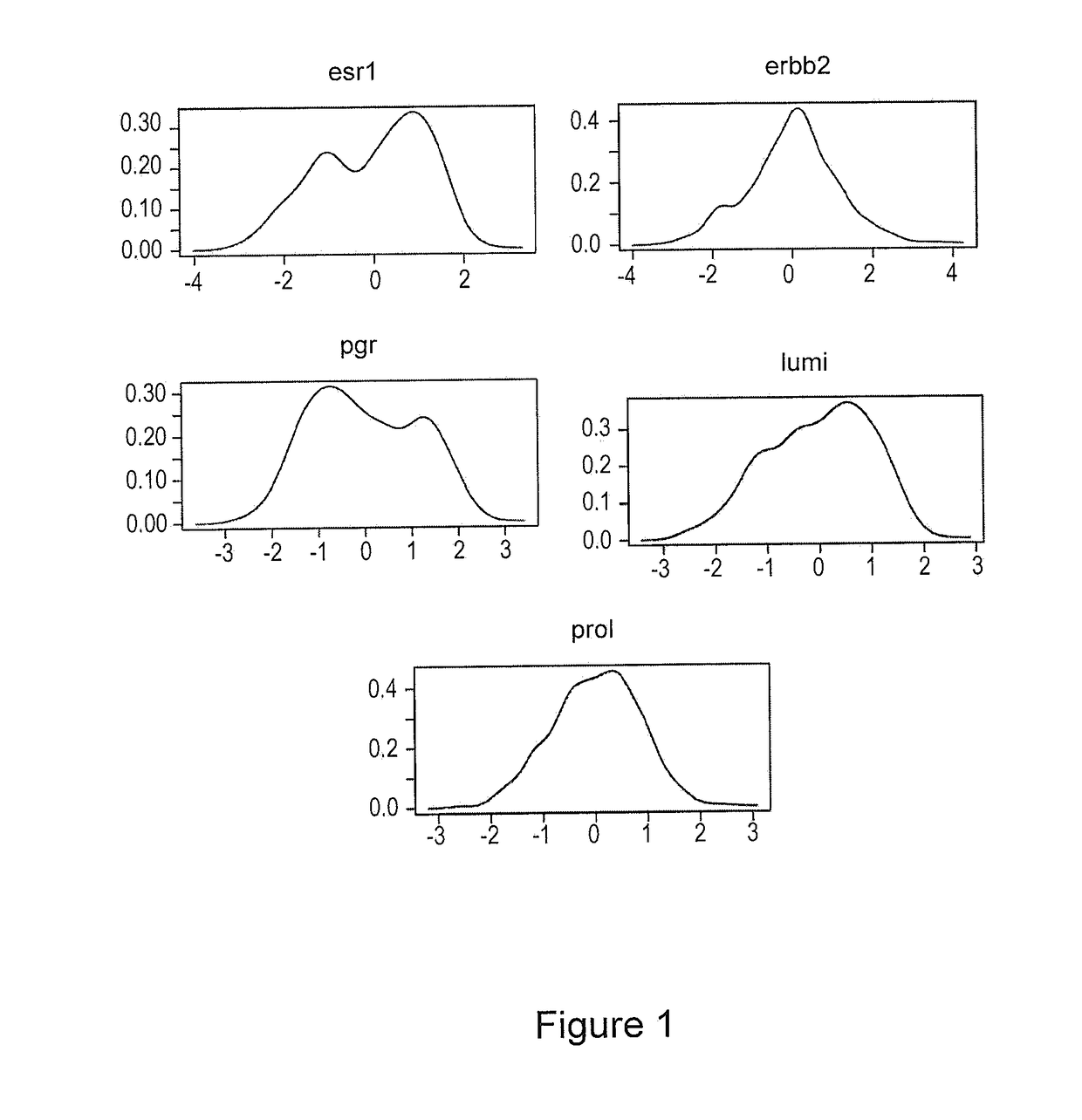
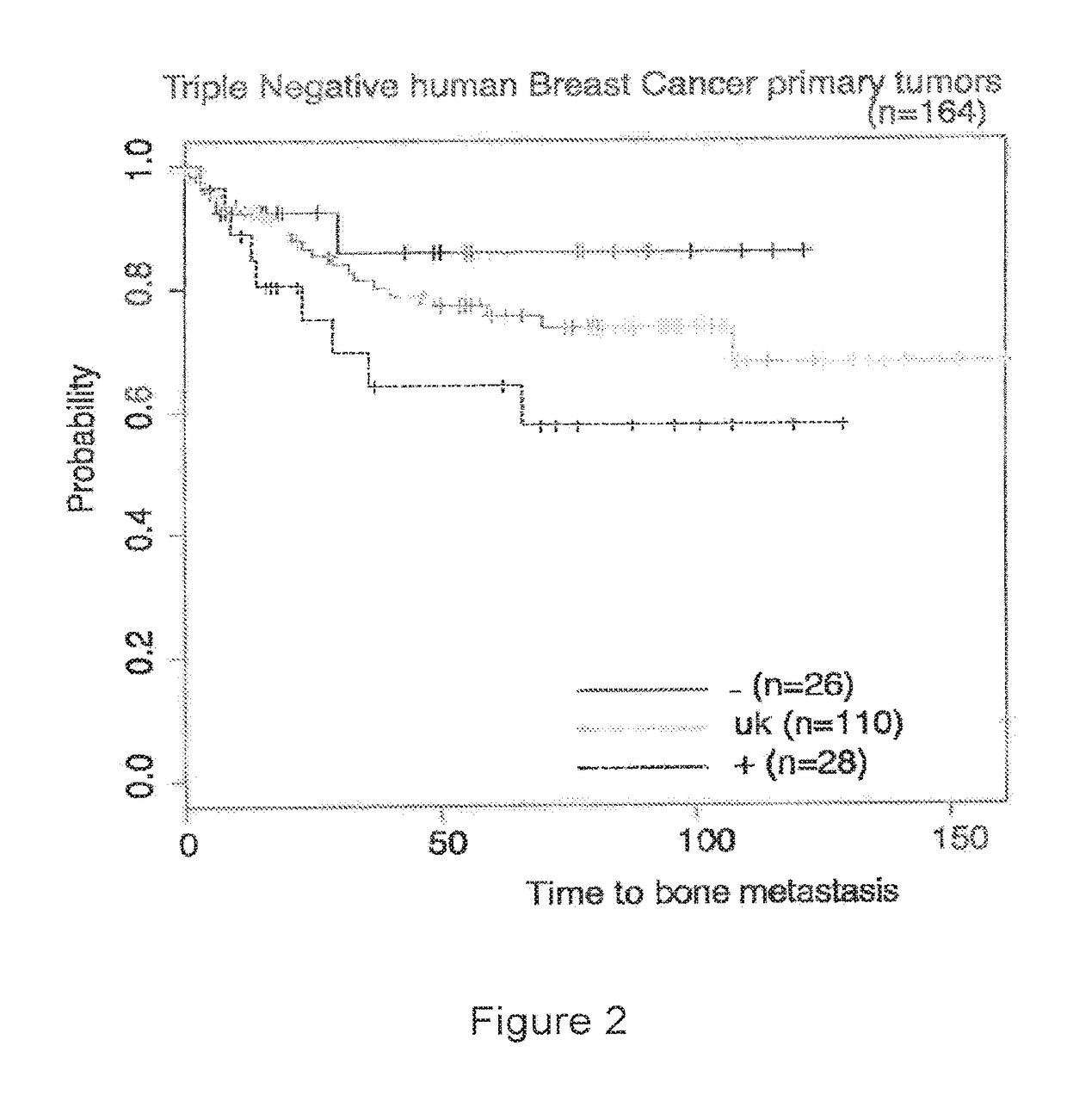
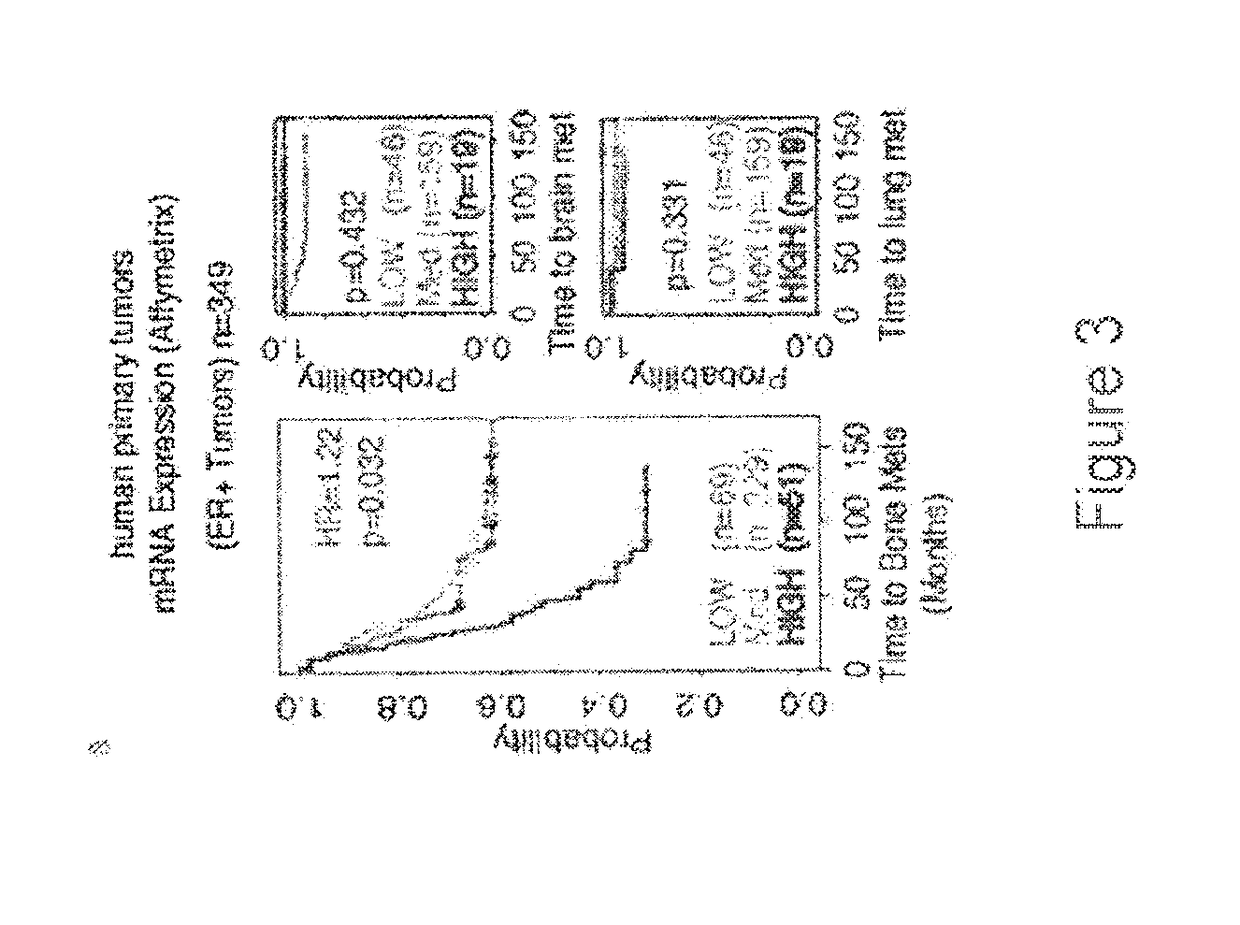
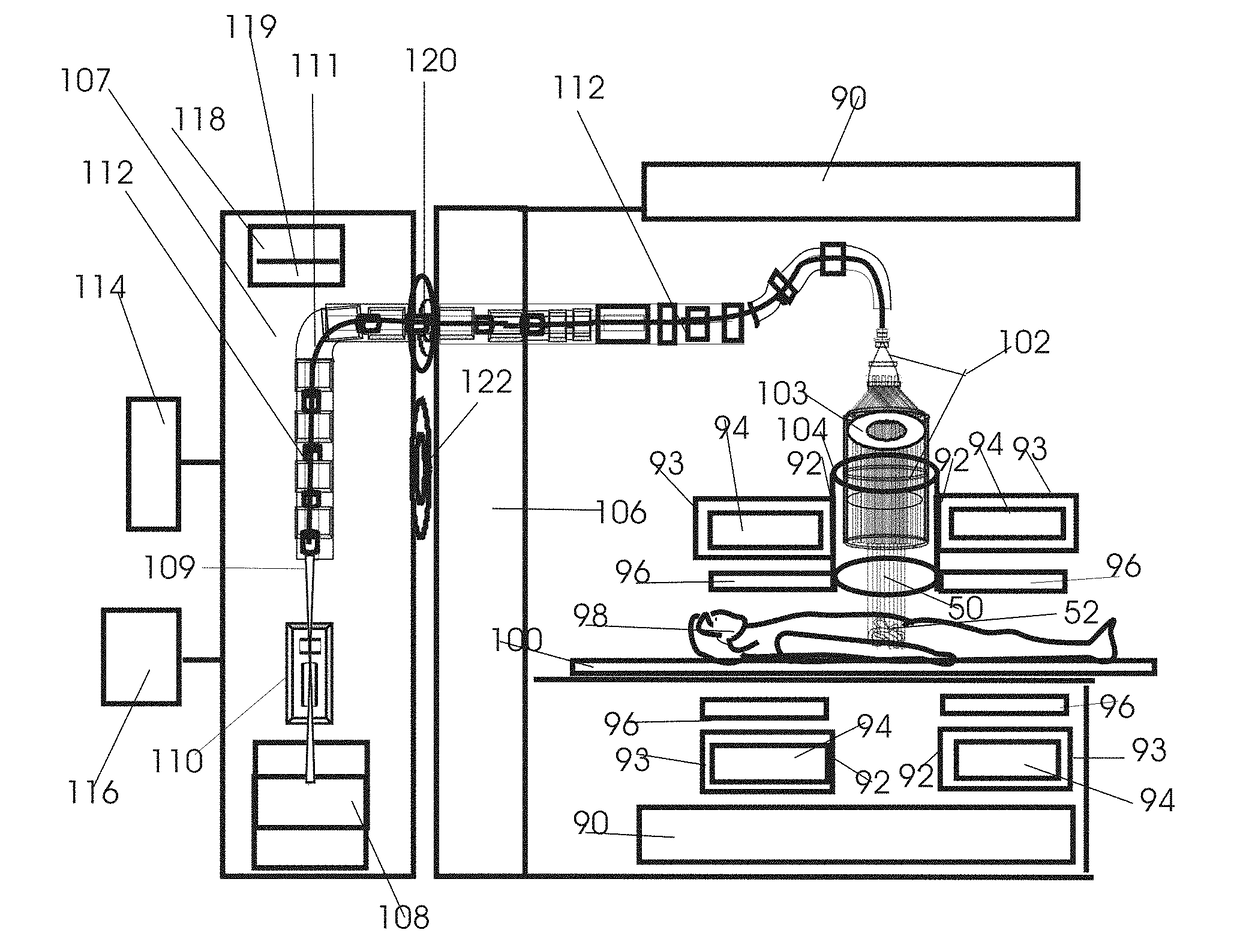
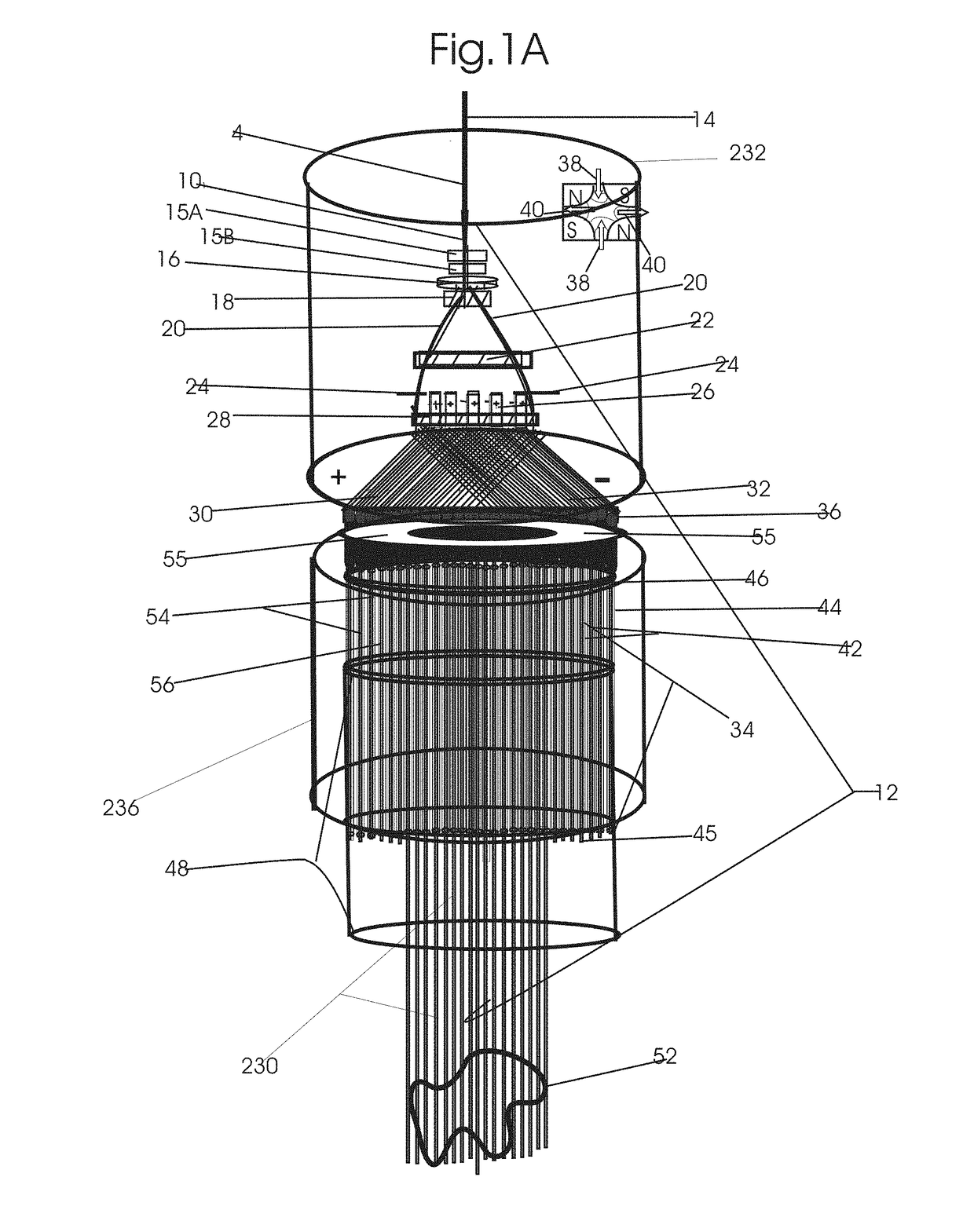
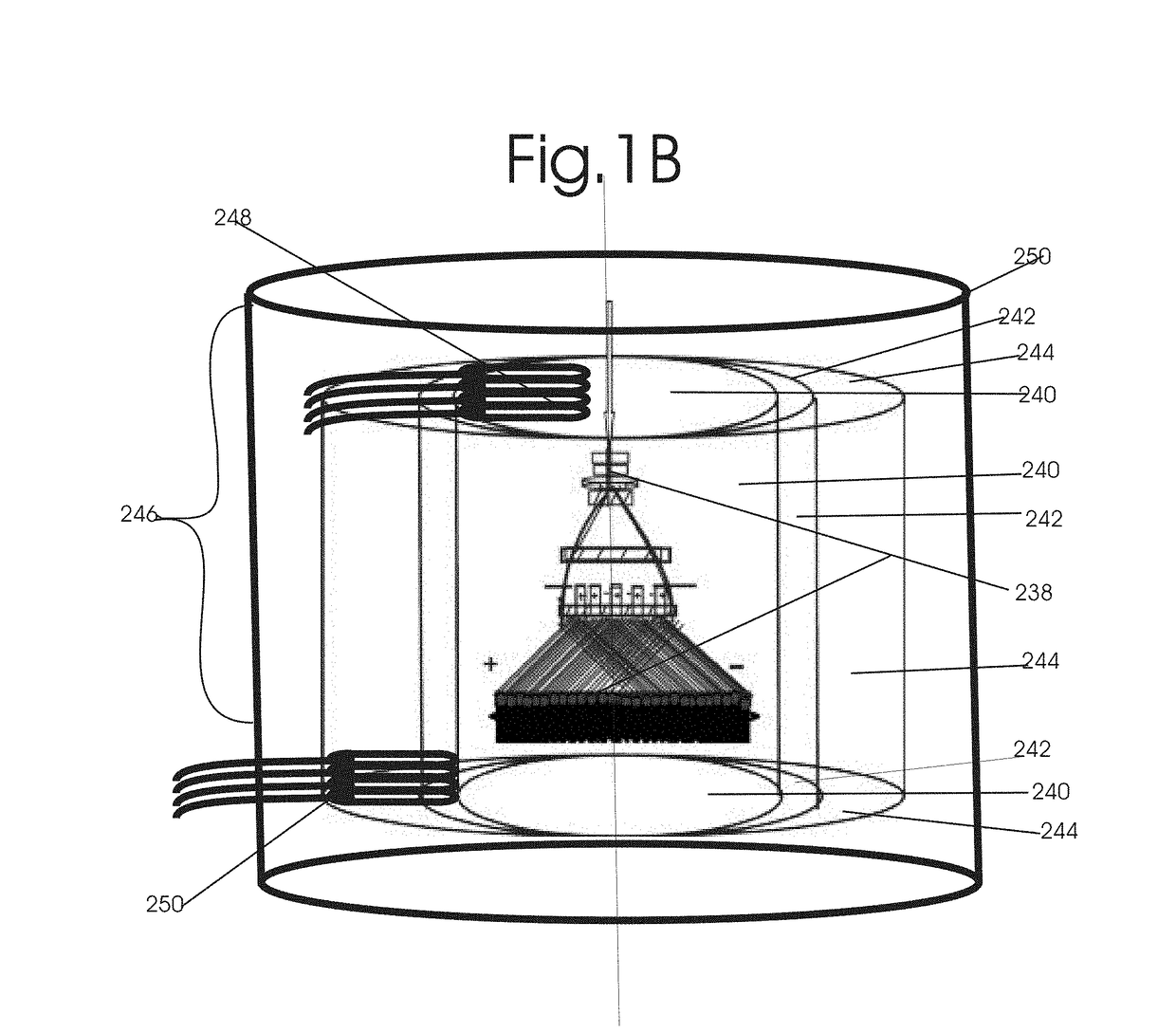
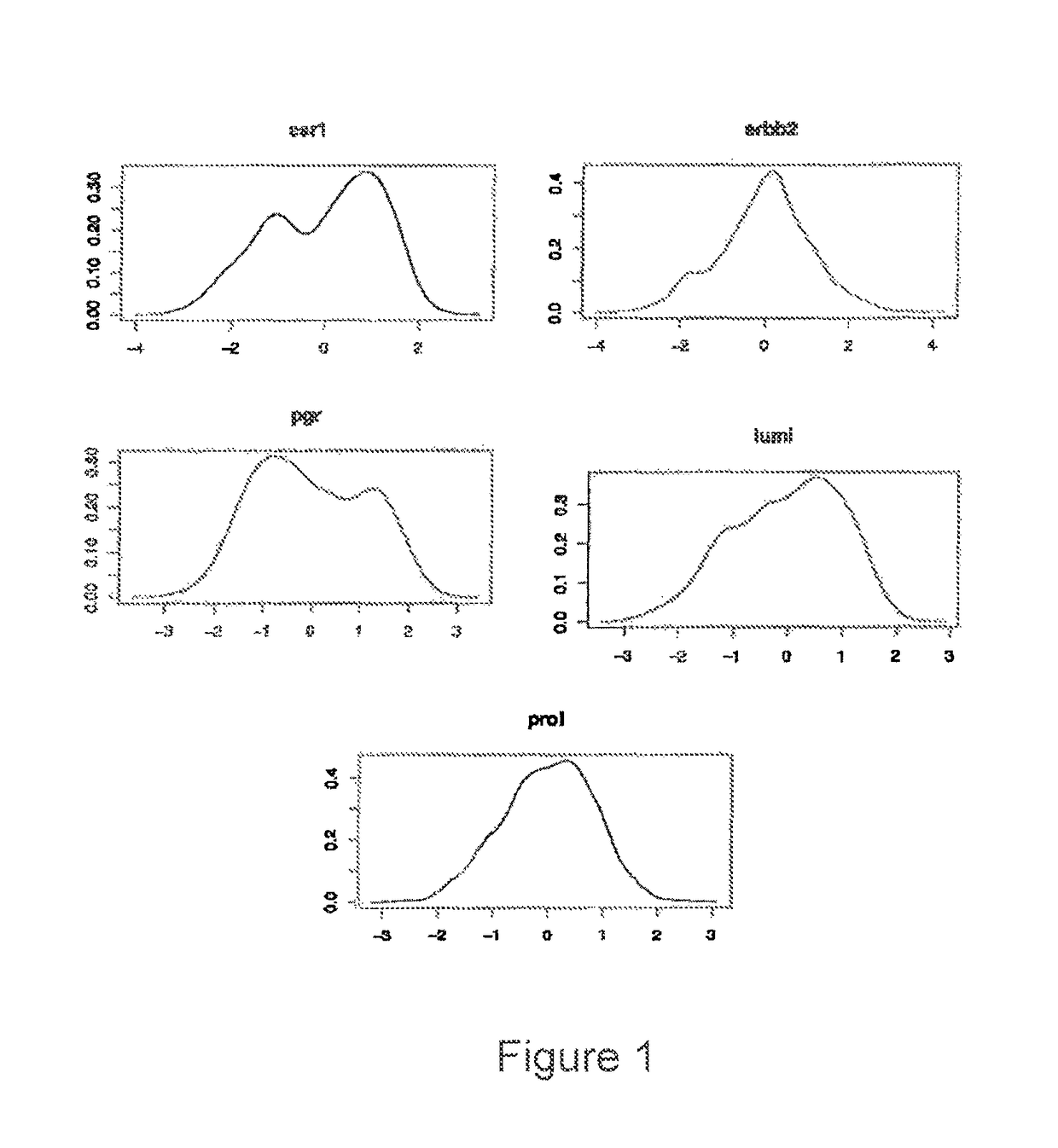
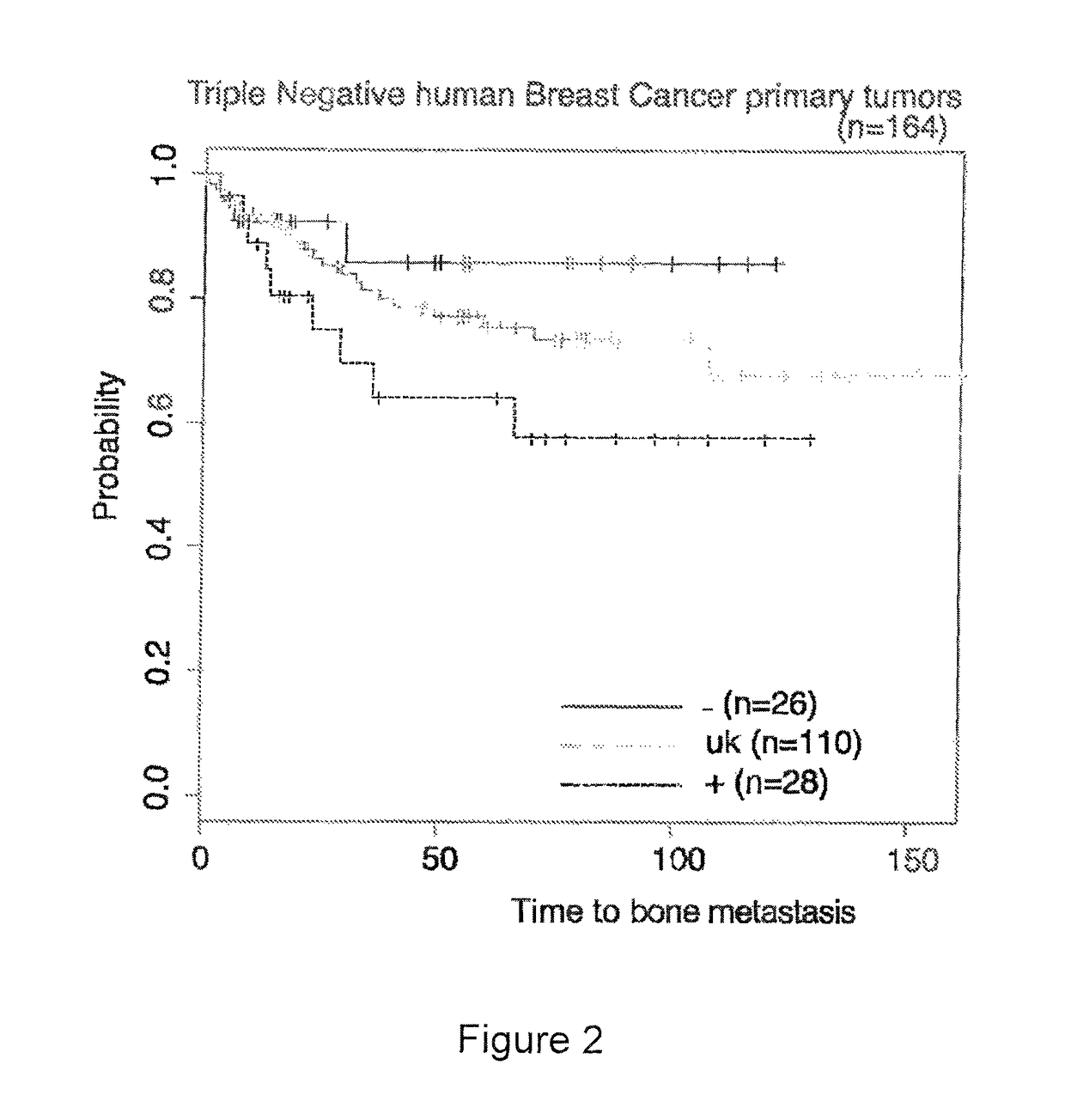
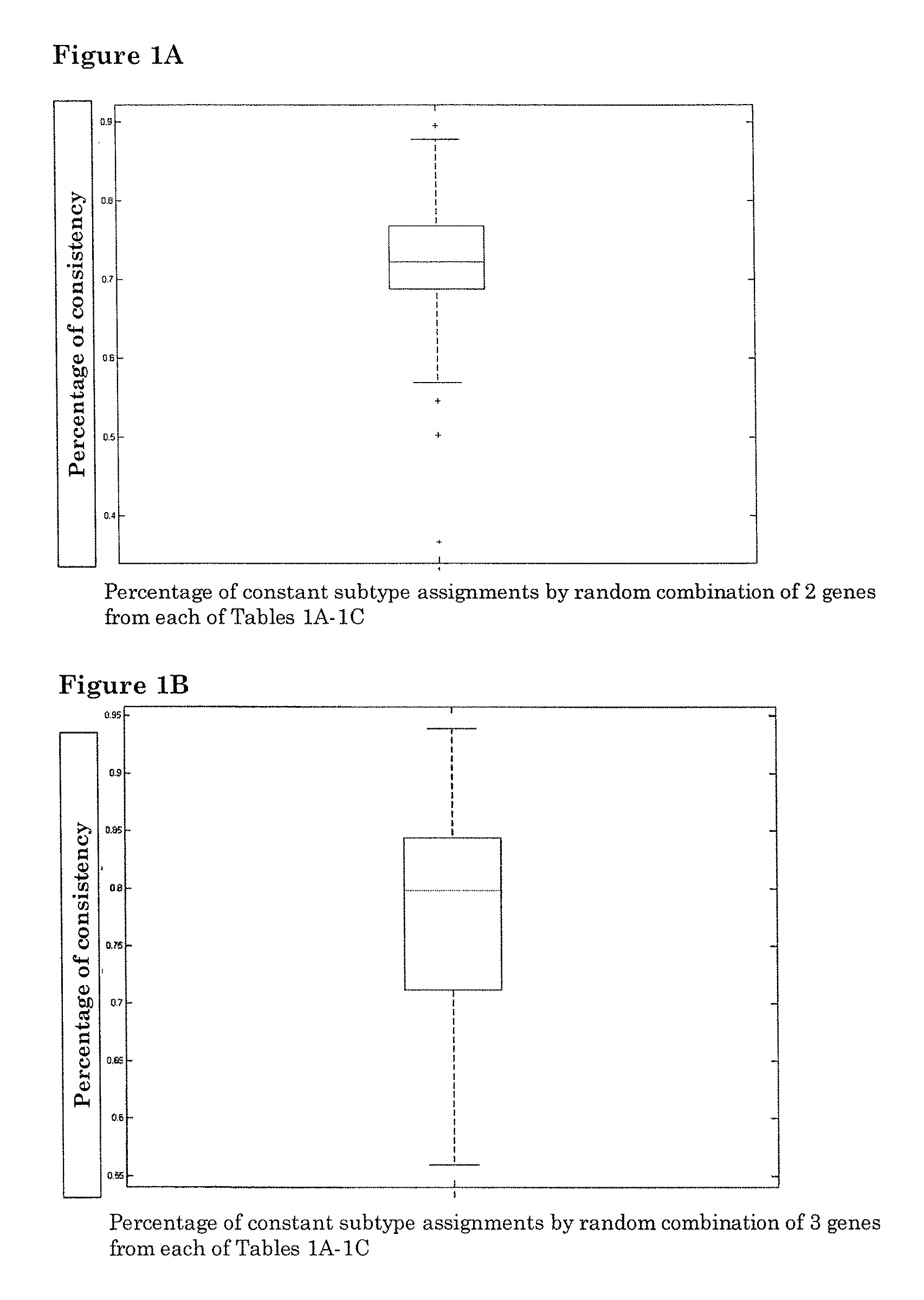
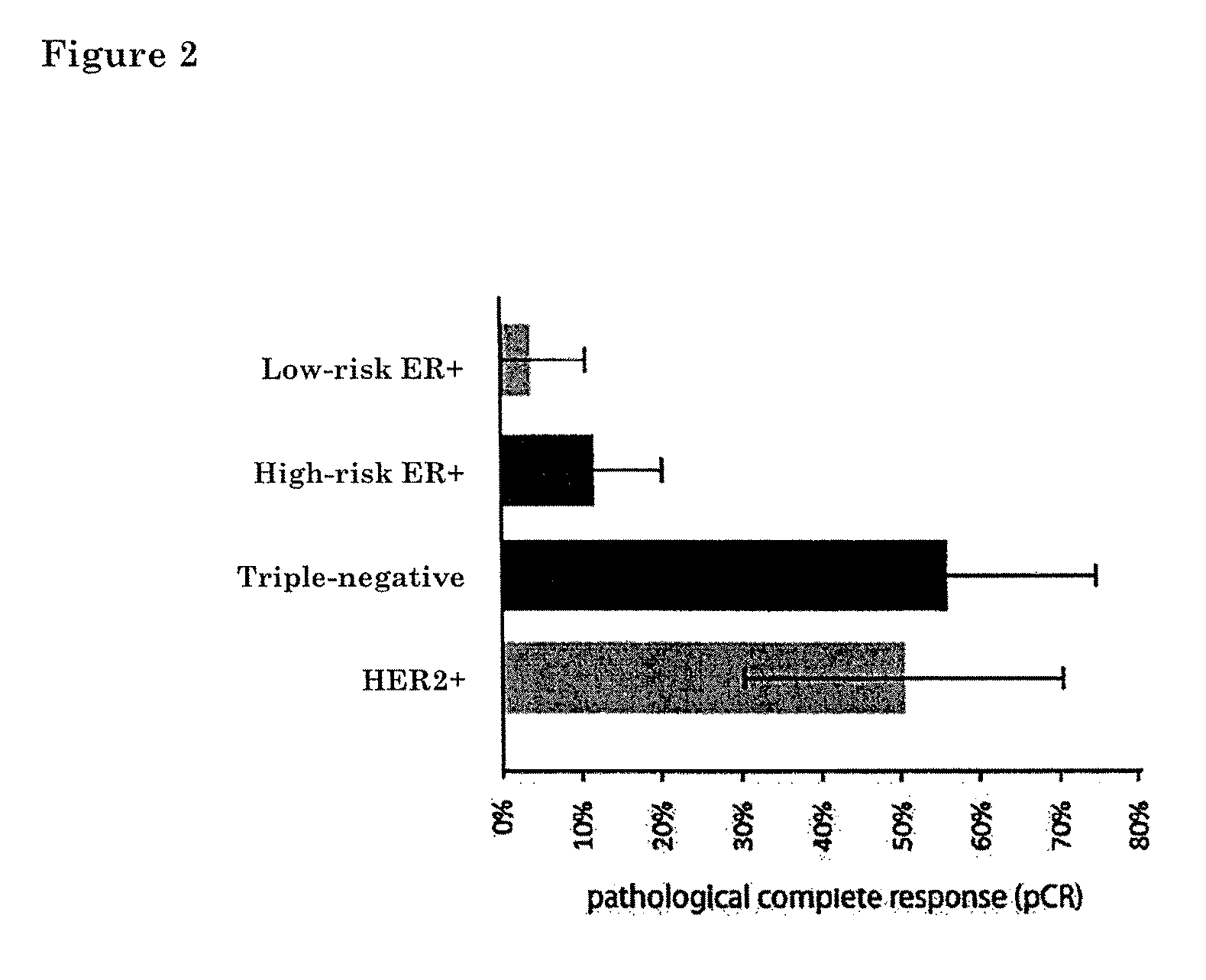
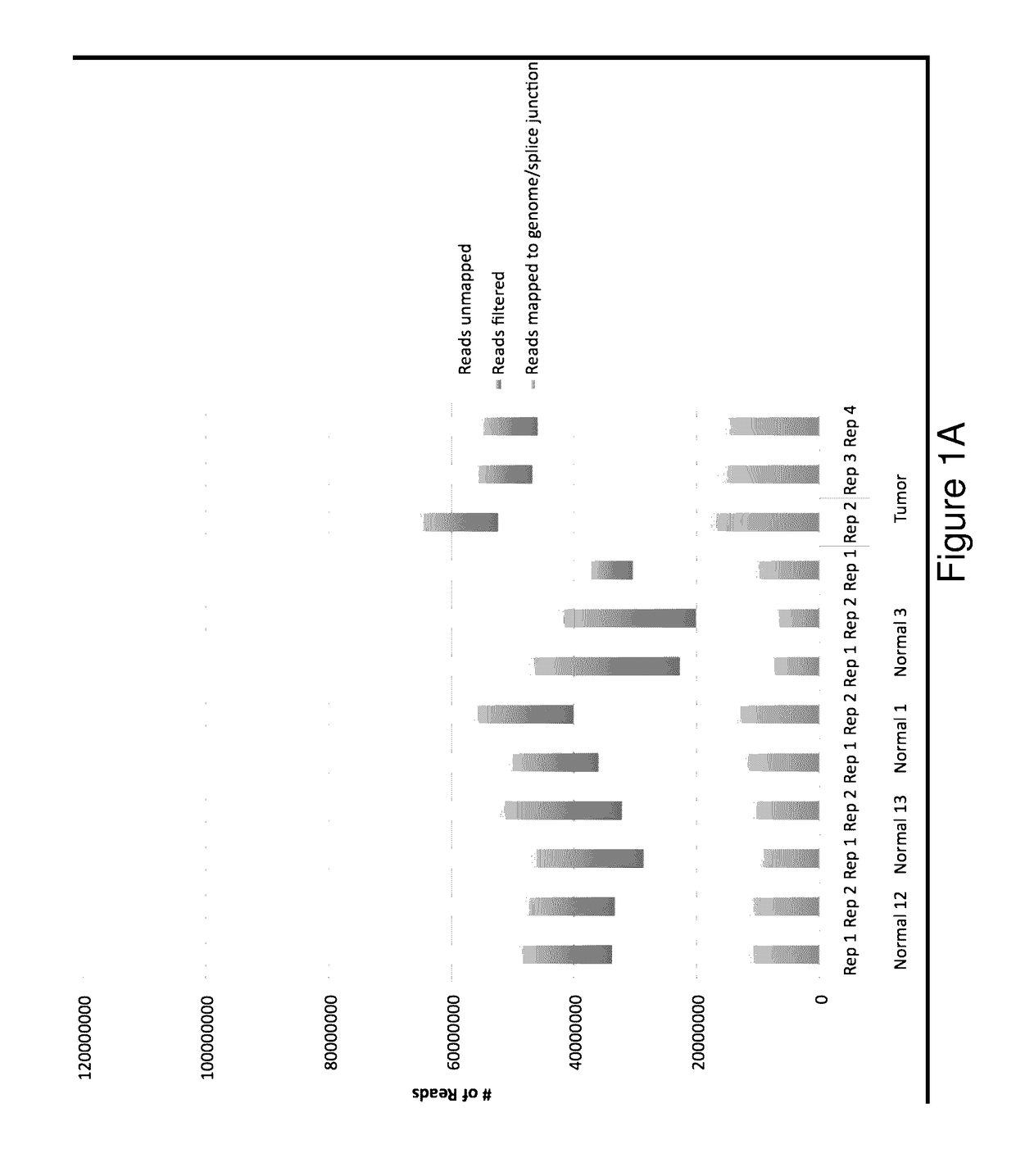
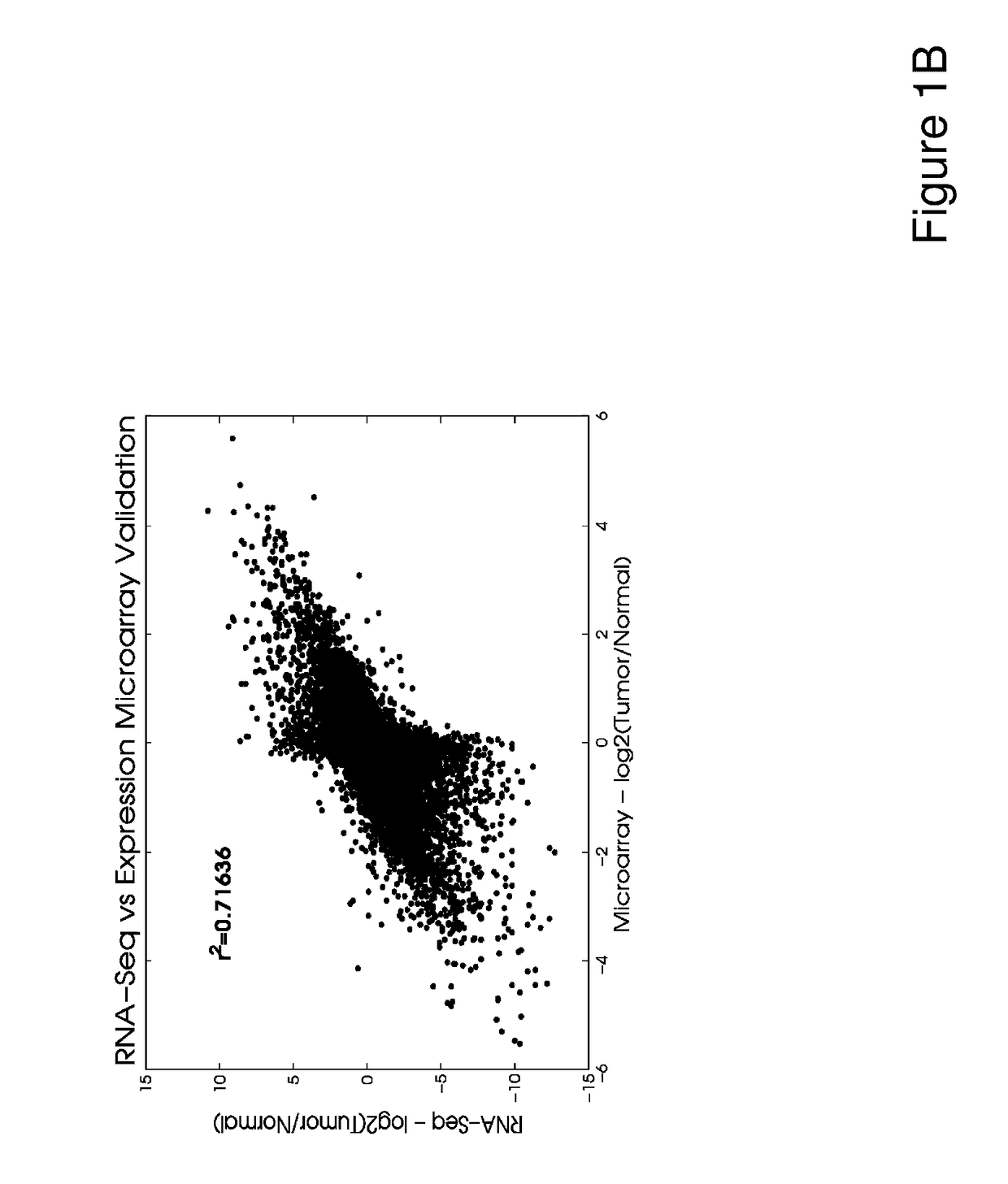
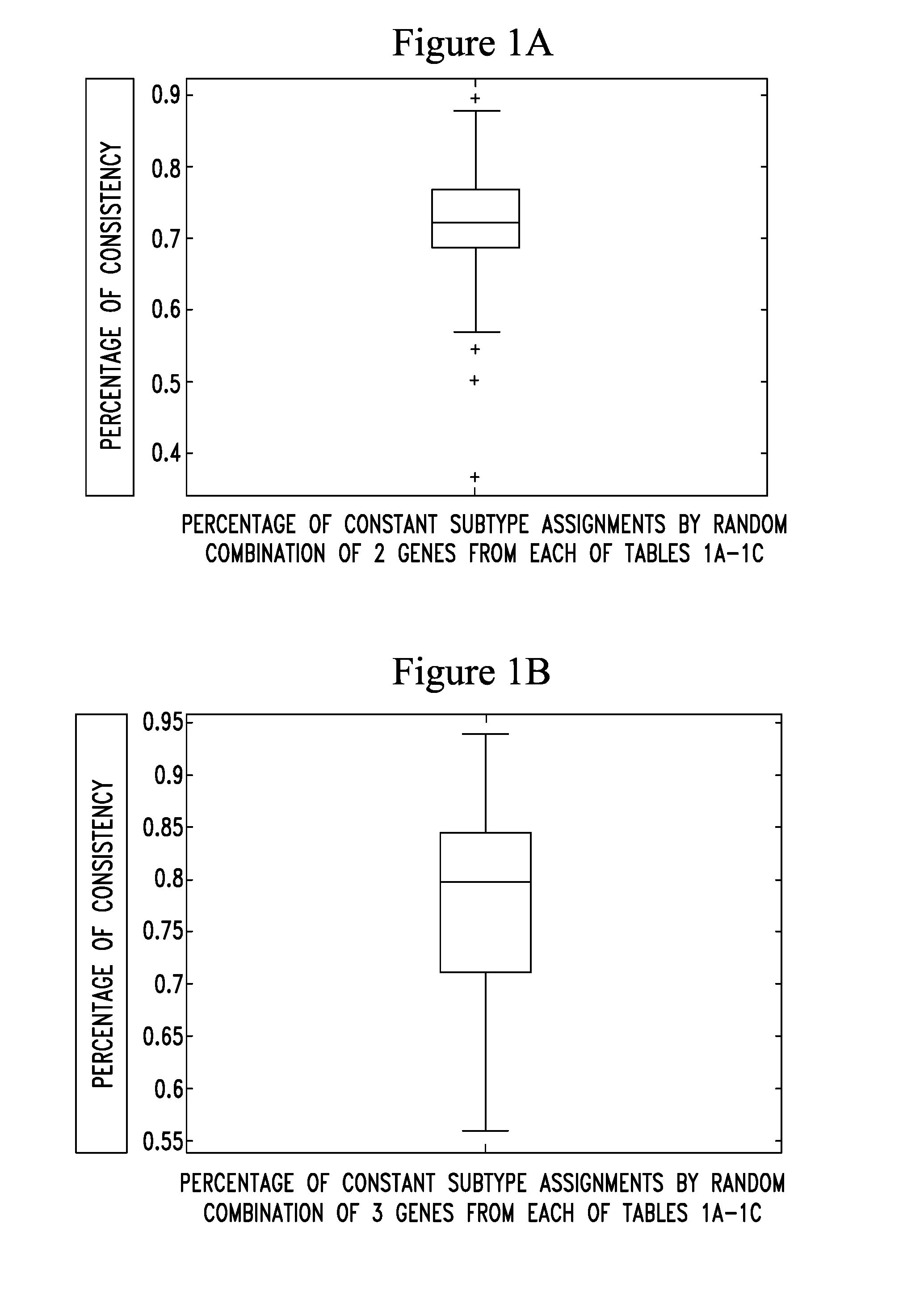
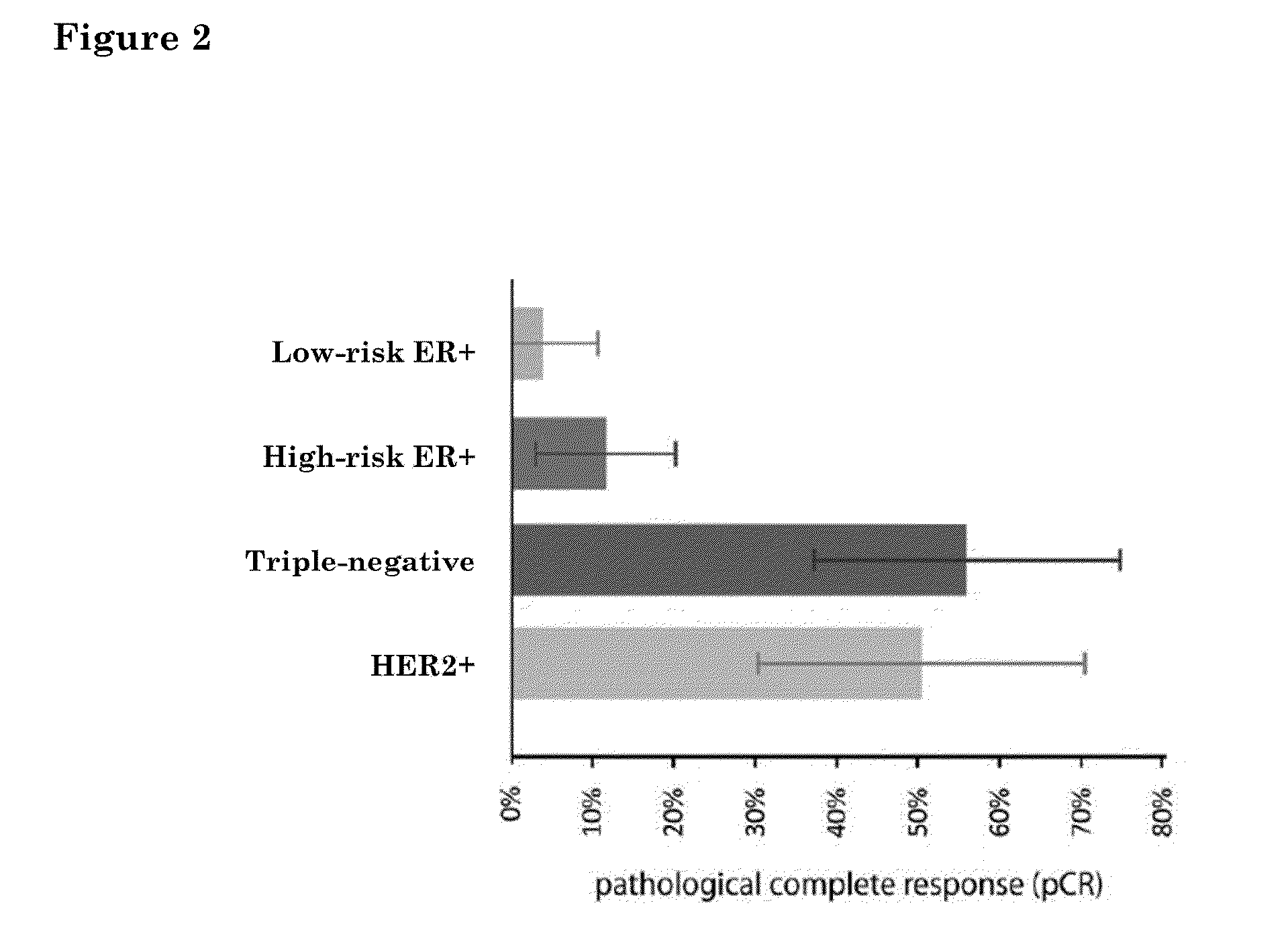
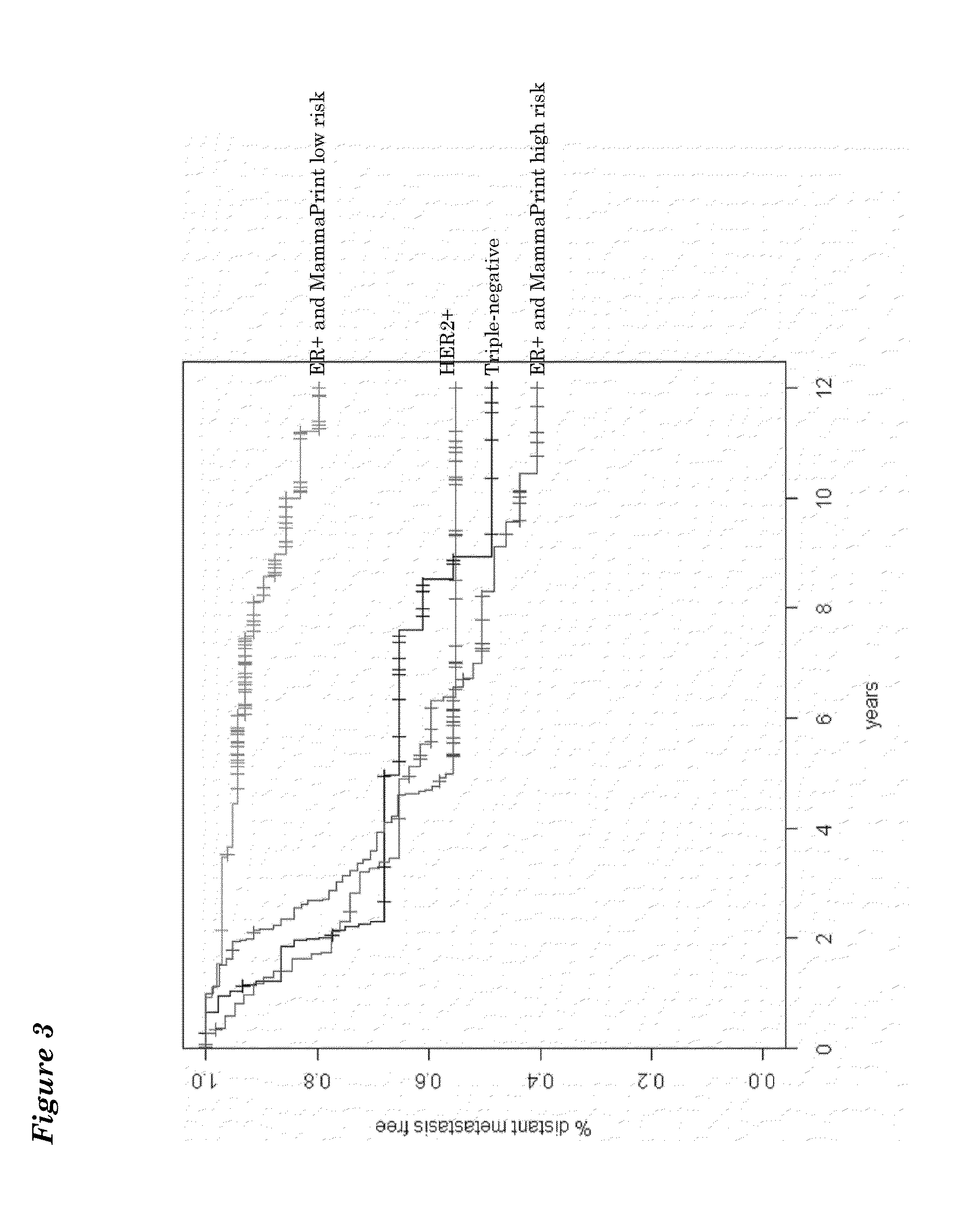
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Triple negative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
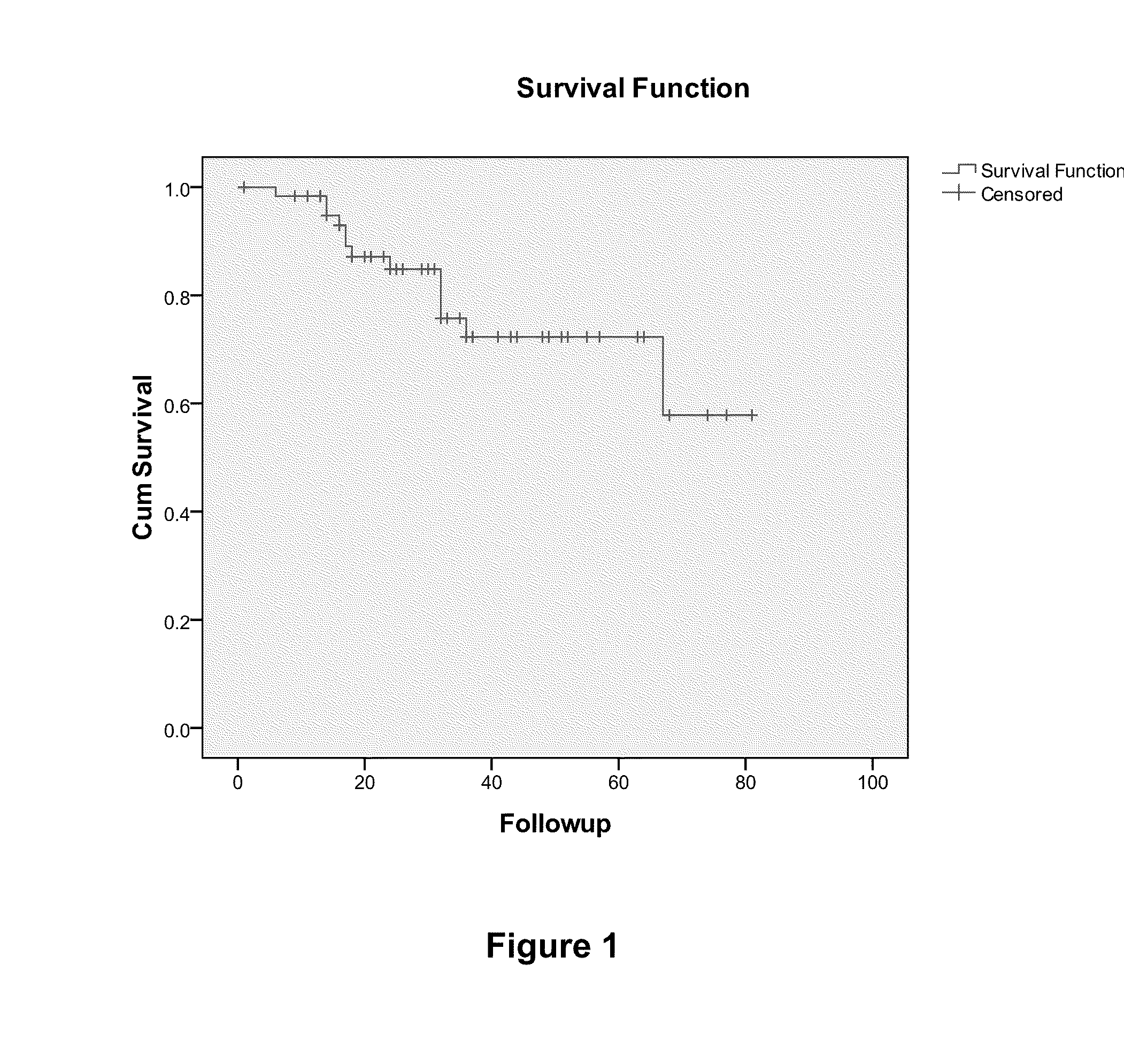
