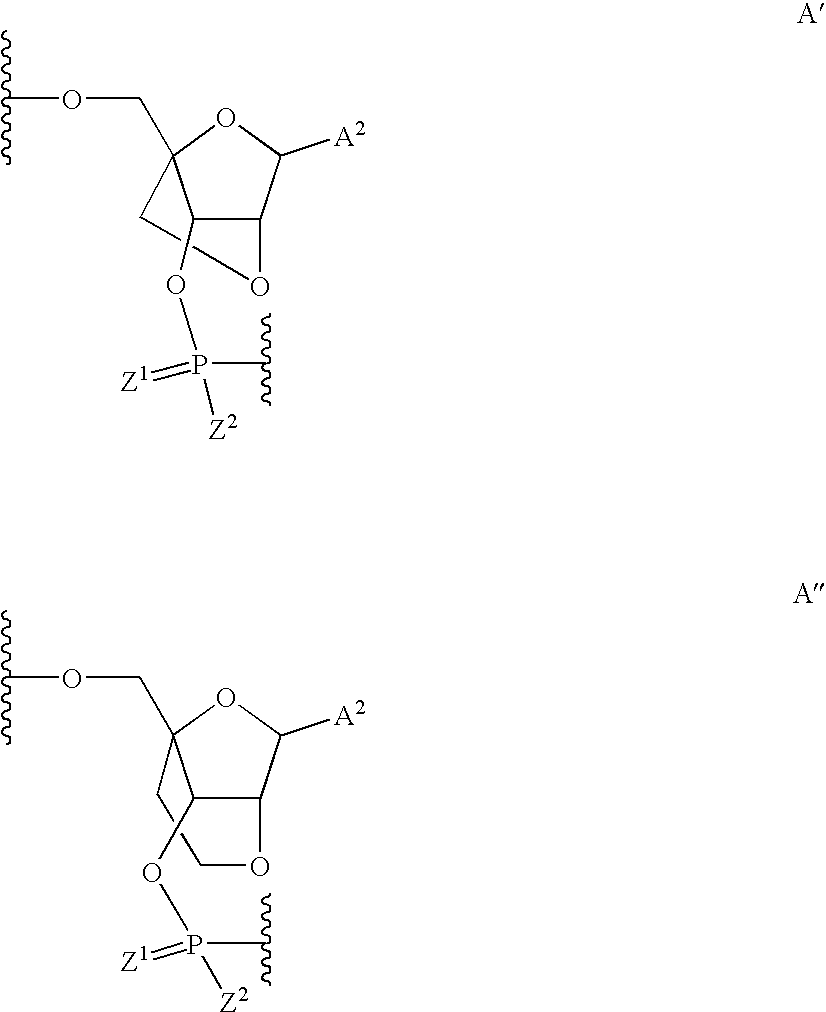
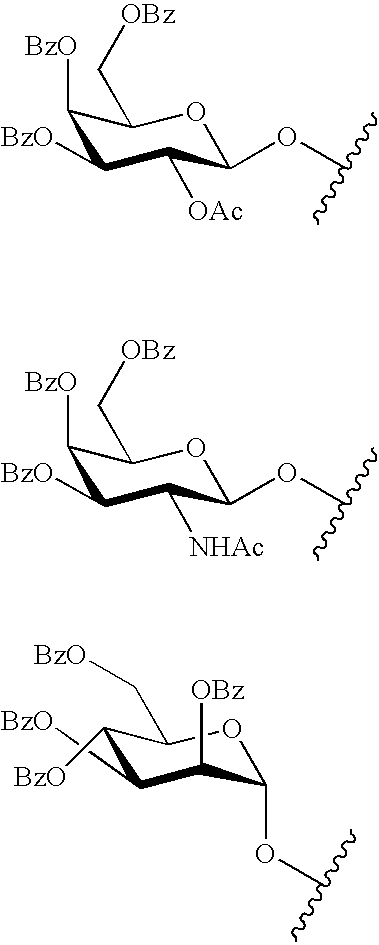
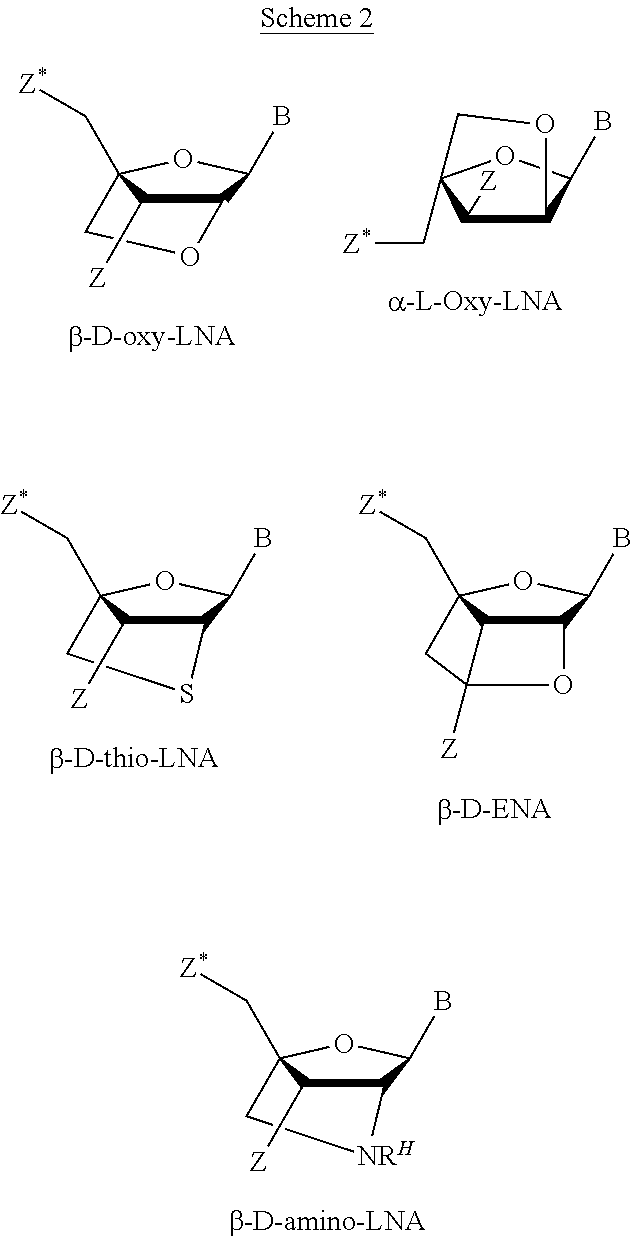
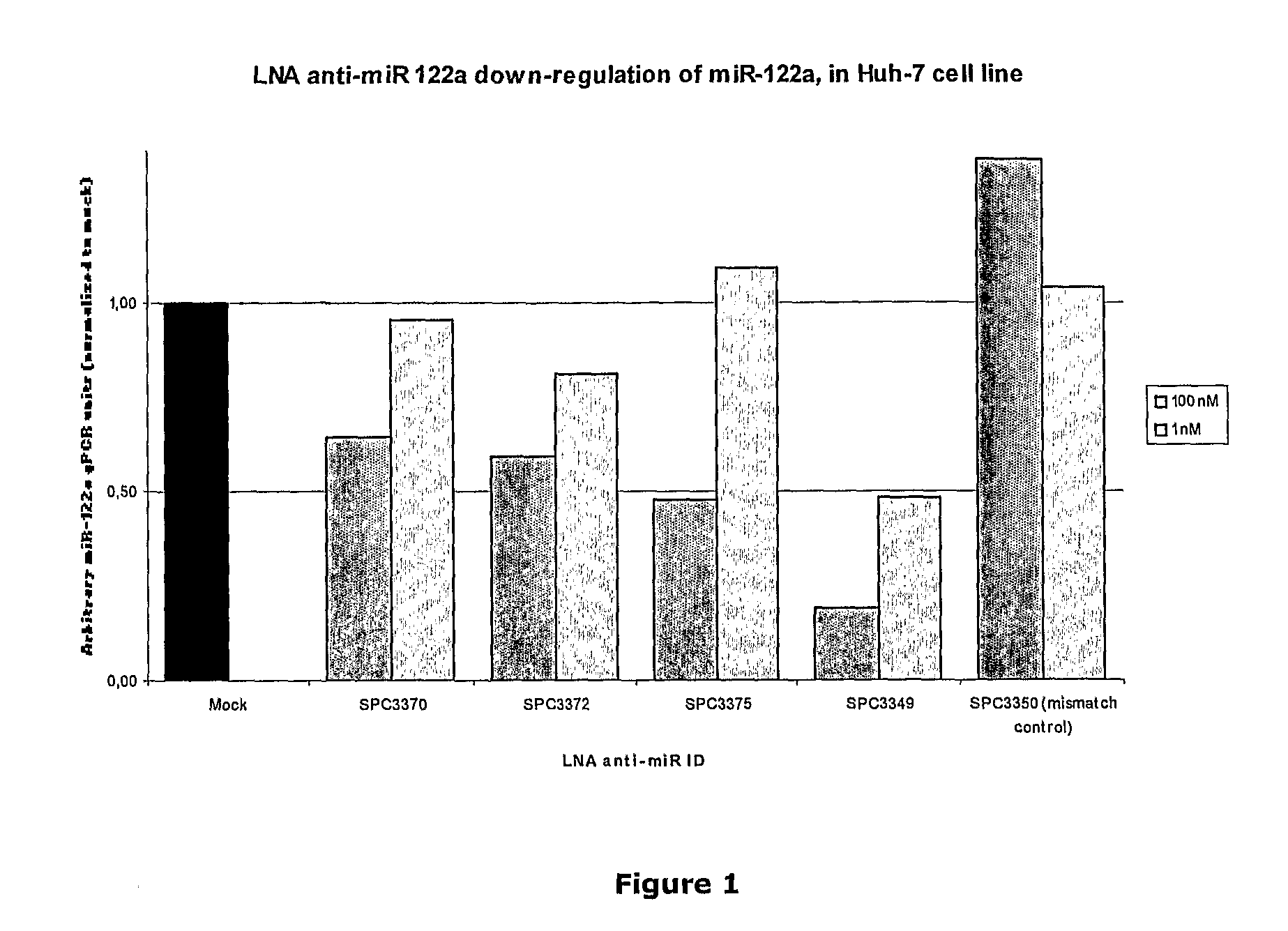
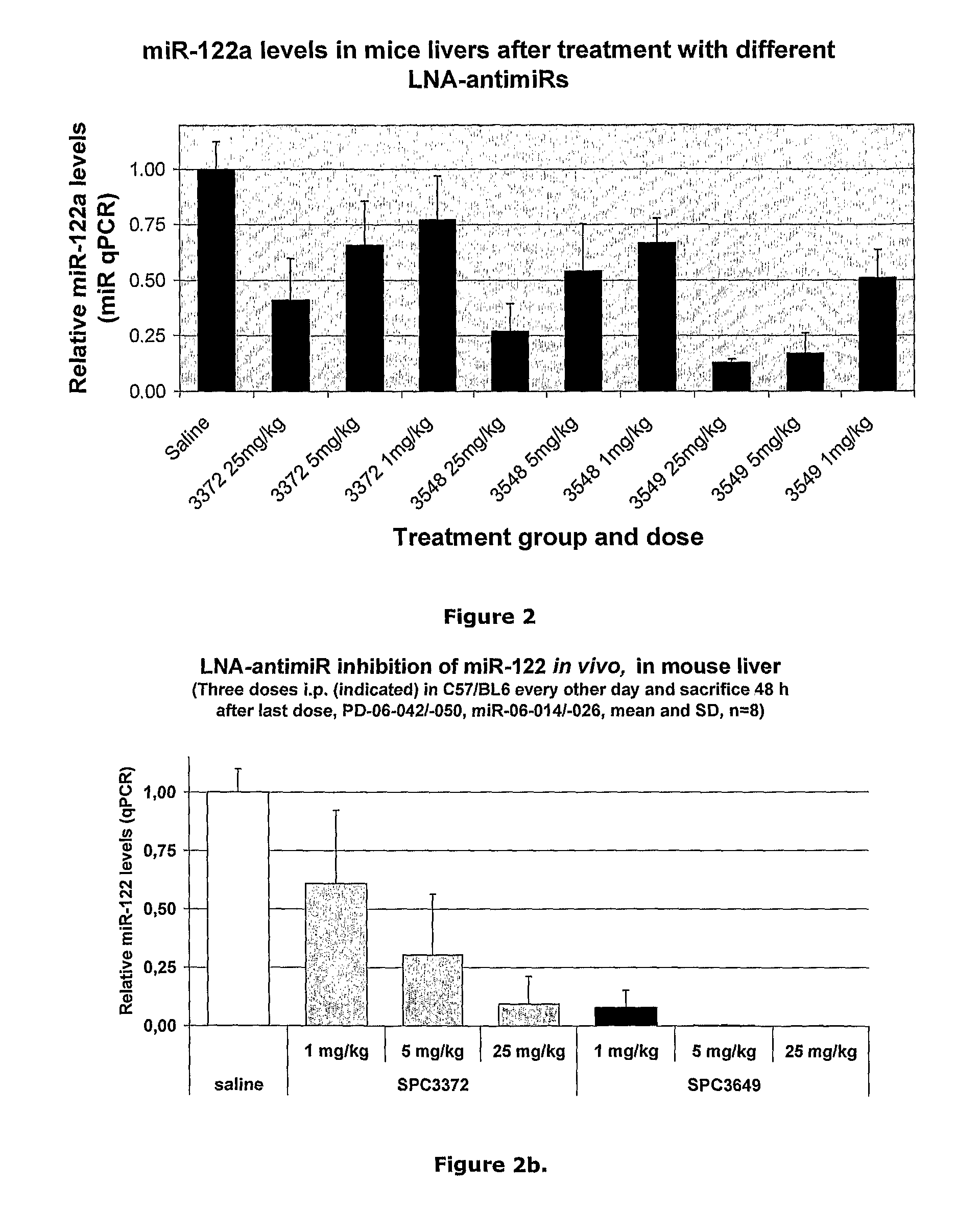
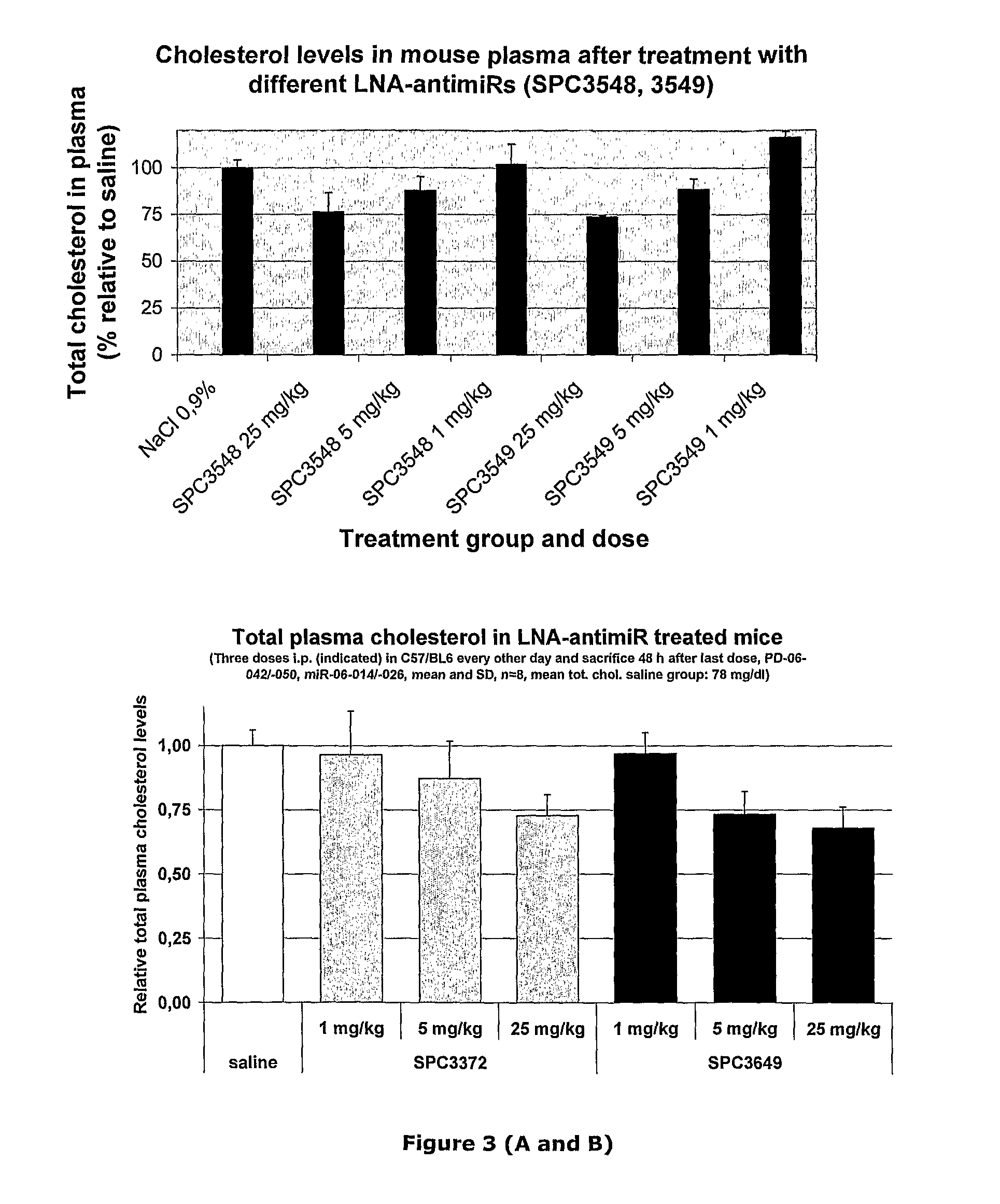
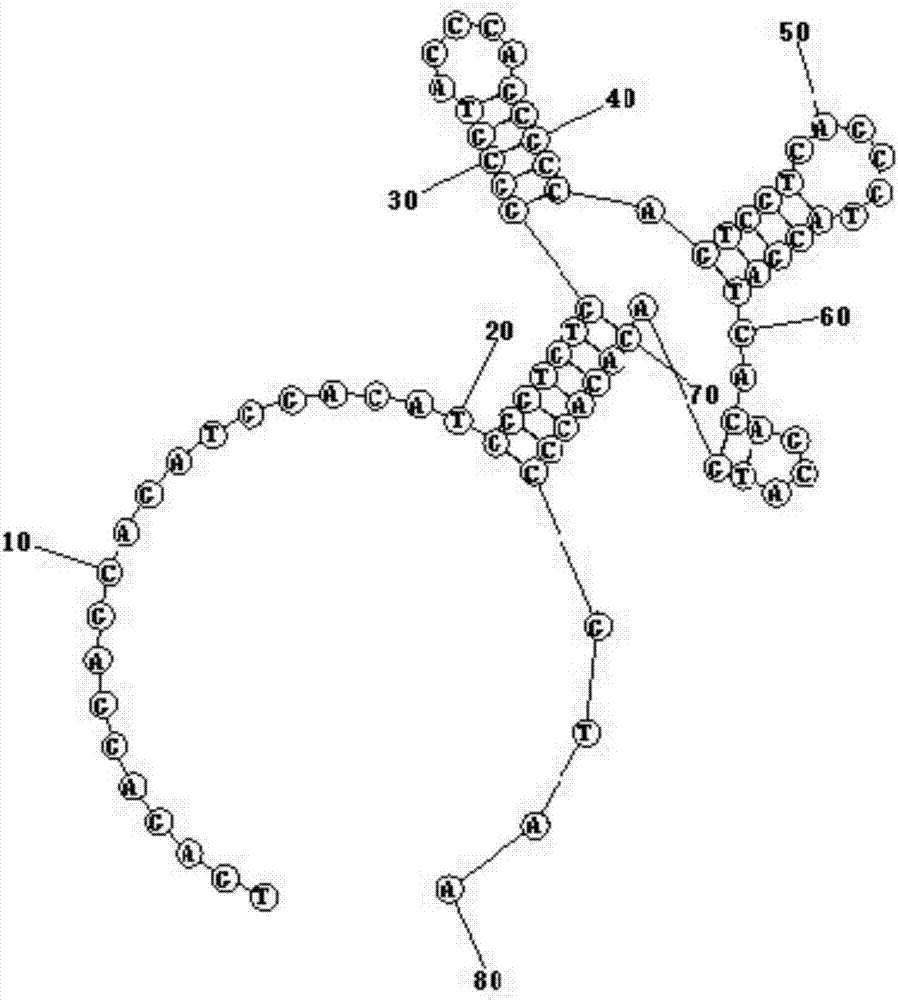
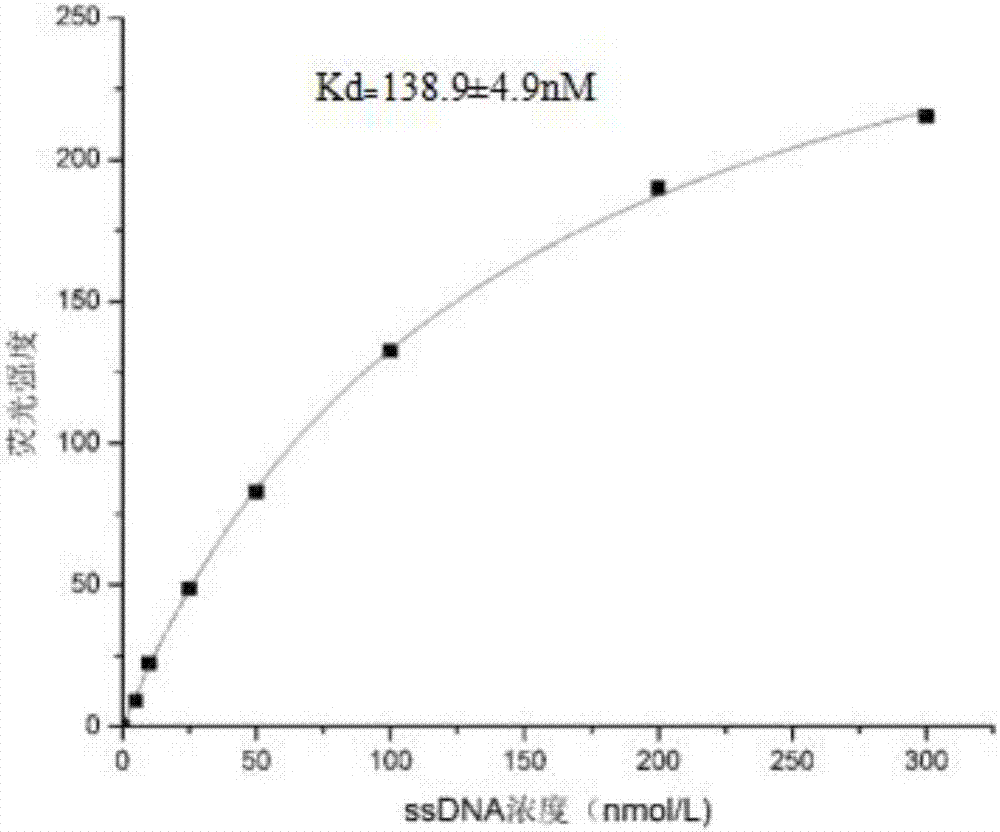
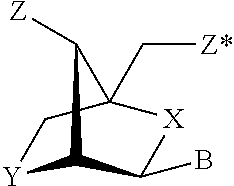
