Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Furin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
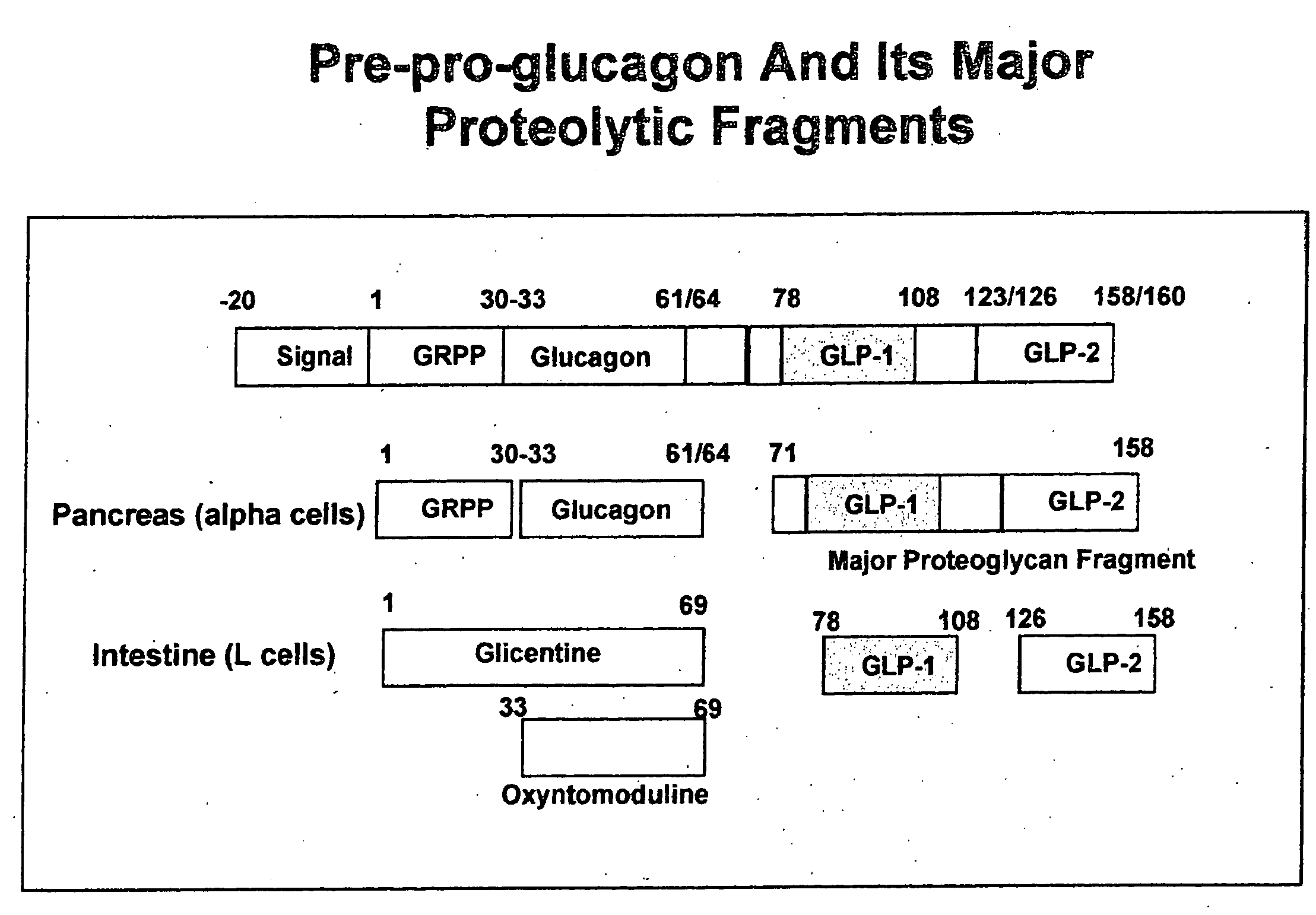
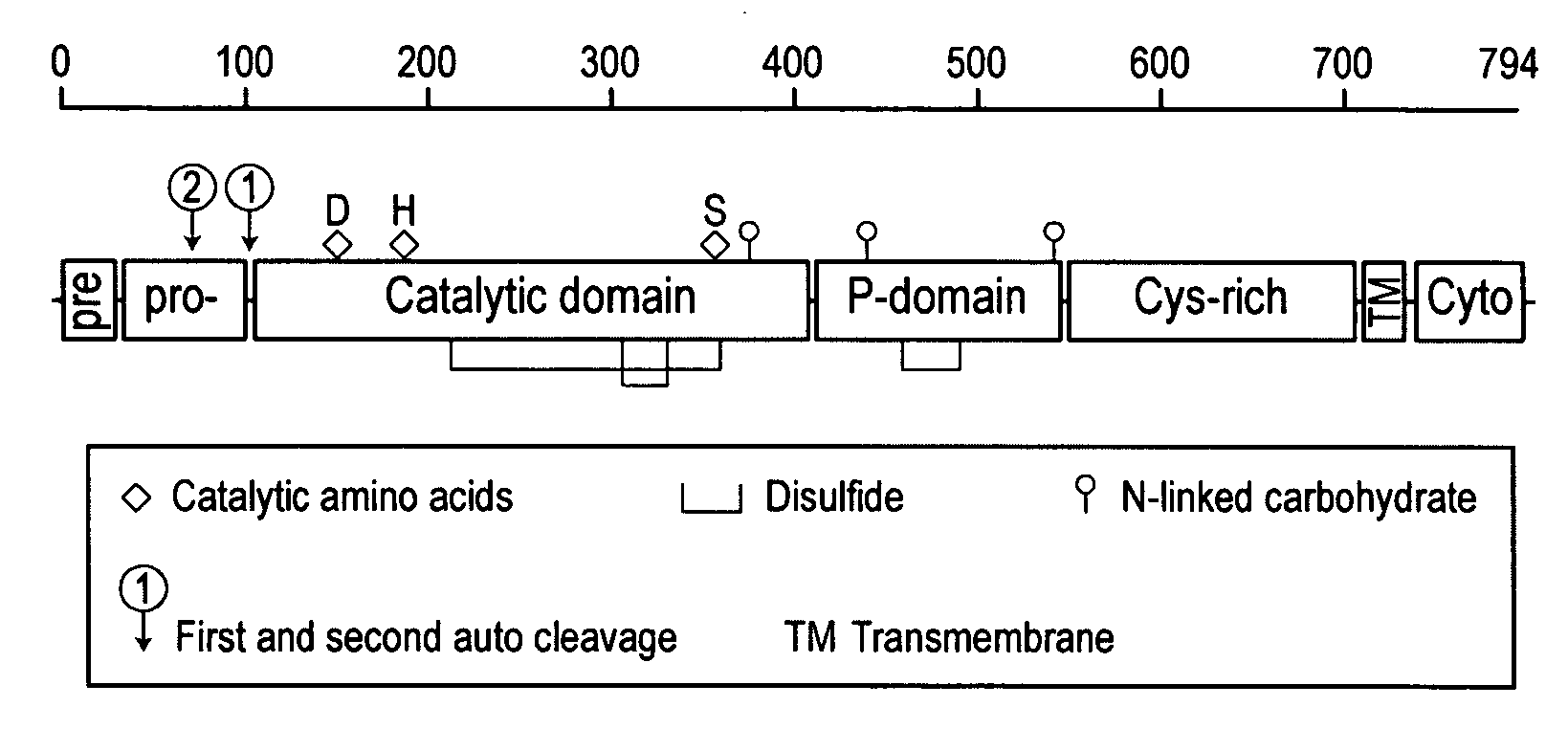
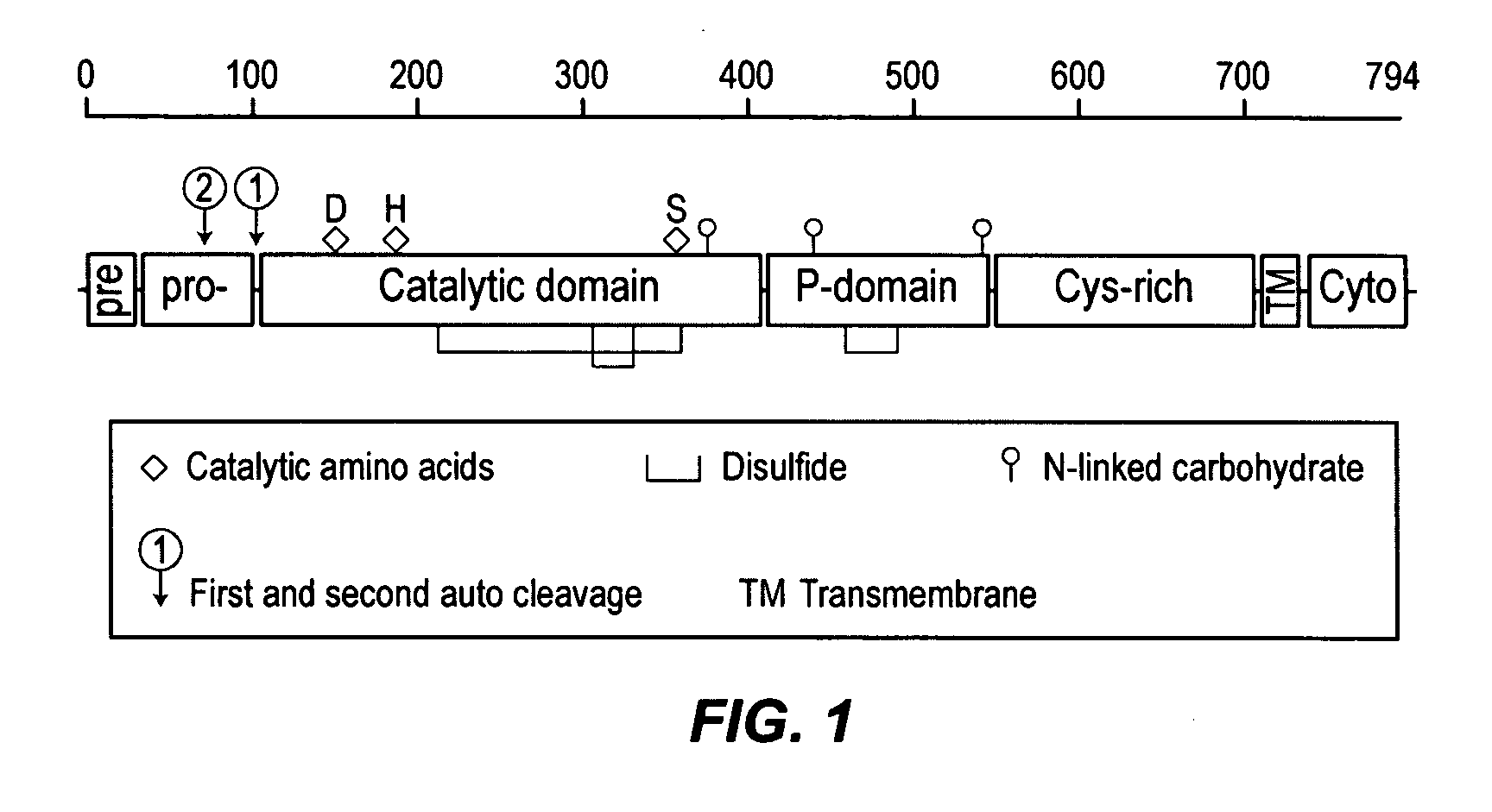
Furin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FURIN gene. Some proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized, and must have sections removed in order to become active. Furin cleaves these sections and activates the proteins. It was named furin because it was in the upstream region of an oncogene known as FES. The gene was known as FUR (FES Upstream Region) and therefore the protein was named furin. Furin is also known as PACE (Paired basic Amino acid Cleaving Enzyme). A member of family S8, furin is a subtilisin-like peptidase.
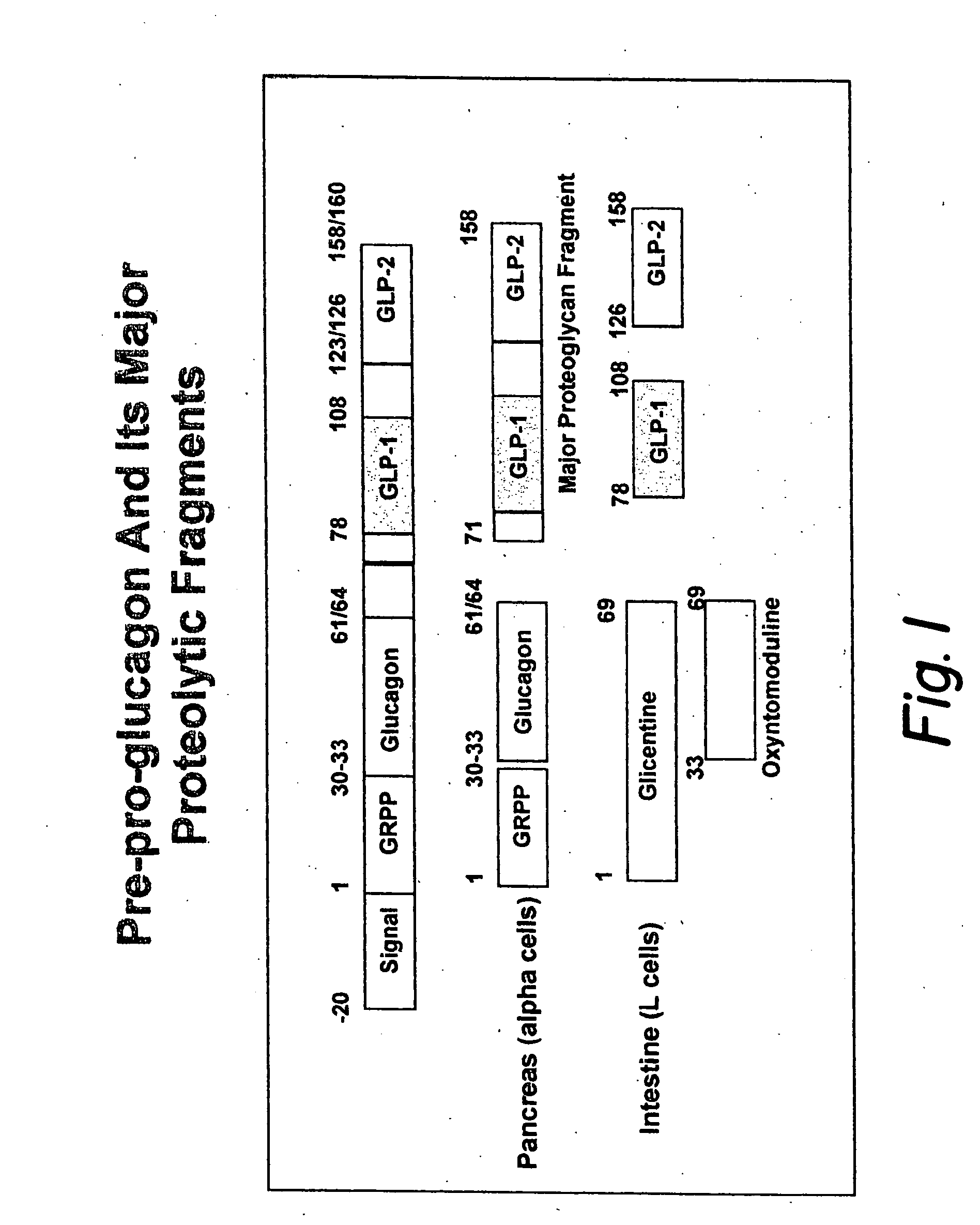
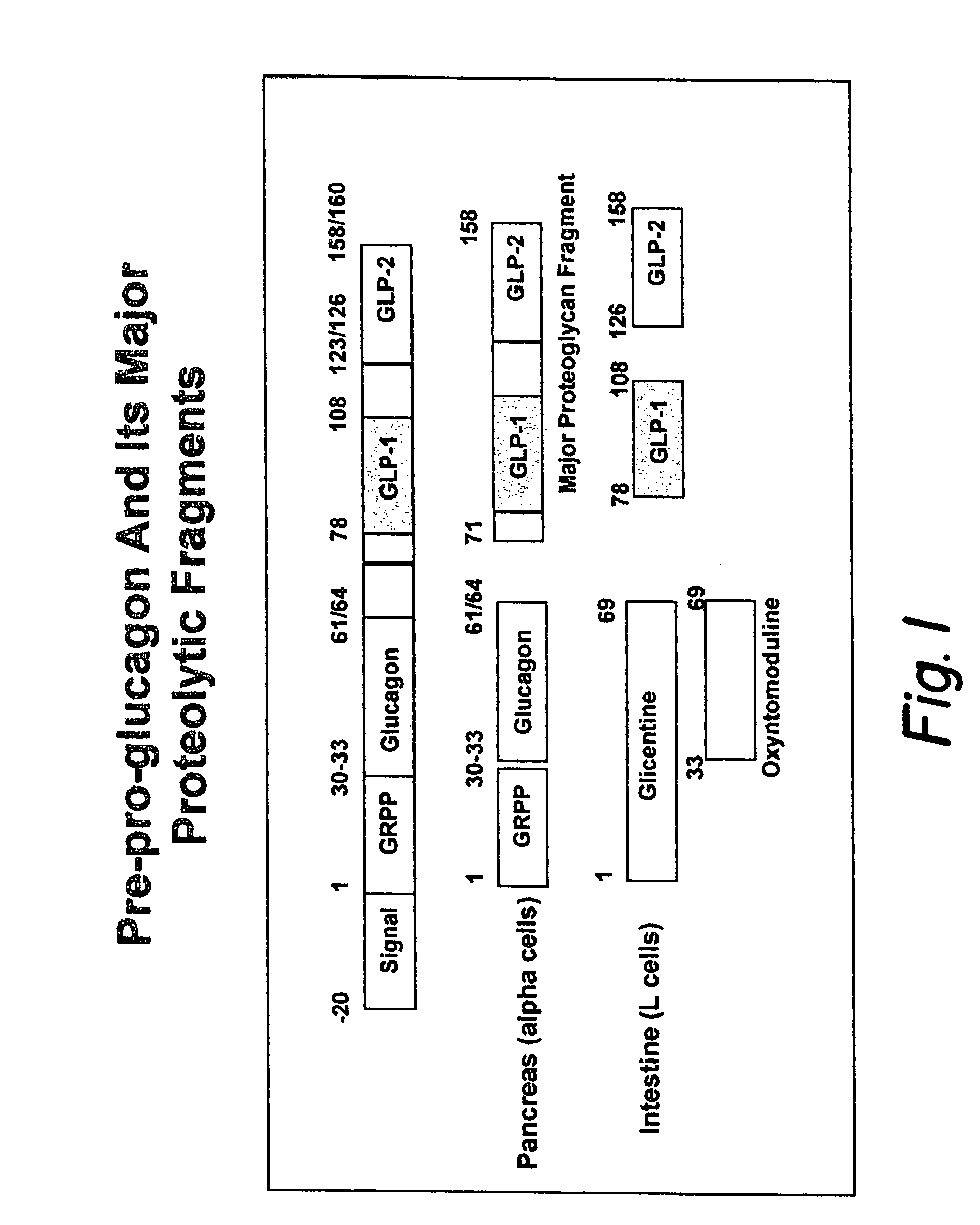
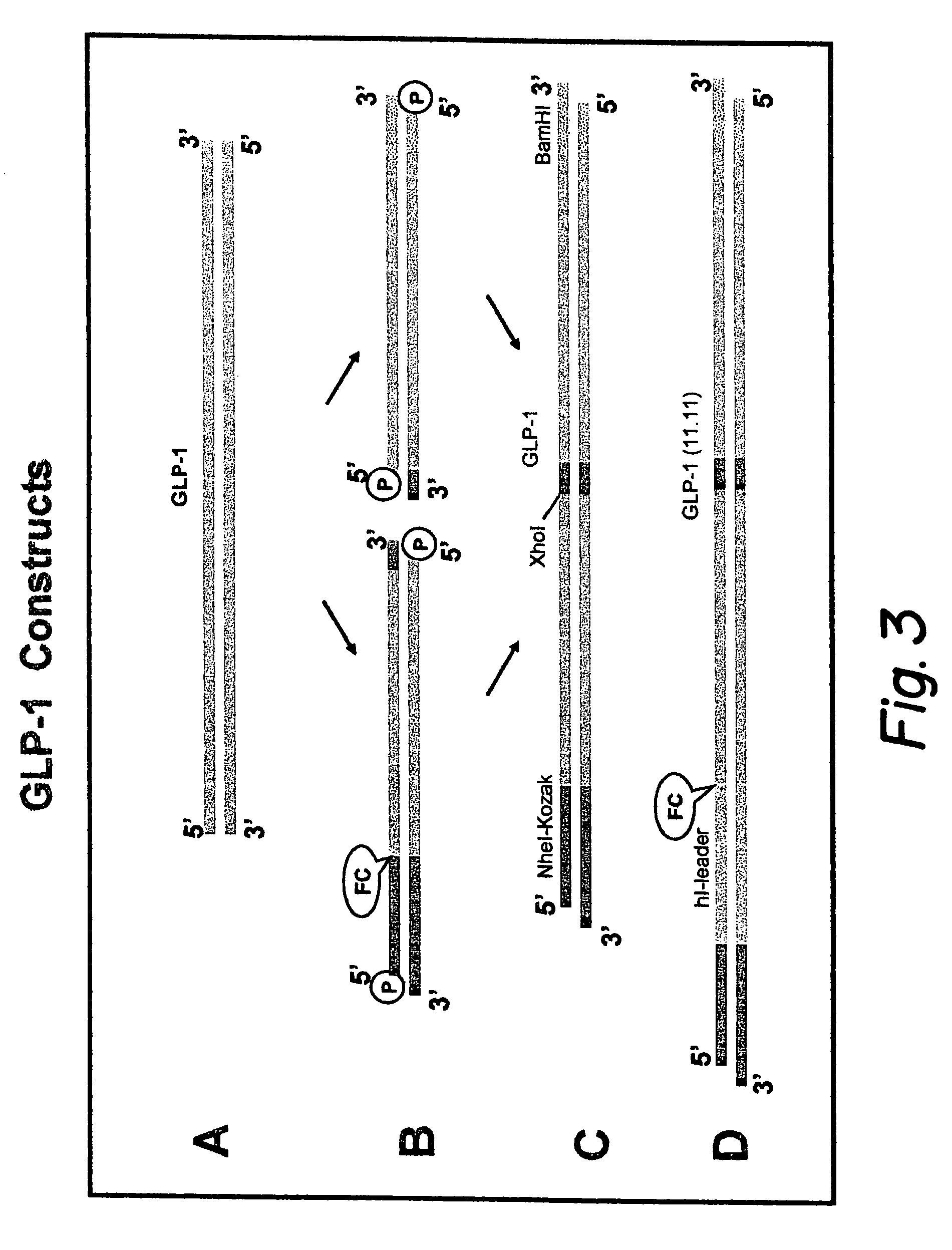
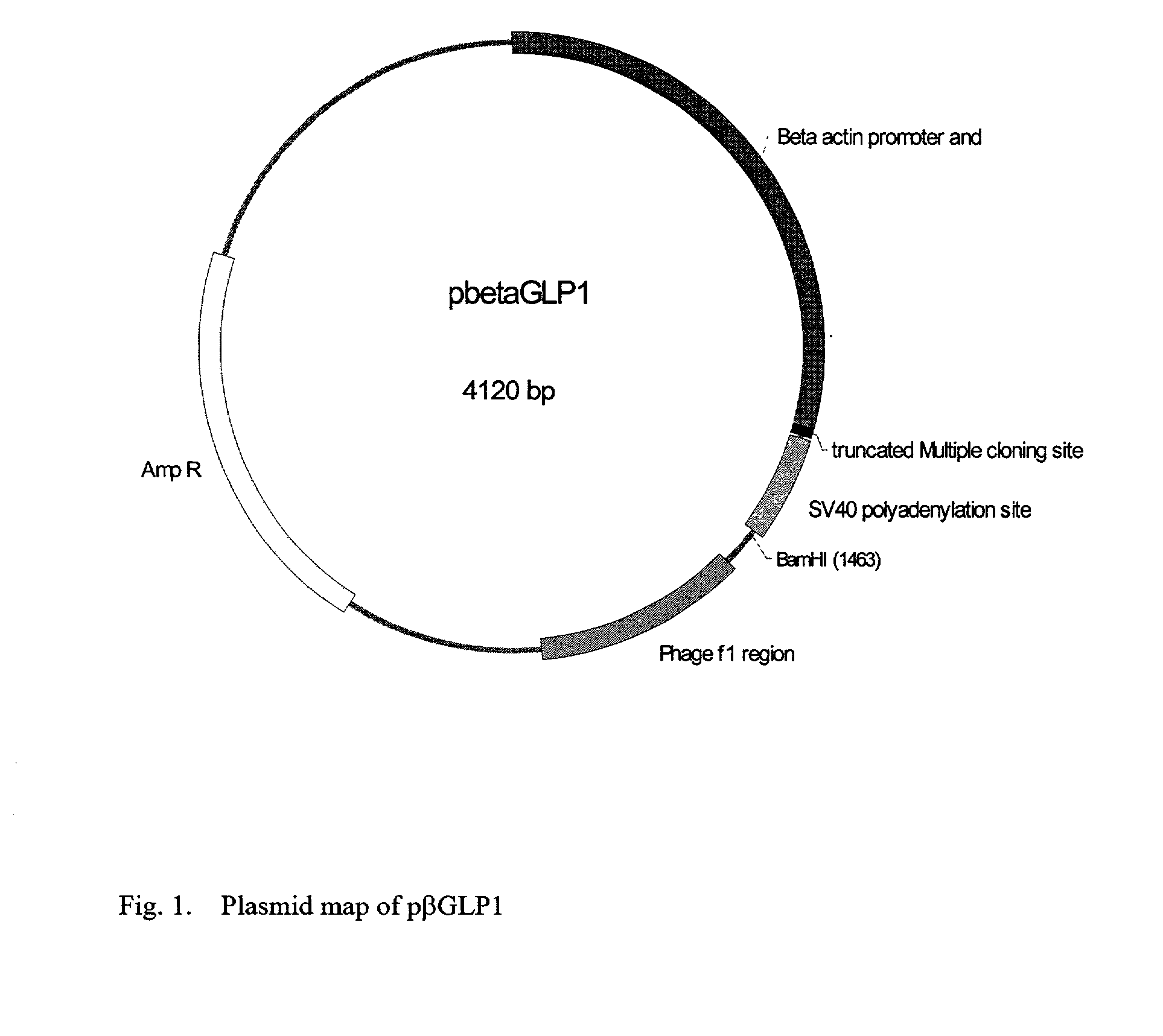
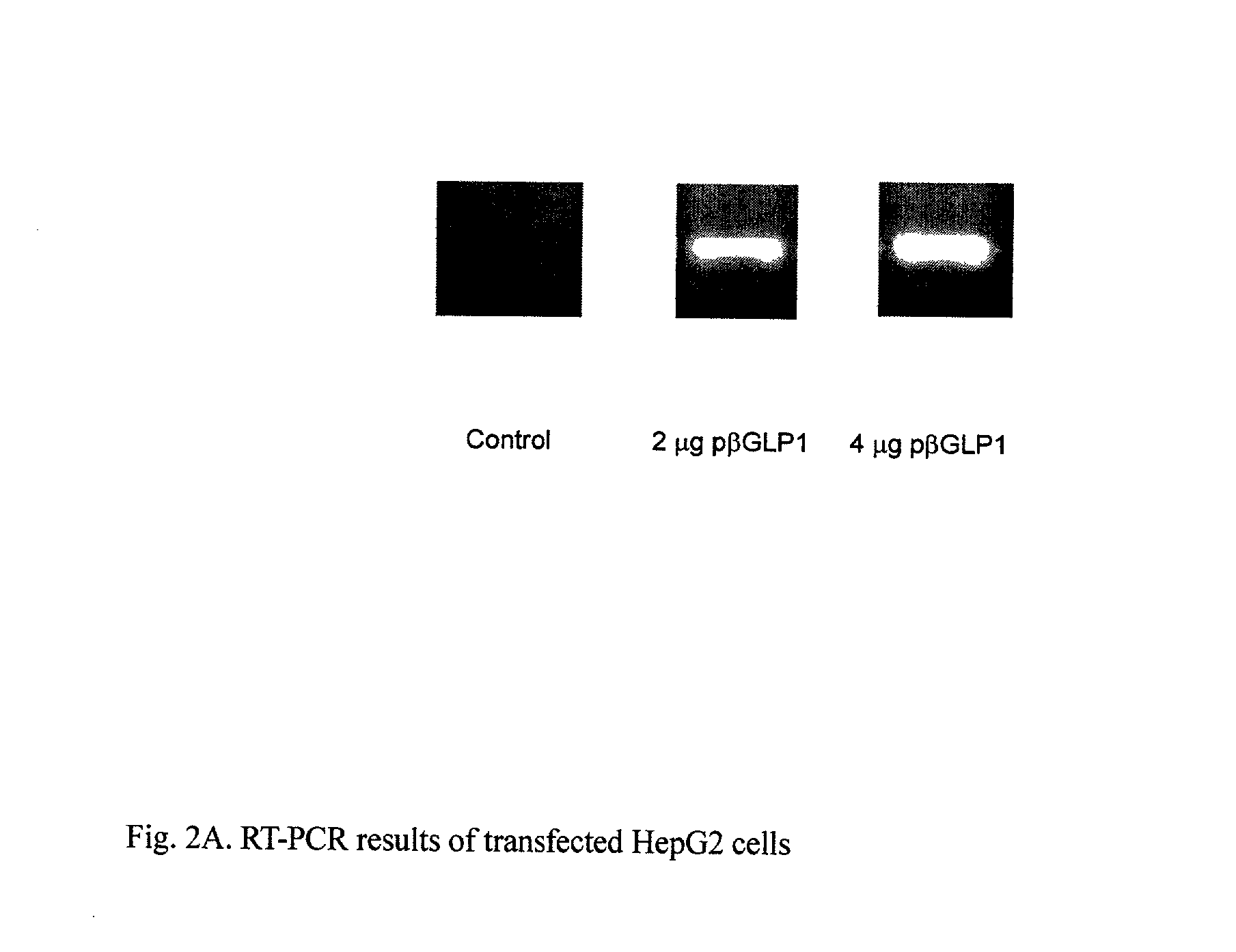
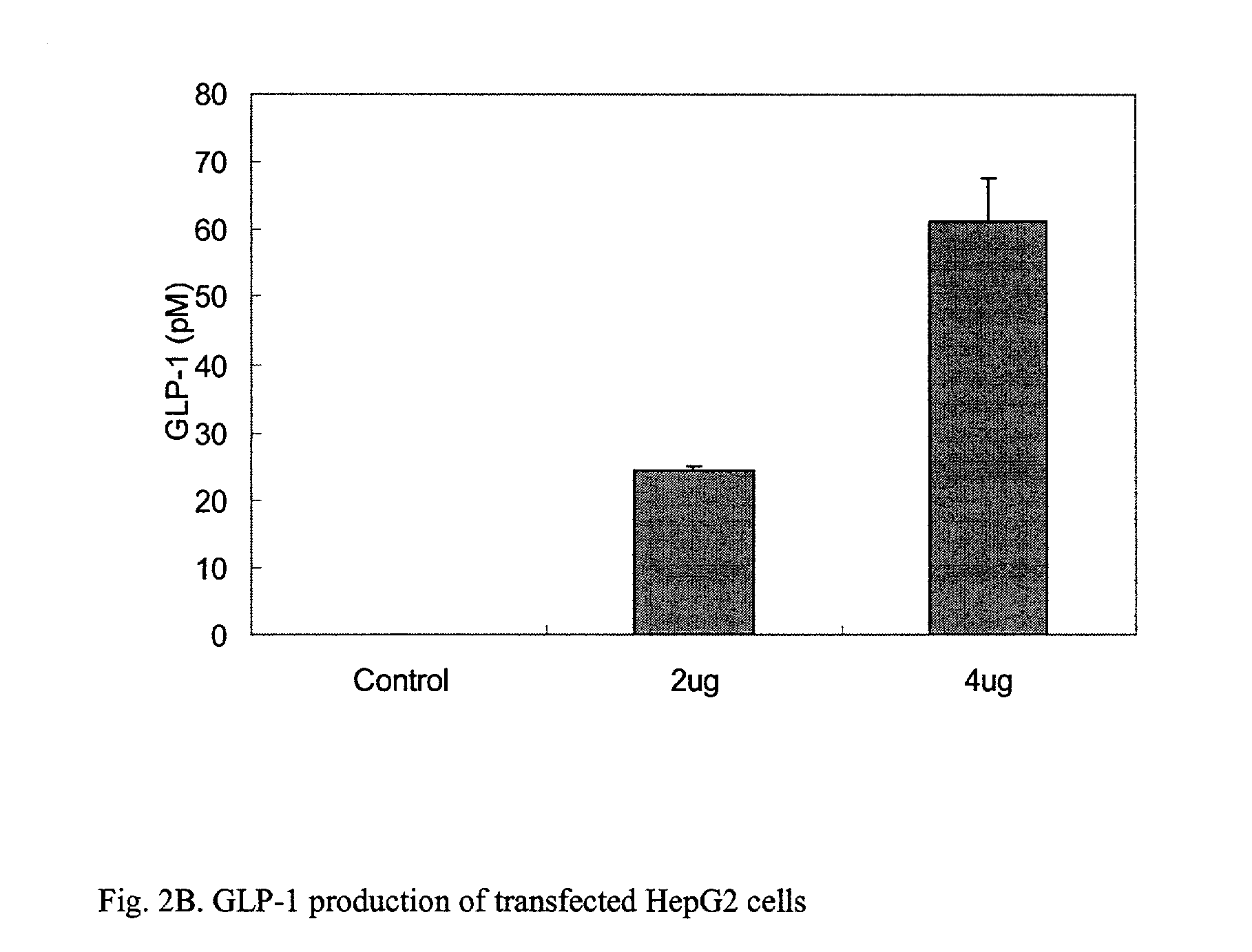
GLP-1 gene delivery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS7374930B2Efficient transfectionEasy to controlSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGlucose polymers
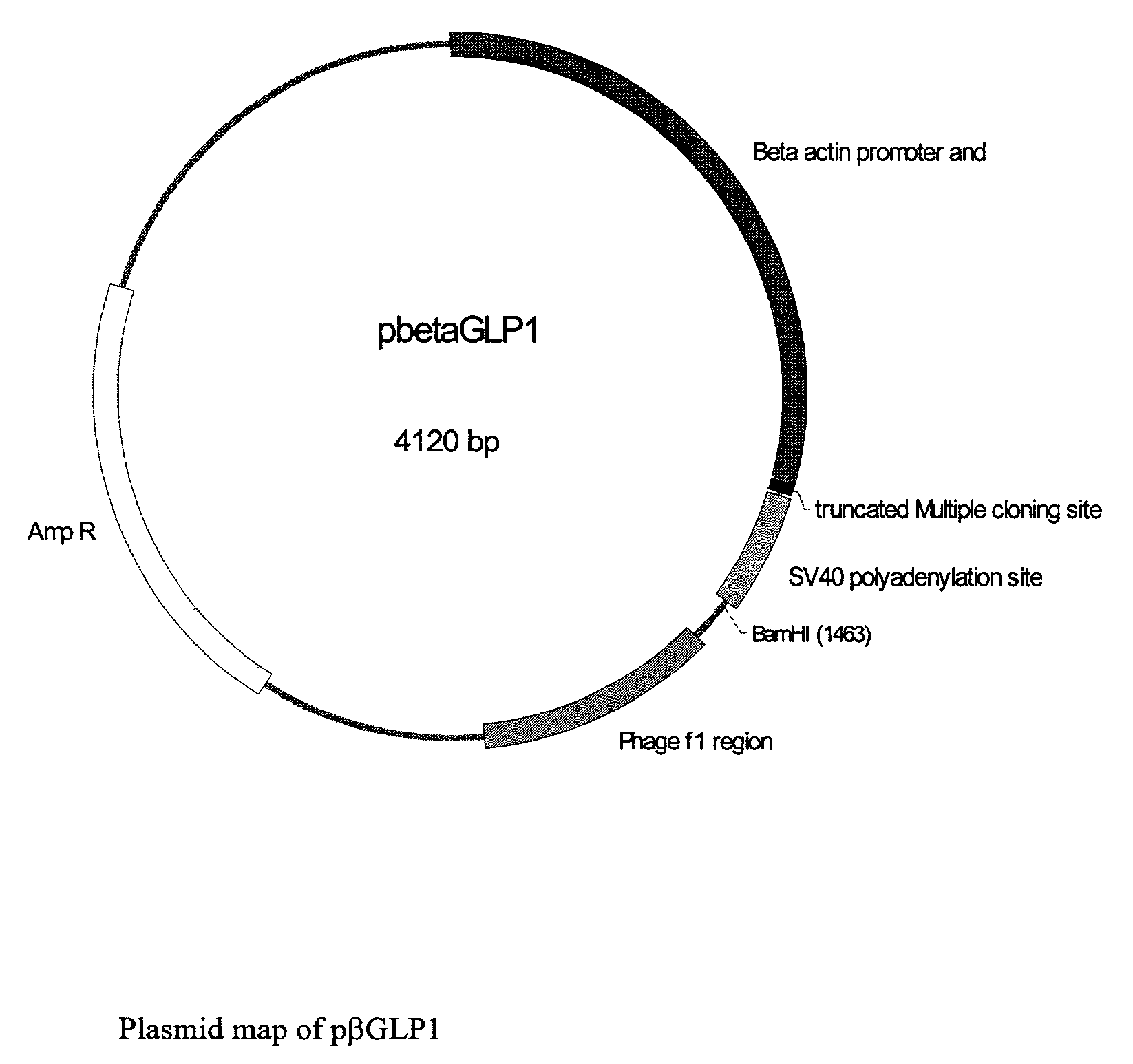
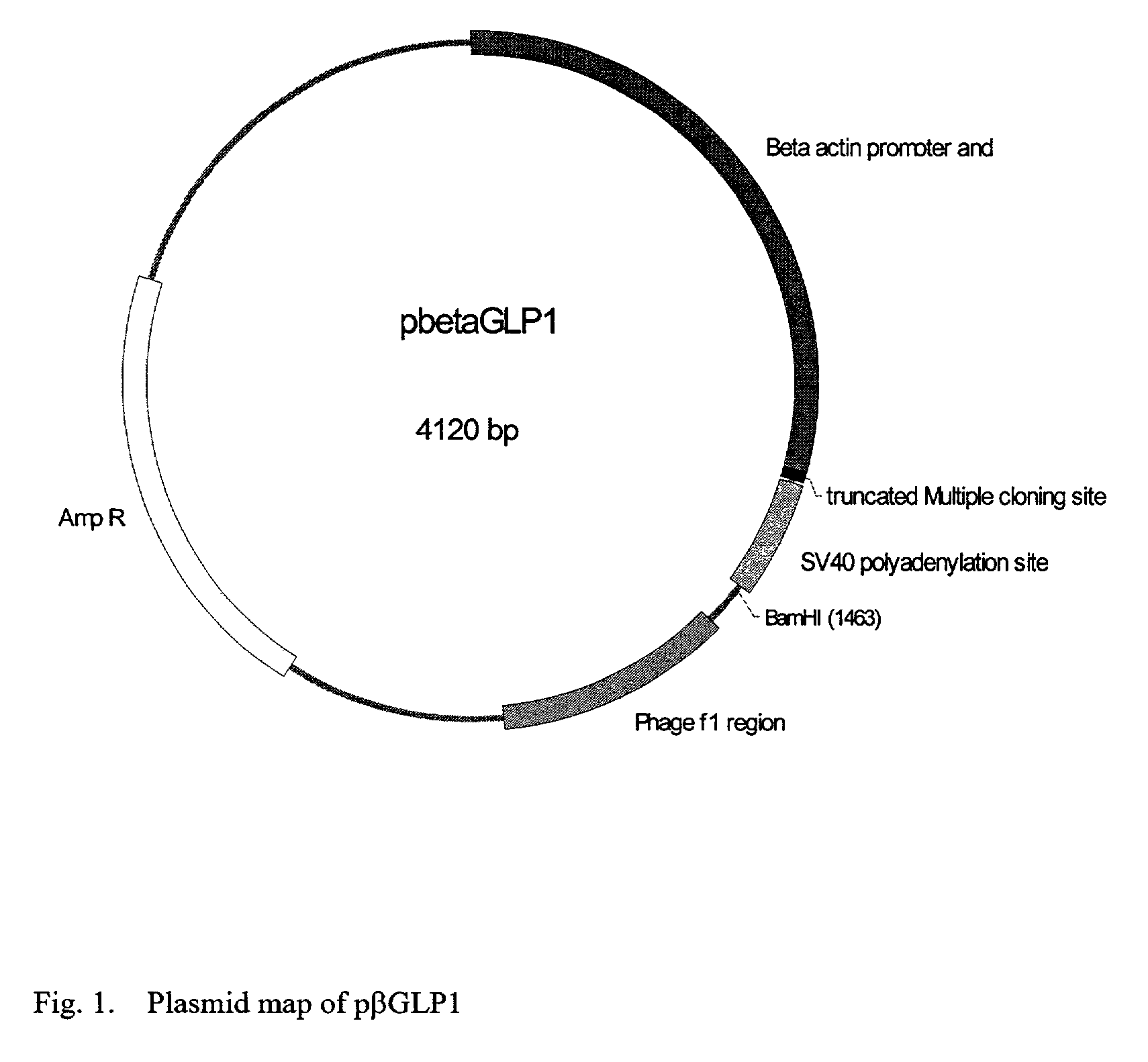
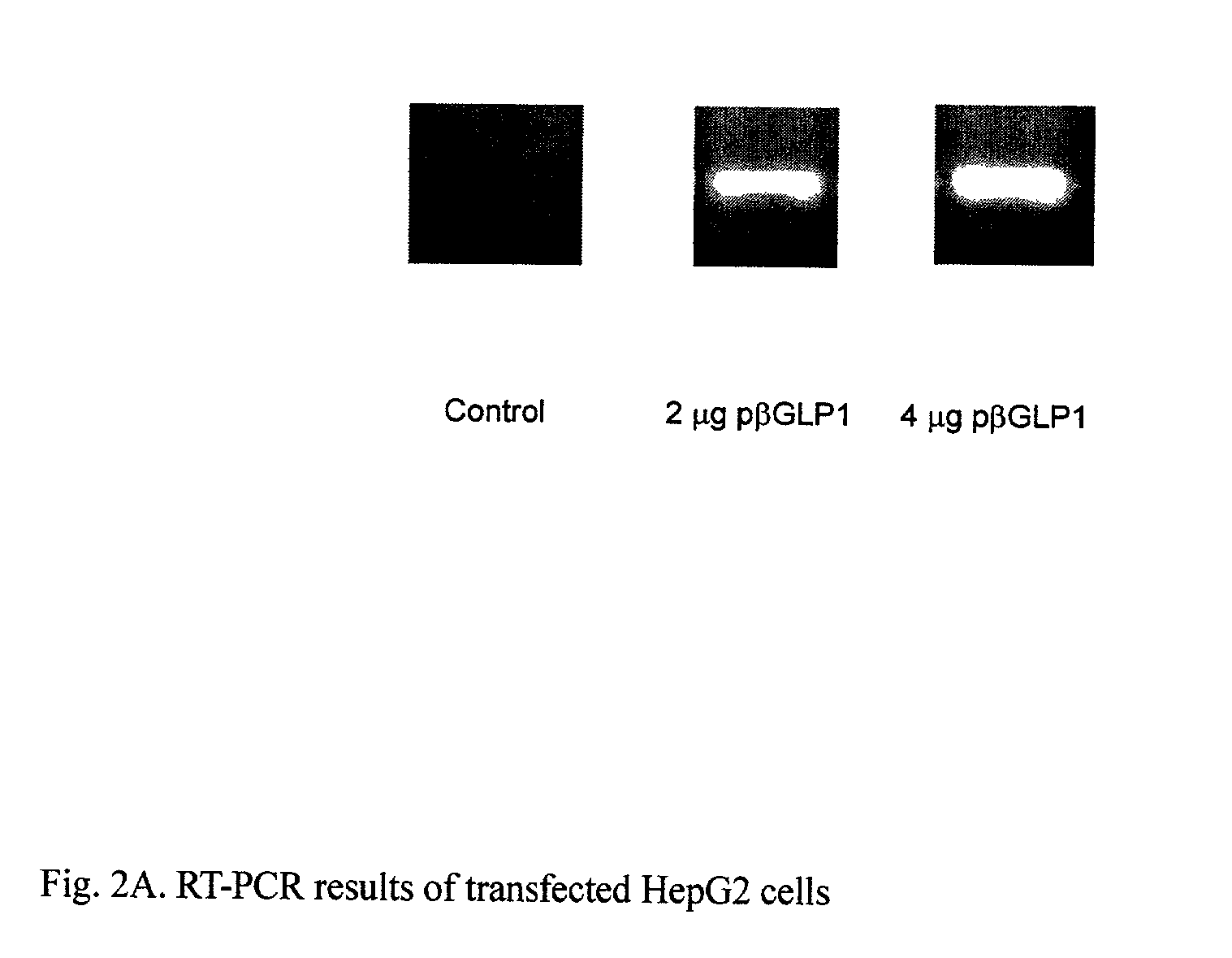
This patent discloses compositions and methods of use thereof to normalize the blood glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes. It relates particularly to a plasmid comprising a chicken β actin promoter and enhancer; a modified GLP-1 (7-37) cDNA (pβGLP1), carrying a furin cleavage site, which is constructed and delivered into a cell for the expression of active GLP-1.