Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Genomic Stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genome instability (also genetic instability or genomic instability) refers to a high frequency of mutations within the genome of a cellular lineage. These mutations can include changes in nucleic acid sequences, chromosomal rearrangements or aneuploidy. Genome instability does occur in bacteria.
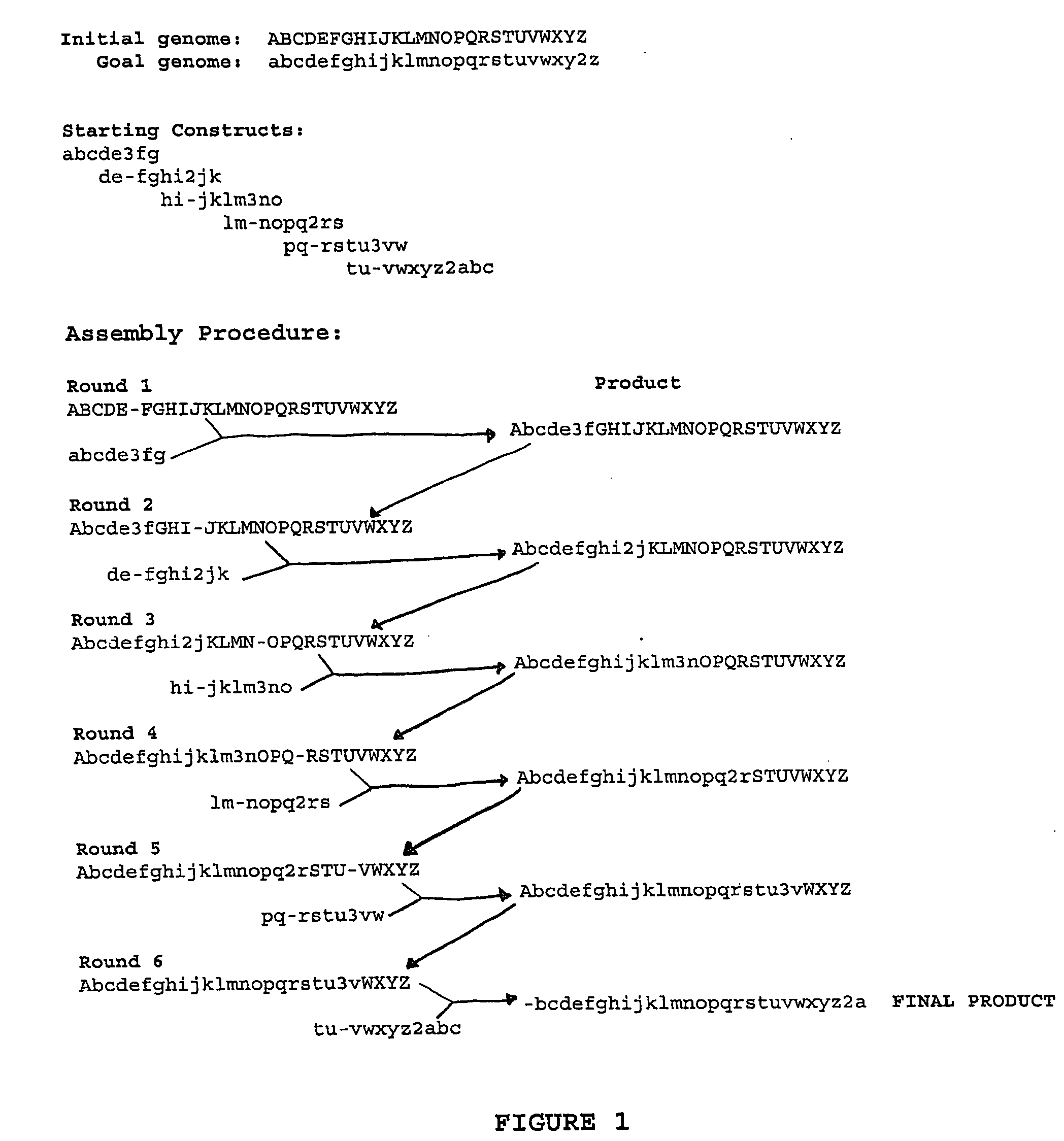
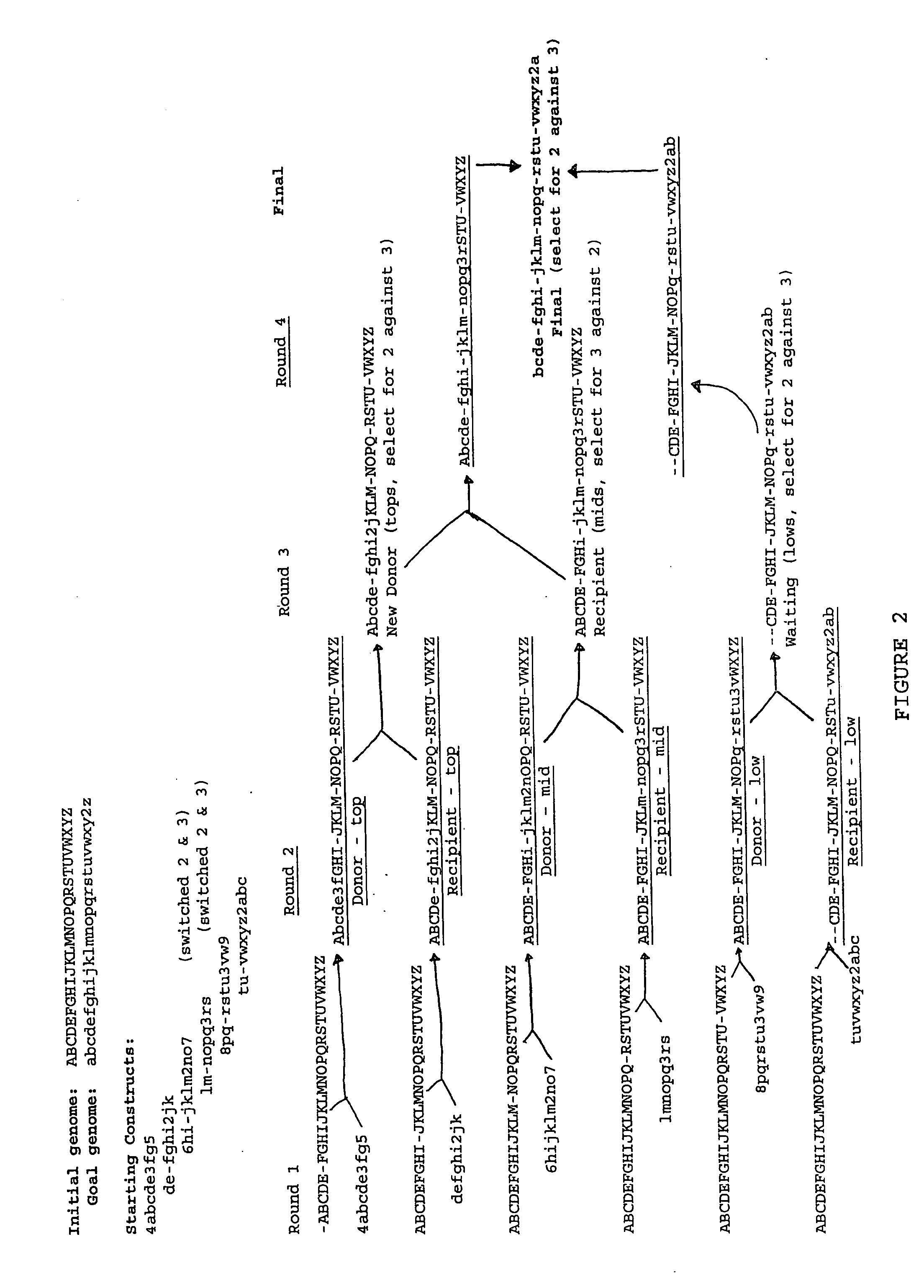
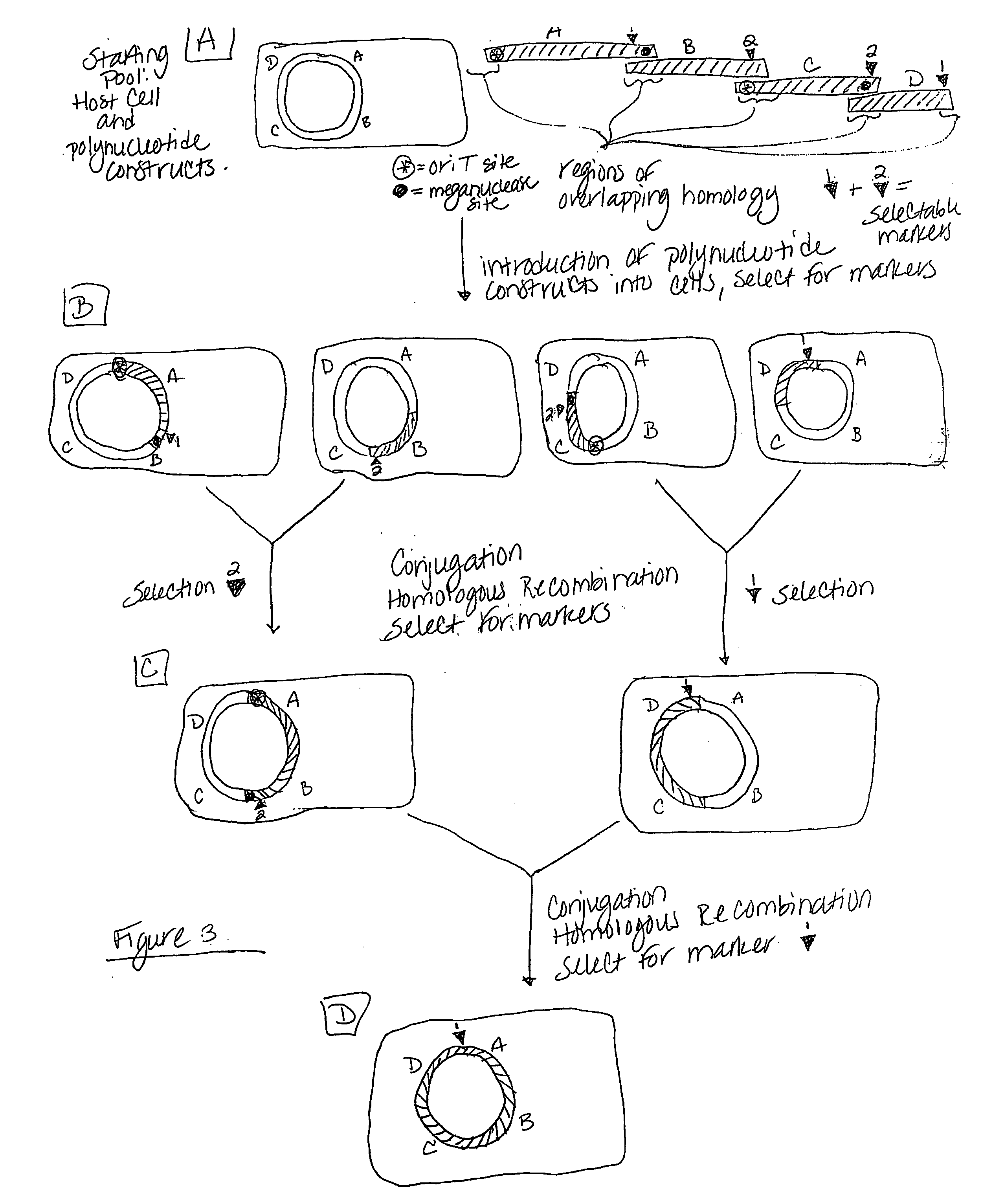
Heirarchical assembly methods for genome engineering
InactiveUS20070004041A1Improve securityImprove propertiesStable introduction of DNAFermentationBiological bodyGenomic Stability
The present invention provides recombination based methods for assembling nucleic acids. In certain aspects the present invention provides hierarchical assembly methods for producing genome sized polynucleotide constructs. The methods may be used for assembling large polynucleotide constructs, for synthesizing synthetic genomes, or for introducing a plurality of nucleotide changes throughout the genome of an organism. In another aspect, the invention provides cells having increased genomic stability. For example, cells comprising alterations in at least a substantial portion of the transposons in the genome are provided.
