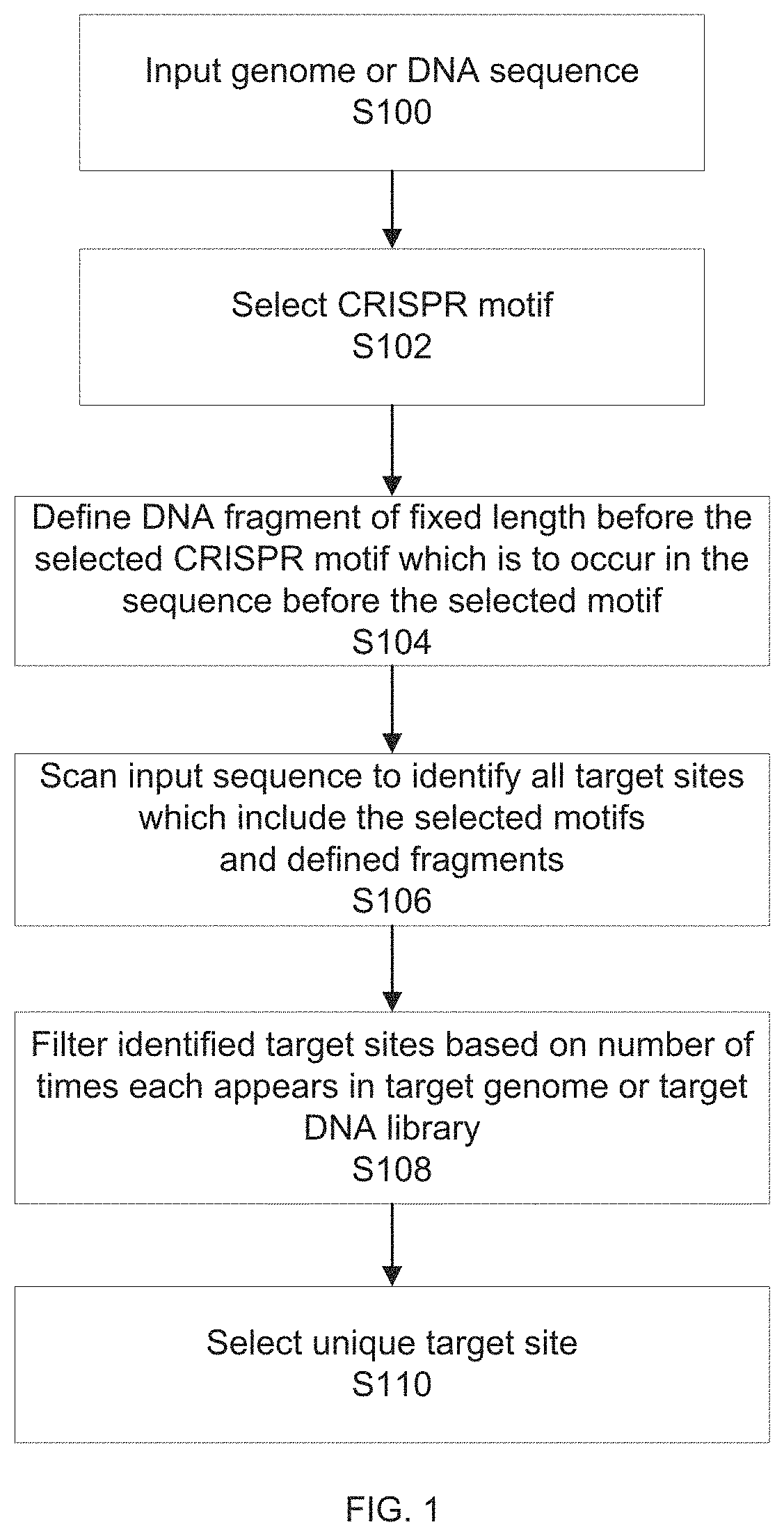
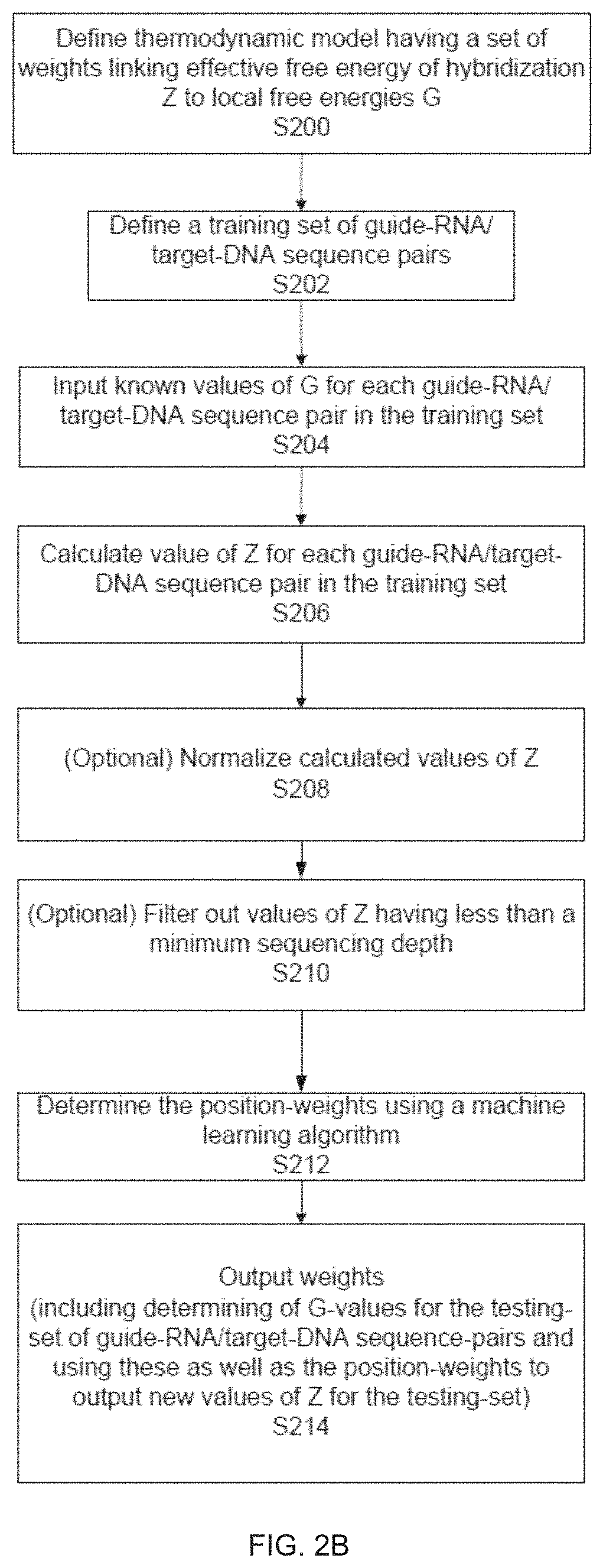
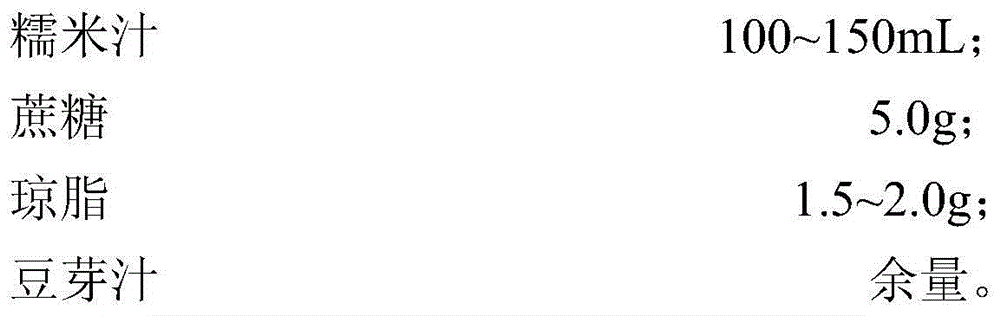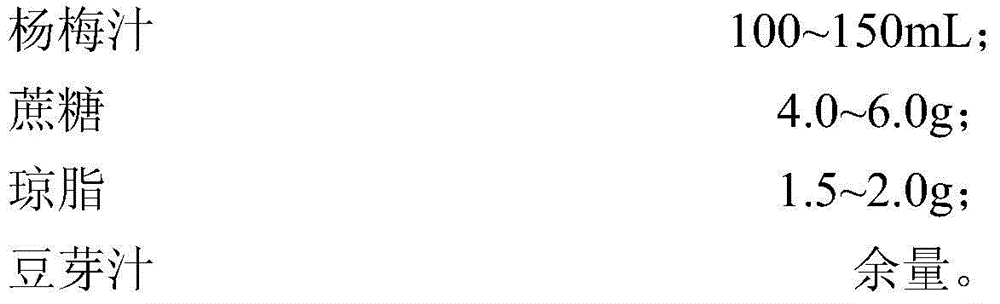Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Genome rearrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A genome rearrangement is a major genomic mutation, usually driven by errors in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. These large-scale changes to the structure of chromosomes are almost always harmful and usually result in the death or sterility of the developing organism, but in very rare cases, they provide a significant advantage.