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Modified nucleotide sequence encoding glucagon-like peptide-1 (glp-1), nucleic acid construct comprising same for production of glucagon-like peptide-1 (glp-1), human cells comprising said construct and insulin-producing constructs, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20080299096A1Reduce weightPromote productionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaNucleotide
An isolated chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequence encoding a human pro-insulin leader, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and a furin cleavable site between the human pro-insulin leader sequence and the GLP-1 is provided. Also provided is an isolated modified chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequence encoding a human pro-insulin leader, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and a furin cleavable site between the human pro-insulin leader sequence and the GLP-1. Recombinant expression vectors comprising the chimeric GLP-1 nucleic acid sequences, which produce GLP-1 constitutively are provided, as are human cells transfected with such an expression vector in combination with an expression vector comprising a proinsulin nucleic acid sequence and an expression vector comprising a furin and a glucose-regulatable TGF-alpha promoter. Methods of producing human GLP-1 constitutively are provided as are method of producing GLP-1 and insulin or in a glucose-dependent manner using such transfected cells. Methods of treating a subject having Type II diabetes and methods of treating a subject prone to hyperglycemia or suffering from hyperglycemia are provided in which transfected cells produce human GLP-1 and insulin in a glucose-dependent manner. Also provided are methods of reducing weight in a subject by implanting into the subject transfected cells which produce human GLP-1 and insulin in a glucose-dependent manner.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Insertion of furin protease cleavage sites in membrane proteins and uses thereof
Cleavage site for the protease furin is inserted between domains of a membrane glycoprotein. Upon cleavage by furin in the trans-Golgi network, the protein is separated into individual membrane-free domain that retains its native conformation. This protocol can be used to produce virus membrane protein domains for structural analysis and for trials as vaccines.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Expression of lysosomal hydrolase in cells expressing pro-N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester α-N-acetyl glucosimanidase
InactiveUS7135322B2The method is simple and reliableReduce stepsSugar derivativesTissue culturePhosphateLysosome
The present invention provides methods of producing a pro-N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiesterαN-acetyl glucosimanidase (phosphodiester α-GlcNAcase), in mammalian cells deficient in the furin proteolytic enzyme and methods of making lysosomal bydrolases having an N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Furin-cleavable peptide linkers for drug-ligand conjugates
InactiveUS20090155289A1Targeted optimizationGood target for cancer cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTrans golgiLigand molecule
Disclosed are certain peptide linkers for conjugating drugs to ligands, and the resulting drug-linker-ligand molecules and compositions thereof. The conjugated molecules useful for the targeted delivery of drugs to the desired cells, and allow for the intracellular release of the drug in cases where the targeted antigen is internalized via the trans Golgi network and not the lysosomal pathway.
