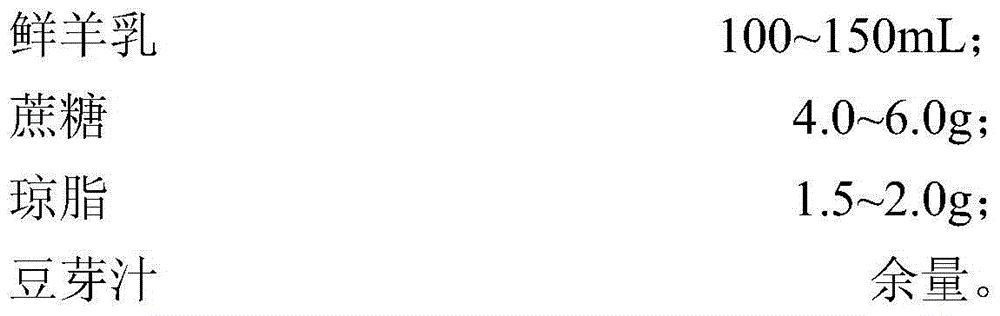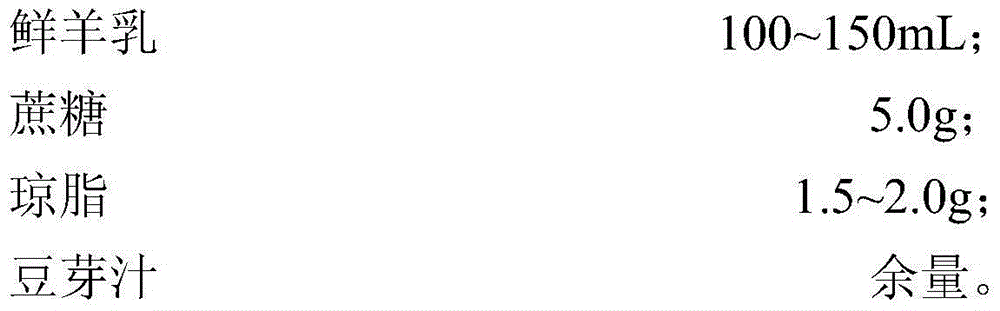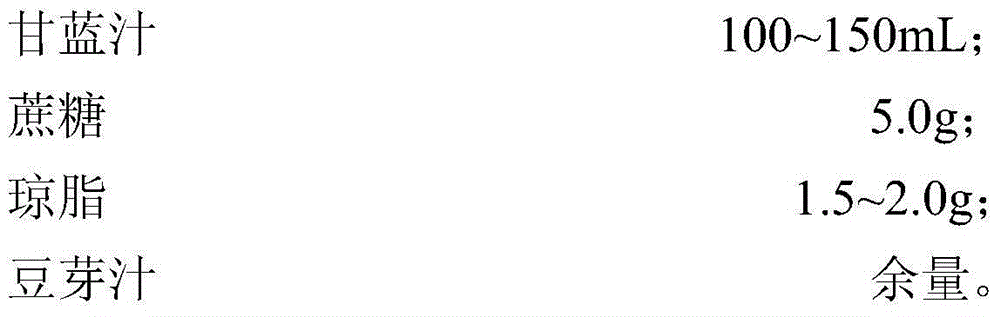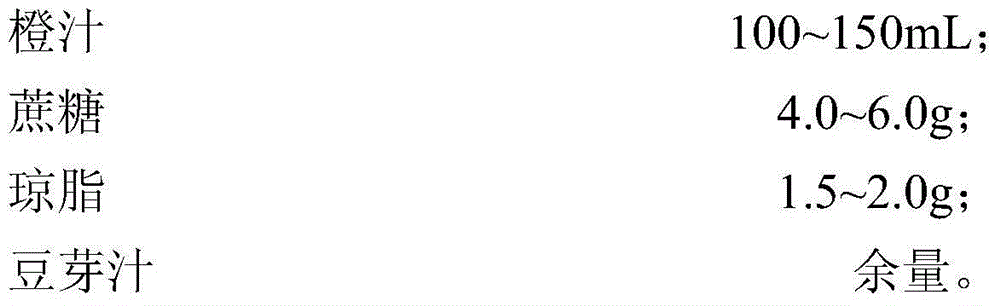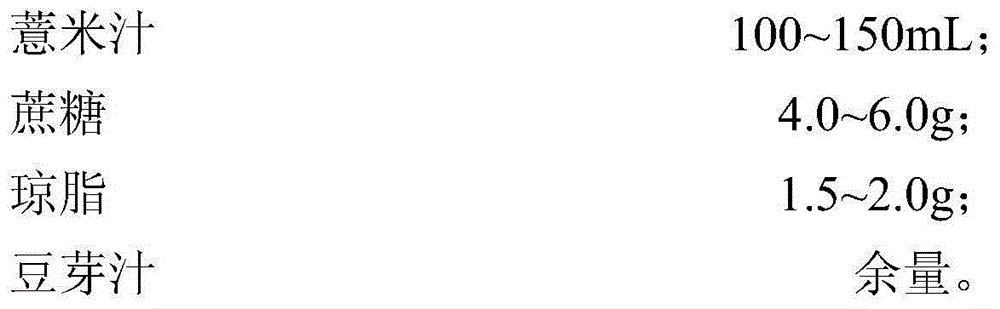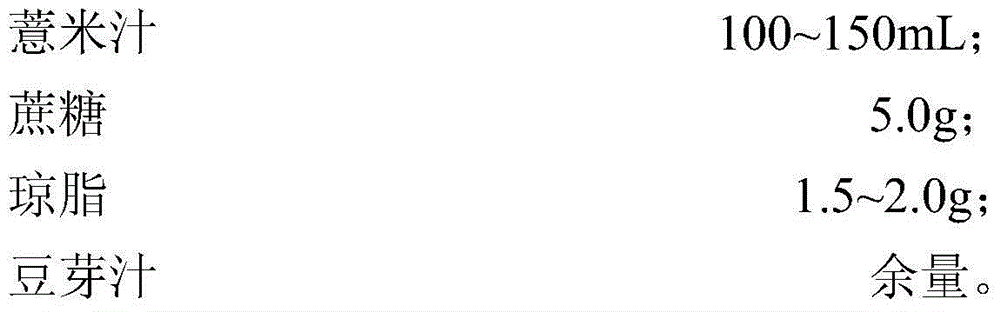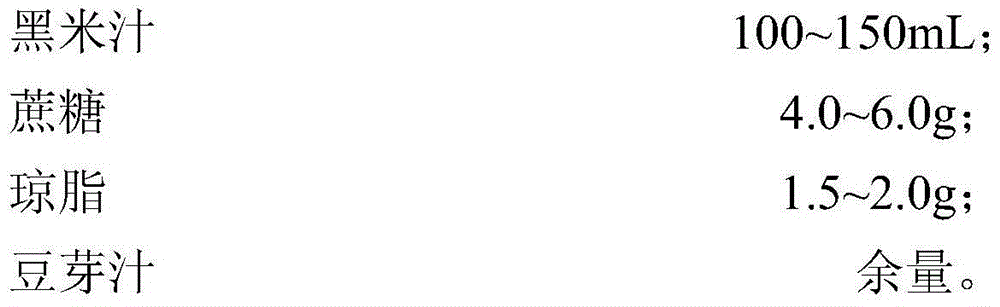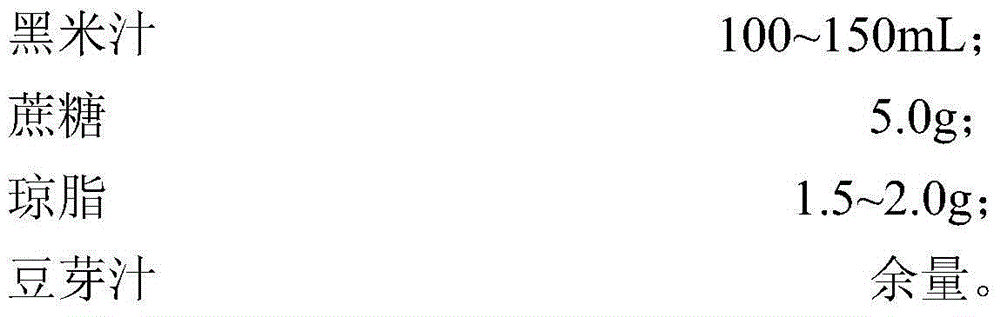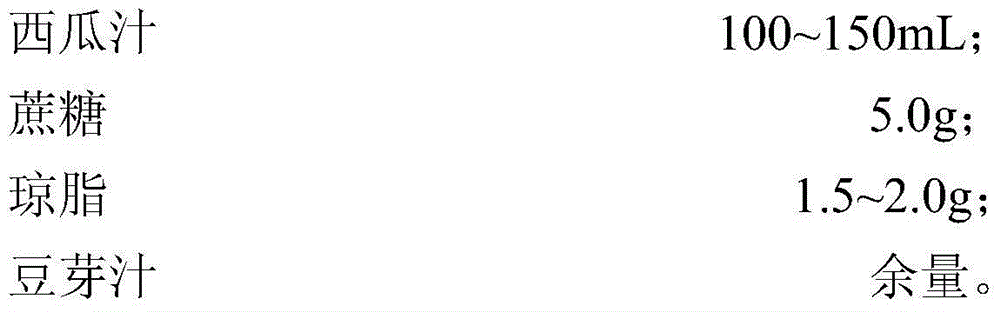Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Genome shuffling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial strain for producing fructosyl transferase and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing fructosyl transferase and a preparation method thereof. The bacterial strain disclosed herein is prepared by the following steps: firstly screening a bacterial strain by lithium chloride and UV mutagenesis, and then changing the property of fructosyl transferase in the bacterial strain by genome shuffling. The bacterial strain is named Aspergillus oryzae scut209, preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan, China, on April 10, 2012 with CCTCC Designation CCTCC No:M 2012106. The bacterial strain has high capability of producing fructosyl transferase and has high industrial application value, wherein the capability of producing fructosyl transferase reaches 34987U / g cell.