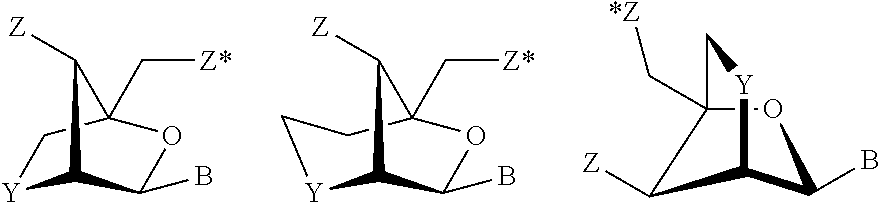
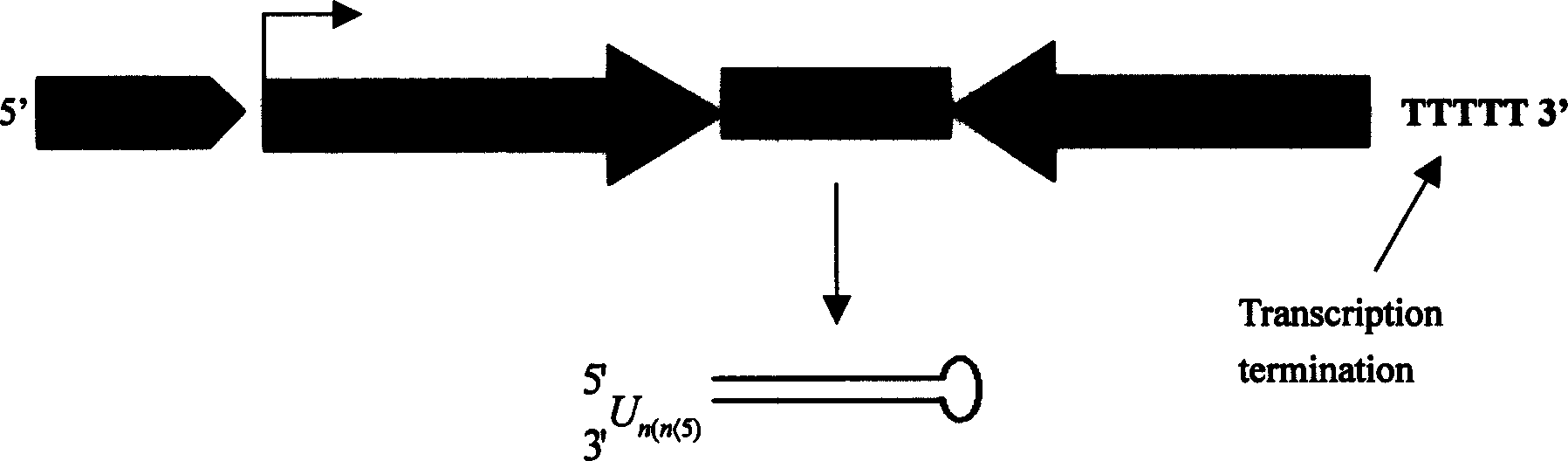
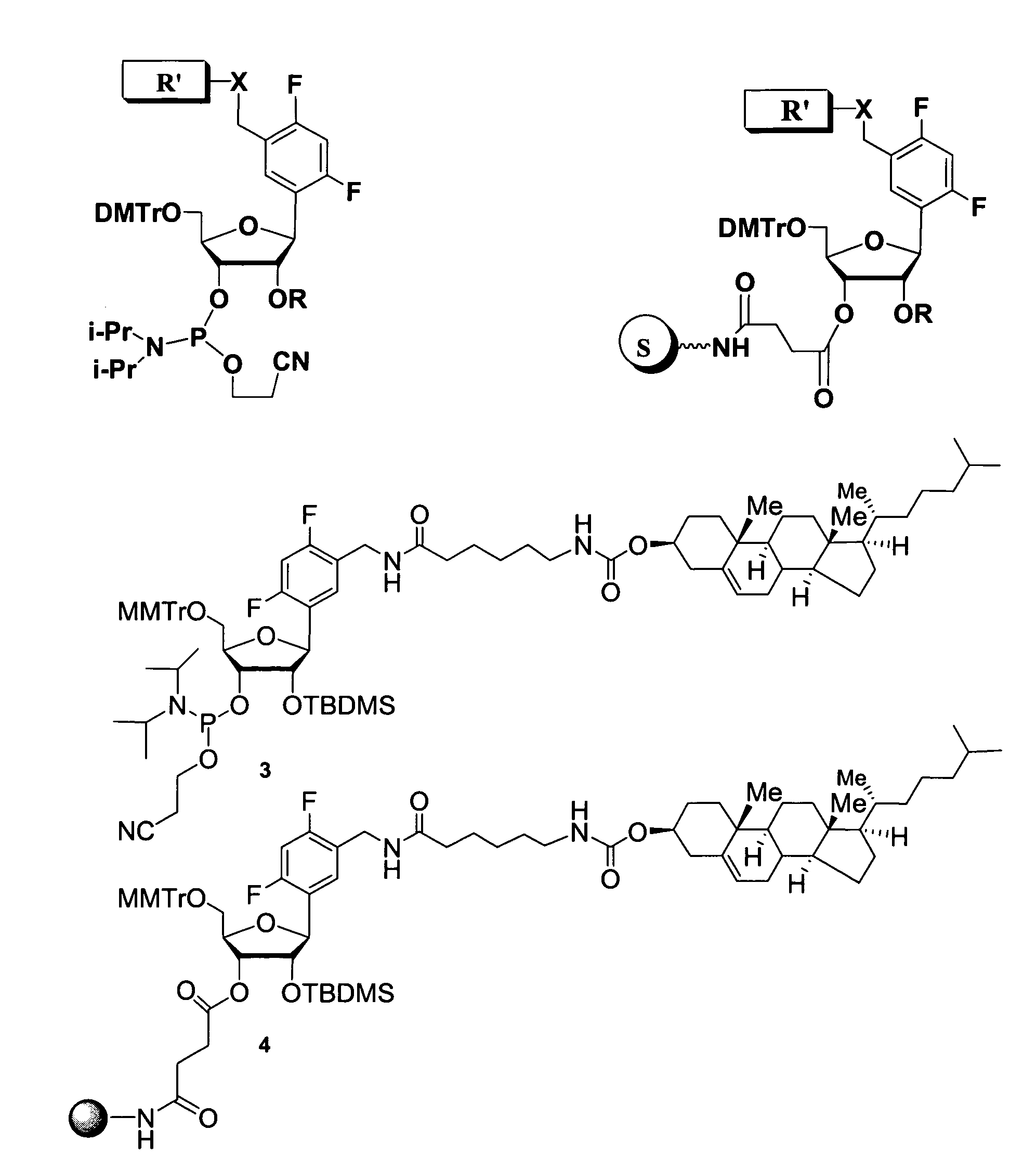
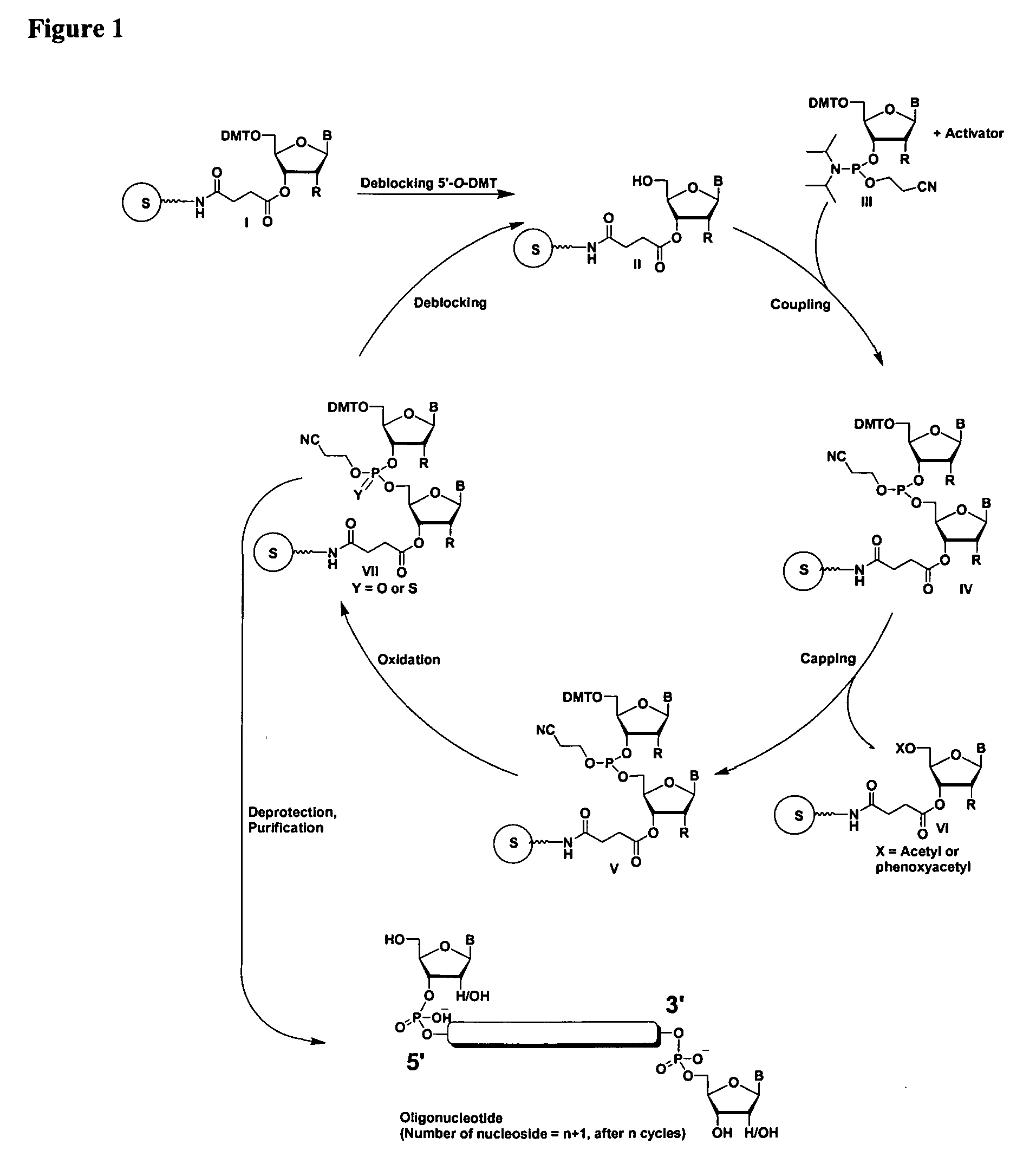
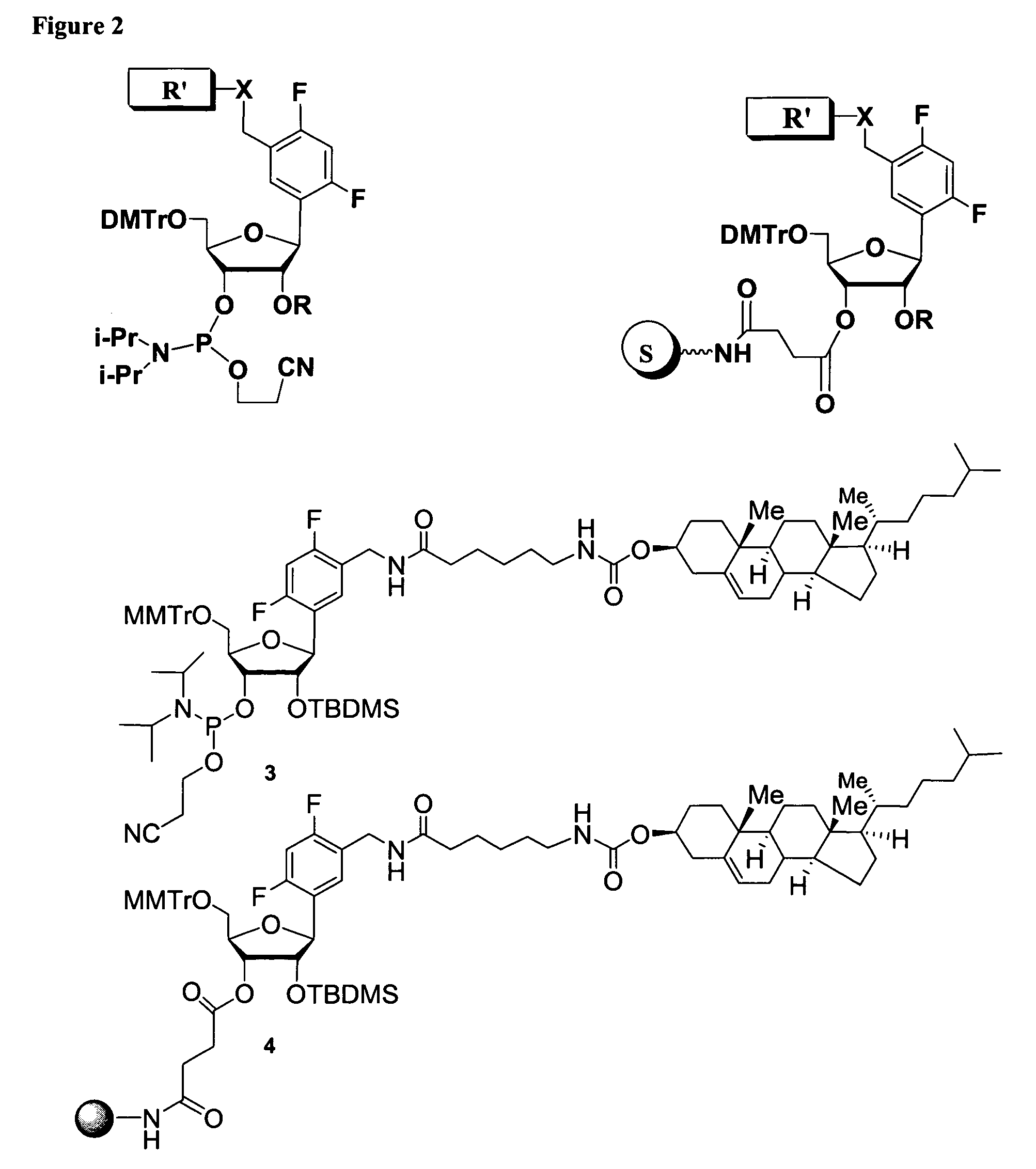
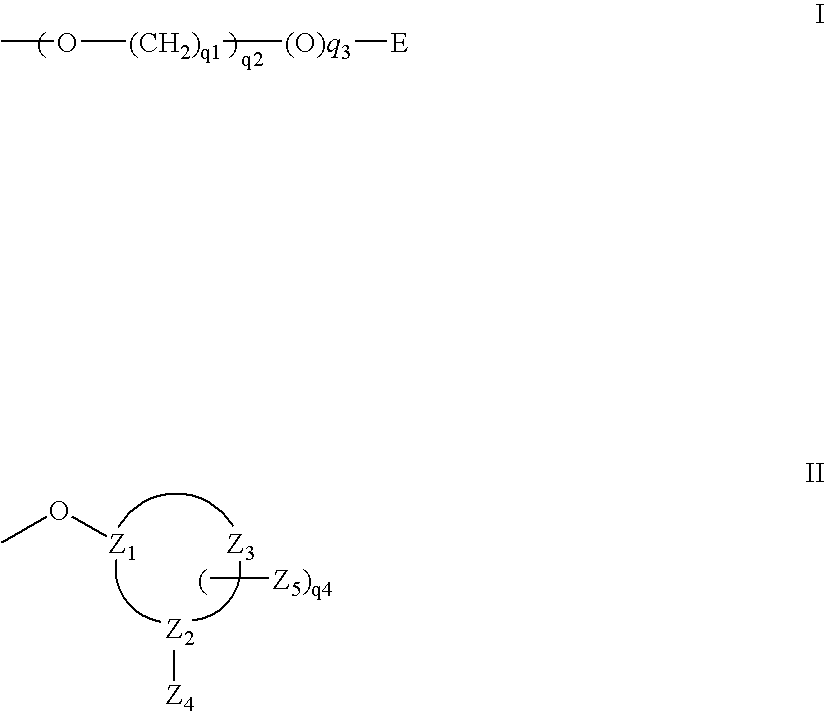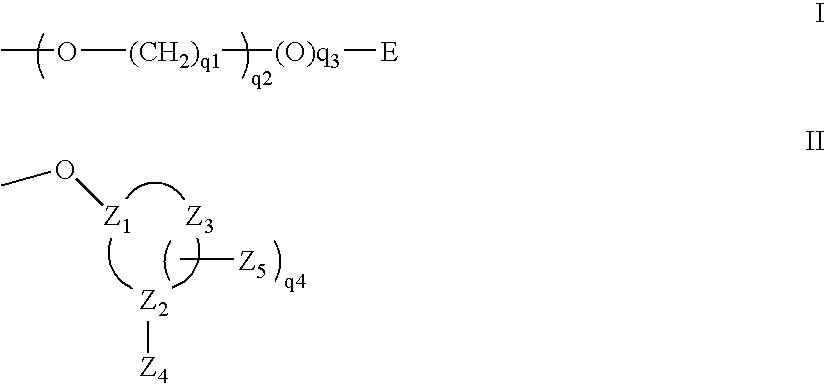Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