Owner:CODON DEVICES
Methods and compositions for treatment of ataxia-telangeictasia
InactiveUS20050009760A1Increase genomic stabilityReduce oxidative stressBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseGenomic Stability
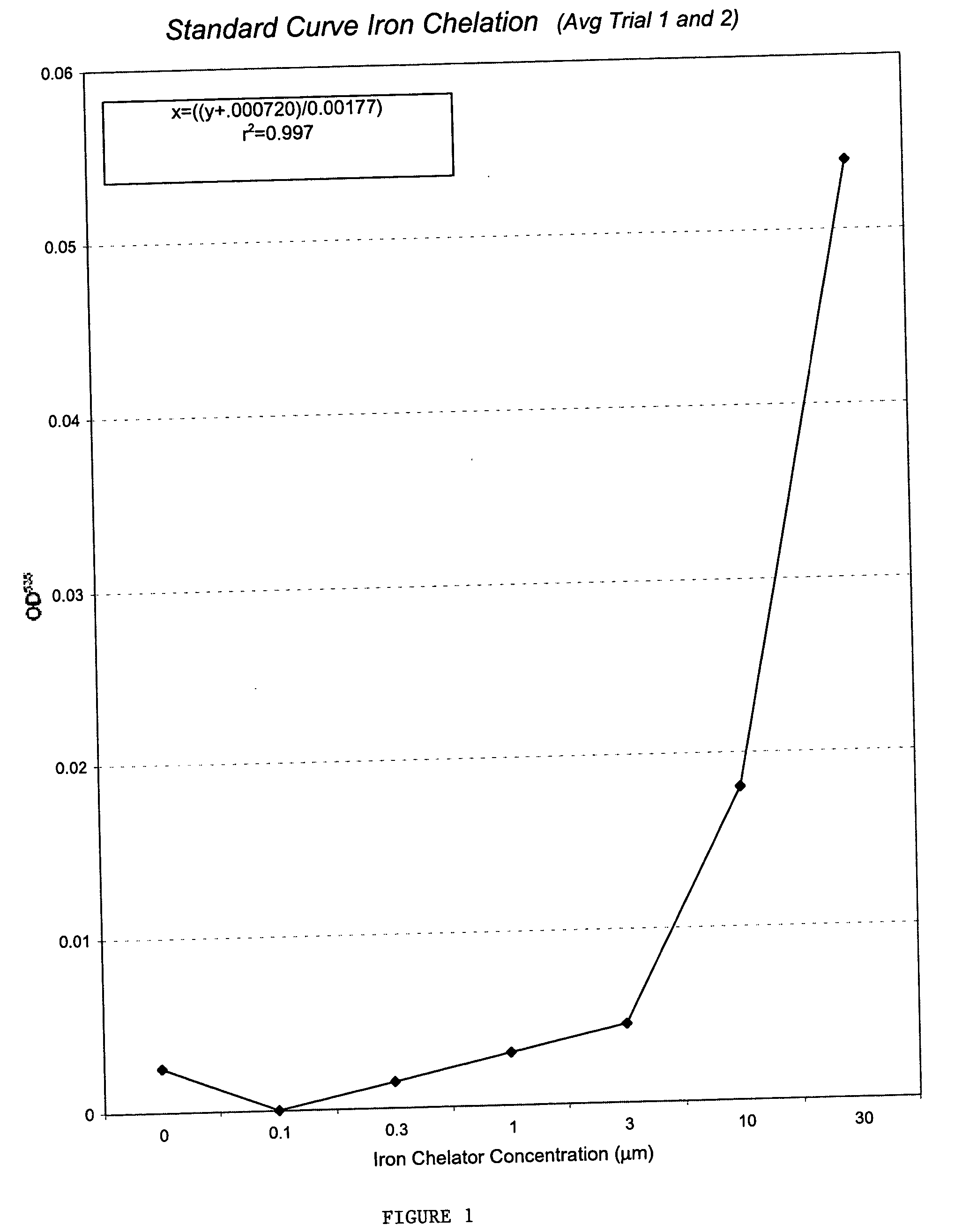
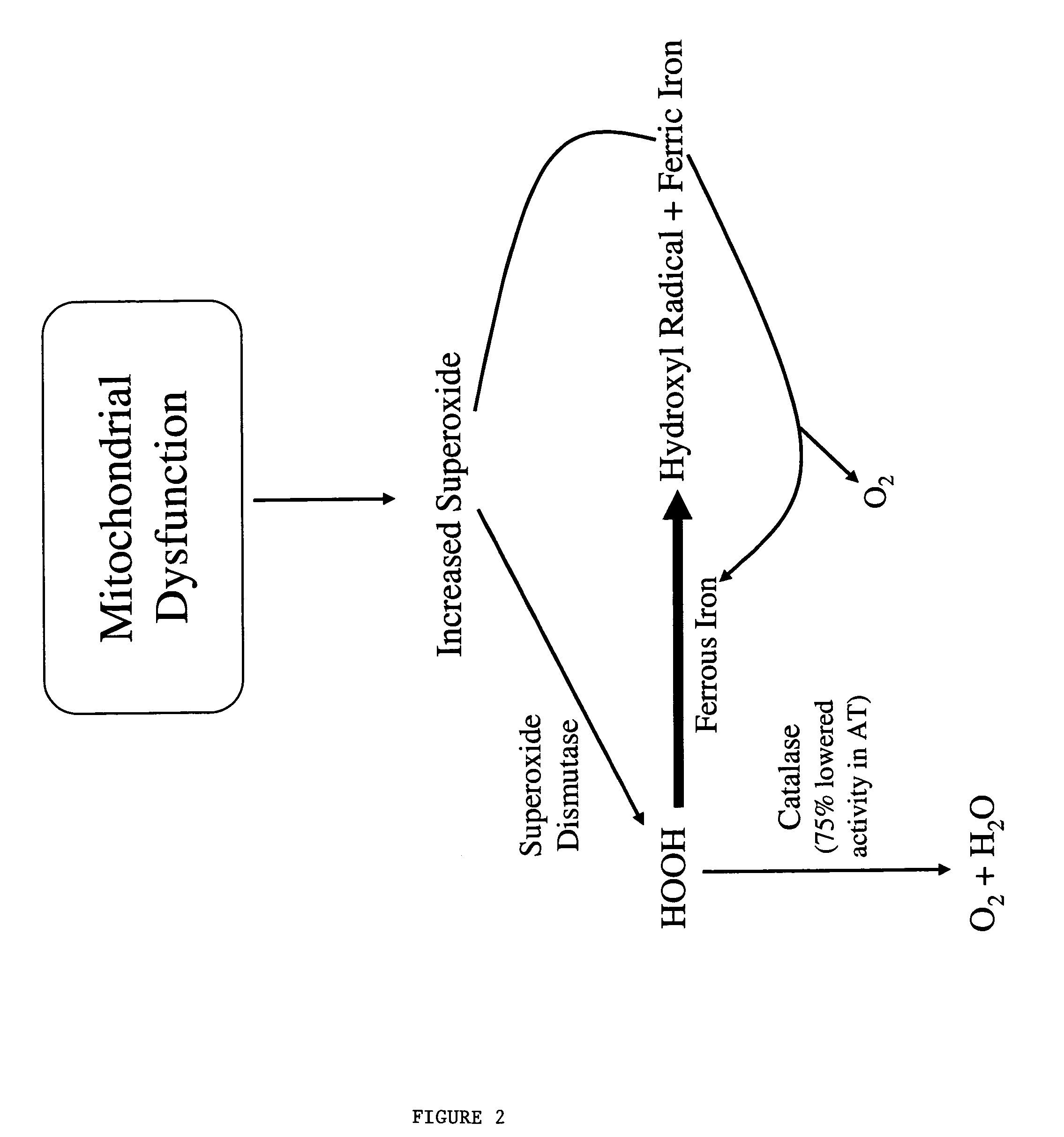
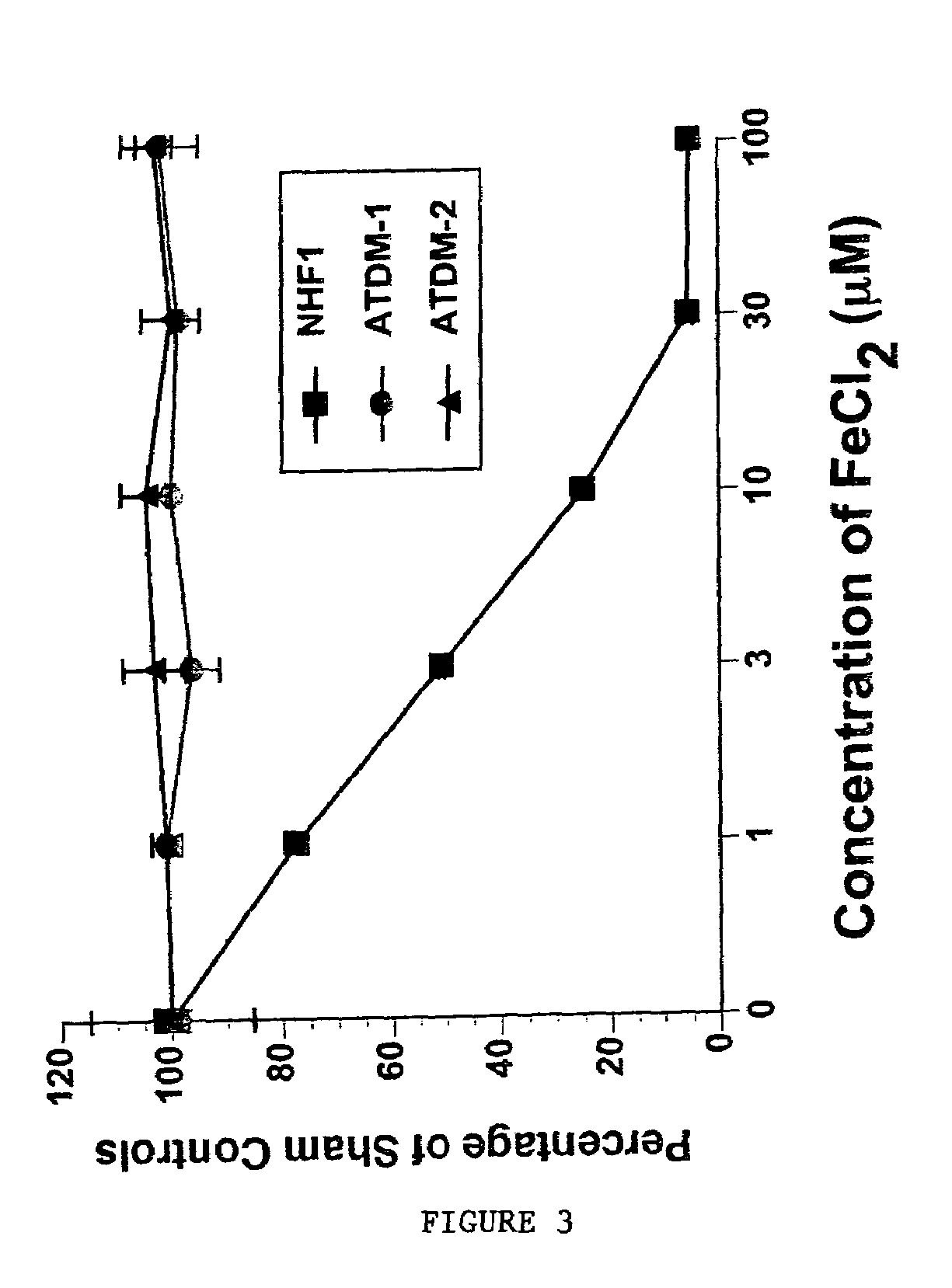
This invention relates to the methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating diseases or disorders associated with oxidative stress and / or genomic instability. In particular, the invention relates to methods for treating ataxia-telangeictasia (AT) and such disease states by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a chelating agent to increase genomic stability and / or decrease oxidative stress.
