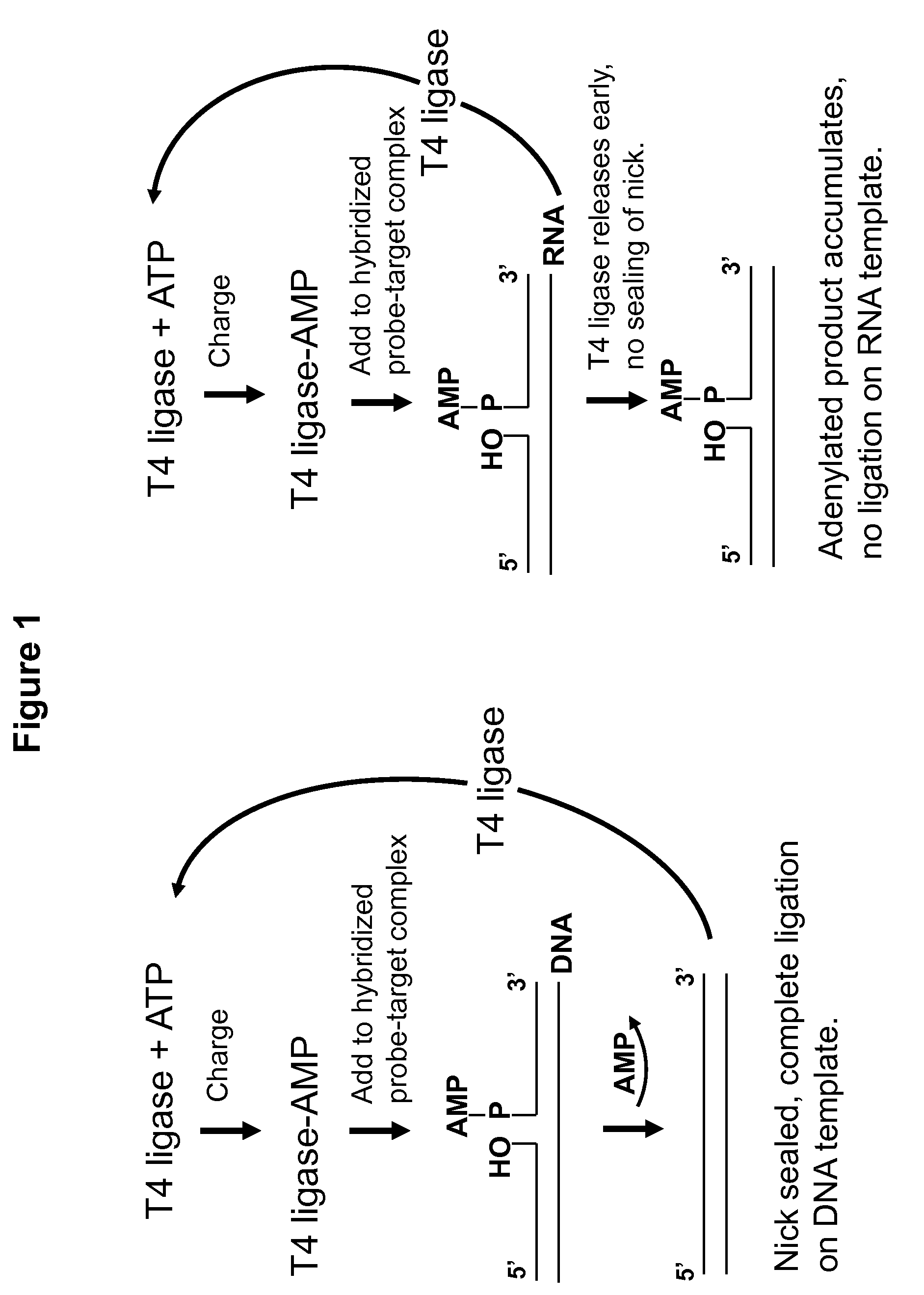
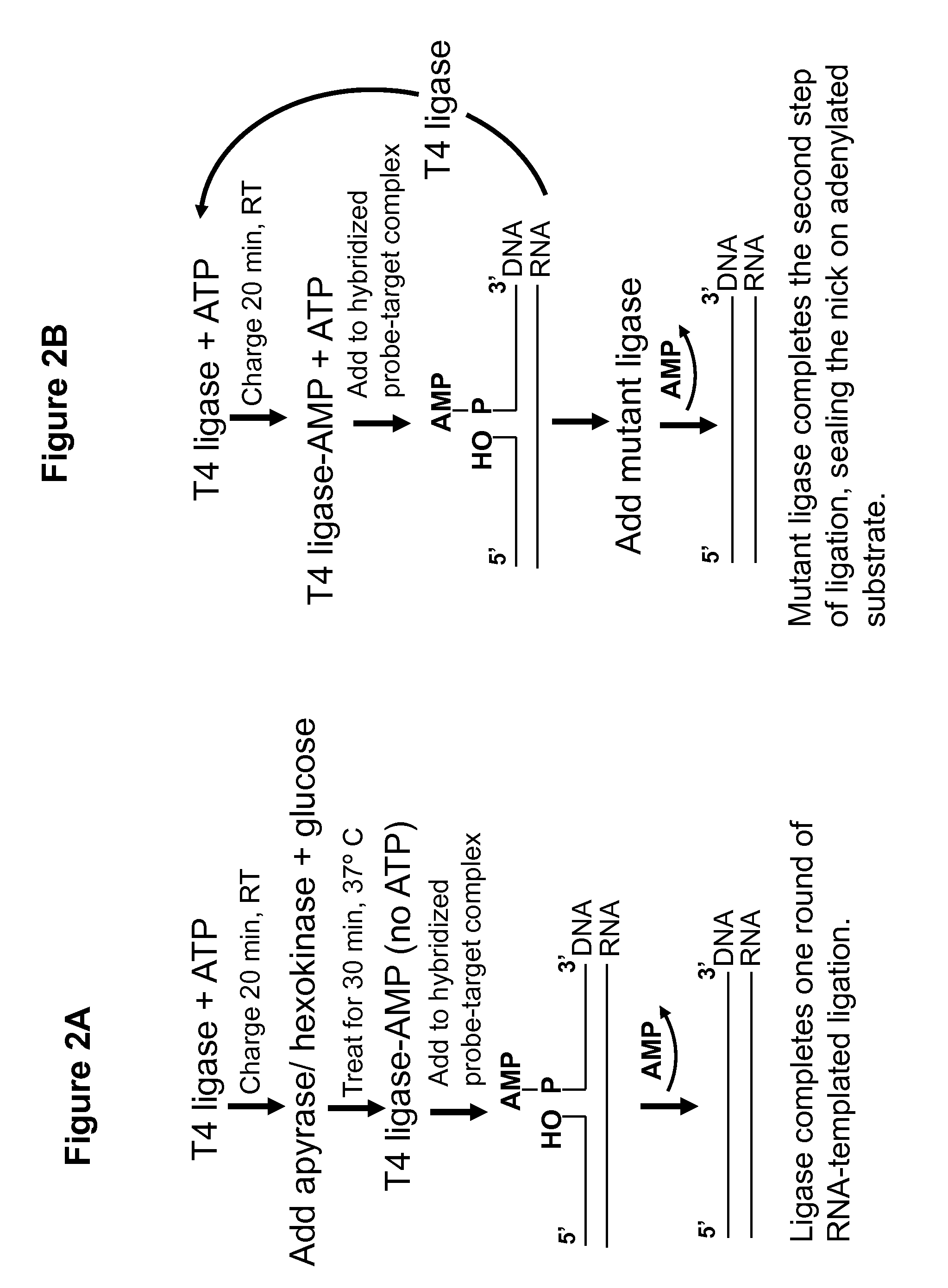
DNA ligation on RNA template
ActiveUS8790873B2High energySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative expressionRNA Sequence
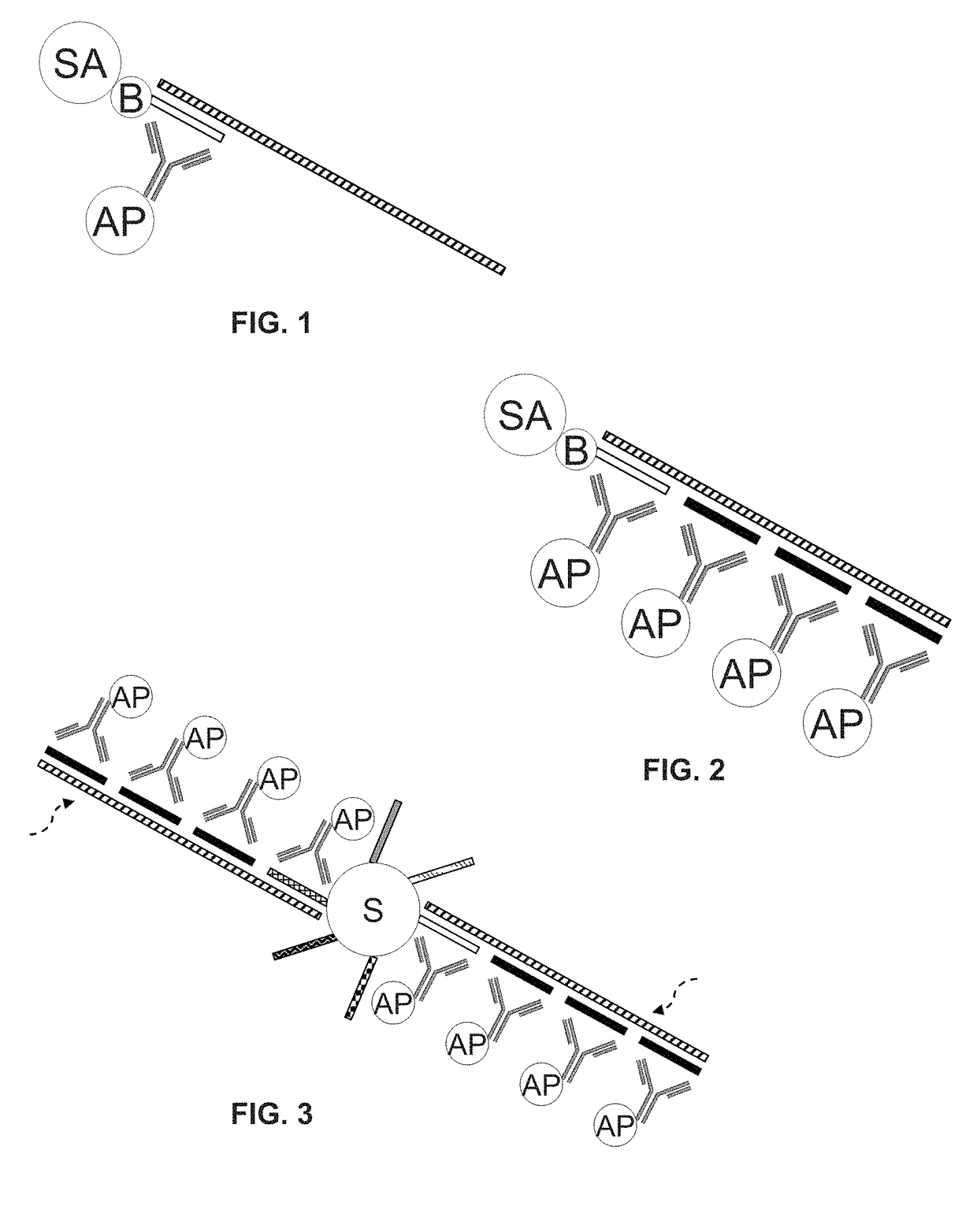
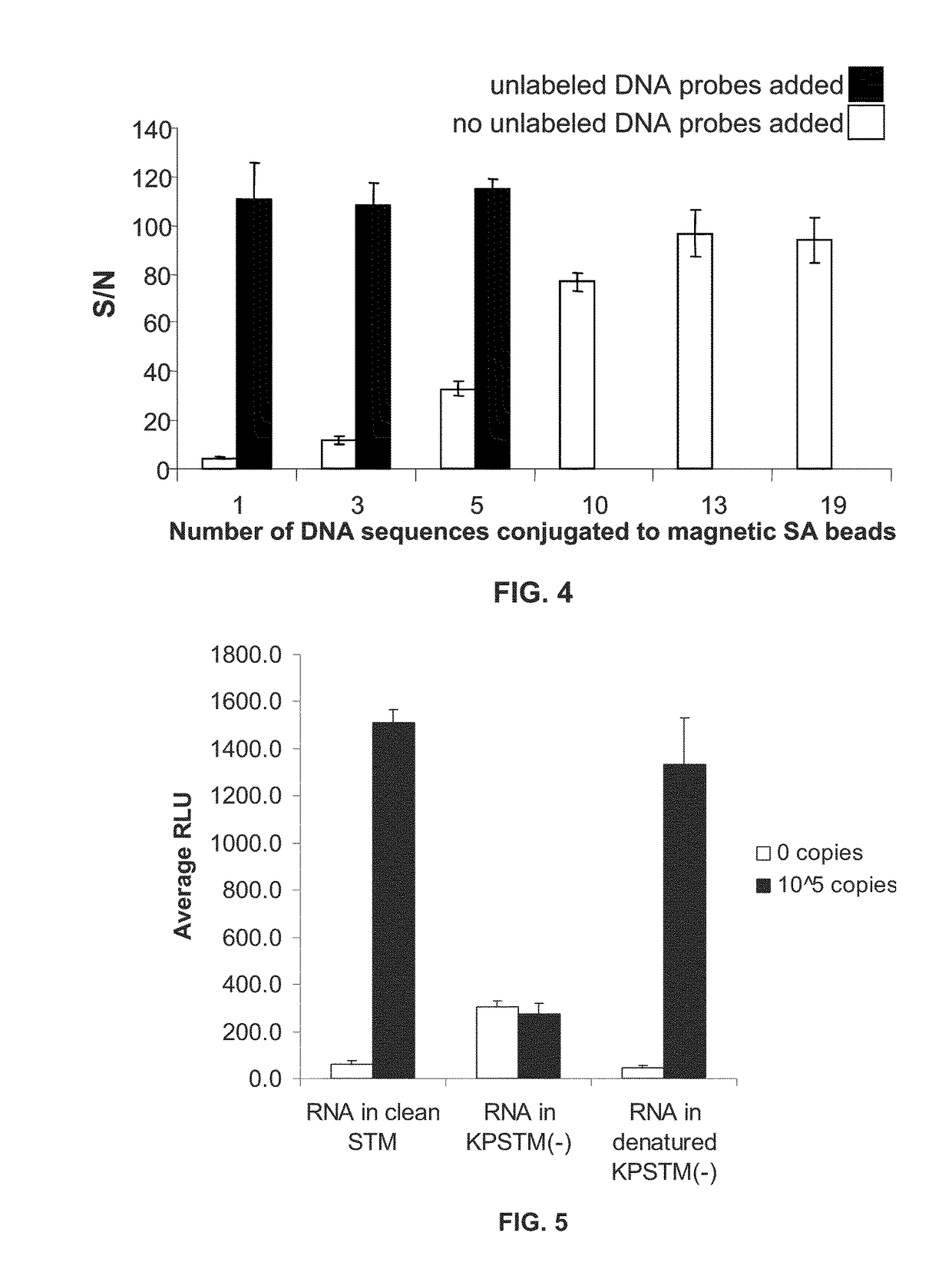
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detection and amplification of nucleic acids, wherein two DNA strands hybridized to an RNA strand are ligated. In one aspect, the disclosed methods include removal of an energy source, such as ATP, upon charging a ligase to form an enzyme-AMP intermediate, and then adding substrate, which results in one complete round of RNA-templated DNA ligation. In another aspect, the ligation reaction is accomplished by use of a mixture of at least two different ligase enzymes. The disclosed methods and compositions for RNA-templated DNA ligation may be particularly useful for detection of RNA sequence variants, for example RNA splice variants, and for quantitative expression analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
DNA ligation on RNA template
ActiveUS20100184618A1High energyLigation is preventedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningQuantitative expressionRNA Sequence
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detection and amplification of nucleic acids, wherein two DNA strands hybridized to an RNA strand are ligated. In one aspect, the disclosed methods include removal of an energy source, such as ATP, upon charging a ligase to form an enzyme-AMP intermediate, and then adding substrate, which results in one complete round of RNA-templated DNA ligation. In another aspect, the ligation reaction is accomplished by use of a mixture of at least two different ligase enzymes. The disclosed methods and compositions for RNA-templated DNA ligation may be particularly useful for detection of RNA sequence variants, for example RNA splice variants, and for quantitative expression analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Improved carriers for delivery of nucleic acid agents to cells and tissues
InactiveUS20090011004A1Reduce deliveryRescue protein expression defectNervous disorderTetracycline active ingredientsDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
This invention relates to drug delivery and specifically to the preparation and use of functionalized carriers such as nanopolymers and nanovesicles for improved delivery of nucleic acid agents (NAA) to tissues and cells. These compounds have broad applicability for treating numerous diseases and disorders, including neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders. The concept encompasses preferably polymeric carriers for delivery of a class of oligonucleotides that modulate RNA splicing.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA HEALTH & EDUCATION CORP +1
Compositions and methods for modulation of smn2 splicing
ActiveUS20100216238A1Increase in exon inclusionSplicing alterationSugar derivativesMedicineDisease cause
Disclosed herein are compounds, compositions and methods for modulating splicing of SMN2 mRNA in a cell, tissue or animal. Also provided are uses of disclosed compounds and compositions in the manufacture of a medicament for treatment of diseases and disorders, including spinal muscular atrophy.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Compositions and methods for modulation of smn2 splicing