207 results about "Single stranded oligonucleotides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
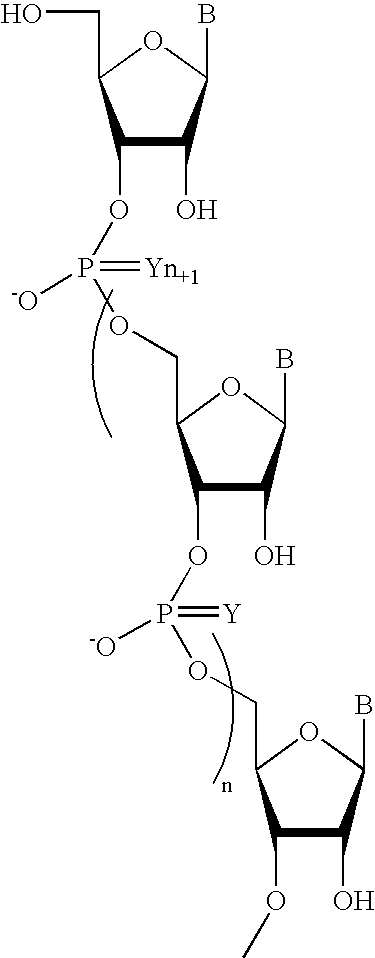
Single-stranded oligonucleotides are important as research tools, as diagnostic probes, in gene therapy and in DNA nanotechnology. Oligonucleotides are typically produced via solid-phase synthesis, using polymer chemistries that are limited relative to what biological systems produce.
