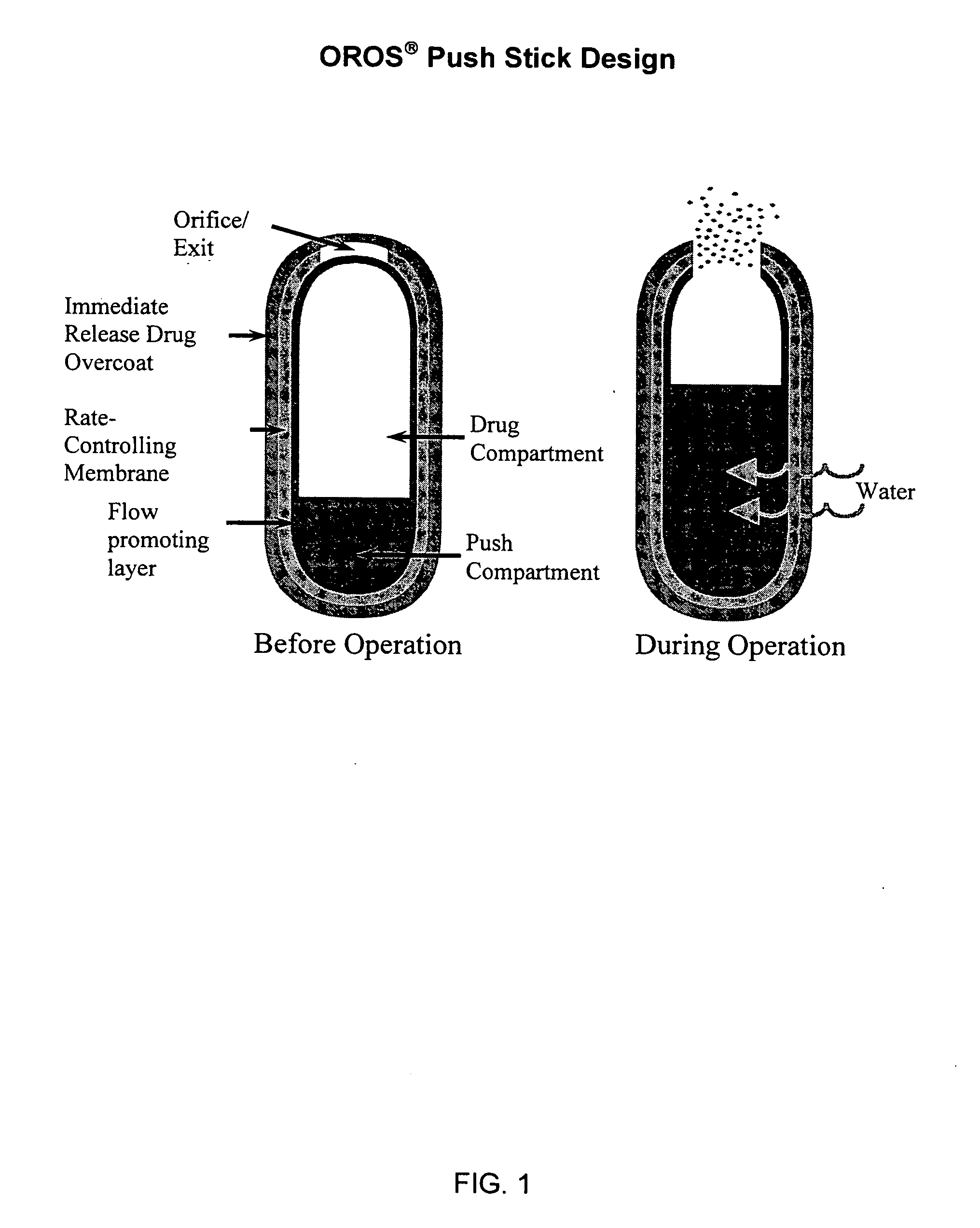
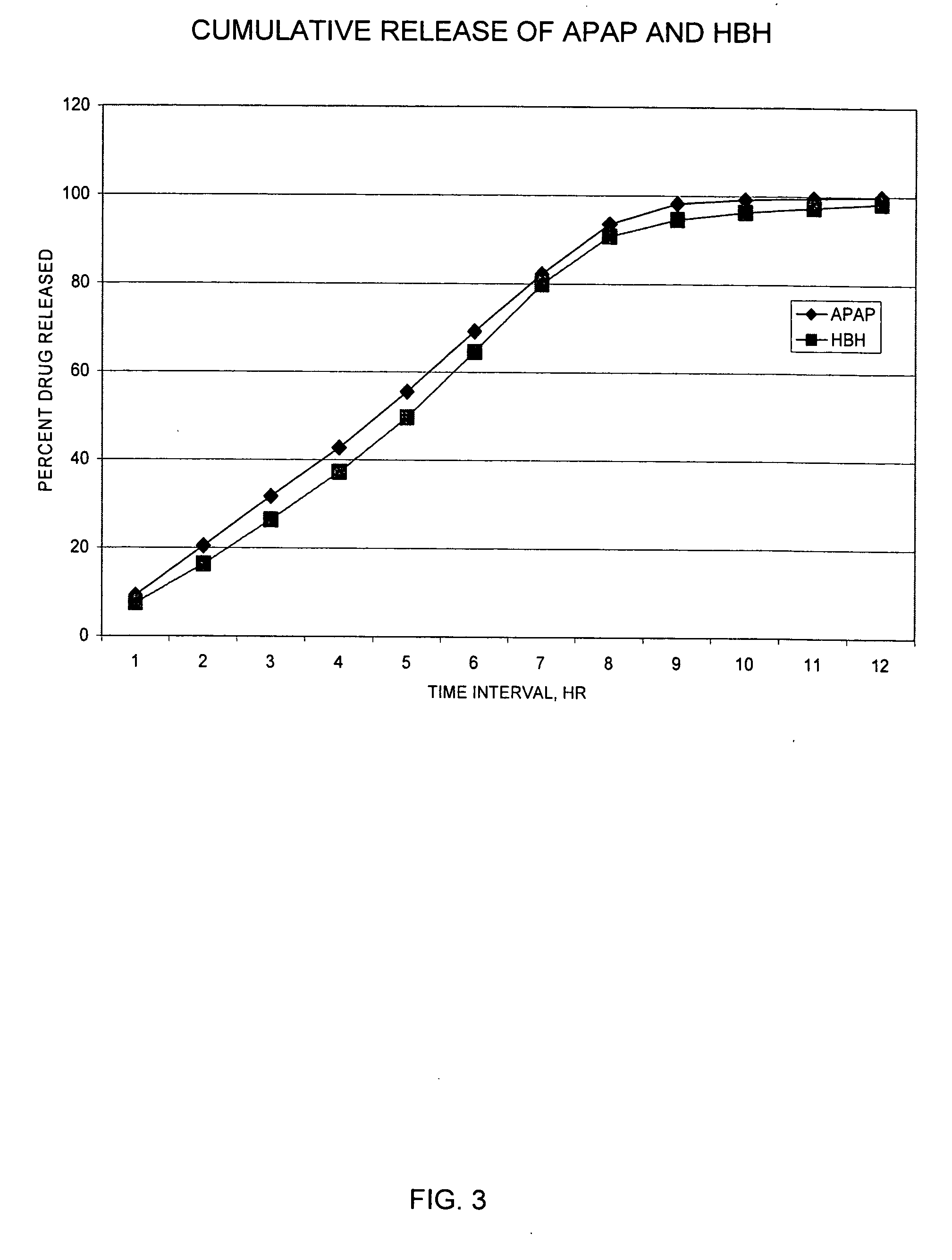
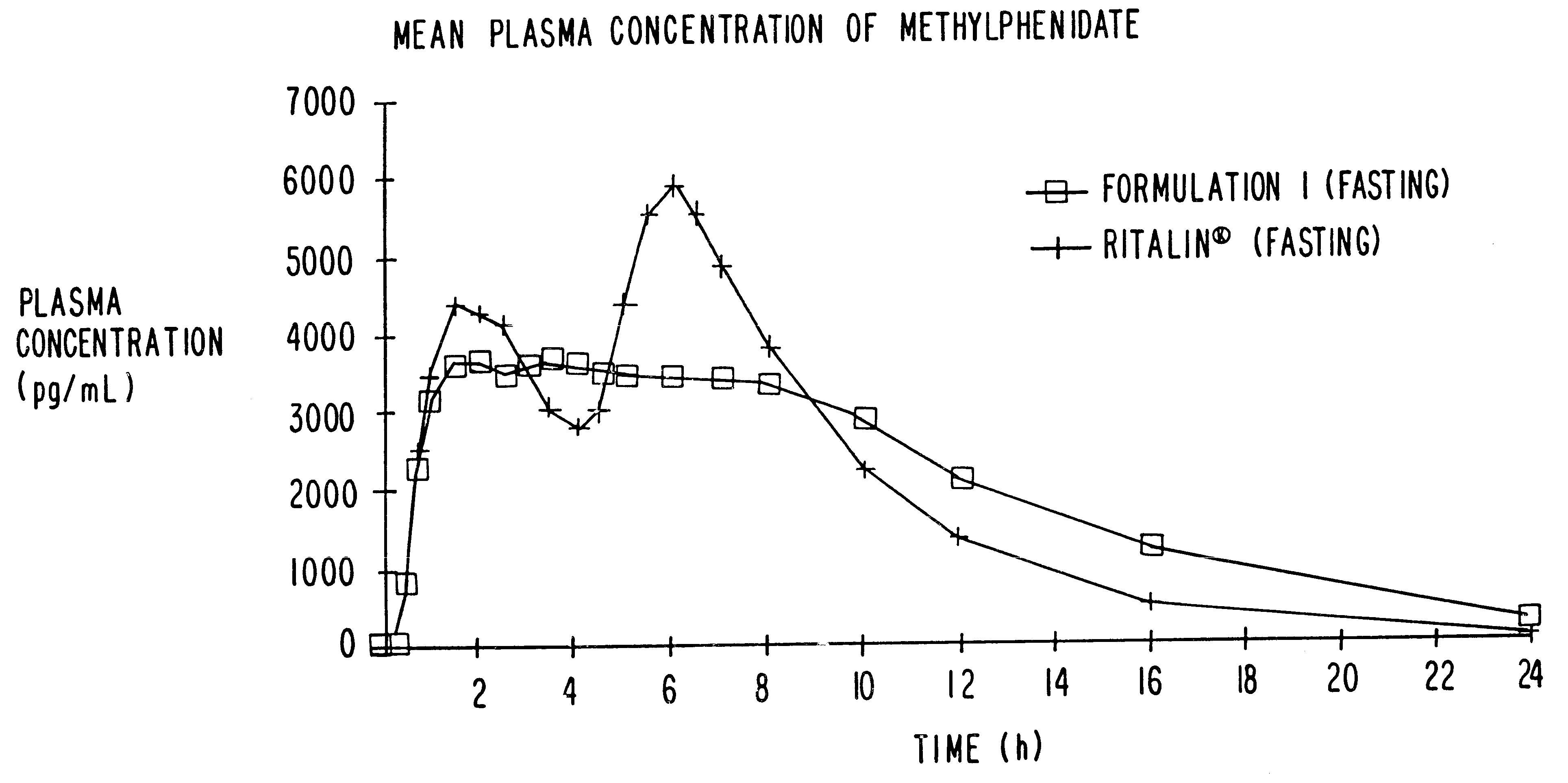
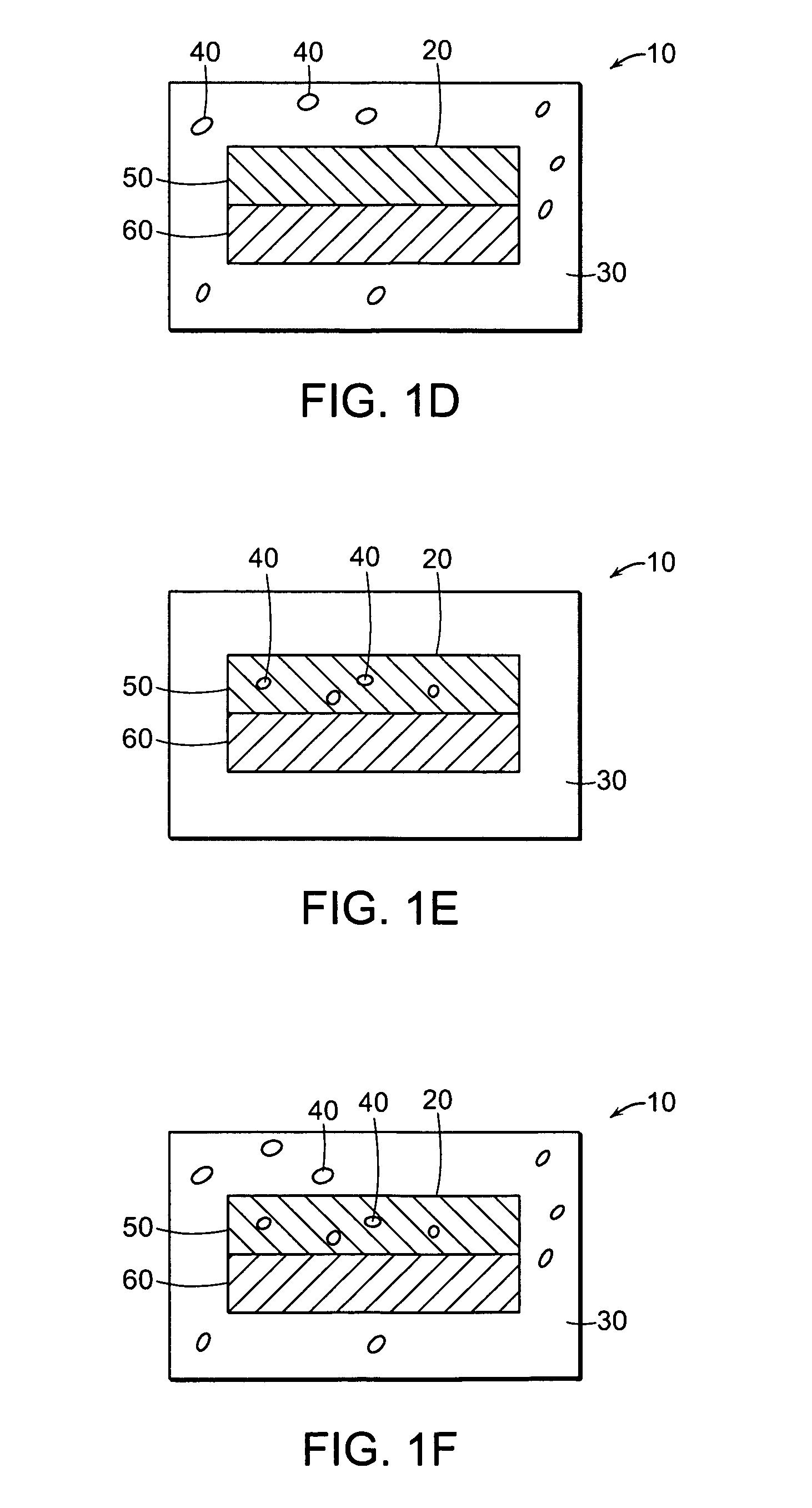
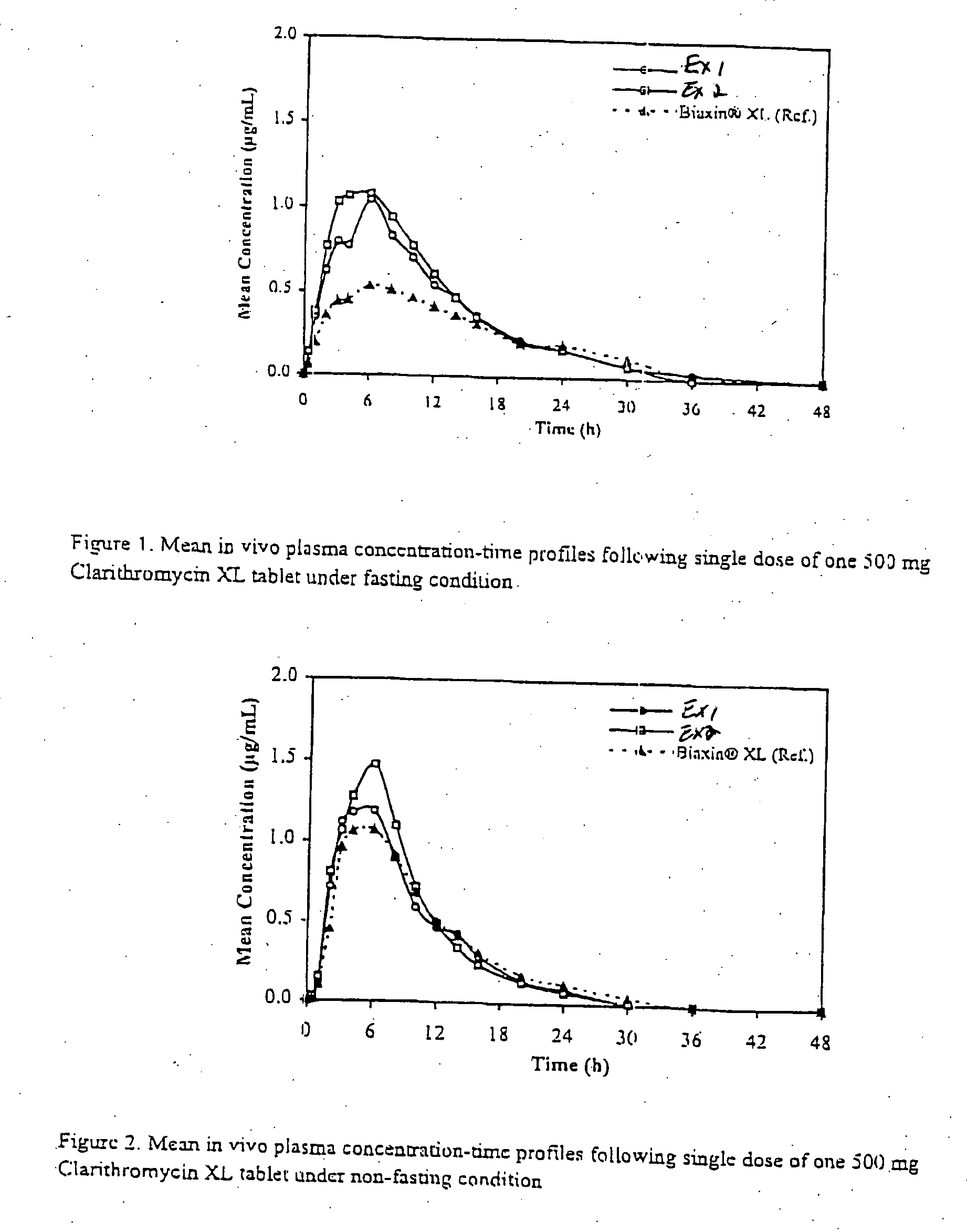
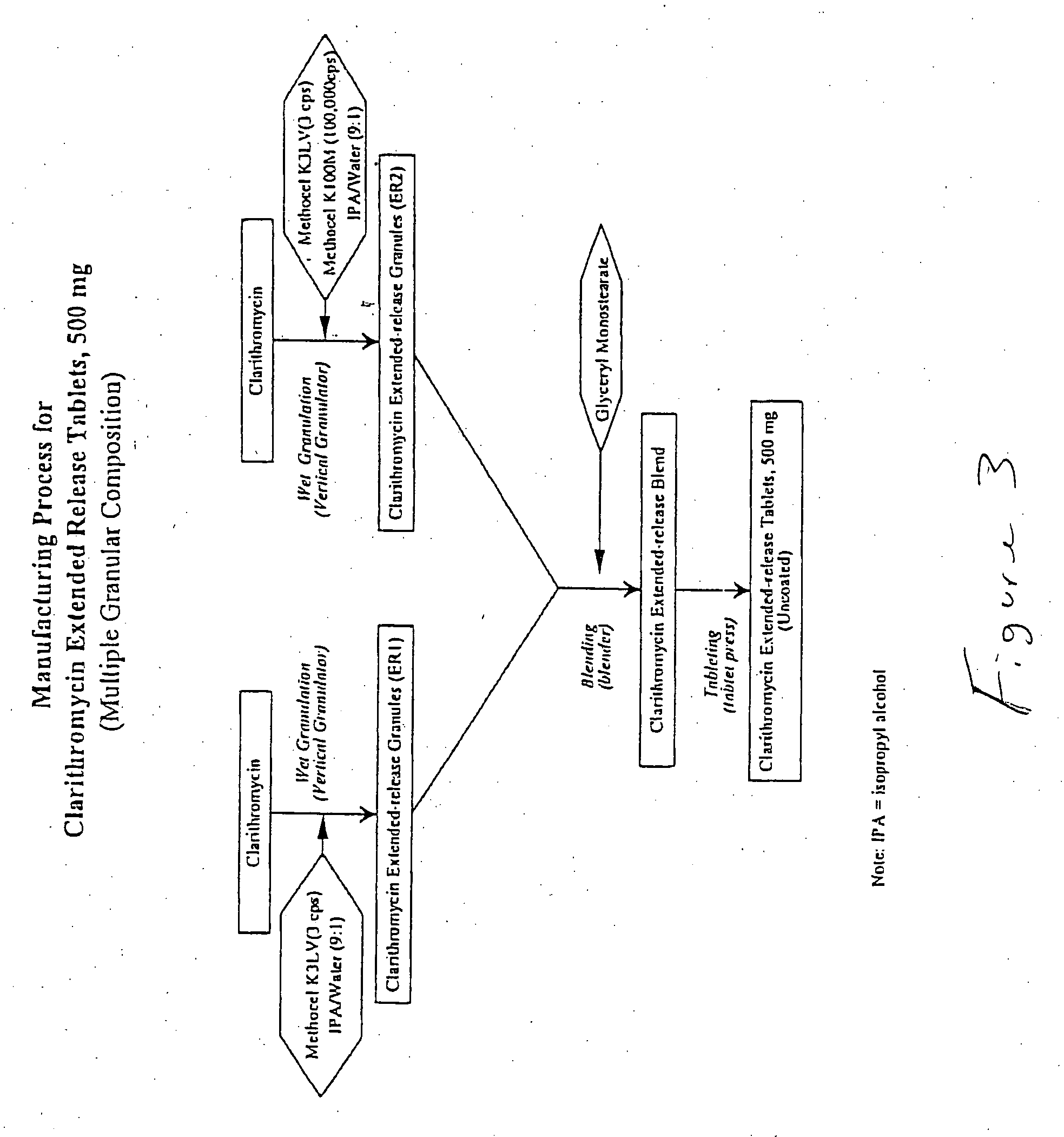
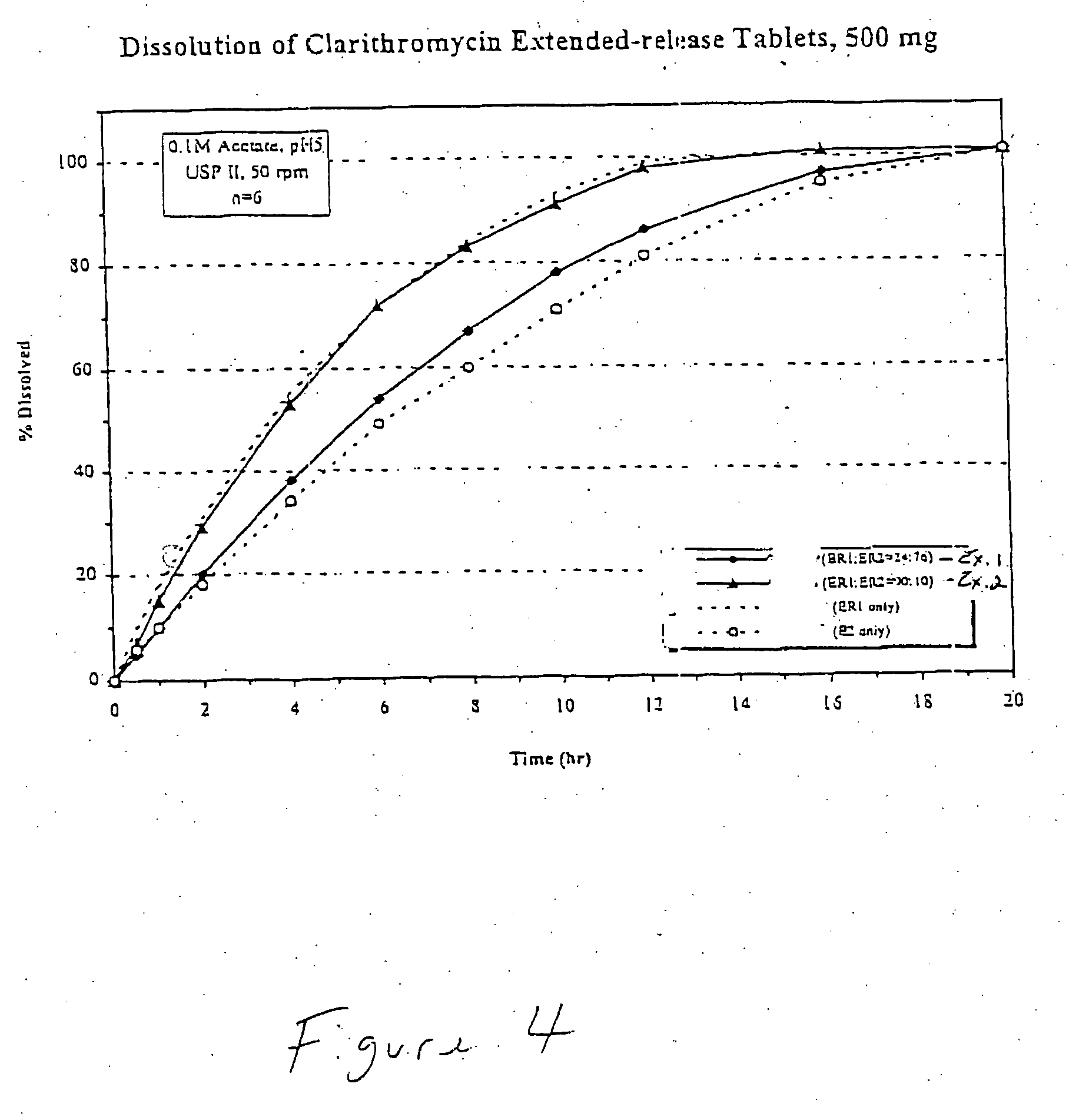
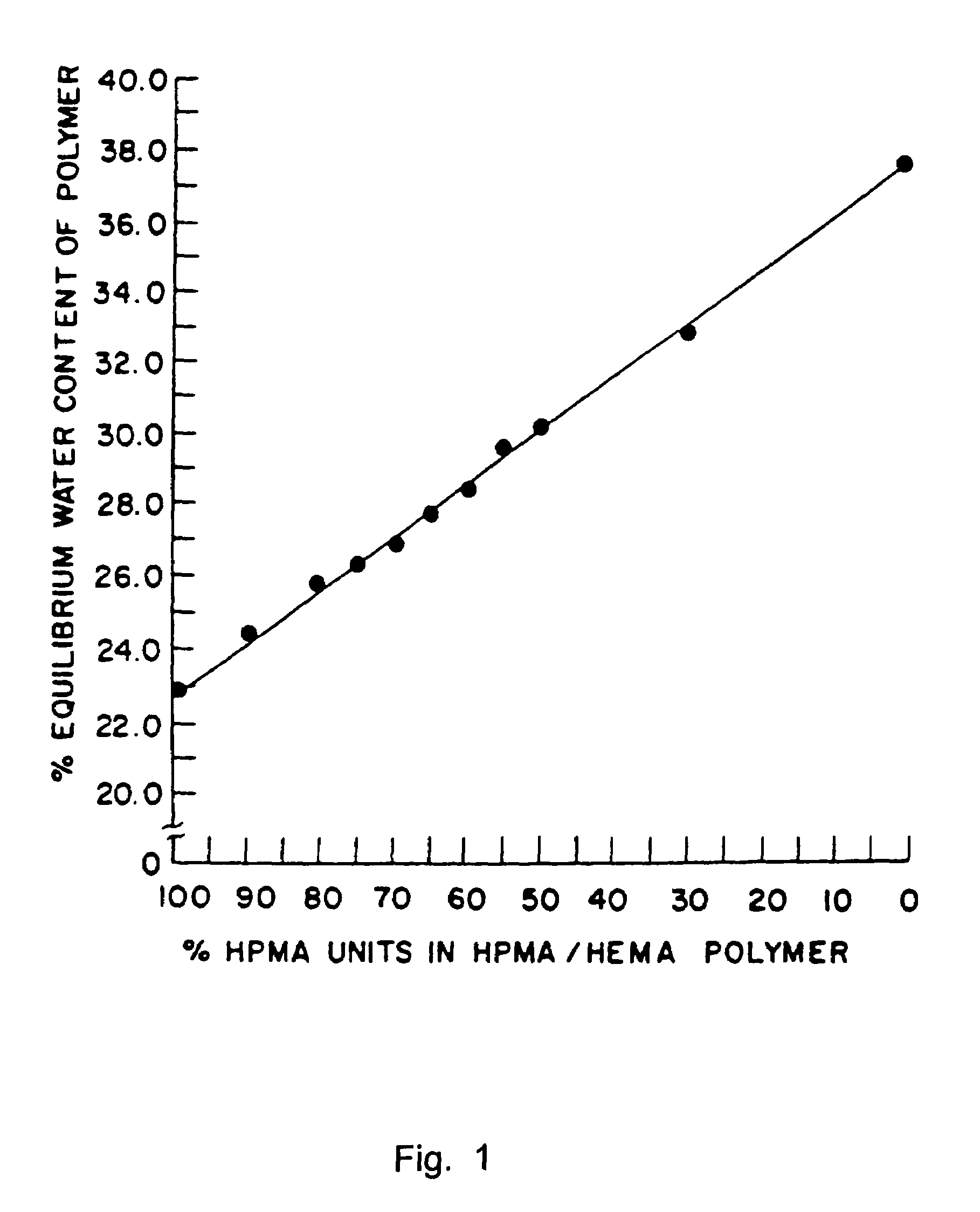
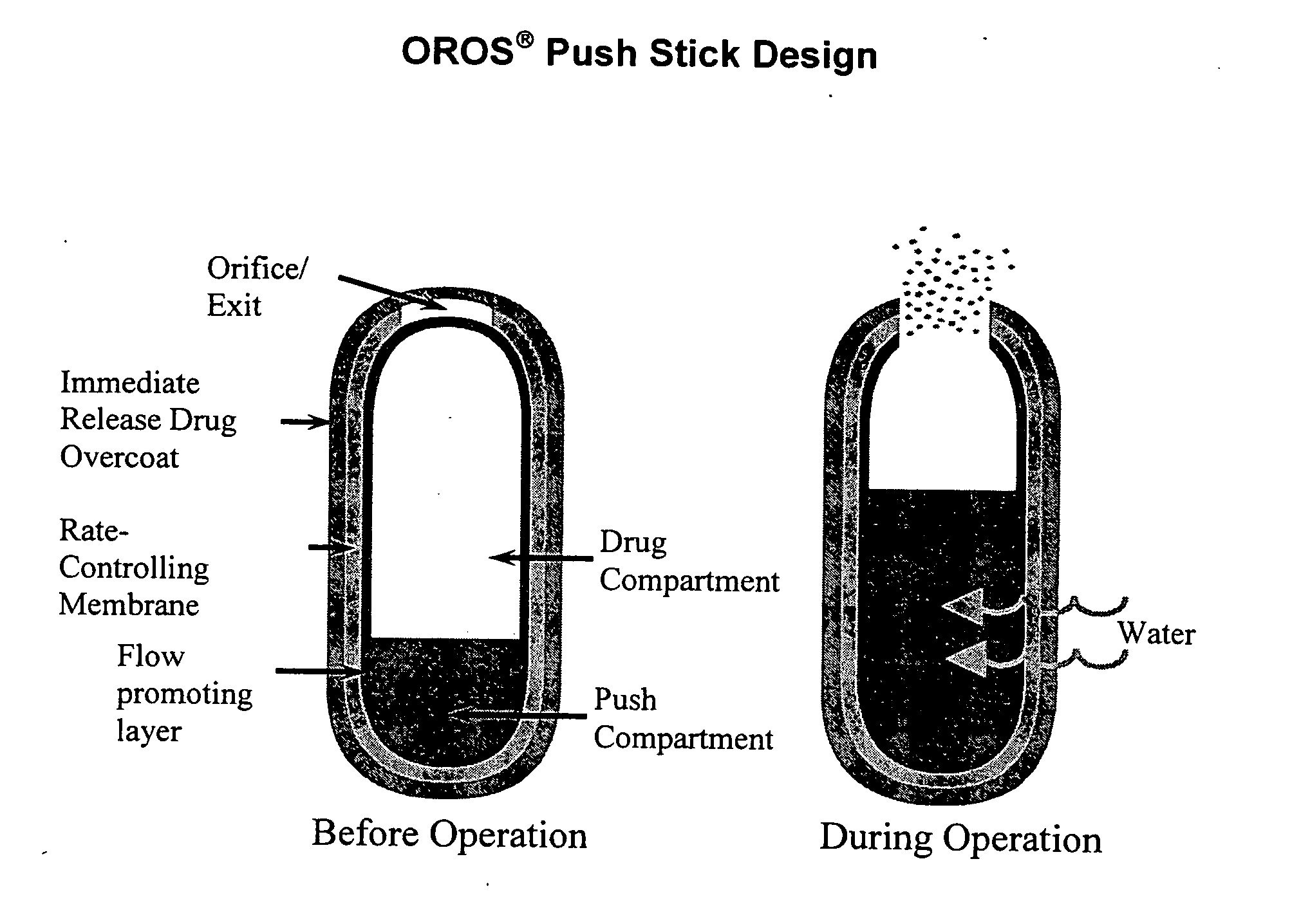
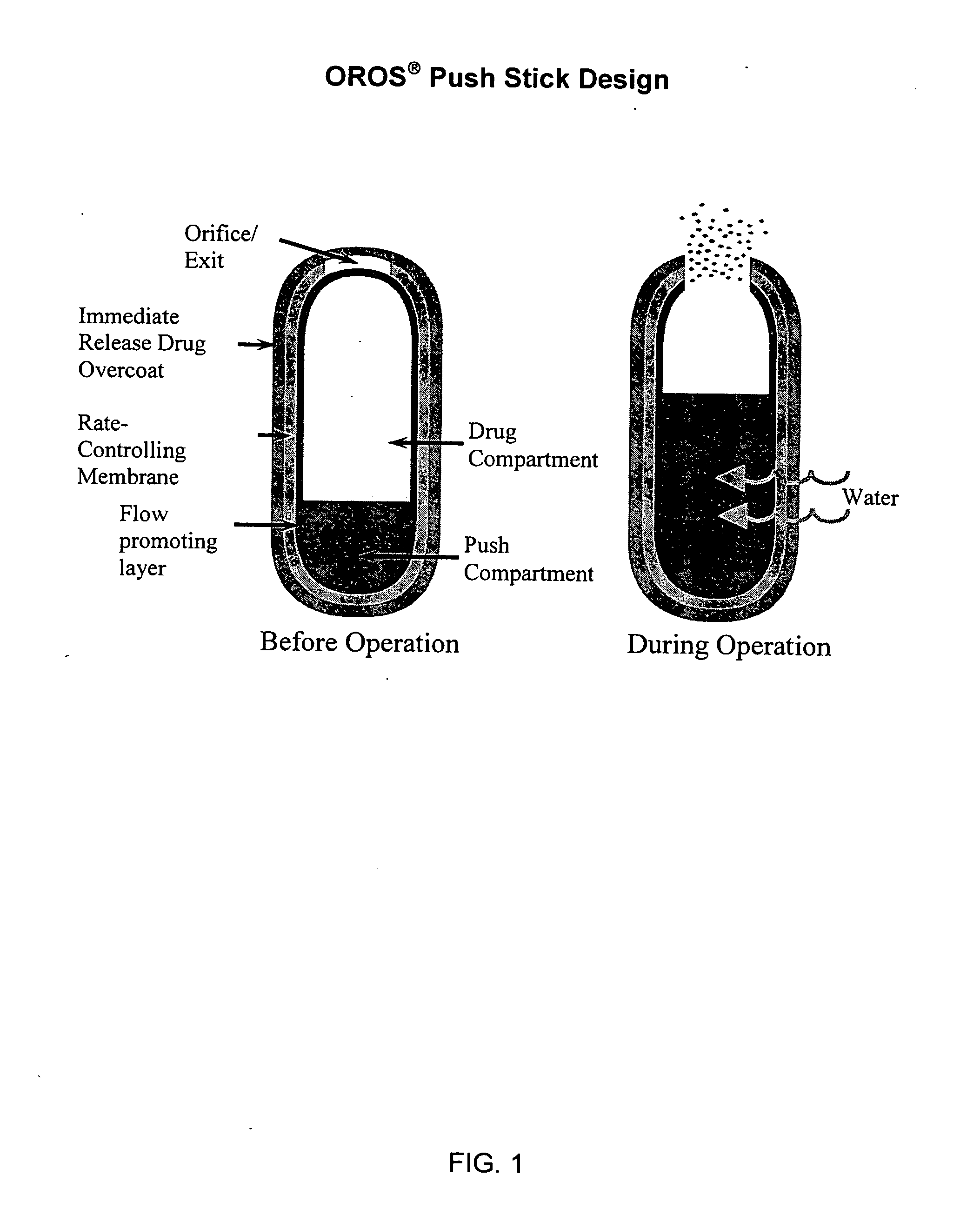
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
421 results about "Controlled-Release Formulations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
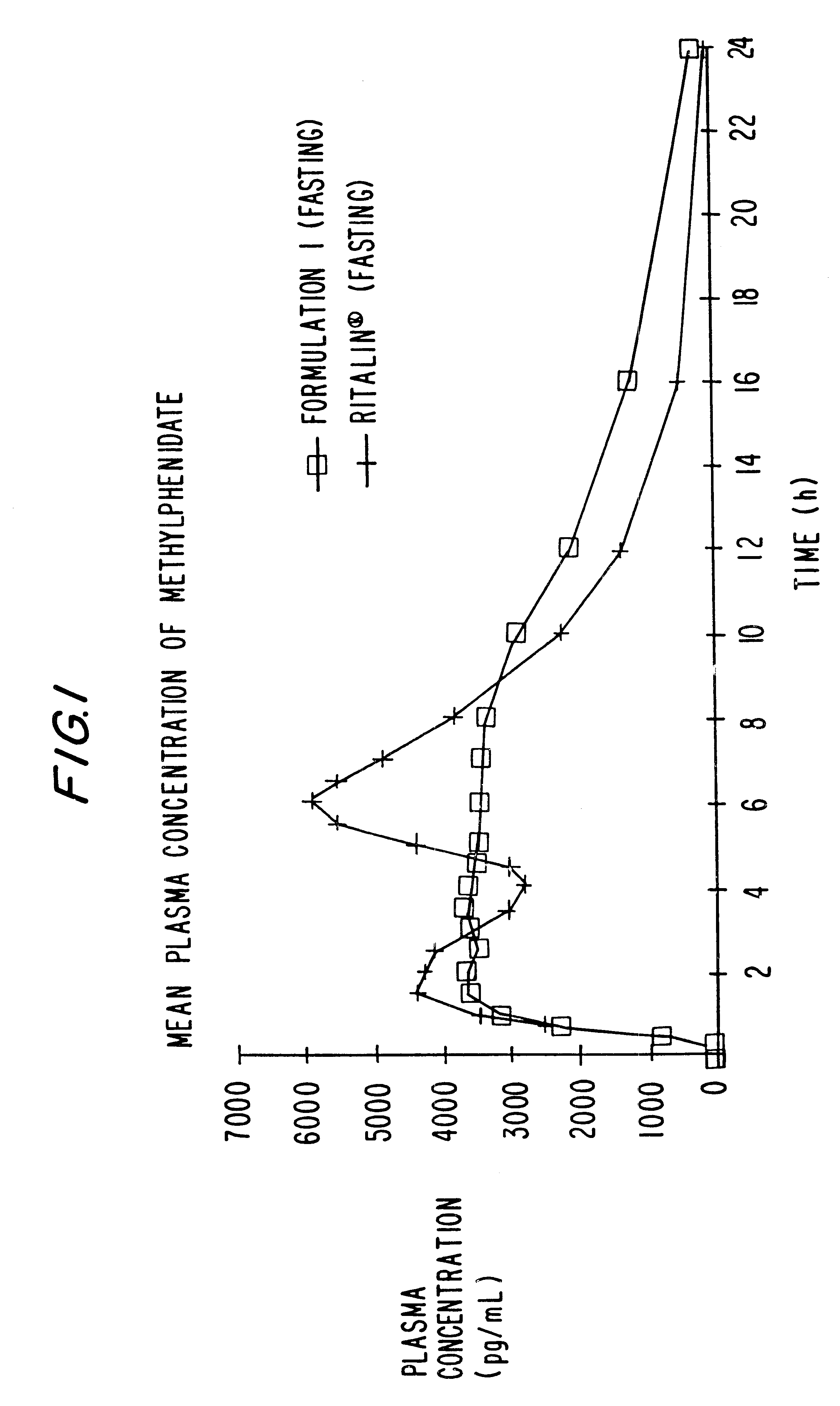
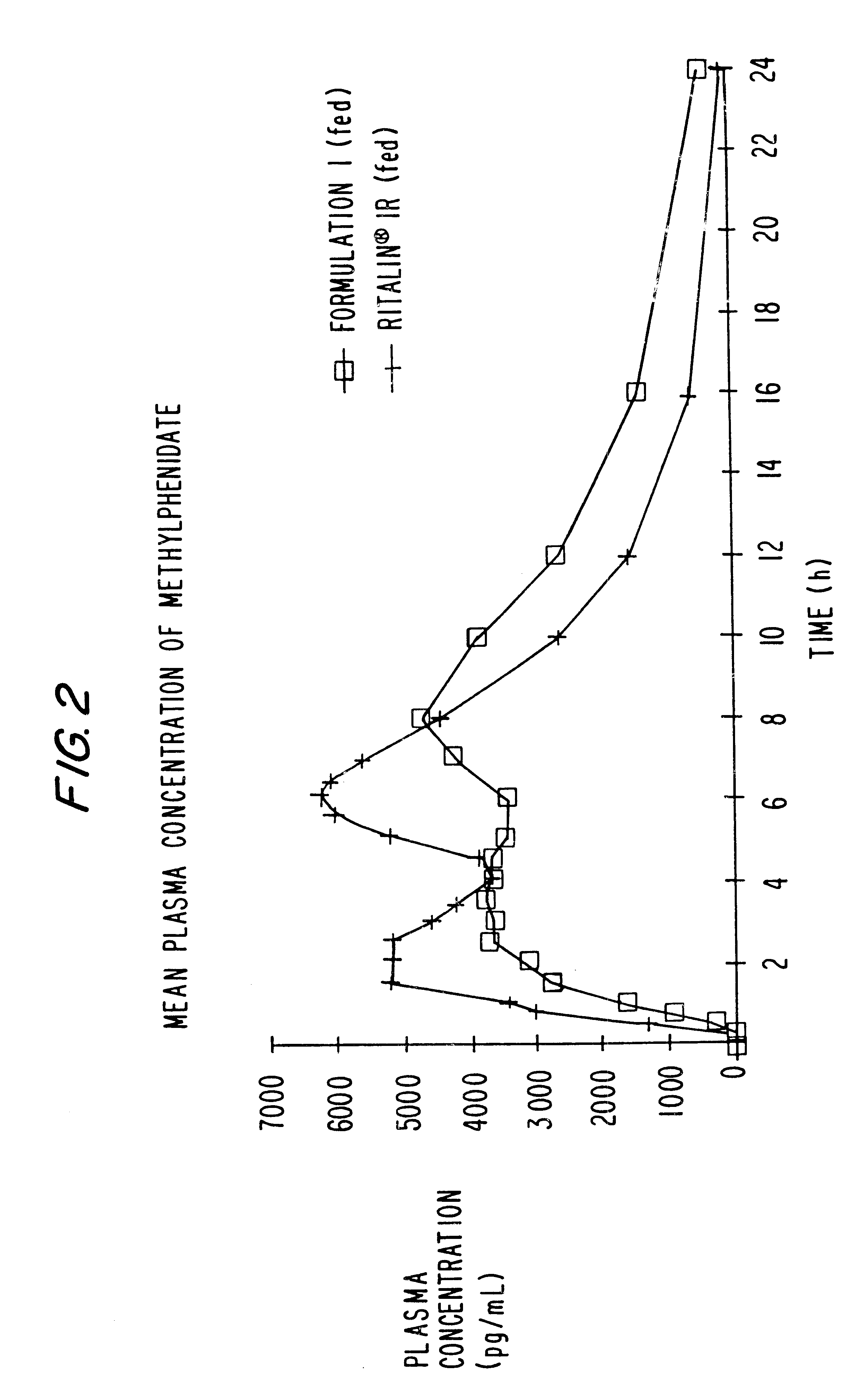
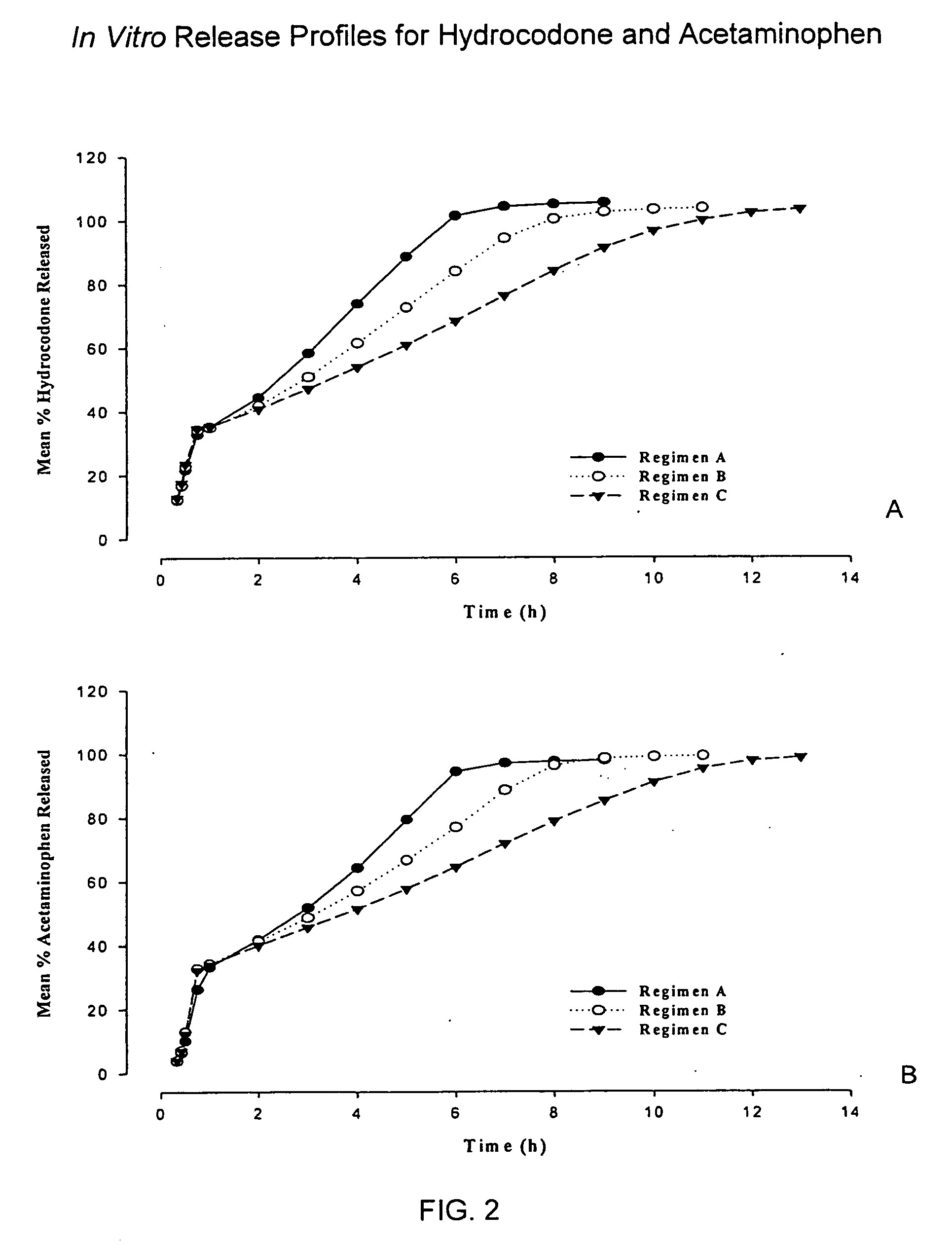
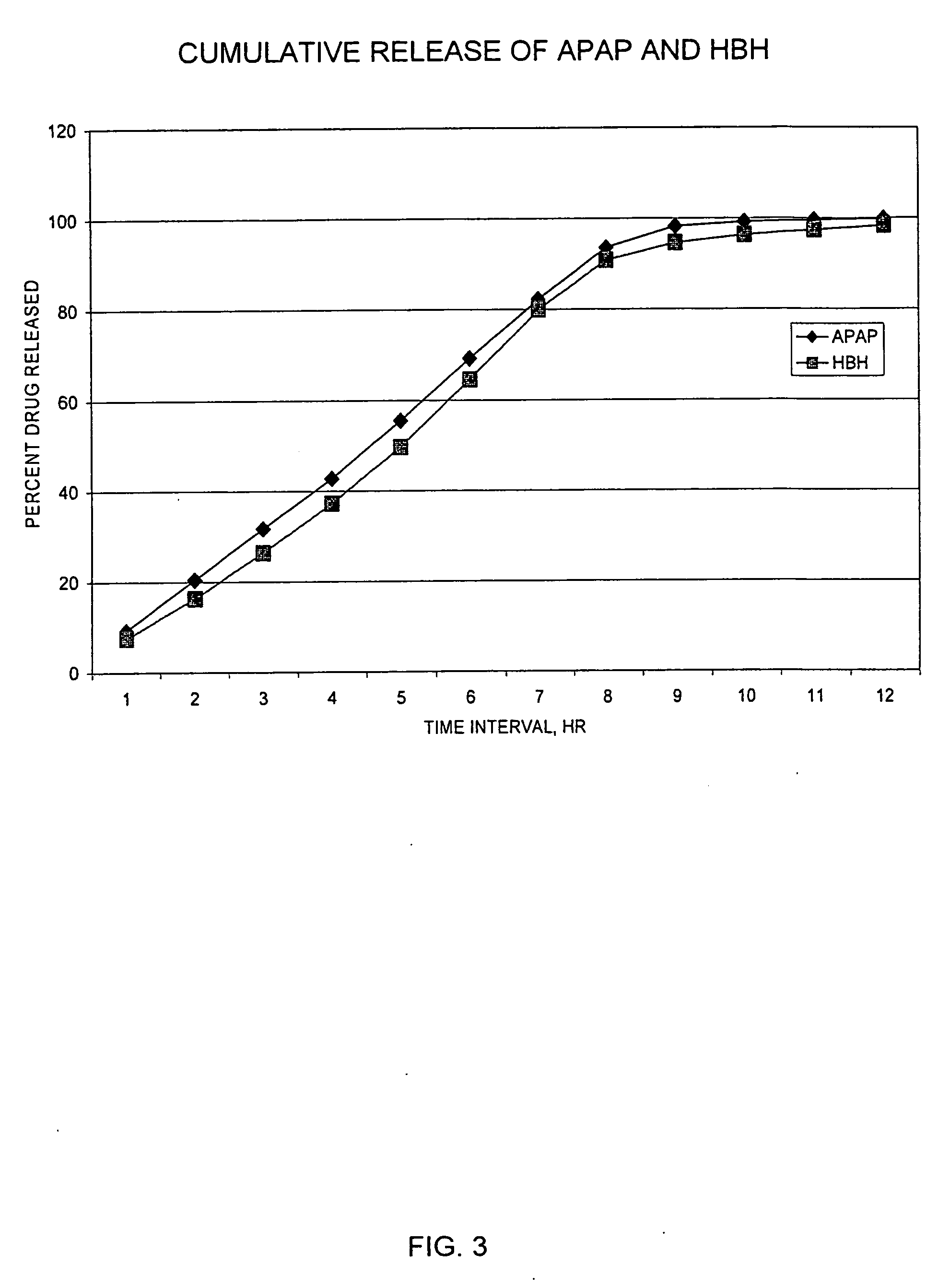
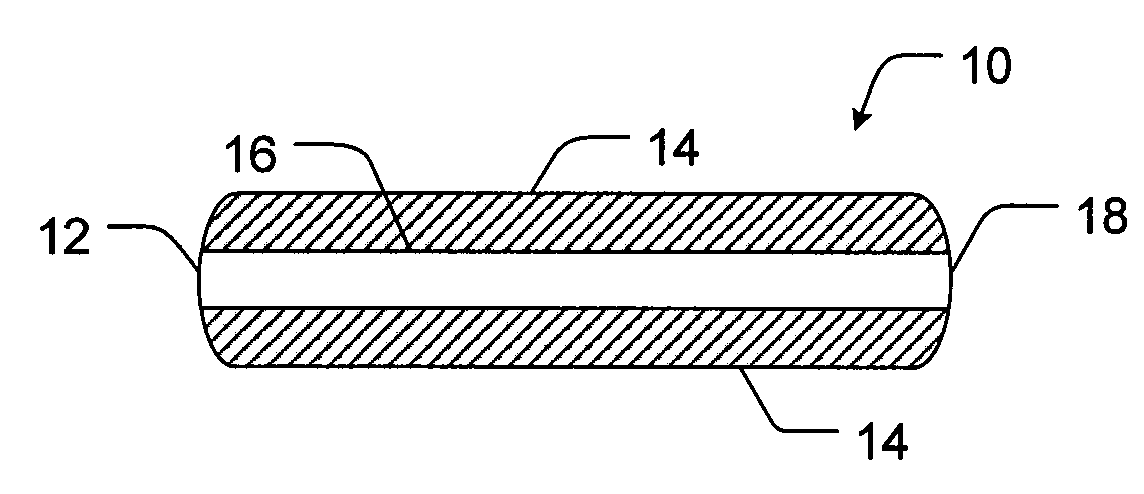
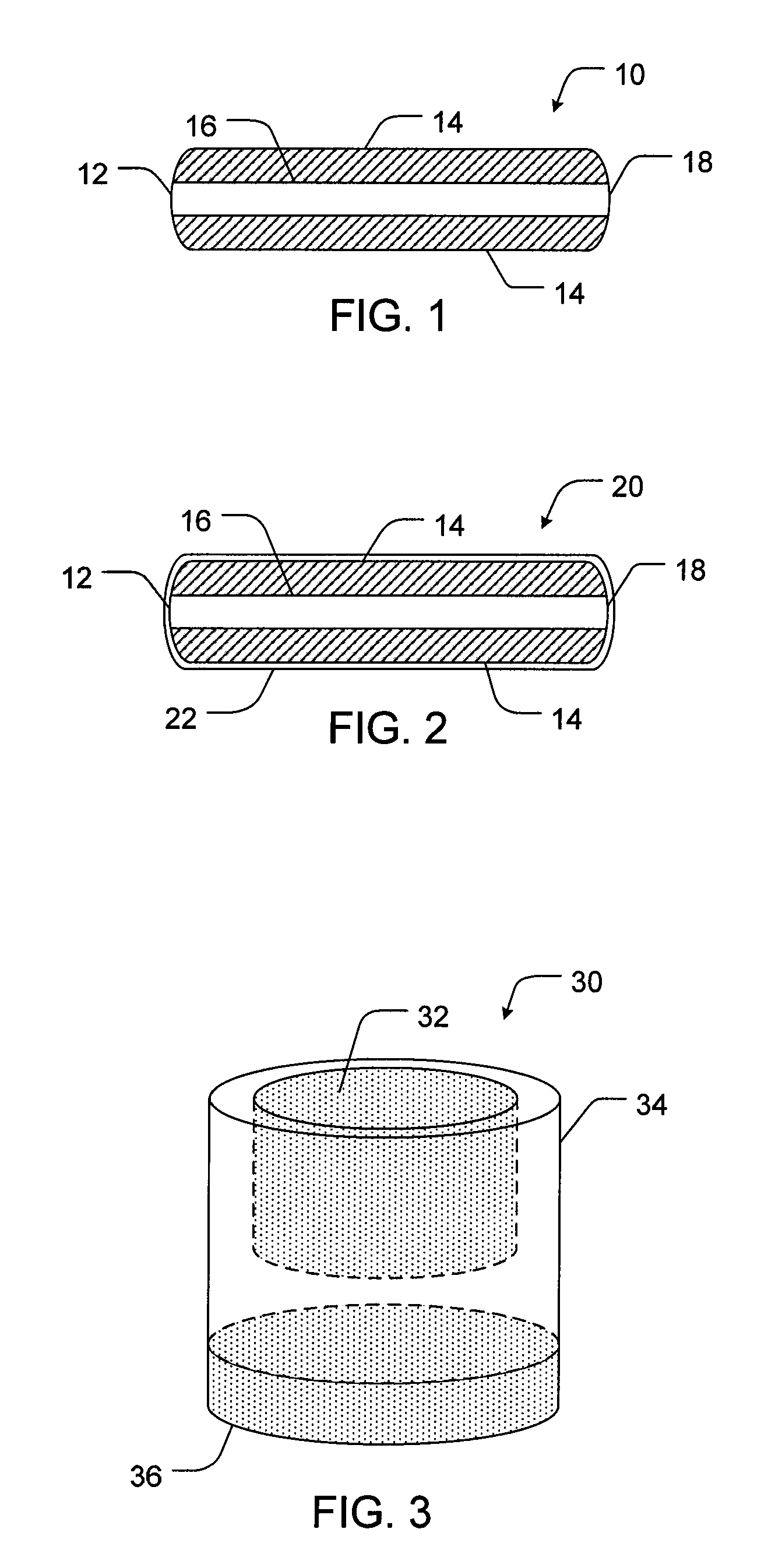
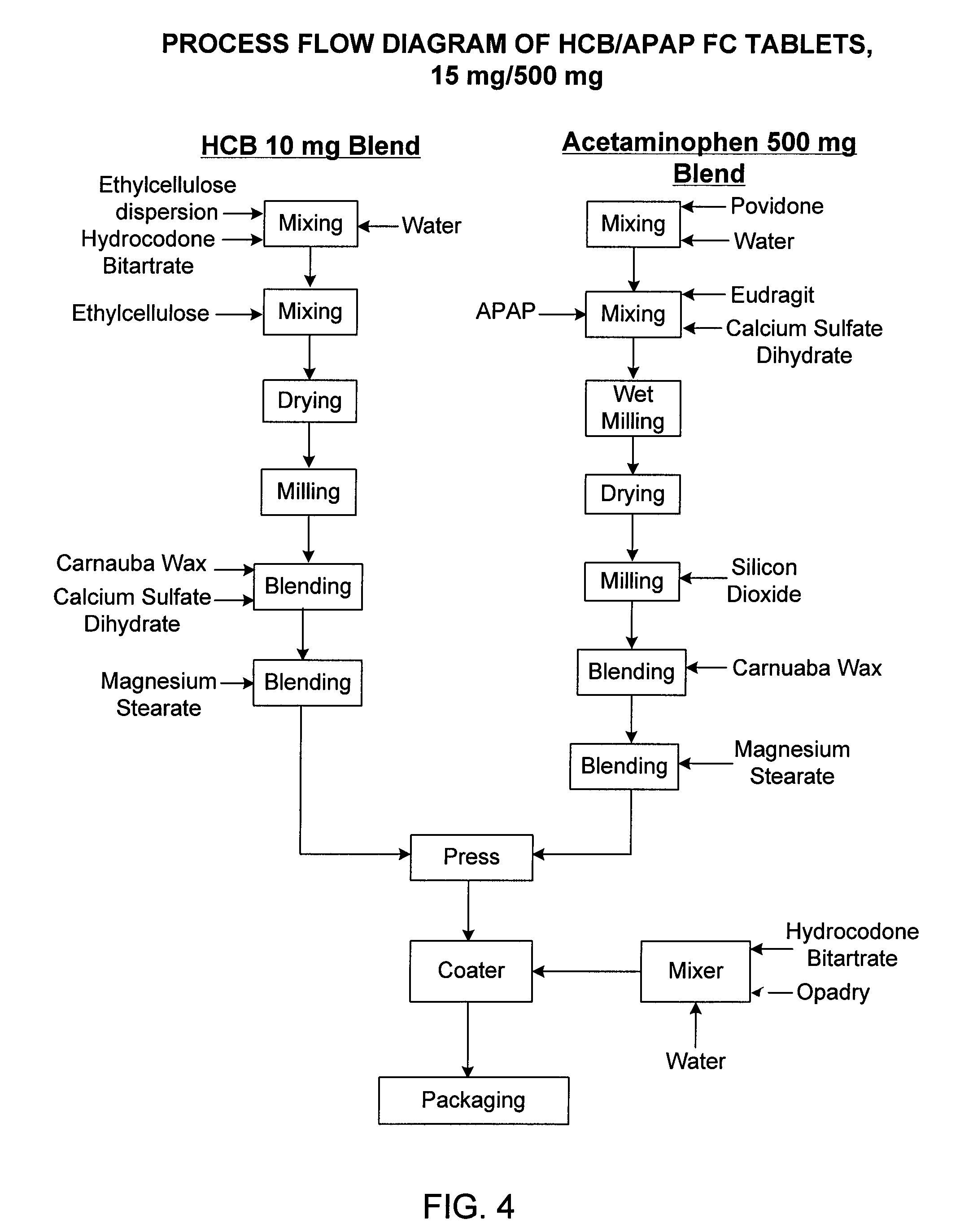
Controlled release formulations of opioid and nonopioid analgesics
InactiveUS20050158382A1Reduce the maximumRapid rise in plasma concentrationBiocideNervous disorderImmediate releaseAnalgesic agents
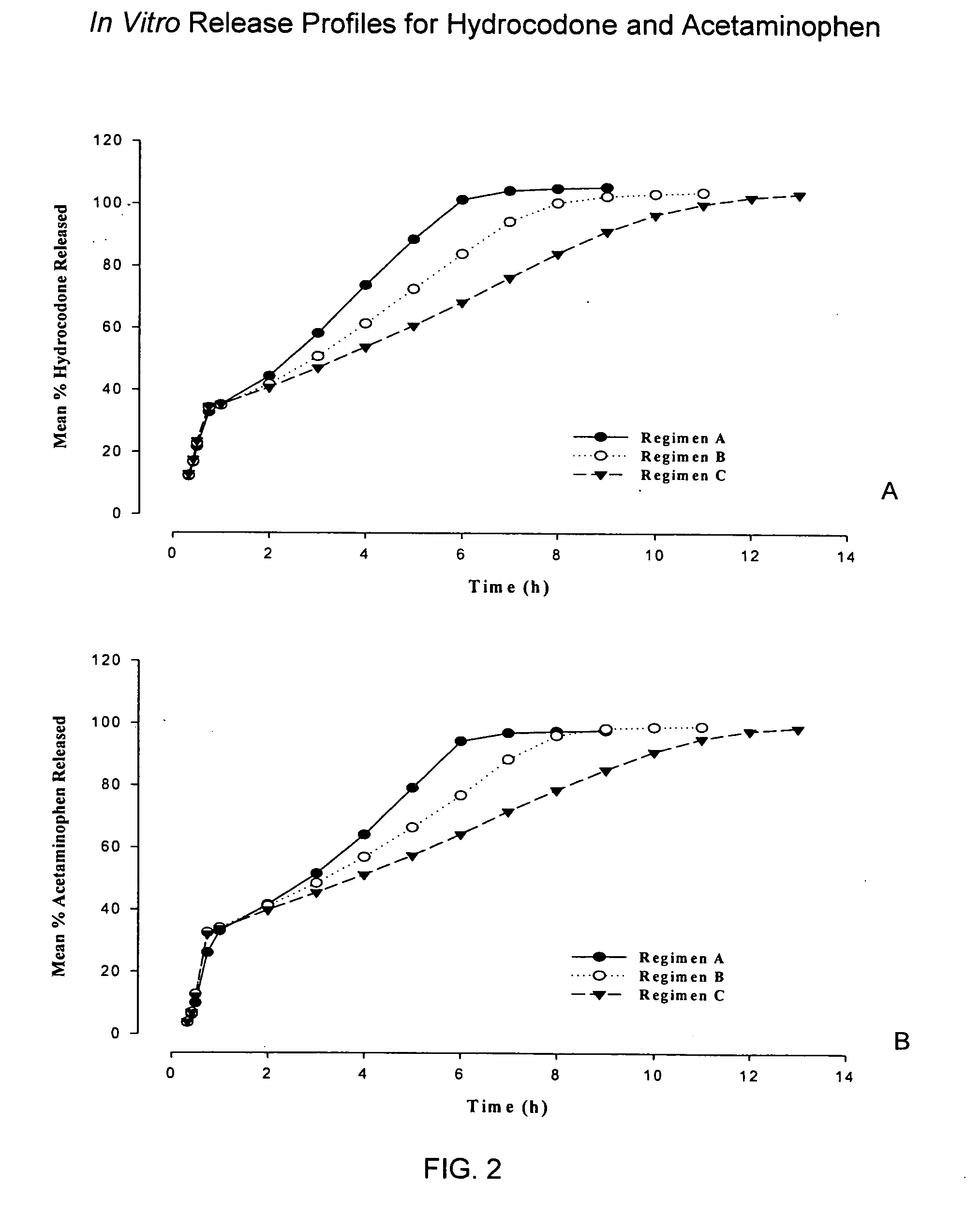
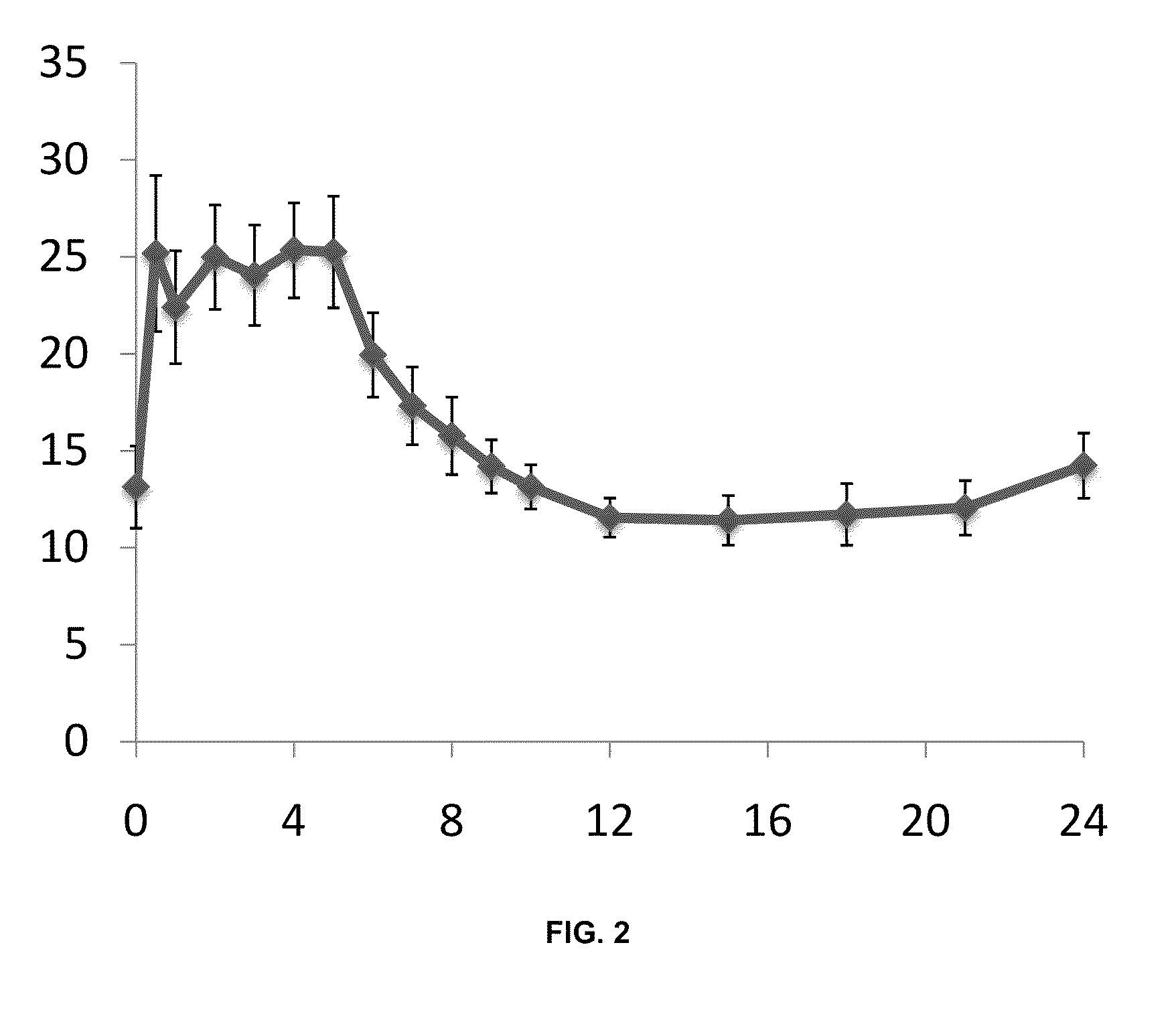
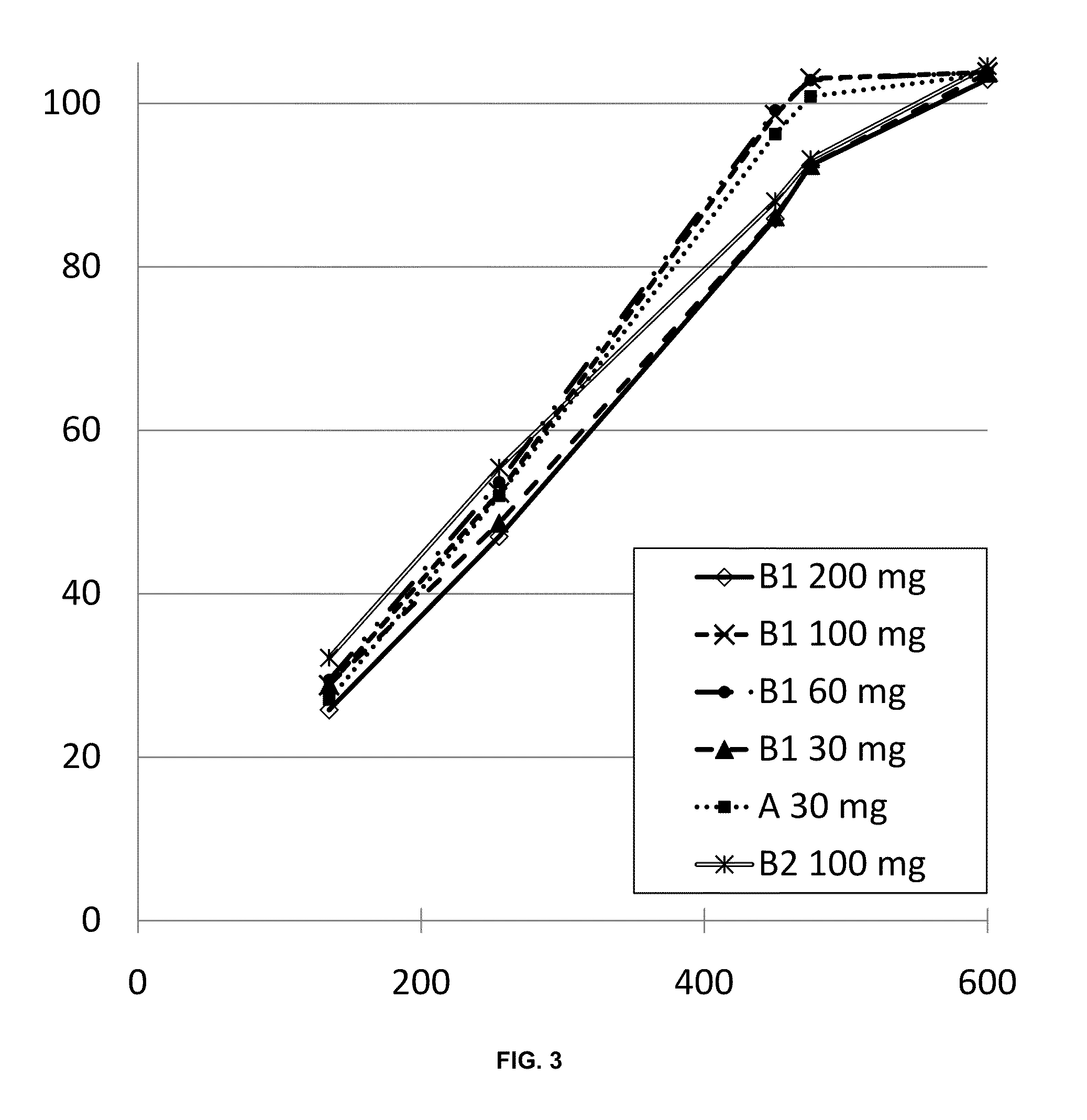
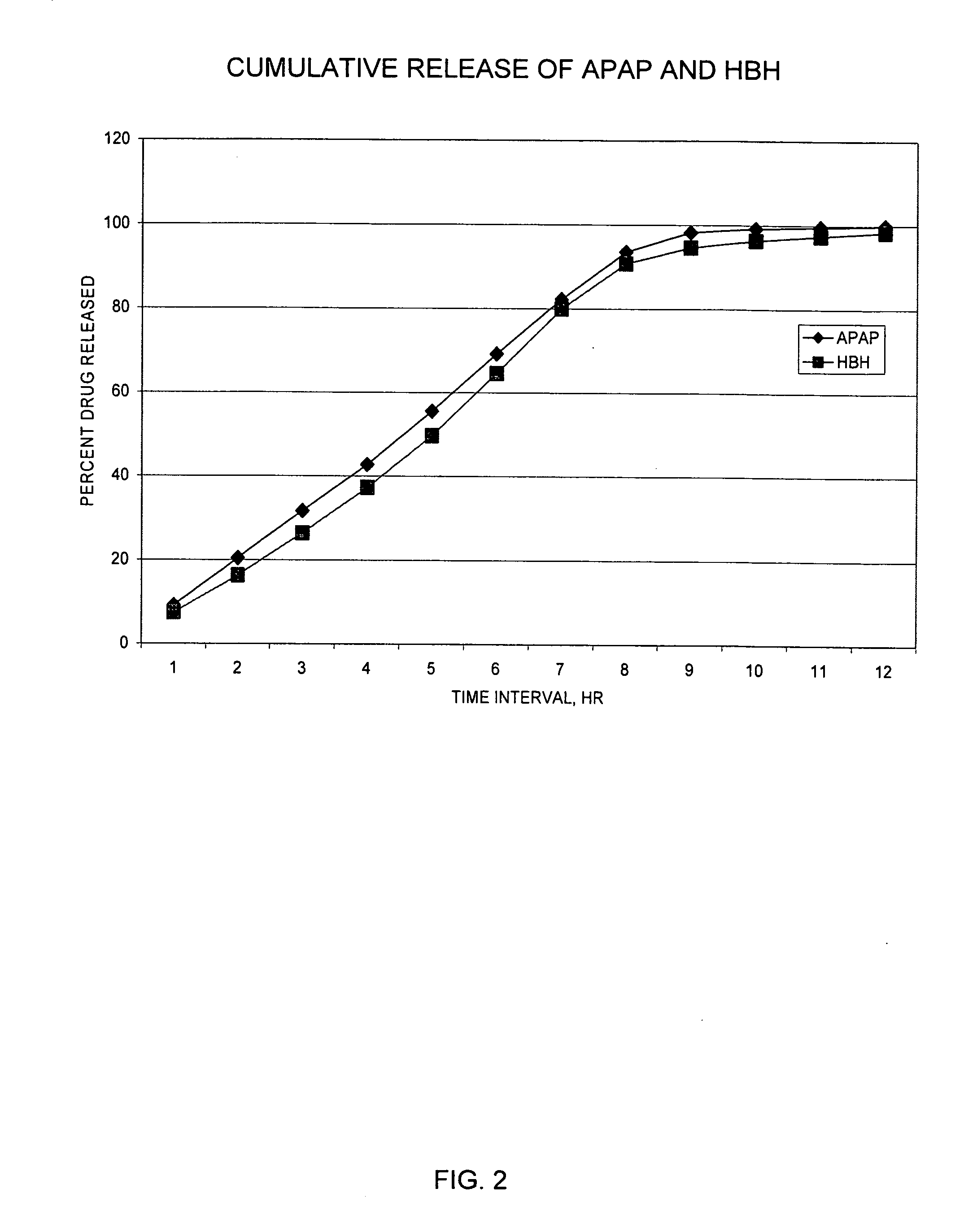
Sustained release dosage forms for twice daily oral dosing to a human patient for providing relief from pain are provided. The sustained release dosage form comprises an immediate release component and a sustained release component, wherein the immediate release component and the sustained release component collectively contain a therapeutically effective amount of an opioid analgesic and a therapeutically effective amount of nonopioid analgesic. In a preferred embodiment, the nonopioid analgesic is acetaminophen and the opioid analgesic is hydrocodone and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and in preferred embodiments, the pharmaceutically acceptable salt is bitartrate. The dosage forms produce plasma profiles in a patient characterized by a Cmax for hydrocodone of between about 0.6 ng / mL / mg to about 1.4 ng / mL / mg and an AUC for hydrocodone of between about 9.1 ng*hr / mL / mg to about 19.9 ng*hr / mL / mg (per mg hydrocodone bitartrate administered) and a Cmax for acetaminophen of between about 2.8 ng / mL / mg and 7.9 ng / mL / mg and an AUC for acetaminophen of between about 28.6 ng*hr / mL / mg and about 59.1 ng*hr / mL / mg (per mg acetaminophen administered) after a single dose.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Controlled release formulations coated with aqueous dispersions of acrylic polymers