Disclosed herein are compounds, compositions and methods for modulating splicing of SMN2 mRNA in a cell, tissue or animal. Also provided are uses of disclosed compounds and compositions in the manufacture of a medicament for treatment of diseases and disorders, including spinal muscular atrophy.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
Compounds for the modulation of smn2 splicing
The present invention relates to oligomer compounds (oligomers) which target nucleic acids encoding human SMN2 in a cell, leading to modulation of SMN2 mRNA splicing which favors full length SMN2 mRNA rather than the poorly functional truncated transcript, SMN2 Δ7. Reduction of SMNA7 mRNA expression and / or increase in full length SMN2 mRNA expression are beneficial for the treatment of diseases or disorders associated with overexpression or undesirably high levels of aberrant forms of SMN2, particularly SMN2 Δ7, such as spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Targeting enzymes of the trna splicing pathway for identification of anti-fungal and/or anti-proliferative molecules
InactiveUS20070178456A1Enhance and improve effectEmission reductionBiocideAntimycoticsCancer preventionHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
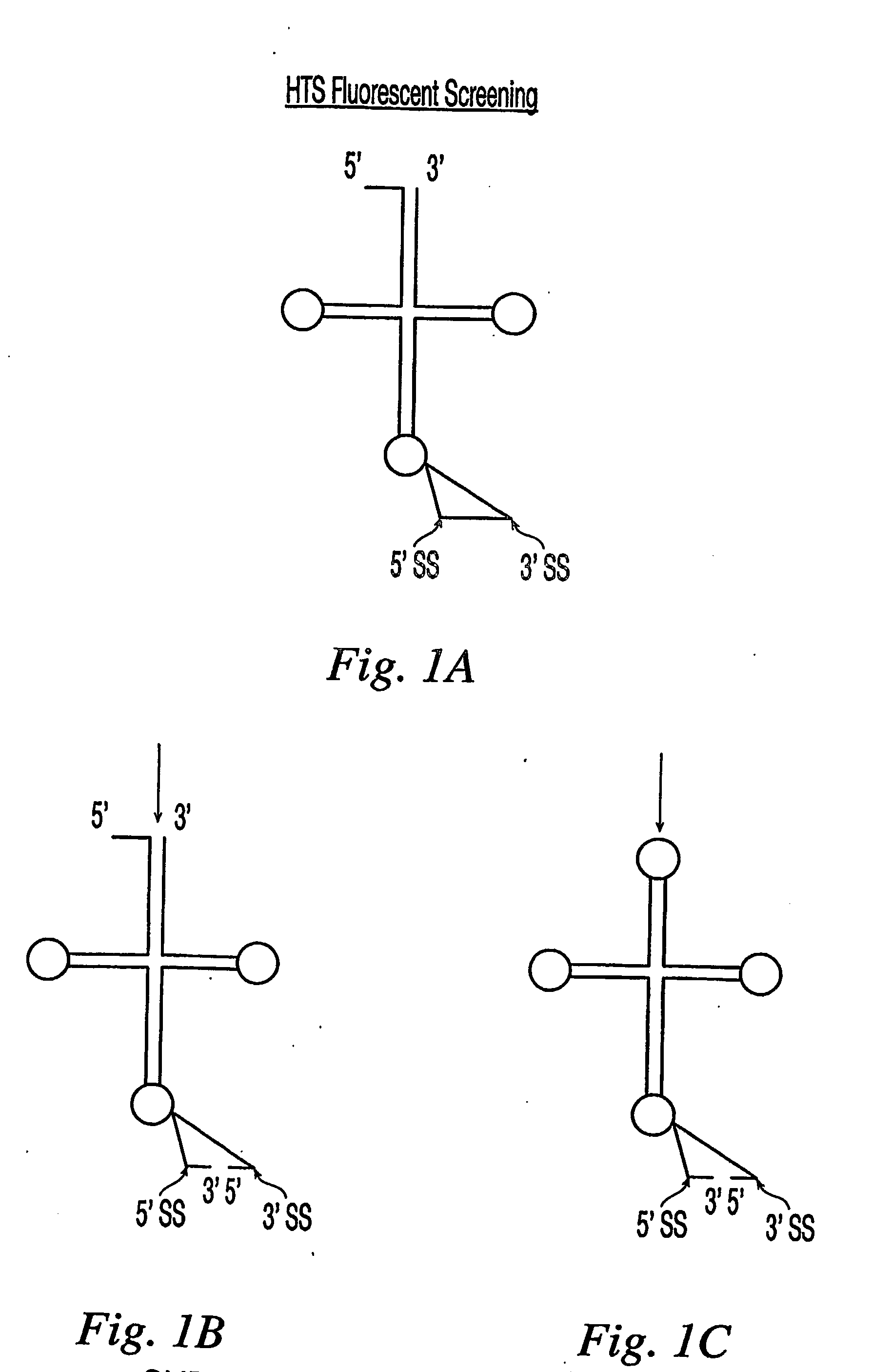
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying compounds that modulate the activity of one or more components in the tRNA splicing pathway. In particular the invention relates to a method for screening and identifying compounds that modulate the activity tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or tRNA splicing ligase. The invention provides assays for the identification of compounds that inhibit animalia tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or animalia tRNA splicing ligase. The invention also provides assays for the identification of compounds that inhibit fungal tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or fungal tRNA splicing ligase. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads useful for treating and / or preventing cancer and / or fungal infections.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
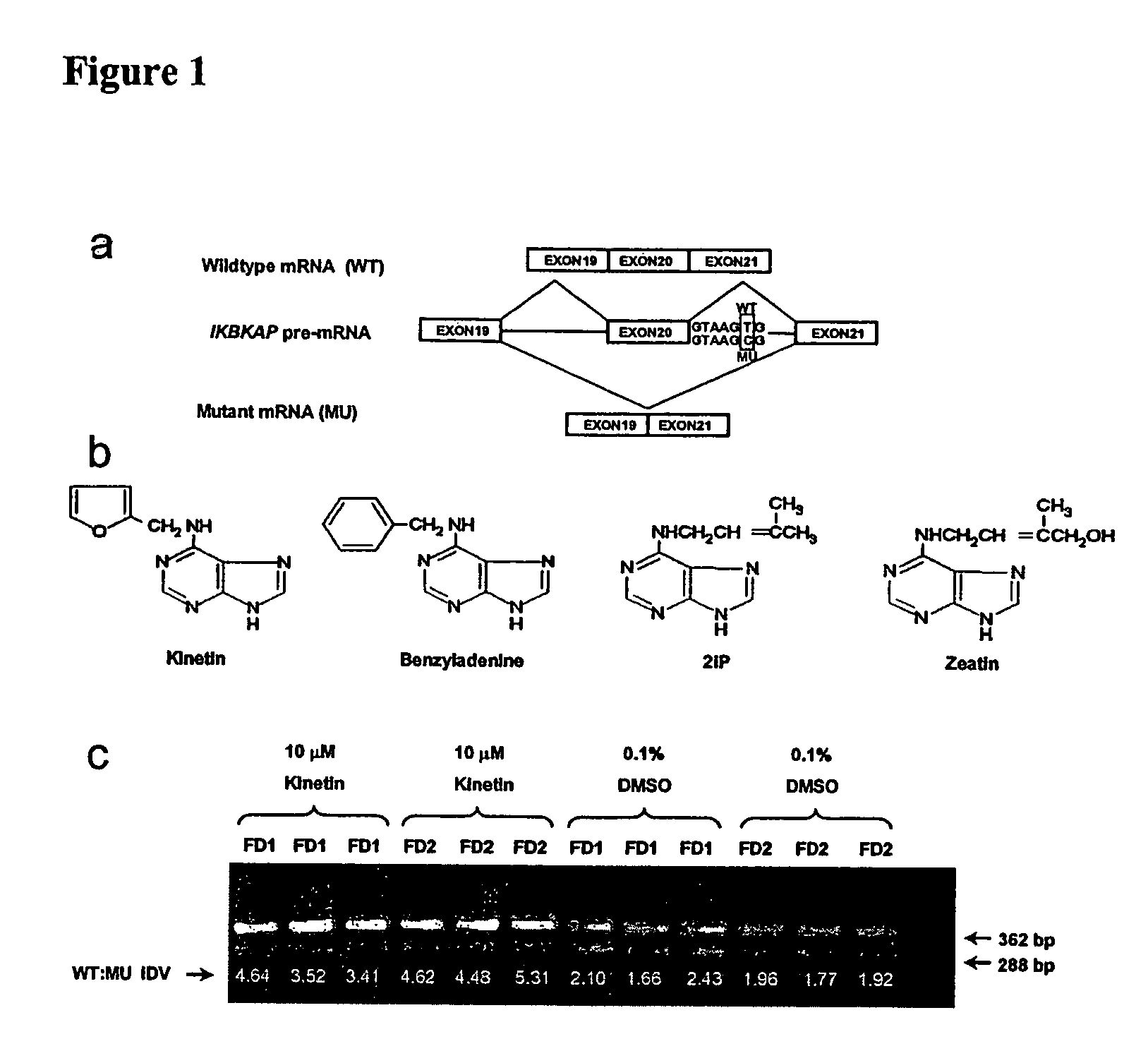
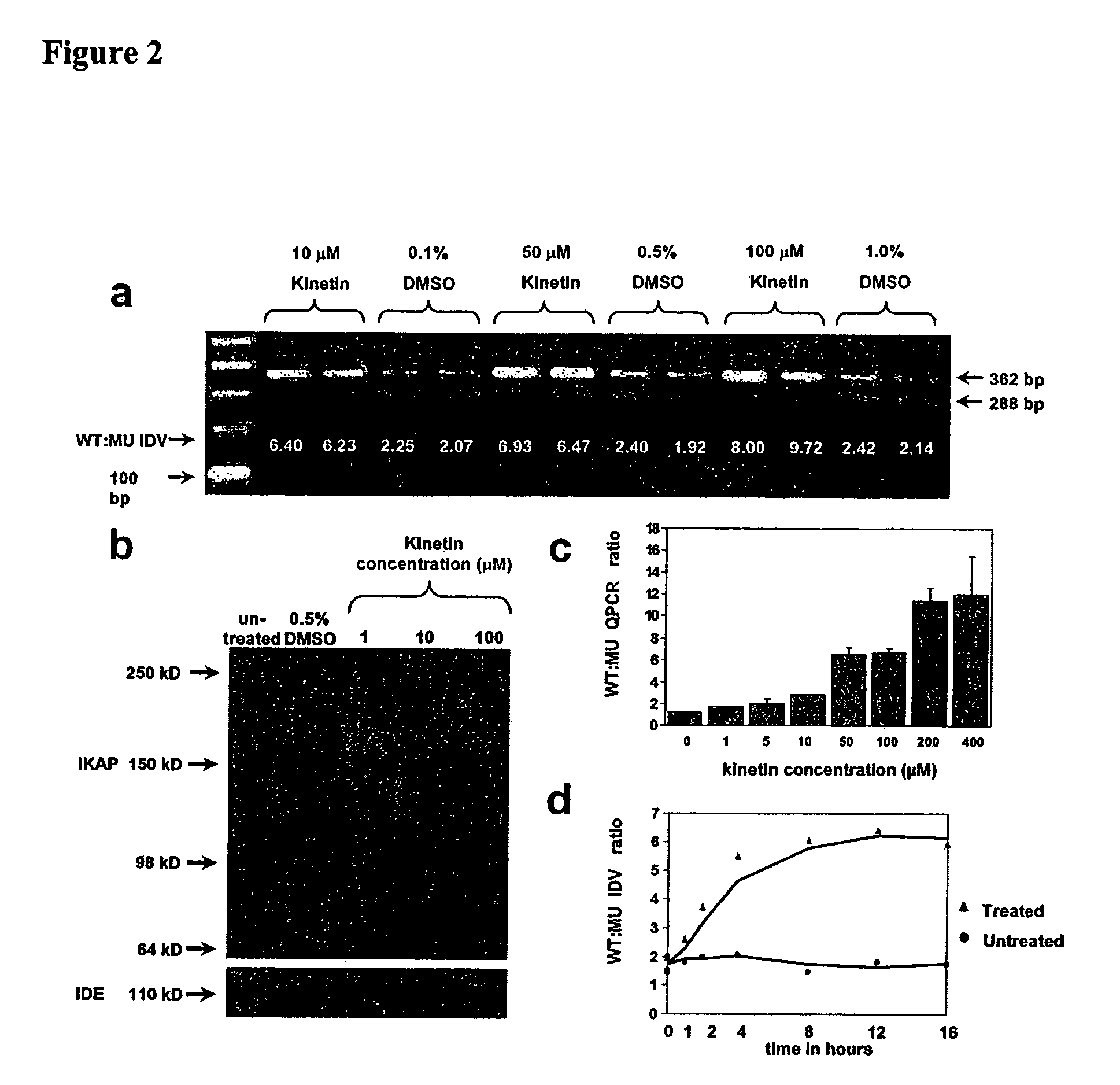
Methods for altering mRNA splicing and treating familial dysautonomia and other mechanistically related disorders
InactiveUS7737110B2Raise the ratioReduce misconnectionBiocideNervous disorderAutonomic bladder dysfunctionDisease
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Adeno-associated virus producer system
InactiveUS20050226847A1Improved propertyReduce inhibitionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdeno associate virusWild type
The present invention provides the use of a replication competent herpes virus which (a) lacks a functional wild-type HSV ICP27 gene; and (b) comprises an ICP27 gene encoding an ICP27 protein which allows replication of said herpes virus to occur and which has a reduced ability to inhibit RNA splicing compared to wild-type HSV ICP27 in the production of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
Lentiviral vector suitable for gene therapy of thalassemia and sickle anemia