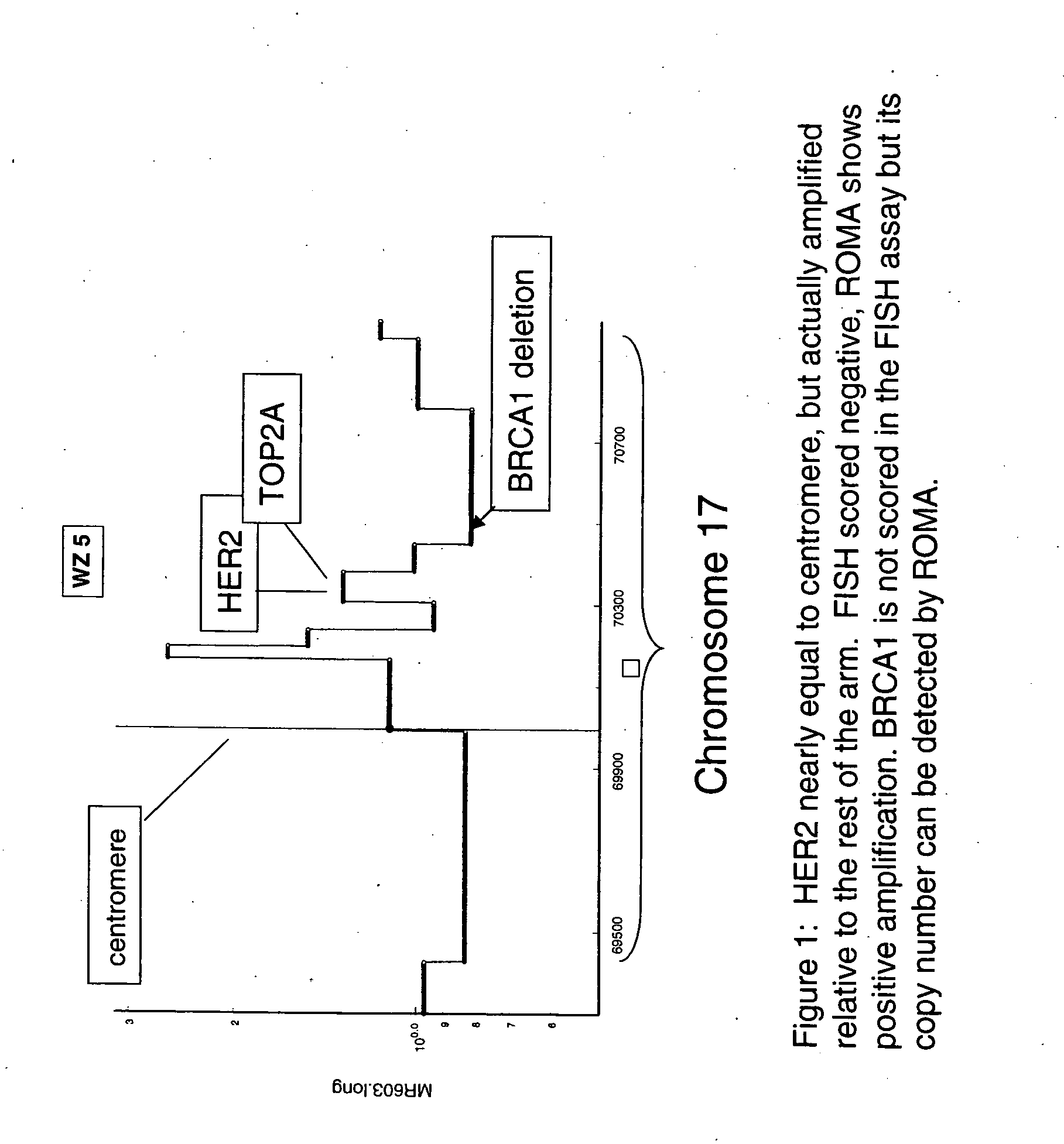
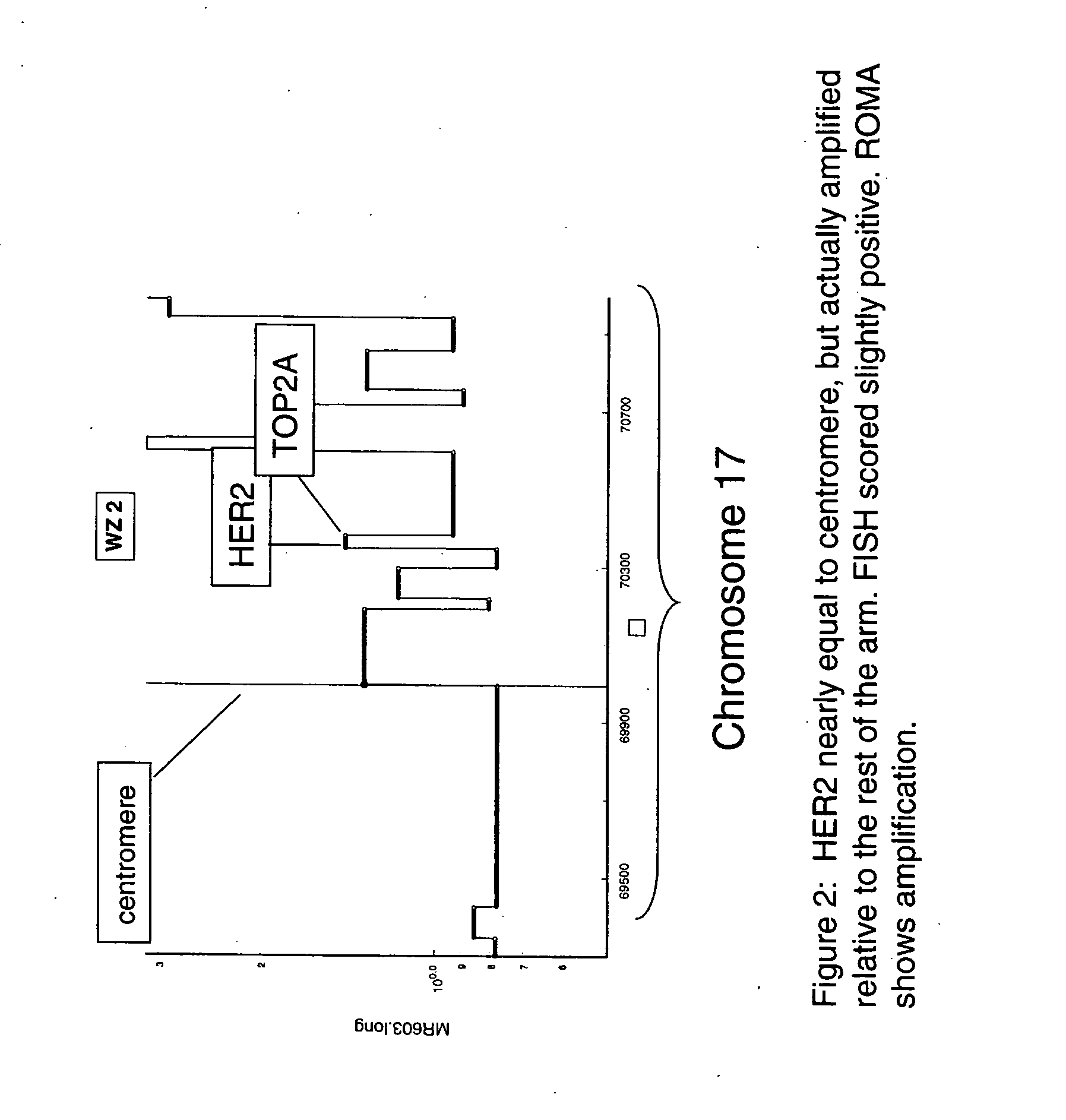
Use of roma for characterizing genomic rearrangements
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for detecting genomic rearrangements (e.g., amplification) at one or more genetic loci and various applications of such methods and compositions. Examples of genetic loci include HER2, TOP2A and other loci on the human chromosome 17.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
Targeted genomic rearrangements using site-specific nucleases
The present invention relates to a method for genomic DNA rearrangements, and more particularly, to a method for deletion, duplication, inversion, replacement, or rearrangement of genomic DNA using pairs of site-specific nucleases targeting two or more sites in the genome, a cell in which genomic DNA is deleted, duplicated, inverted, replaced, or rearranged by the same method, and a method for expressing the site-specific nucleases in cells. Further, the present invention relates to a method for inserting synthetic DNA molecules into the genome using site-specific nucleases targeting a pre-determined site in the genome, a cell in which DNA insertion occurs by the same method, and a method for expressing the site-specific nucleases in cells.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
Long insert-based whole genome sequencing
ActiveUS20150126379A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomic sequencingWhole genome sequencing
The present invention is directed to a method of detecting a genomic rearrangement in a nucleic acid sample with Long Insert Whole Genome Sequencing (LI-WGS). The method may include obtaining a nucleic acid sample and then fragmenting the nucleic acid sample (e.g., via sonication). In particular, the fragmenting may result in the production of a plurality of inserts. Thereafter, the method comprises purifying the plurality of inserts using magnetic beads and then amplifying the purified plurality of inserts. In addition, the method further comprises sequencing the purified and amplified plurality of inserts. In some aspects, the plurality of inserts have a length of between about 800 and about 1,100 base pairs.
Owner:TRANSLATIONAL GENOMICS RESEARCH INSTITUTE
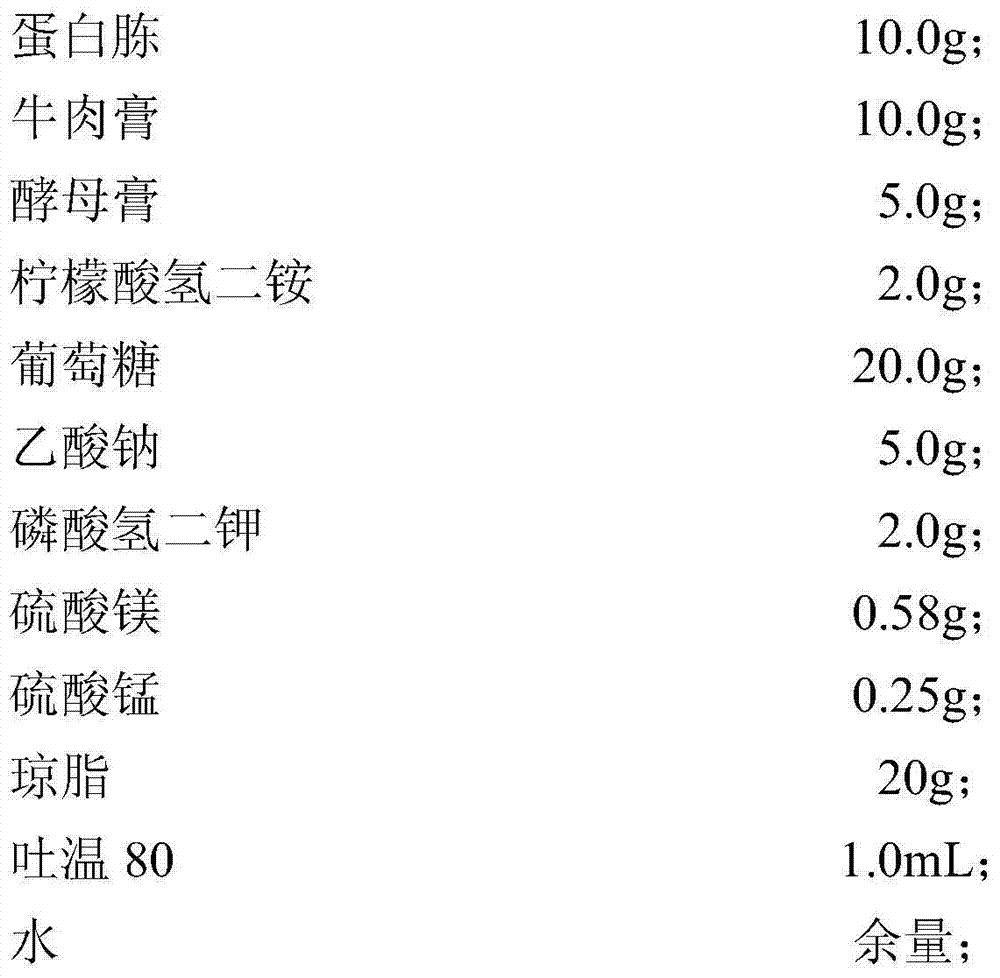
