Application of protein DEPDC1 (Dishevelled and EGL-10, Pleckstrin Domain-Containing protein 1) as marker for diagnosing triple negative breast cancer
A triple-negative breast cancer and marker technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of poor diagnosis and treatment of triple-negative breast cancer, and achieve the effect of promoting cell proliferation and tumor formation with obvious technical effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 DEPDC1 is upregulated in triple negative breast cancer
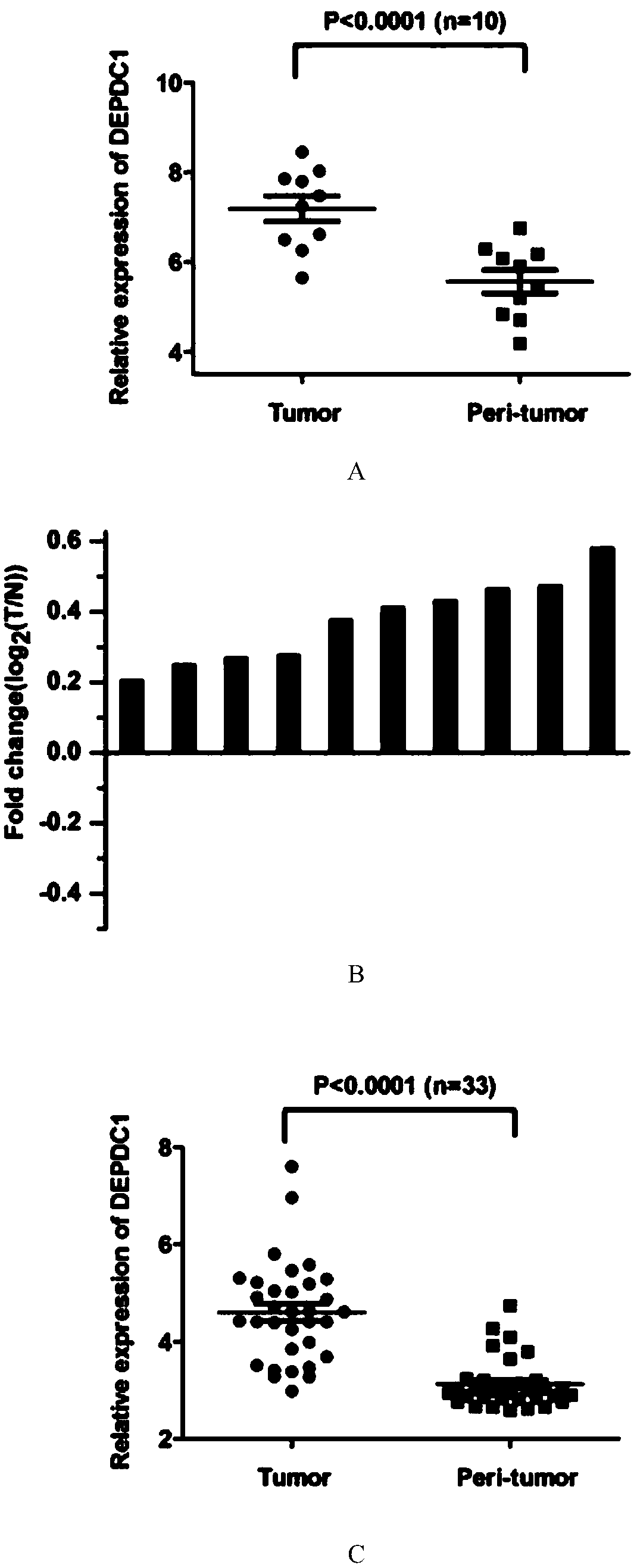
[0046] In order to clarify the role of DEPDC1 in triple-negative breast cancer, the present invention analyzed the data of two sets of chips (GSE76250 and GSE81838) on the Gene Expression Omnibus (website: http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / geo), The expression of DEPDC1 in triple-negative breast cancer and paired paracancerous tissues was clarified. as figure 1 As shown in A and 1B, DEPDC1 expression was significantly increased in TNBC tissues compared with paired paracancerous tissues. Similar results can also be obtained in other databases.