Owner:QUANTUM HI TECH (CHINA) BIO CO LTD +1
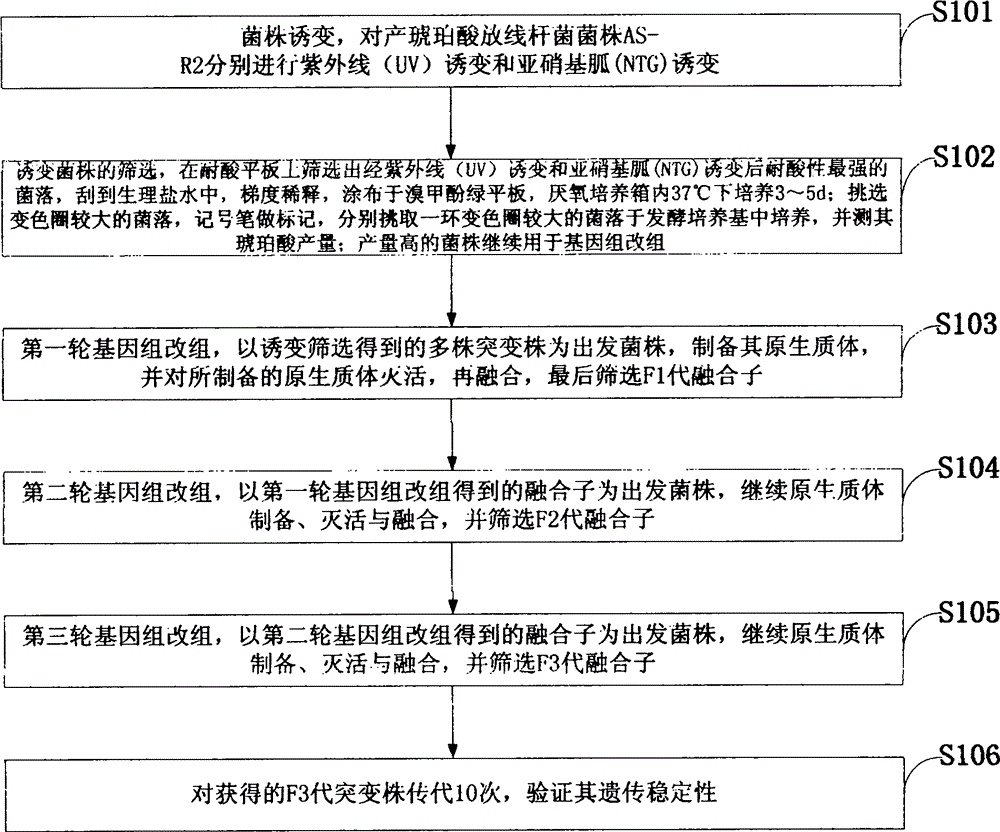
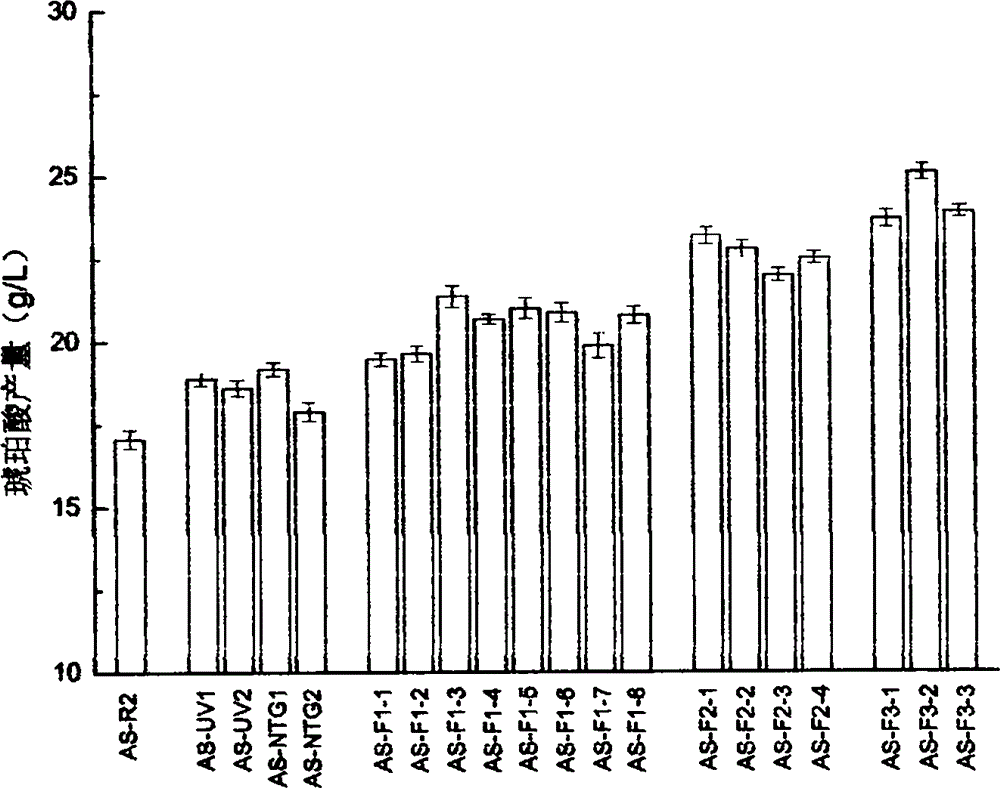
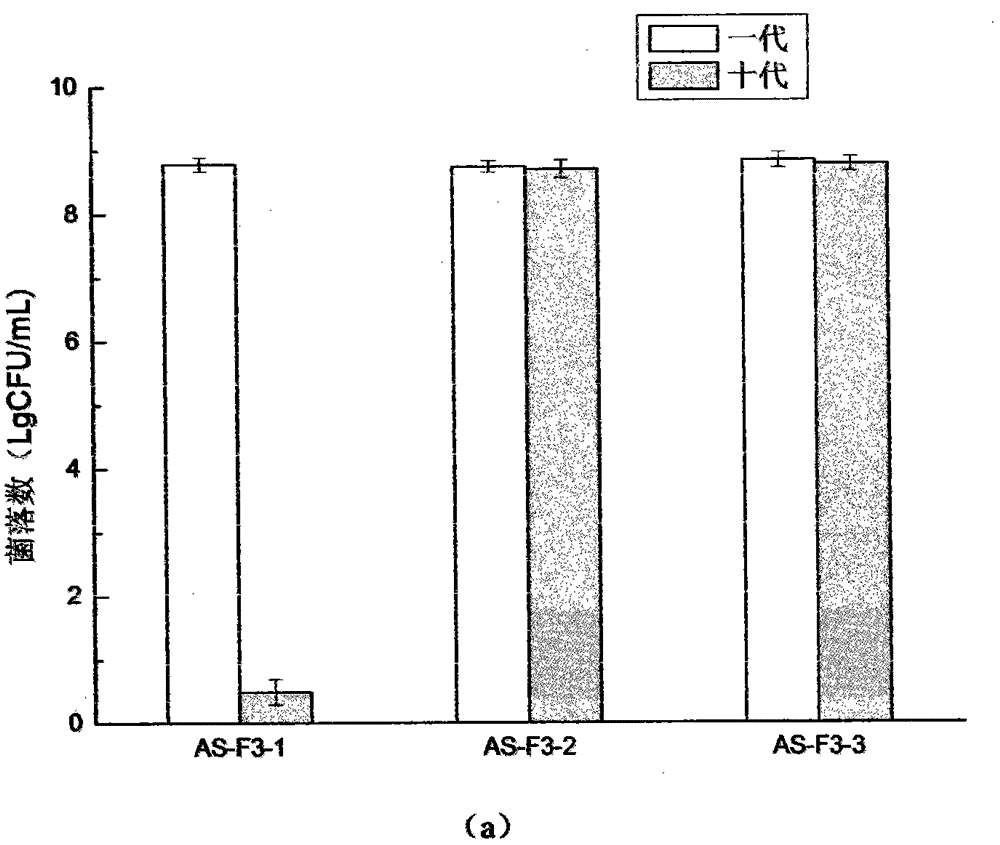
Method for restructuring/breeding Actinobacillus succinogenes strain, and method for producing succinic acid by fermenting Actinobacillus succinogenes strain
InactiveCN101531972AImproved sodium toleranceImprove fermentation characteristicsBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingX-ray
The invention relates to an Actinobacillus succinogenes strain CGMCC 2653 (namely F3-10) with better sodium-ion tolerance and acid-producing performance, a method for breeding the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermenting the strain. Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC 1593 is taken as an original strain and then subjected to X-ray mutation, ultraviolet mutation, diethyl sulfate (EMS) chemical mutation and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) chemical mutation respectively; three strains X-8, UV-17 and SE-6 with improved fermentative acid-producing performance and particularly improved sodium-ion tolerance, as well as a high-yield strain SF-9 with fluoroacetate resistance, are obtained by screening the obtained product; and a genome restructuring method is used for breeding the strains so as to obtain the strain F3-10 with high yield, sodium tolerance and fluoroacetate resistance. The strain F3-10 takes sugarcane molasses as raw material, adopts Na2CO3 to control fermentation pH, and performs fed-batch fermentation in a 5L fermenter, and produces 53.96 grams of succinic acid per liter in 48 hours; the yield of consumed sugar is 89.2 percent; the utilization rate of sugar is 94.0 percent; and the ratio of succinic acid to heteroacid is 6.58:1. Therefore, the strain F3-10 is remarkably improved as compared with the original strain CGMCC 1593.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
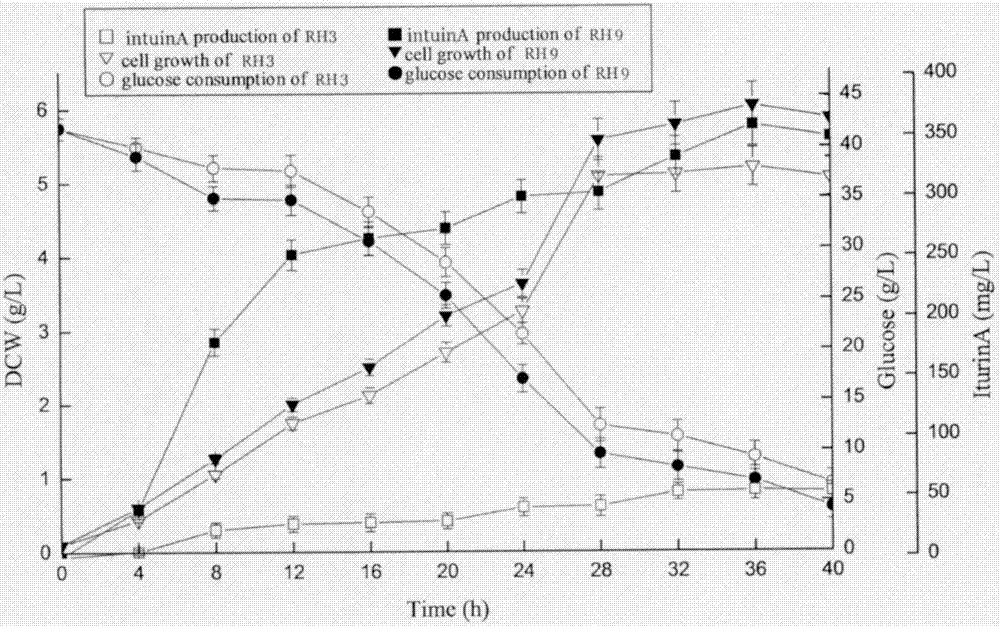
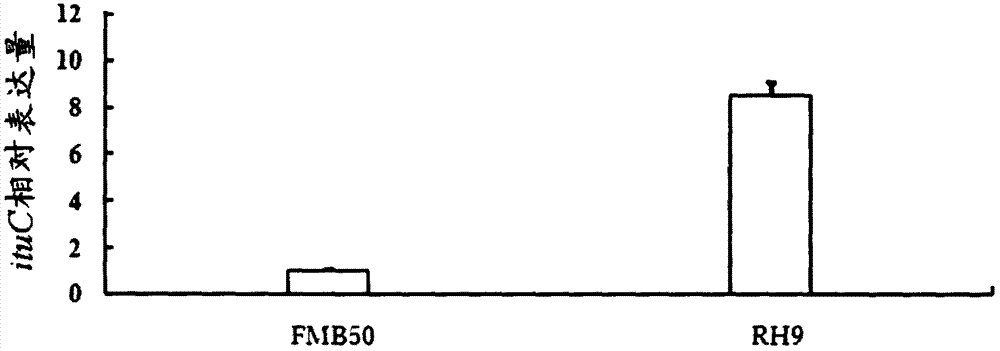
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens RH9, as well as screening method and applications thereof
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens RH9, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens RH9 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC 12489, and has high yield of iturinA, and iturinA produced by bacillus amyloliquefaciens RH9 has very good application prospects in the agriculture, industry and environmental protection. The invention further discloses a screening method of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens RH9. The screening method comprises the following steps: activating the original strains; carrying out penicillin mutation, thus obtaining a first positive mutation strain and a second positive mutation strain; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutation, thus obtaining a third mutation strain and a fourth mutation strain; carrying out genome shuffling on the positive mutation strains, thus obtaining the first round of genome shuffling strains with high yield of iturinA; carrying out genome shuffling on the first round of genome shuffling strains, thus obtaining the second round of genome shuffling strains with high yield of iturinA, and selecting one of the second round of genome shuffling strains which has high yield of iturinA and high hereditary stability, wherein the selected genome shuffling strain is named bacillus amyloliquefaciens RH9.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving cadmium tolerance of bacillus through mutagenesis