High-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and breeding method thereof
ActiveCN103232948AHigh genetic stabilityBack mutationFungiMutant preparationBiotechnologyEthanol yield
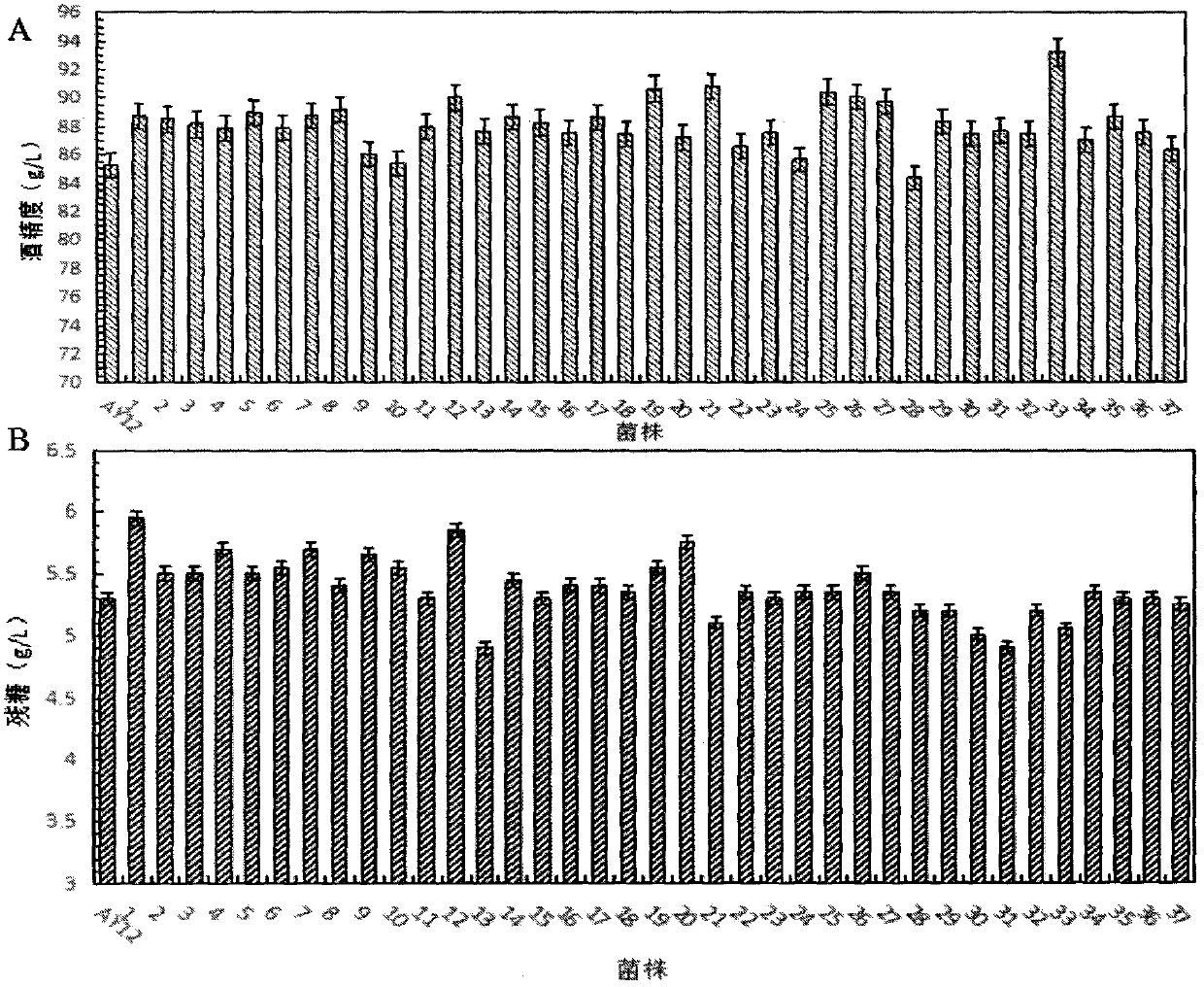
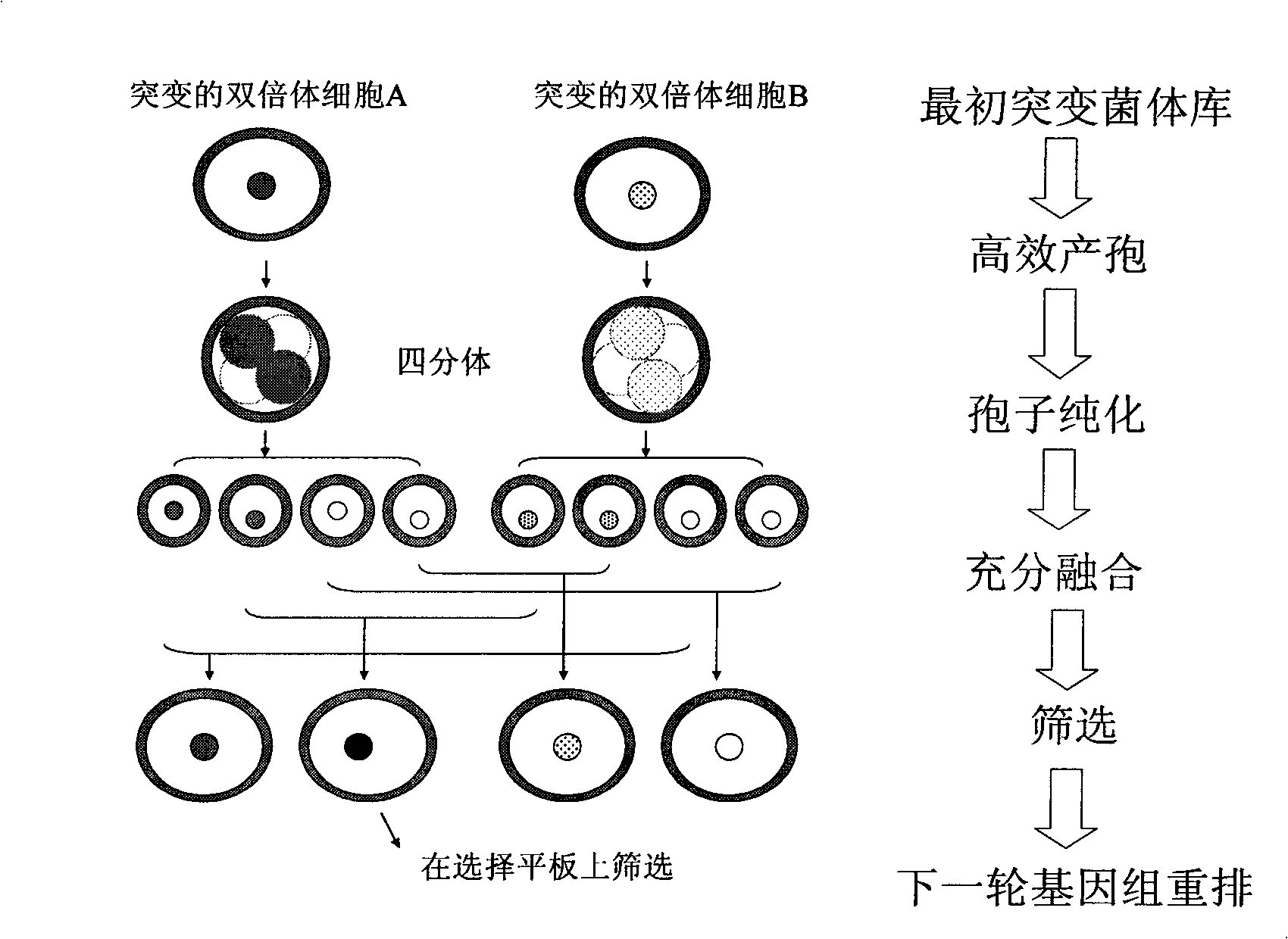
The invention provides a high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a breeding method of the high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) SY-5-11L has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7377. The strain is characterized in that the ethanol yield is 13.9% (v / v) at a condition of fermenting at high temperature of 38 DEG C on the premise that other fermenting performances are not influenced, the yield is improved by 17.8% as compared with that of a parent strain. The ethanol output at the condition of fermenting at high temperature of 40 DEG C is 12.2% (v / v), and is improved by 34.1% as compared with that of the parent strain. The breeding method comprises the following steps of: performing artificial ultraviolet mutagenesis on an initial strain of the saccharomyces cerevisiae; screening out 23 forward mutant strains as a genome rearrangement library, wherein the ethanol output of the forward mutant strains are obviously raised on the condition of fermenting at a high temperature; and performing the genome rearrangement at three rounds, thus gaining the mutant strains with the maximum ethanol output under the high-temperature fermenting condition. The finally bred saccharomyces cerevisiae strain can be subjected to alcoholic fermentation at the high-temperature fermenting condition, brings no special requirements to fermenting equipment and technological conditions, and can be put into service with the equipment and conditions of general plants, thus having a wide application prospect.
Owner:贵州钓鱼台国宾酒业有限公司
Method for creating distiller's yeast ethanol high yield bacterial strain
InactiveCN101323837AIncrease productionLow residual sugarFungiMutant preparationEthylmethane SulfonateSpore
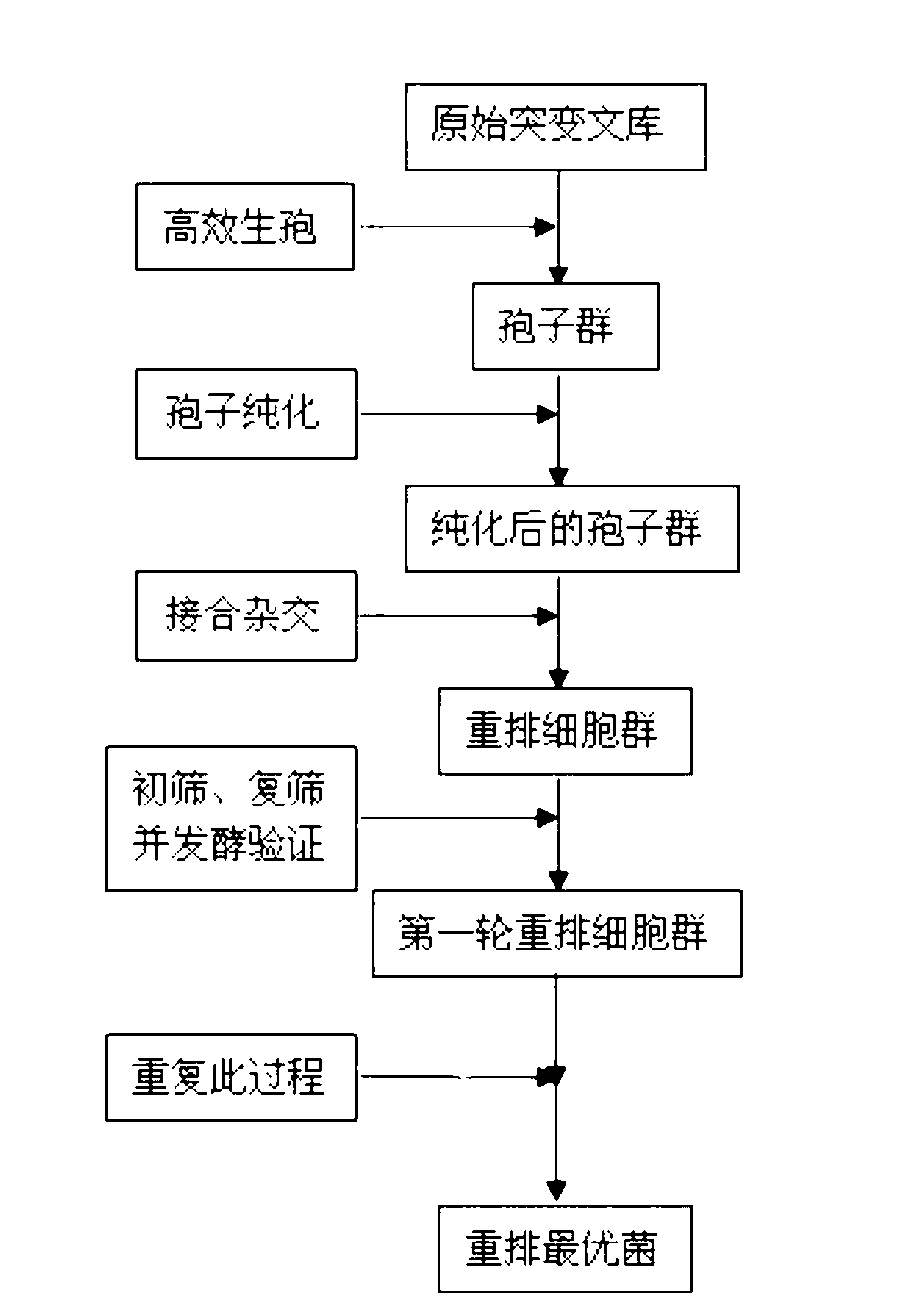
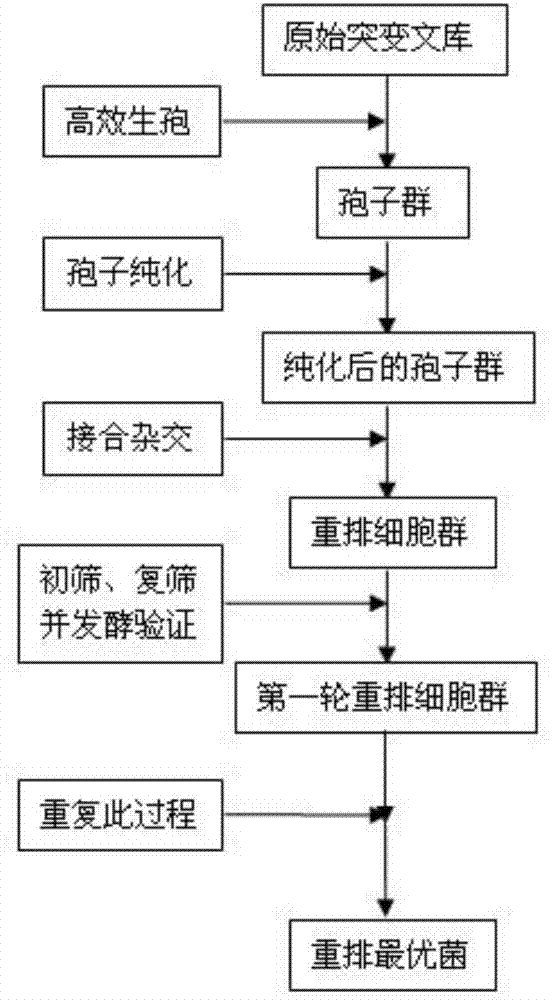