Owner:PANACEA PHARMA
Methods for treating blood coagulation disorders
InactiveUS7615537B2Optimally promote proper disulfide bondingPrecise BondingBiocideVirusesFactor VIIaA-DNA
The present invention relates to a method of treating an individual having a blood coagulation defect (e.g., hemophilia A, hemophilia B), comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a DNA vector encoding modified Factor VII (FVII), wherein the modified Factor VII leads to generation of Factor VIIa in vivo. In a particular embodiment, the invention pertains to a method of treating an individual having a blood coagulation defect comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a nucleic acid encoding a modified FVII wherein the modified FVII comprises a signal which codes for precursor cleavage by furin at the activation cleavage site of the modified FVII. The invention also relates to a method of treating an individual having a blood coagulation disorder comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a nucleic acid encoding the light chain of human FVII and a nucleic acid encoding the heavy chain of human FVII operably linked to a leader sequence. Compositions, expression vectors and host cells comprising nucleic acid which encodes a modified Factor VII, wherein the modified Factor VII leads to generation of Factor VIIa in vivo is also encompassed by the present invention.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Deletions in domain ii of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS20100215656A1Maintain immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
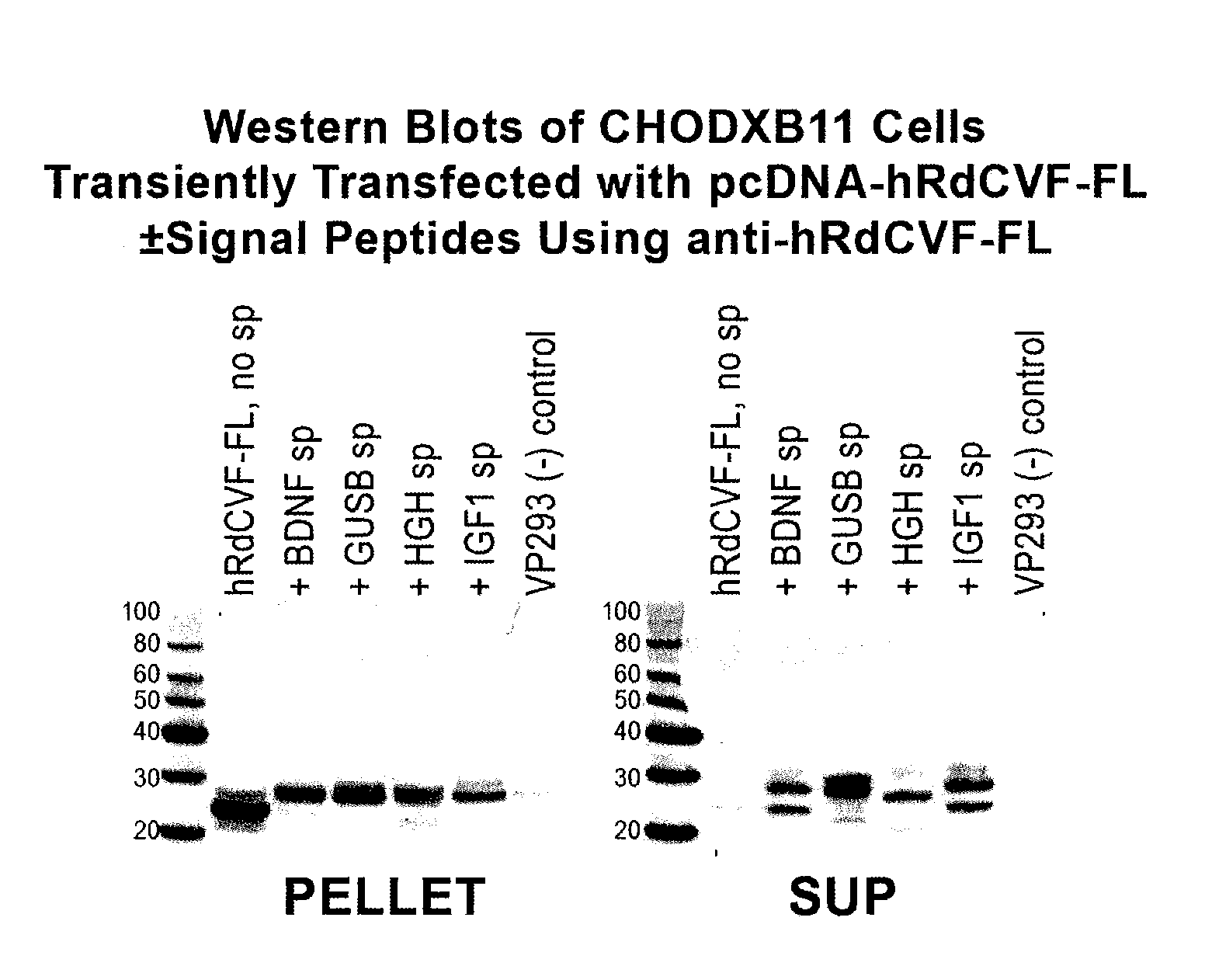
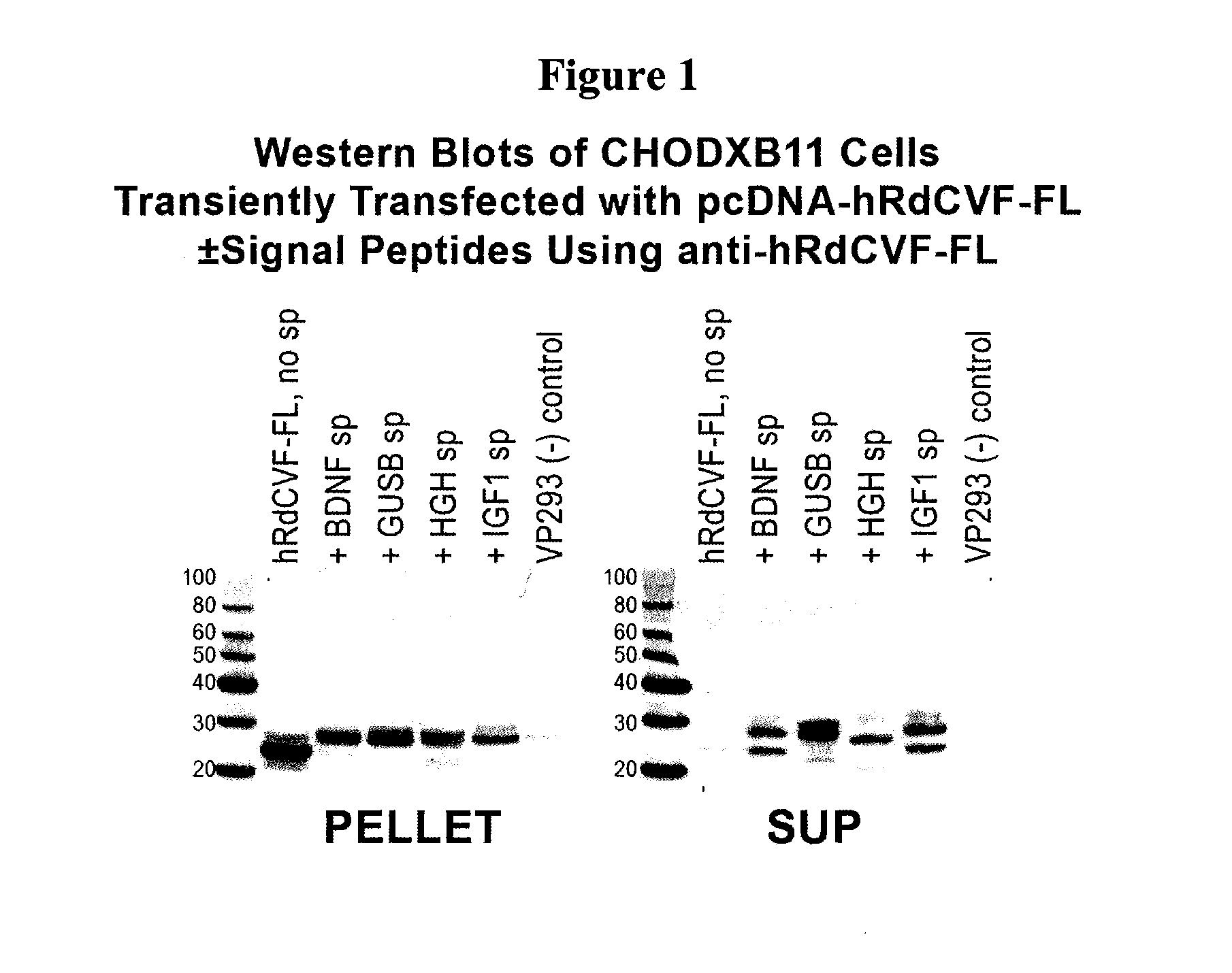
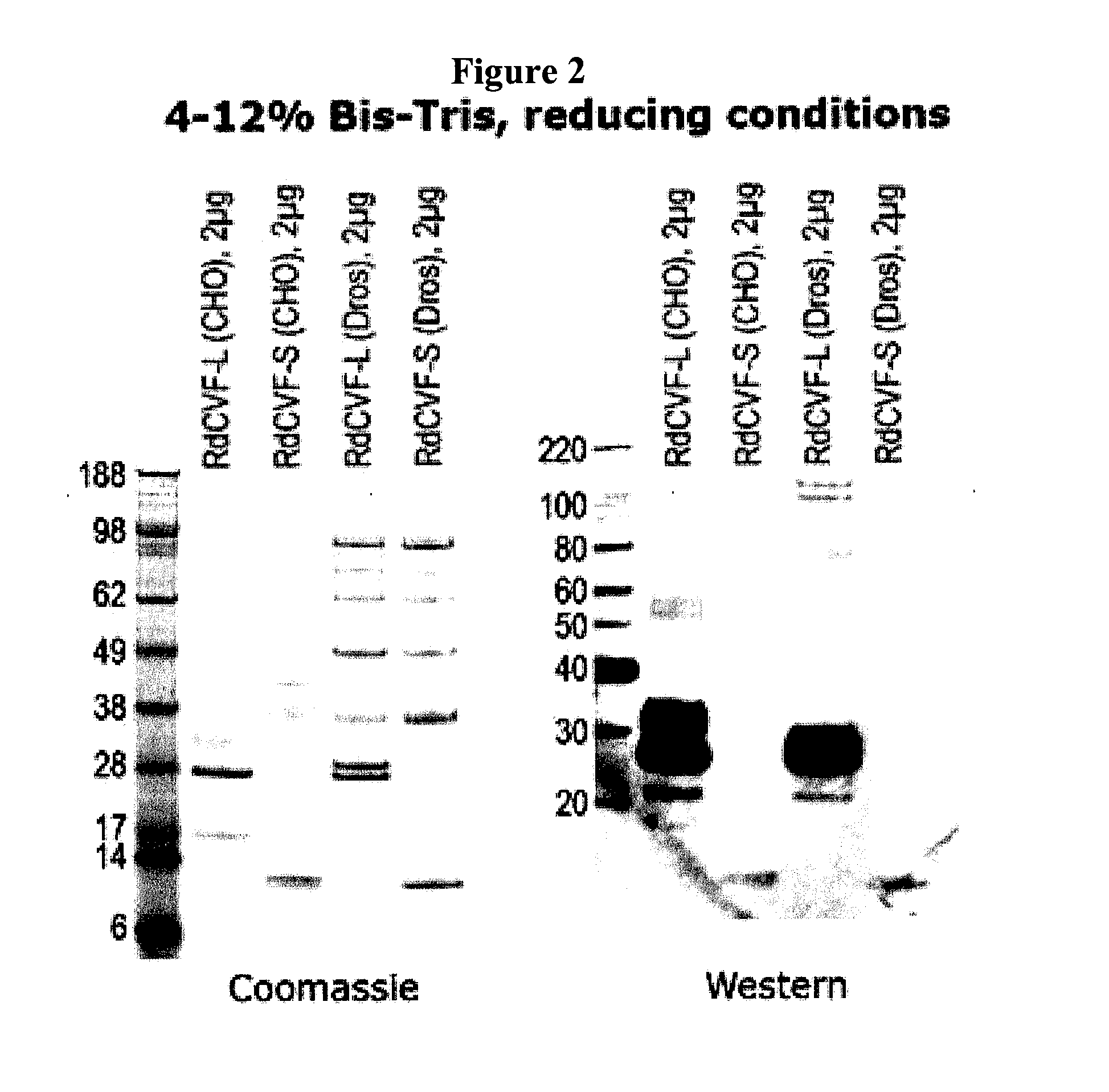
Methods to produce rod-derived cone viability factor (RDCVF)
The invention is related to methods of producing rod-derived cone viability factor (RdCVF). This invention also relates to the treatment of an ocular disease in a mammal using RdCVF. Also provided are expression vectors for high secreted expression of RdCVF of using nucleotide sequences encoding heterologous signal proteins and optionally markers for furin cleavage.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Modified nucleotide sequence encoding glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), nucleic acid construct comprising same for production of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), human cells comprising said construct and insulin-producing constructs, and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7829664B2Reduce weightPromote productionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaNucleotide
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Methods for treating cancer using an immuno-toxin comprising an exotoxin a moiety having a furin cleavage site replaced with a cancer associated protease site cleaved by mmp-2 or mmp-9
The present invention provides a modified toxin having an ETA moiety that has the furin site replaced with a cancer-associated protease site. The present invention also provides modified immunotoxins having a ligand that binds to a cancer cell attached to an ETA moiety that has the furin site replaced with a cancer-associated protease site. Also provided are a method of inhibiting or destroying mammalian cancer cells using the immunotoxins of the invention and pharmaceutical compositions for treating human cancer.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein and subunit vaccine thereof
InactiveCN113234170AIntegrity guaranteedPromote formationSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVaccine antigenTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein and a subunit vaccine thereof. The novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein is characterized in that a furin cleavage site 682-RRAR-685 between an S1 subunit and an S2 subunit of the novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein is replaced with a flexible protein linker; the linker is (GGCAGCGCCAGC), or (GGCGGCGGCAGC)n, or (GGCGGCGGCGGCAGC)n, or (GGC)n, or the linker is GSAS or (GGGS)n or (GGGGS)n or (G) n, n is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 3, and n is an integer; and the amino acid sequence of the novel coronavirus mutant strain S protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 or as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. The S protein has great potential as a vaccine antigen for coping with an SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
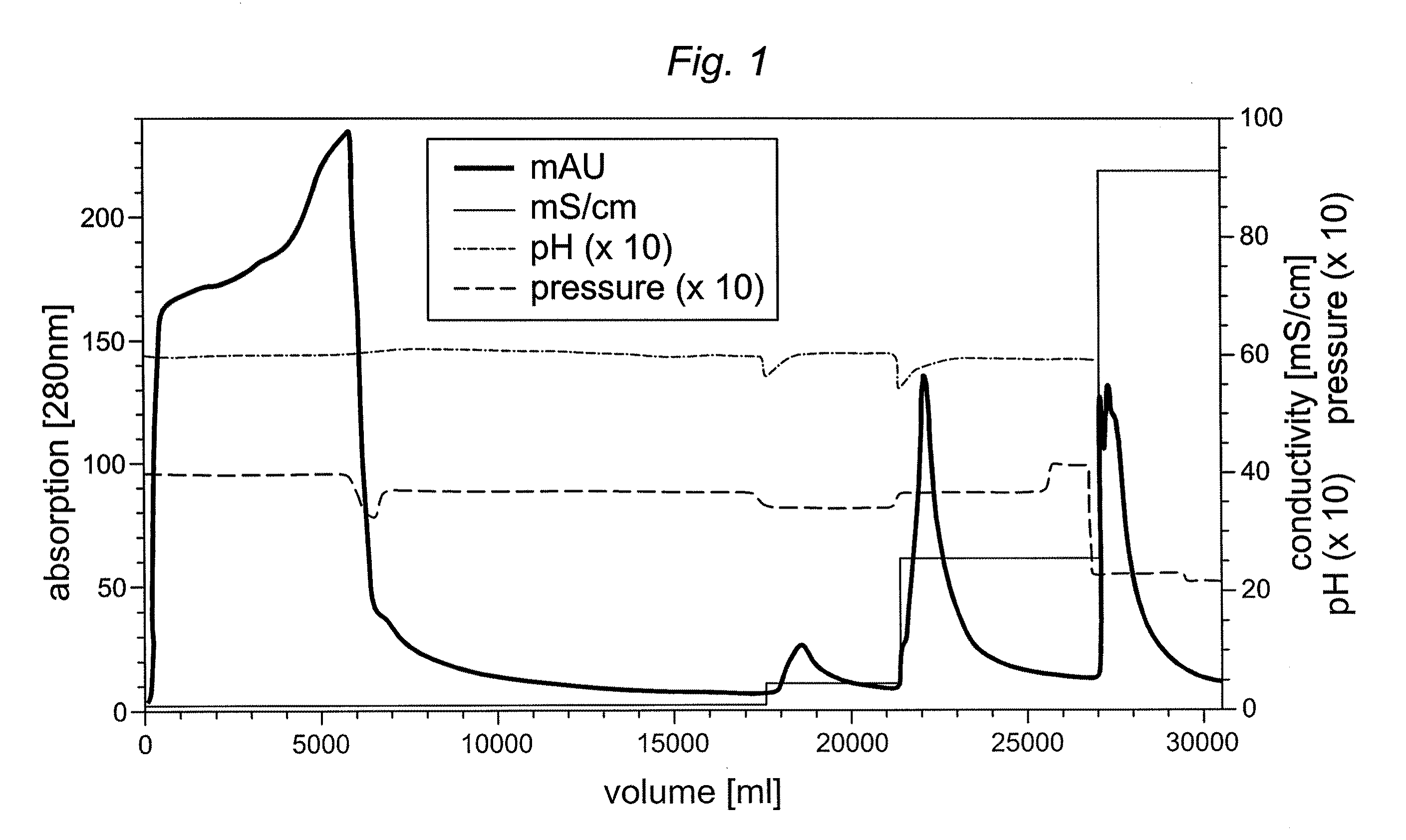
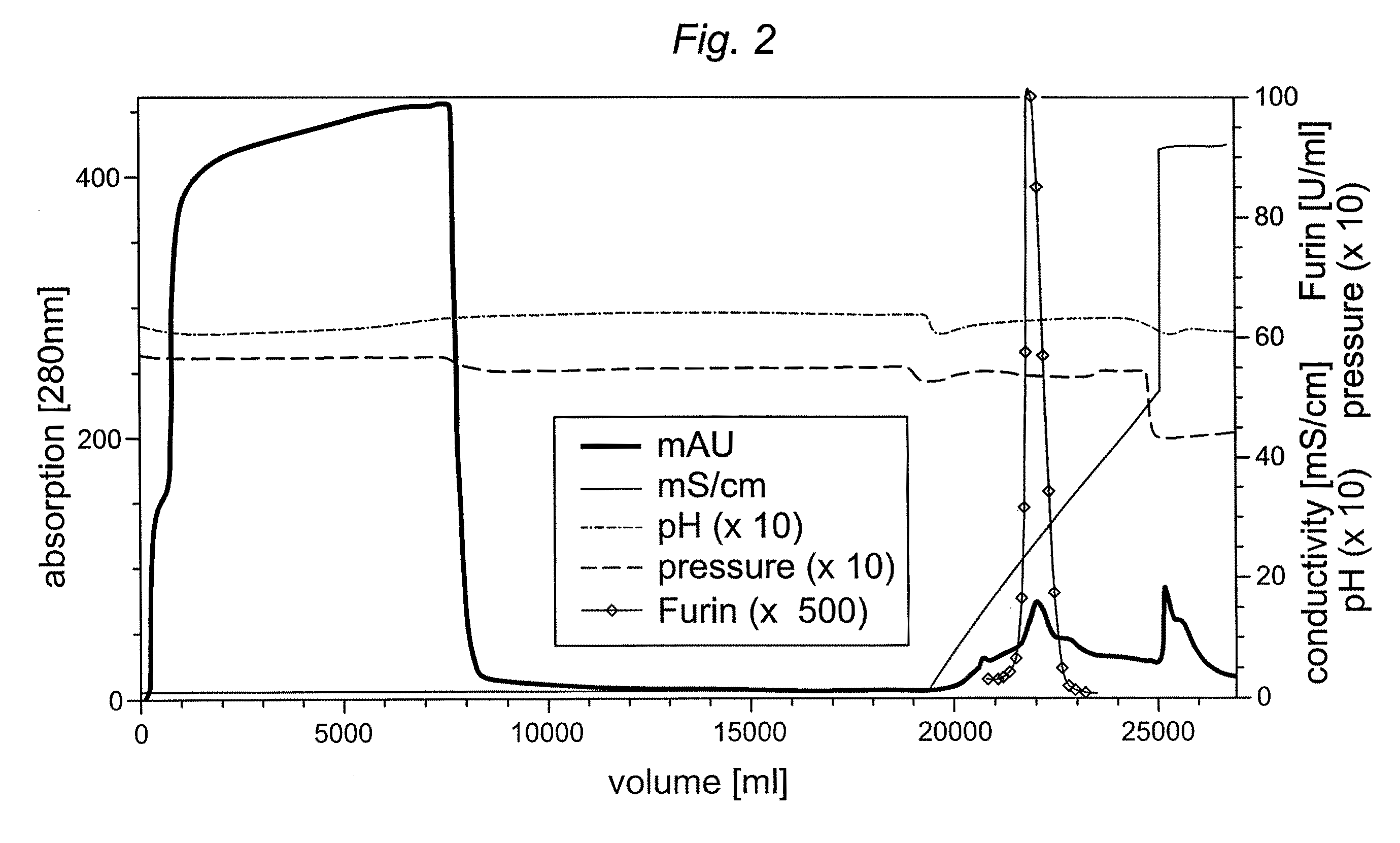
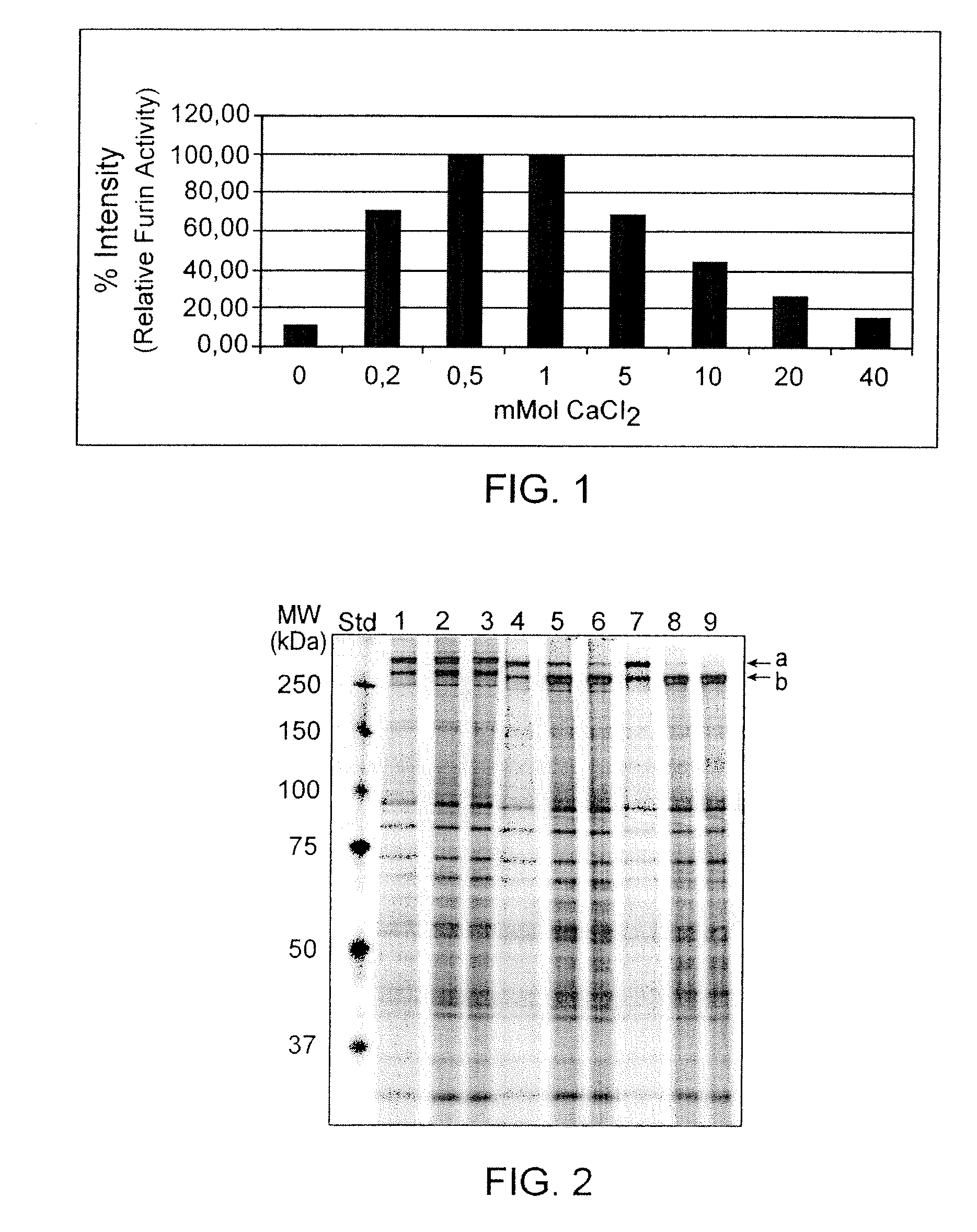
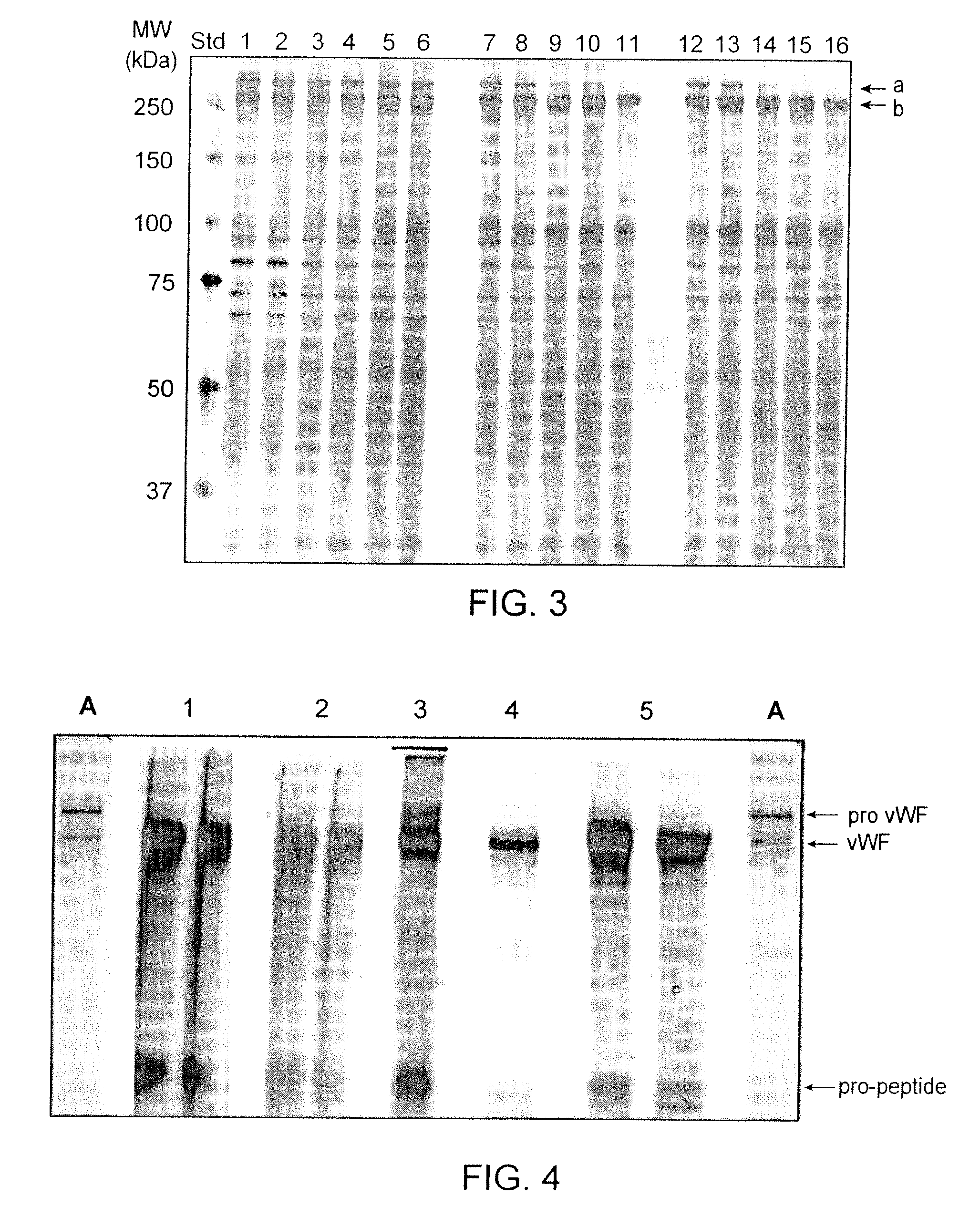
Preparative purification process for human furin
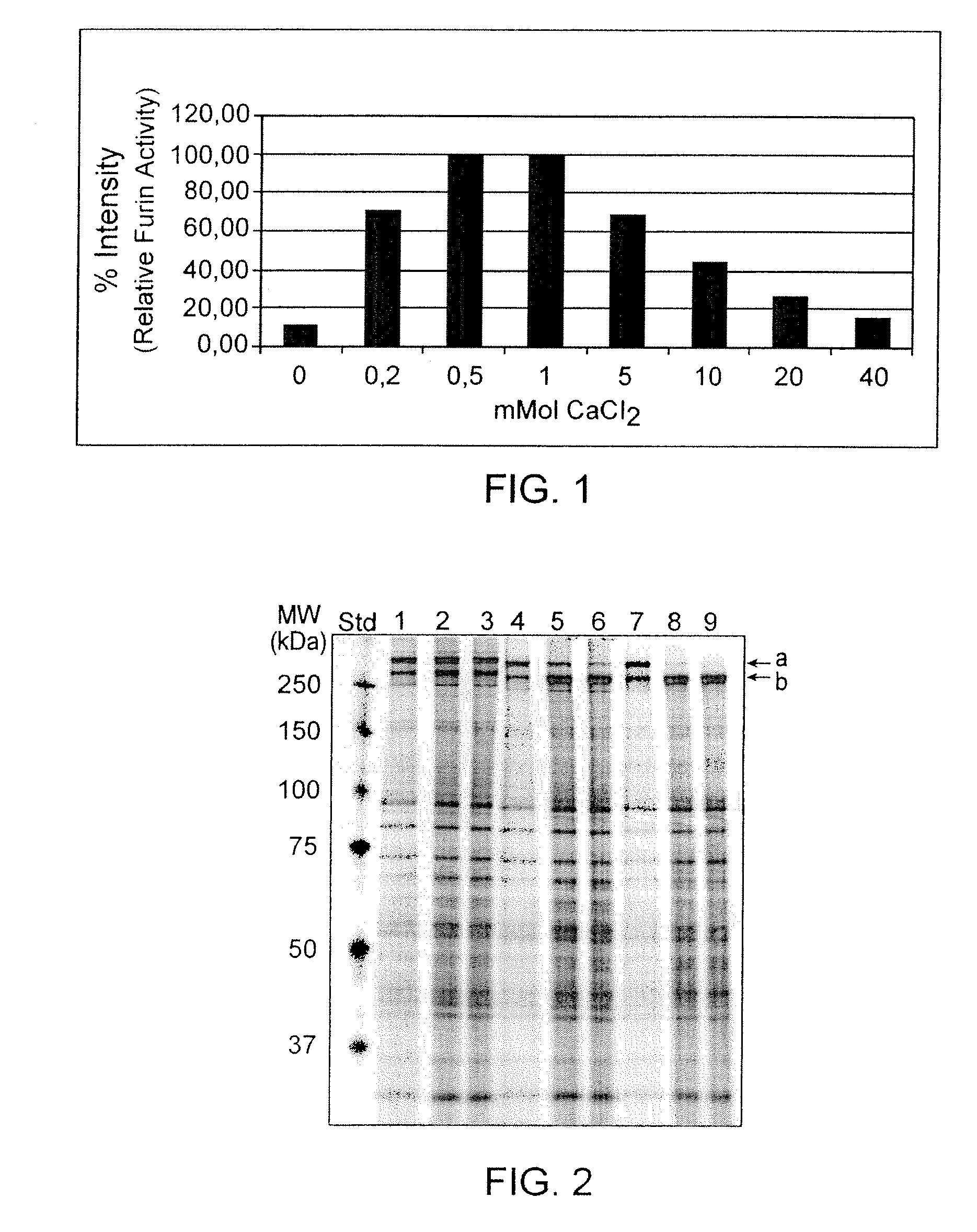
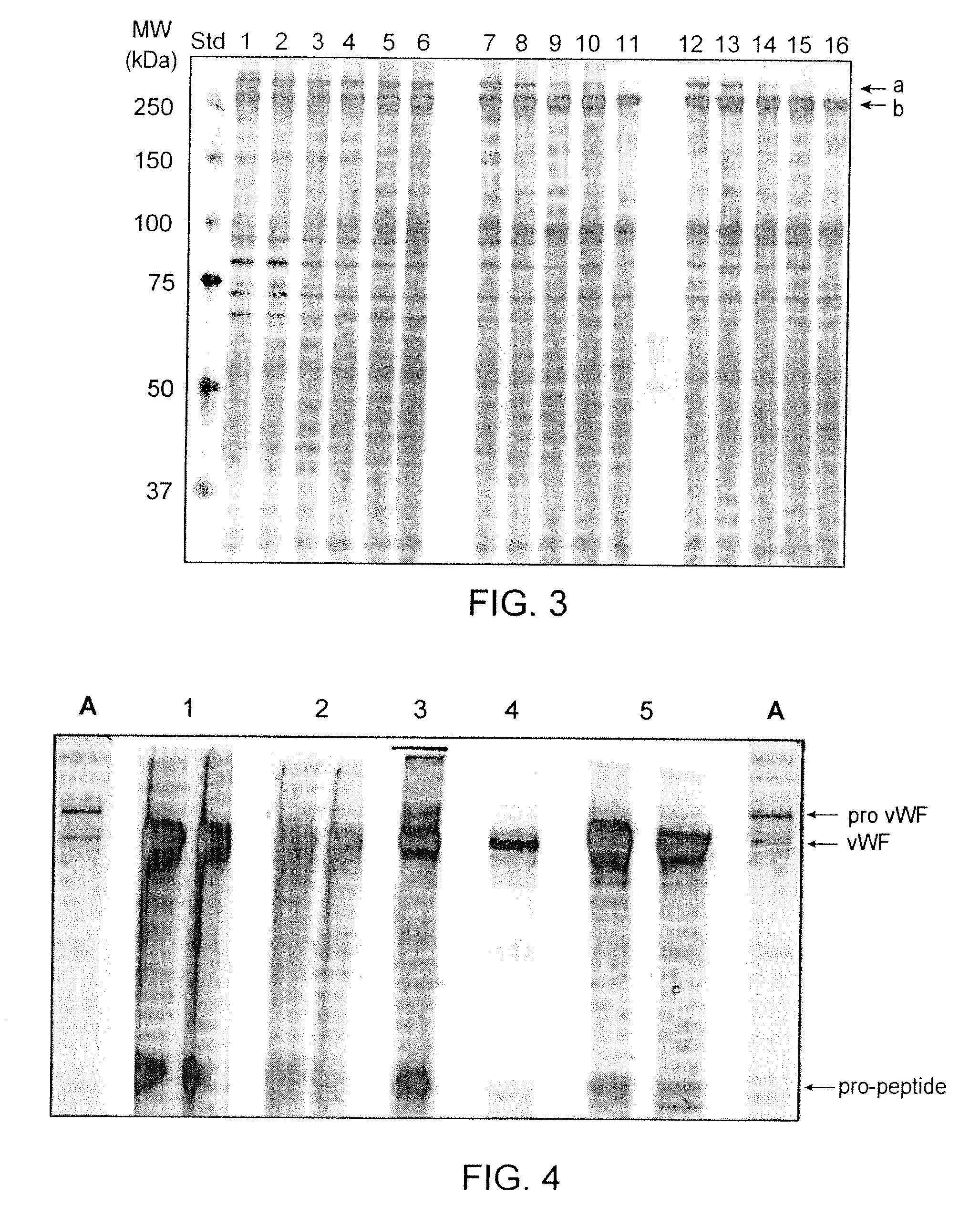
ActiveUS20090304669A1Influence processing costImprove throughputPeptide/protein ingredientsSolid sorbent liquid separationOn columnArginine
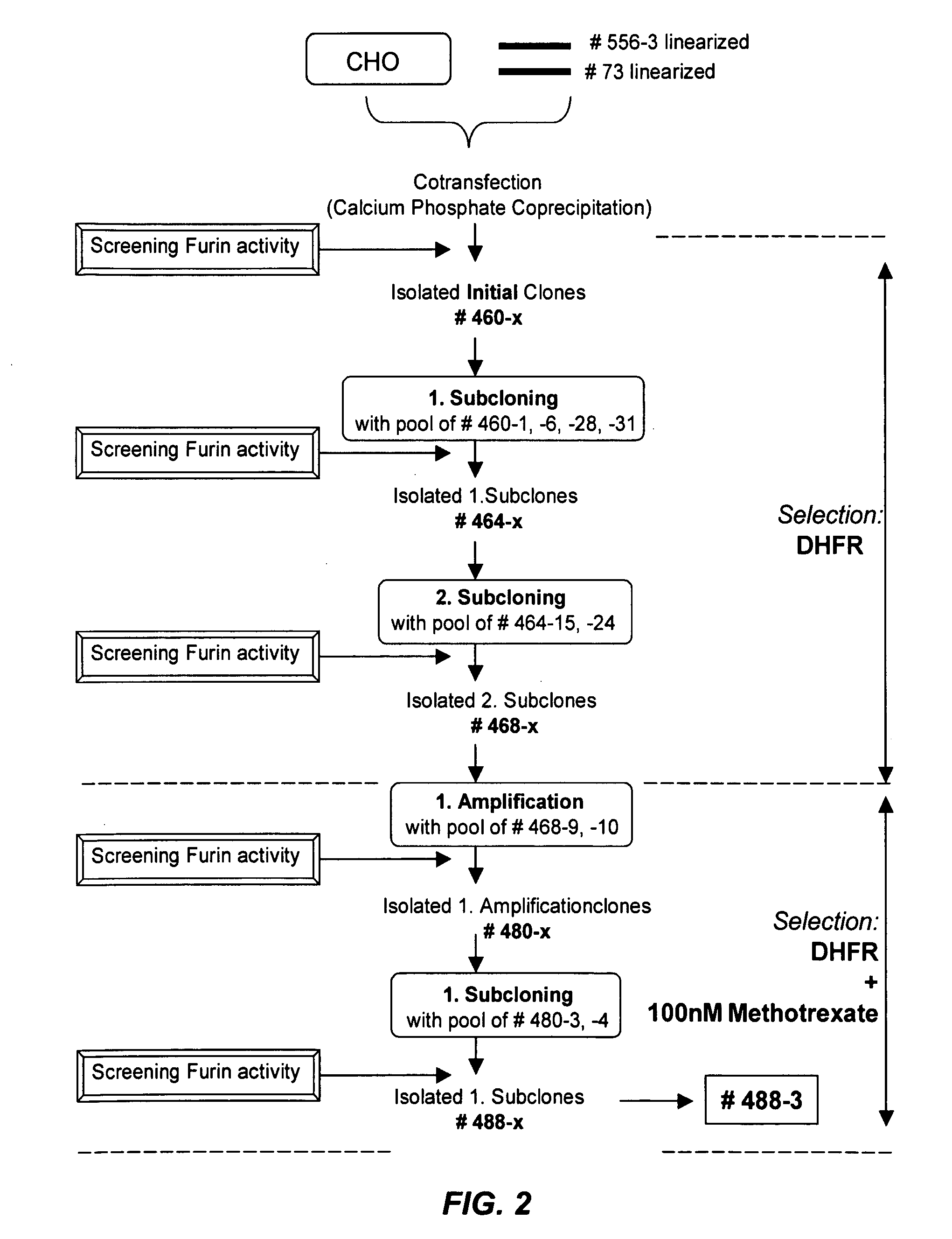