InactiveCN101955925AImprove toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationGenome shufflingCandida tropicalis
The invention relates to a microorganism breeding method, in particular to a method for performing eukaryon and pronucleus microorganism protoplasm multi-parent fusion by establishing genome-based reorganization technology. The technical scheme adopted to fulfill the aim of the invention comprises the following steps of: performing induced mutation on a microorganism and screening so as to obtain a mutated microorganism having high cadmium resistance; and performing slant spore culturing, strain mutagenesis, genome reorganization, screening and multiple recursion infusion by taking the mutated microorganism with the high cadmium resistance as an initial strain by a cell protoplast multi-parent fusion method so as to obtain an anti-cadmium strain with good property. When the cell protoplast multi-parent fusion method established by the invention is used for transforming bacillus subtillis and candida tropicalis which are resistant to cadmium, two high-quality infusion strains which have extremely higher cadmium resistance than that of the bacillus subtillis and the candida tropicalis are obtained.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for improving doramectin preparing bacterium with genome reorganization technique
InactiveCN101343630AEasy to breedEasy to optimizeHybrid cell preparationGenome shufflingMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for preparing strain which can generate protoplast fusion by using marked plasmid. The invention has the advantages that marks can be easily added and removed, thereby being convenient for performing breeding and improvement of the strain based on the gene shuffling technology. The invention also has the advantages that the operation is simple, the cost is low, the requirement for equipment is low, and the chromosome of the strain can not be damaged.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Novel integrase and application thereof to efficiently modifying saccharopolyspora spinosa
The invention provides a novel integrase and application thereof to genetically modifying saccharopolyspora spinosa. The integrase particularly comes from saccharopolyspora endophytica CCTCC AA208003, and exogenous DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be specifically locally integrated on saccharopolyspora endophytica chromosome by the integrase via specific cis-form components. In addition, independent free replication regions of different strain sources are discovered in the saccharopolyspora spinosa by an inventor via research on genetic factors of different strains of the saccharopolyspora spinosa. The novel integrase and the application have the advantages that vectors constructed on the basis of the integrase and sequences of the replication regions can be used for genetically modifying the saccharopolyspora spinosa, accordingly, novel spinosad analogues can be possibly discovered, and the spinosad fermentation yields can be possibly increased; different resistance molecular markers can be carried by plasmids, accordingly, the novel integrase can be used for inter-species or intergenetic genome shuffling operation on the saccharopolyspora spinosa, and efficient genome shuffling can be implemented.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
