Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
144 results about "Nucleic acid structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acid structure refers to the structure of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. Chemically speaking, DNA and RNA are very similar. Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
Chemically modified double stranded nucleic acid molecules that mediate RNA interference
InactiveUS20060217331A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleic acid structureDouble strand
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating gene expression using chemically modified double stranded nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of genes via RNA interference (RNAi). The invention features various modifications to double stranded nucleic acid structures, including chemically modified overhangs and optimized stabilization motifs of guide (antisense) strand and passenger (sense) strands of double stranded nucleic acid molecules that allow for potent RNA interference in therapeutically relevant applications.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
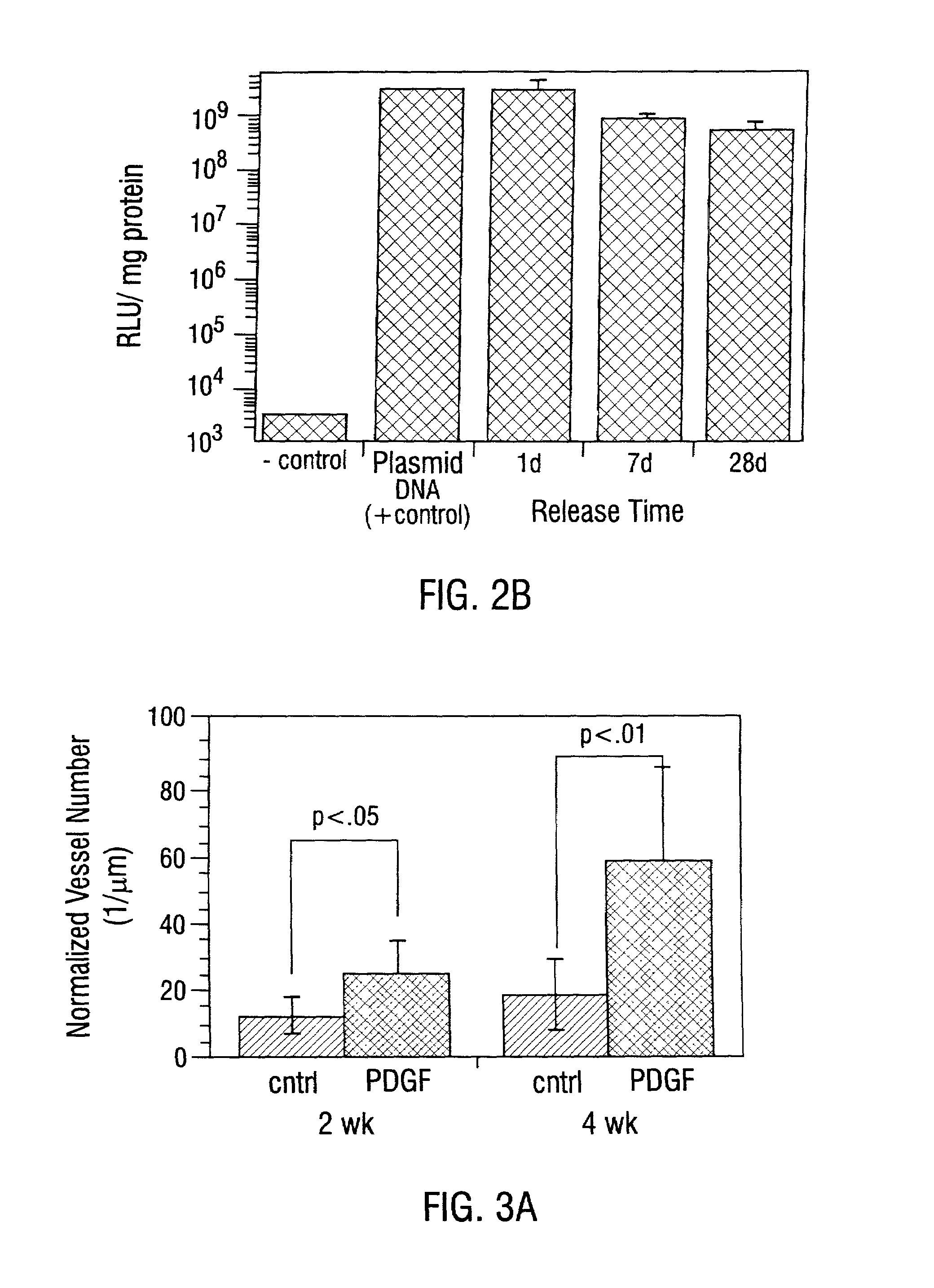
Sustained DNA delivery from structural matrices
InactiveUS7427602B1Improve bioavailabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDna deliveryNucleic acid structure
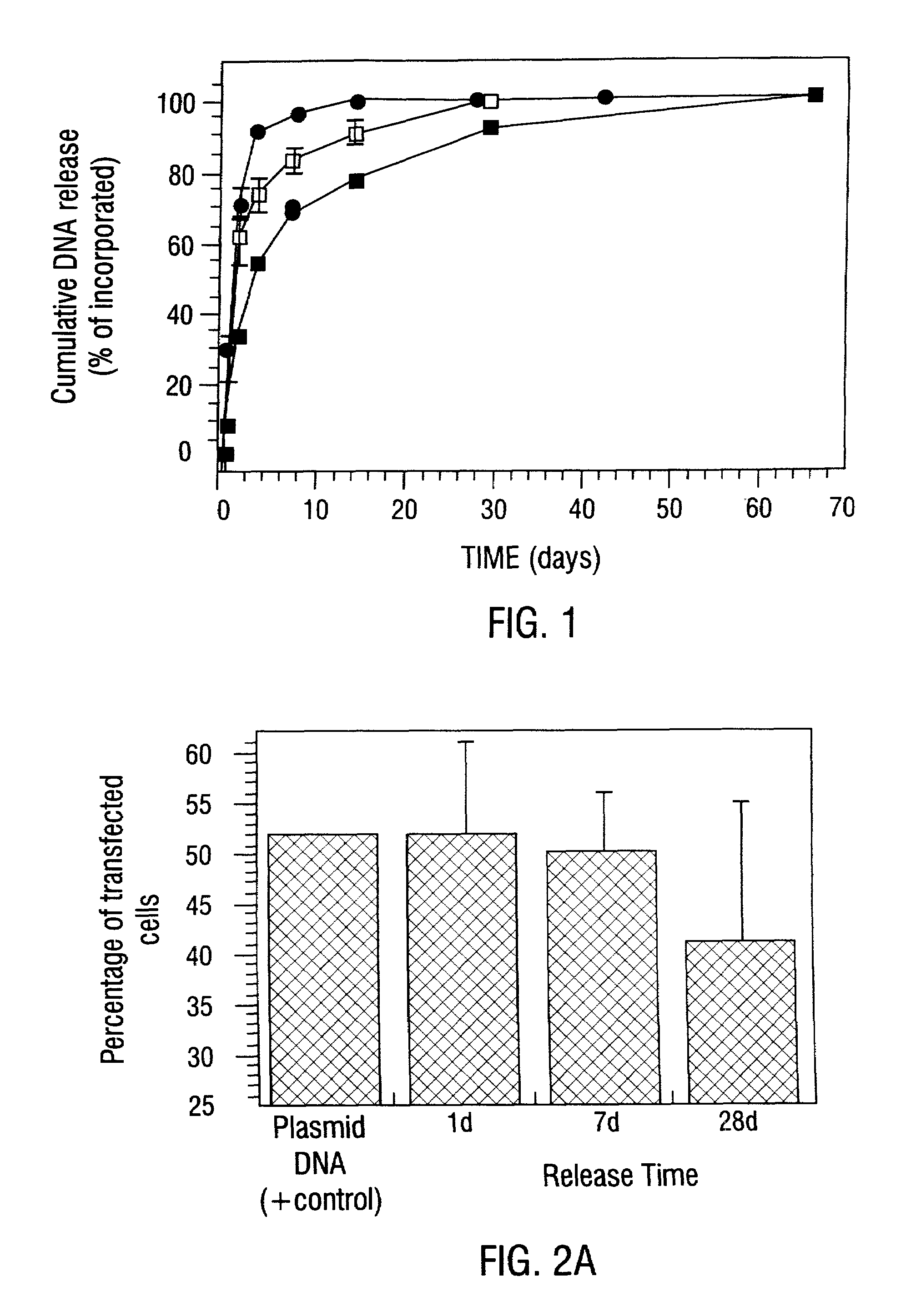
Disclosed are particular 3-dimensional structural matrices containing nucleic acids, various fabrication processes and methods for the prolonged release of nucleic acids in various biological environments. The nucleic acid-matrix materials are created such that they maintain a defined space, allowing cellular migration, transfection and proliferation to occur in a controlled manner. The fabrication processes provide for both high incorporation efficiencies and control over the sustained nucleic acid release. The resultant nucleic acid-containing structural matrices are thus particularly useful in in vivo cell transfection and gene expression in the context of gene therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
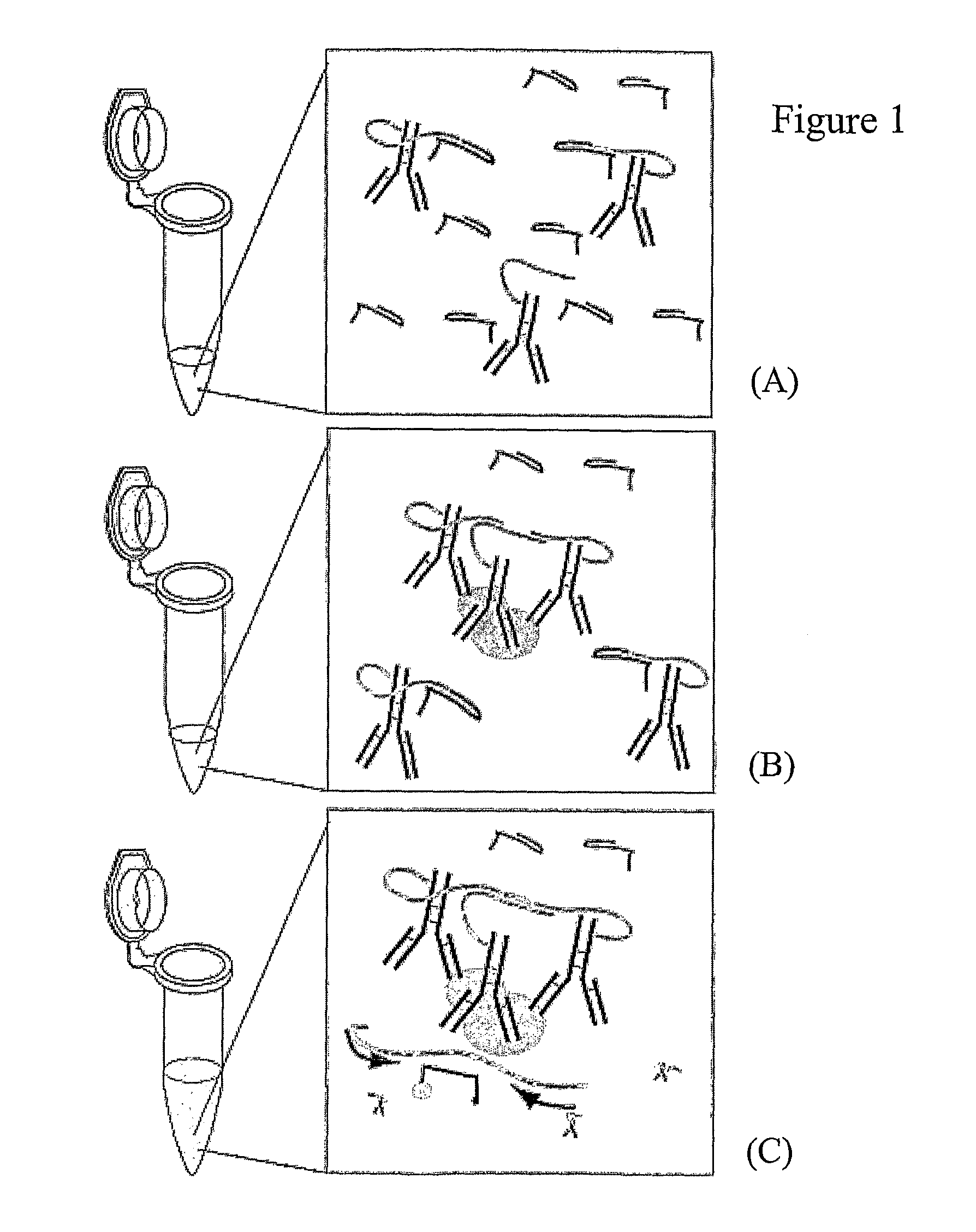
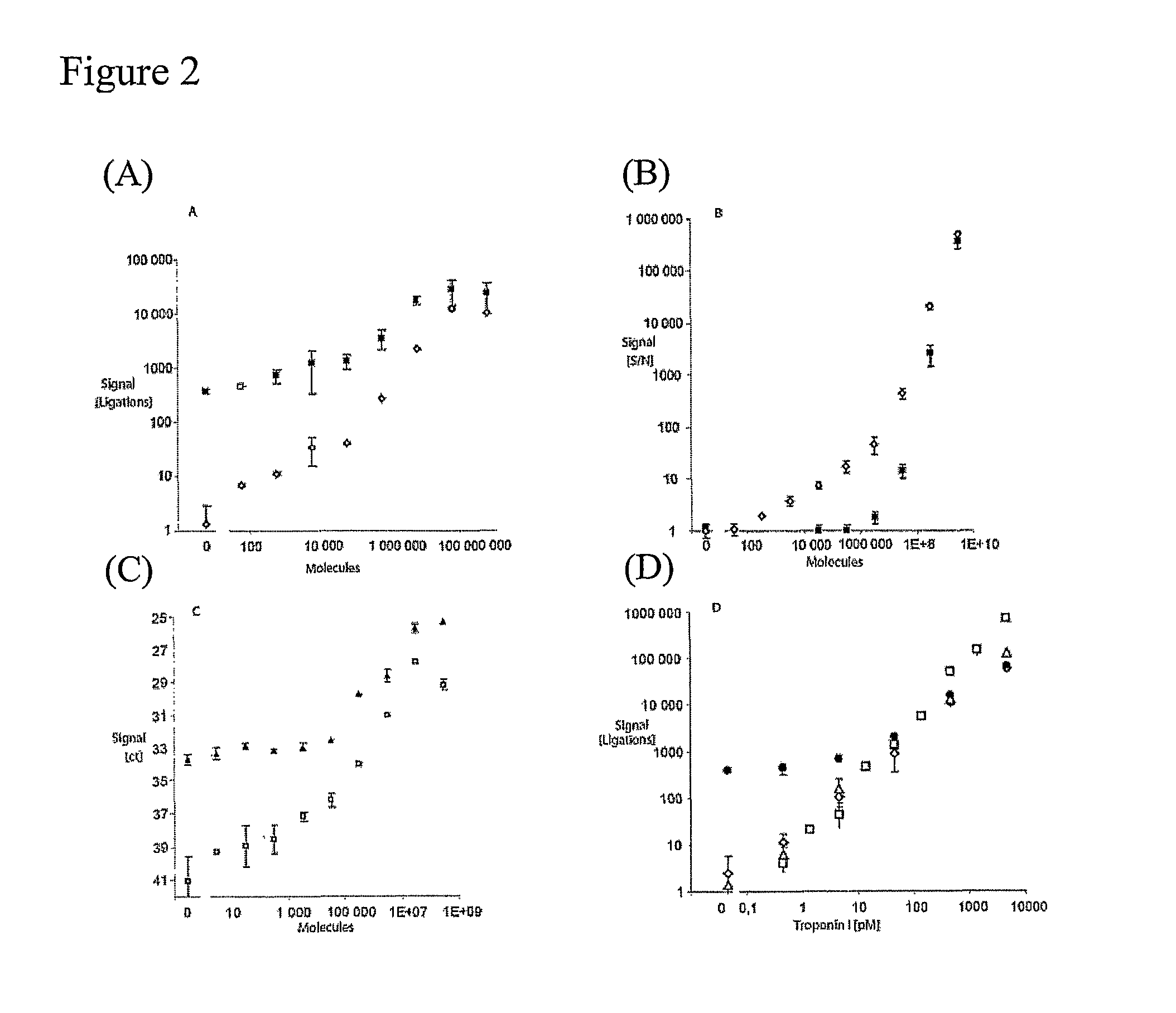
Method for analyte detection using proximity probes
A method for detecting an analyte in a sample, comprising (a) contacting the sample with at least one set of at least first, second and third proximity probes, which probes each include an analyte-binding domain and a nucleic acid domain and can simultaneously bind to the analyte, the nucleic acid domain of the third proximity probe being a splint which is capable of hybridizing at least to the nucleic acid domains of the first and second proximity probes, wherein when all of the at least three proximity probes bind to the analyte, the nucleic acid domains of the first and second proximity probes are conjugatable by means of an interaction mediated by the hybridized splint of the third proximity probe; (b) conjugating the nucleic acids, of the first and second proximity probes; and (c) detecting the conjugation. Also provided is a kit for use in such a method.
Owner:OLINK PROTEOMICS AB
Fusion NANO liposome-fluorescence labeled nucleic acid for in vivo application, uses thereof and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20150211056A1Well formedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsNucleic acid structureCell membrane
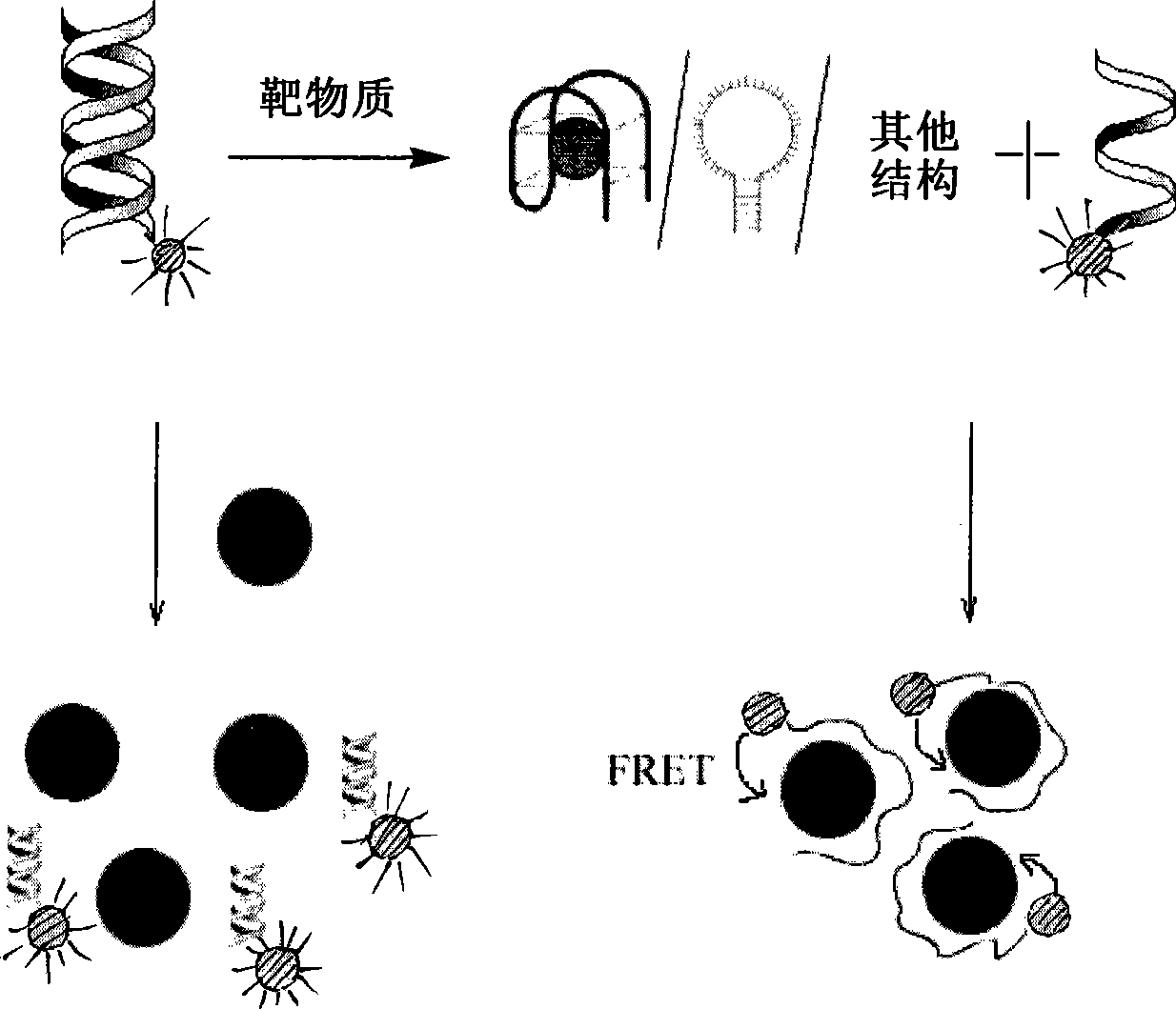
The present disclosure relates to a fusion nano liposome-fluorescence labeled nucleic acid in which a bead having a surface binding with a branch-shaped nucleic acid structure labeled with a fluorophore or a branch-shaped nucleic acid structure having a hairpin loop end is included in an inside of a liposome, and a diagnosis application thereof. The fusion nano liposome-fluorescence labeled nucleic acid, or fusion nano liposome-fluorescence labeled hairpin loop structured nucleic acid may sense an external or internal signal, and high-sensitive diagnosis is possible even when mRNA and miRNA which is present at a low concentration in cells being targeted. Further, various target materials expressed inside and outside of a cell membrane may be targeted, and thus even a type of cancer which is hard to diagnose such as triple negative breast cancer also be flexibly diagnosed. Further, using various fluorophores, multiple cancer may be diagnosed at the same time.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