ActiveCN110564770ALower titerInhibition of activationVectorsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsThalassemiaSickle cell anemia
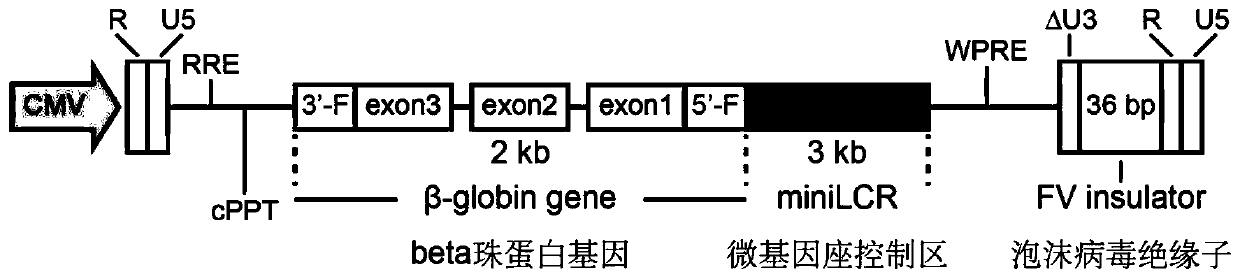
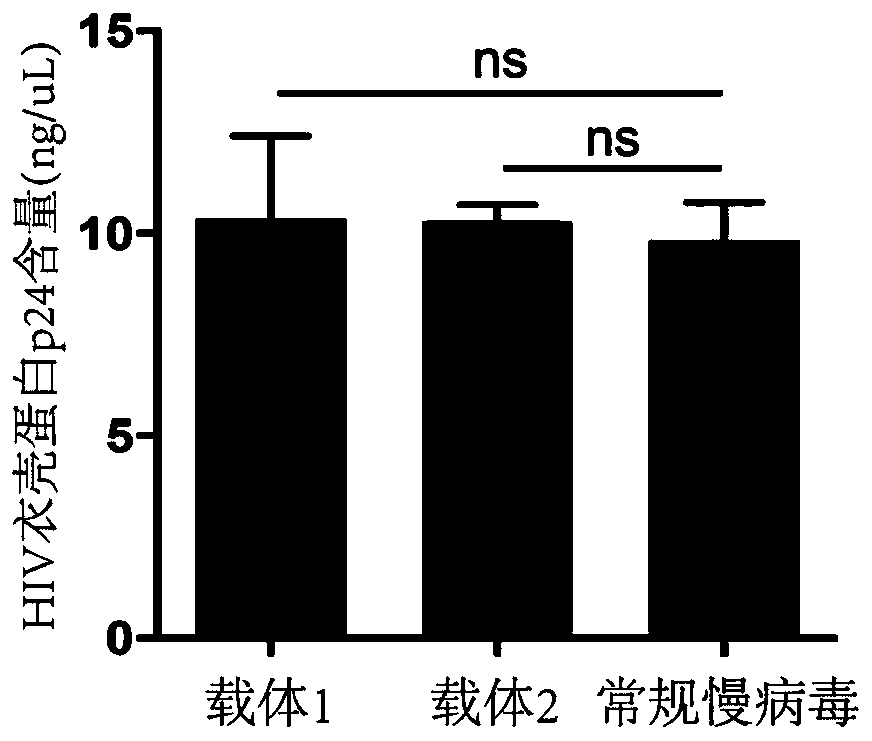
The invention discloses a lentiviral vector suitable for gene therapy of thalassemia and sickle anemia. The lentiviral vector comprises a beta globin expression cassette; the expression cassette comprises a micro-locus control area, a gene sequence of a beta globin, a promoter sequence of a flank of the upstream of the gene sequence of the beta globin, and a flanking sequence of the downstream ofthe gene sequence of the beta globin; the micro-locus control area is a micro-control element which is screened out from the locus control area of beta globin 16kb and does not contain an HS1 area. Compared with the prior art, the screened beta globin expression cassette has both efficiency and specificity, and does not cause reduction of lentivirus titer; a screened insulator sequence which comesfrom foamy virus and is only 36 bp does not contain a hidden RNA splicing signal, and has the functions of maintaining gene expression and preventing gene activation in a region where the insulator sequence is located; the lentiviral vector can be used for gene therapy of thalassemia and sickle anemia.
Owner:SHANGHAI BDGENE TECH CO LTD
Non-target amplification method for detection of RNA splice-forms in a sample
Provided are methods of isolating RNA from a biological sample, methods and means for determining the presence of particular RNA splice-form variants in a biological sample, methods and means for determining the relative ratio of RNA ratios in a biological sample, and methods and means for predicting the progression of precancerous cervical lesions.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
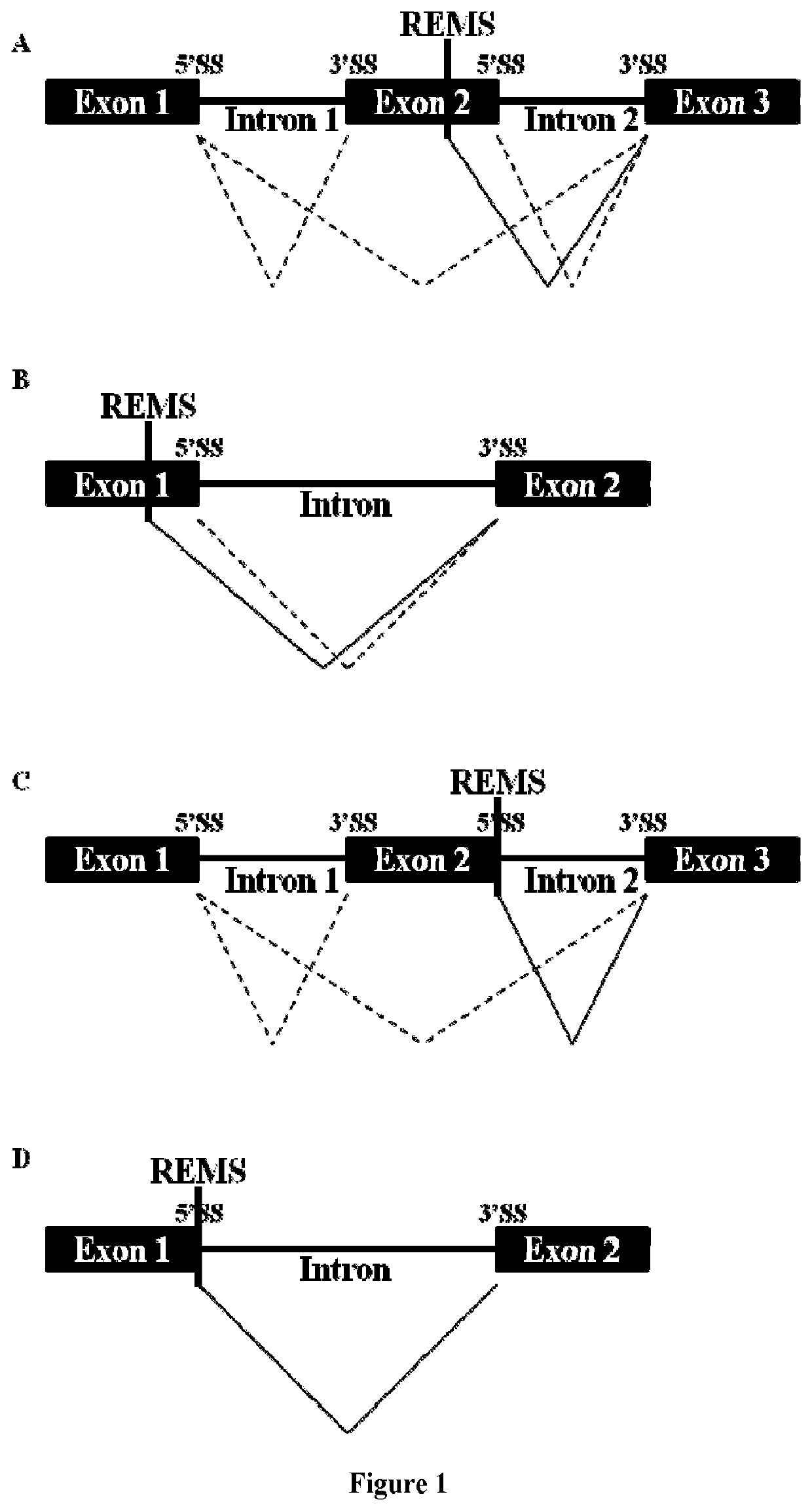
Methods for modulating RNA splicing
ActiveUS20180161456A1High affinityOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationRegulator geneBiology
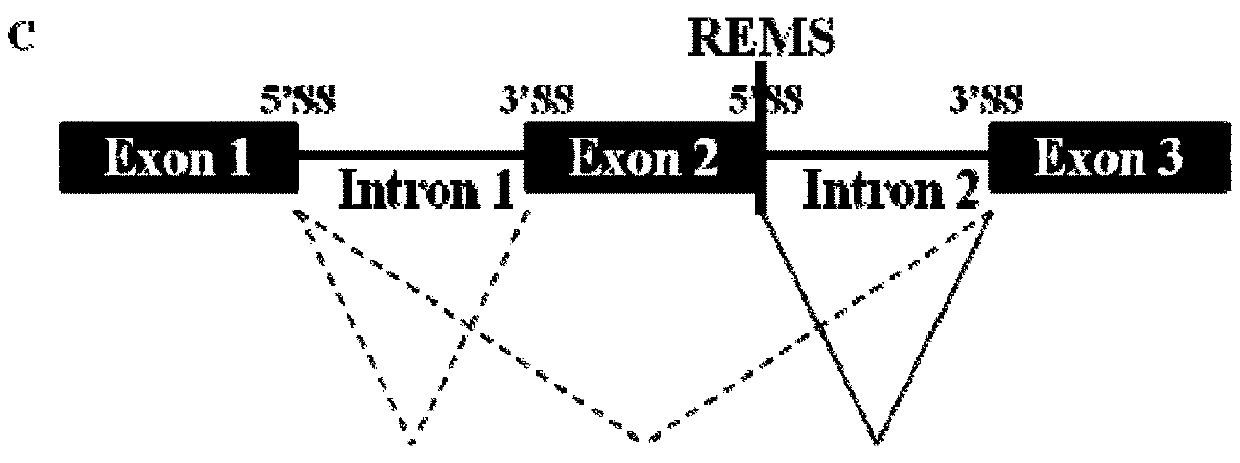
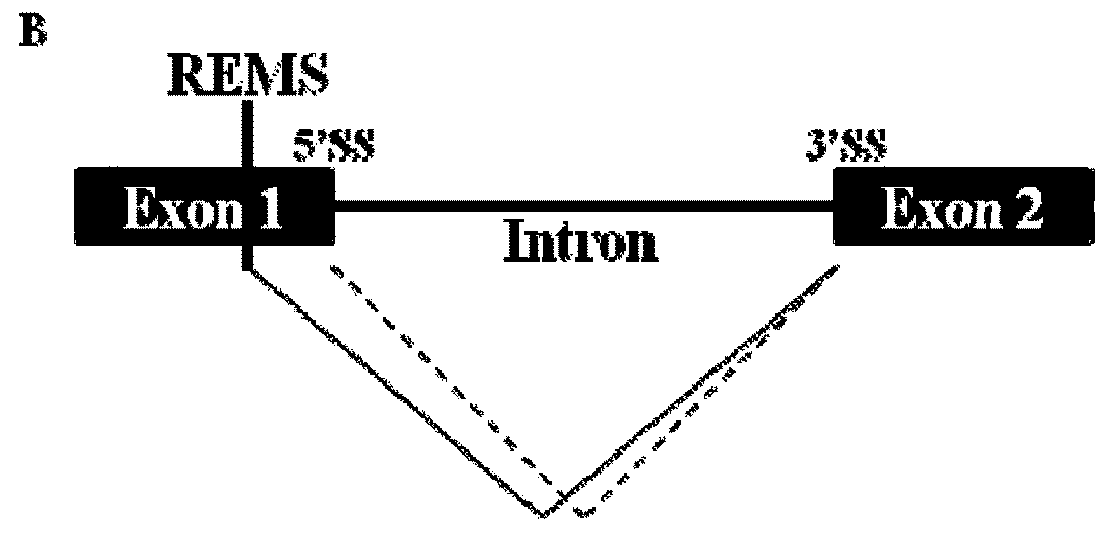
In one aspect, described herein is a recognition element for splicing modifier (REMS) that can be recognized by a compound provided herein. In another aspect, described herein are methods for modulating the amount of a product of a gene, wherein a precursor RNA transcript transcribed from the gene contains a REMS, and the methods utilizing a compound described herein. More particularly, described herein are methods for modulating the amount of an RNA transcript or protein product encoded by a gene, wherein a precursor RNA transcript transcribed from the gene comprises a REMS, and the methods utilizing a compound described herein. In another aspect, provided herein are artificial gene constructs comprising a REMS, and uses of those artificial gene constructs to modulate functional protein production. In another aspect, provided herein are methods for altering endogenous genes to comprise a REMS, and the use of a compound described herein to modulate the functional protein produced from such altered endogenous genes.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
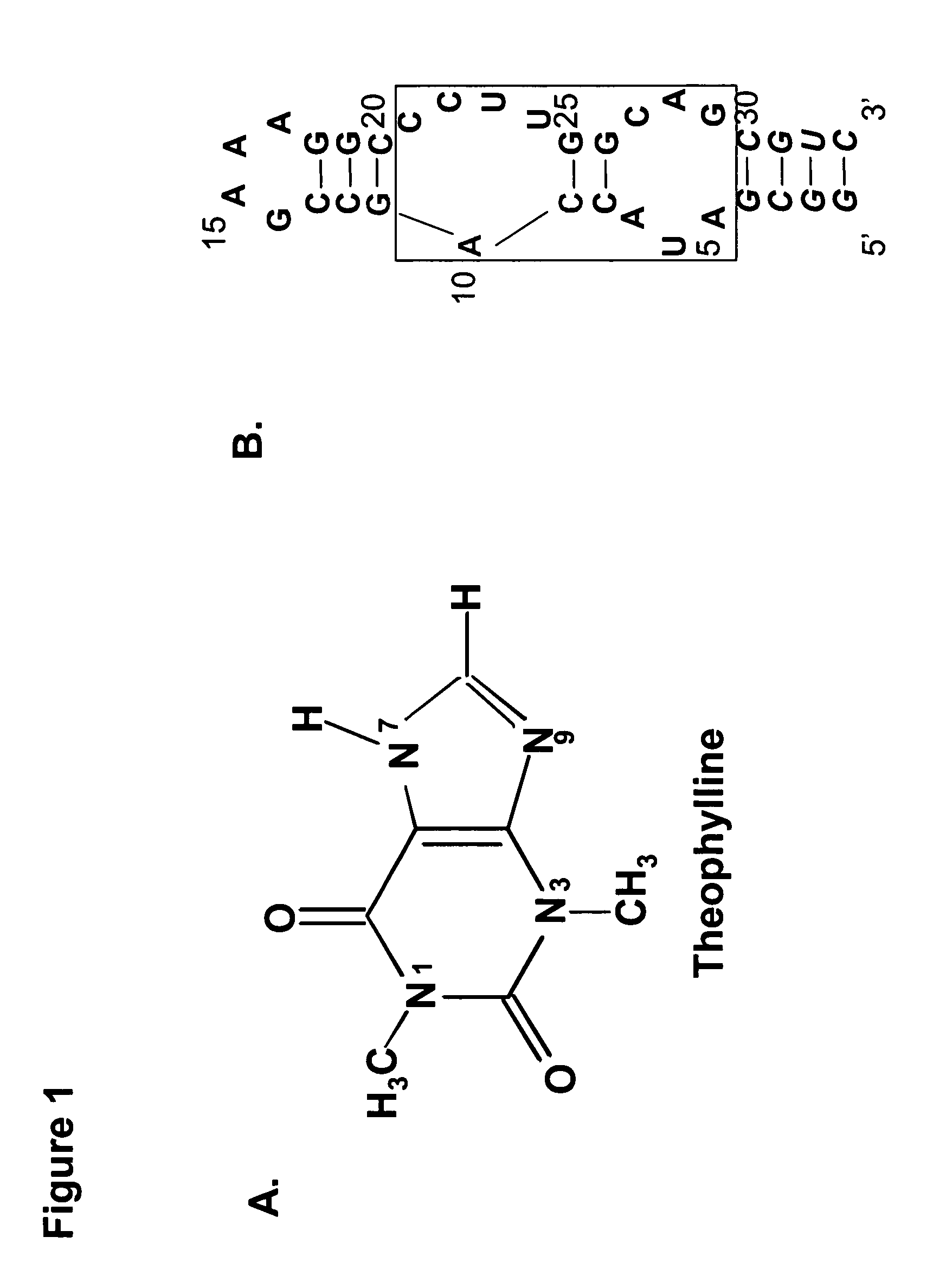
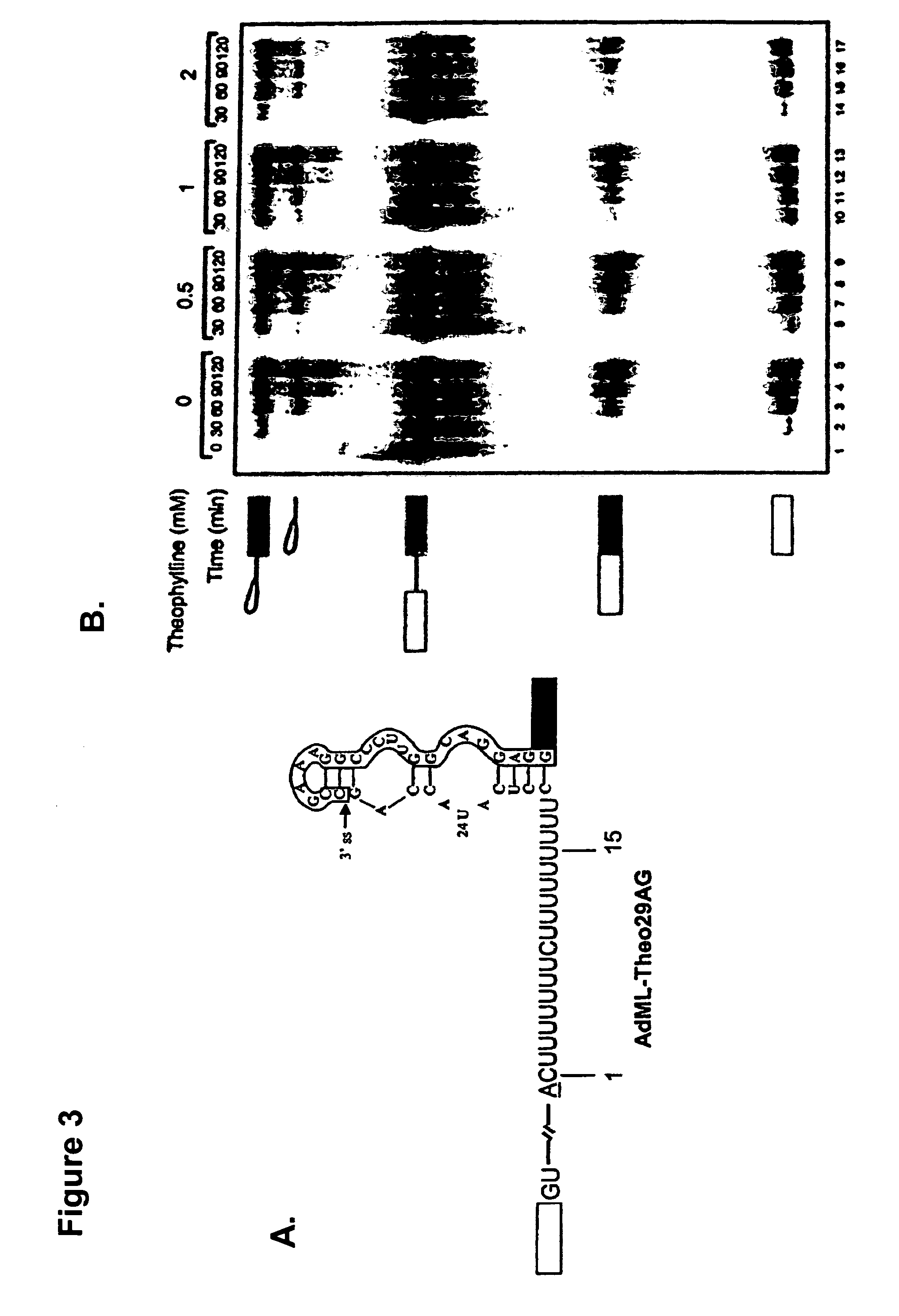
Artificial riboswitch for controlling pre-mRNA splicing