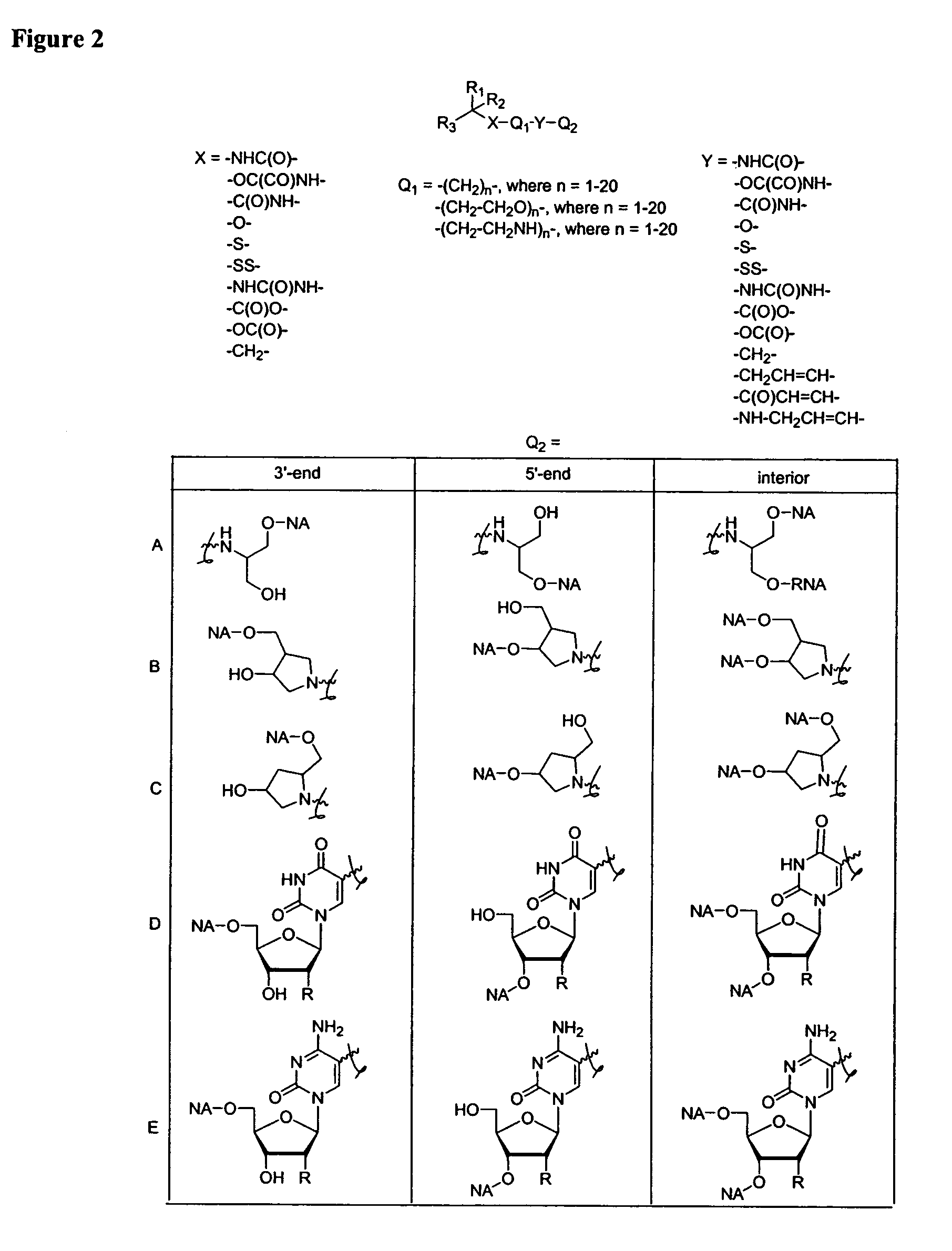
Single-stranded and double-stranded oligonucleotides comprising a 2-arylpropyl moiety
ActiveUS20060008822A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderNucleotidePhosphate
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. The aralkyl ligand improves the pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Pharmaceutical Composition
InactiveUS20100004320A1Reduce depressionEffectively repressedAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideNucleobase
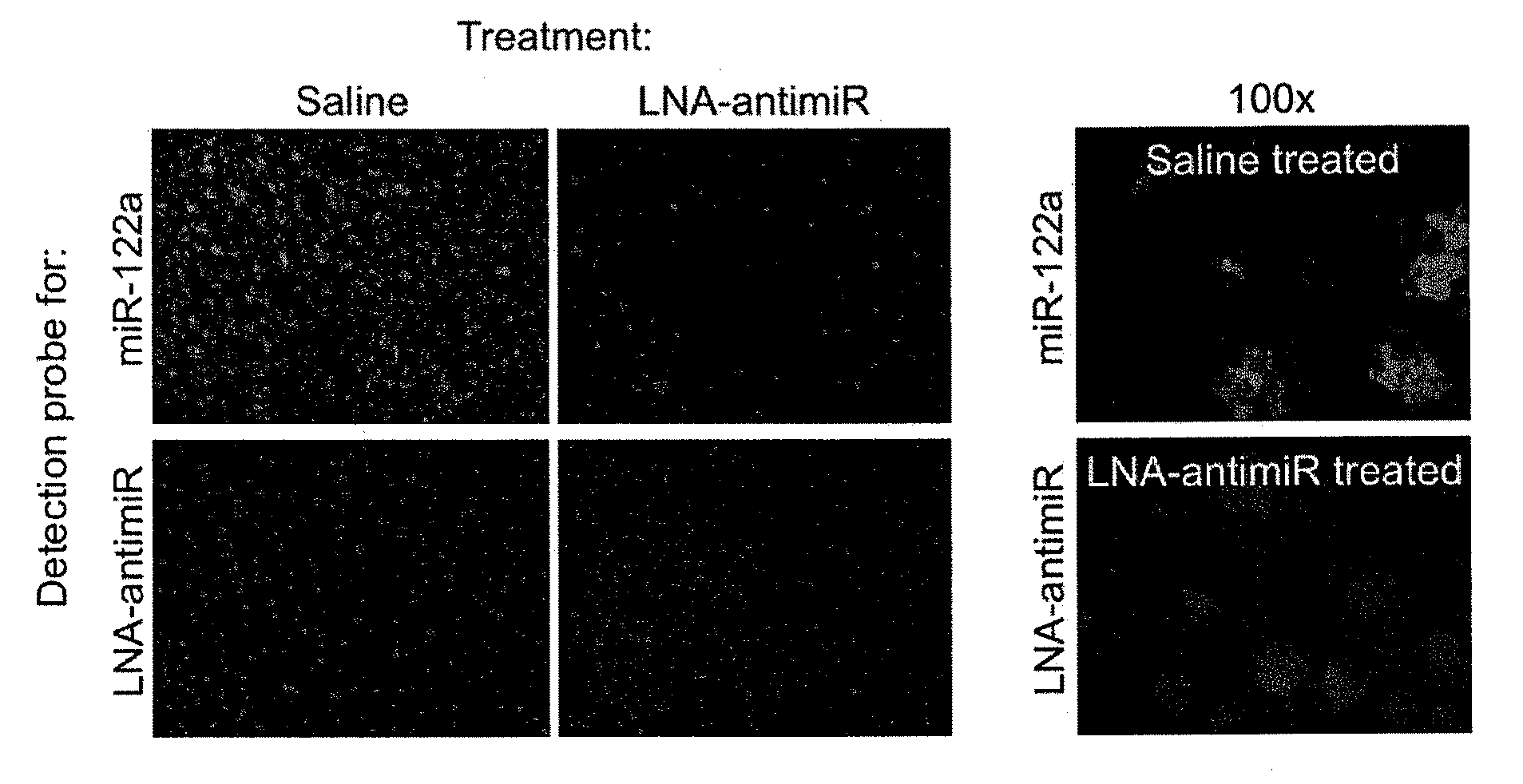
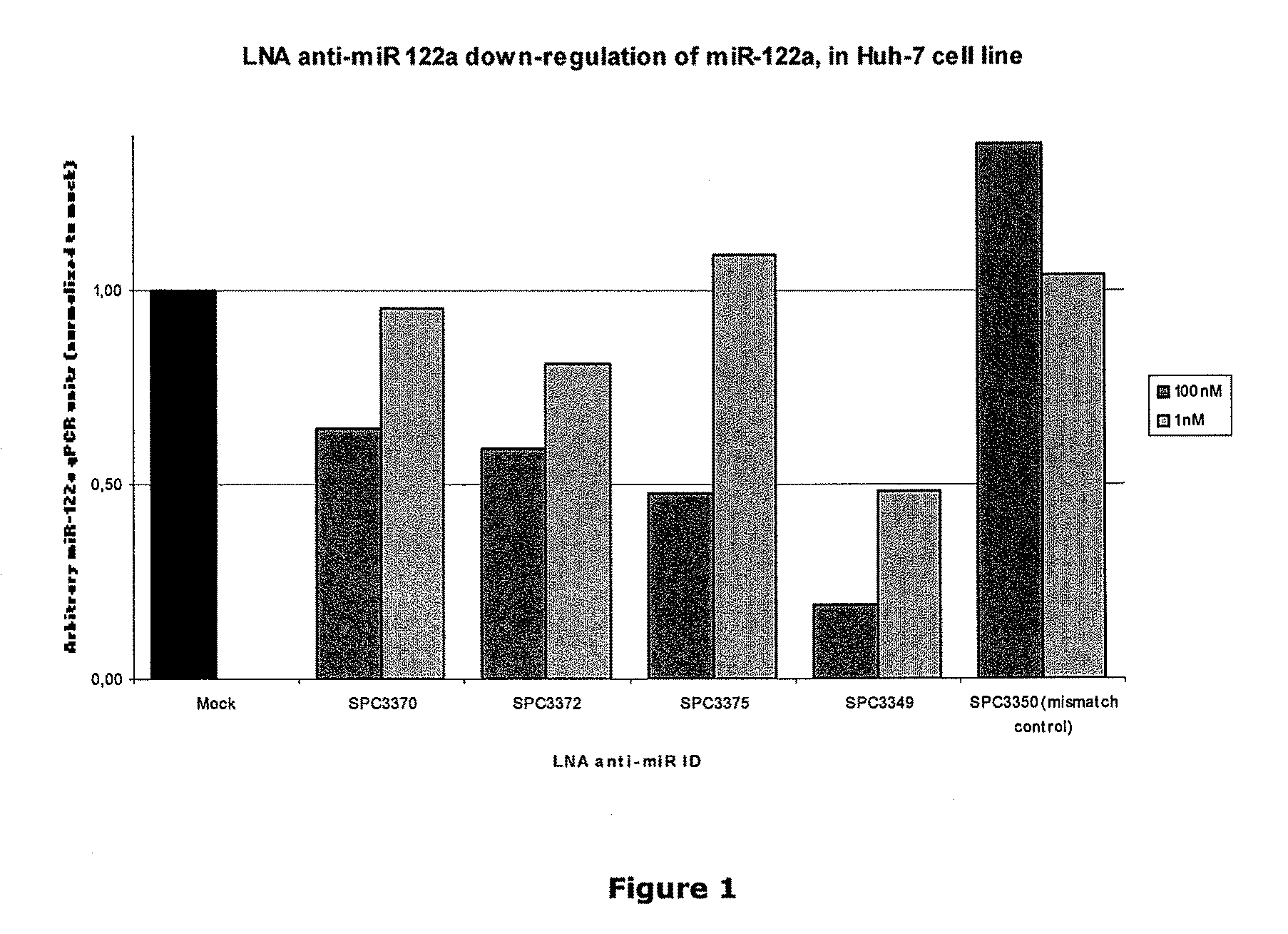
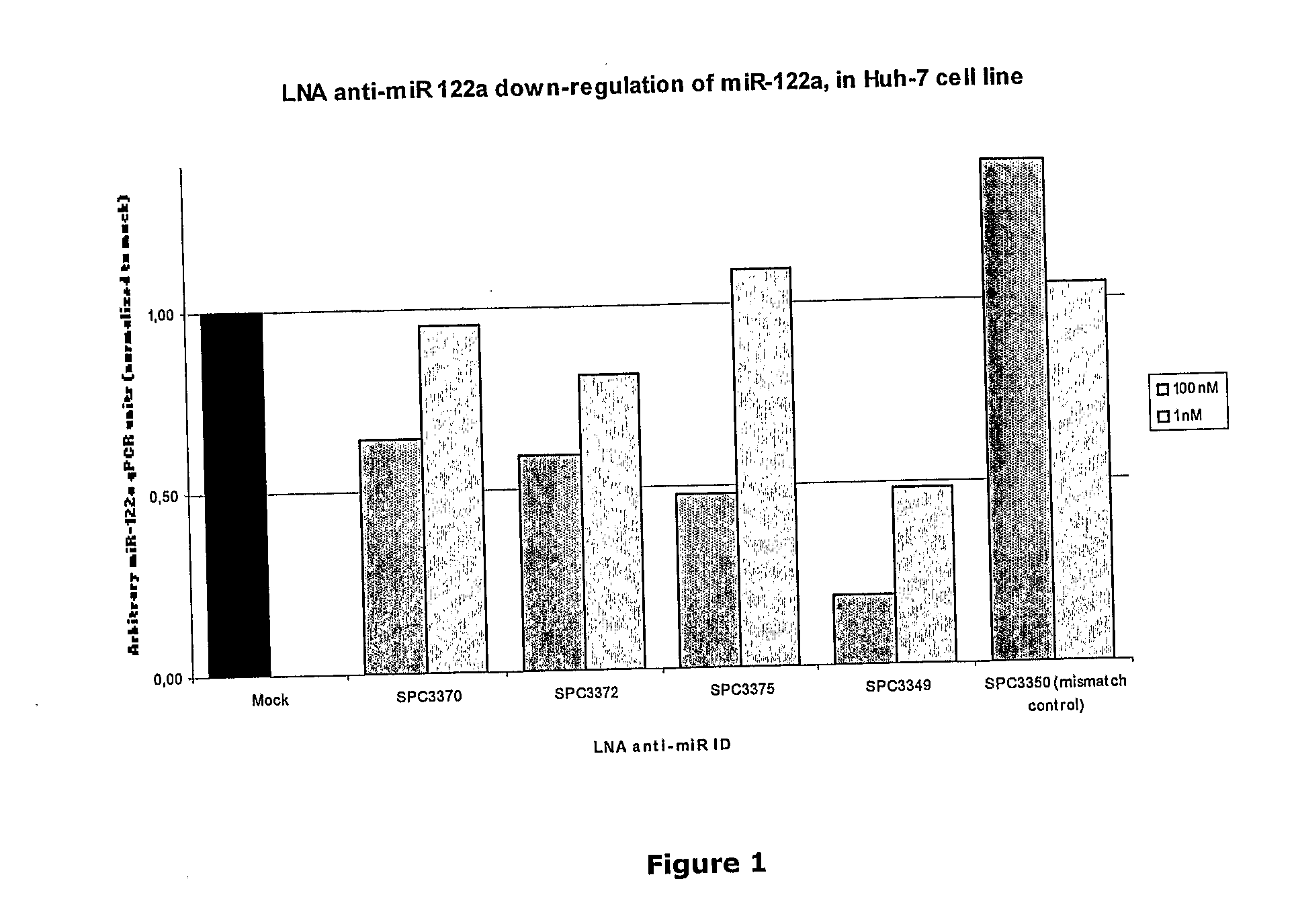
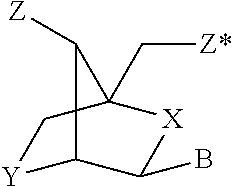
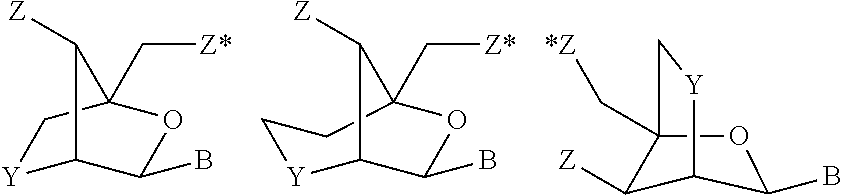
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising short single stranded oligonucleotides, of length of between 8 and 17 nucleobases which are complementary to human microRNAs. The short oligonucleotides are particularly effective at alleviating miRNA repression in vivo. It is found that the incorporation of high affinity nucleotide analogues into the oligonucleotides results in highly effective anti-microRNA molecules which appear to function via the formation of almost irreversible duplexes with the miRNA target, rather than RNA cleavage based mechanisms, such as mechanisms associated with RNaseH or RISC.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
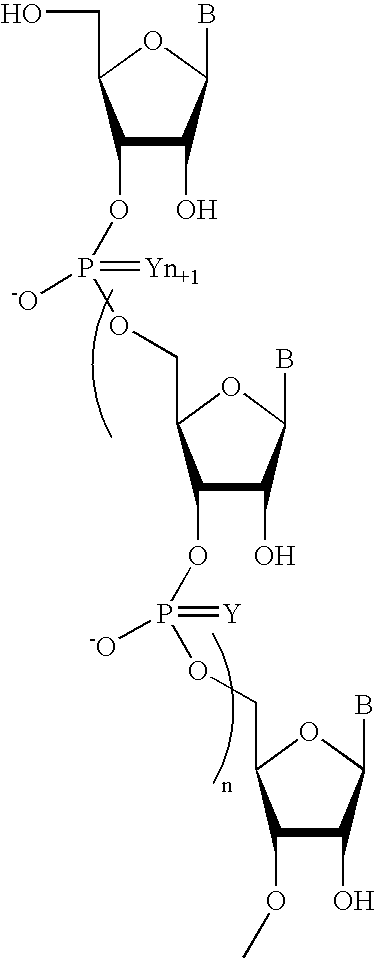
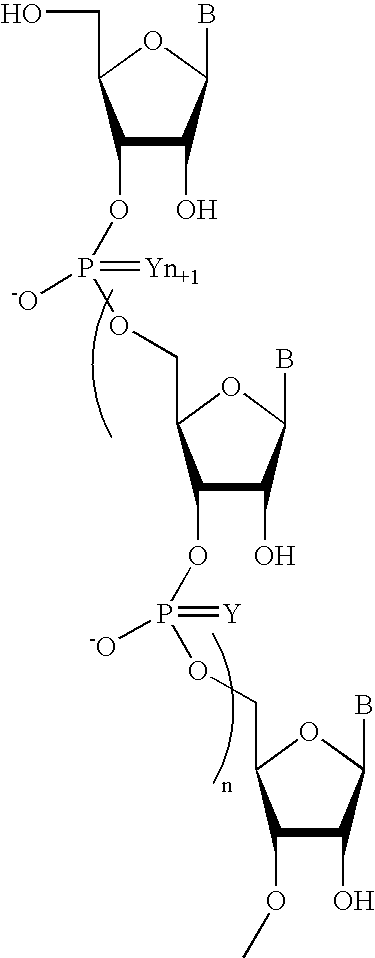
Oligonucleotides comprising a non-phosphate backbone linkage
One aspect of the present invention relates to a ribonucleoside substituted with a phosphonamidite group at the 3′-position. In certain embodiments, the phosphonamidite is an alkyl phosphonamidite. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one non-phosphate linkage. Representative non-phosphate linkages include phosphonate, hydroxylamine, hydroxylhydrazinyl, amide, and carbamate linkages. In certain embodiments, the non-phosphate linkage is a phosphonate linkage. In certain embodiments, a non-phosphate linkage occurs in only one strand. In certain embodiments, a non-phosphate linkage occurs in both strands. In certain embodiments, a ligand is bound to one of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, a ligand is bound to both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one non-phosphate linkage. Representative non-phosphate linkages include phosphonate, hydroxylamine, hydroxylhydrazinyl, amide, and carbamate linkages. In certain embodiments, the non-phosphate linkage is a phosphonate linkage. In certain embodiments, a ligand is bound to the oligonucleotide strand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
2'-f modified RNA interference agents
InactiveUS20110269814A1Inhibit expressionSuppress gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotideSense strand
This invention relates to a method of modulating the expression of a target gene in an organism comprising administering an iRNA agent, wherein the iRNA comprises at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide in the antisense strand and at least one modified nucleotide in the sense strand. The invention also relates to compositions comprising a single-stranded oligonucleotide that contains at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide. siRNA molecule containing these oligonucleotides have decreased immunogenicity.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Oligonucleotides comprising a modified or non-natural nucleobase
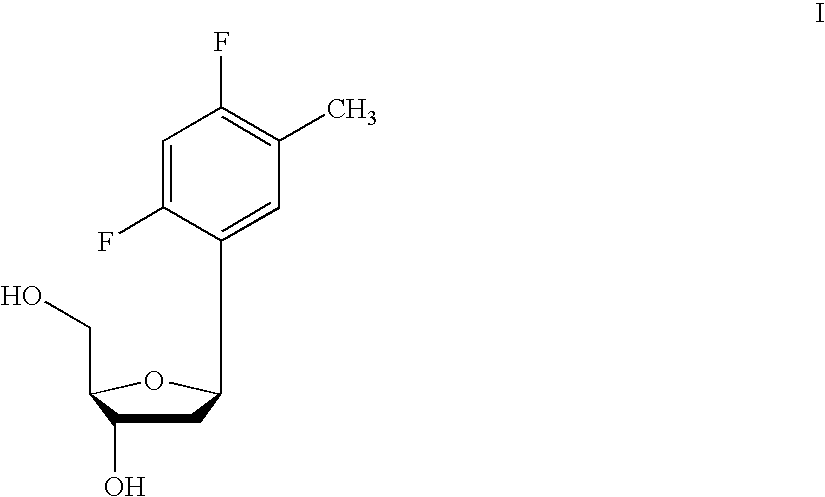
