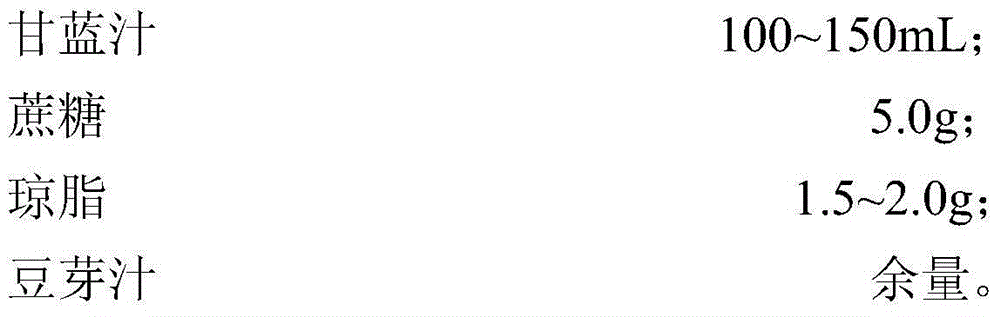Method for producing dietary therapy brassica oleracea by virtue of co-fermentation of bacillus natto and lactobacillus
A technology of co-fermentation and lactic acid bacteria, which is applied in the field of co-fermentation of Bacillus natto and lactic acid bacteria to produce dietary cabbage, can solve the problems of unrelated breeding medium and fermentation medium, low yield of target products, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0103] (h) The preparation of the cabbage juice is obtained by directly squeezing the cabbage juice.
[0104] In the embodiment of the present invention, Bacillus natto 10261 and Bacillus natto 10263 adopt the prior art, and Bacillus natto 10261 comes from China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection Center (CICC), address: 24 Jiuxianqiao Middle Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing No. 6 building; the storage date is 2002, and the strain maintenance number is 10261; Bacillus natto 10263 is from the China Industrial Microbiology Culture Collection Center (CICC), address: Courtyard 6, No. 24, Jiuxianqiao Middle Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing Building No. 1; the storage date was 2002, and the strain maintenance number was 10263; Lactobacillus casei Shirota was from Yakult (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.; the mouse anti-PQQ IgG monoclonal antibody PQQ-mAb was a commercially available product, purchased from Jiaxing Yuanke Biotechnology Co., Ltd., the product number is YK-Ab-013.
Embodiment 1
[0106] The present invention prepares fermented cabbage rich in NK and PQQ through breeding of Bacillus natto and Lactobacillus casei and co-fermentation thereof, comprising the following steps:
[0107] (1) Breeding of Bacillus natto BN-NKPQQ-RWX-404 with high yield of NK and PQQ
[0108] Using the substrate-induced adaptive strategy, the high-yield NK and PQQ Bacillus natto BN-NKPQQ-RWX-404 was obtained through genome rearrangement and high-throughput screening technology. The obtained Bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 producing NK and PQQ were subjected to nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively; then the offspring were mixed for mutagenesis, and cell fusion was carried out (fusogenic agent was polyethylene glycol 4000), subcultured, Realized genome shuffling, optimized and integrated the dominant mutations of all mutagenized progenies of Bacillus natto 10261 and 10623, and bred a high-yield NK and PQQ Natto with high yield, vigorous growth, stable genetics, and suitable as ...
Embodiment 2
[0120] The present invention prepares fermented cabbage rich in NK and PQQ through breeding of Bacillus natto and Lactobacillus casei and co-fermentation thereof, comprising the following steps:
[0121] (1) Breeding of Bacillus natto BN-NKPQQ-RWX-404 with high yield of NK and PQQ
[0122] Using the substrate-induced adaptive strategy, the high-yield NK and PQQ Bacillus natto BN-NKPQQ-RWX-404 was obtained through genome rearrangement and high-throughput screening technology. The obtained NK and PQQ-producing Bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 were subjected to nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis respectively; then the offspring were mixed for mutagenesis, cytoplasmic fusion was carried out (fusogenic agent was polyethylene glycol 4000), subcultured, Realized genome shuffling, optimized and integrated the dominant mutations of all mutagenized progenies of Bacillus natto 10261 and 10623, and bred a high-yield NK and PQQ Natto with high yield, vigorous growth, stable genetics, and suitable ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com