The invention discloses a method for constructing the ethanol high-yield strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which comprises the following steps: (1) ethylmethane sulfonate is utilized to carry out random mutagenesis to the amphiploid strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to cause the final concentration of the volume of the ethylmethane sulfonate in the bacteria liquid to be processed to be 2 to 4 percent and the concentration of the amphiploid strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to be 2 multiplied by 10<6> to 6 multiplied by 10<6> cell / ml; (2) 3 to 5 rounds of the sexual recombination of high efficient sporulation, spore purification and full integration cause genome recombination between strains in a library to construct the ethanol high-yield strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The ethanol output of the recombinant strains constructed by the method of the invention is increased by 8.88 percent compared with that of contrast strains, residual sugar is reduced by 64.37 percent, the fermentation cycle is shortened by 10 hours and ethanol and high osmotic resistance are 5.10 times of that of the contrast strains, thus providing excellent strains for the industrial production of fuel ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method of Inducing Genome Reorganization Via Intracellular Activation of Thermostable Multifrequency Dna-Cleaving Enzyme
InactiveUS20080166809A1Easy to implementThe process is simple and convenientHydrolasesMicroorganismsGenomic DNABiological activation
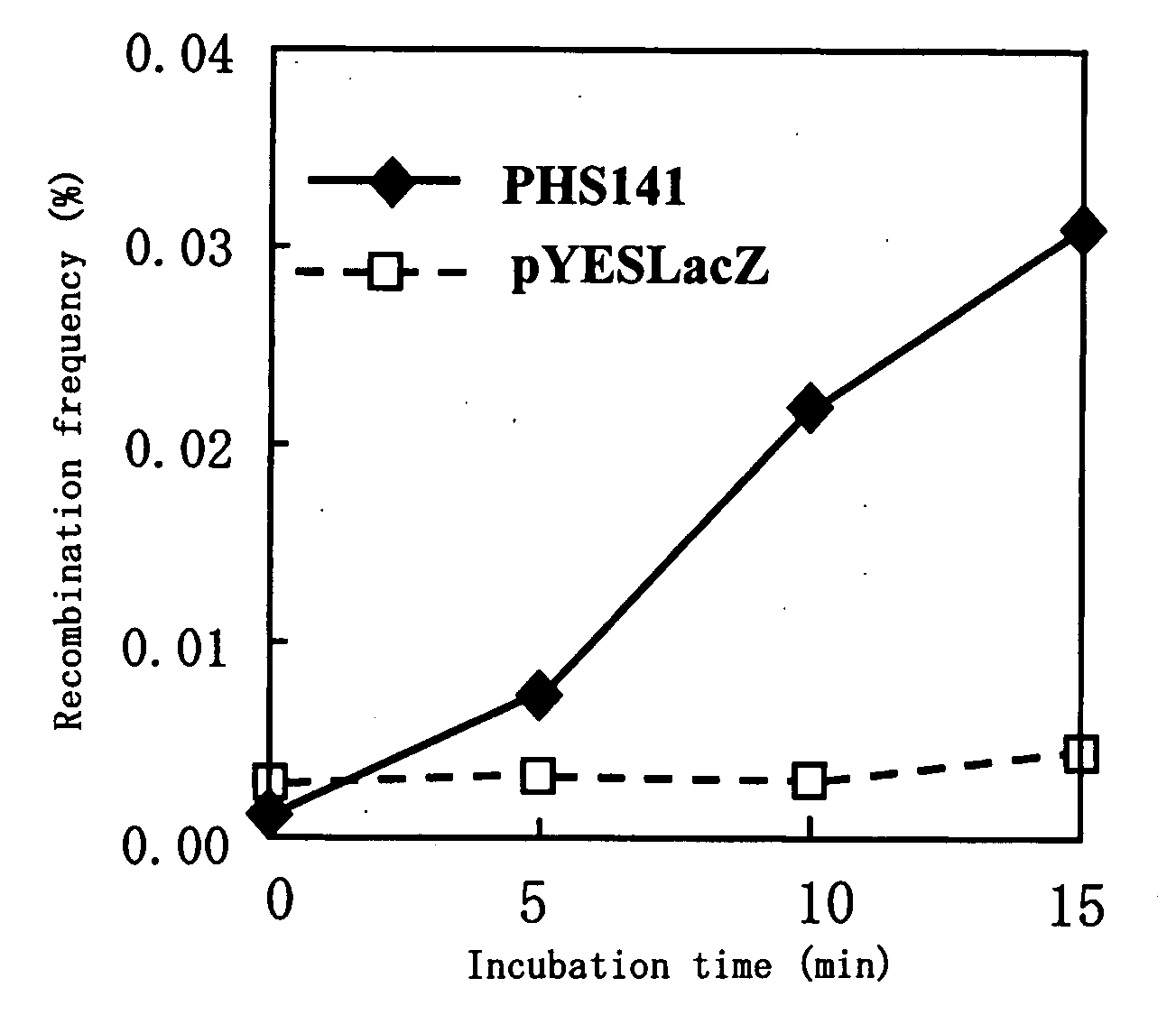
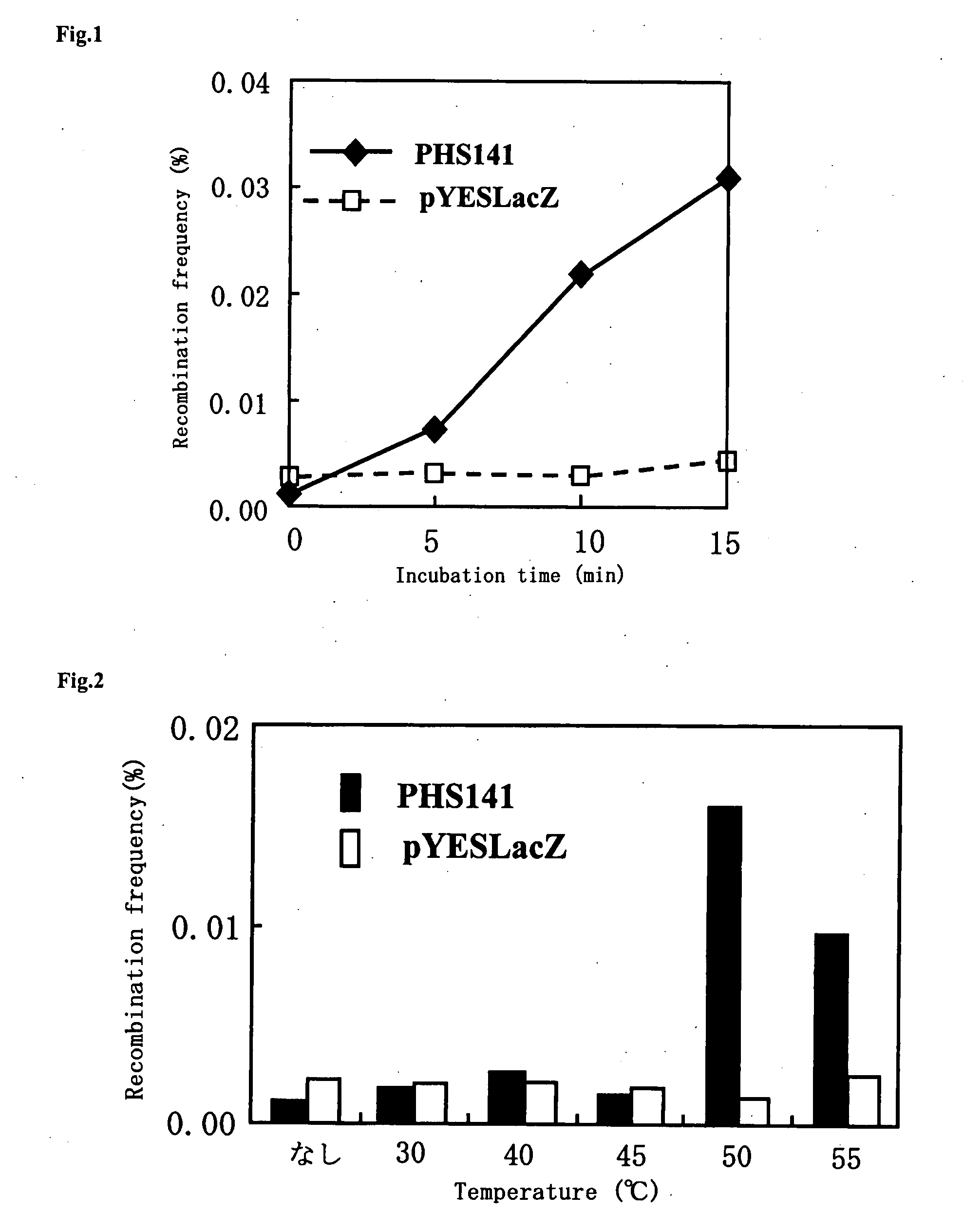
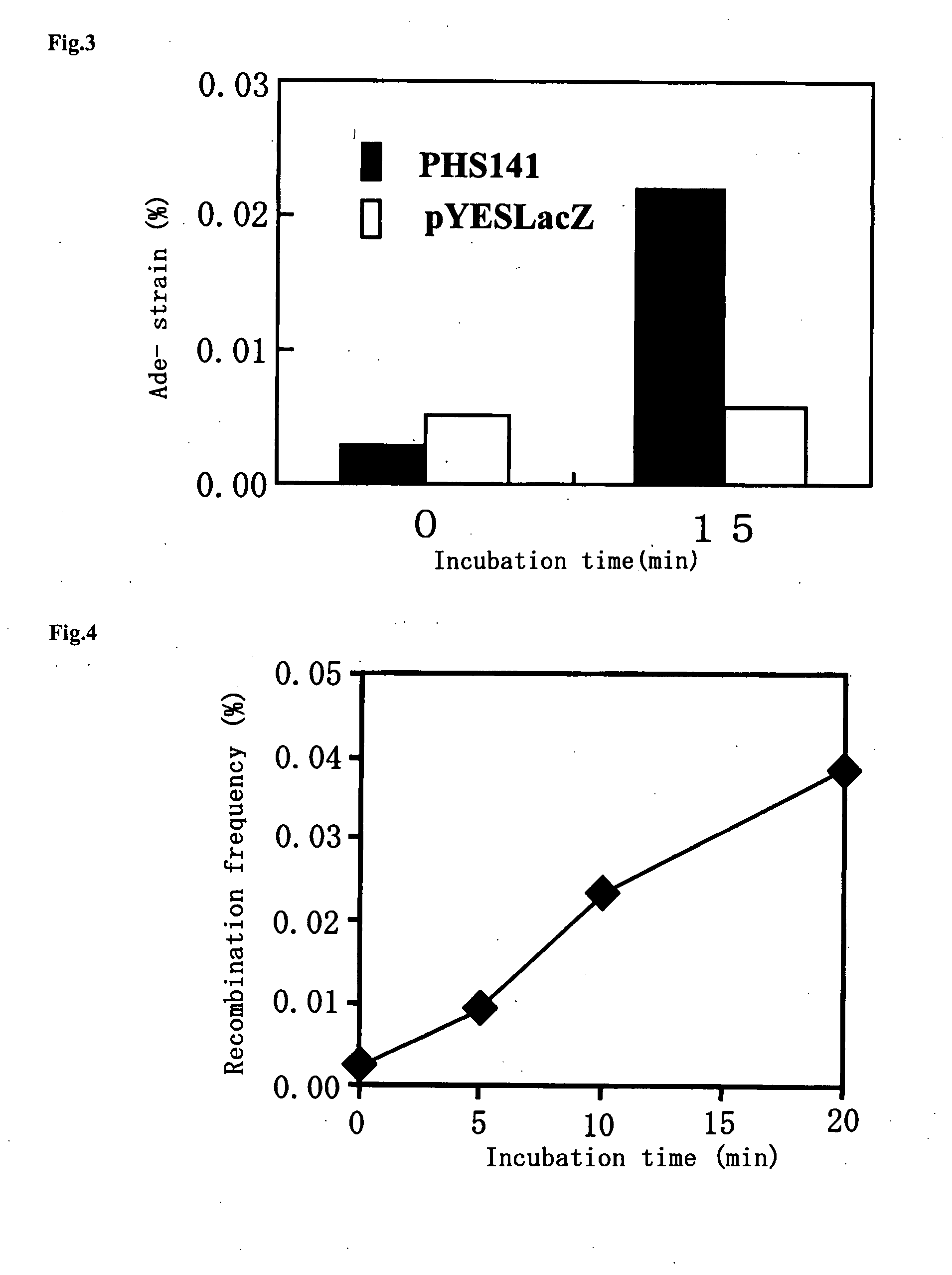
The present invention relates to a method for increasing genetic recombination frequency in a genomic DNA and a method for inducing genome rearrangement. Specifically, according to the present invention there are provided: the method for increasing genetic recombination frequency in a cell in which genetic recombination takes place at any sites in the genome, comprising causing a restriction enzyme to be expressed in the cell, inducing transient activation of the restriction enzyme, and then introducing 2 or more double strand cleavages into any genomic DNA of the cell, so as to increase the genetic recombination frequency; the method for inducing genome rearrangement through the use of the above method; and cells each prepared through the use of the above 2 methods.
