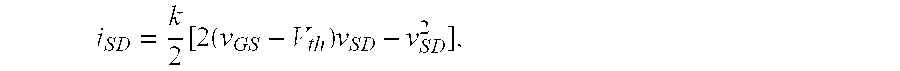Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
754 results about "Molecular recognition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
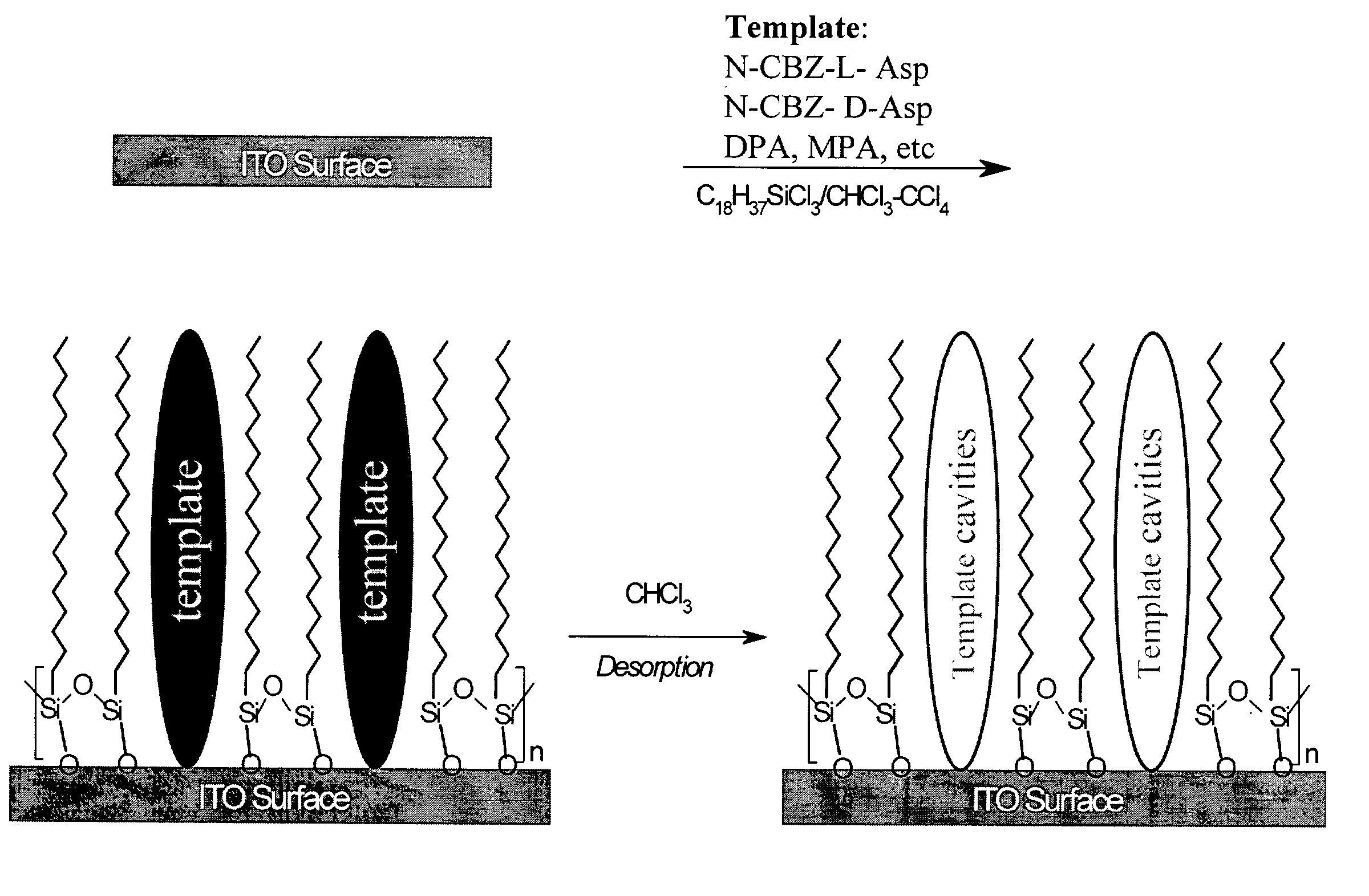
The term molecular recognition refers to the specific interaction between two or more molecules through noncovalent bonding such as hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, π-π interactions, halogen bonding, electrostatic and/or electromagnetic effects. In addition to these direct interactions as well solvent can play a dominant indirect role in driving molecular recognition in solution. The host and guest involved in molecular recognition exhibit molecular complementarity.Exceptions are molecular containers, including e.g. nanotubes, in which portals essentially control selectivity.
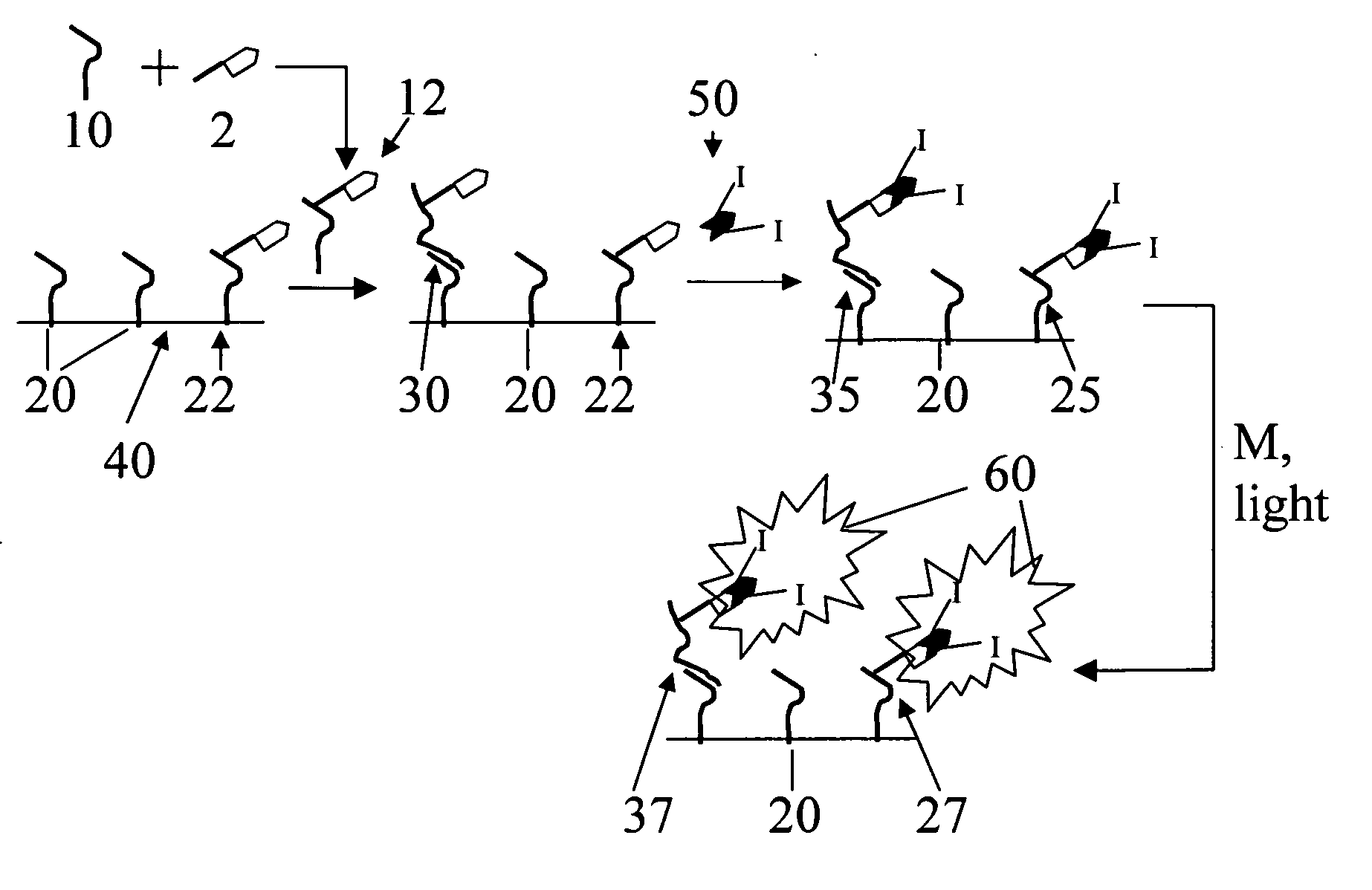
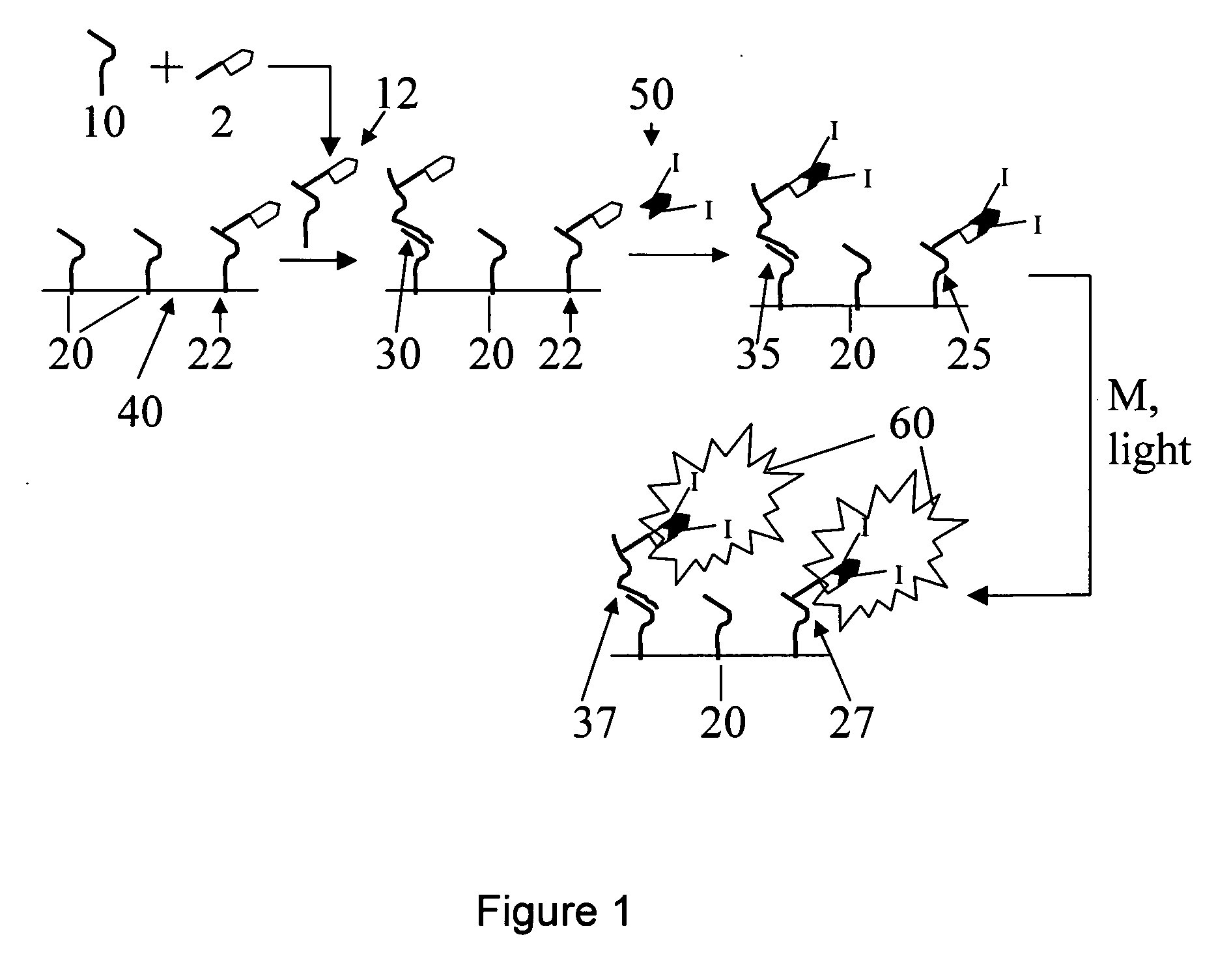
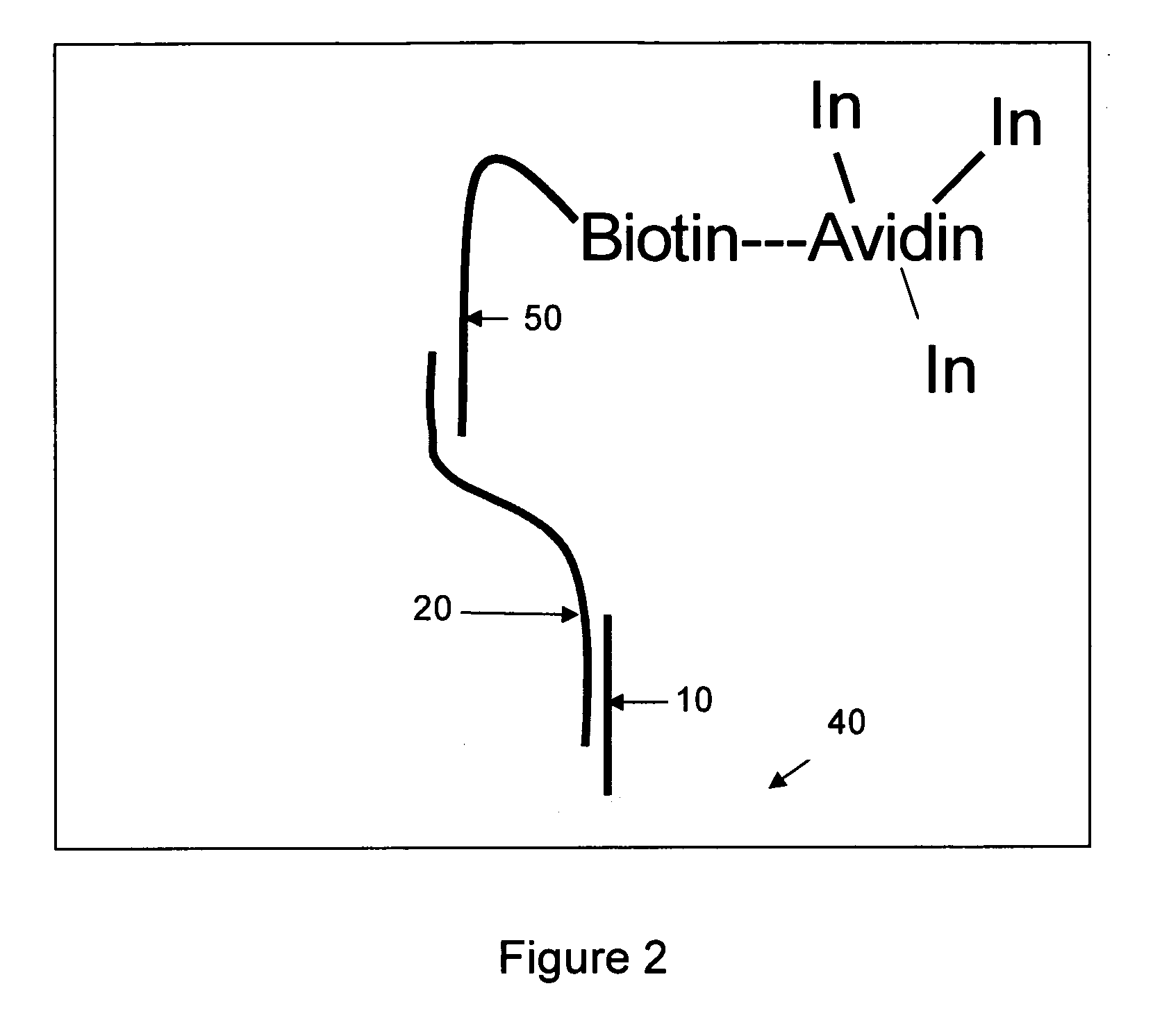
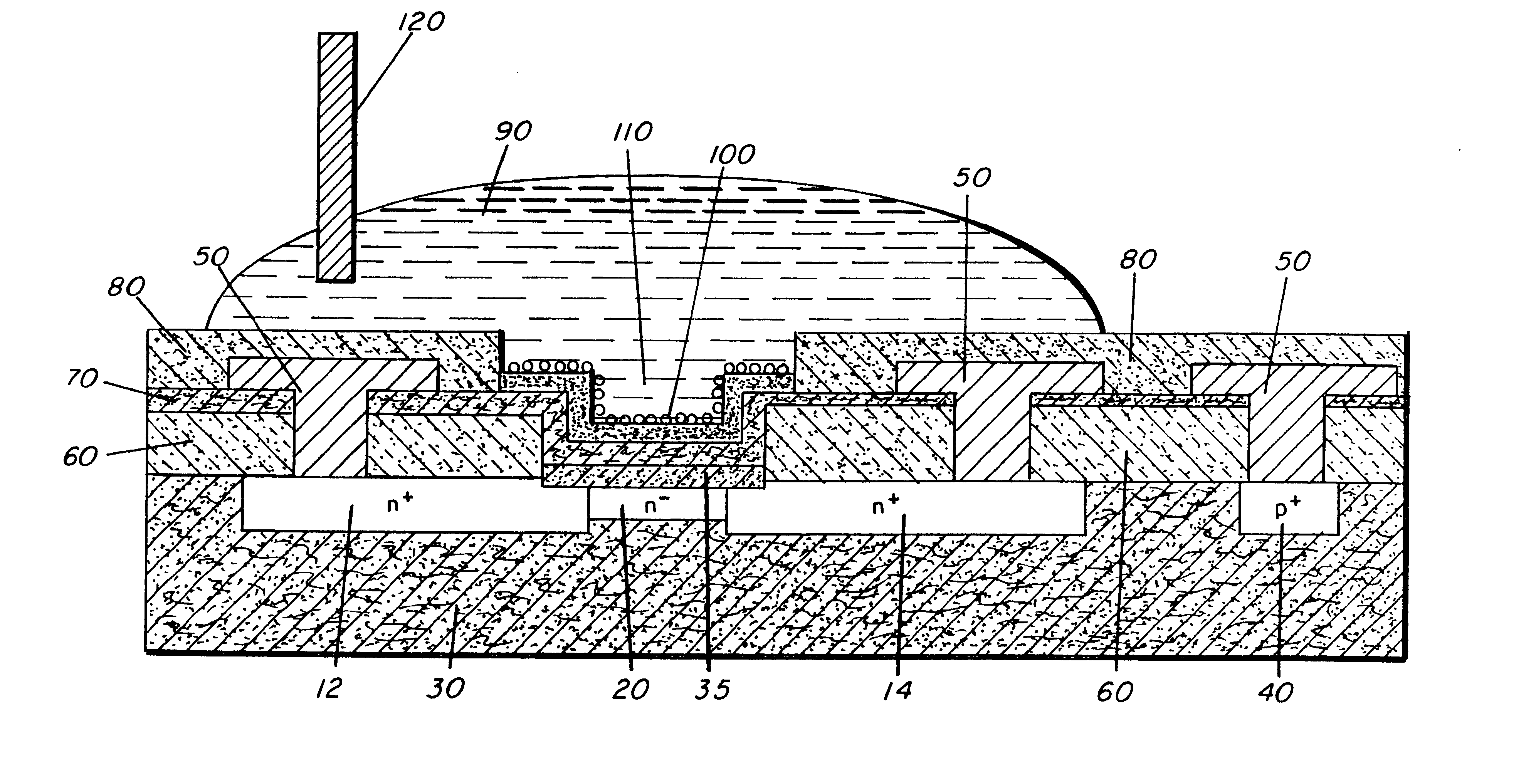
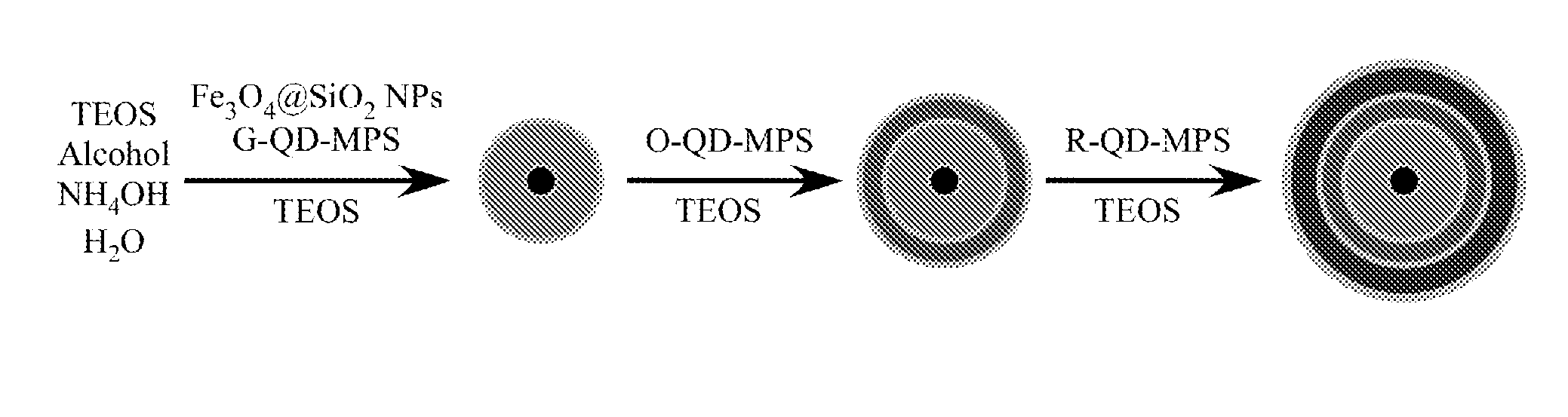
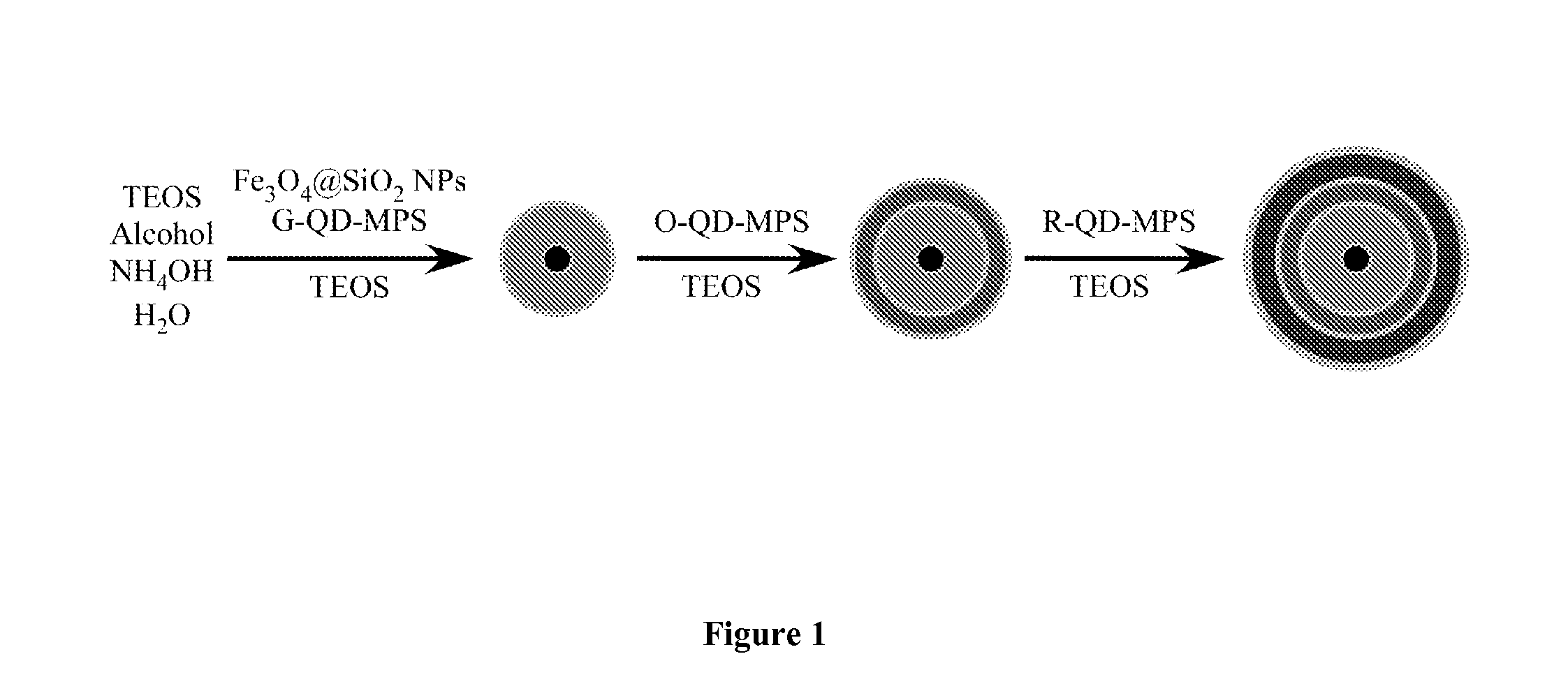
Use of photopolymerization for amplification and detection of a molecular recognition event
InactiveUS20060286570A1Increase the number ofReduce the numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescent polymerConductive polymer
The invention provides methods to detect molecular recognition events. The invention also provides methods to detect the presence of or identify a target species based on its interaction with one or more probe species. The methods of the invention are based on amplification of the signal due to each molecular recognition event. The amplification is achieved through photopolymerization, with the polymer formed being associated with the molecular recognition event. In an embodiment, a fluorescent polymer, a magnetic polymer, a radioactive polymer or an electrically conducting polymer can form the basis of detection and amplification. In another embodiment, a polymer gel swollen with a fluorescent solution, a magnetic solution, a radioactive solution or an electrically conducting solution can form the basis of detection and amplification. In another embodiment, sufficient polymer forms to be detectable by visual inspection.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
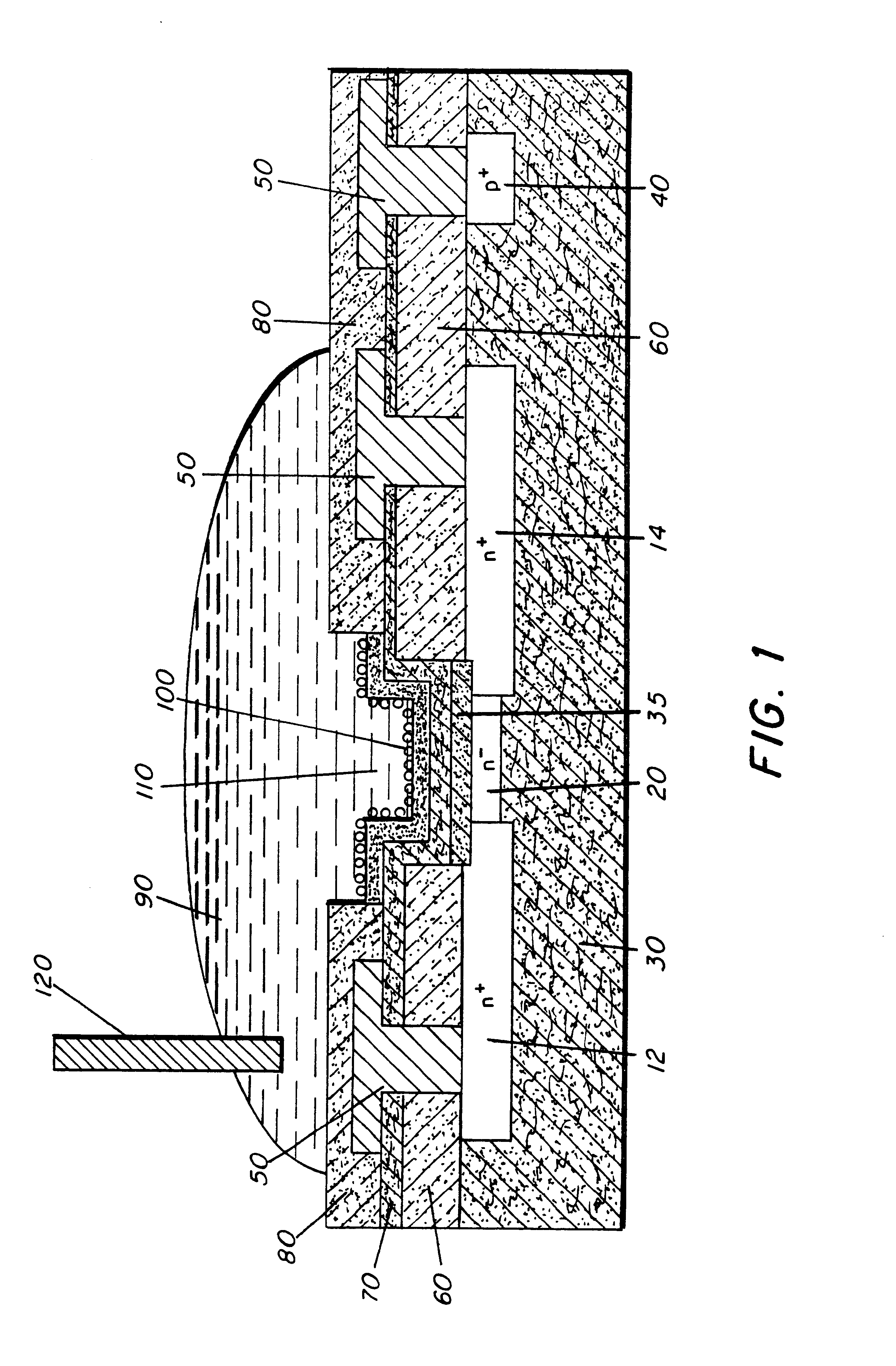
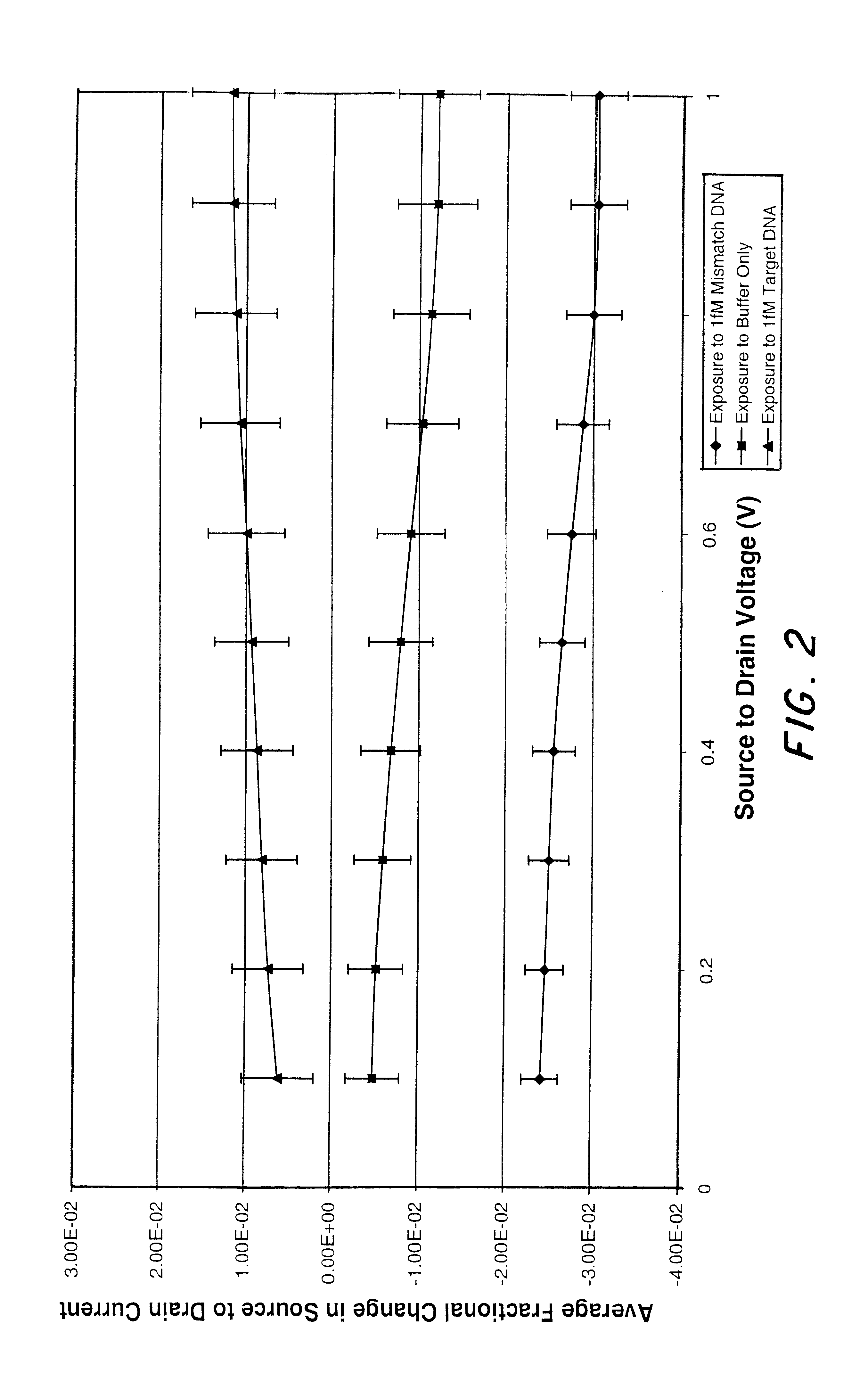
Microelectronic device and method for label-free detection and quantification of biological and chemical molecules
InactiveUS6482639B2Sensitive and accurate detectionWide scope of practical and worthwhile utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceField-effect transistor
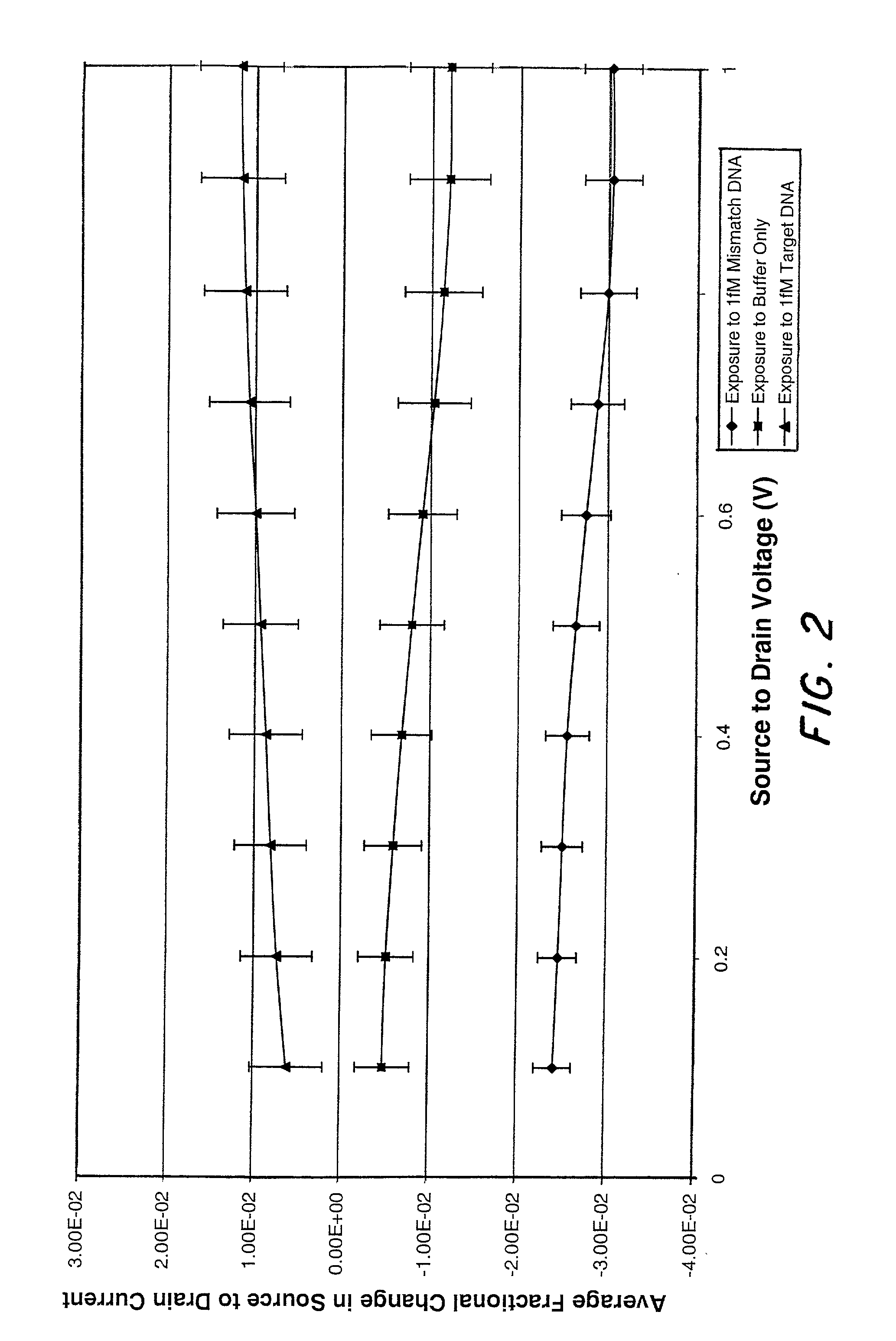