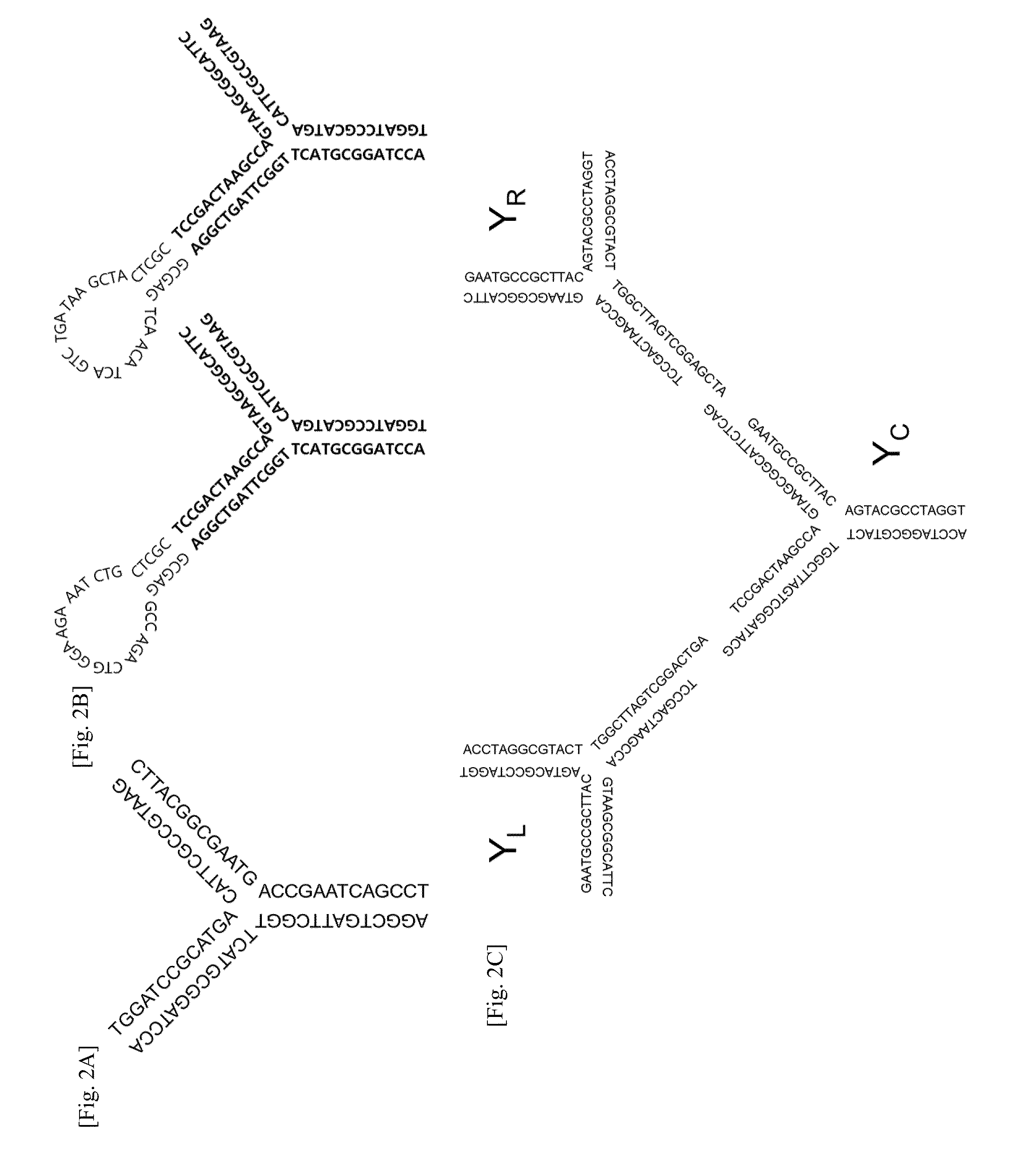
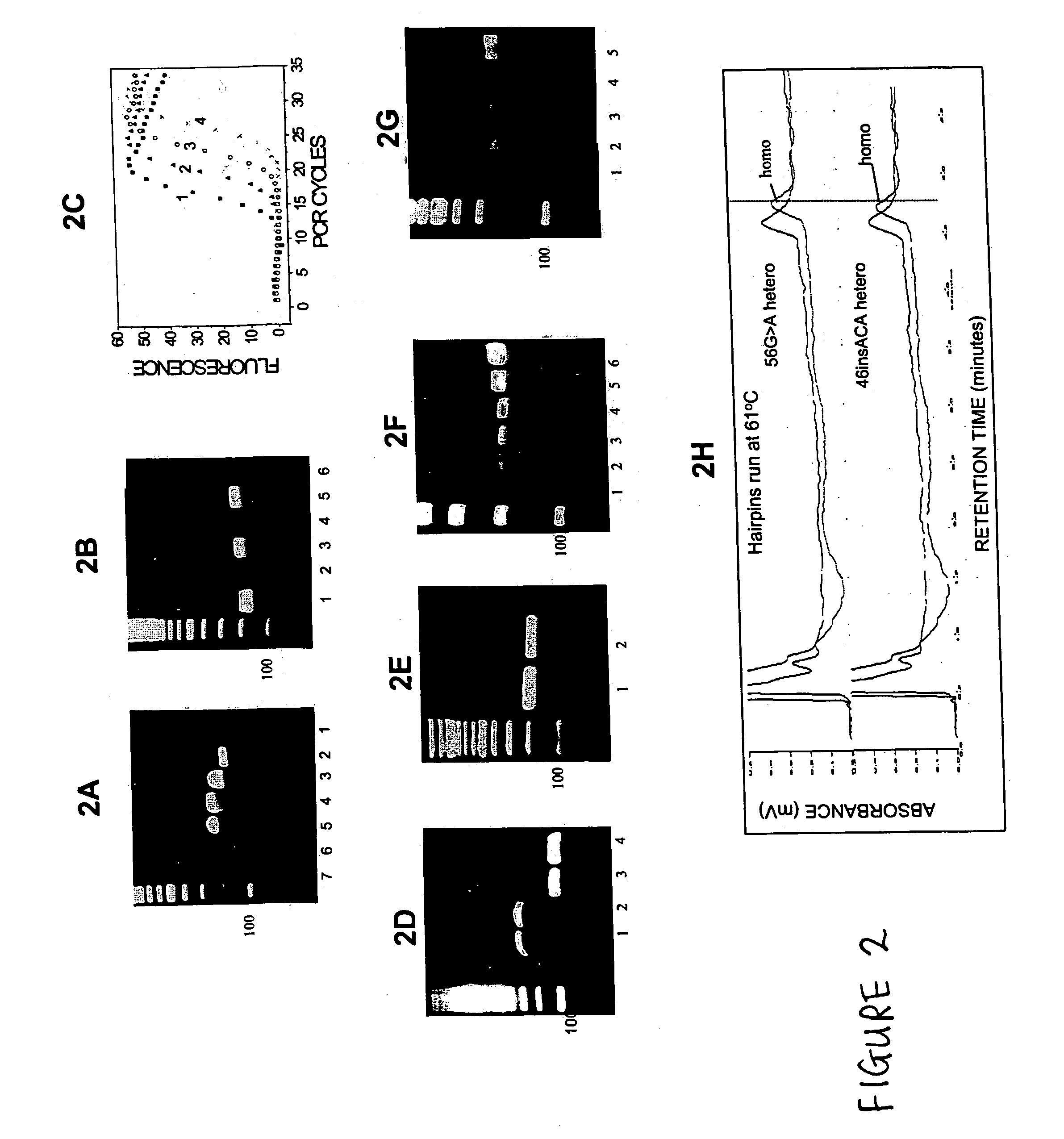
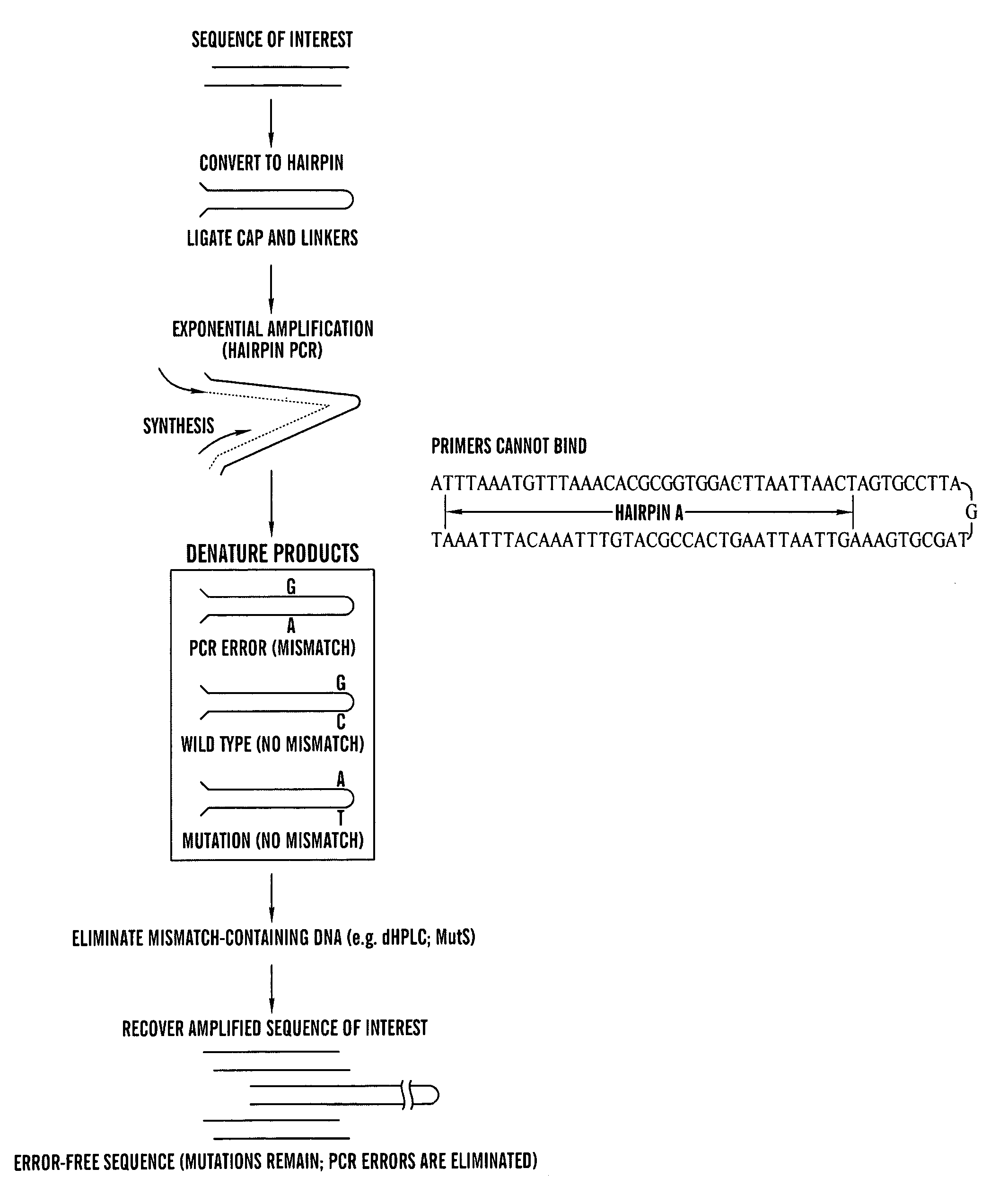
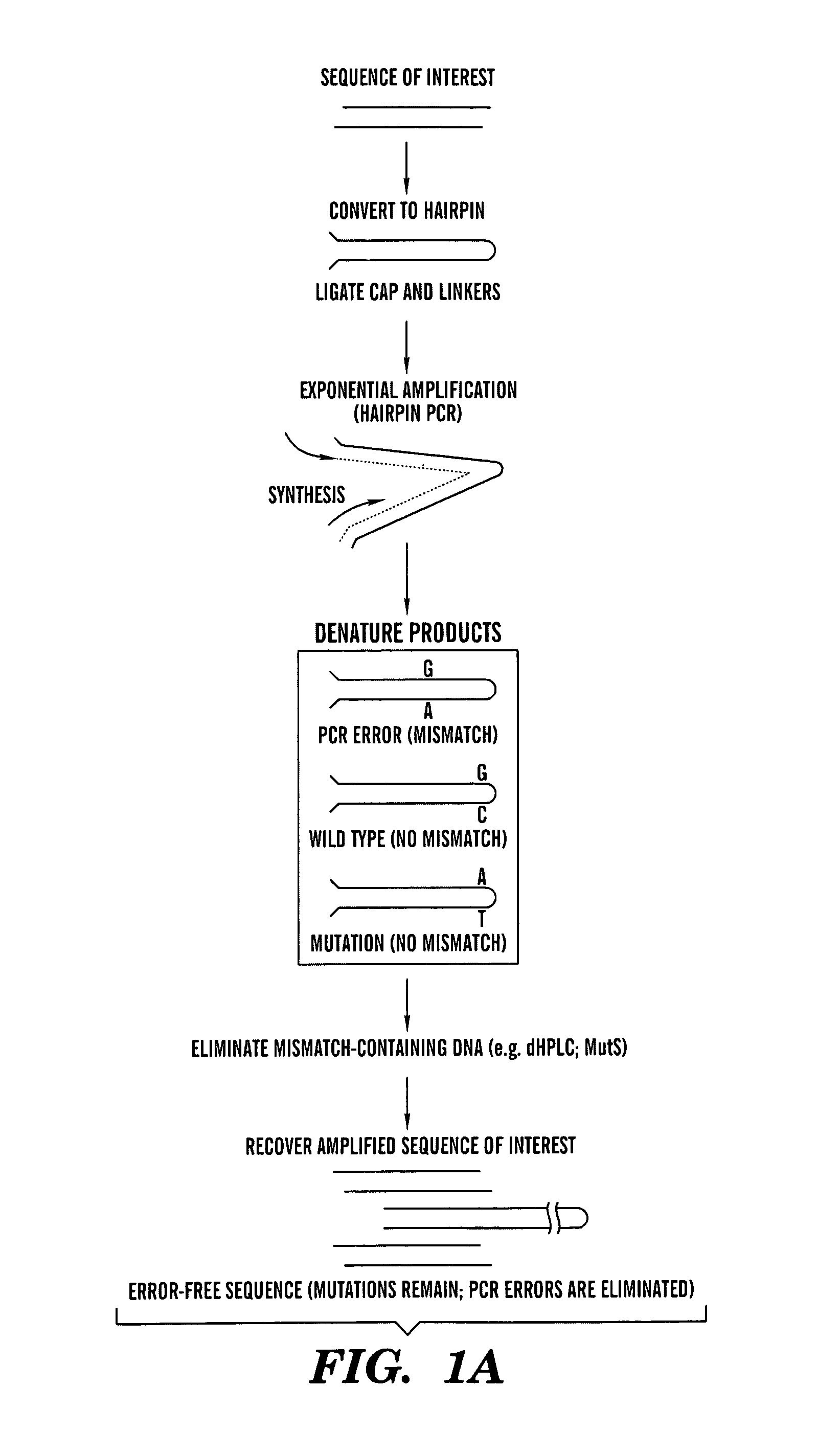
Amplification of DNA in a hairpin structure, and applications
InactiveUS20050142559A1Reduces polymerase induced errorMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid structurePolymerase L
The present invention is directed to a hairpin nucleic acid structure and its use. In a preferred embodiment, the hairpin nucleic acid structure can be used in a method of amplification of a template nucleic acid sequence that substantially reduces polymerase-induced errors.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Closed nucleic acid structures
ActiveUS20140329282A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid structureNucleic acid secondary structure
The invention provides compositions and methods for making closed nucleic acid structures in which one or both strands are continuous. The closed nucleic acid structures can be used as sequencing templates among other applications.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Amplification of DNA in a hairpin structure, and applications
InactiveUS7452699B2Reduces polymerase induced errorMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid structurePolymerase L
The present invention is directed to a hairpin nucleic acid structure and its use. In a preferred embodiment, the hairpin nucleic acid structure can be used in a method of amplification of a template nucleic acid sequence that substantially reduces polymerase-induced errors.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
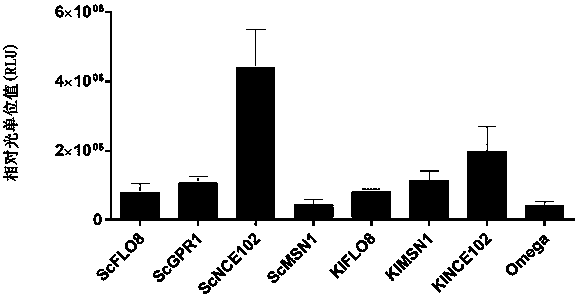
Protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element
The invention provides a protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element and particularly discloses a nucleic acid structure formed by coding sequences of optional promoters, yeast-derived IRES enhancers (such as ScGPR1, ScFLO8, ScNCE102, ScMSN1, KlFLO8, KlNCE102 and KlMSN1) and heterologous proteins. By application of the nucleic acid structure to a yeast in-vitro protein synthesis system, thesynthesized luciferase activity RLU (relative light unit) is extremely high.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Direct, externally imposed control of nucleic acids
InactiveUS6953659B2Reduce inhibitionFacilitate visualBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnergy transferNucleic acid structure
Methods and compositions for rendering nucleic acids directly responsive to an external signal utilizing modulators that themselves respond to the external signal and are associated with the nucleic acid. In response to the external signal, the modulator alters physical properties of the specific nucleic acid molecule(s) with which it is associated, thereby altering the structural and functional properties thereof. The modulator may, for example, transfer applied energy to a nucleic acid, or to a portion of the nucleic acid, thereby changing the nucleic acid structure.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Target molecule detecting method based on nanometer aurum and nucleic acid structure
InactiveCN101424642AVersatilityAchieving Specific DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceNucleic acid structureBiology
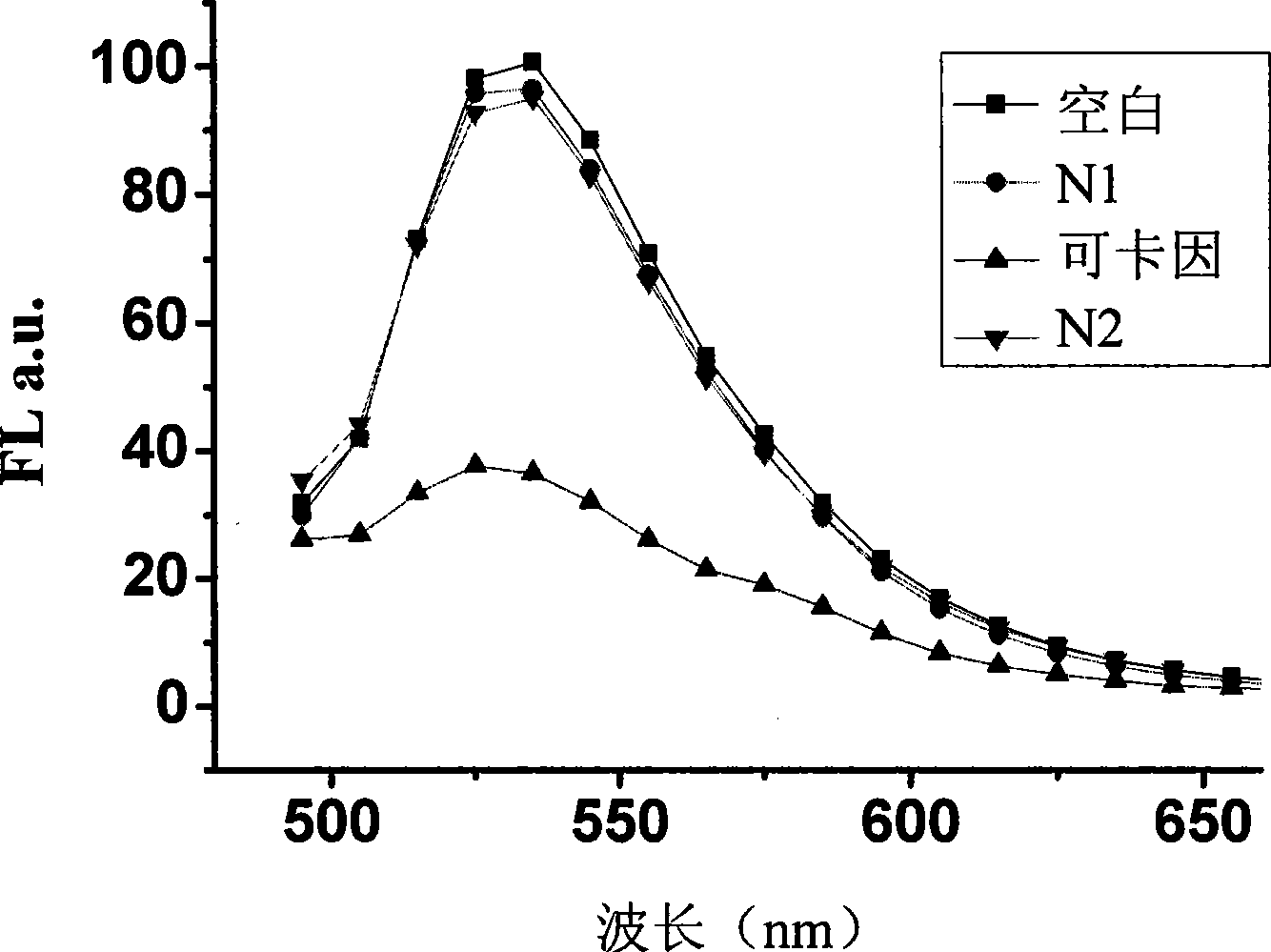
The invention discloses a detection method of target molecules, which is based on manometer gold and a nucleic acid structure and comprises the sequential steps: (1), hybridizing specific DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) with cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) in fluorescence labeling to form a double-stranded capture probe, wherein the specific DNA can be in specificity combination with the target molecules; (2), adding a solution to be detected for reaction; (3), adding a manometer gold solution for reaction and recording a fluorescence spectrum of the reaction solution. The detection method of the invention has commonality and wide range of application so that detection objects can be any target molecule. The invention can be utilized to conveniently realize the rapid, sensitive and selective detection of the target molecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid nano structure for carrying antitumor drugs, preparation method and applications thereof