Owner:RIKEN
High temperature-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and constructing method thereof
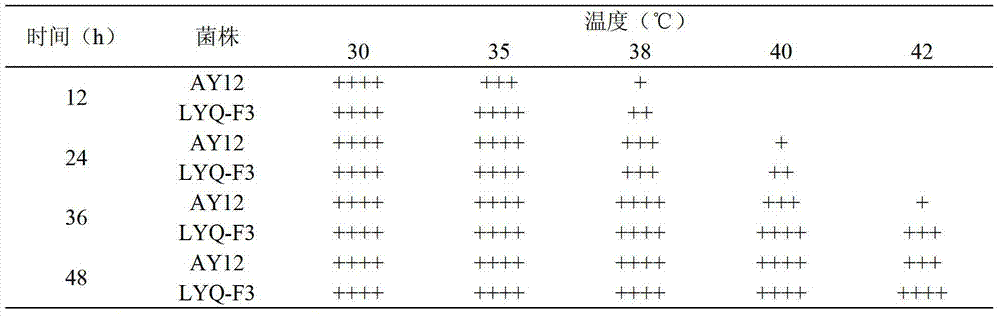
InactiveCN107858298AImprove fermentation effectSimple and fast operationFungiMutant preparationBiotechnologyHydrolysate
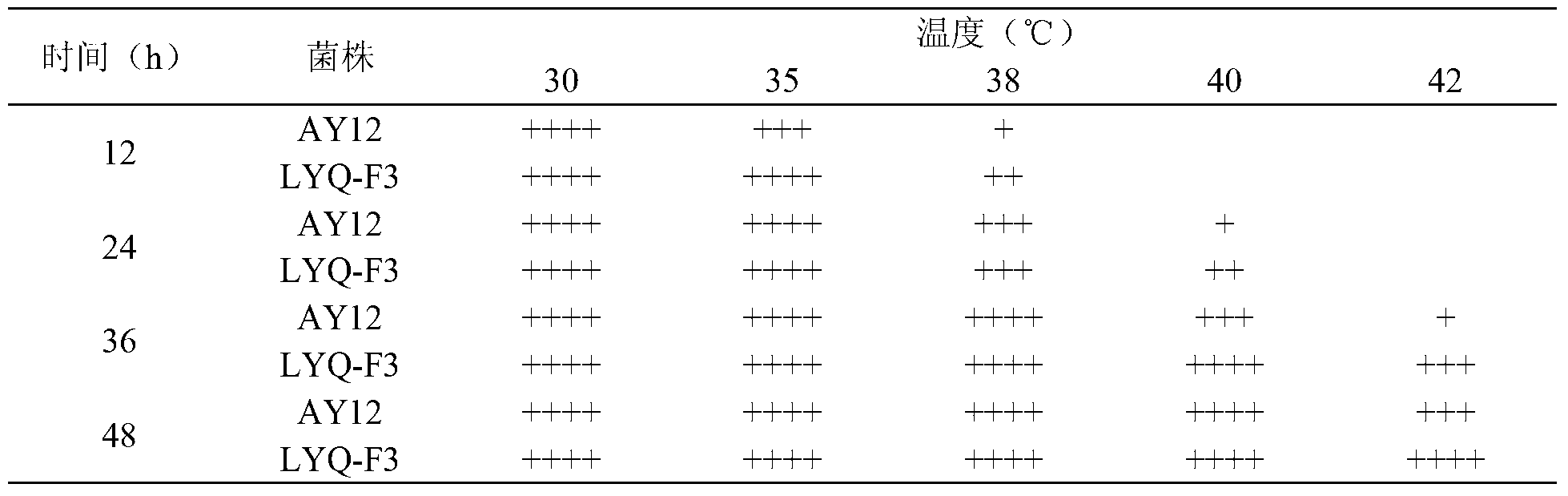
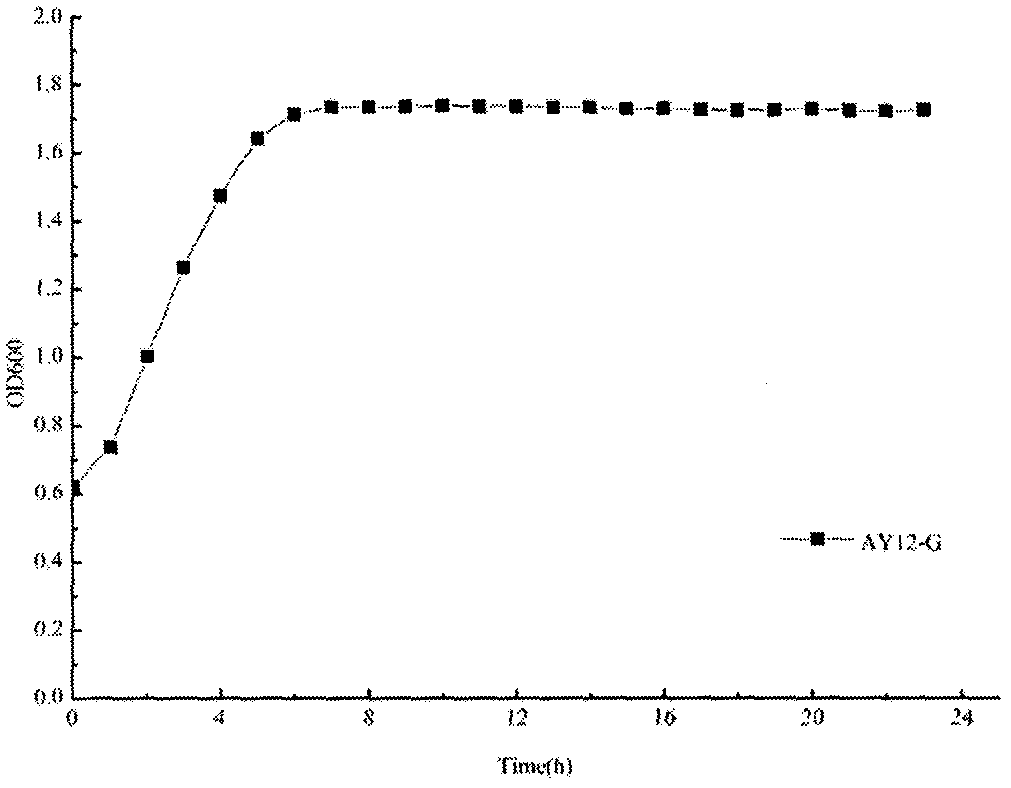
The invention discloses a screening and constructing method for high temperature-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out ARTP plasma mutagenesis on astrain AY12-G used as an original strain, carrying out primary screening at 37 DEG C to obtain 150 strains, carrying out genome rearrangement on the 150 strains, and primarily screening the 150 strains at 37 DEG C to obtain 137 strains; and carrying out 35 DEG C corn hydrolysate fermentation on the 137 strains to obtain 14 strains, carrying out 35 DEG C simultaneous saccharification and fermentation on the 14 strains and 48 h cell survival rate determination to obtain 7 strains having improved high temperature fermentation performances and 48 h cell survival rate, and carrying out 41 DEG C and 42 DEG C high temperature domestication on the 7 strains to finally obtain a strain X-130 having excellent high temperature fermentation performances and significantly improved 48 h cell survival rate. Compared with the original strain AY12-G, the strain X-130 has the advantages of improvement of the 48 h cell survival rate by 84.68%, no obvious change of the 35 DEG C simultaneous saccharification and fermentation performances, and shortening of the fermentation cycle by 12 h through adding acidic protease.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
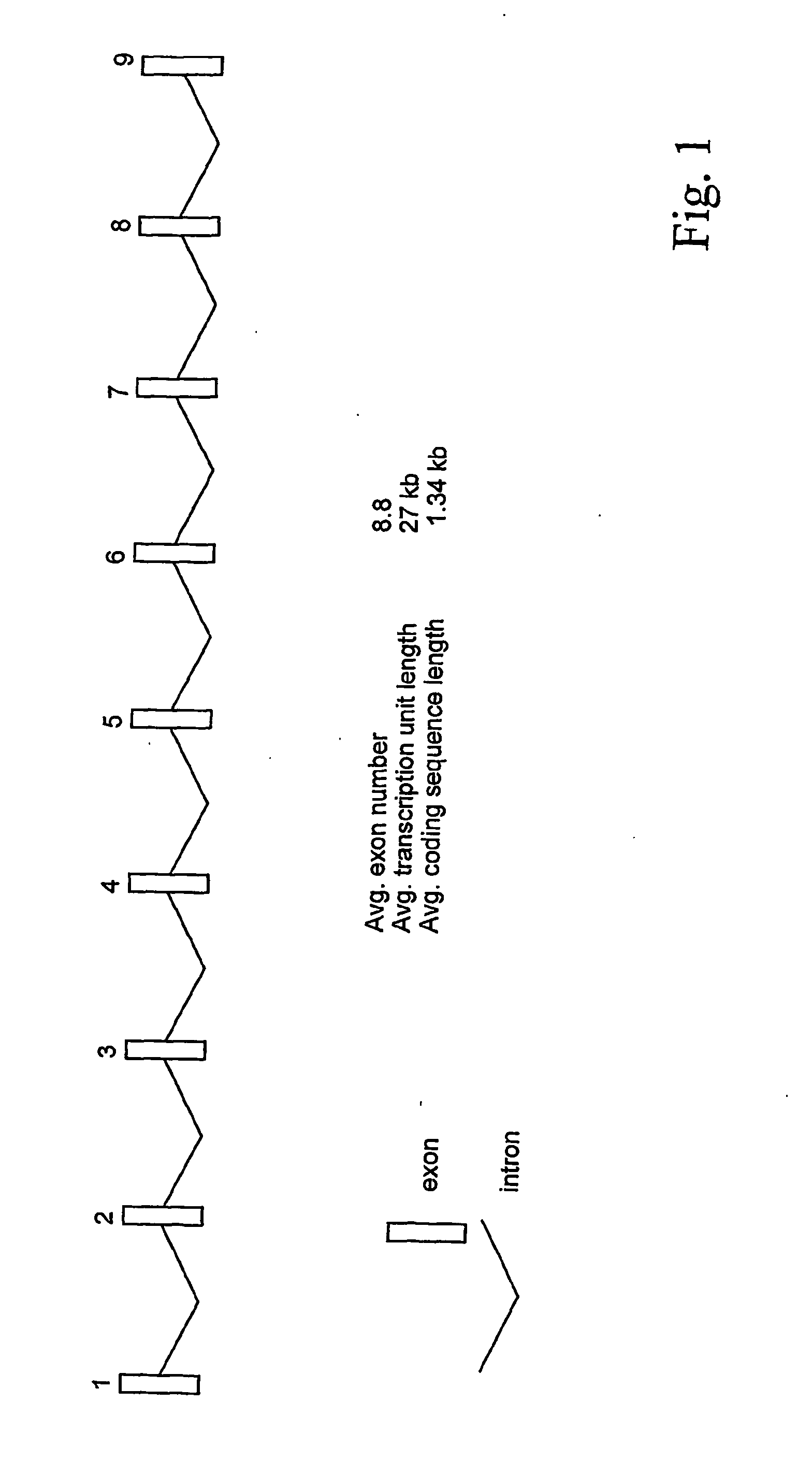
Quantitative multiplex amplification on a genomic scale, and applications for detecting genomic rearrangements
InactiveUS20050244830A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingMultiplex
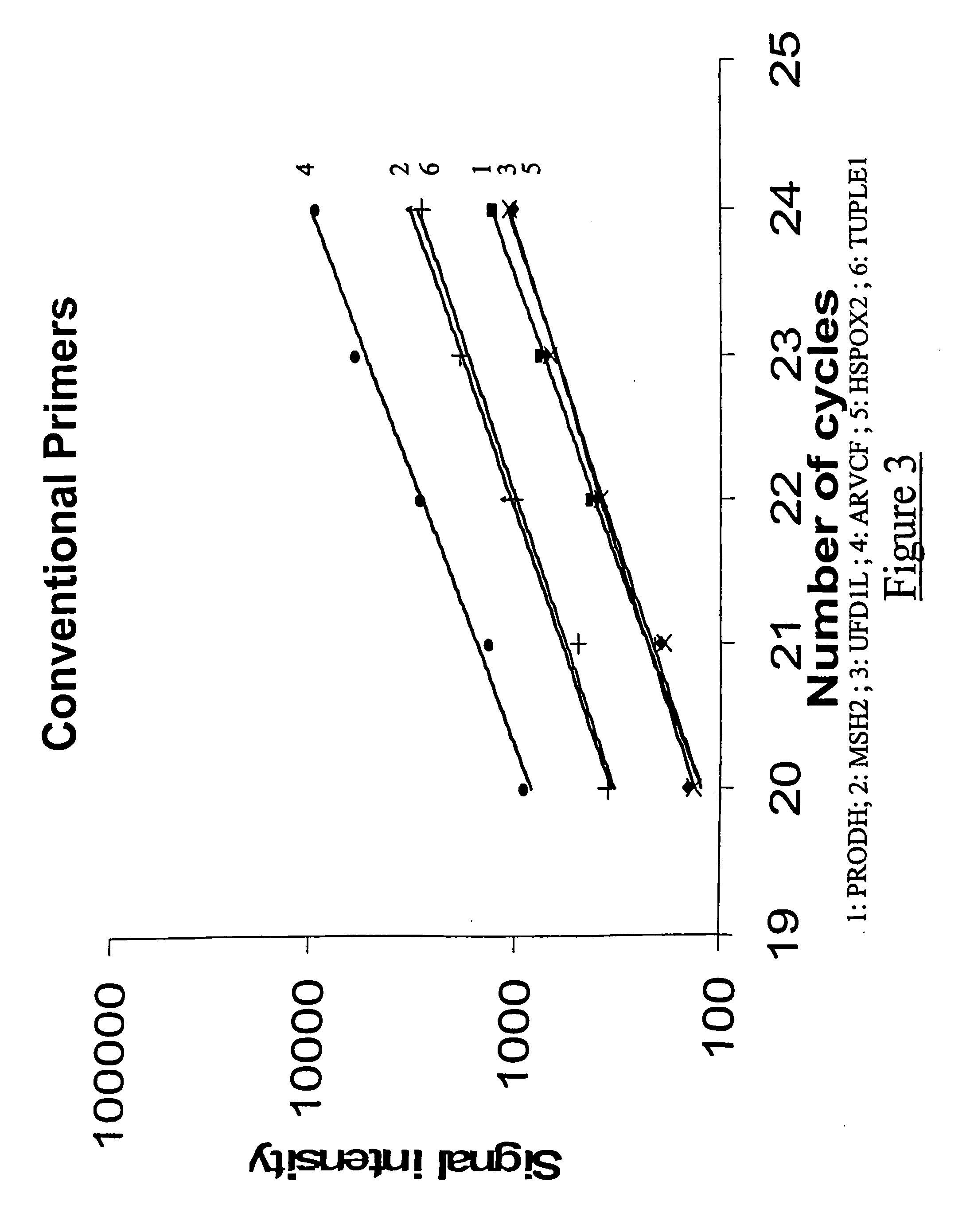
The present application relates to novel composite primers which make it possible to amplify in multiplex at a quantitative level of precision, and to the application of these composite primers for detecting gnomic rearrangements in general and cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in particular. These composite primers contain a tag the sequence of which is absent from or poorly represented in the genome analyzed, and which exhibits a very low propensity to form stable pairings. The composite primers, which contain them, make it possible to carry out multiplex amplifications with quantitative precision on the scale of a genome such as the human genome.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
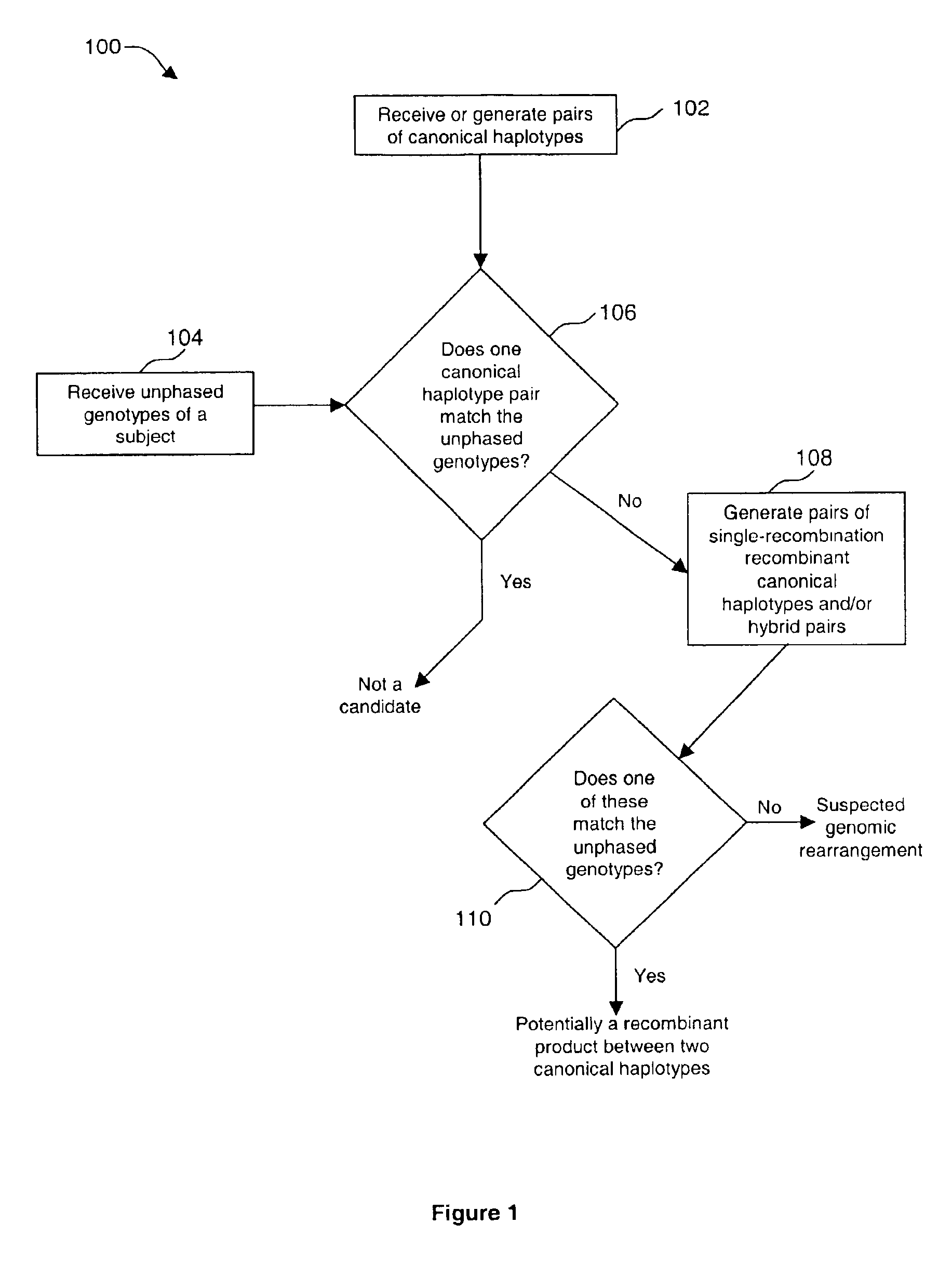
Method of identifying genomic rearrangements
InactiveUS6895337B1Quickly and accurately analyzedImprove accuracyComputer controlRead-only memoriesHeterologousHaplotype