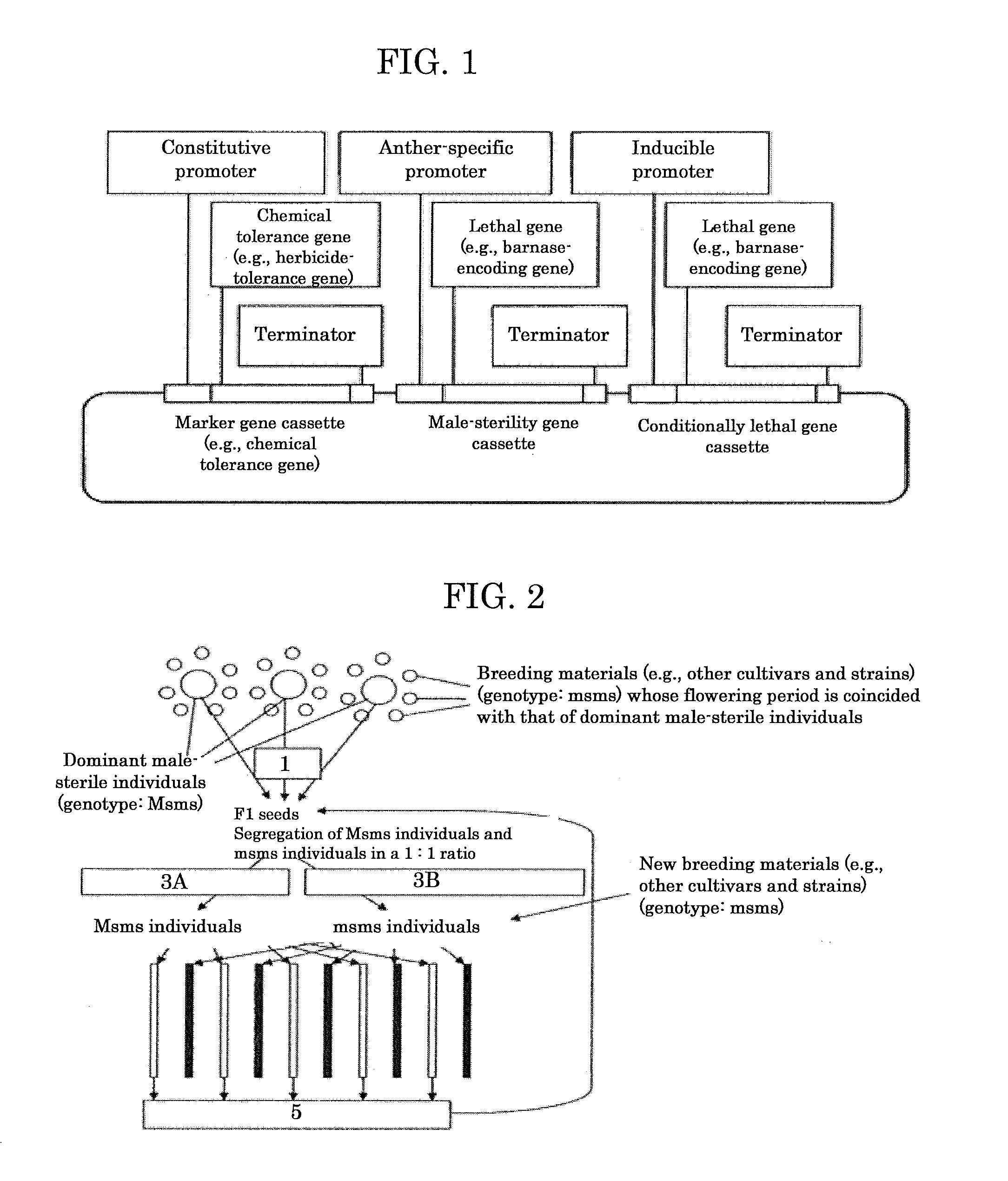
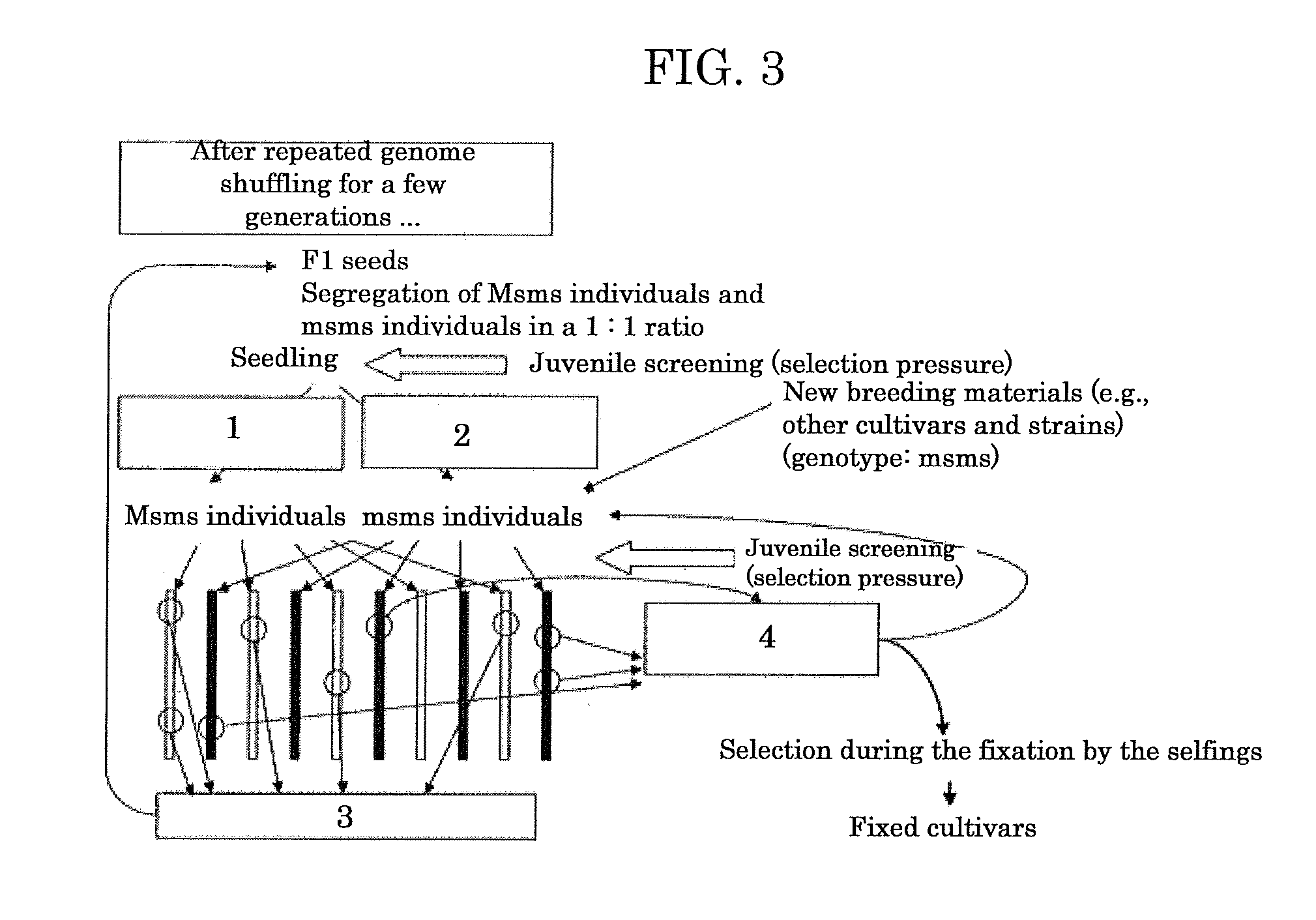
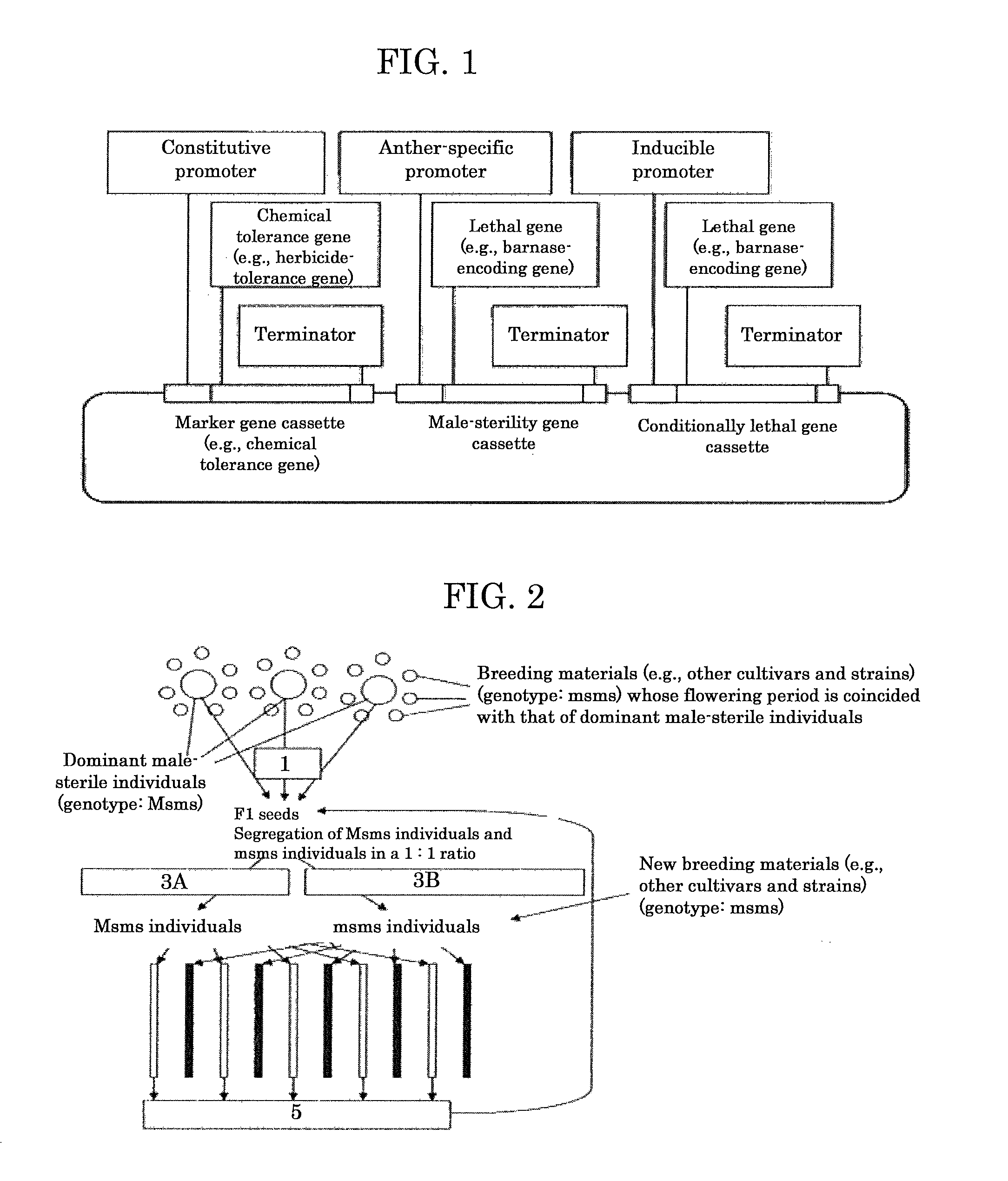
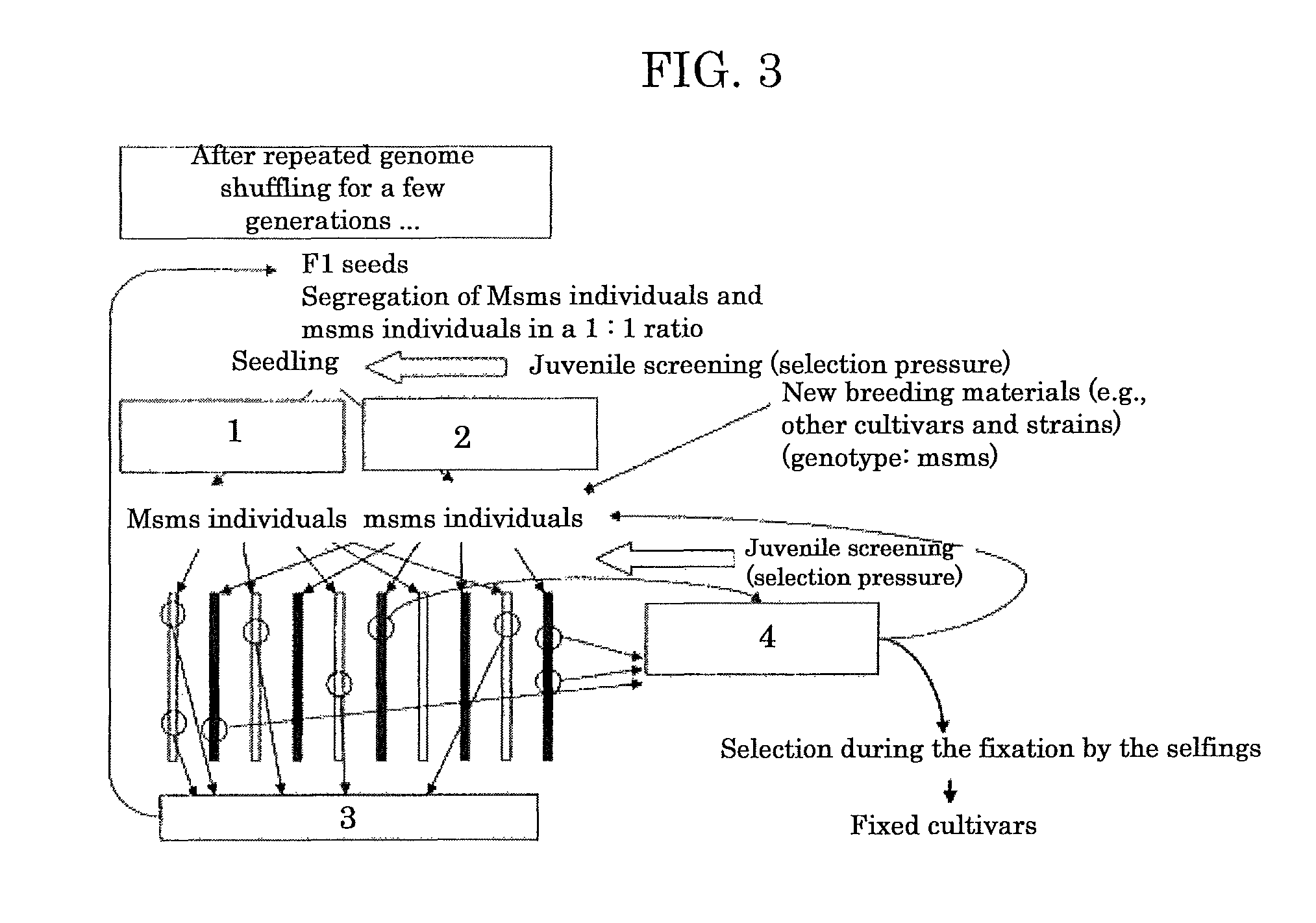
Genome shuffling method for autogamous plants utilizing dominant male sterility obtained by gene engineering technique, and recurrent selection breeding system based on the genome shuffling method
InactiveUS20110099654A1Difficult to outcrossEfficiently outcrossingGenetic engineeringPlant genotype modificationGenome shufflingTransgenic technology
A genome shuffling method for autogamous plants, including producing individuals having the following three traits in a tight coupling linkage by a gene engineering technique selected from a transgenic technique and a gene targeting technique: 1) dominant male sterility, 2) chemical tolerance and 3) lethality inducible by activating an inducible promoter, selecting, from progeny of the individuals, male-sterile individuals by means of the chemical tolerance described in 2) and male-fertile individuals by means of the lethality described in 3), arranging the male-sterile individuals and the male-fertile individuals close together in flowering periods thereof, so that the male-sterile individuals are crossed with the male-fertile individuals, harvesting seeds from the male-sterile individuals, and repeating outcrossing using the seeds from generation to generation.
Owner:TANAKA JUNICHI
Method of preparing novel beer-making yeast through genome recombination technology and obtained novel beer-making yeast
InactiveCN108148829AResistant to high ethanolReduce back mutation rateMicroorganism based processesHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyGenome shuffling
The invention provides a method of preparing a novel beer-making yeast through a genome recombination technology and the obtained novel beer-making yeast, and belongs to the technical field of genomerecombination technologies. According to the method, yeast strains with good ethanol tolerance can be prepared. The method comprises the steps of adopting beer-making yeast and alcohol-resistant low-yield acetaldehyde yeast strains as original strains, and inducing the beer-making yeast and alcohol-resistant low-yield acetaldehyde yeast strains separately by utilizing an optimized spore productioncondition to form ascospores; utilizing a lywallzyme to release haploid spores in the ascospores of the beer-making yeast and alcohol-resistant low-yield acetaldehyde yeast strains, collecting haploid spore suspension liquids, and separating the haploid spores from respective haploid spore suspension liquids; fusing two haploid spores obtained after separation, placing the haploid spores into a wort culture medium in which the ethanol concentration is 12% to conduct culture, and obtaining the novel beer-making yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) SCHL1706, wherein the preservation number is CGMCCNO.14231. The method of preparing the novel beer-making yeast through the genome recombination technology and the obtained novel beer-making yeast can be applied to preparation of the yeast strains with good ethanol tolerance and beer.
