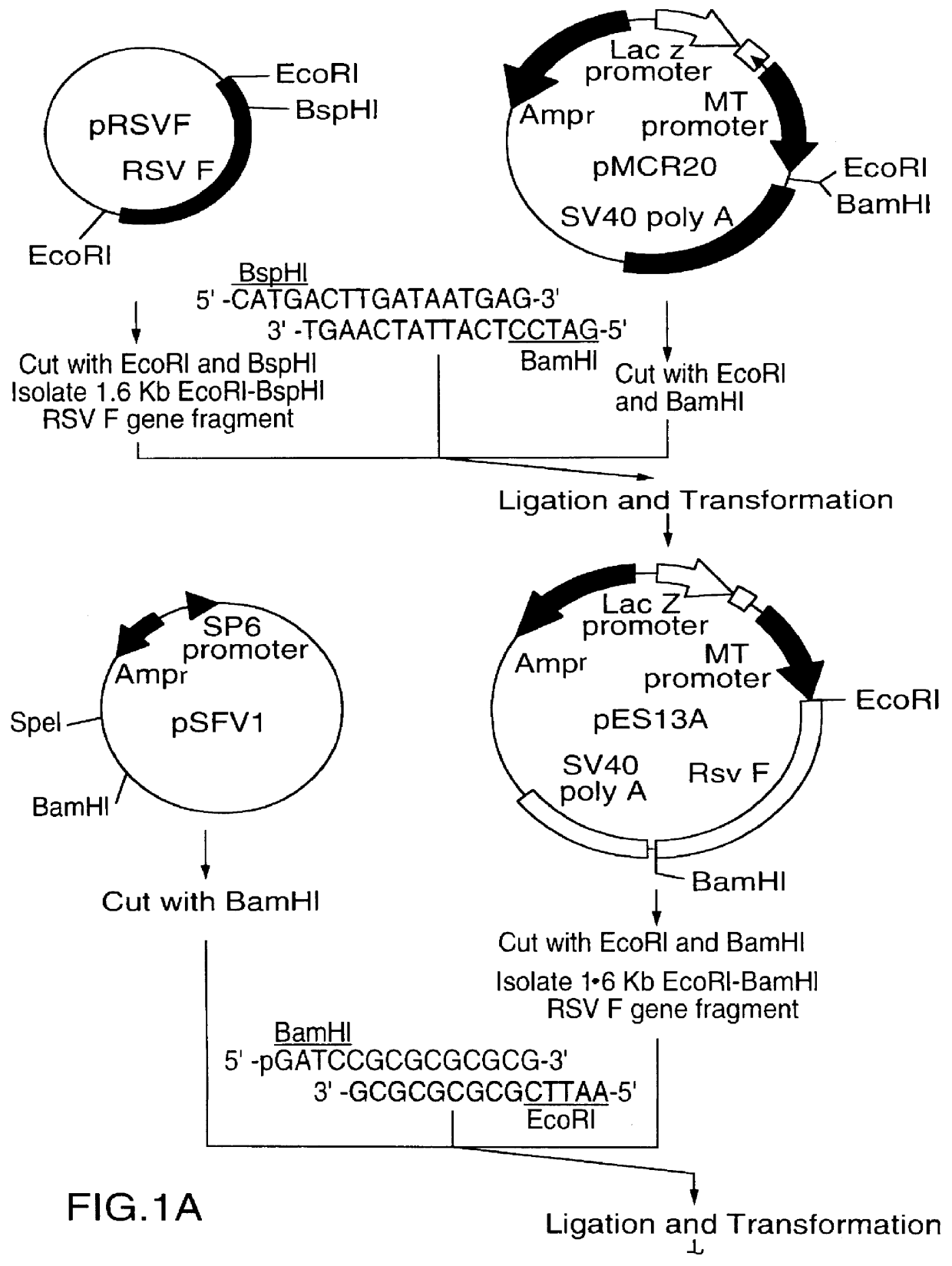
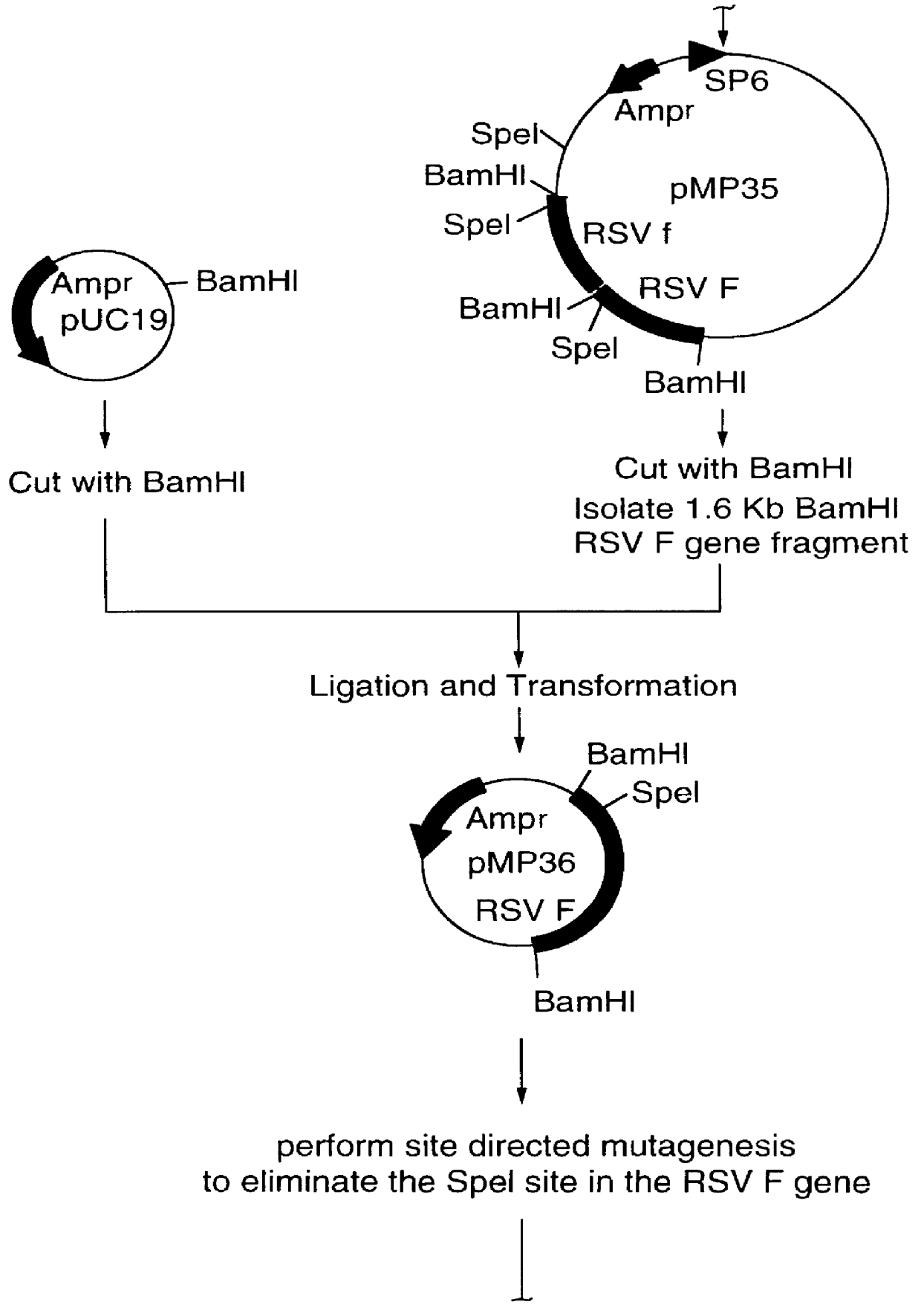
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vaccines or candidate vaccines used to prevent infection with RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUSES.
RNA respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6060308AFaster replicationImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideF proteinViral Vaccine
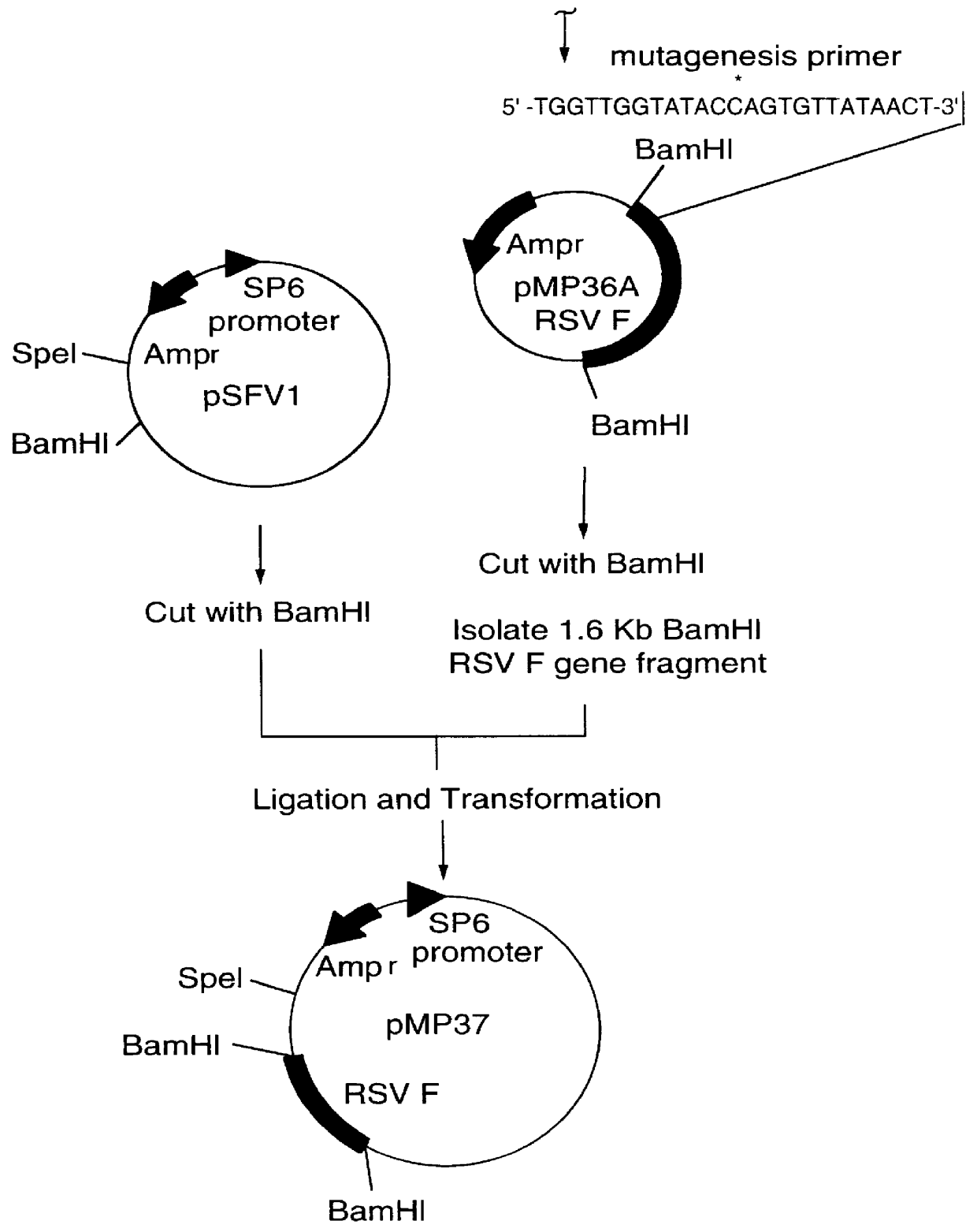
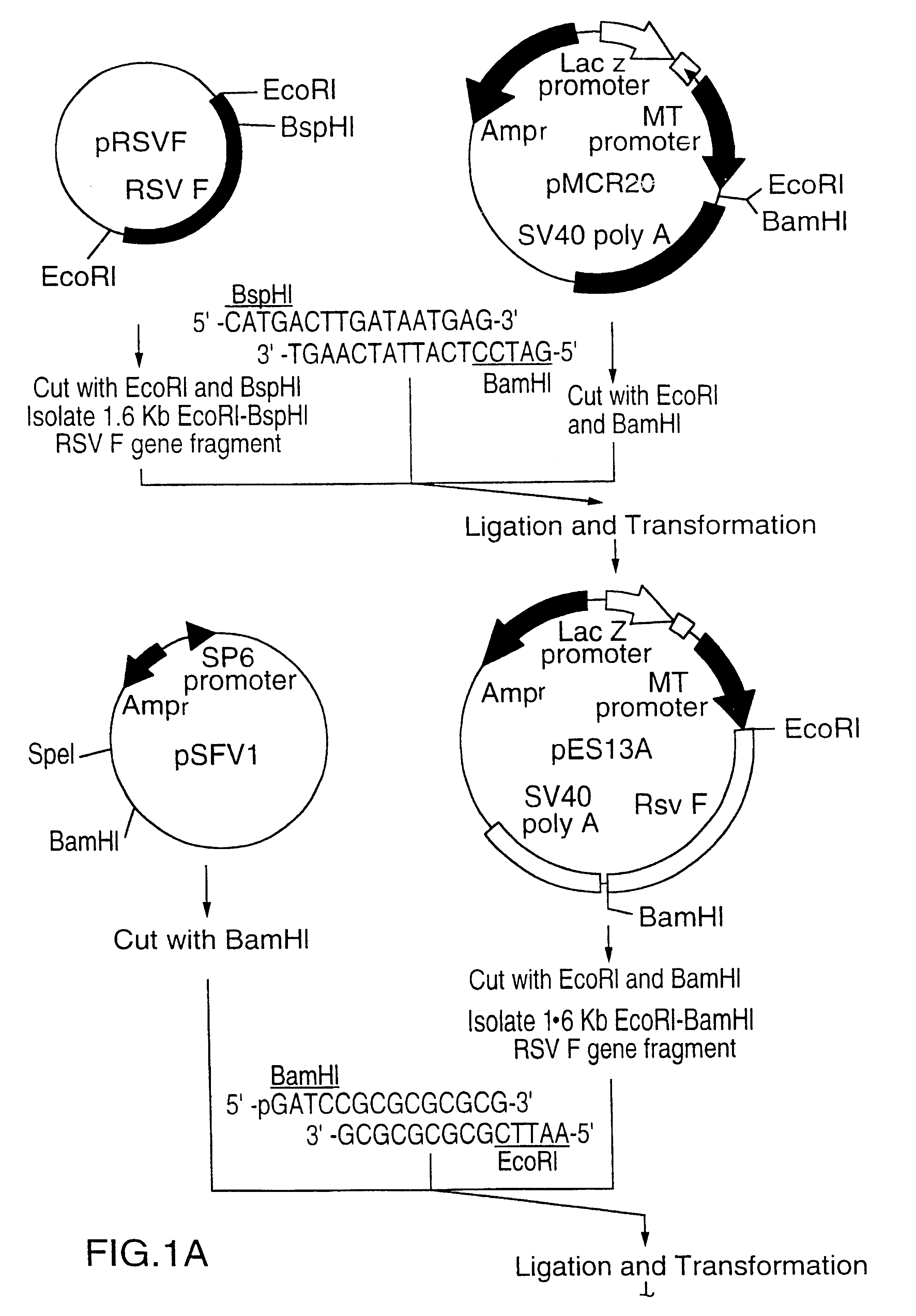
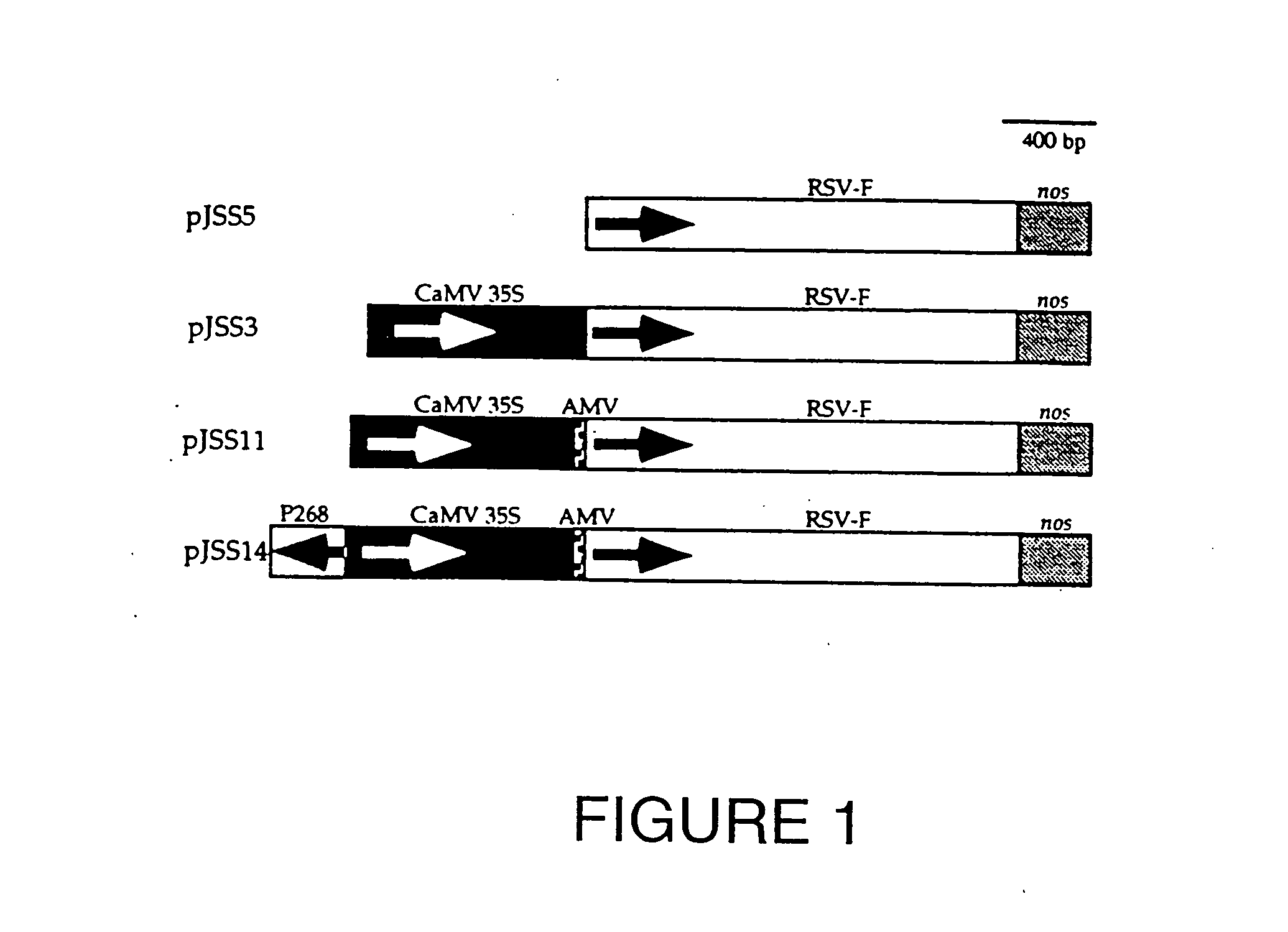
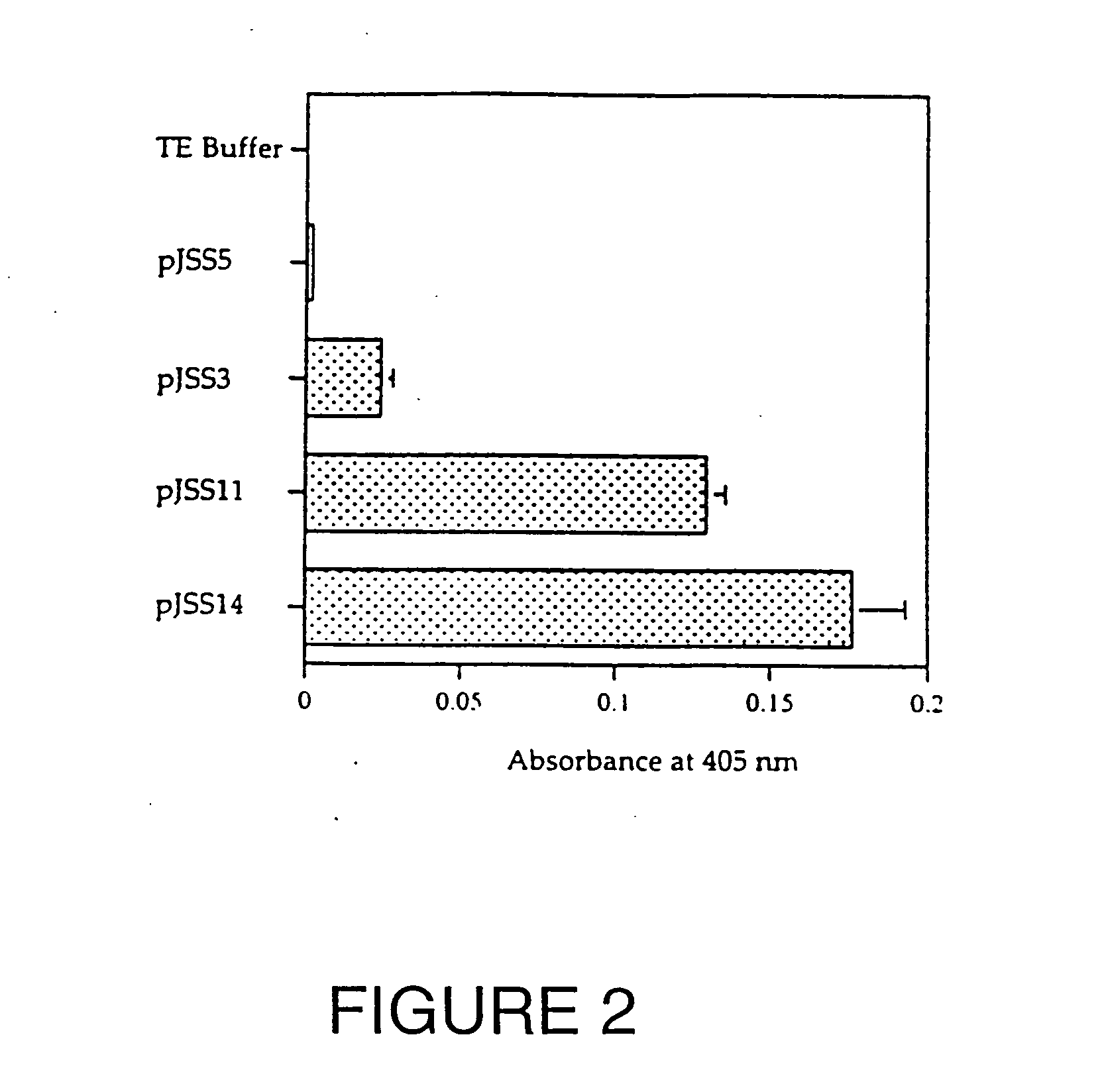
A vector comprising a first DNA sequence which is complementary to at least part of an alphavirus RNA genome and having the complement of complete alphavirus DNA genome replication regions, a second DNA sequence encoding a paramyxovirus protein, particularly