Recombinant truncated human furin was expressed in CHO cells and concentrated approximately 50-fold by ultrafiltration and diafiltration. The concentrate was purified by column chromatography on Capto-MMC(TM) resulting in a 30-50 fold purification factor and a yield of at least 60%. The at least 20% pure preparation obtained after Capto-MMC(TM) chromatography had already a purification degree allowing on-column maturation of pro-VWF. Then an additional Arginine Sepharose chromatography purification was carried out. This two column process for purification of truncated human furin resulted in an almost pure furin preparation with a specific activity of approximately 290,000 U furin / mg protein and a yield of about 50%.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Substantially animal protein-free recombinant furin and methods for producing same
The present invention relates to recombinant furin (rFurin) and methods for producing rFurin. More specifically, the invention relates to substantially animal protein-free rFurin and methods for producing substantially animal protein-free rFurin.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
GLP-1 gene delivery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS20030220274A1Rapid clearanceEasy to controlSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGlucose polymers
This patent discloses compositions and methods of use thereof to normalize the blood glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes. It relates particularly to a plasmid comprising a chicken beta actin promoter and enhancer; a modified GLP-1 (7-37) cDNA (pbetaGLP1), carrying a furin cleavage site, which is constructed and delivered into a cell for the expression of active GLP-1.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion F protein and application thereof
ActiveCN110054668AStable structureExpression did not decreaseSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesF proteinWild type
The invention provides a respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion F protein and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines. The pre-fusion F proteinis formed in the way that the 106th, 108th and 109th amino acids of a wild-type F protein are mutated from Arg to Asn, the 104th amino acid is mutated from Asn to Cys, the 155th amino acid is mutatedfrom Ser to Cys, or the 58th amino acid is mutated from Thr to Cys, and the 190th amino acid is mutated from Ser to Cys. A first furin cleavage site of the mutant wild-type F protein makes the structure of Pre-F more stable, the expression amount is not decreased, and the pre-fusion epitope of M1-F expression in 293T cells is significantly increased. The second mutation of the amino acid site of the F protein forms a disulfide bond, achieves the more stable pre-fusion epitope compared to the wild type, and is suitable for other strains of human RSV. The protein is suitable for various vaccineforms with the RSV F protein as the antigen, such as nucleic acid vaccines, protein vaccines, vector vaccines and recombinant virus particle vaccines.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Mutated anthrax toxin protective antigen proteins that specifically target cells containing high amounts of cell-surface metalloproteinases or plasminogen activator receptors
InactiveUS20090142794A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCompound specificBinding site
The present invention provides methods of specifically targeting compounds to cells overexpressing matrix metalloproteinases, plasminogen activators, or plasminogen activator receptors, by administering a compound and a mutant protective antigen protein comprising a matrix metalloproteinase or a plasminogen activator-recognized cleavage site in place of the native protective antigen furin-recognized cleavage site, wherein the mutant protective antigen is cleaved by a matrix metalloproteinase or a plasminogen activator overexpressed by the cell, thereby translocating into the cell a compound comprising a lethal factor polypeptide comprising a protective antigen binding site.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Modified human thymic stromal lymphopoietin
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
Respiratory syncytial virus F expressing protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109694400AIntegrity guaranteedMaintain immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesSequence designF protein
The invention provides a respiratory syncytial virus F expressing protein and a preparation method thereof, wherein the F protein has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1. Amino acid point mutationis carried out at a Furin recognition site of the soluble F protein; at the same time, a GCN4 fragment is added at a C end to prepare the F protein; through the sequence design, the F protein expressed in an eukaryotic system is guaranteed to avoid being enzymatically hydrolyzed by Furin so as to maintain the integrity of an extracellular fragment and the Pre-fusion state and complete immunogenicity of the F protein are maintained. The F protein is necessary to induce a body to produce antibodies with immunoprotective effect against RSV, and effectively improves the probability to screen positive antibodies in the later stage.