Molecular recognition-based electronic sensor, which is gateless, depletion mode field effect transistor consisting of source and drain diffusions, a depletion-mode implant, and insulating layer chemically modified by immobilized molecular receptors that enables miniaturized label-free molecular detection amenable to high-density array formats. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The conductivity of the active channel is determined by the potential of the sample solution in which the device is immersed and the device-solution interfacial capacitance. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The interfacial capacitance is determined by the extent of occupancy of the immobilized receptor molecules by target molecules. Target molecules can be either charged or uncharged. Change in interfacial capacitance upon target molecule binding results in modulation of an externally supplied current through the channel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS20060115857A1Rapid responseHigh sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Disclosed is a sensor for sensing the presence of an analyte component without relying on redox mediators. This sensor includes (a) a plurality of conductive polymer strands each having at least a first end and a second end and each aligned in a substantially common orientation; (b) a plurality of molecular recognition headgroups having an affinity for the analyte component and being attached to the first ends of the conductive polymer strands; and (c) an electrode substrate attached to the conductive polymer strands at the second ends. The electrode substrate is capable of reporting to an electronic circuit reception of mobile charge carriers (electrons or holes) from the conductive polymer strands. The electrode substrate may be a photovoltaic diode.
Owner:KEENSENSE
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS6979544B2Accurate readingRapid responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Disclosed is a sensor for sensing the presence of an analyte component without relying on redox mediators. This sensor includes (a) a plurality of conductive polymer strands each having at least a first end and a second end and each aligned in a substantially common orientation; (b) a plurality of molecular recognition headgroups having an affinity for the analyte component and being attached to the first ends of the conductive polymer strands; and (c) an electrode substrate attached to the conductive polymer strands at the second ends. The electrode substrate is capable of reporting to an electronic circuit reception of mobile charge carriers (electrons or holes) from the conductive polymer strands. The electrode substrate may be a photovoltaic diode.