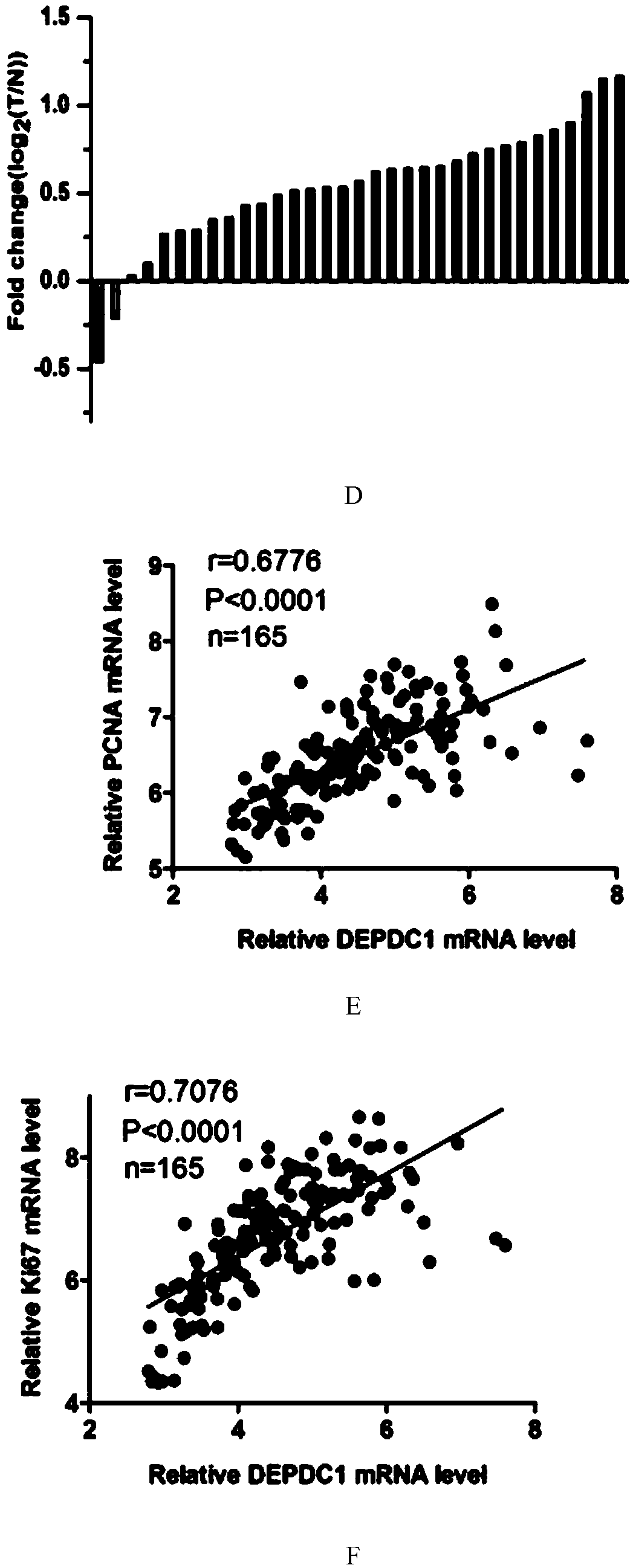
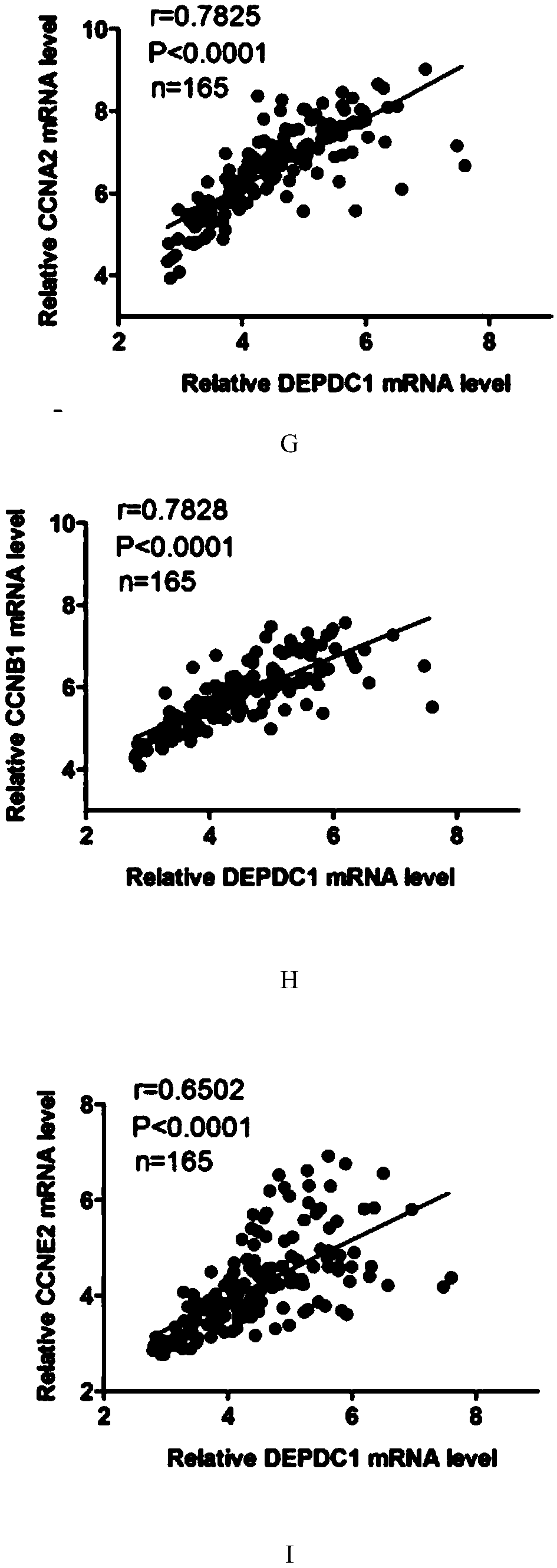
[0047] Among the 33 pairs of triple-negative breast cancer and adjacent tissues, the present invention found that the expression of DEPDC1 in most triple-negative breast cancer tissues was higher than that of adjacent tissues (see figure 1 C and 1D). Moreover, the expression of PCNA (nuclear proliferating antigen) and Ki67 (a marker of proliferation, an important in...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Overexpression of DEPDC1 in triple-negative breast cancer cells can promote cell proliferation and clone formation.
[0049] Then the present invention detects the mRNA expression of DEPDC1 in a group of triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. In these cells, endogenous DEPDC1 expression was significantly higher in MDA-MB-231 than in other cell lines, whereas DEPDC1 expression was lowest in MDA-MB-436 cells (see figure 2 A). Therefore, a DEPDC1 stable overexpression cell line was constructed in MDA-MB-436 cells.
[0050] Real-time quantitative PCR and western blot were used to detect the mRNA and protein expression levels of DEPDC1 to confirm the transfection efficiency ( figure 2 B and 2C). as image 3 As shown in A, the results of CCK-8 detection showed that the cell viability was significantly increased after the overexpression of DEPDC1. BrdU intercalation assay and PCNA expression were used to detect cell proliferation.
[0051] The present inve...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Knocking out DEPDC1 in triple-negative breast cancer can weaken cell proliferation
[0055] In order to determine the physiological function of DEPDC1 in triple negative breast cancer, the present invention also knocked down the expression of DEPDC in MDA-MB-231 cells. The knockout efficiency was also determined by real-time quantitative PCR and western blot ( Figure 4 A and Figure 4 B). like Figure 5 As shown in A, knockdown of DEPDC1 can inhibit the growth of MDA-MB-231 cells. Moreover, both BrdU inhalation and PCNA protein expression levels were attenuated by knocking out DEPDC1 ( Figure 5B and 5C). The results of cell cycle distribution showed that knockdown of DEPDC1 expression increased the proportion of tumor cells in G0 / G1 phase growth arrest (from 56.31% to 78.52%), accompanied by a decrease in S phase cells from 32.41% to 16.31% ( Figure 5 D).
[0056] like Figure 5 As shown in E, knockout DEPDC1 clone formation was inhibited in MDA-MB-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com