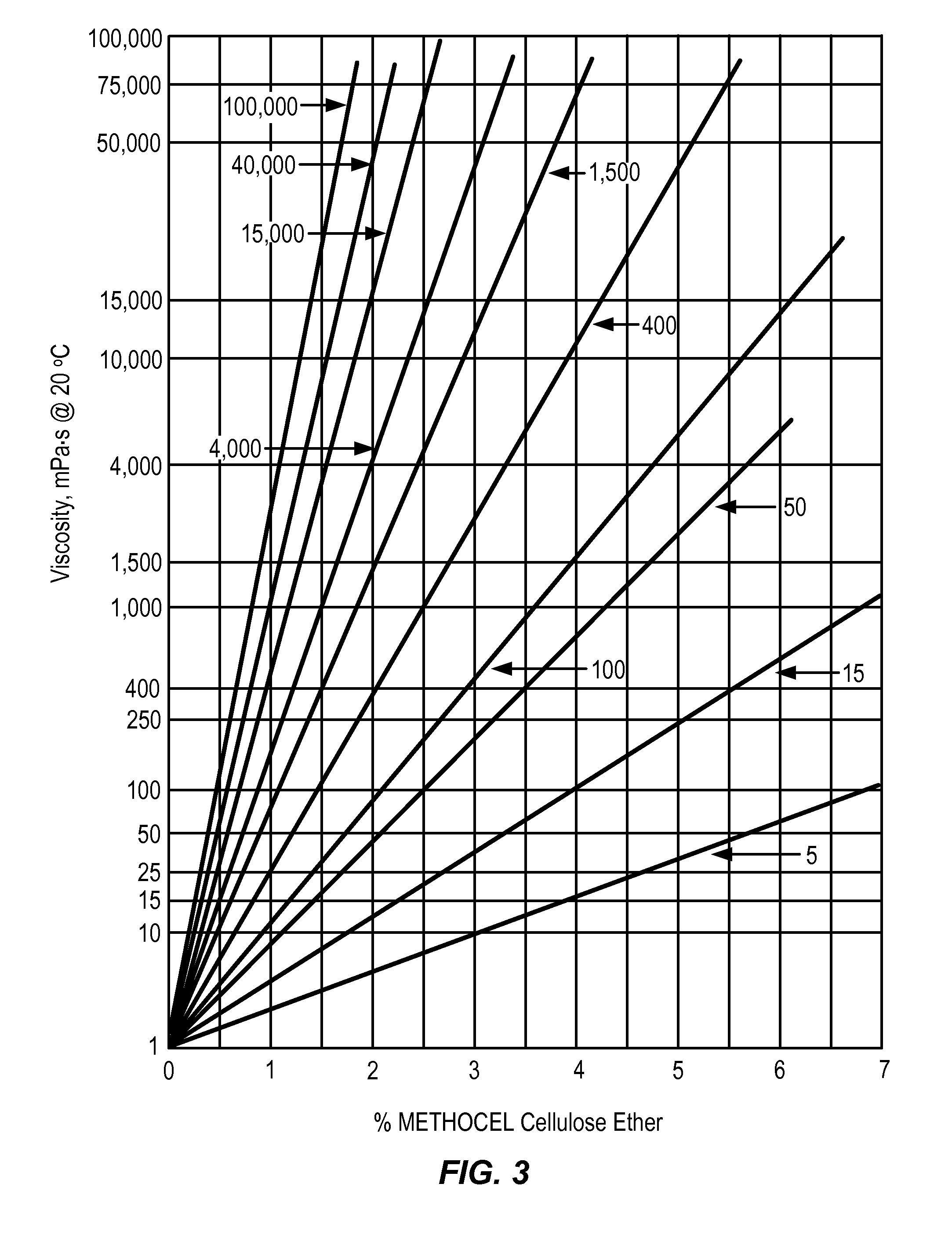
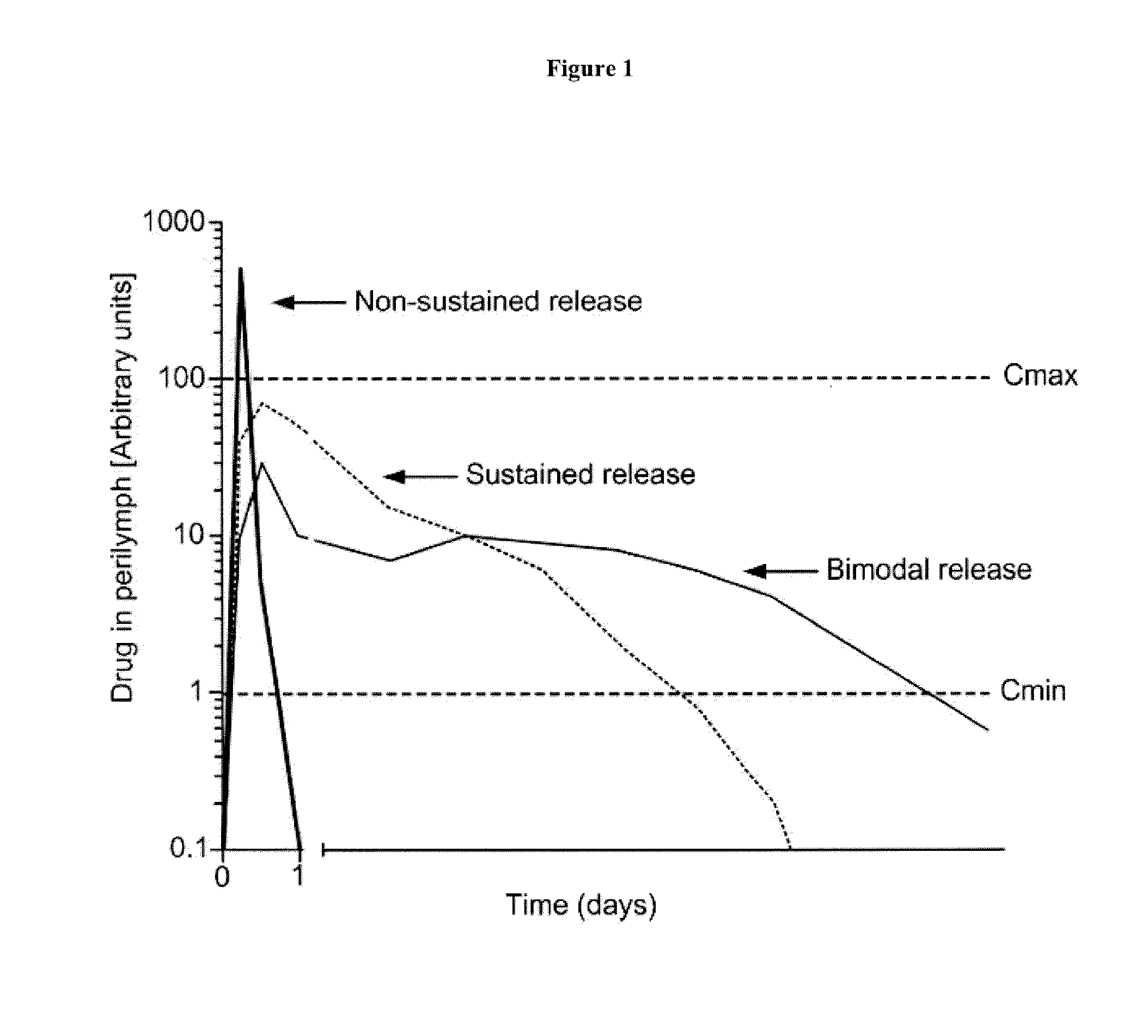
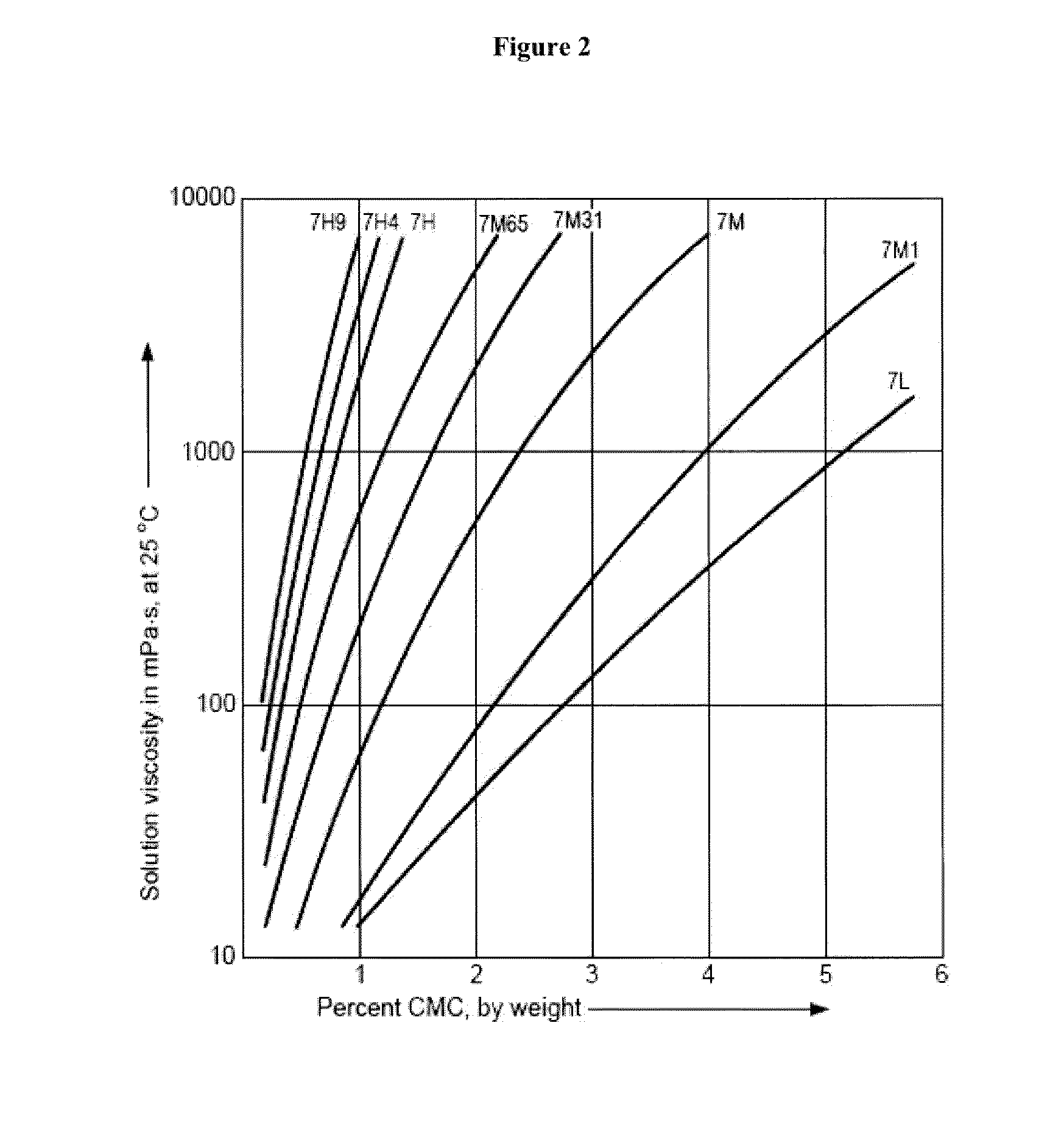
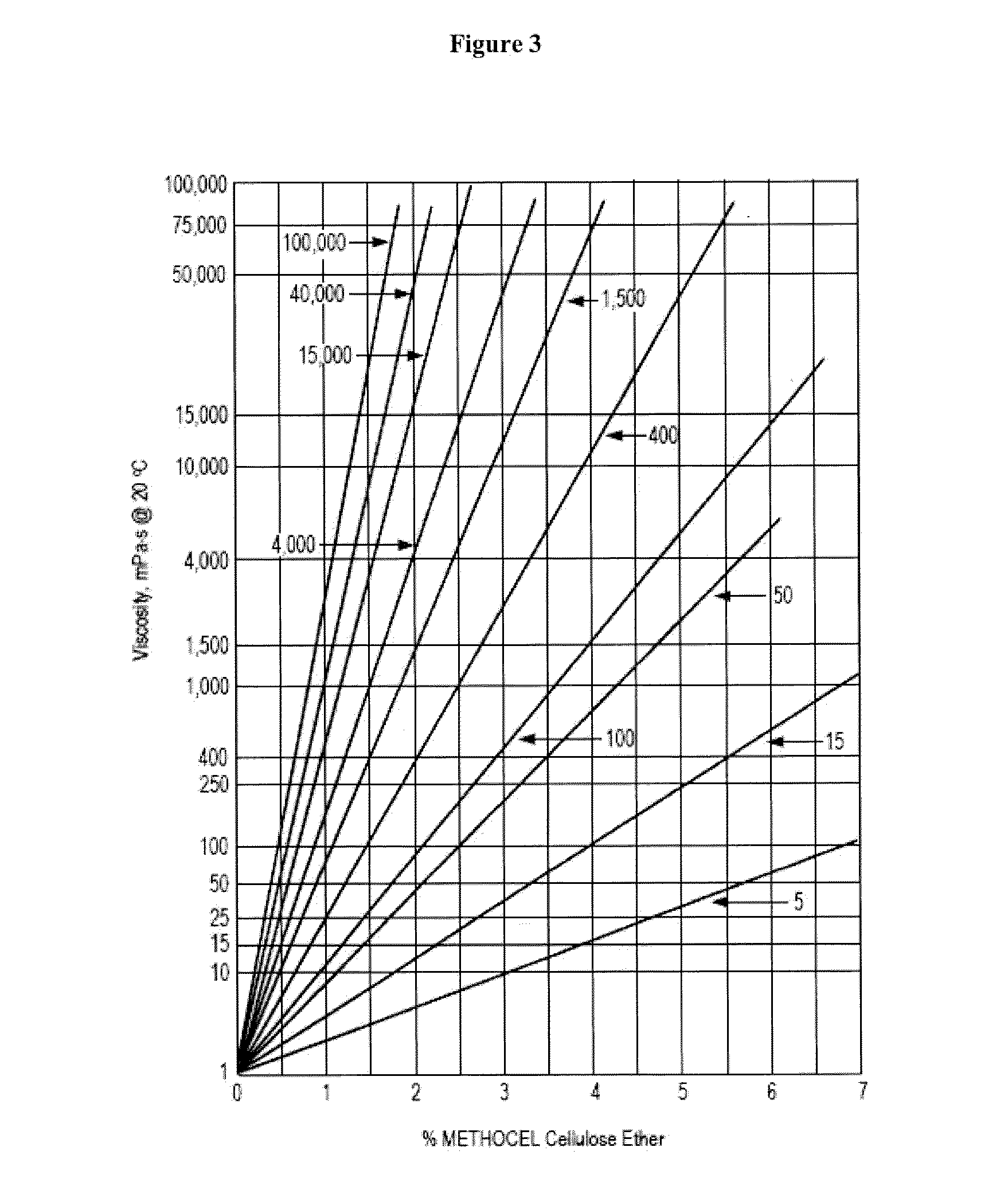
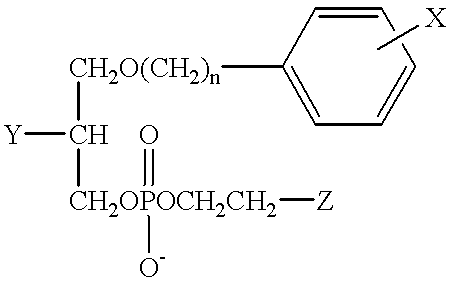
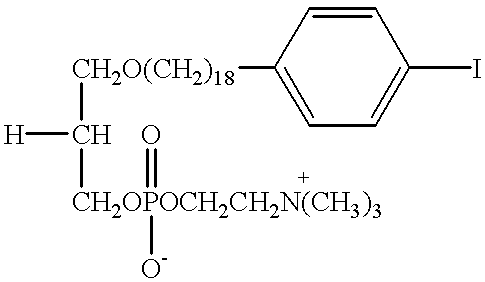Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121results about How to "Rapid clearance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intrathecal administration of rituximab for treatment of central nervous system lymphomas
InactiveUS20020009444A1Prevent intermolecular disulfide formationPromote recoveryBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMeningesImmunocompromised patient
This invention describes methods of using anti-B cell antibodies, preferably anti-CD20 antibodies, and most preferably Rituximab, to treat B cell lymphomas of the brain, especially primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSLs), and to prevent meningeal relapse. The antibodies can be administered intrathecally alone, or in combination with other chemotherapeutics, such as