Owner:苏州高泓利康生物科技有限公司
Minigene
The present invention provides minigenes suitable as a prophylactic or therapeutic vaccine against conditions such as cancer, infectious diseases or autoimmune diseases, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the minigene. The minigenes of the present invention comprise (a) a human tissue plasminogen signal peptide; (b) at least one T-cell epitope; and (c) an E. coli heat labile enterotoxin B subunit; wherein the at least one T-cell epitope is linked to the rest of the minigene, and to any other epitopes, by furin sensitive linkers. In some embodiments of the invention, the minigene comprises T-cell epitopes from one or more of CEA, her-2 / neu and hTERT. Also provided herein are immunogenic peptide epitopes of CEA, her-2 / neu and hTERT, as well as immunogenic peptide analogs, and pharmaceutical compositions and vaccines comprising one or more of said peptides and analogs for prophylaxis and / or treatment of cancer or other disorder. Methods of inducing an immune response in a patient, in addition to methods of treatment using the minigenes, immunogenic peptides, and peptide analogs disclosed herein are also provided.
Owner:MSD ITAL +1
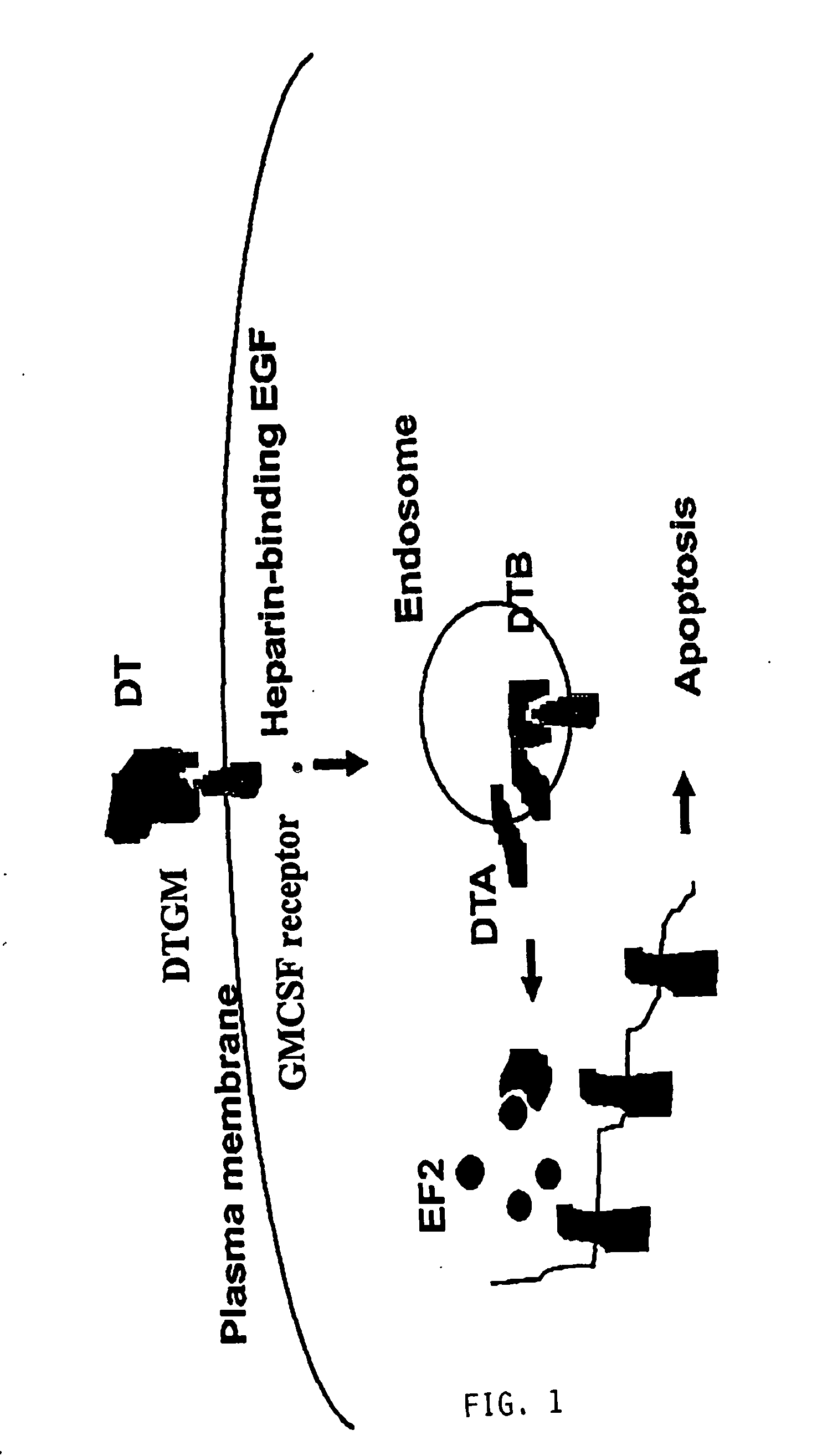
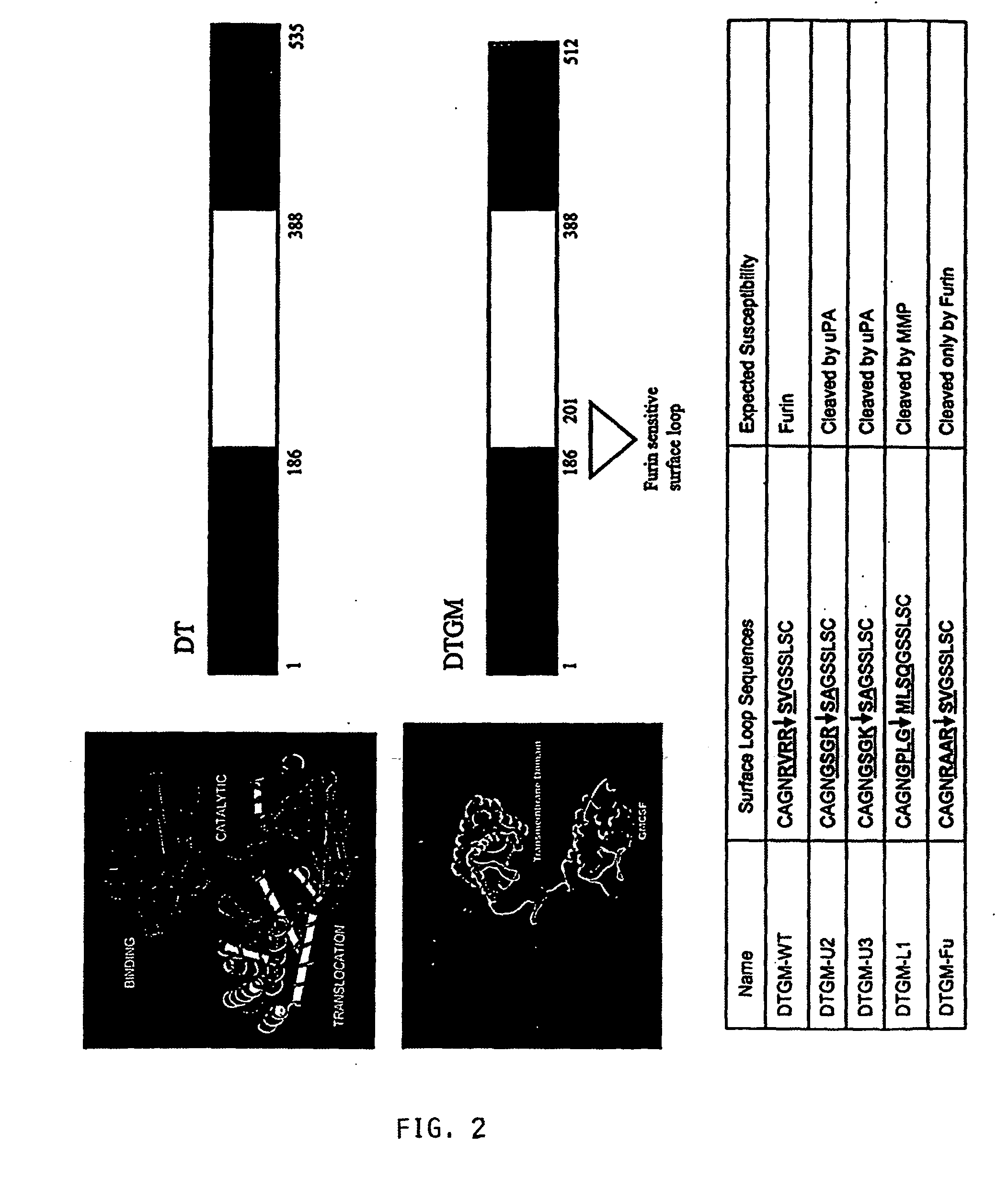
Activation of Recombinant Diphtheria Toxin Fusion Proteins by Specific Proteases Highly Expressed on the Surface of Tumor Cells
The present invention provides compositions and methods for inhibiting abnormal cell growth. In particular, the invention provides nucleic acids encoding Diphtheria toxin fusion proteins comprising residues 1-388 of Diphtheria toxin, wherein the native furin cleavage site has been substituted for a matrix metalloproteinase or plasminogen activator cleavage site, and a heterologous polypeptide and the polypeptides encoded by such nucleic acids. In addition, the invention provides methods of treating cancer by administering such polypeptides.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