Owner:KEENSENSE
Microelectronic device and method for label-free detection and quantification of biological and chemical molecules
InactiveUS20020012937A1Wide scope of practicalWide scope of worthwhile utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceField-effect transistor
Molecular recognition-based electronic sensor, which is gateless, depletion mode field effect transistor consisting of source and drain diffusions, a depletion-mode implant, and insulating layer chemically modified by immobilized molecular receptors that enables miniaturized label-free molecular detection amenable to high-density array formats. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The conductivity of the active channel is determined by the potential of the sample solution in which the device is immersed and the device-solution interfacial capacitance. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The interfacial capacitance is determined by the extent of occupancy of the immobilized receptor molecules by target molecules. Target molecules can be either charged or uncharged. Change in interfacial capacitance upon target molecule binding results in modulation of an externally supplied current through the channel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Chemical, Particle, and Biosensing with Nanotechnology
InactiveUS20080025875A1Reduce manufacturing costEase and flexibility of preparationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological macromoleculeMolecular recognition
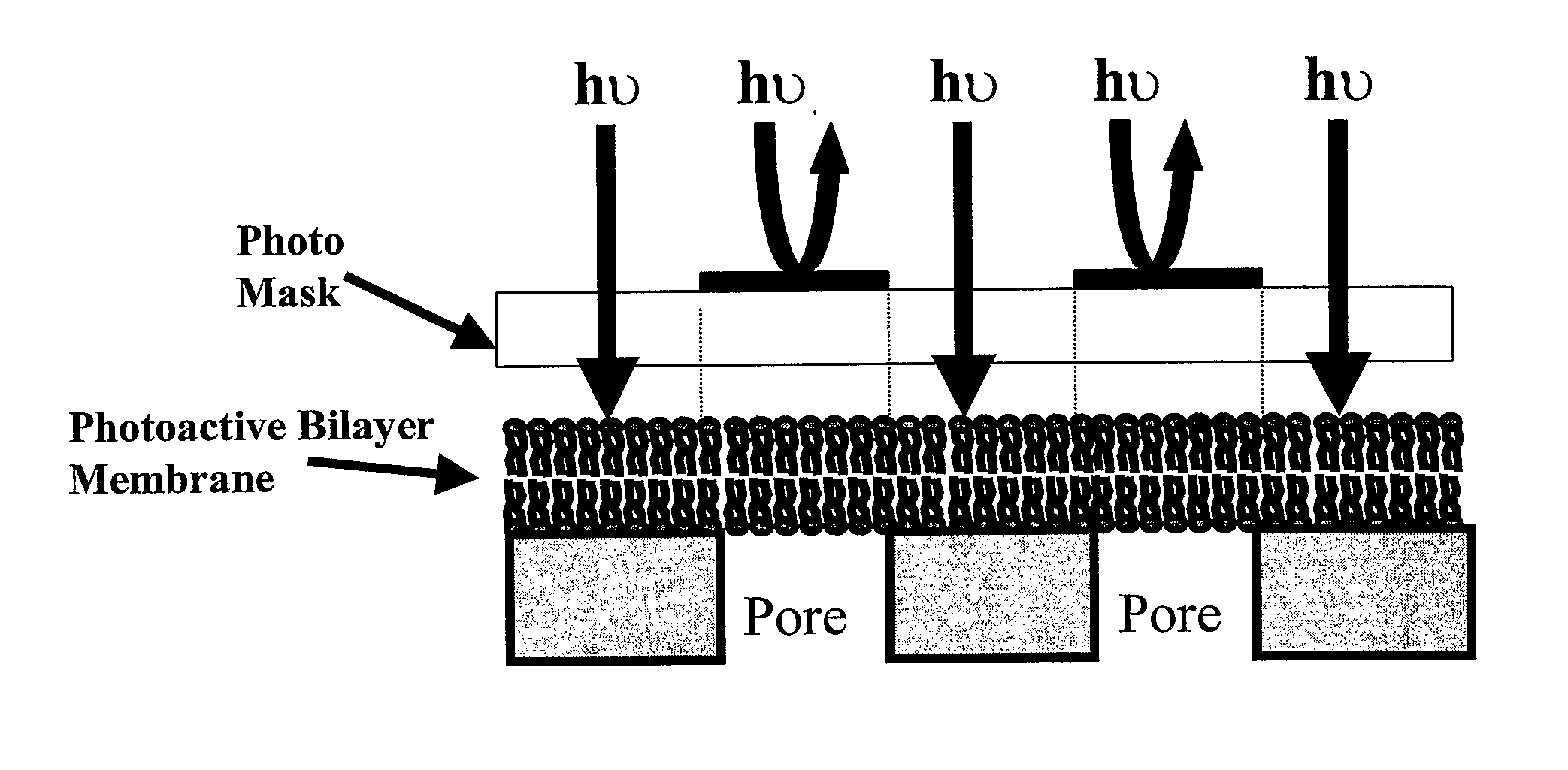
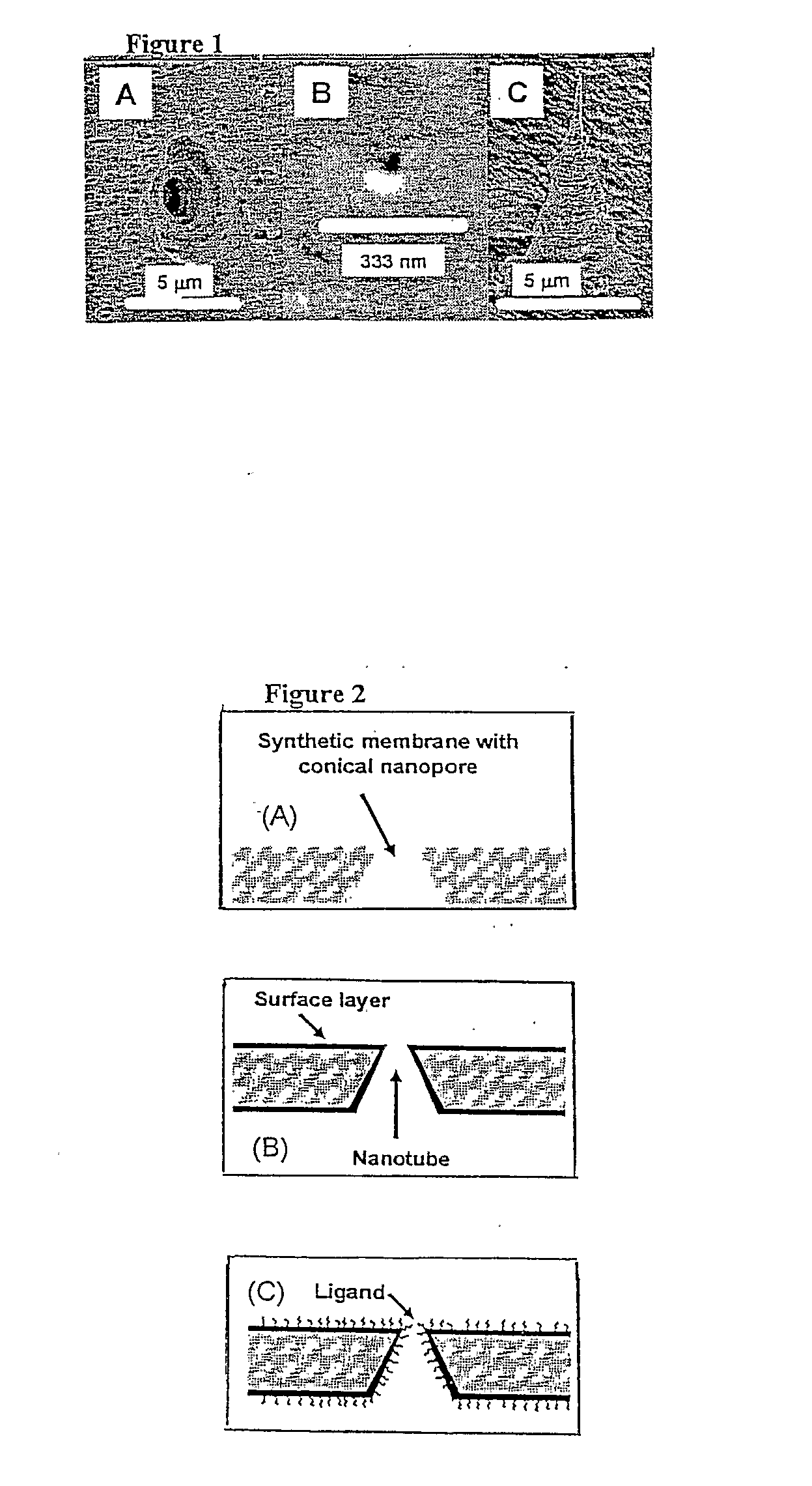
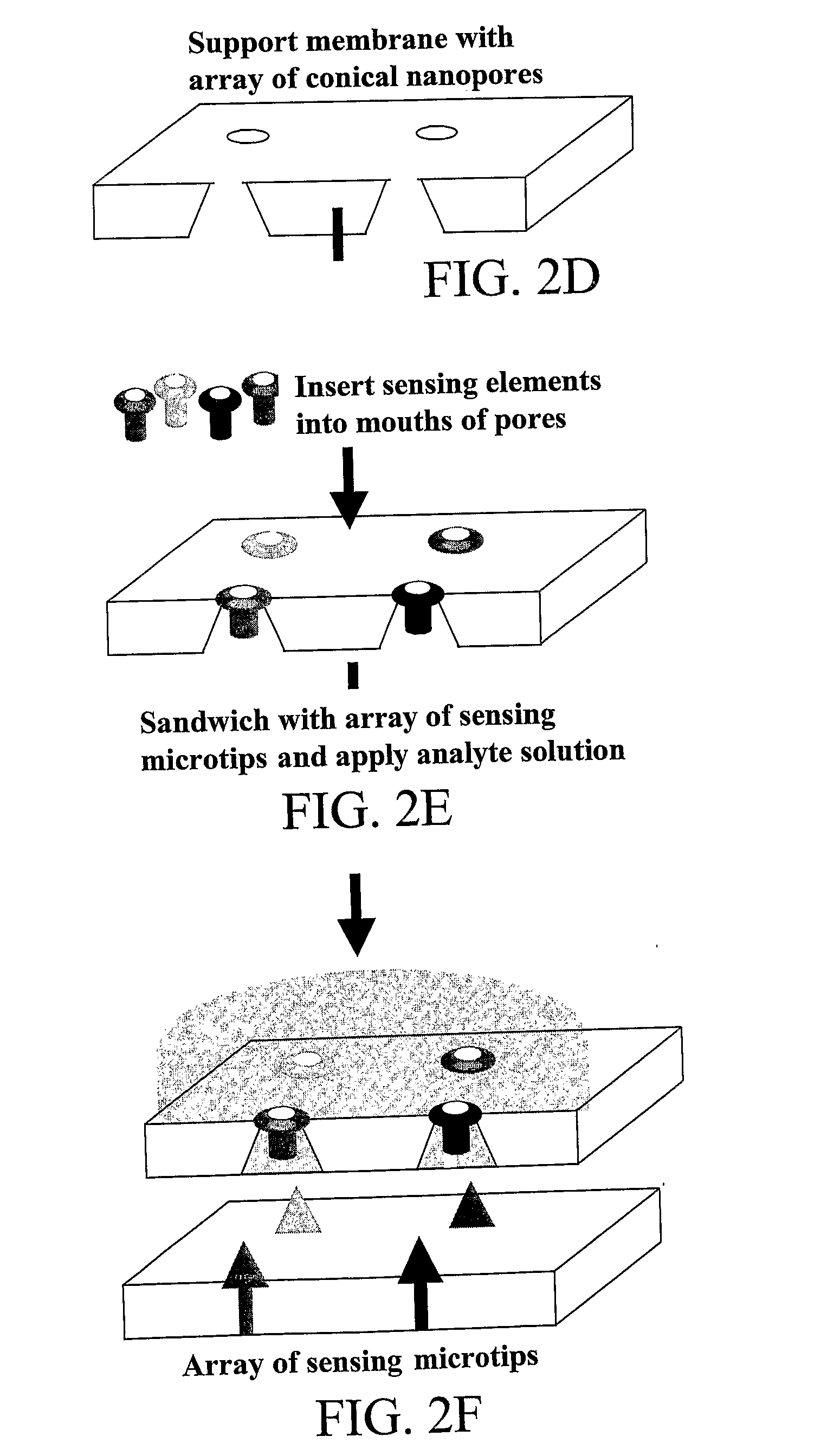
The subject invention provides novel and efficacious systems and methods for particle, chemical, and / or biocompound sensing. In one embodiment, the system of the invention comprises a sensing device that includes a membrane containing at least one nanochannel that spans all or substantially all of the thickness of the membrane. The nanochannel(s) of the invention can be functionalized to enhance target analyte detection and quantification. In one embodiment, the nanochannel is conically shaped and includes a molecular recognition agent for a target analyte. In certain operations, the sensing systems of the invention quantitatively and qualitatively detect biochemical / biomedical species and biomacromolecules, such as proteins, DNA, cells, spores and viruses, with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Force Mediated Assays
InactiveUS20120288852A1High sensitivitySolve the poor convenience of useMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMicroorganismChemical species
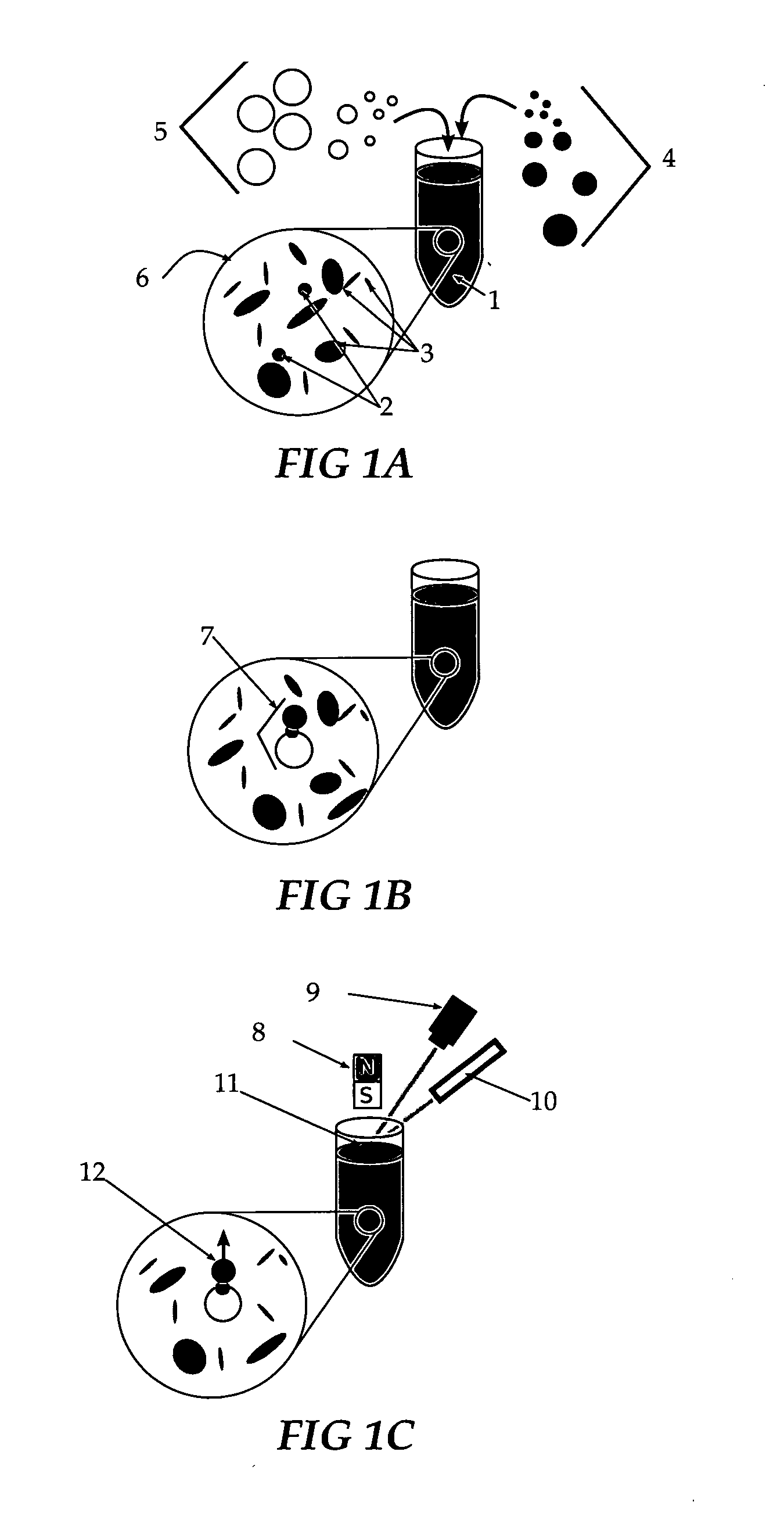
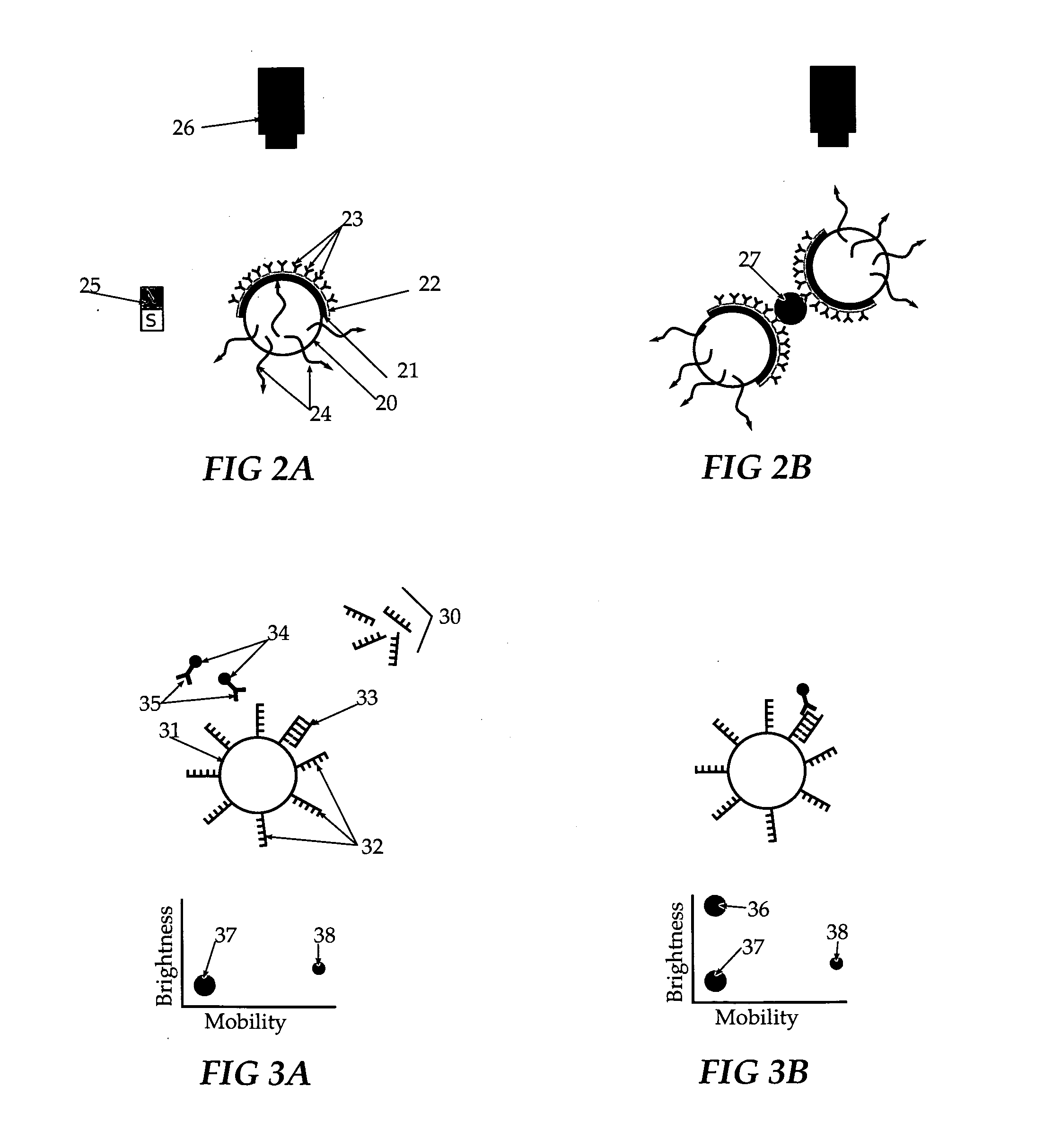
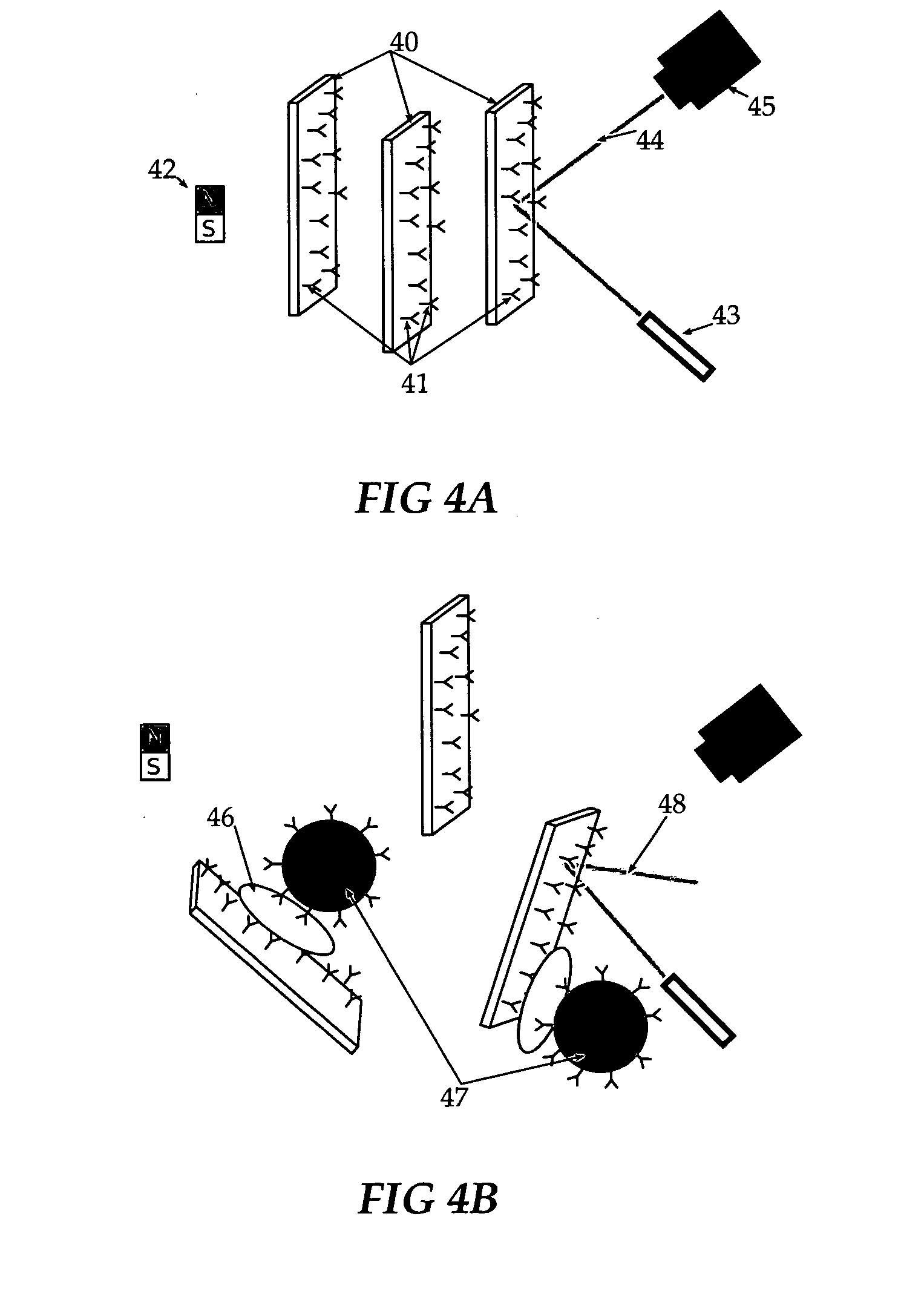
A sensitive and specific method of detecting chemical species, viruses and microorganisms is presented to improve performance of molecular-recognition-based assays utilizing particles decorated with molecular recognition agents such as antibodies and DNA probes, and observing analyte-dependent changes in the response of the particles to forces such as magnetic or gravitational forces or Brownian thermal fluctuations.