methotrexate, or other anti-B cell antibodies to treat PCNSL in both immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised patients. These antibodies can also be used to diagnose patients with CNS lymphoma, especially in immunocompromised patients.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
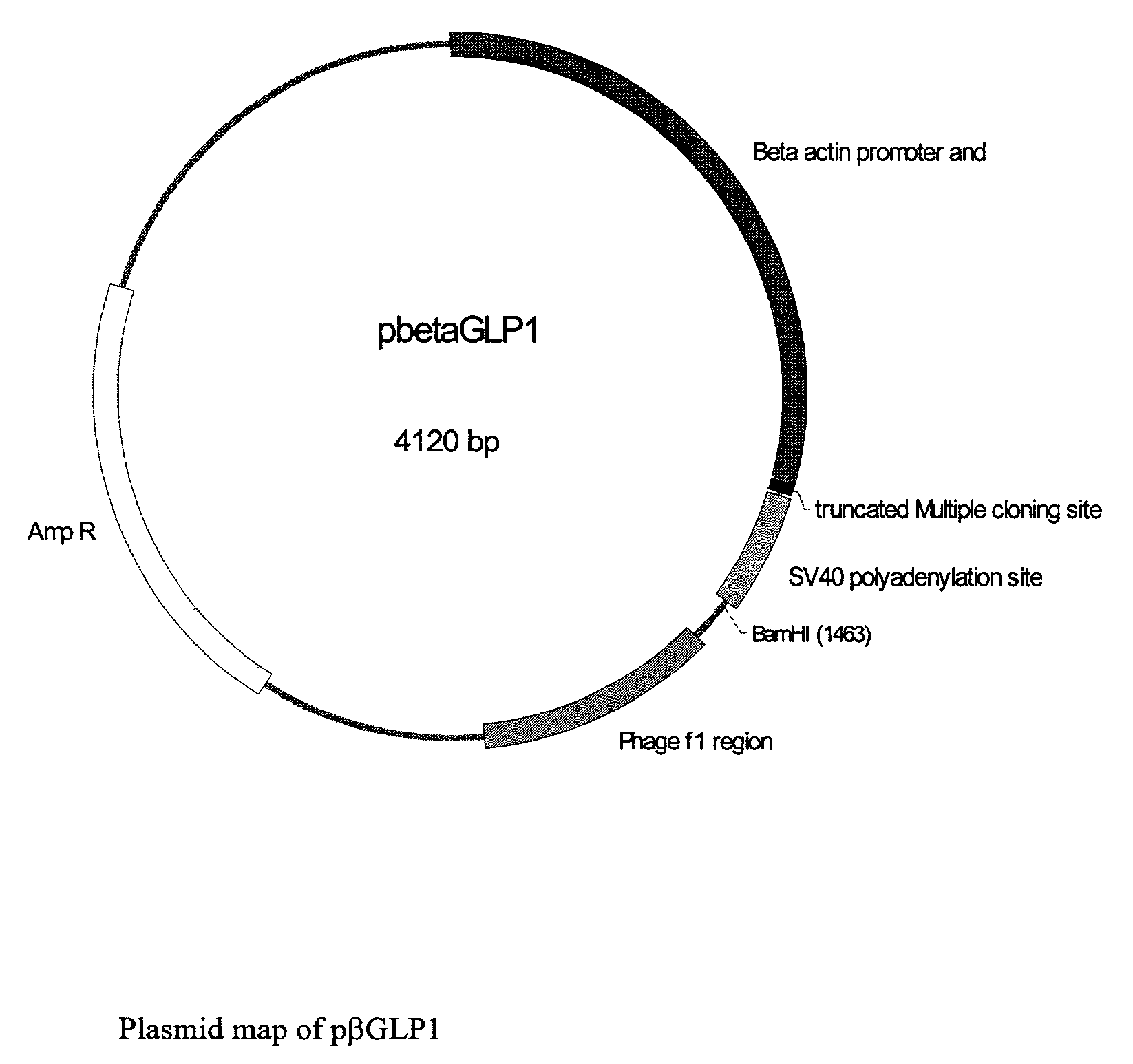
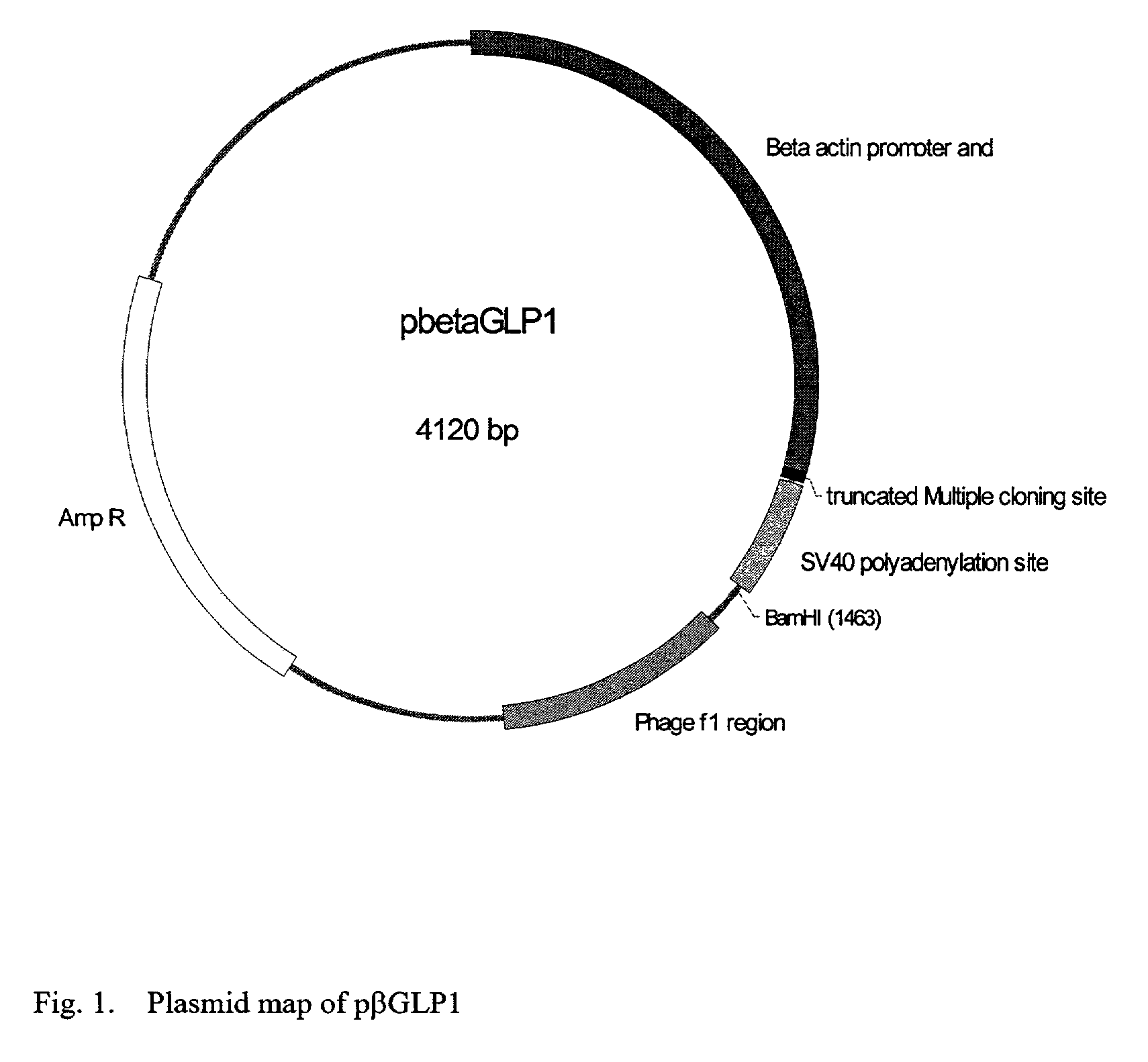
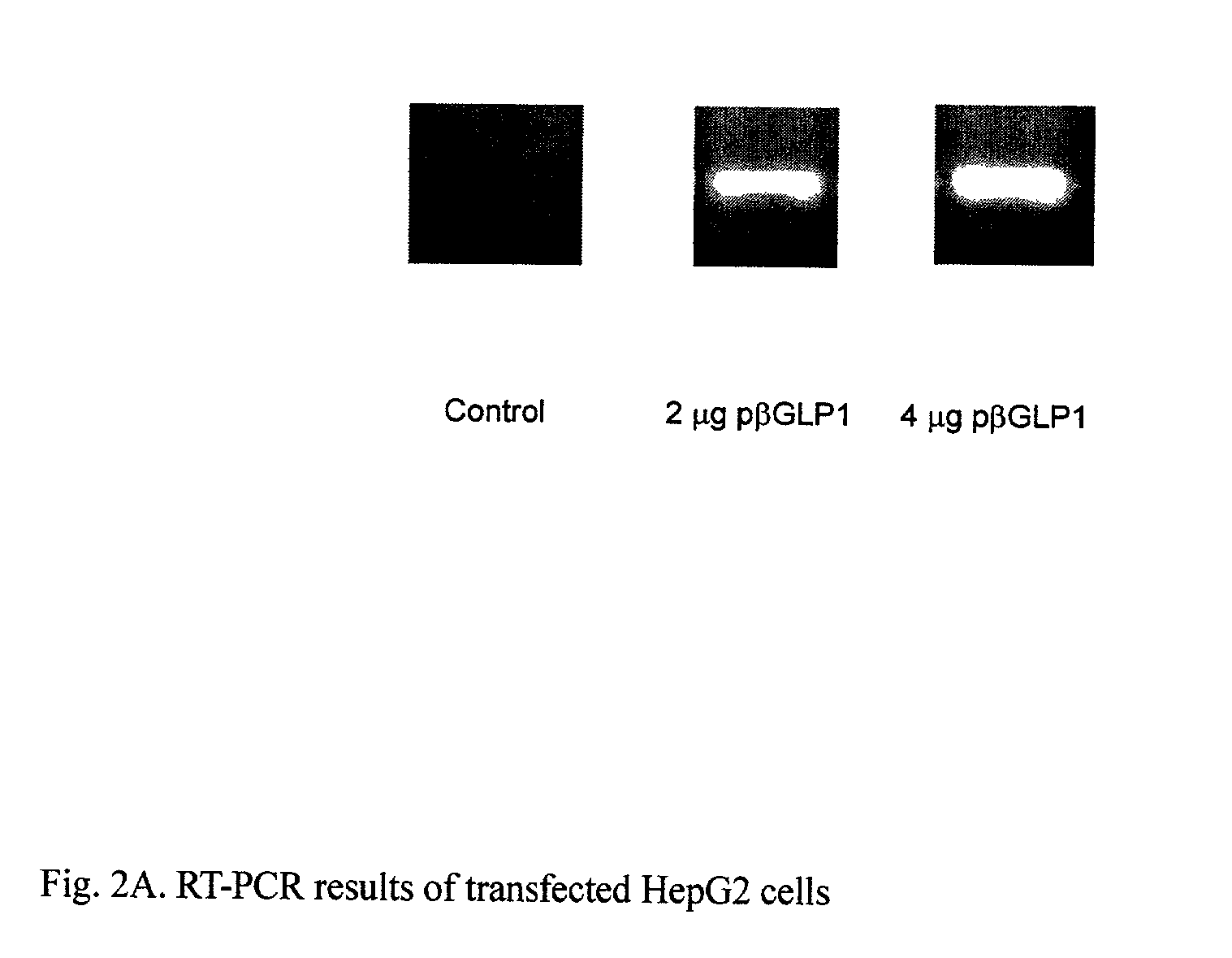
GLP-1 gene delivery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS7374930B2Efficient transfectionEasy to controlSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGlucose polymers
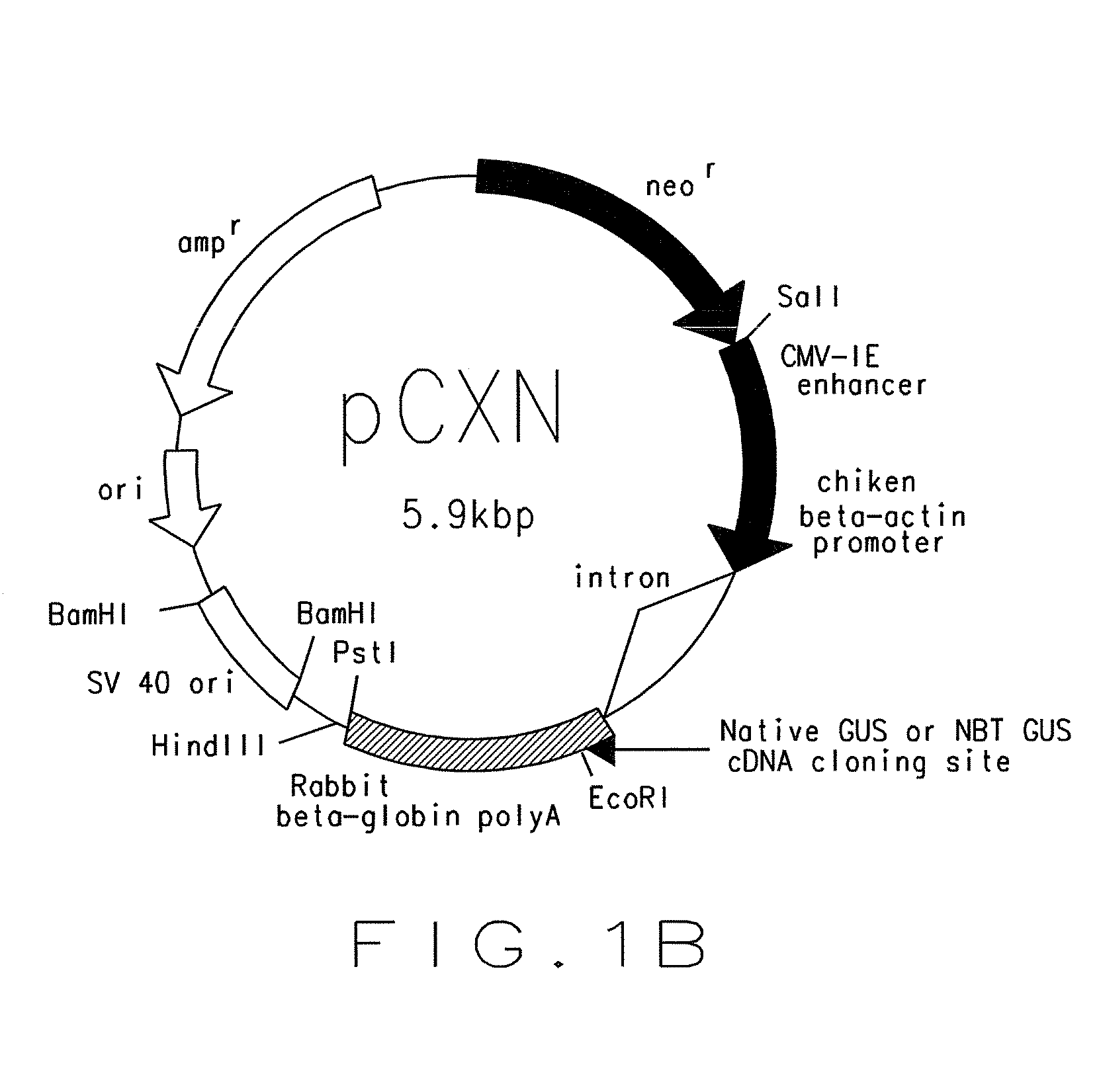
This patent discloses compositions and methods of use thereof to normalize the blood glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes. It relates particularly to a plasmid comprising a chicken β actin promoter and enhancer; a modified GLP-1 (7-37) cDNA (pβGLP1), carrying a furin cleavage site, which is constructed and delivered into a cell for the expression of active GLP-1.