InactiveUS6143353ADissolution stabilityIncrease weight gainPretreated surfacesMedical devicesWater insolubleActive agent
A stable solid controlled release formulation having a coating derived from an aqueous dispersion of a hydrophobic acrylic polymer includes a substrate including an active agent selected from the group consisting of a systemically active therapeutic agent, a locally active therapeutic agent, a disinfecting and sanitizing agent, a cleansing agent, a fragrance agent and a fertilizing agent, overcoated with an aqueous dispersion of the plasticized water-insoluble acrylic polymer. The formulation provides a stable dissolution of the active agent which is unchanged after exposure to accelerated storage conditions.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
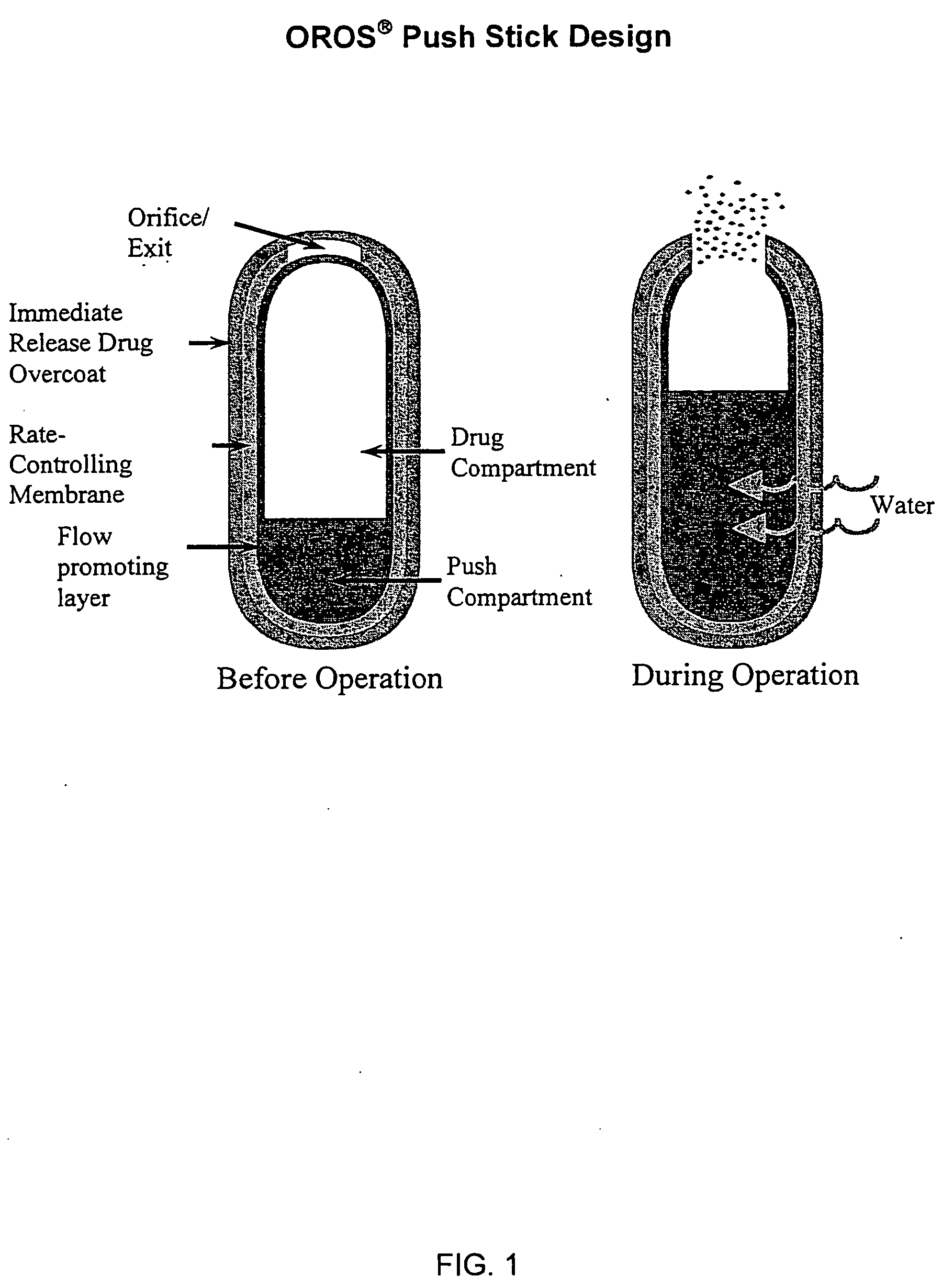
Controlled release formulations having rapid onset and rapid decline of effective plasma drug concentrations
InactiveUS6419960B1Patient compliance is goodGood retarding effectPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsImmediate releasePlasma drug concentration
The invention is directed to oral modified / controlled release drug formulations which provide a rapid initial onset of effect and a prolonged duration of effect. Preferably, the peak concentration is lower than that provided by the reference standard for immediate release formulations of the drug, and the duration of effect falls rapidly at the end of the dosing interval.
Owner:RHODES PHARMA LP
Controlled release formulations of opioid and nonopioid analgesics
InactiveUS20060251721A1Improved ability to treat painLess attentionBiocideNervous disorderImmediate releasePharmaceutical medicine