Owner:WILLSON RICHARD +1
Particulate labels
InactiveUS20120045748A1High sensitivitySolve the poor convenience of useMicrobiological testing/measurementParticulatesMolecular diagnostics
A methodology for bioassays and diagnostics in which a particulate label (ranging in size from nm-scale molecular assemblages to organisms on the scale of tens or hundreds of microns), such as, but not limited to, nanoparticles, bacteria, bacteriophage, Daphnia, and magnetic particles, serve carriers for analytes bound by molecular recognition elements such as antibodies, aptamers, etc. The described methodology is generally applicable to most pathogen assays and molecular diagnostics and also leads to enhanced sensitivity and convenience of use.
Owner:WILLSON RICHARD C +2
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS7220550B2Accurate readingRapid responseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Owner:KEENSENSE
Near-infrared fluorescent molecular probe, synthesizing method and use thereof
InactiveCN101440282APrecise deliveryImplement diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMolecular identification
The invention relates to the field of specific molecular identification and diagnosis reagent and in particular discloses a near infrared fluorescent dye with structural formulas I and II; and the invention also discloses a near infrared molecular probe which is obtained through covalent bonding between the near infrared fluorescent dye with the structural formulas I and II and a ligand of specific molecules. The near infrared molecular probe can be used for early diagnosis of turmour diseases.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
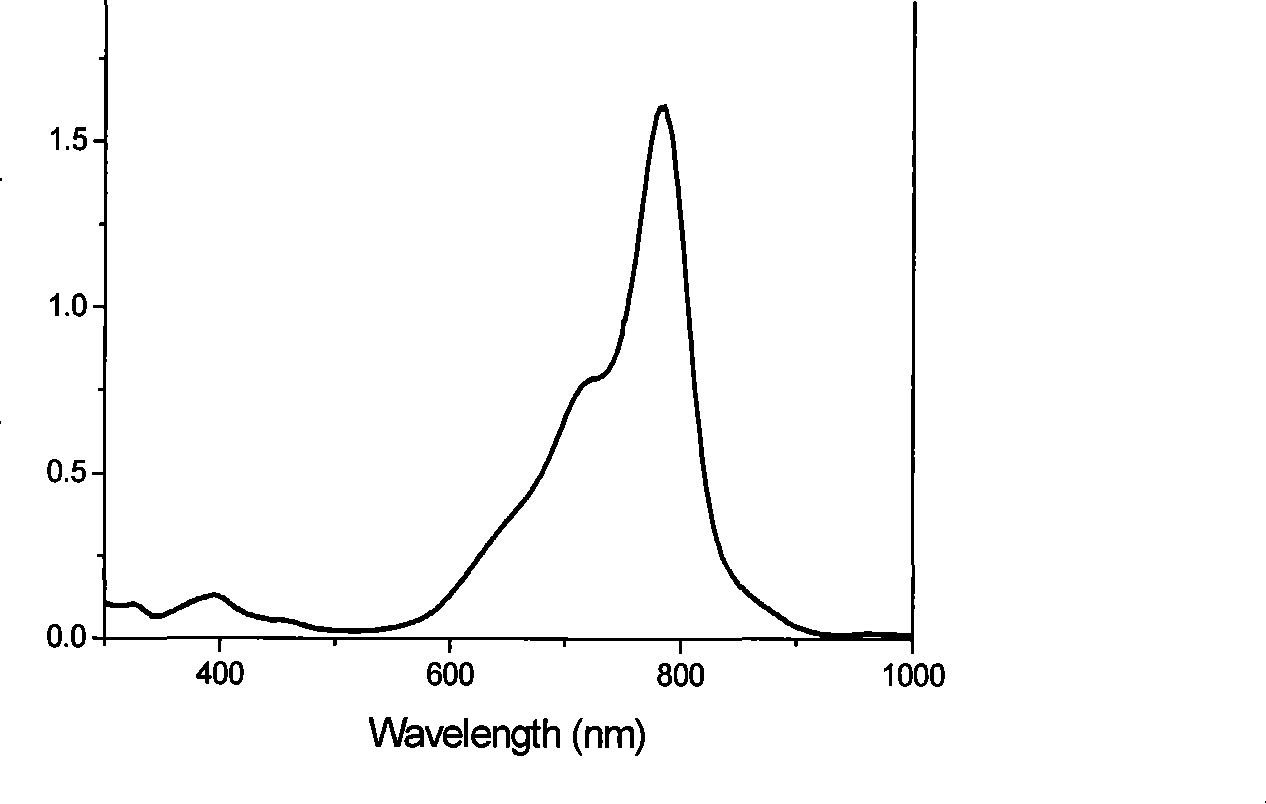
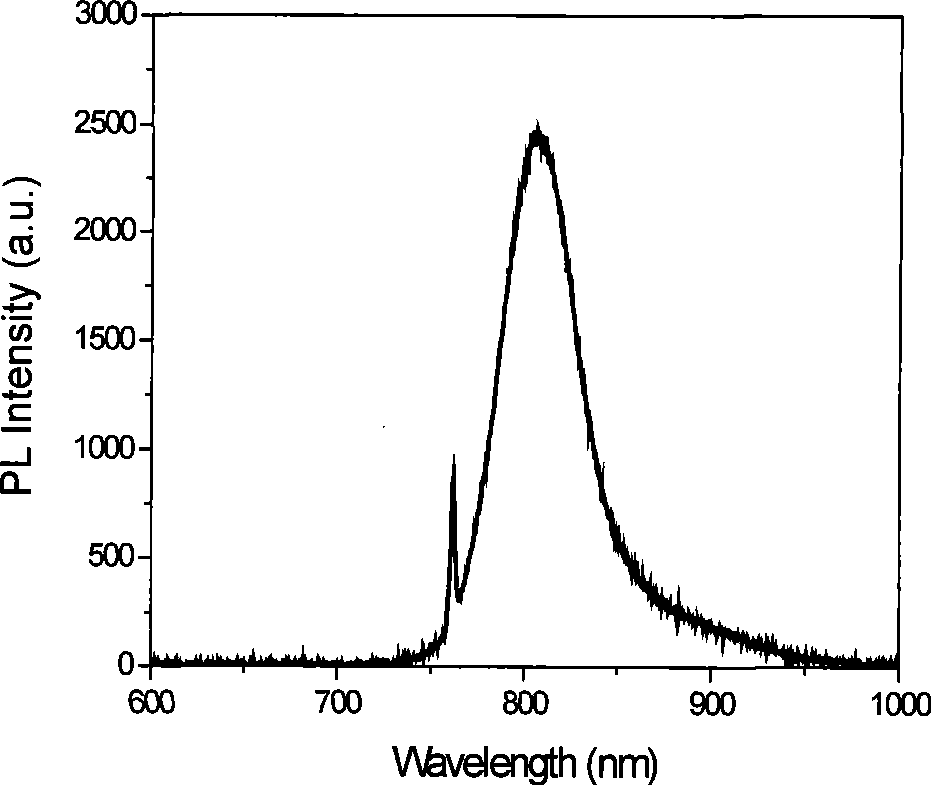
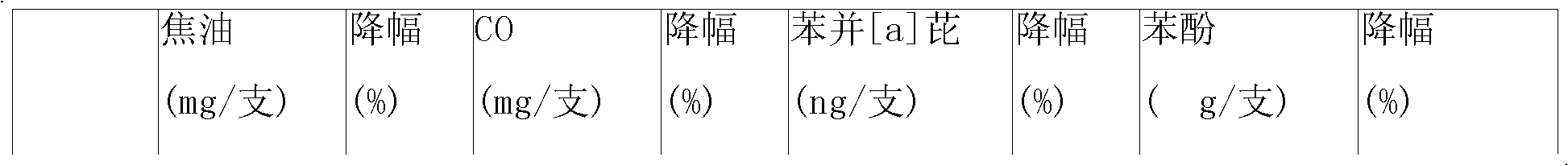
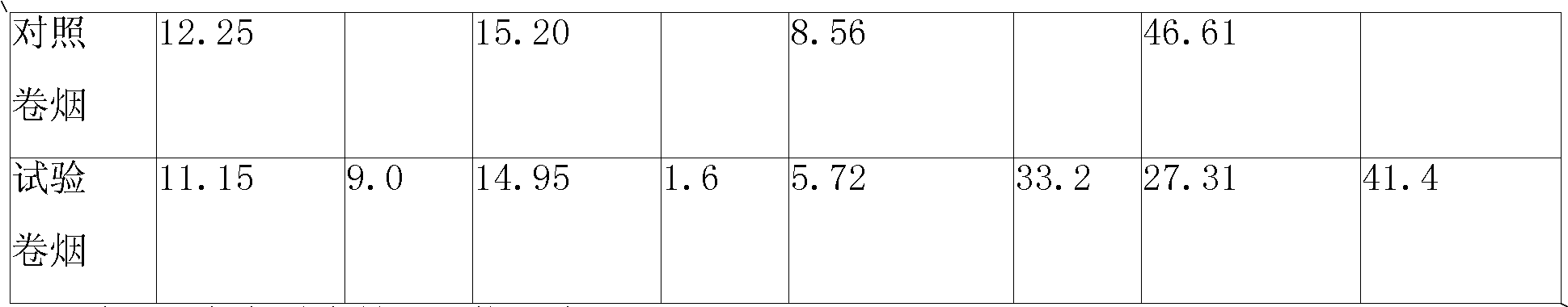
Calixarene additive capable of simultaneously and optionally reducing benzo (alpha) pyrene and phenol contents in cigarette smoke and application method thereof
ActiveCN101664228AReduce benzo[a]pyrene contentReduce phenol contentTobacco smoke filtersCavity sizePhenol
The invention discloses a calixarene additive capable of simultaneously and optionally reducing benzo (a) pyrene and phenol contents in cigarette smoke and an application method thereof. In the invention, deep-cavity P-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl) calyx (8) aromatic compound is selected as the additive material, and the compound is added in a common and conventional filter tip which bettercan be suitable for a compound filter, with the additive amount being arbitrarily adjusted according to the needs. By using the molecular recognition function and the cavity size select effect of thecalyx (8) aromatic compound, the additive can be optionally combined with the benzo (a) pyrene and phenol molecules in the cigarette smoke. When the additive is added into the filler with the amount of 10mg / per cigarette, 33.2 percent of benzo (a) pyrene content and 41.4 percent of phenol content in the cigarette smoke can be simultaneously reduced, and other chemical compositions in the smoke arebasically not influenced, thus achieving the goal of selective harm reduction.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP
Identification of protein binding sites
InactiveUS7972993B2Rapid and straightforward identificationPromote generationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningEpitopeBinding site
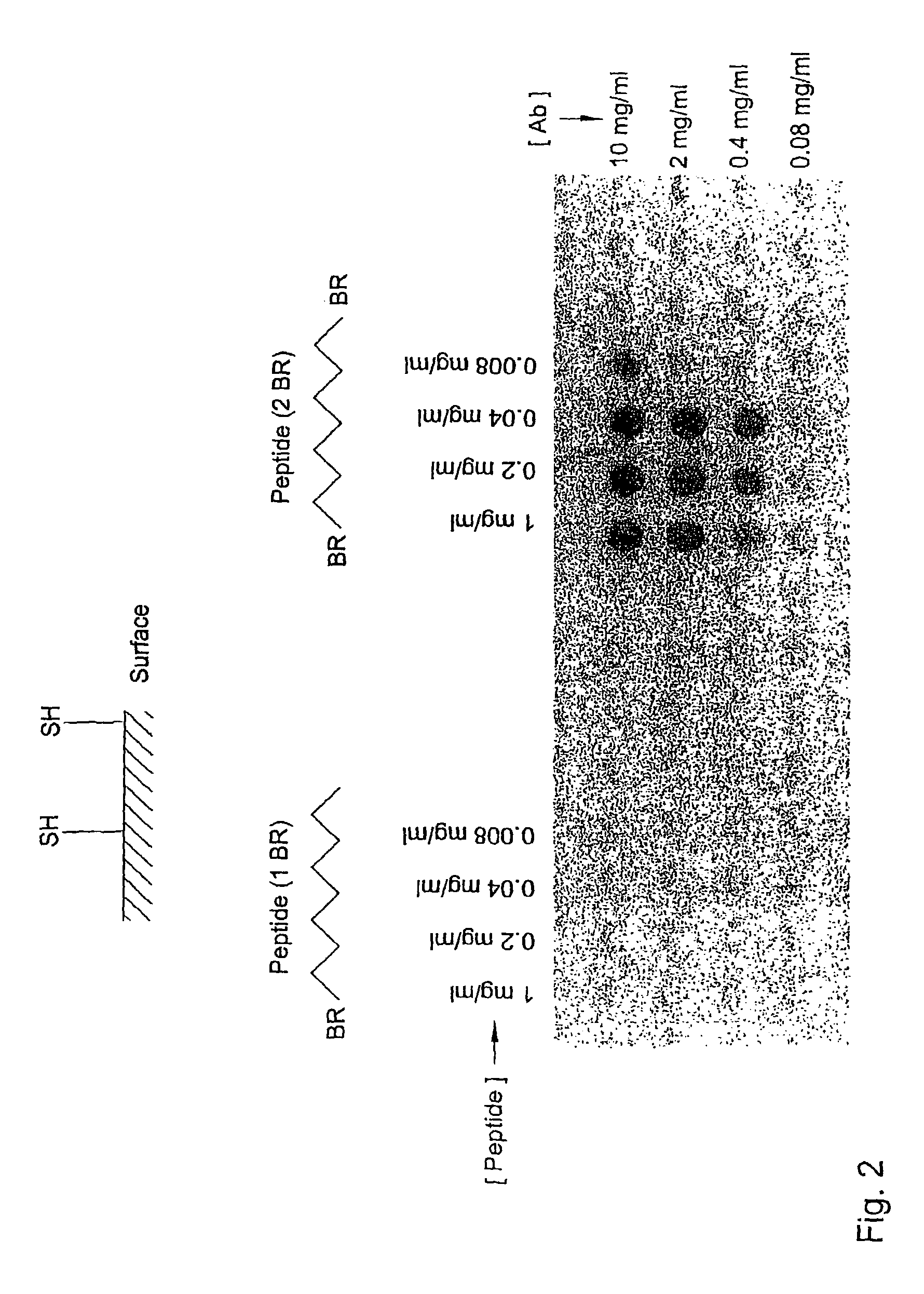
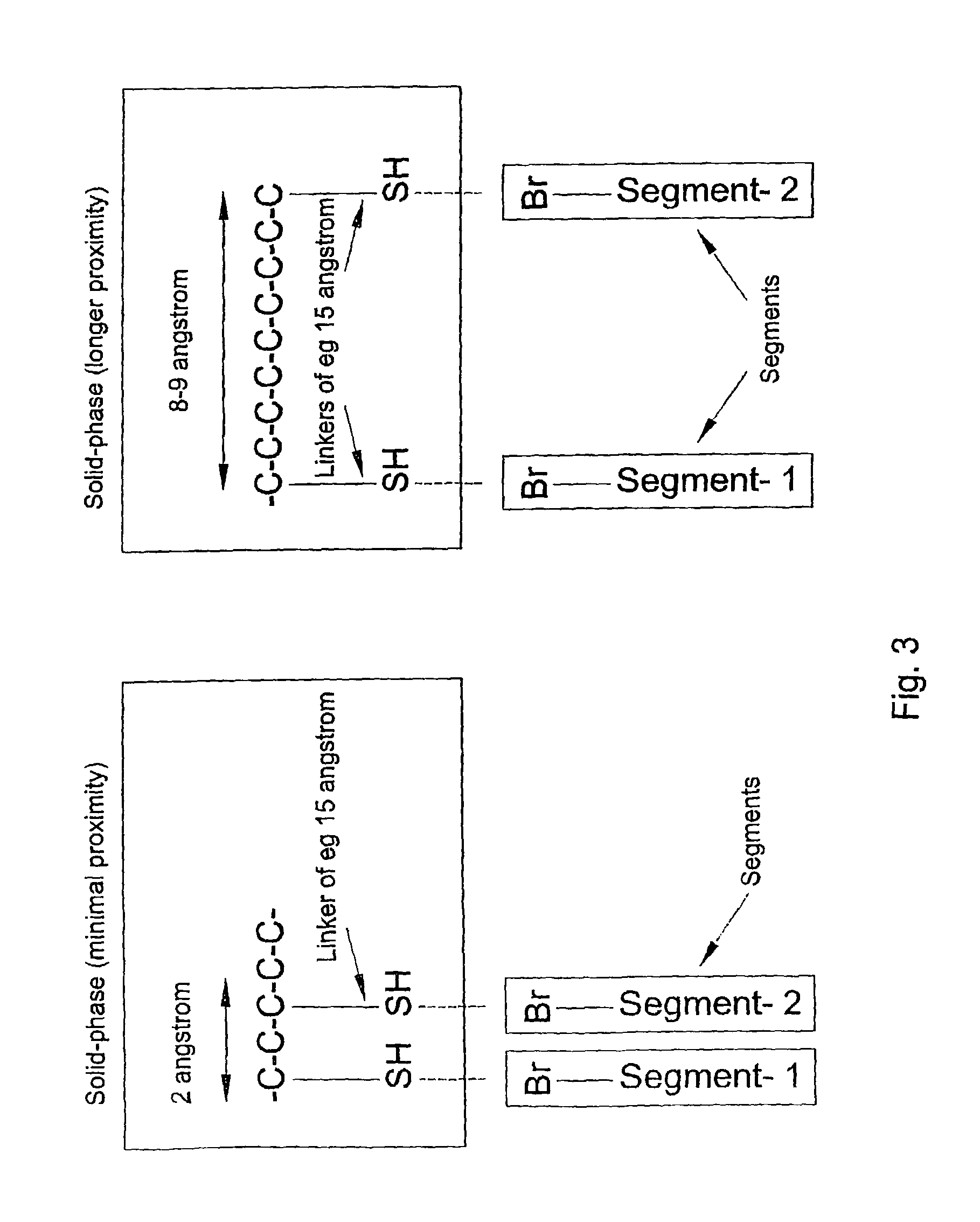
The invention relates to the field of molecular recognition or detection of discontinuous or conformational binding sites or epitopes corresponding to a binding molecule, in particular, in relation to protein-protein, protein-nucleic acid, nucleic acid-nucleic acid or biomolecule-ligand interactions. The invention provides a synthetic molecular library allowing testing for, identification, characterization or detection of a discontinuous binding site capable of interacting with a binding molecule, the library having been provided with a plurality of test entities, each test entity comprising at least one first segment spotted next to a second segment, each segment having the capacity of being a potential single part of a discontinuous binding site.