a respiratory syncytial virus fusion (RSV F) protein or a RSV F protein fragment that generates antibodies that specifically react with RSV F protein, the first and second DNA sequences being under the transcriptional control of a promoter is described. Such vector may be used to produce an RNA transcript which may be used to immunize a host, including a human host, to protect the host against disease caused by paramyxovirus, particularly respiratory syncytial virus, by administration to the host.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Nucleic acid respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6083925AGood immune protectionImprove expression levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousF protein
Non-replicating vectors containing a nucleotide sequence coding for an F protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and a promoter for such sequence, preferably a cytomegalovirus promoter, are described for in vivo immunization. The nucleotide sequence encloding the RSV F protein may lack a sequence encoding the homologous signal peptide but possessing a heterologous signal peptide enhancing RSV F protein expression. Such non-replicating vectors, including plasmids, also may contain a further nucleotide sequence located adjacent to the RSV F protein encoding sequence to enhance the immunoprotective ability of the RSV F protein when expressed in vivo. Such non-replicating vectors may be used to immunize a host against disease caused by infection with RSV, including a human host, by administration thereto, and may be formulated as immunogenic compositions with pharmaceutically-acceptable carriers for such purpose. Such vectors also may be used to produce antibodies for detection of RSV infection in a sample.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Nucleic acid respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6486135B1Good immune protectionImprove expression levelSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousF protein
Non-replicating vectors containing a nucleotide sequence coding for an F protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and a promoter for such sequence, preferably a cytomegalovirus promoter, are described for in vivo immunization. The nucleotide sequence encloding the RSV F protein may lack a sequence encoding the homologous signal peptide but possessing a heterologous signal peptide enhancing RSV F protein expression. Such non-replicating vectors, including plasmids, also may contain a