Owner:WANG SUMING
MiRNA associated with genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and application of miRNA
ActiveCN105821042AReduce riskGood clinical valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic StabilityMesenchymal stem cell
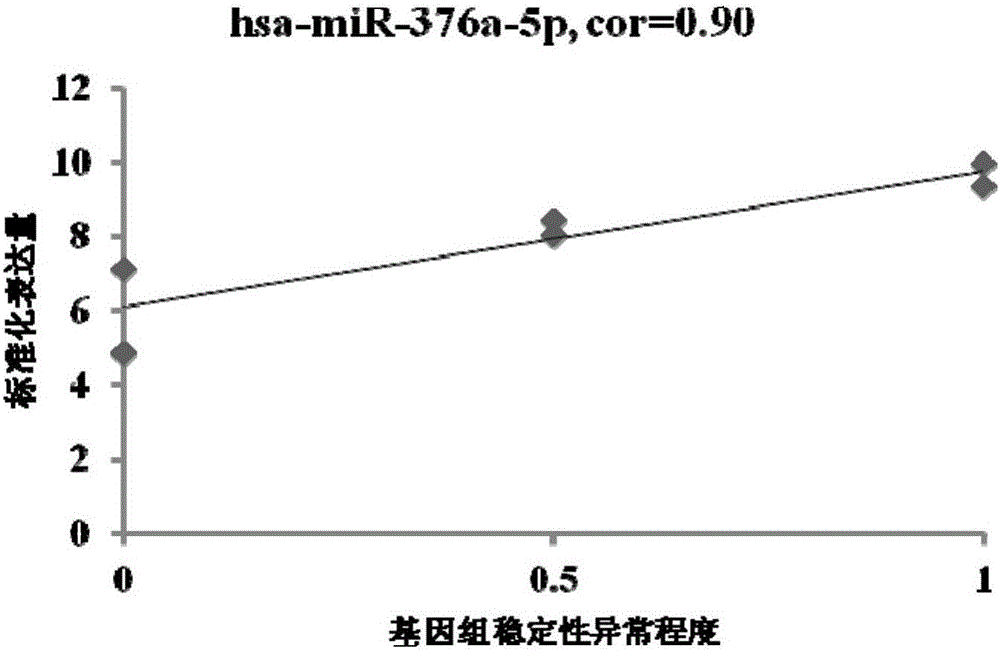
The invention provides an miRNA marker associated with genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and a detection method of the miRNA marker. A new generation of high-throughput sequencing technology is used, in combination with a bioinformatic analysis method of a system, to screen and obtain the miRNA associated with genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells, wherein an RNA sequence is shown in SEQ IDNO.1-5. The invention also provides a specific primer for detecting the miRNA and a detection method of the specific primer, wherein conditions for the detection method of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are optimized. Through the detection of the specific miRNA marker provided by the invention, the genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells after passage or amplification can be estimated effectively, to reduce costs and the risk of subsequent clinical application; the miRNA has excellent clinical application value and broad application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
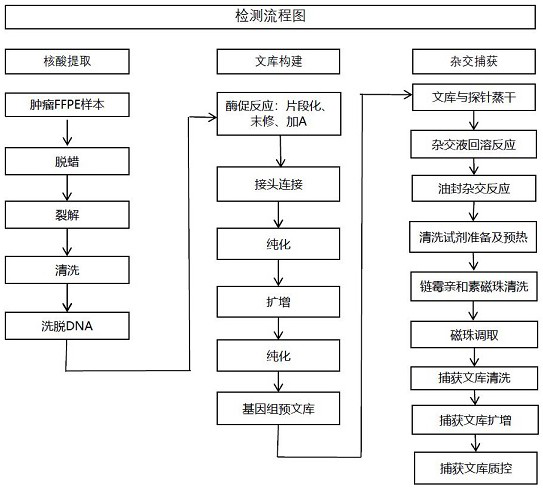
Method and test kit for determining genome instability on basis of next-generation sequencing technology
ActiveCN111676277AHigh detection sensitivityImprove capture efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic StabilityGenome instability
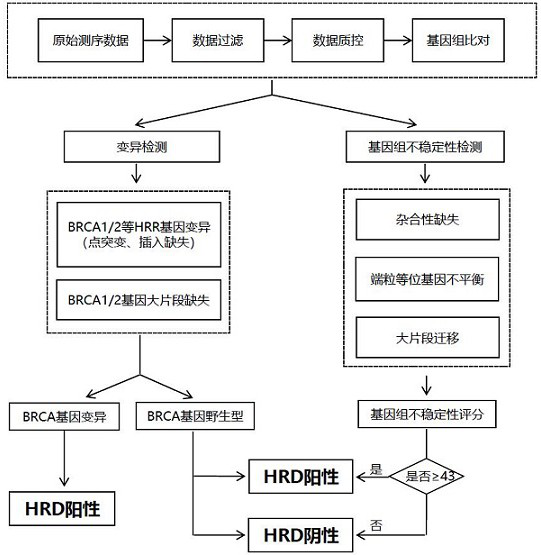
The invention relates to a method and a test kit for determining genome instability on the basis of a next-generation sequencing technology, belonging to the technical field of molecular detection. Inorder to overcome the defect that genome structure variation is not considered during detection of homologous recombination defects in the prior art, the invention provides the method and the test kit for determining genome instability on the basis of the next-generation sequencing technology. The method comprises the following steps: breaking a to-be-detected gene, then adding an A connector fora corresponding PCR reaction, carrying out hybridization capture through a designed probe, then amplifying a captured DNA library, sequencing the library, and carrying out evaluating through a software so as to determine the homologous recombination defect state. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention can comprehensively evaluate the HRD state, is reliable in data results and is applicable to popularization.
Owner:臻和(北京)生物科技有限公司 +1
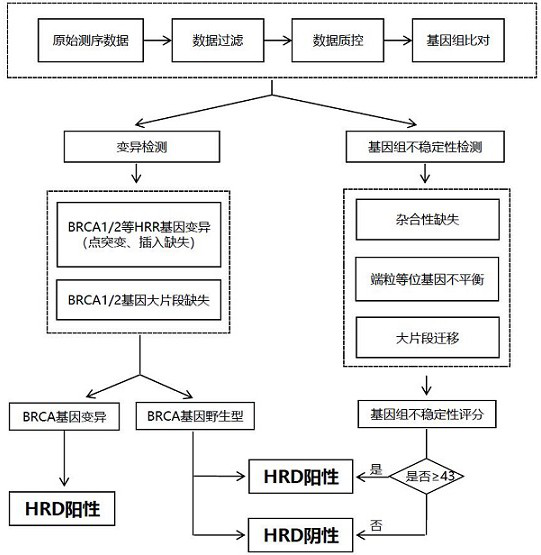
Homologous recombination defect judgment method based on DNA sequencing data
ActiveCN111462823AOvercoming the Difficulty of Data InsufficiencyThe result is easy to judgeBiostatisticsSequence analysisGenomic StabilityGenome instability
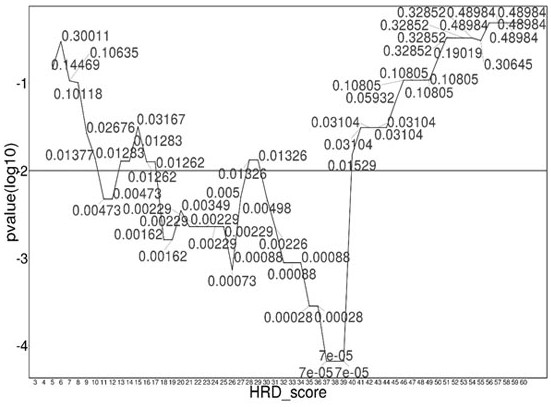
The invention discloses a homologous recombination defect judgment method based on DNA sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring characteristic attributes; extracting validdata; based on a triple learning method framework, selecting three different base classifiers H1, H2 and H3 by considering good generalization ability, high accuracy and processing efficiency for multi-dimensional feature attributes; performing iterative training on the H1, H2 and H3 to obtain an extended training set, and updating a model to complete a training process; and marking a unmarked sample set U by using the trained model, and completing judgment of the HRD state according to the marking result. According to the method, the limitation that HRD state judgment is carried out by usinglocal characteristics such as a single genome instability state or a small number of genome instability states and the like is solved, the difficulty that the number of samples with clinically known HRD states is extremely small is overcome, learning of multi-characteristic attributes under existing sample data is achieved, and the performance of the HRD judgment method can be improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