Owner:CLSN LAB
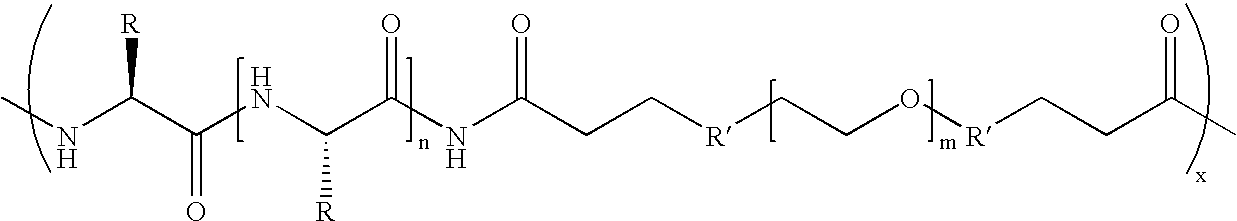
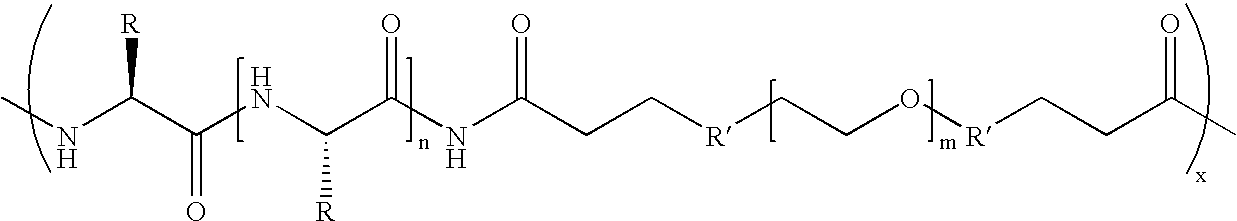
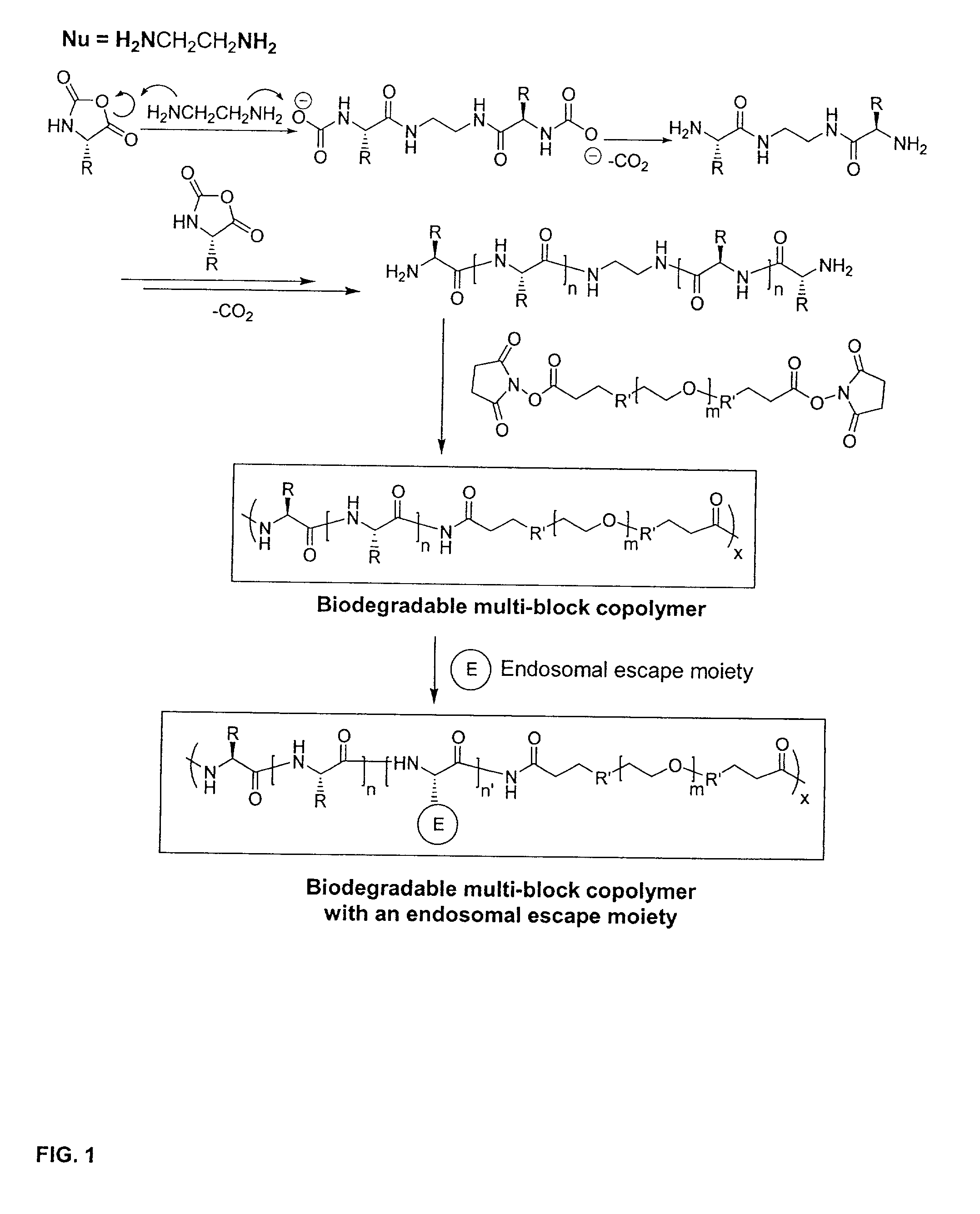
Biodegradable multi-block copolymers of poly(amino acid)s and poly(ethylene glycol) for the delivery of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20030147958A1Easy to chargeSmall sizePowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsCarbamateHydrophilic polymers
This patent discloses the synthesis of a multi-block copolymer containing poly(amino acids) (PAA) and a hydrophilic polymer which are degradable under physiological conditions. Control over the degradation rate of the obtained copolymers is achieved by introducing ester, amide or urethane groups as a biodegradable linkage connecting the PAA and the hydrophilic polymer. The biodegradable multi-block copolymers display high transfection efficiency in plasmid delivery with low cytotoxicity.
Owner:EXPRESSION GENETICS INC
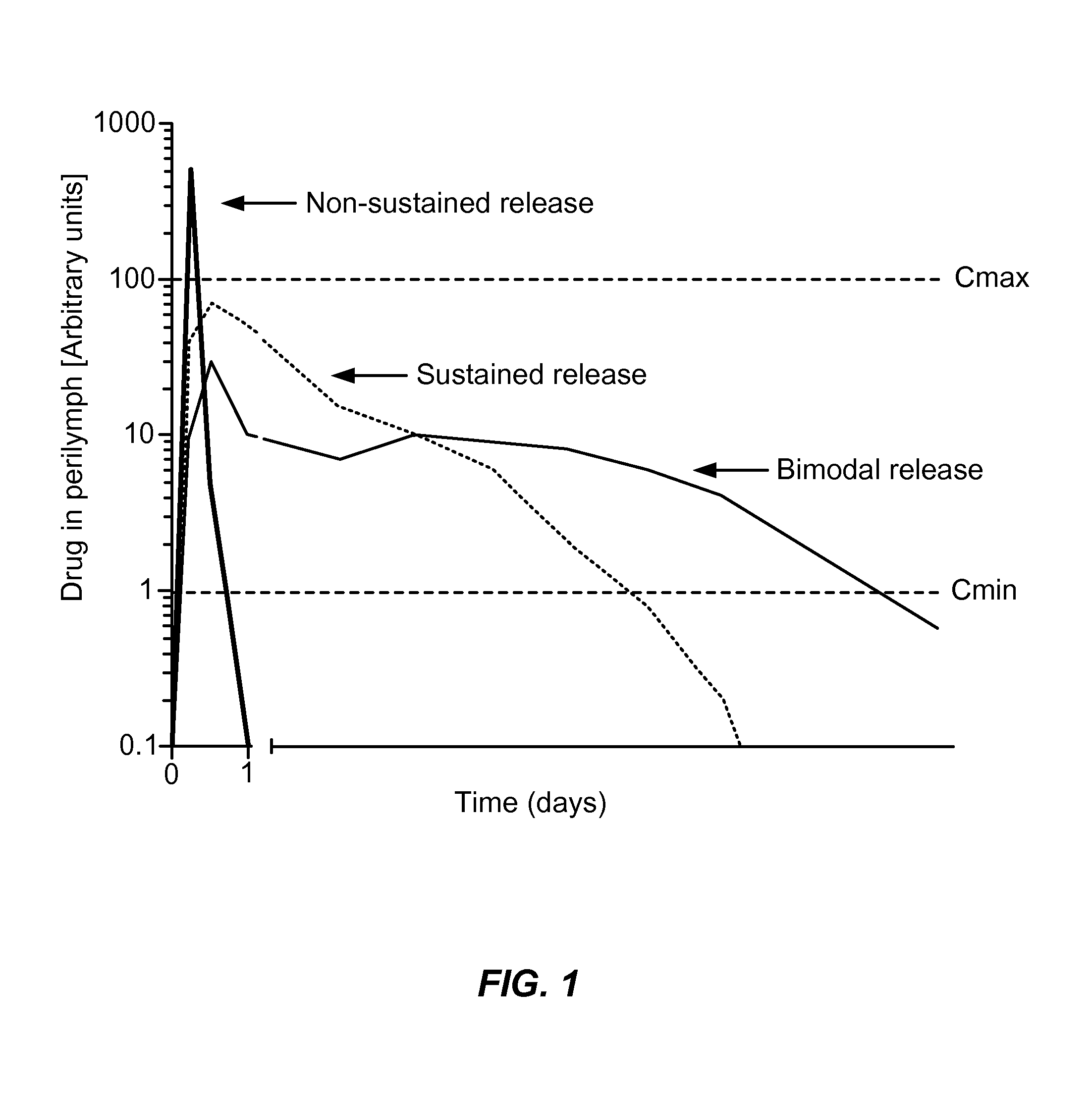
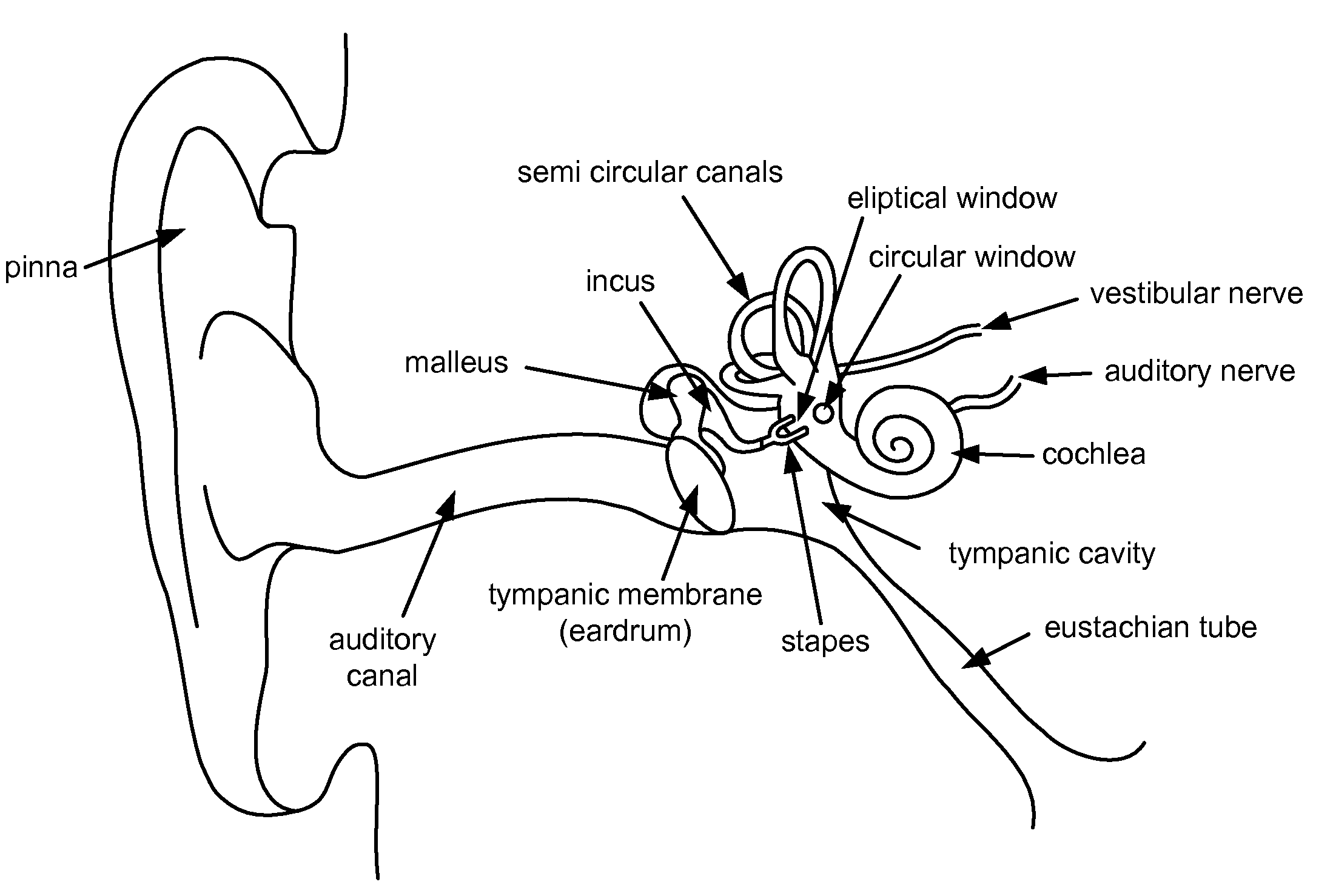
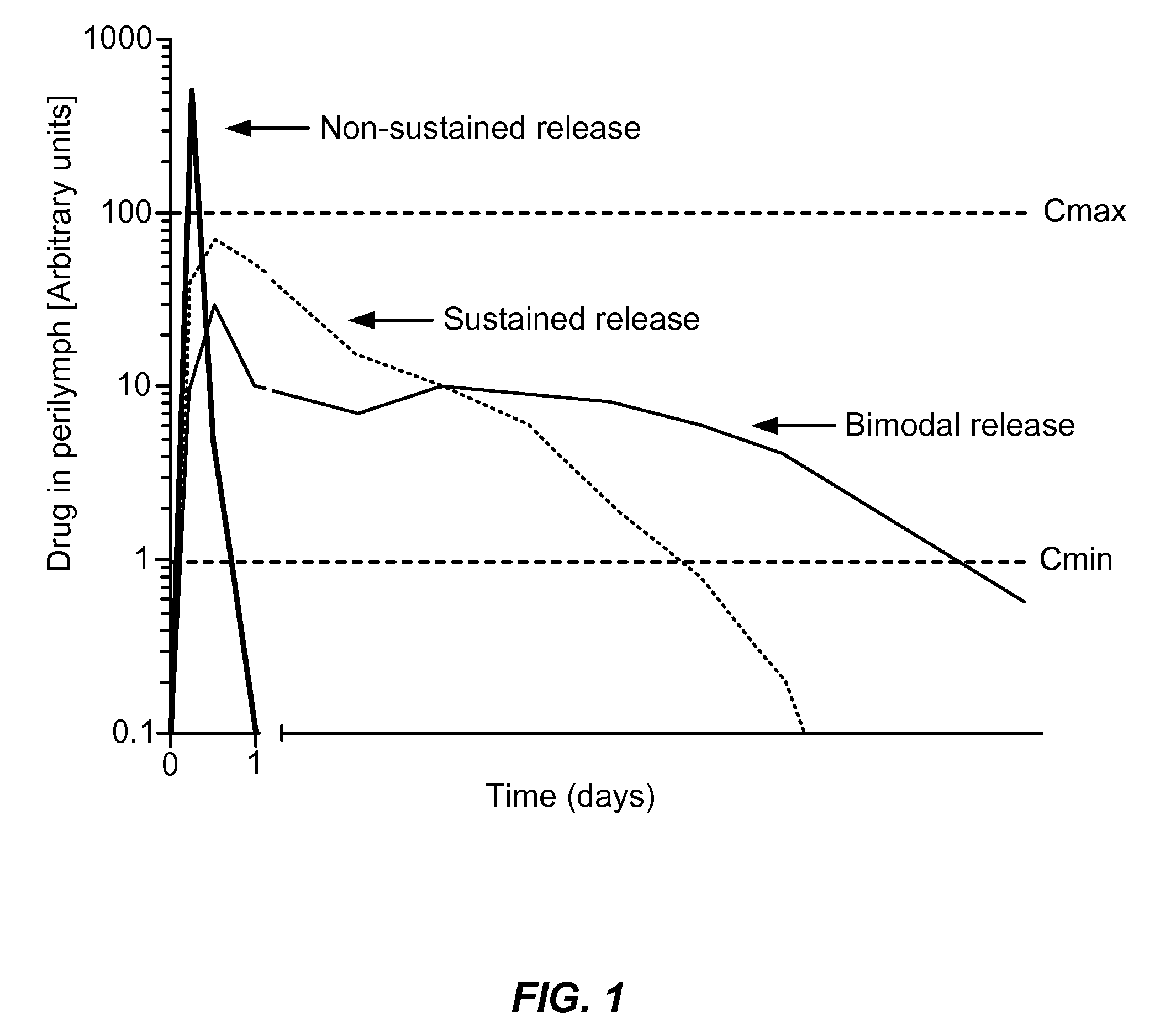
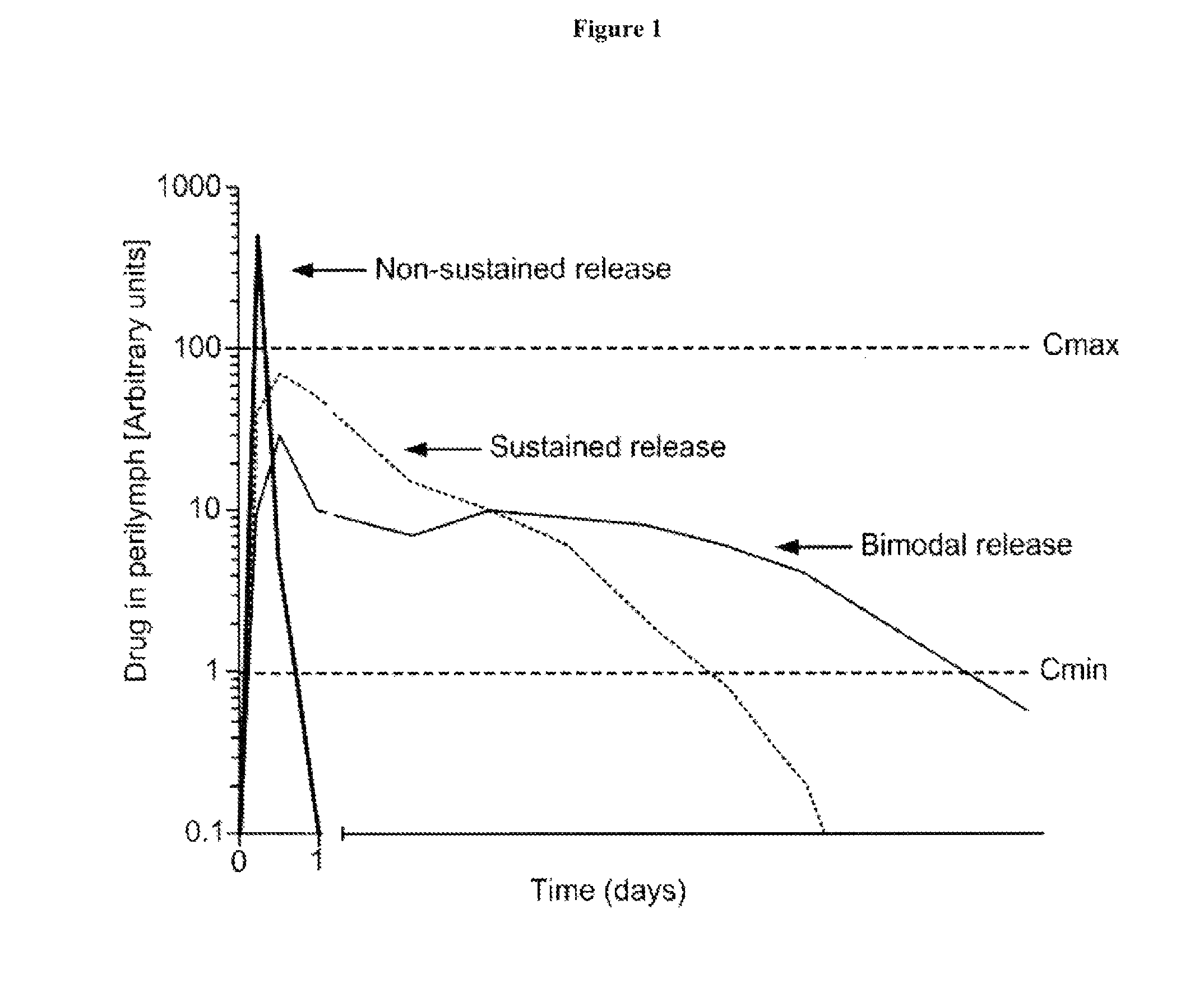
Controlled-release otic structure modulating and innate immune system modulating compositions and methods for the treatment of otic disorders
ActiveUS20100021416A1Reduce dosing frequencyReduce riskBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseControlled release
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of otic disorders with otic structure modulating compositions administered locally to an individual afflicted with an otic disorder, through direct application of these compositions and compositions onto or via perfusion into the targeted auris structure(s).