Owner:PEPSCAN SYST
Polymer-based cantilever array with optical readout
InactiveUS20060075803A1Good chemical resistanceEasy and fast processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGold layerOptical sensing
A cantilever array for use as a sensor, e.g. a bio / chemical sensor is disclosed. The cantilever array comprises a platform and a multitude of polymer-based cantilevers attached to the platform. Each of the cantilevers is coupled to an optical sensing means adapted to sense deformations of an individual cantilever. The cantilevers may be coated with a first and / or a second layer, the first layer being a metal layer, such as a gold layer, the second layer being a molecular layer capable of functioning as a receptor layer for molecular recognition. Further, two methods of fabricating a cantilever array are disclosed, one being based on photolithography, the other being based on micromoulding.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
MOF-based hierarchical porous materials, methods for preparation, methods for pore regulation and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140212944A1Improve thermal stabilityGood reproducibilityMaterial nanotechnologyMethane captureGasolineHierarchical porous
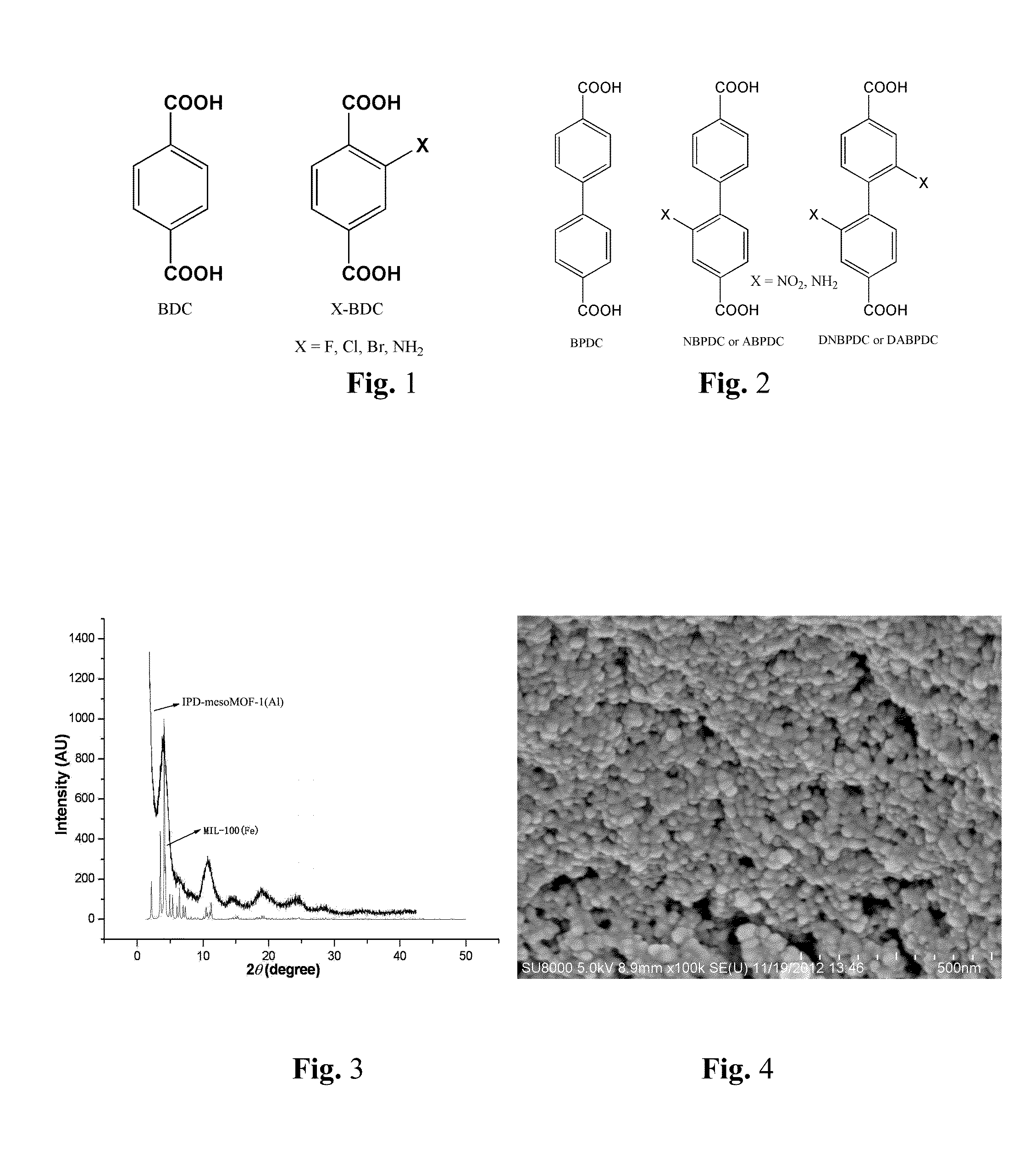
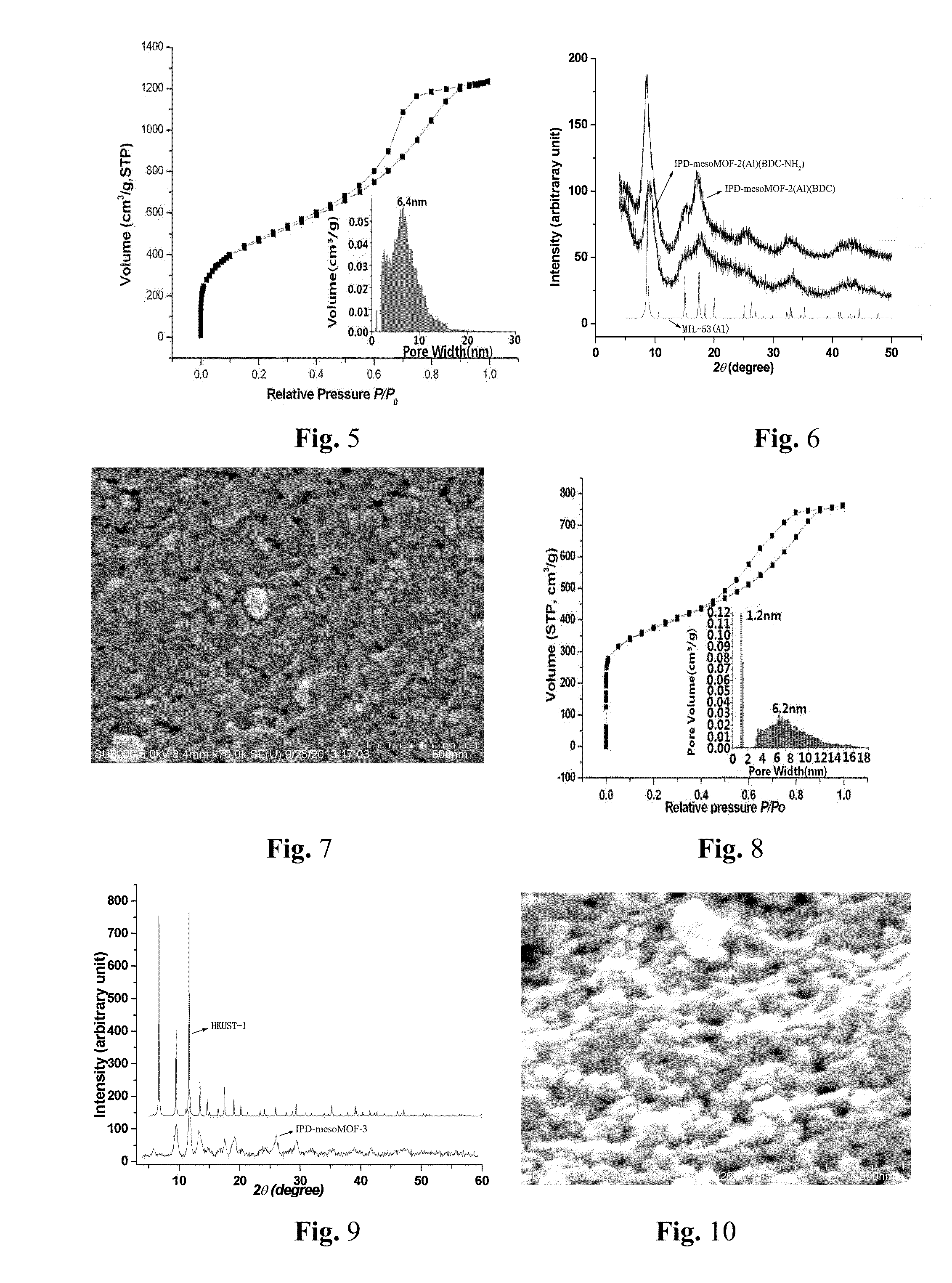
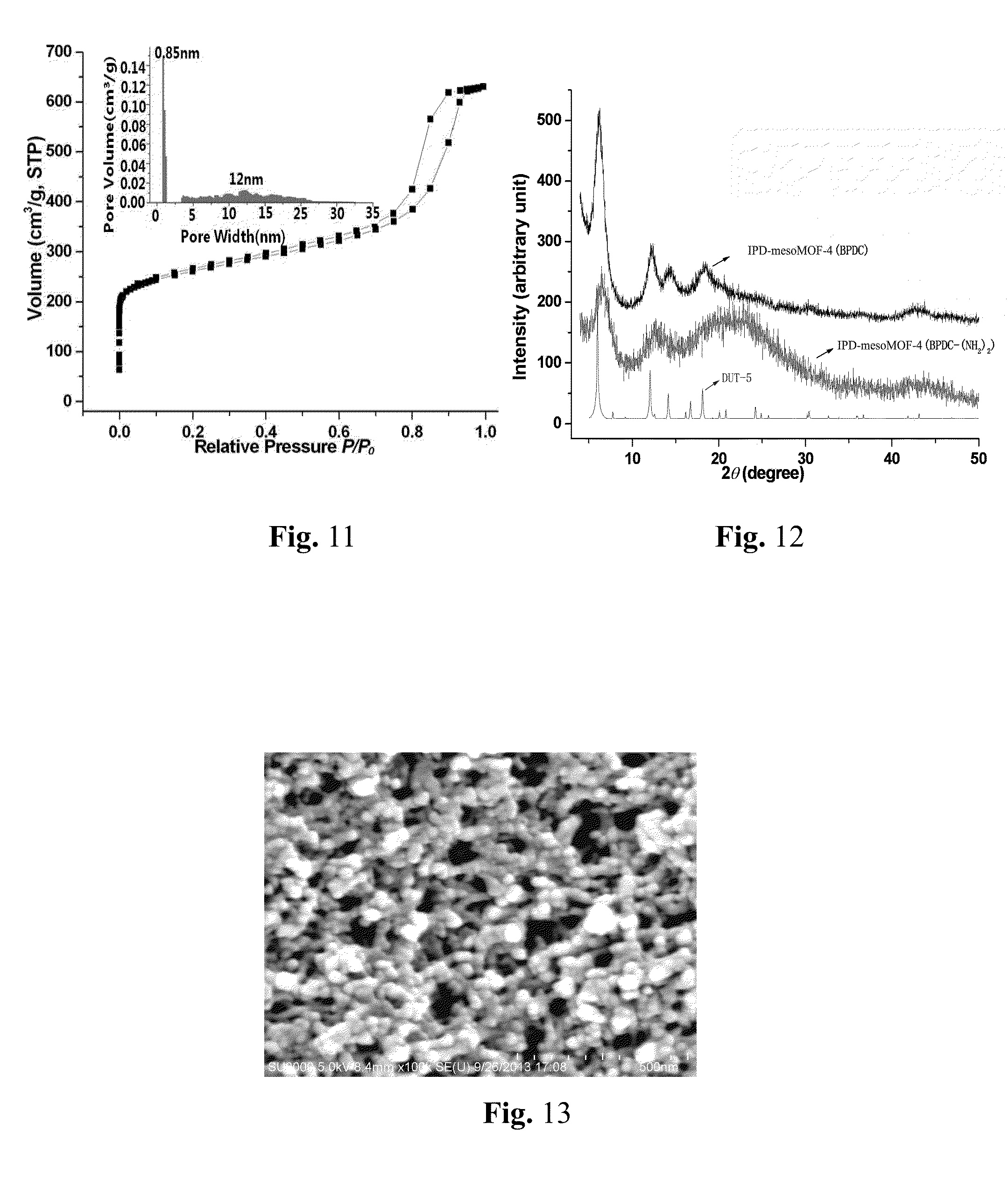
A series of MOF-based hierarchical porous material, namely IPD-mesoMOF-1˜9, based on nanoscale MOFs of MIL-100(Al, Fe, Cr, Sc and In), MIL-53(Al), HKUST-1, DUT-5, DUT-4, MIL-101(Cr), MIL-101NDC(Cr), MIL-101BPDC(Cr) and MIL-110 respectively, forming the permanent interparticle porosities by using close (or relatively close) packing, and preparation methods thereof. Modulated or functionalized IPD-mesoMOFs can be applied for gas adsorption and molecule separation (such as CH4- and CO2-adsorption, gasoline / diesel desulfurization and purification), catalyst loadings and molecular recognition / immobilization of biological macromolecules and enzymes.
Owner:BEIJING SIDAAN NEW MATERIAL TECH
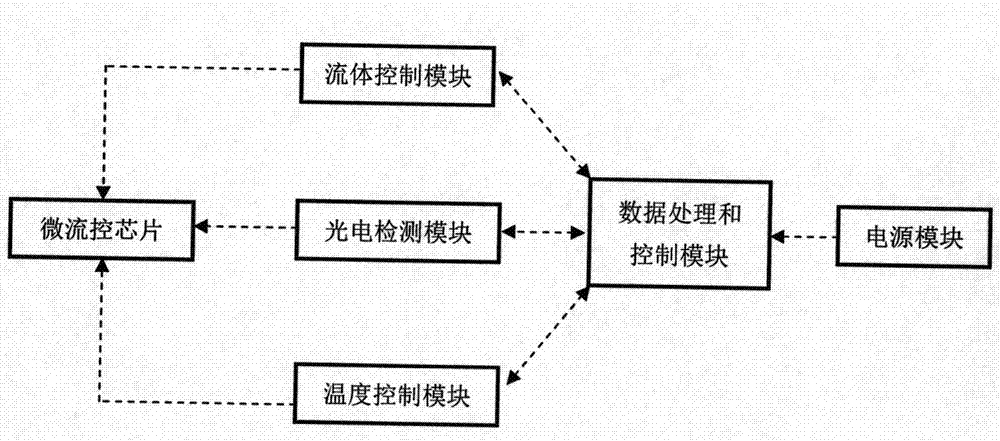
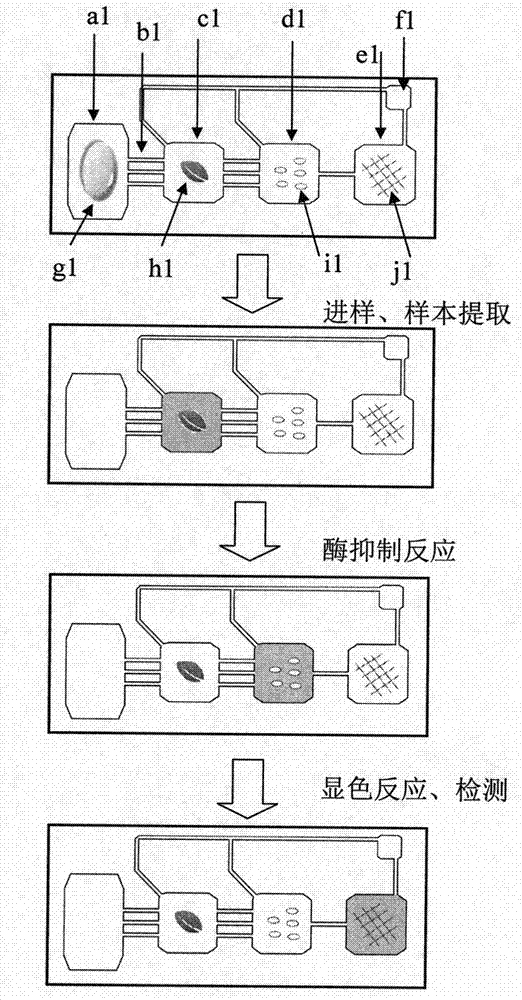
Full-automatic and high-throughput micro-fluidic chip system and method for detecting pesticide residue
InactiveCN104502617AAvoid preparation workQuick checkMaterial analysisEnzyme inhibitionPesticide residue
The invention provides a full-automatic and high-throughput micro-fluidic chip system and method for detecting pesticide residue, used for field detection of pesticide residue based on enzyme inhibition reaction. The full-automatic and high-throughput micro-fluidic chip system is mainly composed of a portable analytical detector and a disposable micro-fluidic chip; the plastic polymer material of the micro-fluidic chip is manufactured through existing micro-machining technology; the micro-fluidic chip is composed of a central clamping groove, an extraction chamber, a sample chamber, a reaction chamber, a detection chamber, a micro-groove, a micro-hole and a quality control bar code; reagents (comprising an extracting solution, enzyme, a colour developing agent and the like) required for detecting pesticide residue are fixed in the micro-fluidic chip; the functions of sampling automatically and quantitatively, distributing a fluid, carrying out biochemical reaction and molecular recognition and the like can be realized; a fluid operation and control module, a photoelectric detection module, a data analyzing and processing module and an information storage and communication module are integrated in the portable analytical detector; operation and control of biochemical reaction in the micro-fluidic chip and rapid analysis and detection of to-be-detected indexes and pesticide residue can be realized; and thus, the micro-fluidic chip system and the method provided by the invention are particularly applied to full-automatic and high-throughput detecting and screening of pesticide residue in the samples, such as fruits, vegetables, soil and water.
