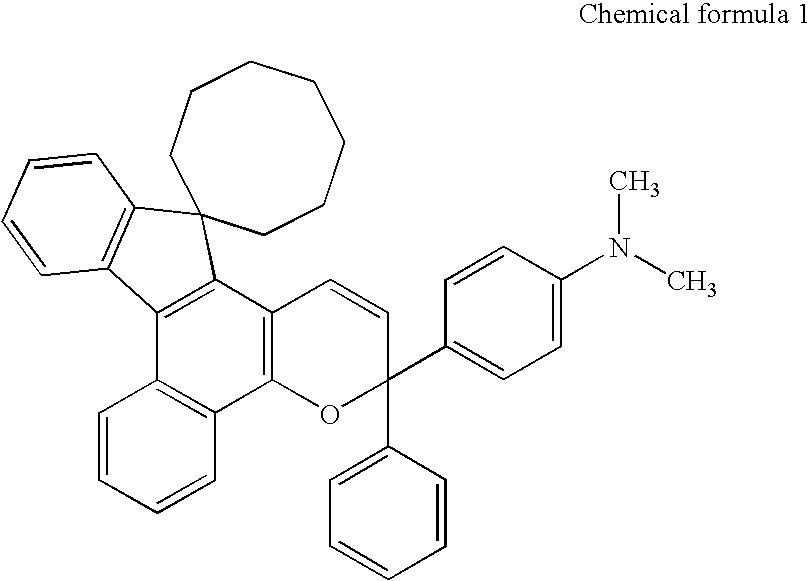
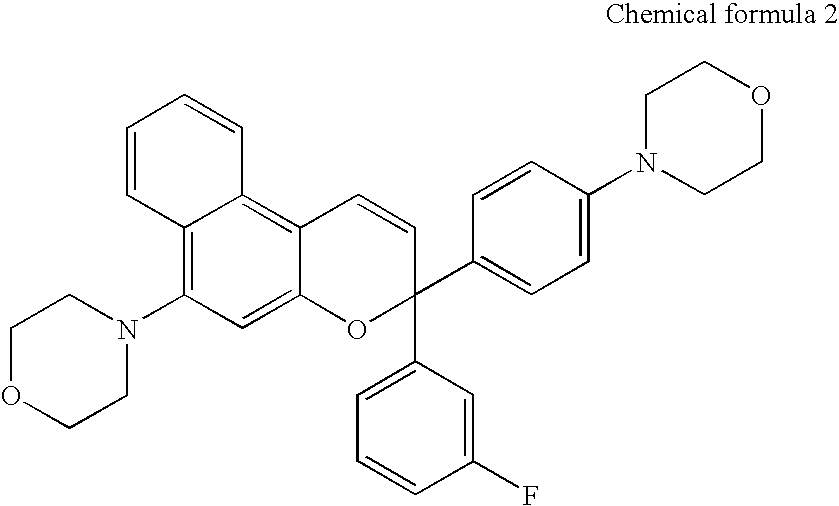
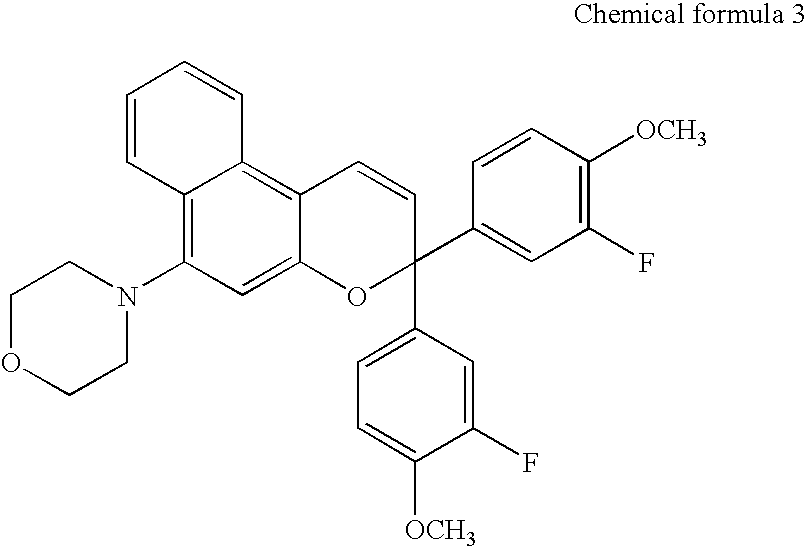
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
217results about How to "Precise Bonding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
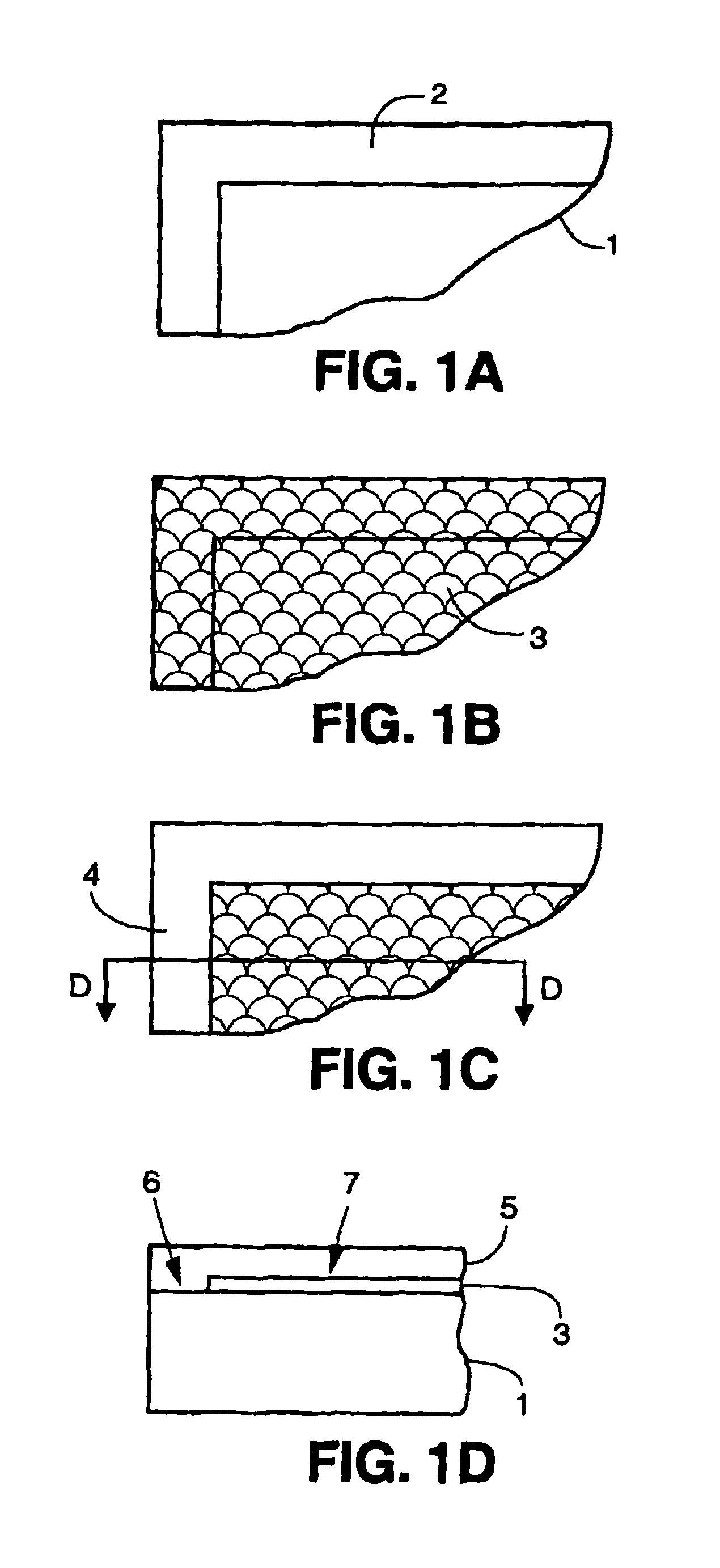
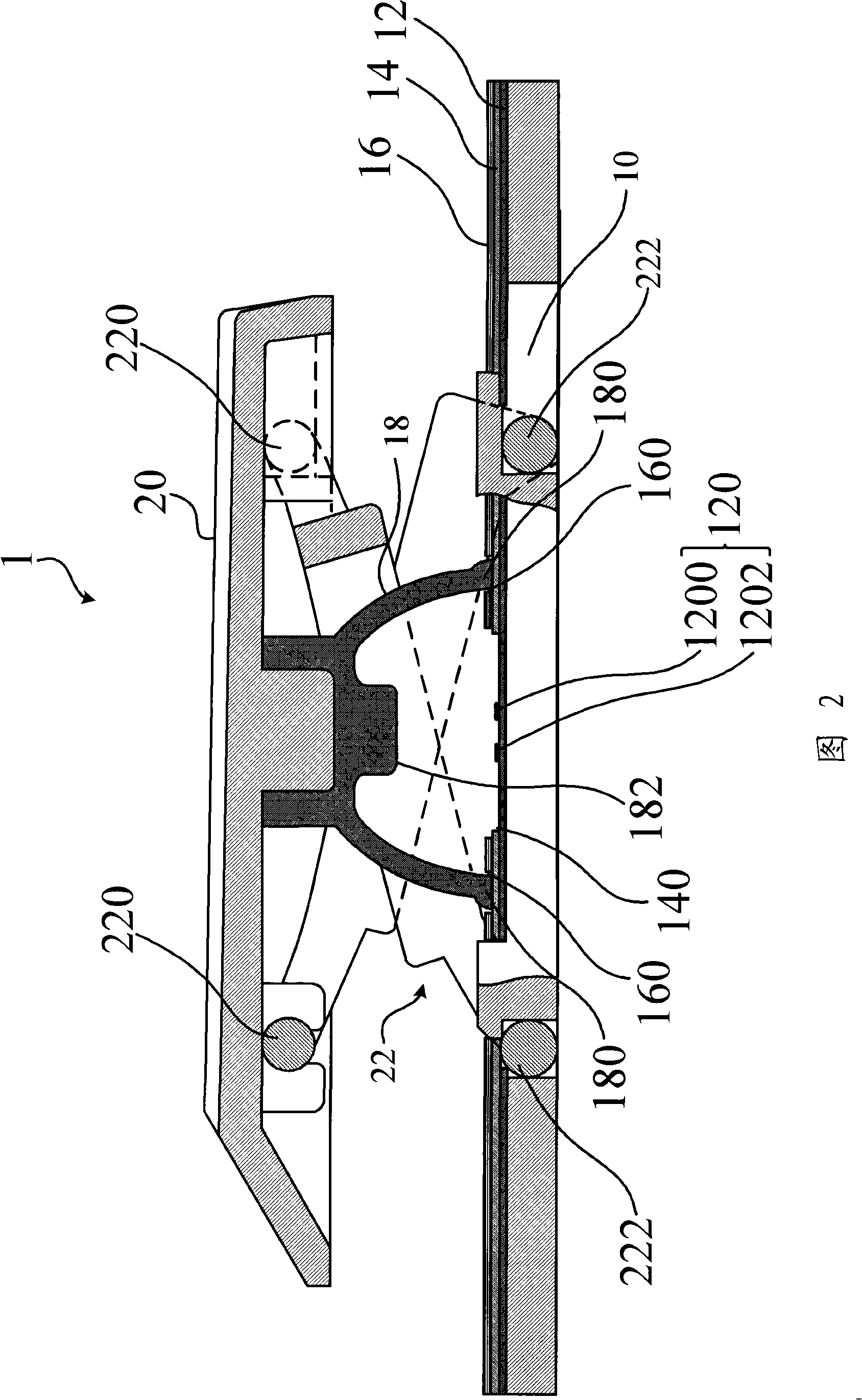
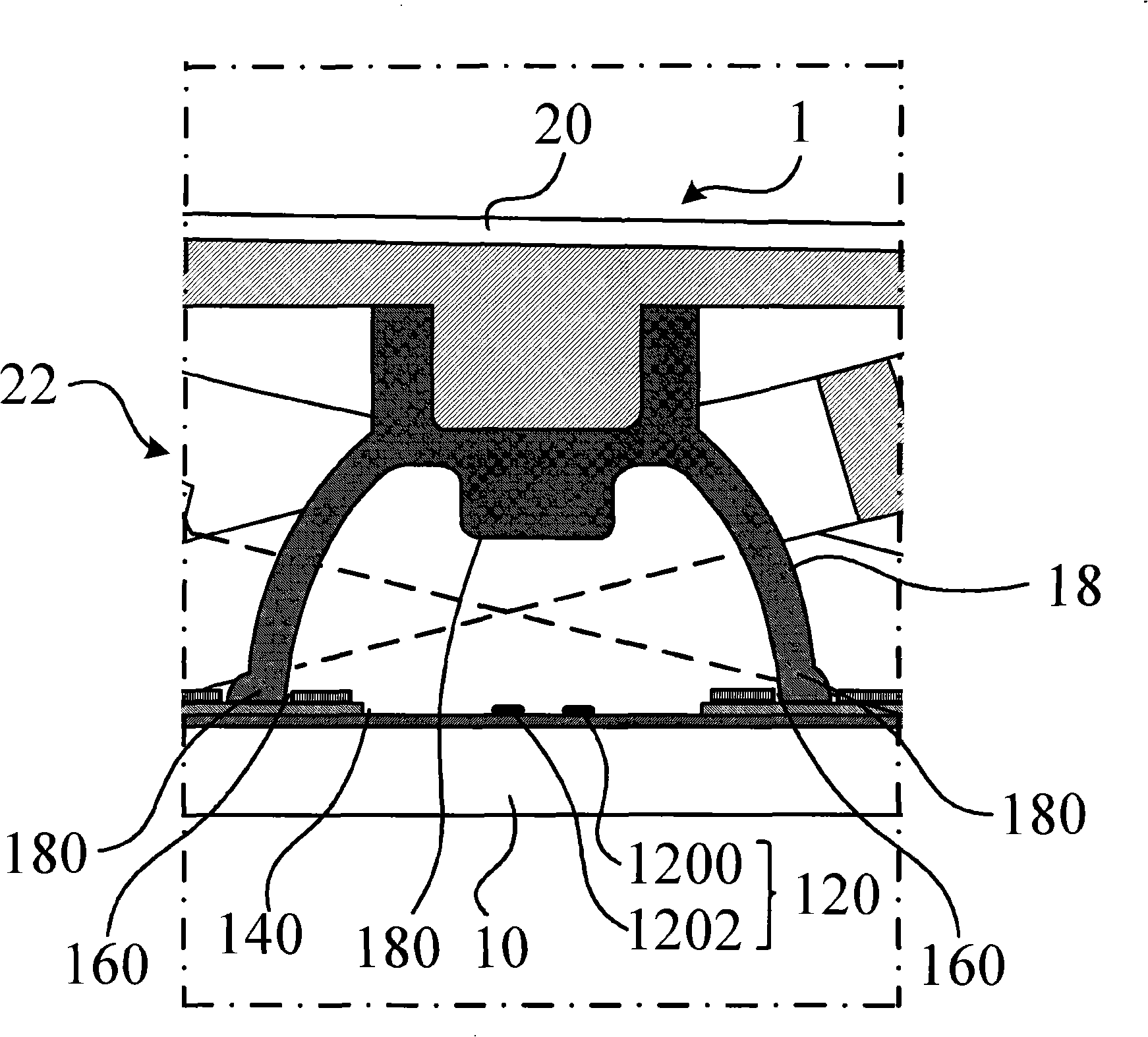
Flow control of photo-polymerizable resin
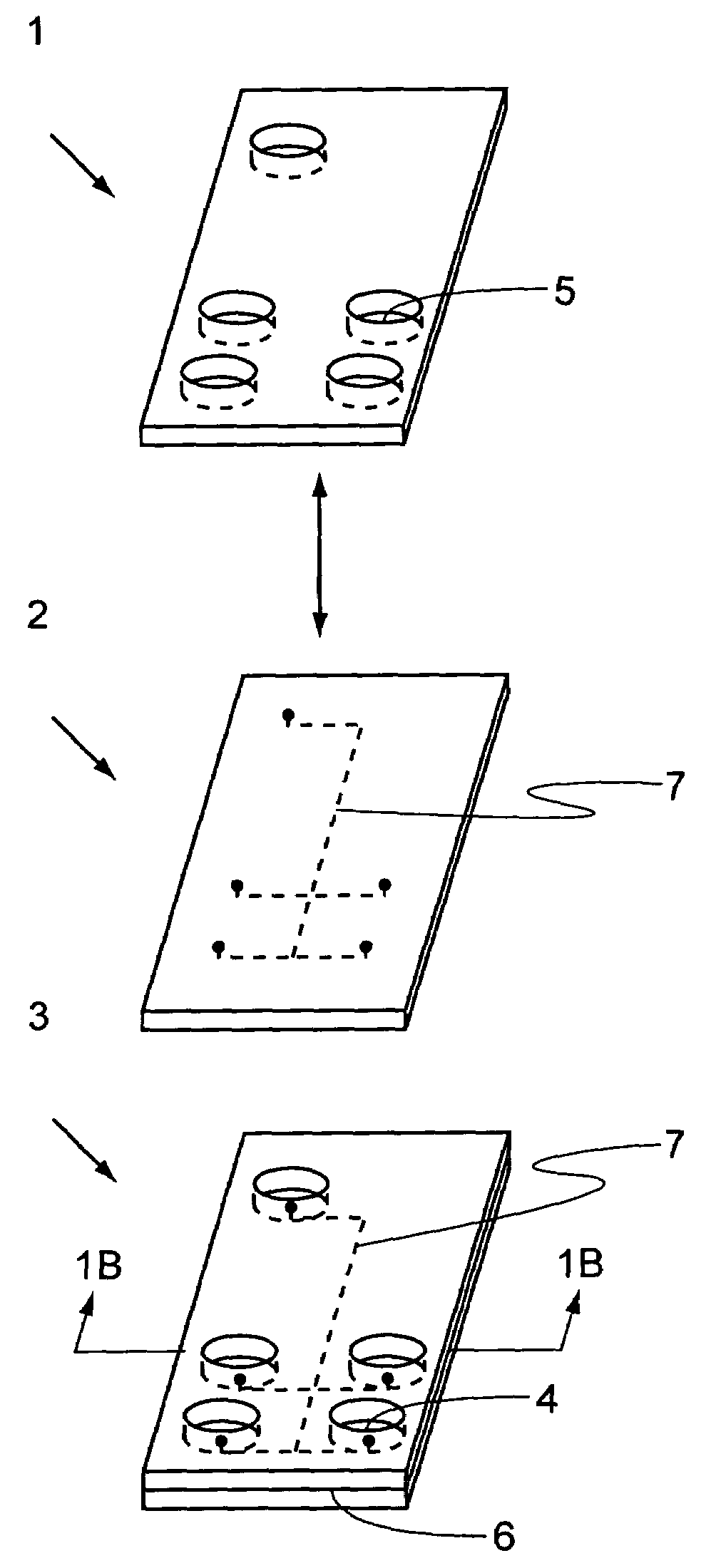
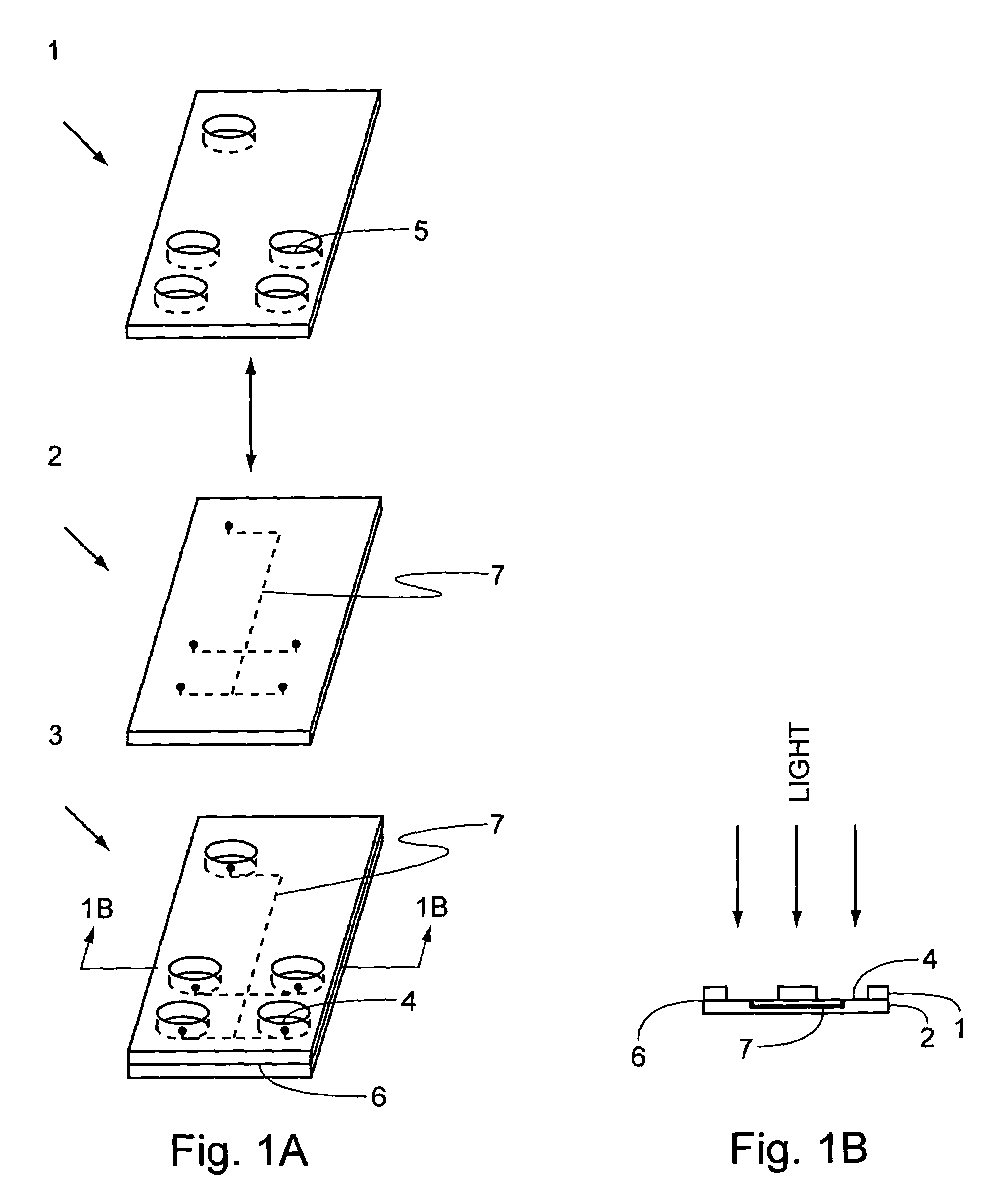
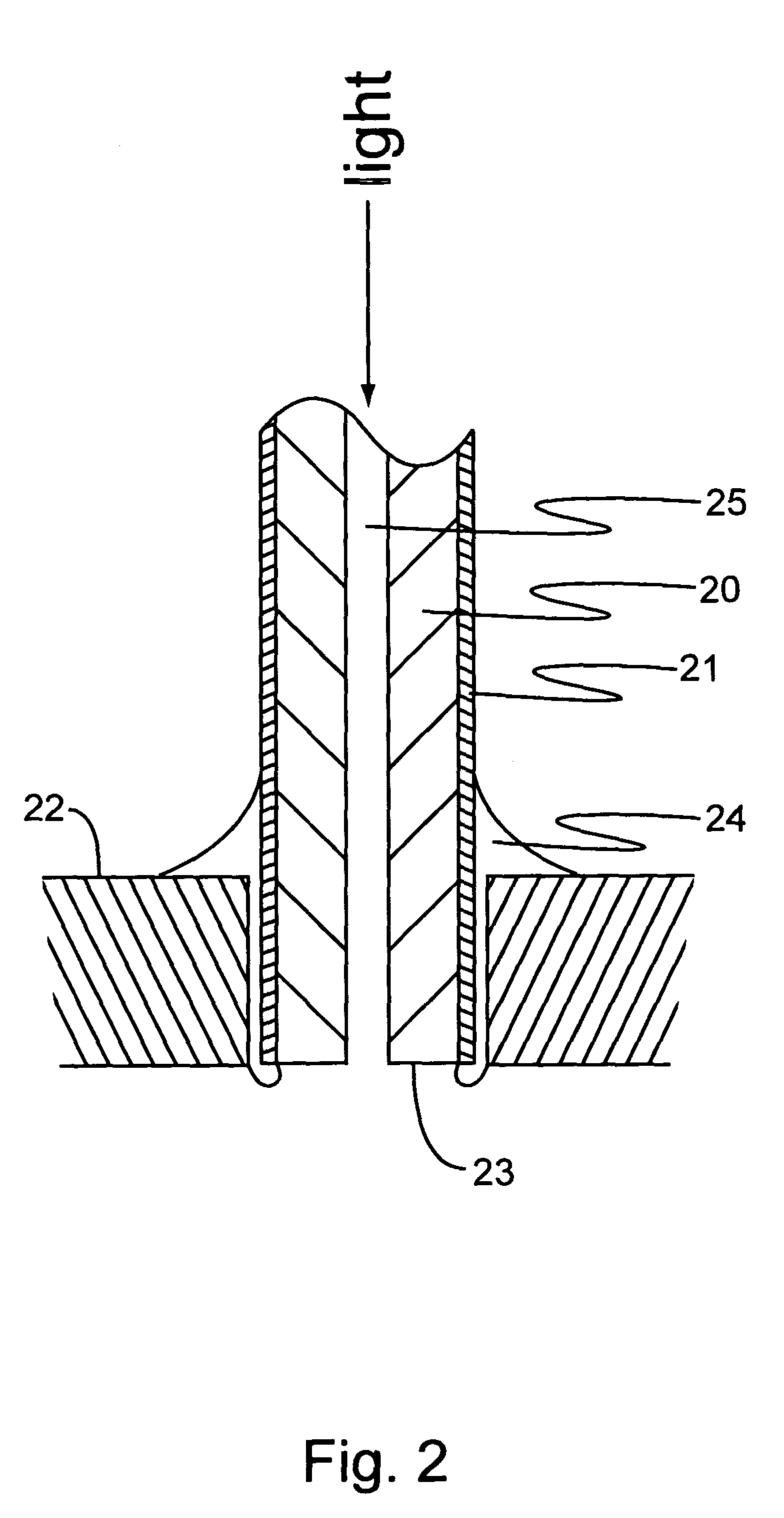
ActiveUS7001853B1Avoid flowPrecise BondingPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsSubstrate surface
This invention provides methods and systems, e.g., to control the flow of photo-polymerizable resins. In the method, e.g., flow of a photo-polymerizable resin is restricted from illuminated resin exclusion regions on a substrate surface by precisely situated flow barriers. A system to control photo-polymerizable resin flow includes, e.g., a light source, a mask and a substrate.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
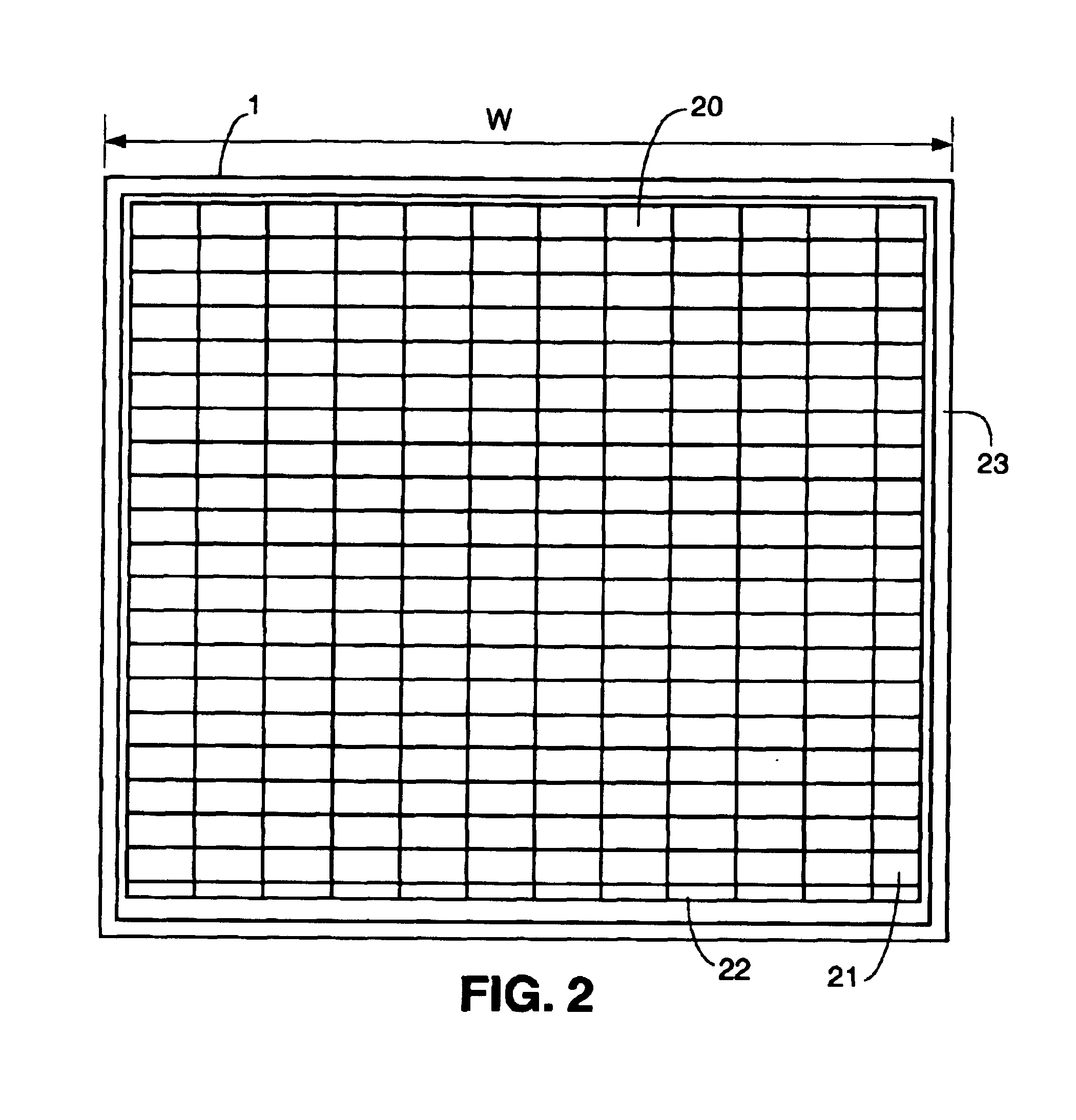
Electronic system modules and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6927471B2Good dimensional stabilityLow costPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureDielectricEngineering
This specification describes techniques for manufacturing an electronic system module. The module includes flexible multi-layer interconnection circuits with trace widths of 5 microns or less. A glass panel manufacturing facility, similar to those employed for making liquid crystal display, LCD, panels is used to fabricate the interconnection circuits. A polymer base layer is formed on a glass carrier with an intermediate release layer. Alternate layers of metal and dielectric are formed on the base layer, and patterned to create an array of multi-layer interconnection circuits on the glass panel. A thick layer of polymer is deposited on the interconnection circuit, and openings formed at input / output (I / O) pad locations. Solder paste is deposited in the openings to form wells filled with solder. After dicing the glass carrier to form separated interconnection circuits, IC chips are stud bumped and assembled using flip chip bonding, wherein the stud bumps on the components are inserted into corresponding wells on the interconnection circuits. The IC chips are tested and reworked to form tested circuit assemblies. Methods for connecting to testers and to other modules and electronic systems are described. Module packaging layers are provided for hermetic sealing and for electromagnetic shielding. A blade server embodiment is also described.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Flip chip package structure and carrier thereof
