Acid resistance and high succinic acid yield strain and preparation method thereof
A succinic acid and acid-resistant technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as large demand for petrochemical materials and power consumption, cultivation conditions and yield limitations, and environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
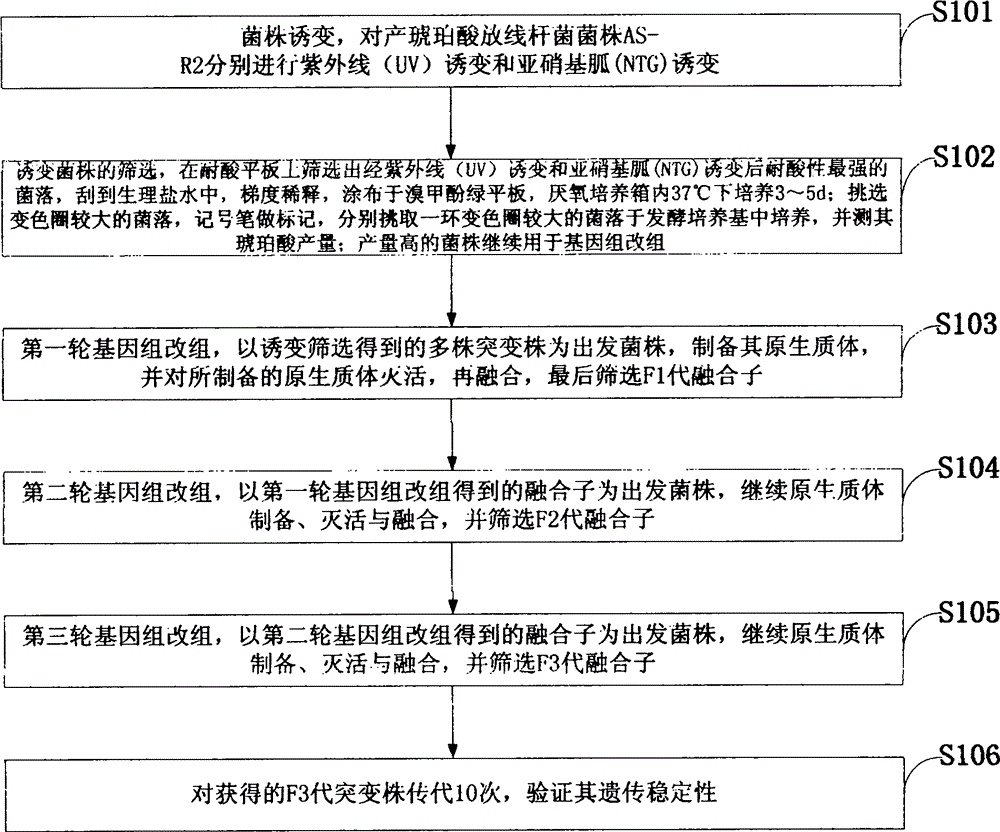
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for preparing the acid-resistant and high-yield succinic acid strain of the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0039] S101: strain mutagenesis, ultraviolet (UV) mutagenesis and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutagenesis were performed on the Actinobacillus succinogenes strain AS-R2, respectively;
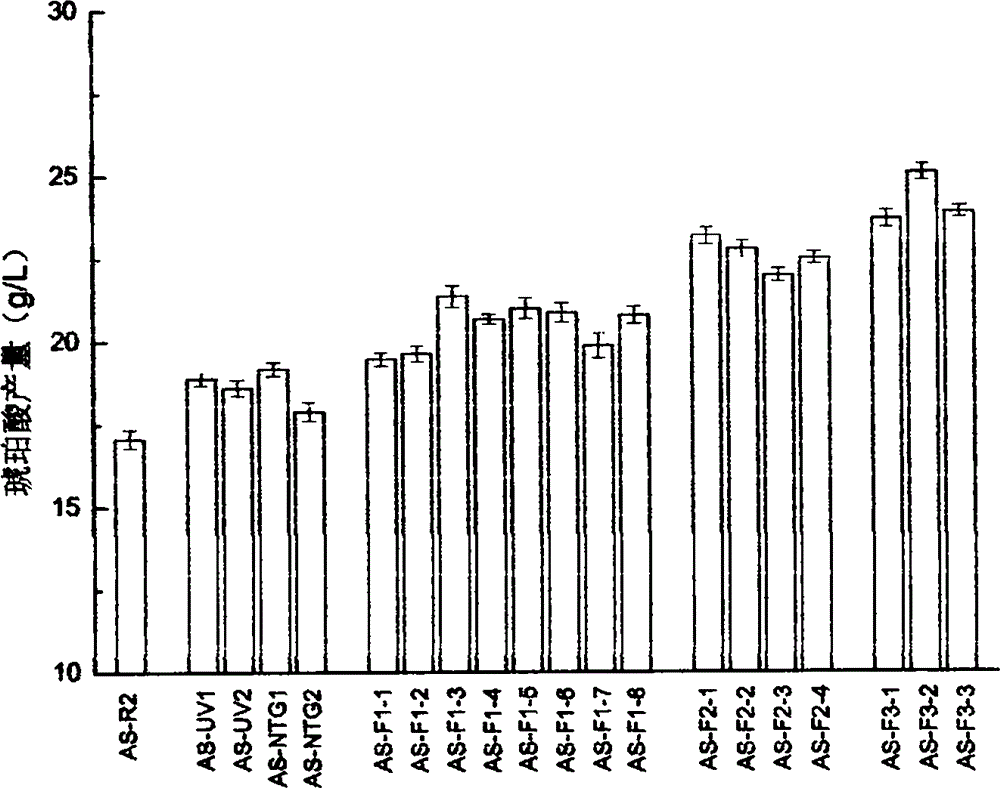
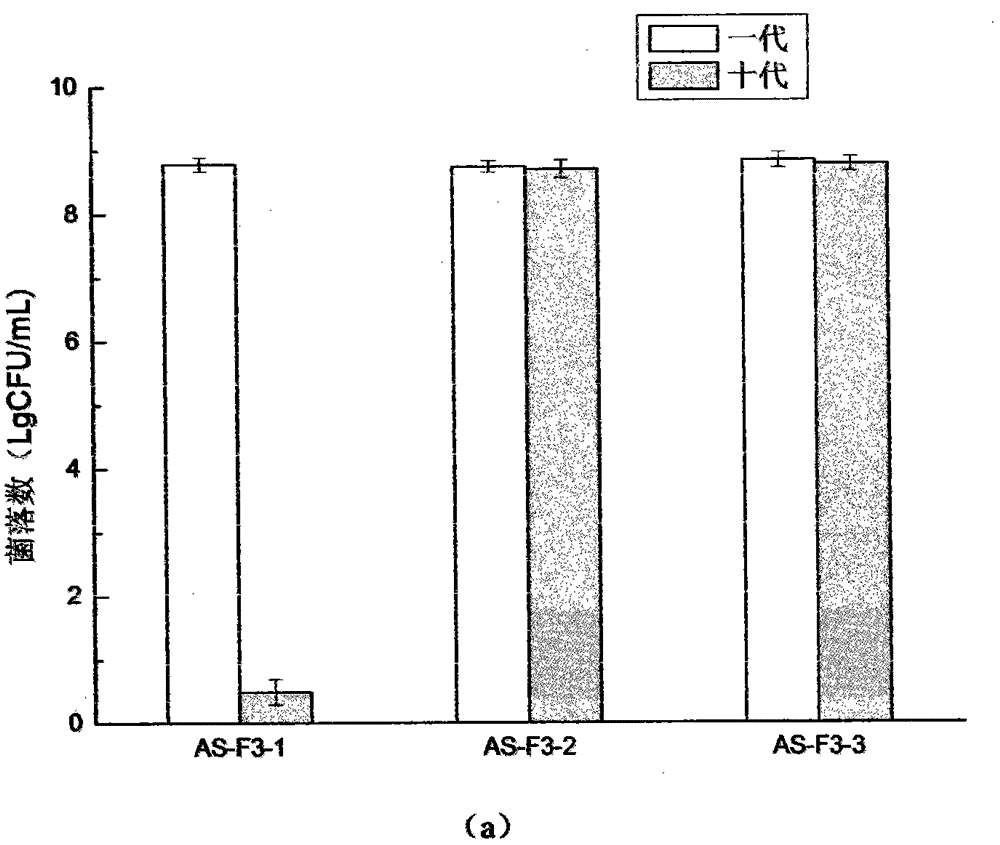
[0040] S102: Screening of mutagenized strains, screen out the most acid-resistant colony after ultraviolet (UV) mutagenesis and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutagenesis on an acid-resistant plate, scrape into normal saline, serially dilute, and spread Cultivate on bromocresol green plate at 37°C for 3-5 days in an anaerobic incubator; select colonies with larger color-changing circles, mark them with a marker pen, and pick a colony with larger color-changing circles to culture in the fermentation medium , and measured its succinic acid production; strains with high production continued to be used for genome shuffling;...
Embodiment 1
[0089] Protoplast preparation conditions:
[0090] Pick one loop of each mutant strain in the activation medium to activate the first generation (cultivate for 24 hours), activate it for the second time in the activation medium (cultivate for 24 hours) with 3% inoculum, then inoculate with 3% inoculum to contain 1.0% In the fermentation medium of glycine, cultivate for 6 hours, take 10ml of the culture solution in a sterilized centrifuge tube, centrifuge at a speed of 8000r / min for 15min, pour out the supernatant, and resuspend the bacterial cell pellet in 10ml of osmotic pressure stabilization solution. Centrifuge and wash the bacteria twice, continue to resuspend the bacteria pellet in 10ml osmotic pressure stabilization solution, shake well, add lysozyme solution with a final concentration of 0.08mg / ml, and enzymolyze in a water bath at 37°C for 40min at constant temperature; After the solution is completed, take it out from the water bath and centrifuge at a speed of 6000r...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Protoplast inactivation:
[0093] The protoplast suspension obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of each mutant strain was mixed evenly in equal amounts, and then divided into two parts, one was inactivated by heat inactivation, and the other was inactivated by ultraviolet inactivation;
[0094] Heat inactivation: put the protoplast suspension used for heat inactivation in a 60°C water bath, and inactivate at a constant temperature in the dark for 30 minutes;
[0095] Ultraviolet inactivation: Divide the protoplast suspension used for ultraviolet inactivation equally, each portion contains 10ml of protoplast suspension, pour it into a sterilized petri dish, put it into a sterilized magnetic stirring bar, and place it under the ultraviolet light for 30cm UV irradiation on a magnetic stirrer for 35 minutes, when the time is up, turn off the magnetic stirrer;
[0096] The above-mentioned inactivation process must be carried out in the dark;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com