Owner:HANGZHOU TINKER BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
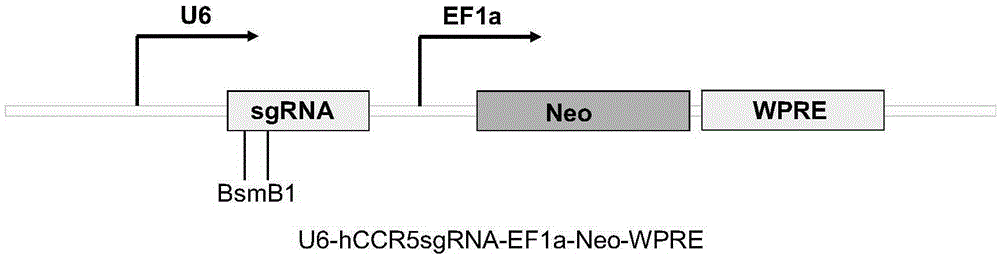
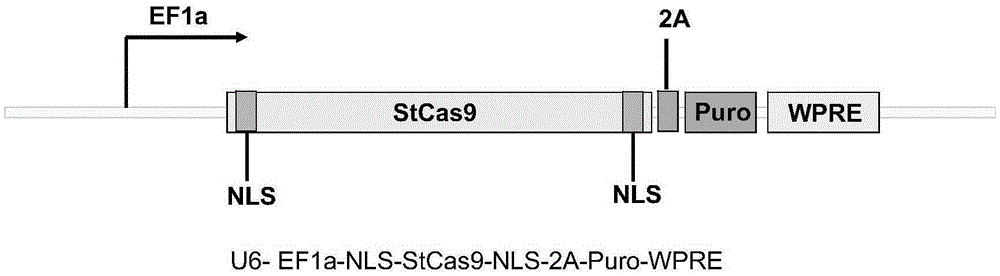
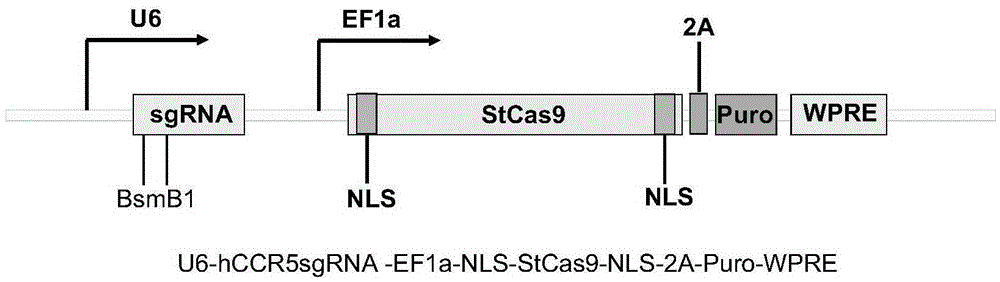
Target sequence, recognized by streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR-Cas9 system, of human CCR5 gene, sgRNA and application of CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN105400779AHIV prevention and/or treatmentAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGenetic engineeringStreptococcus thermophilus
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a target sequence, recognized by a streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR-Cas9 system, of a human CCR5 gene, sgRNA and an application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system. The target sequence is shown as any one of the nth bit to the 30th bit of the SEQ ID NO:1-30, and n is equal to 1-12. The invention further relates to the sgRNA of the sequence -3' with the sequence of 5'-recognition sequence-recruiting Cas9 protein and a coded DNA molecule thereof. The DNA sequence corresponding to the recognition sequence is identical to the target sequence. The invention further relates to the CRISPR-Cas9 system. The system comprises Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or the coded sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a carrier of the coded sequence of the sgRNA. The invention further relates to the application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system in editing the CCR5 gene and preparing medicine for HIV infection. Editing of the human CCR5 gene can be achieved, and therefore Aids is prevented and treated.
Owner:张竞方
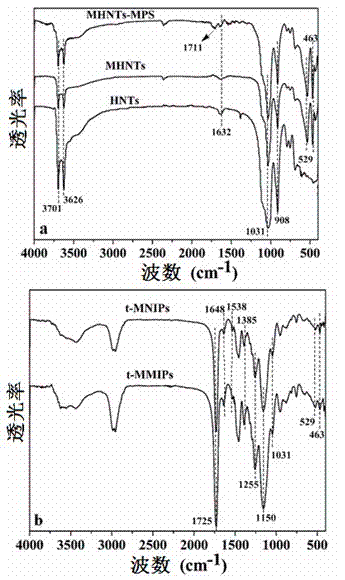
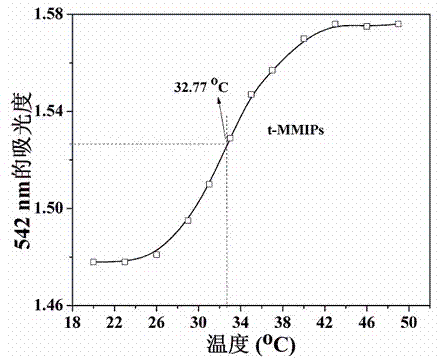
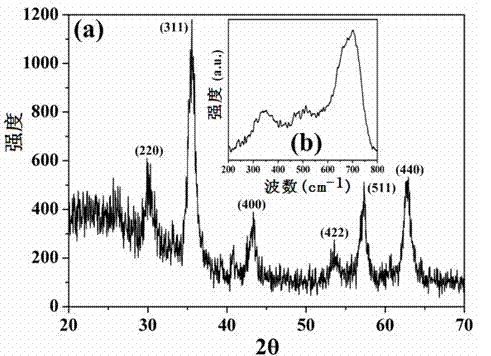
Magnetic composite material surface imprinting thermosensitive adsorbent, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102527349AHigh mechanical strengthImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationMethacrylateMagnetic stability
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of environment functional materials, in particular to a magnetic composite material surface imprinting thermosensitive adsorbent, and a preparation method and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, a ferroferric oxide / nerchinskite nanotube magnetic composite material is prepared by a solvent thermal synthesis method; secondly, the magnetic composite material is modified on ethenyl by using 3-(methacrylo) propyltrimethoxyl silane; and finally, the nerchinskite nanotube magnetic composite material is prepared by using the ethenyl-modified magnetic composite material as a substrate material, 2, 4, 5-trichlorophenol as a template molecule, methacrylate as a functional monomer, N-isopropylacrylamide as a thermosensitive functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a cross-linking agent, and 2,2'-azodiisobutyronitrile as an initiator. The prepared thermosensitive imprinting adsorbent is obvious in thermal stability and magnetic stability, sensitive in magnetic effect and thermosensitive effect, relatively high in adsorption capacity, obvious in reversible absorption / release function along with temperature and obvious in tertiary calcium phosphate (TCP) molecule recognition performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
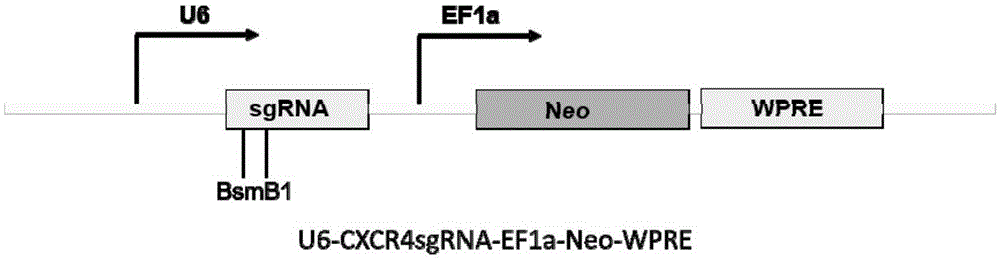
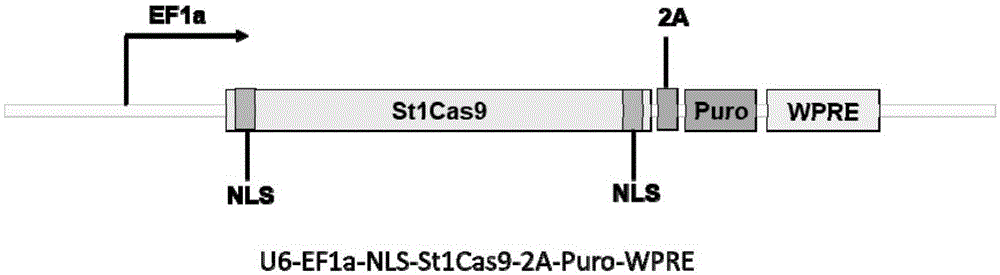
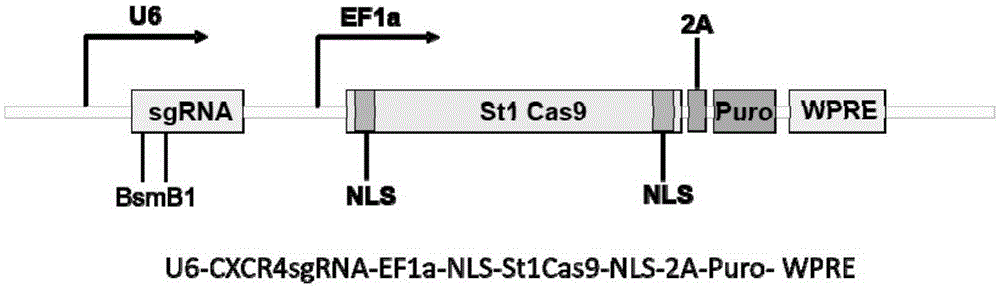
Streptococcus thermophilus derived human CXCR3 gene target sequence recognizable by CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 (CRISPR associated 9) system and sgRNA (single guide ribonucleic acid) and application thereof