ActiveUS7791211B2Amount of solder that may be coated thereon is alsoIncrease productionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A flip chip package structure including a chip, a carrier, and a plurality of bumps is provided. The chip has a bonding surface and a plurality of bump pads thereon. The carrier is disposed corresponding to the chip and includes a substrate and a plurality of pre-solders. The substrate has a carrying surface and a patterned trace layer thereon. The patterned trace layer has a plurality of traces, and each of the traces has an outward protruding bonding portion corresponding to the bump. The line width of the bonding portion is greater than that of the trace. The pre-solders are disposed on the bonding portions, respectively. The bumps are disposed between the bump pads and the corresponding pre-solders such that the chip is electrically connected to the carrier through the bumps.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS20060115730A1Increase flexibilityPrevent curingFinal product manufactureActive material electrodesParticulatesFluorocarbon
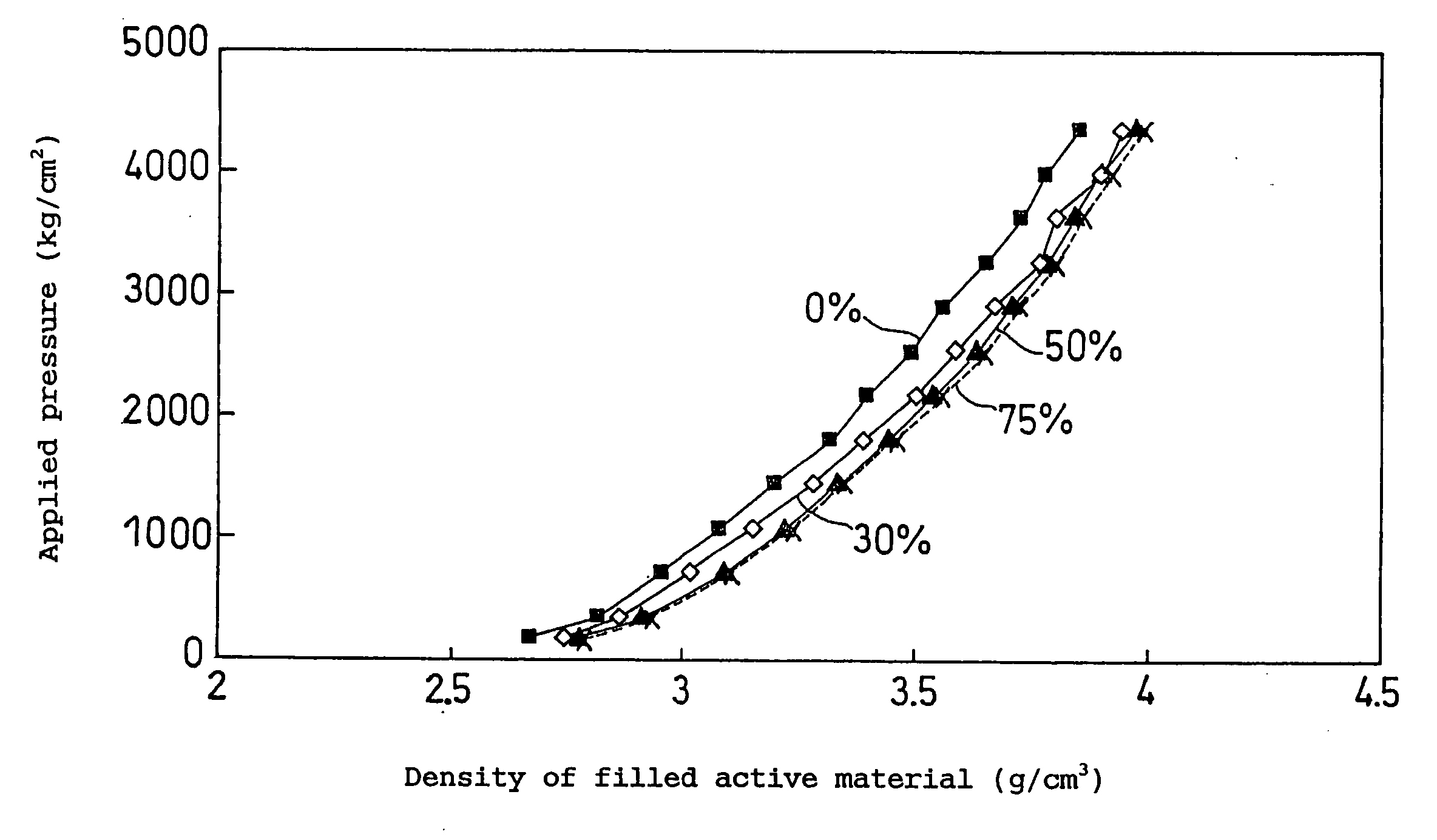
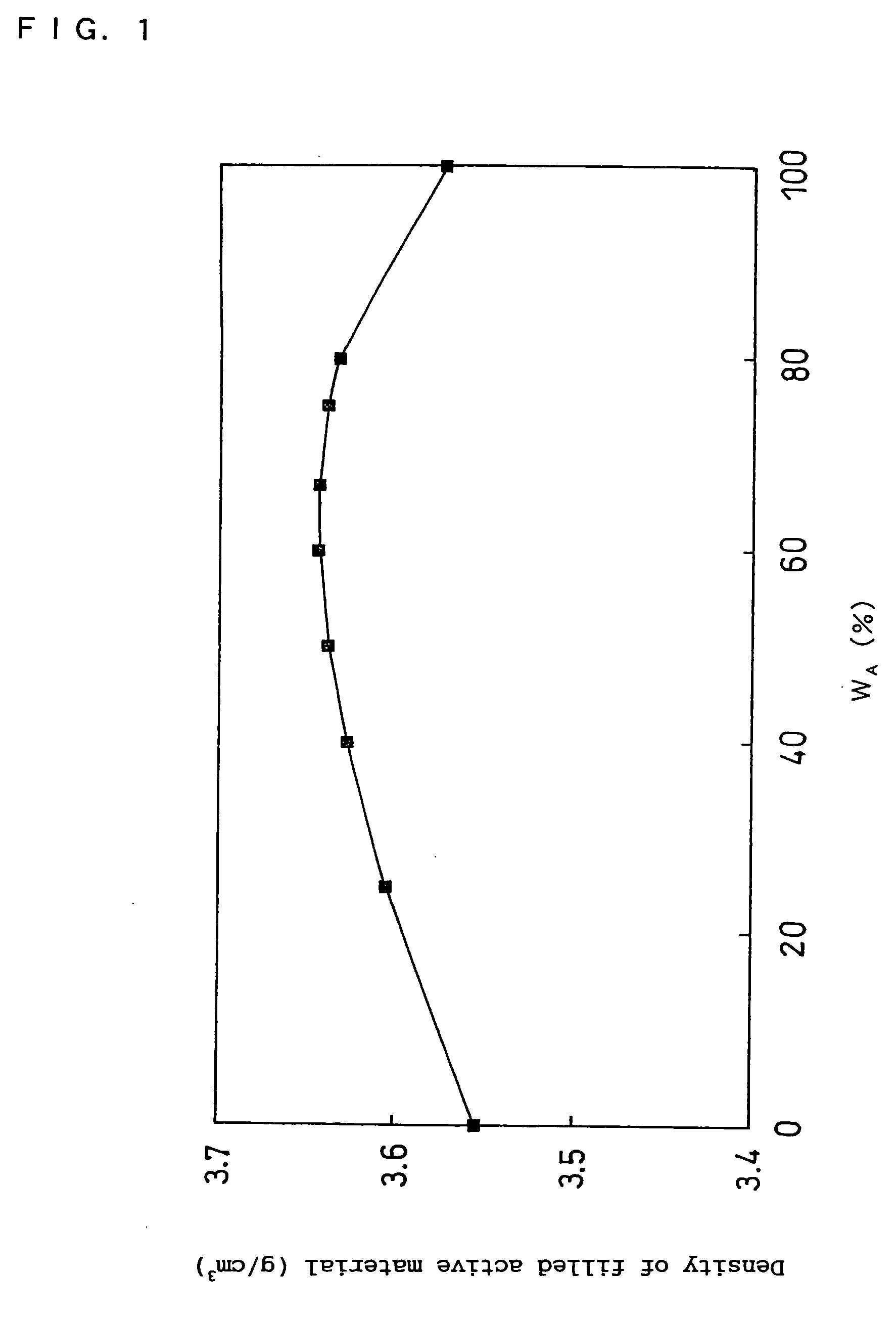
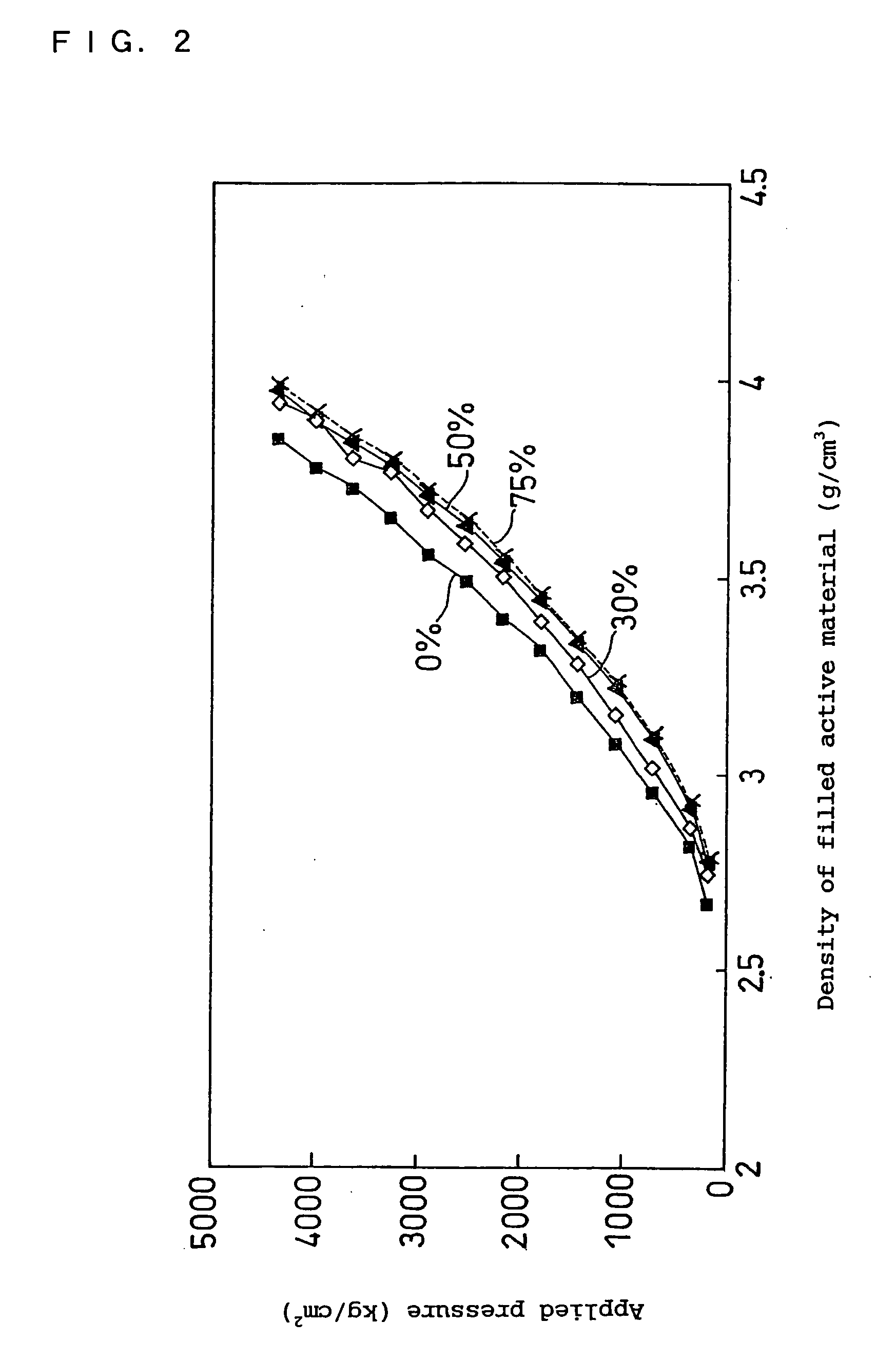
Disclosed is a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery having an electrode group in which a positive electrode and a negative electrode are spirally wound with a separator interposed therebetween. The positive electrode contains a positive electrode active material and a binder. The positive electrode active material contains a mixture of two different particulate substances having different average particle sizes. The two different particulate substances are lithium composite metal oxides containing nickel as an essential element. The binder includes fluorocarbon resin and rubber particles. The fluorocarbon resin contains at least a vinylidene fluoride unit. The amount of the rubber particles per 100 parts by weight of the fluorocarbon resin is 1 to 25 parts by weight.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Pod for shipping prepasted orthodontic appliances
ActiveUS20150021210A1Precise BondingMaximizing bonding strengthArch wiresBracketsEngineeringAdhesive
A pod for shipping a prepasted orthodontic appliance including a compartment having a cover or lid. The appliance includes uncured adhesive on its base and is removably attached to the underside of the lid and removable from the pod upon lifting of the lid. It is thereafter removable from the cover for placement on a tooth. The appliance is removably mounted on the lid by a compressible element frictionally engagable with an opening or openings of the appliance. When the lid is in closed position the appliance is suspended above the bottom of the pod so that the uncured adhesive does not touch the interior walls of the pod.