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl, nitroindolyl, nitropyrrolyl, or nitroimidazolyl. In a preferred embodiment, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl. In certain embodiments, only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide contains a non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide independently contain a non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one non-natural nucleobase. In a preferred embodiment, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl. In certain embodiments, the ribose sugar moiety that occurs naturally in nucleosides is replaced with a hexose sugar, polycyclic heteroalkyl ring, or cyclohexenyl group. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Oligonucleotides comprising a C5-modified pyrimidine
ActiveUS20050288244A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderBenzoic acidPhosphate
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one ligand. In certain embodiments, a ligand is bound to only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, both of the oligonucleotide strands of the double-stranded oligonucleotide independently comprise a bound ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, a phosphate linkage in one or both of the strands of the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the ligand is cholesterol or 5β-cholanic acid. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, a phosphate linkage of the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the ligand is cholesterol or 5β-cholanic acid. The ligand improves the pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Circular DNA vectors for synthesis of RNA and DNA
InactiveUS20080227160A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
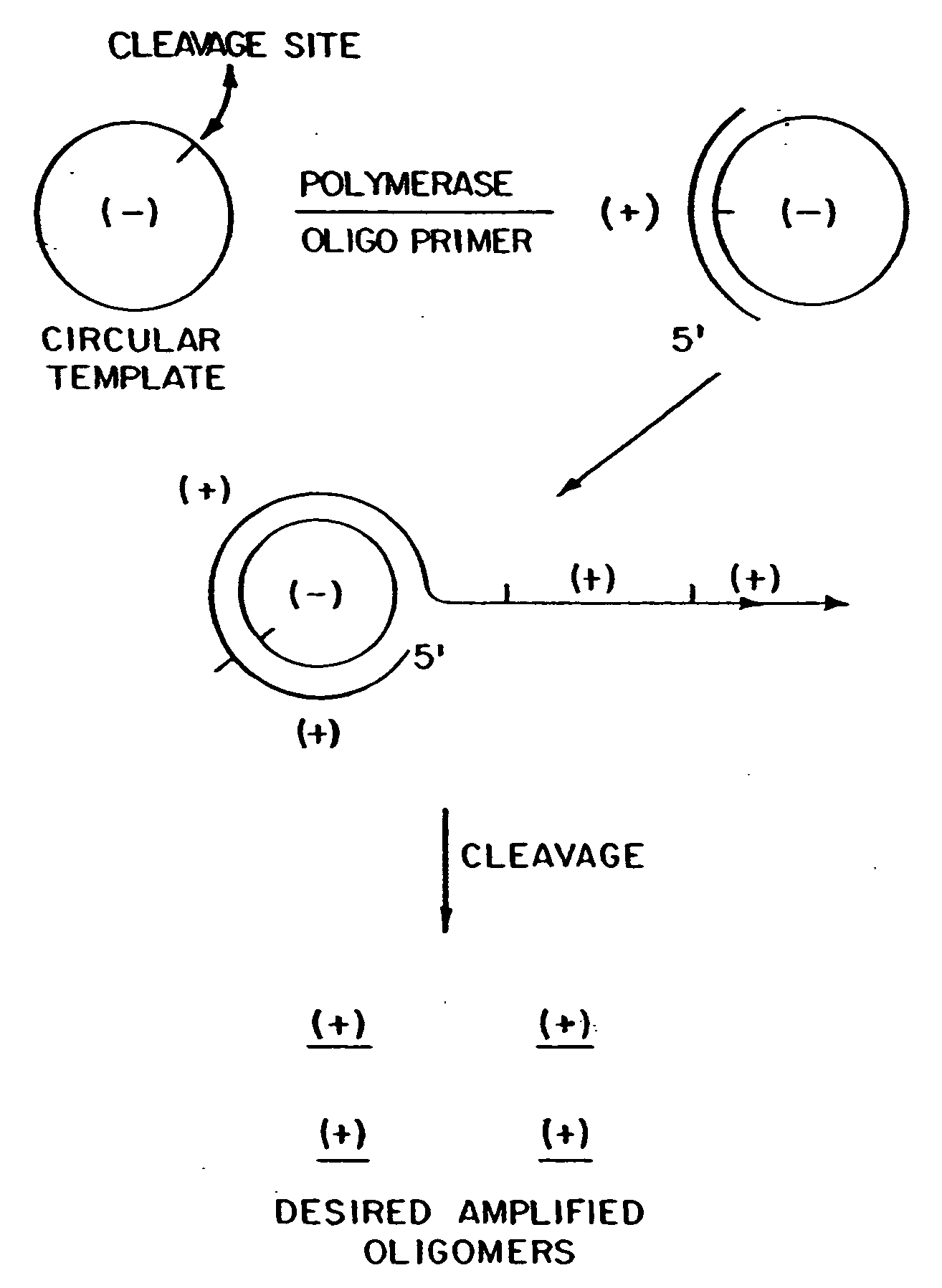
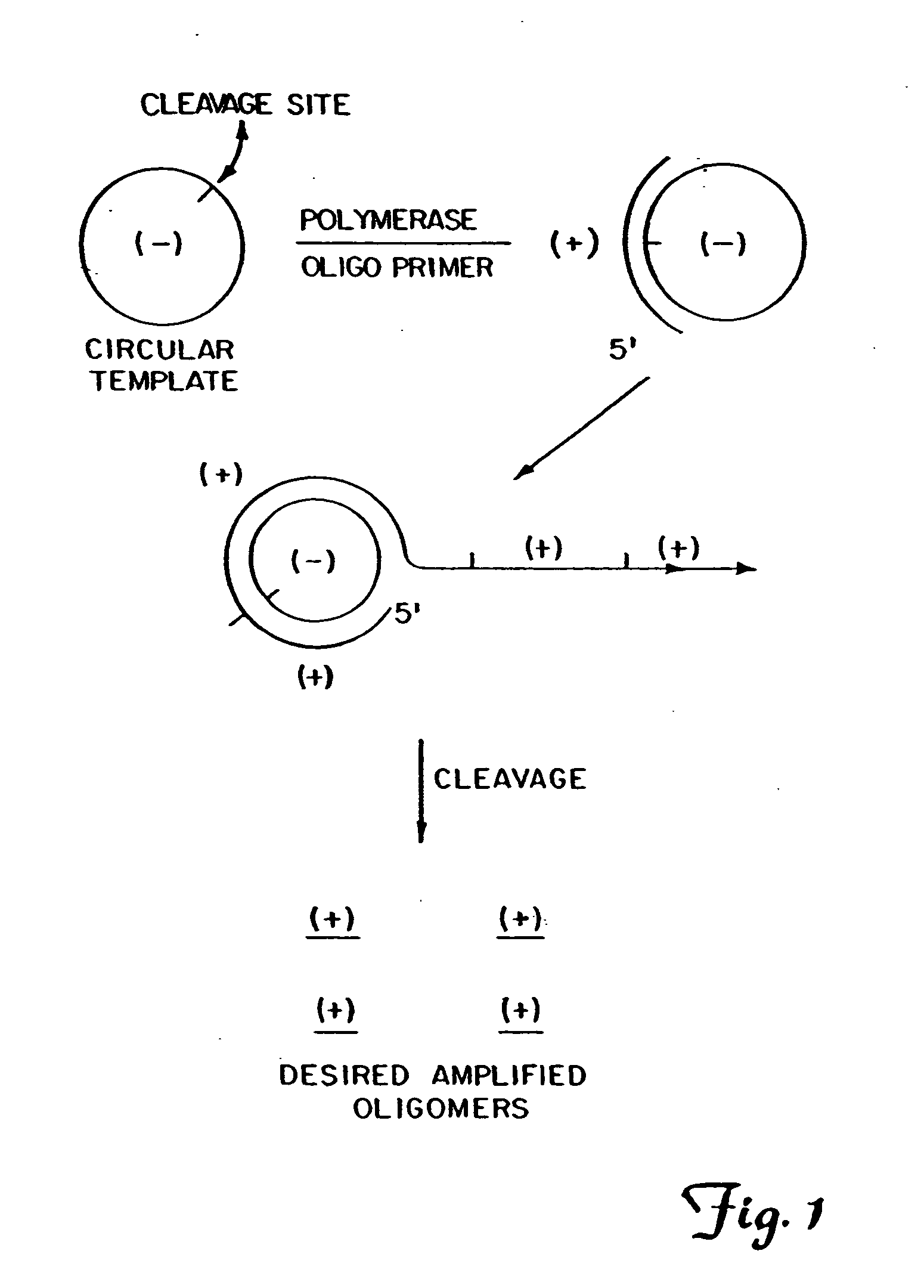
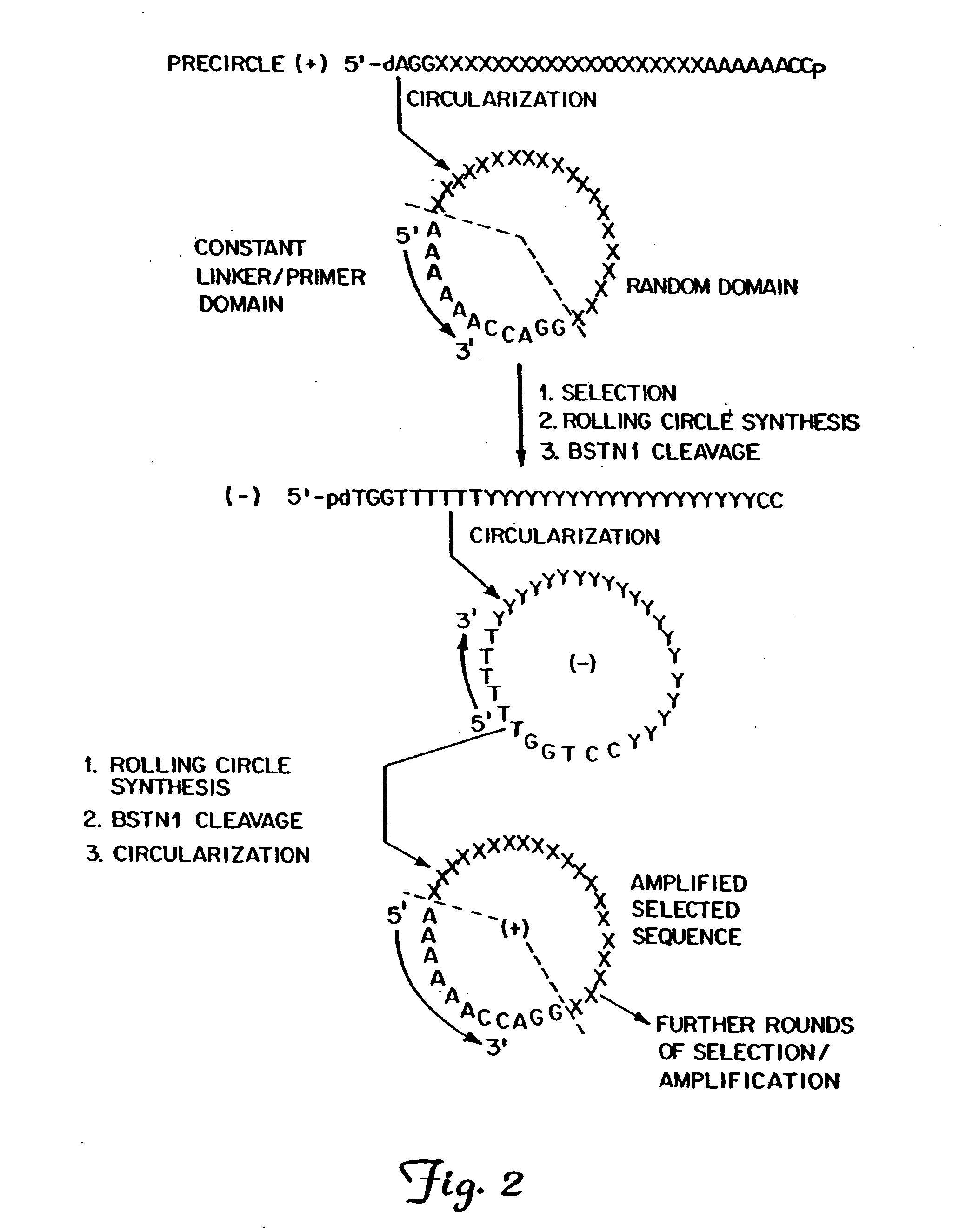
The present invention provides methods for synthesis and therapeutic use of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides and analogs. RNA oligonucleotides are synthesized using a small, circular DNA template which lacks an RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The RNA synthesis is performed by combining a circular single-stranded oligonucleotide template with an effective RNA polymerase and at least two types of ribonucleotide triphosphate to form an RNA oligonucleotide multimer comprising multiple copies of the desired RNA oligonucleotide sequence. Preferably, the RNA oligonucleotide multimer is cleaved to produce RNA oligonucleotides having well-defined ends. Preferred RNA oligonucleotide multimers contain ribozymes capable of both cis (autolytic) and trans cleavage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Anti-Mirna Antisense Oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20100286234A1Reduced microRNA levelAvoid off-target effectsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleobaseRNA Cleavage
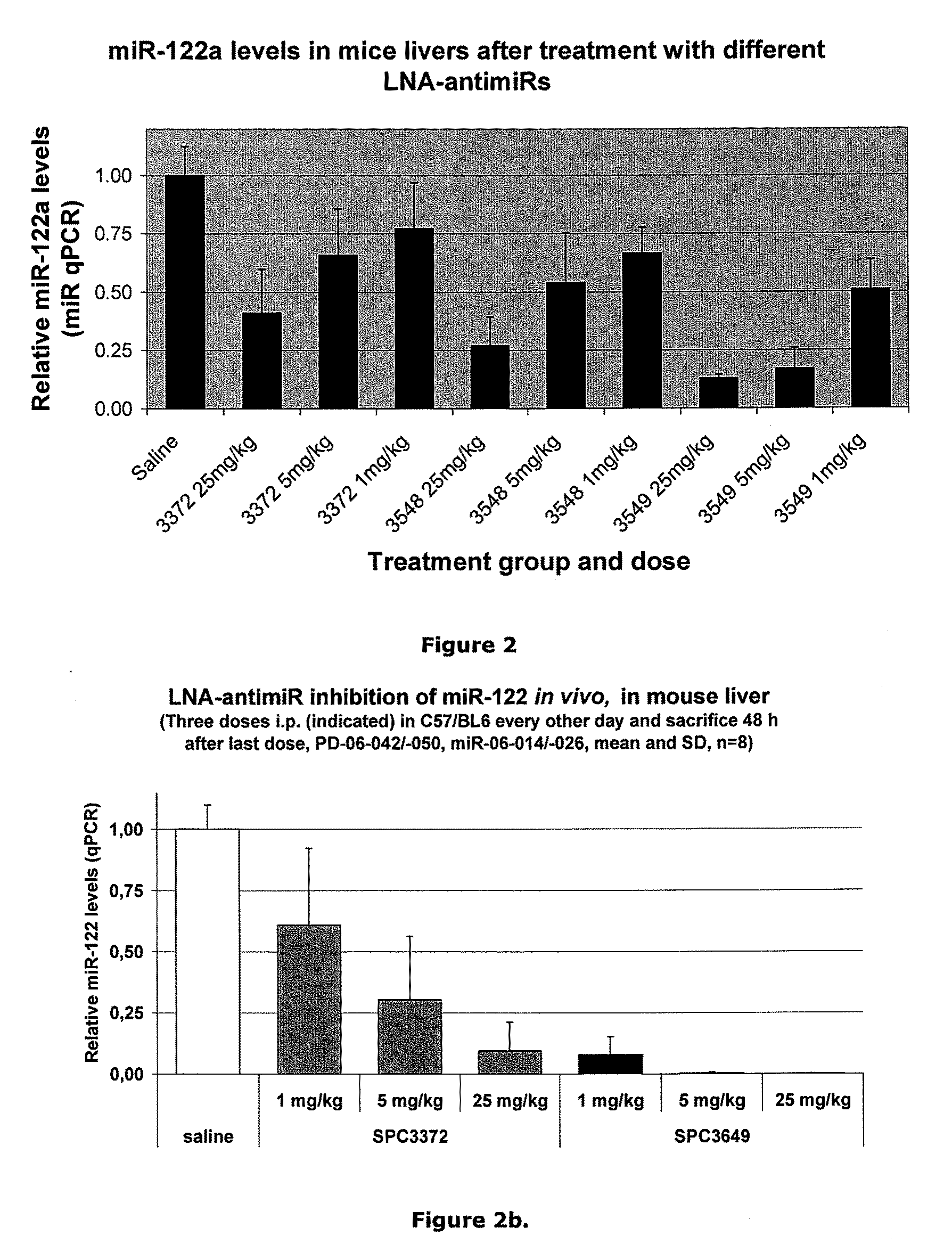
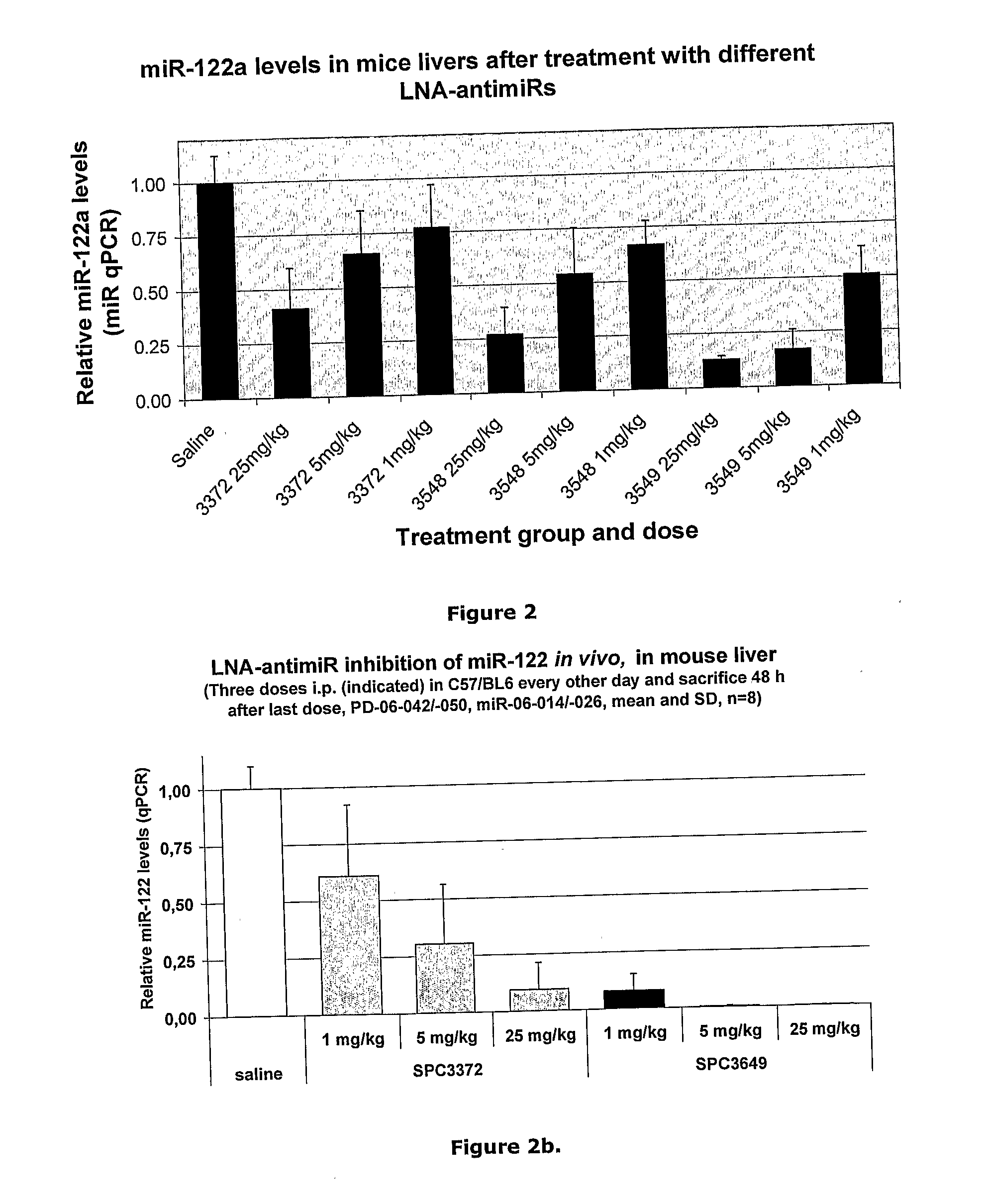
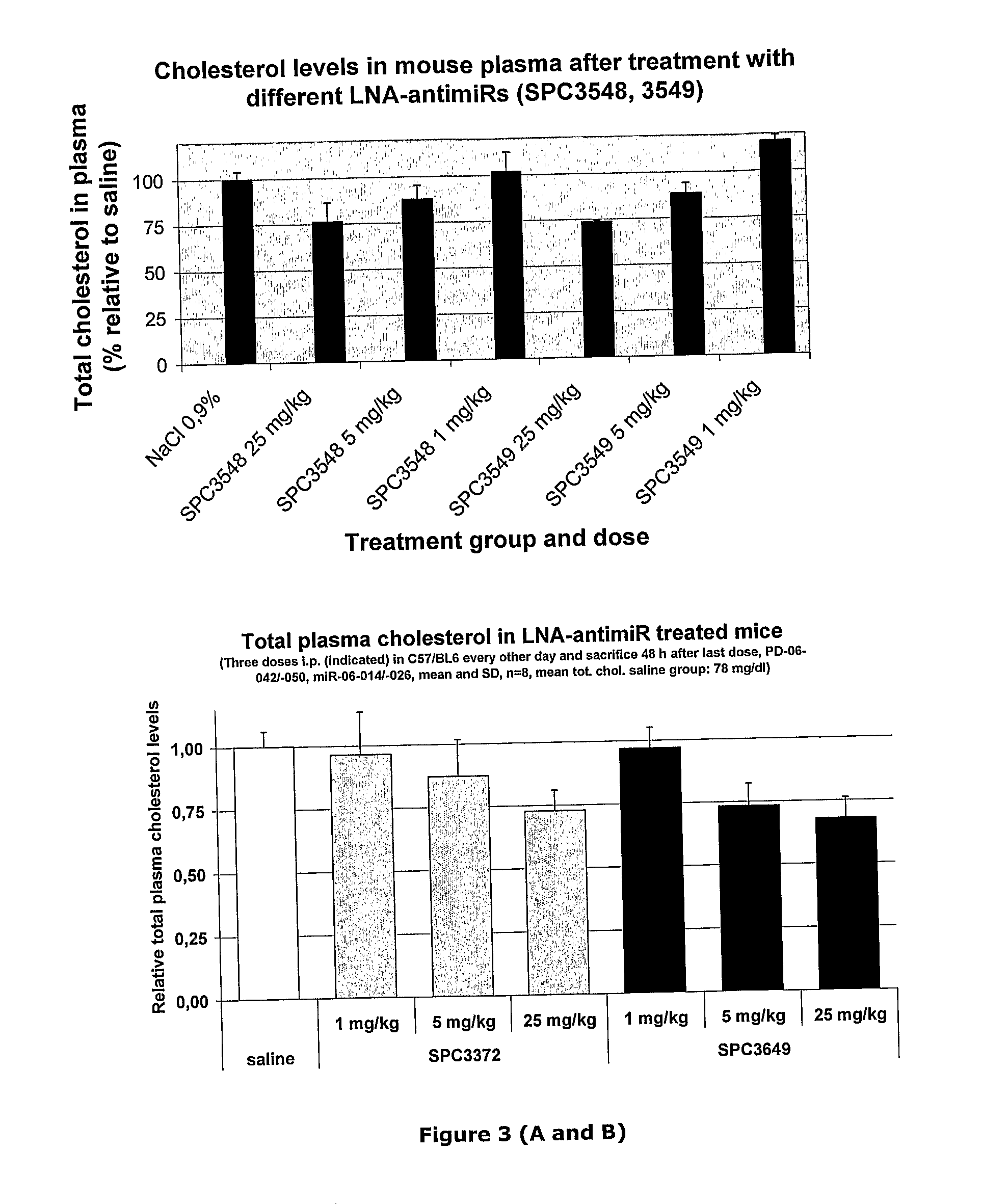
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising short single stranded oligonucleotides, of length of between 8 and 26 nucleobases which are complementary to human microRNAs selected from the group consisting of miR19b, miR21, miR122a, miR155 and miR375. The short oligonucleotides are particularly effective at alleviating miRNA repression in vivo. It is found that the incorporation of high affinity nucleotide analogues into the oligonucleotides results in highly effective anti-microRNA molecules which appear to function via the formation of almost irreversible duplexes with the miRNA target, rather than RNA cleavage based mechanisms, such as mechanisms associated with RNaseH or RISC.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Compositions and methods for modulating gene expression