InactiveCN105316324AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesProtein recruitmentA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, discloses a streptococcus thermophilus derived target sequence recognizable by a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 (CRISPR associated 9) system and further discloses a sgRNA (single guide ribonucleic acid) and a coding DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule thereof. The target sequence is shown as n-20th of any one of SEQ ID NO:1-63, wherein n=1-5. A sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-recognition sequence- Cas9 protein recruitment sequence-3', and a DNA sequence corresponding to the recognition sequence is identical to the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system, and the CRISPR-Cas9 system comprises Cas9 proteins and sgRNA and / or comprises carriers carrying a Cas9 protein coding sequence and a sgRNA coding sequence. The invention further discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to CXCR4 gene editing and preparation of medicines for treating HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection. CXCR4 gene editing can be realized to protect cells from HIV infection.
Owner:张竞方
Surface imprinting: integration of molecular recognition and transduction
InactiveUS20040058380A1High sensitivityEnhanced signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCouplingElectrostatic interaction
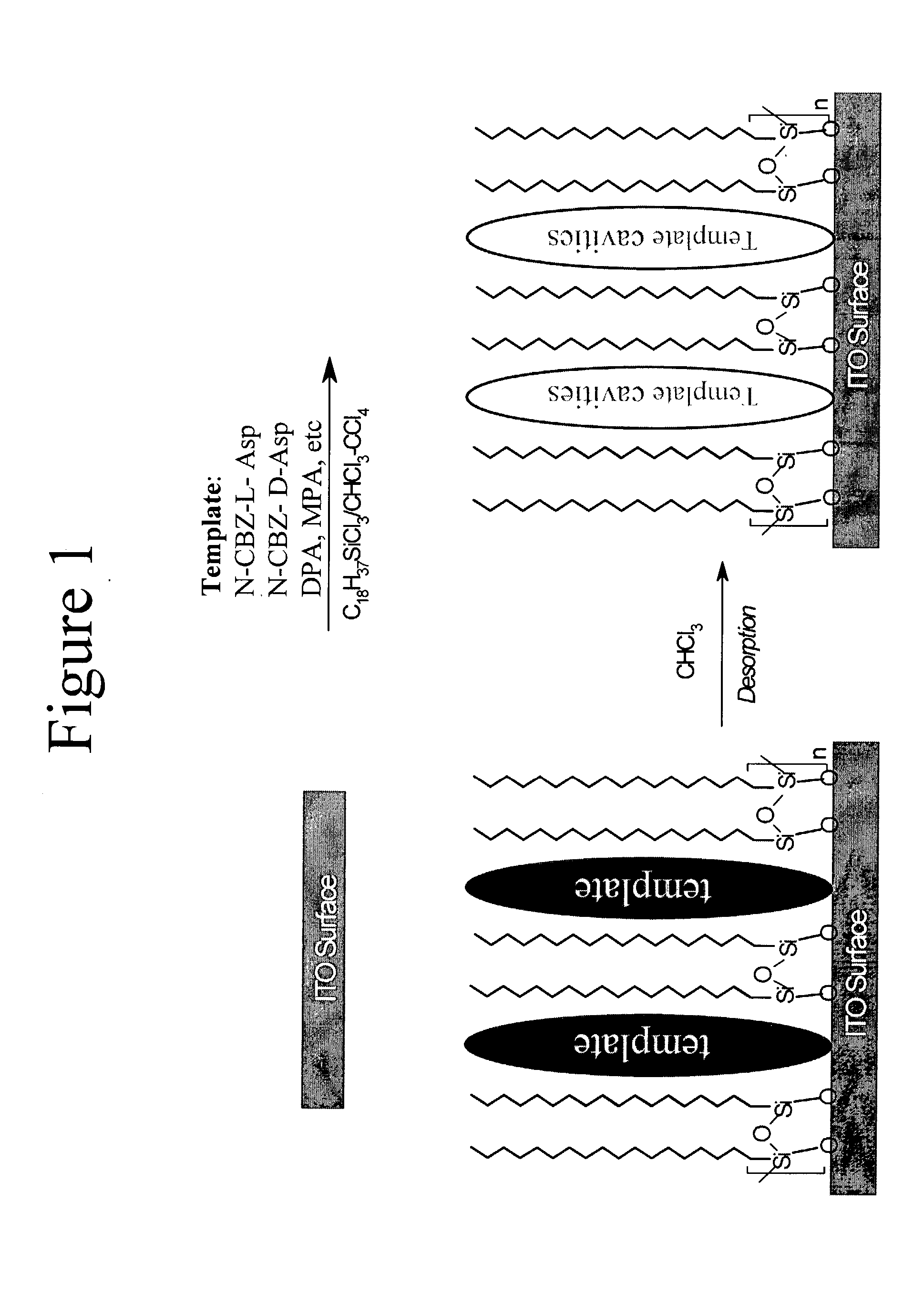
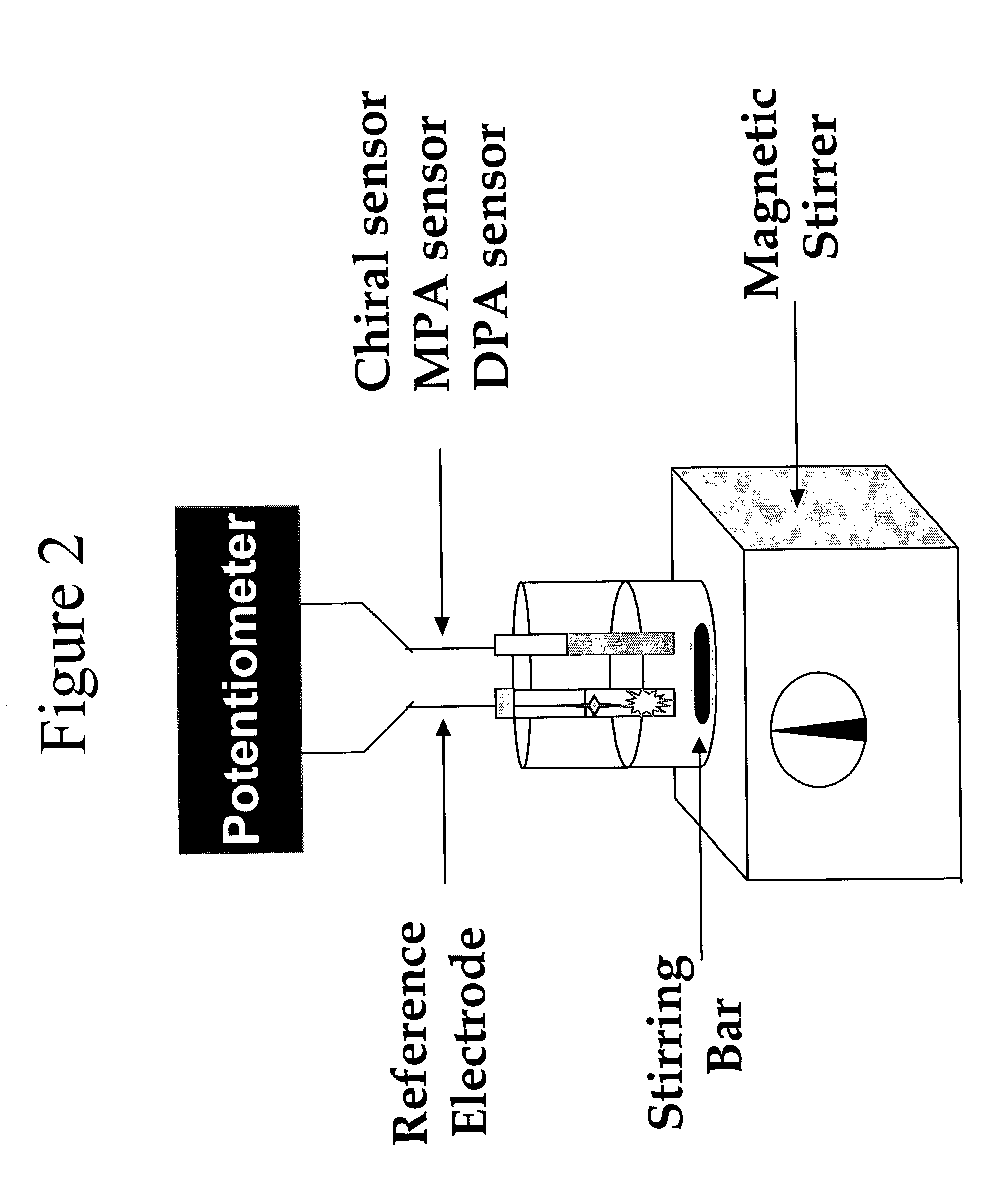
Surface-molecularly imprinted sensors were fabricated for detecting ionic molecules. Target molecules are recognized by the combination of a hydrophobic interaction with the imprinted polymer layer to provide specificity and an electrostatic interaction to provide sensitivity Coupling surface imprinting techniques with an electrochemical detection method, such as potentiometry, allows specific recognition of target molecules and translation of the recognition event into an output signal by the sensor.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
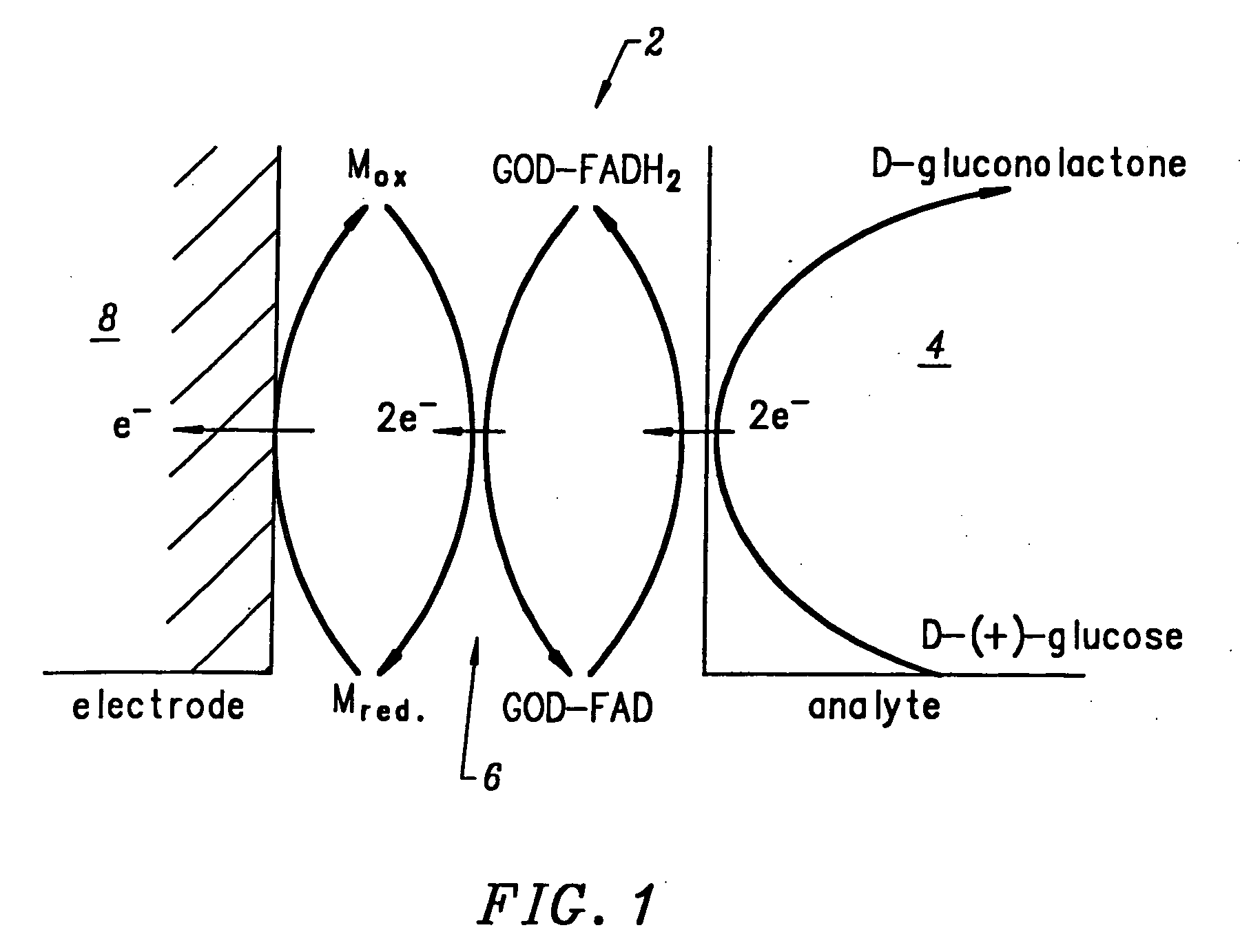
Intelligent polymerized crystalline colloidal array carbohydrate sensors
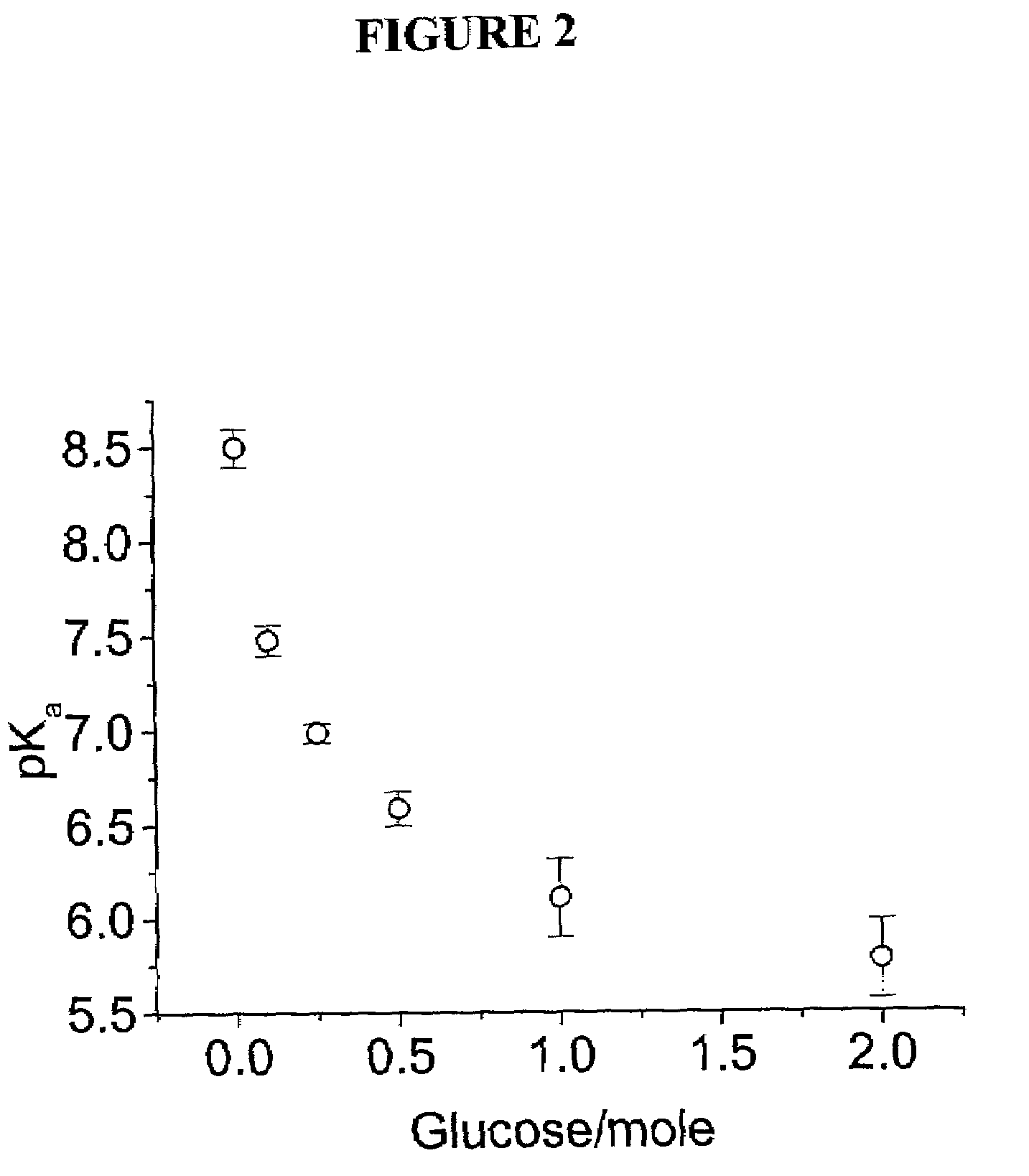
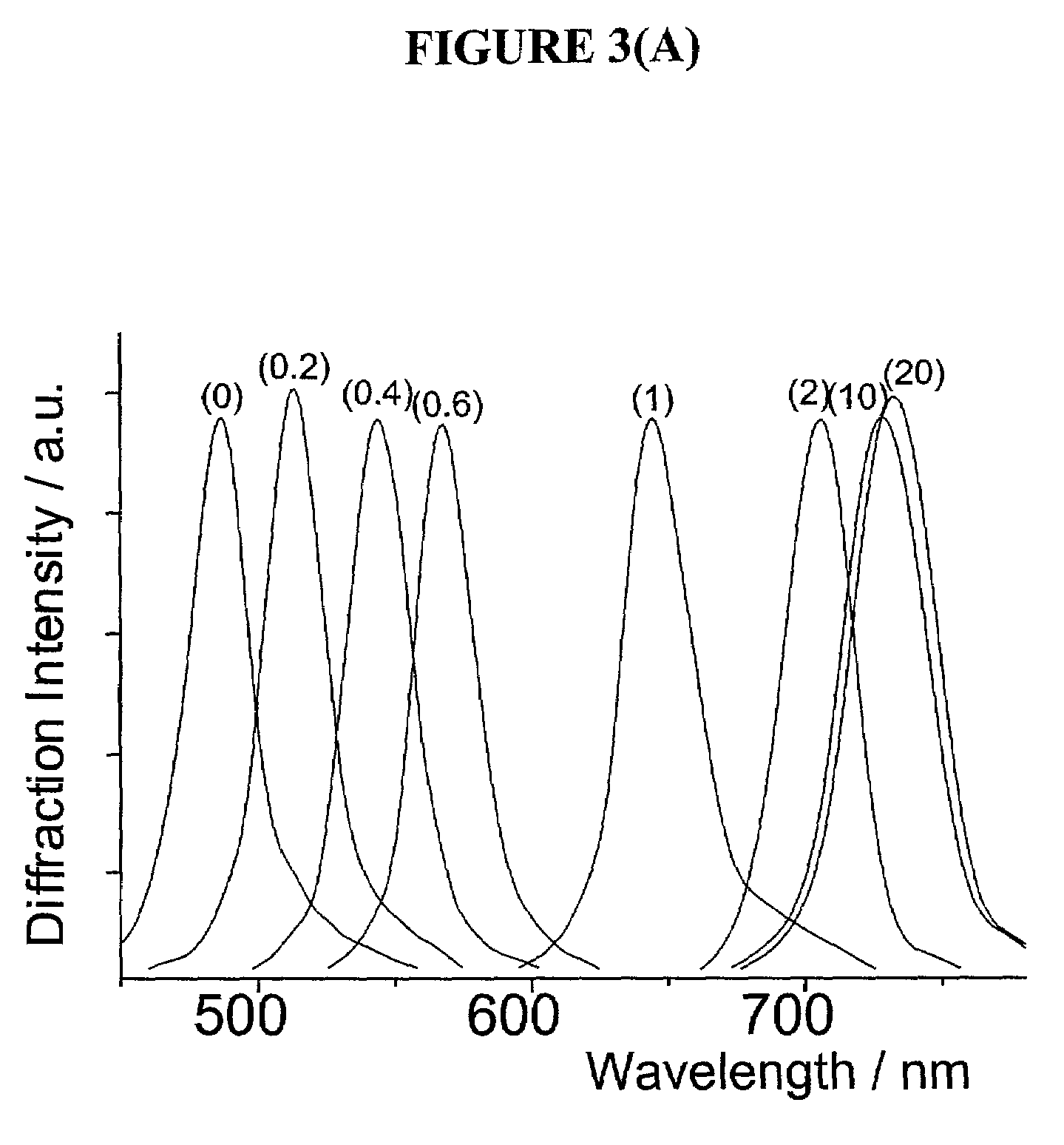
InactiveUS7105352B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
The present invention is related to glucose sensors that are capable of detecting the concentration or level of glucose in a solution or fluid having either low or high ionic strength. The glucose sensors of the present invention comprise a polymerized crystalline colloidal array (PCCA) and a molecular recognition component capable of responding to glucose. The molecular recognition component may be a boronic acid, such as a phenylboronic acid, glucose oxidase, a combination of phenylboronic acid and poly(ethylene)glycol or crown ether, or another component capable of detecting glucose in various fluids and solutions. The glucose sensors of the present invention may be useful in the development of noninvasive or minimally invasive in vivo glucose sensors for patients having diabetes mellitus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
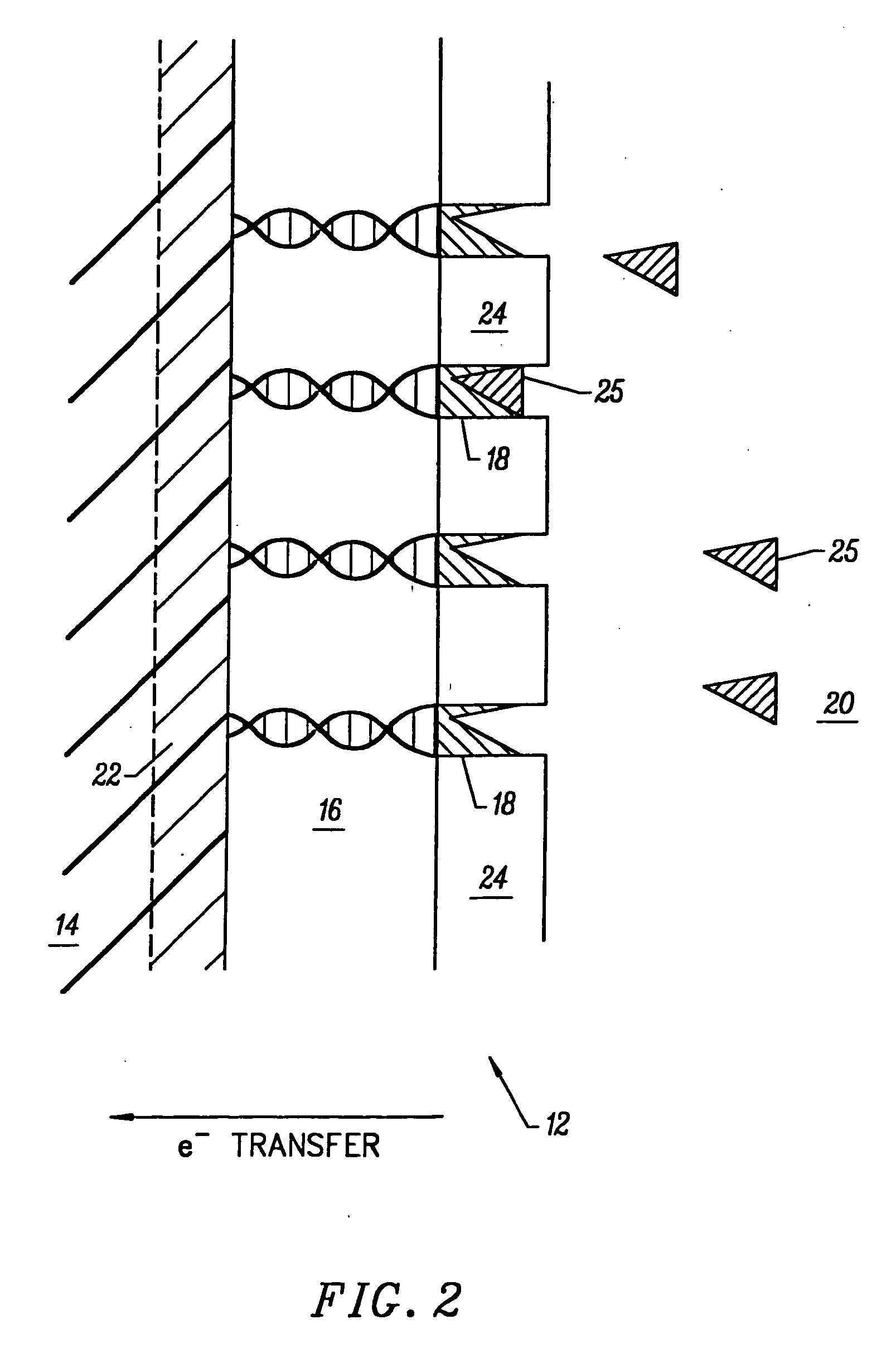
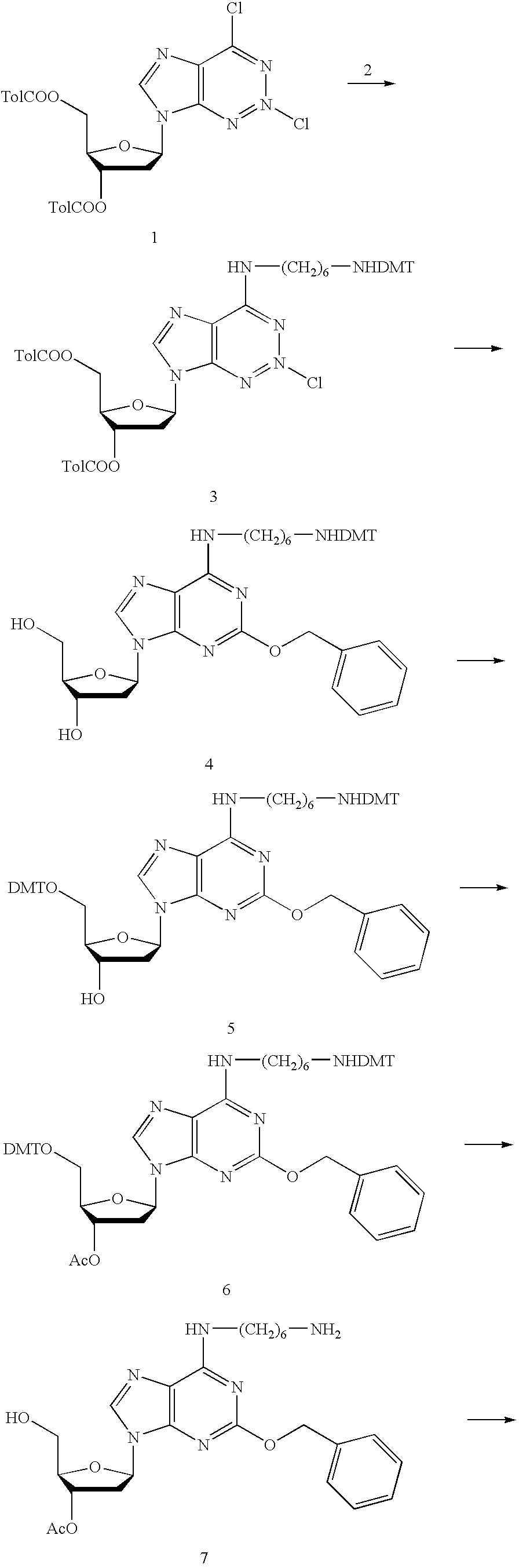
Solid support assay systems and methods utilizing non-standard bases
Solid support assays using non-standard bases are described. A capture oligonucleotide comprising a molecular recognition sequence is attached to a solid support and hybridized with a target oligonucleotide. In some instances, the molecular recognition sequence includes one or more non-standard bases and hybridizes to a complementary tagging sequence of the target oligonucleotide. In other instances, incorporation of a non-standard base (e.g., via PCR or ligation) is used in the assay.