Owner:TP ORTHODONTICS
Process for producing a nonwoven material, plant for implementing it and nonwoven thus obtained
This invention concerns a method and an installation for producing a spunbonded fabric, characterized in that it consists in: producing a spunbonded lap (5) against the surface of which is delivered at least a web (V1 and / or V2) of discontinuous fibers, obtained by carding. The formed complex is compacted by pressing and is continuously transferred onto a line (10) for water jet binding treatment, driving the fibers in the direction of thickness, the fibers which are bound together like a splice between and around the continuous filaments while remaining visible at the surface. After drying, the final product is obtained.
Owner:RIETER PERFOJET
Press key using film switch circuit and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101315841AImprove manufacturing qualityHigh product yieldInput/output for user-computer interactionElectric switchesMembrane switchEngineering
The invention provides a membrane switching circuit and a keystroke using the membrane switching circuit. An insulating layer of the membrane switching circuit is provided with an annular opening. The bottom of an elastic element is matched with the annular opening of the insulating layer and bonded to the annular opening by an adhesive. The annular opening can assist the elastic element to be accurately bonded to a designated position. In addition, the annular opening can prevent the adhesive from overflowing out of the annular opening.
Owner:DARFON ELECTRONICS CORP
Manufacturing method and bonding apparatus with vacuum chuck with independent retaining portions for liquid crystal (LCD) device
ActiveUS7050141B2Increase bonding areaPrecise BondingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A manufacturing method and a bonding apparatus for a liquid crystal display device is provided for that makes it possible to expel remaining bubbles from a liquid crystal and to bond an array substrate and a color filter substrate while maintaining their positional relationship. In a step for bonding an array substrate with a liquid crystal applied thereto and a color filter substrate, vacuum holding of only a central retaining region of an upper vacuum chuck of the bonding apparatus is stopped. This causes the central portion of the color filter substrate to come in contact with the array substrate due to its own weight. The contact region is pressed by a holder to secure the positional relationship between the array substrate and the color filter substrate. Thereafter, with the elapse of time, the upper vacuum chuck increases the retaining region for which a vacuum retaining operation is stopped so as to expand the area of contact between the array substrate and the color filter substrate. As a result, bubbles in the liquid crystal are expelled externally.
Owner:TWITTER INC
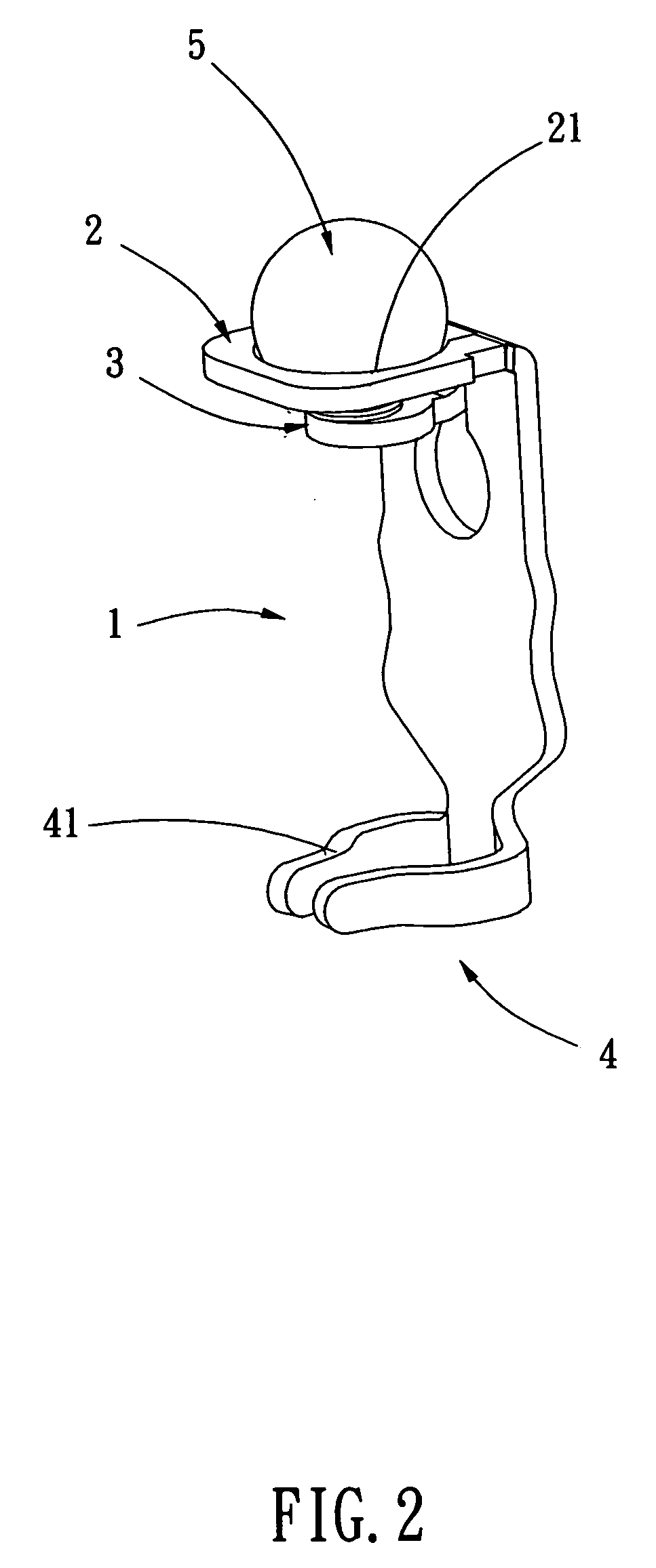
Captive fastener
A captive fastener includes a mounting base member bonded to a first panel frame, a locking shank loaded with a spring member and axially movably mounted in the mounting base member hole for engaging into a mounting through hole of a second panel frame to detachably lock the second panel frame to the first panel frame, and a driving member, which is coated with a color index coating for identification and connected to the locking shank after bonding the mounting base member to the first panel frame and operable to move the locking shank between a locking position where the first panel frame and the second panel frame are locked and an unlocking position where the first panel frame is detachable from the second panel frame.
Owner:HANWIT PRECISION IND LTD
Method of manufacturing an ink jet print head
InactiveUS8272130B2Short timePrecise BondingPrinted circuit assemblingInking apparatusProduction rateAdhesive