Owner:TSINGTAO BREWERY
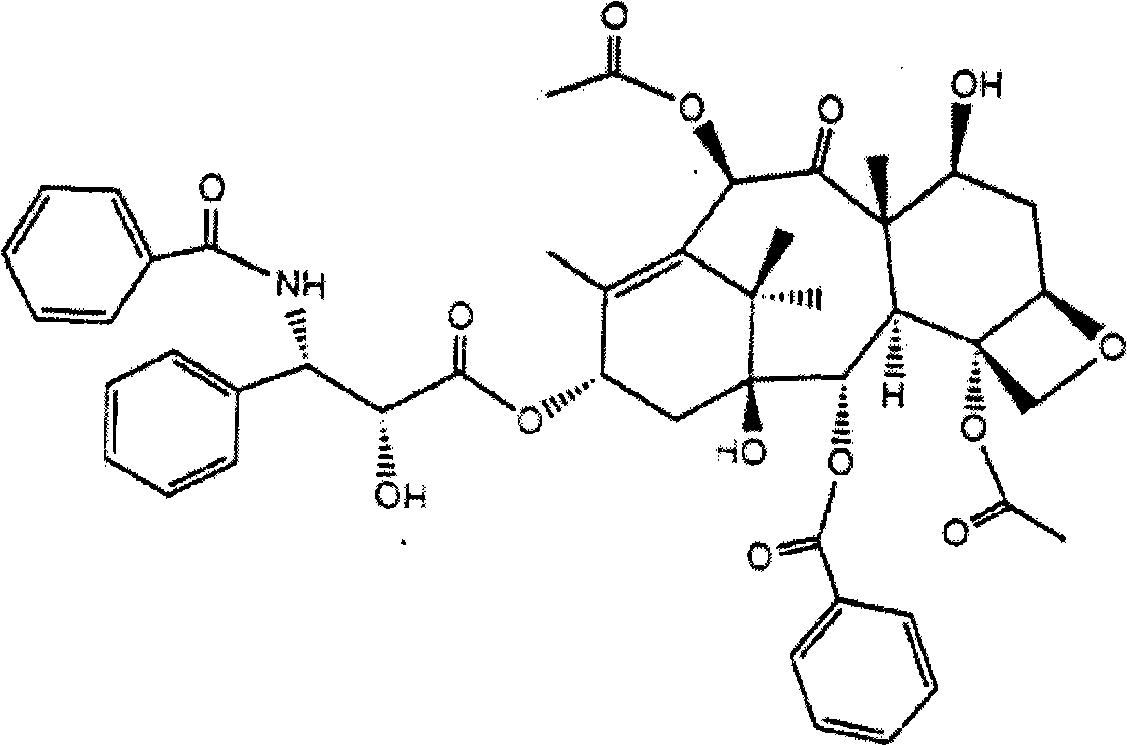
Paclitaxel genome rearrangement bacterial strain HDFS4-26 and breeding method of high-yield bacterial strain
InactiveCN101280281ABreeding is simpleGood effectFungiHybrid cell preparationMicroorganismGenome shuffling
The invention relates to paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain HDFS4-26 and a seed selection method of high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain, which belongs to the paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain and the seed selection method of the paclitaxel engineering bacterial strain and solves the problem that the paclitaxel output of the bacterial strain which can be used in the paclitaxel microorganism fermentation at present is still relatively low. The paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain HDFS4-26 is nodulisporium sylviforme and belongs to the nodulisporium and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation date is February 28, 2008, the preservation number is CCTCC M 208026. The seed selection method of the high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain adopts firstly, the protoplast preparation; secondly, the inactivation of the protoplast; thirdly, the interfusion of the protoplast; fourthly, the regeneration of the protoplast; fifthly, the genome shuffling and sieving, therefore to obtain the high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain. The paclitaxel output of the bacterial strain HDFS4-26 is 516.37ug / L. The seed selection method of the high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain provided by the invention is simple, the effect is good, and the paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain HDFS4-26 and the seed selection method of high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain lay the foundation of industrial production of bacterial strain providing high yield paclitaxel.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
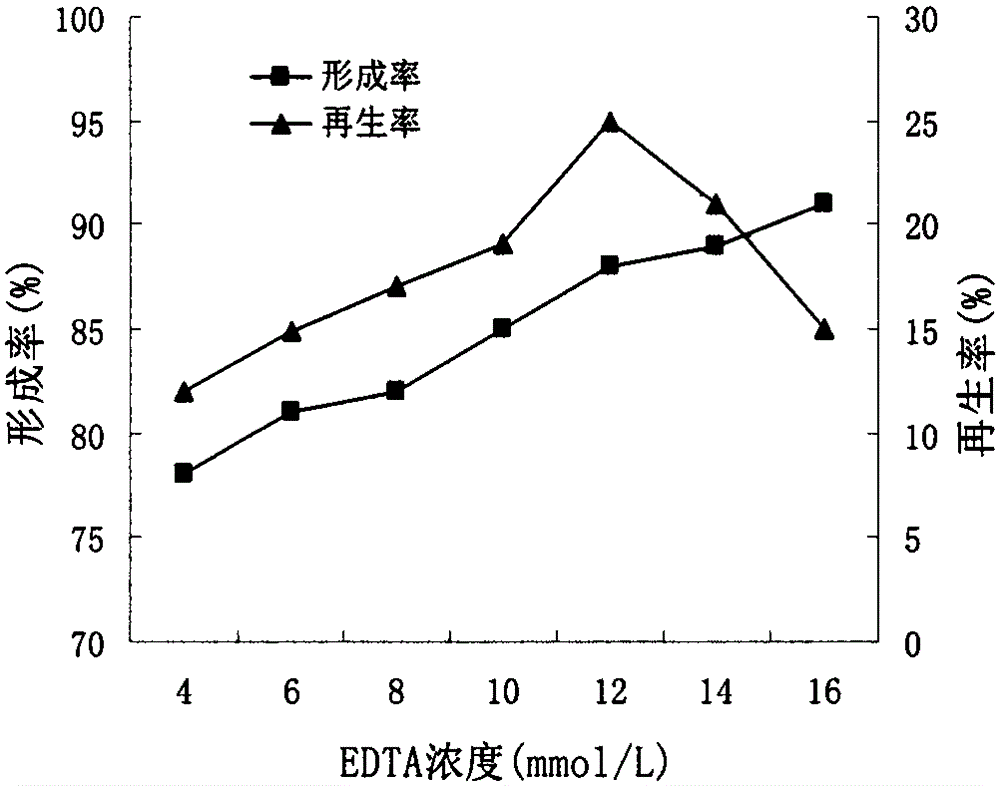
Method for preparing and regenerating sphingomonas sp protoplast
ActiveCN106591167AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismGenome shuffling
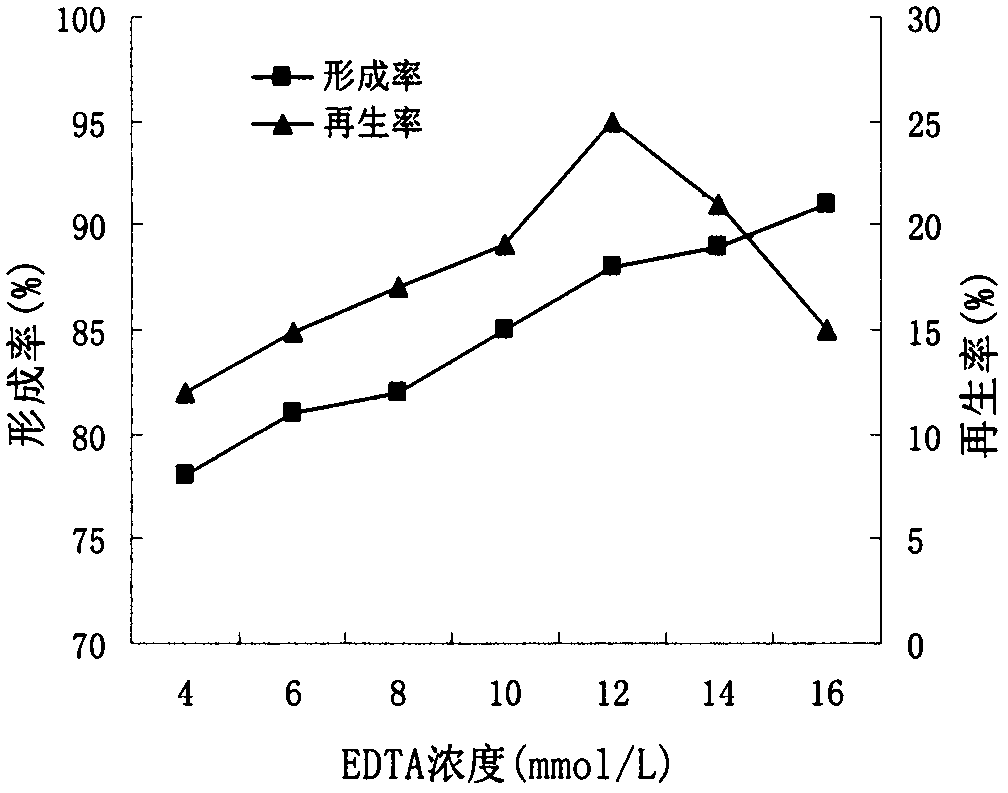
The invention provides a method for preparing and regenerating sphingomonas sp protoplast, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. According to the method, sphingomonas sp is used as an original strain; the sphingomonas sp protoplast is prepared by an enzymolysis method; the formation rate of the obtained protoplast is 97.3 percent; and the regeneration rate is 33.9 percent. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient; the preparation rate of the protoplast is high; the activity is high; and the further breeding of the excellent sphingomonas sp strain by using protoplast fusion and genome shuffling is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Method for preparing fermented goat milk rich in pyrroloquinoline quinine and nattokinase by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei
InactiveCN104430853APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMilk preparationMutant preparationBiotechnologySheep milk