Methods, computer program products and systems are provided for detecting large genomic rearrangements based on unphased genotype data obtained using common genotyping techniques that do not differentiate different alleles. In the method, unphased genotypes at a plurality of nucleotide variant markers of a particular gene in a diploid subject are compared with a canonical haplotype collection of the gene for a heterogeneous subject population. If the unphased genotypes cannot be reduced to a pair of canonical haplotypes within the canonical haplotype collection, it would indicate an increased likelihood that an allele of the gene in the diploid subject harbors a genomic rearrangement.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
Method for quickly and efficiently constructing good S yeast strain
InactiveCN101525612AGood fermentation propertiesImprove salt toleranceMutant preparationHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyGenetic diversity
The invention relates to a method for quickly and efficiently constructing good S yeast strain. On the basis of determining the optimal acting time of EMS (methyl methane sulfonate) on amphiploid cells of S yeast (namely, Saccharomycesrouxii used in soya sauce enterprises), S yeast amphiploid of non-conventional yeast strains is subjected to random mutagenesis by using EMS to generate an S yeast genetic diversity strain library, and genome rearrangement is generated among the strains in the library through multiple sexual recombination of efficient spore generation, spore purification, full integration and salt-resistant screening so as to construct S yeast recombinant strain with good fermentation performance. The salt resistance of the recombinant strain constructed by the method is obviously improved, the fermentation period is shortened by 10 days, the generated flavor substances are obviously improved compared with wild strains, and an important flavor substance 4-EG is also generated; and the good strain can generate thick and ester-flavor soya sauce flavor in high salt liquid state fermentation, has better physicochemical standard, and is provided for the industrial production of soya sauce.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genome-wide detection of genomic rearrangements and use of genomic rearrangements to diagnose genetic disease
The disclosure relates to the genome-wide identification of “rearrangement hotspots”. The disclosure also relates to a microarray chip system for use in detecting genomic rearrangements and a method of manufacturing a microarray chip system useful for detecting genomic rearrangements. The disclosure also relates to methods for detecting genomic rearrangements associated with genetic diseases. The disclosure further relates to methods for using copy number variants in chromosome 2 for detecting Tourette Syndrome.