InactiveUS20150141320A1Expression of target gene can be increasedLevel of expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesRegulator geneCancer research
Aspects of the invention provide single stranded oligonucleotides for activating or enhancing expression of a target gene. Further aspects provide compositions and kits comprising single stranded oligonucleotides for activating or enhancing expression of a target gene. Methods for modulating expression of a target gene using the single stranded oligonucleotides are also provided. Further aspects of the invention provide methods for selecting a candidate oligonucleotide for activating or enhancing expression of a target gene.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Method for improving gene targeting efficiency and method for carrying out in-situ repair on base on beta-globulin gene locus
InactiveCN106244555AShorten the construction experiment cycleHigh miss rateNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsGene Modification
The invention provides a method for improving the gene targeting efficiency and a method for carrying out in-situ repair on the base on a beta-globulin gene locus. The method for improving the gene targeting efficiency comprises the following steps of: S10, determining a gene locus to undergo in-situ repair; and S20, introducing a CRISPR / Ca system to cleave editing lotus DNA to cause DNA damage and simultaneously providing a repair template segment. Based on the deficiency of existing gene modification, the gene modification efficiency, the timeliness and the modification quality are improved after single-stranded oligonucleotides (ss ODNs) and a small molecule compound participate in a CRISPR / Cas9 gene modification system.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical composition comprising anti-mirna antisense oligonucleotide
ActiveUS8163708B2Effectively repressedHigh affinitySugar derivativesMetabolism disorderNucleobaseRNA Cleavage
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Nano-Scale Bridge Biosensors
ActiveUS20100227416A1Rapid and inexpensiveLarge-scale and inexpensive fabricationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanoparticleMolecular hybridization
Devices, systems, and methods for detecting nucleic acid hybridization, including single nucleic base mutations at low concentrations, are disclosed, using capture units having nanoparticles with attached single-stranded oligonucleotides that are capable of hybridizing target oligonucleotides and reporter molecules having nanoparticles with attached single-stranded oligonucleotides, without the use of labeling or target modification.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Oligonucleotides comprising a modified or non-natural nucleobase
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Compositions and methods for modulating mecp2 expression
InactiveUS20150152410A1High expressionPrevents repressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMECP2Cancer research
Aspects of the invention provide single stranded oligonucleotides for activating or enhancing expression of MECP2. Further aspects provide compositions and kits comprising single stranded oligonucleotides for activating or enhancing expression of MECP2. Methods for modulating expression of MECP2 using the single stranded oligonucleotides are also provided. Further aspects of the invention provide methods for selecting a candidate oligonucleotide for activating or enhancing expression of MECP2.