Sustained release dosage forms for twice daily oral dosing to a human patient for providing relief from pain are provided. The sustained release dosage form comprises an immediate release component and a sustained release component, wherein the immediate release component and the sustained release component collectively contain a therapeutically effective amount of an opioid analgesic and a therapeutically effective amount of nonopioid analgesic. In a preferred embodiment, the nonopioid analgesic is acetaminophen and the opioid analgesic is hydrocodone and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and in preferred embodiments, the pharmaceutically acceptable salt is bitartrate. The dosage forms produce plasma profiles in a patient characterized by a Cmax for hydrocodone of between about 0.6 ng / mL / mg to about 1.4 ng / mL / mg and an AUC for hydrocodone of between about 9.1 ng*hr / mL / mg to about 19.9 ng*hr / mL / mg (per mg hydrocodone bitartrate administered) and a Cmax for acetaminophen of between about 2.8 ng / mL / mg and 7.9 ng / mL / mg and an AUC for acetaminophen of between about 28.6 ng*hr / mL / mg and about 59.1 ng*hr / mL / mg (per mg acetaminophen administered) after a single dose.
Owner:ALZA CORP
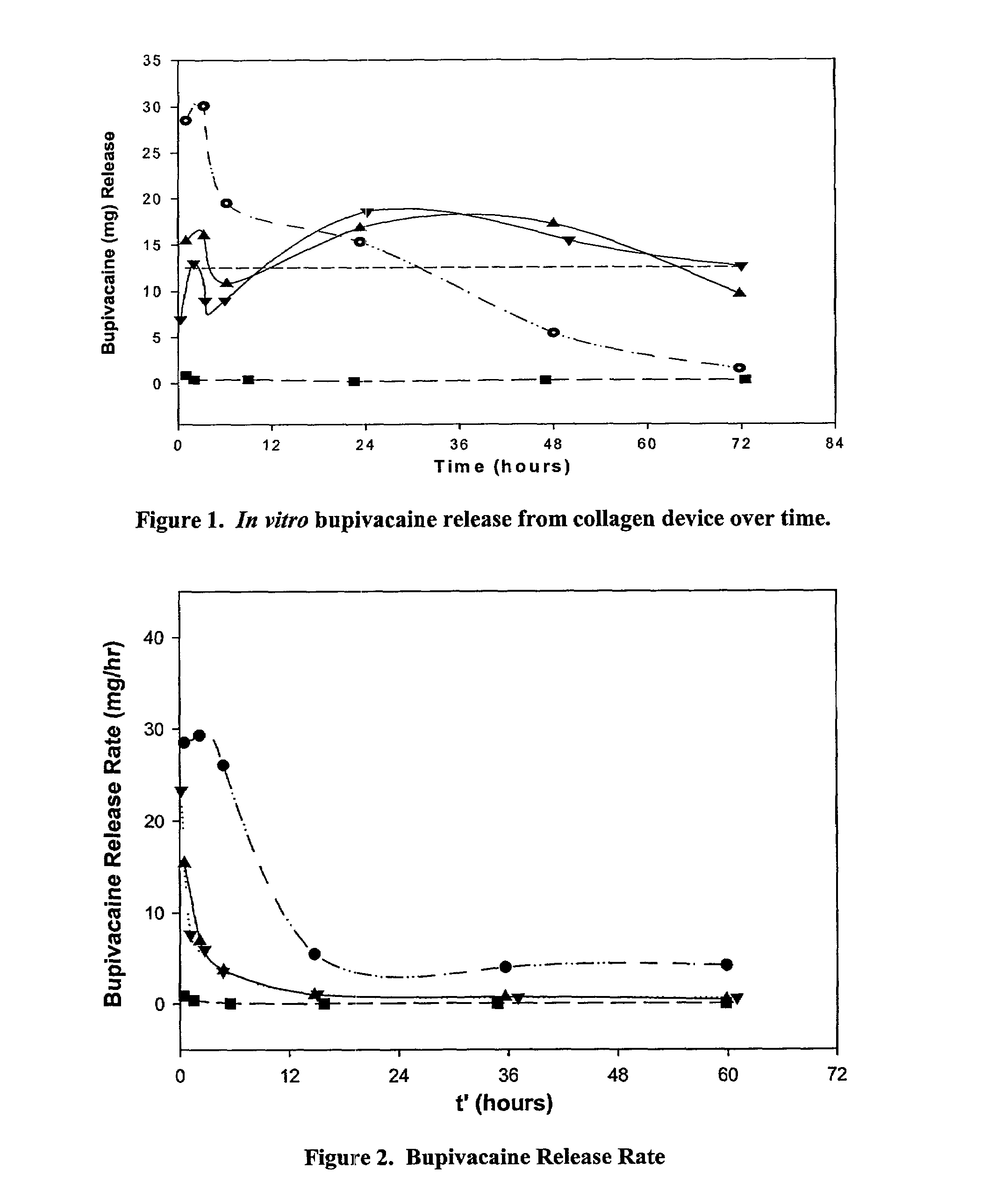
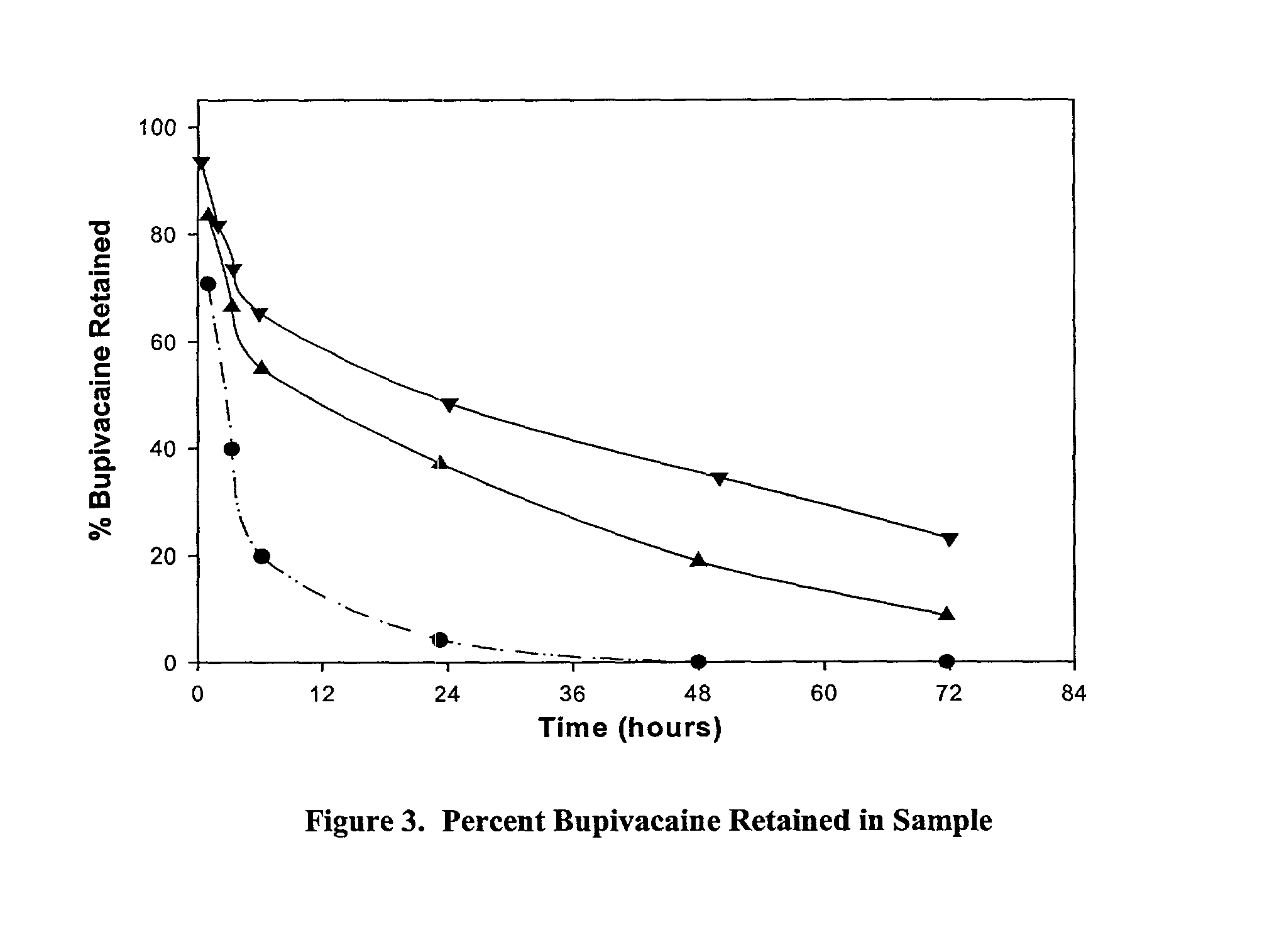
Methods and compositions for improved articular surgery using collagen
InactiveUS7119062B1Alleviate patient painShorten recovery timePeptide/protein ingredientsSurgerySide effectIncisional pain
The invention provides methods for treating post-surgical articular or incisional pain and / or discomfort in a patient. The invention further provides improved surgical methods and controlled release formulations for treating an articular injury of a joint in a patient, in which a collagen formulation is used in conjunction with a surgical procedure to treat the articular injury or the side effects of the surgical procedure. Collagen formulations of the invention and their use, in addition to the surgical procedure, may provide at least one or more of the following benefits: reduced patient pain, shortened recovery time and / or improved joint condition (including treatment of the underlying articular injury). Moreover, the methods and compositions of the invention can be used in conjunction with essentially any surgical procedure used to treat an articular injury. The invention further provides compositions and methods for treating post-surgical articular or incisional pain in a patient as well as a catheter for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:SURGICAL SPECIALTIES CORP LTD
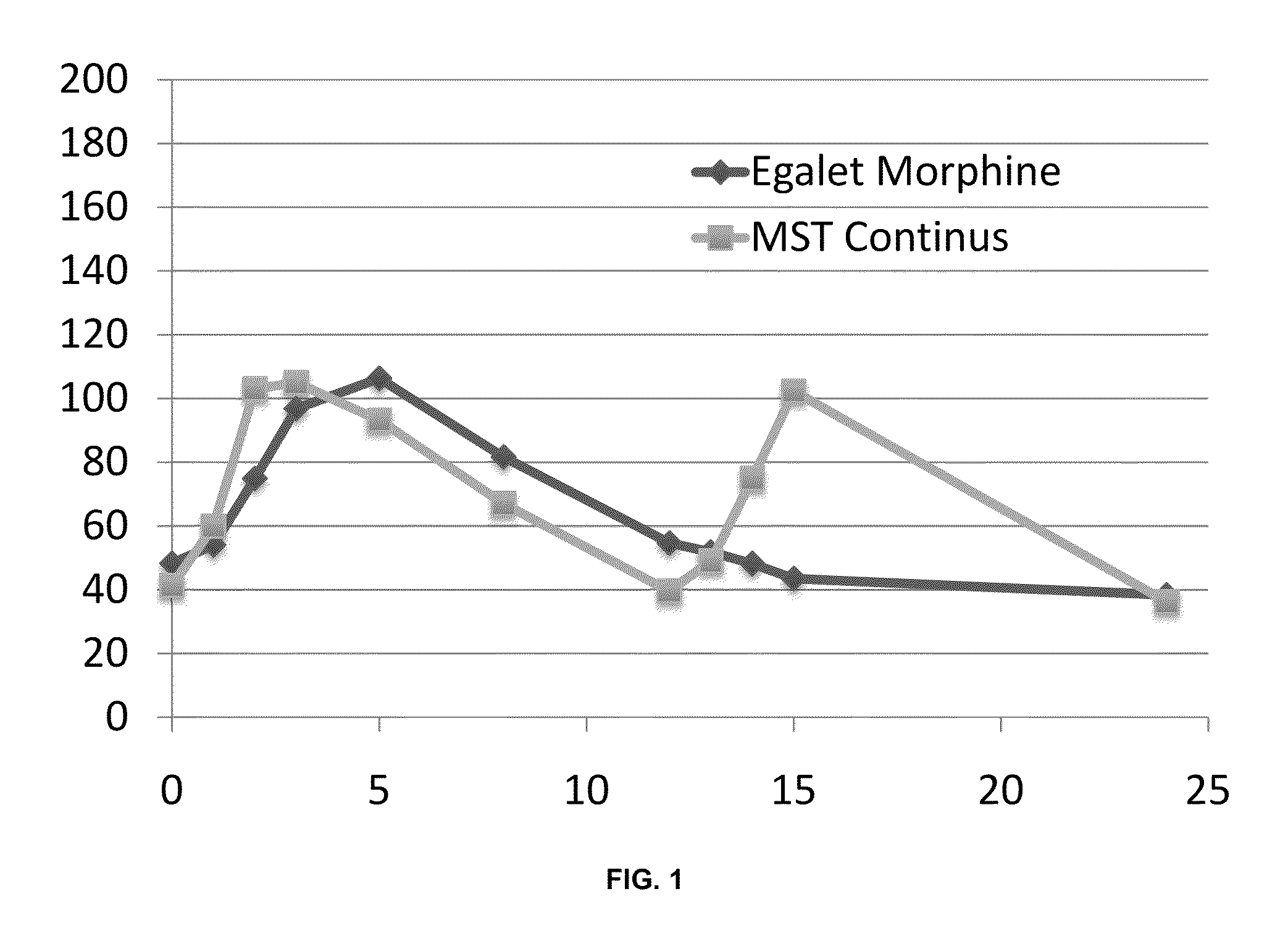
