Gene knock-in composition and use method and application thereof
A gene knock-in and composition technology, applied in the field of gene knock-in composition, can solve problems such as low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
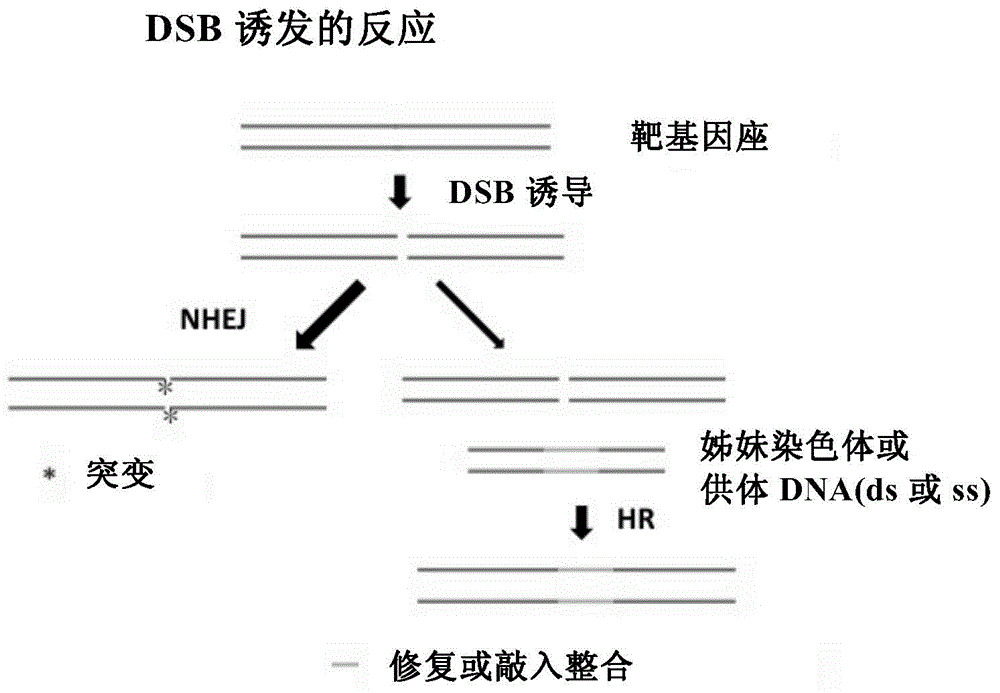
[0191] Example 1. Localization of potential nicks at the rat Bassoon integration target site
[0192] The goal of rat Bassoon genetic modification is to construct a transgenic rat strain that expresses Basson-EOS3.2 fusion protein at the endogenous Bassoon gene locus without changing other genome sequences. The operation of the corresponding transgene is integrated into the EOS3.2 DNA coding frame (ORF) within the front frame (in-frame) of the stop codon (stop codon) of Bassoon.
[0193] First, determine the integration site in the target site area, that is, near the stop codon of Bassoon, that is, select the single-strand gap (nick) site, and the integration site can be selected at the nick site or at a specific site between the cooperative nick sites. on the nucleotides.
[0194] This embodiment adopts Cas9 that has been genetically engineered, that is, Cas9-D10A and Cas9-H840A, hereinafter referred to as D10A and H840A, and the supporting sgRNA (upstream chain PAM: CCT T...
Embodiment 2
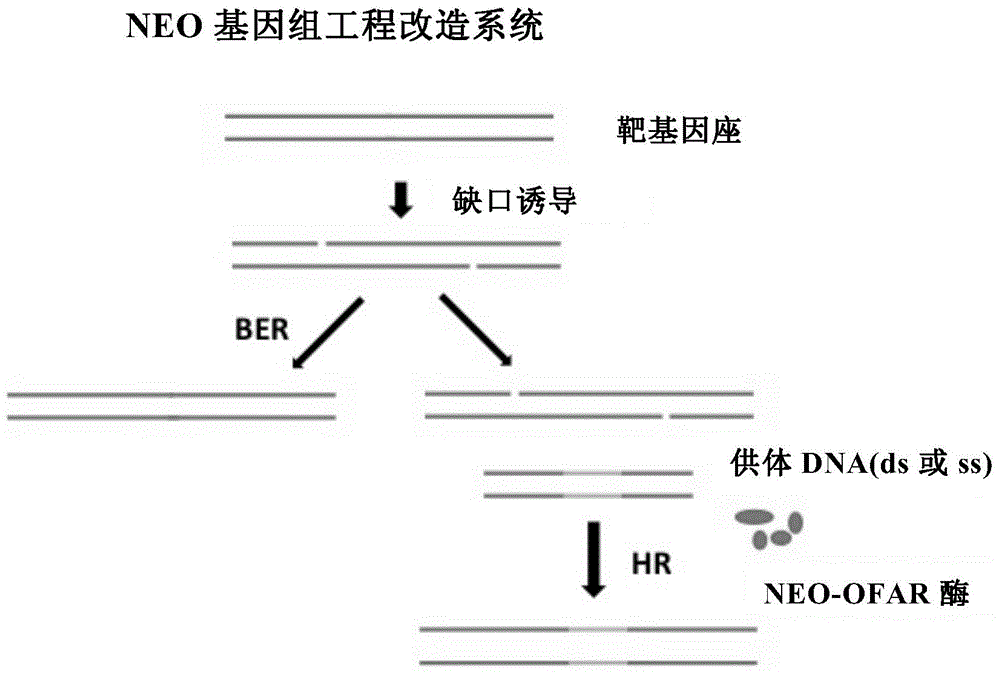
[0201] Example 2. Design of Exogenous Donor DNA Templates
[0202] Such as image 3 The donor DNA template was designed as shown, with 1 kb of homologous sequence upstream of the upstream nick (upstream homology arm) and 1 kb of homologous sequence downstream of the downstream nick (downstream homology arm). The EOS3.2 coding sequence was added at the integration site, and a linker region was added at the junction of EOS3.2 and Bassoon gene to reduce the effect of fluorescent protein on the function of Bassoon gene protein. This element comprising the upstream and downstream homology arms and the EOS3.2 coding frame (ORF) is molecularly cloned into the pBluescript II vector (Agilent's plasmid vector), and the plasmid is amplified and extracted to become an exogenous donor DNA (nucleotide sequence See SEQ ID NO: 15).
[0203] Donor DNA Construction:
[0204] 1kb upstream homology arm - CCTCA* + coding region of polyG linker + EOS3.2 coding region containing TAA stop codon *T...
Embodiment 3
[0205] Example 3. Preparation of recombinant enzyme complex
[0206] Four recombination factors derived from Escherichia coli (E.coli), collectively called OFAR (RecO, RecF, RecA, RecR) reading frame sequences were cloned from the genome of DH5alpha strain. After sequencing verification, the mammalian codons were optimized, and the nuclear localization sequence was added respectively. Then the SP6 promoter sequence (ATTTA GGTGA CACTA TAGAA, SEQ ID NO: 16) was added upstream of the entire sequence, and the in vitro transcription kit (mMESSAGE mMACHINE T7 / SP6kit, Life Technologies) and transcription vector pSP73 (Promega, USA) were used to obtain Capped and polyA-added mRNAs were mixed and frozen at -80°C with a working concentration of 100ng / ul.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com