A method of manufacturing an ink jet print head capable of bonding the printing element substrate to the support surface with high precision in a reduced period of time is provided. For this purpose, raised flat portions are formed in the support surface of the supporting member to provide in an adhesive layer between the printing element substrate and the supporting member a portion of the thermosetting adhesive that is thinner than others. After the relative positions of the printing element substrate and the supporting member are adjusted, the thin portions of the adhesive layer are hardened. This enables the printing element substrate to be bonded to the supporting member in a relatively short period of time. As a result, if there are undulations on the support surface, the printing element substrate can be bonded to the supporting member with high precision, improving the mass productivity of the print head.
Owner:CANON KK
Slip resistant roof underlayment
ActiveUS20080020662A1Quality improvementIncrease resistanceRoofingSynthetic resin layered productsFiberEngineering
A roofing underlayment having a slip-resistant surface includes a woven polypropylene scrim laminated to a top layer made from a non-woven spun-bond polypropylene fabric. During lamination, the scrim is bonded to the top layer by a polypropylene coating that impregnates the scrim, thereby forming a structural bottom layer comprising the polypropylene-impregnated scrim. The non-woven fibers of the top layer provide a micro-textured, slip-resistant surface. A second polypropylene coating may be applied to the bottom surface of the bottom structural layer. An adhesive layer may optionally be applied either to the bottom surface of the bottom structural layer, or, if used, to the bottom surface of the second polypropylene coating.
Owner:KIRSCH RES & DEV
Fabrication methods for electronic system modules
InactiveUS20050140026A1Good dimensional stabilityRobust processingPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureDielectricElectromagnetic shielding
This specification describes techniques for manufacturing an electronic system module. The module includes flexible multi-layer interconnection circuits with trace widths of 5 microns or less. A glass panel manufacturing facility, similar to those employed for making liquid crystal display, LCD, panels is used to fabricate the interconnection circuits. A polymer base layer is formed on a glass carrier with an intermediate release layer. Alternate layers of metal and dielectric are formed on the base layer, and patterned to create an array of multi-layer interconnection circuits on the glass panel. A thick layer of polymer is deposited on the interconnection circuit, and openings formed at input / output (I / O) pad locations. Solder paste is deposited in the openings to form wells filled with solder. After dicing the glass carrier to form separated interconnection circuits, IC chips are stud bumped and assembled using flip chip bonding, wherein the stud bumps on the components are inserted into corresponding wells on the interconnection circuits. The IC chips are tested and reworked to form tested circuit assemblies. Methods for connecting to testers and to other modules and electronic systems are described. Module packaging layers are provided for hermetic sealing and for electromagnetic shielding. A blade server embodiment is also described.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Substrate assembly apparatus and method
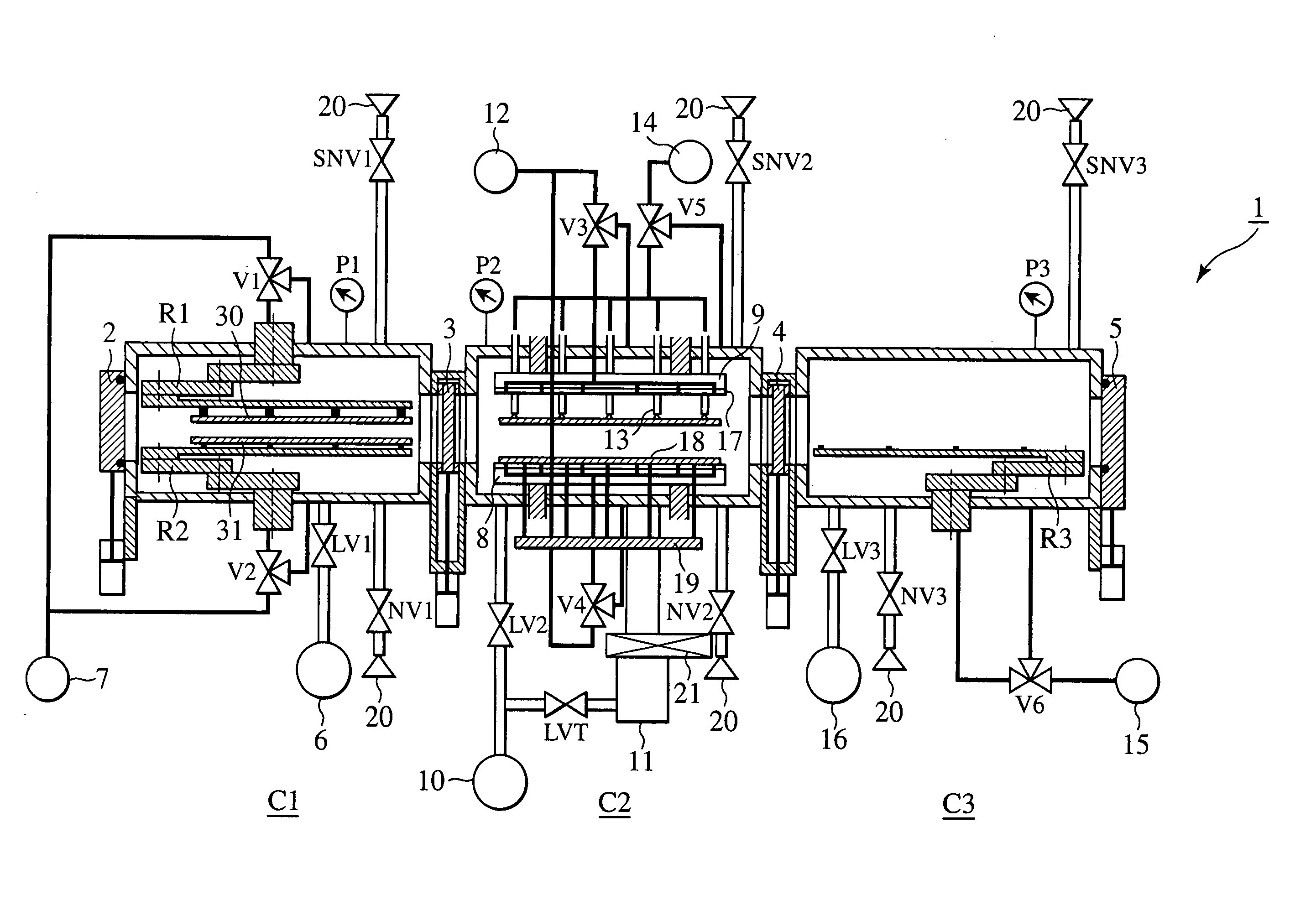
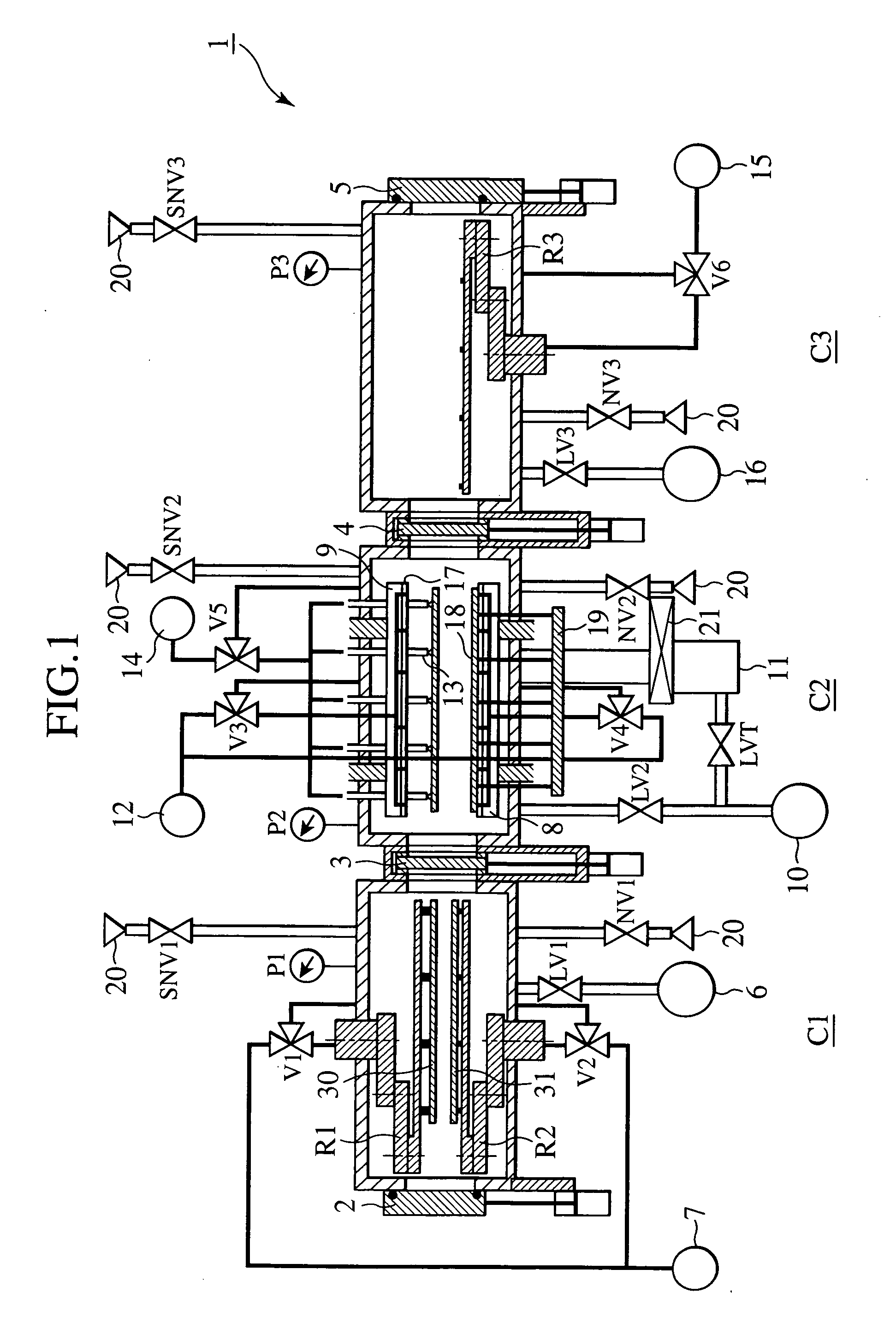
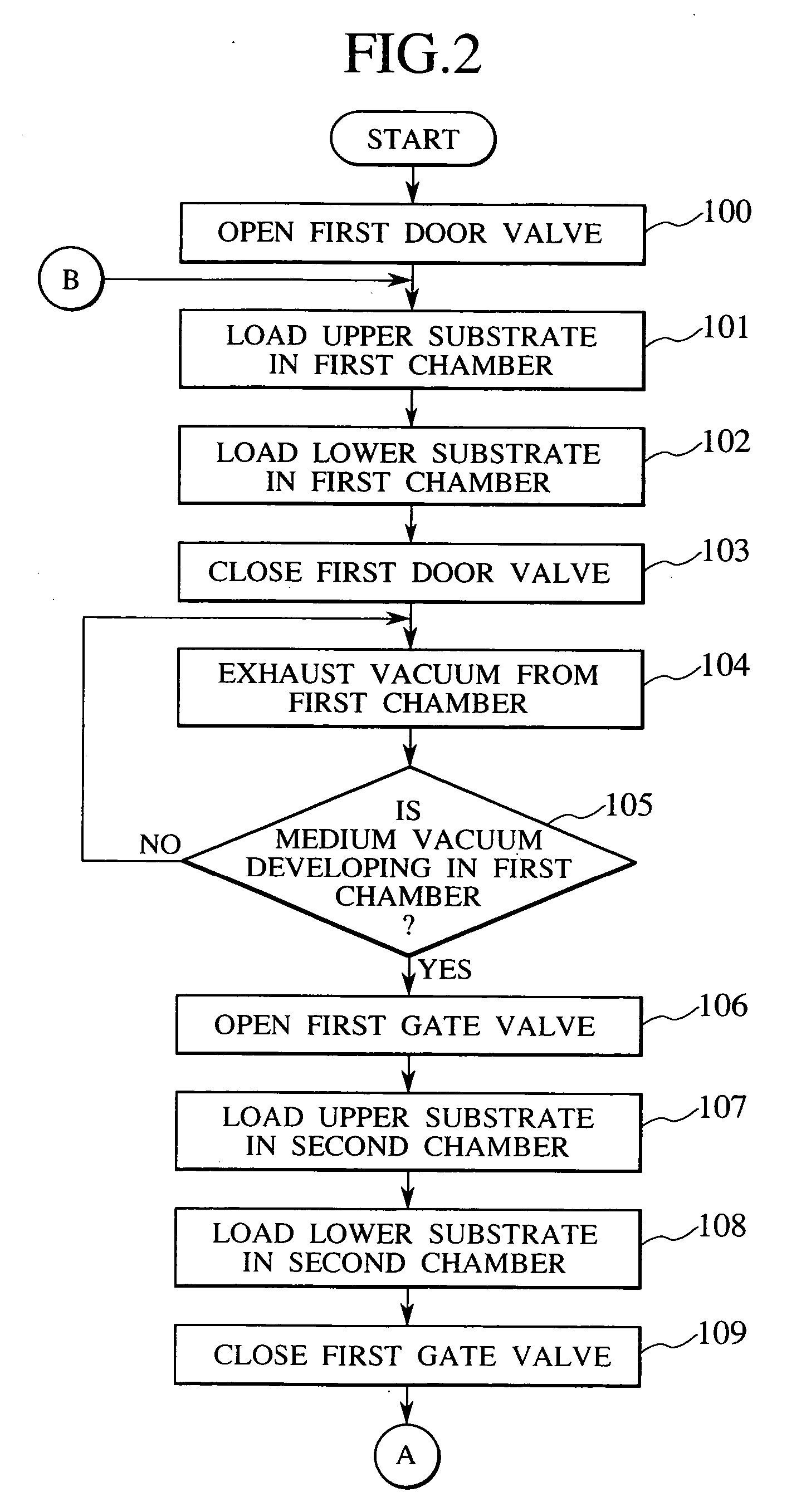
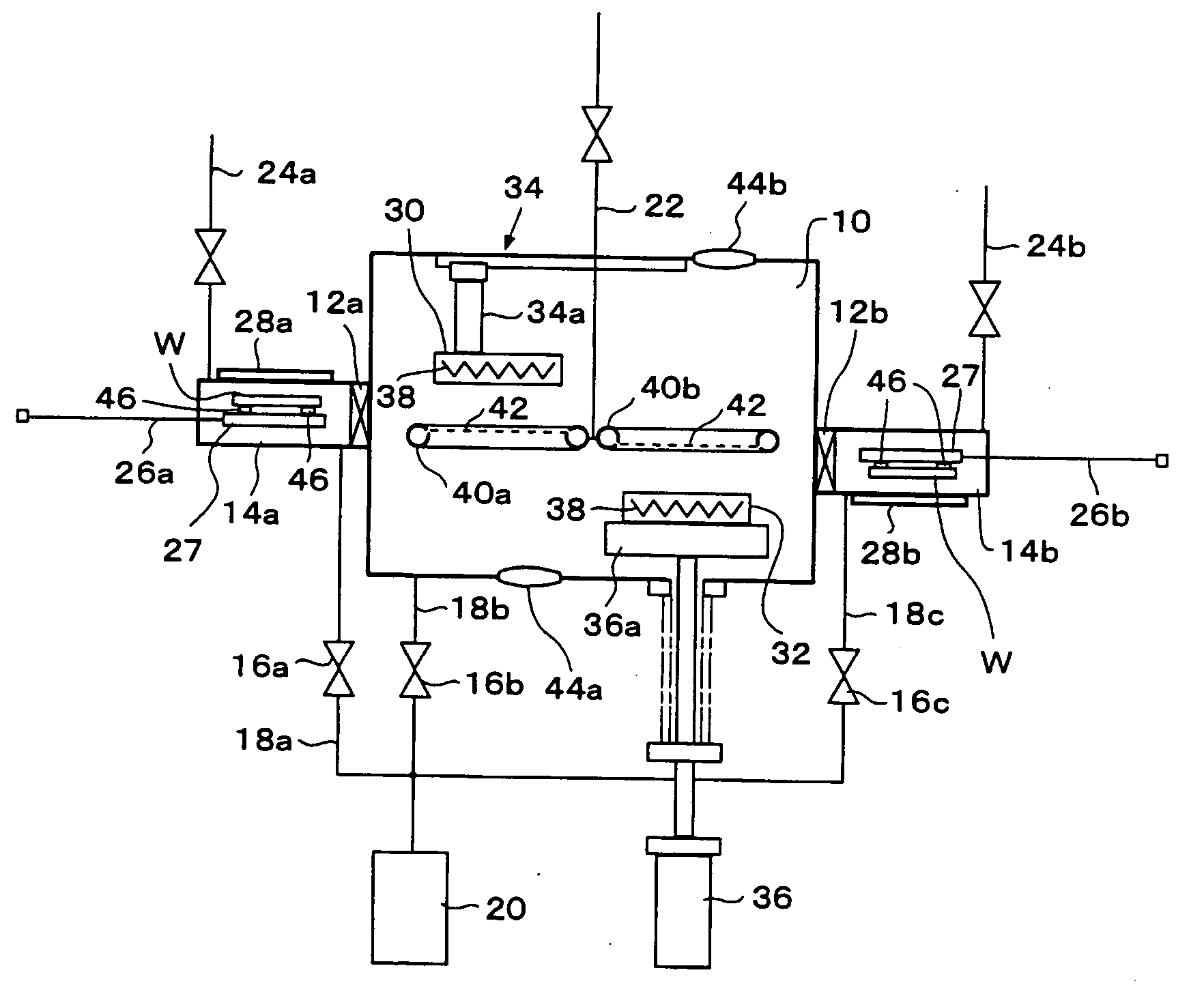
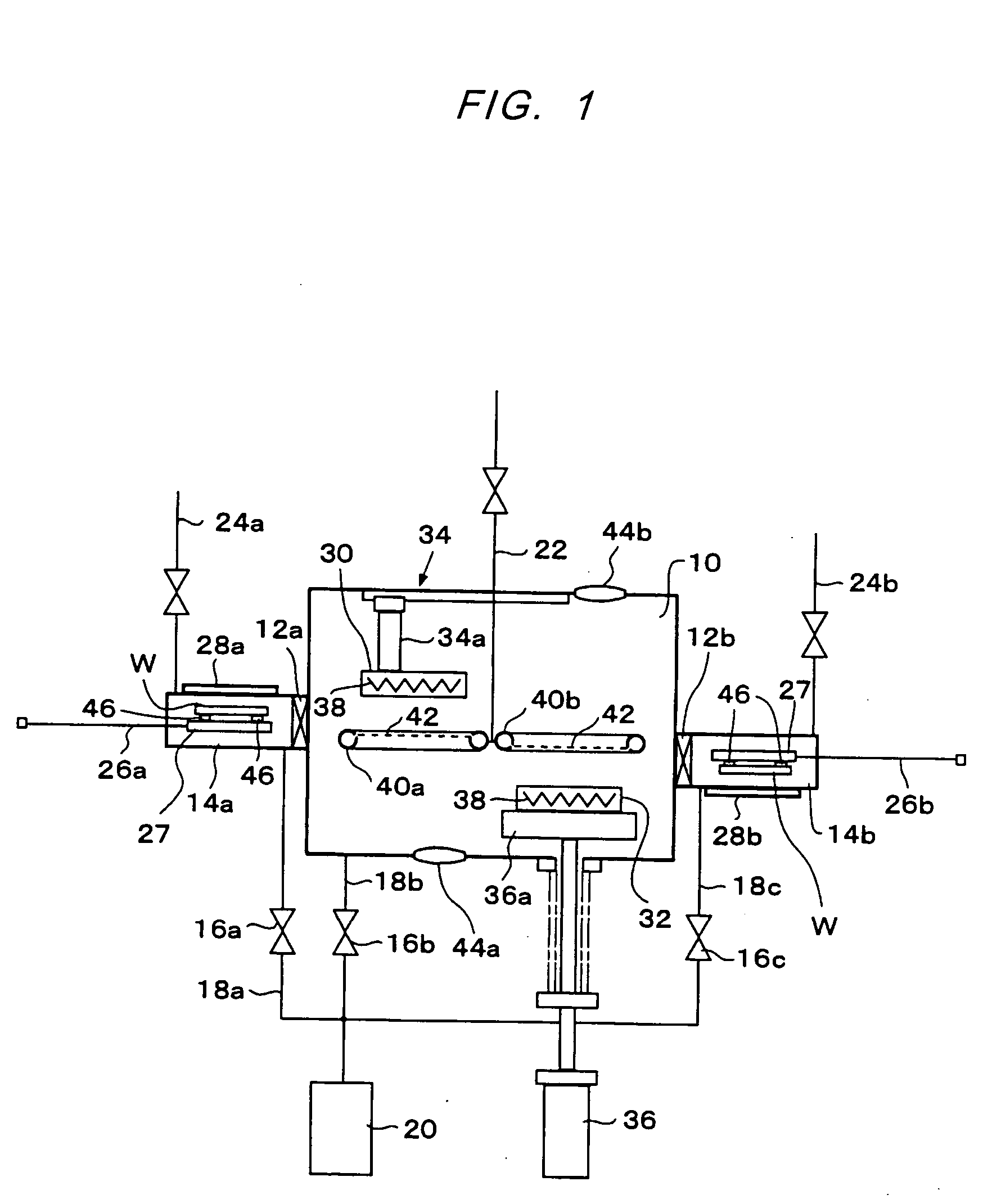
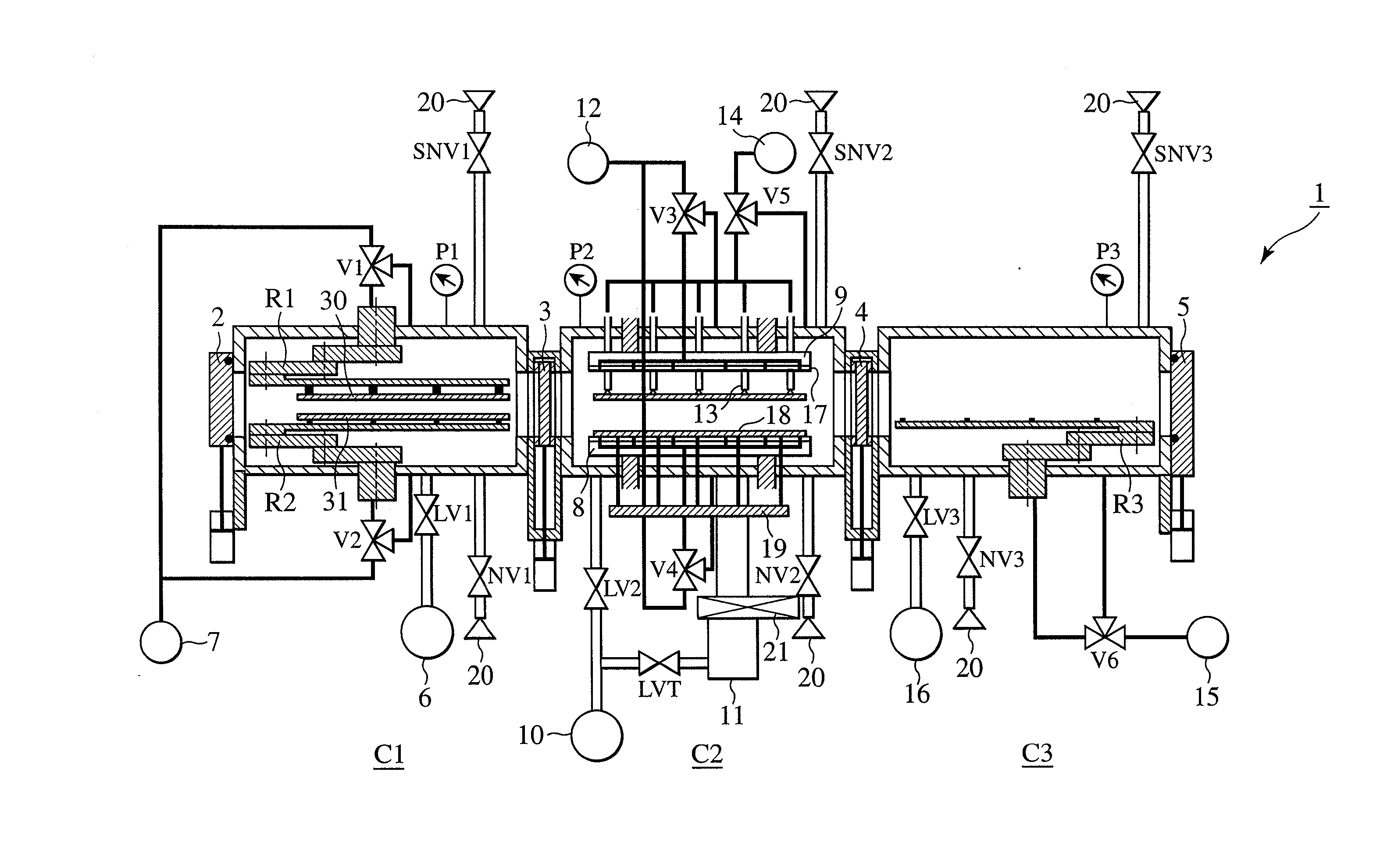
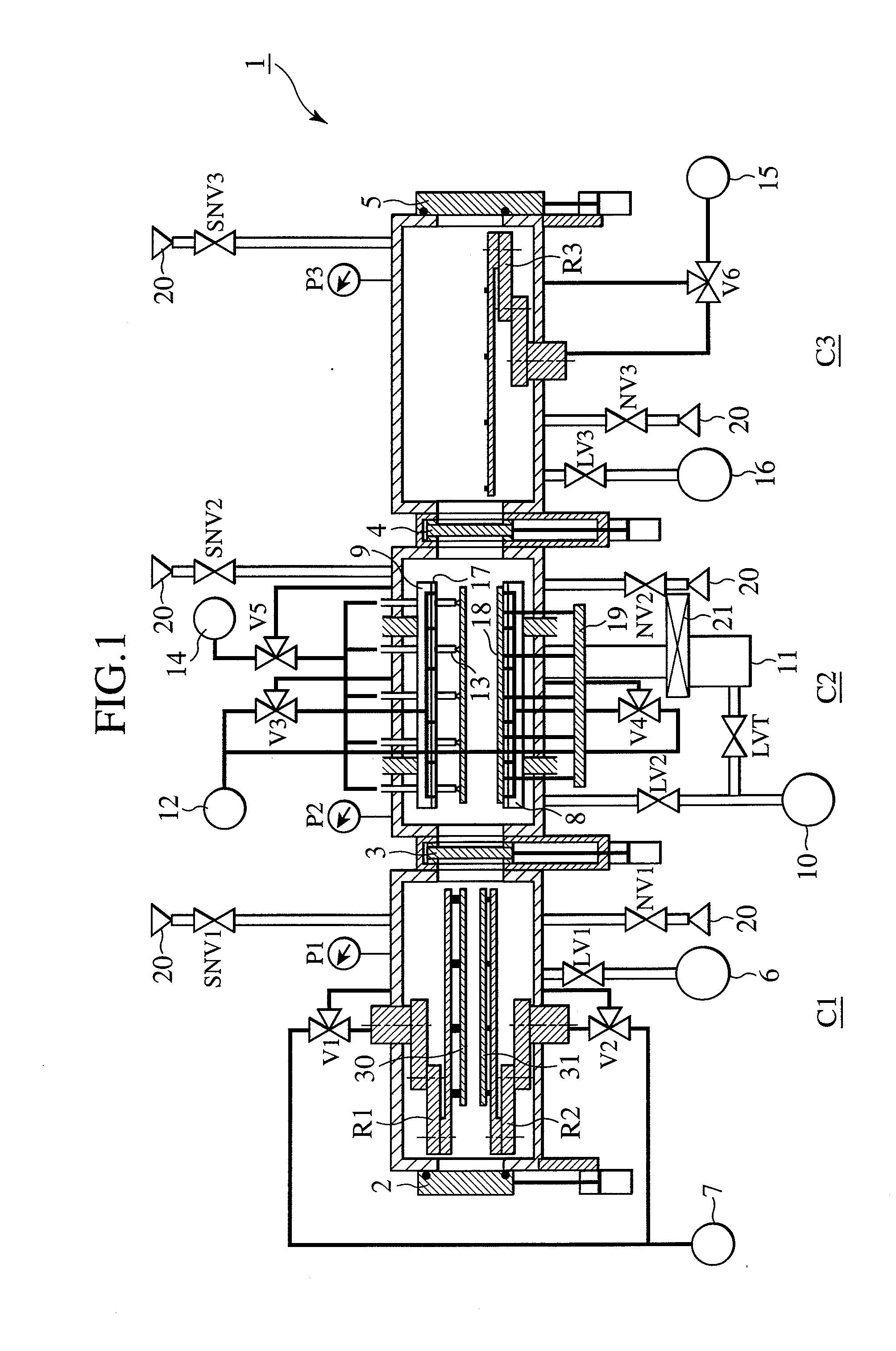
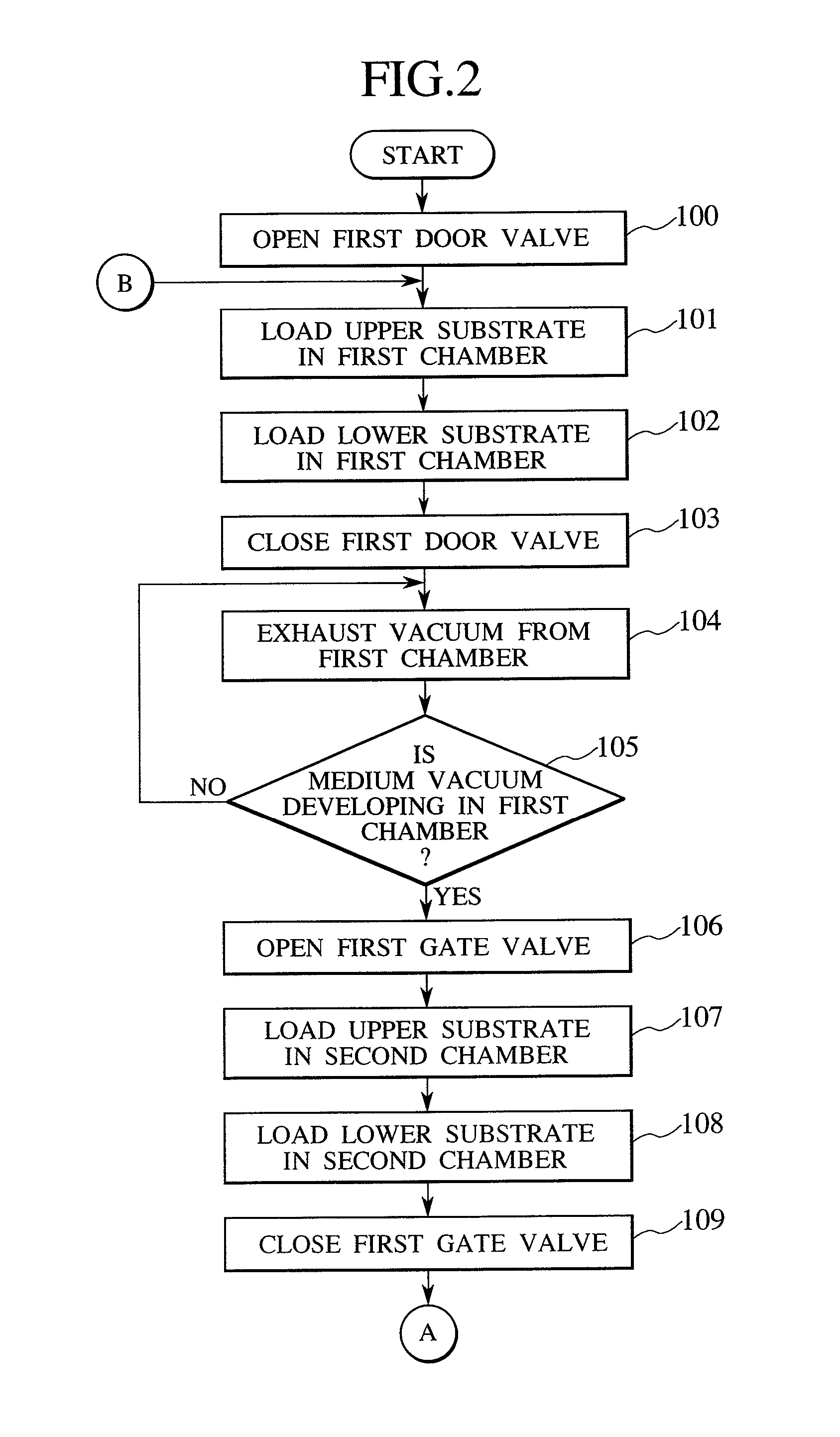
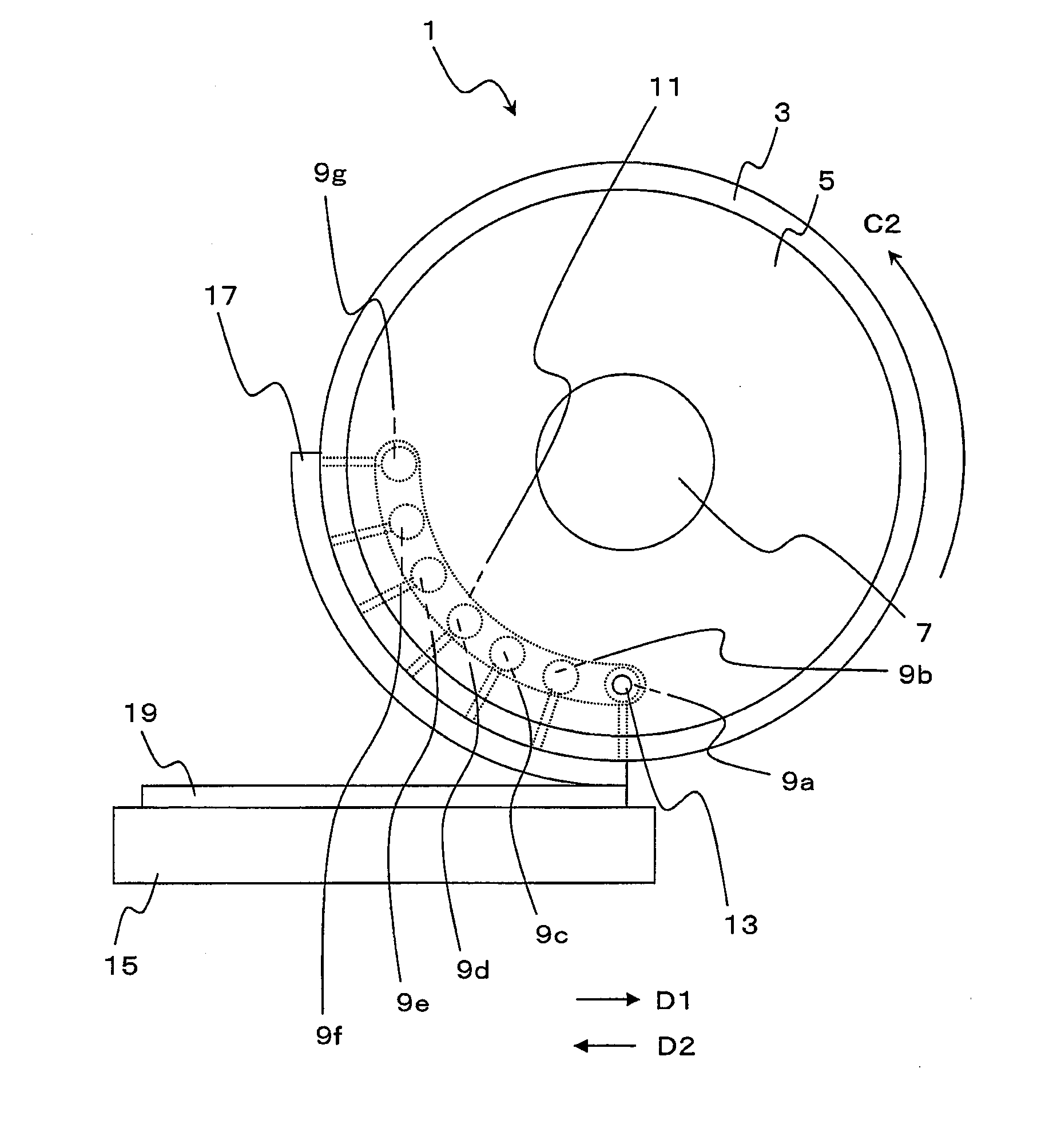
InactiveUS20070051462A1High precisionShorten evacuation timeLayered product treatmentLaminationAtmospheric pressureElectrical and Electronics engineering
A substrate bonding apparatus for bonding substrates together in a vacuum at high speeds, with a high degree of accuracy includes a first chamber C1, a second chamber C2, and a third chamber C3. Two substrates to be bonded together are loaded in the first chamber C1. The two substrates are bonded together in the second chamber C2. The two substrates bonded together are unloaded in the third chamber C3. The first and third chambers are variably controlled from an atmospheric pressure state to a medium vacuum state. The second chamber is variably controlled from the medium vacuum state to a high vacuum state.