Controlled release formulations with continuous efficacy
InactiveUS20100203129A1Effective treatment regimenFacilitated releaseBiocidePowder deliveryControlled-Release FormulationsTreatment regimen
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions, which provide controlled release of a drug. The compositions are suitable for continuous administration as they remain effective throughout the treatment regimen. The present invention also relates to the use of the compositions for preparation of a medicament for continuous treatment of an individual.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Polymeric drug delivery system for hydrophobic drugs
InactiveUS20050249799A1Low oral bioavailabilityStable against aggregationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryHydrophobic polymerImmediate release
An oral delivery system for Class II drugs that have low oral bioavailability due to their insolubility in water and slow dissolution kinetics and method for making such a drug delivery system are disclosed herein. The formulation may be a controlled release or immediate release formulation. The immediate release formulation contains a Class II drug, together with a hydrophobic polymer, preferably a bioadhesive polymer. In one embodiment, the drug and polymer are co-dissolved in a common solvent. The solution is formed into small solid particles by any convenient method, particularly by spray drying. The resulting particles contain drug dispersed as small particles in a polymeric matrix. The particles are stable against aggregation, and can be put into capsules or tableted for administration. The controlled release formulations contain a BCS Class II drug and a bioadhesive polymer. The controlled release formulations may be in the form of a tablet, capsules, mini-tab, microparticulate, or osmotic pump. Enhancement of oral uptake of the drug from use of bioadhesive polymers occurs through (1) increased dissolution kinetics due to stable micronization of the drug, (2) rapid release of the drug from the polymer in the GI tract; and (3) prolonged GI transit due to bioadhesive properties of the polymers. The combination of these effects allows the preparation of a compact, stable dosage form suitable for oral administration of many class II drugs.