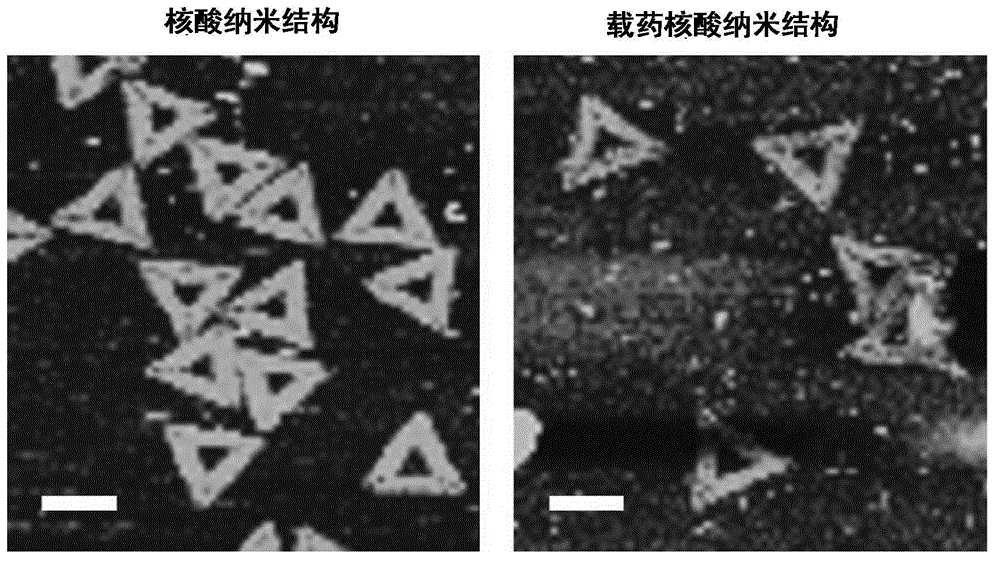
InactiveCN104368004AGuaranteed antitumor activityImprove targetingNanomedicinePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNano structuringWhole body
The invention discloses a nucleic acid nano structure for carrying antitumor drugs, a preparation method and applications thereof. The nucleic acid nano structure is a random two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional nano structure constructed through a DNA origami technology. The nucleic acid nano structure is obtained through self-assembly between a scaffold chain and a staple chain for auxiliary folding, wherein the scaffold chain and the stable chain are hybridized according to the base paring principle. The provided nucleic acid nano structure taken as the carrier of antitumor drugs can guarantee the antitumor activity of the carried antitumor drugs, and further improves the targeting property of the antitumor drugs. Thus the antitumor drugs can be enriched in the tumor tissues, and the overall toxicity due to the non-specificity of the antitumor drugs is greatly reduced. Furthermore, the preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, convenience, and easy application.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA +1
Target molecule detection method based on nano-Au and nucleic acid structure
InactiveCN101561398AAchieving Specific DetectionHigh affinityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementWAS PROTEINNucleic acid structure
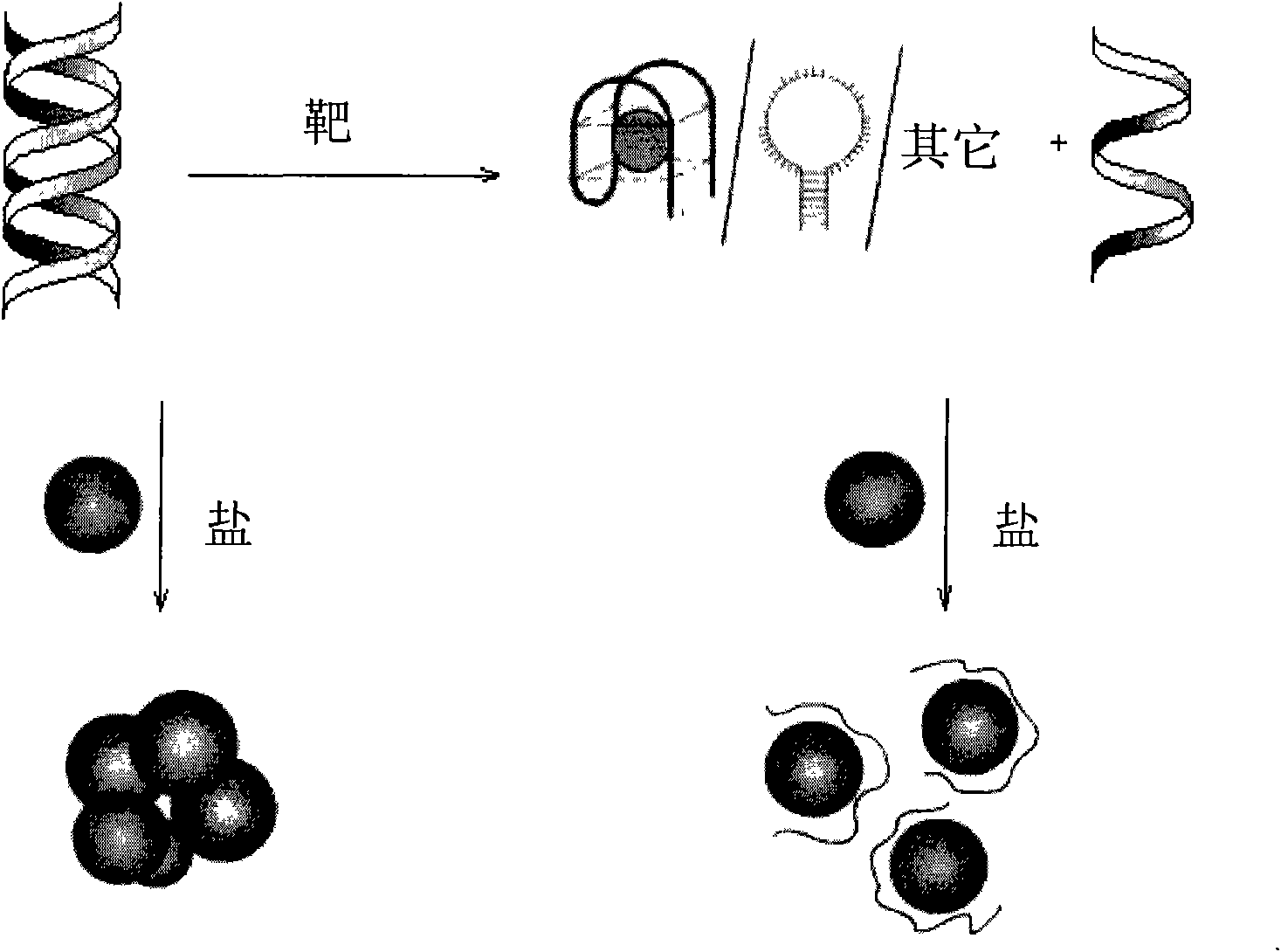
The invention discloses a target molecule detection method based on nano-Au and nucleic acid structure. The detection method sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) specific DNA which can specifically react with target molecules is sufficiently hybridized with the cDNA of the DNA to form a double-chain capture probe, wherein the target molecules are proteins or ions; (2) target molecule solution is added for full reaction; (3) nano-Au solution with the mol number of 0.01-1 time of that of the specific DNA is added, and the solution is red after reaction; (4) high salting solution with the final concentration of 1-100 mM is added, and the color change of the solution is observed. The detection method has commonality, wide application range, good specificity and high sensitivity, can quickly detect any proteins or any ions with low cost, and does not need DNA mark or dear instruments.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid molecules inducing RNA interference, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130273657A1Novel structureGood effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense RNAAntisense DNA
The present invention relates to an RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having a new structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a novel nucleic acid molecule having a structure comprising a first strand, which is 24-121 nt in length and comprises a region complementary to a target nucleic acid, and a second strand which is 13-21 nt in length and has a region that binds complementarily to the region of the first strand, which is complementary to the target nucleic acid, so that the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the expression of a target gene with increased efficiency, and to a method of inhibiting the expression of a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule structure of the present invention increases the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. Alternatively, the nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can either increase the ability of the siRNA to bind to the target gene or cause synergistic cleavage, by introduction of antisense DNA, antisense RNA, ribozyme or DNAzyme, thereby increasing the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. In addition, when the nucleic acid molecule according to the present invention is used, the efficiency with which the target gene is inhibited can be maintained for an extended period of time. Accordingly, the RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of cancer or viral infection in place of conventional siRNA molecules.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Colorimetric detection method based on nanometer-gold and nucleic acid structure and kit thereof