Owner:HITACHI PLANT TECH LTD
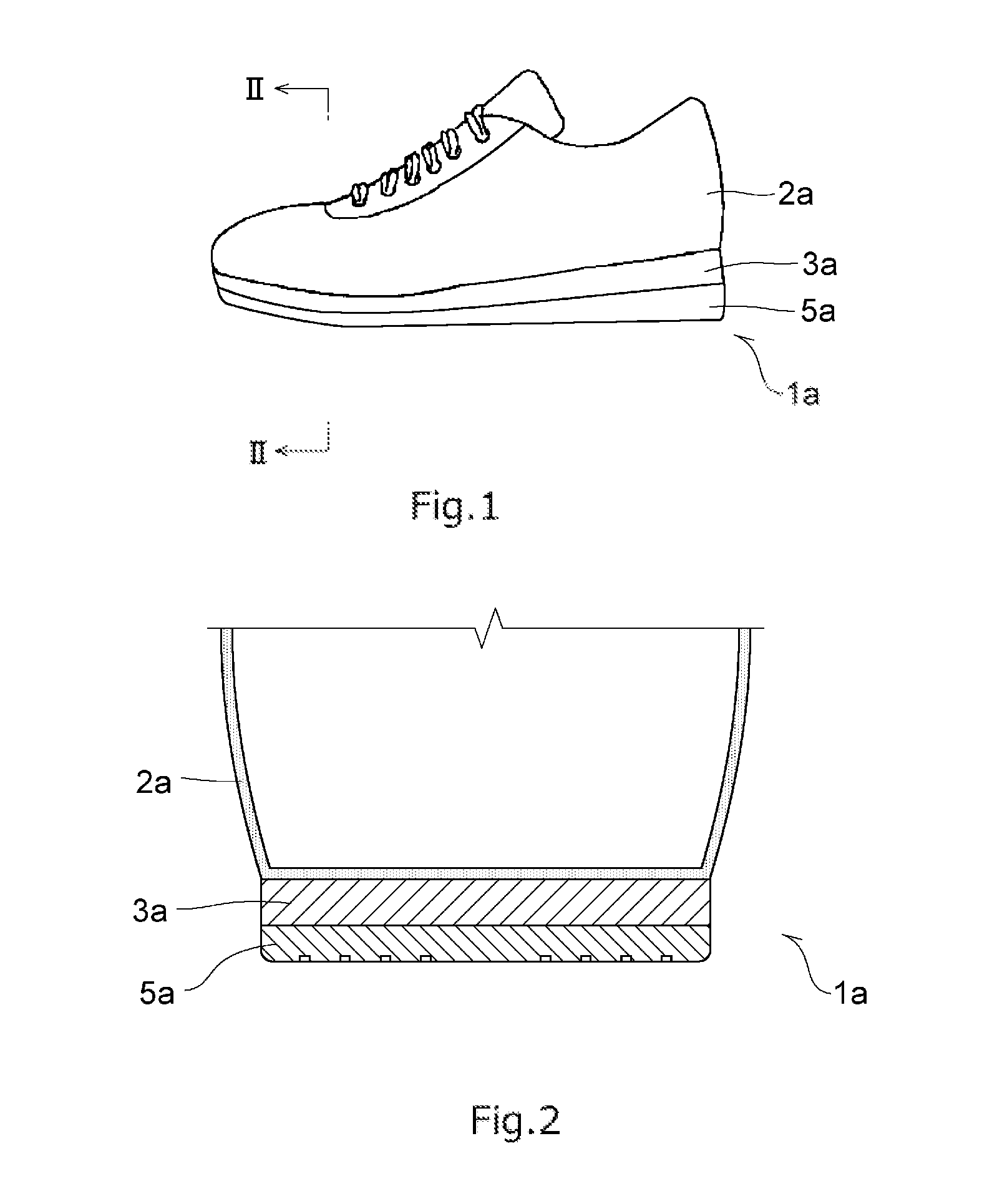
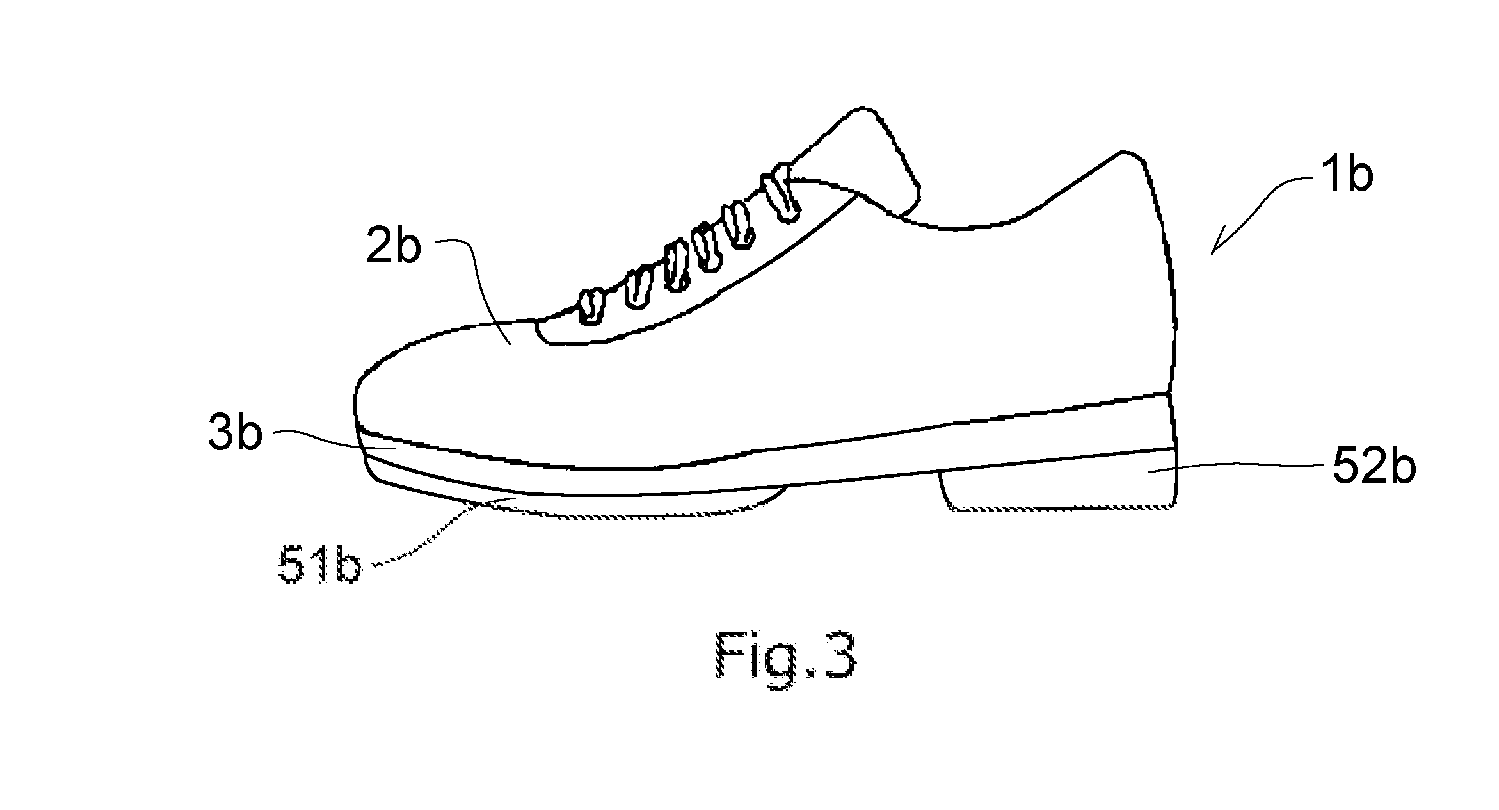
Foamed Sole and Shoe
A foamed sole according to the present invention includes a foam molding containing a rubber component and a resin component, wherein the maximum value of a loss factor [tan δ] at a frequency of 10 Hz and at 30° C. to 80° C. of the foam molding is 0.18 or less, and a peak of a loss factor [tan δ] at a frequency of 10 Hz of the foam molding lies within the range of 100° C. or higher. The foamed sole has a feature that it hardly shrinks when it is heated.
Owner:ASICS CORP
Bonding apparatus and bonding method
InactiveUS20060118598A1Precise positioningIncreased durabilityHigh frequency current welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsHermetic sealElectronic component
A bonding apparatus can bond contacts of electronic components directly to each other without the need for solder. The bonding apparatus include a hermetically sealed processing chamber, a plurality of bases for holding at least two workpieces having respective bonding regions in the processing chamber, a gas inlet for introducing a processing gas to clean the bonding regions into the processing chamber, a pressure controller for controlling a predetermined pressure to be developed in the processing chamber, a heater for heating the workpieces in the processing chamber, and a bonding unit for pressing and bonding the bonding regions of the workpieces to each other in the processing chamber.
Owner:EBARA CORP
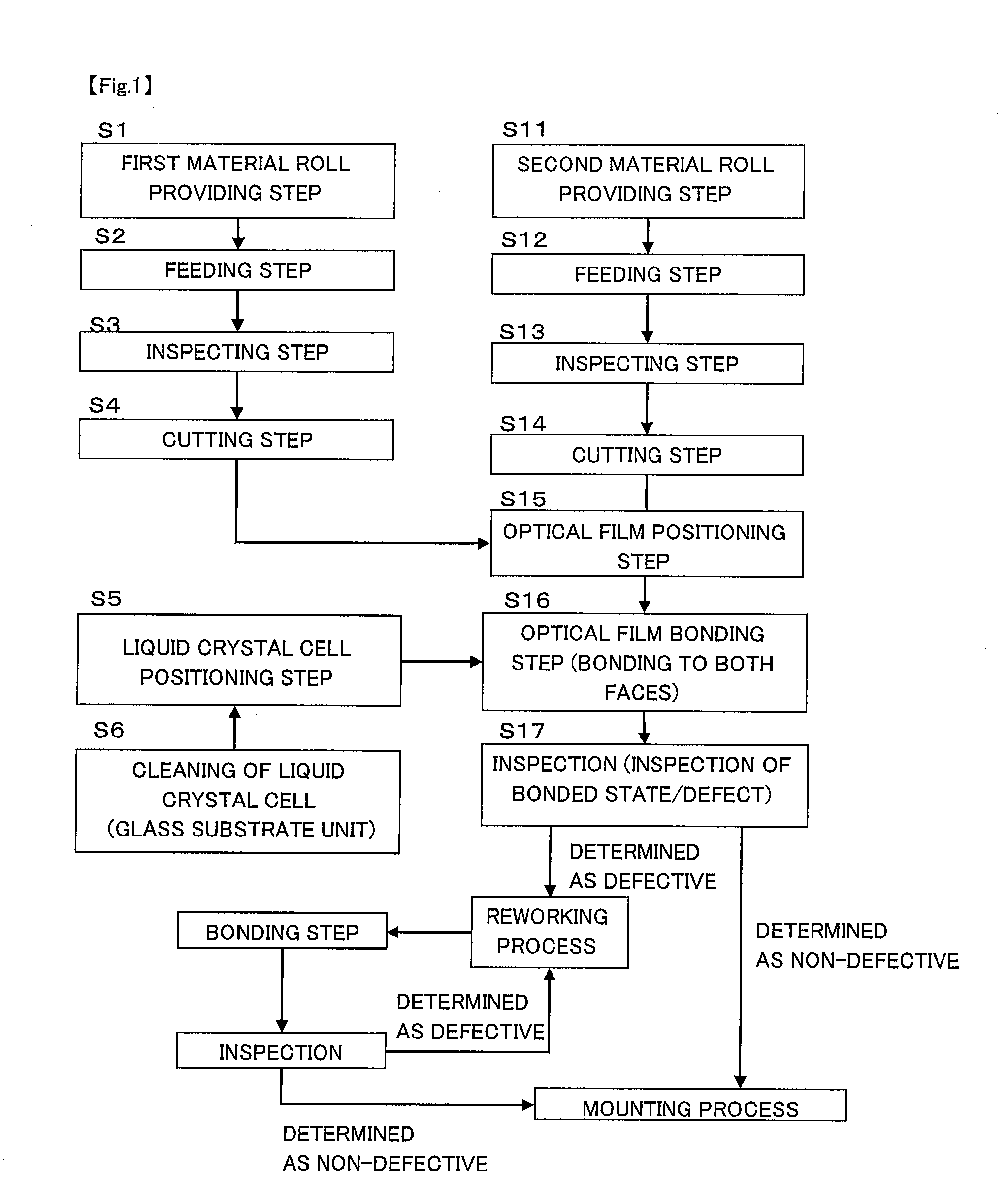
Optical display device manufacturing system and method for manufacturing optical display device
InactiveUS20110025958A1Simple constitutionHigh optical contrastNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceEngineering
Provided are an optical display device manufacturing system and a method for manufacturing an optical display device which can bond optical films to both surfaces of a liquid crystal cell in good condition with a simpler constitution. A first optical film F11 is fed in an orthogonal direction with respect to the width direction from a first material roll R1 formed by winding the first optical film F11 in such a manner that an absorption axis B1 extends in the orthogonal direction, and then the first optical film F11 is cut and bonded to one surface of a liquid crystal cell. A second optical film F21 is fed in an orthogonal direction with respect to the width direction from a second material roll R2 formed by winding the second optical film F21 in such a manner that an absorption axis B2 extends in the width direction, and then the second optical film F21 is cut and bonded to the other surface of the liquid crystal cell. Accordingly, it is possible to bond the first optical film F11 and the second optical film F21 in the crossed nicols relation, without the provision of the mechanism for rotating the liquid crystal cell W or the like.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Substrate assembly apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080053619A1Improve productivityPrecise BondingLayered product treatmentLaminationEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
A substrate bonding apparatus for bonding substrates together in a vacuum at high speeds, with a high degree of accuracy includes a first chamber C1, a second chamber C2, and a third chamber C3. Two substrates to be bonded together are loaded in the first chamber C1. The two substrates are bonded together in the second chamber C2. The two substrates bonded together are unloaded in the third chamber C3. The first and third chambers are variably controlled from an atmospheric pressure state to a medium vacuum state. The second chamber is variably controlled from the medium vacuum state to a high vacuum state.
Owner:NAKAYAMA YUKINORI +2
Vacuum adsorption control mechanism device, film pasting device, method of pasting film, and display device
ActiveUS20100206485A1Precise BondingSimple structureLamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationDisplay deviceEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a vacuum suction control mechanism apparatus capable of accurately bonding a film to a bonding object with a simple structure. A vacuum suction control mechanism apparatus according to the present invention includes a first member including a plurality of suction holes formed in a surface thereof, the plurality of suction holes being connectable to a decompression source, and a second member capable of contacting the plurality of suction holes, the second member being movable relative to the first member, wherein the second member includes connecting member connecting some of the suction holes, the number of which corresponds to a relative position between the first member and the second member, to the decompression source.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Rotor construction in an electric motor
InactiveUS20090140598A1Increasing manufacturing costPrecise BondingMagnetic circuit rotating partsEngineeringElectric motor
A rotor of an electric motor with a cylindrical shaft and a magnetically conducting laminated core, the laminated core having a central shaft duct. The laminated core can be fastened reliably and permanently to the rotor shaft, without significantly increasing manufacturing costs. This task is accomplished by adhesively connecting the shaft to the laminated core in the area of its inside contour as by welding.
Owner:BUHLER MOTOR GMBH
Process for producing photochromic optical articles
ActiveUS20090324956A1Without deterioration of coating propertySimple methodSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsEmulsionColloid
Provided is a method for producing a photochromic optical article having a photochromic coating layer exhibiting photochromism formed on an optical base such as a plastic lens which has good optical characteristics and photochromic characteristics, and also has good adhesion between the base and the photochromic layer. The method enables to easily produce such a photochromic optical article by improving wettability of a photochromic coating agent for a primer. In this method, the photochromic optical article is produced by forming a primer layer on the optical base surface by coating a primer comprising an emulsion which has a colloidally dispersed urethane resin in a dispersion medium, and then forming on the primer layer.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Binder to process book blocks and method of binding
A perfect binder for processing book blocks, including: a conveying device adapted to convey the book blocks along a closed circulating path, the conveying device including a plurality of clamping devices each adapted to convey a book block; and a plurality of processing stations arranged successively along the closed circulating path. One of the processing stations includes a spine-processing station, and another one of the processing stations includes an end sheet feed station following the spine-processing station. According to another aspect of the invention there is provided a method forthe perfect binding of book blocks, comprising: conveying the book blocks around a closed circulating path with each book block clamped in a clamping device of a conveying device, wherein a pluralityof processing stations are arranged successively along the closed circulating path; milling the spine of each book block at one of the processing stations; and subsequently, inserting at least one endsheet into the clamping device at a downstream end sheet feed station.