Owner:GENESIS GROUP
Methods for the detection, visualization and high resolution physical mapping of genomic rearrangements in breast and ovarian cancer genes and loci brca1 and brca2 using genomic morse code in conjunction with molecular combing
InactiveUS20130130246A1Reduce background noiseRobustnessMicrobiological testing/measurementCombingOvarian cancer
Methods for detecting genomic rearrangements in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes at high resolution using Molecular Combing and for determining a predisposition to a disease or disorder associated with these rearrangements including predisposition to ovarian cancer or breast cancer. Primers useful for producing probes for this method and kits for practicing the methods.
Owner:BENSIMON AARON +4
Co-production fermentation method for astaxanthin and mannan and application of astaxanthin and mannan
PendingCN107974447ARealize co-production fermentationEffective thinningOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesAdhesiveBetaxanthins
The invention discloses a co-production fermentation method for astaxanthin and mannan and application of the astaxanthin and the mannan. The co-production fermentation method for the astaxanthin andthe mannan comprises: mutagenesis, preparation of protoplast, genome rearrangement, obtainment of the astaxanthin and extraction of the mannan. The astaxanthin is applied as an antioxidant additive infeeds, food and cosmetics; and the mannan can be applied in adhesives, fixatives, feed additives, cosmetic additives, embedding materials in wastewater treatment, dust preventives, chromatographic packing materials and food preservation. The beneficial effects are as follows: high-yield phaffia rhodozyma strains are obtained by a dual induction method, a strain for the high yield of the astaxanthin is screened out by a genome rearrangement and cell fusion method, so that a genetically stable phaffia rhodozyma strain is obtained, and the astaxanthin and the mannan are obtained by co-productionfermentation; the application ranges of the astaxanthin and the mannan are wide, and economic value is high.
Owner:杭州皇冠农业生物工程技术研究中心有限公司
Method for identifying or detecting genomic rearrangements in a biological sample
ActiveUS9133514B2Improves structural and functional analysisHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseImage resolution
Owner:GENOMIC VISION
Novel integrase and application thereof to efficiently modifying saccharopolyspora spinosa
The invention provides a novel integrase and application thereof to genetically modifying saccharopolyspora spinosa. The integrase particularly comes from saccharopolyspora endophytica CCTCC AA208003, and exogenous DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be specifically locally integrated on saccharopolyspora endophytica chromosome by the integrase via specific cis-form components. In addition, independent free replication regions of different strain sources are discovered in the saccharopolyspora spinosa by an inventor via research on genetic factors of different strains of the saccharopolyspora spinosa. The novel integrase and the application have the advantages that vectors constructed on the basis of the integrase and sequences of the replication regions can be used for genetically modifying the saccharopolyspora spinosa, accordingly, novel spinosad analogues can be possibly discovered, and the spinosad fermentation yields can be possibly increased; different resistance molecular markers can be carried by plasmids, accordingly, the novel integrase can be used for inter-species or intergenetic genome shuffling operation on the saccharopolyspora spinosa, and efficient genome shuffling can be implemented.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Unbiased identification of double-strand breaks and genomic rearrangement by genome-wide insert capture sequencing
ActiveUS10689691B2Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenome editingGenomic Stability
The invention provides for systems, methods, compositions, and kits for the complete characterization of targeted nuclease specificity which necessitates techniques that can assess the full possibility space of off-target activity and genomic stability following genome editing. Also provided are the materials and techniques which enable the comprehensive genomic stability accompanying a range of cellular perturbations, including genome editing (ZFN, TALEN, CRISPR, and future technologies) and disease modeling among other applications.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Improved methods of determining nucleic acid structural information
ActiveCN106029909AMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsNucleic acid structureNucleic acid sequencing
Methods of double-stranded nucleic acid sequence determination and assembly that are able to identify insertions, deletions, repeat region sizes and genomic rearrangements, for example, are disclosed herein, which can use relatively large labeled nucleic acid fragments to analyze the structure of even larger genetic regions. In some embodiments these methods involve the use of certain parameters which unexpectedly improve overall method performance. In some embodiments these methods involve sample labeling that does not result in the formation of single-stranded nucleic acid fragment labeling intermediaries.
Owner:BIONANO GENOMICS
Method for preparing food therapy brown rice juice by co-fermenting bacillus natto and lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN104489831APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationHybrid cell preparationLactic acid bacteriumPyrroloquinoline quinone
The invention discloses a method for preparing food therapy brown rice juice by co-fermenting bacillus natto and lactic acid bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 which can be used for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinone, then mixing bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 to mutate an offspring, carrying out cell fusion subculture, further by adopting a matrix induction adaptive strategy on the technical basis of genome rearrangement, screening at high flux to obtain the bacillus natto used for producing the nattokinase and the pyrroloquinoline quinone at high yield; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei, and screening out the methionine auxotroph lactobacillus casei; co-fermenting brown rice juice by using the screened bacillus subtilis natto and lactobacillus casei to obtain the brown rice juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinone. The brown rice juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinone, which is obtained through the method disclosed by the invention, achieves the pyrroloquinoline quinone content at 35-49 ng / mL and the nattokinase activity at 242-331 U / mL.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for Detecting a Genomic Fusion Event
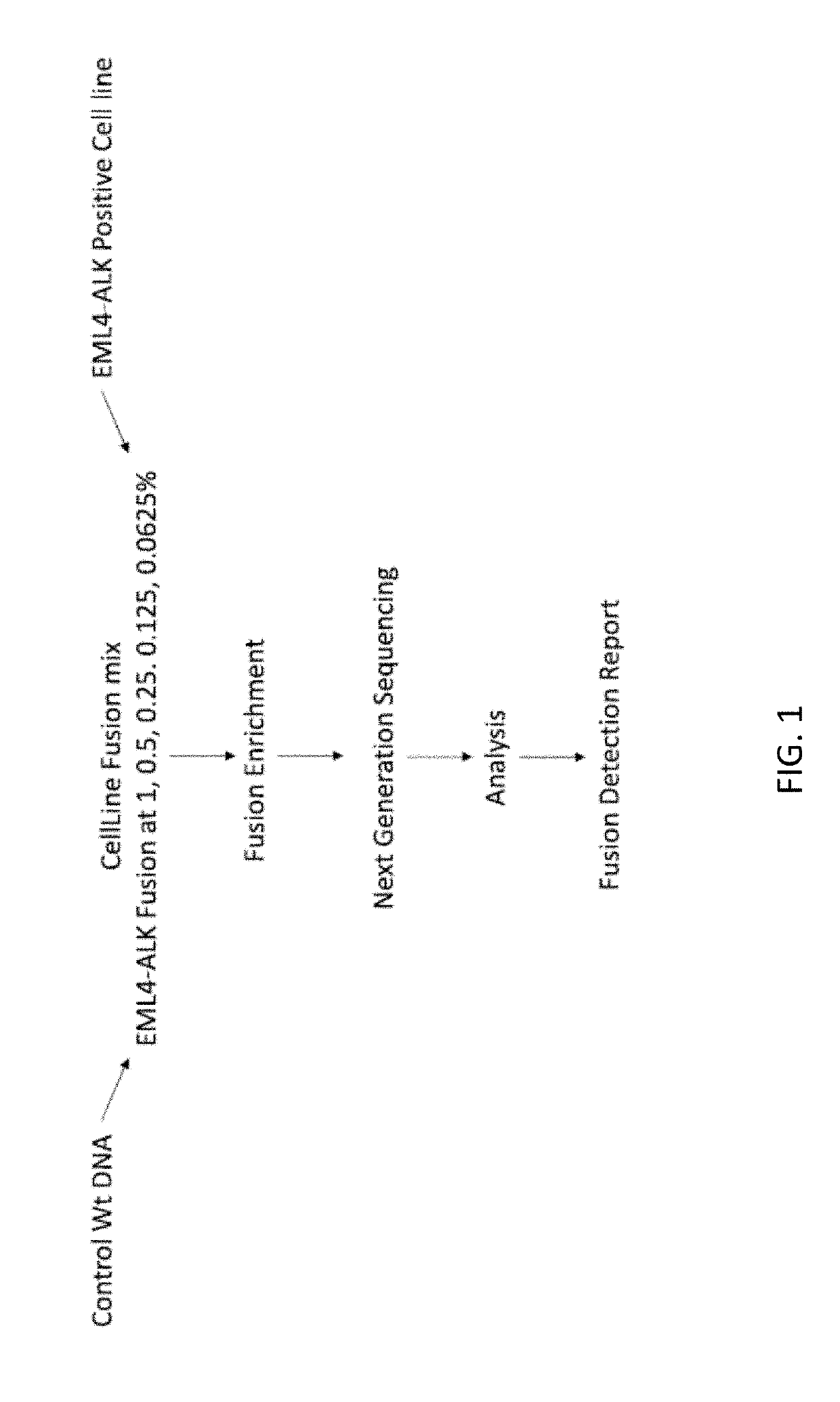
The present disclosure relates to methods for detecting and targeting genomic rearrangements, in particular gene fusion events, by targeting a DNA molecule of interest with a set or pool of primers, wherein the forward primers and reverse primers produce a PCR amplification product when a genomic rearrangement is present. The present disclosure also relates to methods of bioinformatic analysis to determine whether or not the detection of an amplification product from the selective PCR is actually indicative of the presence of a gene fusion. The present disclosure also related to related methods of diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions associated with such genomic rearrangements, in particular cancers, such as lung cancer.