Owner:OTONOMY INC +1
Controlled release immunomodulator compositions and methods for the treatment of otic disorders
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of otic disorders with immunomodulating agent compositions and formulations administered locally to an individual afflicted with an otic disorder, through direct application of these compositions and formulations onto or via perfusion into the targeted auris structure(s).
Owner:OTONOMY INC +1
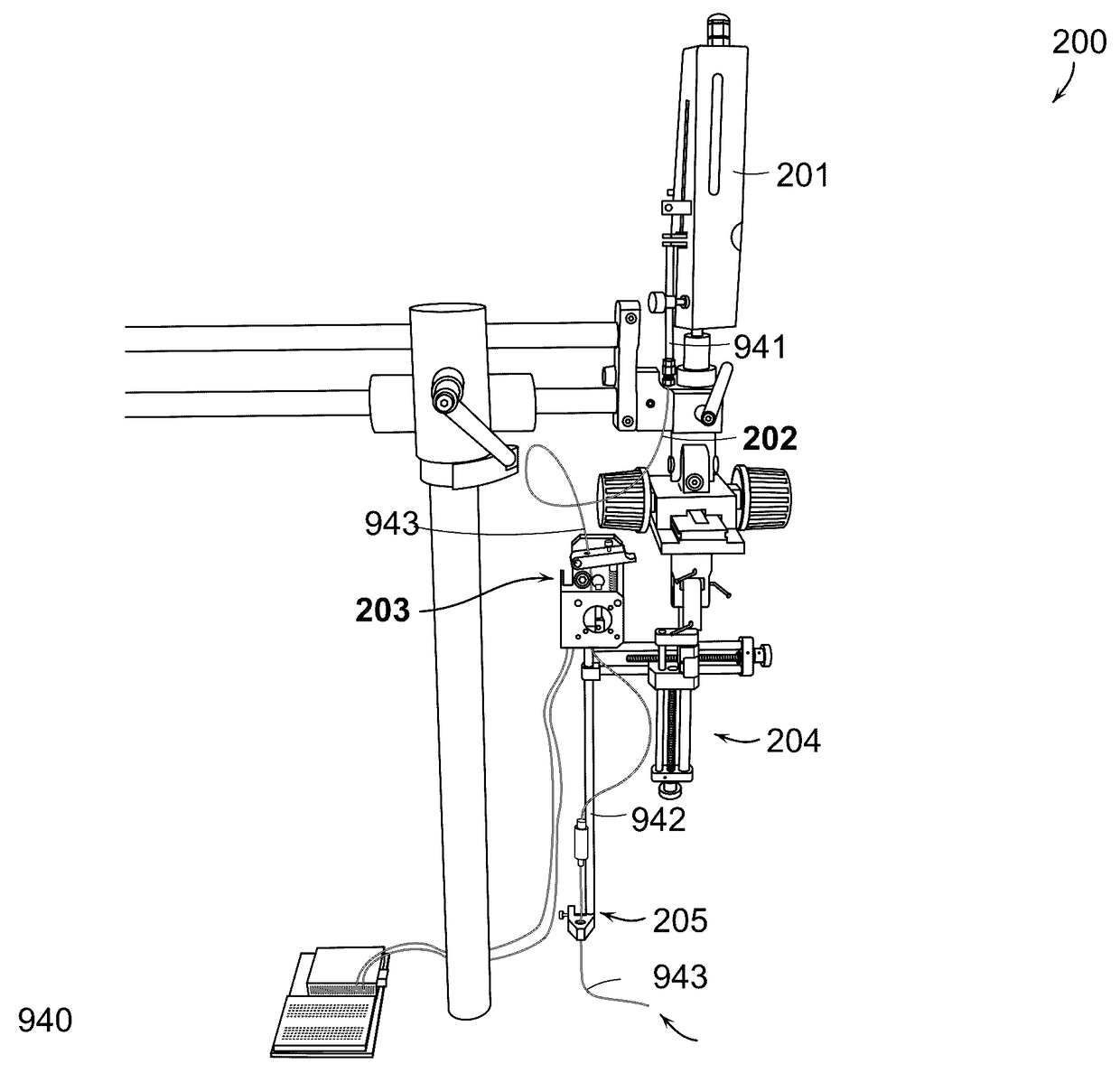
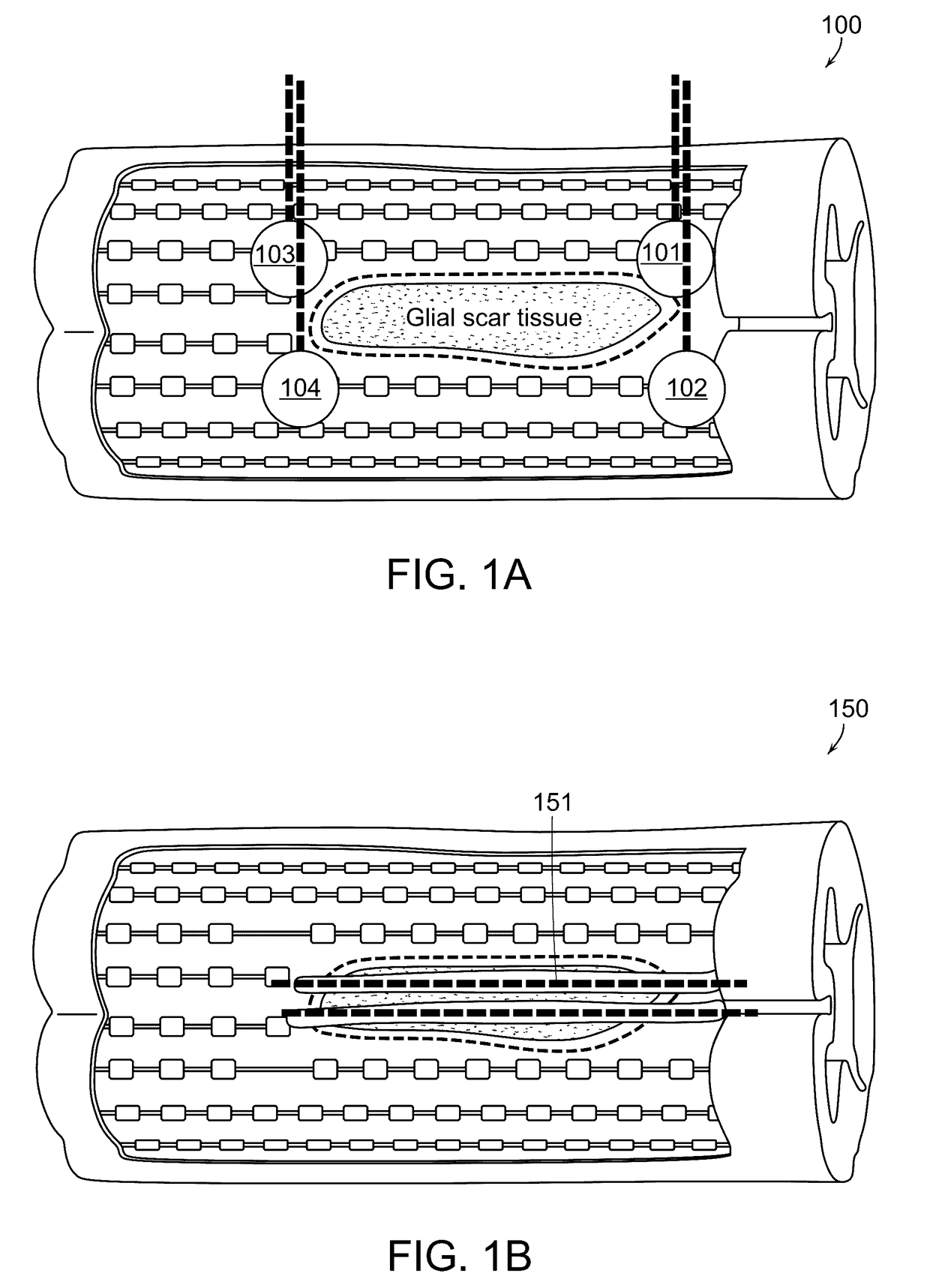
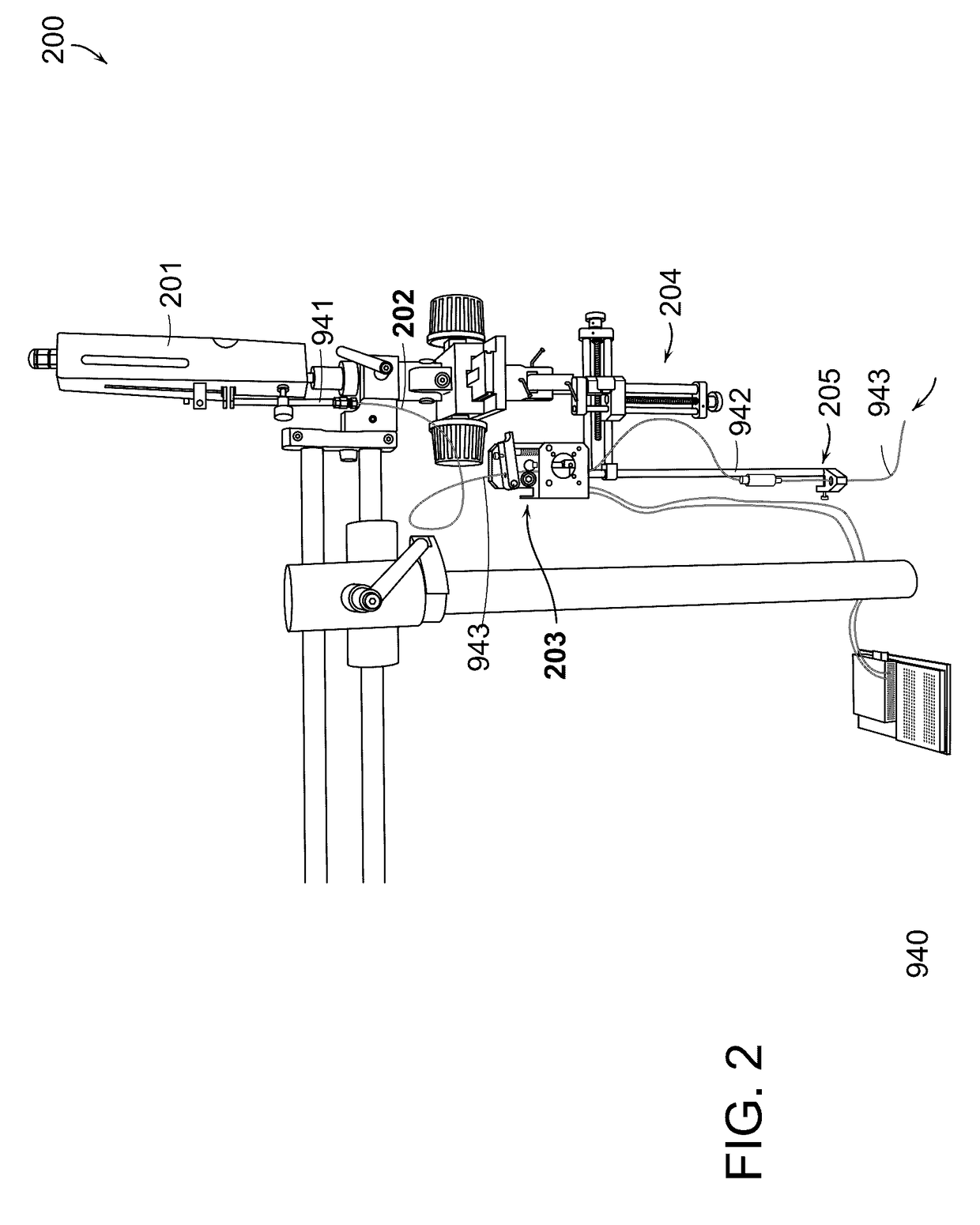
Methods and Systems for Delivery of a Trail of a Therapeutic Substance into an Anatomical Space
InactiveUS20170151416A1Easy to manageRapid clearanceGuide needlesPeptide/protein ingredientsCentral nervous systemPathology diagnosis
Injection devices and methods for delivering a trail of therapeutic cells and / or one or more therapeutic substances or diagnostic substances or injectable medium into an anatomical space of an animal or human subject, particularly a trail of therapeutic cells and / or one or more therapeutic substances or diagnostic substances or injectable medium into the spinal cord of a subject and to deliver a trail of therapeutic cells and / or one or more therapeutic substances or diagnostic substances or injectable medium inside the spinal cord, to treat an injury or disorder of the central nervous system requiring injection of cells and / or one more therapeutic substances. The devices and methods are useful for the treatment of a variety of traumas, conditions and diseases, in particular, spinal cord injuries, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis and spinal ischemia as well as other spinal cord degenerative conditions and pathologies.