Owner:RANA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Oligonucleotides comprising a non-phosphate backbone linkage
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
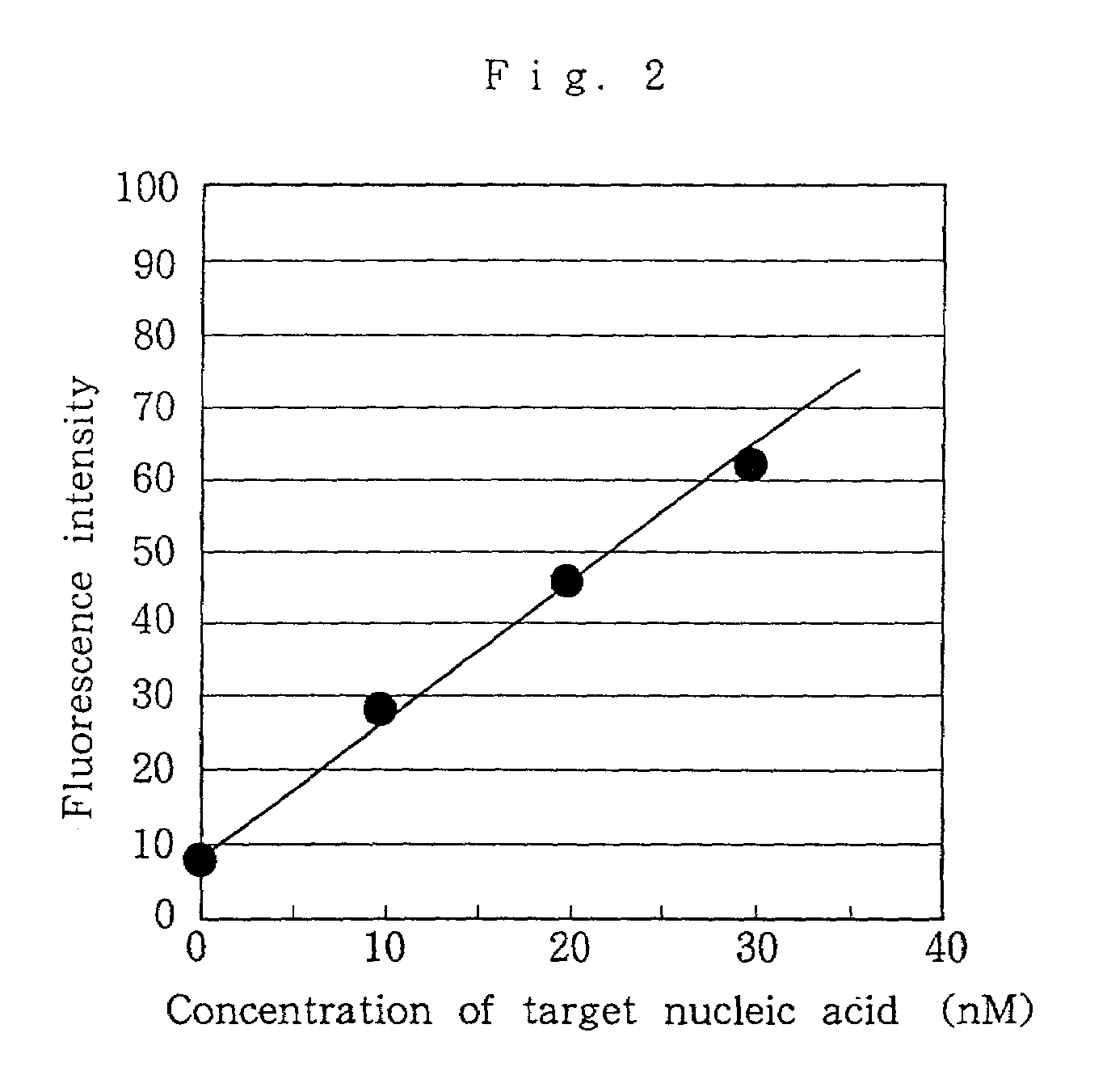
Nucleic acid probes, method for determining concentrations of nucleic acid by using the probes, and method for analyzing data obtained by the method
InactiveUS7354707B2Reduce measurementEasy to measureMonoazo dyesSugar derivativesFluorescenceNucleic Acid Probes
Nucleic acid probes are provided, each of which is formed of a single-stranded oligonucleotide which can hybridize to a target nucleic acid and is labeled with a fluorescent dye or with a fluorescent dye and a quencher substance. The nucleic acid probes can be easily designed, permit determination, polymorphous analysis or real-time quantitative PCR of nucleic acids in short time, and are not dissociated during reactions. Nucleic acid determination methods, polymorphous analysis methods and real-time quantitative PCR methods, which make use of the nucleic acid probes, are also provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Processes and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis and purification
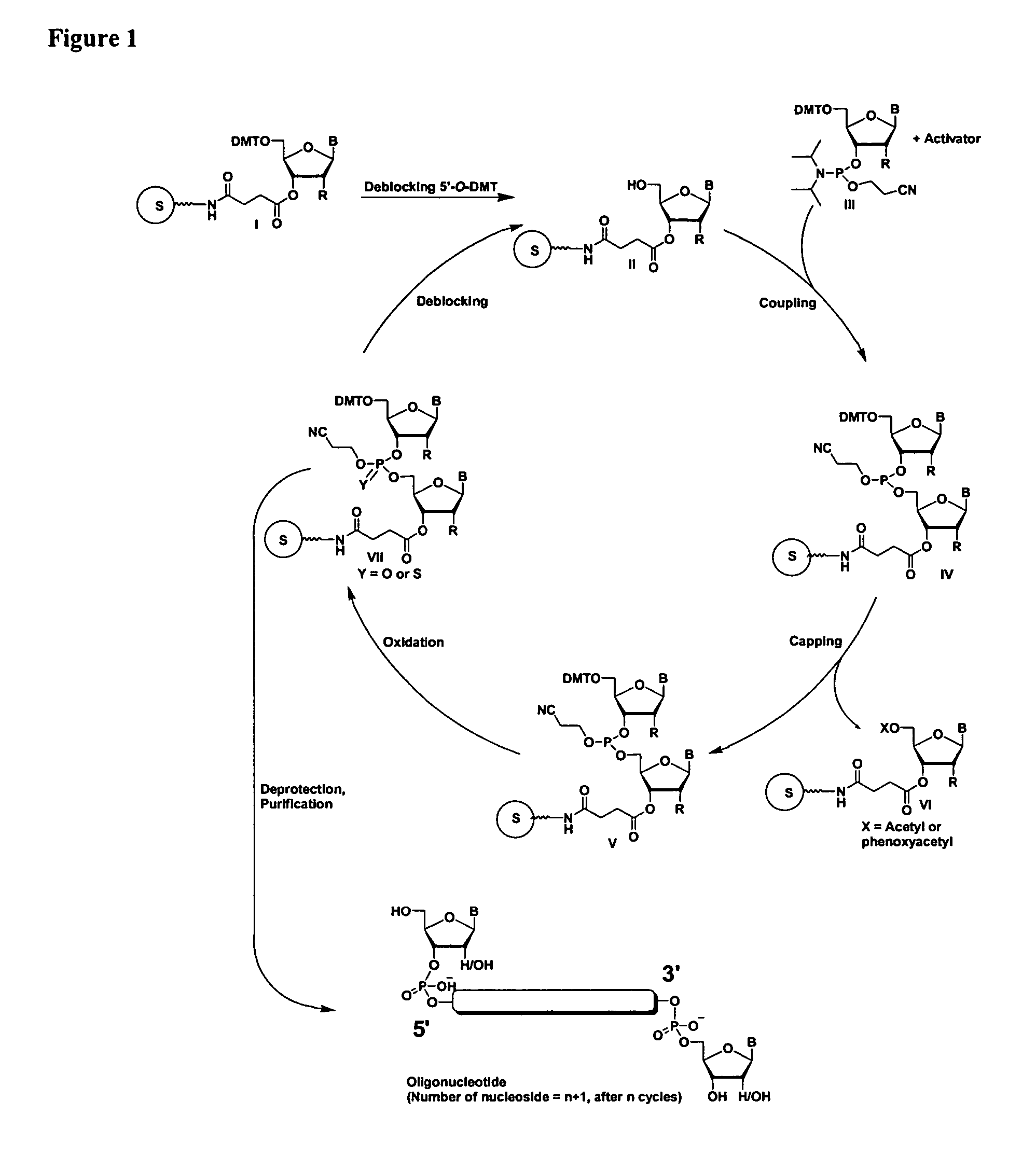
The present invention relates to processes and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis and purification. One aspect of the present invention relates to compounds useful for activating phosphoramidites in oligonucleotide synthesis. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing oligonucleotides via the phosphoramidite method using an activator of the invention. Another aspect of the present invention relates to sulfur-transfer agents. In a preferred embodiment, the sulfur-transfer agent is a 3-amino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-5-one. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a phosphorothioate by treating a phosphite with a sulfur-transfer reagent of the invention. In a preferred embodiment, the sulfur-transfer agent is a 3-amino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-5-one. Another aspect of the present invention relates to compounds that scavenge acrylonitrile produced during the deprotection of phosphate groups bearing ethylnitrile protecting groups. In a preferred embodiment, the acrylonitrile scavenger is a polymer-bound thiol. Another aspect of the present invention relates to agents used to oxidize a phosphite to a phosphate. In a preferred embodiment, the oxidizing agent is sodium chlorite, chloroamine, or pyridine-N-oxide. Another aspect of the present invention relates to methods of purifying an oligonucleotide by annealing a first single-stranded oligonucleotide and second single-stranded oligonucleotide to form a double-stranded oligonucleotide; and subjecting the double-stranded oligonucleotide to chromatographic purification. In a preferred embodiment, the chromatographic purification is high-performance liquid chromatography.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Marine fish mitochondrial genome control area amplification primer, as well as design and amplification methods
The invention belongs to the field of research of marine fish mitochondrial genome control areas, and relates to an amplification primer of the marine fish mitochondrial genome control area. The amplification primer is composed of two chains of single-chain oligonucleotide, wherein a light-chain primer is a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1 and a heavy-chain primer is a nucleotide sequenceshown in SEQ ID No.2. The invention also provides a design method of the amplification primer and a method for amplifying the marine fish mitochondrial genome control area utilizing the amplificationprimer. The amplification primer provided by the invention can efficiently and specifically amplify the marine fish mitochondrial genome control area, and can be applicable to large-scale investigation and analysis of fish seed resources, thereby providing a powerful tool for rapidly and efficiently obtaining the marine fish mitochondrial genome control area sequence to carry out variety identification, seed resource investigation and control area evolution research.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Methods and devices based upon a novel form of nucleic acid duplex on a surface
InactiveUS20090011949A1Easy to manufactureCapacity retentionSequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesPhosphateNucleotide
Provided herein are biomolecular hybridization devices comprising a substrate with a permanently and covalently attached surface of functional groups and an adsorbed monolayer of unmodified, single-stranded oligonucleotides all of which are 10 to about 24 bases in length as a saturated film of constrained oligonucleotides on the surface via direct non-covalent phosphate-surface adsorptive contact of substantially all phosphate groups of each oligonucleotide. The constrained oligonucleotides are effective to dissociably hybridize to a complementary single-stranded nucleic acid with asymmetric, non-helical base pairing and without oligonucleotide dissociation from the surface of the device. Also, provided are methods for hybridizing solution-state target nucleic acids to probe nucleic acids and for identifying a nucleotide sequence to which a nucleotide-binding protein binds using the biomolecular hybridization devices.
Owner:GMSBIOTECH INC +1
High affinity adapter body capable of specifically binding with saxitoxin acetate and application thereof
ActiveCN104894135AGreat potentialAntagonistic inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsSingle strand dnaBiology
The invention relates to biological technical field, and provides a high affinity adapter body capable of specifically binding with saxitoxin acetate, and the sequence of single-stranded DNA adapter body as SEQ ID NO: 2. By mutation and truncation of an in vitro screened adapter body, a high affinity single-stranded oligonucleotide adapter body capable of specifically identifying the saxitoxin acetate can be obtained. The adapter body has a broad application prospect, and can be used for separation and enrichment of trace concentrations of STX (saxitoxin) in a sample, rapid detection of saxitoxin, and preparation of a drug for neutralization of saxitoxin sodium ion channel inhibition effect, and removal of toxins in water.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
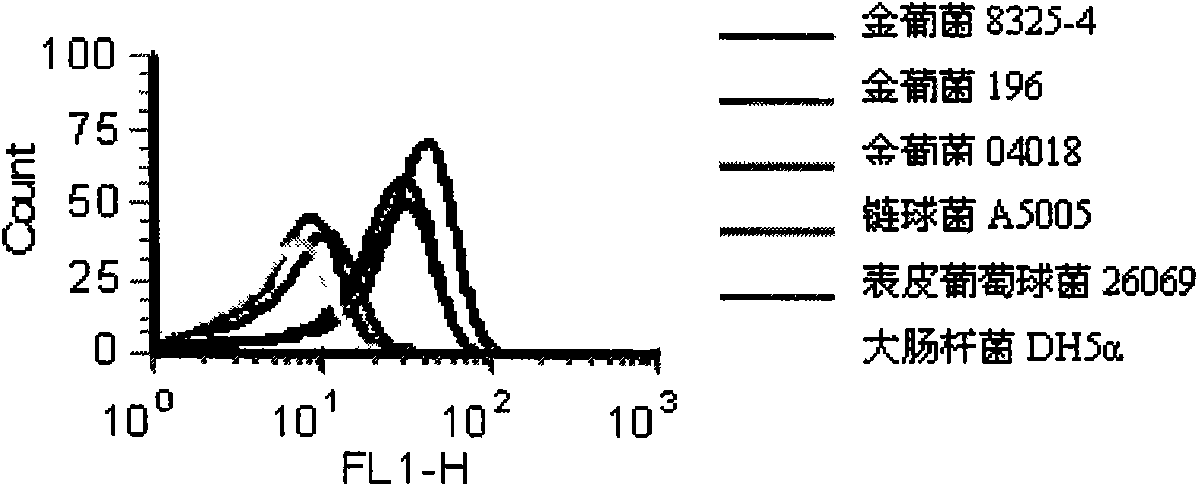
Oligonucleotide aptamer group for specifically identifying staphylococcus aureus and use thereof
ActiveCN101665821AEasy to operateLower synthesis costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and relates to the sequences of five oligonucleotide aptamers for specifically identifying staphylococcus aurei and use thereof. The fivesinge-chain DNA oligonucleotide aptamers for specifically identifying the staphylococcus aureus are obtained by a bacterial subtraction SELEX technology. After FITC is marked, the five aptamers are proved by fluorescent staining to be capable of specifically identifying the strain of the staphylococcus aurei. After being used in combination, the five ligands can improve sensibility in identification of target bacteria and the ratios of detected different staphylococcus aureus strains and the detected staphylococcus aurei in different growth states. Therefore, the sequences of the five aptamershave wide application prospects in quick detection of the staphylococcus aurei in samples including suspected terrorist attack biological agents and identification of the staphylococcus aurei and other gram-positive cocci.