further nucleotide sequence located adjacent to the RSV F protein encoding sequence to enhance the immunoprotective ability of the RSV F protein when expressed in vivo. Such non-replicating vectors may be used to immunize a host against disease caused by infection with RSV, including a human host, by administration thereto, and may be formulated as immunogenic compositions with pharmaceutically-acceptable carriers for such purpose. Such vectors also may be used to produce antibodies for detection of RSV infection in a sample.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Subunit respiratory syncytial virus vaccine preparation
InactiveUS6020182ASlow and sustained releaseImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsIon exchangeViral Vaccine
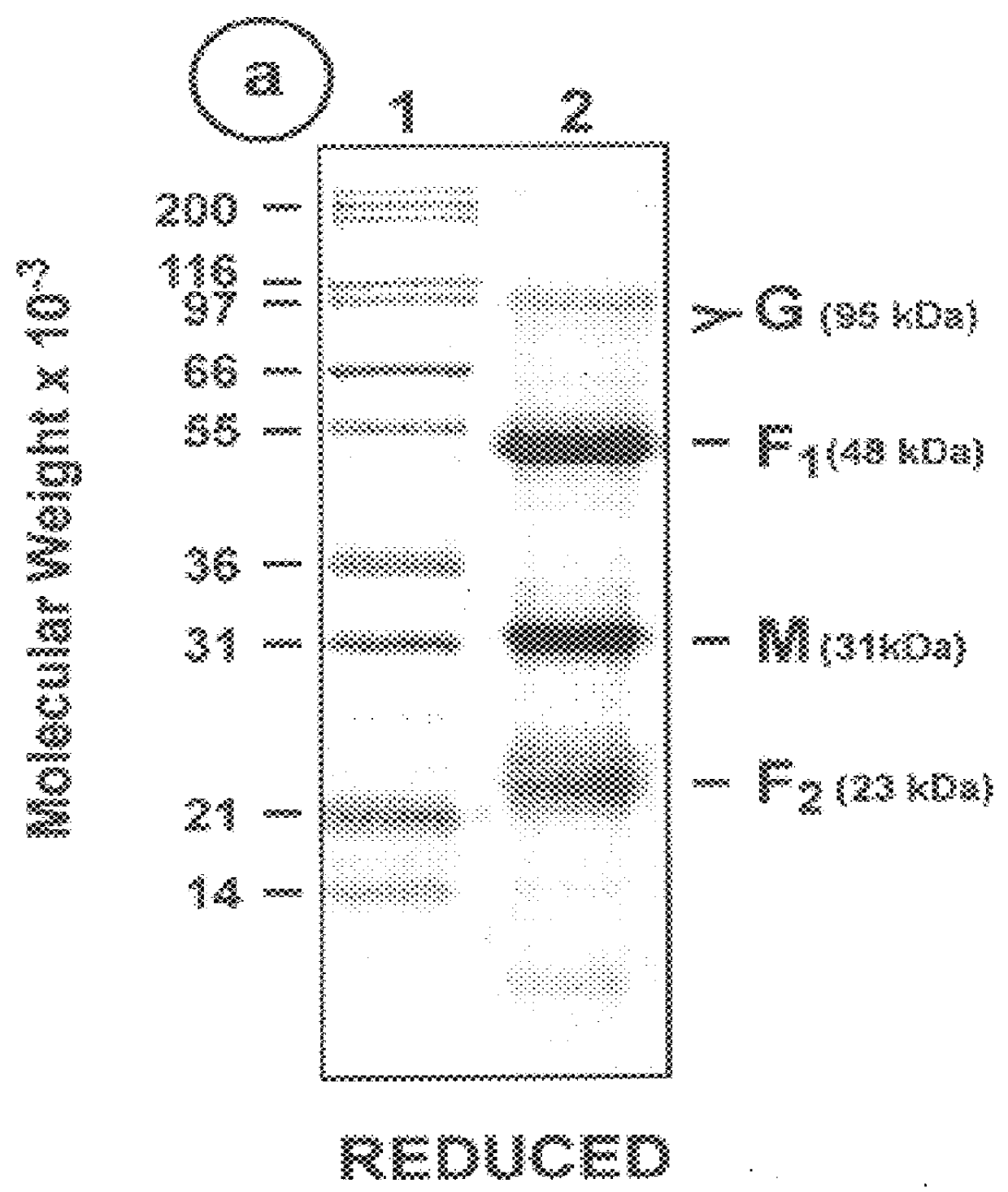
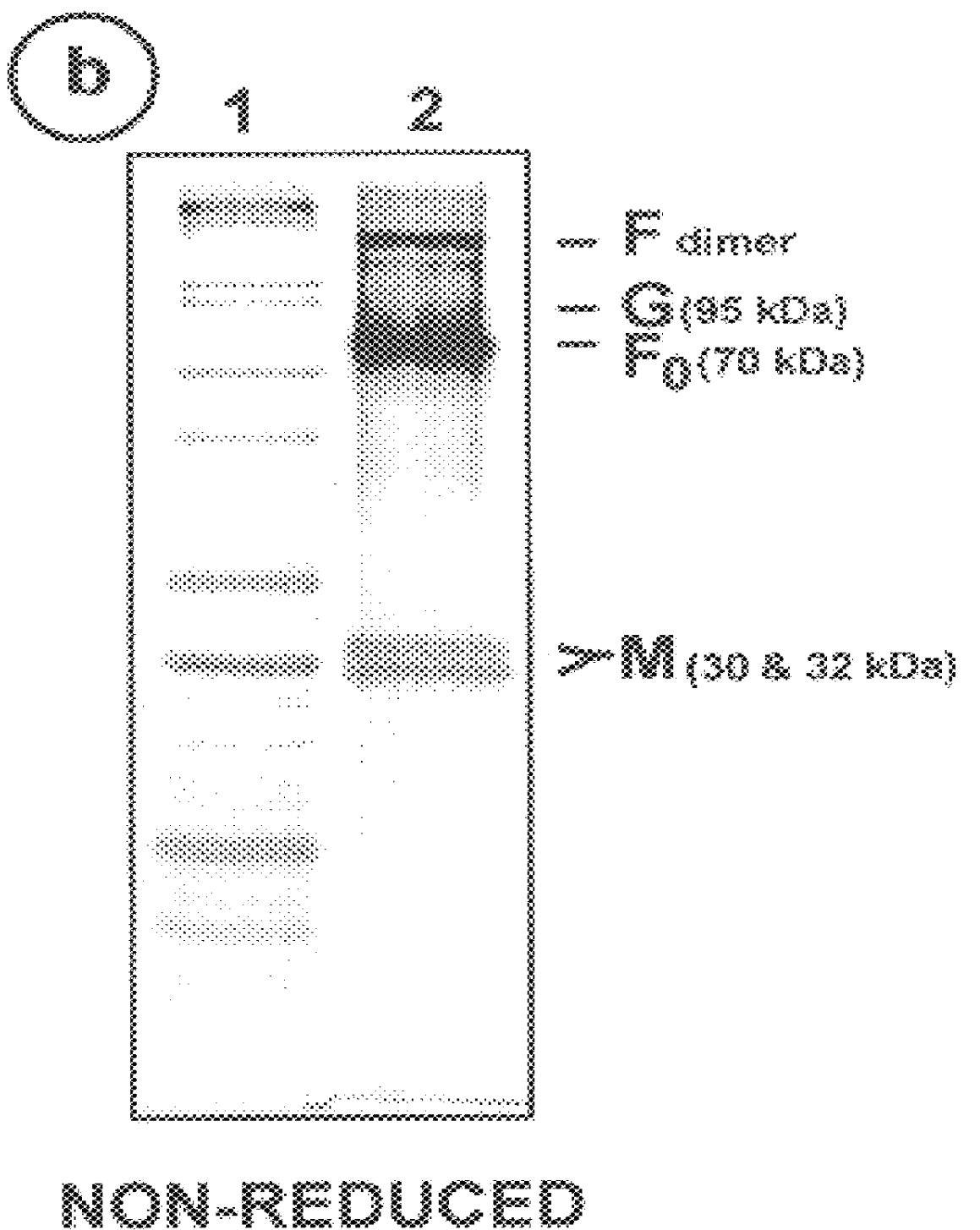