The invention discloses a method for preparing fermented goat milk rich in pyrroloquinoline quinine and nattokinase by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing the two mutagenesis progenies, implementing cell fusion and subculture, and conducting high-throughput screening by further adopting a substrate-induced adaptive strategy on the basis of the genome shuffling technology so as to obtain bacillus natto for the high production of nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening out methionine auxotrophic lactobacillus casei; and co-fermenting fresh goat milk by virtue of the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei so as to obtain the fermented goat milk rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine. In the fermented goat milk rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine prepared by the method disclosed by invention, the content of the pyrroloquinoline quinine reaches 100-134ng / mL and the activity of the nattokinase reaches 1725-1900U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
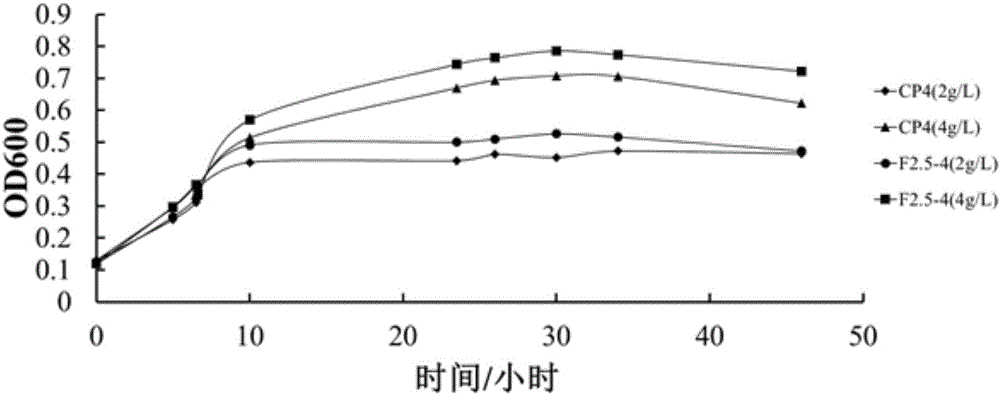
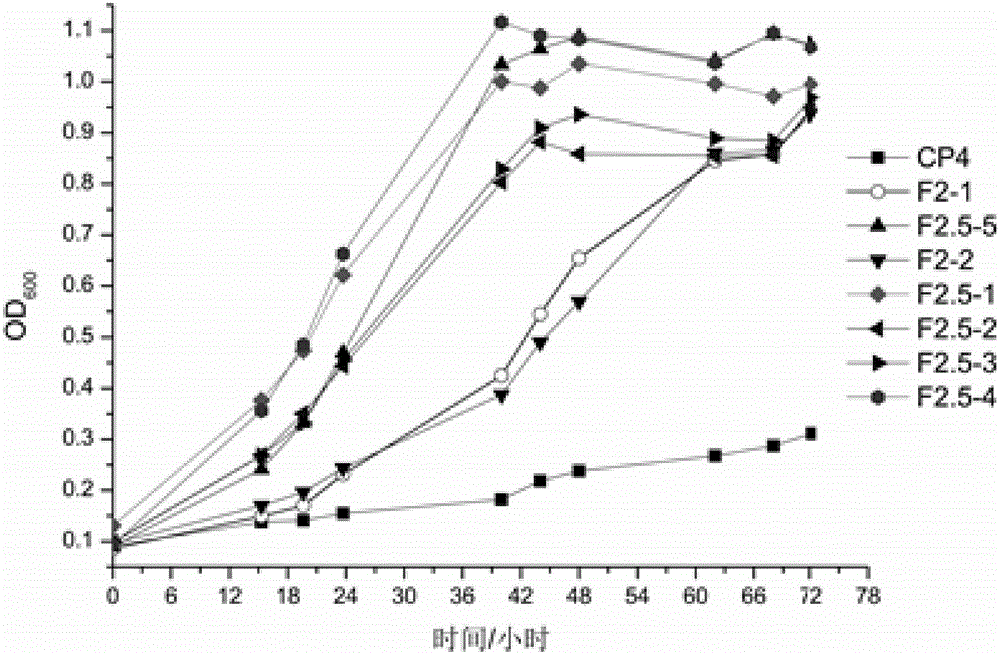
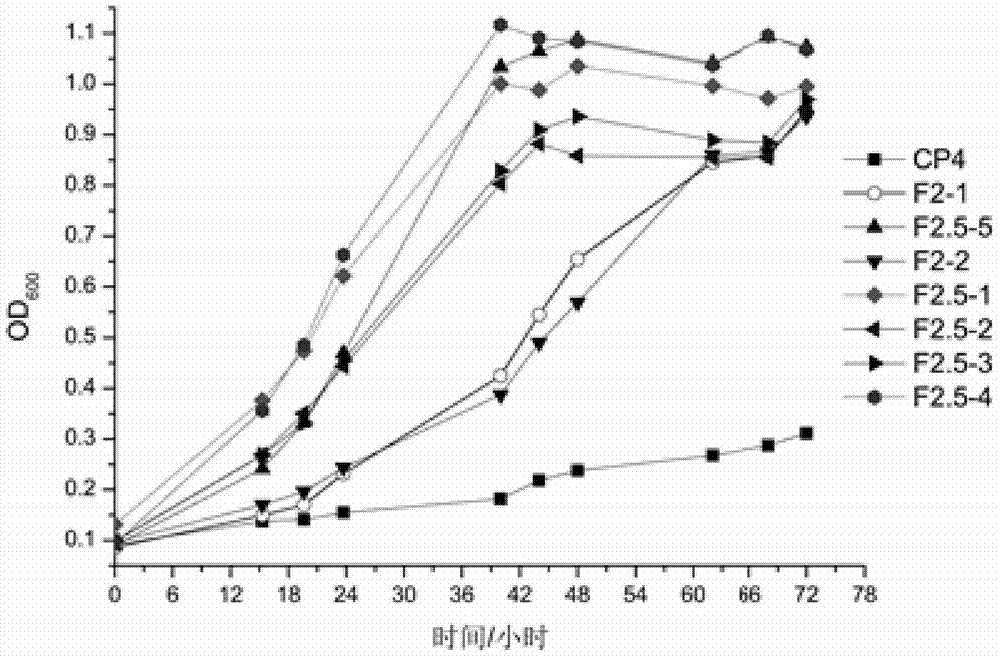
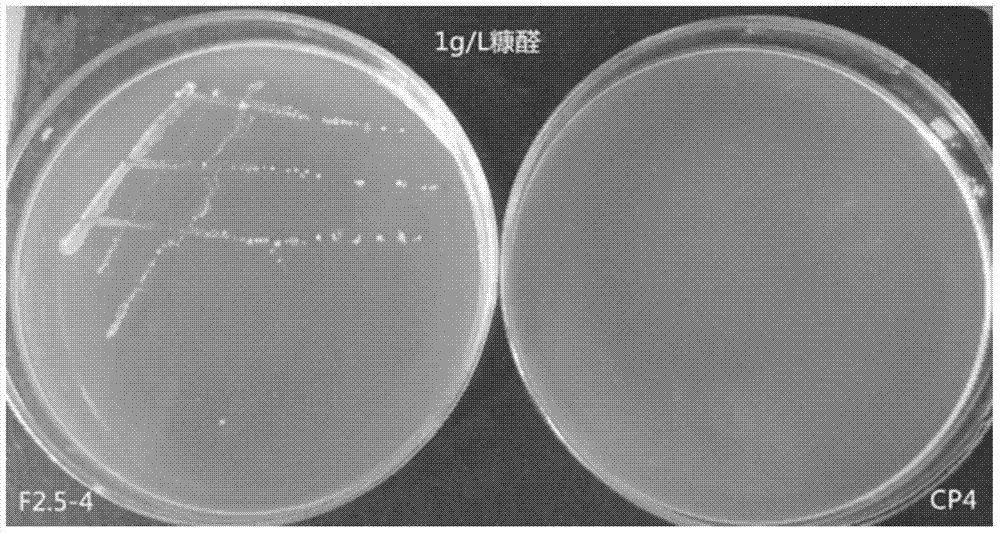
Error-prone whole-genome shuffling method of zymomonas mobilis and furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis
ActiveCN105132348AEfficient growth processFast and effective growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenome shufflingMicrobiology
The invention discloses an error-prone whole-genome shuffling method of zymomonas mobilis and furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis. The furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis is classified and named as zymomonas mobilis F2.5-4 with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M2015366. The furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis obtained by the method is capable of growing in an RM culture medium with 3g / L furfural efficiently. Compared with a traditional whole-genome shuffling technology, the error-prone whole-genome shuffling method has the advantages that since the error-prone PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology is applied effectively, the furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis can be obtained rapidly and effectively without physical and chemical mutagenesis and protoplast fusion. Growth of a starting zymomonas mobilis strain in the culture medium with the 3g / L furfural is inhibited severely, and the furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis obtained by the method is stronger than the starting zymomonas mobilis strain in furfural tolerance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Genome shuffling method for autogamous plants utilizing dominant male sterility obtained by gene engineering technique, and recurrent selection breeding system based on the genome shuffling method
InactiveUS8629322B2Efficient recurrent selection breedingEfficiently outcrossingHydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyGenome shuffling
A genome shuffling method for autogamous plants, including producing individuals having the following three traits in a tight coupling linkage by a gene engineering technique selected from a transgenic technique and a gene targeting technique: 1) dominant male sterility, 2) chemical tolerance and 3) lethality inducible by activating an inducible promoter, selecting, from progeny of the individuals, male-sterile individuals by means of the chemical tolerance described in 2) and male-fertile individuals by means of the lethality described in 3), arranging the male-sterile individuals and the male-fertile individuals close together in flowering periods thereof, so that the male-sterile individuals are crossed with the male-fertile individuals, harvesting seeds from the male-sterile individuals, and repeating outcrossing using the seeds from generation to generation.