InactiveCN101832936ALow costVersatilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleic acid structure
The invention discloses a colorimetric detection method based on a nanometer-gold and nucleic acid structure and a kit thereof. The colorimetric detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing specific DNA which can be specifically combined with the target molecules with a solution to be detected for reaction; (2) mixing the reaction solution which is obtained in the step (1) with a nanometer-gold solution of which the number of moles is 0.01 to 1 time that of the specific DNA for reaction; and (3) adding a high-salt solution with the reaction concentration between 10 and 600 mM, and observing color change of the solution. In the operation process of the invention, DNA is not needed to be marked, expensive equipment is not needed need, and the existence of the target molecules can be determined only by observing the color change of the nanometer-gold solution. Therefore, the invention is simple, convenient and fast, has low cost, high specificity and high sensitive detection of any target molecules, is especially suitable for open-air analysis and high-throughput screening, and has wide application range.
Owner:苏州市长三角系统生物交叉科学研究院有限公司
Methods and compositions for detection of specific nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6100040AMinimize false positive signalHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThree levelNucleic acid structure
Methods and compositions are provided for the detection of specific nucleic acid sequences purified from cellular or tissue sources. More particularly, the present invention includes methods and compositions for the detection of nucleic acid sequences using a protection molecule that forms a protected nucleic acid sequence (PNAS) such as a triplex or duplex nucleic acid structure that includes the target nucleic acid sequence. An assay using the methods of the present invention may include one, two or three levels of specificity to minimize false positive signals. An assay using the methods or compositions of the present invention can be performed on large amounts of purified DNA in a single test, with high levels of sensitivity, thus eliminating the need for DNA amplification procedures.
Owner:CYGENE
Nucleic acid structure and expression carrier for enhancing recombinant protein production and mass-production of recombinant protein
InactiveCN1712534AImprove propertiesProtection from decompositionHaemoglobins/myoglobinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid structureGene product
Nucleic acid construction and expression carrier for improving recombinant protein production and production of recombinant protein are disclosed. The process is carried out by cloning first nucleic acid sequence of coded thioredoxin and second nucleic acid sequence of coded ferrohemoglobin into recombinant host cell, reinforcing the recombinant host cell production and helping to release intracellular stress.
Owner:FENG CHIA UNIVERSITY
Microscopy tip
InactiveUS20070082352A1No chemical safety concernsHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCrystallographyAtomic force microscopy
Disclosed is a tip for use in atomic force microscopy. The tip includes a substrate and a three-dimensional, double-stranded nucleic acid structure attached thereto. The nucleic acid structure may have a single-stranded nucleic acid attached thereto, such as an aptamer sequence. In use, the tip having the nucleic acid structure can be brought into contact with a surface to be imaged.
Owner:CUMPSON PETER JONATHAN
Nucleic acid molecules inducing RNA interference, and uses thereof
ActiveUS9637742B2Good effectNovel structureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntisense DNAAntisense RNA