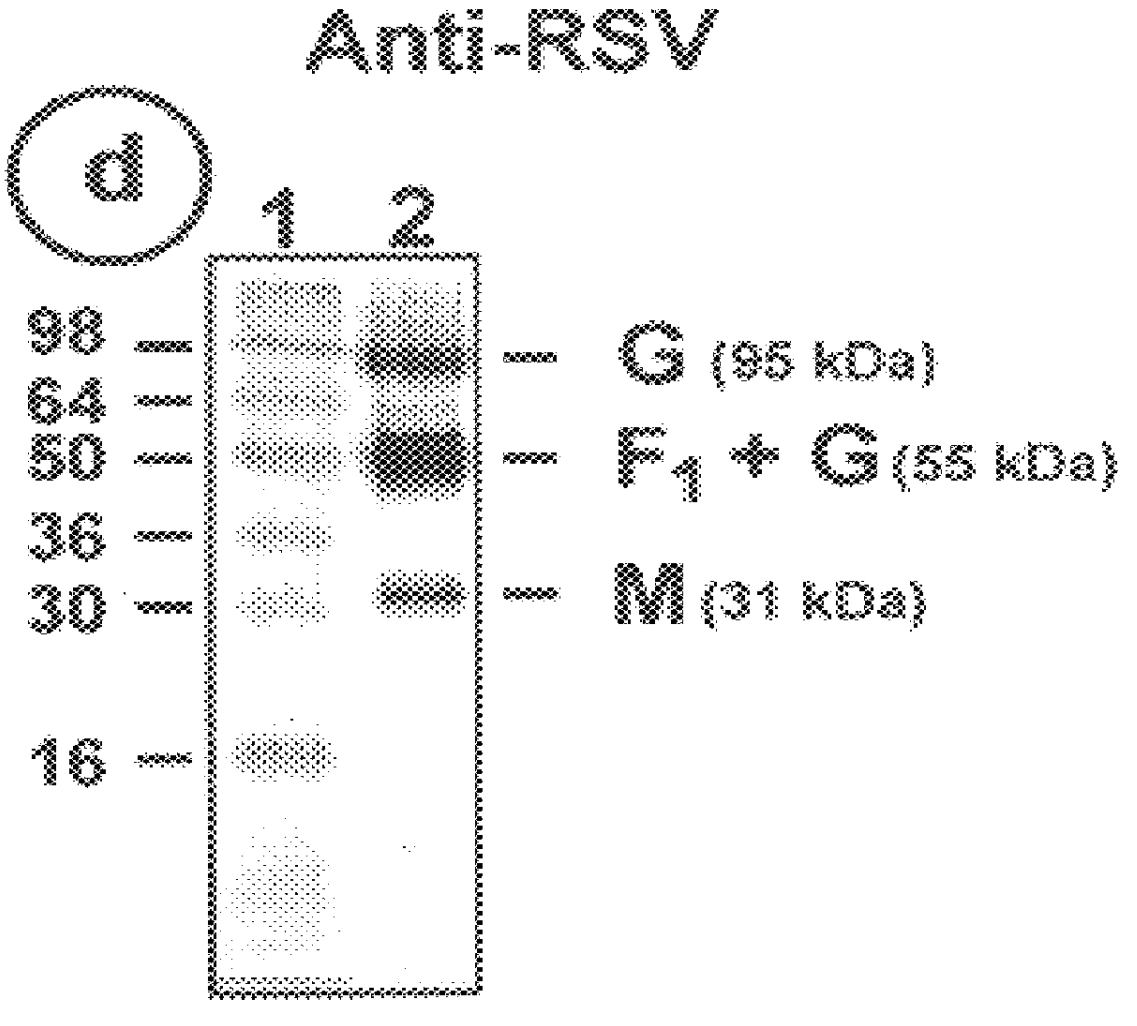
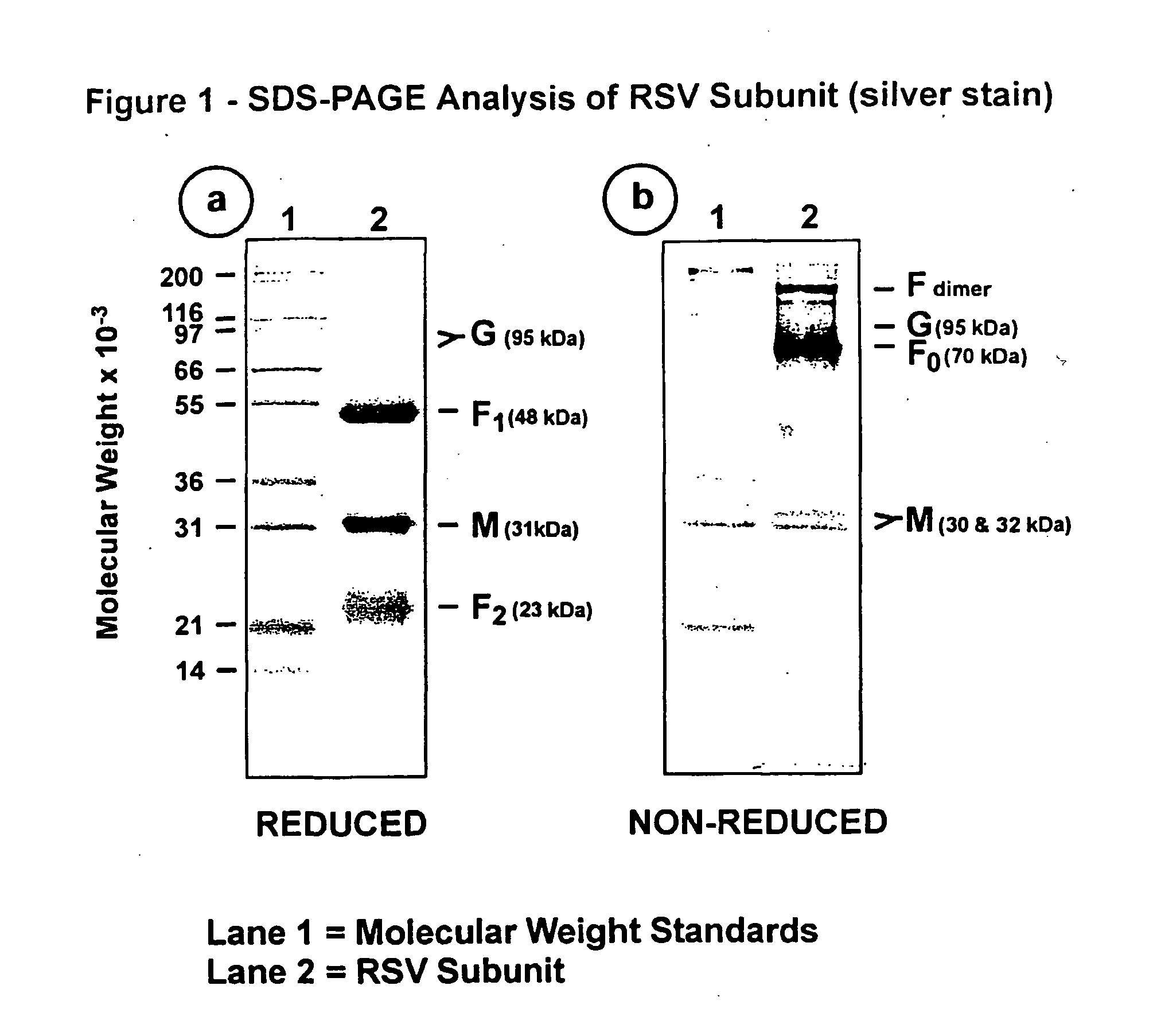
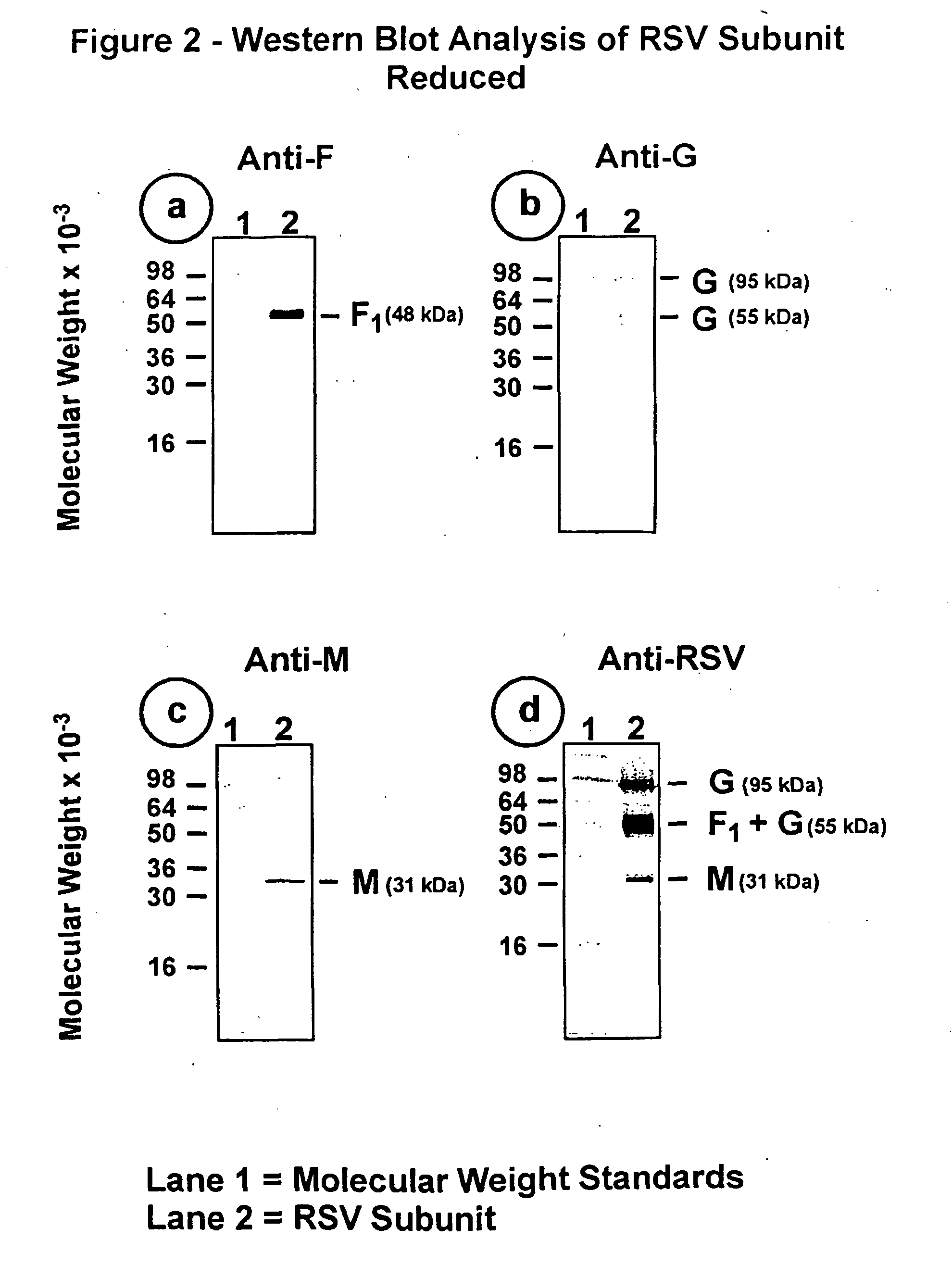
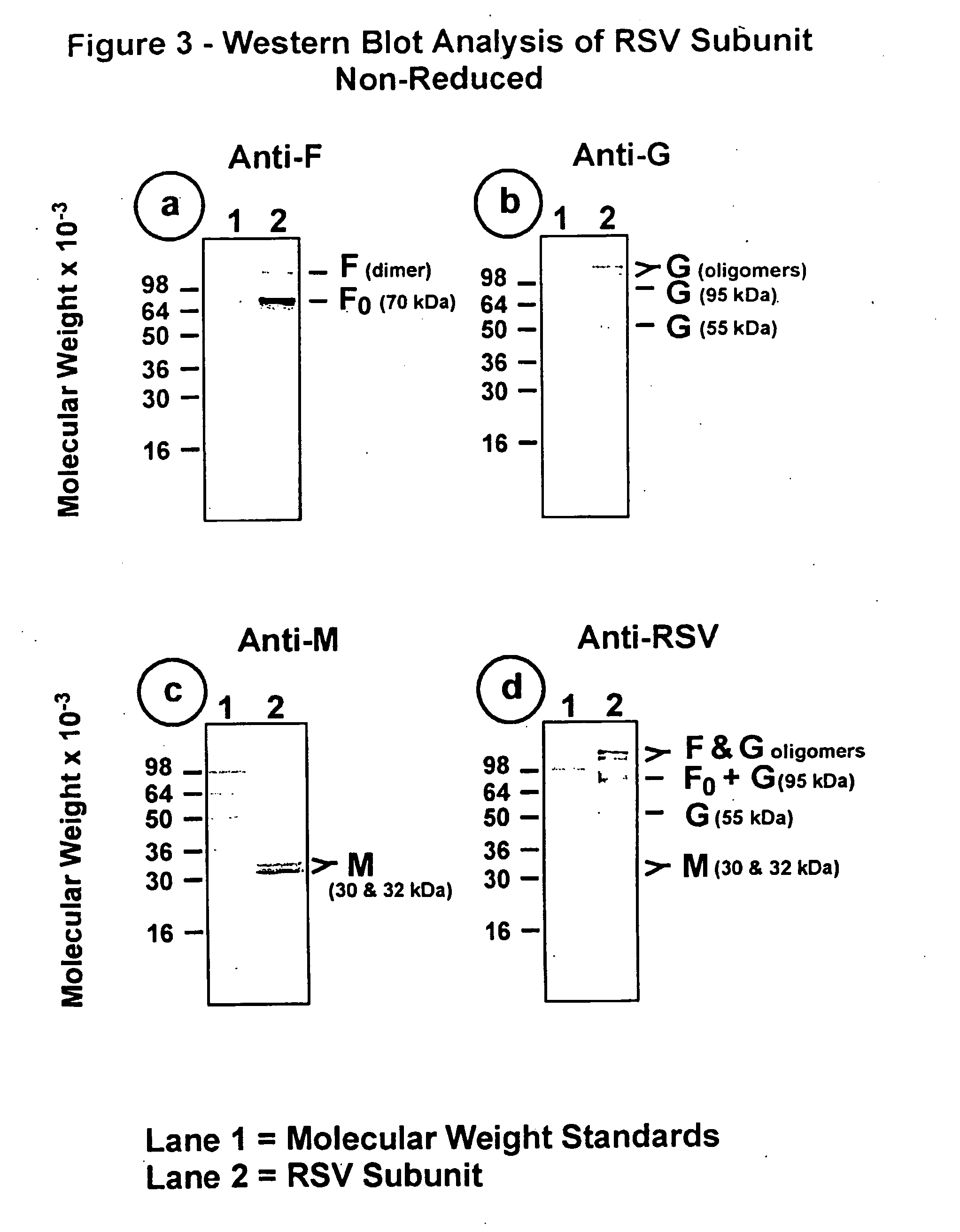
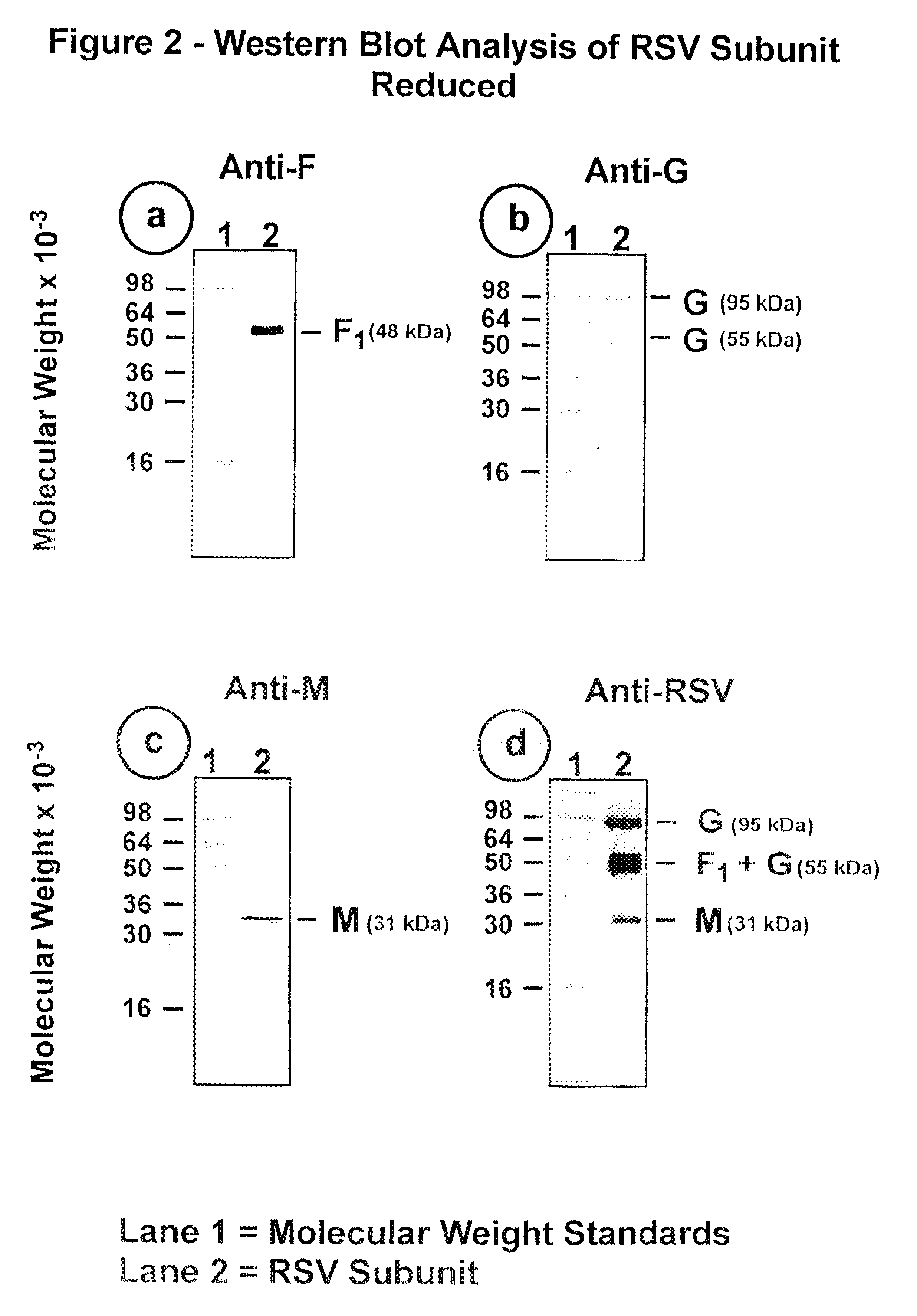
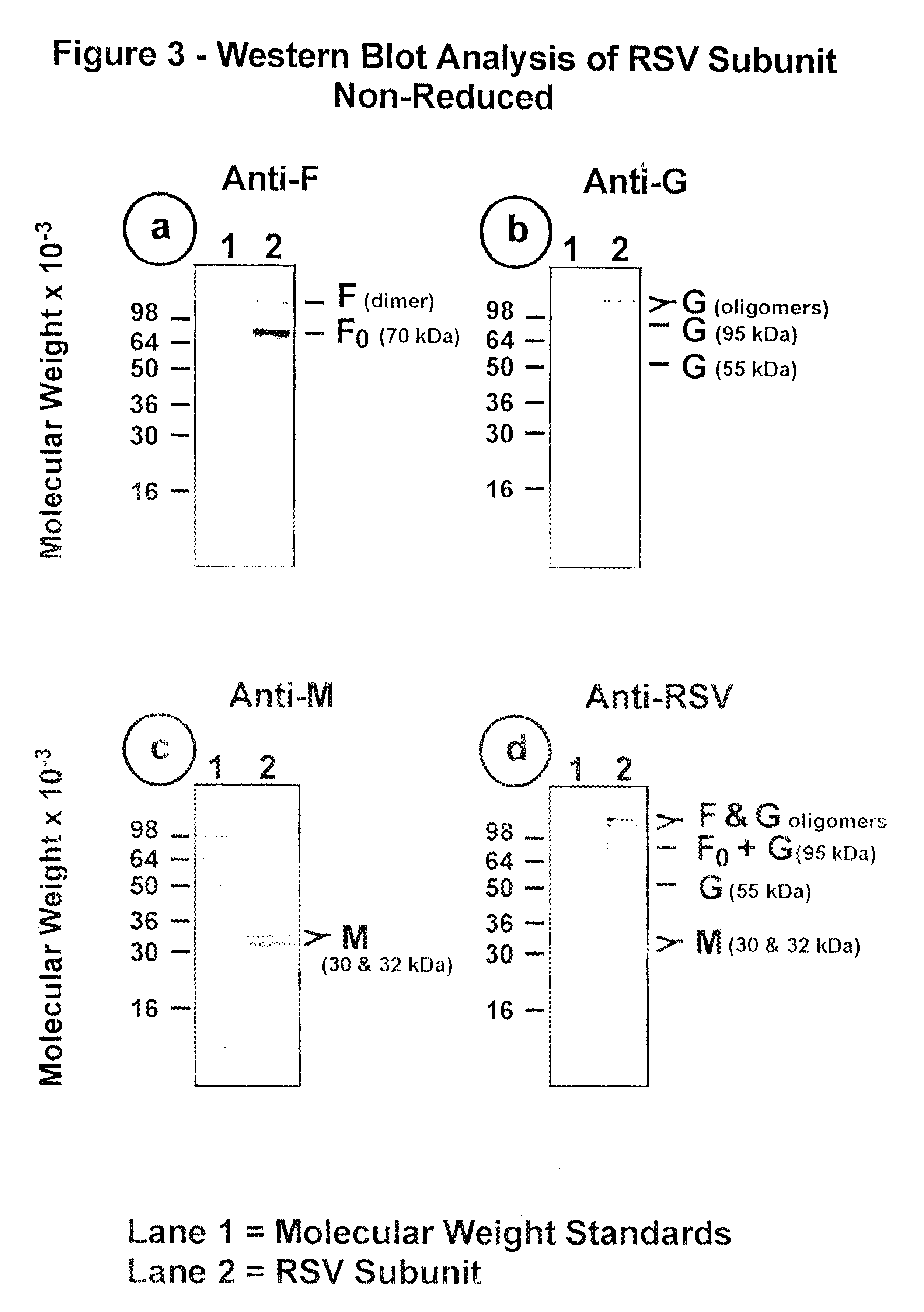
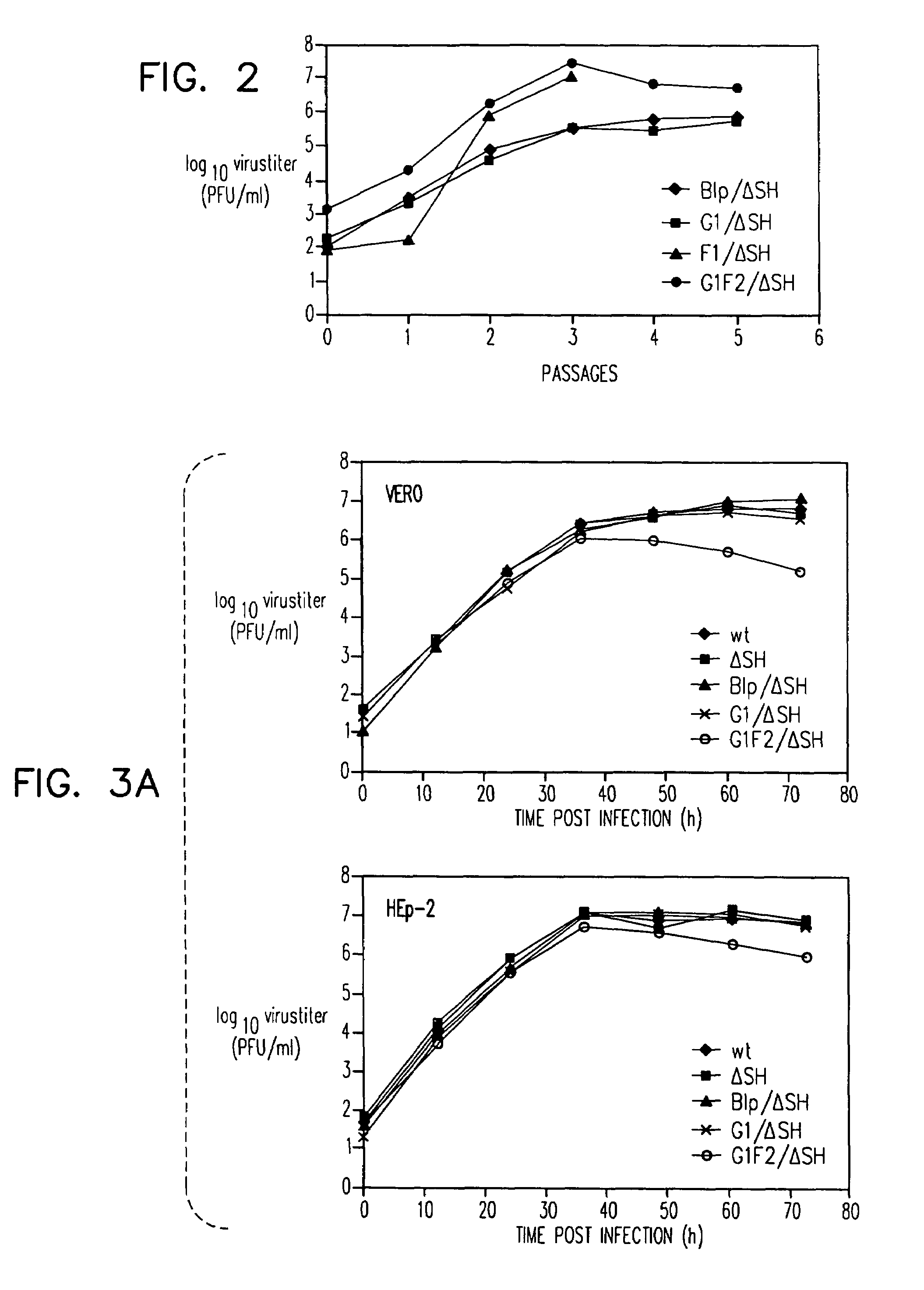
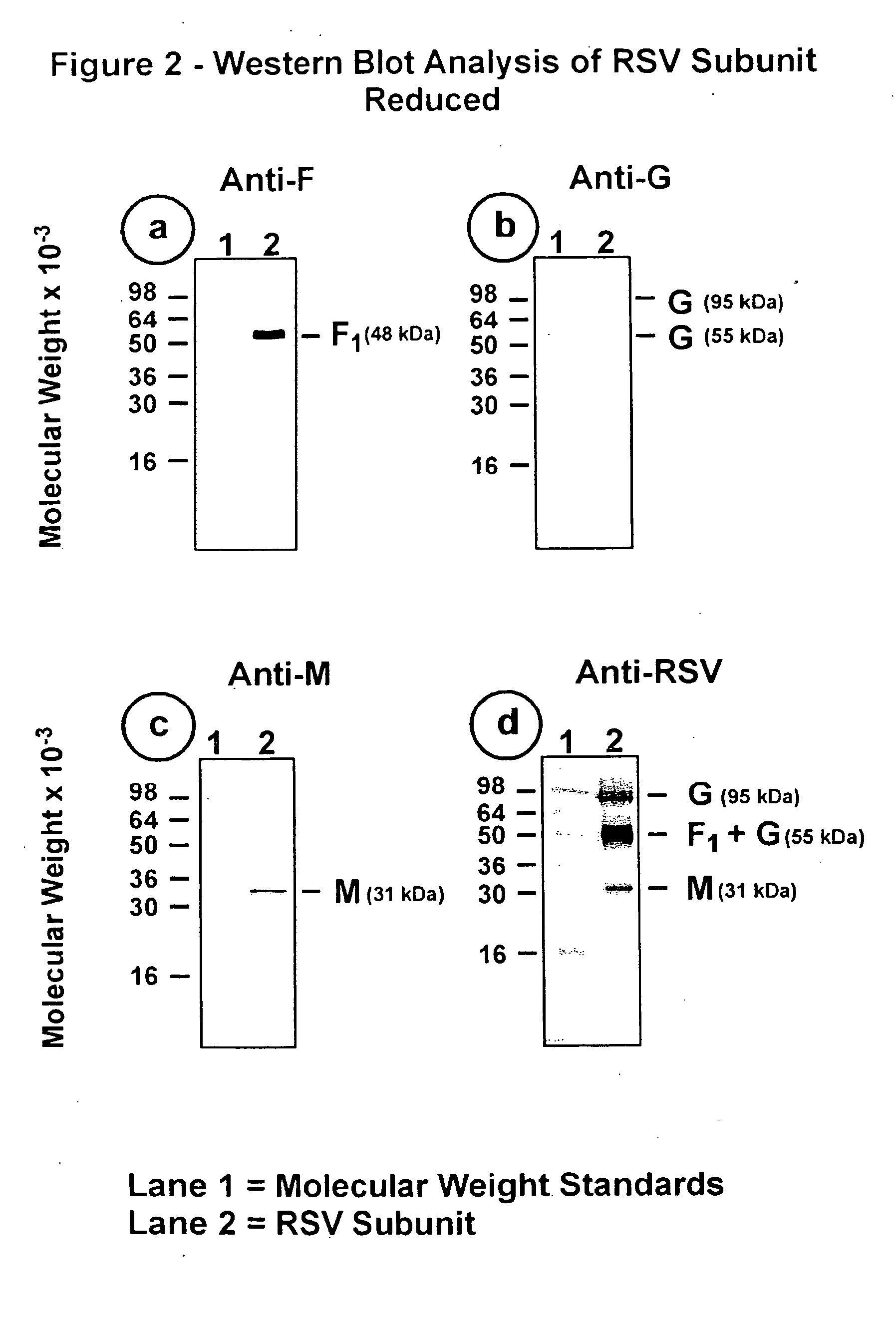
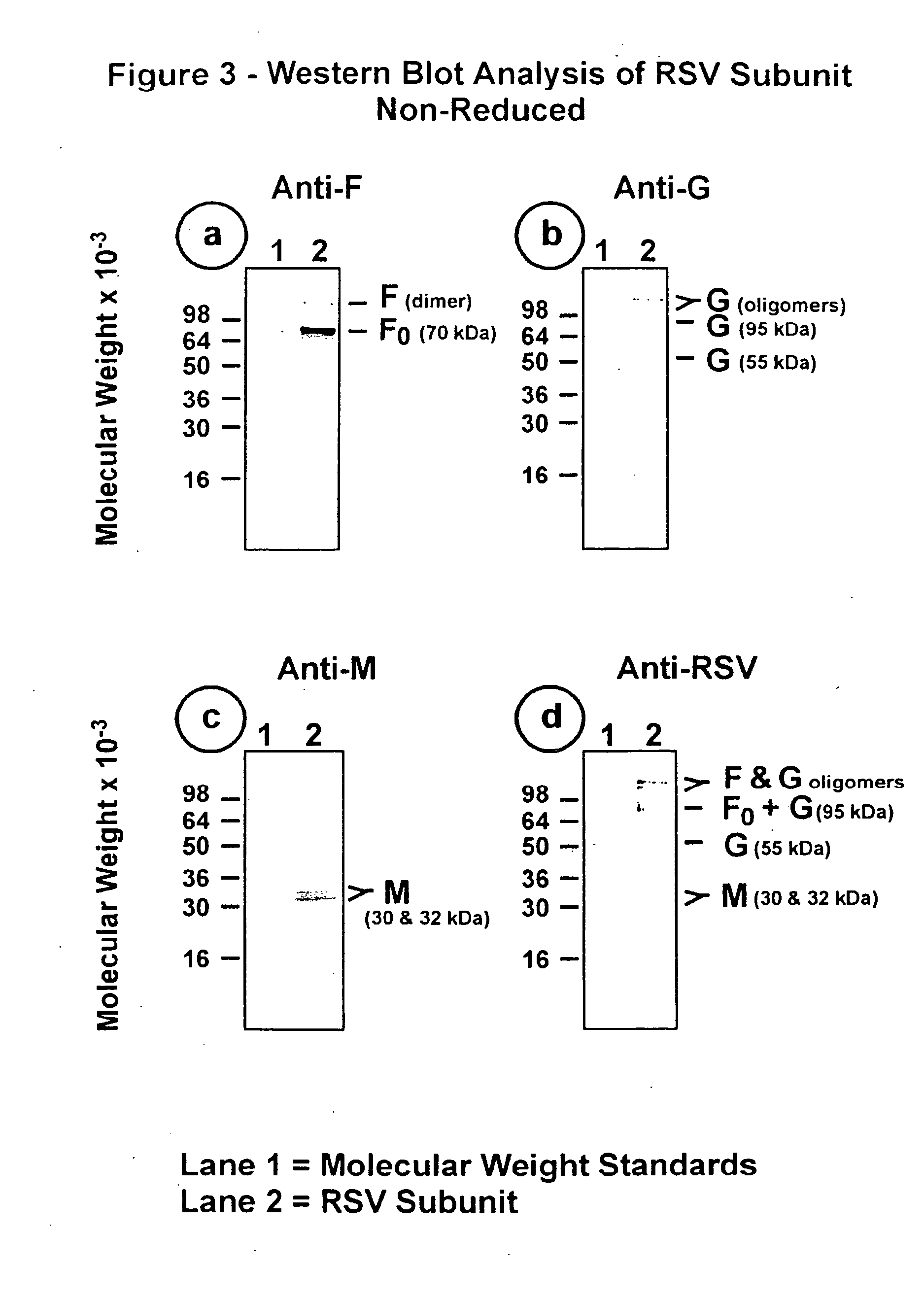
The fusion (F) protein, attachment (G) protein and matrix (M) protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are isolated and purified from respiratory syncytial virus by mild detergent extraction of the proteins from concentrated virus, loading the protein onto a hydroxyapatite or other ion-exchange matrix column and eluting the protein using mild salt treatment. The F, G and M proteins, formulated as immunogenic compositions, are safe and highly immunogenic and protect relevant animal models against respiratory syncytial virus.