Owner:TANAKA JUNICHI
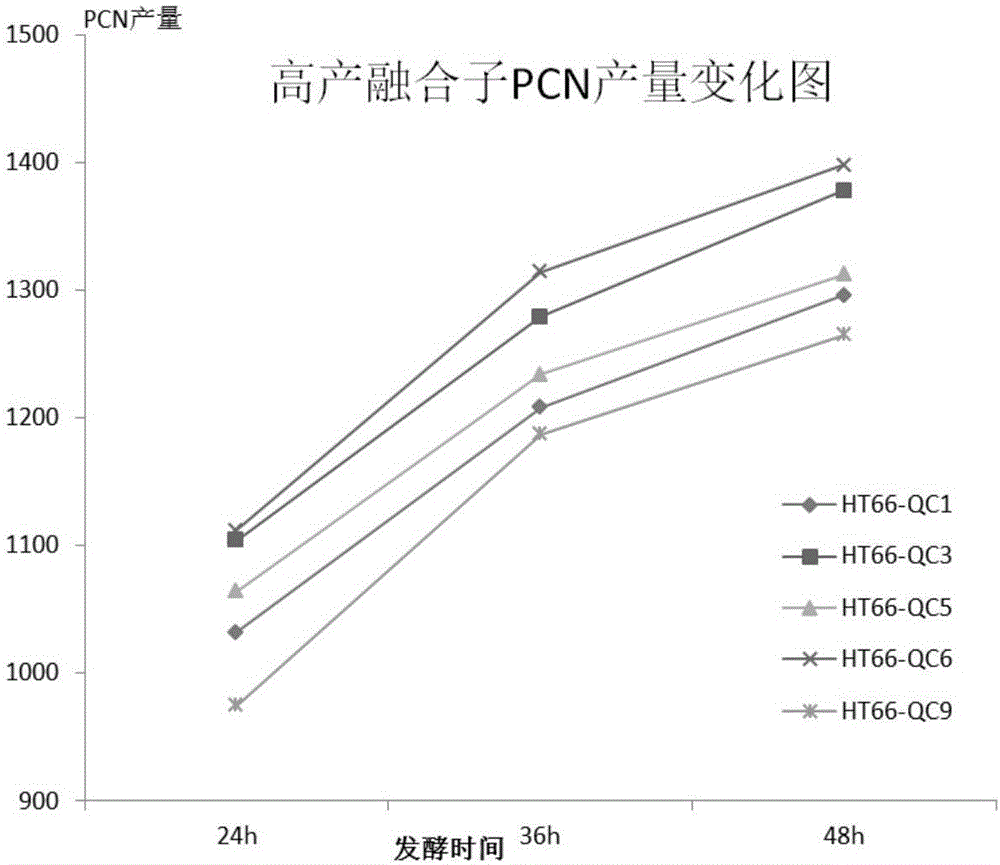
Breeding method of strain with high yield of phenazine-1-formamide based on genome shuffling
InactiveCN106399158AIncrease productionImprove the efficiency of restructuringBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingPhenazine
The invention relates to a breeding method of a strain with high yield of phenazine-1-formamide based on genome shuffling. The breeding method comprises the following steps: by taking pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 as an initial strain, carrying out mutagenesis treatment, thus obtaining a genome library containing various different positive mutations, and screening out a plurality of mutant strains with high PCN yield; and carrying out protoplast preparation and protoplast fusion on the mutant strains, and screening out fusants with high PCN yield. The breeding method has the beneficial effects that the mutant strains of pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 are screened by adopting the method combining mutagenesis treatment with the genome shuffling technology, the relevant parameters of protoplast preparation and fusion are optimized, the genome shuffling efficiency is improved, the strain with high yield of phenazine-1-formamide is obtained, and compared with that of the initial strain, the yield of phenazine-1-formamide of the obtained strain is improved by 2.8 times to the maximum. The method provided by the invention is easy to operate, and the parent strain does not need to be labeled, so that the labor cost is greatly reduced, and the screening period is shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Acid resistance and high succinic acid yield strain and preparation method thereof
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for producing dietary therapy brassica oleracea by virtue of co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus
InactiveCN104431853APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationHybrid cell preparationGenome shufflingMutagenesis
The invention discloses a method for producing dietary therapy brassica oleracea by virtue of co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing the two mutagenesis progenies, implementing cell fusion and subculture, and conducting high-throughput screening by further adopting a substrate-induced adaptive strategy on the basis of the genome shuffling technology so as to obtain bacillus natto for the high production of nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening out methionine auxotrophic lactobacillus casei; and co-fermenting brassica oleracea by virtue of the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei so as to obtain the fermented brassica oleracea rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine. In the fermented brassica oleracea rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine prepared by the method disclosed by invention, the content of the pyrroloquinoline quinine reaches 82-117ng / mL and the activity of the nattokinase reaches 416-811U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
Polypeptide for Genome Shuffling in Plants, and Use Therefor
ActiveUS20180305708A1Reduce the impactHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDna breakageGenome shuffling
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Method for restructuring/breeding Actinobacillus succinogenes strain, and method for producing succinic acid by fermenting Actinobacillus succinogenes strain
InactiveCN101531972BReduce manufacturing costGood fermentation propertiesBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingX-ray
The invention relates to an Actinobacillus succinogenes strain CGMCC 2653 (namely F3-10) with better sodium-ion tolerance and acid-producing performance, a method for breeding the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermenting the strain. Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC 1593 is taken as an original strain and then subjected to X-ray mutation, ultraviolet mutation, diethyl sulfate(EMS) chemical mutation and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) chemical mutation respectively; three strains X-8, UV-17 and SE-6 with improved fermentative acid-producing performance and particularly improved sodium-ion tolerance, as well as a high-yield strain SF-9 with fluoroacetate resistance, are obtained by screening the obtained product; and a genome restructuring method is used for breeding the strains so as to obtain the strain F3-10 with high yield, sodium tolerance and fluoroacetate resistance. The strain F3-10 takes sugarcane molasses as raw material, adopts Na2CO3 to control fermentation pH, and performs fed-batch fermentation in a 5L fermenter, and produces 53.96 grams of succinic acid per liter in 48 hours; the yield of consumed sugar is 89.2 percent; the utilization rate of sugar is 94.0 percent; and the ratio of succinic acid to heteroacid is 6.58:1. Therefore, the strain F3-10 is remarkably improved as compared with the original strain CGMCC 1593.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing dietary therapy orange juice by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei
InactiveCN104432323APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationHybrid cell preparationGenome shufflingMutagenesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing dietary therapy orange juice by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing the two mutagenesis progenies, implementing cell fusion and subculture, and conducting high-throughput screening by further adopting a substrate-induced adaptive strategy on the basis of the genome shuffling technology so as to obtain bacillus natto for the high production of nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening out methionine auxotrophic lactobacillus casei; and co-fermenting orange juice by virtue of the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei so as to obtain the orange juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine. In the orange juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine prepared by the method disclosed by invention, the content of the pyrroloquinoline quinine reaches 50-95ng / mL and the activity of the nattokinase reaches 366-780U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
Method for breeding epsilon-poly-L-lysine tolerant high-producing strain
InactiveCN104789550AMicroorganism based processesHybrid cell preparationMicroorganismHigh concentration
The invention belongs to the field of microbial breeding and relates to a method for screening an epsilon-poly-L-lysine tolerant high-producing strain through restructuring a genome. The method is characterized in that 16g / L epsilon-poly-L-lysine is added in a restructured strain regeneration medium by using a 4-5 cycle progressive protoplast fusion method, and finally, the yield-increased restructured strain capable of growing at high concentration is obtained.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Daunorubicin hydrochloride bacterium and yield increasing method thereof
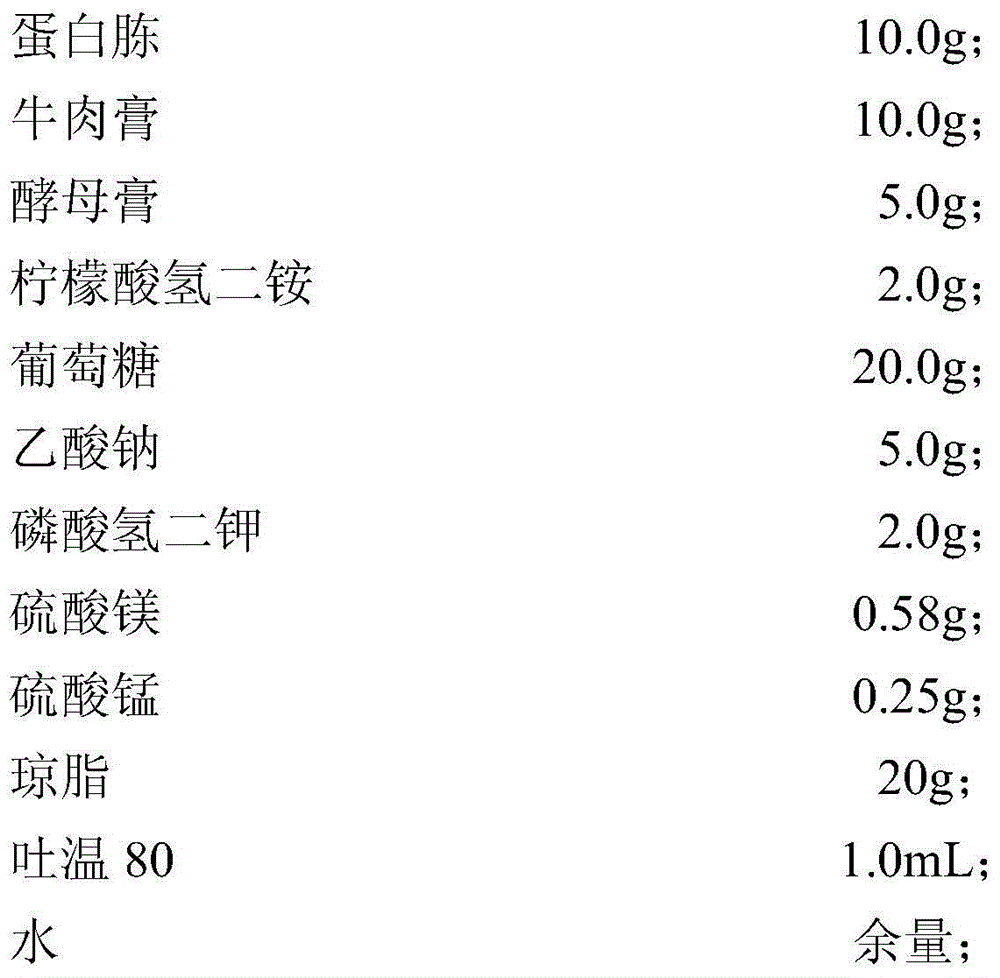
The invention provides a daunorubicin hydrochloride bacterium and a yield increasing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: Q1, preparing protoplast; Q2, regenerating the protoplast; Q3, performing ultraviolet mutagenesis of the protoplast; Q4, performing ion implantation mutagenization treatment of the prepared protoplast suspension according to the following steps; Q5, performing genome shuffling treatment by using bacterial colonies respectively treated in Q3 step and cultured in Q4 step as parents with different genetic backgrounds; Q6, culturing heterozygous regenerated offspring mycelia; Q7, preparing heterozygous offspring protoplast and performing protoplast fusion; Q8, performing multi-time fusion and regeneration of offspring protoplast, that is, performing multi-time repeated fusion and of offspring according to Q1-Q7, and screening to obtain a mutant strain with greatly increased daunorubicin yield.