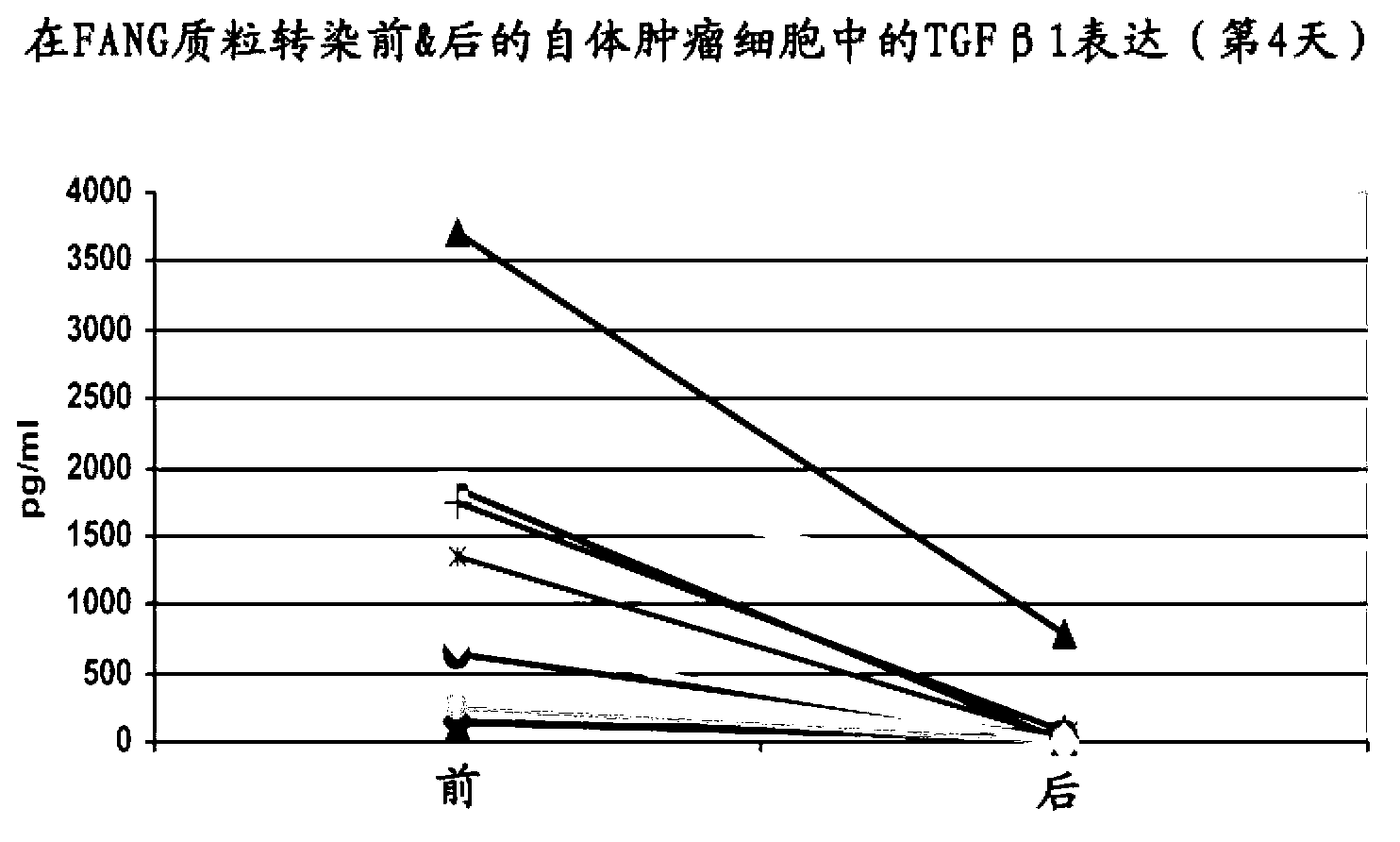
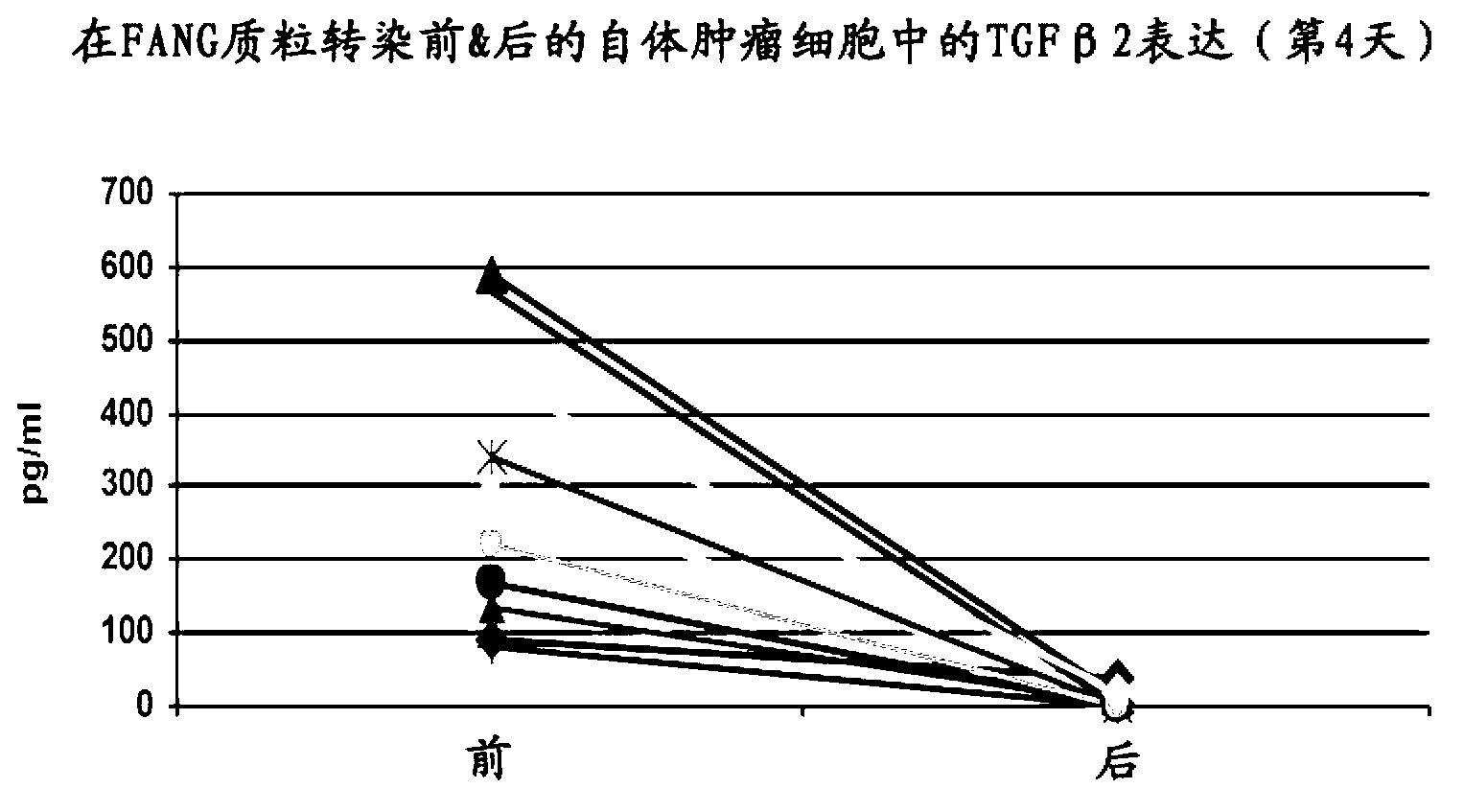
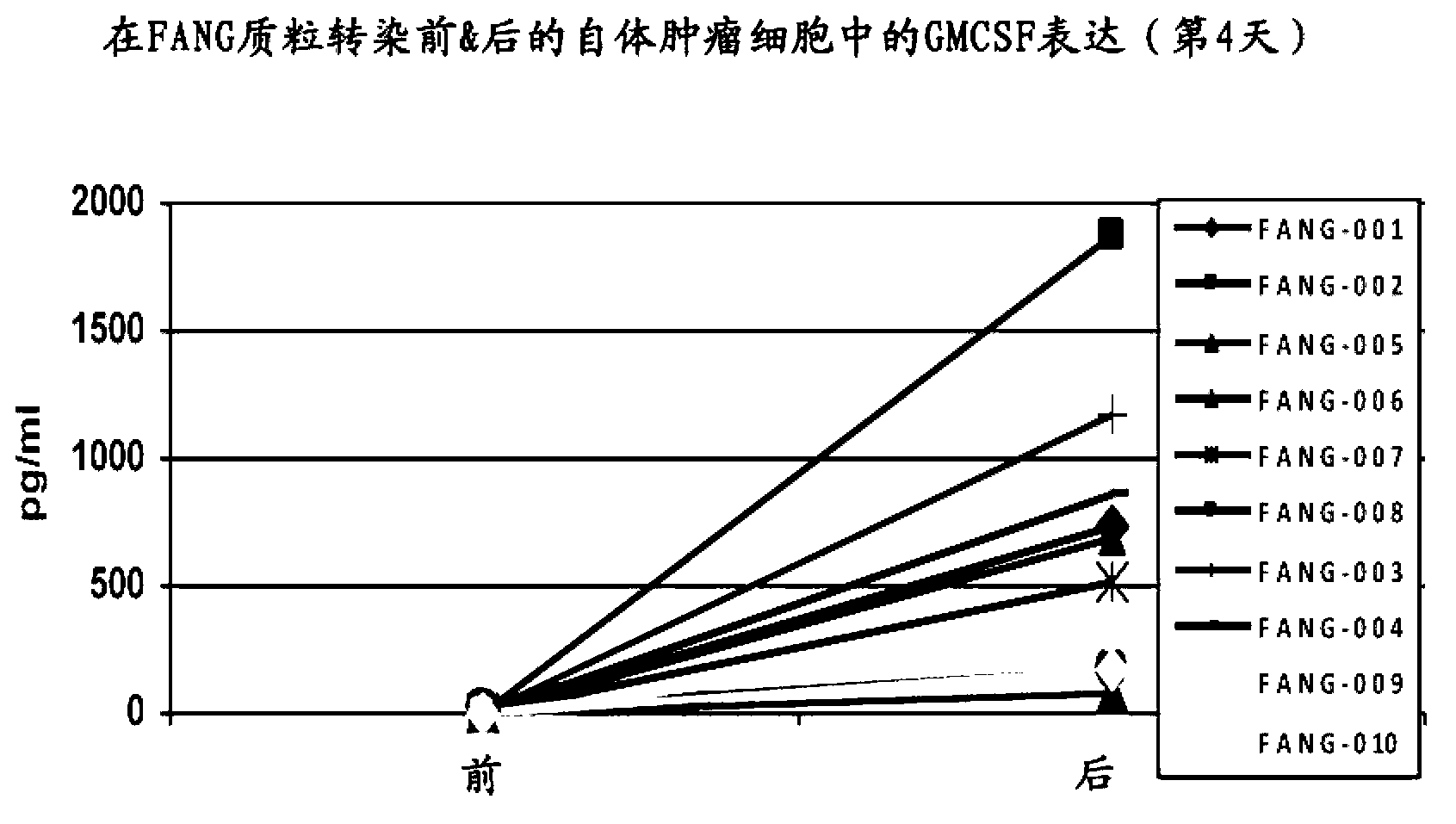
Furin-knockdown and GM-CSF-augmented (FANG) cancer vaccine
The present invention includes compositions and methods for cancer treatment. More specifically the present invention describes an autologous cancer vaccine genetically modified for Furin knockdown and GM-CSF expression. The vaccine described herein attenuates the immunosuppressive activity of TGF-ss through the use of bi-functional shRNAs to knock down the expression of furin in cancer cells, and to augment tumor antigen expression, presentation, and processing through expression of the GM-CSF transgene.
Owner:GRADALIS
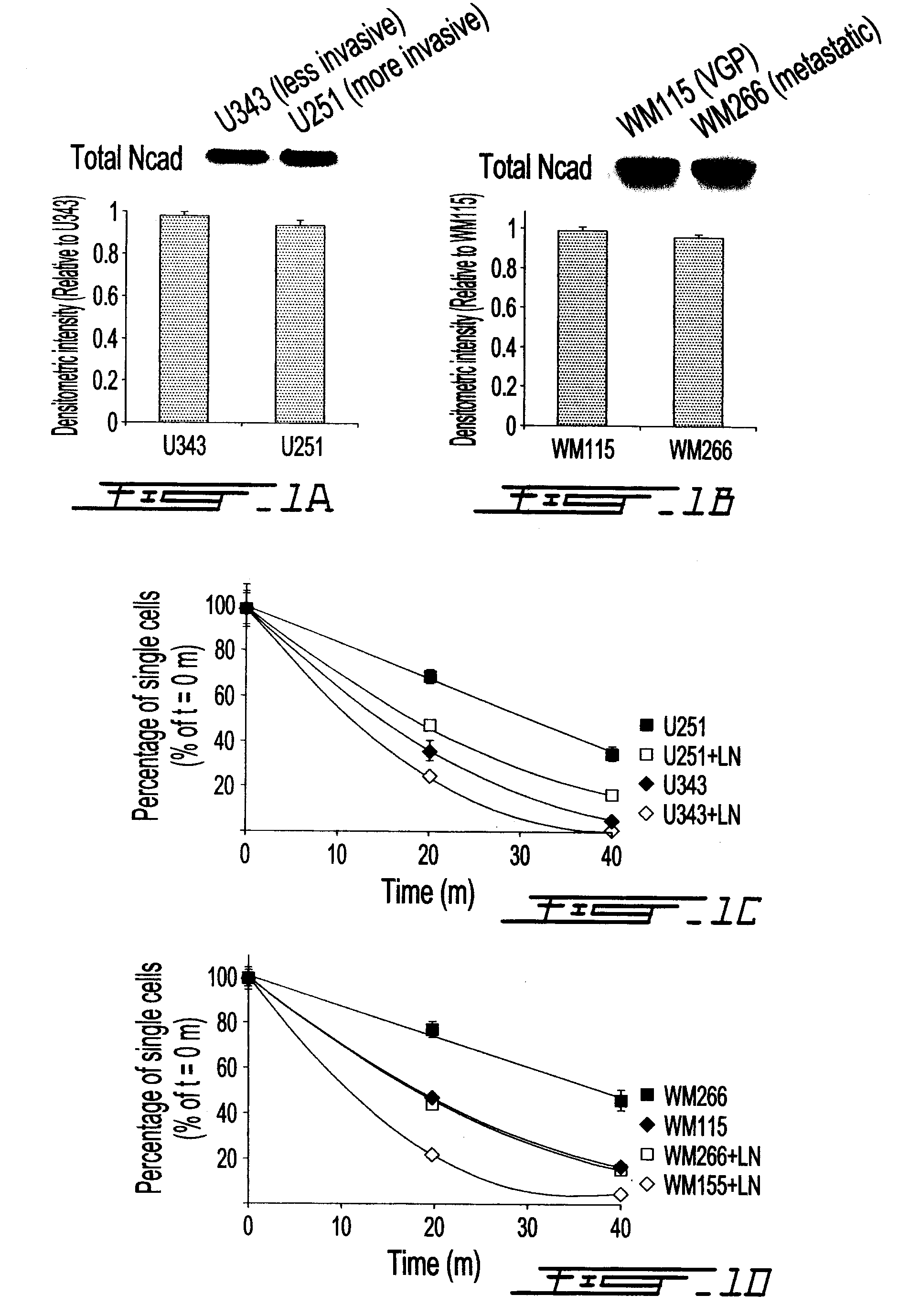
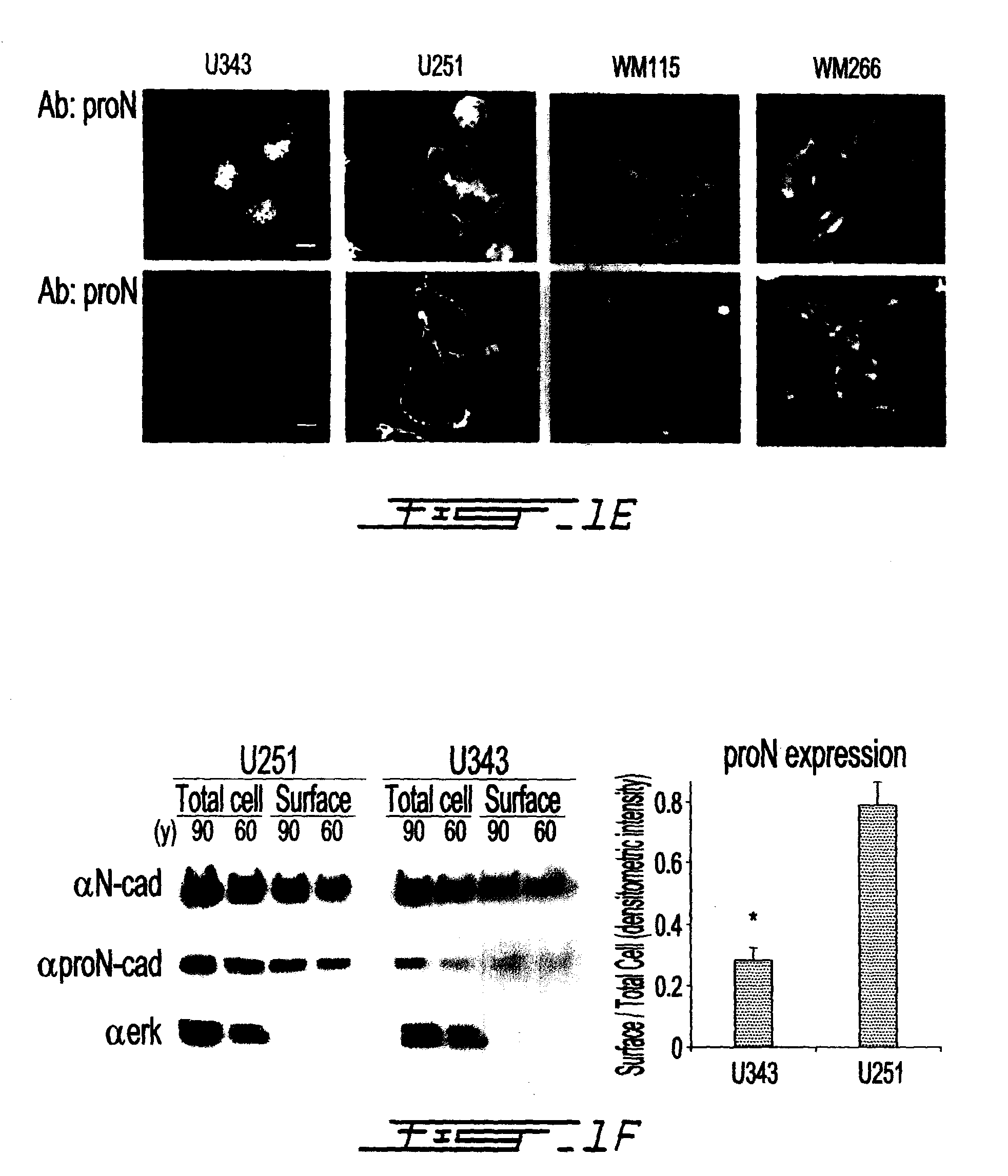
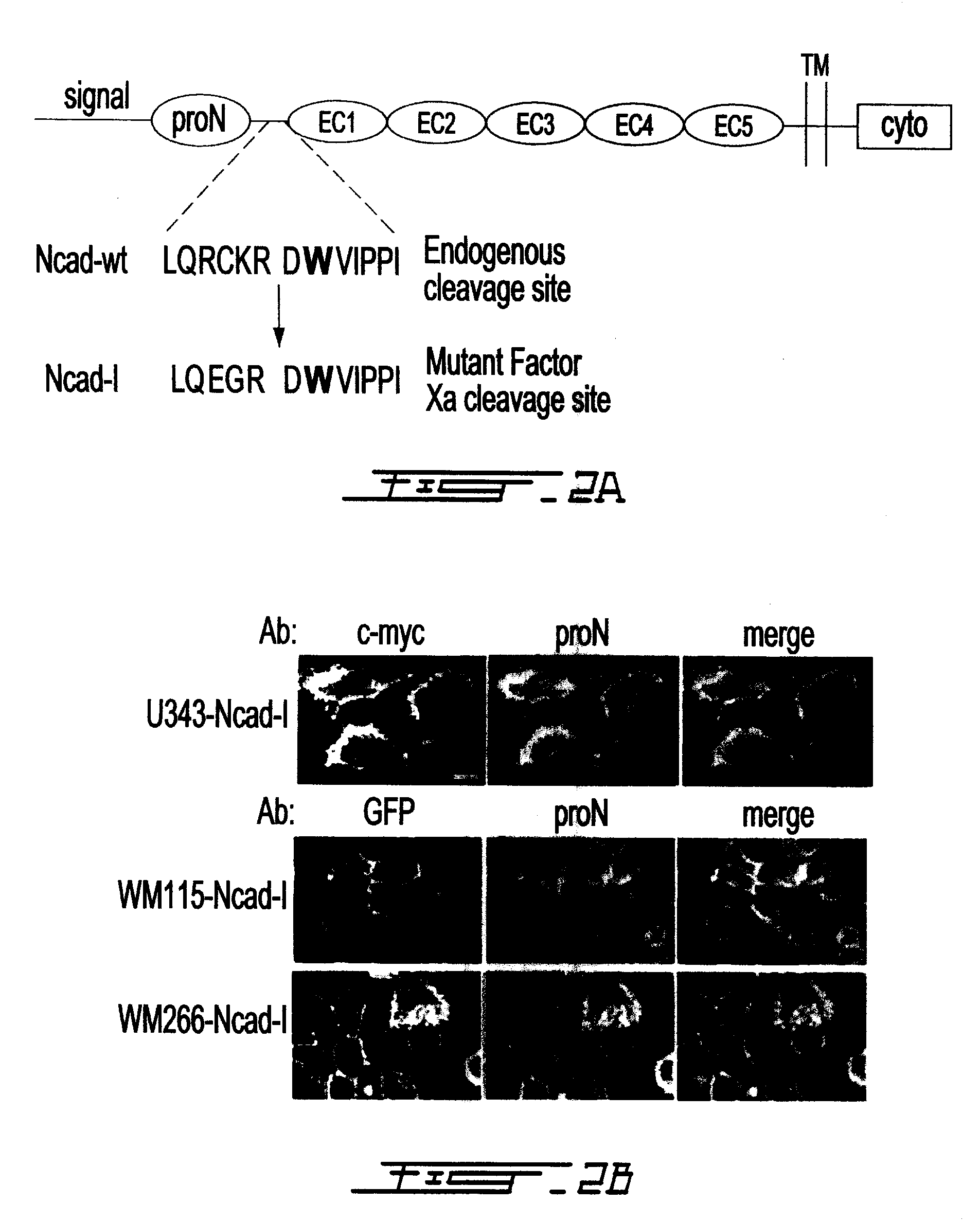
Altered n-cadherin processing in tumor cells by furin and proprotein convertase 5a (PC5A)
InactiveUS20100310451A1Increase productionReduce productionOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLymphatic SpreadCancer cell
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosis and / or prognosis of cancer and for monitoring the progression of cancer and / or the therapeutic efficacy of an anti-cancer treatment in a subject by determining the molecular form of cadherin at the cell surface of cancer cells in the subject. The invention also relates to a method for preventing, inhibiting or treating cancer or its metastasis in a subject by increasing the adhesive forms of cadherin and / or decreasing the non-adhesive forms of cadherin at the cell surface. The invention also relates to a method step of determining the expression level of furin and proprotein convertase 5A (PC5A).