The present invention relates to an RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having a new structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a novel nucleic acid molecule having a structure comprising a first strand, which is 24-121 nt in length and comprises a region complementary to a target nucleic acid, and a second strand which is 13-21 nt in length and has a region that binds complementarily to the region of the first strand, which is complementary to the target nucleic acid, so that the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the expression of a target gene with increased efficiency, and to a method of inhibiting the expression of a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule structure of the present invention increases the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. Alternatively, the nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can either increase the ability of the siRNA to bind to the target gene or cause synergistic cleavage, by introduction of antisense DNA, antisense RNA, ribozyme or DNAzyme, thereby increasing the efficiency with which the nucleic acid molecule inhibits the target gene. In addition, when the nucleic acid molecule according to the present invention is used, the efficiency with which the target gene is inhibited can be maintained for an extended period of time. Accordingly, the RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of cancer or viral infection in place of conventional siRNA molecules.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Nucleic acid hybridization probes
Compositions of nucleic acid hybridization probes for detecting a nucleic acid target sequence and methods for their production are described. In one preferred embodiment, the nucleic acid hybridization probe includes a hybridization domain, an adaptor, a linker, and a signaling domain. The hybridization domain includes a nucleic acid sequence having complementarity to the nucleic acid target sequence. The adaptor is a nucleic acid sequence. The linker includes a moiety having at least one abasic site, such that the moiety blocks extension by an elongating polymerase on a nucleic acid template containing the moiety. The signaling domain comprises a nucleic acid having at least one label or a nucleic acid having at least one nucleic acid domain for binding at least one additional nucleic acid.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
RNA-interference-inducing nucleic acid molecule able to penetrate into cells, and use therefor
ActiveCN104755620AIdentify other featuresOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDelivery problemsMolecular Structure of Nucleic Acids: A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
The present invention relates to a novel, RNAi-inducing nucleic acid molecule having cell penetrating ability and the use thereof, and more particularly, to a novel, RNAi-inducing double-stranded nucleic acid molecule, which has a replacement of the phosphate backbone of at least one nucleotide with phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate, and has a lipophilic compound conjugated thereto, and thus has high target gene-silencing efficiency while having the ability to penetrate cells without needing a separate intracellular delivery vehicle, and to a method of silencing a target gene using the nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid structure according to the present invention has both cholesterol modification and phosphorothioate modification introduced therein, and thus has high gene silencing efficiency while having the ability to penetrate cells without needing a separate intracellular delivery vehicle. Thus, it can be delivered into an actual target area in an amount sufficient for induction of RNAi, and thus can overcome the in vivo delivery problem occurring in the prior art. Therefore, the nucleic acid molecule according to the invention can effectively substitute for conventional siRNA molecules to treat cancer or viral infections.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
Signal Amplification
ActiveUS20140017669A1Guaranteed detection effectMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid structureEnzyme
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the use of enzymes composed of nucleic acid and / or protein enzymes to generate and amplify a signal indicative of the presence of a target. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions comprising nucleic acid structures that serve as partial or complete enzyme substrates and methods for using these structures to facilitate detection of targets.