Owner:INIVATA LTD
Method for rapid optimization of yeast cell plants
InactiveCN107641605AImproving Specific Recombination TechnologyImprove rearrangement efficiencyFungiStable introduction of DNAYeastBiotechnology
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a method for rapid optimization of yeast cell plants. The feature that diploids can be formed among haploid brewing yeasts through mating is utilized, the specific recombination technology of a Cre-LoxP system is improved, and genome rearrangement efficiency is greatly improved, target strains are simply and rapidly optimized and high-producing strains are screen out on the basis of a yeast strain library rearranged by a large number of genomes. Compared with a certain gene optimization technology in the prior art, the method is popular, low in cost and efficient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Detection of Fusion Events Using Replicate PCR Reactions
Owner:INIVATA LTD
Making method of dietary therapy fermented leaf mustard
InactiveCN104522586APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesMethionine biosynthesisPyrroloquinoline quinone
The invention discloses a making method of dietary therapy fermented leaf mustard. The making method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 generating nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing mutagenic descendants of the bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 generating the nattokinase and the pyrroloquinoline quinine for cell fusion subculture, carrying out high throughput screening to obtain the bacillus natto which can generate nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine in high yield by further adopting a substrate-induced adaptive strategy based on a genome rearrangement technology; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening methionine auxotroph lactobacillus casei; and co-fermenting fermented leaf mustard by using the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei to obtain the fermented leaf mustard rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinone. According to the fermented leaf mustard rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinone disclosed by the invention, the content of pyrroloquinoline quinone reaches 93-144ng / mL and the activity of nattokinase reaches 500-1210 / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
Strain of agaricus bisporus and breeding method thereof
InactiveCN108865899AHigh substrate utilizationGood genetic stabilityFungiFungi productsMyceliumEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a strain of agaricus bisporus and a breeding method thereof. The strain of agaricus bisporus has preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2017244. The strain has colony fully growingon a flat plate for 9d, the flat plate mycelium is white, the formed primordium number is 151-202 / m<2>, mature fruiting body pileusis is brown, and the per unit area yield of factory cultivation is 26kg / m<2> or above. The strain of agricus bisporus is bred by adopting a genome rearrangement technology, and has the advantages of high flat plate growth rate, dense mycelium growth, obviously increased induction number of fruiting body primordium, improved yield of agaricus bisporus, high matrix utilization rate, easy factory cultivation, and increased economic benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of fermented pineapple juice
InactiveCN104382155APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationHybrid cell preparationNitrosoguanidinesPyrroloquinoline quinone
The invention discloses a preparation method of fermented pineapple juice. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively mutating bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 used for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinone by using nitrosoguanidine, mixing mutated products of the bacillus natto 10261 and 10263, performing cell fusion subculture, and performing high-throughput screening by further adopting a substrate induction adaptive strategy based on a genome rearrangement technology to obtain the bacillus natto which realizes high yield of the nattokinase and the pyrroloquinoline quinone; mutating lactobacillus casei by using the nitrosoguanidine, and screening methionine auxotroph lactobacillus casei; co-fermenting the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei with pineapple juice to obtain the pineapple juice rich in the nattokinase and the pyrroloquinoline quinone. In the prepared pineapple juice rich in the nattokinase and the pyrroloquinoline quinone, the content of the pyrroloquinoline quinone is as high as 55ng / mL to 93ng / mL, and the activity of the nattokinase is as high as 420U / mL to 765U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
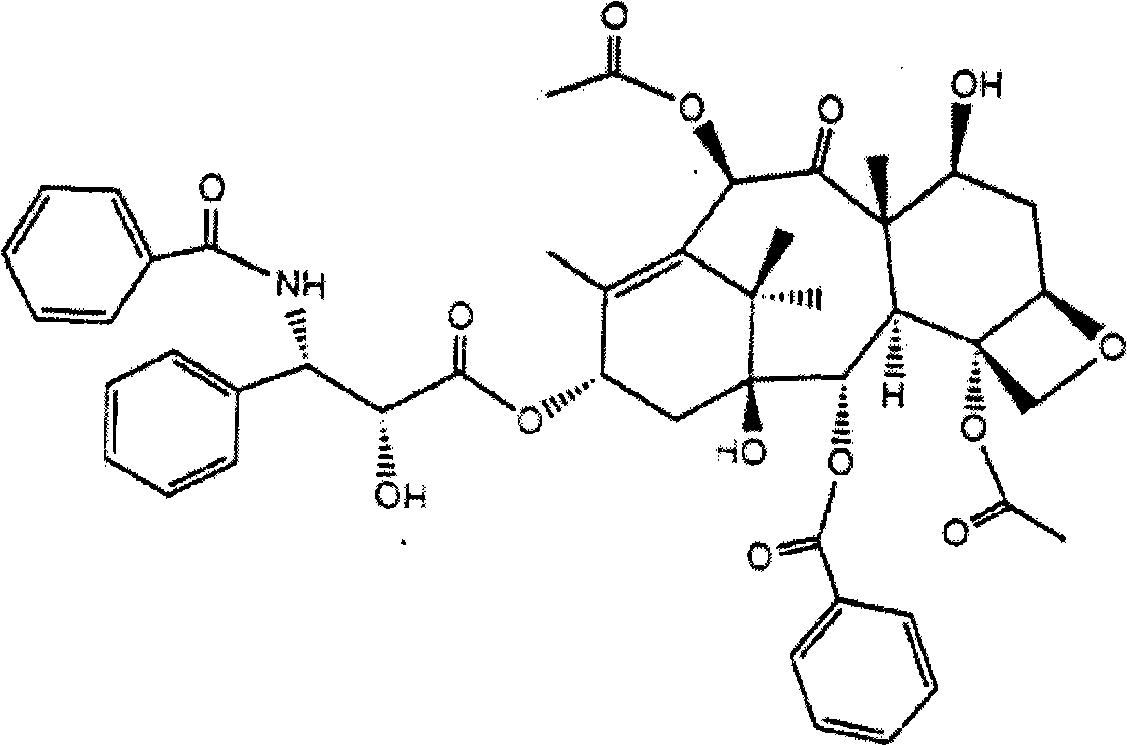
Paclitaxel genome rearrangement bacterial strain HDFS4-26 and breeding method of high-yield bacterial strain
InactiveCN101280281ABreeding is simpleGood effectFungiHybrid cell preparationMicroorganismGenome shuffling
The invention relates to paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain HDFS4-26 and a seed selection method of high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain, which belongs to the paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain and the seed selection method of the paclitaxel engineering bacterial strain and solves the problem that the paclitaxel output of the bacterial strain which can be used in the paclitaxel microorganism fermentation at present is still relatively low. The paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain HDFS4-26 is nodulisporium sylviforme and belongs to the nodulisporium and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation date is February 28, 2008, the preservation number is CCTCC M 208026. The seed selection method of the high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain adopts firstly, the protoplast preparation; secondly, the inactivation of the protoplast; thirdly, the interfusion of the protoplast; fourthly, the regeneration of the protoplast; fifthly, the genome shuffling and sieving, therefore to obtain the high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain. The paclitaxel output of the bacterial strain HDFS4-26 is 516.37ug / L. The seed selection method of the high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain provided by the invention is simple, the effect is good, and the paclitaxel genome shuffling bacterial strain HDFS4-26 and the seed selection method of high yield paclitaxel bacterial strain lay the foundation of industrial production of bacterial strain providing high yield paclitaxel.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing fermented rice cake from bacillus natto and lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN104522513APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesLactic acid bacteriumAcetic acid bacteria
The invention discloses a method for preparing fermented rice cake from bacillus natto and lactic acid bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: respectively performing nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine, then mixing the bacillus natto 10261 and 10263 for progeny mutagenesis, performing cell fusion subculture, further by adopting a substrate induction adaptation strategy based on a genome rearrangement technology, performing high throughput screening to obtain bacillus natto for producing nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine with a high yield; performing nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on bacillus natto, screening out methionine auxotrophic lactobacillus casei from the bacillus natto; co-fermenting the screened-out bacillus natto and the lactobacillus casei in sticky rice juice, and then decocting to obtain the fermented rice cake rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinoline quinine. In the fermented rice cake obtained by the method disclosed by the invention, the content of pyrroloquinoline quinine is up to 99-185ng / ml, and the activity of nattokinase is up to 830-1300U / mL.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel method for finding mutations caused by the insertion of repeated dnas
The present invention provides a method of for identifying repeat insertion mutation, a method for identifying or classifying genetic diseases characterized by genome rearrangement, as well as a method for mapping complex traits controlled by repeat insertion mutations in a plant or mammalian subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for improving efficiency of screening of 1,3-propylene glycol fusion bacteria
InactiveCN102311947AIncrease production intensityImprove toleranceHybrid cell preparationFiltrationScreening method
The invention discloses a method for improving the efficiency of the screening of 1,3-propylene glycol fusion bacteria. The main process of the method comprises: selecting a parent strain; subjecting the parent strain to enzymolysis wall removal to obtain a protoplast; inactivating a protoplast; subjecting the inactivated protoplast to protoplast fusion; selecting a fusant, and selecting target fusion bacteria with high performance; and subjecting the high-quality fusion strain serving as a parent to a next genomic rearrangement process till a strain with high comprehensive performance is obtained, wherein the protoplast obtained by the enzymolysis wall removal of the parent strain or inactivated protoplast are subjected to membrane filtration treatment first and then to subsequent treatment operation. Compared with the convention gene engineering fusion bacterium screening method, the method has the advantages of high target strain screening efficiency, convenience for operation, no need of expensive experimental instrument, suitability for industrial strain breeding and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and breeding method thereof
ActiveCN103232948BHigh genetic stabilityBack mutationFungiMutant preparationBiotechnologyEthanol yield
The invention provides a high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a breeding method of the high-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) SY-5-11L has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7377. The strain is characterized in that the ethanol yield is 13.9% (v / v) at a condition of fermenting at high temperature of 38 DEG C on the premise that other fermenting performances are not influenced, the yield is improved by 17.8% as compared with that of a parent strain. The ethanol output at the condition of fermenting at high temperature of 40 DEG C is 12.2% (v / v), and is improved by 34.1% as compared with that of the parent strain. The breeding method comprises the following steps of: performing artificial ultraviolet mutagenesis on an initial strain of the saccharomyces cerevisiae; screening out 23 forward mutant strains as a genome rearrangement library, wherein the ethanol output of the forward mutant strains are obviously raised on the condition of fermenting at a high temperature; and performing the genome rearrangement at three rounds, thus gaining the mutant strains with the maximum ethanol output under the high-temperature fermenting condition. The finally bred saccharomyces cerevisiae strain can be subjected to alcoholic fermentation at the high-temperature fermenting condition, brings no special requirements to fermenting equipment and technological conditions, and can be put into service with the equipment and conditions of general plants, thus having a wide application prospect.
Owner:贵州钓鱼台国宾酒业有限公司
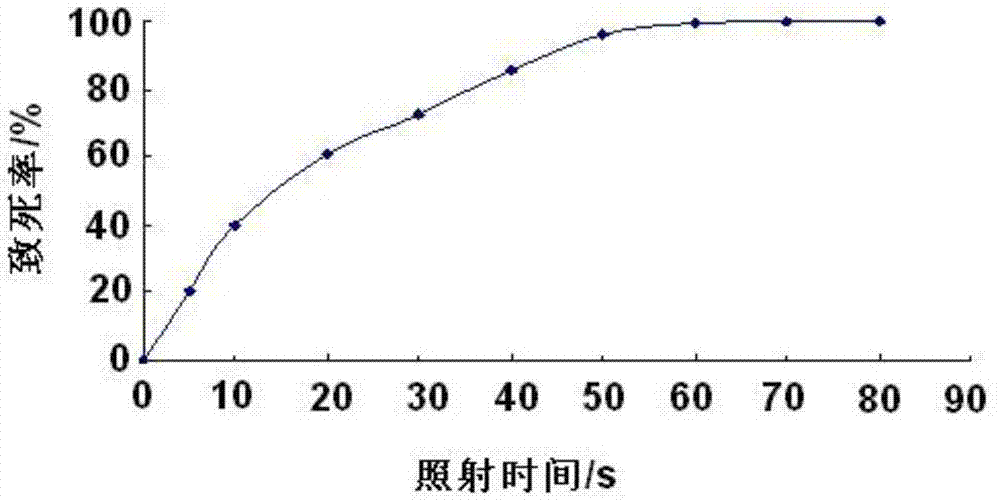
Preparation method of dietary therapeutic fermented bayberry juice
InactiveCN104432326APromote productionLower cholesterol levelsMicroorganismsMutant preparationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh-throughput screening
The invention discloses a preparation method of dietary therapeutic fermented bayberry juice. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on nattokinase and pyrroloquinolinequinone-generating bacillus natto 10261 and 10263, mixing the mutagenesis descendants to carry out cell-fusion subculture, and carrying out high-throughput screening to obtain the bacillus natto which is high in yield of nattokinase and pyrroloquinolinequinone by using a substrate-induced adaptive strategy on the basis of a genome rearrangement technology; carrying out nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis on lactobacillus casei and screening the methionine nutrition-defective lactobacillus casei; fermenting bayberry juice by using the screened bacillus natto and lactobacillus casei so as to obtain the bayberry juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinolinequinone. In the bayberry juice rich in nattokinase and pyrroloquinolinequinone, the content of the pyrroloquinolinequinone is up to 63-129ng / mL and the activity of nattokinase is up to 575-855U / mL.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUANPEITE BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com