ActiveUS7563601B1Efficient modulationConvenient distanceSplicing alterationSugar derivativesSplice Site SNPPrecursor mRNA
The present invention relates to riboswitches that have been engineered to regulate pre-mRNA splicing. In particular, the insertion of a high affinity theophylline binding aptamer into the 3′ splice site region, 5′ splice site region, or branchpoint sequence (BPS) of a pre-mRNA modulates RNA splicing in the presence of theophylline. Accordingly, the aspects of the present invention include, but are not limited to, theophylline-dependent riboswitches which modulate RNA splicing, methods of modulating RNA splicing using theophylline and its corresponding riboswitches, methods of improving / identifying theophylline-dependent riboswitches, methods of treating diseases associated with or caused by abnormal RNA splicing.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Method for regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution
PendingCN109295053APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsCytosine deaminaseIntein
A method of regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution is disclosed, the method comprises expressing targeted cytidine deaminase in cellsto induce AG to AA mutation of 3' splicing site of intron of interested of gene of interested in the cells, or GT to AT mutation of 5' splicing site of the intron of interested of the gene of interested in the cells, or respective mutation of multiple C in a polypyrimidine region of the intron of interested of the gene of interested to T. The method can specifically block the exon recognition process, regulates the alternative splicing process of endogenous mRNA, induces exon skipping, activates alternative splicing sites, induces mutual exclusive exon conversion, induces intron retention andenhances exon retention.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
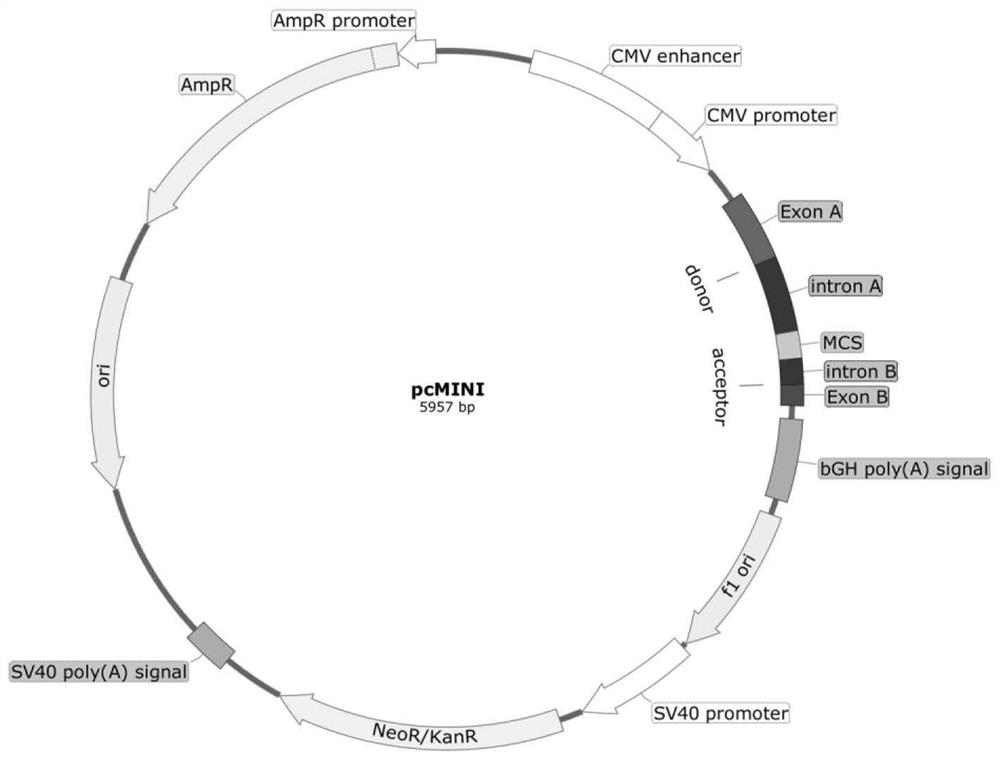
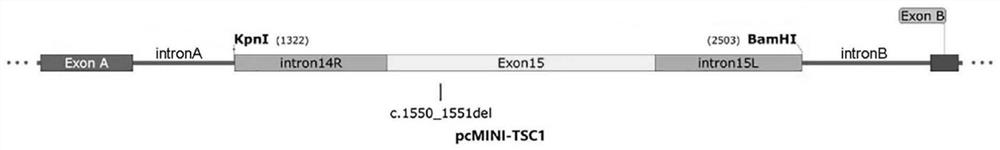
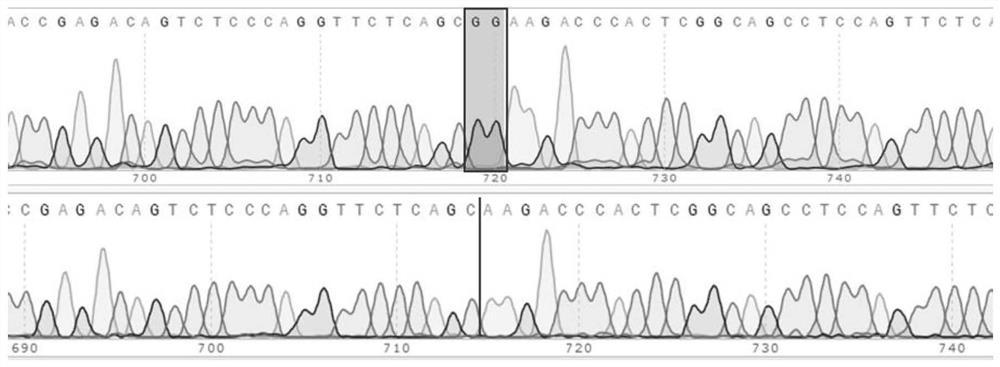
PcMINI vector as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN113736812ASimple and fast operationEfficient constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenes mutationCloning Site
The invention discloses a pcMINI vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pcMINI vector is formed by modifying a vector pcDNA3.1+, the pcMINI vector comprises a CMV enhancer, a PCMV promoter, a multiple cloning site (MCS), an exon-intron gene fragment and a BGH_PA_terminator terminator, and the multiple cloning site (MCS) is used for being inserted into a gene fragment with mutation at an exon-intron combination position. According to a pcMINI vector system, detection on different gene mutations can be achieved only by replacing inserted DNA fragments, the application range is wide, and the operation is easy and convenient; according to the constructed pcMINI vector, dNA fragments needing to be inserted are smaller, and vector construction is more efficient and faster; and meanwhile, an intron element of the pcMINI vector comprises an efficient splicing acceptor and a splicing donor site, so that effective RNA splicing of an inserted DNA fragment can be ensured. The invention provides a complete and feasible prokaryotic mRNA abnormal splicing verification method based on the pcMINI vector.