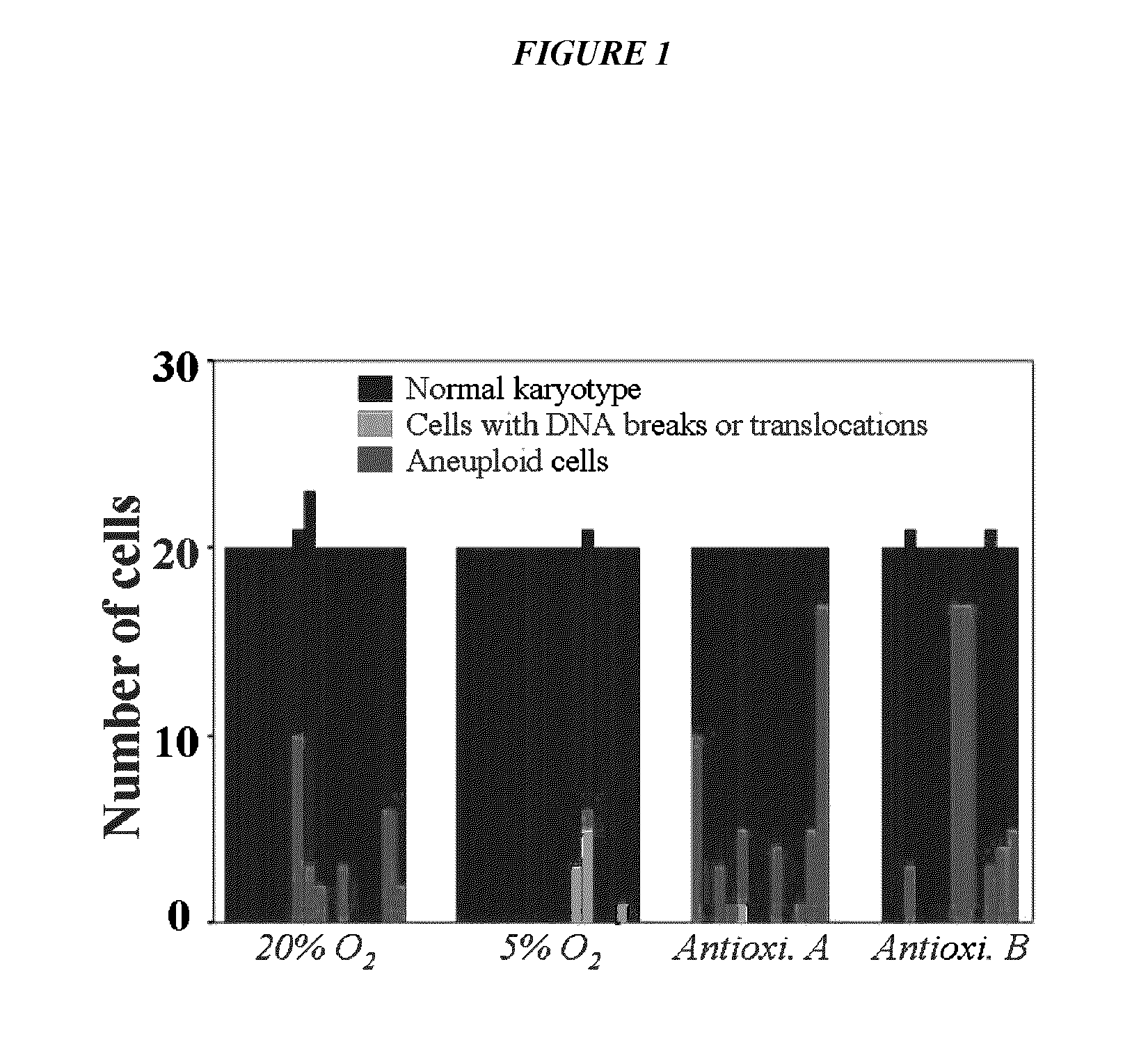
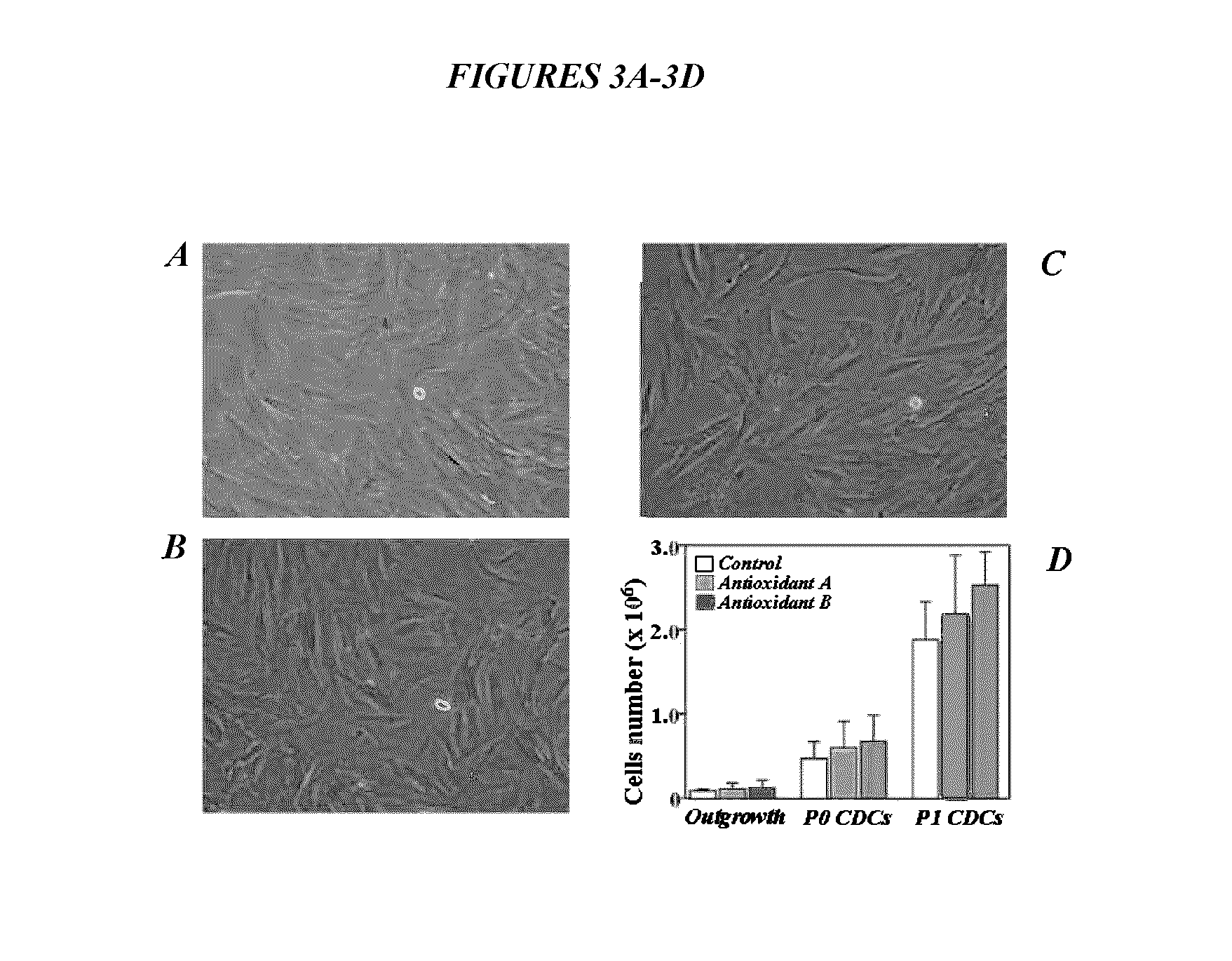
Maintenance of genomic stability in cultured stem cells
ActiveUS9845457B2Low efficacyImprove stabilityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGenomic StabilityAntioxidant
The present application relates to methods and compositions for the generation of therapeutic cells having reduced incidence of karyotypic abnormalities. In several embodiments cardiac stem cells are cultured in an antioxidant-supplemented media that reduces levels of reactive oxygen species, but does not down regulate DNA repair mechanisms. In several embodiments, physiological oxygen concentrations are used during culture in order to increase the proliferation of stem cells, decrease the senescence of the cells, decrease genomic instability, and / or augment the functionality of such cells for cellular therapies.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Kit and probe for measuring instability of genome and application of kit and probe
ActiveCN112662767AEfficient analysisLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genome sequenceGenome instability
The invention provides a kit for measuring genome instability and application thereof, and a probe set contained in the kit is determined by the following steps: dividing a reference genome sequence into a plurality of first-level regions, wherein the first-level regions contain at least one known SNP site; performing SNP filtering on each of the plurality of primary regions; selecting a notch region; dividing the gap region into at least one secondary region based on an expected interval; for each of the at least one secondary region, respectively carrying out secondary high-frequency SNP search: carrying out extension treatment from the central point of the secondary region to two sides for at least one time, and after extending for a preset length for at least one time, searching for the SNP with the highest frequency in the obtained region, and determining a third-level region on the basis of taking the summary of the first-level high-frequency SNP and the second-level high-frequency SNP as the starting point SNP; and based on the third-level region, constructing a probe for specifically identifying the third-level region. By utilizing the method, the probe combination which can be effectively used for analyzing the instability of the genome can be effectively obtained.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +2
Method for constructing target set for homologous recombination repair defect detection
ActiveCN113462784AImprove the detection rateReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic StabilityGenome instability
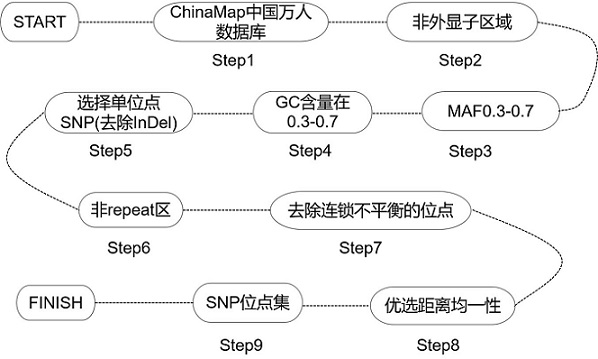
The invention relates to a method for constructing a target set for homologous recombination repair defect detection. The target set comprises a homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene and SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) loci, the HRR gene comprises 40 genes represented by BRCA1 and BRCA2, and the SNP loci comprise 10913 SNP loci. The SNP loci capable of fully representing genome instability are screened and combined with the HRR gene to construct the target set, the probe composition is designed, HRR gene variation can be detected by utilizing the probe composition, meanwhile, genome instability is accurately evaluated, the positive detection rate of homologous recombination repair defects can be effectively increased. The detection cost is reduced.