Owner:INVIVO THERAPEUTICS CORP
Polymer conjugates of GLP-1
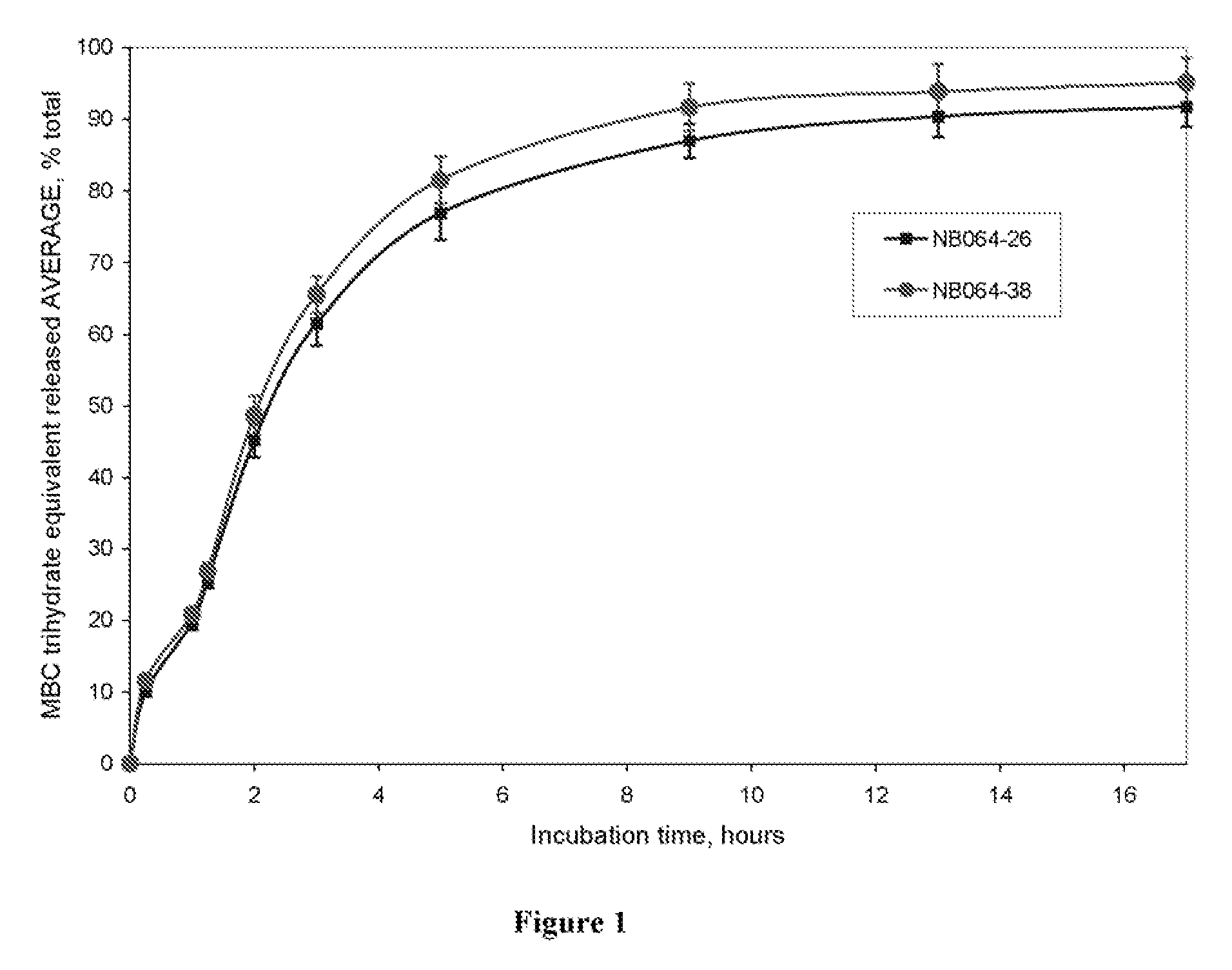
ActiveUS8293869B2Rapid clearanceGood release effectMetabolism disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsWater solubleMethyl group
Conjugates of a GLP-I moiety may be covalently attached to one or more water-soluble polymers. For instance, a GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety releasably attached at its N-terminus to a water-soluble polymer. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety possesses an N-methyl substituent. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached at a polymer attachment site to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety is glycosylated at a site separate from the polymer attachment site.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
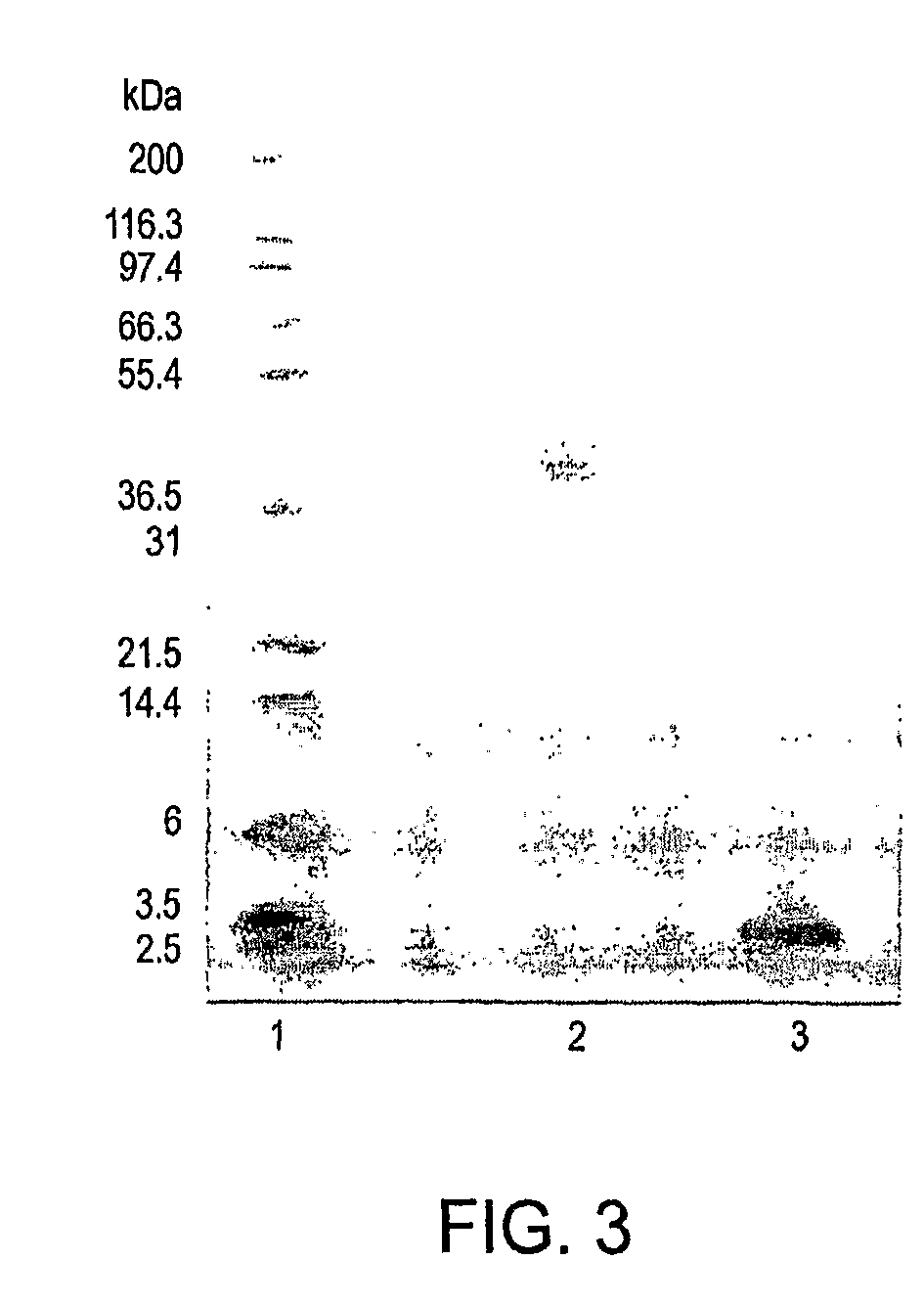
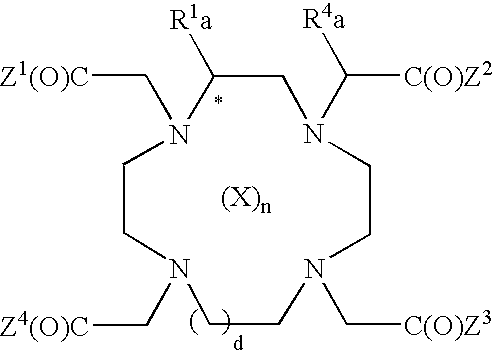
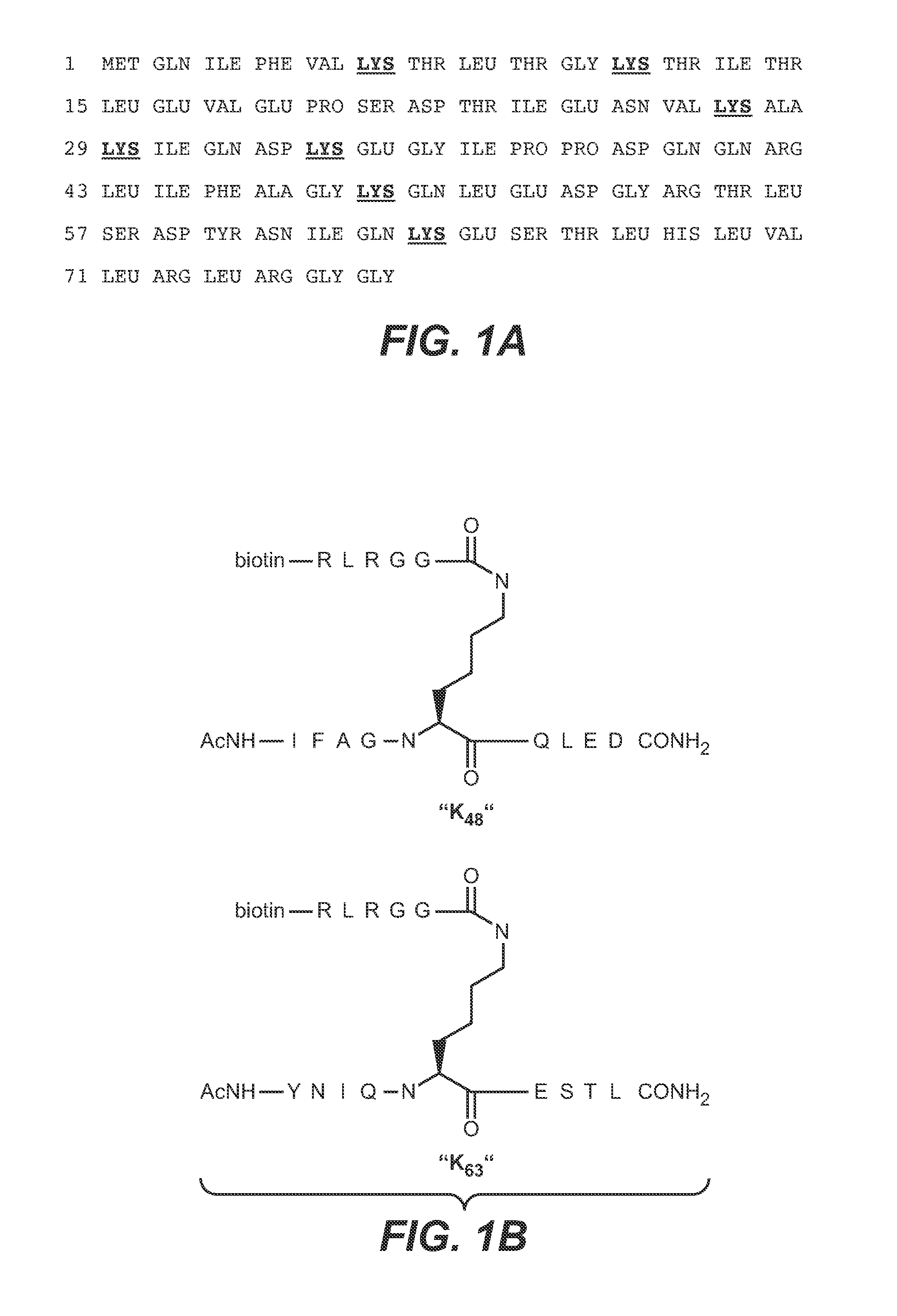
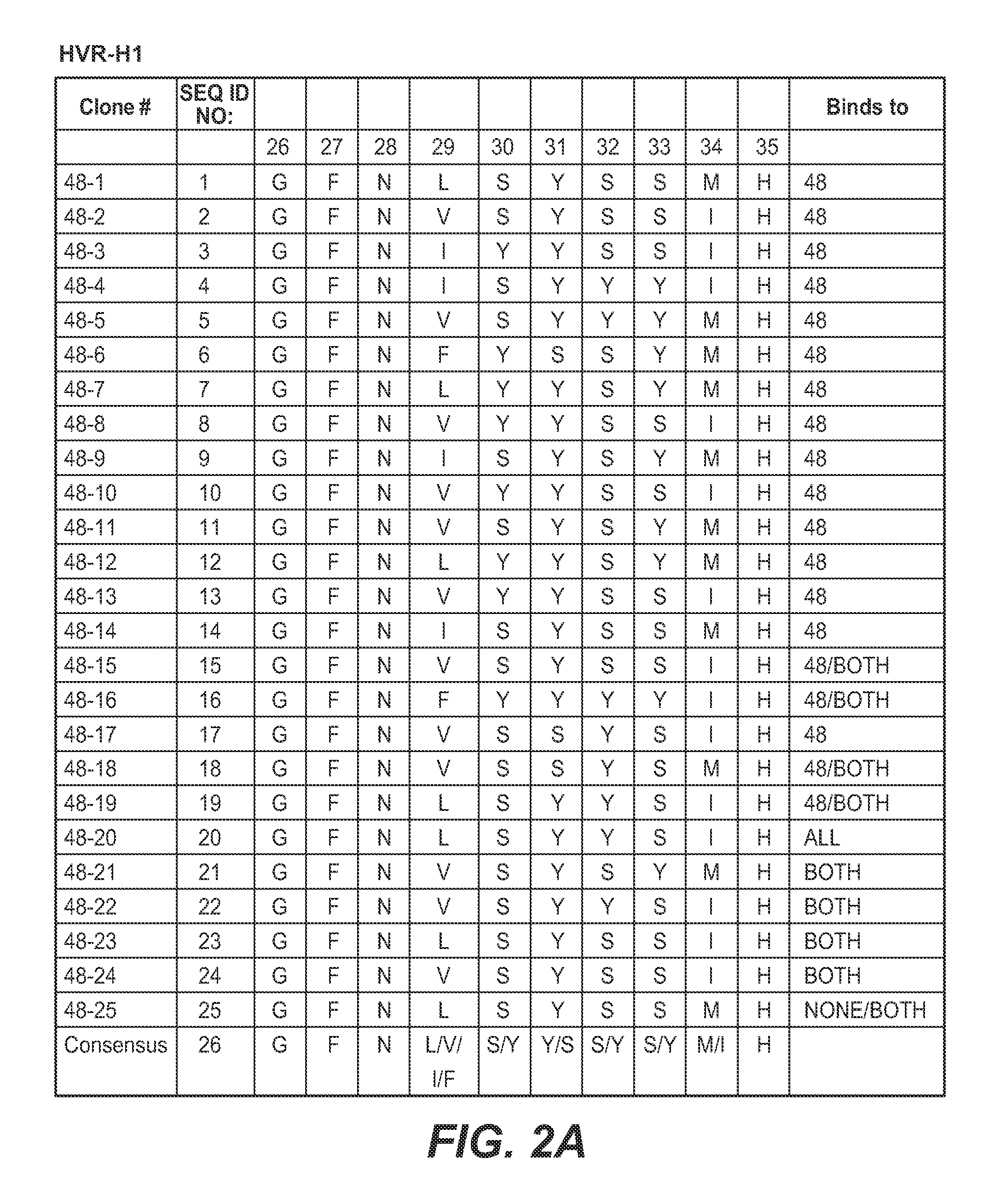
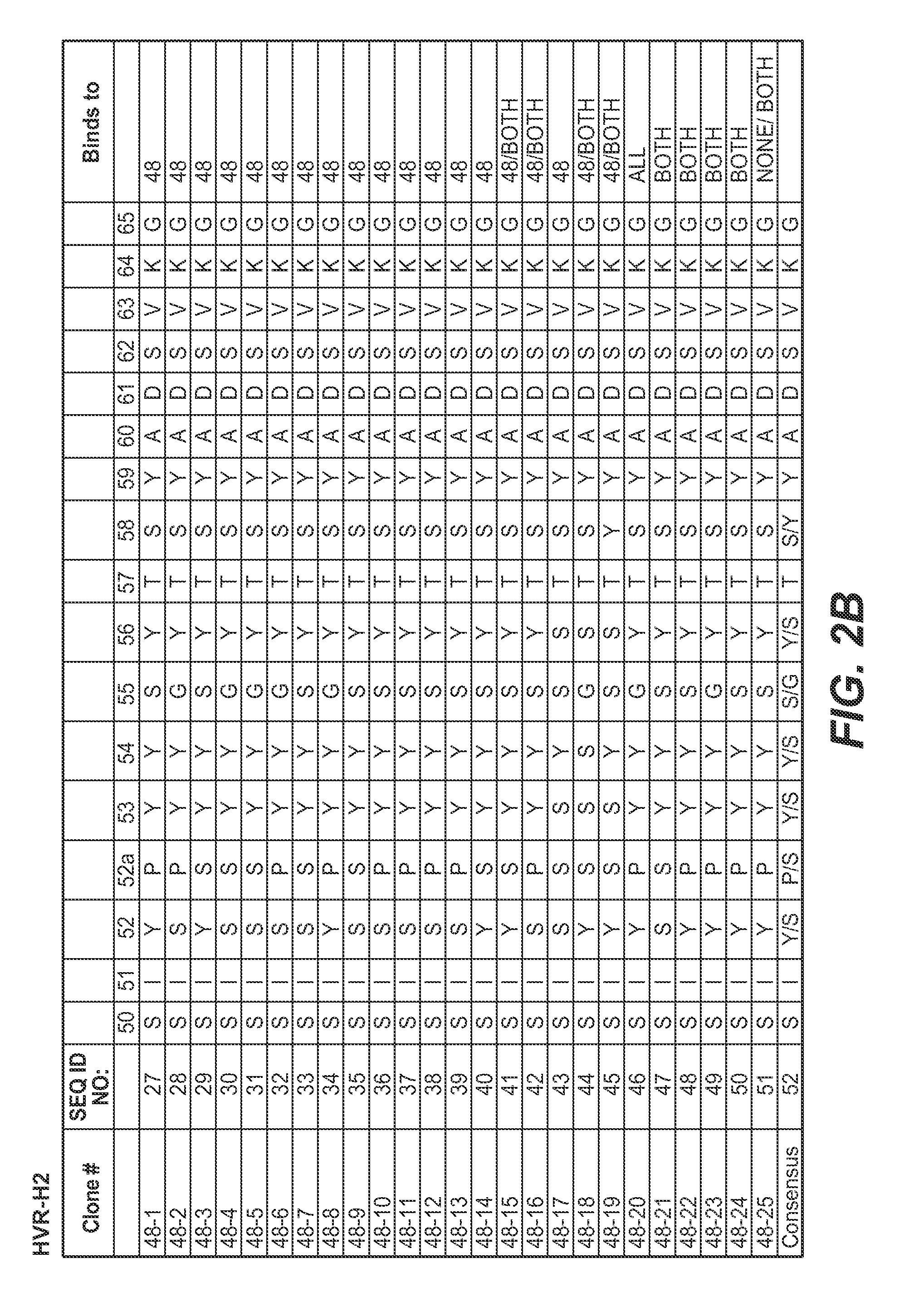
Methods and compositions for targeting polyubiquitin
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Glycosylation-Disrupted Factor VII Variants
InactiveUS20080058255A1Improve biological activityRapid clearancePeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical drugsNucleotideFactor VII
The present invention relates to human coagulation Factor VII polypeptides, as well as polynucleotide constructs encoding such polypeptides, vectors and host cells comprising and expressing the polynucleotide, pharmaceutical compositions comprising Factor VII polypeptides, uses and methods of treatment; and any additional inventive features related thereto.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Controlled release compositions for modulating free-radical induced damage and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20100022661A1Rapid clearanceReduce dosing frequencySenses disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseControlled release
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of otic diseases or conditions with free-radical modulating agent compositions and formulations administered locally to an individual afflicted with an otic disease or condition, through direct application of these compositions and formulations onto or via perfusion into the targeted auris structure(s).