Owner:中国人民解放军军事医学研究院
Nucleic acid aptamer for specifically identifying ochratoxin A and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107446929AImprove solubilityAvoid fixationBiological testingLibrary creationAptamerOchratoxin A
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer for specifically identifying ochratoxin A and a preparation method thereof. The sequence of the single-chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) aptamer is a sequence I. The nucleic acid aptamer for specifically identifying the ochratoxin A is characterized in that by adopting the index enrichment ligand system advancing technology based on graphene oxide separation, and in-vitro screening, the single-chain oligonucleotide aptamer with high affinity and ability of specifically identifying the OTA toxin is obtained; the specificity is good, the stability is high, the cost is low, the synthesizing and modifying are easy, the convenience in use is realized, the toxicity is avoided, and the like; the nucleic acid aptamer can be applied to studying of biological sensors and solid-phase affinity purifying columns based on the nucleic acid aptamer, and analyzing methods for quick detection on agricultural products, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
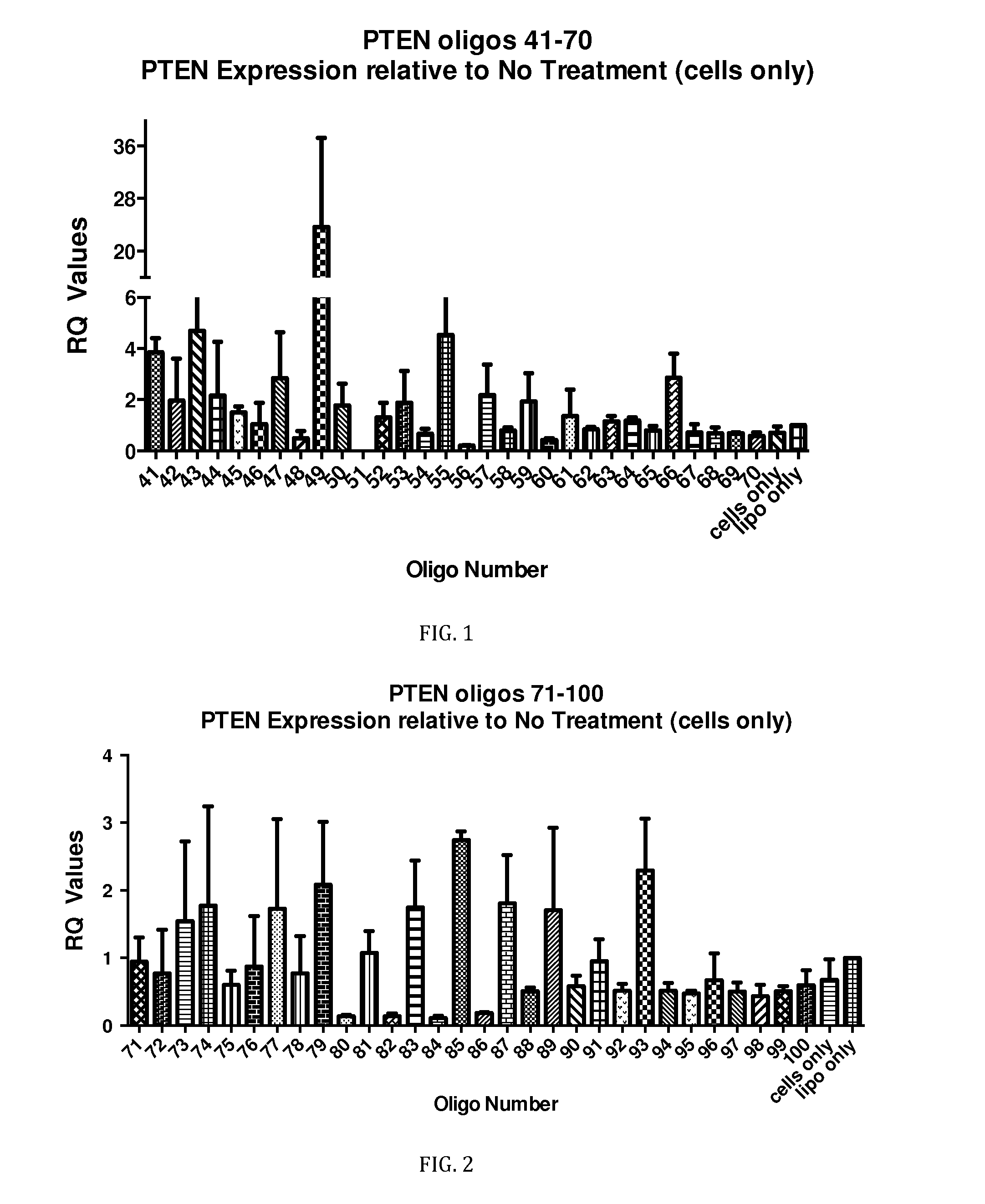
Compositions and methods for modulating pten expression
InactiveUS20150159161A1Activate and enhance expression of PTENRelieving and preventingOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCancer researchSingle stranded oligonucleotides
Aspects of the invention provide single stranded oligonucleotides for activating or enhancing expression of PTEN. Further aspects provide compositions and kits comprising single stranded oligonucleotides for activating or enhancing expression of PTEN. Methods for modulating expression of PTEN using the single stranded oligonucleotides are also provided. Further aspects of the invention provide methods for selecting a candidate oligonucleotide for activating or enhancing expression of PTEN.
Owner:RANA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
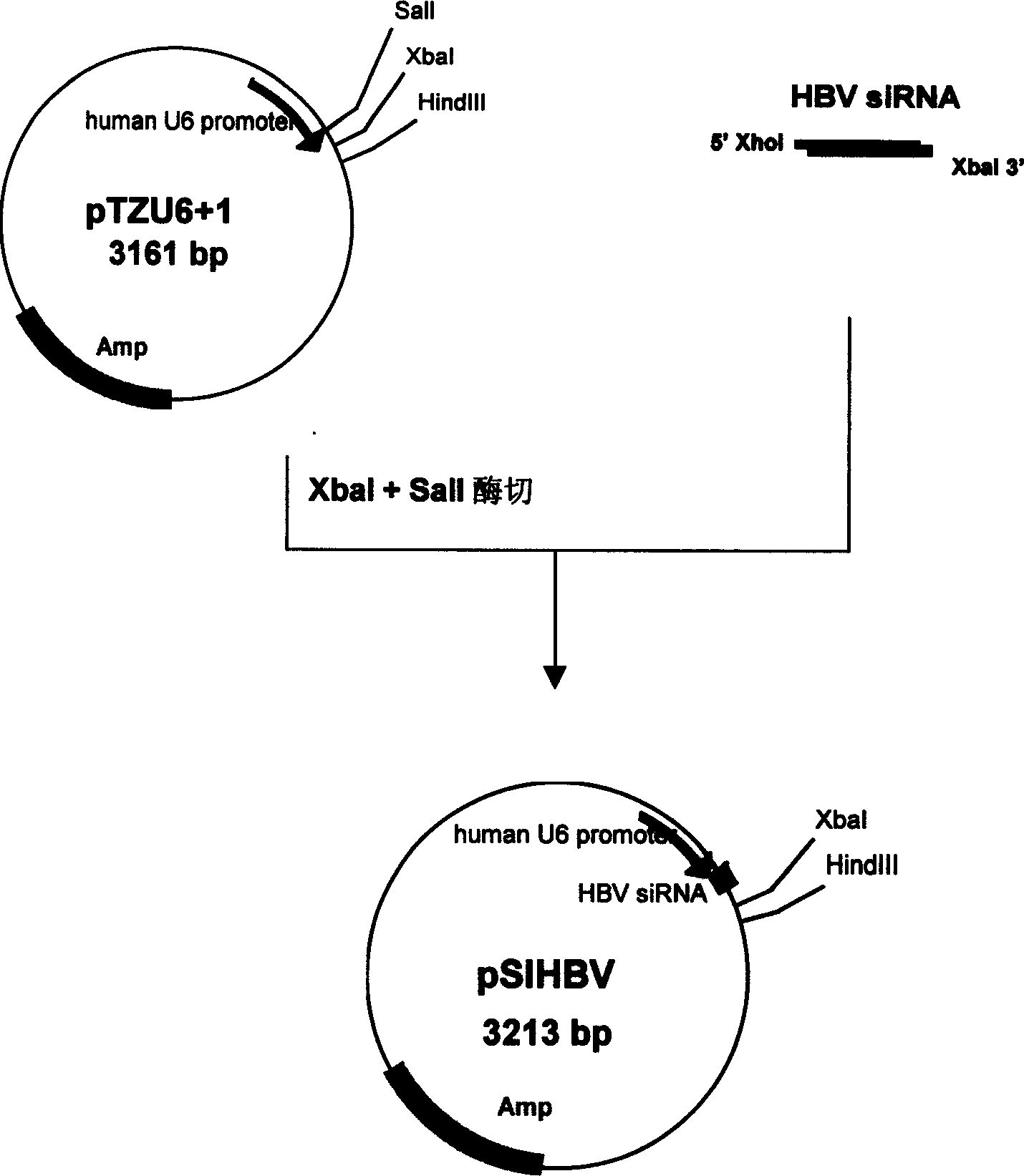
Construction of hepatitis B virus siRNA expression vector and its application in antivirus treatment
InactiveCN1523113AInhibit expressionInhibition of replicationGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyChemical synthesisConserved sequence
The present invention relates to construction of hepatitis B virus siRNA expression vector and its antiviral therapeutic application. According to the design principle said construction includes the following steps: respectively selecting nucleotide sequence of HBV envelope protein (MS) coding region 69nt-87nt, polymerase(p) coding region 708nt-726nt and core protein (c) coding region 2052 nt-2070nt, designing correspondent siRNA sequence, using BLAST software to analyze homogenously to confirm that it is HBV highly conservative sequence, then chemically synthesizing single-stranded oligonucleotide, external annearing to form double-stranded DNA, connecting it with eukaryotic expression vector pTZU6+1, enzyme excision identification and sequence determination and analysis show that siRNA extression vectors of three target hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene sequences are constructed. The tests show that HBV siRNA has the strong action of inhibiting virus replication and expression.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Marine fish mitochondrion 12S rRNA (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) gene amplification primer and design and amplification method thereof
InactiveCN102912012AAmplify high efficiency and specificityImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of marine fish mitochondrial genome research, and particularly relates to a marine fish mitochondrion 12S rRNA (ribosomal ribonucleic acid) gene amplification primer. The primer is composed of two single-chain oligonucleotide chains, wherein a light chain primer is a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a heavy chain primer is a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a design method of the amplification primer and a method for amplifying a marine fish DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) solution by using the amplification primer. The invention can efficiently and specifically amplify multiple marine fish mitochondrion 12S rRNA genes and can be used for the analytical study on the system evolution of different taxonomic categories of fishes, thereby providing a powerful tool for fish species identification, germplasm resource survey and system evolution research.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method of the electrochemical detection of nucleic acid oligomer hybrids
InactiveUS7056664B1Improve responseEconomical and simple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCyclic voltametryDouble strand
The invention relates to a method for the electrochemical detection of sequence-specific nucleic acid oligomer hybridization events. To this end single DNA / RNA / PNA oligomer strands which at one end are covalently joined to a support surface and at the other, free end, covalently linked to a redox pair, are used as hybridization matrix (probe). As a result of treatment with the oligonucleotide solution (target) to be examined, the electric communication between the conductive support surface and the redox pair bridged by the single-strand oligonucleotide, which communication initially is either absent or very weak, is modified. In case of hybridization, the electric communication between the support surface and the redox pair, which is now bridged by a hybridized double-strand oligonucleotide, is increased. This permits the detection of a hybridization event by electrochemical methods such as cyclic voltametry, amperometry or conductivity measurement.
Owner:FRIZ BIOCHEM FUR BIOANALYTIK MBH
Oligonucleotides comprising a ligand tethered to a modified or non-natural nucleobase
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one ligand tethered to an altered or non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl, nitropyrrolyl, or nitroimidazolyl. In certain embodiments, the ligand is a steroid or aromatic compound. In certain embodiments, only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide contains a ligand tethered to an altered or non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide independently contain a ligand tethered to an altered or non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one ligand tethered to an altered or non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl, nitropyrrolyl, or nitroimidazolyl. In certain embodiments, the ligand is a steroid or aromatic compound. In certain embodiments, the ribose sugar moiety that occurs naturally in nucleosides is replaced with a hexose sugar, polycyclic heteroalkyl ring, or cyclohexenyl group. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
High variation zone amplication primer of rockfish mitochondrial genome and its design method
InactiveCN1900318AAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementConserved sequenceLong pcr
The present invention relates to one pair of PCR primers named as G-dloop, and provides one pair of amplification primers capable of amplifying the high variation zone of rockfish mitochondrial genome in high efficiency and its design method. The amplification primers consist of two single strand oligonucleotides. Through logging-on Genebank to search vertebrate mitochondrion DNA cytochrome b gene and the high conservation area of 16S rRNA gene sequence and homologous comparison, one pair of amplification primers is obtained. Through long PCR amplification, the target segments of 32 varieties of rockfish are obtained and sequenced. The obtained sequences are compared by means of using homologous comparison software Clustal X 1.83 to fine the conservation sequences in the cytochrome b5' ends and the 12S rRNA 3' ends of the mitochondrial genomes of the 32 varieties of rockfish, and the said amplification primers are designed based on the degeneracy principle.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Chimeric RNA oligonucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140171492A1Reduce the frequency of occurrenceReduce severitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic disorderDna methyl transferase
The present invention relates to chimeric RNA oligonucleotides that are single-stranded oligonucleotides. These compounds are capable of targeting particular genes and reducing DNA methyltransferase activity. Accordingly, these compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of disease associated with aberrant DNA methyltransferase activity, such as cancer or a genetic disorder.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically recognizing shigella, screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN102010866ARapid diagnosisAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAptamerFluorescein
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically recognizing shigella, a screening method and application thereof. In the technical scheme, the single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide aptamer capable of specifically recognizing shigella is obtained through the SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential enrich-m ent) technology, and the aptamer can be converted to a report aptamer for detecting shigella through marking a marker such as fluorescein, so that the invention has wide application prospects of quick and accurate detection of shigella in food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com