Owner:LUMINEX
Modular nanoparticles for adaptable vaccines
ActiveUS20100104503A1Rapid productionWell representedPowder deliveryBacterial antigen ingredientsVaccine deliveryAdjuvant
Modular nanoparticle vaccine compositions and methods of making and using the same have been developed. Modular nanoparticle vaccine compositions comprise an antigen encapsulated in a polymeric particle and adaptor elements which modularly couple functional elements to the particle. The modular design of these vaccine compositions, which involves flexible addition and subtraction of antigen, adjuvant, immune potentiators, molecular recognition and transport mediation elements, as well as intracellular uptake mediators, allows for exquisite control over variables that are important in optimizing an effective vaccine delivery system.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Fluidic force discrimination
InactiveUS20040253744A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrometer scaleUltimate tensile strength
This invention describes a method of using controlled fluidic forces to improve the performance of a biochemical binding assay where a target molecule is captured by specific molecular recognition onto a substrate surface with an affinity coating, and then labeled with a detectable micrometer-scale particle using a second specific molecular recognition reaction with the target. By using specific ranges of label sizes and laminar flow conditions, controlled fluidic forces can be applied to the label particles in order to selectively remove molecules bound to a surface according to their binding strength, and thereby increase the ratio of specifically bound labels to more weakly attached non-specifically bound labels. This method can be used with a wide variety of label types and associated detection methods, improving the sensitivity and selectivity of a broad range of binding assays.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Surface-functionalized molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of a surface-functionalized molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere. The crosslinking degree of the molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere is above 60 percent, and therefore, the molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere has excellent molecule recognition to a template molecule and the particle size of 1-5 microns and is provided with an active function group on the surface. The molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere is prepared by adopting a new method of controllable / active free radical deposition and polymerization. The invention has the advantages of simple method, wide application range, pure product and the like. The prepared molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere has a wide application potential in mass fields of chromatographic stationary phase, biological sample analysis, medial clinic immunity analysis, food and environment monitoring, analogy enzyme catalysis, biomimetic sensors and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of bionic artemisinin molecular imprinting composite membrane
InactiveCN104231166AHigh selectivityEasy to separateOther chemical processesMethacrylateFunctional monomer
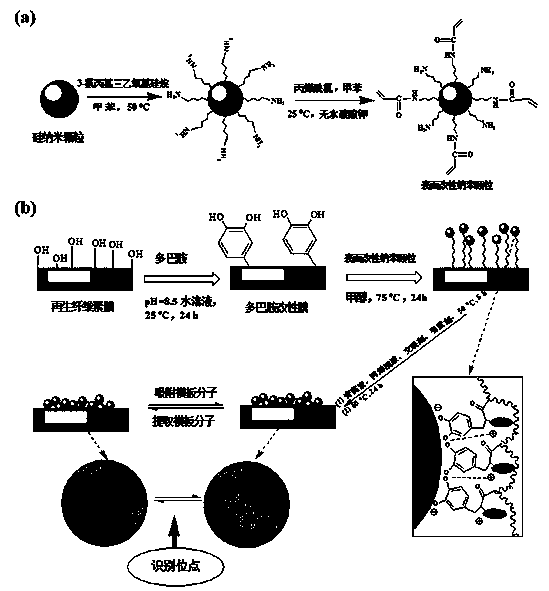
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bionic artemisinin molecular imprinting composite membrane, belonging to the technical field of environmental material preparation. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: by taking a regenerated cellulose membrane as a substrate, artemisinin as a template molecule, acrylamide (AM) as a functional monomer and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as a cross-linking agent, inlaying silicon dioxide nanoparticles with functional monomer modified surfaces to the surface of a membrane material by combination with a dopamine bionic principle, and performing two-step temperature polymerization to prepare the bionic artemisinin molecular imprinting composite membrane. The static adsorption experiment is used for making a research on the adsorption balance, dynamics and selective recognition performance of the prepared imprinting membrane. A result shows that the artemisinin imprinting membrane prepared by adopting the method is relatively high in adsorption capacity and superior in artemisinin molecular recognition penetration performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of fly ash superbead magnetic composite material surface imprinting adsorbent
InactiveCN102350319AAvoid embedding too deeplyAvoiding non-elutable problemsOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMolecularly imprinted polymerMolecular recognition
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fly ash superbead magnetic composite material surface imprinting adsorbent. The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental material preparation. Through a microemulsion method, cross-linked chitosan is used for coating nano-grade gamma-Fe2O3 and micrometer-grade ball-shaped fly ash superbeads, such that the fly ash superbead magnetic composite material is obtained; the fly ash superbead magnetic composite material is adopted as a substrate, molecularly imprinted polymer modification is carried out on the surface of the substrate through a suspension polymerization method; template molecules bisphenol A are eluted, such that the fly ash superbead magnetic composite material surface imprinting adsorbent is obtained. The ball-shaped imprinting adsorbent has substantial thermal and magnetic stabilities. 1H-NMR shows that hydrogen bonding among the molecules is an identification framework of the imprinting adsorbent. As a result of a static absorbing experiment, the fly ash superbead magnetic composite material surface imprinting adsorbent provided by the invention has relatively high adsorption capacity, rapid adsorption dynamic property and substantial BPA molecule identification performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
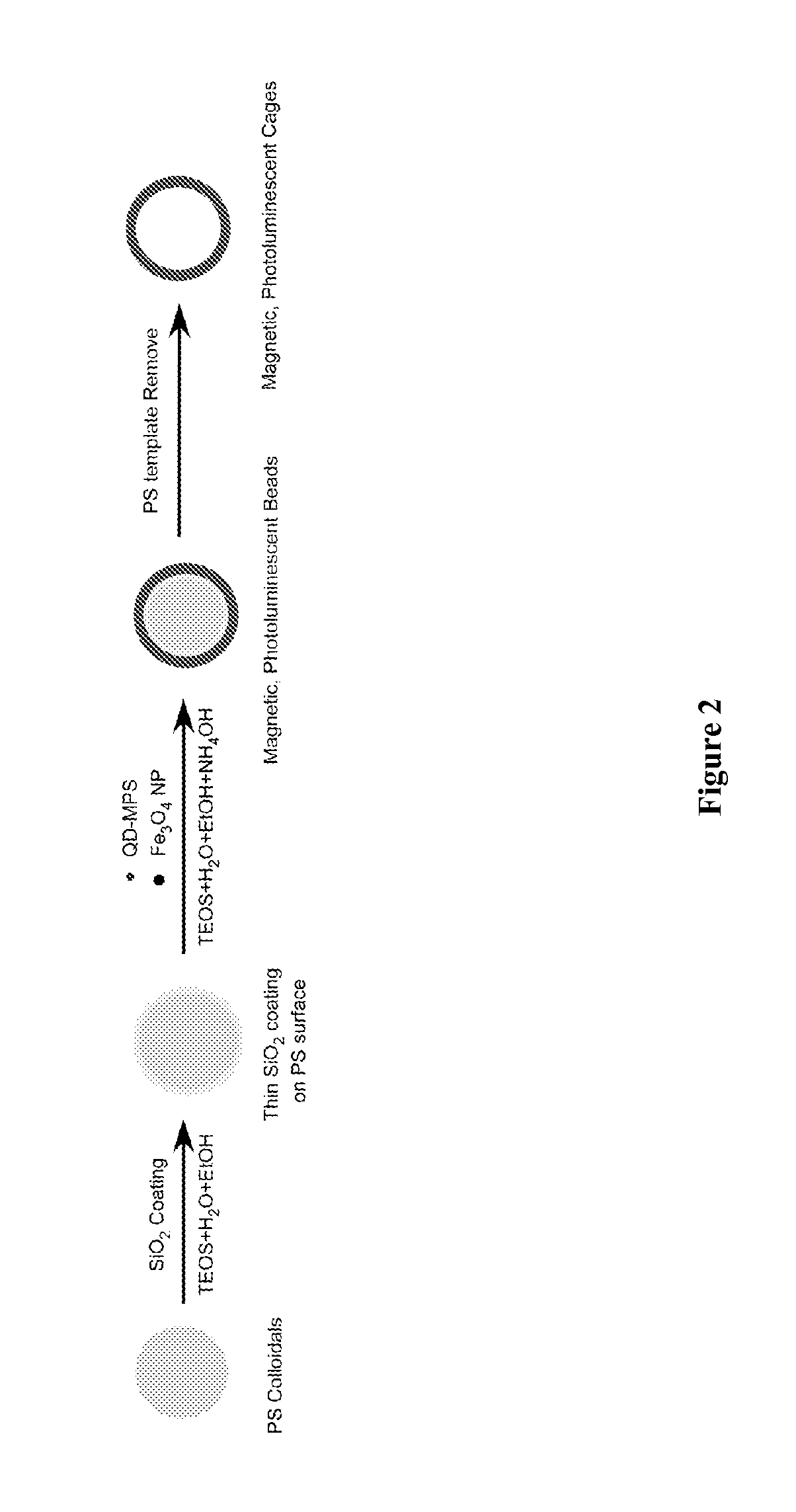
Quantum Dot Barcode Structures and Uses Thereof
The present invention provides novel barcode microstructures and methods for making and using the microstructures for molecular recognition, and / or delivery of therapeutic, diagnostic, contrast, and imaging agents.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
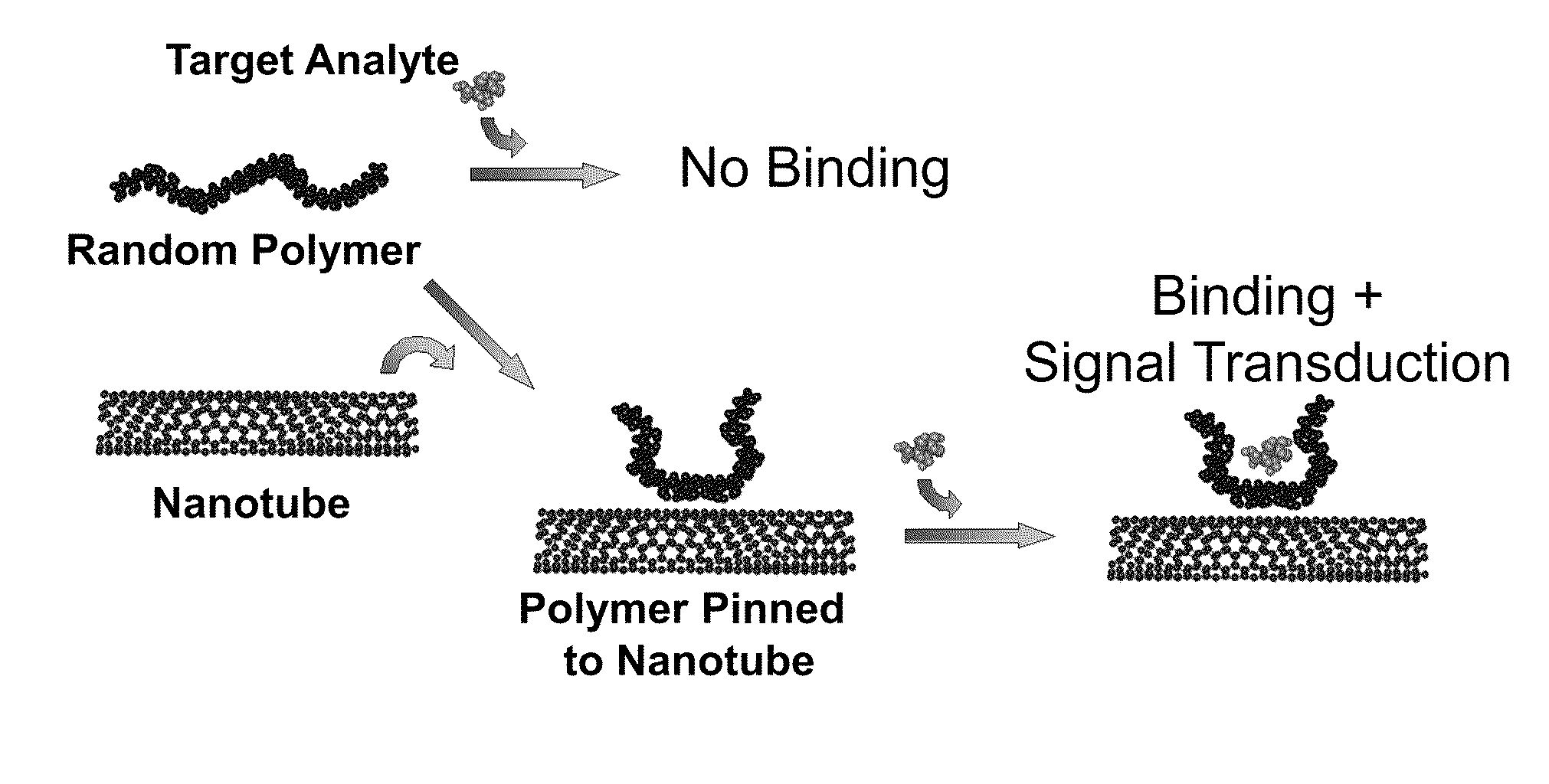
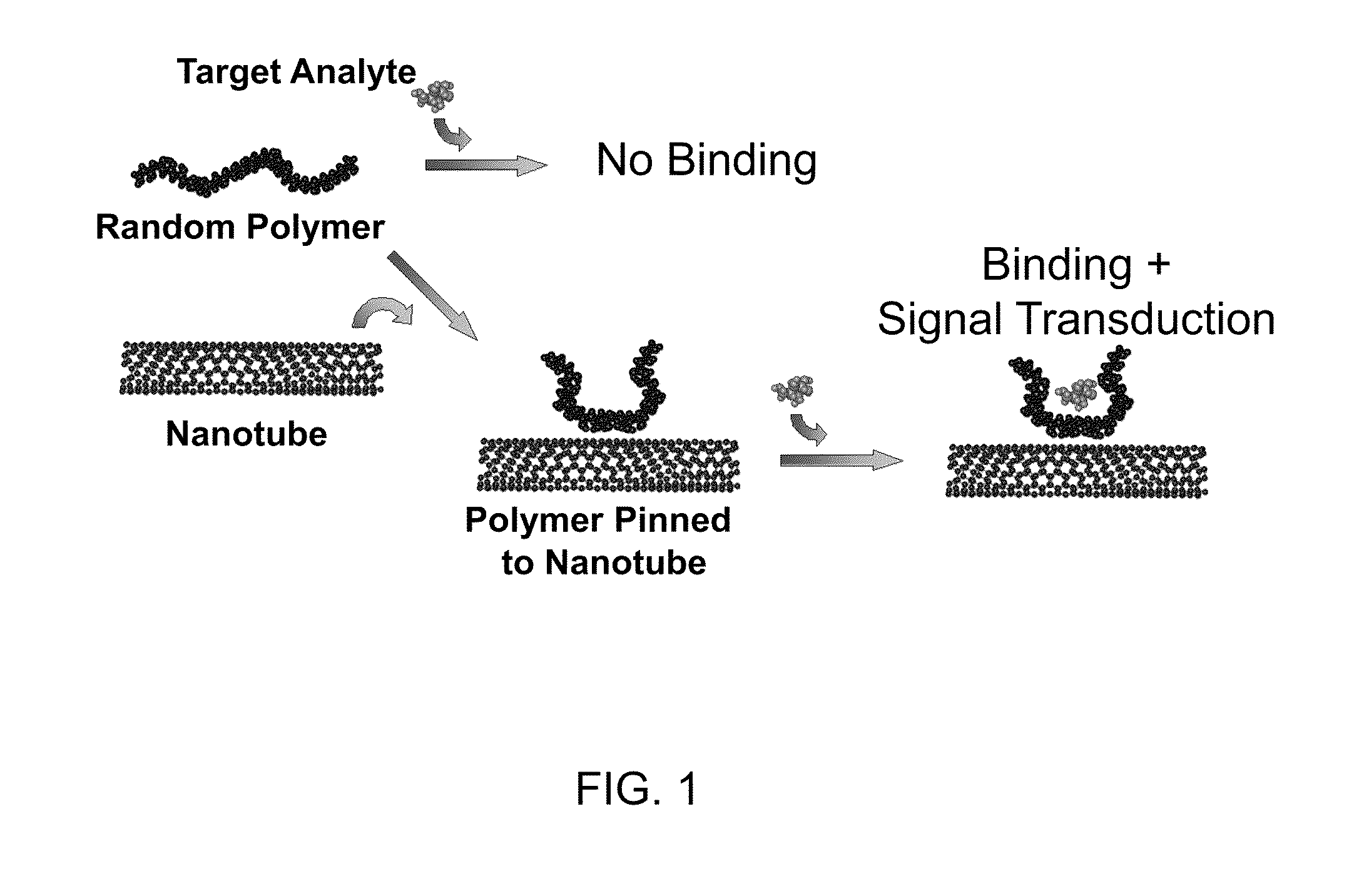
Polymer-nanostructure composition for selective molecular recognition
ActiveUS20110257033A1Material nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalytePhotoluminescence
A composition can include a complex, where the complex includes a photoluminescent nanostructure and a polymer free from selective binding to an analyte, the polymer adsorbed on the photoluminescent nanostructure, and a selective binding site associated with the complex.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation method of macrolide antibiotics molecular engram polymer microsphere
InactiveCN101507916AOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesWater bathsFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a method for preparing macrolide antibiotics molecular engram polymer microspheres, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: dissolving a dispersant, namely polyvinyl alcohol or hydroxyethyl cellulose into secondary distilled water to prepare a water-phase dispersion liquid; dissolving engram molecules and functional monomers into an organic solvent to prepare an oil-phase mixture; adding the oil-phase mixture into the water-phase dispersion liquid under the action of stirring, adding an initiator, namely azo-bis-iso-butyrynitrile into the mixture, performing thermal initiation polymerization on the mixture in water bath, and obtaining polymer microspheres; and adopting an ultrasonic extraction method to elute the engram molecules in a butyl acetate aqueous solution or a methanol solution of acetic acid, using distilled water to wash the engram molecules, and performing vacuum drying on the engram molecules to obtain the macrolide antibiotics molecular engram polymer microspheres. Through the method, the macrolide antibiotics molecular engram polymer microspheres are prepared in water phases and are recognized in the water phases; the reorganization result is close to that obtained by a natural biological molecular recognition system; and the invention provides a method for recognizing, separating and analyzing hydrophilic medicaments .
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Electrochemical sensor based on molecular engram and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102721727AQuick analysisBest preparation conditionsMaterial electrochemical variablesHigh concentrationPeak current
The invention relates to an electrochemical sensor based on a molecular engram and a preparation method and an application thereof. The electrochemical sensor based on the molecular engram comprises a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode, wherein the base electrode of the working electrode is a gold electrode; sulfonated graphene is modified on the surface of the gold electrode; after airing, polymerization is performed in an acid buffer solution containing o-phenylenediamine and dopamine till the oxidation peak current of the o-phenylenediamine falls to zero, and then dopamine is eluted in a sulfuric acid medium; and the reference electrode and the counter electrode are a saturated calomel electrode and a platinum wire electrode respectively. Under an optimal condition, a molecular engram sensor with molecule identifying performance is prepared by an appropriate eluting method, so that rapid analysis and detection of the dopamine are realized. The electrochemical sensor based on the molecular engram has the advantages of quick response, high selectivity, high sensitivity and the like on the molecular engram, the aim of identifying molecules is fulfilled, and detection of the dopamine in the presence of high-concentration ascorbic acid is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com