Owner:OTONOMY INC +1
Ligand
InactiveUS20060257406A1Rapid clearanceRapid productionVirusesSugar derivativesVariable domainTargeting ligands
The invention provides a dual-specific ligand comprising a first immunoglobulin variable domain having a first binding specificity for a target ligand and a complementary or non-complementary immunoglobulin variable domain having a second binding specificity for a receptor of the target ligand.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
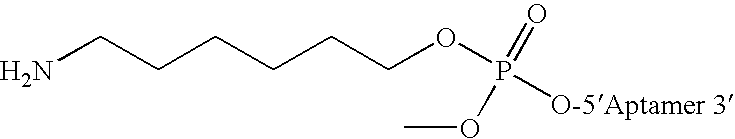
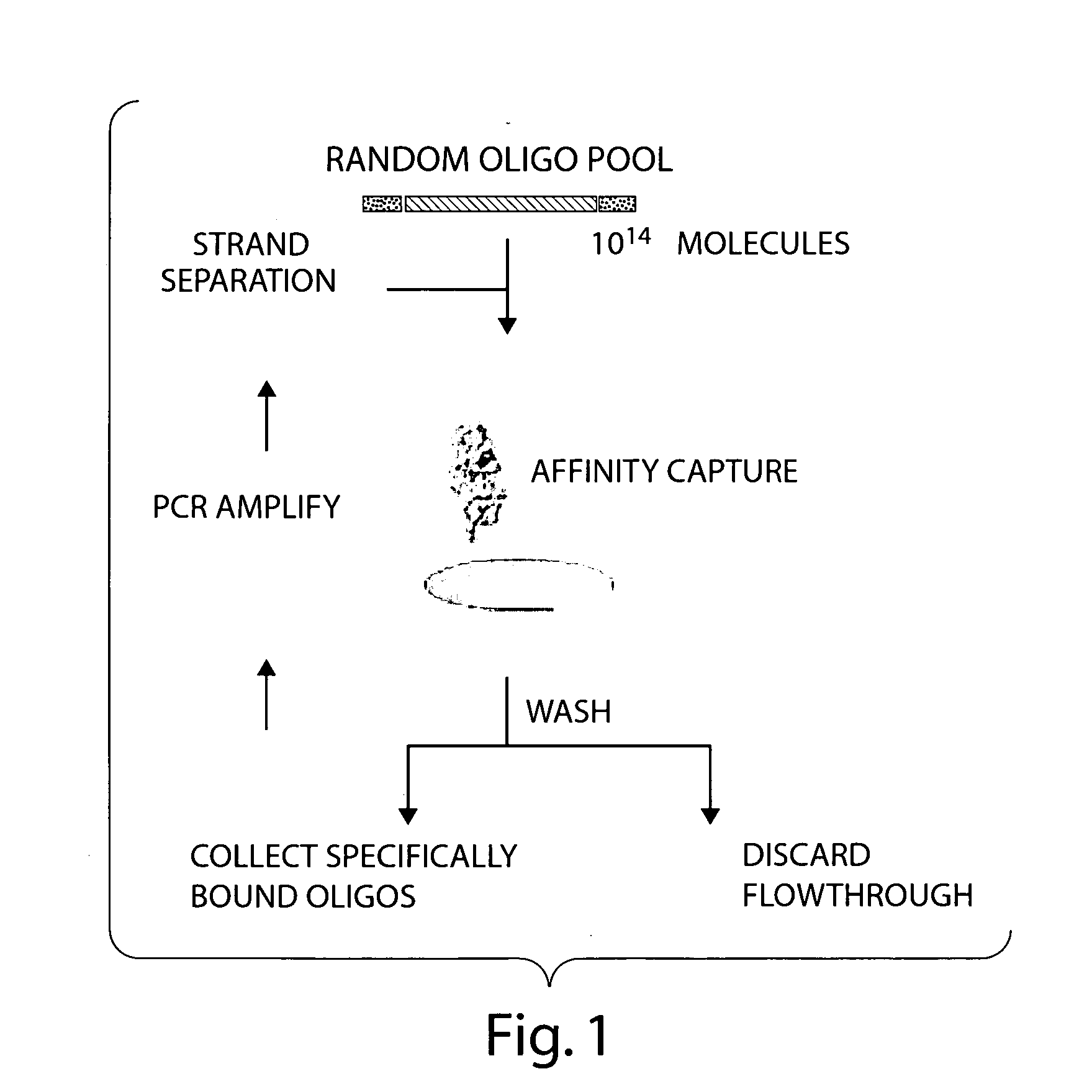
Controlled modulation of the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of aptamer therapeutics
InactiveUS20060030535A1Reduce distributionReduce ratePowder deliveryActivity regulationControl mannerBiodistribution
Materials and methods are provided to modulate, in a controlled manner, the pharmacokinetic and biodistribution properties of nucleic acid aptamers, and to enhance their safety and efficacy properties as therapeutic agents.
Owner:ARCHEMIX CORP
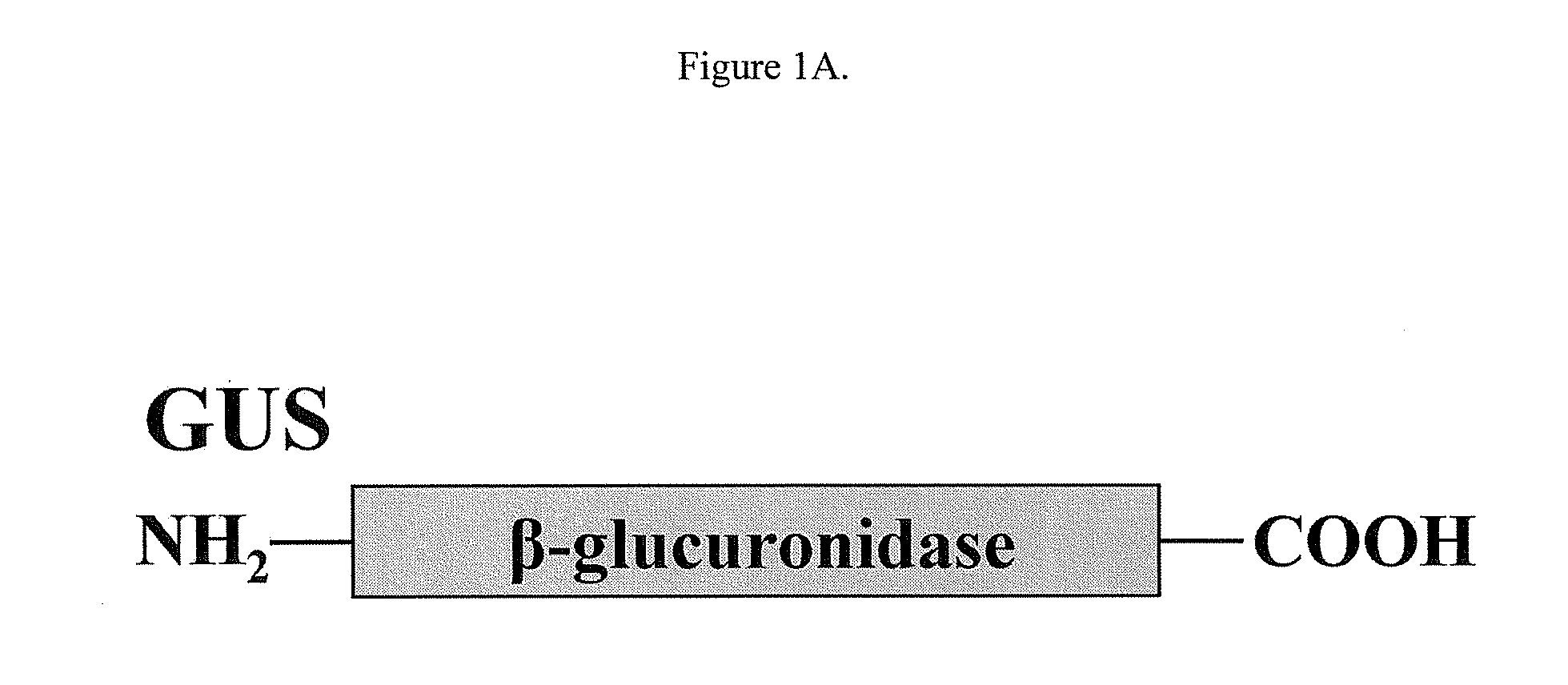
Modified enzyme and treatment method
InactiveUS20090041741A1Extended half-lifeConvenient treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesLysosomeCompound (substance)
There is disclosed an isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase wherein the modification is having its carbohydrate moeties chemically modified so as to reduce its activity with respect to mannose and mannose 6-phosphate cellular delivery system while retaining enzymatic activity Also disclosed are methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage disease in mammals wherein the mammal is administered a therapeutically effective amount of isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase whereby said storage diseased is relieved in the brain and visceral organs of the mammal. Also disclosed are other lysosomal enzymes within the scope of the invention.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Methylene Blue Derivatives
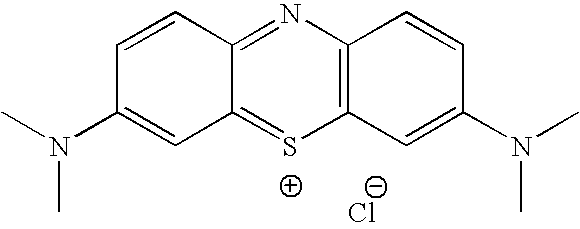
InactiveUS20070116757A1Facilitated releaseRapid uptakeOrganic chemistryPill deliveryImmediate releaseFatty acid
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a fatty acid salt, a dicarboxylic acid salt, an alkyl sulfate salt, an aryl sulfate salt or an alkyl aryl sulfonate salt of methylene blue or a derivative of methylene blue are described herein. The compositions are preferably administered orally and can be administered as tablets, soft or hard shell capsules (e.g. soft gelatin capsules), suspensions or solutions. The composition can also be formulated as a suppository or enema or rectal administration. The compositions further comprise a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and optionally one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. Suitable excipients include diluents, binders, plasticizers, lubricants, disintegrants, colorants, stabilizers, surfactants, and combinations thereof. The fatty acid salts, alkyl sulate salts, aryl sulfate salts or alkyl aryl sulfonate salts can be co-mixed or co-melted with one or more fatty acids to make more hydrophobic compositions, which may result in less staining formulations. The compositions can be formulated for immediate release, controlled release such as extended release, delayed release, and pulsatile release, or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the derivative of methylene blue is methylene dodecylsulfate.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Radioiodinated phospholipid ether analogs and methods of using the same
InactiveUS6255519B1Reduce accumulationReduce the amount requiredRadioactive preparation carriersIsotope introduction to organic compoundsHalf-lifePhospholipid Ethers
Improved radioiodinated phospholipid ether analogs are described which exhibit significant tumor avidity and longer plasma half-life relative to shorter chain analogs. Use of these compounds results in superior imaging and visualization of neoplastic lesions and tumor-specific cytotoxic cancer therapy.
Owner:MICHIGAN RGT UNIV
Engineered antibody fragment that irreversibly binds an antigen
InactiveUS20060063209A1Rapid clearanceSolid tumor permeabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesDiseaseAntibody fragments
The present invention provides mutant antibodies with infinite affinity for a target antigen. The antibodies comprise a mutant amino acid at a position within or proximate to a complimentarity determining region of the antibody and a linker covalently bound to the mutant amino acid, the linker comprising a reactive functional group. Subsequent to binding an antigen, the reactive functional group is converted to a covalent bond by reaction with a group of complementary reactivity on the bound antigen. The invention also provides bispecific antibodies with infinite binding affinity that comprise a second domain that specifically binds a metal chelate. The invention further provides methods of using such antibodies to diagnose and treat diseases and conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Non-glycosylated recombinant monovalent antibodies
InactiveUS20100325744A1Effect plasma residence timeRapid clearanceFungiSenses disorderAntiendomysial antibodiesPharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides non-glycosylated monovalent antibodies with a long half-life when administered in vivo, methods of making such monovalent antibodies, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such antibodies, and uses of the monovalent antibodies.
Owner:GENMAB AS
Methods and compositions for targeting polyubiquitin
ActiveUS7763245B2Expand accessRapid clearanceNervous disorderAntipyreticProtein.monoclonalMonoclonal antibody
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Polymer conjugates of glp-1
ActiveUS20100210505A1Lower blood sugar levelsRapid clearanceMetabolism disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsWater solubleMethyl group
Conjugates of a GLP-I moiety may be covalently attached to one or more water-soluble polymers. For instance, a GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety releasably attached at its N-terminus to a water-soluble polymer. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety possesses an N-methyl substituent. The GLP-I polymer conjugate may include a GLP-I moiety covalently attached at a polymer attachment site to a water-soluble polymer, wherein the GLP-I moiety is glycosylated at a site separate from the polymer attachment site.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Responsive liposomes for ultrasonic drug delivery
InactiveUS20060002994A1Enhanced response to ultrasoundStably incorporated into liposomeLiposomal deliveryDopantCritical micelle concentration
This invention relates to biotechnology, more particularly, to an improved liposomal drug delivery system. Liposomes treated with or incorporating a surface active dopant, such as those containing polymers or oligomers of ethylene glycol as their hydrophilic “headgroup” component, have strongly increased permeabilizability when exposed to ultrasound. Permeabilizability was measured by the rate of release of self-quenching fluorescent dye at concentrations that caused no increase in permeability in the absence of ultrasound. The surface active dopants reached maximal effectiveness at about 1% of their critical micelle concentration. As disclosed by the present invention, surface active dopants, such as a PEG-lipid and a PLURONIC® triblock copolymer and a PEG-PBLA block copolymer, can be irreversibly incorporated into liposomes to give formulations for use as drug delivery vehicles.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES INST
Anti-gcc antibody molecules and related compositions and methods
ActiveUS20130315923A1Decrease and eliminate immunogenicityReduce the possibilityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBiological material analysisAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
Antibodies and antigen-binding fragments of antibodies that bind GCC are disclosed. In some embodiments, the antibodies are humanized, chimeric or human. Nucleic acids and vectors encoding the antibodies or portions thereof, recombinant cells that contain the nucleic acids, and compositions comprising the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments are also disclosed. The invention also provides therapeutic and diagnostic methods utilizing the antibodies and antigen-binding
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Sheath assembly and multihole catheter for different fields of endoscopic surgery involving suction, irrigation and material removal
ActiveUS20180289394A1Small sizeMinimally invasiveCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryMaterial removal
A sheath assembly for different fields of endoscopic surgery involving suction, irrigation and material removal which would on one hand enable reducing the size of keyhole to do the endoscopic surgery making it minimally invasive surgery, minimal damage to surrounding organ and practically no bleeding, faster recovery and early discharge and yet on the other hand provide for the advantages of big hole surgery. The sheath assembly of the invention would enable using variety of sheath sizes of different length and width of working sheath and thus facilitate applying to neonates as well as morbidly obese patients. The sheath assembly would enable endoscopic surgery such as percutaneous renal surgery with even about 3.0 mm inner diameter tubular sheath for large varieties of stones which would further add comfort and extra safety both for the patient as well as the surgeons.