Owner:SPHERICS
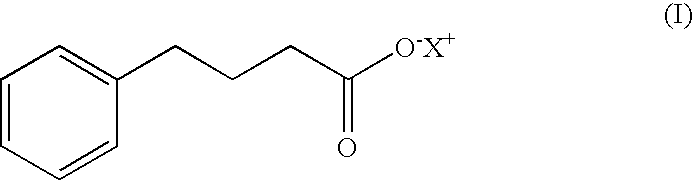
4-phenylbutyric acid controlled-release formulations for therapeutic use
InactiveUS20060045912A1Low costReduce the amount requiredBiocideNervous disorderHalf-lifeNeuro-degenerative disease
Controlled-release formulations and dosage forms containing 4-phenylbutyric acid sodium salt, or other pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters or prodrugs, and a controlled release material for use in the treatment of diseases and disorders including neoplastic disorders and neurodegenerative diseases The formulations provide extended release and extended half-life.
Owner:LUNAMED
Controlled Release Formulations
InactiveUS20080057123A1Modulate release of the active agentBiocideAnimal repellantsActive agentCentral layer
Controlled release oral dosage formulations containing one or more active agent, and methods of use thereof, are provided for the once-a-day treatment. The formulation can be in the form of a trilayer tablet containing a core or central layer and one or more barrier layers. The core may contain one or more enteric materials or polymeric materials which modulates the release of the active agent.
Owner:JAGOTEC AG
Misuse Preventative, Controlled Release Formulation
ActiveUS20090175937A1Control releasePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsActive agentMicroparticle
Disclosed is a misuse preventative, controlled release formulation comprising a core comprising a superabsorbent material (for example, polycarbophil), a controlled release coat surrounding the core, and a plurality of controlled release microparticles having a pharmaceutically active agent (for example, an opioid analgesic) disposed within the core, the coat, or both the core and the coat. When crushed, either intentionally or accidentally, and exposed to an aqueous medium, the superabsorbent material present in the core swells to encapsulate the microparticles, which remain substantially intact thereby retarding the release of the pharmaceutically active agent from the formulation. Also disclosed is a method of using the misuse preventative, controlled release formulation to deliver a pharmaceutically active agent to a mammal, for example, a human, in need thereof.
Owner:LABOPHARM BARBADOS LTD 36646
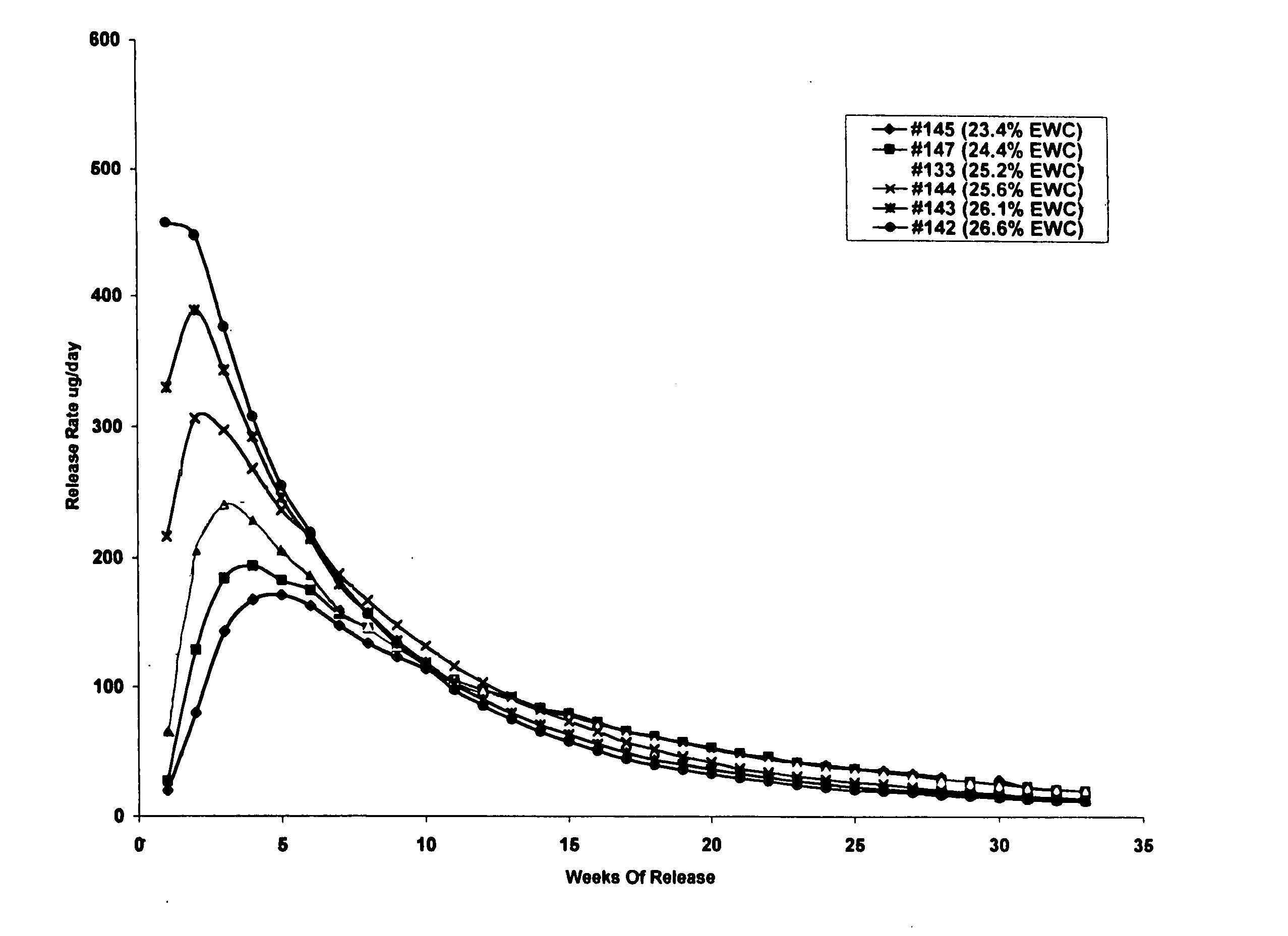
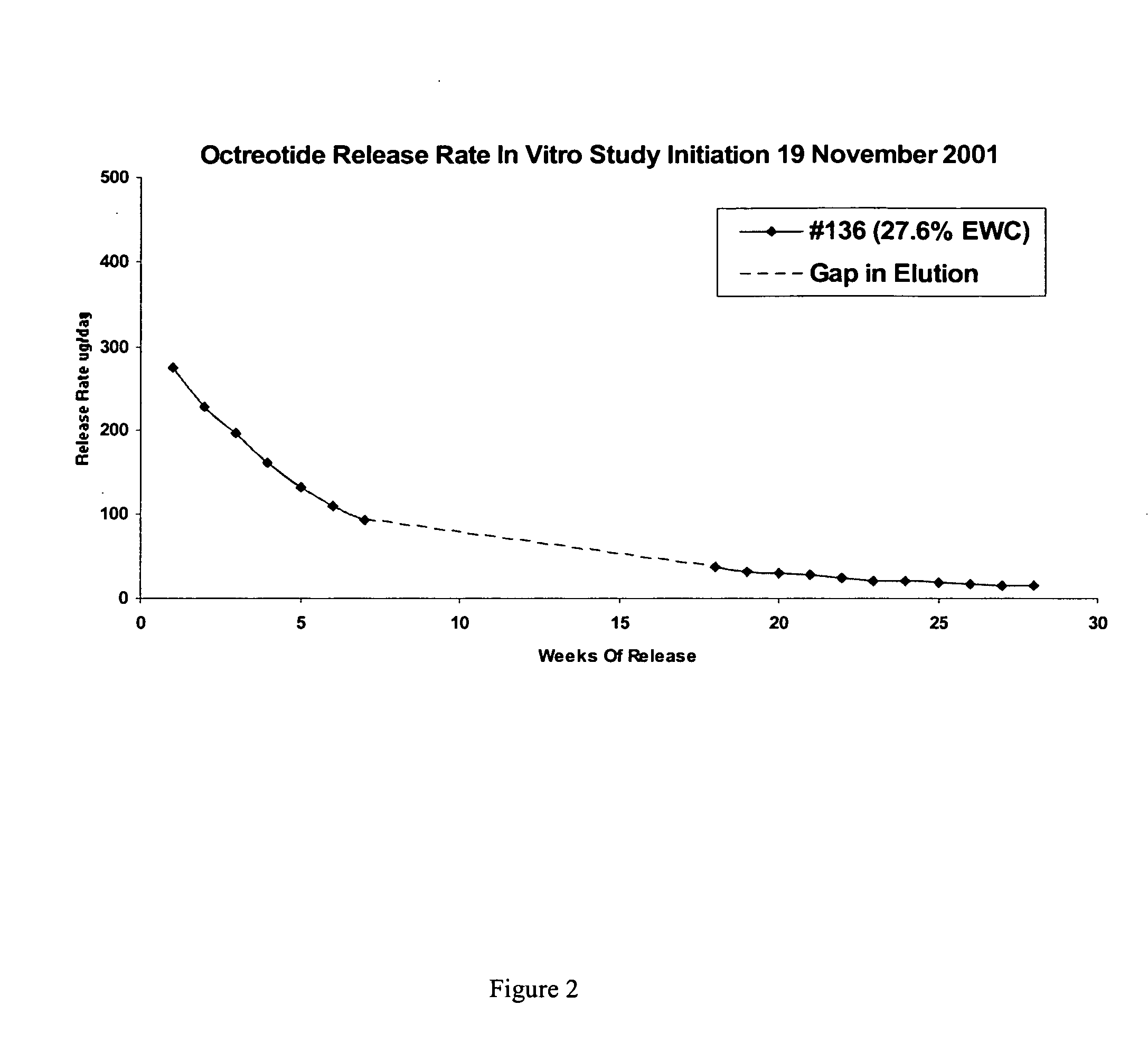
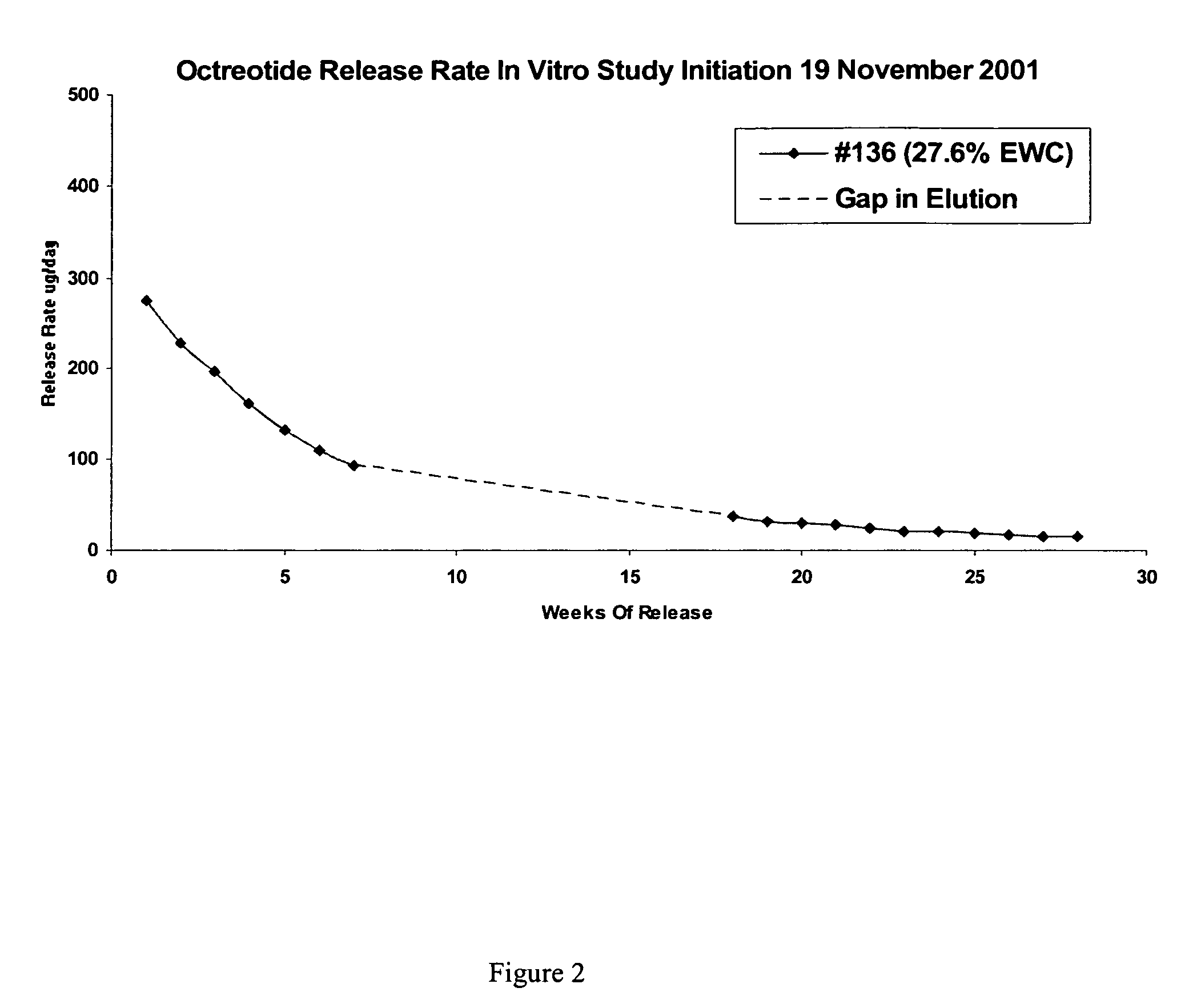
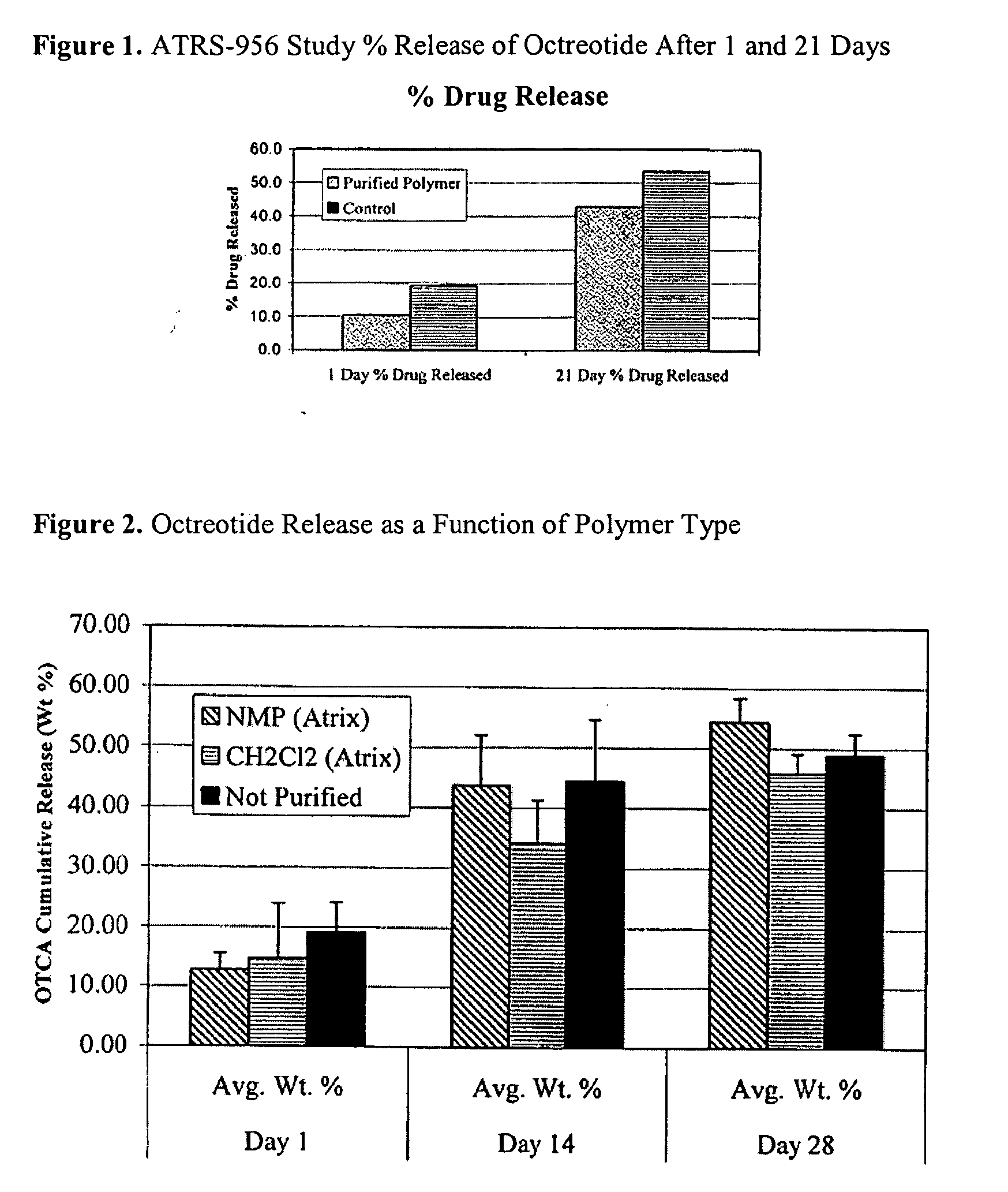
Controlled release formulations of octreotide
ActiveUS20060204540A1Avoid large peakImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAcromegalyMalignant carcinoid tumors
A formulation of octreotide or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, which provides controlled release of a therapeutically effective amount of octreotide for a period of at least about two months. Methods of treating acromegaly, decreasing growth hormone, decreasing IGF-1, and treating conditions associated with carcinoid tumors and VIPomas by administering a controlled release formulation of octreotide are provided herein.
Owner:ENDO PHARMA SOLUTIONS
Controlled Release Formulations and Associated Methods
A pharmaceutical formulation having a geometric configuration that affects the release characteristics of active agents contained therein and associated methods are provided. In one aspect, a sustained release oral dosage pharmaceutical tablet may include a first layer having a first active agent, where the first layer is disposed between two adjacent controlled release layers, at least one of the adjacent layers including at least one second active agent. The two adjacent layers are arranged such that they cover a portion of the first layer. The two adjacent layers may be separate layers or they may be joined into a single continuous layer, depending on the overall configuration and geometric design of the oral dosage form.