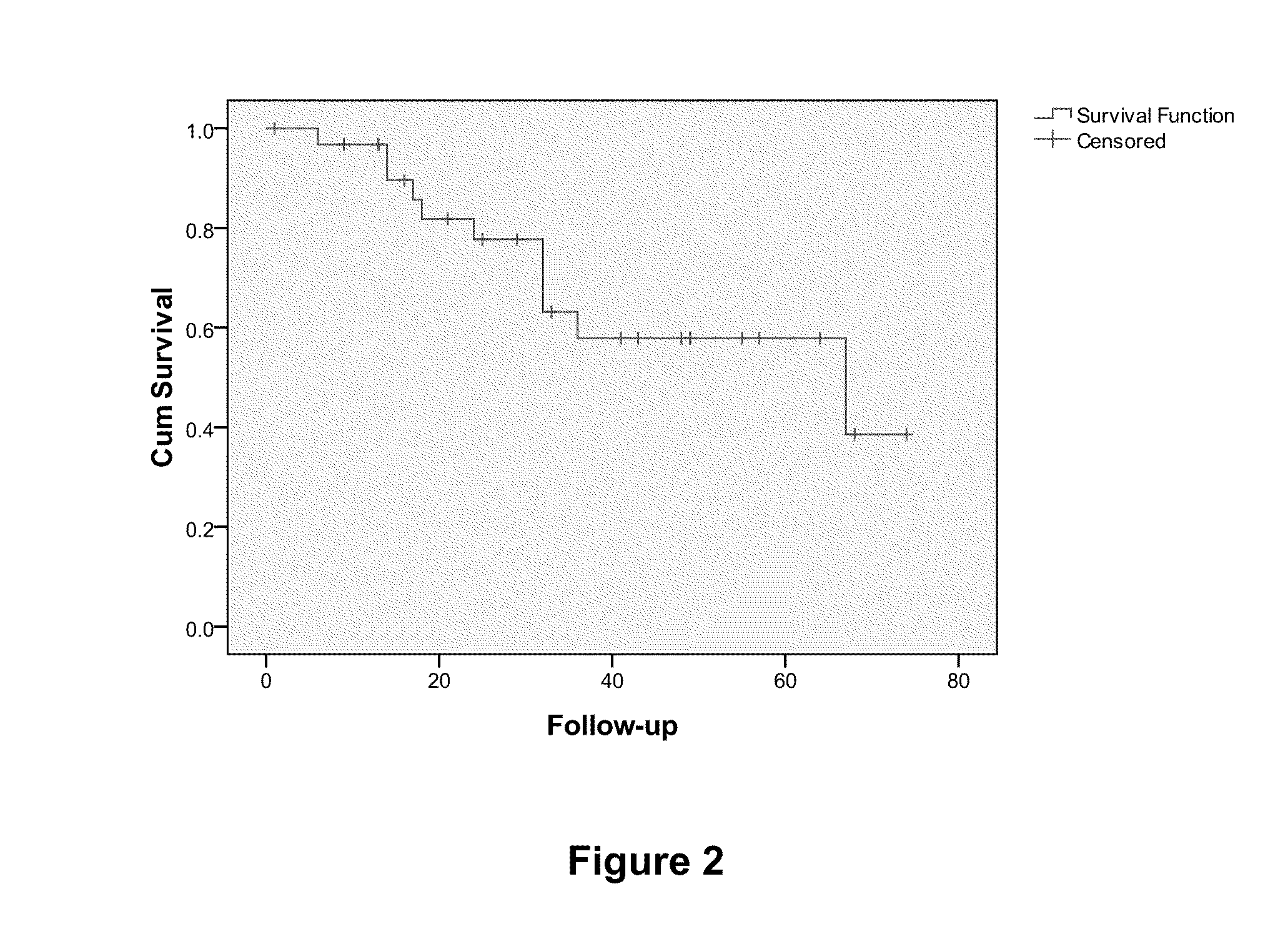
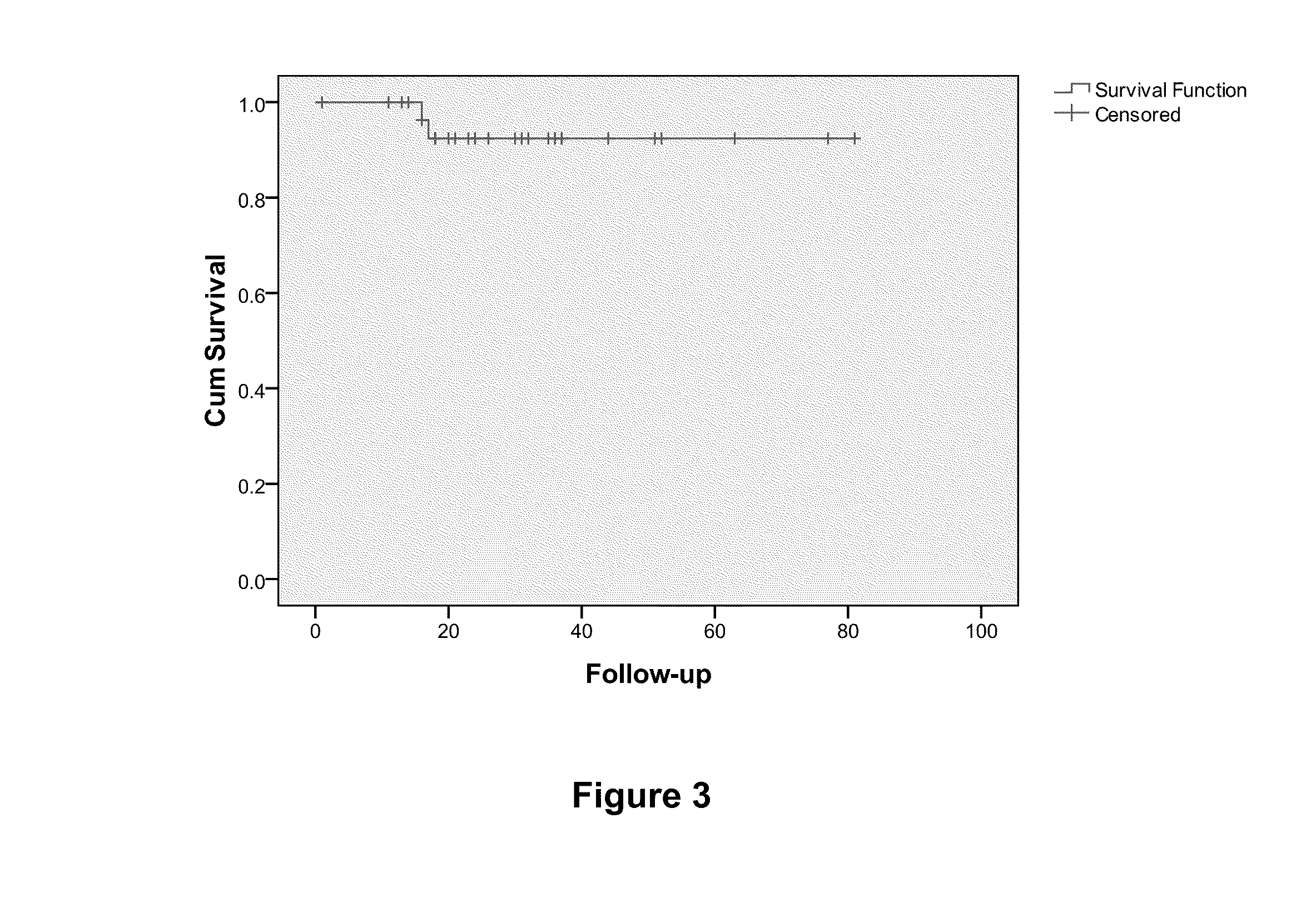
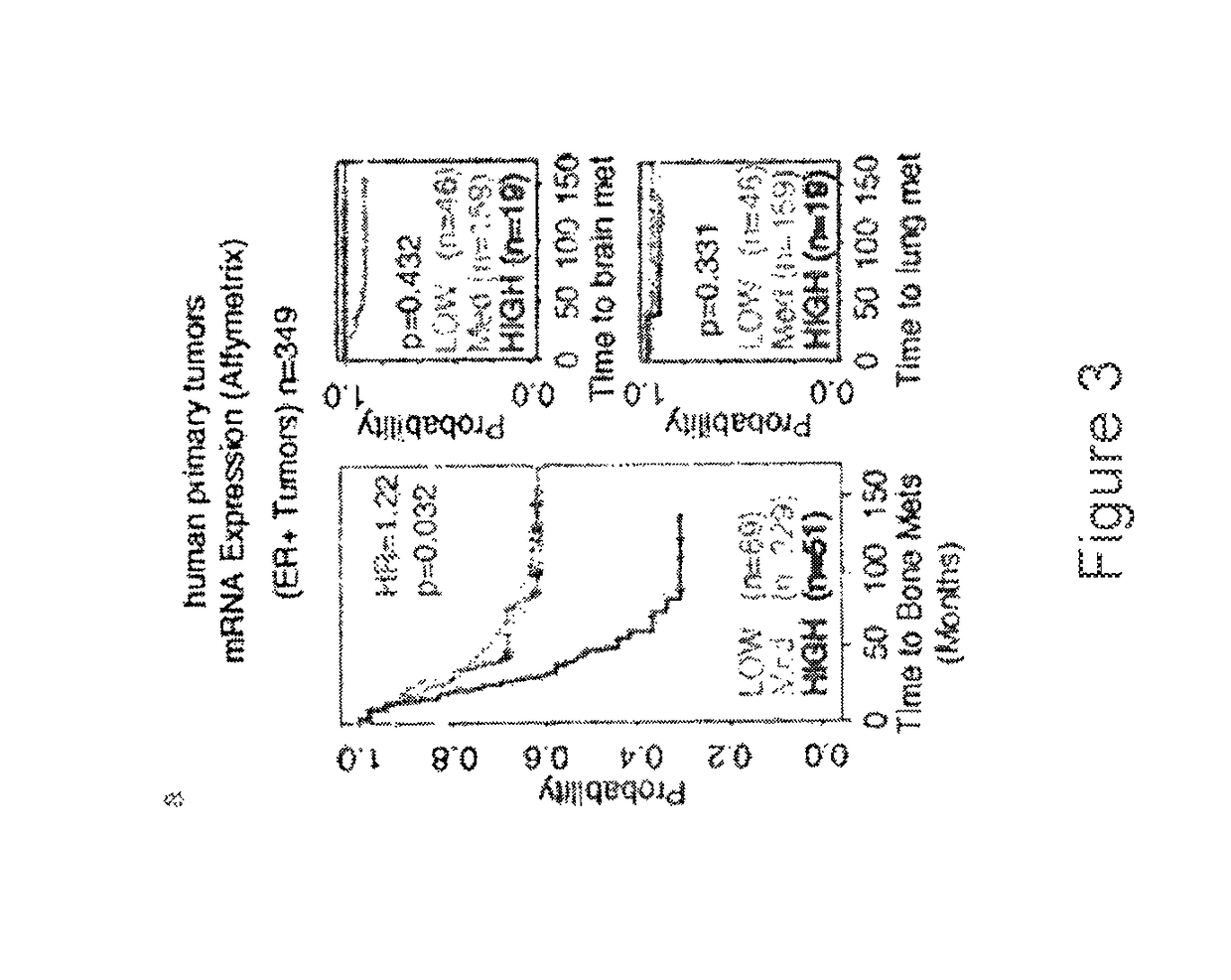
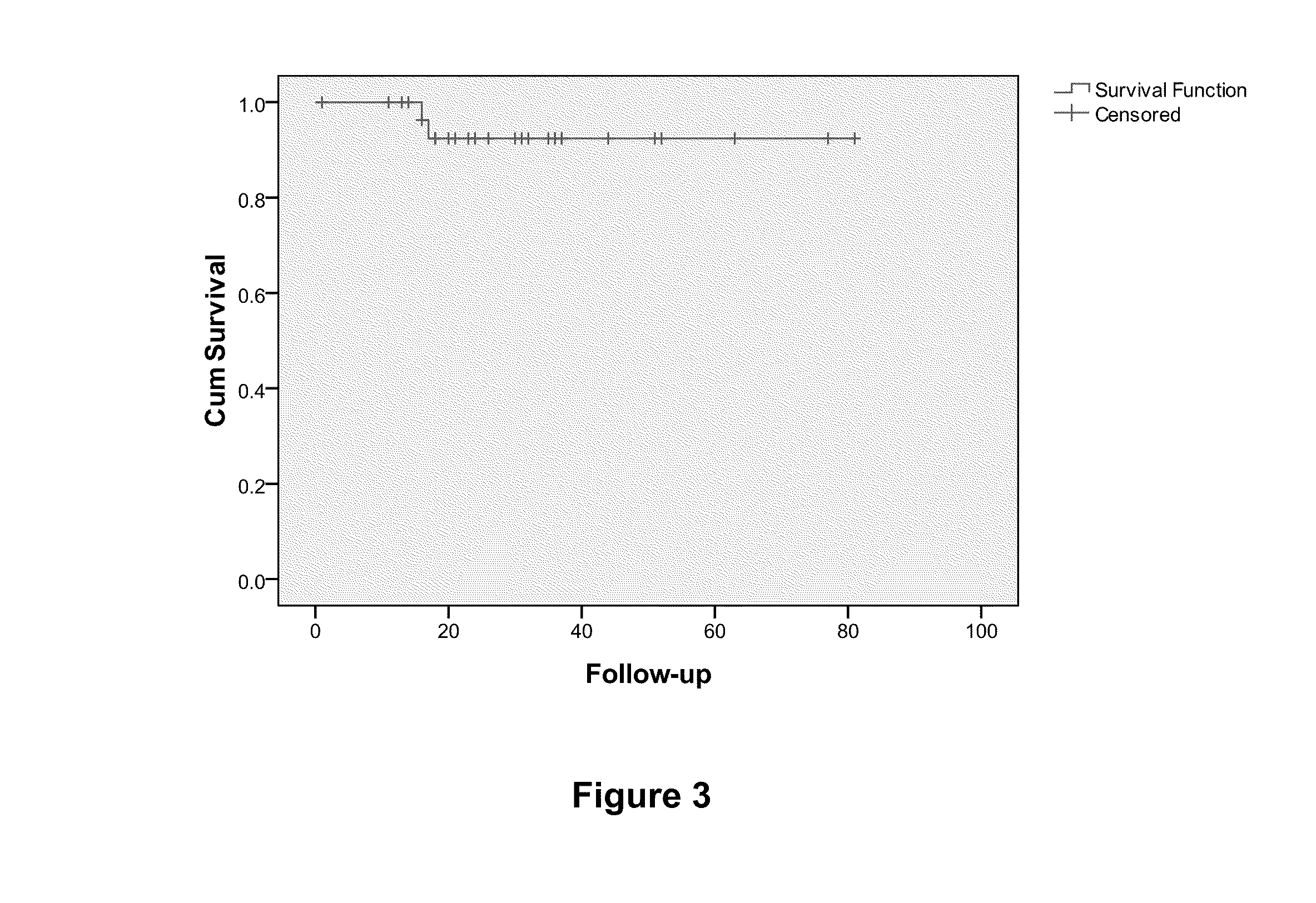
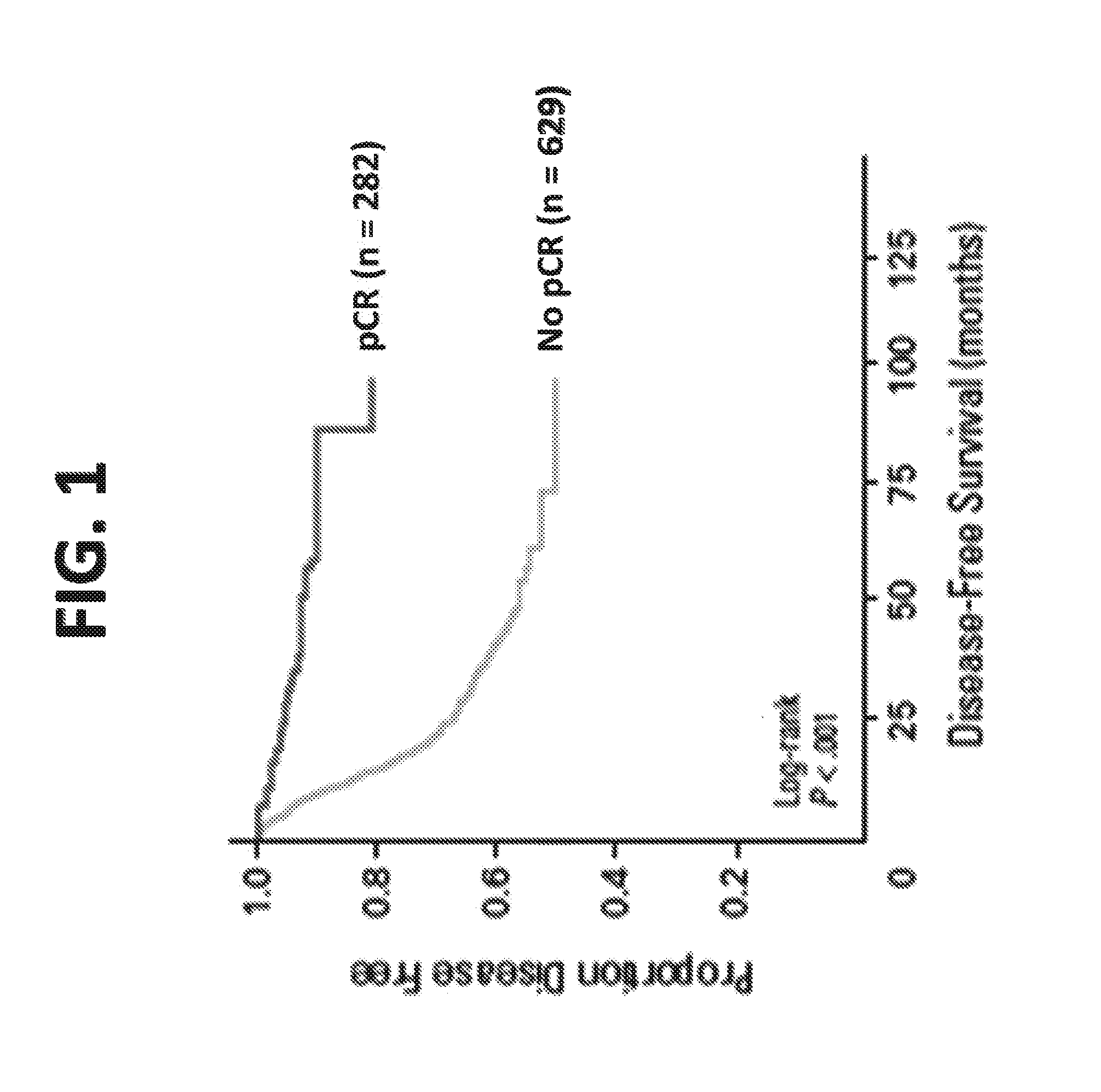
Prognostic biomarkers to predict overall survival and metastatic disease in patients with triple negative breast cancer
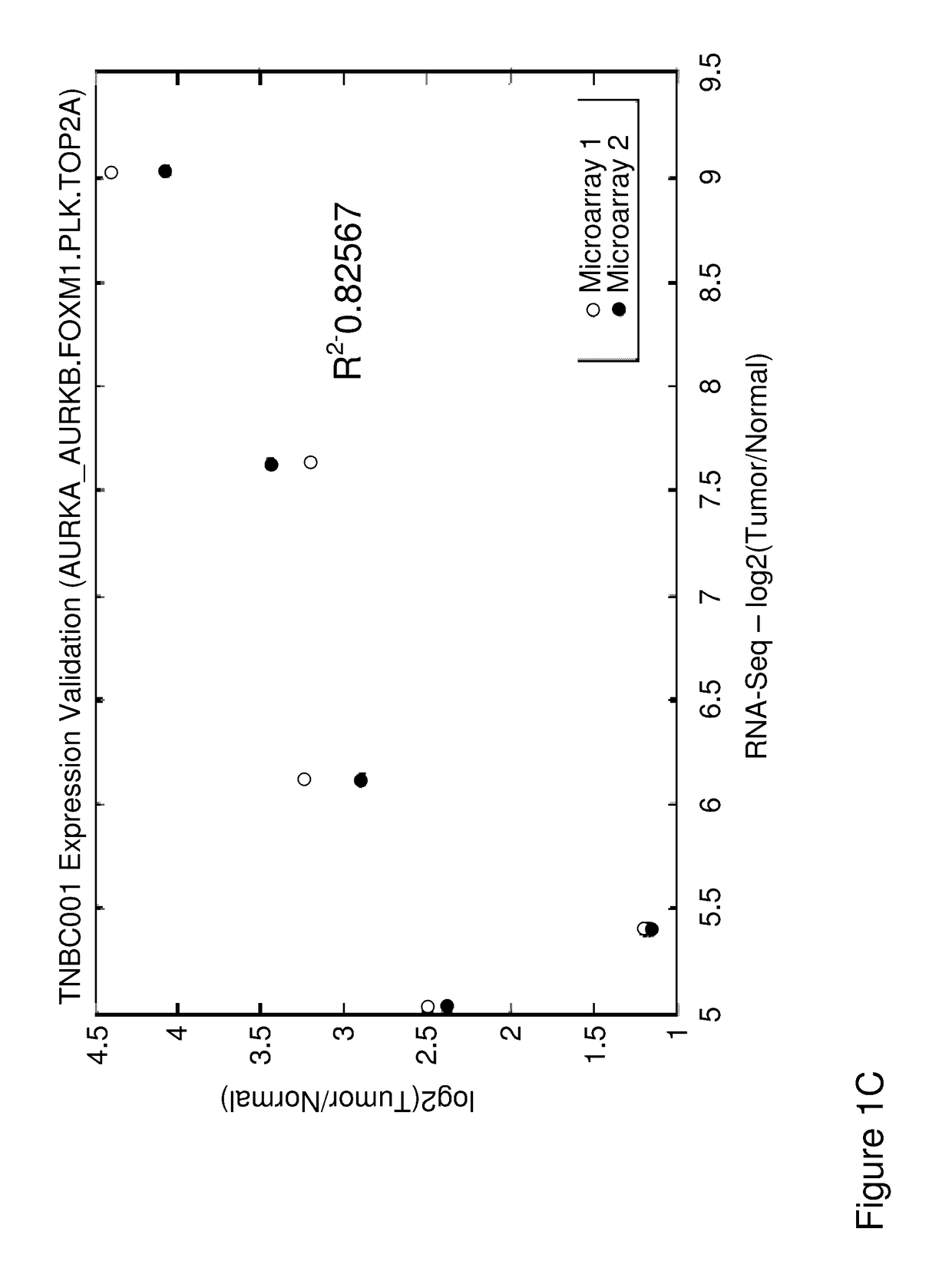
The present invention relates to a method for prognosing cancer in a subject with triple negative (TN) breast cancer, whose tumors lack expression of the estrogen receptor (ER), the progesterone receptor (PR) and normal (not amplified) levels of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). Methods and biomarkers are disclosed that are useful for predicting the overall survival (OS) potential of cancer in a subject with triple negative breast cancer or for predicting metastatic disease in a subject with triple negative breast cancer. For example, the method comprises detecting in a sample from a subject one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of ANK3, CD24, EIF1, KLF6, KRAS, KRT1, MAP2K4, SDC4, SLC2A3, STK3, TFAP2C, and WRN. An increase or decrease in one or more biomarkers as compared to a standard is prognostic of OS of TN breast cancer. Likewise, in another example, the method comprises detecting in a sample from a subject one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of ANG, DICER1, EIF1, and MSH6. An increase or decrease in one or more biomarkers as compared to a standard is prognostic of metastasis of TN breast cancer.