Owner:武汉翼康基因科技有限公司 +1
Compositions and methods for exon profiling
InactiveUS7807447B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesCell type
The present invention provides methods for analyzing exon expression profiles of a cell or type of cell. In the invention, the expression levels of a plurality of individual exons or multiexons for each of a plurality of genes in the genome of an organism are measured and analyzed to determine the biological state, such as the exon expression state or transcriptional state, of the cell or type of cell. The methods of the invention are useful for determination of alternative RNA splicing in a plurality of genes. The invention also provides nucleic acid probe arrays for determining in parallel the expression levels of a plurality of exons or multiexons for each of a plurality of genes in the genome of an organism. The invention further provides methods for determining the effects of perturbations, such as perturbations by drugs, on exon expression and alternative RNA splicing pathways.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
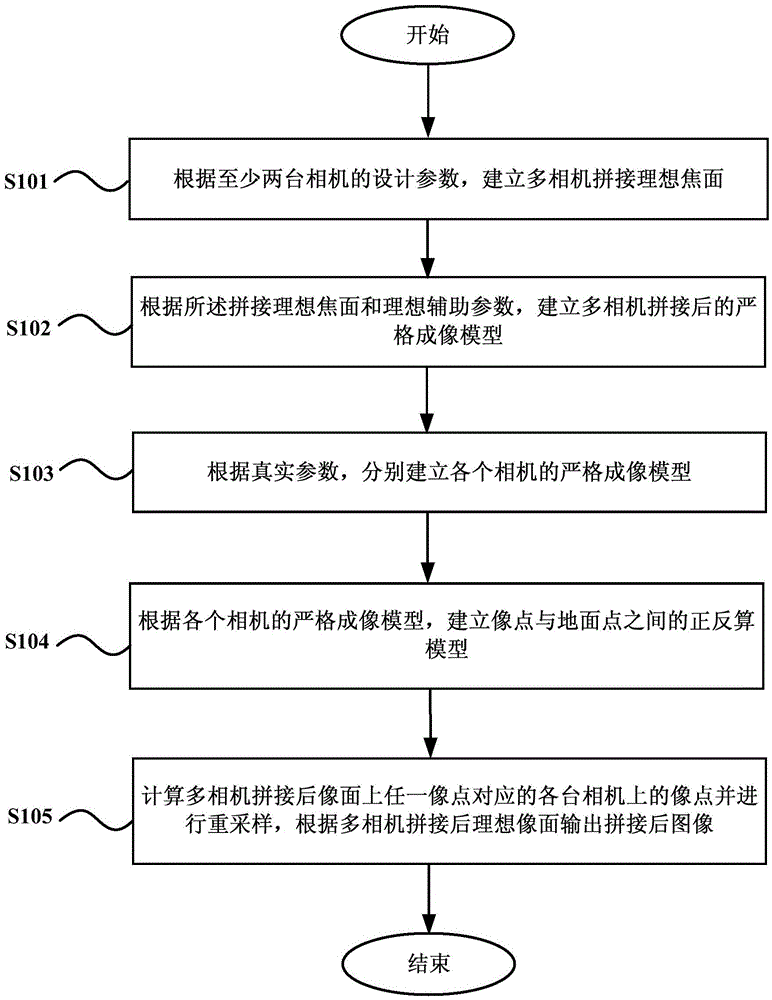
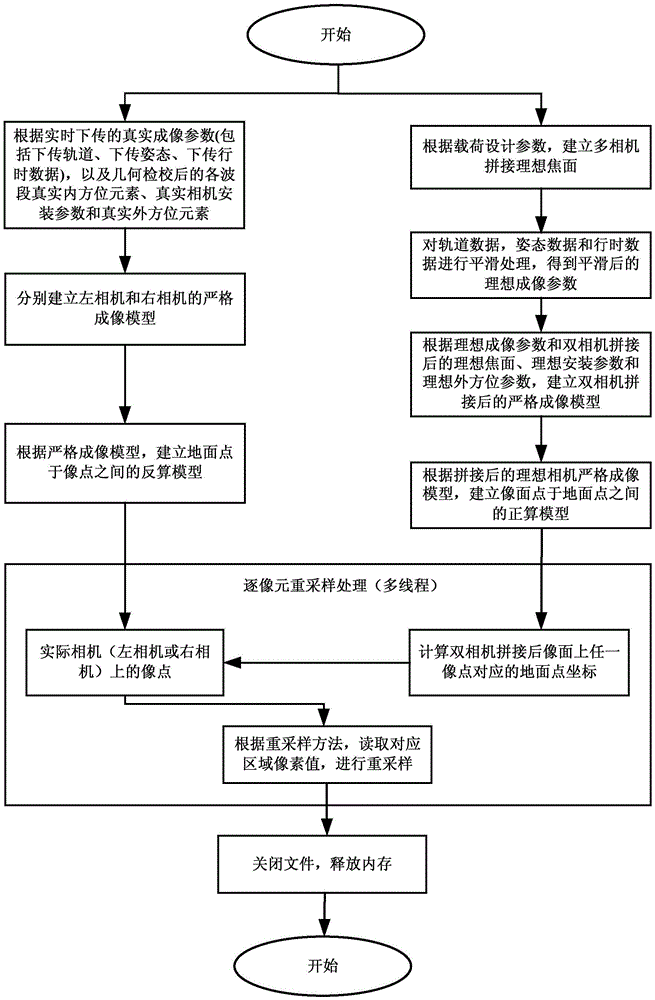
Multi-camera data splicing method based on strict imaging model
ActiveCN105550982ASolve the problem of low splicing accuracy and poor stabilityHigh precisionGeometric image transformationIdeal imageMulti camera
The invention provides a multi-camera data splicing method based on a strict imaging model. The method comprises steps that an ideal multi-camera splicing focal plane is established according to design parameters of at least two cameras; according to the ideal splicing focal plane and ideal auxiliary parameters, a strict imaging model after multi-camera splicing is established; according to actual parameters, a strict imaging model of each camera is established; according to the strict imaging models of the cameras, a positive and negative computation model between image points and ground points is established; after multi-camera splicing, image points of the cameras corresponding to any image point on an image are calculated, re-sampling is further carried out, after multi-camera splicing, an image after splicing is outputted from the ideal image plane. Through the method, multi-camera splicing precision can be improved, problems of low multi-camera splicing precision and poor stability in the prior art are solved, through experiment verification, splicing precision is stable, splicing is not influenced by an image texture status factor, and the splicing precision is high.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
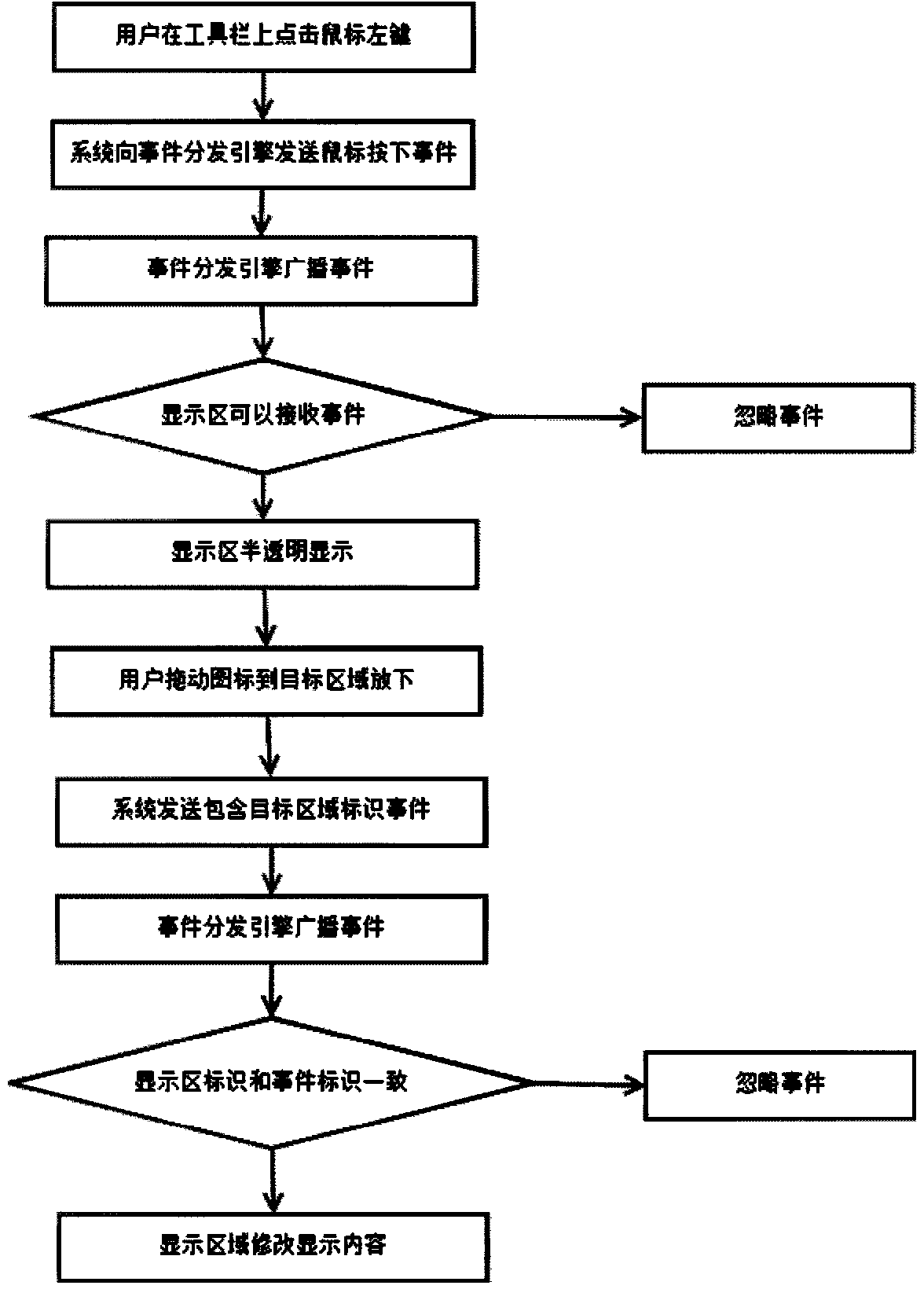
Event-driven large screen display method suitable for multi-screen splicing
InactiveCN104049875ASolve the problem of uncoordinated linkageImprove experienceDigital output to display deviceState of artLarge screen
The invention relates to an event-driven large screen display method suitable for multi-screen splicing. The method includes a method for changing the content of a functional area with a mouse dragging mode and a method for inputting parameters of the functional area with the mouse dragging mode. According to the method for changing the content of the functional area with the mouse dragging mode, a functional picture is dragged into a functional display area with the mode of clicking the functional picture on a tool bar through a mouse, and the content of the functional display area can be immediately changed into the function represented by the functional picture. According to the method for inputting the parameters of the functional area with the mouse dragging mode, a user drags an element in one functional area to another functional area capable of receiving the parameters, the functional area can recognize the parameter meaning represented by the dragged icon, and the analysis operation is carried out. According to the event-driven large screen display method, the large screen display purpose is finished through the mouse operation, a good user experience is provided for the user, and the problem that all large screens cannot be coordinated or be linked when different functions are displayed in the prior art is solved.