Owner:WATSON LAB INC
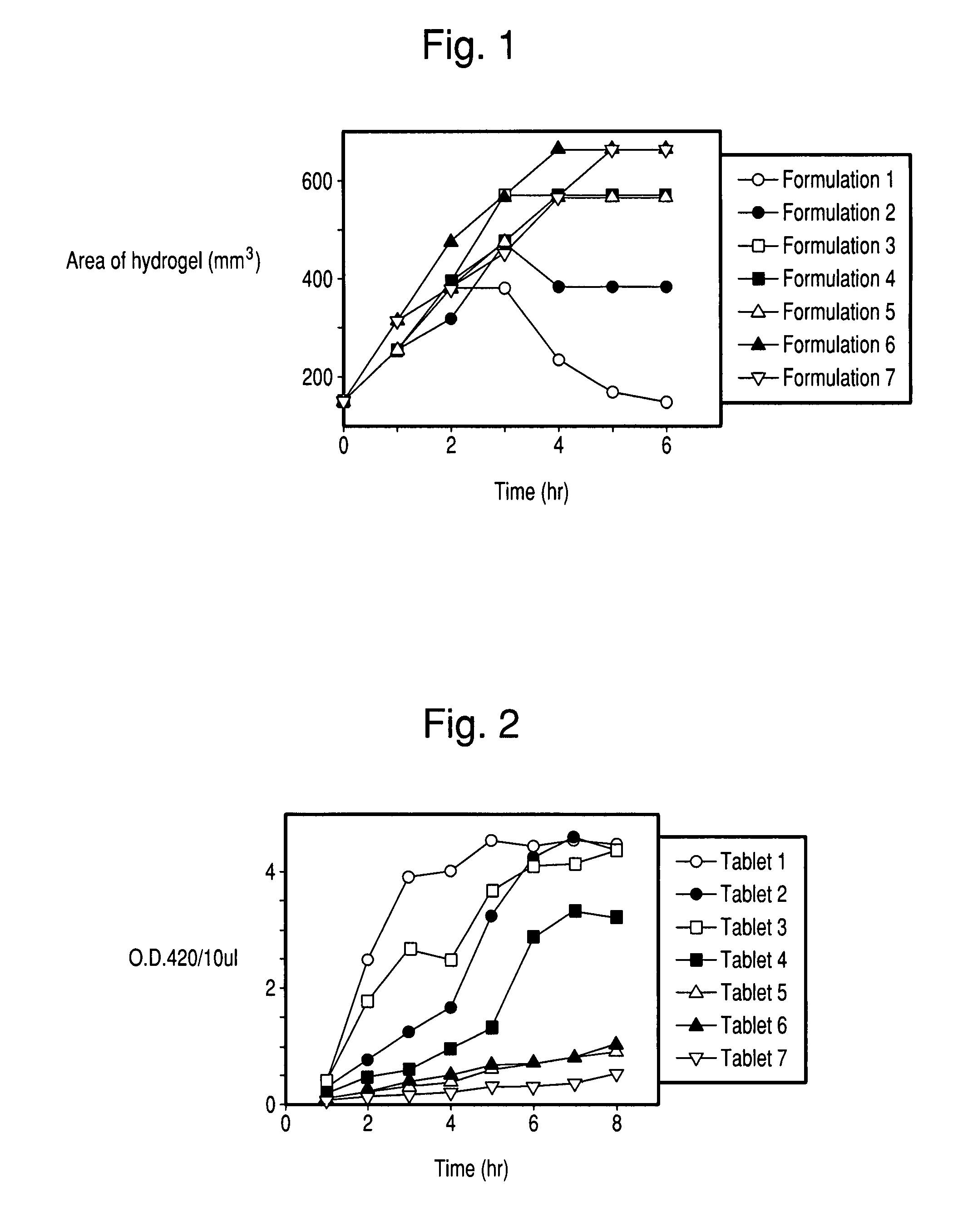
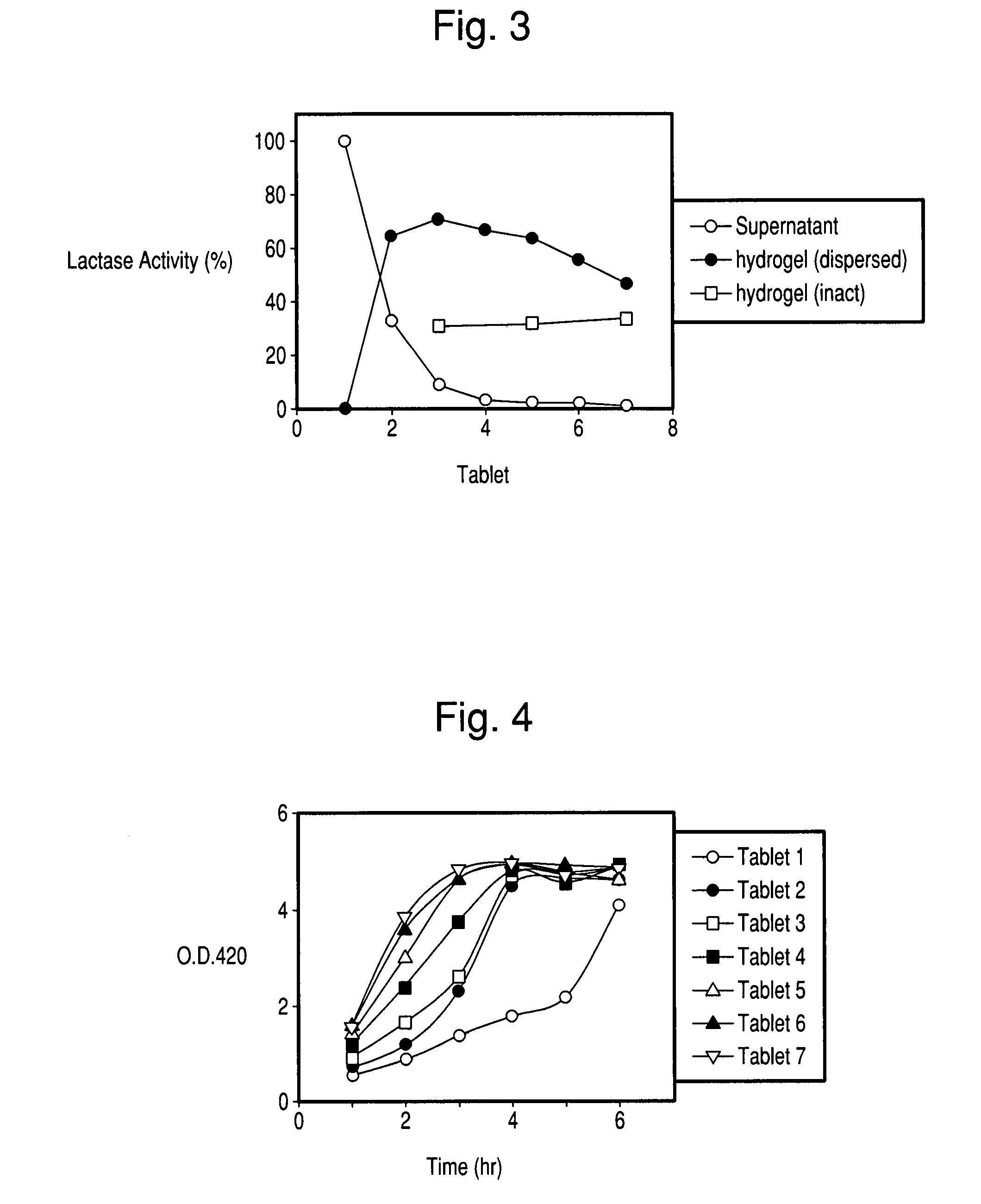
Controlled release formulations of enzymes, microorganisms, and antibodies with mucoadhesive polymers
InactiveUS20080020036A1Easy to exportDisintegrates quicklyPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismWater soluble
There is provided a composition comprising at least one mucoadhesive polymer that is capable of forming a hydrogel and at one least water soluble polymer, and one or more enzymes, microorganisms, or antibodies. The formulation forms a hydrogel in aqueous solution that has mucoadhesive properties and that is capable of releasing the enzymes, microorganisms, or antibodies over an extended period of time and / or of entrapping enzymes, microorganisms, or antibodies within the hydrogel that is active for an extended time.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME USA CO LTD +1
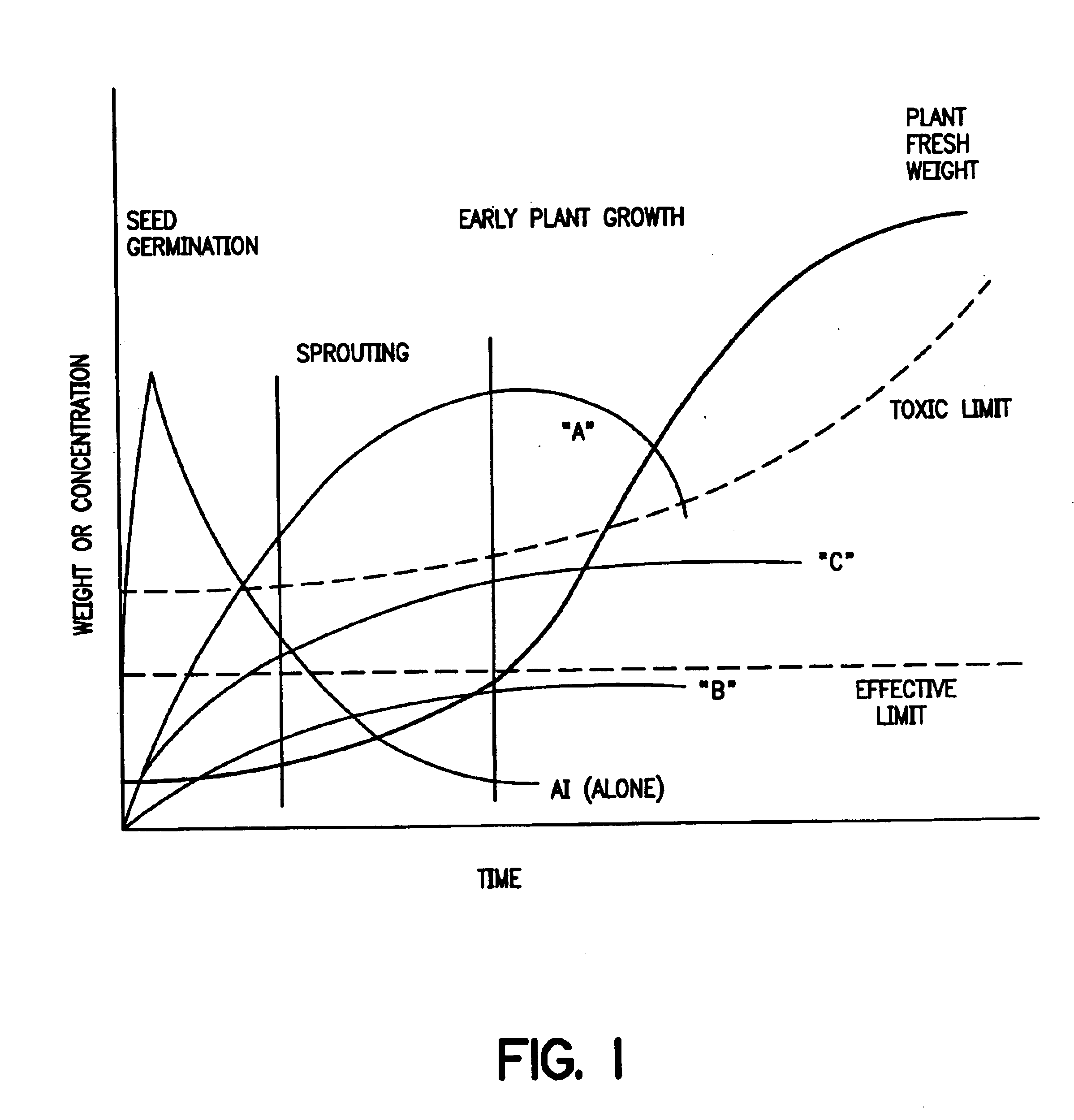
Controlled release formulations and methods for their production and use
Controlled release formulations for pesticides and herbicides contain an active ingredient, a matrix polymer and a matrix polymer plasticizer which is present in an amount sufficient to provide a release rate for the active ingredient from the formulation that matches a selected release rate. Methods for making and using the formulation, and seeds and plants that have been treated with the formulations are also included.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Microencapsulated and controlled-release formulations of isoflavone from enriched fractions of soy and other plants
InactiveUS6890561B1Facilitate user complianceMaintain activityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAdditive ingredientBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
There is provided an orally-administrable formulation for the controlled release or stable storage of a granulated isoflavone-enriched fraction or mixture of such fractions, comprising at least one granulated isoflavone-enriched fraction and at least one carrier, diluent or excipient therefor. Preferably, the formulation is characterized in that the total in vitro dissolution time of said formulation required for release of 75% of the active ingredients available from the formulation is between about 4 and about 18 hours, as determined by the U.S.P. XXIII paddle method at a paddle speed of 75 rpm, using simulated intestinal fluid without the digestive enzymes normally found in intestinal fluid, at pH 6.8, and a temperature of 37° C. A process for the preparation of such a formulation is also provided.
Owner:LYCORED BIO
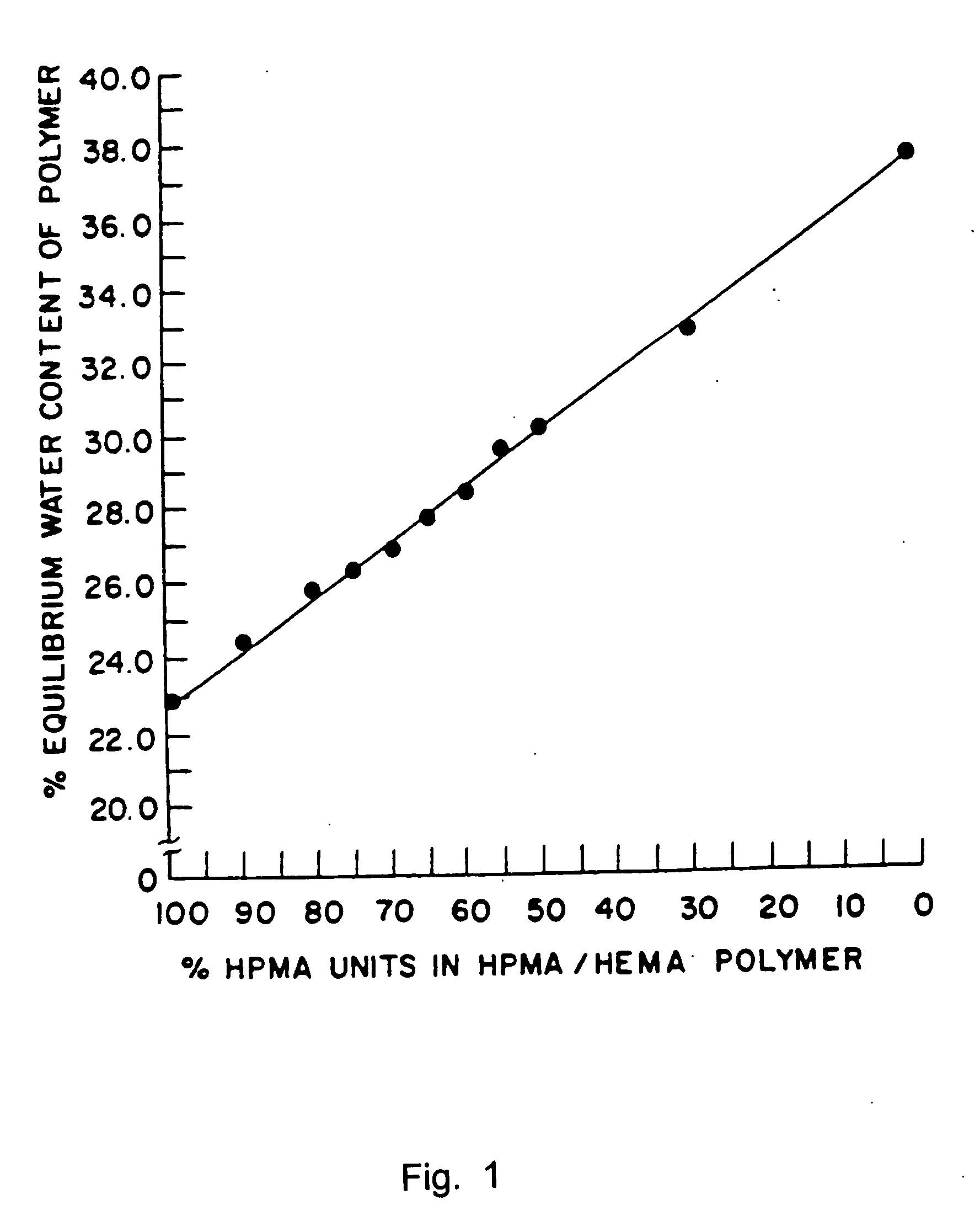
Controlled release formulations using intelligent polymers
InactiveUS6893661B1Promote absorptionMaintenance of therapeutically effective blood levelPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSmart polymerWater contact
An extended release dosage composition of pharmaceutically active substances that have a water contact angle (θ) such that cos θ is between +0.9848 and −0.9848 presented as a matrix tablet containing the said pharmaceutically active substances, with / without suitable pharmaceutical excipients in intimate mixture with two groups of intelligent polymers having opposing wettability characteristics, one demonstrating a stronger tendency towards hydrophobicity and the other a stronger tendency towards hydrophilicity, the polymer combination being between the ratios of 1:50 and 50:1 amounts effective to control the release of said pharmaceutically active substances in a mathematically predictable manner, wherein the polymer demonstrating a stronger tendency towards hydrophobicity is not less than 5% wt / wt and preferably between 5-70% wt / wt of the final formulation composition. The intelligent polymers being ethylcellulose (EC) as a more strongly hydrophobic and hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) and / or hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) as more strongly hydrophilic (the ratio of HEC to HPMC being between 1:100 and 100:1). The matrix tablet is optionally coated with an enteric coat, 0-5%-15% wt / wt to prevent the initial burst effect seen in such systems and to impart gastrointestinal tract (GIT) “stealth” characteristics especially in the presence of food.
Owner:VALEANT INT BERMUDA
Controlled release formulations for the delivery of HIF-1 inhibitors
ActiveUS8962577B2Controlled drug and drug release profileReduce solubilityBiocidePowder deliveryDiseaseSide effect
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Oral extended-release composition
InactiveUS20050064034A1Antibacterial agentsPowder deliveryControlled-Release FormulationsExtended release
The invention is directed to controlled release formulations containing drugs which are preferably considered sparingly soluble to insoluble and which are suitable for administration to a patient in need of treatment related thereto, and methods of manufacturing the same.
Owner:ANDRX PHARMA INC
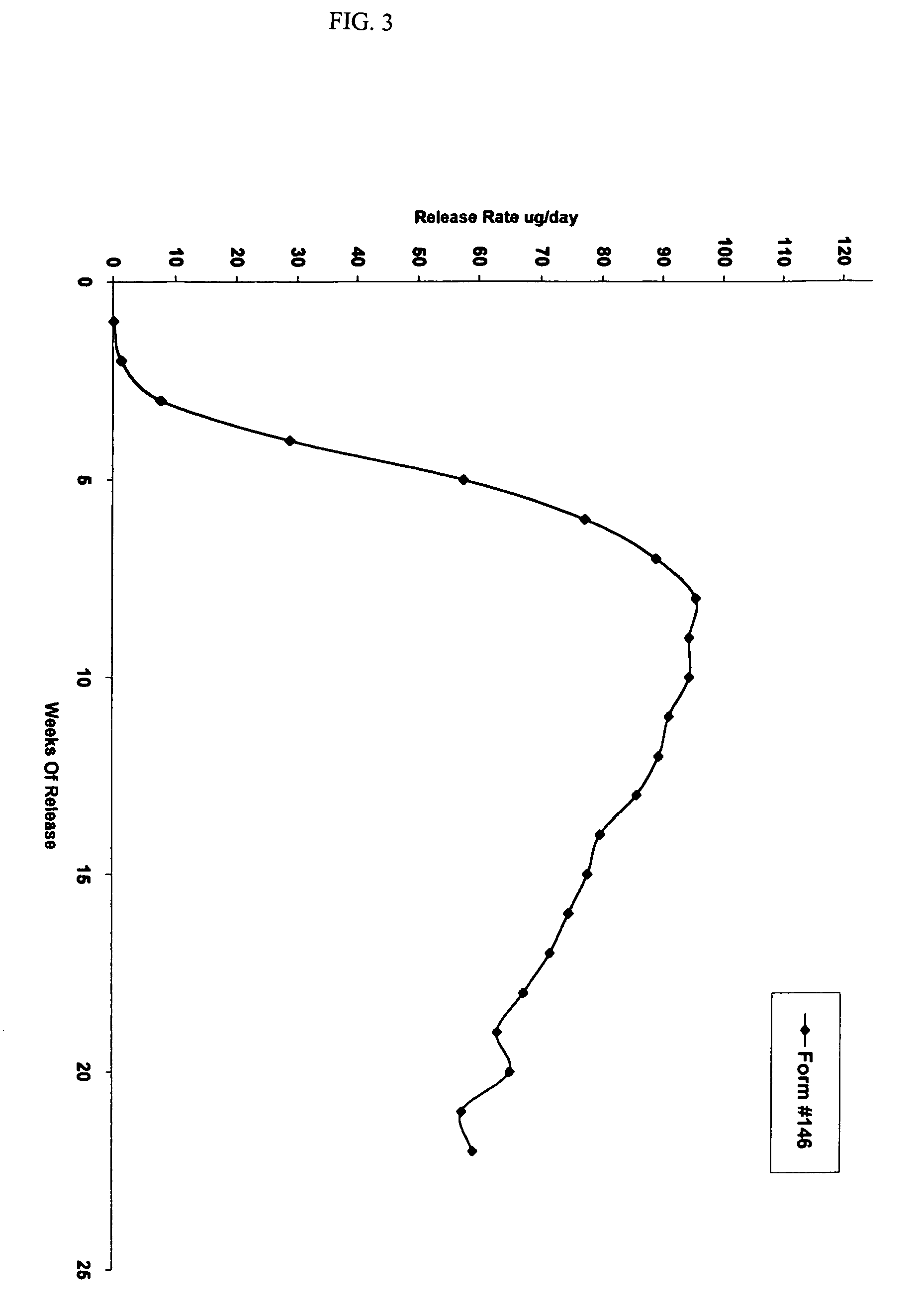
Controlled release formulations of octreotide