Owner:QIAGEN SUZHOU TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE CO LTD
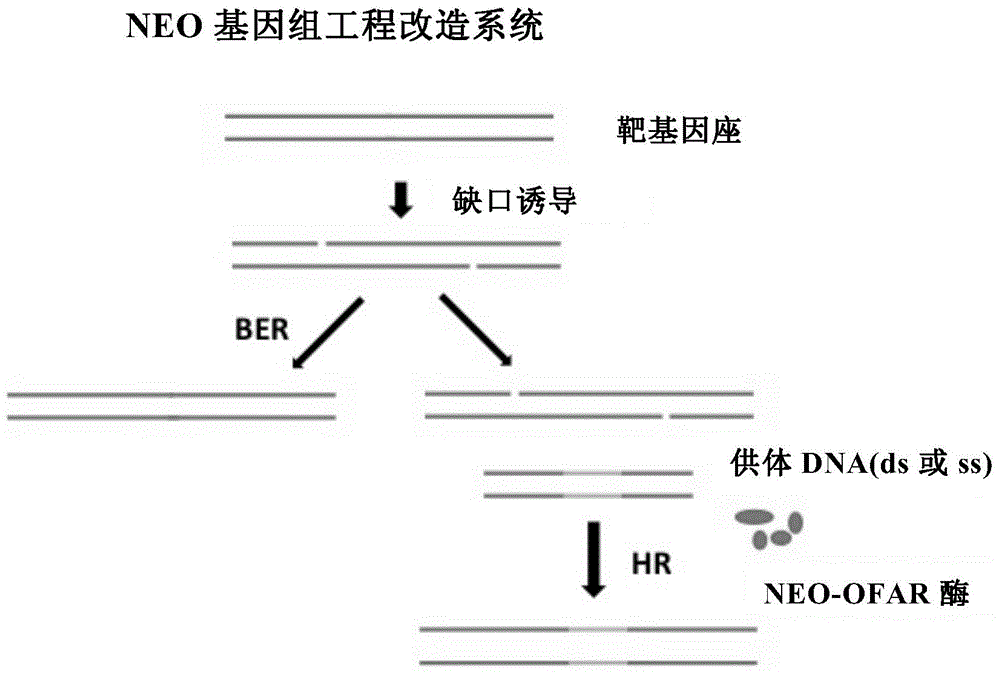
Gene knock-in composition and use method and application thereof
InactiveCN104946621AImprove the efficiency of homologous recombinationAvoid the disadvantages of instabilityRecombinant DNA-technologyForeign genetic material cellsGenome instabilityGenomic Stability
The invention provides a gene knock-in composition containing a single incision enzyme or polynucleotide coding the same, recombinase or polynucleotide coding the same, and an optional donor DNA containing an exogenous gene. The invention also provides a corresponding gene knock-in method and a method for preparing a transgenic non-human mammal model. The composition and the methods provided by the invention can be used for realizing efficient homologous recombination integration, and meanwhile various defects of insertion or deletion, genome instability and the like which are generated easily in the prior art can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
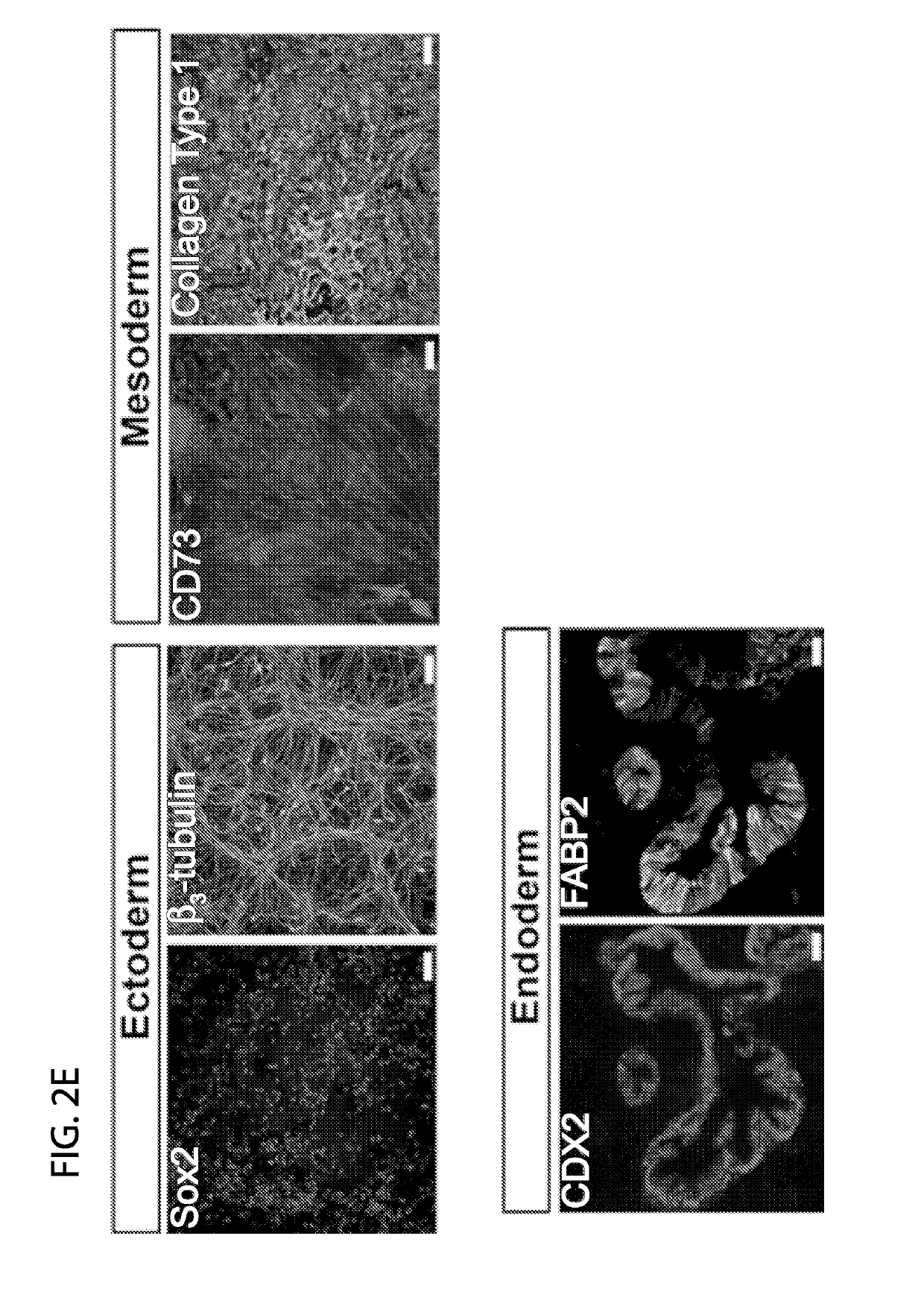
Novel and efficient method for reprogramming blood to induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20170362574A1Reduced feature requirementsCulture processCell culture supports/coatingReprogrammingGenomic Stability
Described herein are methods and compositions related to generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Improved techniques for establishing highly efficient, reproducible reprogramming using non-integrating episomal plasmid vectors. Using the described reprogramming protocol, one is able to consistently reprogram non-T cells with close to 100% success from non-T cell or non-B cell sources. Further advantages include use of a defined reprogramming media E7 and using defined clinically compatible substrate recombinant human L-521. Generation of iPSCs from these blood cell sources allows for recapitulation of the entire genomic repertoire, preservation of genomic fidelity and enhanced genomic stability.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method for removing genomically unstable ips cells and synthetic peptide used therefor
ActiveUS20160252523A1Highly efficient and highly reliable evaluationGood effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic StabilityCalreticulin
The present invention provides a method that allows highly efficient and highly reliable evaluation of genomic stability of pluripotent stem cells, a method for removing pluripotent stem cells that have been identified as genomically unstable by the evaluation method from a culture of pluripotent stem cells to be evaluated, and a synthetic peptide that can be used for the methods. The methods provided by the present invention include preparing a culture of pluripotent stem cells of interest and analyzing an expression level of calreticulin for the pluripotent stem cells in the culture followed by identifying genomic stability or genomic instability of the stem cells on the basis of the expression level of calreticulin.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD +1
Methods and compositions for modulating tumor suppression
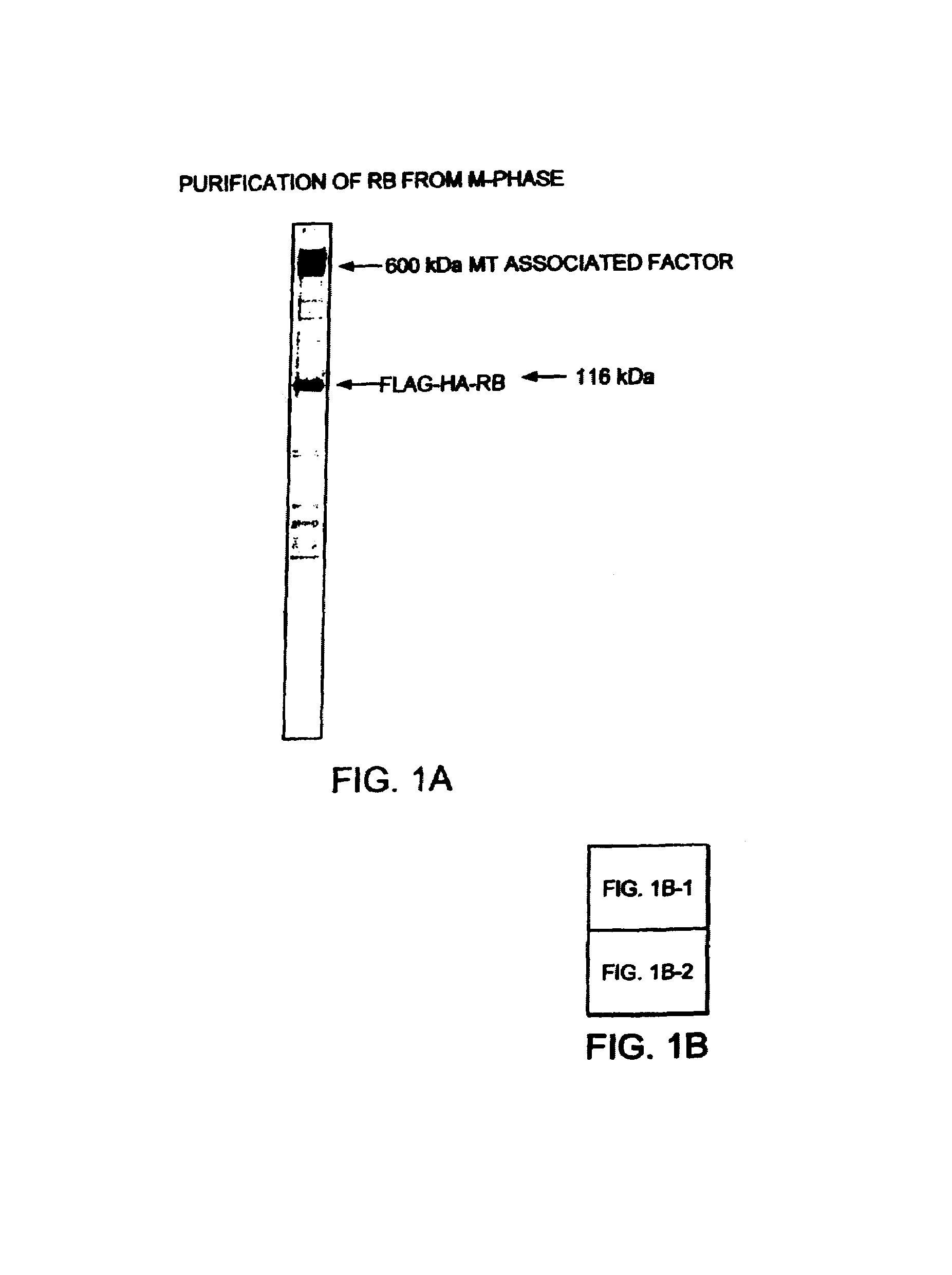
The purification of native RB (retinoblastoma) as a complex, including P107, P130, and a 600 kDa subunit, termed MTAF600 (microtubule associated factor 600) is described. MTAF600 binds to RB regardless of the phosphorylation status of RB, and binds to RB without disrupting the interaction between RB and E2F. It is further shown that E2F and DP proteins co-purified with MTAF600 and RB, such that hypophosphorylated RB may gain access to E2F as a complex with MTAF600. In addition, MTAF600 binds to microtubules and plays a role in active repression of E2F-responsive genes, cell cycle arrest, and genomic stability. The sequence of MTAF600 is described herein, along with its binding properties to proteins such as RB and microtubules, and its sequence homology. Further, methods and reagents for assaying the presence of MTAF600 or mutants thereof, pharmaceutical formulations, and methods for treating disease are also described.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Methods and compositions for treatment of Ataxia-telangeictasia
InactiveUS7176239B2Improve stabilityReduce oxidative stressBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseGenomic Stability
This invention relates to the methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating diseases or disorders associated with oxidative stress and / or genomic instability. In particular, the invention relates to methods for treating ataxia-telangeictasia (AT) and such disease states by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a chelating agent to increase genomic stability and / or decrease oxidative stress.