Owner:VM INST OF RES
Multi-gene classifiers and prognostic indicators for cancers
InactiveUS20110130296A1Increase doseIncrease frequencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary breast cancerOncology
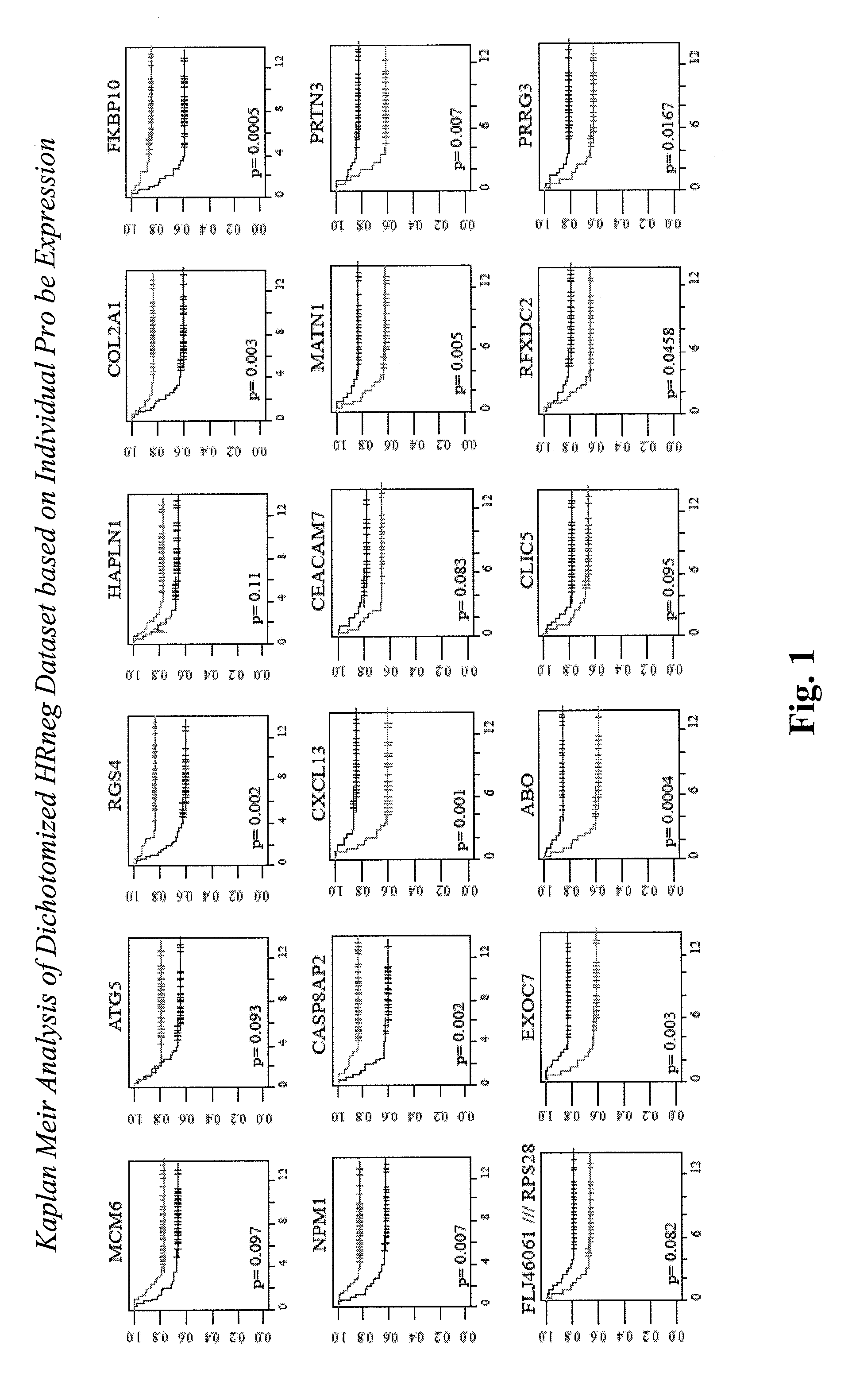
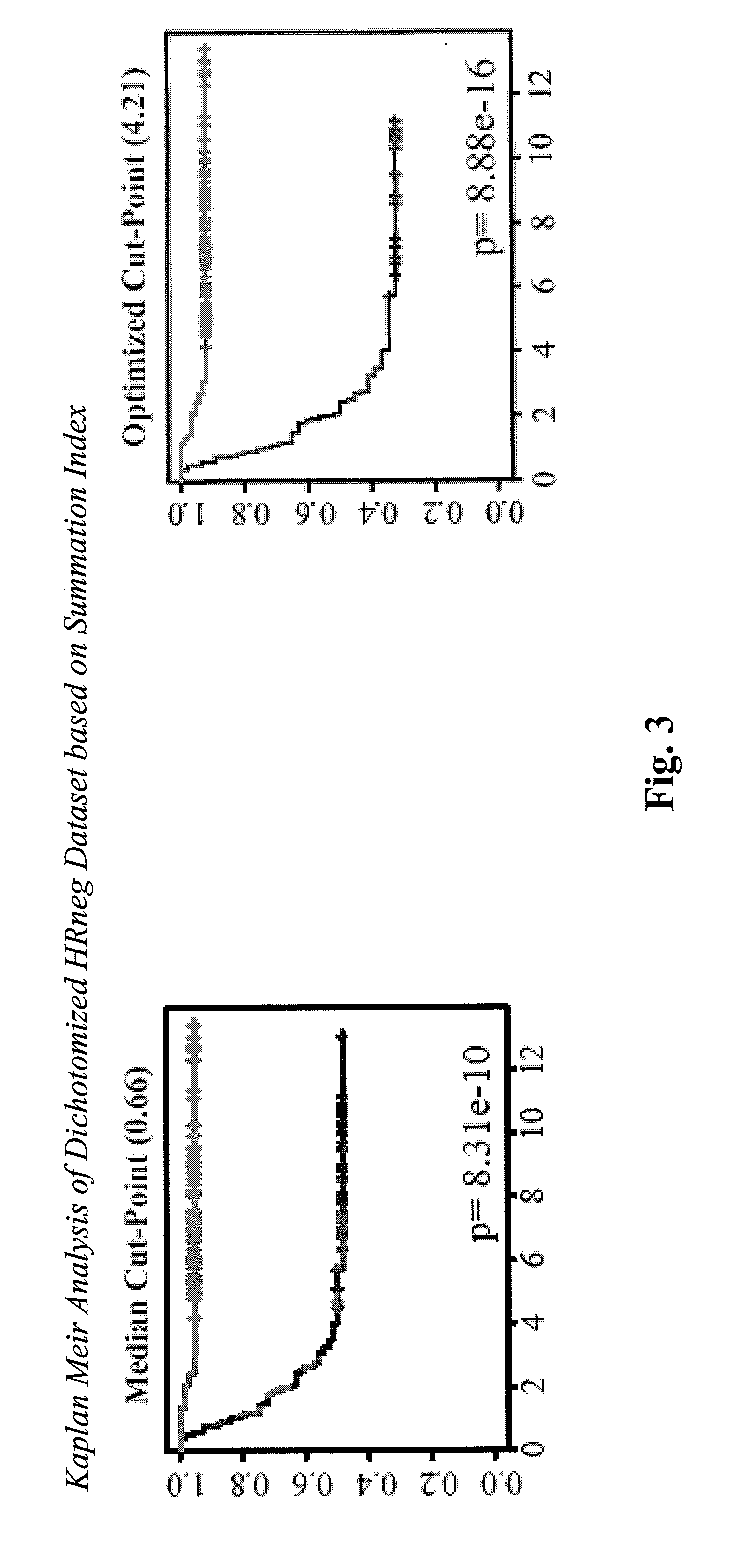
The present invention relates to the identification of marker genes useful in the diagnosis and prognosis of clinically problematic subsets of primary breast cancers. More specifically, the invention relates to the identification of two sets of marker genes that are differentially expressed in and useful for the diagnosis and prognosis of subsets of hormone receptor-negative (HRneg; i.e., ER and PR negative) and triple-negative (Tneg; i.e., ER, PR and HER2 negative) primary breast cancers at highest risk for early metastatic relapse. The invention further provides methods for determining the best course of treatment for patients having one of these clinically problematic subsets of primary breast cancers. The invention also provides methods for identifying compounds that prevent or treat a subtype of breast cancer based on their ability to modulate the activity or expression level of one or more marker genes identified herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
DNA Repair Proteins Associated With Triple Negative Breast Cancers and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090239229A1High riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMedicineBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention provides methods of detecting triple negative breast cancer recurrence using biomarkers.
Owner:DNAR
Biomarkers and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20140024539A1Sensitive to treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMedicineBiomarker (petroleum)
Methods useful in the prediction and detection of a triple negative cancer subtype using biomarkers are provided herein.
Owner:TRANSLATIONAL GENOMICS RESEARCH INSTITUTE
Method for the prognosis and treatment of cancer metastasis
ActiveUS20170370935A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBreast cancer metastasisBreast cancer classification
Owner:INSTITUCIO CATALANA DE RECERCA I ESTUDIS AVANCATS +1
Device and Methods for Broadbeam and Microbeam Chemo-Radiosurgery Combined with Its Tumor Exosome Apheresis
InactiveUS20170368373A1Breathing protectionOther blood circulation devicesImmune complex depositionAtm kinase
Conventional single fraction 20-Gy broadbeam photonbeam or protonbeam chemo-radiosurgery does not sterilize EMT-MET cancer stem cell radiodurans but single fraction 100 to 10,000 Gy microbeam radiosurgery sterilizes them. Device and methods for microbeam chemo-radiosurgery including 250 MeV wakefield electronbeam is disclosed.Surgery, chemotherapy and broadbeam and microbeam radiosurgery releases billions of abscopal metastasis causing, tumor specific plasma soluble proteins, cell membranes, apoptotic bodies, DNA and RNAs, exosomes like telomere-telomerase, ATM-ATM kinase and others. They and adaptive resistance to chemo-radiosurgery, paraneoplastic and non-paraneoplastic diseases causing immune complexes are removed by pulse flow combined continuous flow ultracentrifugation apheresis and immune affinity chromatography. Chemotherapy and high dose radiation exposed tumor cells and their exosomes are made sensitive to telomerase inhibiting and apoptosis inducing and least toxic epigallocatechin and to heparin bound receptors. They convert triple negative breast tumors into receptor positive tumors which open new avenues for treating most aggressive breast cancers.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Method for the prognosis and treatment of cancer metastasis
ActiveUS9702878B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBreast cancer metastasisBreast cancer classification
The present invention relates to a method for the prognosis of bone metastasis in triple negative (including basal-like) breast cancer or, alternatively, ER+ breast cancer (including luminal A and B) which comprises determining if the c-MAF gene is amplified in a primary tumor sample. Likewise, the invention also relates to a method for determining the tendency to develop bone metastasis with respect to metastasis in other organs, which comprise determining the c-MAF gene expression level, amplification or translocation. The invention also relates to a method for predicting early bone metastasis in a subject suffering breast cancer. The invention also relates to a c-MAF inhibitor as therapeutic agent for use in the treatment of triple negative (including basal-like) breast cancer metastasis or, alternatively, ER+ breast cancer (including luminal A and B) metastasis. The invention relates to kits for predicting bone metastasis and predicting the clinical outcome of a subject suffering from bone metastasis. Finally, the invention relates to a method for typing of a subject suffering breast cancer and for classifying a subject from breast cancer into a cohort.
Owner:INSTITUCIO CATALANA DE RECERCA I ESTUDIS AVANCATS +1
Compositions and methods of treatment of drug resistant cancers
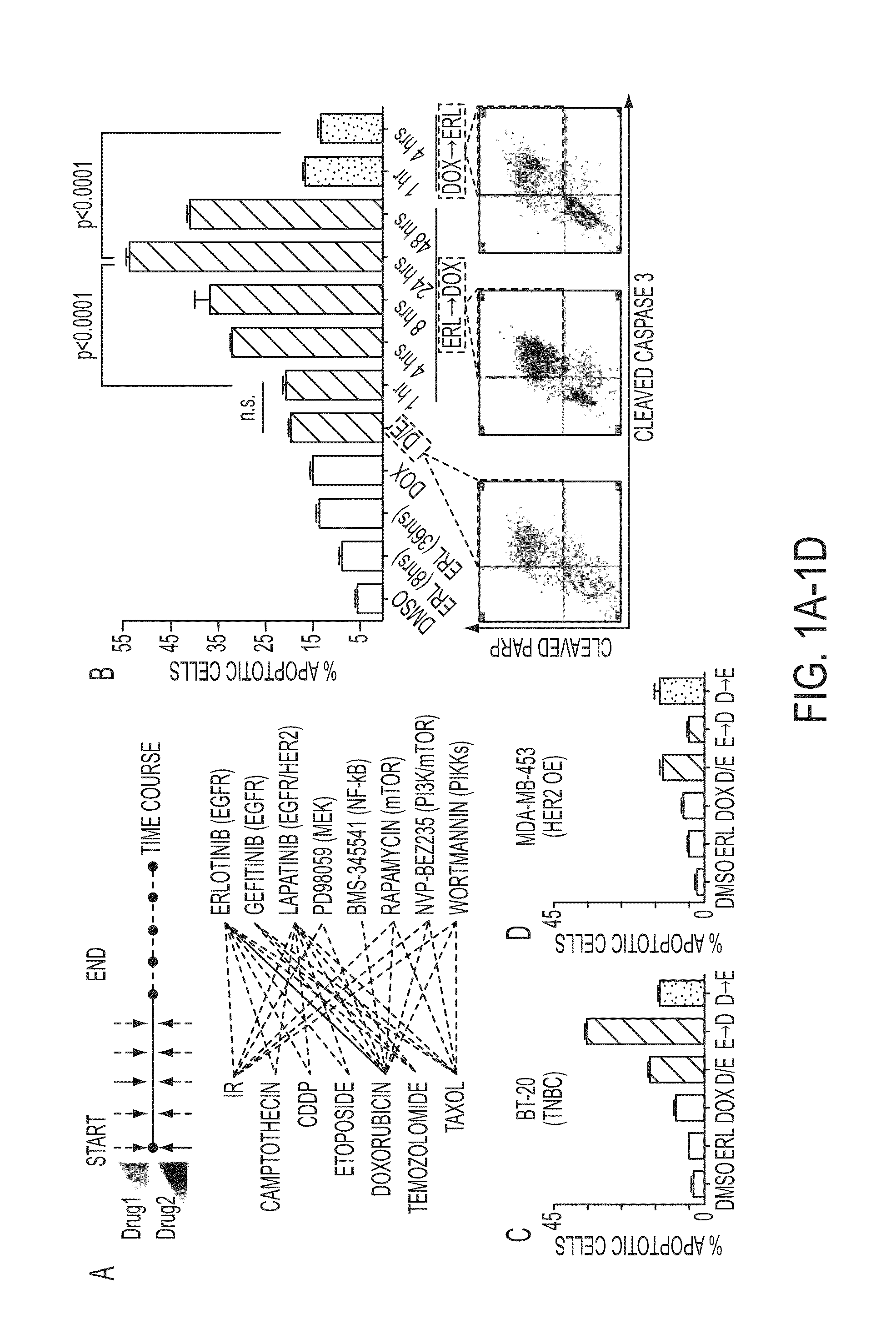
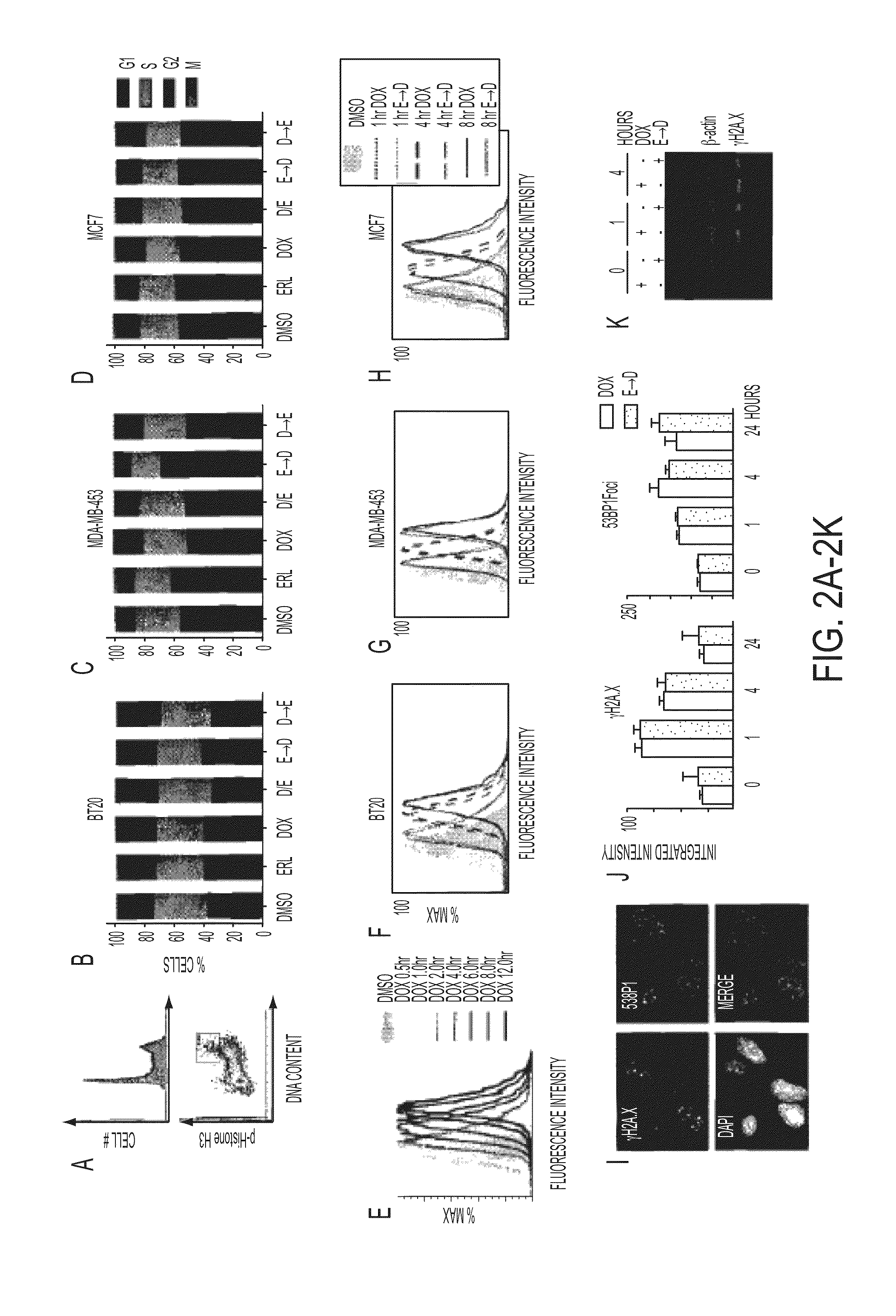
ActiveUS20140011759A1Synergize their apoptotic responseBiocideSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthPhosphorylation
Time-staggered inhibition of EGFR, in combination with DNA damaging agents, is a useful therapeutic strategy for treating cancers, particularly drug resistant cancers such as a subset of triple-negative tumors, particularly those with high basal levels of phosphorylated EGFR. The staggered therapy was also demonstrated to be applicable to other types of tumors, especially lung cancers, which contain either high levels of phosphorylated wild-type EGFR or mutations within EGFR itself. EGFR inhibition dramatically sensitizes cancer cells to DNA damage if the drugs are given sequentially, but not simultaneously. The first drug must be administered in a dosage and for a period of time sufficient for the dynamic network rewiring of an oncogenic signature maintained by active EGFR signaling to unmask an apoptotic process that involves activation of caspase-8.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Prognostic biomarkers to predict overall survival and metastatic disease in patients with triple negative breast cancer
The present invention relates to a method for prognosing cancer in a subject with triple negative (TN) breast cancer, whose tumors lack expression of the estrogen receptor (ER), the progesterone receptor (PR) and normal (not amplified) levels of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). Methods and biomarkers are disclosed that are useful for predicting the overall survival (OS) potential of cancer in a subject with triple negative breast cancer or for predicting metastatic disease in a subject with triple negative breast cancer. For example, the method comprises detecting in a sample from a subject one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of ANK3, CD24, EIF1, KLF6, KRAS, KRT1, MAP2K4, SDC4, SLC2A3, STK3, TFAP2C, and WRN. An increase or decrease in one or more biomarkers as compared to a standard is prognostic of OS of TN breast cancer. Likewise, in another example, the method comprises detecting in a sample from a subject one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of ANG, DICER1, EIF1, and MSH6. An increase or decrease in one or more biomarkers as compared to a standard is prognostic of metastasis of TN breast cancer.