Owner:SPEEDX
Compositions and methods relating to nucleic acid nano- and micro-technology
ActiveUS9796749B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid structureSynthesis methods
The invention provides nucleic acid structures of controlled size and shape, comprised of a plurality of oligonucleotides, and methods for their synthesis. The structures are formed, at least in part, by the self-assembly of single stranded oligonucleotides. The location of each oligonucleotide in the resultant structure is known. Accordingly, the structures may be modified with specificity.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for identifying ligands that target nucleic acid molecules and nucleic acid structural motifs
ActiveUS20080188377A1Microbiological testing/measurementSaccharide librariesNucleic acid structureDNA
Disclosed are methods for identifying a nucleic acid (e.g., RNA, DNA, etc.) motif which interacts with a ligand. The method includes providing a plurality of ligands immobilized on a support, wherein each particular ligand is immobilized at a discrete location on the support; contacting the plurality of immobilized ligands with a nucleic acid motif library under conditions effective for one or more members of the nucleic acid motif library to bind with the immobilized ligands; and identifying members of the nucleic acid motif library that are bound to a particular immobilized ligand. Also disclosed are methods for selecting, from a plurality of candidate ligands, one or more ligands that have increased likelihood of binding to a nucleic acid molecule comprising a particular nucleic acid motif, as well as methods for identifying a nucleic acid which interacts with a ligand.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and kit for detecting mutation or nucleotide variation of organism
InactiveUS20050106575A1Efficient migrationMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid-state devicesDiseaseNucleotide
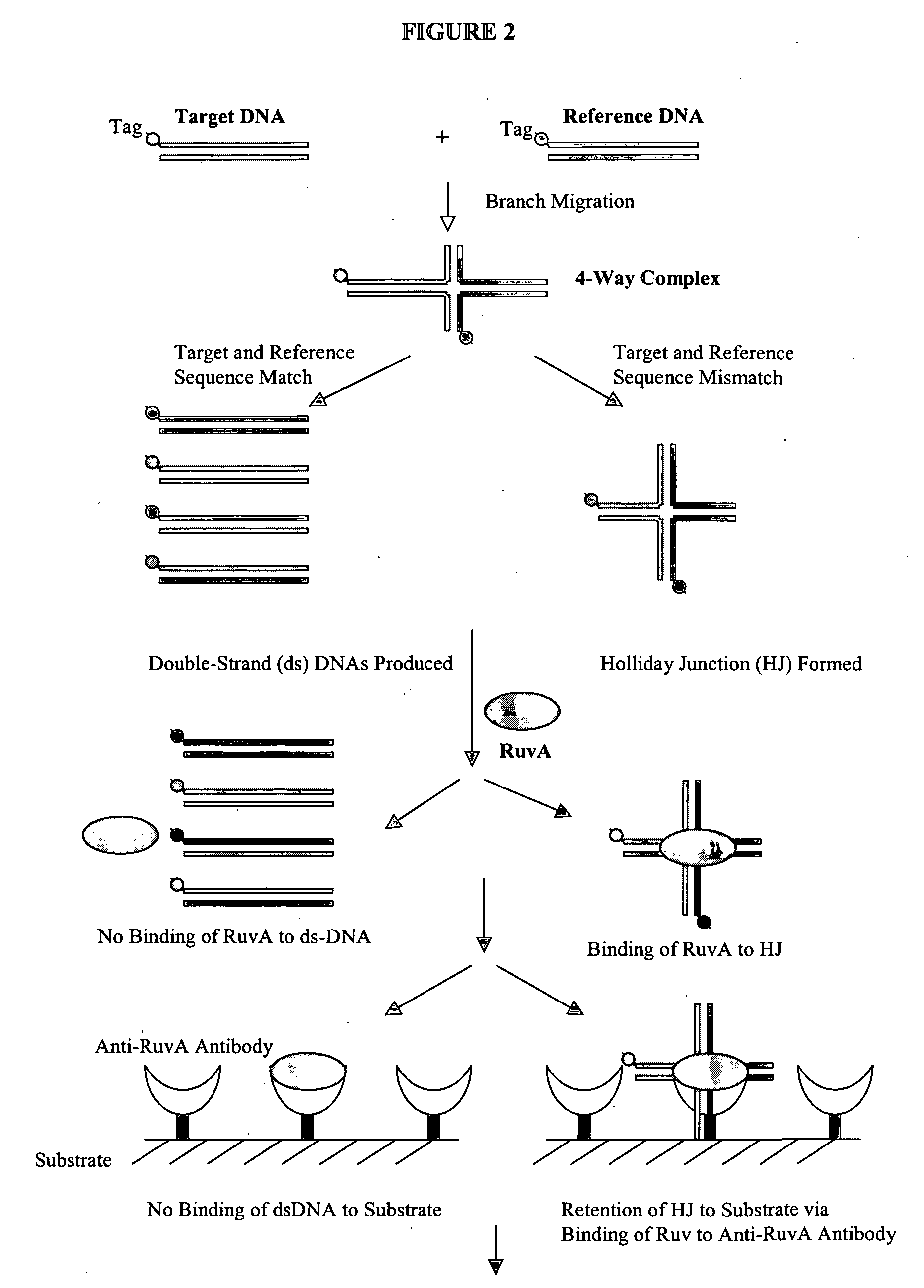
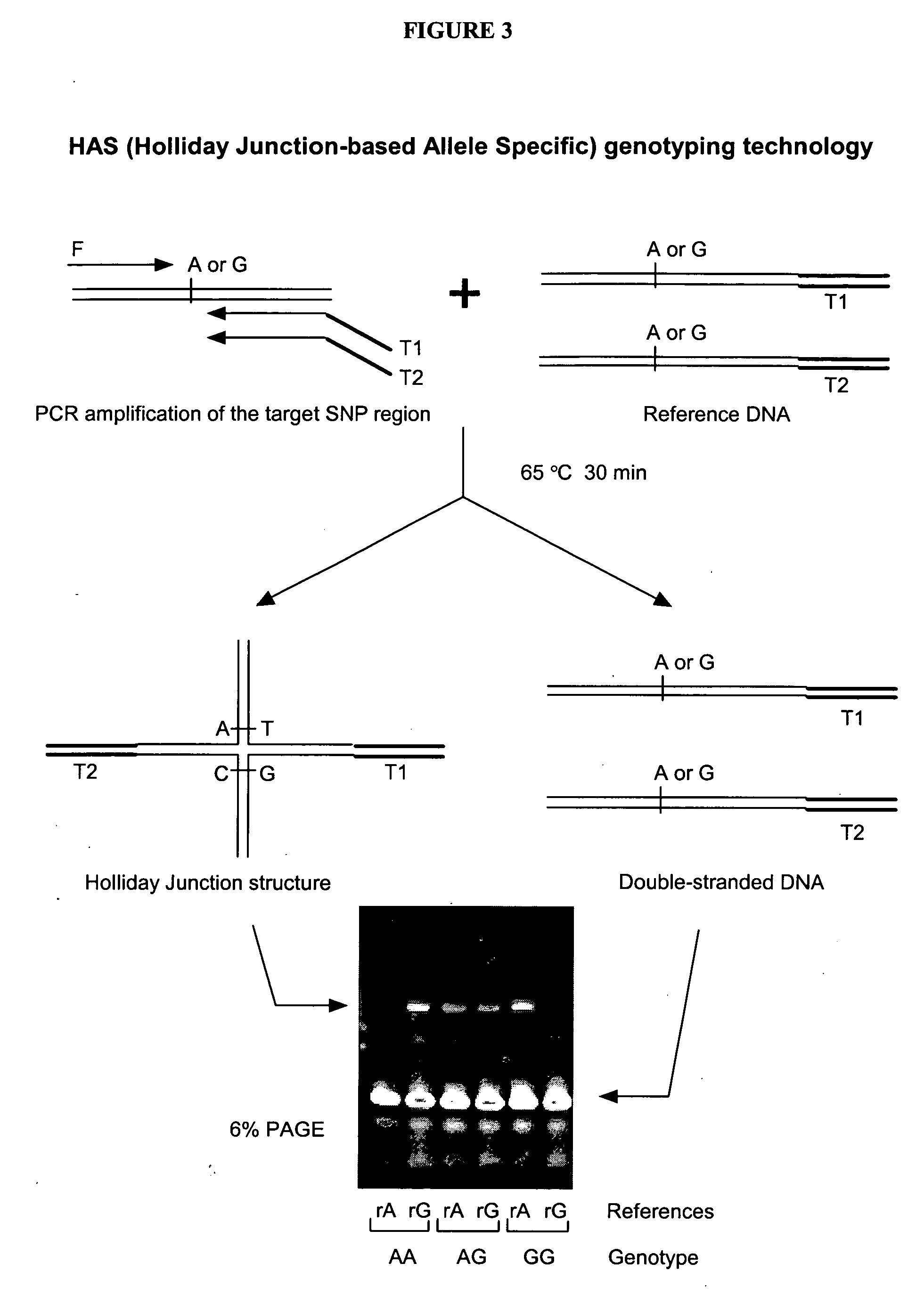
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for highly efficient, high throughput detection of mutation or nucleotide variation of an organism. By exploiting the molecular interactions between strands of nucleic acid and between nucleic acid and protein, assays have been developed to detect nucleotide variation, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in various biological samples including human genomic DNA and virus. In preferred embodiments, immunoassays are developed to specifically capture a nucleic acid-protein complex formed between a 4-way nucleic acid structure called Holliday junction and a protein that specifically recognizes the Holliday junction. These assays can be used in a wide variety of applications such as diagnostics, genotyping, genetic profiling, mutation detection, disease prevention, therapeutic treatment, and screening for therapeutic targets or therapeutics.
Owner:PANOMICS
Copper ion detection method based on click chemistry and detection kit
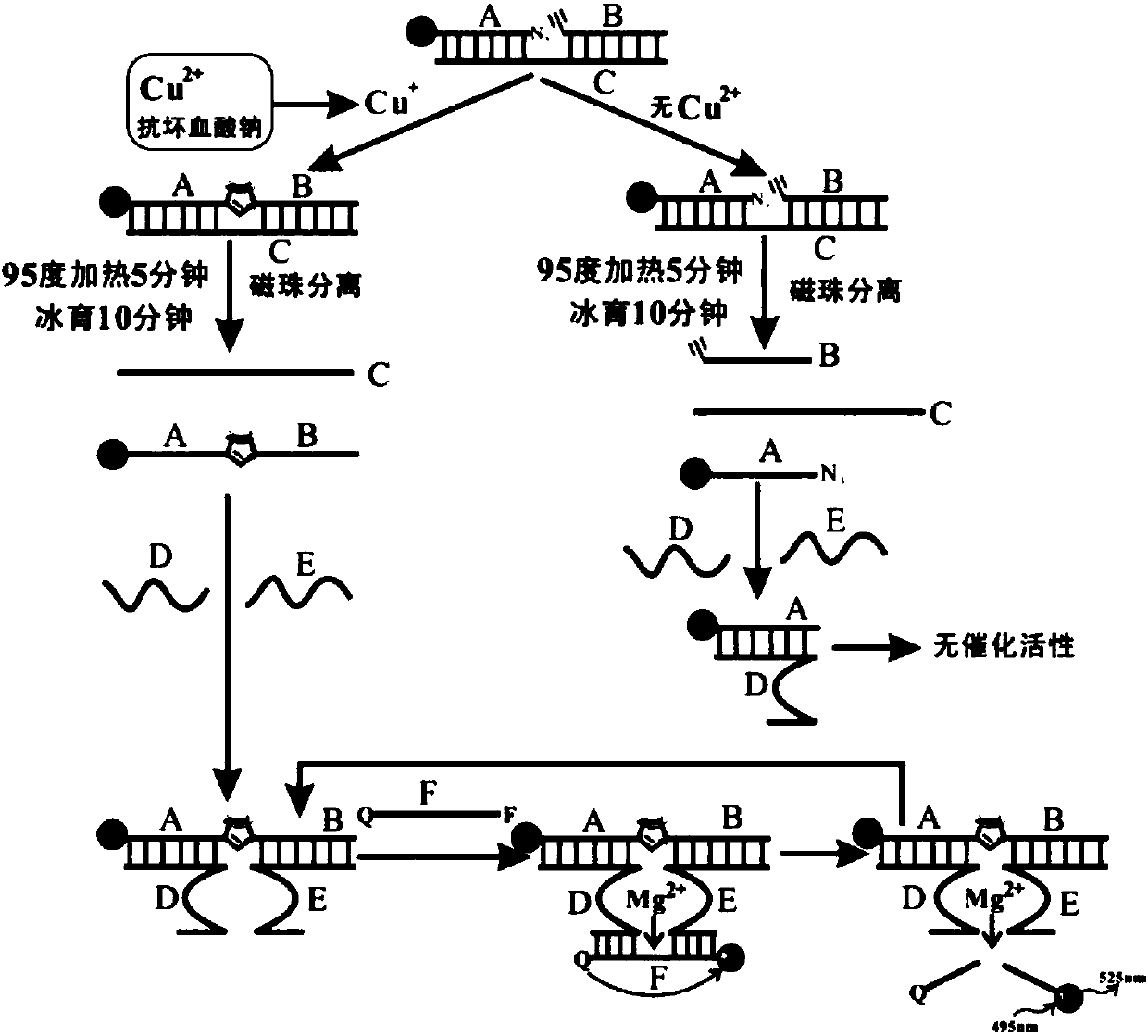
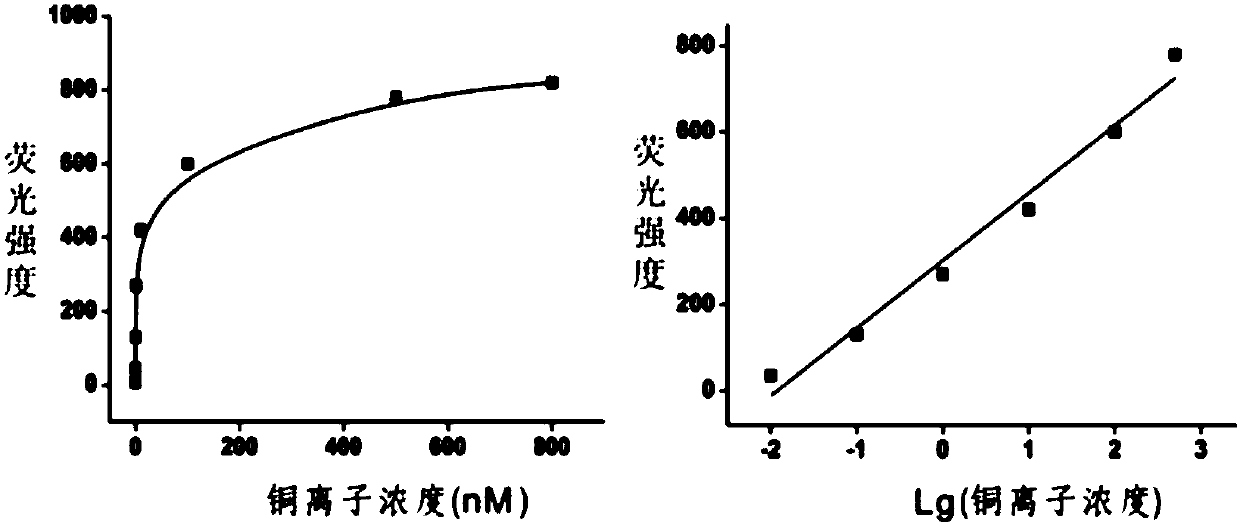
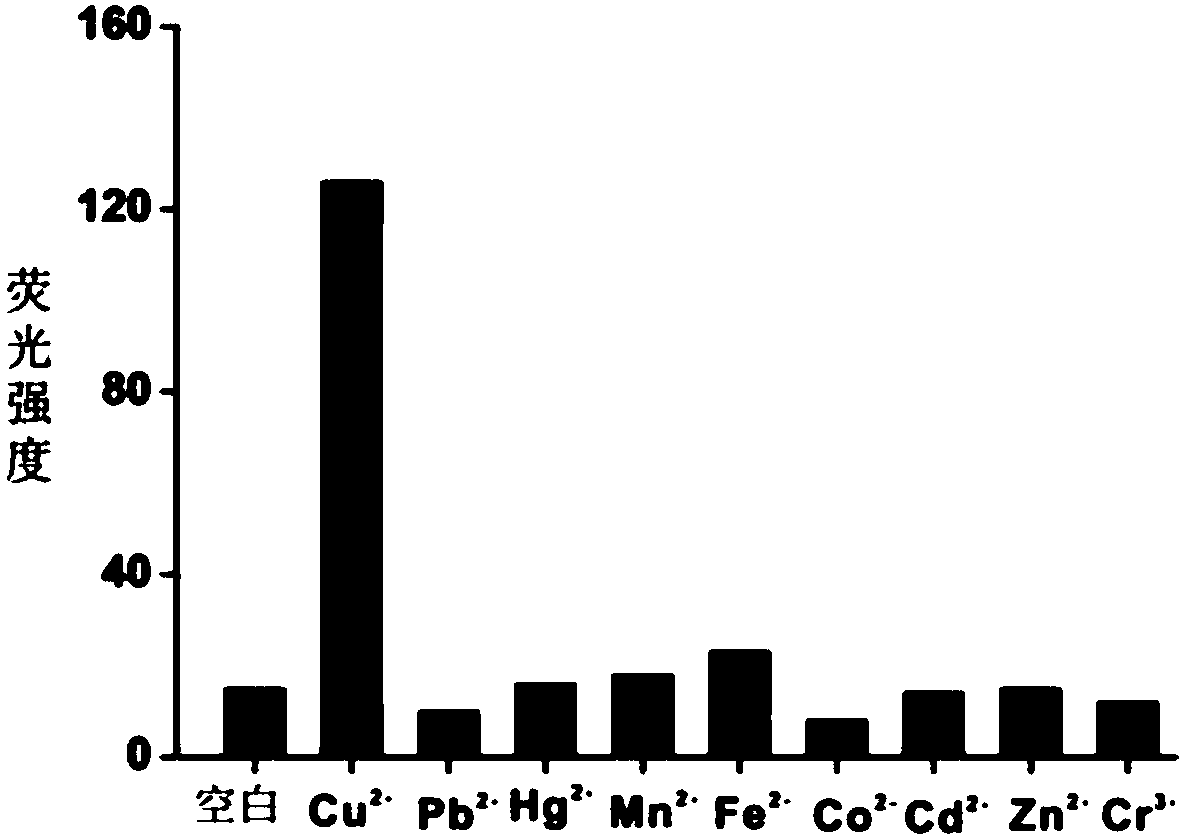
ActiveCN107064515AHigh sensitivityGood choiceBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical reactionFluorescence