Owner:WANG SUMING
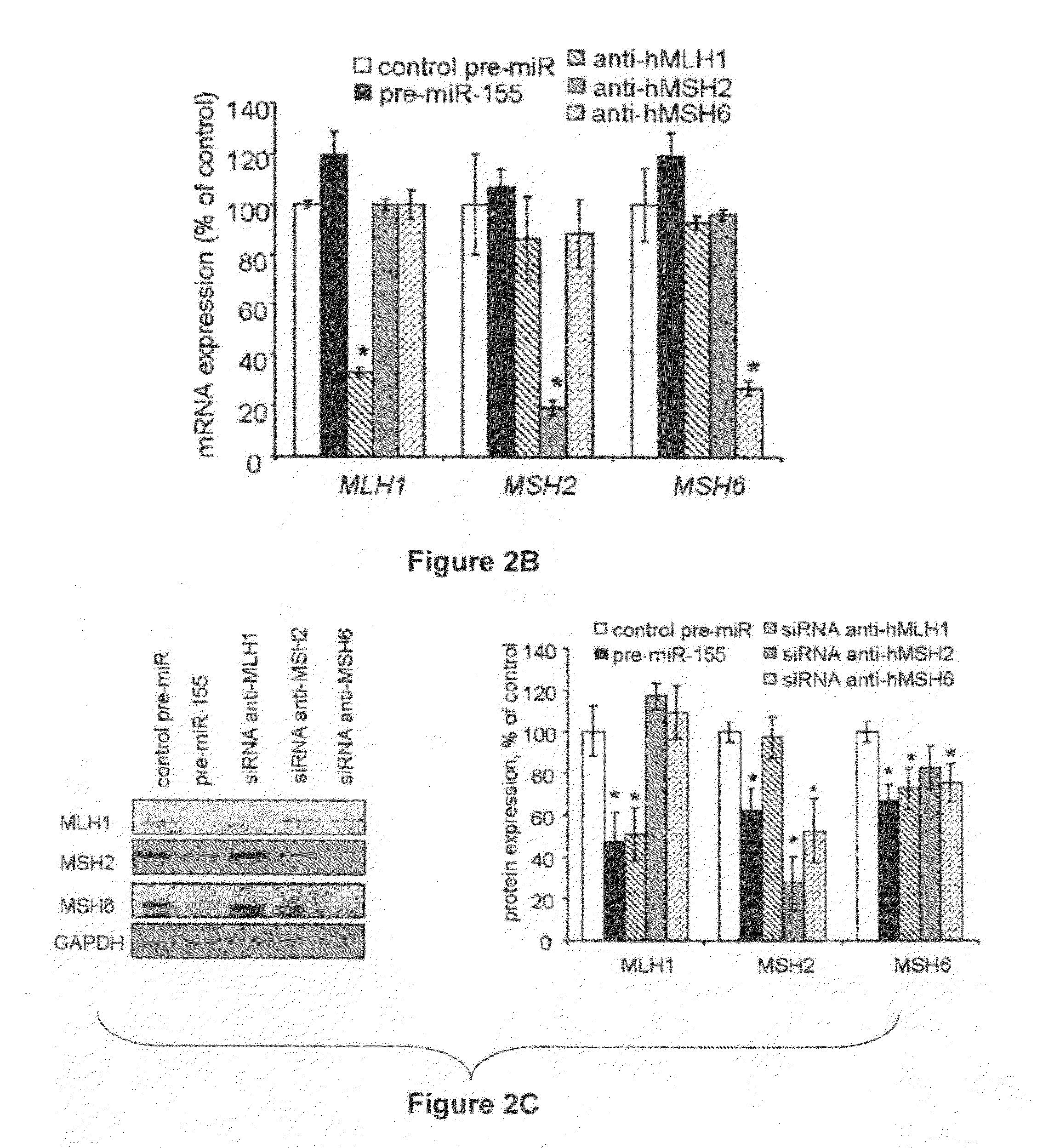
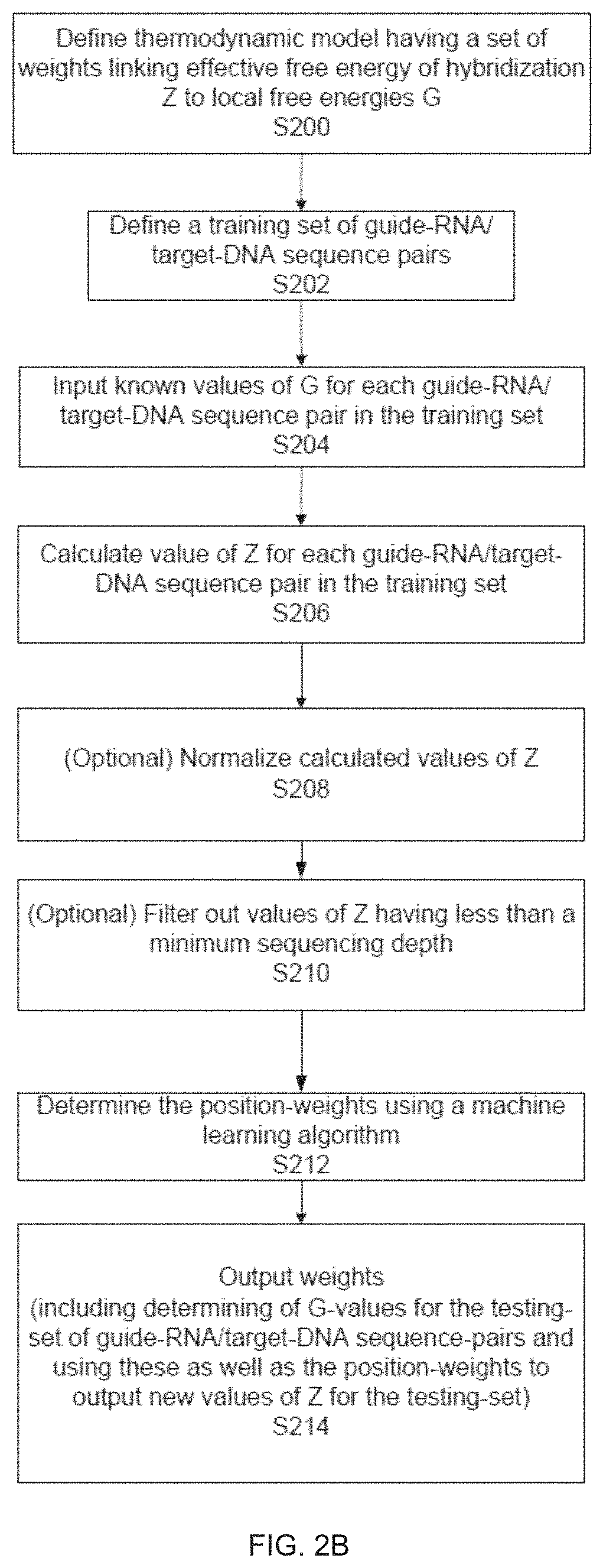
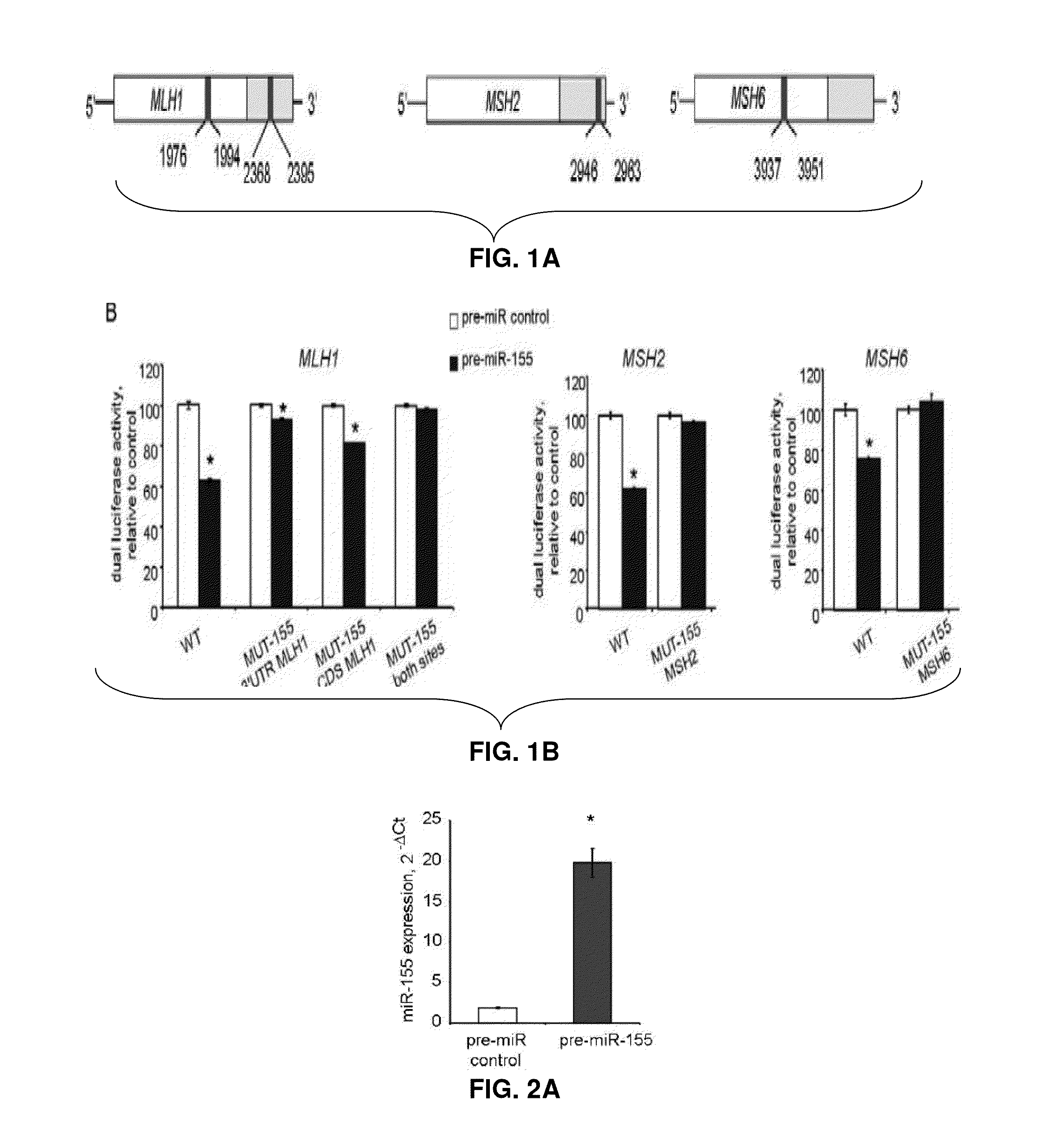
Materials and Methods Related to Modulation of Mismatch Repair and Genomic Stability by miR-155
InactiveUS20130065946A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGenomic StabilityProviding material
The present invention provides materials and methods related to modulation of mismatch and genomic stability by miR-155.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Maintenance of genomic stability in cultured stem cells
ActiveUS20160108365A1Low efficacyEnhanced genomic stabilityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGenomic StabilityAntioxidant
The present application relates to methods and compositions for the generation of therapeutic cells having reduced incidence of karyotypic abnormalities. In several embodiments cardiac stem cells are cultured in an antioxidant-supplemented media that reduces levels of reactive oxygen species, but does not down regulate DNA repair mechanisms. In several embodiments, physiological oxygen concentrations are used during culture in order to increase the proliferation of stem cells, decrease the senescence of the cells, decrease genomic instability, and / or augment the functionality of such cells for cellular therapies.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
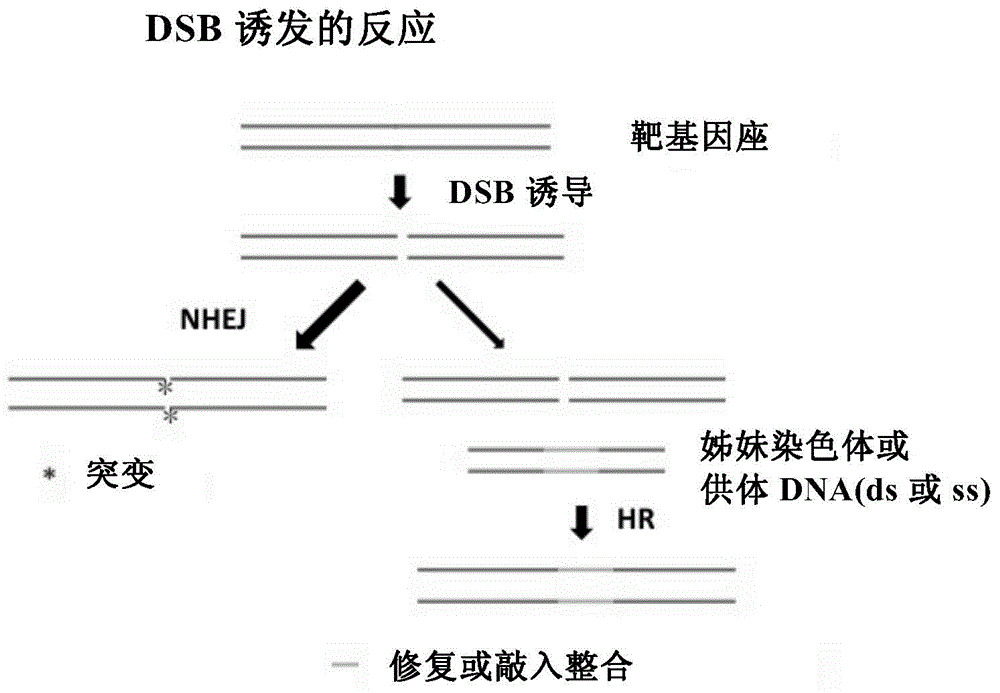
Unbiased identification of double-strand breaks and genomic rearrangement by genome-wide insert capture sequencing
ActiveUS10689691B2Simplify methodologyImprove abilitiesHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenome editingGenomic Stability
The invention provides for systems, methods, compositions, and kits for the complete characterization of targeted nuclease specificity which necessitates techniques that can assess the full possibility space of off-target activity and genomic stability following genome editing. Also provided are the materials and techniques which enable the comprehensive genomic stability accompanying a range of cellular perturbations, including genome editing (ZFN, TALEN, CRISPR, and future technologies) and disease modeling among other applications.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Materials and Methods Related to Modulation of Mismatch Repair and Genomic Stability by miR-155
The present invention provides materials and methods related to modulation of mismatch repair and genomic stability by miR-155.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Methods and compositions for modulating tumor suppression
The purification of native RB (retinoblastoma) as a complex, including P107, P130, and a 600 kDa subunit, termed MTAF600 (microtubule associated factor 600) is described. MTAF600 binds to RB regardless of the phosphorylation status of RB, and binds to RB without disrupting the interaction between RB and E2F. It is further shown that E2F and DP proteins co-purified with MTAF600 and RB, such that hypophosphorylated RB may gain access to E2F as a complex with MTAF600. In addition, MTAF600 binds to microtubules and plays a role in active repression of E2F-responsive genes, cell cycle arrest, and genomic stability. The sequence of MTAF600 is described herein, along with its binding properties to proteins such as RB and microtubules, and its sequence homology. Further, methods and reagents for assaying the presence of MTAF600 or mutants thereof, pharmaceutical formulations, and methods for treating disease are also described.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Efficient method for reprogramming blood to induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS10221395B2Reduced feature requirementsCulture processCell culture supports/coatingReprogrammingGenomic Stability
Described herein are methods and compositions related to generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Improved techniques for establishing highly efficient, reproducible reprogramming using non-integrating episomal plasmid vectors. Using the described reprogramming protocol, one is able to consistently reprogram non-T cells with close to 100% success from non-T cell or non-B cell sources. Further advantages include use of a defined reprogramming media E7 and using defined clinically compatible substrate recombinant human L-521. Generation of iPSCs from these blood cell sources allows for recapitulation of the entire genomic repertoire, preservation of genomic fidelity and enhanced genomic stability.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Methods and compositions for maintaining genomic stability in cultured stem cells
ActiveUS20110269230A1Low efficacyEnhanced genomic stabilityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAntioxidantGenomic Stability
The present application relates to methods and compositions for the generation of therapeutic cells having reduced incidence of karyotypic abnormalities. In several embodiments cardiac stem cells are cultured in an antioxidant-supplemented media that reduces levels of reactive oxygen species, but does not down regulate DNA repair mechanisms. In several embodiments, physiological oxygen concentrations are used during culture in order to increase the proliferation of stem cells, decrease the senescence of the cells, decrease genomic instability, and / or augment the functionality of such cells for cellular therapies.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Novel and efficient method for reprogramming blood to induced pluripotent stem cells