Owner:VM INST OF RES
Means and methods for molecular classification of breast cancer
ActiveUS20130178381A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBreast cancer classificationMolecular classification
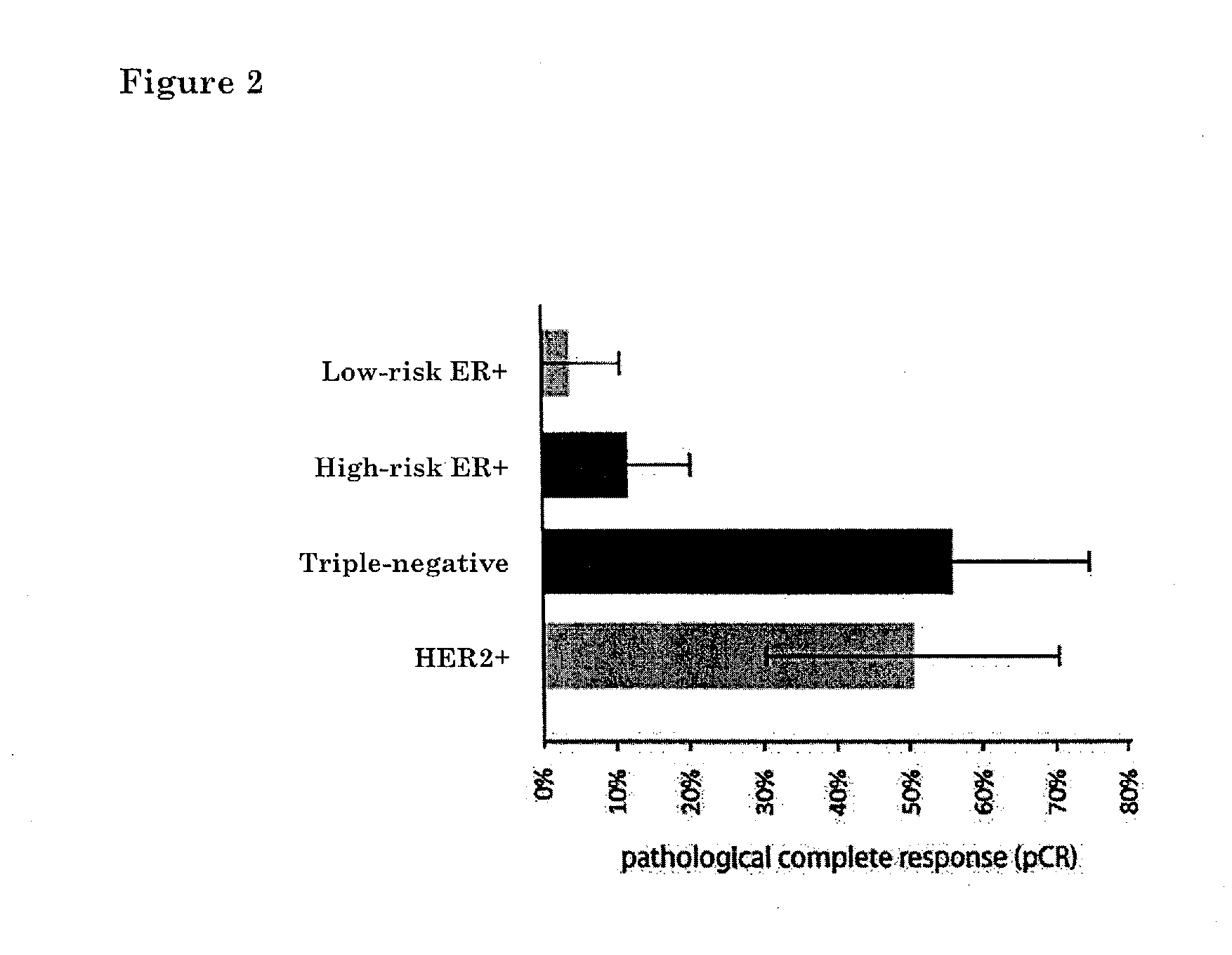
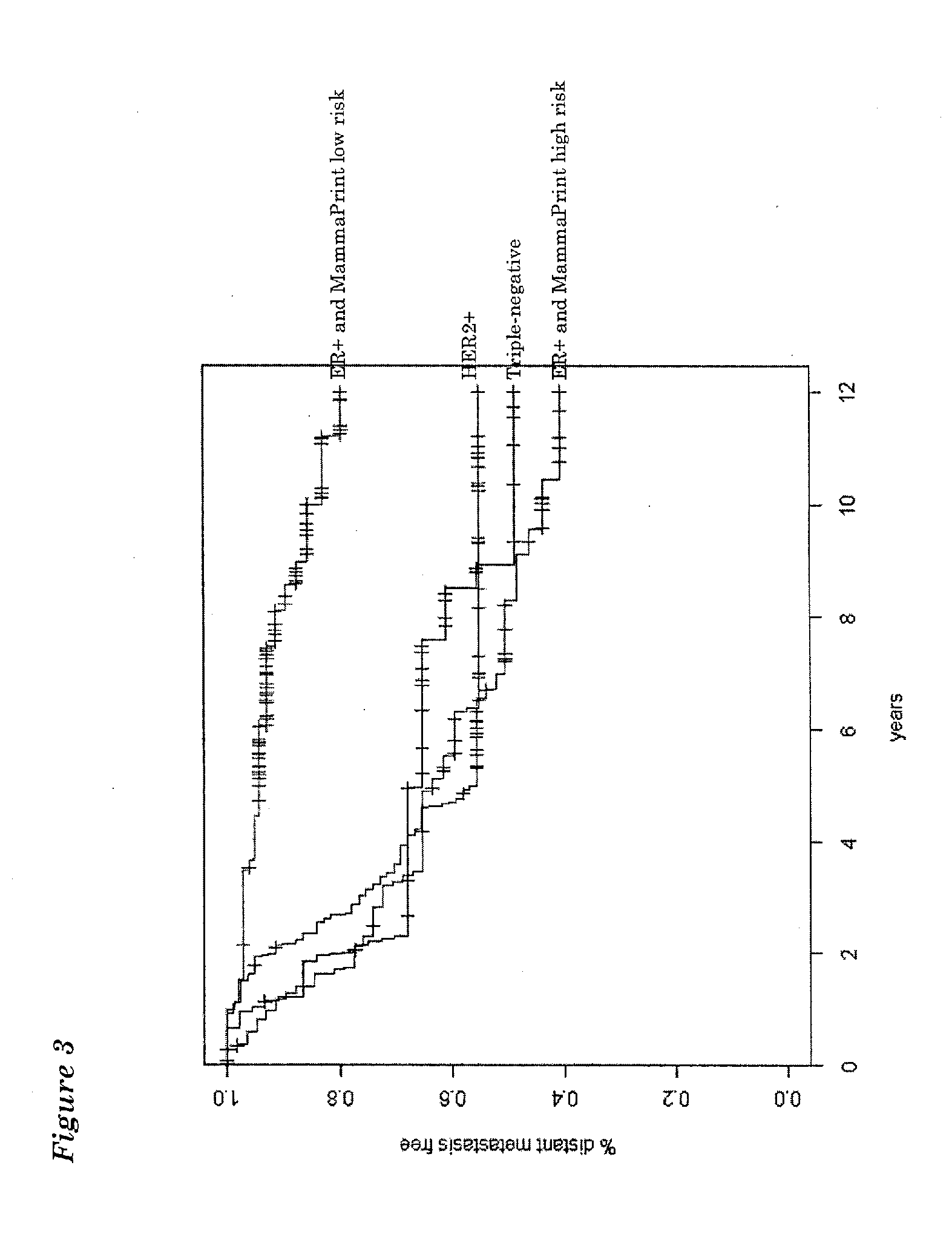
The invention relates to a method of typing a sample from a breast cancer patient. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for classification of breast cancer according to the presence or absence of Estrogen Receptor (ER), Progesterone Receptor (PR) and Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2 (ERBB2; HER2). More specifically, the invention provides methods and means to classify breast cancer as ER positive, triple negative (ER−, PR− and HER2−) and HER2+.
Owner:AGENDIA NV
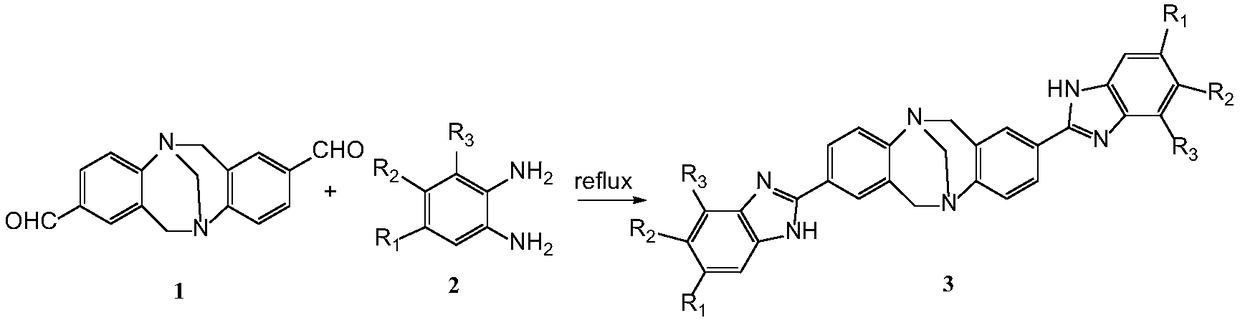
Benzimidazole-containing Tr*ger's base type compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108864111AEasy to prepareMild reaction conditionsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryStructural formulaNon-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
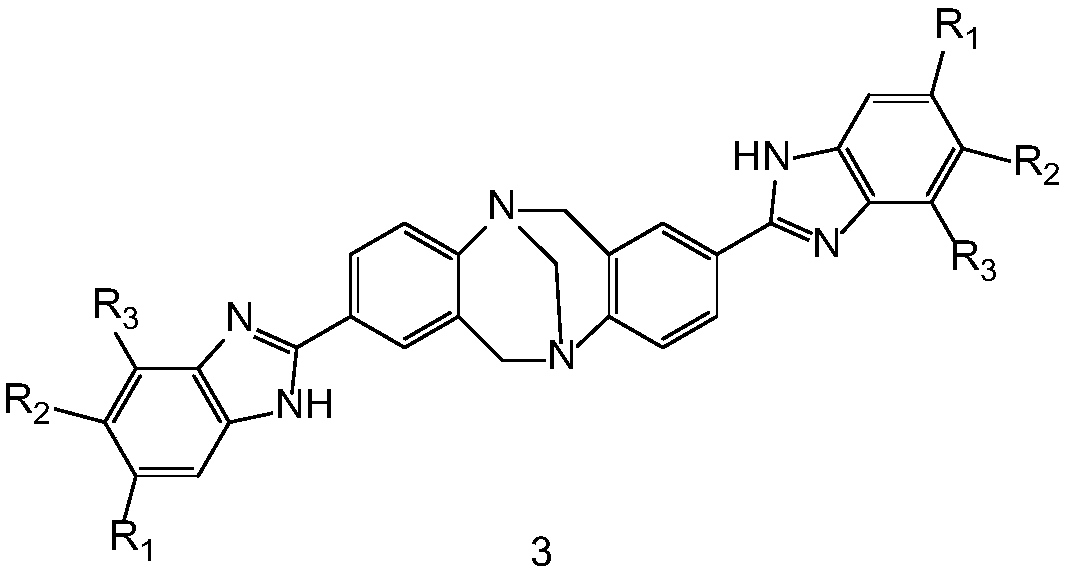
The invention discloses a benzimidazole-containing Tr*ger's base type compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A structural formula of the compound is shown as a formula 3; the compound is prepared by carrying out aldimine condensation reaction on 2,8-dialdehyde-Tr*ger's base and substituted o-phenylenediamine. An in-vivo experiment shows that the benzimidazole-containingTr*ger's base type compound has relatively high inhibition activity on non-small cell lung cancer cells (A549), triple-negative breast cancer cells (231) and triple-positive breast cancer cells (MCF-7), and has low toxicity in human normal cells; the benzimidazole-containing Tr*ger's base type compound can be mixed with human body acceptable acid-forming salt or a medical carrier to form an anti-tumor drug. The invention provides a candidate compound for researching and developing a novel drug for treating triple-negative and triple-positive breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. The formula 3 is shown in the description.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
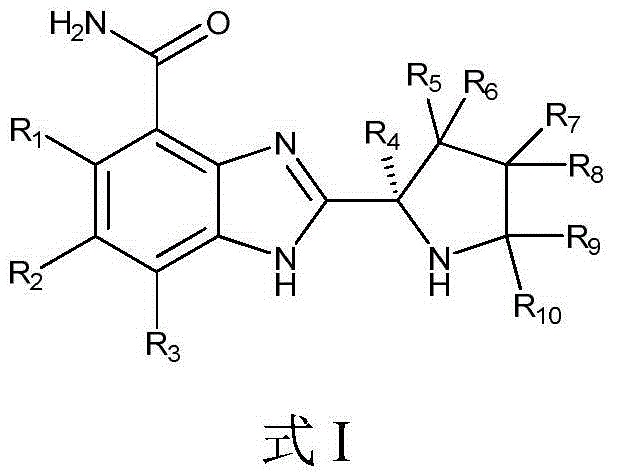
Tumor-treating compound and application thereof
ActiveCN104926793AHas antitumor activityStrong therapeutic activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsMelanomaHalf-life
Provided in the present invention are a compound for treating tumours and a use thereof, and also provided are a compound as shown in formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compound provided in the present invention has a high medicine peak concentration, a high medicine absorption and a long elimination half life, and can improve the efficacy of the medicine in clinical use and reduce the frequency of the dosages. The compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof prepared by the present invention can act as a PARP inhibitor medicine, have a certain anti-tumour activity, and especially have a good therapeutic activity on triple negative, primary or metastatic breast cancer, colon cancer, uterine cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, stomach cancer, leukemia, melanoma, solid tumors or intracranial tumors, and provide a new choice for clinical medication.
Owner:HINOVA PHARM INC
Biomarker for breast cancer
ActiveCN103547923AHigh precisionImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingIntraductal breast papillomaMammary gland structure
Owner:J PHARMA
miR-506 targeting PENK gene of triple negative breast cancer cells and application of miR-506
PendingCN110760513AInhibit progressAffect proliferationAntineoplastic agentsAnimal husbandryMiRBaseOncology
The invention relates to a miR-506 targeting PENK gene of triple negative breast cancer cells and application of the miR-506. By screening miRWalk2.0, miRBase, TargetScanHuman 7.0 databases and detecting tissue samples of triple negative breast cancer patients by using a qRT-PCR technology, it is confirmed that the expression of miR-506 in the triple negative breast cancer is decreased significantly, and is averagely down-regulated by 88.95%, a dual-luciferase reporter experiment confirms that miR-506 can directly interact with Penk, and it is indicated that miR-506 can target PENK. Accordingto the miR-506 targeting the PENK gene of the triple negative breast cancer cells and the application of the miR-506, it is proved that miR-506 affects the proliferation, metastasis and invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells by increasing the content of penk in a targeting mode; the effectiveness of miR-506 targeting penk in inhibiting the progression of the triple negative breast canceris detected through a nude mouse breast cancer model; and the results show that the miR-506 can inhibit the development of the triple negative breast cancer through targeting penk.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Means and methods for molecular classification of breast cancer
ActiveUS9175351B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBreast cancer classificationMolecular classification
Owner:AGENDIA NV
Biomarkers and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20170166981A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsMedicineBiomarker (petroleum)
Methods useful in the prediction and detection of a triple negative cancer subtype using biomarkers are provided herein.
Owner:TRANSLATIONAL GENOMICS RESEARCH INSTITUTE
Biomarker for breast cancer
ActiveUS9618512B2Effective cancer therapyEasy to optimizeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingIntraductal breast papillomaHigh level expression
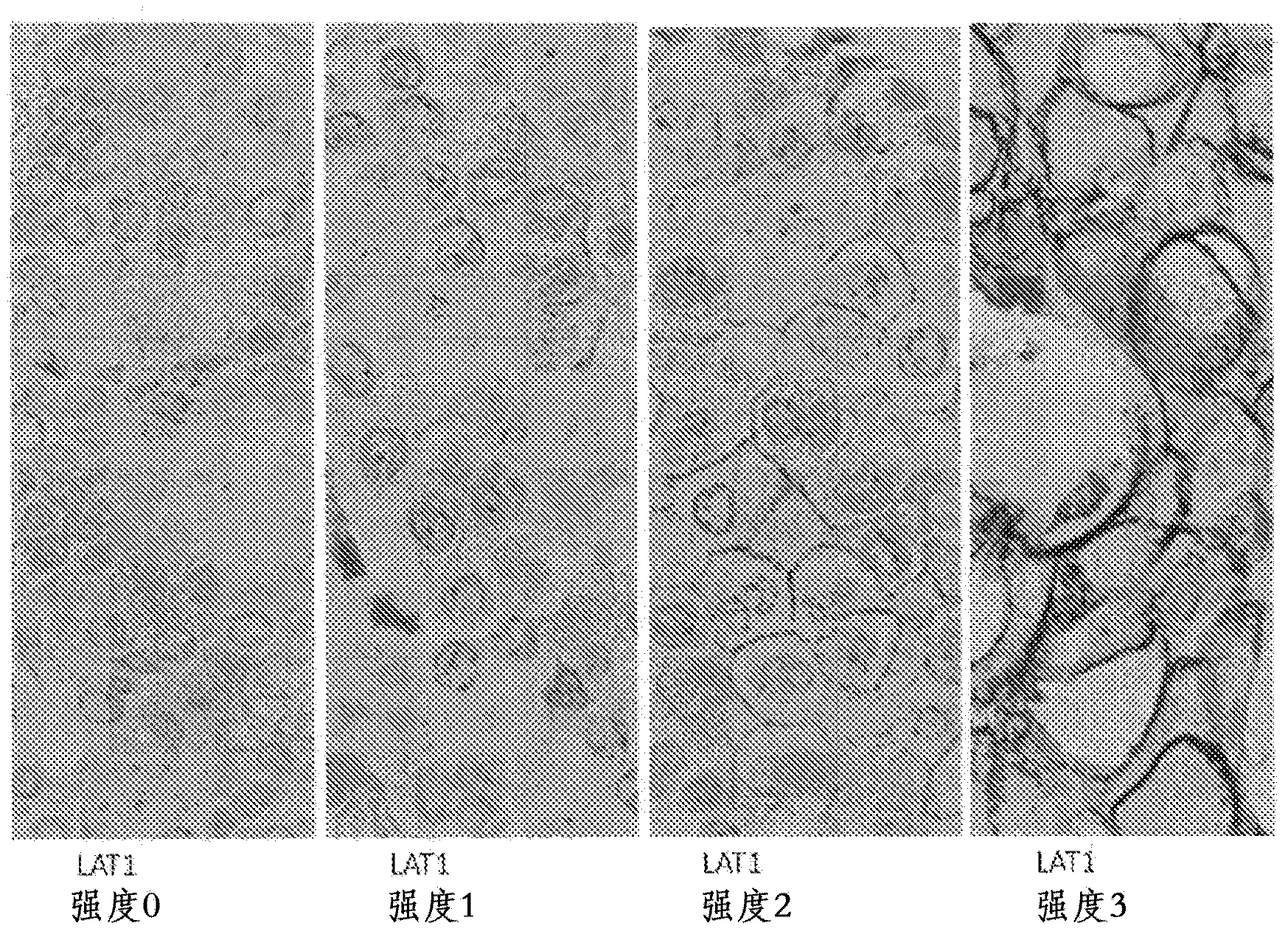
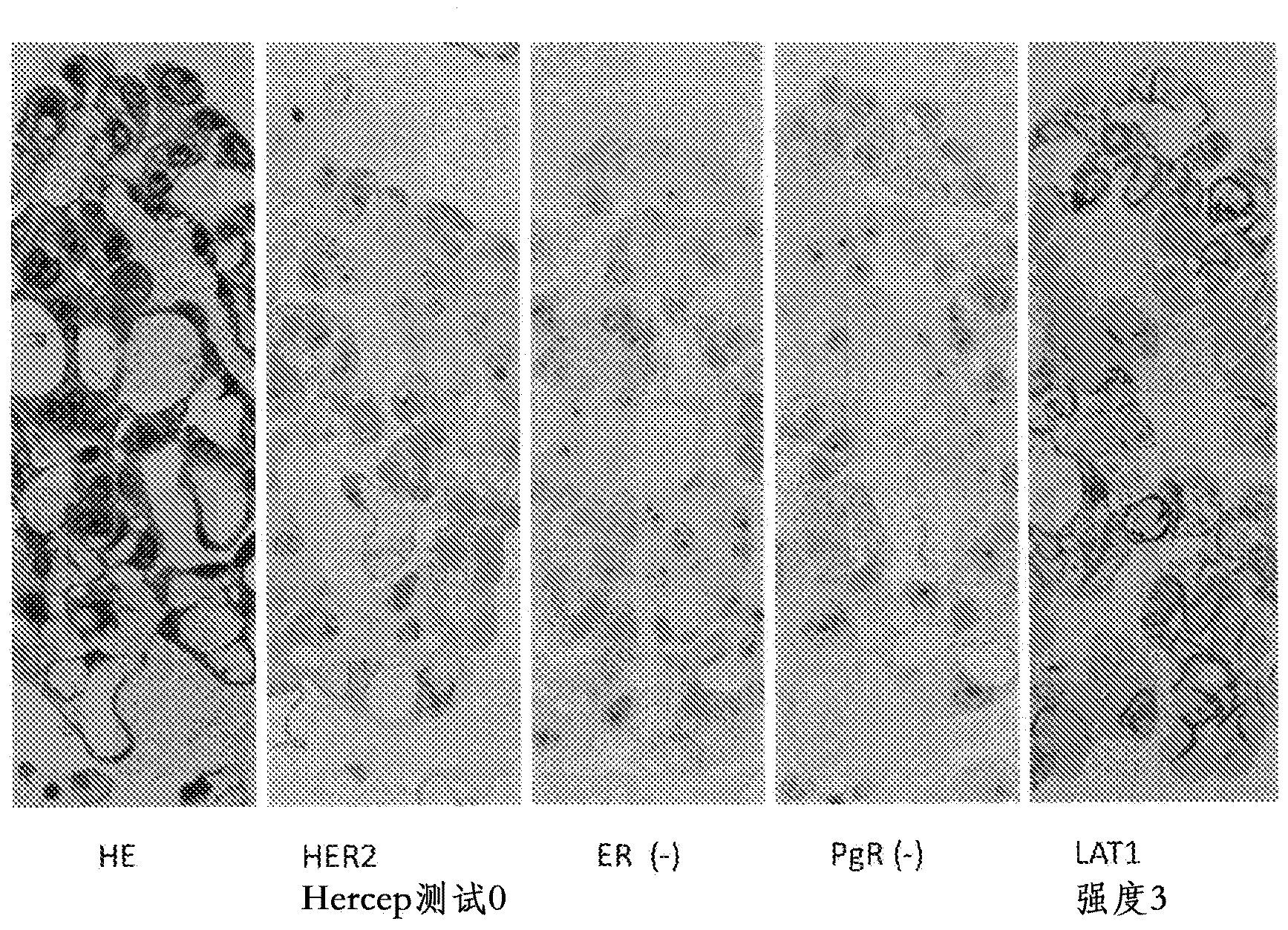