ActiveUS7452868B2Reduce needLower Level RequirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAcromegalyMalignant carcinoid tumors
Owner:ENDO PHARMA SOLUTIONS
Controlled release formulations exhibiting an ascending rate of release
InactiveUS20070259033A1Low profileReduce solubilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSustained release drugActive agent
A sustained release dosage form is comprising a pharmaceutically active agent and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and adapted to release as an erodible solid over a prolonged period of time, wherein the dosage form provides an ascending rate of release of the pharmaceutically active agent for at least about 4 hours. The dosage form is able to deliver high doses of poorly soluble or slowly dissolving active agents. When additional pharmaceutically active agents are present, the agents are released from the dosage form at rates that are proportional to the respective weights of each active agent in the dosage form. Methods of using the dosage forms to treat disease or conditions in human patients are also disclosed.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Controlled release of chemical admixtures
InactiveUS7879146B2Improved modulation of slump lossImprove performanceSolid waste managementChemical admixtureSuperplasticizer
A controlled release formulation for a cement-based composition can be produced by intercalating an admixture (e.g. an accelerator, a set retarder, a superplasticizer) for the cement-based composition into a layered inorganic material (e.g. a layered double hydroxide (LDH)). A cement-based composition containing a cement-based material (e.g. cement, mortar or concrete) and such a controlled release formulation has better workability, especially in respect of slump-loss characteristics. With such a formulation release of an admixture in a cement-based composition may be controlled.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Alcohol resistant dosage forms
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
Controlled release formulations and methods for their production and use
Controlled release formulations for pesticides and herbicides contain an active ingredient, a matrix polymer and a matrix polymer plasticizer which is present in an amount sufficient to provide a release rate for the active ingredient from the formulation that matches a selected release rate. Methods for making and using the formulation, and seeds and plants that have been treated with the formulations are also included.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
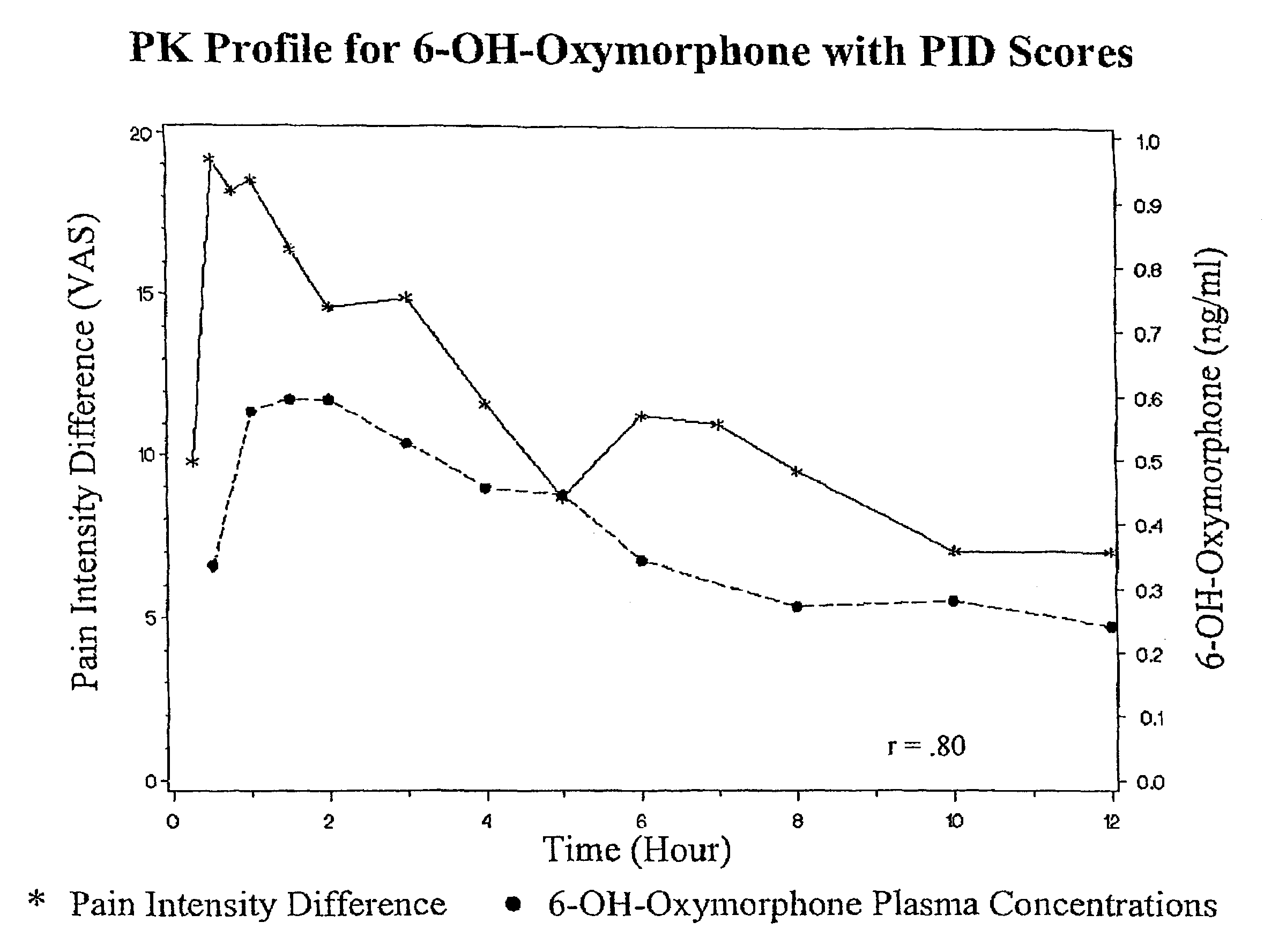
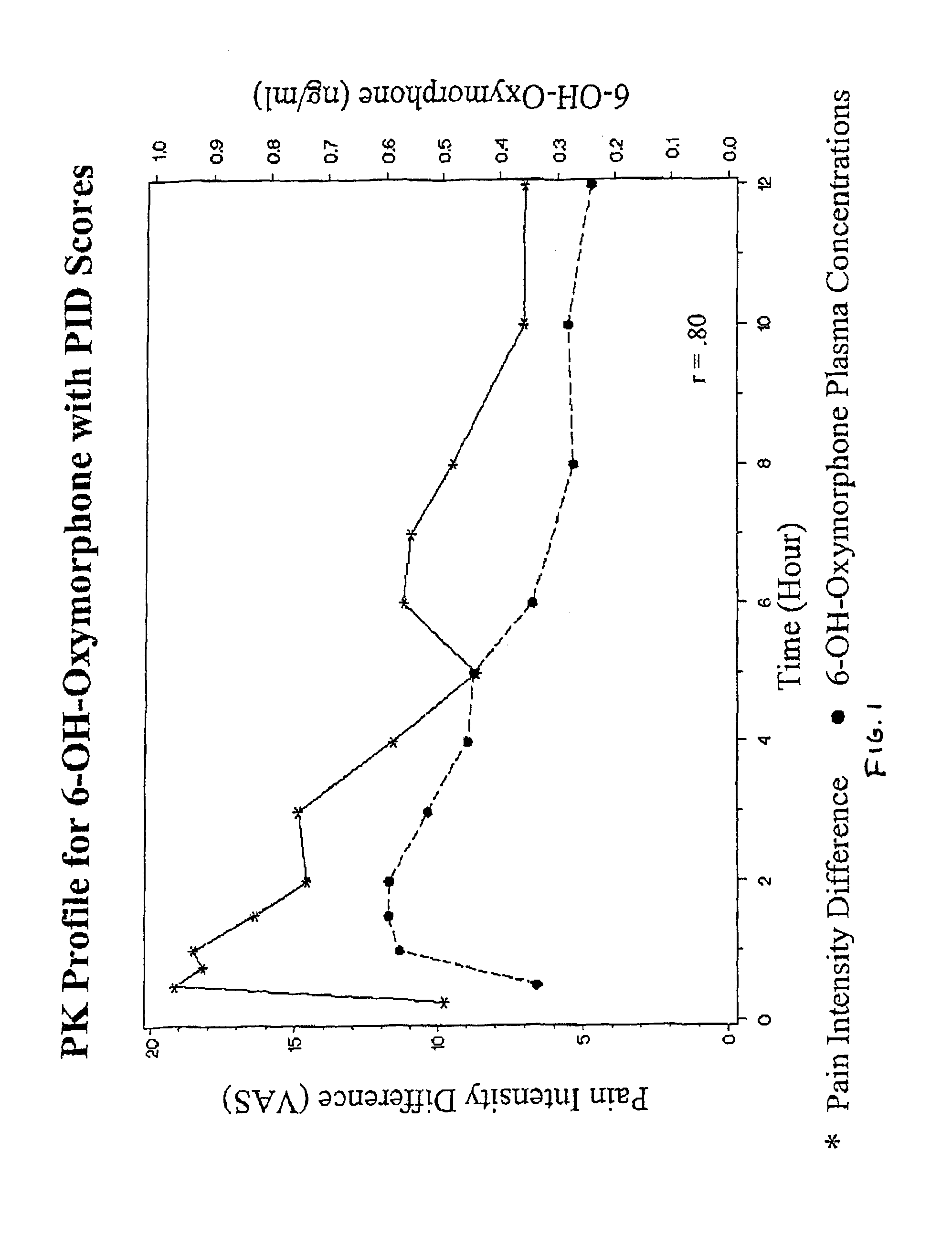
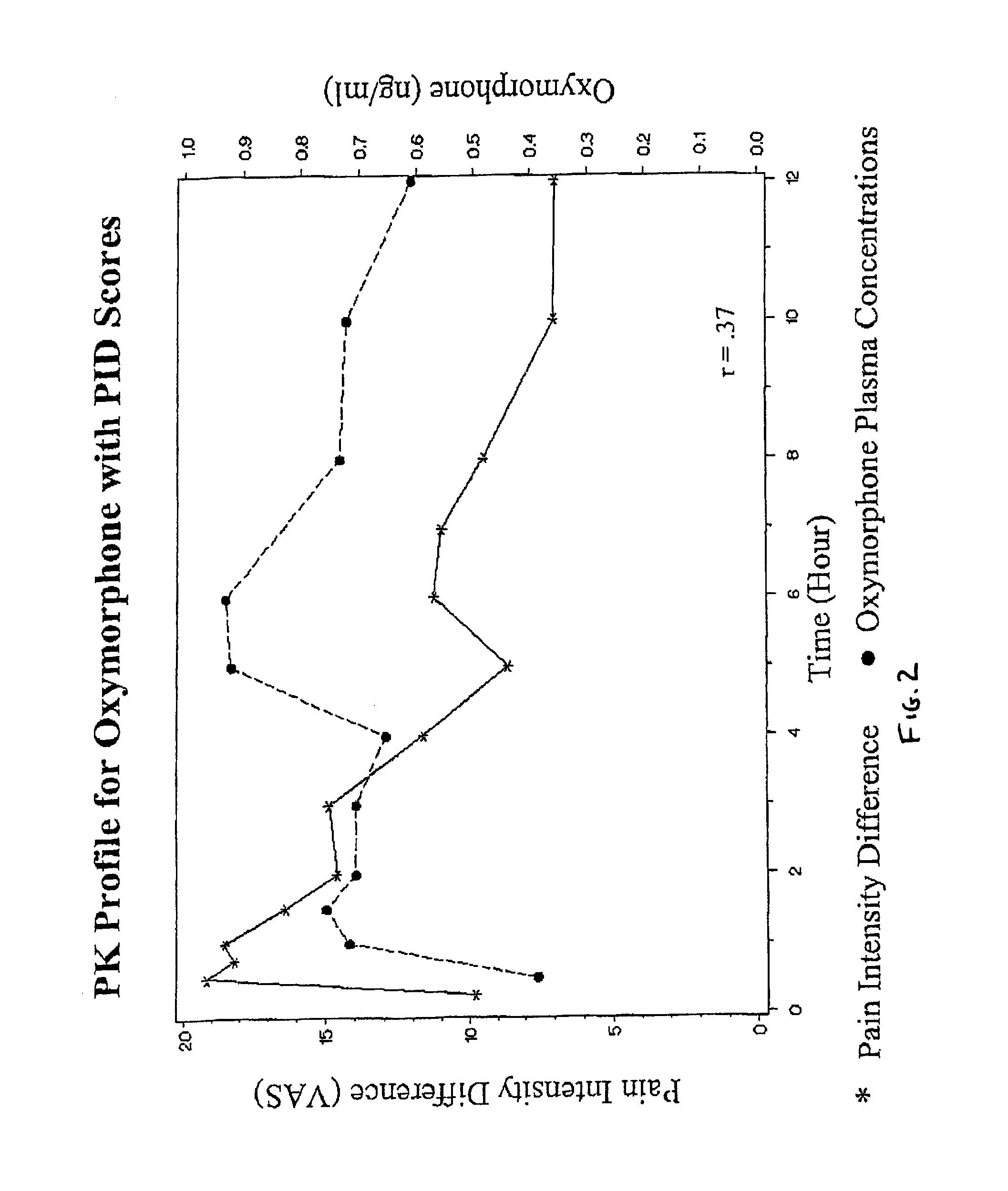
Oxymorphone controlled release formulations
The invention pertains to a method of relieving pain by administering a controlled release pharmaceutical tablet containing oxymorphone which produces a mean minimum blood plasma level 12 to 24 hours after dosing, as well as the tablet producing the sustained pain relief.
Owner:ENDO PHARMA INC
Method for the preparation of controlled release formulations
ActiveUS20060228414A1Prevent degradationReducing and preventing degradationBiocideNanotechActive agentPolymer chemistry
The methods disclosed herein are of use for the production of controlled release compositions. In particular, the methods provide the contacting of an organic phase containing a bioactive agent and a polymer with an aqueous phase containing an organic ion to create controlled release compositions containing bioactive agents. The present invention also includes controlled release compositions including a polymer, an organic ion and a bioactive agent. The present invention also includes methods of using such controlled release compositions. The usefulness of the present invention is that the methods result in the production of controlled release compositions containing bioactive agent capable of administration in a concentrated low-dose form, having low burst and reduced production of degraded bioactive agent.
Owner:PR PHARMA +1
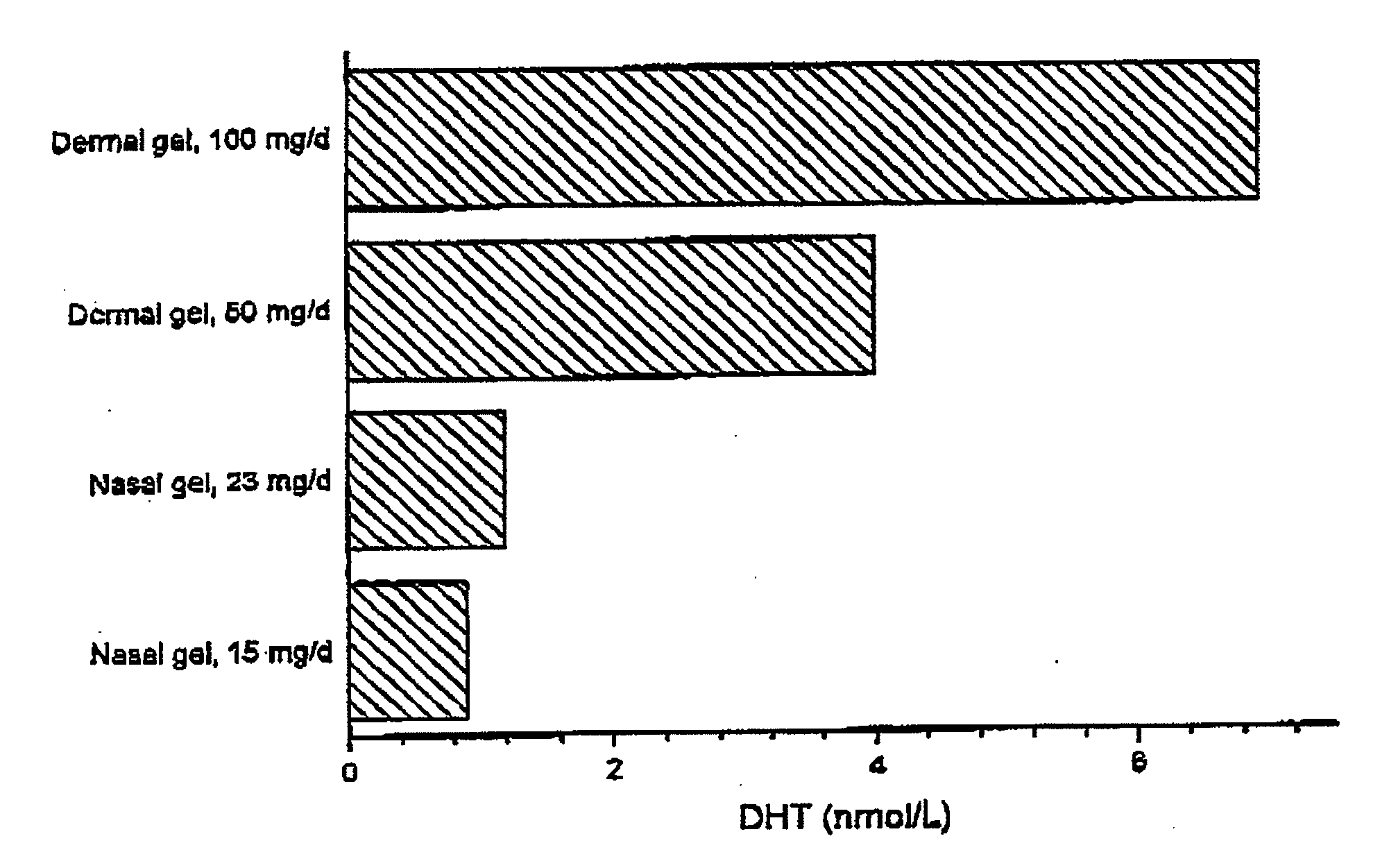
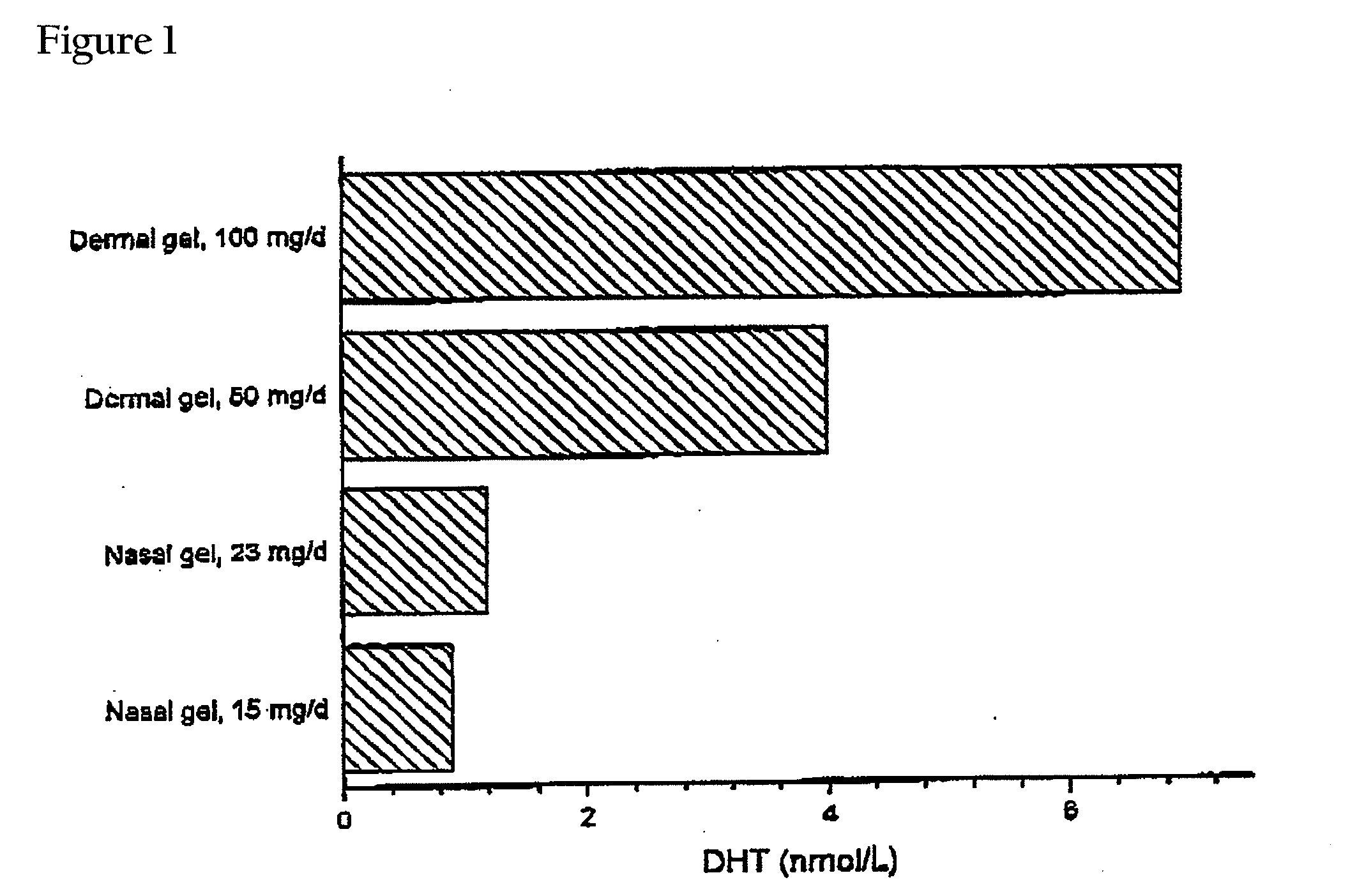
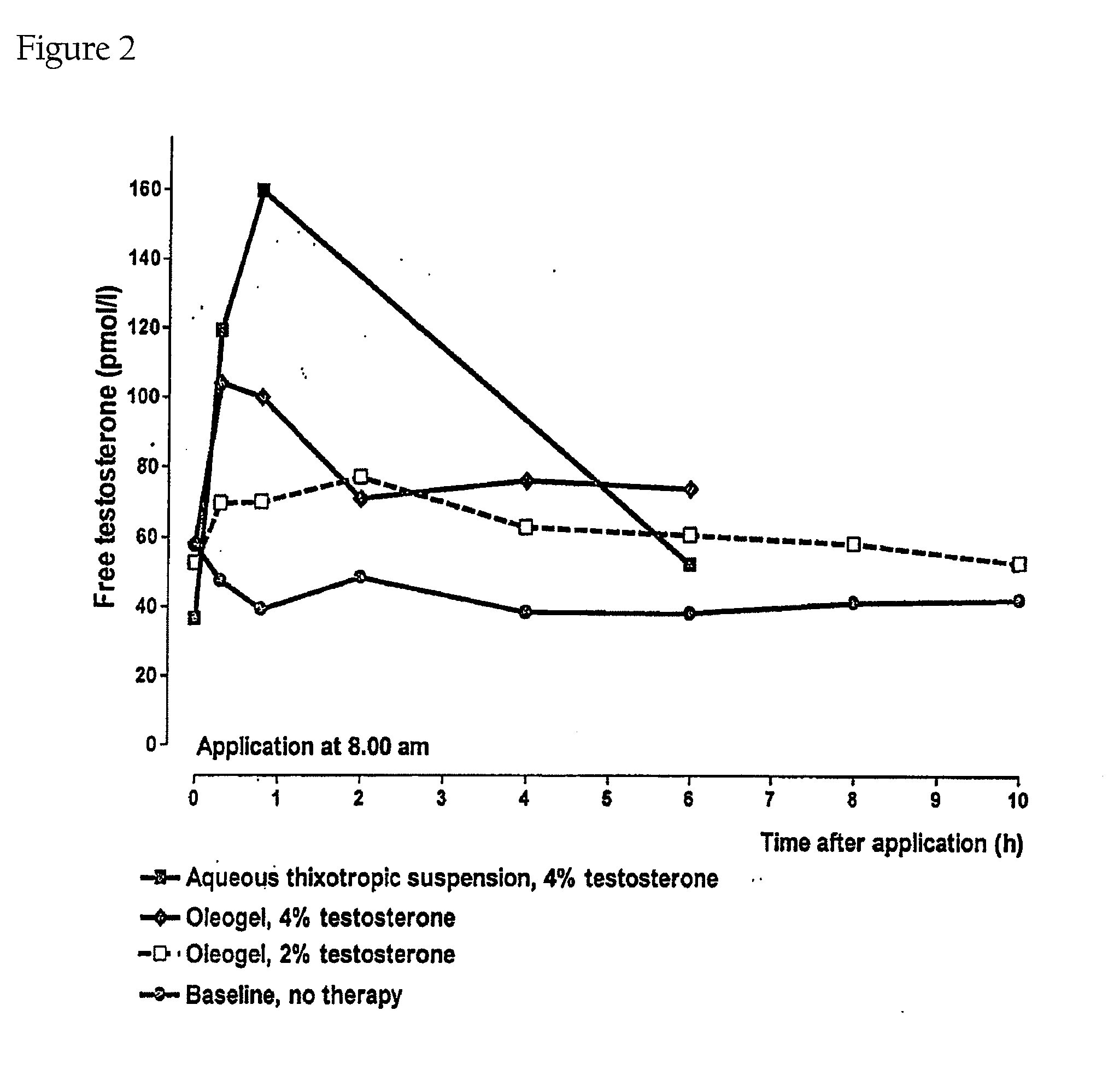
Controlled Release Delivery System for Nasal Applications and Method of Treatment
InactiveUS20070149454A1Improve bioavailabilityImproved profileOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFemale Sexual Arousal DisorderNasal cavity
This invention relates to a gel formulation for nasal administration of a controlled release formulation of hormones to the systemic circulation and / or to the brain. The special lipophilic or partly lipophilic system of the invention leads to higher bioavailability of the active ingredient caused by sustained serum levels in plasma but also leads to a more favorable serum level profile. The special lipophilic or partly lipophilic system also allows for the modulation of brain functioning. The invention also relates to the nasal administration of steroid hormones for treatment of female sexual dysfunction (FSD) or female arousal disorder.