Described herein are methods and compositions related to generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Improved techniques for establishing highly efficient, reproducible reprogramming using non-integrating episomal plasmid vectors. Using the described reprogramming protocol, one is able to consistently reprogram non-T cells with close to 100% success from non-T cell or non-B cell sources. Further advantages include use of a defined reprogramming media E7 and using defined clinically compatible substrate recombinant human L-521. Generation of iPSCs from these blood cell sources allows for recapitulation of the entire genomic repertoire, preservation of genomic fidelity and enhanced genomic stability.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
A method for constructing a target collection for homologous recombination repair defect detection
ActiveCN113462784BImprove the detection rateReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic StabilityGenome instability
The invention relates to a method for constructing a target set for homologous recombination repair defect detection. The target set includes homologous recombination repair (homologous recombination repair, HRR) genes and SNP sites, the HRR genes include 40 genes represented by BRCA1 and BRCA2, and the SNP sites include 10913 SNP sites. The present invention screens SNP sites that can fully characterize genomic instability and constructs a target set in combination with HRR genes, and designs a probe composition, which can detect HRR gene variation and simultaneously detect genomic instability Accurate assessment can effectively expand the detection rate of positive homologous recombination repair defects and reduce detection costs.
Owner:QIAGEN SUZHOU TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE CO LTD
A method and kit for determining genome instability based on next-generation sequencing technology
ActiveCN111676277BHigh detection sensitivityImprove capture efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic StabilityGenome instability
Owner:臻和(北京)生物科技有限公司 +1
The miRNA related to genome stability of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and its application
ActiveCN105821042BReduce riskGood clinical valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic StabilityMesenchymal stem cell
The invention provides an miRNA marker associated with genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells and a detection method of the miRNA marker. A new generation of high-throughput sequencing technology is used, in combination with a bioinformatic analysis method of a system, to screen and obtain the miRNA associated with genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells, wherein an RNA sequence is shown in SEQ IDNO.1-5. The invention also provides a specific primer for detecting the miRNA and a detection method of the specific primer, wherein conditions for the detection method of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are optimized. Through the detection of the specific miRNA marker provided by the invention, the genomic stability of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells after passage or amplification can be estimated effectively, to reduce costs and the risk of subsequent clinical application; the miRNA has excellent clinical application value and broad application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Increasing genomic stability and reprogramming efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells
PendingCN114502576AGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNAReprogrammingGenomic Stability
The present disclosure relates to methods and compositions for producing induced pluripotent stem cells with improved efficiency and genomic stability. In particular aspects, induced pluripotent stem cells are produced from somatic cells after inhibiting, lowering, or down-regulating a particular protein or gene. In some embodiments, the protein is a p53-binding protein or 53BP1.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Assay method, device, terminal device and computer readable storage medium for measuring genomic instability
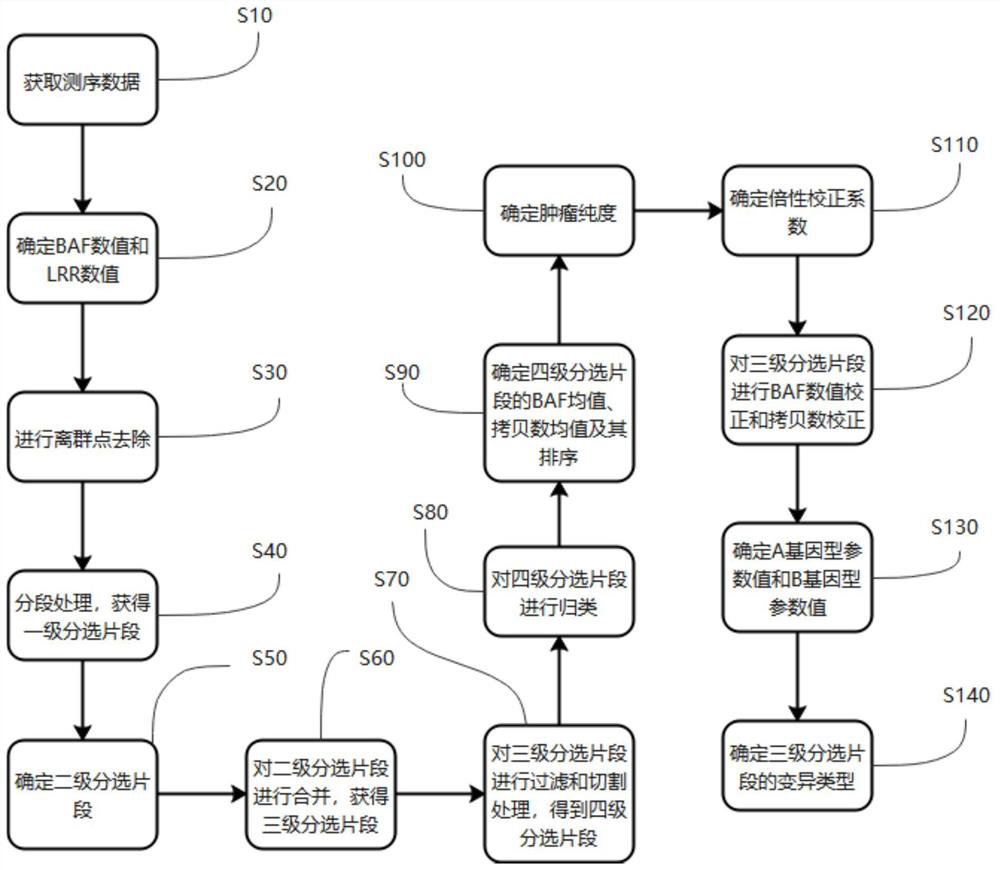
The invention provides a detection method for measuring genome instability, comprising: (1) obtaining sequencing data; (2) determining BAF values and LRR values; (3) performing outlier removal; (4) at least one round of analysis segment processing; (5) merging of breakpoint sets; (6) merging of the second-level sorting segments; (7) filtering and cutting of the third-level sorting segments, (8) same distribution test; (9) determination BAF mean value, copy number mean value; (10) Carry out plane coordinate axis clustering and plotting to the BAF mean value, copy number mean percentage ordinal number of the four-level sorting fragments, so as to determine the tumor purity of the tumor sample in the test sample; (11) determine The ploidy correction factor of the sample to be tested; (12) performing BAF value correction and copy number correction; (13) determining the A genotype parameter value and the B genotype parameter value; (14) determining the variation type.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +2
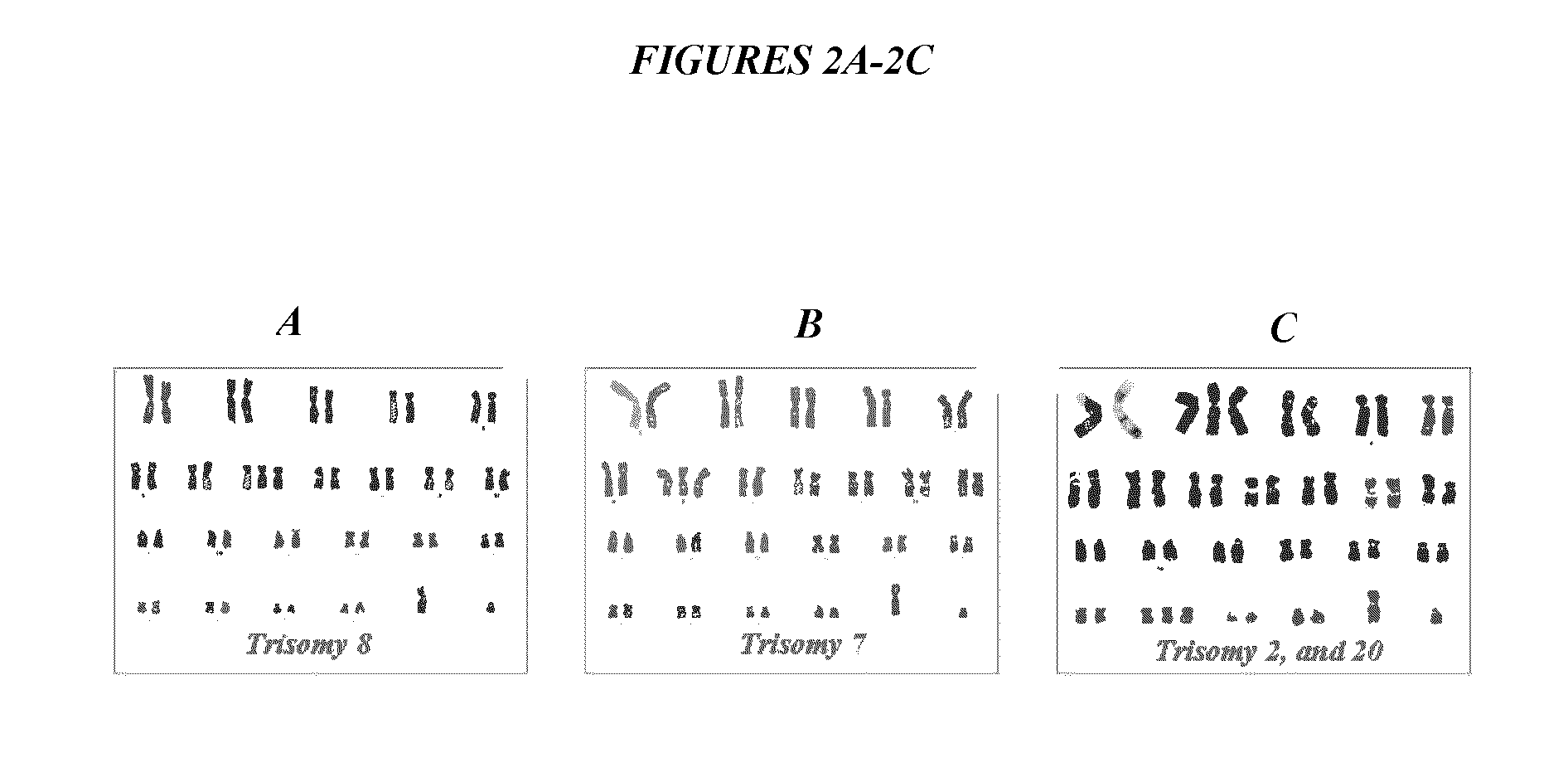
Trisome syndrome gene nucleic acid detection quality control product based on CRSIPR-Cas9 and organoid culture and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN112391461AImprove stabilityRealize all-round monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsTelomeraseGenomic Stability