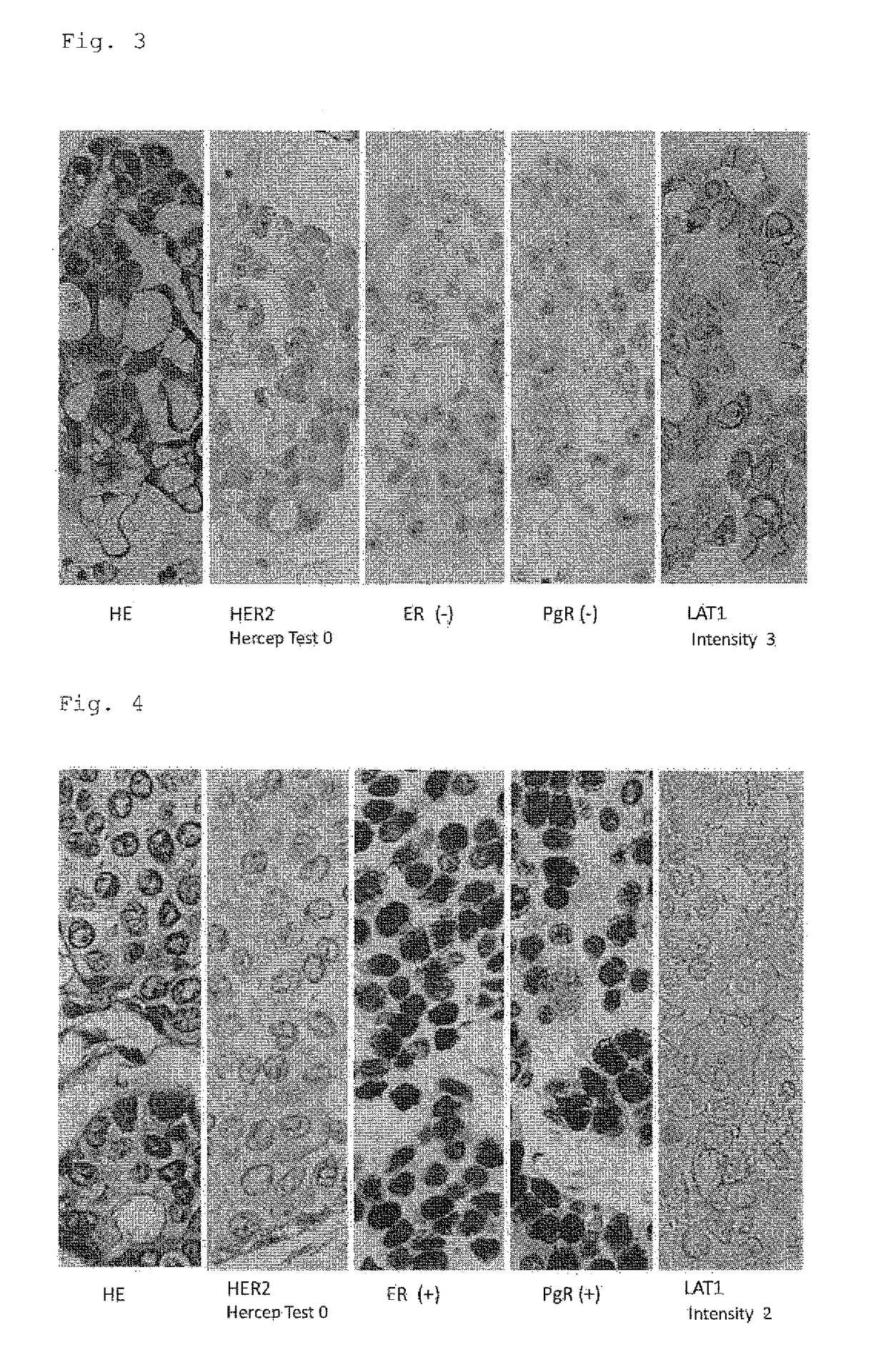
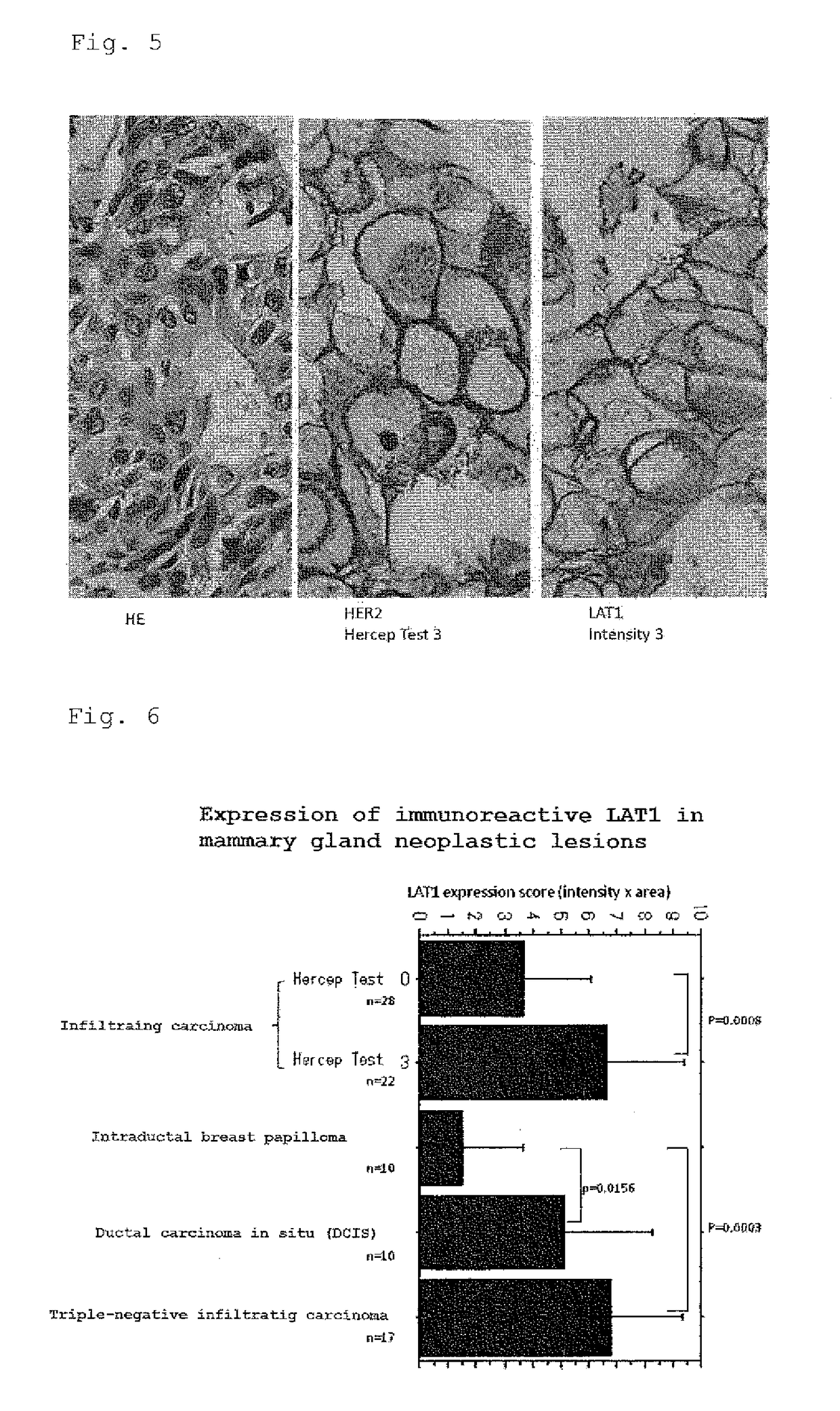
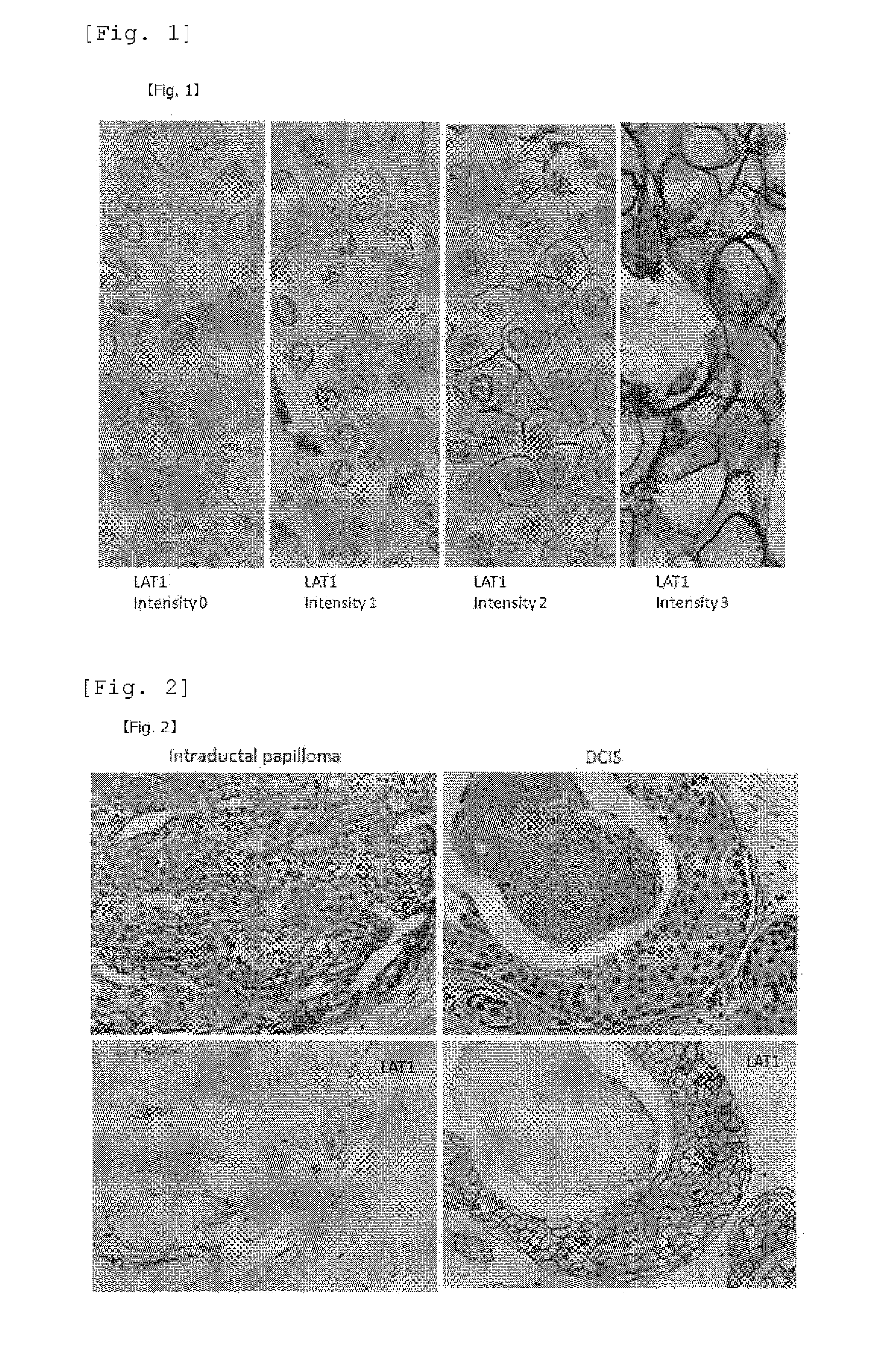
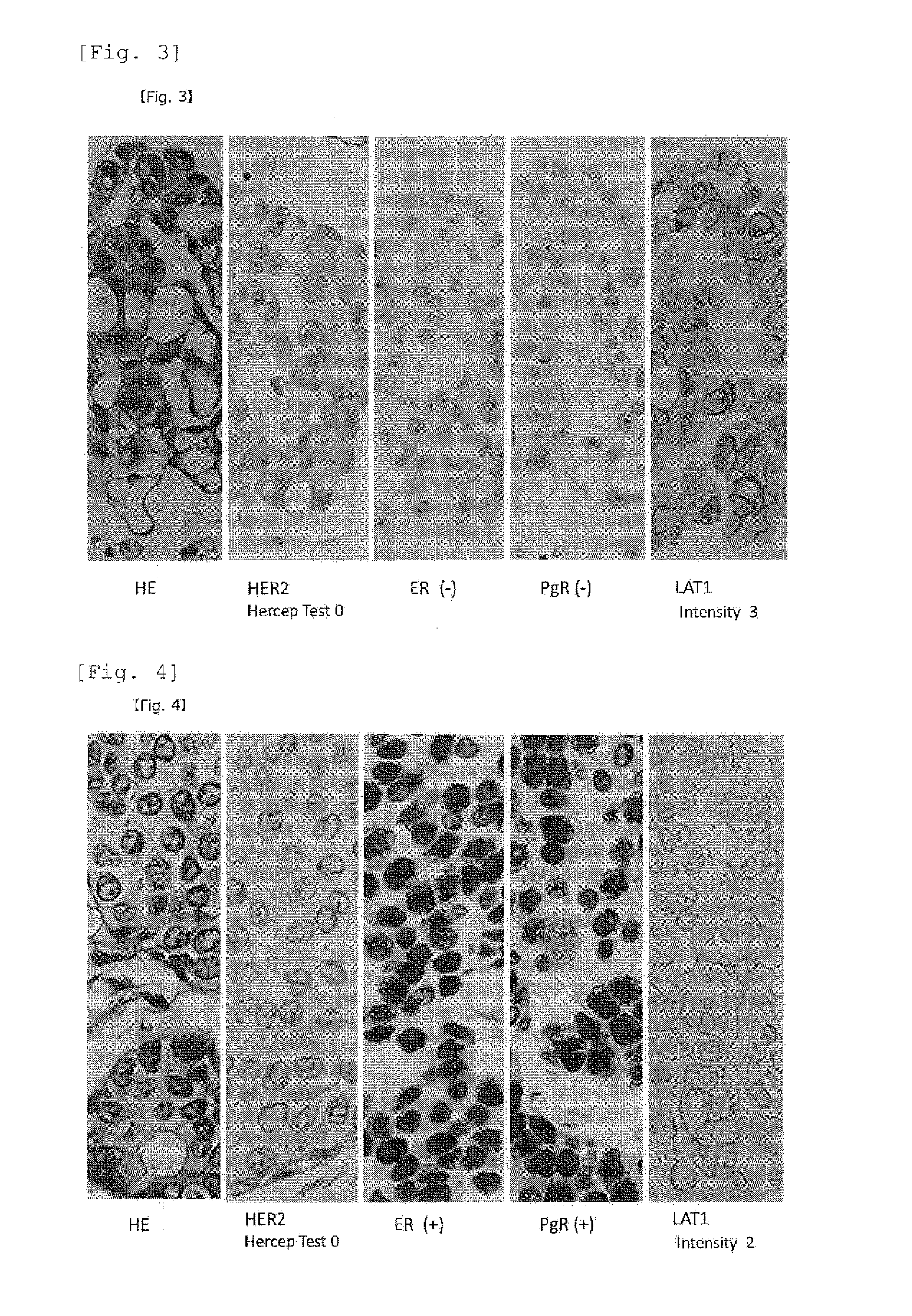
A method for the diagnosis of breast cancer using an anti-LAT1 monoclonal antibody. Among intraductal breast neoplastic lesions, duct carcinoma in situ, which is malignant, expresses LAT1 at a significantly high level, as compared to intraductal breast papilloma, which is benign. An anti-LAT1 monoclonal antibody is useful for the discrimination between these two lesions. Further, LAT1 is expressed at a high level in most of triple negative infiltrating carcinomas, which are negative for all of ER, PgR, and HER2 that are conventional molecular targeting markers for breast cancer. Therefore, LAT1 can be used as a novel molecular targeting marker for the triple negative breast cancer.
Owner:J PHARMA
Diagnosis and prognosis of triple negative breast and ovarian cancer
InactiveUS20140087400A1Enhanced untreatedEnhanced treated prognosisBiological testingDisease progressionReceptor for activated C kinase 1
In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a method of predicting disease progression comprising: (a) obtaining a sample of breast tissue that is estrogen receptor negative, progesterone receptor negative and does not over-express human epidermal growth factor 2 receptor protein; and (b) determining the expression of glia maturation factor beta, wherein expression of glia maturation factor beta is indicative of lymph node metastatis. In another aspect, the present disclosure provides a method of predicting disease progression comprising: (a) obtaining a sample of breast tissue that is estrogen receptor negative, progesterone receptor negative and does not over-express human epidermal growth factor 2 receptor protein; and (b) determining the expression of glia maturation factor beta, wherein expression of glia maturation factor beta is indicative of an untreated or treated prognosis that is reduced compared to an absence of the expression.
Owner:ALPER BIOTECH
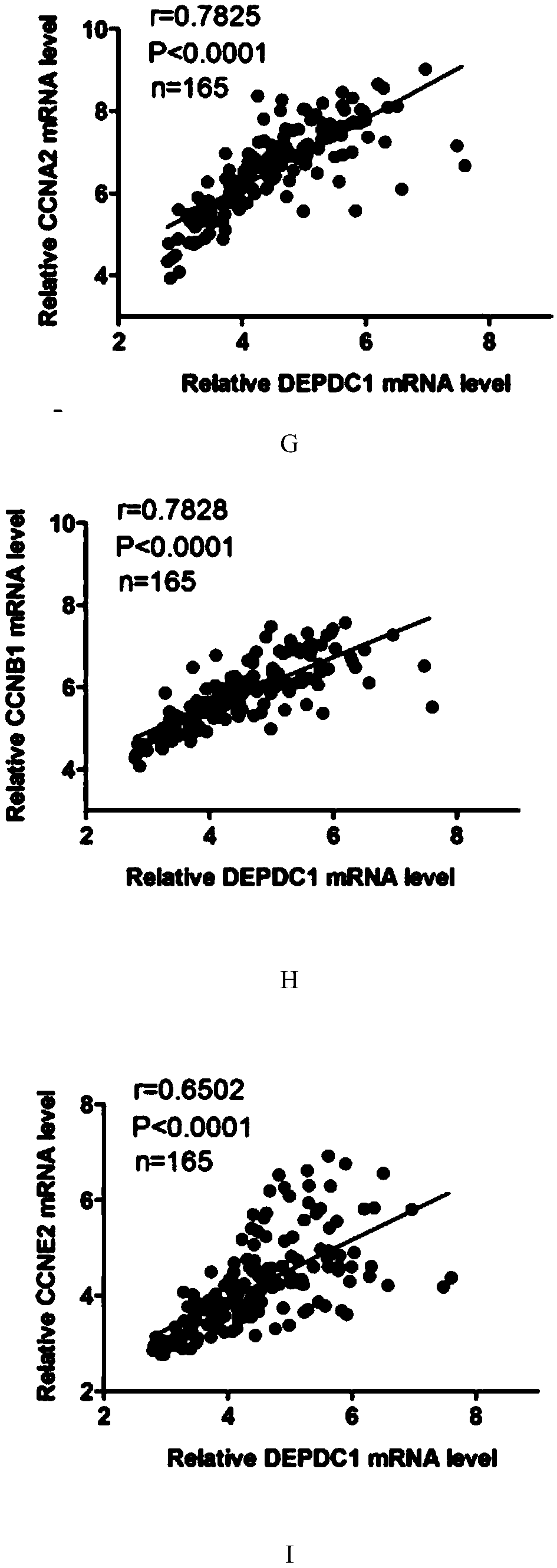
Application of protein DEPDC1 (Dishevelled and EGL-10, Pleckstrin Domain-Containing protein 1) as marker for diagnosing triple negative breast cancer
ActiveCN109321656APositive and obvious technical effectPromote growthOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell growthWilms' tumor
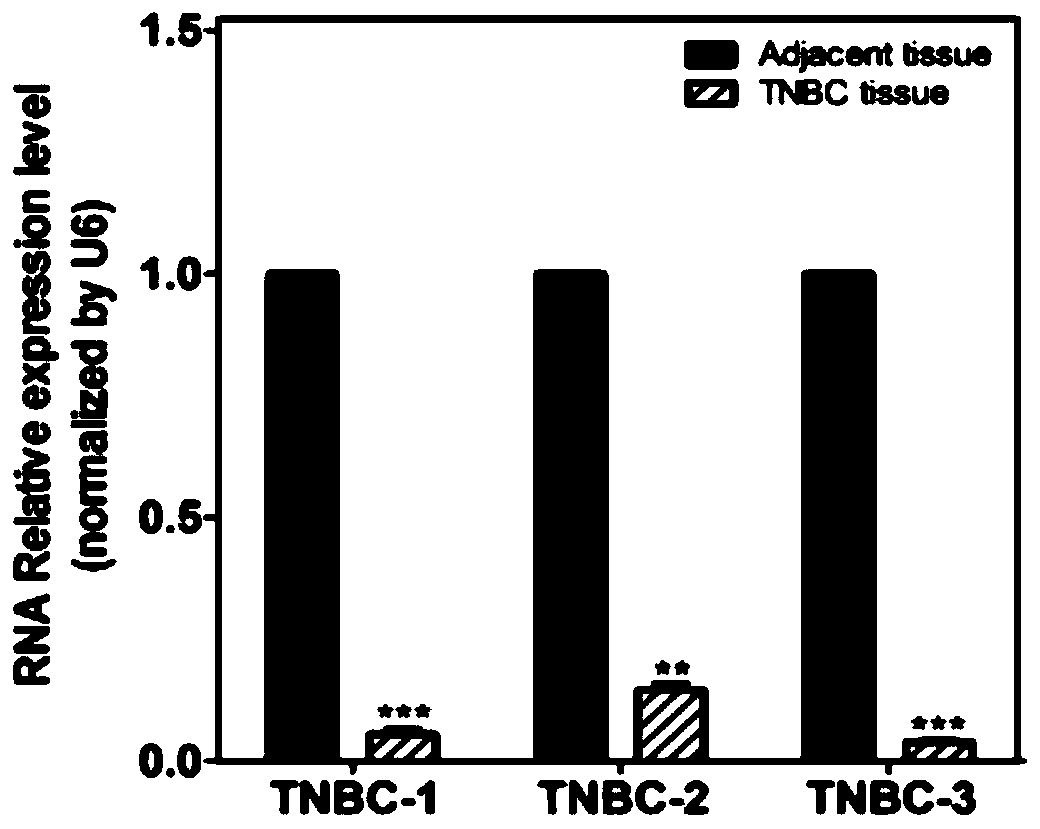
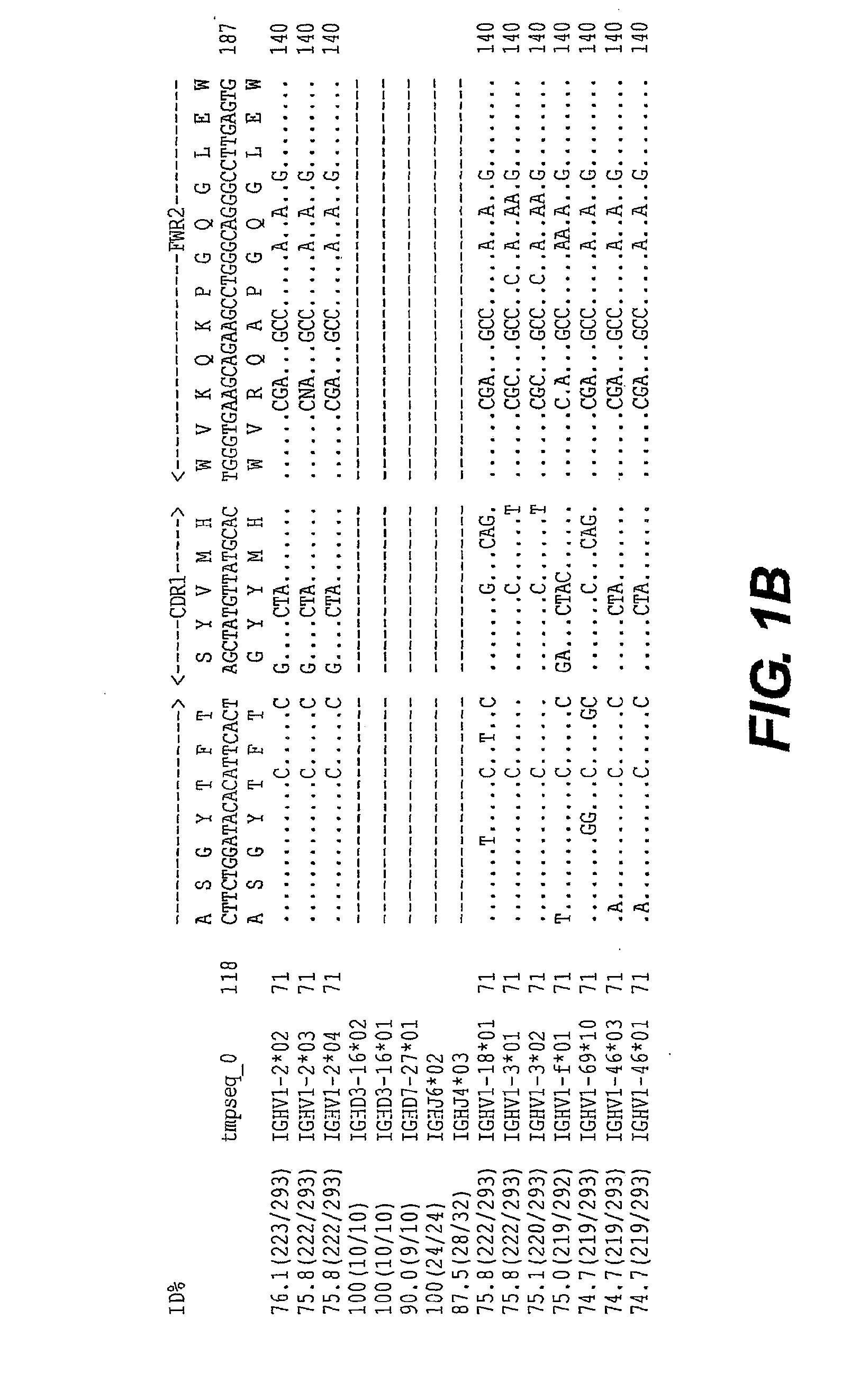
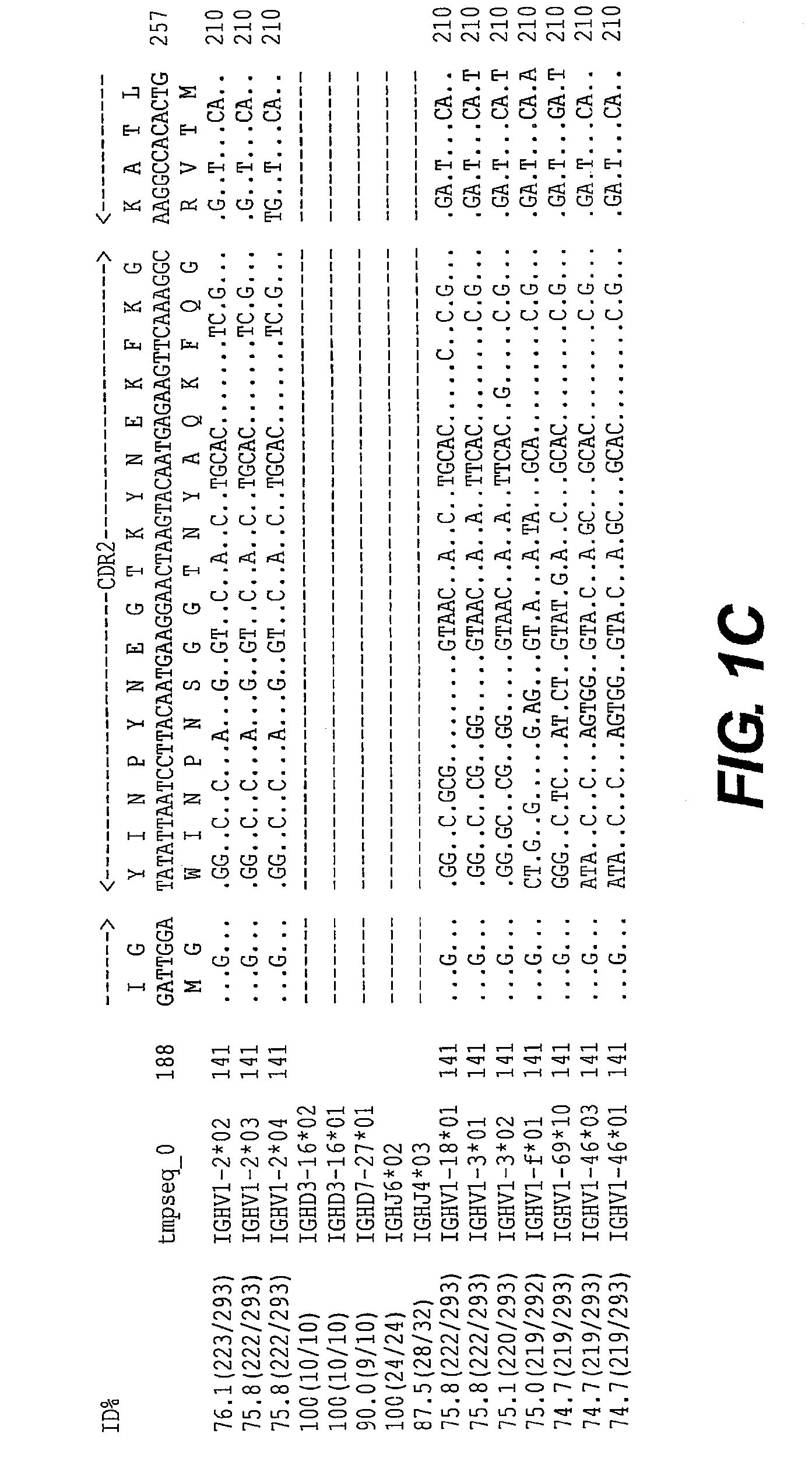
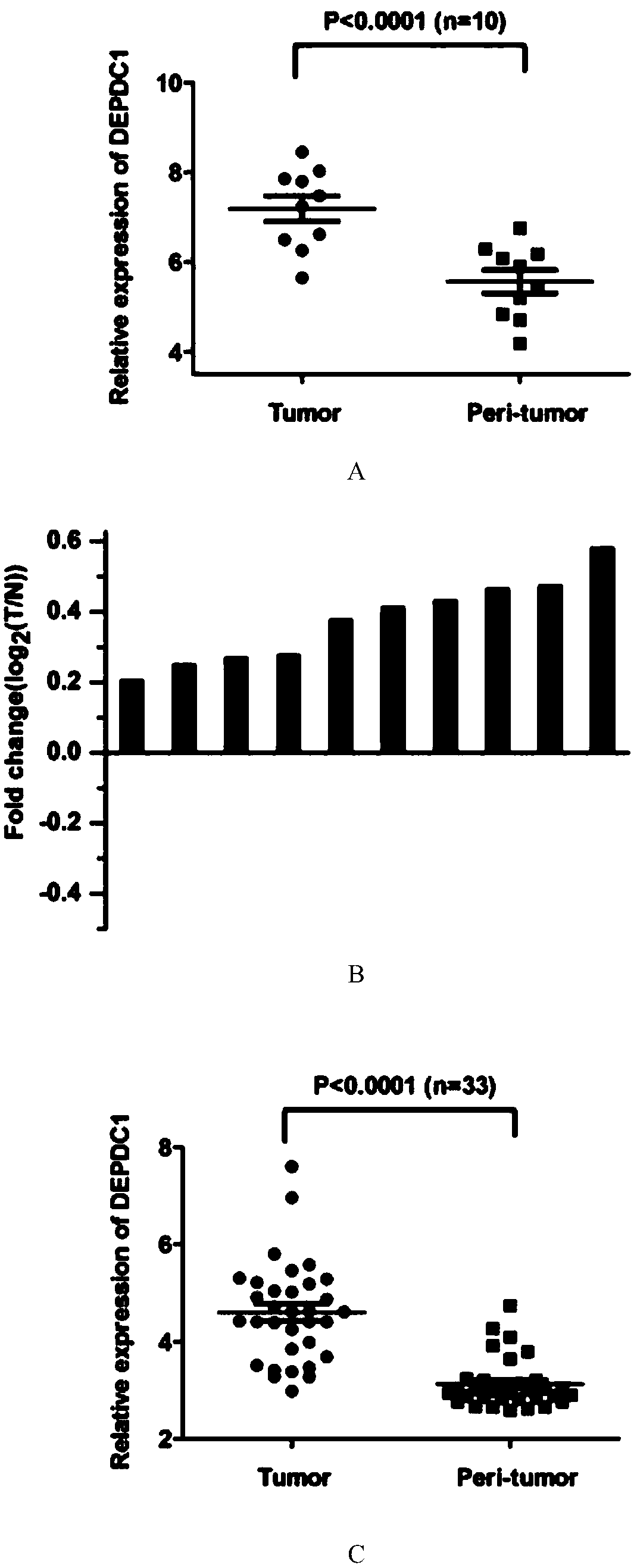
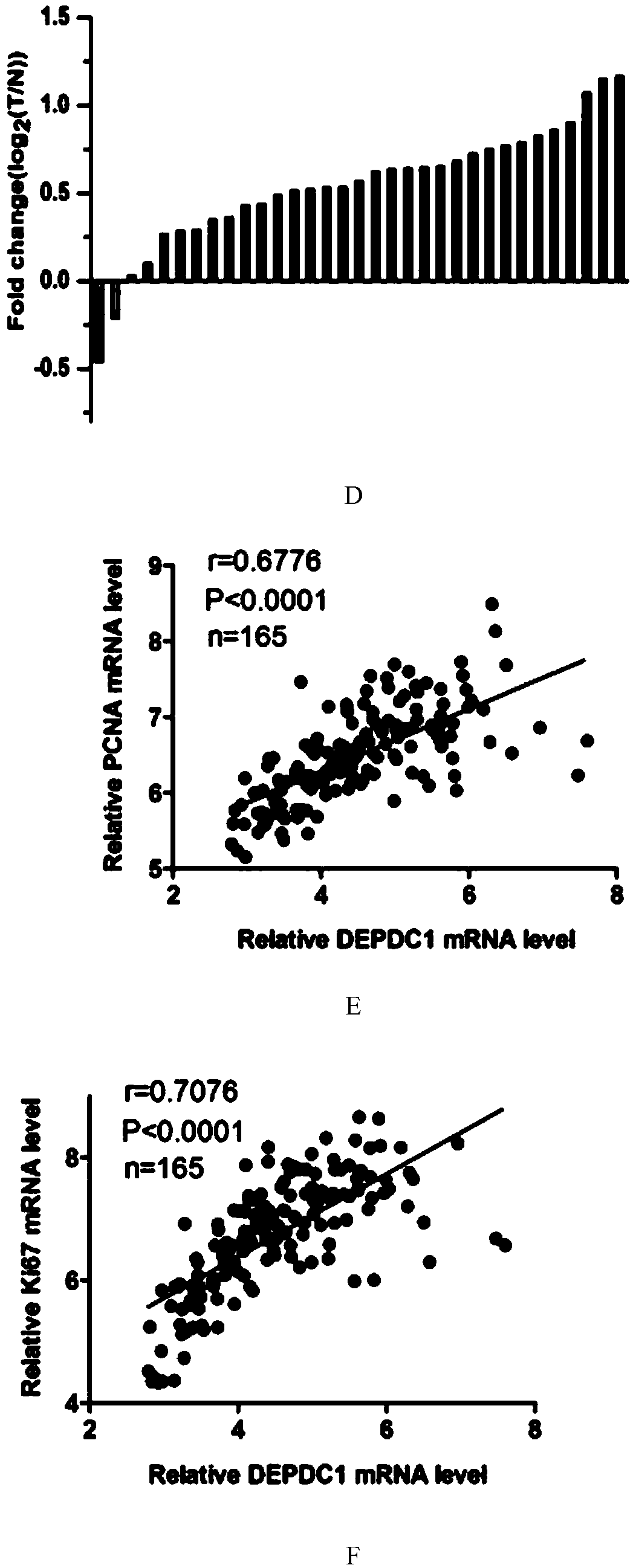
The invention provides application of protein DEPDC1 (Dishevelled and EGL-10, Pleckstrin Domain-Containing protein 1) as a marker for diagnosing the triple negative breast cancer, and also provides application of miR-26b for preparing a medicine for treating the triple negative breast cancer. The invention also provides application of miR-26b for preparing a medicine for inhibiting DEPDC1 mRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) expression. The invention finds that DEPDC1 expression is obviously higher than a paired para-carcinoma tissue in a triple negative breast cancer tissue. In the triple negative breastcancer cell, overexpression DEPDC1 can accelerate cell growth and tumor formation through FOXM1 (Forkhead box protein M1) expression up-regulation. On the contrary, after the DEPDC1 is knocked down,an inverse function is displayed. In addition, in the triple negative breast cancer, miR-26b serves as a tumor inhibiting factor to directly inhibit DEPDC1 expression and weaken the acceleration function of the DEPDC1 for cell growth and clone formation. The invention points out a new important mechanism for the occurrence, the development, the regulation and the control of the triple negative breast cancer.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Inos-inhibitory compositions and their use as breast cancer therapeutics
InactiveUS20170020835A1Unexpected benefitEasy to useInorganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsRefractoryHuman breast
Disclosed are methods for treating one or more mammalian cancers, and in particular, methods for treating human breast cancer employing one or more iNOS pathway-inhibitory compounds, either alone, or in combination with one or more selected antihypertensive agents, including calcium channel antagonists, either alone, and further in combination with one or more conventional chemotherapeutic or anti-cancer regimens. Also disclosed are particular therapeutic formulations including these compositions, and methods for their use in treating refractory, metastatic, and relapsed cancers, and for managing or reversing treatment resistance in human triple-negative breast cancers in particular.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL
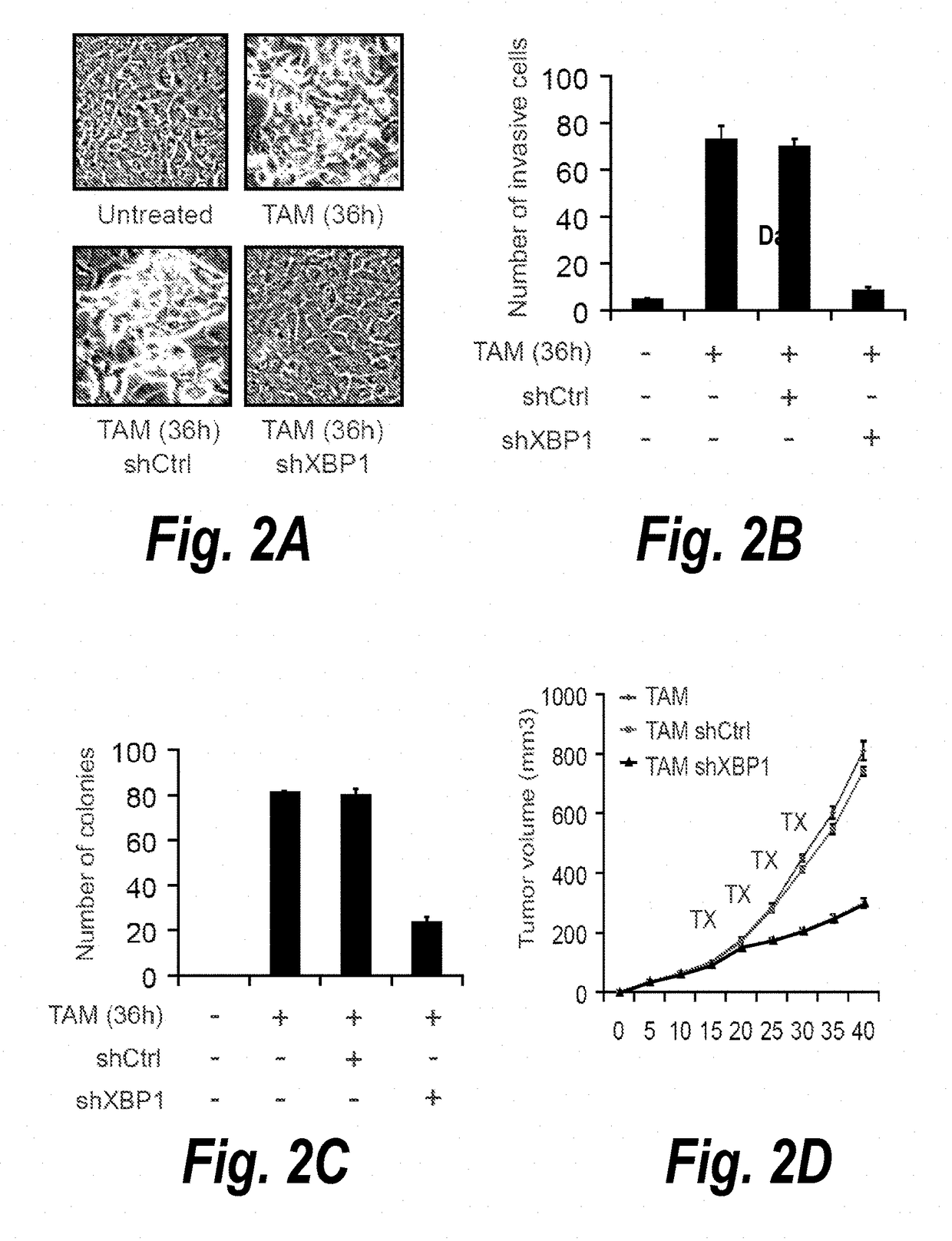
Modulation of breast cancer growth by modulation of xbp1 activity
ActiveUS20170240903A1Treatment option is limitedSuppressed growth and invasivenessCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsXBP1Short survival
Described herein is a previously unknown function of XBP1 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). It is shown that XBP1 is preferentially spliced and activated in TNBC, and that deletion of XBP1 significantly blocks triple negative breast tumor growth. Strikingly, XBP1 is required for the self-renewal of breast tumor initiating cells (TICs). Genome-wide mapping of the XBP1 transcriptional regulatory network identified a fundamental role for XBP1 in regulating the response to hypoxia via the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α). Importantly, activation of this pathway appears to carry prognostic implications, as expression of the XBP1-dependent signature is associated with shorter survival times in human TNBC.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