Owner:BEIJING TRANSPORTATION INFORMATION CENT
Genetic variant of cytomegalovirus (CMV)
The present invention relates to a genetic variant of CMV, said genetic variant lacking intron 2 of the IE region of CMV (CMV IEΔi2) The present invention also relates to various uses of this genetic variant as well as RNA splice variants transcribed therefrom, and proteins expressed from the RNA splice variants, such as in the diagnosis of a CMV related cancer disease, and identification of individuals at risk of developing cancer or risk of transferring the CMV IEΔi2 virus with a human sample and prevention and treatment through targeting of unique CMV IE proteins for immunotherapy and vaccination.
Owner:NAUCLER CECILIA
Repeated positioning precision detection method of white vehicle body main splicing clamp switching system
InactiveCN106949863AMeet the precision requirementsRealize real-time detectionMeasurement devicesComputer visionRNA splicing
The invention discloses a repeated positioning precision detection method of a white vehicle body main splicing clamp switching system. The method comprises following steps of a, selecting multiple to-be-tested points on a clamp substrate of the main splicing, and fixedly arranging multiple probes corresponding to the to-be-tested points; b, using a displacement sensor to measure a distance value between each to-be-tested point and the corresponding probe; c, repeating the step b and acquiring distance values between multiple groups of to-be-tested points and the corresponding probes; d, calculating the absolute position precision Xij of each to-be-tested point and the ideal position thereof; e, calculating repeated positioning precision R of the main splicing; and f, comparing the calculated repeated positioning precision R with the theoretical precision value, and judging whether the working state of the main splicing is normal or not. According to the invention, real-time detection can be conducted on the repeated positioning precision of the main splicing clamp switching system; obtained results are displayed on a computer in forms of graphs and data; and the system is capable of judging whether to give an alarm about stopping lines by judging whether the repeated positioning precision is in an error permissible range, thereby ensuring that the vehicle body meets a precision requirement.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
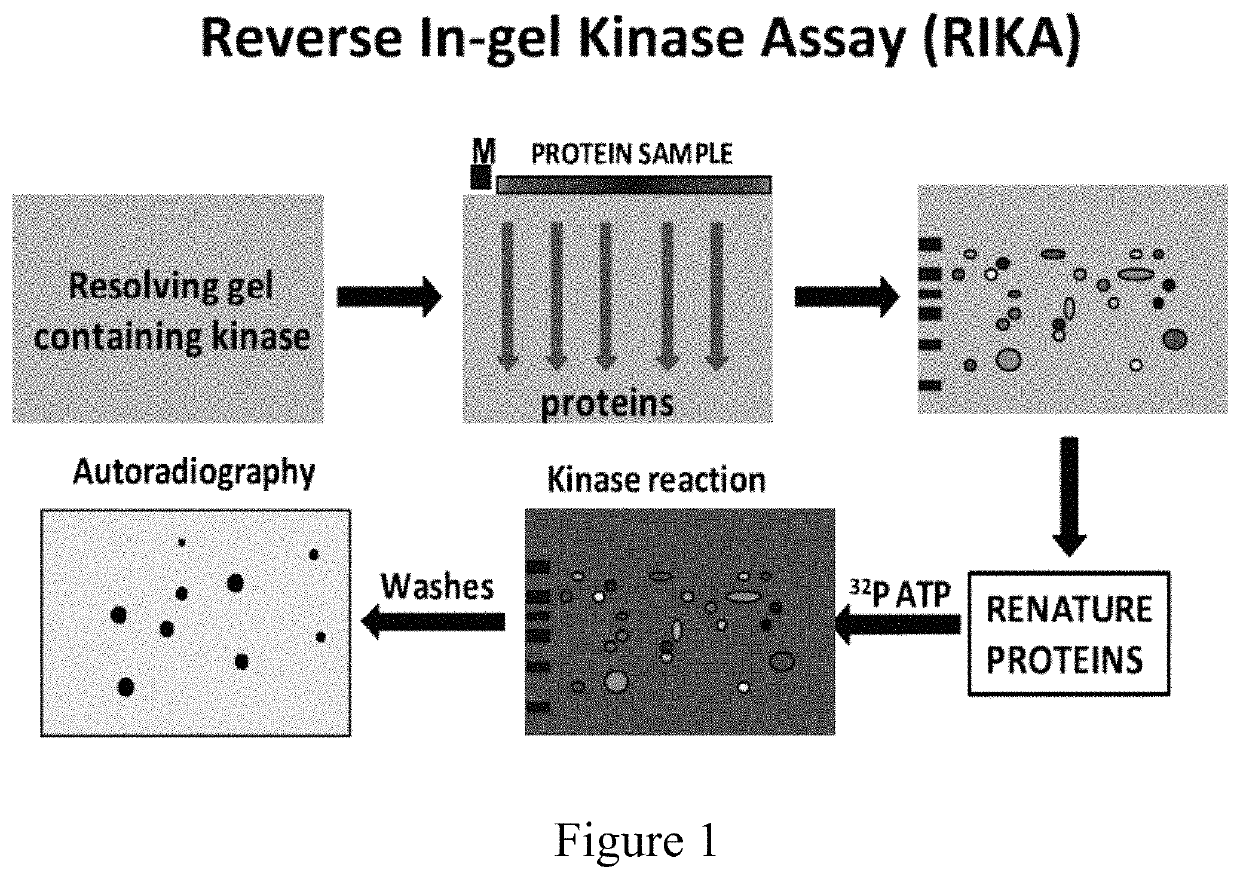
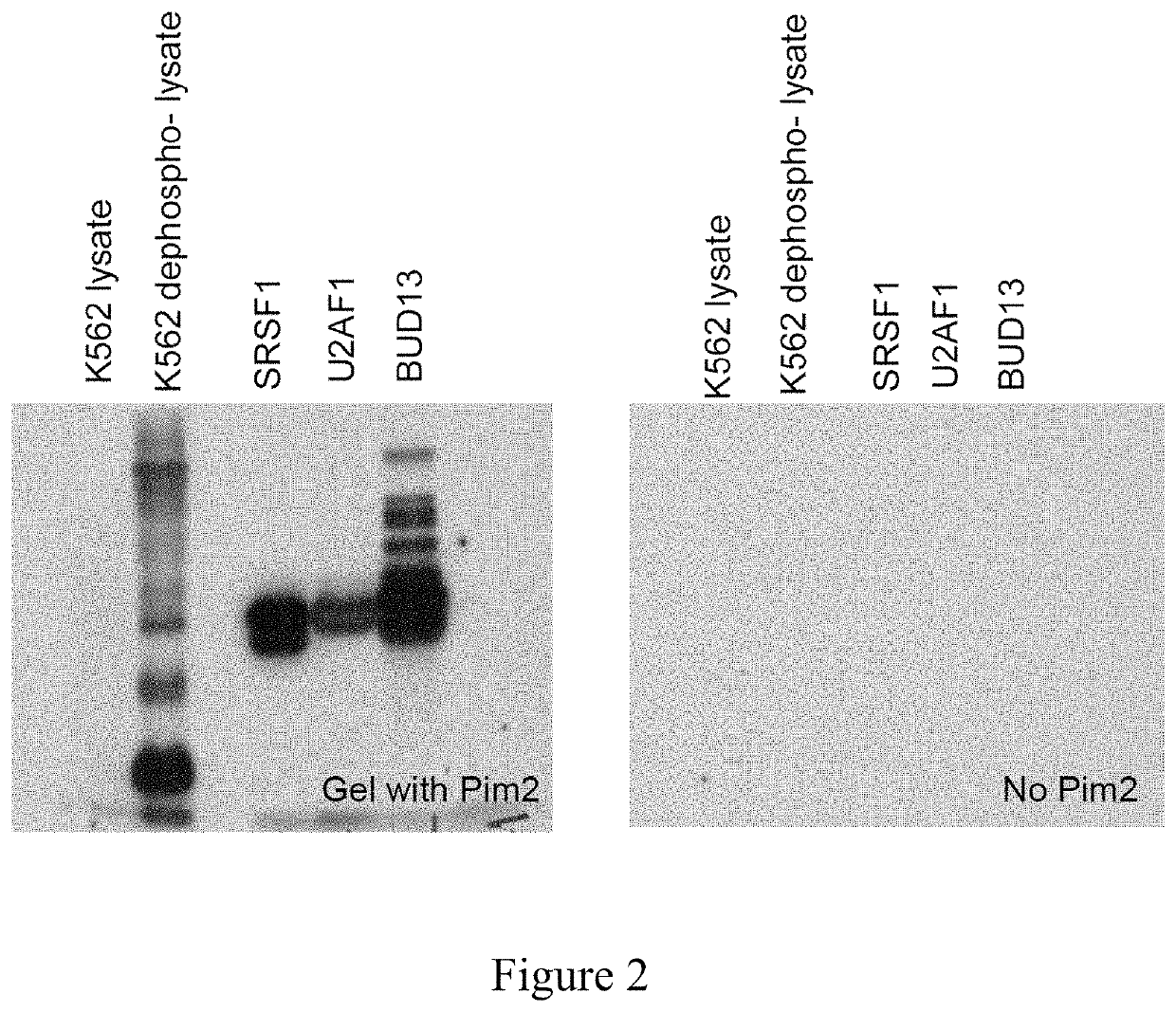
PIM kinase inhibitors in combination with RNA splicing modulators/inhibitors for treatment of cancers