Owner:MATTERN PHARMA
Low burst polymers and methods to produce polymer
ActiveUS20100292195A1Increase release rateReduced initial burstAntibacterial agentsBiocideDrug biological activityCopolymer
A PLG copolymer material, termed a PLG(p) copolymer material, adapted for use in a controlled release formulation for a bioactive material is provided, wherein the formulation exhibits a reduced “initial burst” effect when introduced into the tissue of a patient in need thereof. A method of preparation of the PLG copolymer material is also provided, as are methods of use.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
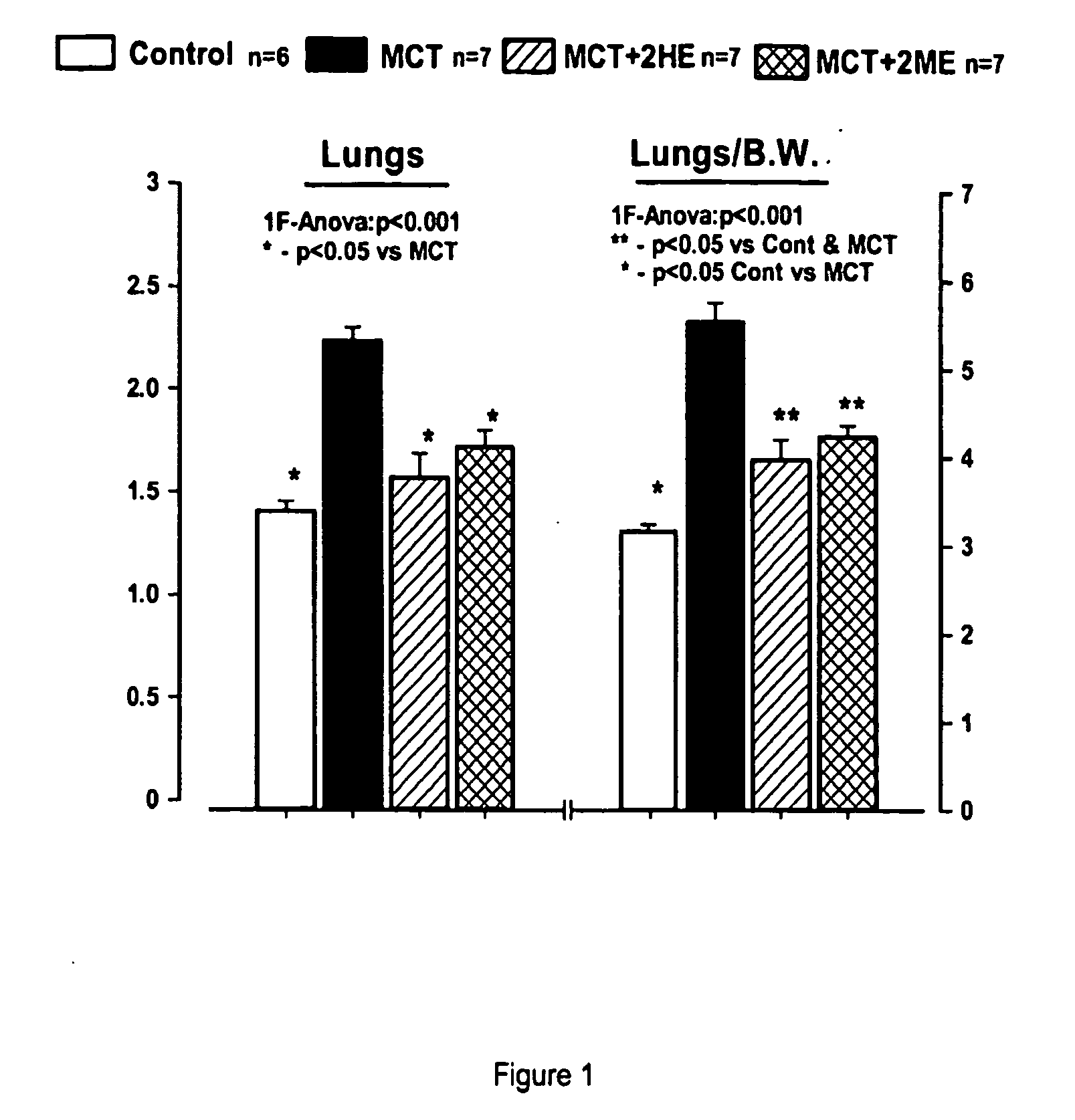
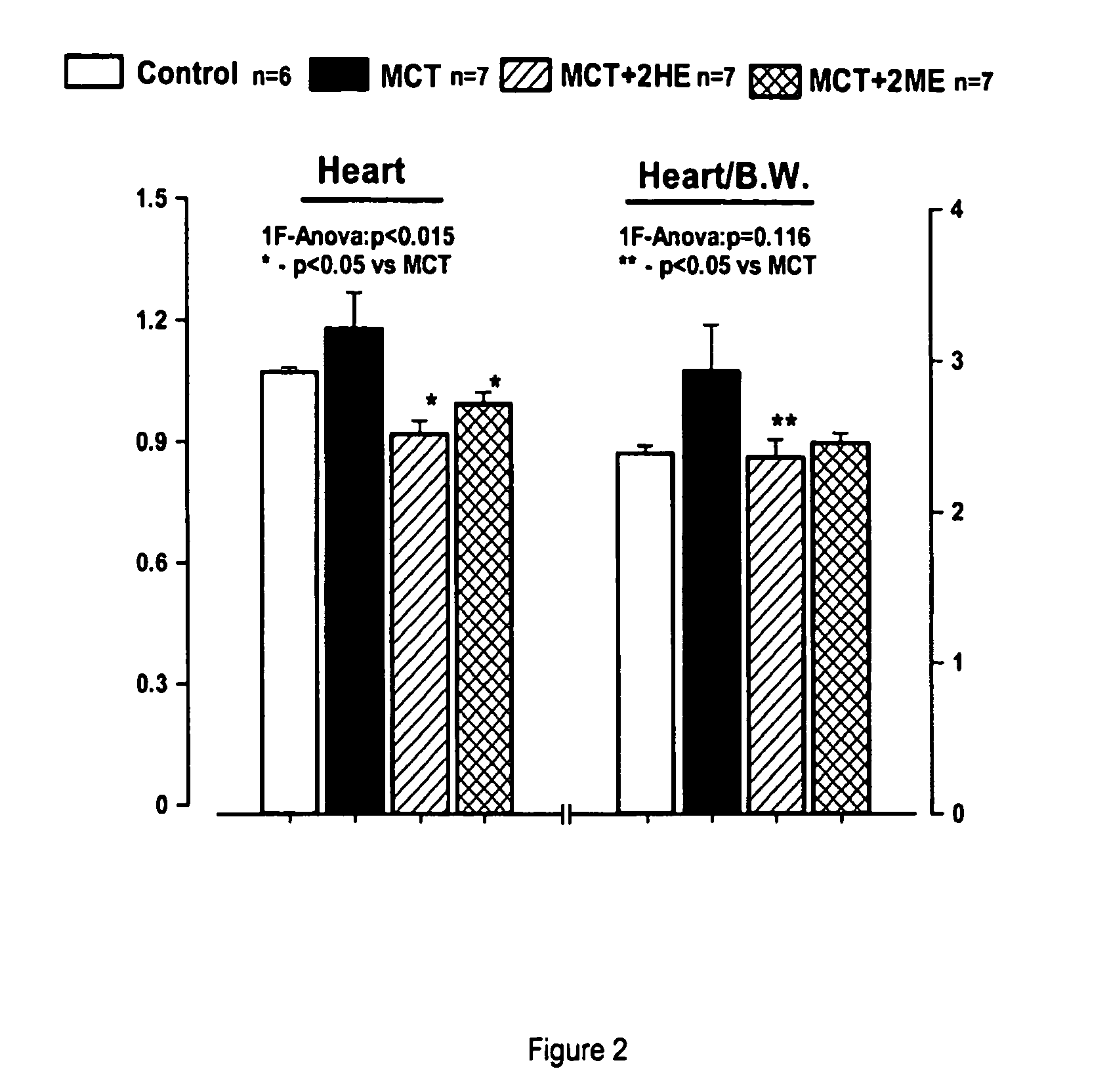
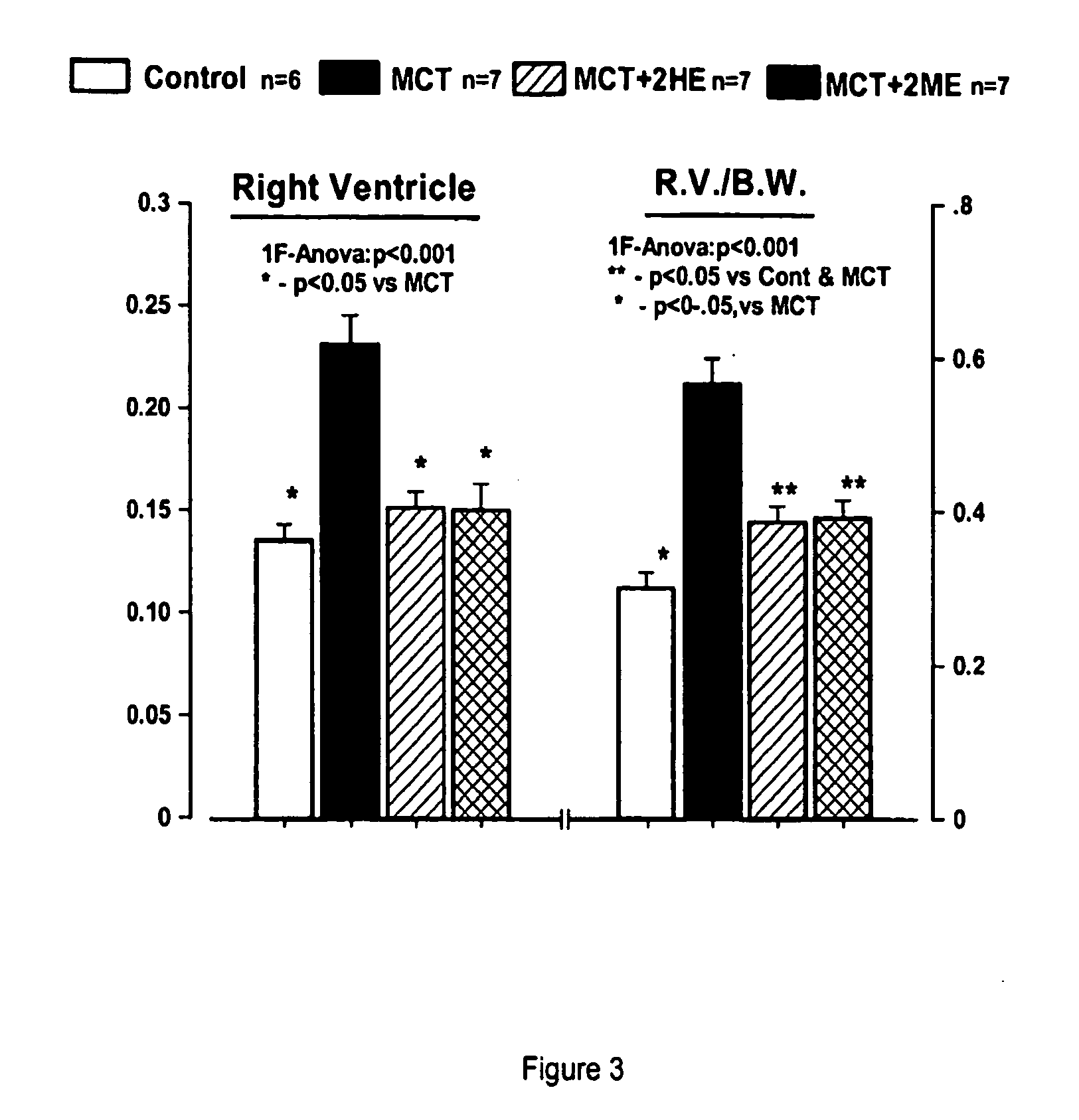
Estradiol metabolites for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension
InactiveUS20060194775A1Decrease lung weightDecrease right ventricular hypertrophyOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDisease4-Methoxyestradiol
Methods are provided for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension and other conditions associated therewith. In particular, the methods include treatment of pulmonary hypertension with an estradiol metabolite or alkoxy analogue of an estradiol metabolite. The estradiol metabolite or alkoxy analogue thereof may be associated with biodegradable microparticles or nanoparticles alone or in combination with other therapeutic agents. Preferred estradiol metabolites include 2-methoxyestradiol, 4-methoxyestradiol, 2-hydroxyestradiol, and 4-hydroxyestradiol and preferred alkoxy analogues of estradiol metabolites include 2-ethoxyestradiol, and / or to synthetic derivatives and analogues thereof or prodrugs thereof. The compositions may also be in the form of a controlled release formulation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
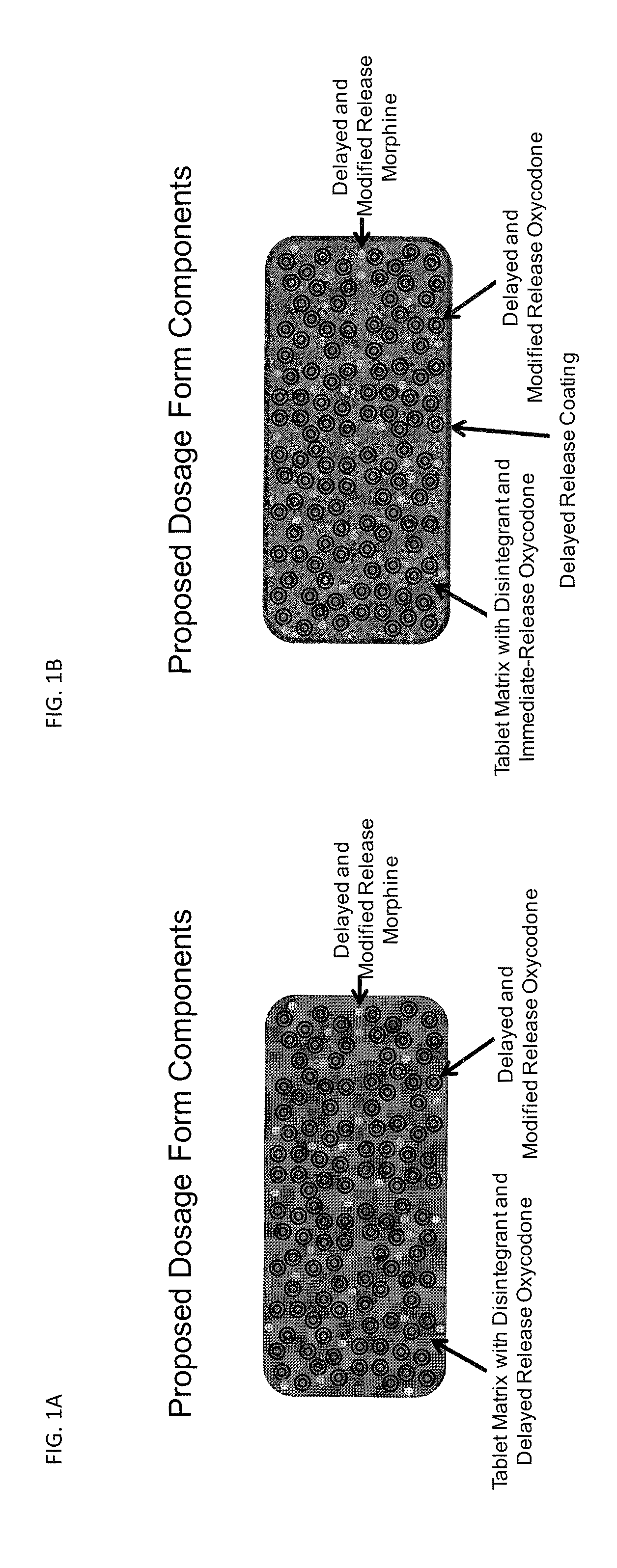
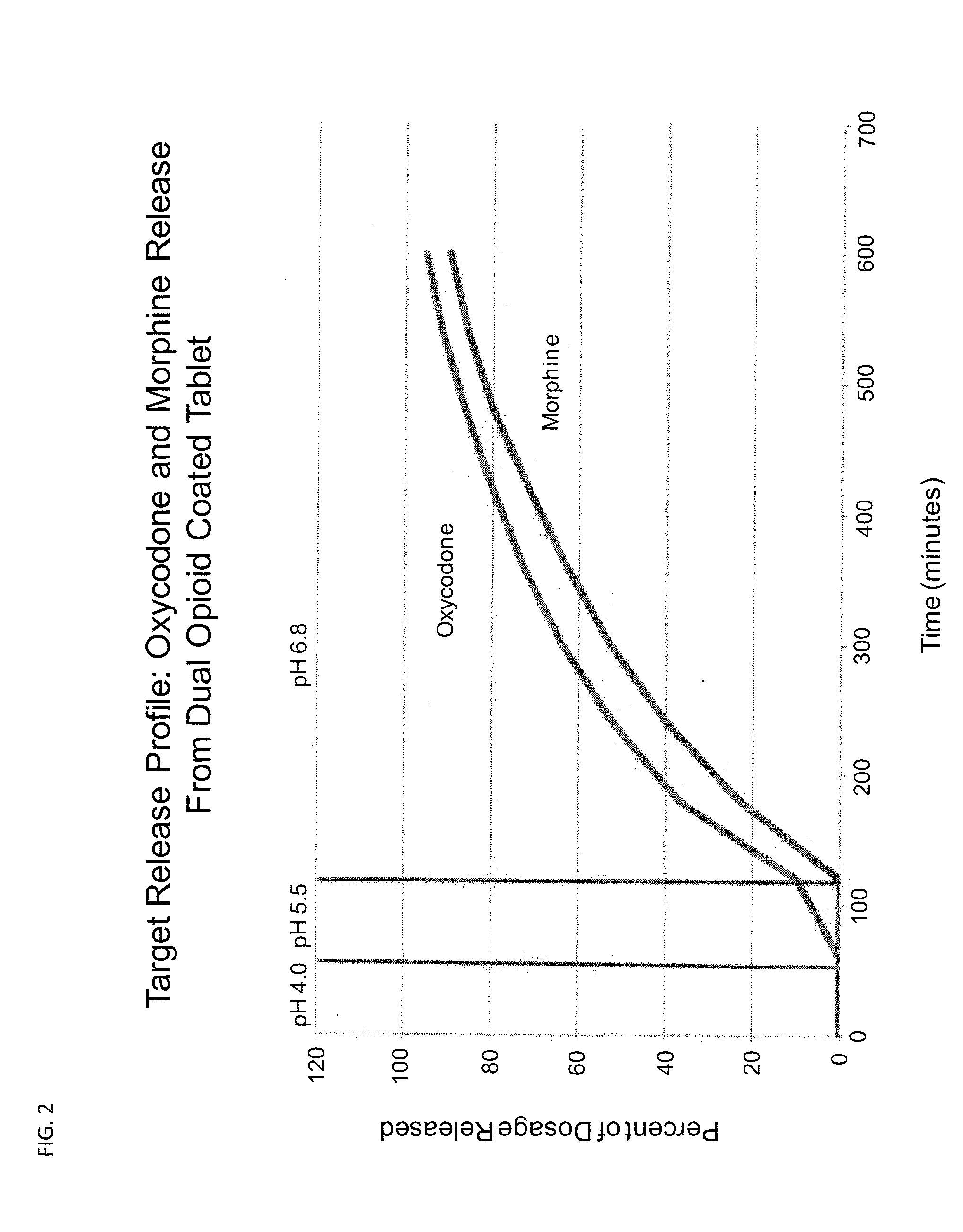
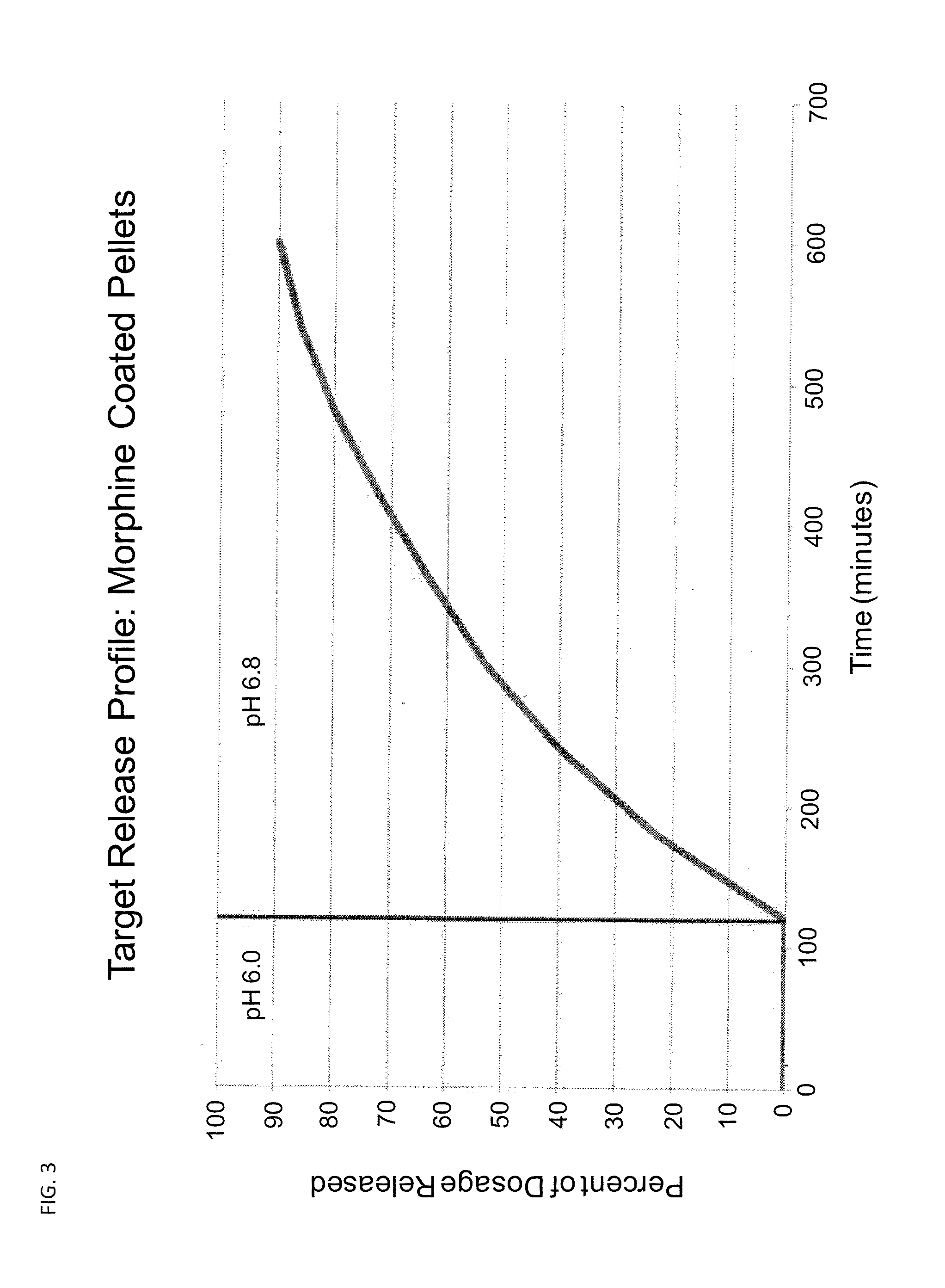
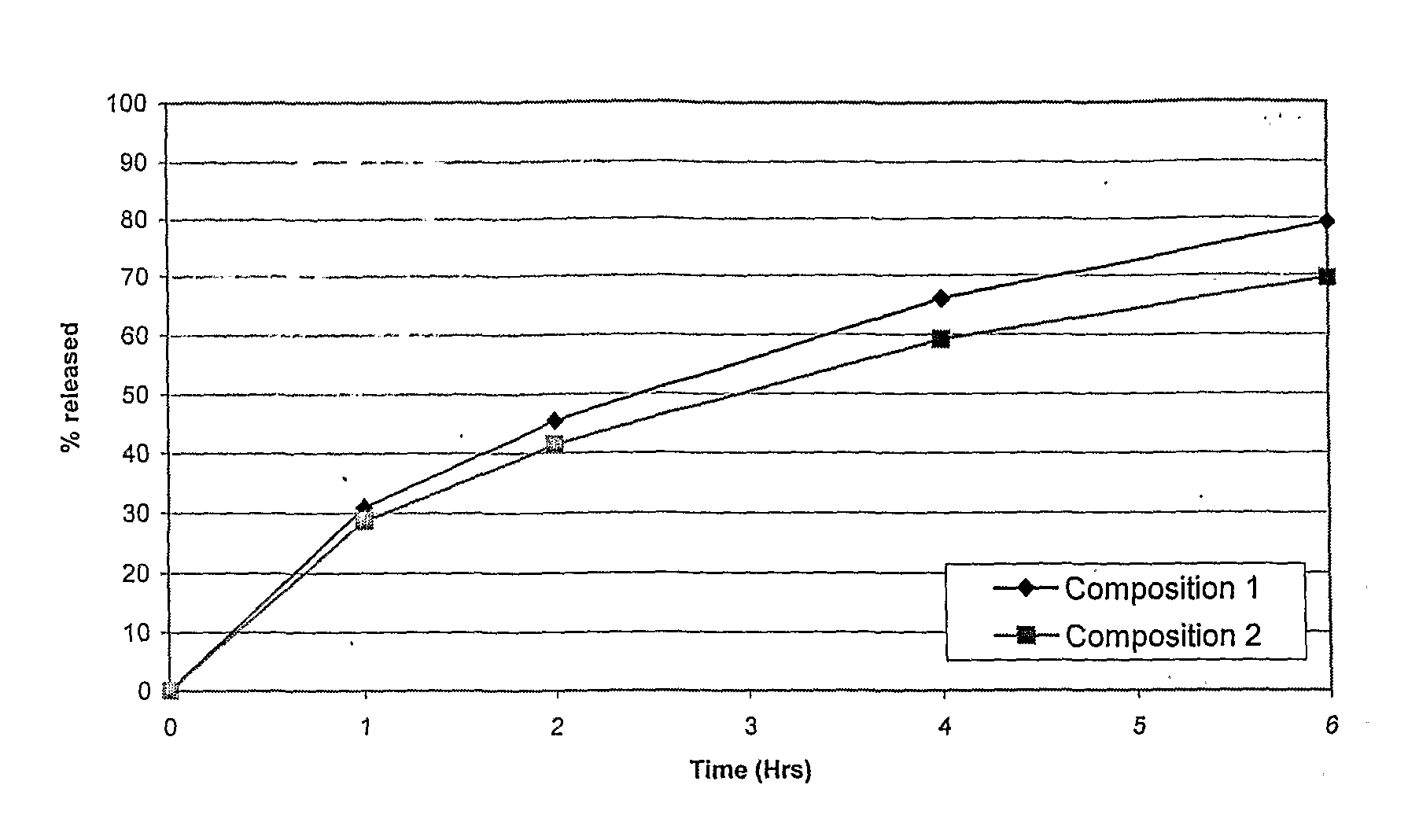
Controlled Release Formulations of Opioids
Pharmaceutical formulations containing opioid components that each has a release profile. The components may provide immediate or controlled release of the opioid. The invention is also directed to methods of controlling release of one or more opioid compounds and methods of treating pain.
Owner:QRXPHARMA
Controlled Release Formulation
InactiveUS20080248107A1Reduced initial burst releaseGood physical propertiesPowder deliveryBiocideSolubilityActive agent
The present invention provides a controlled release formulation comprising an therapeutically effective amount of pharmacologically active substance having high water solubility, at least one non-polymeric release retardant, and at least one pH independent non-swelling release retarding polymer. The said dosage form provides controlled release of the active agent with reduced initial burst release.
Owner:RUBICON RES PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com