Nucleic acid structure of which interchain exchange is achieved by support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and synthesis method thereof
A synthesis method and strand exchange technology, which can be used in DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulty in precise control of size and shape.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
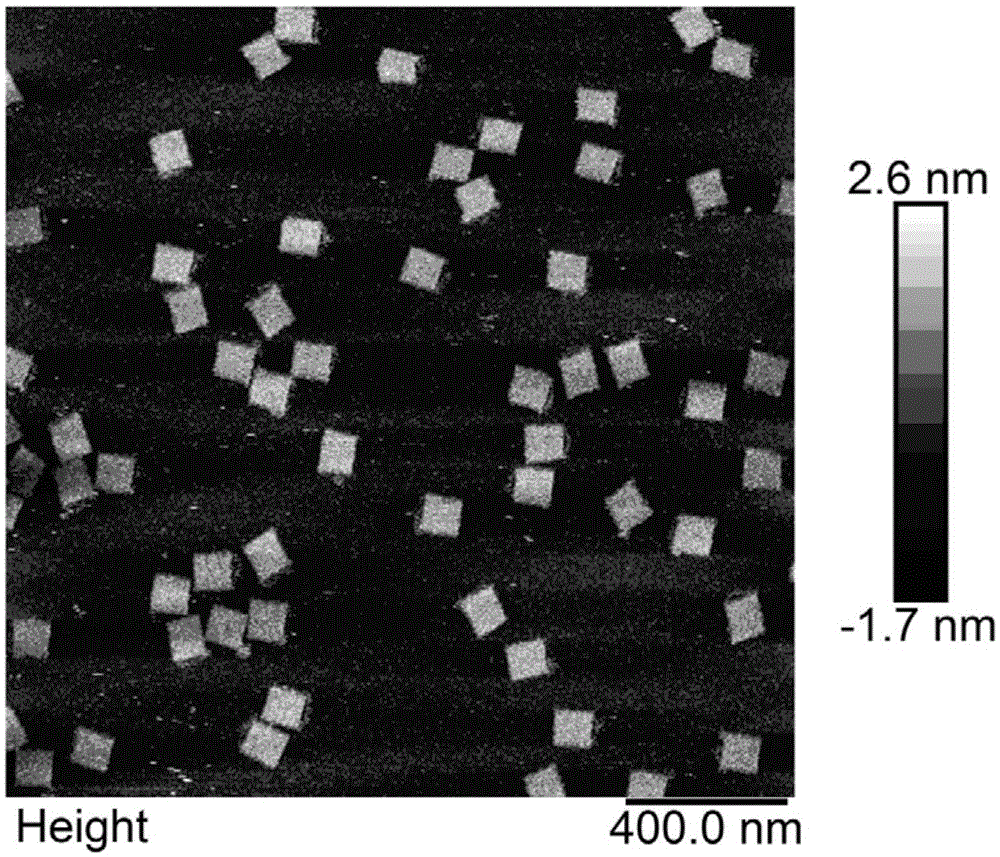
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
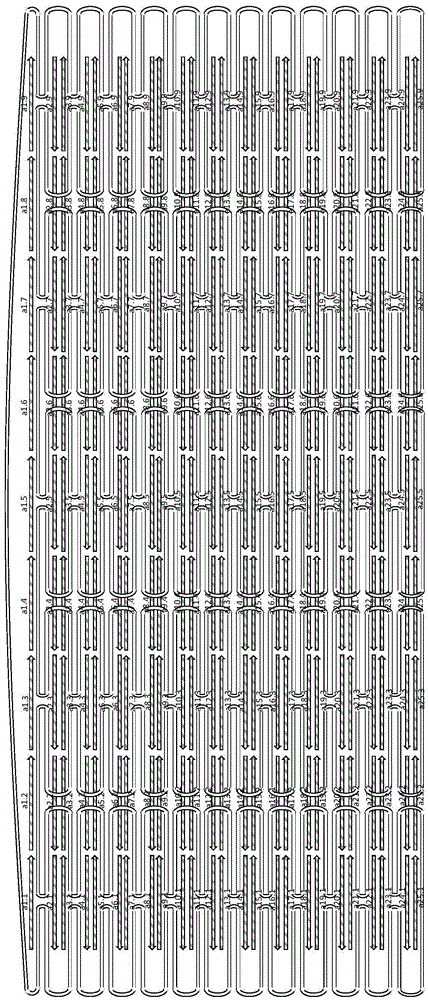
[0107] like Figure 13 Shown, the preparation process that the present invention relates to comprises the following steps:
[0108] 1. Sample preparation:
[0109] The short-chain DNA was synthesized by Bioneer Company, and all the short-chain DNA needed to form a single nucleic acid structure was absorbed with equal volume, and DEPC water was added to make the concentration of each short-chain DNA in the final mixed solution 500nM. The dilution factor is based on the starting concentration from the manufacturer's specification sheet and no additional internal corrections are performed, so the stoichiometry of short-strand DNA does not need to be precisely controlled.
[0110] The M13mp18 in the scaffold DNA was purchased from NEB Company, and an appropriate amount of pure water was added to make the initial scaffold DNA concentration 100 nM.
[0111] 2. Annealing reaction
[0112] Mix 10nM scaffold DNA with 200nM short-chain DNA in a buffer solution (10mM Tris, pH8.0, 2mM ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com