The invention discloses a copper ion detection method based on click chemistry and a detection kit. The bivalent copper ion is reduced to the cuprous ion under the effect of a reducing agent, so that the click chemistry reaction is activated; two sections of nucleotide sequences are connected with each other; a catalytic nucleic acid structure with catalytic activity can be further assembled after the magnetic bead separation; a substrate nucleic acid can be cut, so that fluorescence groups and quenching groups at the two ends of the substrate nucleic acid can be separated; and the copper ion concentration can be identified through fluorescence detection. The copper ion detection method has higher sensitivity; a detection limit to copper ions is 2pM; the detection has excellent specificity; the other conventional interfering ions have no influence on the detection; and the detection process is simple in operation, low in cost and suitable for quick detection for the copper ion concentration in practical samples.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Method for selective removal of a substance from samples containing compounds having nucleic acid structure
InactiveUS20050267295A1Simple methodCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationSurface layerSorbent
A method for purifying a desired substance by separating from each other a substance (I) from a substance (II), one of which is the desired substance, both of which have affinity for the same ligand structure, and wherein substance (I) is smaller than substance (II). The method comprising the steps of: (i) providing substances I and II in a liquid; (ii) contacting the liquid with an adsorbent which selectively adsorbs substance I; (iii) recovering the desired substance; The adsorbent has (a) an interior part which carries a ligand structure that is capable of binding to substances I and II, and is accessible to substance I, and (b) an outer surface layer that does not adsorb substance II, and is more easily penetrated by substance I than by substance II.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Double block molecular probe and rapid nucleic acid detection method thereof
ActiveCN105400781ANo retouching requiredReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDisplacement reactionsNucleic Acid Probes
The invention discloses a double block molecular probe and a rapid nucleic acid detection method thereof. Target nucleic acid sequences and initiating zones of the tail ends of the double block molecular probes interact mutually, strand displacement reaction is triggered, and hairpin structures of the double block molecular probes are opened sequentially and combined with target DNA, so that a lot of Y-type nucleic acid structures with three polyA tails can be generated. The polyA tails of the Y-type nucleic acid structures can be combined with a plurality of nanogold respectively, so that colors of the nanogold can be changed from red into blue, the detection result can be observed by naked eyes, and the nucleic acid concentration and the color change degree are in direct correlation. According to the double block molecular probe and the rapid nucleic acid detection method thereof, the operation is easy, protease and marking are not required, the reaction condition is mild, the detection limit to nucleic acid is 0.01 pM, single nucleic acid mutation can be distinguished, and the detection result can be used for quantitative analysis and nucleic acid rapid spot detection.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Fluorescence detection kit based on aptamer
ActiveCN107870242AEasy to prepareEasy to storeBiological material analysisBiological testingAptamerWater source
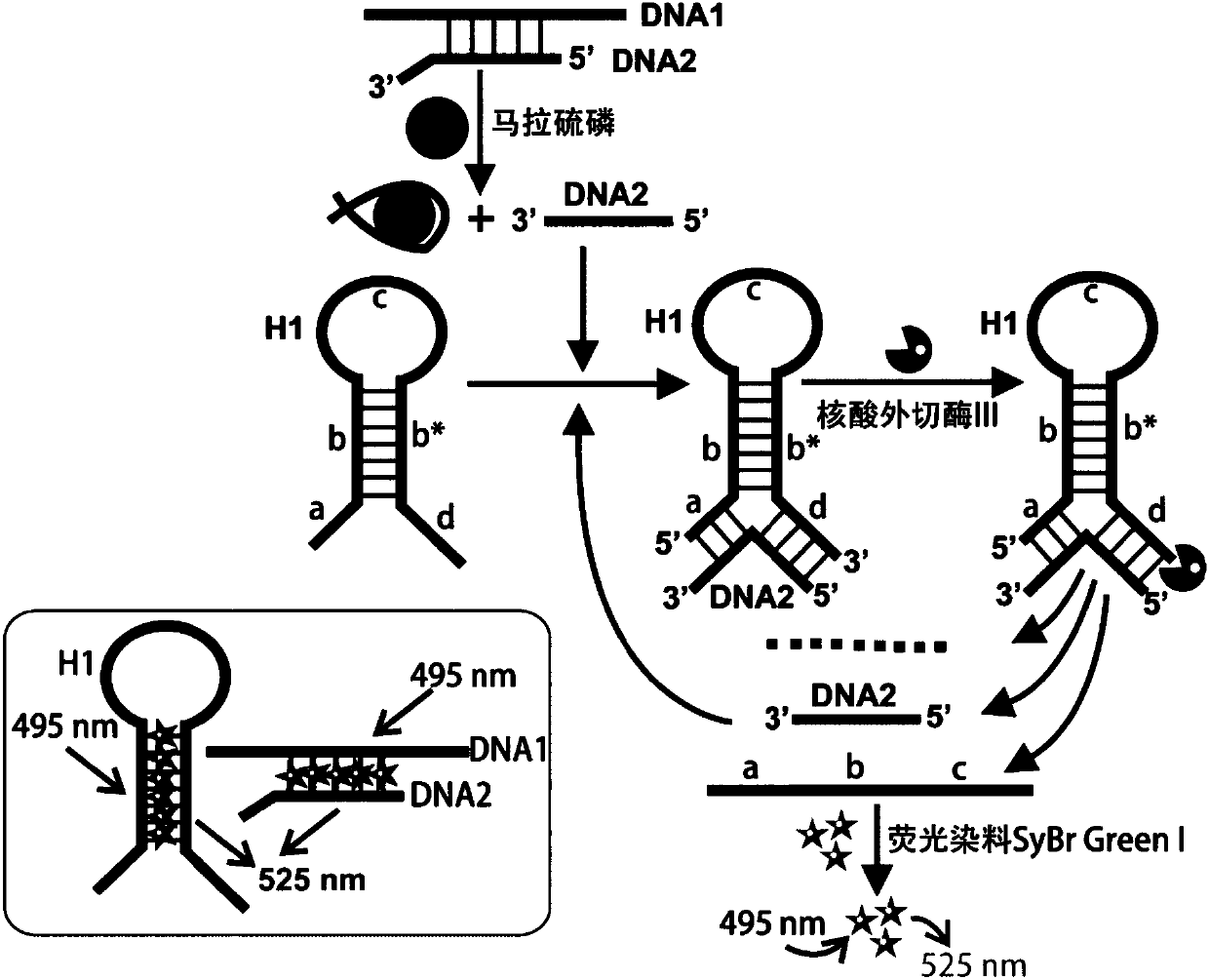
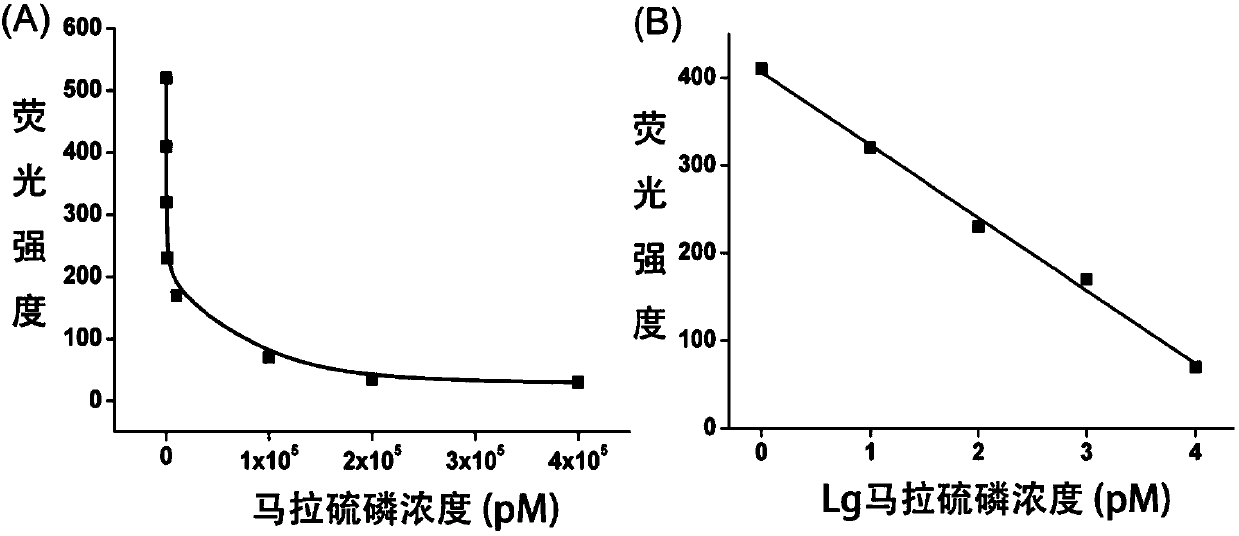
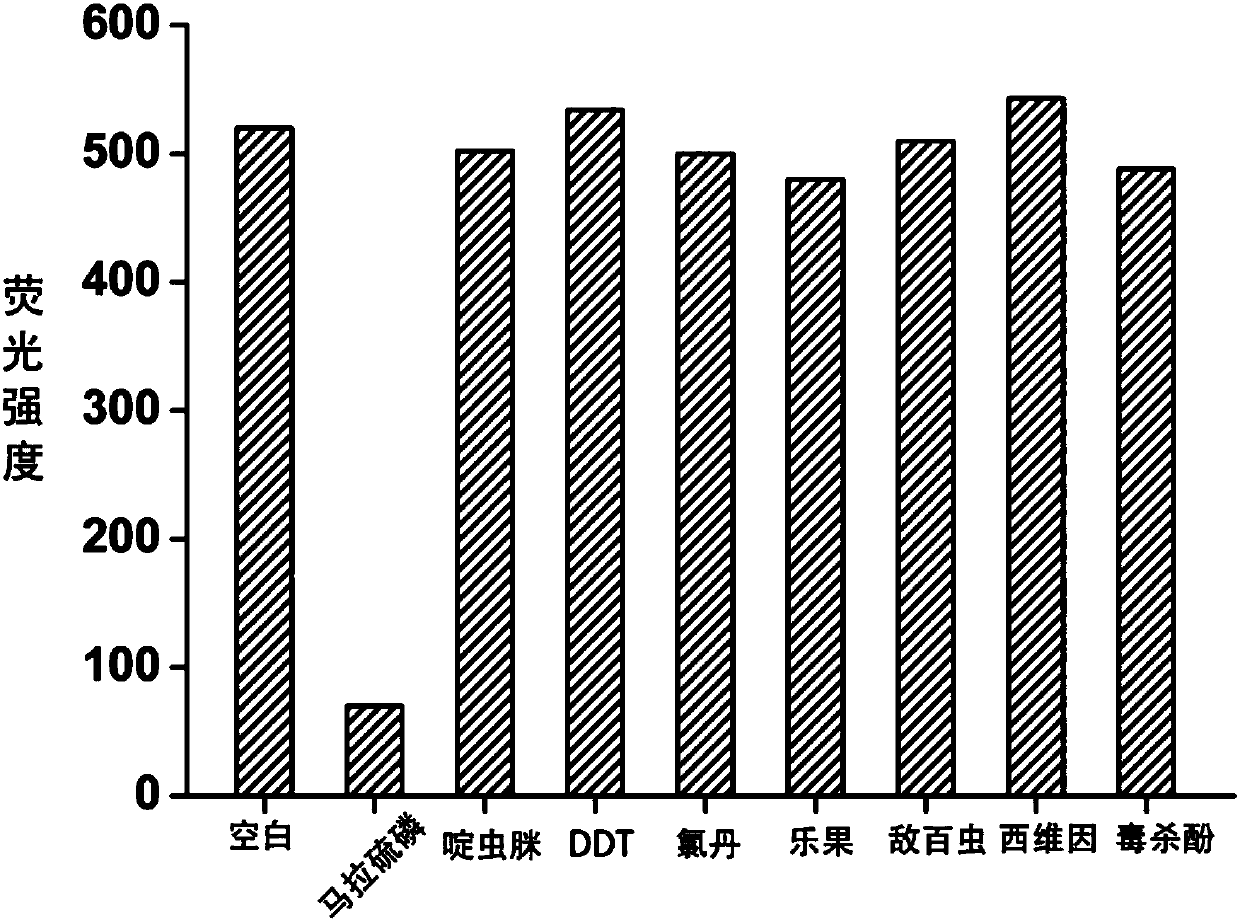