Owner:JIANGSU HECHANG BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for improving doramectin preparing bacterium with genome reorganization technique
InactiveCN101343630BEasy to breedEasy to optimizeHybrid cell preparationGenome shufflingMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for preparing strain which can generate protoplast fusion by using marked plasmid. The invention has the advantages that marks can be easily added and removed, thereby being convenient for performing breeding and improvement of the strain based on the gene shuffling technology. The invention also has the advantages that the operation is simple, the cost is low, the requirement for equipment is low, and the chromosome of the strain can not be damaged.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
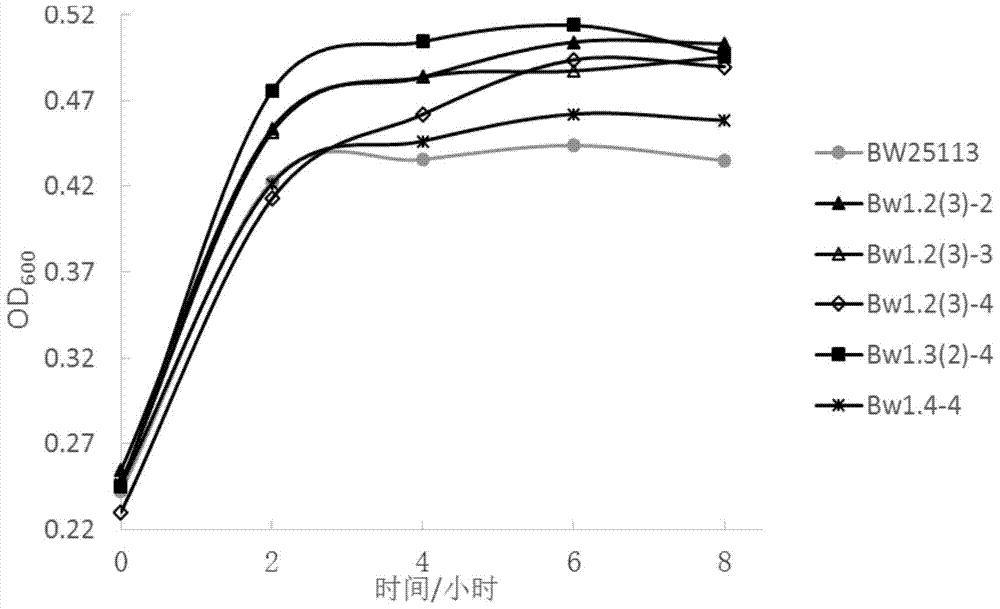
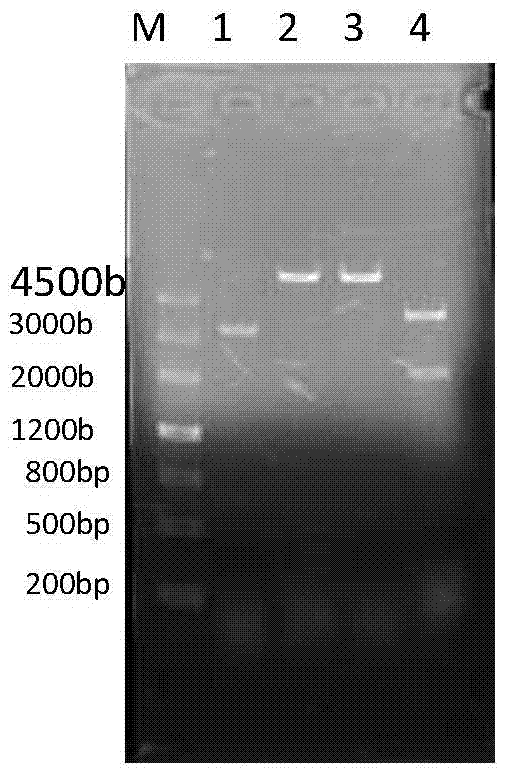
Error-prone whole-genome shuffling approach for Escherichia coli and butanol-tolerant Escherichia coli
ActiveCN105002218BFast and effective growthHigh tolerance traitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGenome shuffling
The invention discloses an error-prone whole-genome shuffling method for escherichia coli and the escherichia coli tolerating butanol. The escherichia coli tolerating the butanol is classified and named escherichia coli Bw1.8-4(Escherichia coli)Bw1.8-4, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2015365. The escherichia coli tolerating the butanol obtained through the method can grow efficiently in an LB liquid medium of 0.85% V / V butanol. According to the error-prone whole-genome shuffling method for the escherichia coli and the escherichia coli tolerating the butanol, an error-prone PCR technology is adopted for obtaining the escherichia coli tolerating the butanol fast and effectively without physicochemical mutagenesis and protoplast fusion, pollution of chemical reagents and radiation due to traditional physicochemical mutagenesis bacteria is avoided, and the defect of a long period due to continuous acclimatization is overcome. Compared with a traditional whole-genome shuffling technology, the escherichia coli tolerating the butanol and obtained through the method is higher in butanol tolerating capability than original strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing coix seed juice rich in pyrroloquinoline quinine and nattokinase by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei
InactiveCN104432378APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMicroorganismsMutant preparationGenome shufflingHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a method for preparing coix seed juice rich in pyrroloquinoline quinine and nattokinase by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing the two mutagenesis progenies, implementing cell fusion and subculture, and conducting high-throughput screening by further adopting a substrate-induced adaptive strategy on the basis of the genome shuffling technology so as to obtain bacillus natto for the high production of nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening out methionine auxotrophic lactobacillus casei; and co-fermenting coix seed juice by virtue of the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei so as to obtain the coix seed juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine. In the coix seed juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine prepared by the method disclosed by invention, the content of the pyrroloquinoline quinine reaches 80-101ng / mL and the activity of the nattokinase reaches 528-716U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
Preparation method for diet therapy fermented black rice juice
InactiveCN104397815APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationHybrid cell preparationGenome shufflingHigh-throughput screening
The invention discloses a preparation method for diet therapy fermented black rice juice. The preparation method comprises the following steps: conducting nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 generating nattokinase and pyrrolequinoline respectively; mixing mutagenized subsequent generation of the bacillus natto 10261 and 10263; conducting cell fusion subcultring; adopting a substrate induced adaptability strategy based on a genome shuffling technique; conducting high throughput screening to obtain bacillus natto generating nattokinase and pyrrolequinoline in high yield; conducting nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei; screening methionine auxotroph lactobacillus casei; fermenting the screened bacillus natto and the lactobacillus casei to obtain the black rice juice rich in nattokinase and pyrrolequinoline. In the black rice juice, the content of the pyrrolequinoline reaches 64-128 ng / mL; the nattokinase activity reaches 481-774 U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
A method for preparing and regenerating protoplasts of Welan gum synthetic bacteria
ActiveCN106591167BEasy to operateGood repeatabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSphingomonas sp.
The invention provides a method for preparing and regenerating sphingomonas sp protoplast, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. According to the method, sphingomonas sp is used as an original strain; the sphingomonas sp protoplast is prepared by an enzymolysis method; the formation rate of the obtained protoplast is 97.3 percent; and the regeneration rate is 33.9 percent. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient; the preparation rate of the protoplast is high; the activity is high; and the further breeding of the excellent sphingomonas sp strain by using protoplast fusion and genome shuffling is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Method for preparing dietary therapy watermelon juice by virtue of breeding and co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei
InactiveCN104432352APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationLactobacillusGenome shufflingGenetics
The invention discloses a method for preparing dietary therapy watermelon juice by virtue of breeding of bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei and co-fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing the two mutagenesis progenies, implementing cell fusion and subculture, and conducting high-throughput screening by further adopting a substrate-induced adaptive strategy on the basis of the genome shuffling technology so as to obtain bacillus natto for the high production of nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening out methionine auxotrophic lactobacillus casei; and co-fermenting watermelon juice by virtue of the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei so as to obtain the watermelon juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine. In the watermelon juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine prepared by the method disclosed by invention, the content of the pyrroloquinoline quinine reaches 51-100ng / mL and the activity of the nattokinase reaches 377-875U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
Error-prone whole-genome shuffling approach for Zymomonas mobilis and furfural-tolerant Zymomonas mobilis
ActiveCN105132348BEfficient growth processFast and effective growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenome shufflingMicrobiology
The invention discloses an error-prone whole-genome shuffling method of zymomonas mobilis and furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis. The furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis is classified and named as zymomonas mobilis F2.5-4 with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M2015366. The furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis obtained by the method is capable of growing in an RM culture medium with 3g / L furfural efficiently. Compared with a traditional whole-genome shuffling technology, the error-prone whole-genome shuffling method has the advantages that since the error-prone PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology is applied effectively, the furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis can be obtained rapidly and effectively without physical and chemical mutagenesis and protoplast fusion. Growth of a starting zymomonas mobilis strain in the culture medium with the 3g / L furfural is inhibited severely, and the furfural-tolerant zymomonas mobilis obtained by the method is stronger than the starting zymomonas mobilis strain in furfural tolerance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
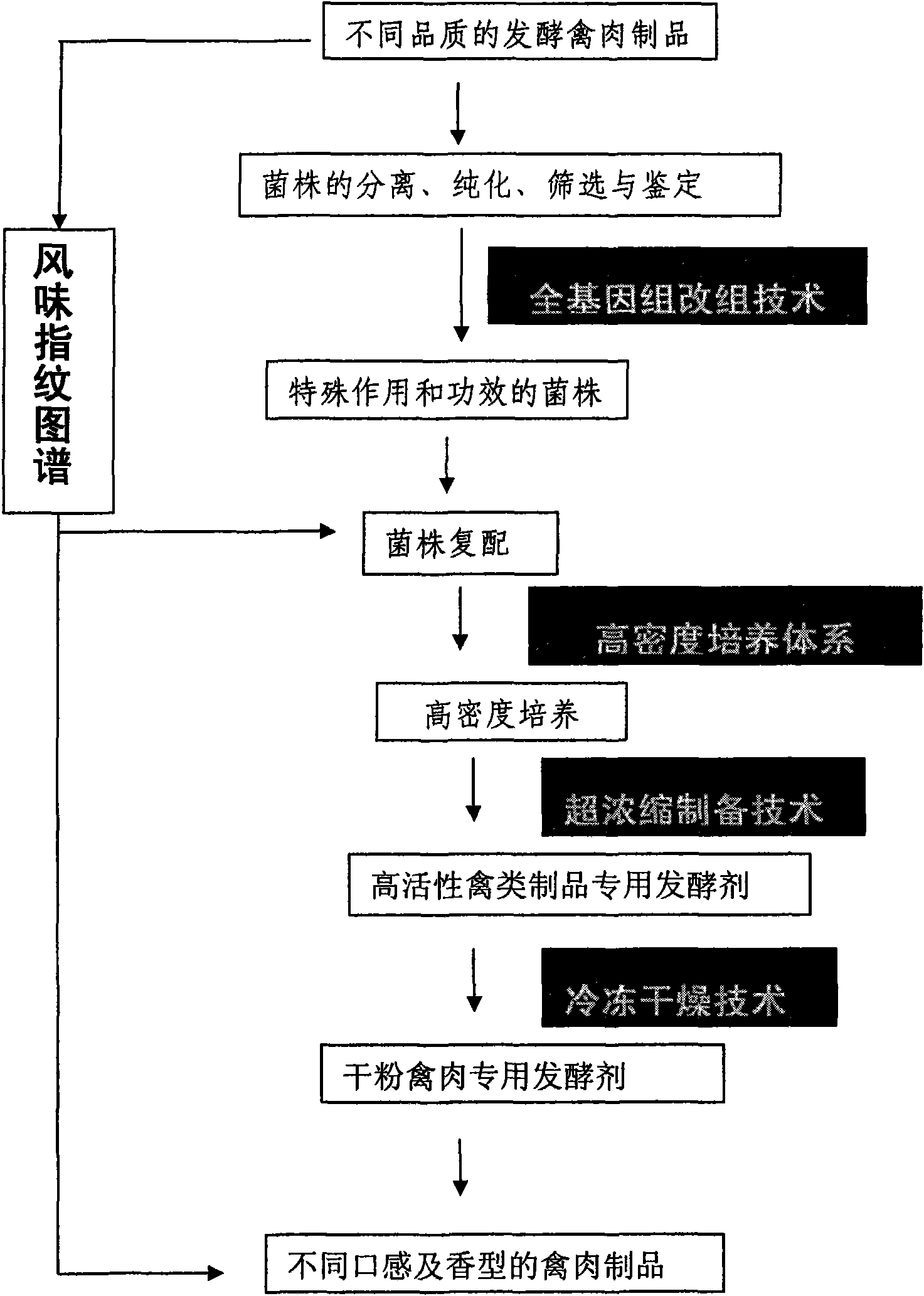
Production method of characteristic fermented poultry meat products
InactiveCN101940332AStrong heat resistanceThere is no GMO safety controversyFood preparationBiotechnologyGenome shuffling
The invention relates to a food processing method, in particular to a production method of characteristic fermented poultry meat products. The production method comprises the steps of separating and screening microbial strains with special roles and effects, such as the strains for producing aroma, producing freshness and the like, carrying out fast improvement on production traits of excellent microbes by adopting the complete genome shuffling technology, and breeding fermentation agent strains with excellent traits, stable performances, strong stress resistance and safe administration in a directional manner, thereby developing modern fermented poultry meat new products with low cholesterol, low salt, delicious taste, strong aroma, easy digestion and reasonable nutrition, upgrading the processing level of the poultry meat products, enriching the types of the fermented meat products and meeting the demands of broad consumers on the medium and high grade fermented meat products.
Owner:赵保雷
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com