The present invention provides for a method of treating cancer and / or reducing proliferation of cancer cells, the method comprising administering to a subject in need of such treatment a composition comprising a PIM kinase inhibitor that exhibits changes of mRNA splicing in combination with a compound that modulates / inhibits activity of an RNA splicing factor protein. Further, changes in splicing of mRNAs and phosphorylation of RNA splicing factors can be used as biomarkers for patient responsiveness to anti-PIM treatment and also suggest effective combinatorial therapies, including synergistic combination.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
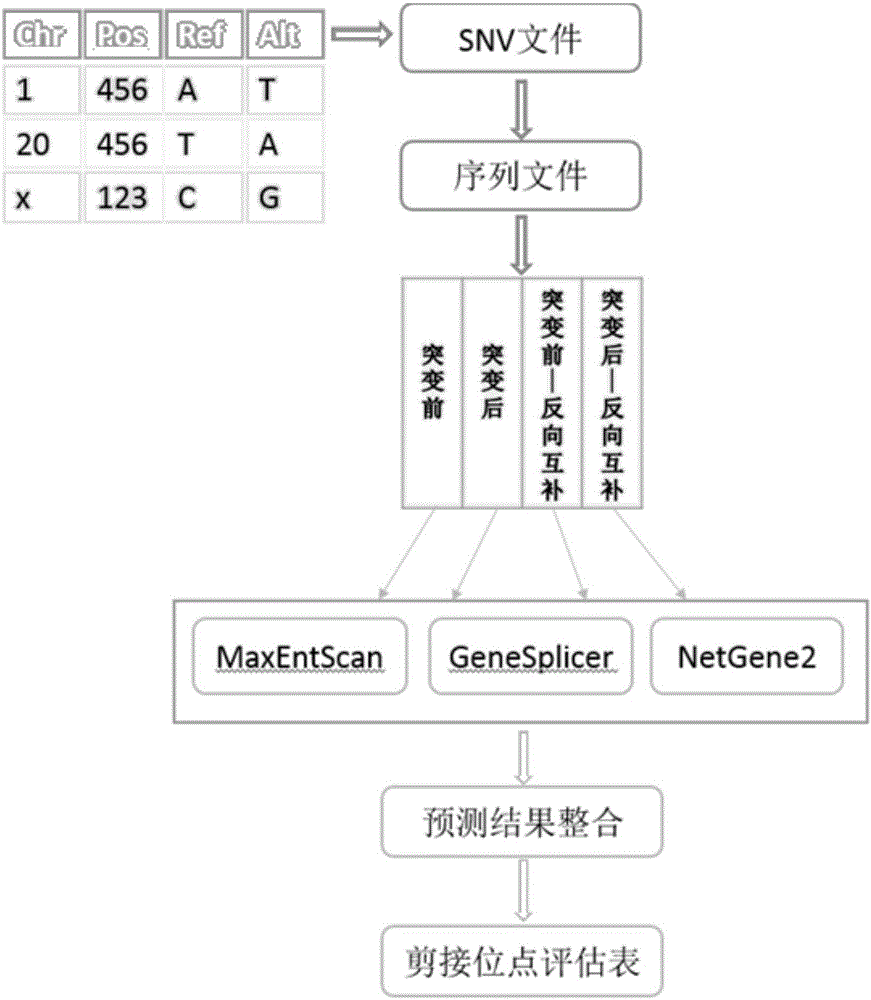
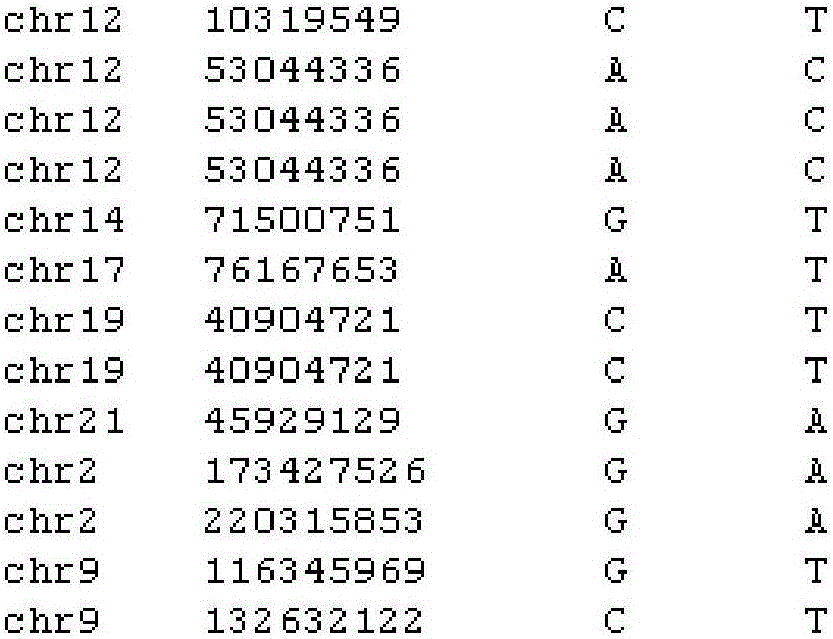
SNV detection system affecting RNA splicing
InactiveCN105956415AImprove accuracySystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsPrediction scoreGenome
The invention provides an SNV detection system affecting RNA splicing. The SNV detection system comprises the following steps of: step 1), according to locus information and genome sequence information of an SNP file, extracting upstream and downstream sequences at 100bp and a reverse complementary sequence of the locus before and after mutation; step 2), using the sequences extracted in step 1) to respectively predict splice loci based on three different methods, that is, a maximum entropy principle, a Markov model and an artificial neural network; and step 3), integrating according to a prediction score result of the three methods, and screening out the SNV having an effect on the RNA splicing. According to the SNV detection system affecting the RNA splicing provided by the invention, changes of the RNA splicing before and after mutation are predicted by integrating these three methods and taking SNV data as input, and the SNV affecting the RNA splicing is acquired, thereby effectively improving the prediction accuracy and providing reference for biological experiments and clinical researches.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
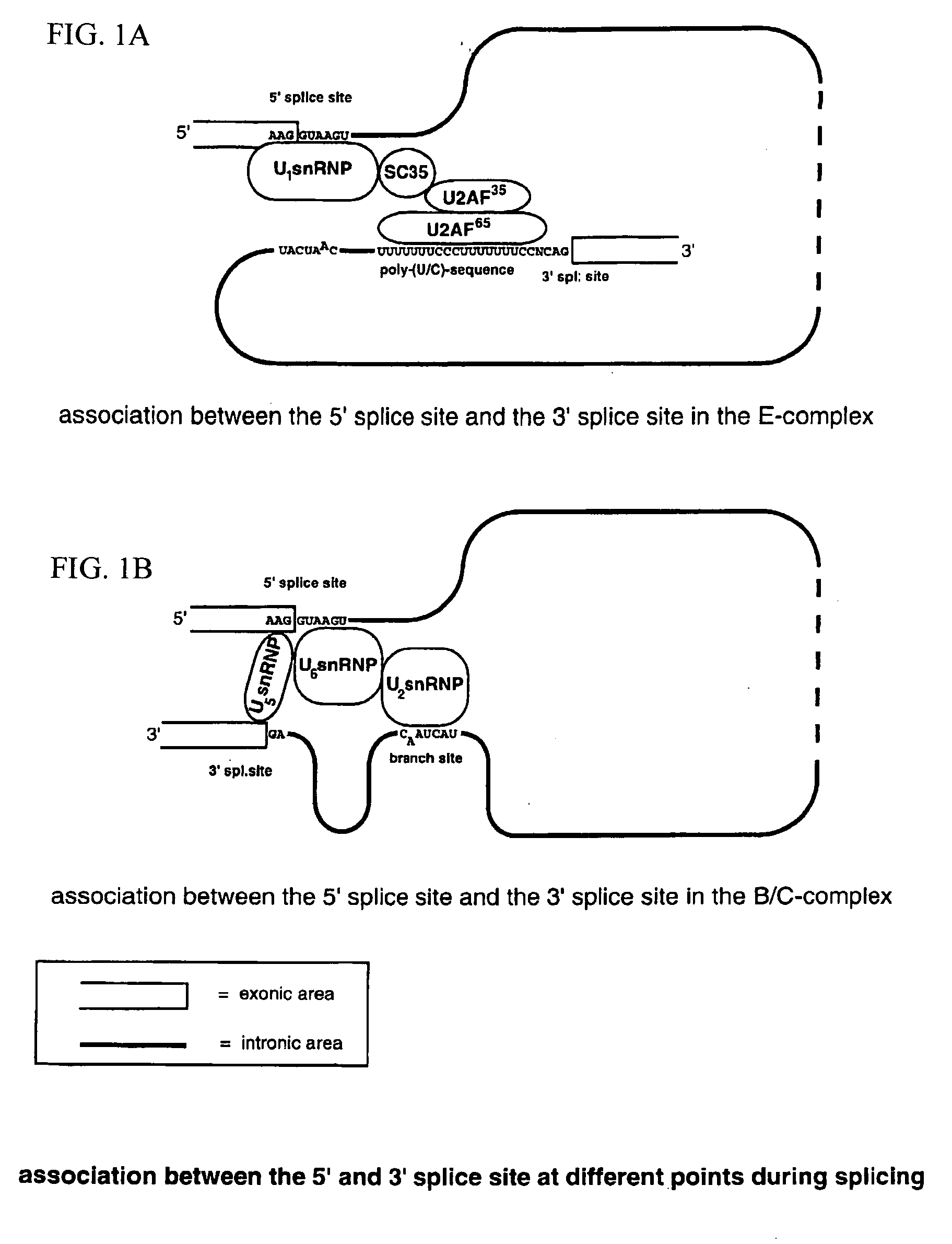
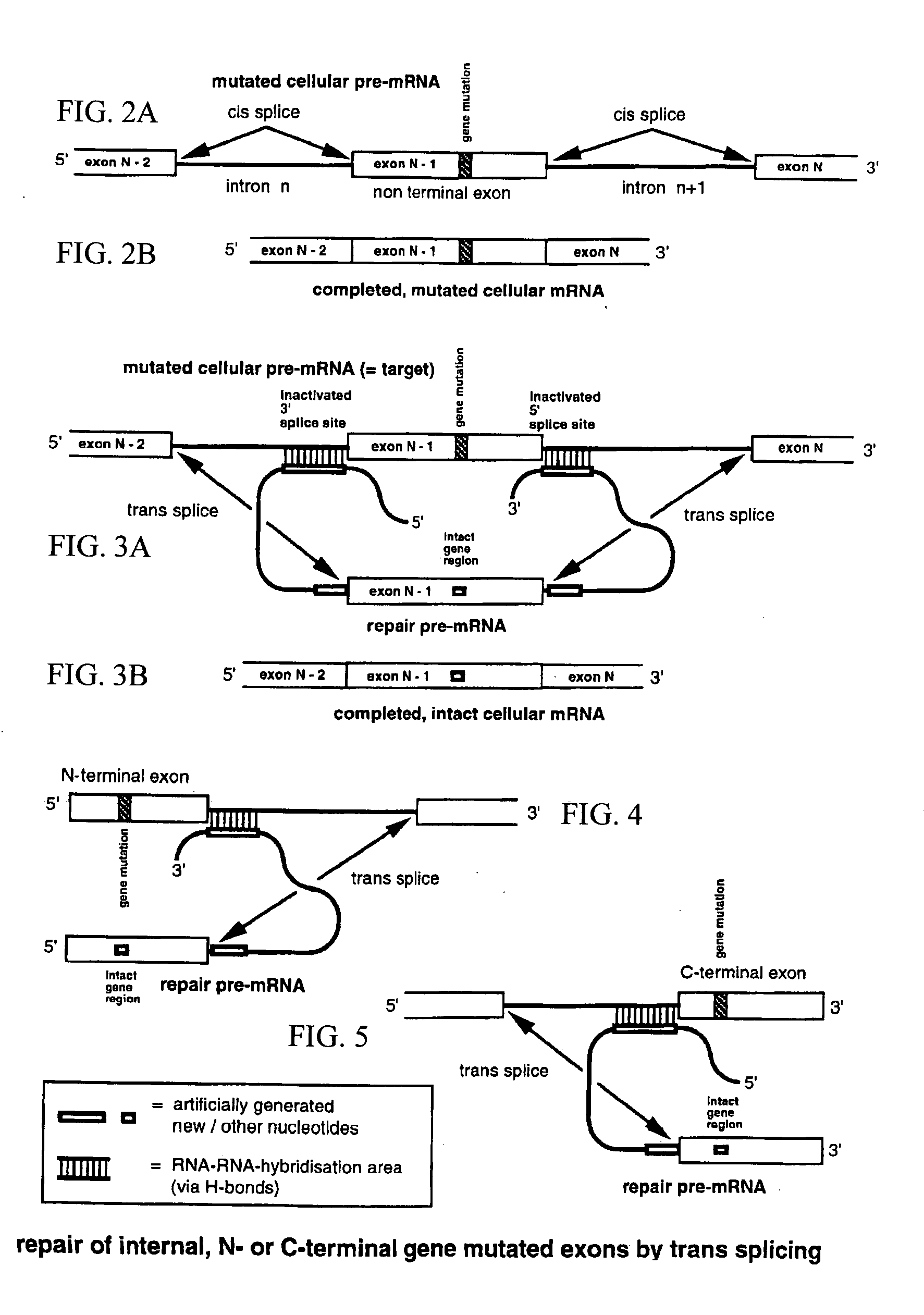
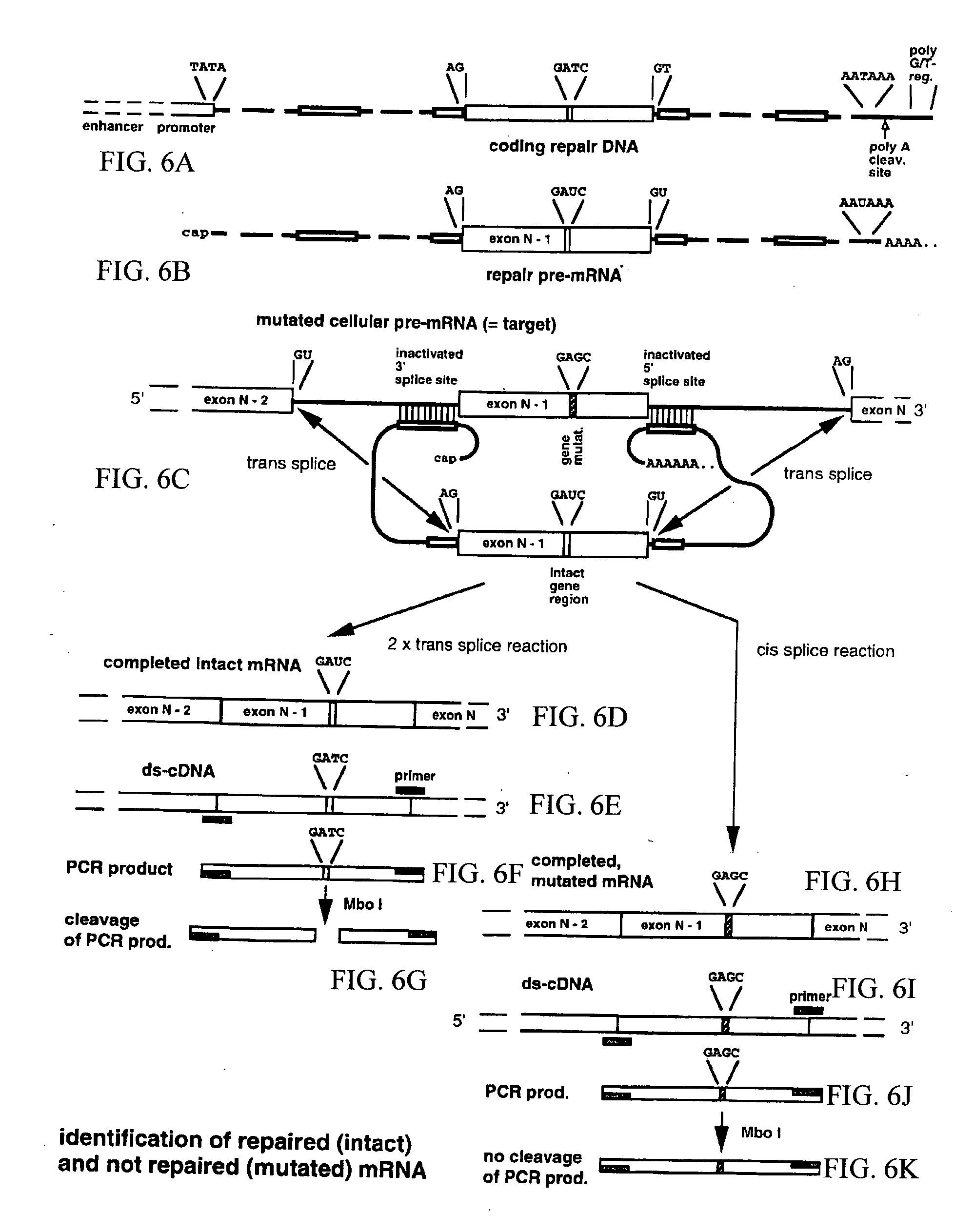
Method for the repair of mutated RNA from genetically defective DNA and for the specific destruction of tumor cells by RNA trans-splicing, and a method for the detection of naturally trans-spliced cellular RNA
InactiveUS20060094675A1Allow useMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsRNA Trans-SplicingTumor cells
Methods and products for the repair of genetically defective DNA in the region of a mutated exon, for the specific destruction of tumor cells, and for the identification of naturally trans-spliced RNA. The methods inter alia are based on the utilization of cellular RNA splicing components.