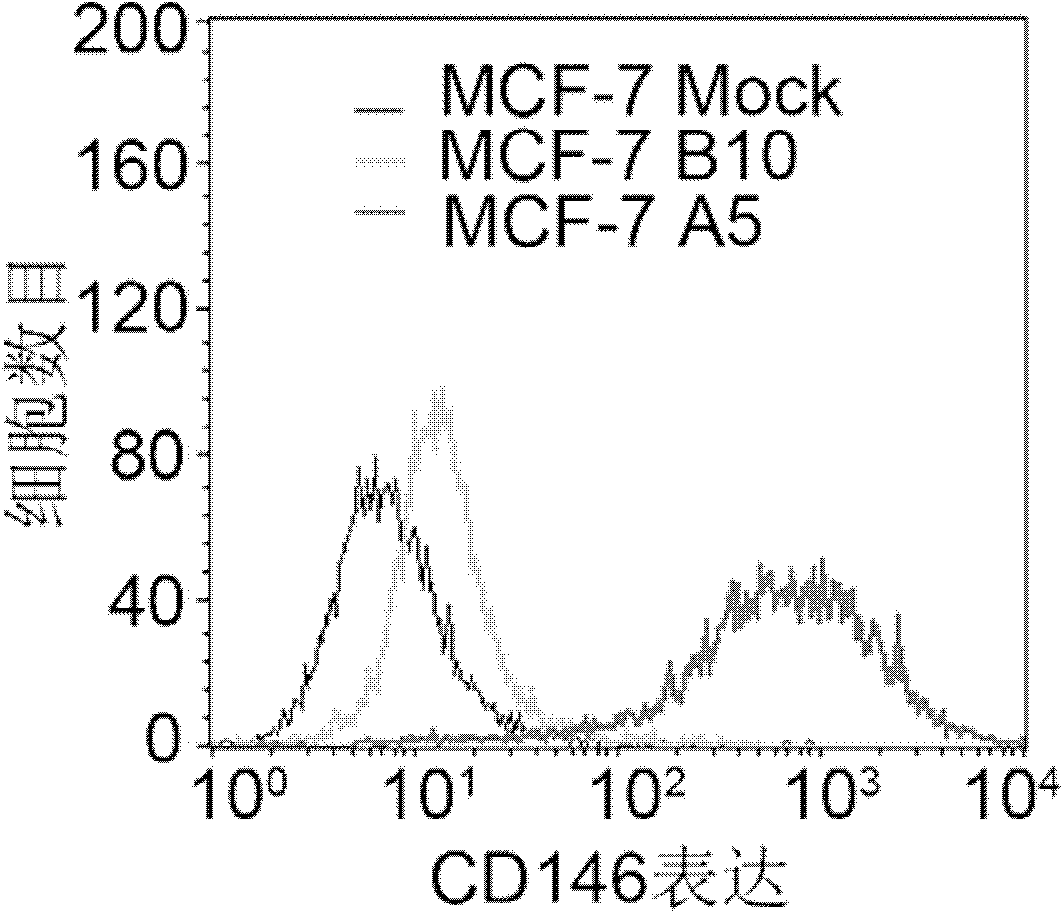
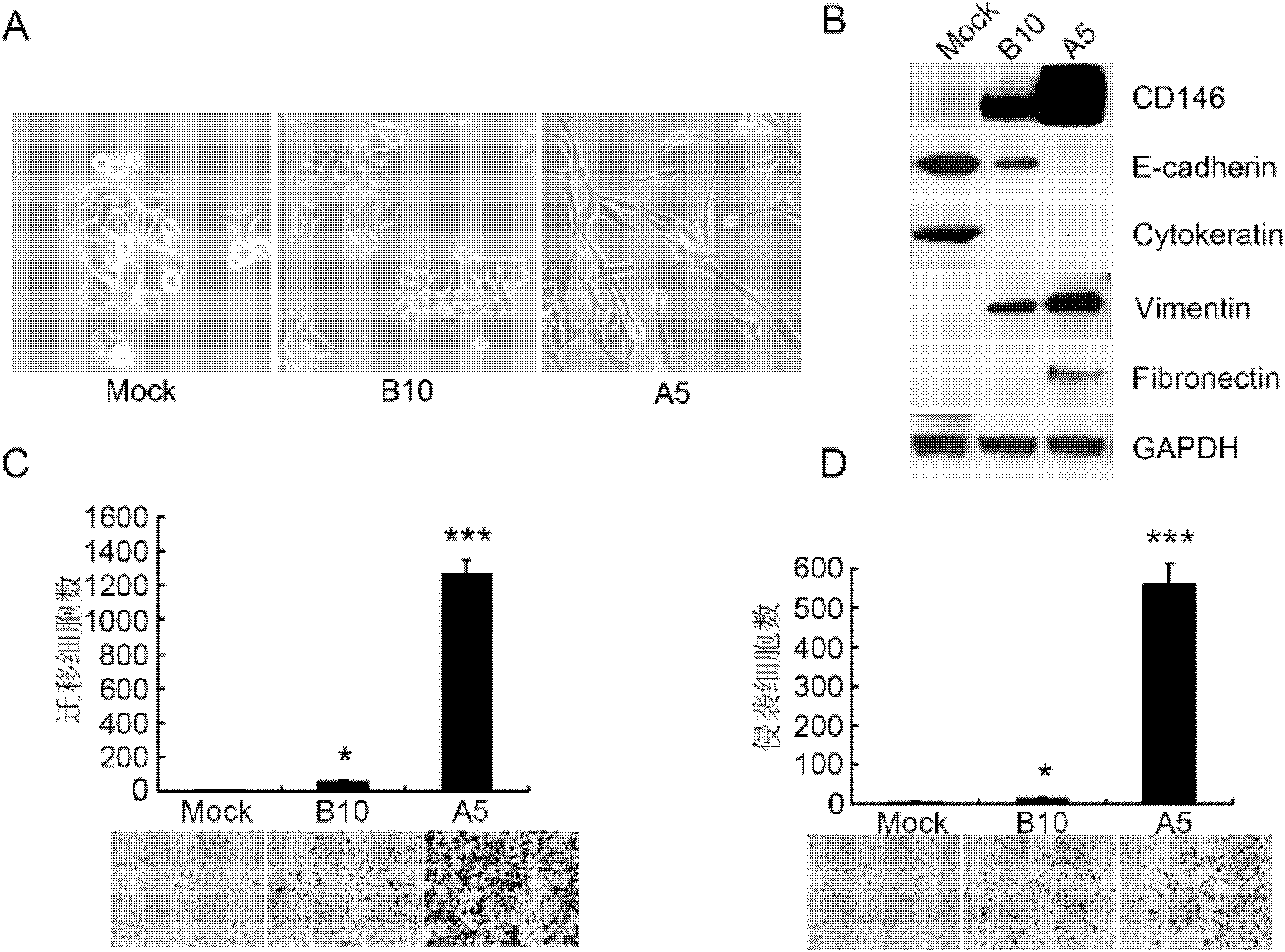
CD146 and antibody diagnosis thereof, and application in treating triple negative breast cancer
The invention relates to CD146 and antibody diagnosis thereof, and an application thereof in treating triple negative breast cancers. For a first time, the invention provides that CD146 is a novel target of triple negative breast cancer, and an anti-CD146 antibody might become a novel targeting medicine for treating the disease. Therefore, the invention provides an application of CD146 or anti-CD146 antibody or a functional form of the antibody in preparing medicines used for diagnosing and / or treating triple negative breast cancers. CD146 molecules are subjected to specific high expression in triple negative breast cancer tissues, and induce the occurrences of transformation of epithelial cell to mesenchymal cell in tumor cells. Therefore, tumor invasion migration is promoted. Therefore, the mechanism for CD146 antibody to treat triple negative breast cancer is mainly that the CD146 antibody inhibits the mesenchymal cell characteristics of triple negative breast cancer, and reduces the metastasis invasion capacity thereof. Compared with common chemotherapy medicines, the anti-CD146 antibody has the advantages of low side effects and clear target. The anti-CD146 antibody does not cause whole-body side effect.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
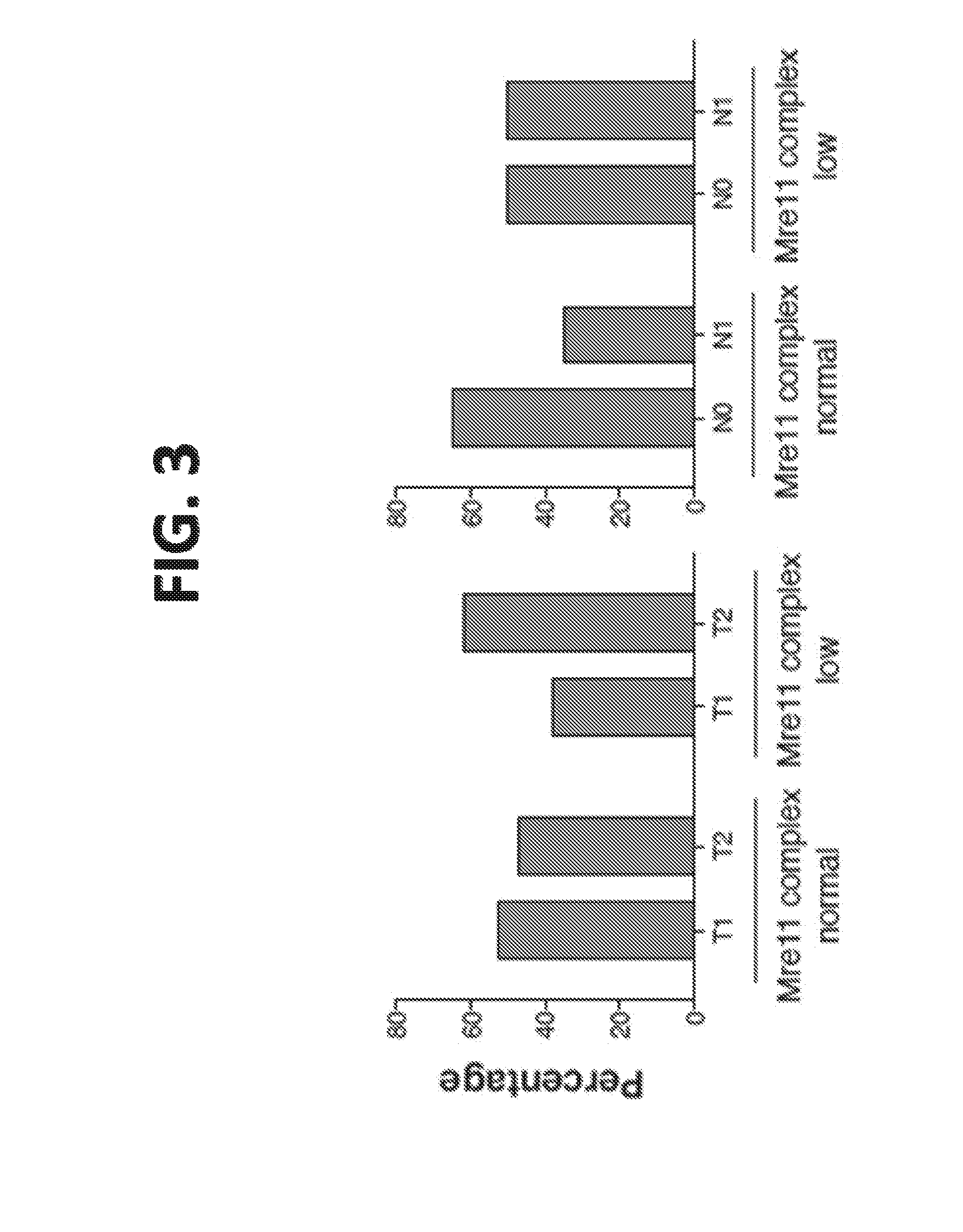
Compositions and methods for the treatment of cancers associated with a deficiency in the mre11/rad50/nbs1 DNA damage repair complex
InactiveUS20150313922A1Excessive levelHigh sensitivityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCytotoxicityHormones regulation
Provided are compositions and methods for the identification and treatment of cancers exhibiting reduced MRE11 / RAD50 / NBS1 (MRN) complex formation and / or functionality as well as methods for the identification and use of cytotoxic agents, including clastogenic agents, for the treatment of cancers exhibiting reduced MRN complex formation and / or functionality. Also provided are methods for detecting and treating cancers, in particular breast cancers, such as hormone-negative breast cancers (HNBCs) and triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs), colorectal cancers, urothelial cancers, and other cancers that exhibit reduced MRN complex formation and / or functionality and are correspondingly sensitive to growth and / or survival inhibition by one or more cytotoxic agents.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
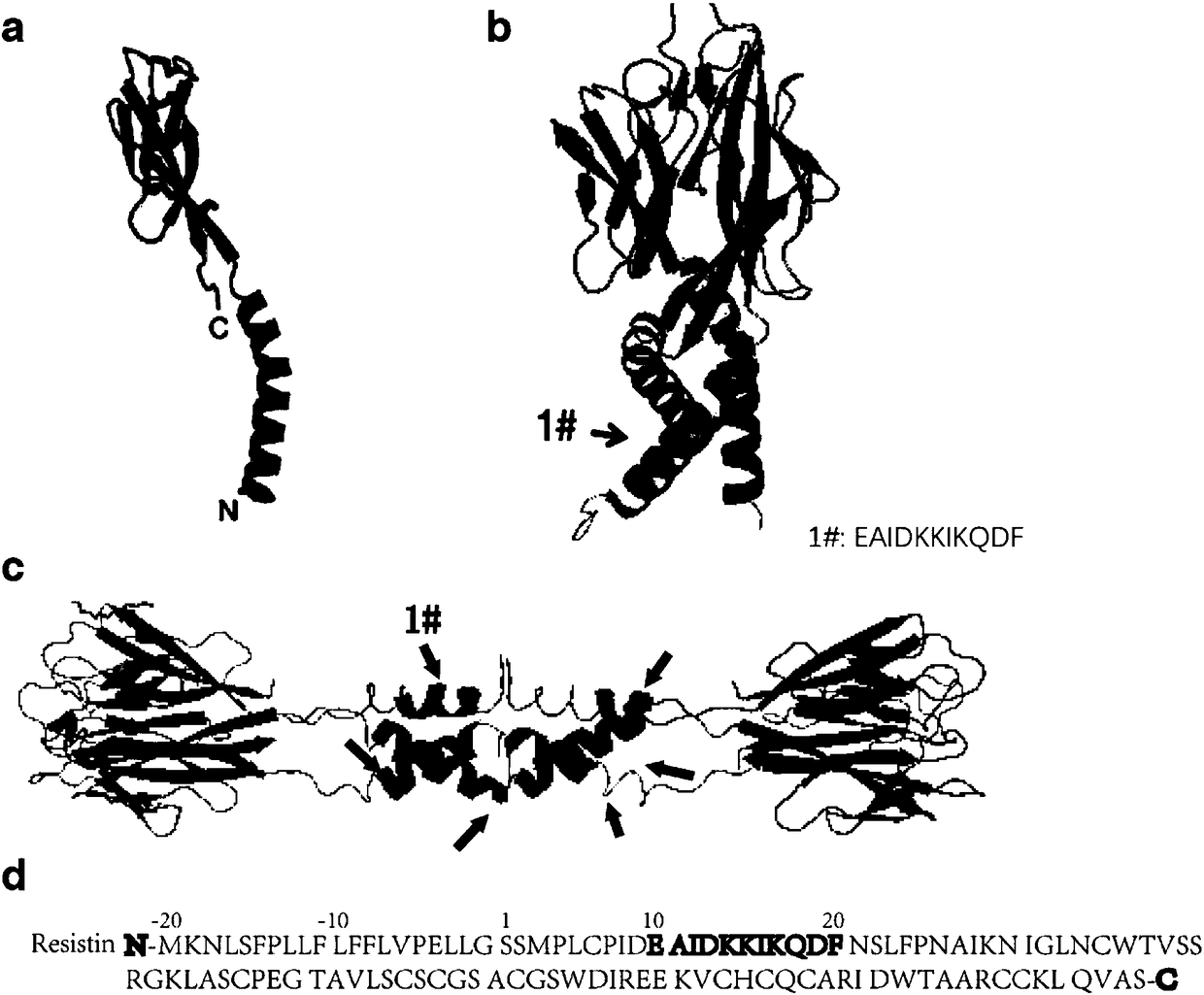
Resistin polypeptide vaccine and application thereof to treatment of mammary cancer
ActiveCN108379568AGrowth inhibitionPromote growthPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsSubcutaneous injectionLymphocyte
The invention discloses a resistin polypeptide vaccine and application thereof to the treatment of a mammary cancer, and belongs to the technical field of biology. A polypeptide vaccine provided by the invention is prepared from a Resistin-protein specific polypeptide segment and an immunologic adjuvant, and becomes the Resistin polypeptide vaccine. Through multiple subcutaneous injections, the vaccine can be used for activating the lymphocyte of an organism, and generates an immune neutralizing antibody aiming at Resistin protein. The Resistin polypeptide vaccine does not influence the sugartolerance and insulin tolerance levels of the organism at all. The Resistin polypeptide vaccine can be used for obviously inhibiting the growth of an ER (Estrogen Receptor) positive mammary tumor anda triple-negative mammary tumor under a mouse model; in addition, the Resistin polypeptide vaccine can be used for obviously inhabiting the growth of the ER positive mammary tumor and the triple-negative mammary tumor of a mouse under an obesity model induced by a high fat diet, and a new way is provided for ameliorating a current treatment method of the mammary cancer by the resistin polypeptidevaccine.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
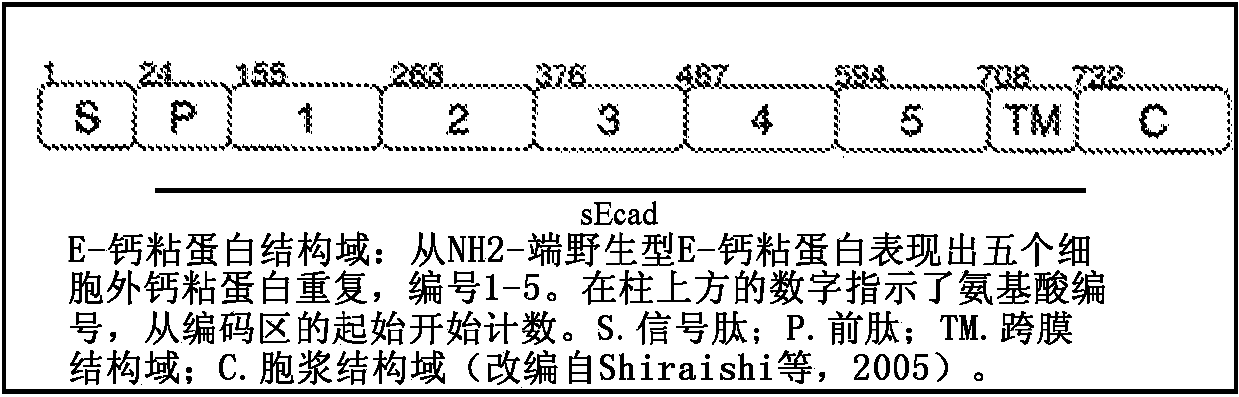
Combination therapies including inhibitors of the extracellular domain of E-cadherin
InactiveCN104519899AGrowth factor receptorPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTube formationLymphatic Spread
The present invention is based on our work with E-cadherin, including soluble portions of this integral membrane glycoprotein. The compositions of the present invention include therapeutically effective amounts of a first agent that targets epitopes within one or more of the EC2-EC5 subdomains of the ectodomain of E-cadherin (induing these domains in the shed sEcad fragment) and a second agent that inhibits one or more of: endothelial tube formation; angiogenesis; the human epidermal growth factor receptor family (i.e. HER1-4); an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R); any other receptor tyrosine kinase receptor family member; the P13K-MAPK pathway; and the P13K / Akt / mTOR pathway. The compositions can be used in the treatment of epithelial cancers, and may effectively inhibit cellular proliferation, migration, and / or invasiveness. Thus, the present compositions can be used to inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. The present compositions can be used in the treatment of "triple negative" breast cancer patients (in whom breast cancer cells test negative for estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and HER2), as well as HER2 -positive and other HER2 -negative tumors. In addition to therapeutic and prophylactic treatment methods, the invention features methods in which cancer is staged depending on the relative amounts of full-length (FL) E-cadherin and soluble E-cadherin (sEcad) and / or with another predictive biomarker for cancer. The greater the amount of sEcad relative to the amount of FL E-cadherin, the more advanced the cancer.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Biomarker for breast cancer