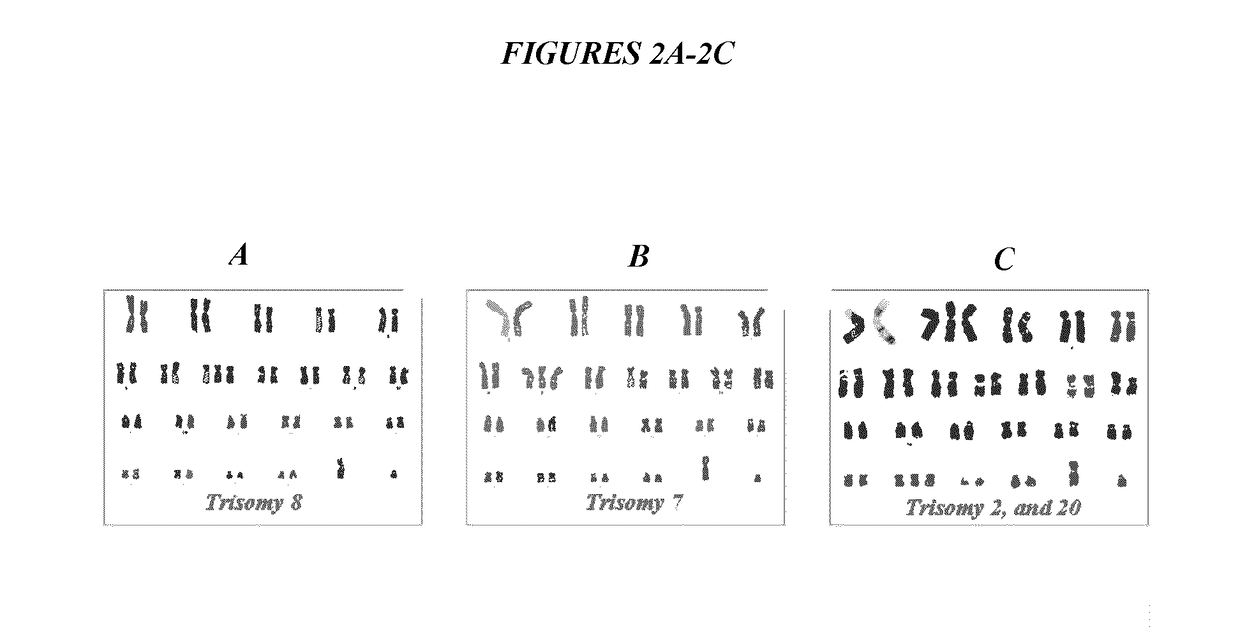
The invention provides a trisome syndrome gene nucleic acid detection quality control product based on CRSIPR-Cas9 and organoid culture. The quality control product is applied to omni-directional monitoring on a trisome syndrome gene detecting process. A preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out telomerase TERT knock-in expression on peripheral blood lymphocytes derived from a trisome syndrome sufferer by using a CRISPR-Cas9 technology, so as to construct gene-edited lymphocytes capable of stably amplifying and dividing; (2) constructing a brand-new organoid culture system, carrying out large-scale amplification on the gene-edited lymphocytes, and verifying maintaining conditions of chromosomal aberration states of amplified cells through chromosomal karyotype analysis; and (3) mixing the product with wild type human-derived lymphocytes according to a specific proportion, and carrying out accurate quantitative verification, thereby preparing the trisome syndrome gene nucleic acid detection quality control product. A foundation biological genetic background is closer to that of an actual sufferer, the stability is higher compared with that of a genome of a quality control derived from an ordinary sufferer, and omni-directional monitoring on trisome syndrome gene detection is achieved.
Owner:苏州艾可瑞斯生物科技有限公司
C terminal specific human Eme1 polypeptide and antibody preparation method
InactiveCN101318998AHigh potencyHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansGenomic StabilityCarrier protein
The invention discloses C-terminal specific human Eme1 polypeptide, as well as an antibody and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the biomedicine technical field. The amino acid sequence of the C-terminal specific human Eme1 polypeptide is VRRGEGVTSTSRRIG.. Antihuman EME1 polypeptide antibody is prepared according to the following method that: (1) human EME1 epitope is analyzed; (2) human EME1 C-terminal polypeptide is synthesized; (3) synthesized polypeptide is crosslinked with carrier protein; (4) rabbit anti-human EME1 polypeptide antibody is prepared; (5) serum containing the antibody is obtained through collection and separation, and the antibody is purified, and then the antihuman EME1 polypeptide antibody can be obtained. The C-terminal specific antihuman BTRC synthesized polypeptide antibody is high in potency, strong in affinity, good in specificity, capable of having specific conjugation with natural human Eme1; purified antibody can be completely used for immunoblot and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, as well as the establishment of in vitro immunization analytical method. The antibody provides a useful tool for the research on the biological effects of Eme1 in DNA damage and genomic stability.
Owner:BEIJING IMMUNOHUNT CORP
N terminal specific human Eme1 polypeptide and antibody preparation method
InactiveCN101318999AHigh potencyHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansGenomic StabilityCarrier protein
The invention discloses N-terminal specific human Eme1 polypeptide, as well as an antibody and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the biomedicine technical field. The amino acid sequence of the N-terminal specific human Eme1 polypeptide is LKKEPSSTKRRQPER. Antihuman EME1 polypeptide antibody is prepared according to the following method that: (1) human EME1 epitope is analyzed; (2) human EME1 N-terminal polypeptide is synthesized; (3) synthesized polypeptide is crosslinked with carrier protein; (4) rabbit anti-human EME1 polypeptide antibody is prepared; (5) serum containing the antibody is obtained through collection and separation, and the antibody is purified, and then the antihuman EME1 polypeptide antibody can be obtained. The N-terminal specific antihuman BTRC synthesized polypeptide antibody is high in potency, strong in affinity, good in specificity, capable of having specific conjugation with natural human Eme1; purified antibody can be completely used for immunoblot and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, as well as the establishment of in vitro immunization analytical method. The antibody provides a useful tool for the research on the biological effects of Eme1 in DNA damage and genomic stability.
Owner:BEIJING IMMUNOHUNT CORP
Method for removing genomically unstable IPS cells and synthetic peptide used therefor
ActiveUS10067145B2Highly efficient and highly reliable evaluationGood effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic StabilityInstability
The present invention provides a method that allows highly efficient and highly reliable evaluation of genomic stability of pluripotent stem cells, a method for removing pluripotent stem cells that have been identified as genomically unstable by the evaluation method from a culture of pluripotent stem cells to be evaluated, and a synthetic peptide that can be used for the methods. The methods provided by the present invention include preparing a culture of pluripotent stem cells of interest and analyzing an expression level of calreticulin for the pluripotent stem cells in the culture followed by identifying genomic stability or genomic instability of the stem cells on the basis of the expression level of calreticulin.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com