Owner:MULLER MARTINI HLDG
Methods for treating blood coagulation disorders
InactiveUS7615537B2Optimally promote proper disulfide bondingPrecise BondingBiocideVirusesFactor VIIaA-DNA
The present invention relates to a method of treating an individual having a blood coagulation defect (e.g., hemophilia A, hemophilia B), comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a DNA vector encoding modified Factor VII (FVII), wherein the modified Factor VII leads to generation of Factor VIIa in vivo. In a particular embodiment, the invention pertains to a method of treating an individual having a blood coagulation defect comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a nucleic acid encoding a modified FVII wherein the modified FVII comprises a signal which codes for precursor cleavage by furin at the activation cleavage site of the modified FVII. The invention also relates to a method of treating an individual having a blood coagulation disorder comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a nucleic acid encoding the light chain of human FVII and a nucleic acid encoding the heavy chain of human FVII operably linked to a leader sequence. Compositions, expression vectors and host cells comprising nucleic acid which encodes a modified Factor VII, wherein the modified Factor VII leads to generation of Factor VIIa in vivo is also encompassed by the present invention.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
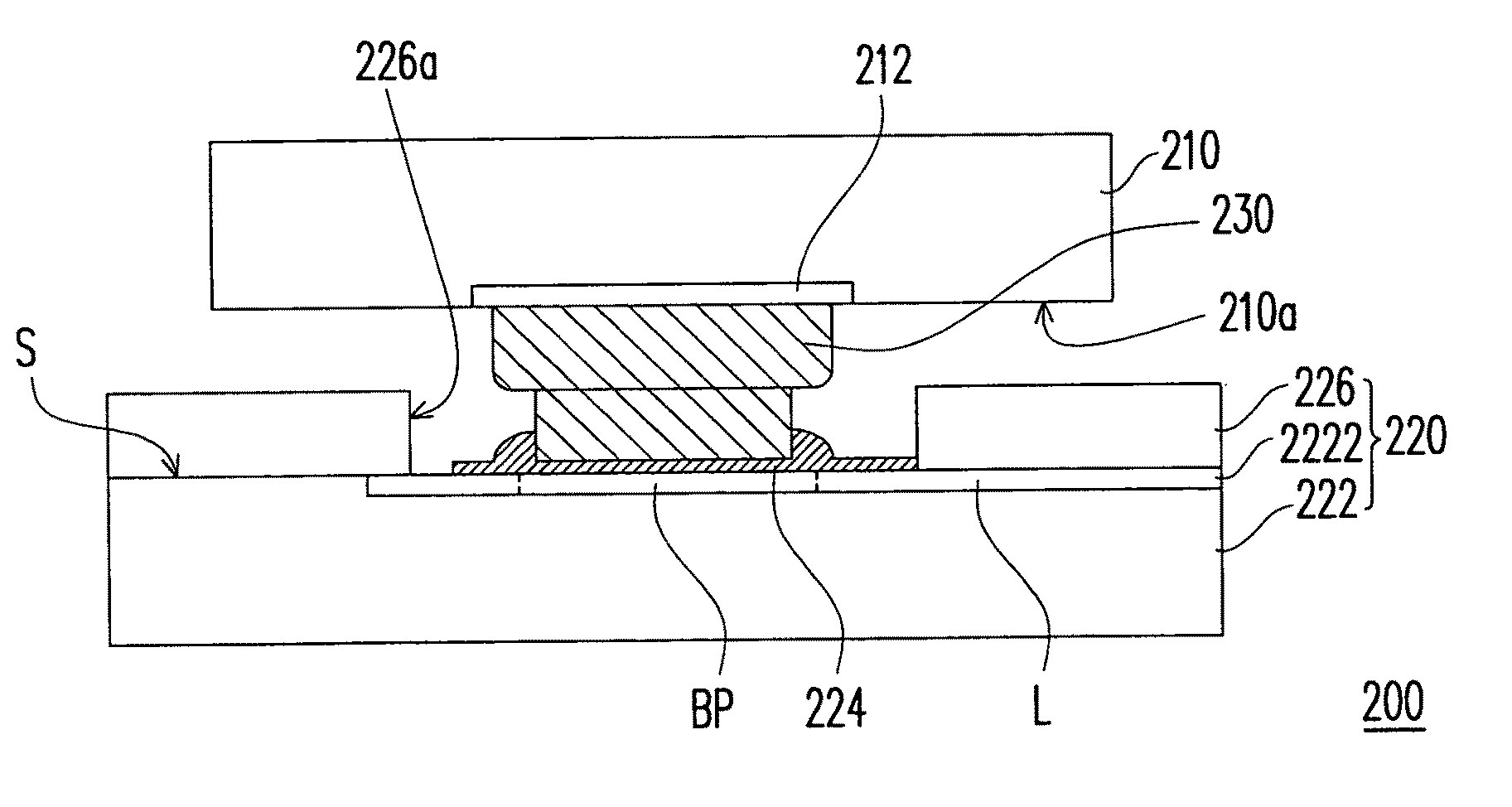
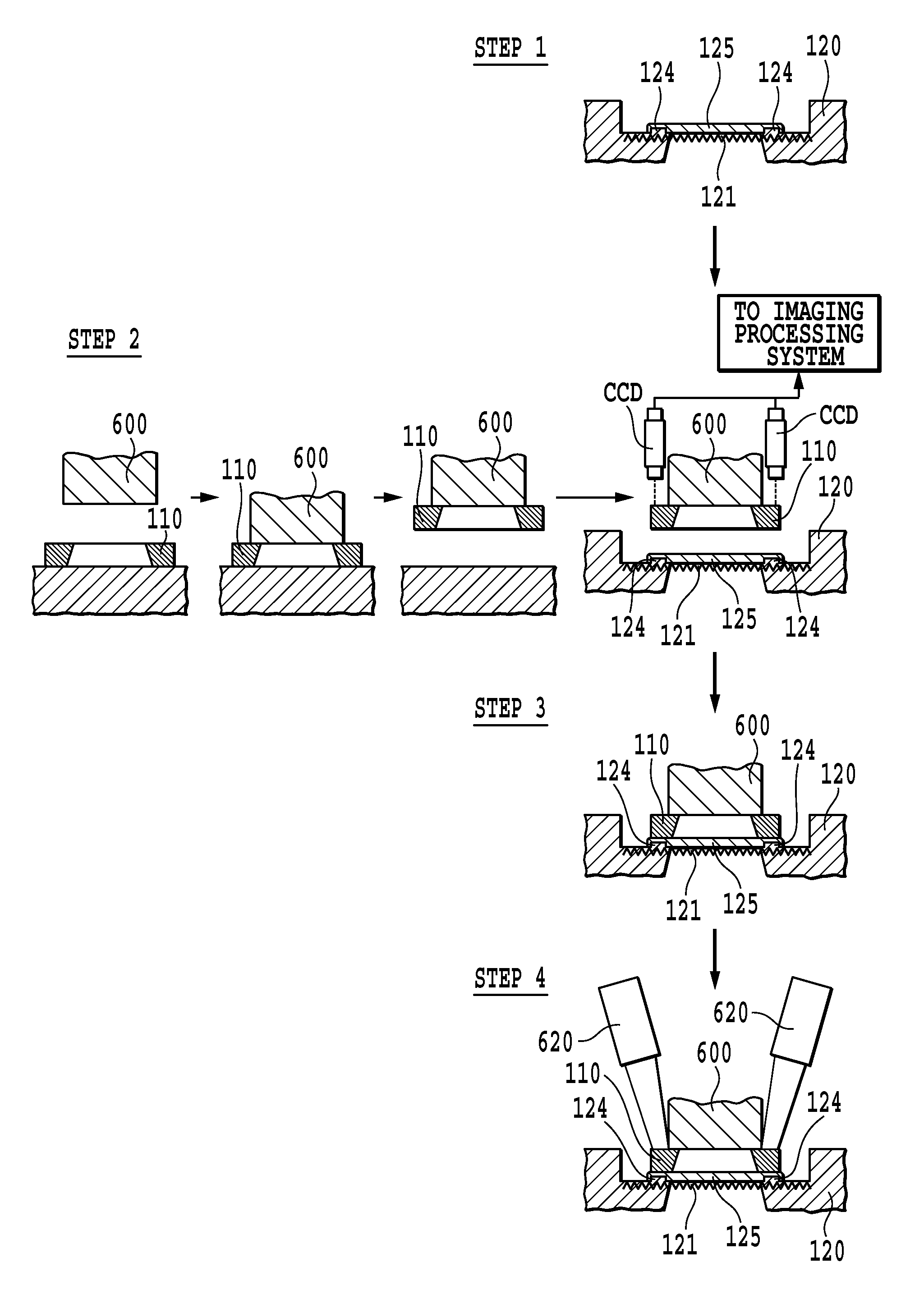
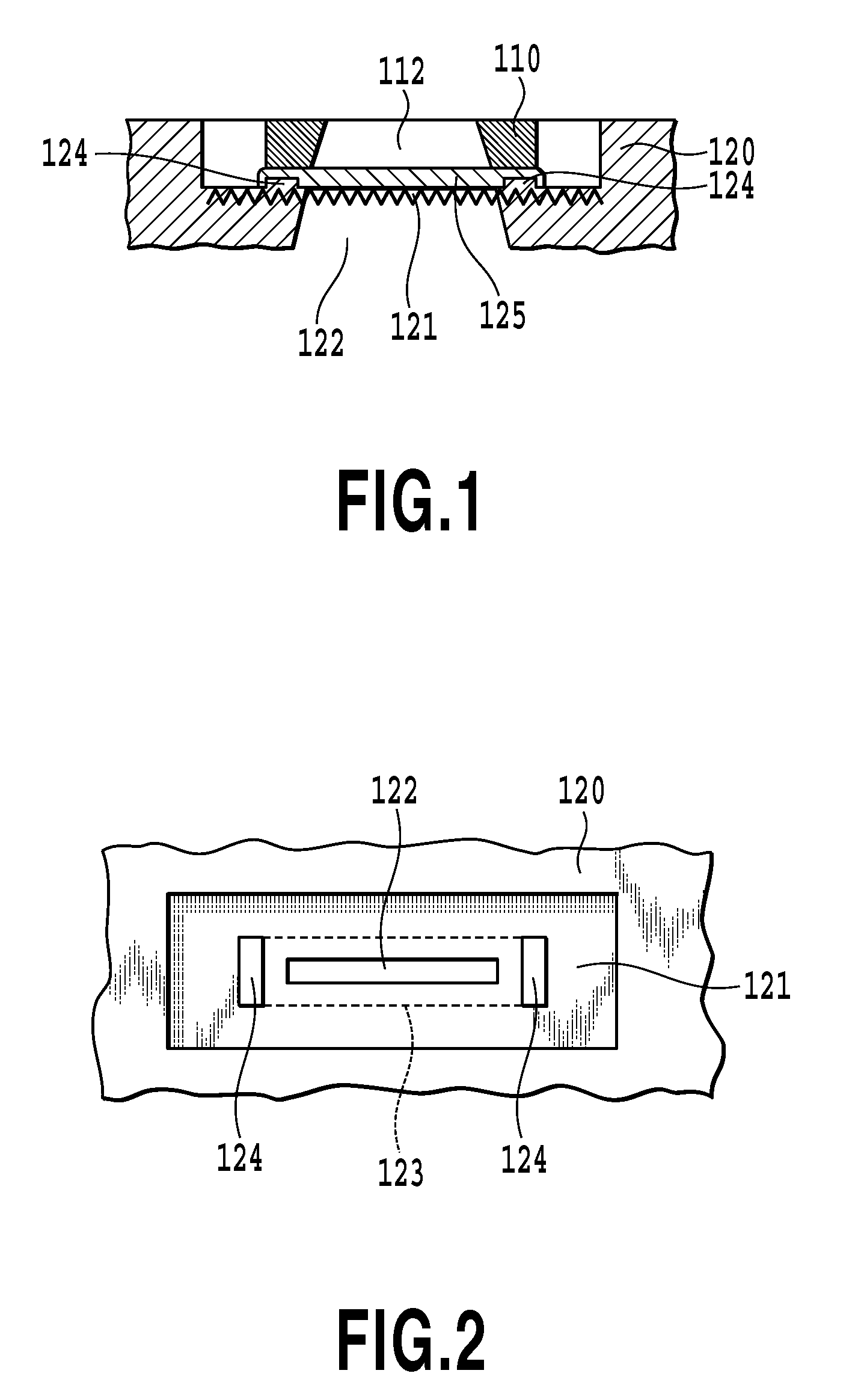
Contact terminal structure
InactiveUS20060258190A1Improve adhesionPrecise BondingFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsSolder ballEngineering
An improvement on a contact terminal structure to be disposed into the terminal block on the base of an integrated circuit, comprises a main body, a soldering end extending vertically from one end of said main body and providing with an aligning portion of an arcuate hollow shape for placing a solder ball, a supporting portion extending vertically from said main body and being used for supporting said solder ball, and a contact end extending vertically from another end of said main body and providing contortedly with a corresponding contact portion at an appropriate position thereon. This structure can allow said solder ball bond more precisely with said soldering portion on said contact terminal.
Owner:WONTEN TECH
Techniques for debris reduction when performing edge deletion on coated articles having temporary protective coatings applied thereto
InactiveUS8449348B2Reduce dispersionPrecise bondingEdge grinding machinesGrinding feed controlAspiratorEngineering