ActiveUS20140106377A1Easy diagnosisEffective cancer therapyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingIntraductal breast papillomaHigh level expression
A method for the diagnosis of breast cancer using an anti-LAT1 monoclonal antibody. Among intraductal breast neoplastic lesions, duct carcinoma in situ, which is malignant, expresses LAT1 at a significantly high level, as compared to intraductal breast papilloma, which is benign. An anti-LAT1 monoclonal antibody is useful for the discrimination between these two lesions. Further, LAT1 is expressed at a high level in most of triple negative infiltrating carcinomas, which are negative for all of ER, PgR, and HER2 that are conventional molecular targeting markers for breast cancer. Therefore, LAT1 can be used as a novel molecular targeting marker for the triple negative breast cancer.
Owner:J PHARMA
Methods and compositions for tnbc stratification and treatment
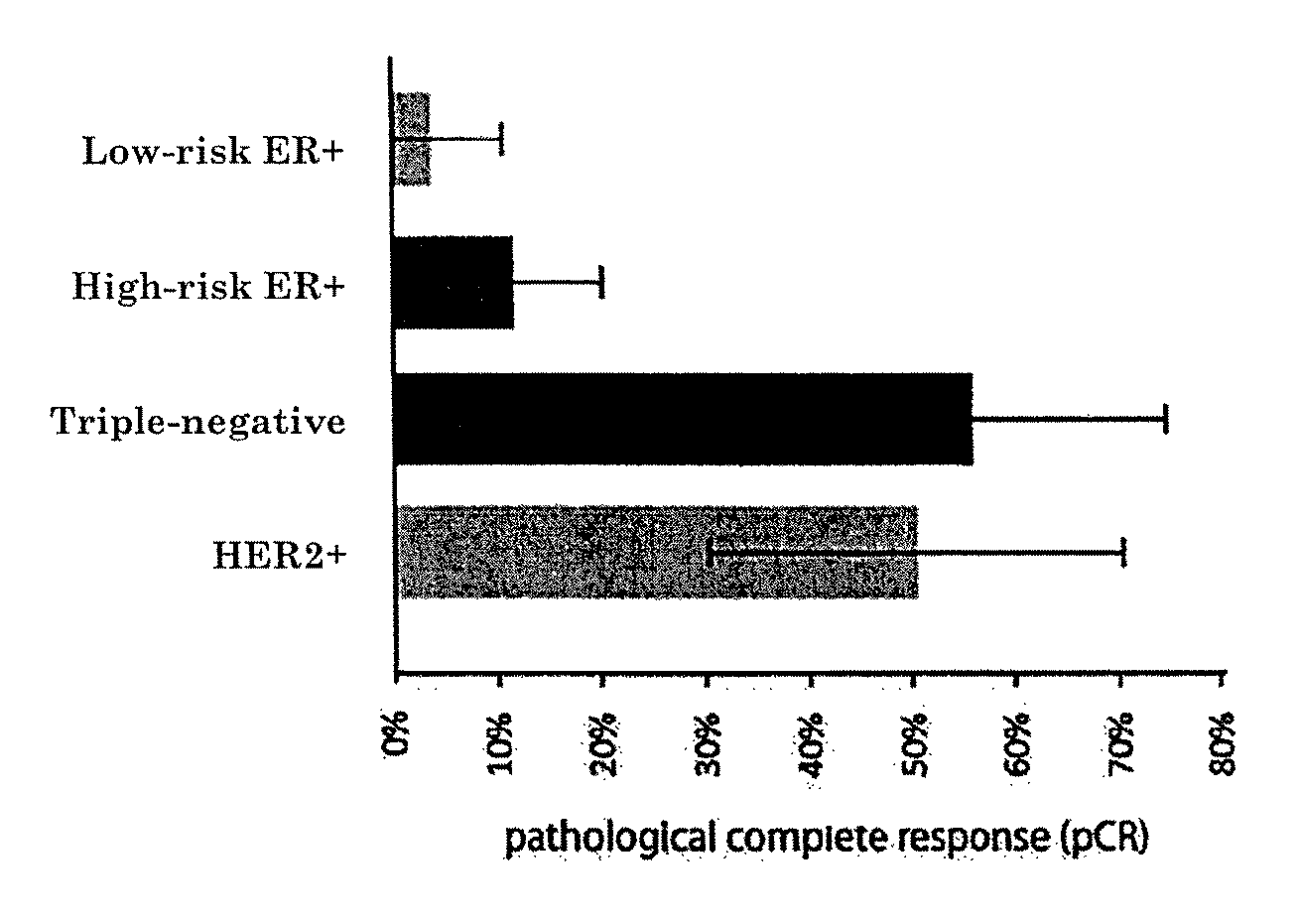
PendingCN111656194AGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsBiological material analysisET combinationOncology
Provided herein are methods for diagnosing and / or treating a new subtype of triple negative breast cancers (TNBC), as well as compositions and kits that can be used in such methods.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (ptpn11) and triple-negative breast cancer
The present invention relates to a method for treating breast cancer in a subject having a breast cancer of the triple-negative type, which method comprises the step of administering to said subject a therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) gene or of its gene product (Shp2). The present invention also relates to a method for treating breast cancer in a subject having a breast cancer over-expressing the “SHP2 signature” genes, as compared to normal breast tissue samples, which method comprises the step of administering to said subject a therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (PTPN11) gene or of its gene product (Shp2), wherein said “SHP2 signature” genes consist of the genes SGCB, ZSCAN12, ID4, ZIC3, CPVL, HLA-A, MCOLN3, SPATA18, TMEM45A, GNAL, CYBRD1, TSPAN7, ZEB1, CNTLN, NEFL, CENPV, ARL6, HPRT1, LRRC34, PDPN, BEND7, SLC16A10, FAM27E1, PLEKHA1, HERC5, CHIC1, PHF6, ELOVL4, ANTXR1, PRAME, SCML1, CLIP4, CECR2, CNOT10, IGF2BP3, NAP1L3, GPC3, KIAA1804, DGKE, FAS, EPHA6, KDELC1, CRISPLD1, DOCK3, ACSL4, CNTNAP3, PLEKHM3, RDX, TBX18, RRAGD, HOXB5, SNCA, FUNDC2, ITGA8, HFM1, IGF2BP2, CCND2, SGTB, MKX, CRYBG3, WBP5, LPHN3, BEX4, CPNE8, GLDC, SLC35F1, HOXA13, SERPINF1, NEFM, SYCP2L, FHL1, APOBEC3C, CALD1, FKBP10, HOXD11, DENND2C, LRRC49, FAM55C, KIAA0408, HOXB9, C160RF62, ACN9, TUSC3, ELOVL2, SPOCK3, HOXB6, WDR35, MPP1, FBX038, PRKAA2, SLAIN1, NPHP3, KIAA1524, PRPS1, GJC1, AMOT, SLC9A6, KCTD12, NUP62CL, DZIP3, JAM3, HOXA9, ANKRD19, CDKN2A, BCAT1, OAT, LPHN2, CCDC82, HSD17B11, SAMHD1, WDR17, STK33, GSTP1, TRPC1, CKB, LIN28B, ALDH1L2, SACS, CLGN, MY03A, EPB41L3, SLC25A27, VCAN, GPX8, GALNT13, PVRL3, MOXD1, HEY1, MAP7D3, ESD, MPP6, EYA4, SPG20, ZDBF2, ZNF204, IFT57, AKR1B1, ADAT2, ZNF717, CCDC88A, ZNF215, MIDI, FBN2, LOC100130876, TCEAL8, IGF2BP1, ANKRD18B, PLAGL1, PM20D2, LDHB, C150RF51, PTPN11, EPB41L2, TLE4, GOLM1, C60RF192, HOXD13, SLIT2, UCHL1, DYNC2H1, CPS1, GPR180, PYGL, NRN1, PRTFDC1, SLC16A1, DSC3, TMC01, LRCH2, SLC6A15, DZIP1, HOXA5, HSPA4L, CDR1, PLS3, ECHDC1, SMARCA1, CXORF57, HOXD10, and IRS4.
Owner:NOVARTIS FORSCHUNGSSTIFTUNG ZWEIGNIEDERLASSUNG FRIEDRICH MIESCHER INSTITTUE FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
TGF beta2 gene, TGF beta 2 polypeptide and application thereof
InactiveCN105483134ARapid Molecular TypingMolecular typing is convenientMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTGF beta 2Oncology
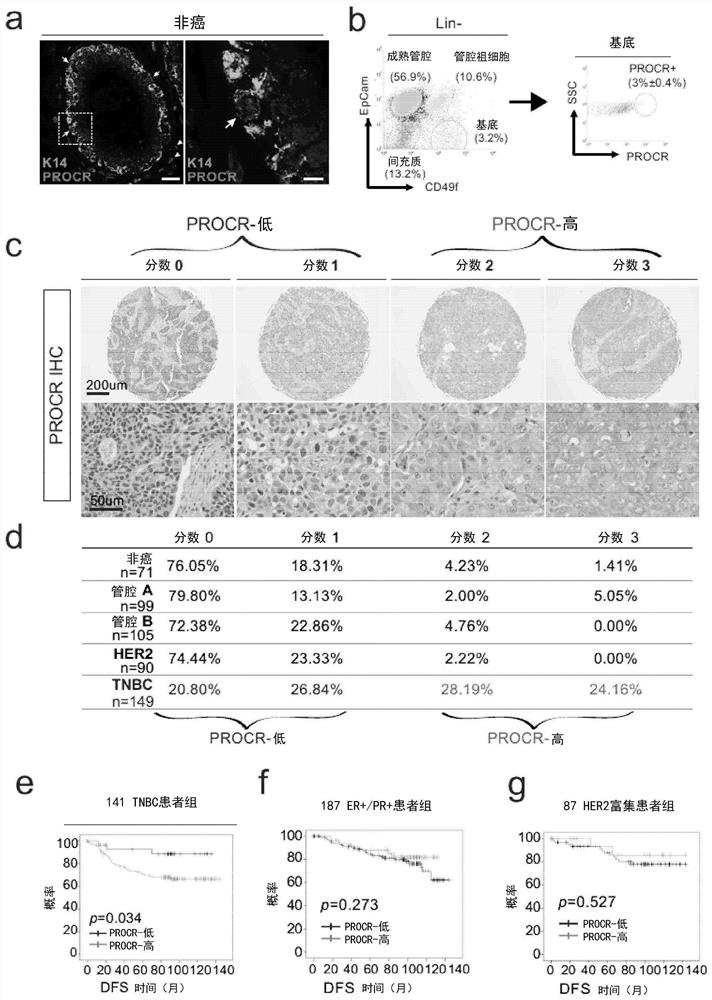
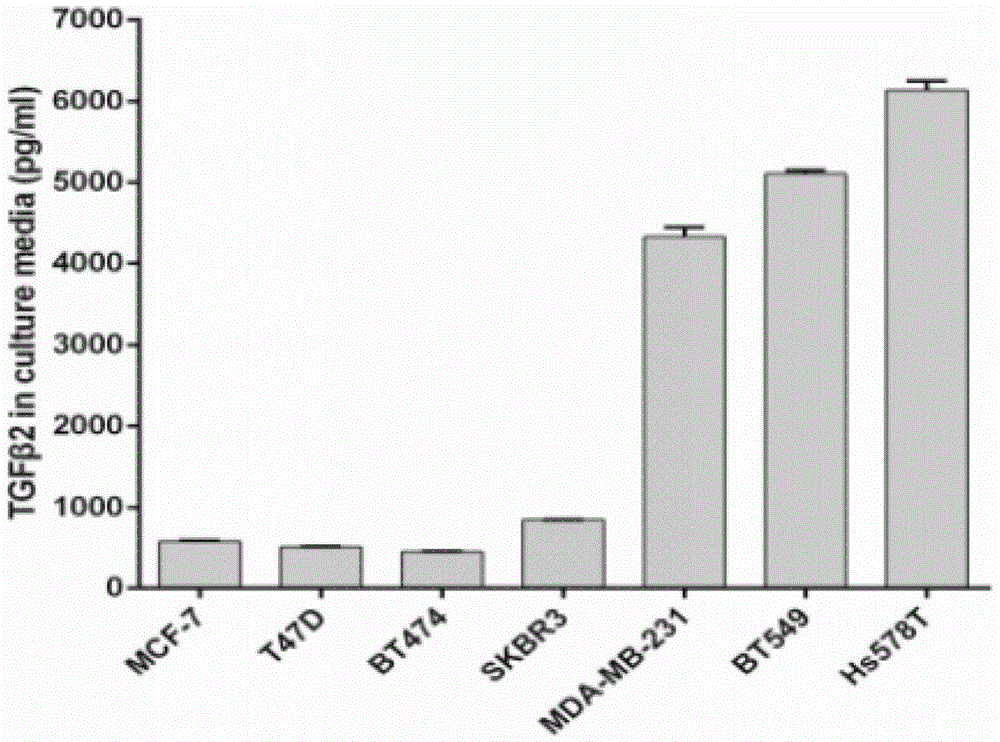
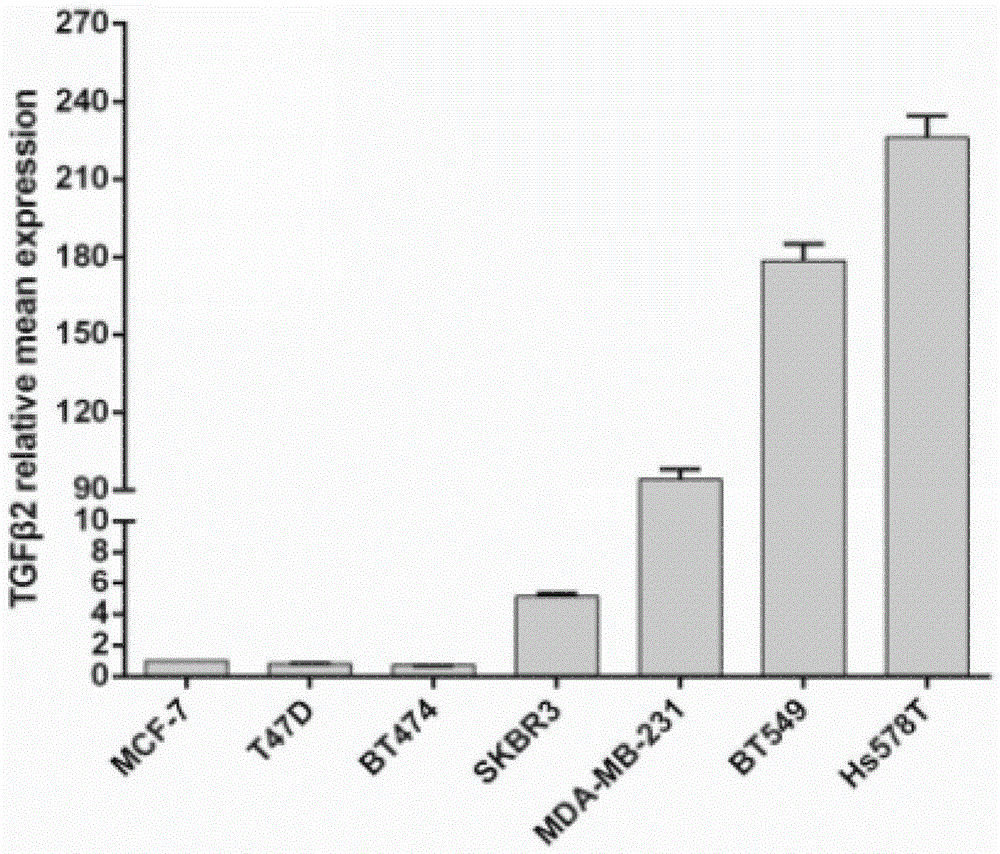
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and relates to a TGF beta2 gene, a TGF beta 2 polypeptide and application thereof, especially application thereof serving as novel molecular subtyping markers of breast cancer. The circumstance that increase of expression of the TGF beta 2 gene mainly occurs in triple negative breast cancer is verified for the first time, and expression of the TGF beta2 gene in serum of a patient with the triple negative breast cancer is obviously increased than in serum of patients of other molecular subtypes. Novel data are provided for molecular subtyping of the breast cancer, and a novel target and a serologic quick detection method are provided for detecting triple negative molecular subtyping of the breast cancer.
Owner:CANCER CENT OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Means and methods for molecular classification of breast cancer
ActiveUS20160115552A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBreast cancer classificationMolecular classification
The invention relates to a method of typing a sample from a breast cancer patient. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for classification of breast cancer according to the presence or absence of Estrogen Receptor (ER), Progesterone Receptor (PR) and Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2 (ERBB2; HER2). More specifically, the invention provides methods and means to classify breast cancer as ER positive, triple negative (ER−, PR− and HER2−) and HER2+.
Owner:AGENDIA NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com