Owner:MCGILL UNIV +2
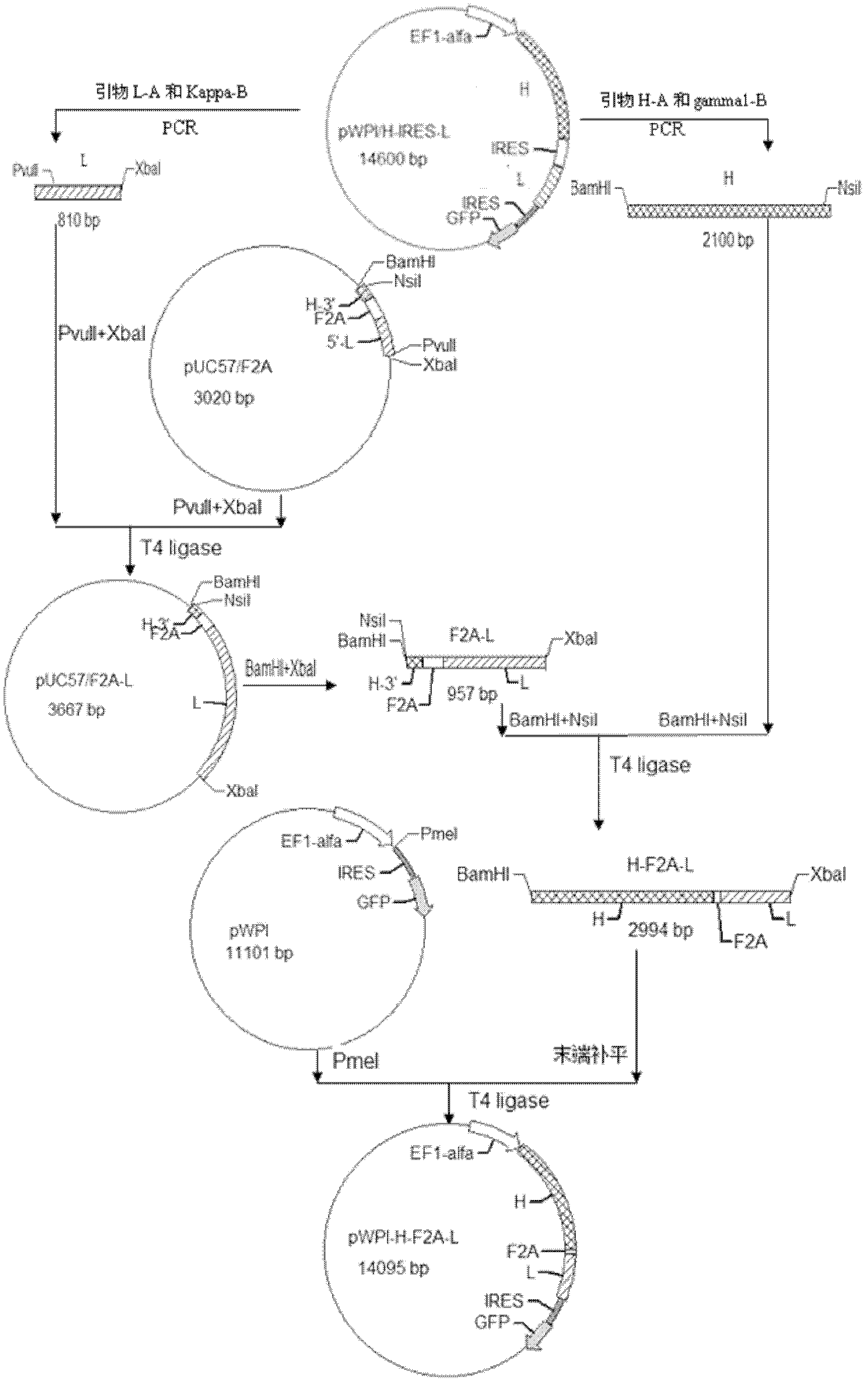
Lentivirus expression vector of anti-p185erdB2 human mouse chimeric antibody containing F/2A sequence and construction method of lentivirus expression vector
InactiveCN102618583AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionOpen reading frameHeavy chain
The invention discloses a lentivirus expression vector of an anti-p185erdB2 human mouse chimeric antibody containing an F / 2A sequence, and a construction method of the lentivirus expression vector. Furin or foot and mouth disease virus / 2A polypeptide (F / 2A) with self shearing capacity is connected with a heavy chain and a light chain of the human-mouse chimeric antibody to form an open reading frame (ORF), and the ORF is inserted into a lentivirus expression vector pWPI to construct the expression vector pWPI / H-F2A-L of the recombination anti-p185erdB2 overall-length human mouse chimeric antibody. According to sequencing identification, the pWPI / H-F2A-L is consistent to expected design. The infection efficiency of recombination lentivirus is 87.68%, and the expressions of the chimeric heaving chain and light chain are formed after the recombination lentivirus is infected with 293T cells. Compared with that of a lentivirus expression vector of an IRES (Internal Ribosome Entry Site) chimeric antibody, the expression level of the chimeric antibody mediated by the F / 2A is higher than that of the chimeric antibody mediated by IRES, thereby laying a foundation for research on anti-p185erdB2 engineering antibodies.
Owner:广西壮族自治区肿瘤防治研究所
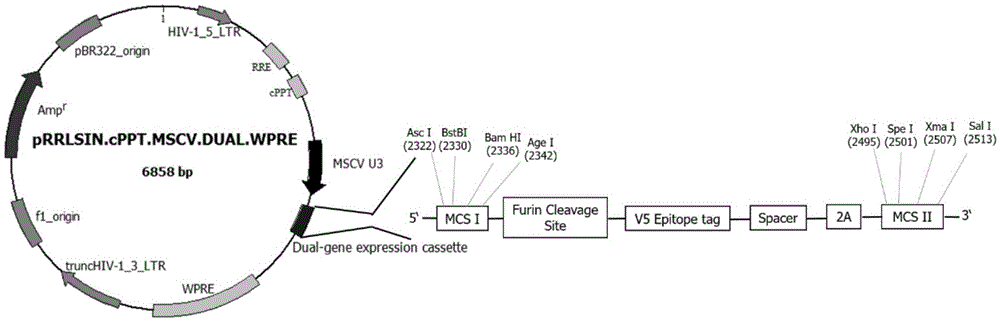
Lentiviral expression vector, as well as preparation method and application of lentiviral expression vector, and preparation method of recombinant lentivirus
The invention discloses a lentiviral expression vector, as well as a preparation method and an application of the lentiviral expression vector, and a preparation method of a recombinant lentivirus. The lentiviral expression vector is a pRRLSIN.cPPT.MSCV-Dual.WPRE vector, which is obtained by replacing the GFP sequence of a pRRLSIN.cPPT.MSCV / GFP.WPRE vector with a double gene expression box Dual, wherein the double gene expression box Dual comprises the following structure sequentially arranged from the 5' terminal to the 3' terminal: a first polyclonal site-a furin cleavage site-a V5 label-Spacer-2A peptide-a second polyclonal site, the mark '-' represents the connection relation. According to the lentiviral expression vector, 2A peptide is utilized for realizing the expression of double exogenous genes in cells of mammals, 2A peptide has the 'self-shearing' property, in the translation process of protein, 2A peptide changes the activity of ribosome, promotes the hydrolysis of ester chains between peptide residue Gly and tRNAGly of 2A, releases upstream polypeptides and starts the translation of upstream polypeptides from a transcribed compound, and the realizes double gene expression in the level of translation.
Owner:SHENZHEN GENTARGET BIOTHERAPEUTICS CO LTD
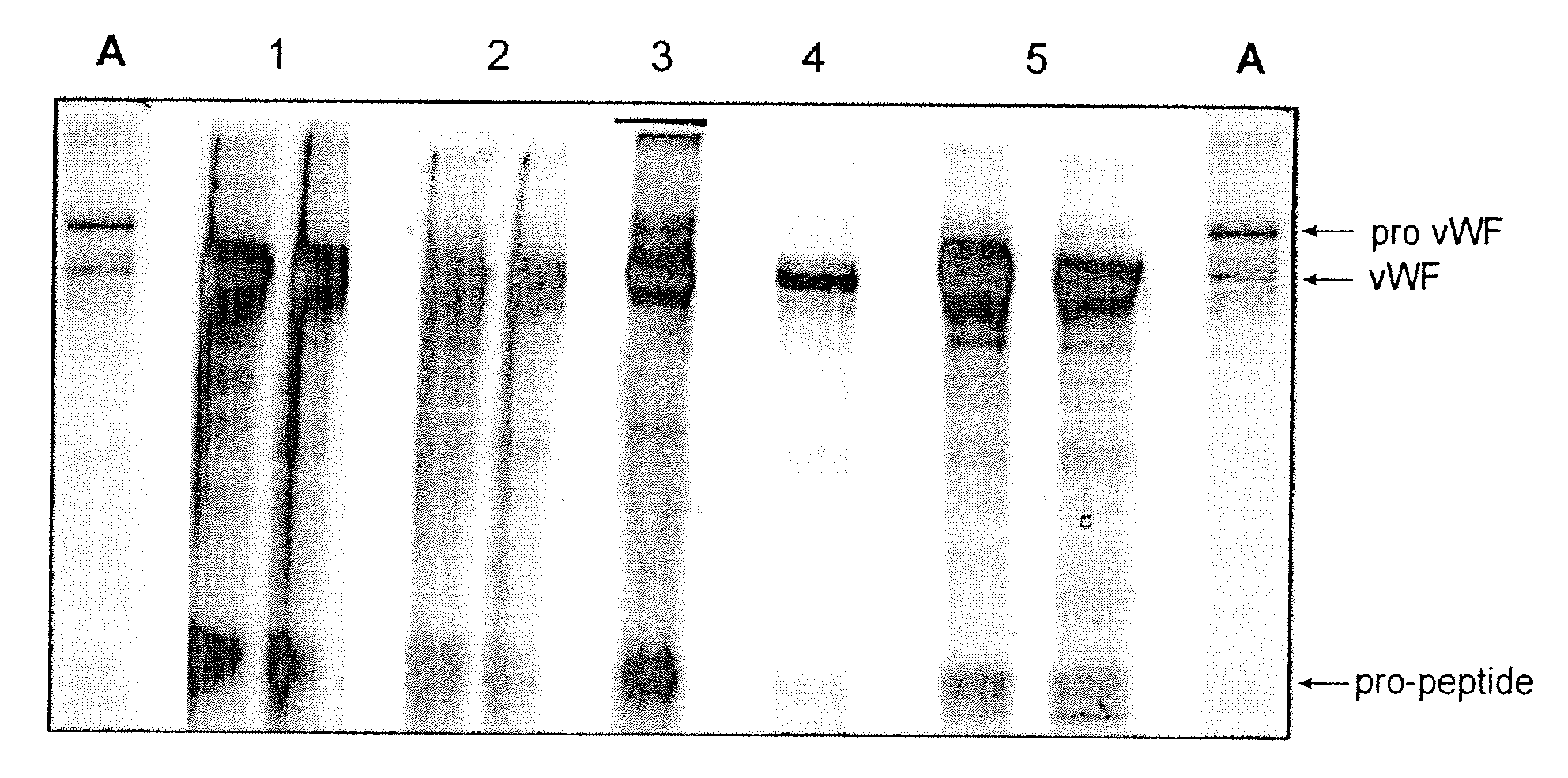
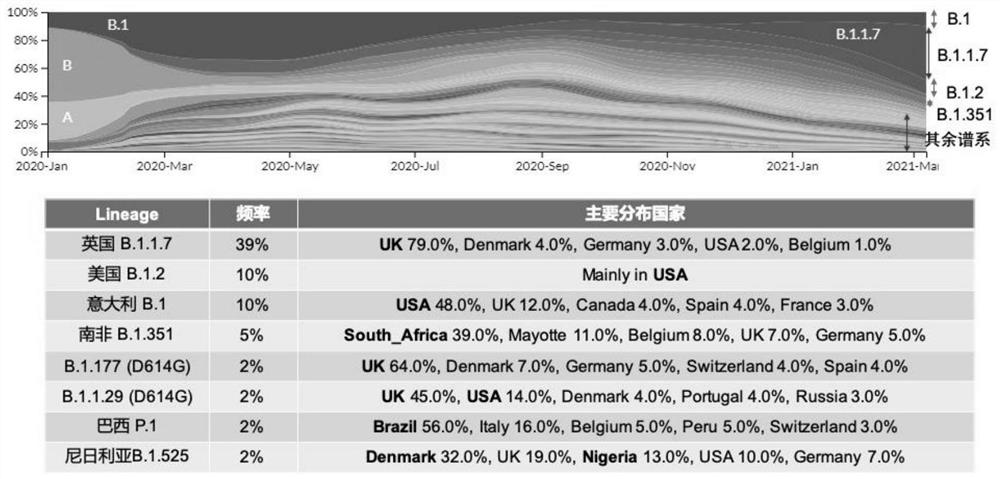
Method for producing mature VWF from VWF pro-peptide
ActiveUS8058411B2High specific activity and purityEfficient productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFactor VIII vWFPhysical chemistry
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Method for producing mature VWF from VWF Pro-Peptide
ActiveUS20090029918A1High specific activity and purityEfficient productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFactor VIII vWFElution
The present invention relates to a method for producing a mature von Willebrand Factor (VWF) from von Willebrand Factor pro-peptide comprising the steps: immobilizing VWF pro-peptide on an ion exchange resin, incubating the immobilized VWF pro-peptide with furin to obtain immobilized mature VWF, and isolating mature VWF from the ion exchange resin by elution.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Albumin-proaerolysin prodrugs
ActiveUS20180008668A1Improve permeabilityImprove retentionTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAerolysinProstate-specific antigen
The present invention relates to the field of cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer using albumin-proaerolysin prodrugs. Accordingly, in one aspect, the present invention provides prodrug compositions. In certain embodiments, a prodrug composition comprises a prostate-specific antigen (PSA)-activated pro-aerolysin (PA), wherein a PSA cleavable linker replaces the native furin cleavage site within PA; and human serum albumin (HSA) or a fragment thereof fused to the N-terminus of the PSA-activated PA.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain S protein and subunit vaccine thereof
ActiveCN113929786AIntegrity guaranteedPromote formationSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVaccine antigenTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain S protein and a subunit vaccine thereof. A furin cleavage site 682-RRAR-685 between the S1 subunit and the S2 subunit of the SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain S protein is replaced with a flexible protein linker; the linker is (GGCAGCGCCAGC), or (GGCGGCGGCAGC)n, or (GGCGGCGGCGGCAGC)n, or (GGC)n; or the linker is GSAS or (GGGS)n or (GGGGS)n or (G)n, wherein n is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 3, and n is an integer; the amino acid sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain S protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 or as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. The S protein has great potential as a vaccine antigen for coping with the SARS-CoV-2 mutant strain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Non-activated polypeptides having a function of tissue regeneration and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS8268590B2Stimulating formation and regenerationImproving cirrhosisProtozoaSkeletal disorderEscherichia coliCell membrane
Non-activated tissue-regeneration polypeptides (TRPs) and their preparation methods are disclosed. The TRPs include: a protein transduction domain (PTD) making the polypeptides to permeate a cell membrane without cell membrane receptors; a furin activation domain (FAD) which has at least one proprotein convertase cleavage site and which can be cleaved by the proprotein convertase and activate a tissue regeneration domain (TRD) in cells; and a tissue regeneration domain (TRD) which can be activated by the proprotein convertase cleavage of the FAD to stimulate the growth or formation of tissues or to induce the regeneration of tissues. The TRPs can be mass-produced by cultured bacteria, such as recombinant E. coli, are in a non-activated state before in vivo administration, and their separation, purification, handling, storage and administration are simple and convenient. The in vivo administration of the TRPs is useful to stimulate the formation or regeneration of tissues, such as bones or cartilages, or to improve the fibrosis and cirrhosis of organs, such as kidneys, liver, lungs and heart by pharmacological mechanisms completely different from those of prior rhBMPs or TGF-β proteins.
Owner:MET LIFE SCI CO LTD
Recombinant foot and mouth disease vaccine
InactiveUS8409588B2SsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsProteinase activityStructural protein
A foot and mouth disease virus (FMDV) vaccine and method for producing same is described wherein the N terminal portion of the FMDV polyprotein, encoding the four structural proteins, 1A, 1B, 1C, and 1D, are each separated by a non-FMDV protease, preferably a cellular protease, for example, furin. The expression system may be transformed into a cell expressing the non-FMDV protease and the resulting particles recovered for use as a vaccine.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com