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to techniques for edge deleting coatings supported by coated articles while a temporary protective coating is applied thereto. More particularly, a stationary, enlarged, and higher powered aspirator is connected to flexible tubing, which itself has an enlarged diameter, that has a nozzle located proximate to a grinding wheel on an edge deletion unit is provided in connection with an edge deletion table. Advantageously, the edge deletion table and aspirator of certain example embodiments are capable of performing edge deletion and removal of a temporary protective coating substantially simultaneously (e.g., from a common area of interest), during which process the debris produced when edge deletion is performed is controlled and removed from the substrate of interest.
Owner:GUARDIAN EURO S A R L
Method and device of adhering polarizer onto substrate
Provided is a method for sticking a polarizing plate to a liquid crystal panel particularly suitable for sticking the polarizing plate to the large size liquid crystal panel by mounting a polarizing plate sticking unit on a conveyance line of the liquid crystal panel, thus adopting a structure with no stage and saving space and making the structure compact as far as possible. A device for sticking the polarizing plate is constructed in such a way that a release sheet E of the polarizing plate B is released so as to expose an adhesive layer and subsequently the polarizing plate B is stuck to a substrate A while transferring the substrate A such as the liquid crystal panel along the conveyance line 2 in one direction from the carry-in side to the carry-out side.
Owner:SHARP KK
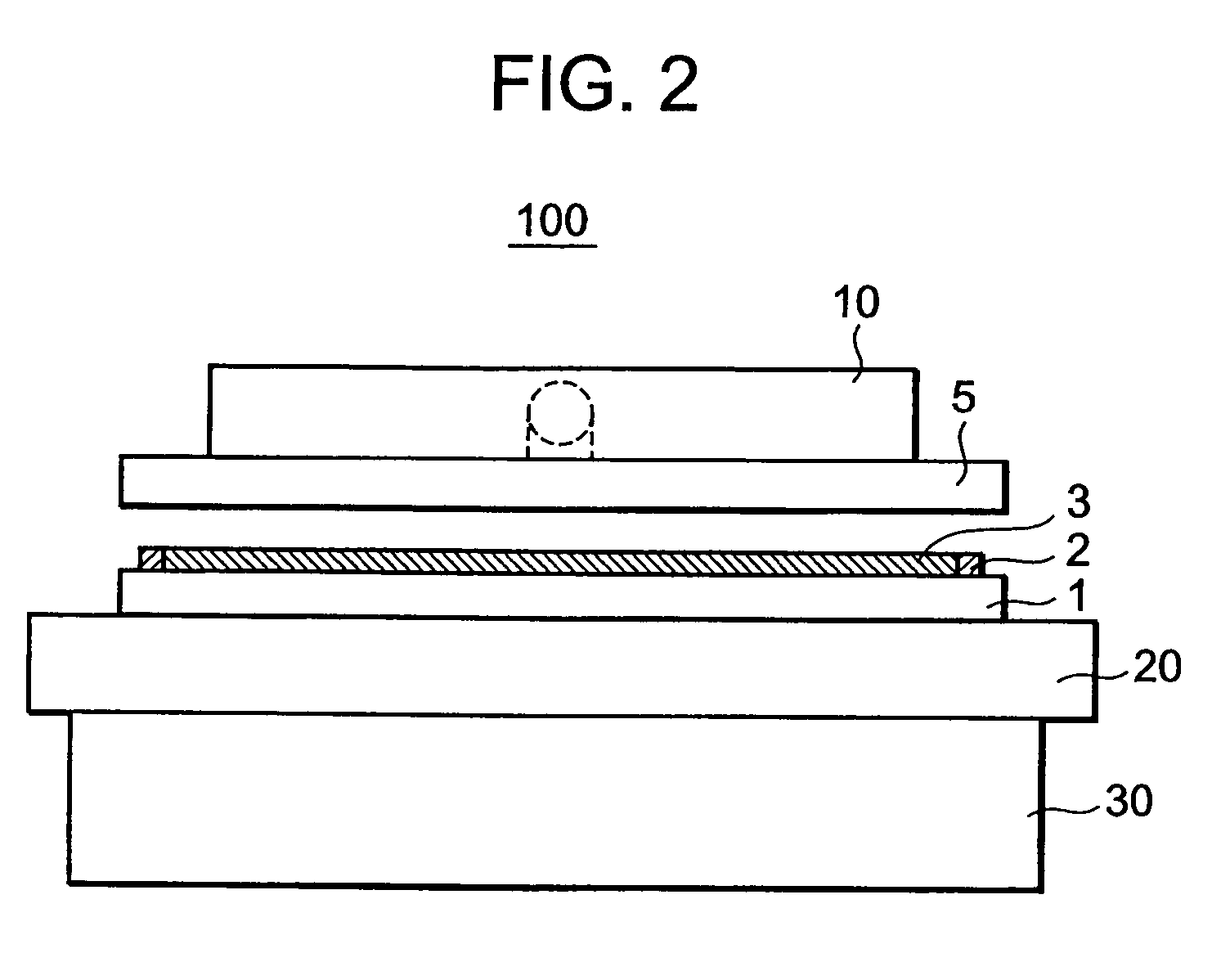
Solid-state imaging device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20040189855A1Avoid flowApply evenlyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveElectrical and Electronics engineering
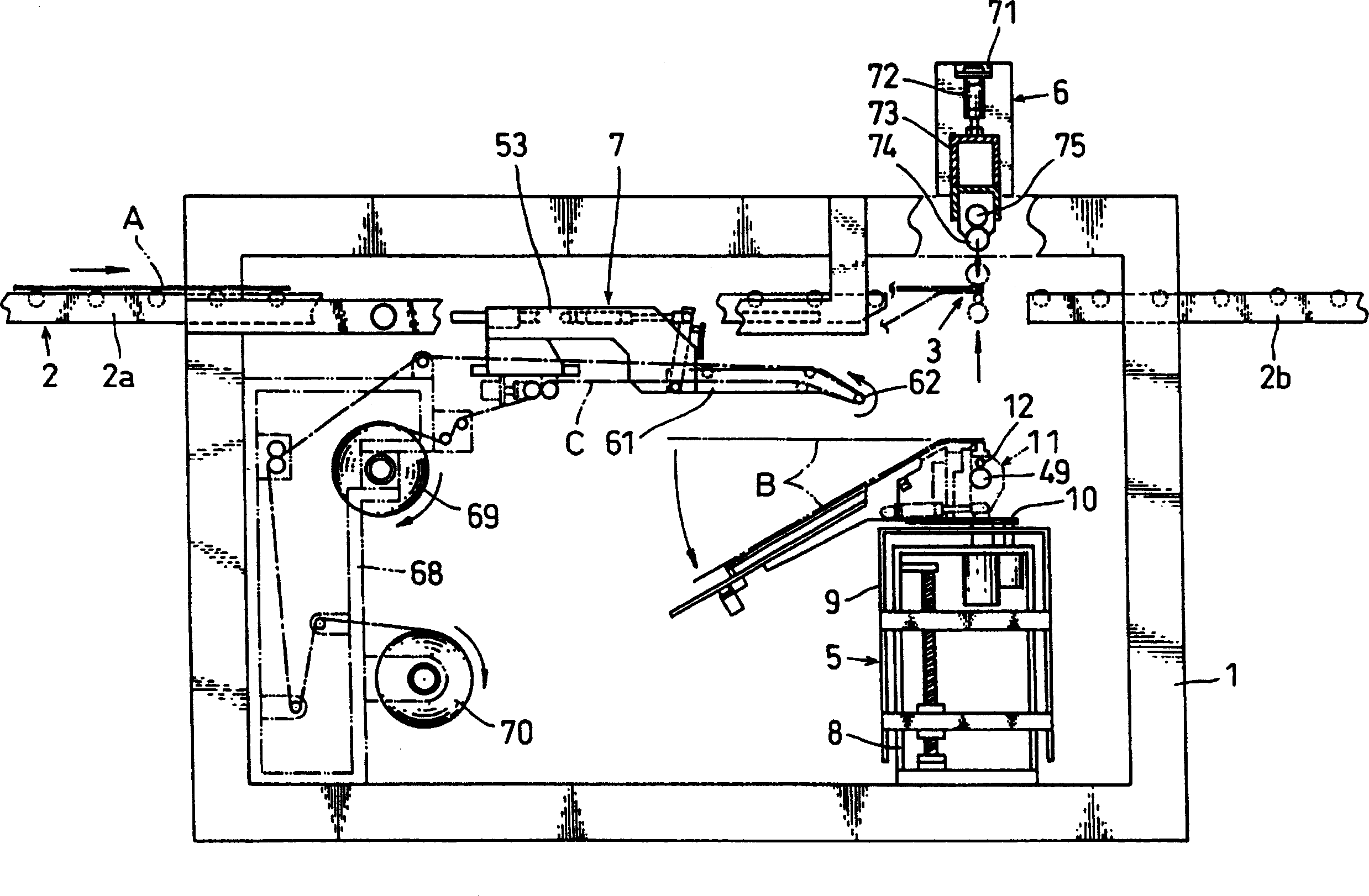
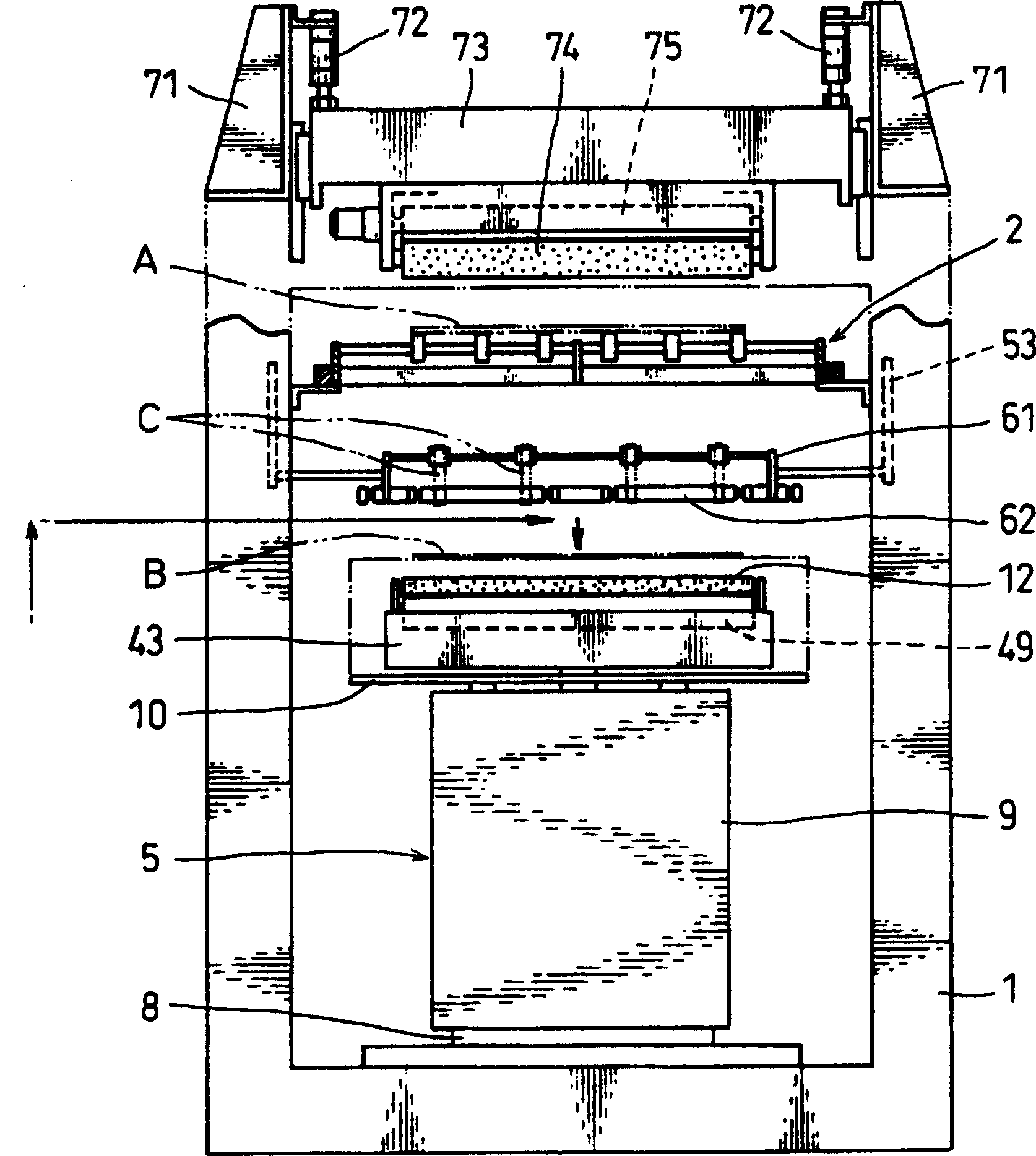
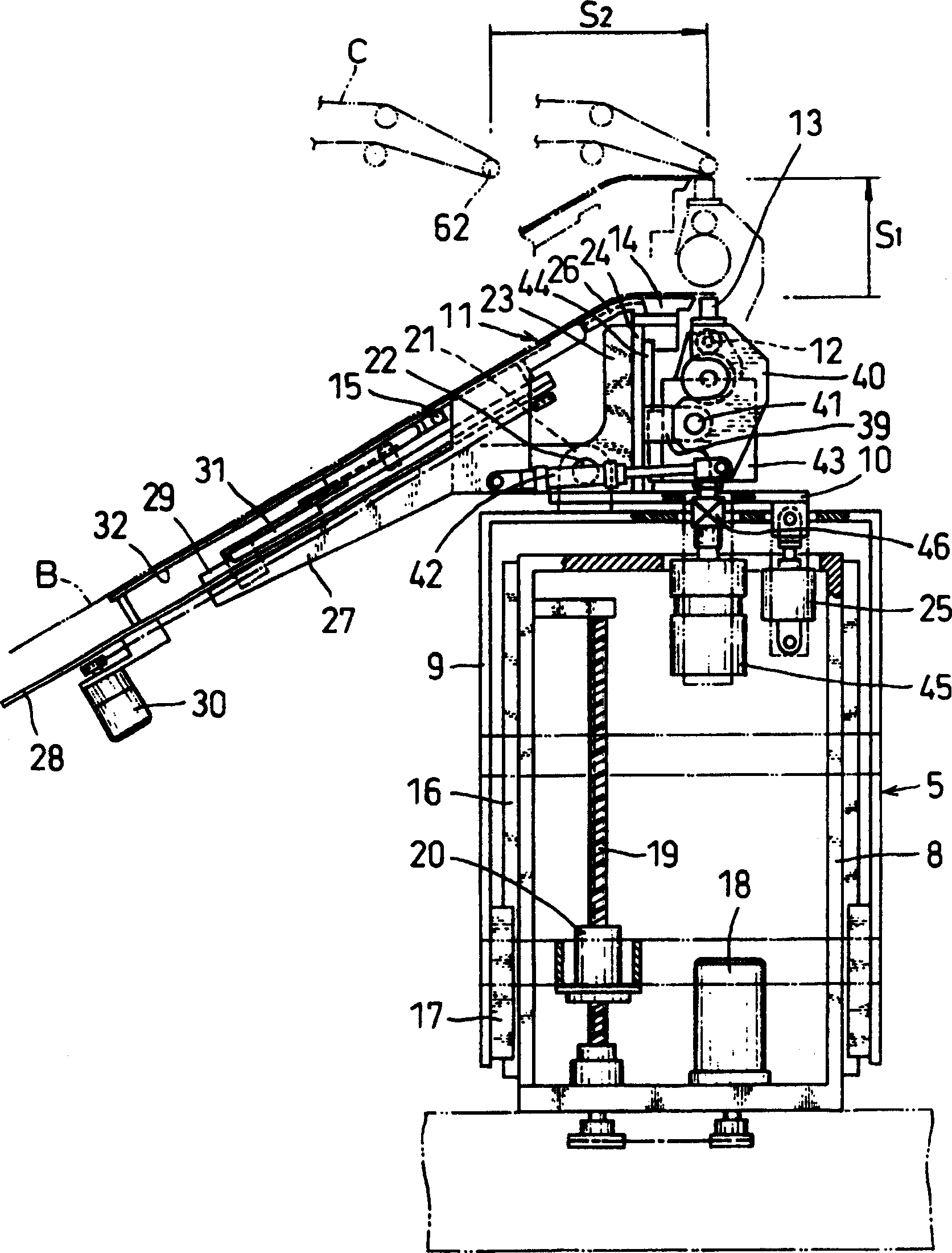
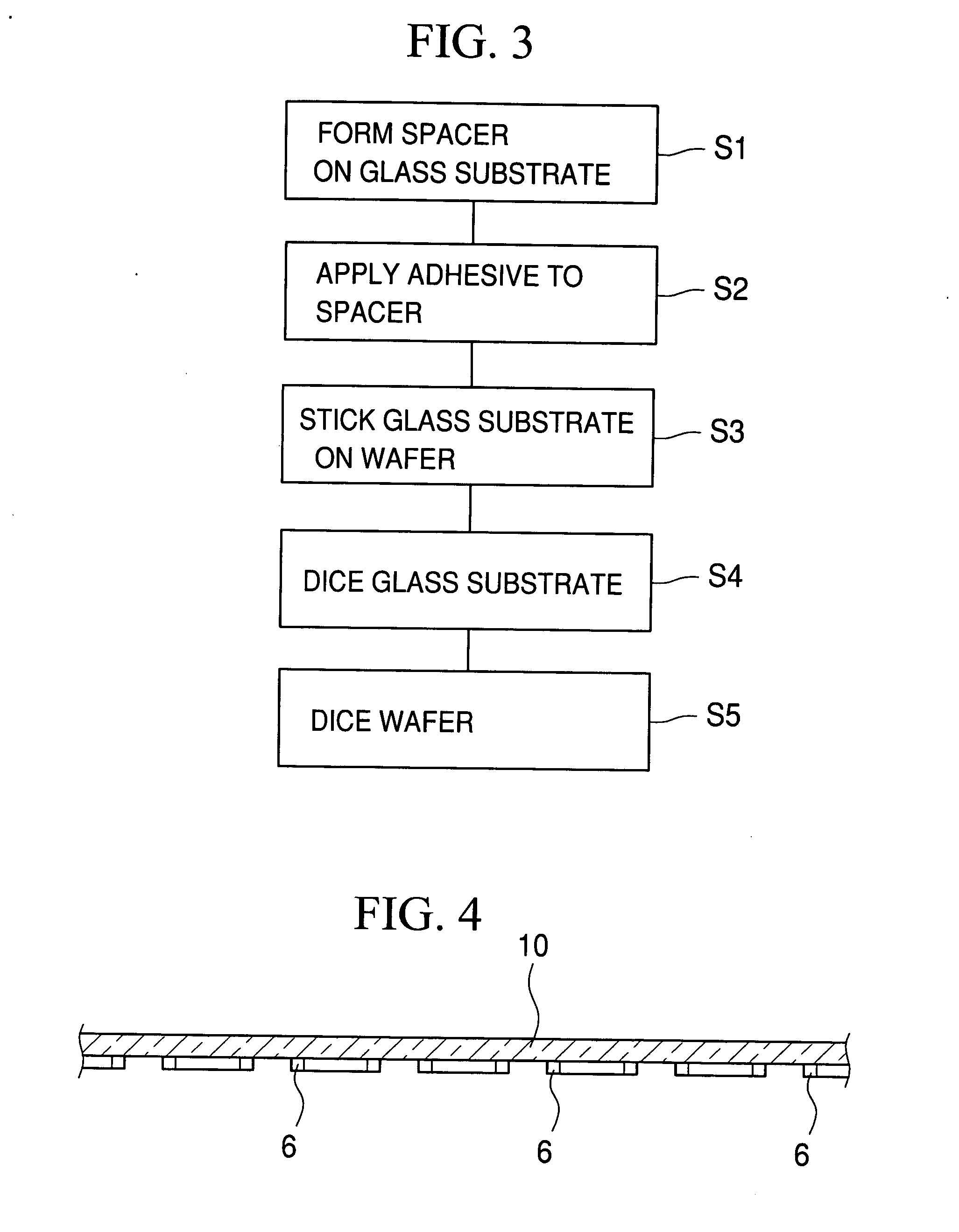
A transfer film, on which an adhesive is applied, is glued to plural spacers formed on a glass substrate. The glass substrate is laid on a working table, and one end of the transfer film is fixed to a winding roller. A peeling guide is set at a position over the transfer film. The winding roller is driven to wind the transfer film while the working table moves horizontally. While winding the transfer film, the angle between the glass substrate and the transfer film is kept constant. After the transfer film is peeled off, the adhesive is uniformly transferred to each of the spacers.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
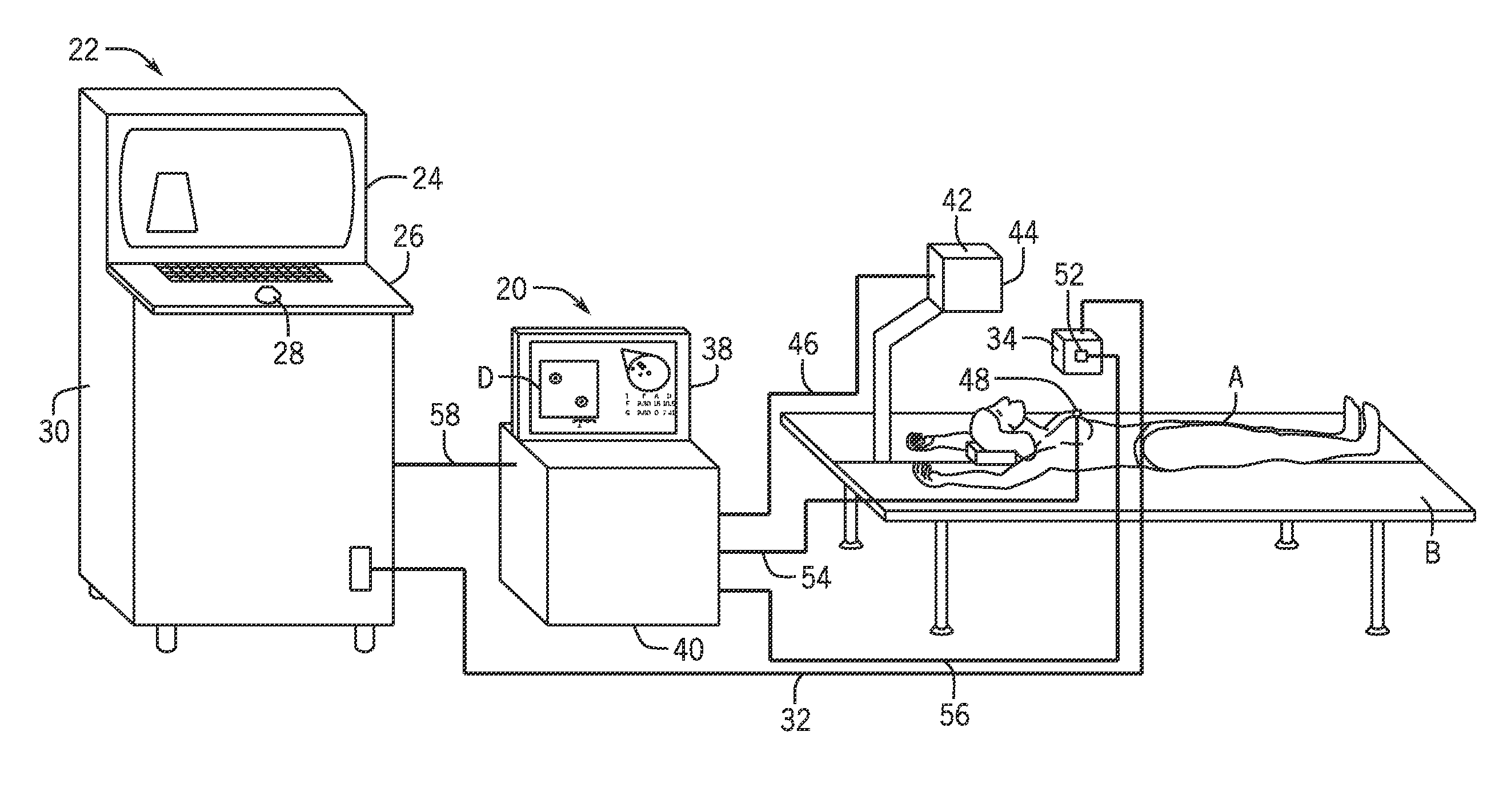
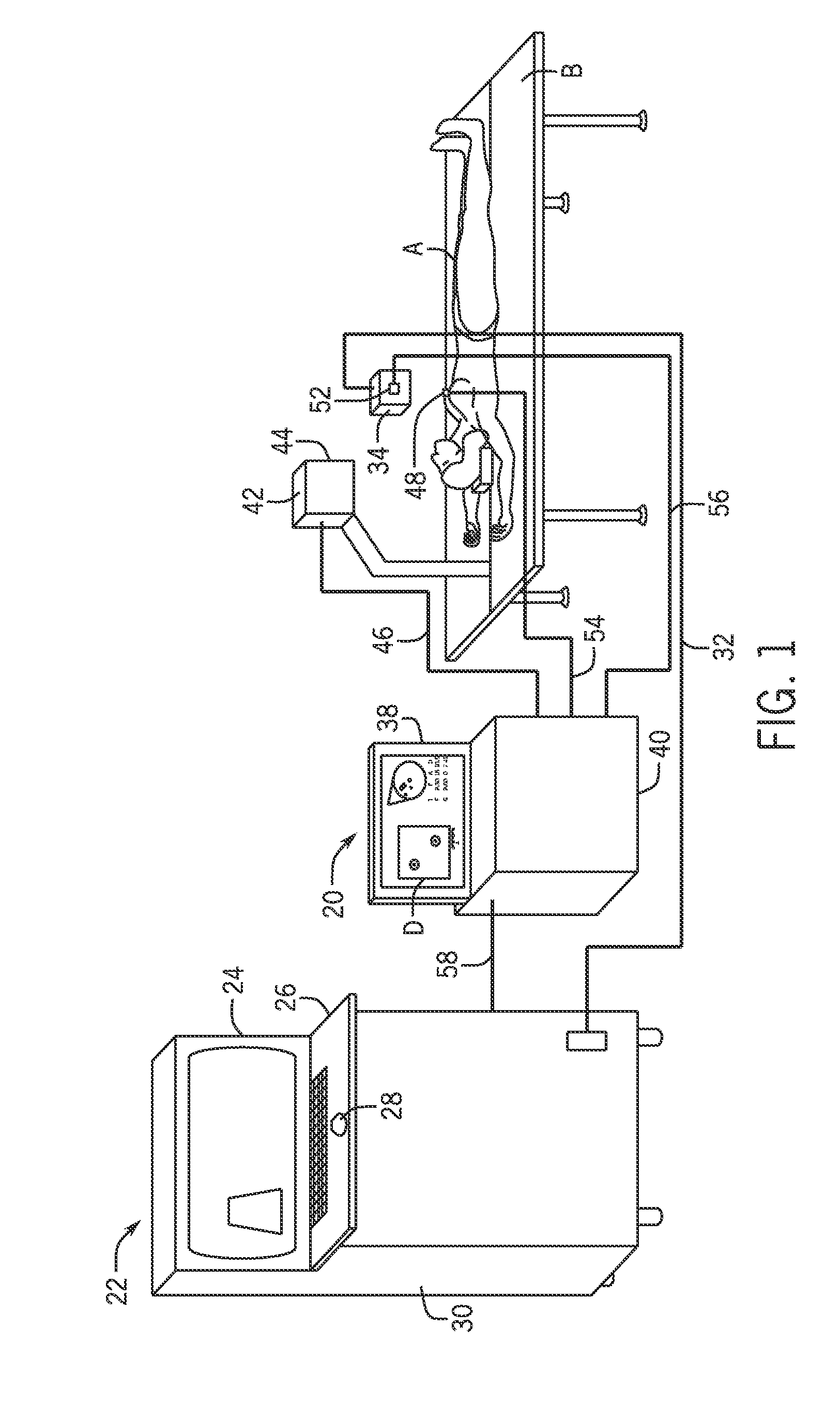
Sensor Attachment for Three Dimensional Mapping Display Systems for Diagnostic Ultrasound Machines
ActiveUS20150011858A1Shorten the timePrecise positioningOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic ultrasoundBiomedical engineering
A sensor attachment for use with three dimensional ultrasound mapping devices is presented. According to the invention, one or more sensors are attached to specific locations on the body, such as the nipple and sternum, the inventive sensor attachments enabling accurate recording of target information, including location and size; the present invention especially helpful in subsequent and comparative examinations. A method of use is also presented.