The invention discloses a fluorescence detection kit based on an aptamer. The fluorescence detection kit comprises exonuclease III, a reaction buffer solution, DNA1, DNA2 and stem-loop structure nucleic acid H1. The aptamer is used for specific recognition of a molecular recognition element, a 3' double-chain nucleic acid structure with a flush end is obtained, and circular signal amplification isperformed after exonuclease III is added, so that a large amount of double-chain DNA become single-chain DNA; after fluorescent dye is added, the content of to-be-detected molecules is detected by distinguishing fluorescence intensity change. The linear range for malathion detection is 10 pM to 100 nM, and the limit of detection is 5 pM; meanwhile, the detection system has good specificity and the detection results cannot be interfered by other common analogues. No separation and purification processes are required in the detection process, the kit can be used for detection after simple mixing, has the advantages of being simple to operate, low in cost, rapid in response and the like and can be used for rapid and high-sensitivity detection of pesticide residues in food, water sources, soil and other samples.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
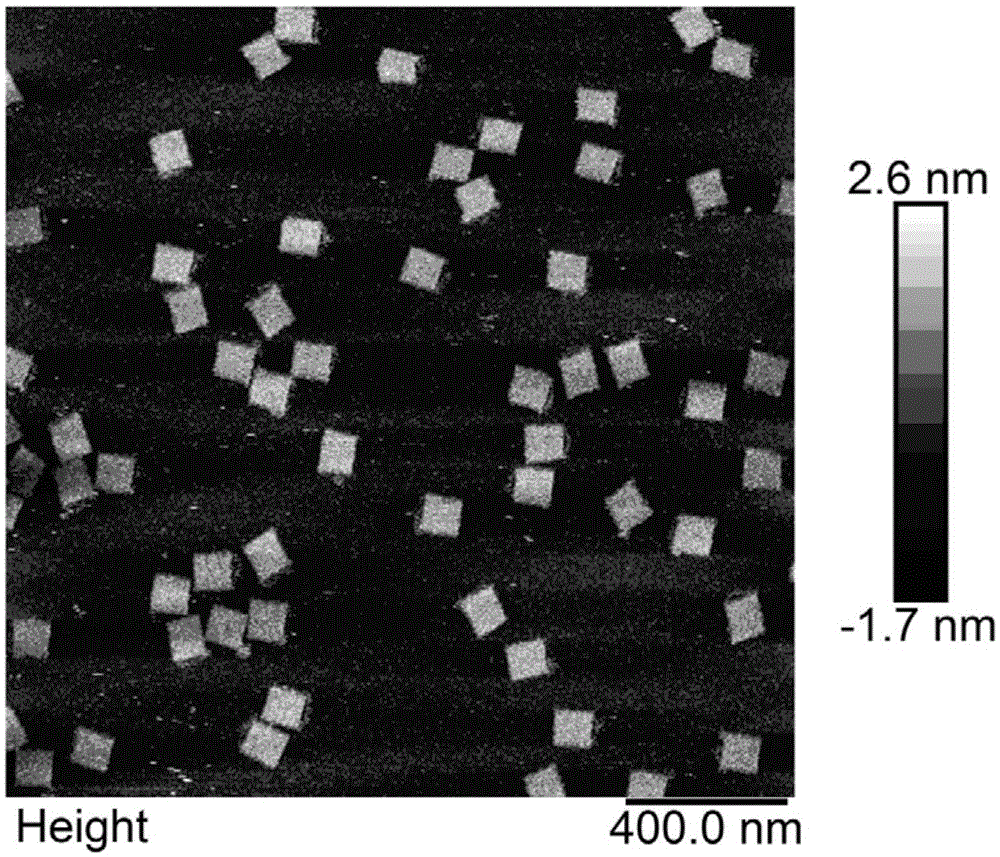
Nucleic acid structure of which interchain exchange is achieved by support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and synthesis method thereof
PendingCN105602949AHigh yieldSimple designDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA origamiNucleic acid structure
The invention discloses a nucleic acid structure of which the interchain exchange is achieved by a support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The nucleic acid structure is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional nucleic acid structure with controllable size and shape, which is formed by achieving interchain exchange by the support DNA. The nucleic acid structure comprises a set of parallel double helices connected by interchain exchange and a single-chain DNA segment, wherein the double helices are formed by carrying out folding and interchain exchange by the support DNA, carrying out specific matching with a plurality of short-chain DNAs and carrying out annealing reaction; and the single-chain DNA is the part of the support DNA which does not form the double helices. The invention provides the multiple nucleic acid structures and synthesis methods thereof. The nucleic acid structure is a variant technique based on DNA paper folding. The invention aims to form the nucleic acid structure with controllable size, shape, complexity and modification by achieving interchain exchange by using the support DNA. The nucleic acid structure is completed by the support DNA / short-chain DNA self-assembly process, and has the advantages of higher yield and simple design; and the predicated two-dimensional and three-dimensional structures can be simultaneously synthesized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
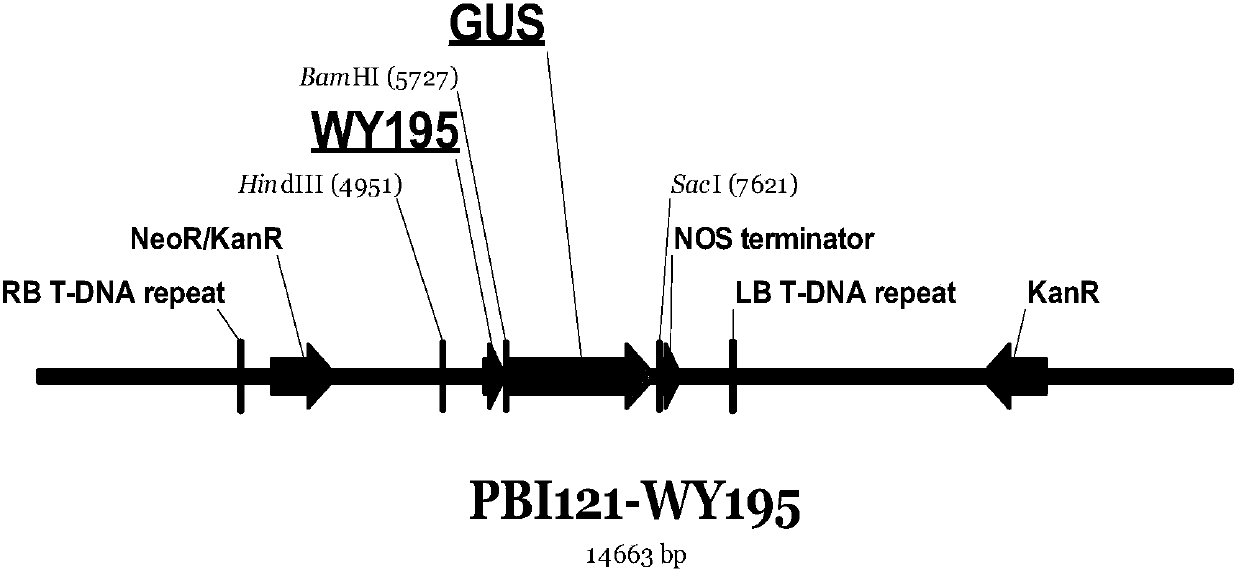
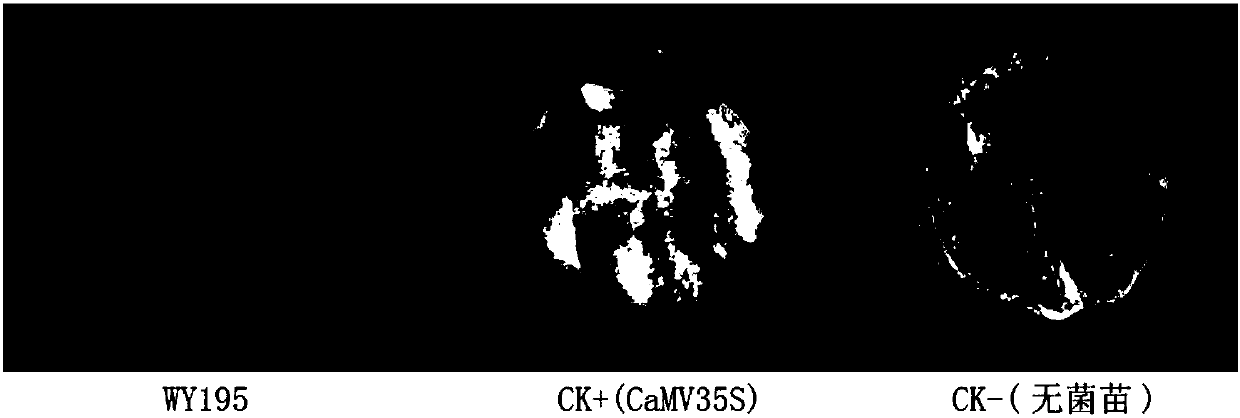
Promoter WY195 and application thereof
The invention relates to a promoter derived from powdery mildew of rubber trees and application of the promoter. The invention provides a novel promoter derived from powdery mildew of rubber trees, and the promoter has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, or a variant with functions of the promoter. The invention further relates to a nucleic acid structure, a vector, a recombinant cell,a transgenic plant, explants and calluses with the promoter. The invention further relates to application of the promoter to regulation and control of target gene expression in fungi. The promoter canbe used for regulating and controlling expression of exogenous target genes in dicotyledon and monocotyledon, and a completely novel tool and option are provided for gene expression of transgenic plants.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com