Owner:NEY ANDREAS DR
Method of establishing mouse genome mutant embryonic stem cell library
InactiveCN1548535AMeet research needsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHigh fluxGene Mutant
The method of utilizing gene capture technology in establishing mouse genome mutant embryonic stem cell library includes the following steps: introducing gene capture carrier, which has the from-5'-to-3' structure of LTR-RNA splice acceptor sequence-promoter-screening gene-RNA splice donor sequence-LTR, with the screening gene containing no polyA area, into embryonic stem cell; screening survival embryonic stem cell with the screening gene; and merging the survival embryonic stem cell to obtain mutant embryonic stem cell library. The present invention also provides the identification method of mutant gene site. The present invention lays the foundation for obtaining gene mutant mouse in large scale and high flux.
Owner:MABPLEX INT LTD
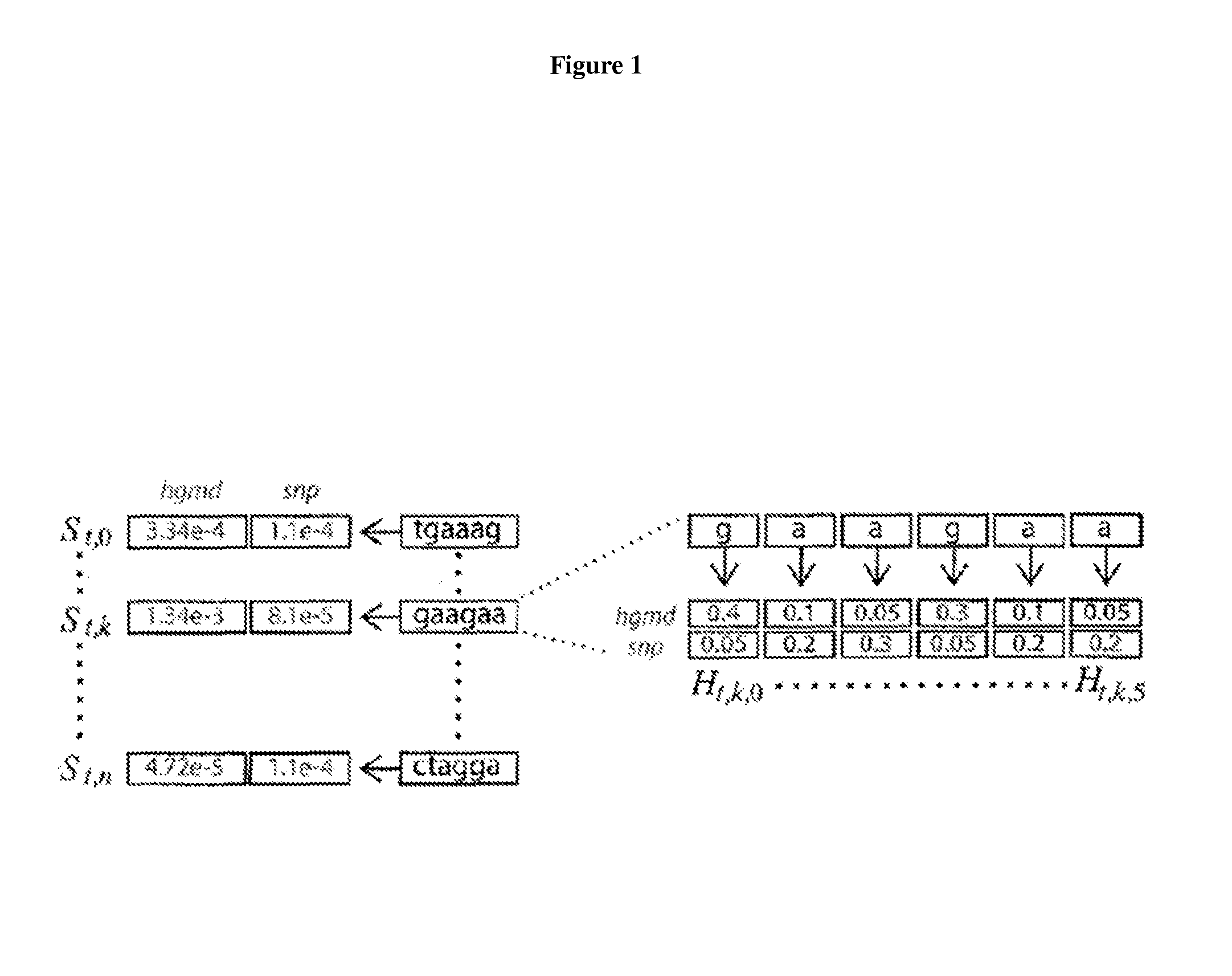
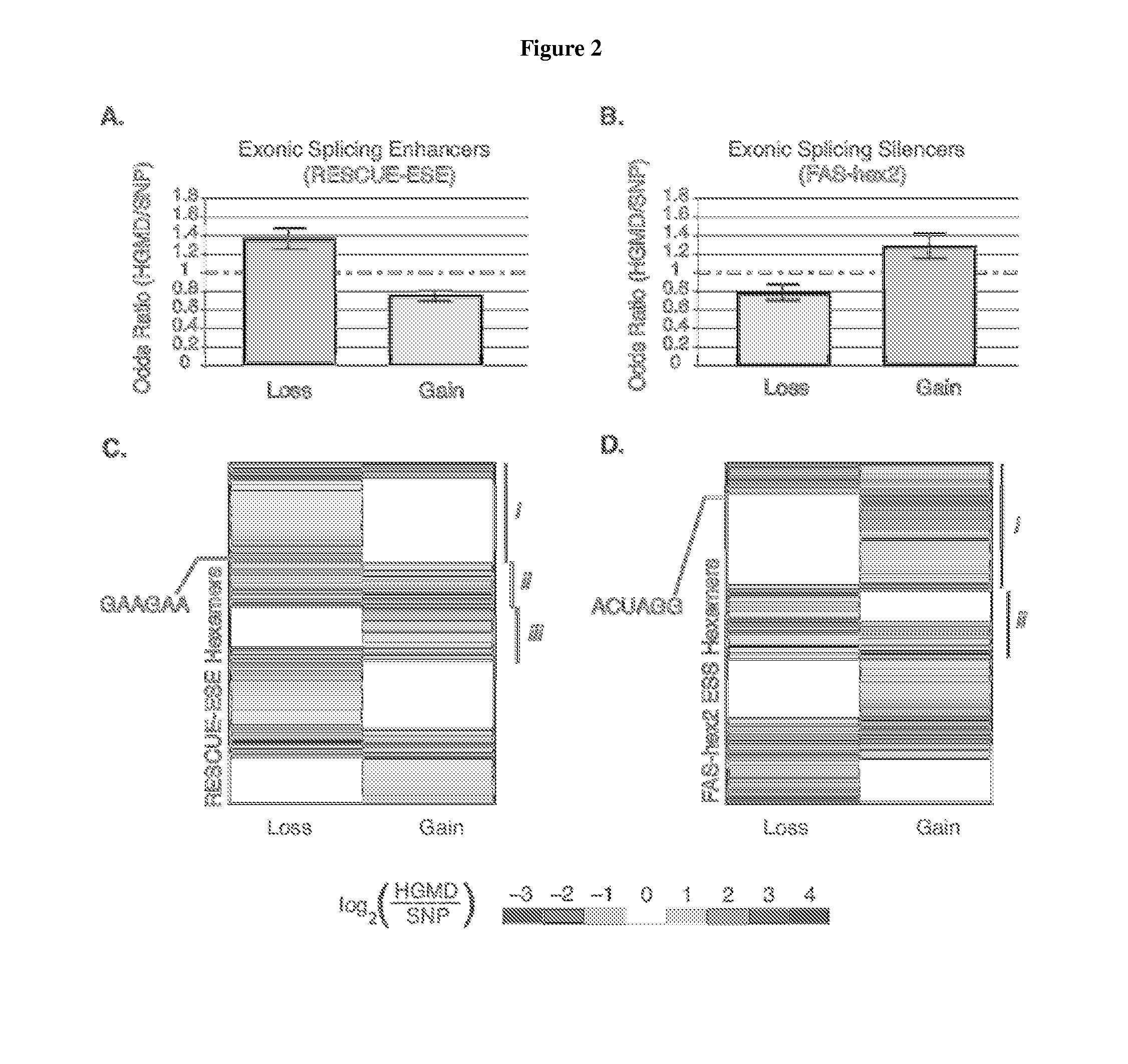
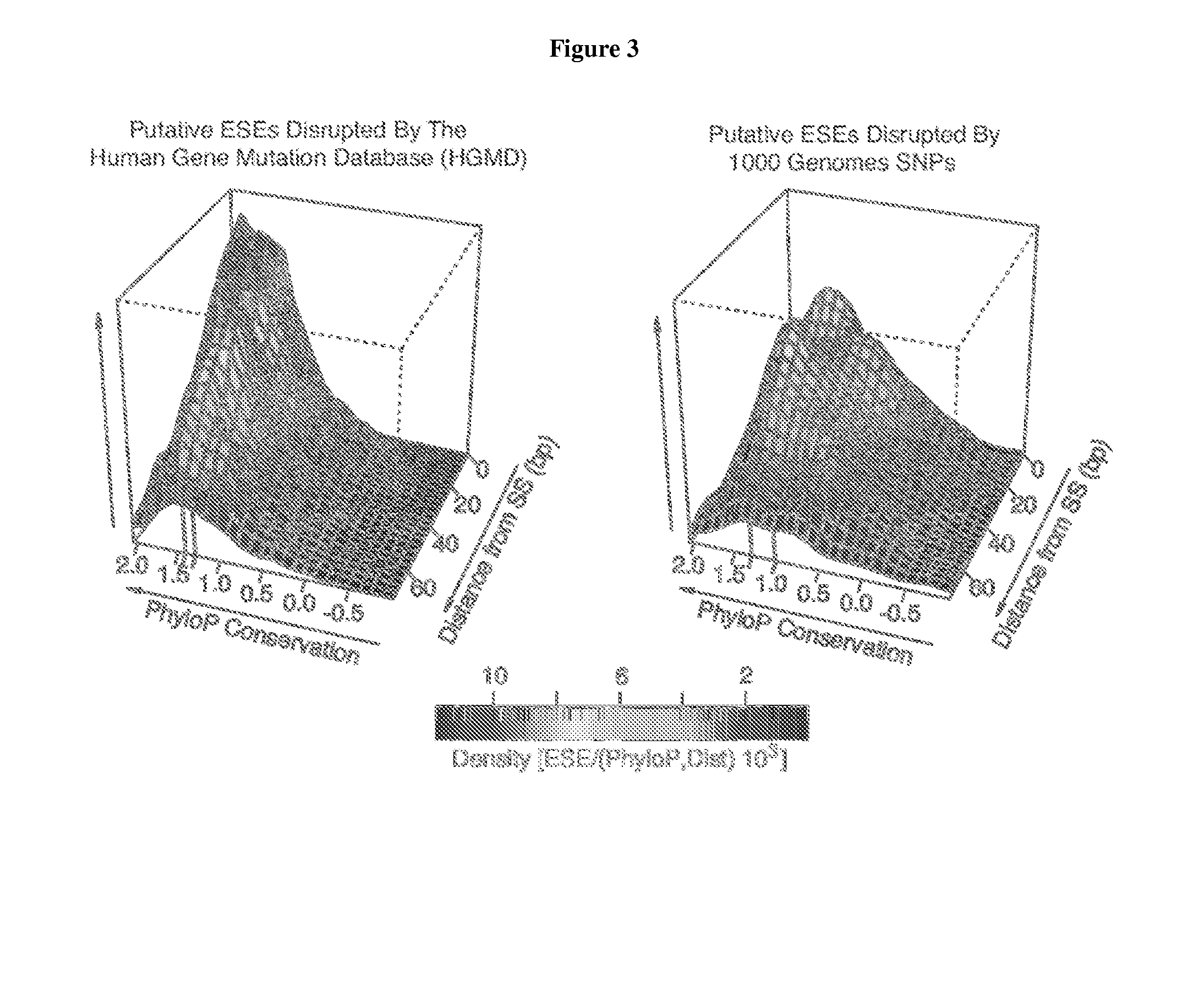
Exonic splicing enhancers and exonic splicing silencers
ActiveUS20140193821A1Maximum efficiencyHigh strengthSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseaseExonic splicing silencer
Compounds and methods for regulation of exonic splicing enhancers and exonic splicing silencers. Compounds include polynucleotides targeted to aberrant exonic splicing enhancers and exonic splicing silencers. Compounds and methods for the diagnosis of diseases and conditions associated with aberrant exonic splicing enhancers and exonic splicing silencers. Methods for identifying splicing-sensitive disease mutations, and functional RNA elements as targets for amelioration of aberrant pre-mRNA splicing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for modulating RNA splicing
ActiveUS10668171B2High affinityOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationRegulator geneFunctional protein
In one aspect, described herein is a recognition element for splicing modifier (REMS) that can be recognized by a compound provided herein. In another aspect, described herein are methods for modulating the amount of a product of a gene, wherein a precursor RNA transcript transcribed from the gene contains a REMS, and the methods utilizing a compound described herein. More particularly, described herein are methods for modulating the amount of an RNA transcript or protein product encoded by a gene, wherein a precursor RNA transcript transcribed from the gene comprises a REMS, and the methods utilizing a compound described herein. In another aspect, provided herein are artificial gene constructs comprising a REMS, and uses of those artificial gene constructs to modulate functional protein production. In another aspect, provided herein are methods for altering endogenous genes to comprise a REMS, and the use of a compound described herein to modulate the functional protein produced from such altered endogenous genes.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com