Owner:METRITRACK
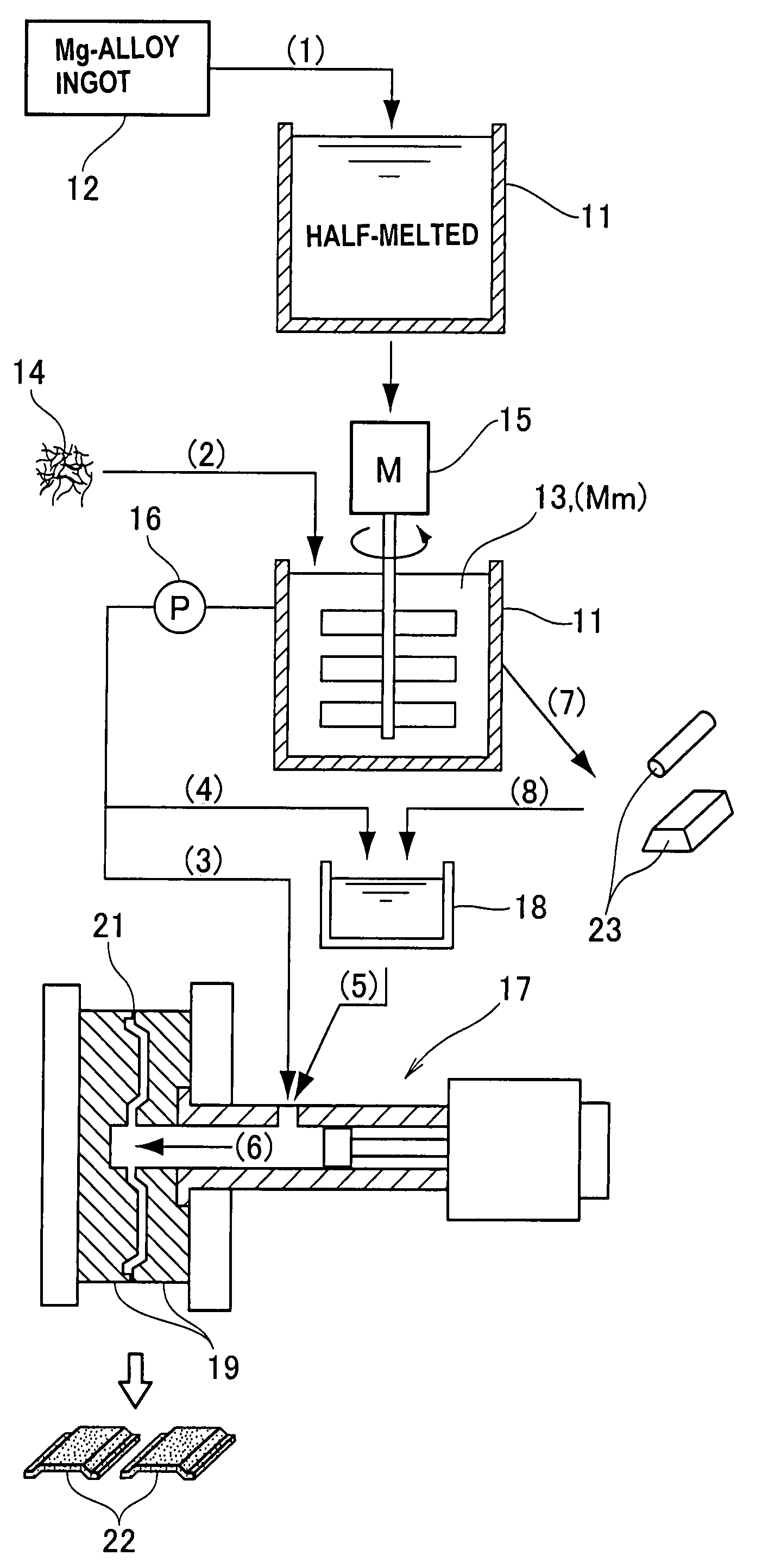
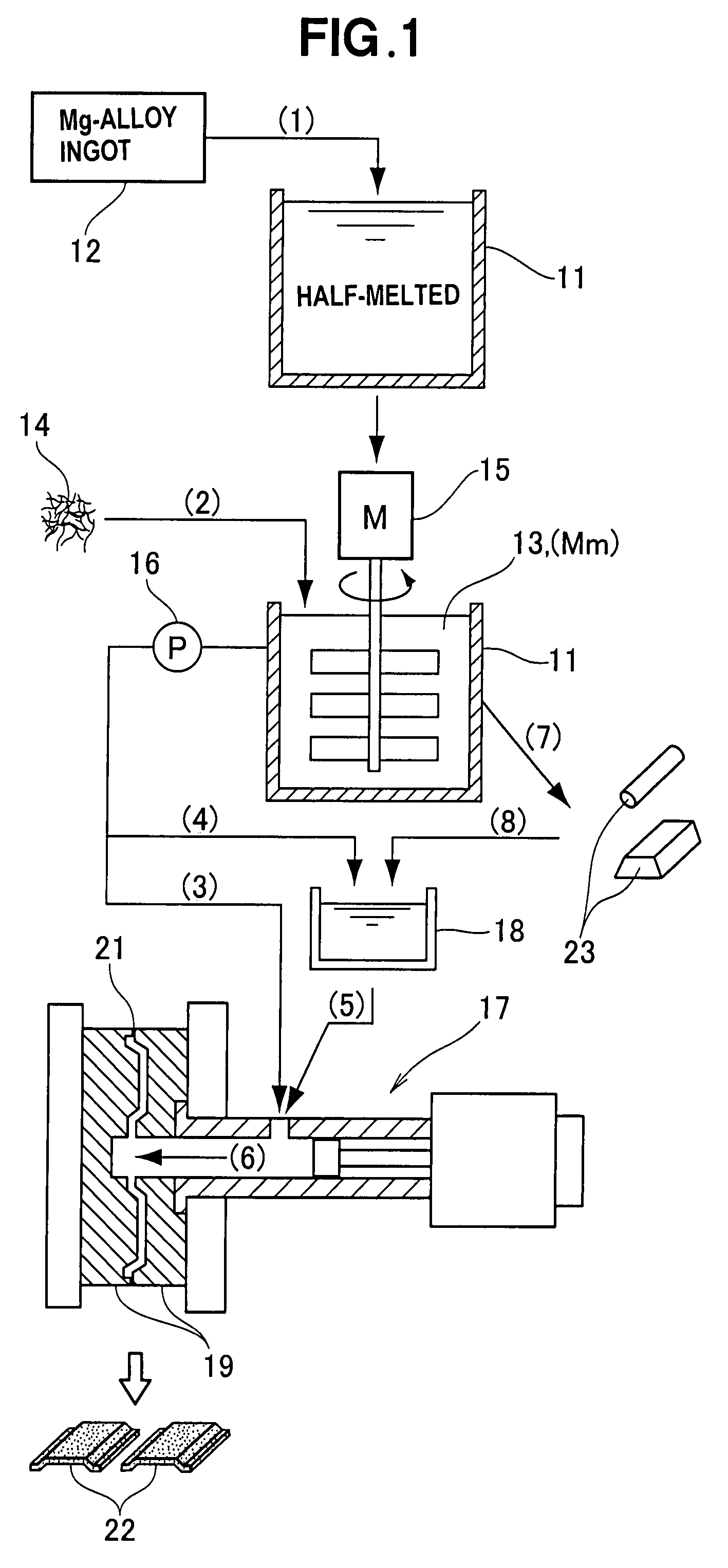
Method for manufacturing composite metal material and method for manufacturing composite-metal molded article
InactiveUS7712512B2Improve wettabilityPrecise BondingAngiosperms/flowering plantsMolten stateMetal alloy
A method for manufacturing a composite metal material combined with a nanocarbon material comprises heating a metal alloy to a half-melted state in which both liquid and solid phases are present. Next, a nongraphitized nanocarbon material is added to the half-melted metal alloy and stirred to form a composite metal material combined with a nanocarbon.
Owner:NISSEI PLASTIC IND CO LTD
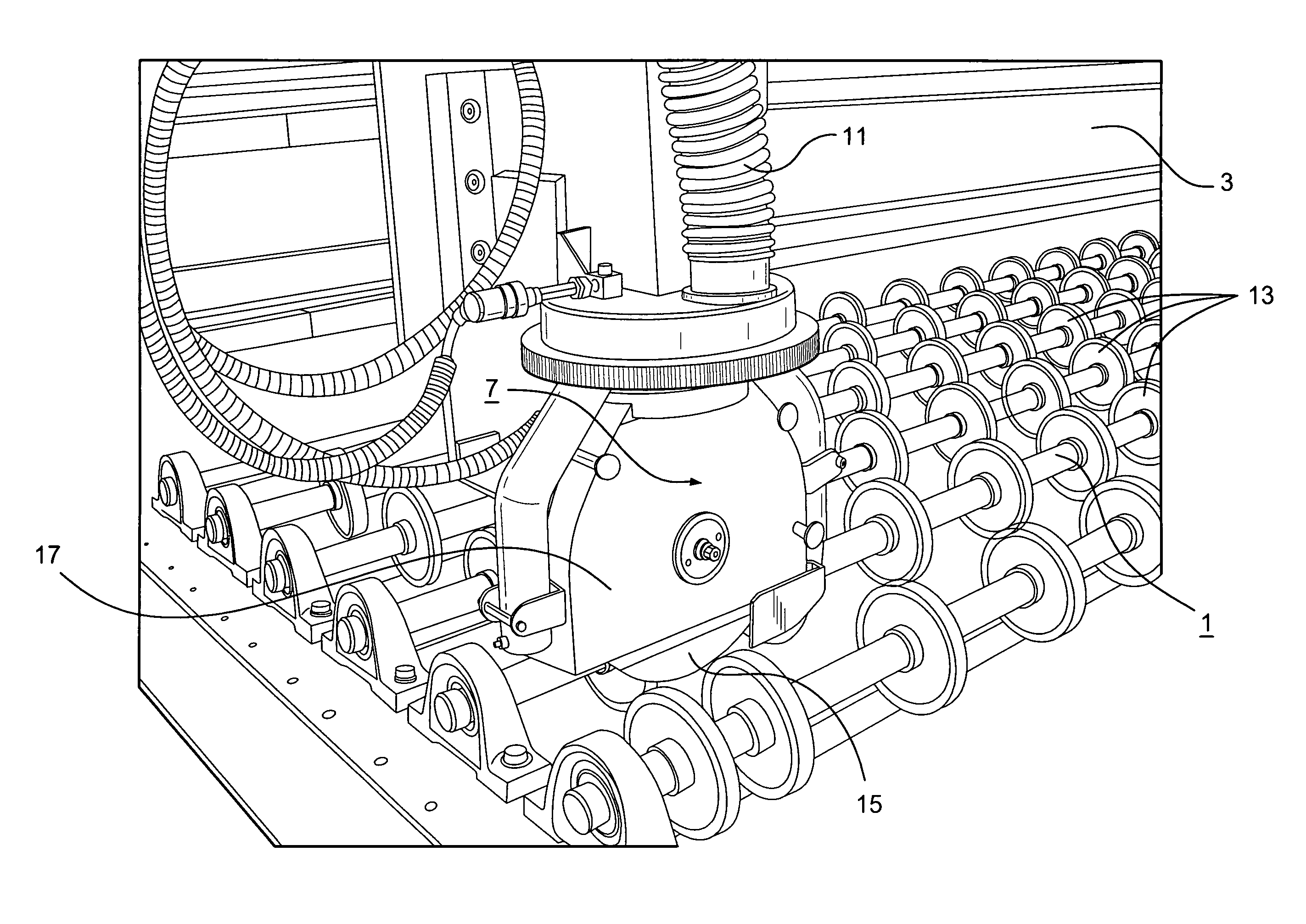
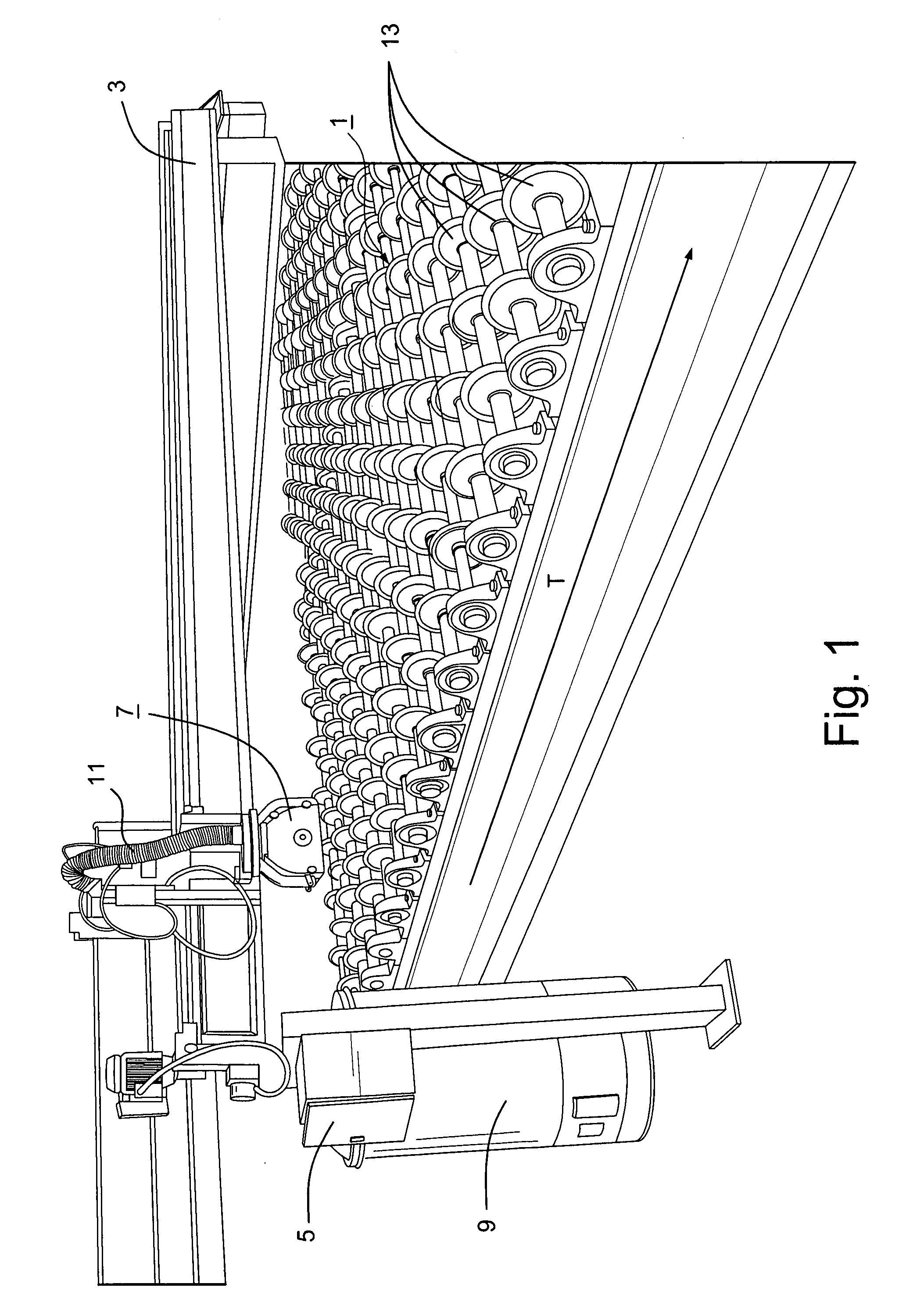
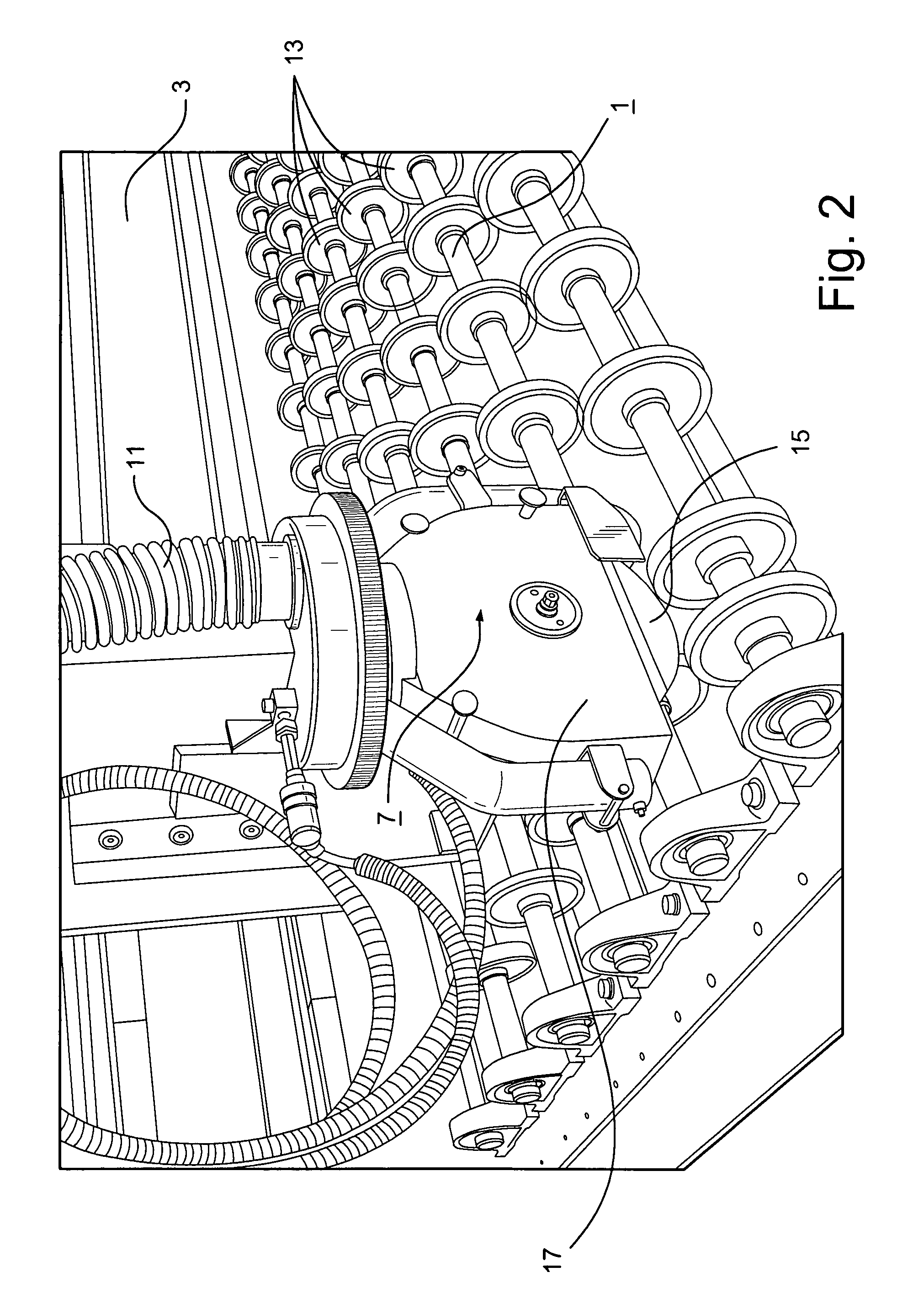
Method for producing a continuous bonding agent carpet and road finisher
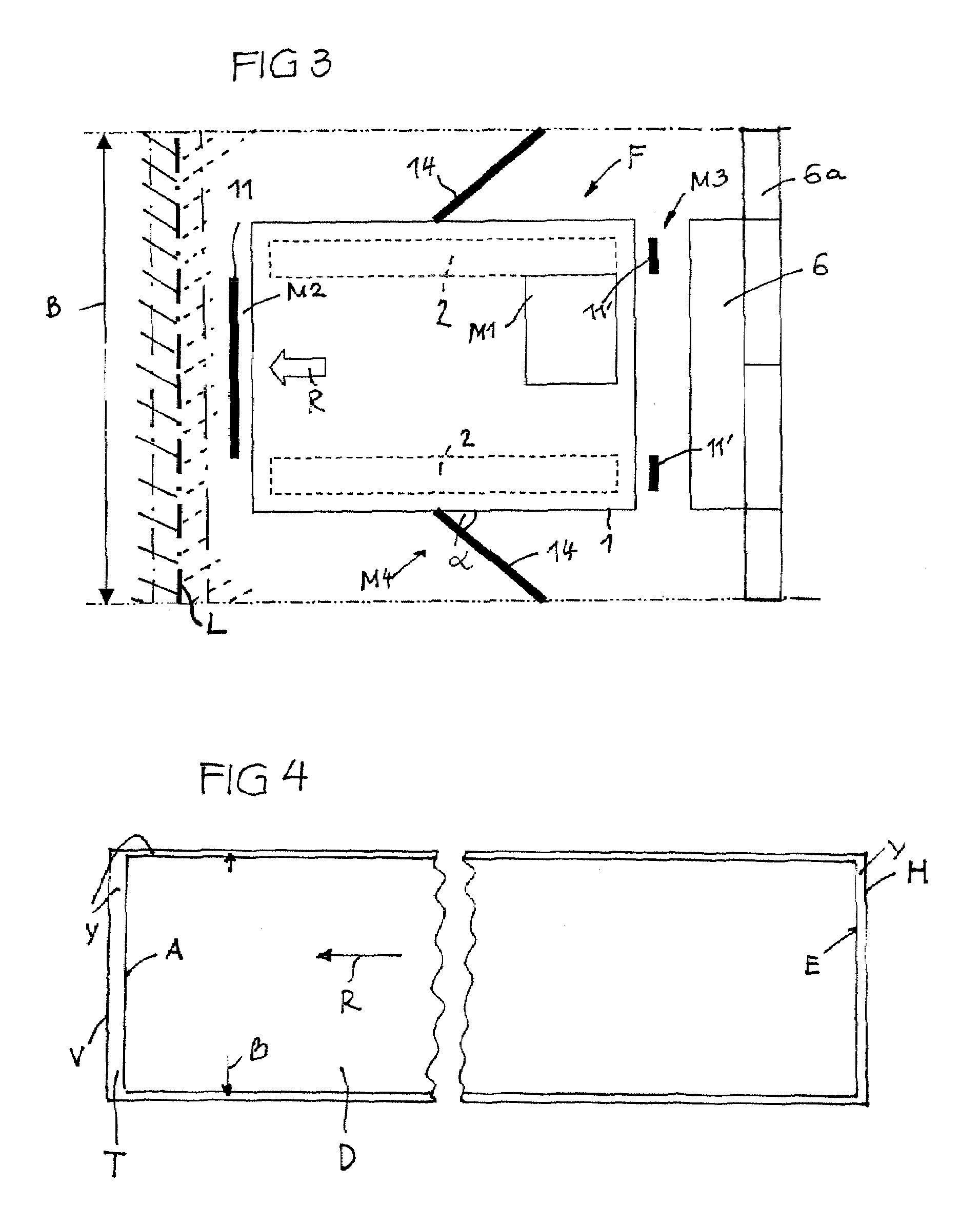
A road finisher F for producing a continuous sprayed carpet T of a bonding agent on a planum has a spraying system S on a vehicle having at least two spraying facilities 11, 11′, 14, 14′ which are located offset to each other in the and laterally to the traveling motion direction R and a control device which operates the spraying facilities using a method such that during a traveling motion of the vehicle a sprayed carpet T is produced with front and rear boundaries V, H which are continuous over the width of the sprayed carpet and which are parallel to a respective reference line L which is placed on the planum in front of the spraying facility which is the frontmost in traveling motion direction. The sprayed carpet T is produced such that each spraying facility 11, 11′, 14, 14′ first is activated or deactivated depending on the traveling motion with a predetermined distance from the or when reaching the respective reference line L.
Owner:JOSEPH VOEGELE AG
Method for producing a continuous bonding agent carpet and road finisher
A road finisher F for producing a continuous sprayed carpet T of a bonding agent on a planum has a spraying system S on a vehicle having at least two spraying facilities 11, 11′, 14, 14′ which are located offset to each other in the and laterally to the traveling motion direction R and a control device which operates the spraying facilities using a method such that during a traveling motion of the vehicle a sprayed carpet T is produced with front and rear boundaries V, H which are continuous over the width of the sprayed carpet and which are parallel to a respective reference line L which is placed on the planum in front of the spraying facility which is the frontmost in traveling motion direction. The sprayed carpet T is produced such that each spraying facility 11, 11′, 14, 14′ first is activated or deactivated depending on the traveling motion with a predetermined distance from the or when reaching the respective reference line L.
Owner:JOSEPH VOEGELE AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com