Owner:SHAH KAUSHIKKUMAR VALLABHADAS
Controlled release immunomodulator compositions and methods for the treatment of otic disorders
InactiveUS8648119B2Reduce dosing frequencyReduce riskBiocideSenses disorderControlled releaseDisease
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods for the treatment of otic disorders with immunomodulating agent compositions and formulations administered locally to an individual afflicted with an otic disorder, through direct application of these compositions and formulations onto or via perfusion into the targeted auris structure(s).
Owner:OTONOMY INC +1
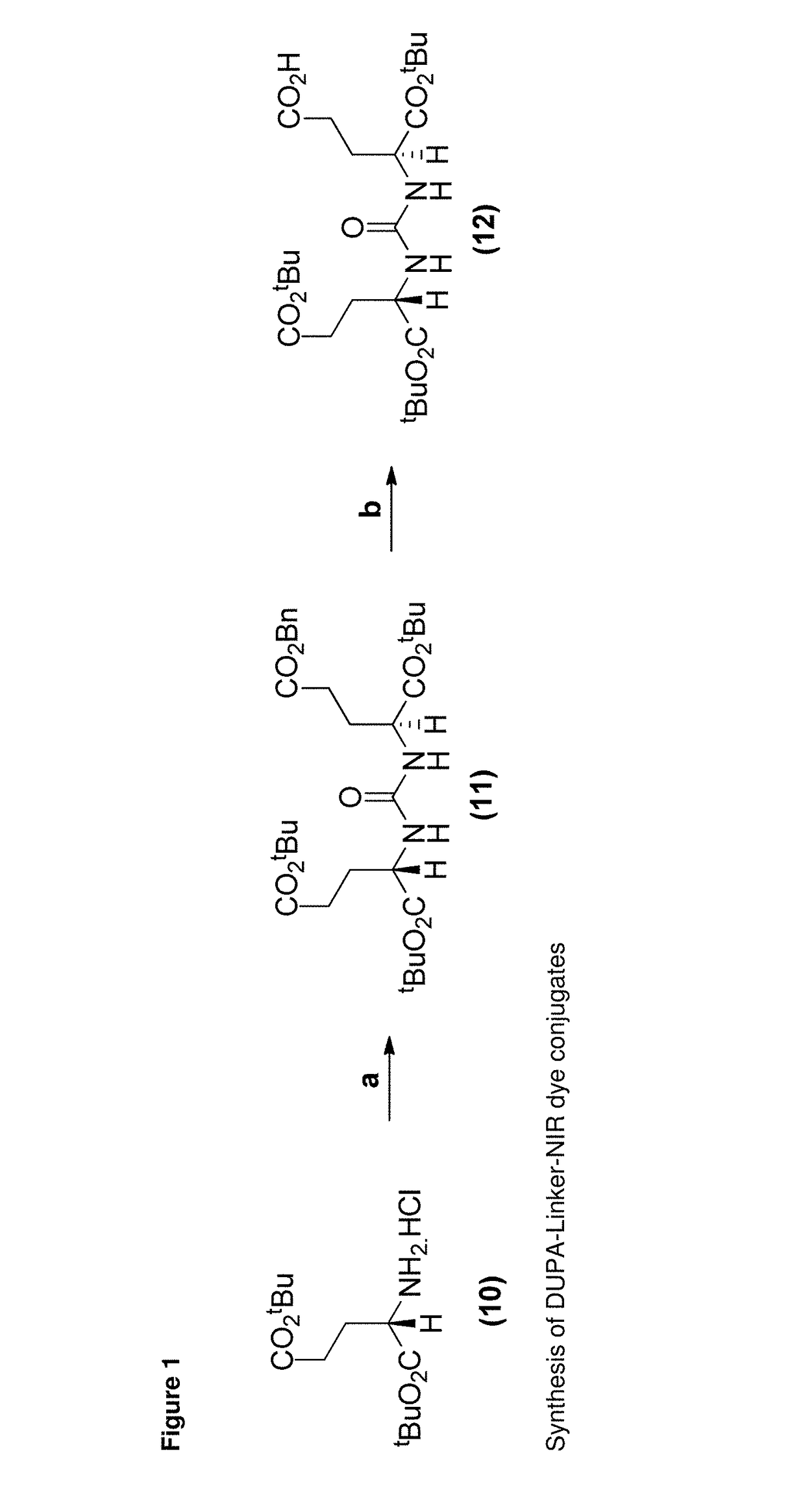
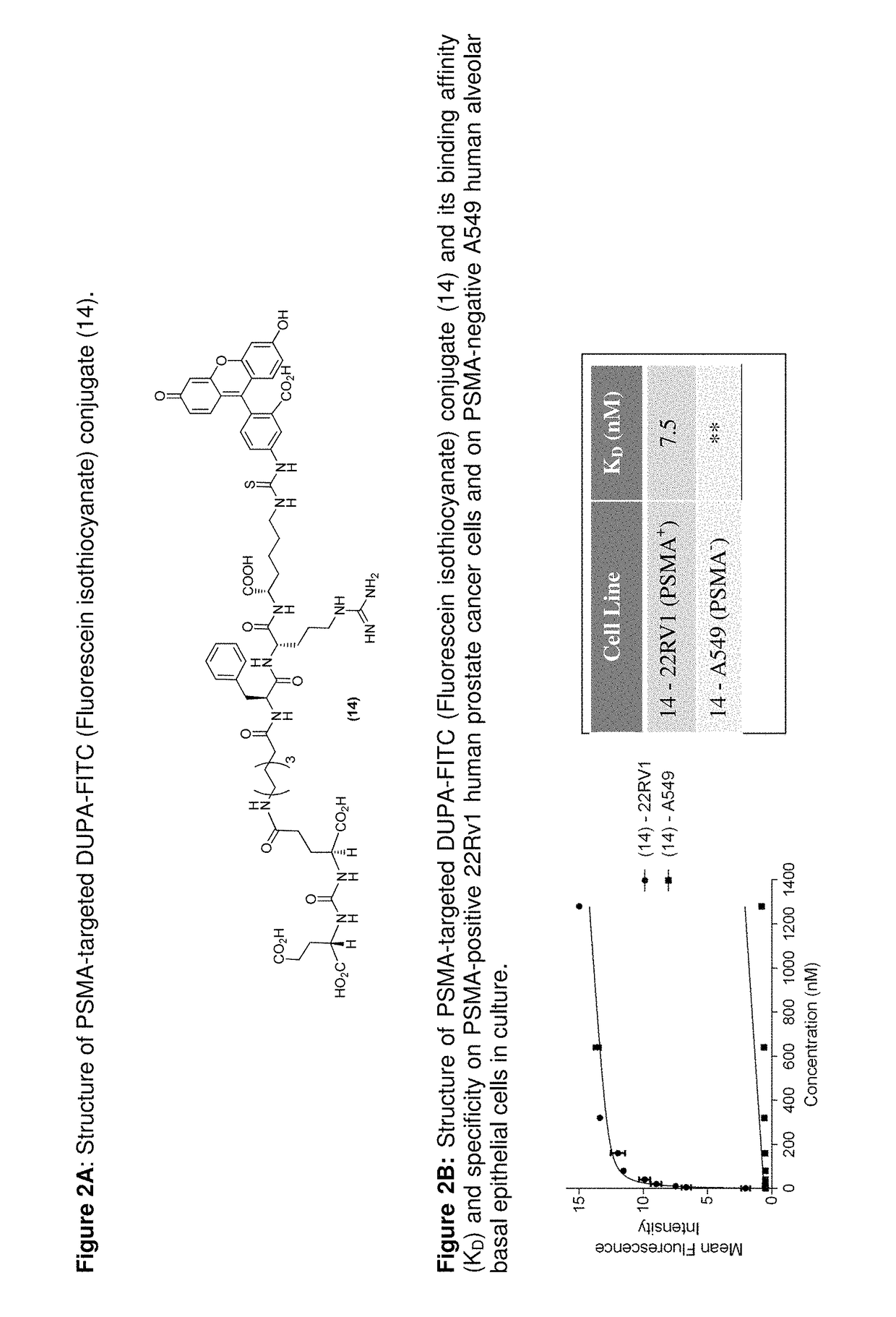
PSMA-targeted NIR dyes and their uses
ActiveUS9801956B2Promote rapid accumulationFluorescence enhancementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAntigenDisease
The present disclosure relates to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeted compounds conjugated to near-infra red (NIR) dyes and methods for their therapeutic and diagnostic use. More specifically, this disclosure provides compounds and methods for diagnosing and treating diseases associated with cells and / or vasculature expressing prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA), such as prostate cancer and related diseases. The disclosure further describes methods and compositions for making and using the compounds, methods incorporating the compounds, and kits incorporating the compounds.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Complex of bi-specific antibody and digoxigenin conjugated to a therapeutic or diagnostic agent
ActiveUS20120269723A1Easy to monitorImprove therapeutic efficacyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsDrugCompound s
The present invention relates to complexes of a) bi-specific antibodies and antibody fragments against a target protein and b) a digoxigenin conjugated to a therapeutic or diagnostic agent, methods for their production, their use as a delivery platform for therapeutic or diagnostic agents, pharmaceutical compositions containing said antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Novel Compound Having Affinity for Amyloid
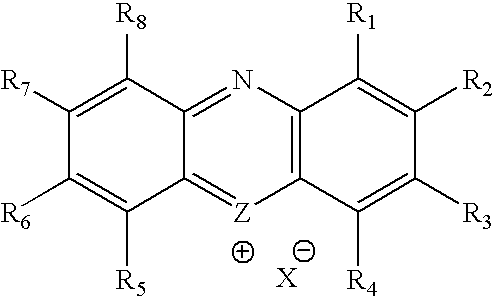
InactiveUS20090252679A1Fast clearanceExcellent in amyloid imagingTin organic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersHalogenChemistry
The present invention provides a compound which has affinity with amyloid, shows sufficiently rapid clearance from normal tissues and is suppressed in toxicity such as mutagencity. Provided is a compound represented by the following formula (1) or a salt thereof:wherein A1, A2, A3 and A4 independently represents a carbon or nitrogen; R1 is a halogen substituent; R2 is a halogen substituent; and m is an integer of 0 to 2, provided that at least one of R1 and R2 is a radioactive halogen substituent, at least one of A1, A2, A3 and A4 represents a carbon, and R1 binds to a carbon represented by A1, A2, A3 or A4 as well as a low-toxic diagnostic agent comprising a compound represented by the preceding formula or a salt thereof.
Owner:NIHON MEDI PHYSICS CO LTD
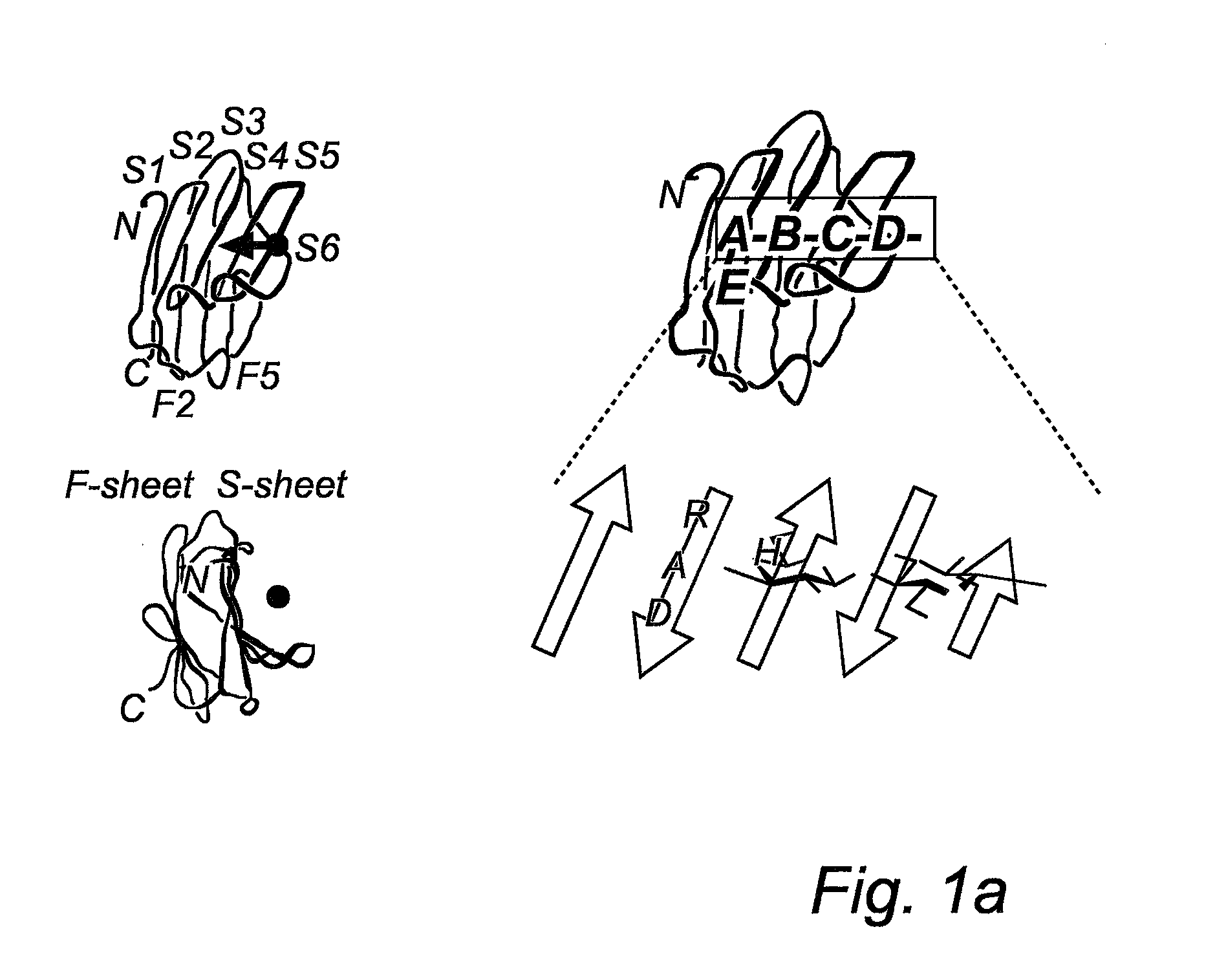
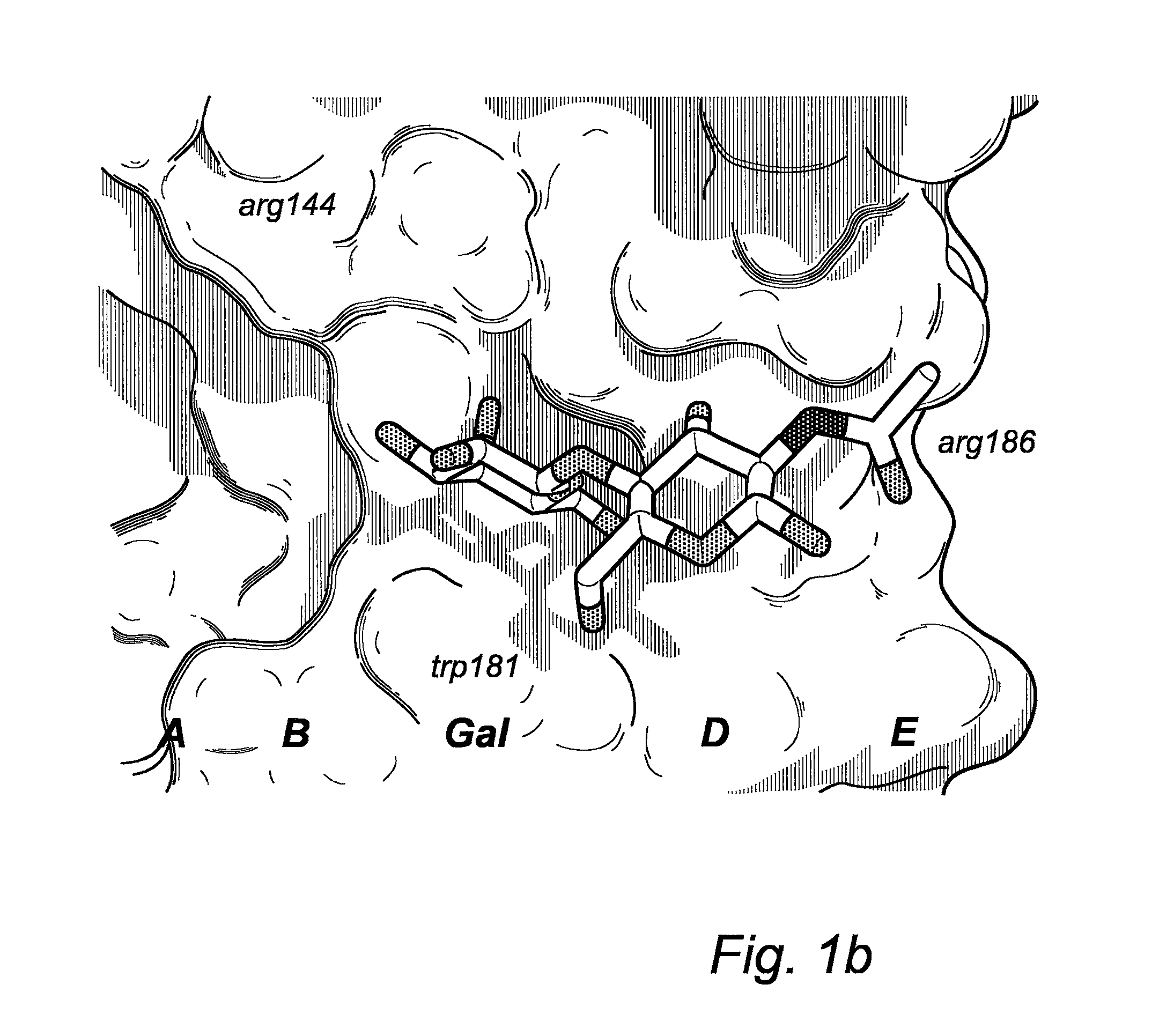
Novel galactoside inhibitors of galectins
Compounds having an effect as i.a. galectin inhibitors, to the use of said compounds as a medicament, as well as for the manufacture of a medicament for treatment of disorders relating to the binding of galectin to receptors in a mammal, where in the galectin is preferably a galectin-3. The novel compounds are defined by the general formula:
Owner:GALECTO BIOTECH
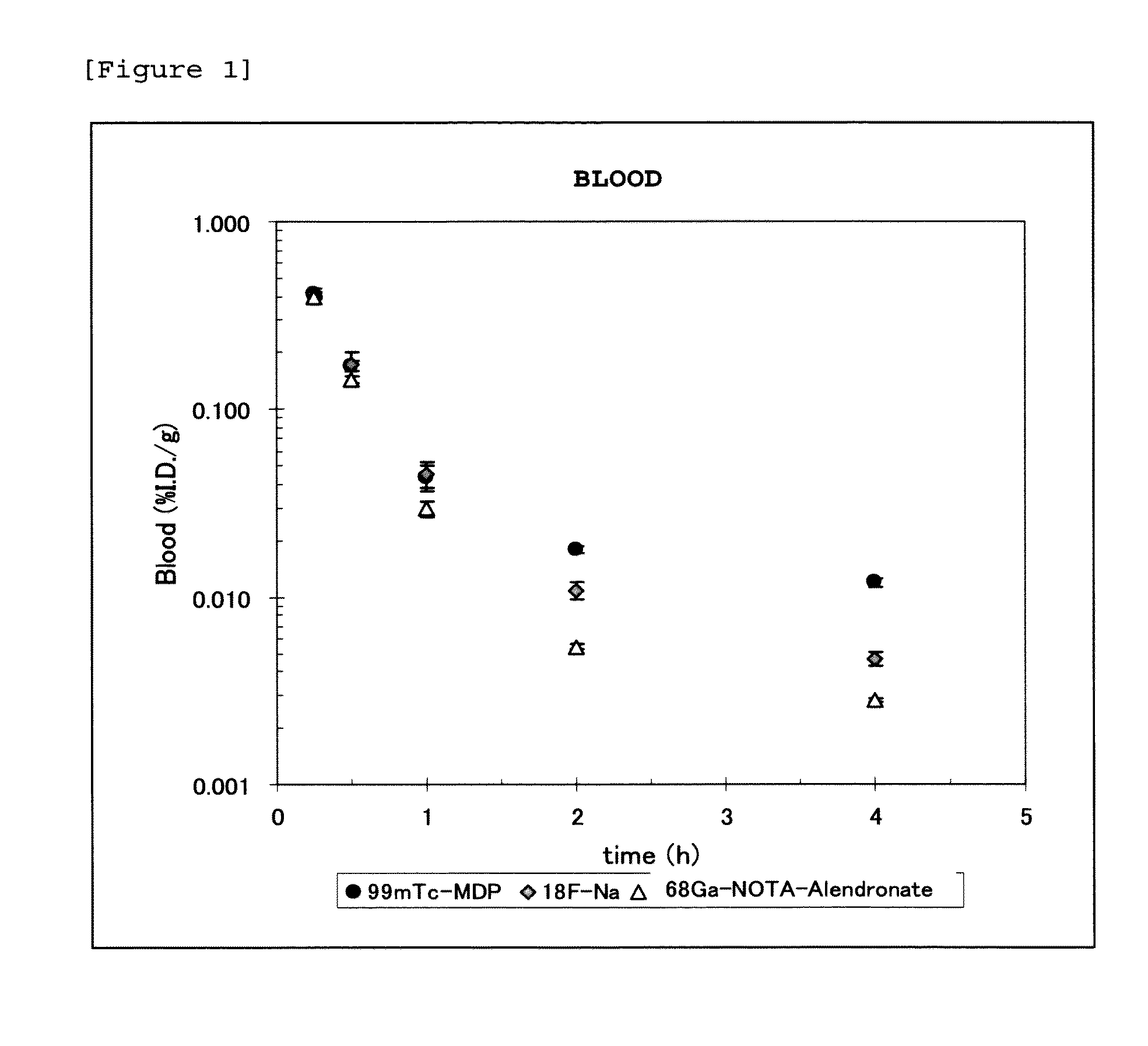
Bisphosphonic acid derivative and compound thereof labeled with radioactive metal nuclide
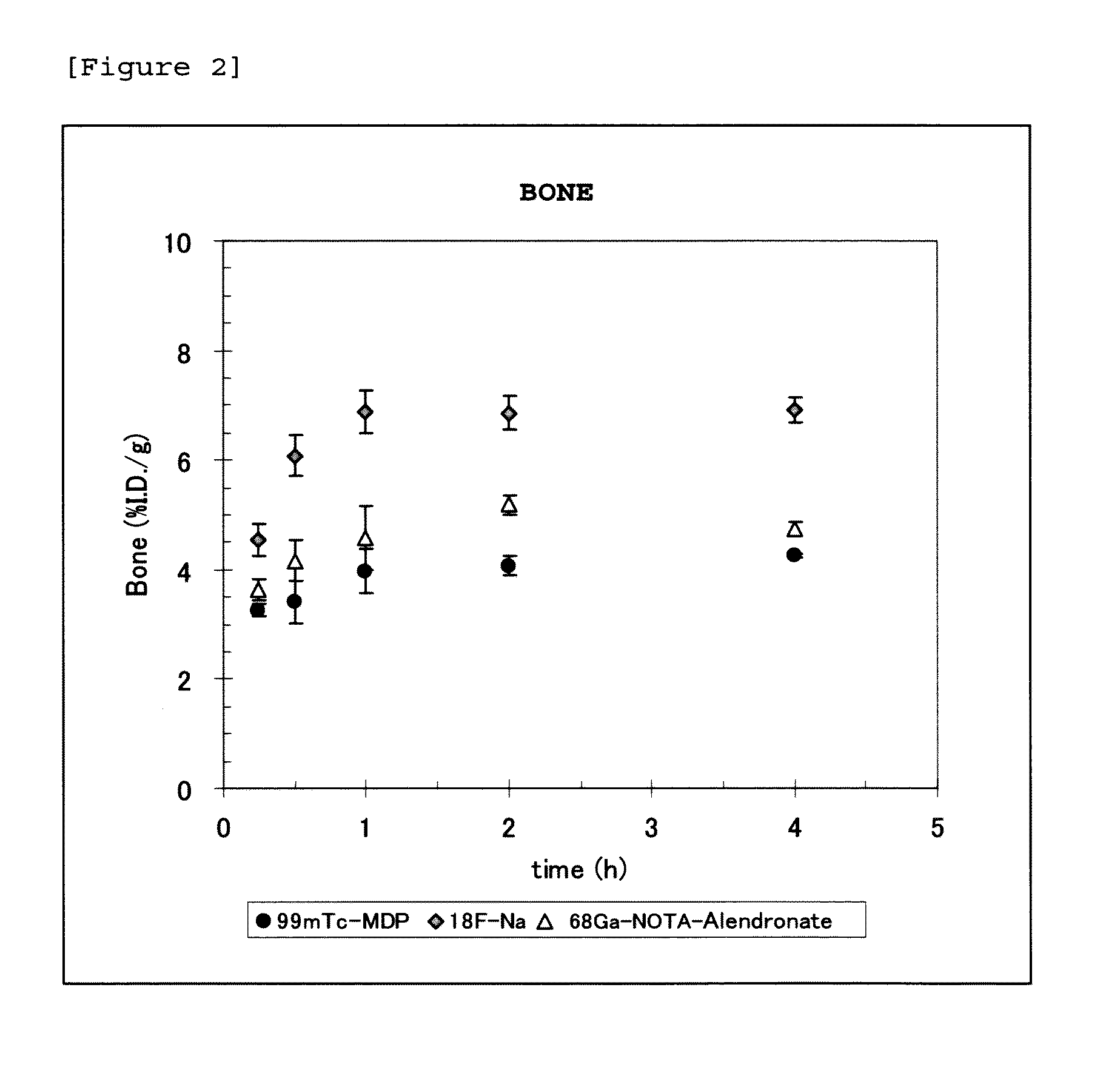
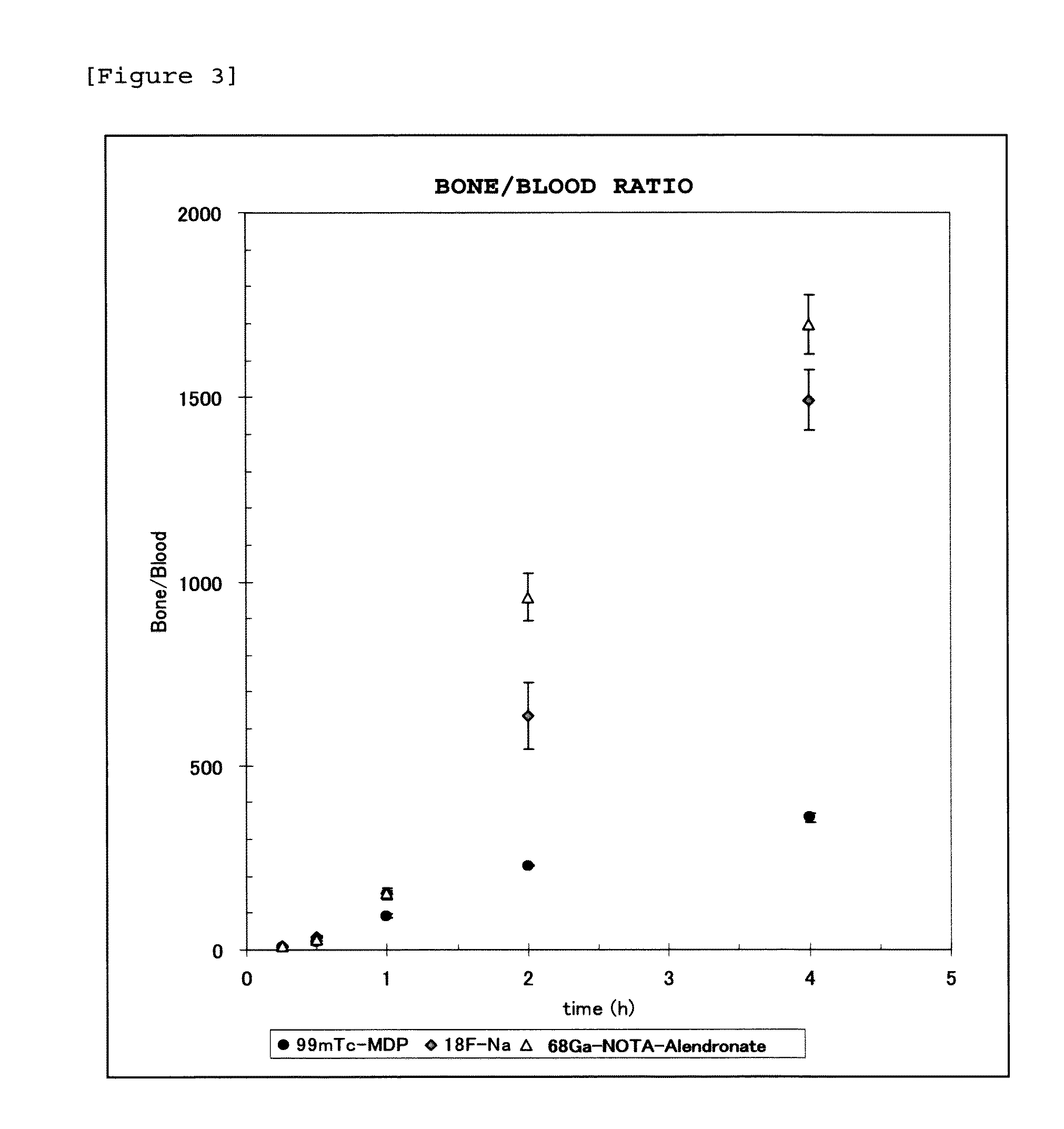
InactiveUS20120148492A1Rapid clearanceRaise the ratioIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsStage iibHalogen
Disclosed is a radioactive bone diagnostic agent which gives a high ratio of radioactivity accumulation in bone to that in blood from an early stage after administration of the agent and allows capturing an image in a short time after administration. Also disclosed is a bisphosphonic acid derivative represented by the following chemical formula (II) or a salt thereof, wherein X represents —(CH2)mCO—, Y represents —(CH2)n—, R represents H, OH, or a halogen atom, m and n are independent of each other and m represents an integer of 1 to 3, and n represents an integer of 0 to 4.
Owner:FUJIFILM RI PHARMA
Method of Treating An Acute Vascular Disorder
InactiveUS20090221540A1Rapid clearanceHigh riskBiocideAnimal repellantsSteroid CompoundVascular disease
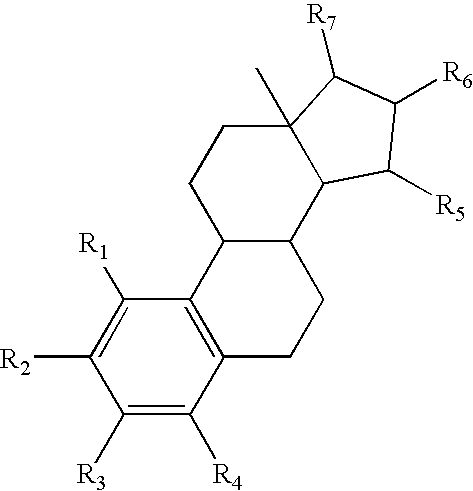
The invention relates to a method of treating an acute vascular disorder in a mammal. The method comprises orally administering to the mammal an effective amount of a steroid. The steroid is selected from the group consisting of: substances represented by formula (I), in which R1, R2, R3, R4 independently are a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group or an alkoxy group with 1-5 carbon atoms; each of R5, R6, R7 is a hydroxyl group; no more than 3 of R1, R2, R3, R4 are hydrogen atoms; precursors capable of liberating a substance according to the aforementioned formula when used in the present method; and mixtures of one or more of the aforementioned substances and / or precursors.
Owner:PANTARHEI BIOSCI
Oligonucleotide antagonist for human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)
InactiveUS7309786B2Strong specificityHigh affinitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsL929 cellHigh concentration
The present invention relates to a group of new oligonucleotides sequences with human tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibiting activity, which includes DNA sequences and RNA sequences. These oligonucleotides or aptamer can specifically be bound to TNF-α and inhibit the cytoxicity of TNF-α to L929 cells. Therefore, the aptamer of the present invention may be used to detect TNF-α and provide a therapeutic method for diseases related to the increasing level of TNF-α. Compared with other TNF antagonists such as monoclonal antibody and soluble receptor, the present invention has high specificity, high affinity, quick penetration to target tissue, rapid plasma clearance, and lower immunogenecity. Turthermore, it can be used repeatedly and keeps high concentration in target tissue and the like. It has the advantages of affinity and specificity similar to monoclonal antibodies and also has permeability and pharmacokinetics characteristics similar to small molecular polypeptide. The present invention also refers to derivative of the oligonucleotides sequence, including modified sequence. The present invention may further be manufactured as medicine for therapy and diagnosis of TNF-α related diseases.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com