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promoter-proximal genes
InactiveUS6923971B2Altered immunogenicitySmall sizeSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesProtective antigenGene Position
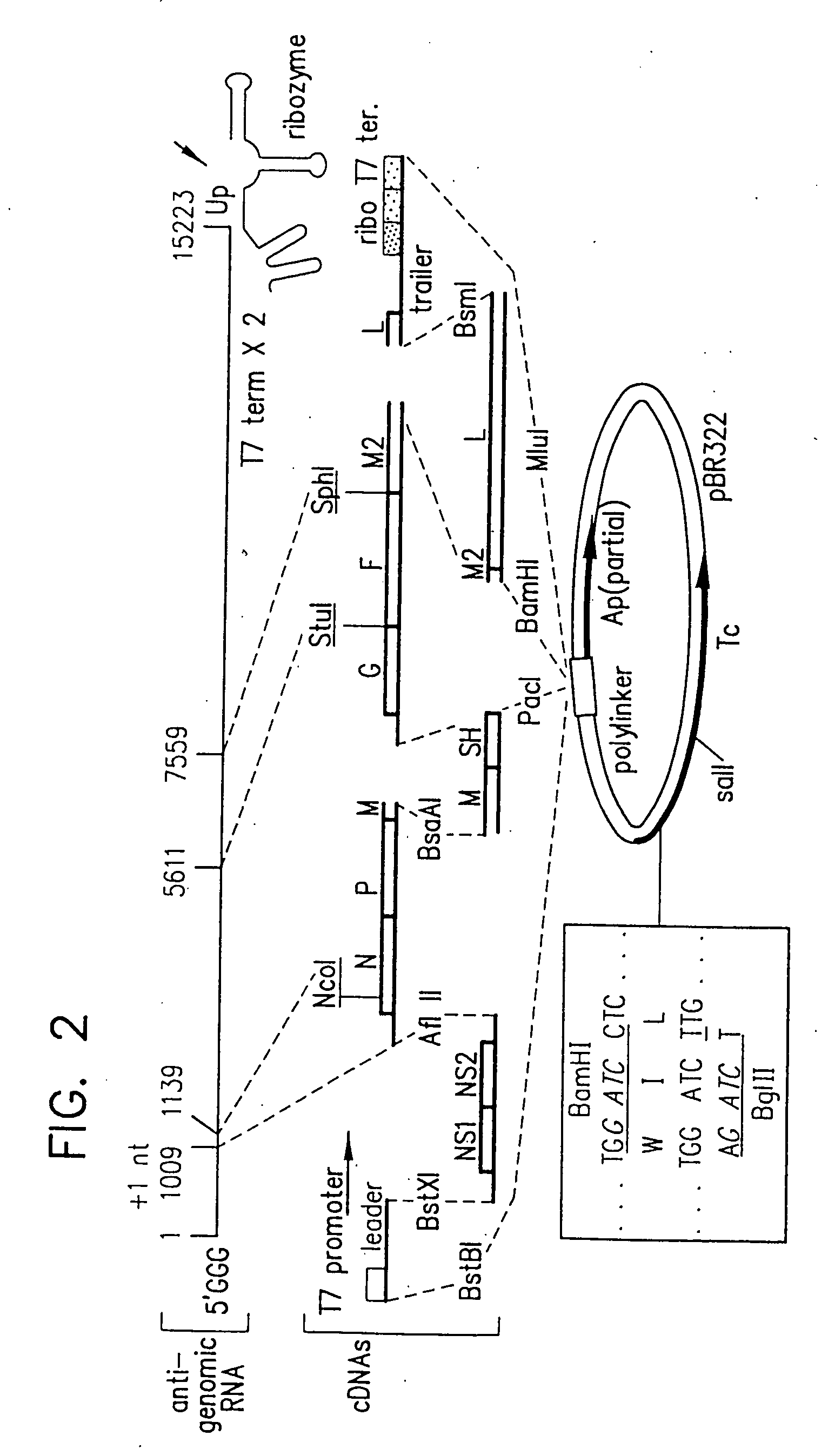
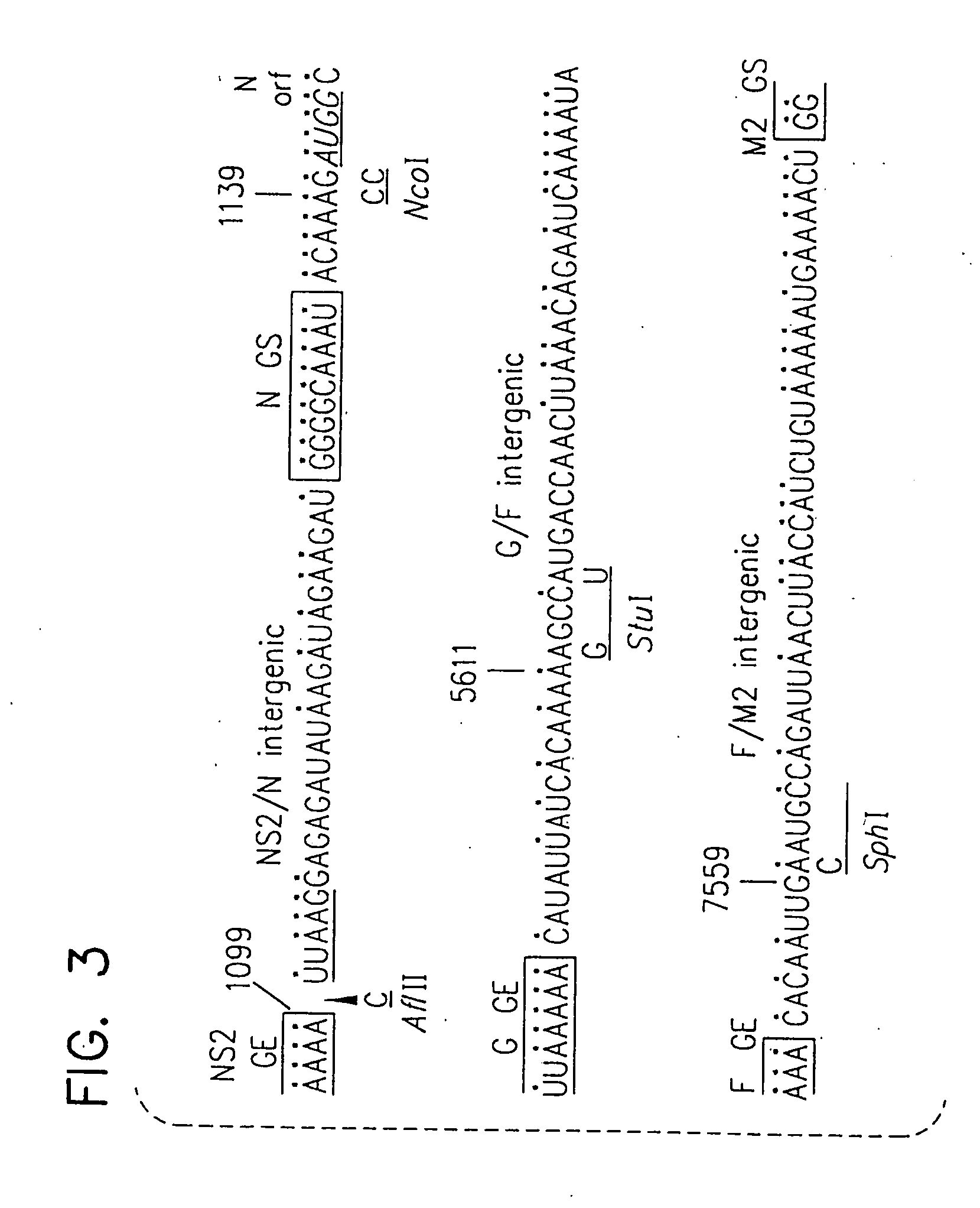
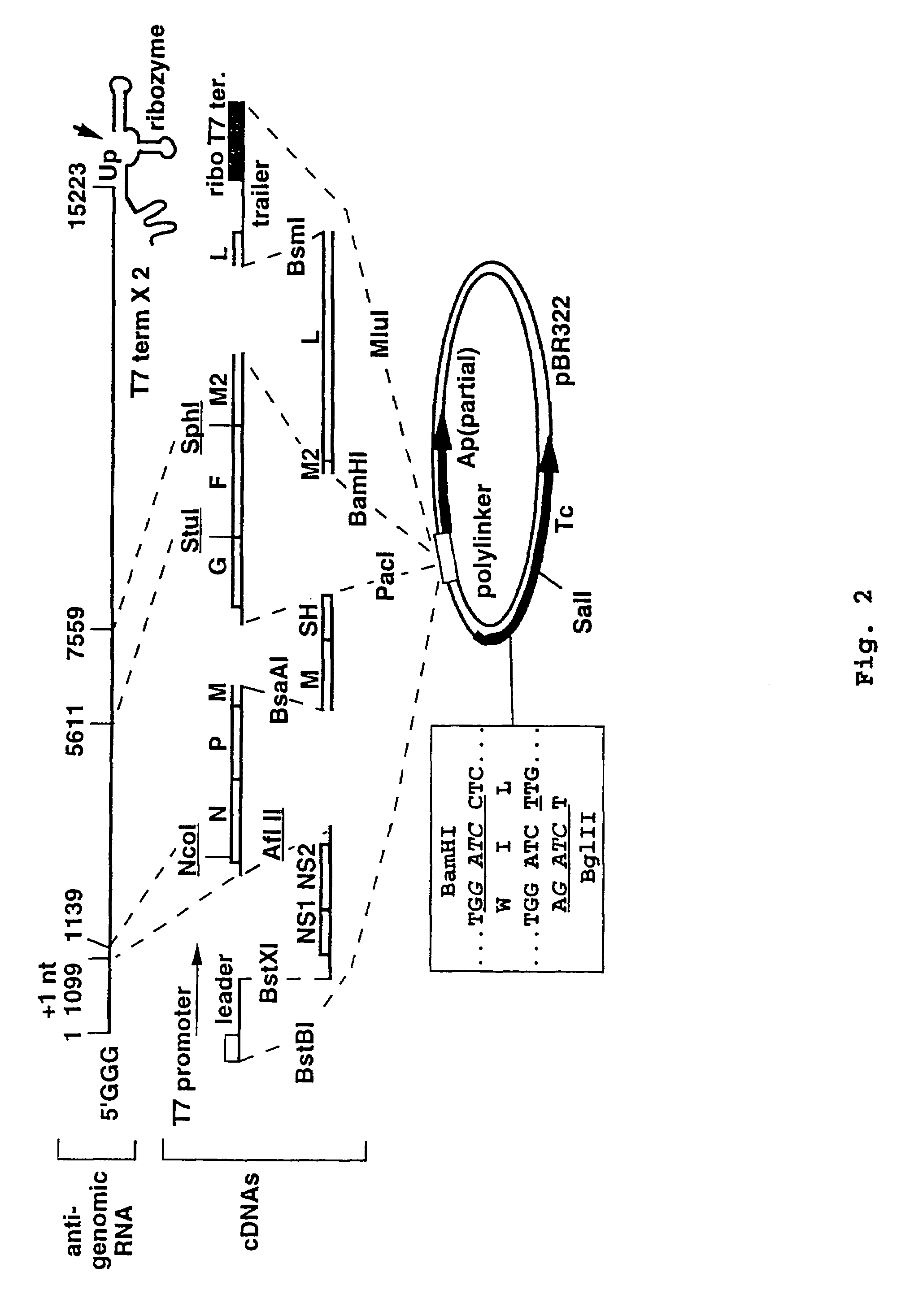
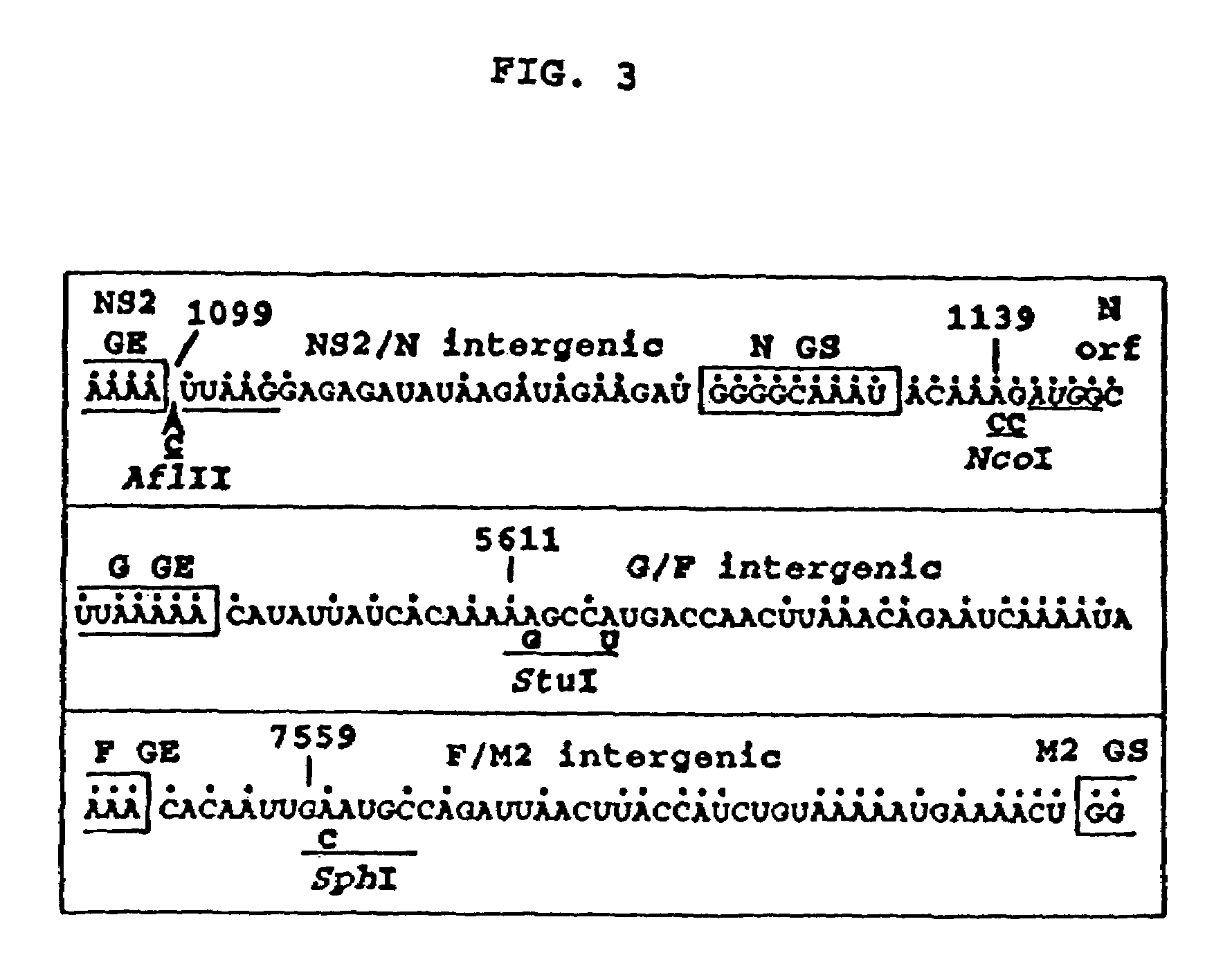
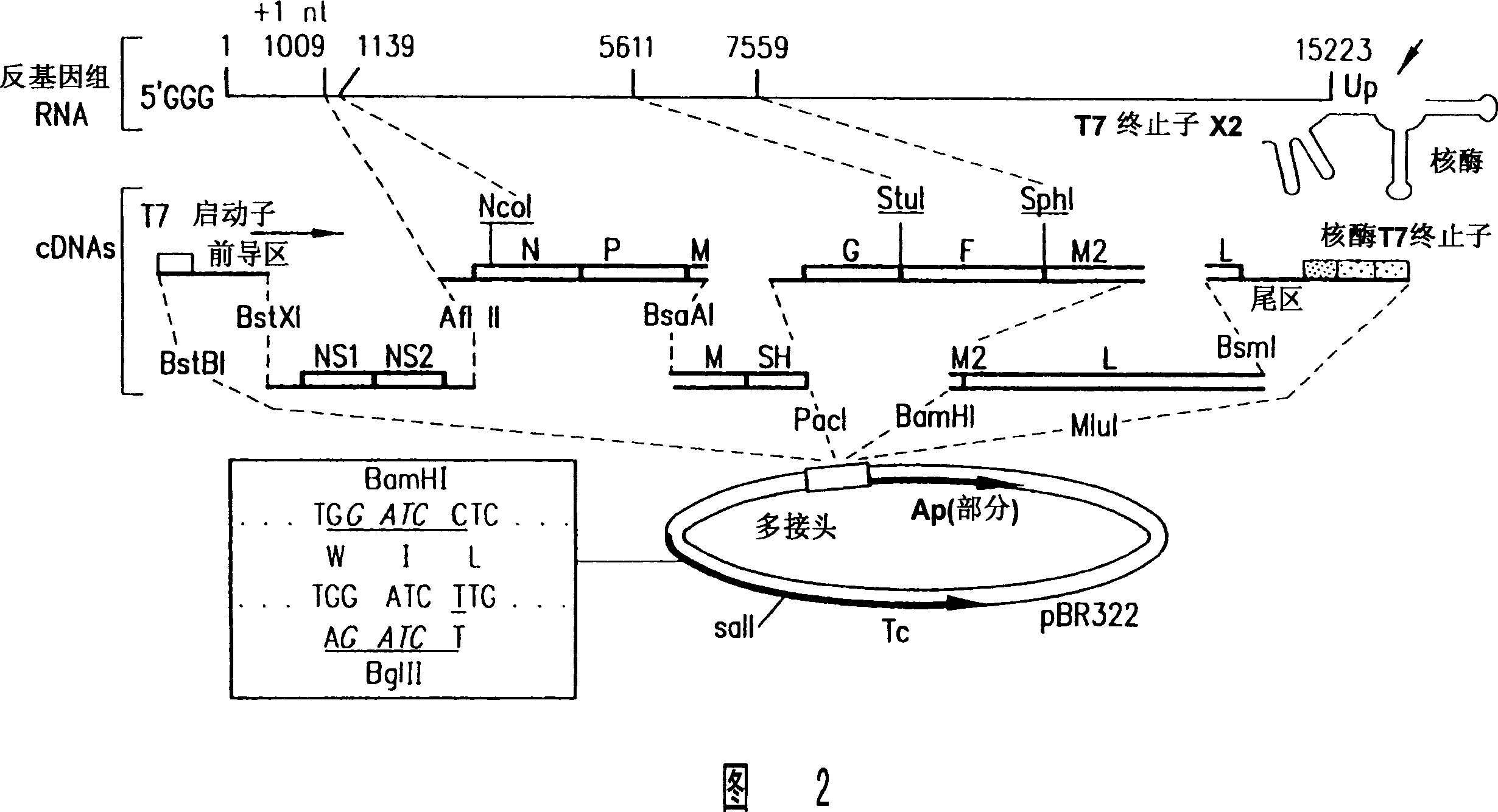
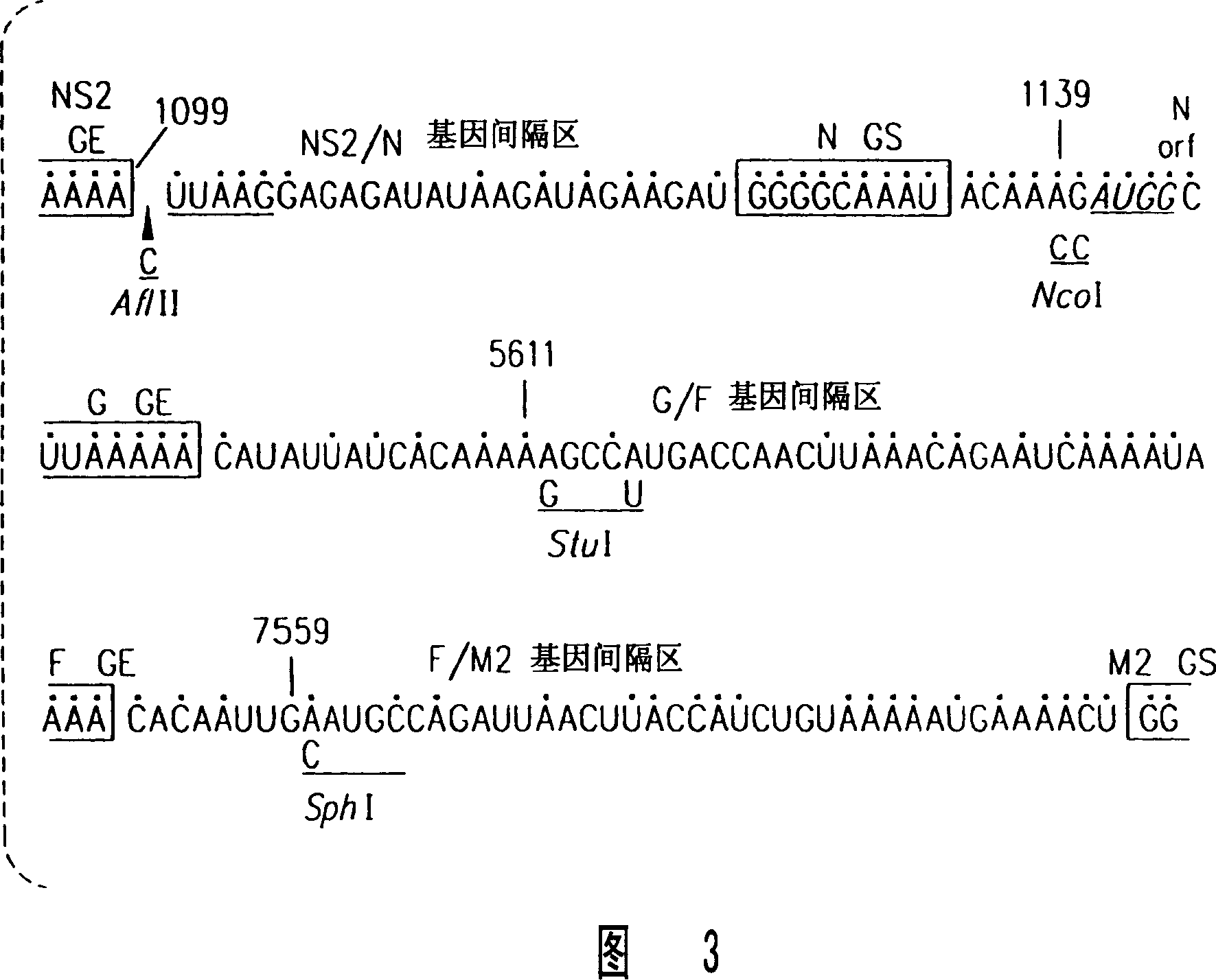
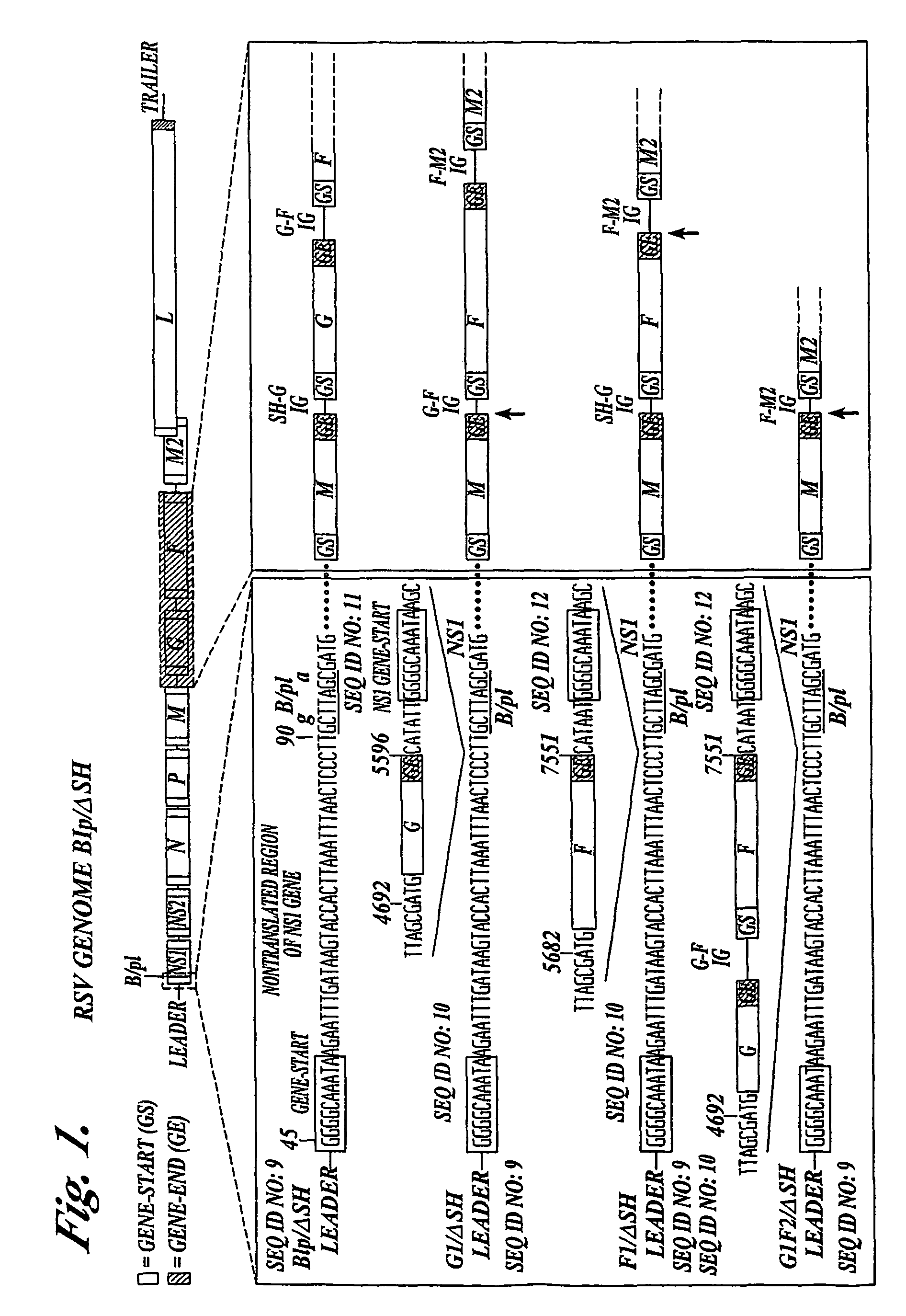
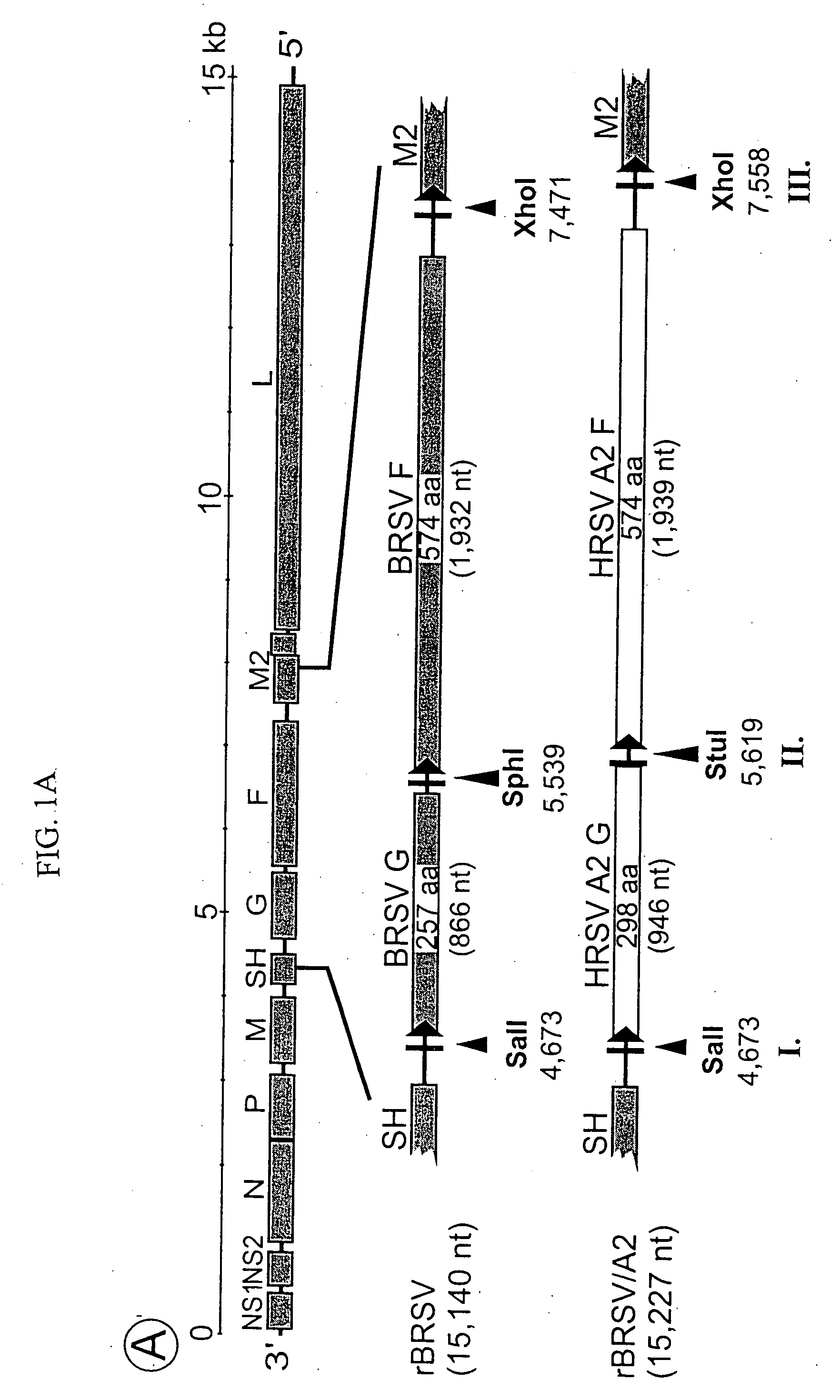
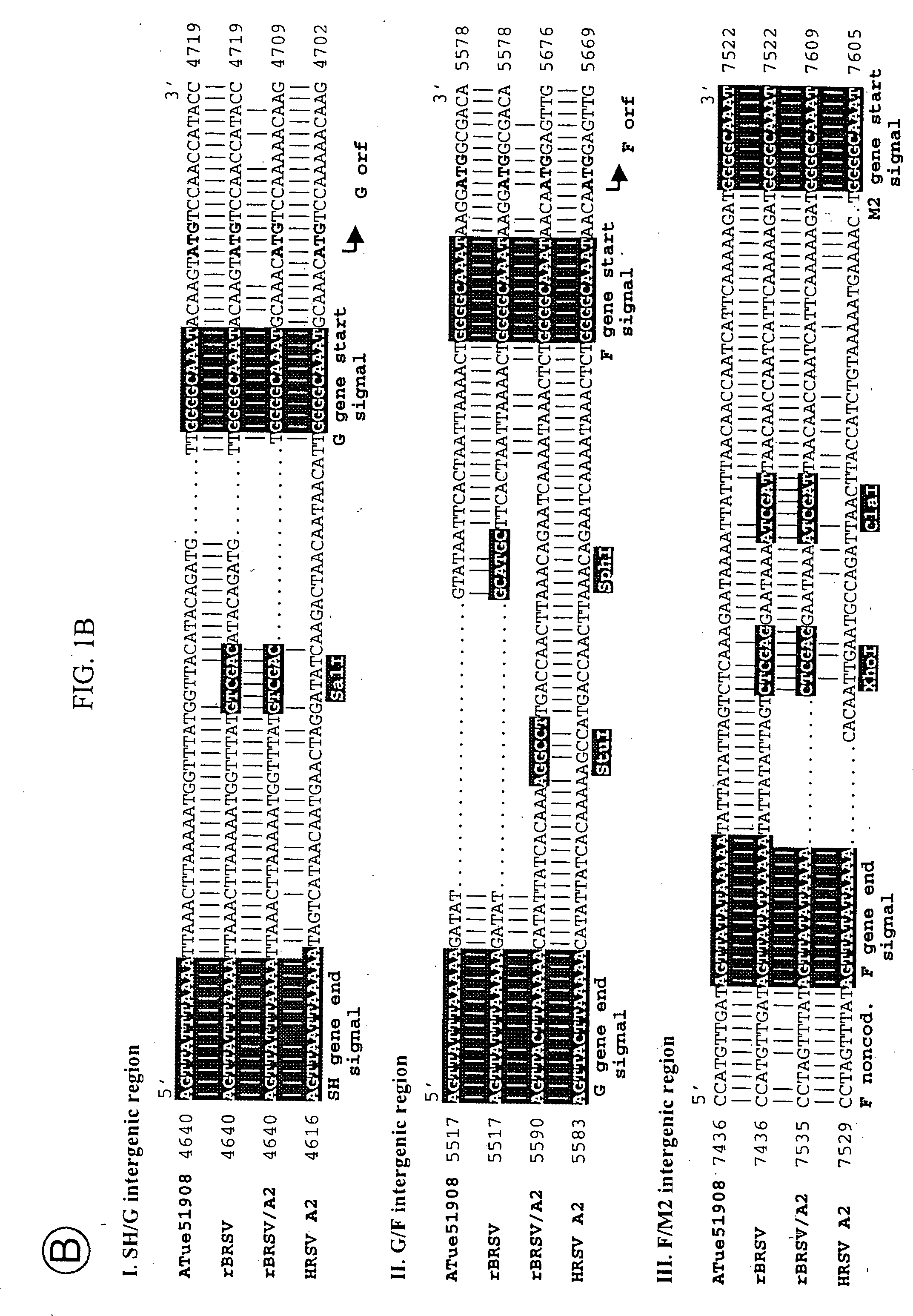
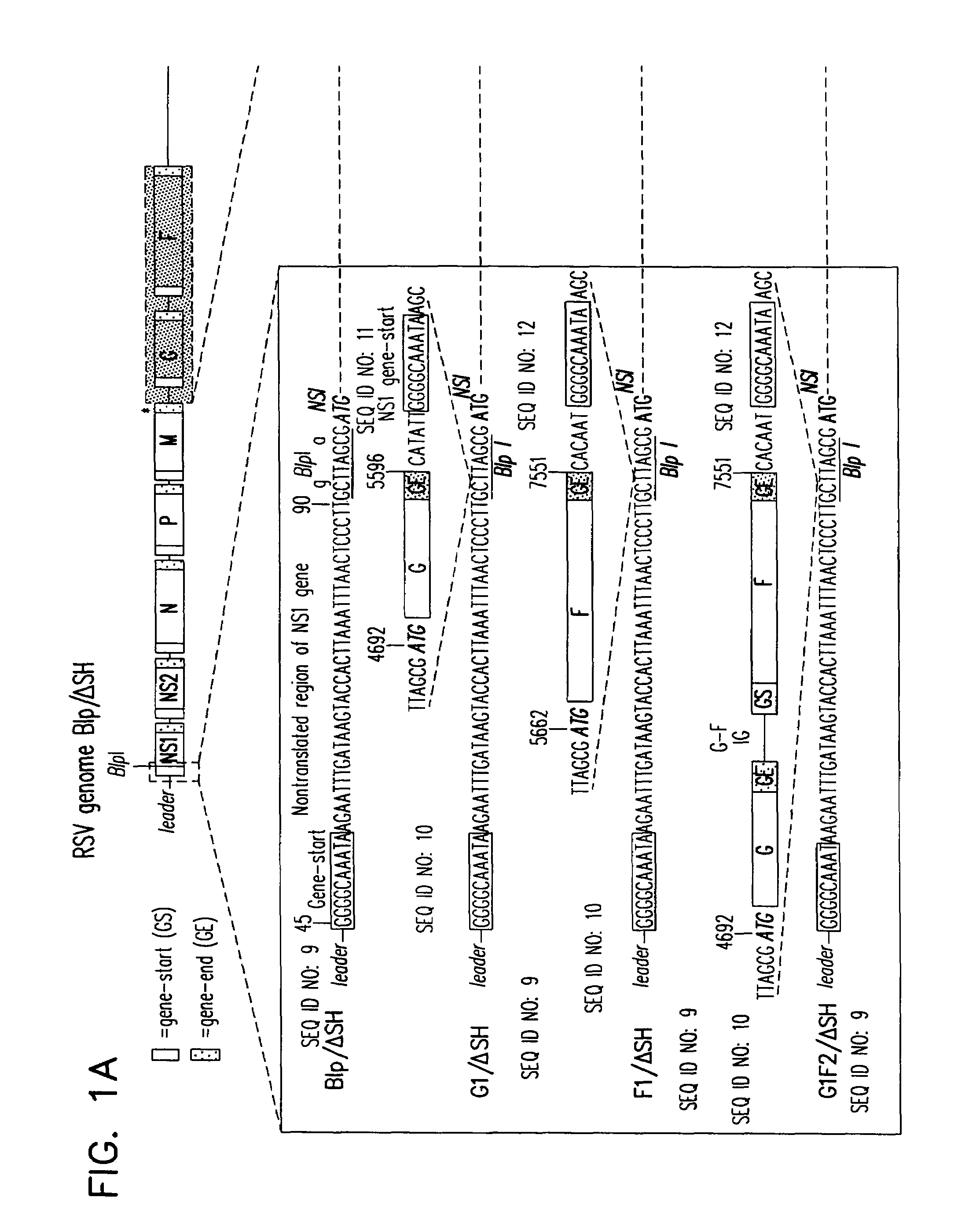
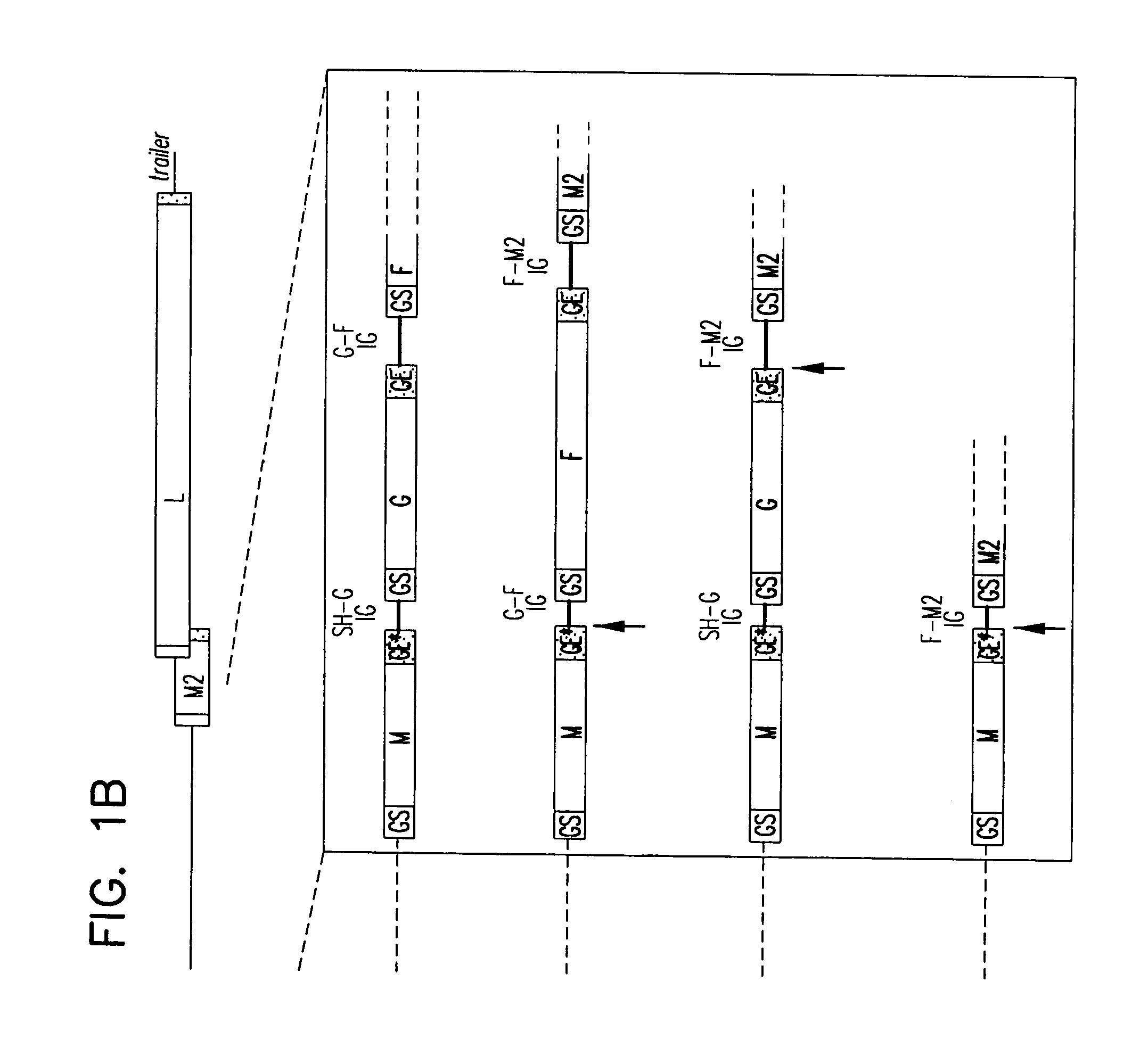
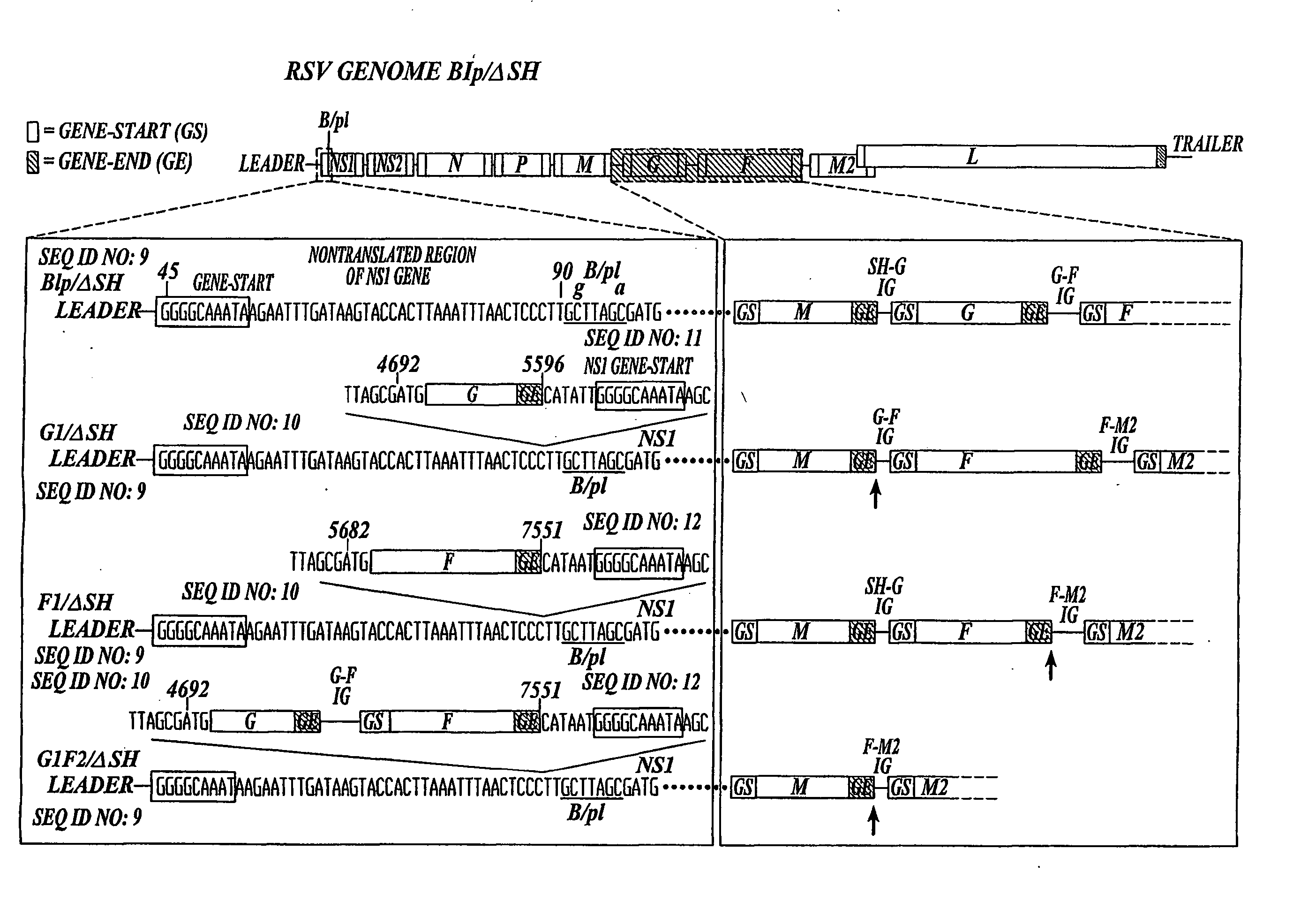
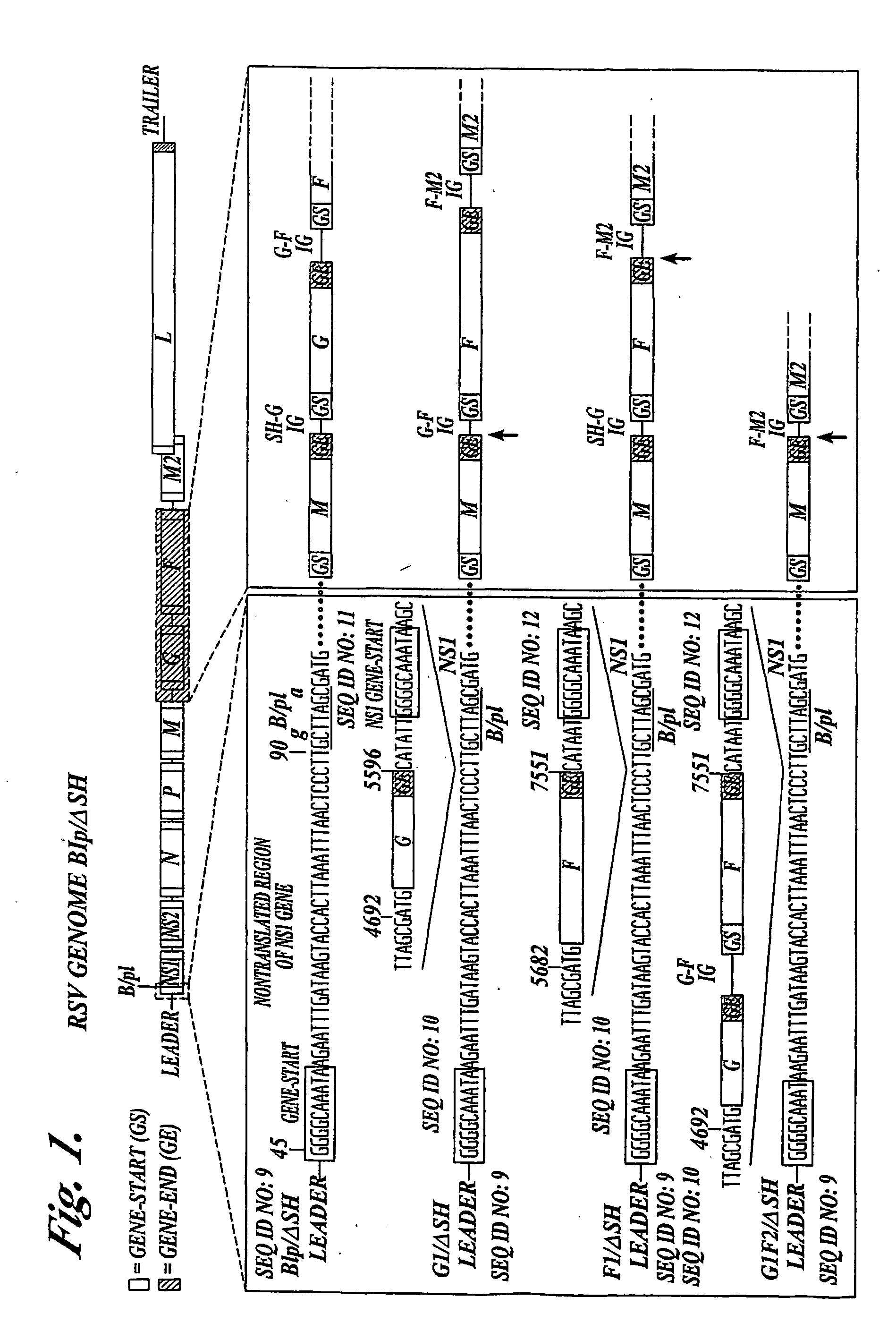
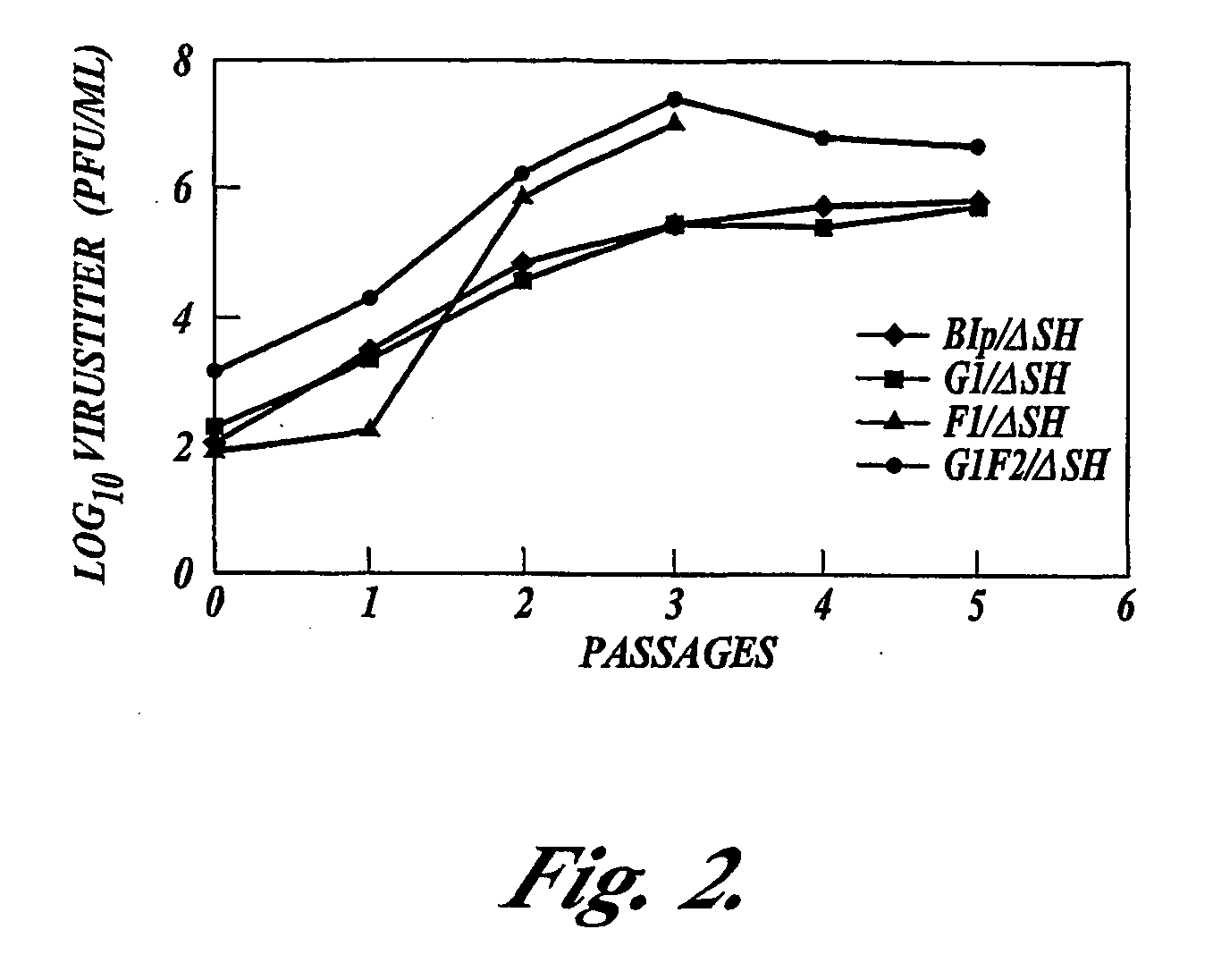
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene. In one embodiment, expression of RSV glycoproteins is upregulated by shifting one or more glycoprotein-encoding genes to a more promoter-proximal position. Genes of interest for manipulation to create gene position-shifted RSV include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment that may be part of a gene or extragenic. Additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within gene position-shifted RSV to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE +1
Production of attenuated chimeric respiratory syncytial virus vaccines from cloned nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS20050100557A1Satisfactory level of attenuationReduce the possibilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHeterologousProtective antigen
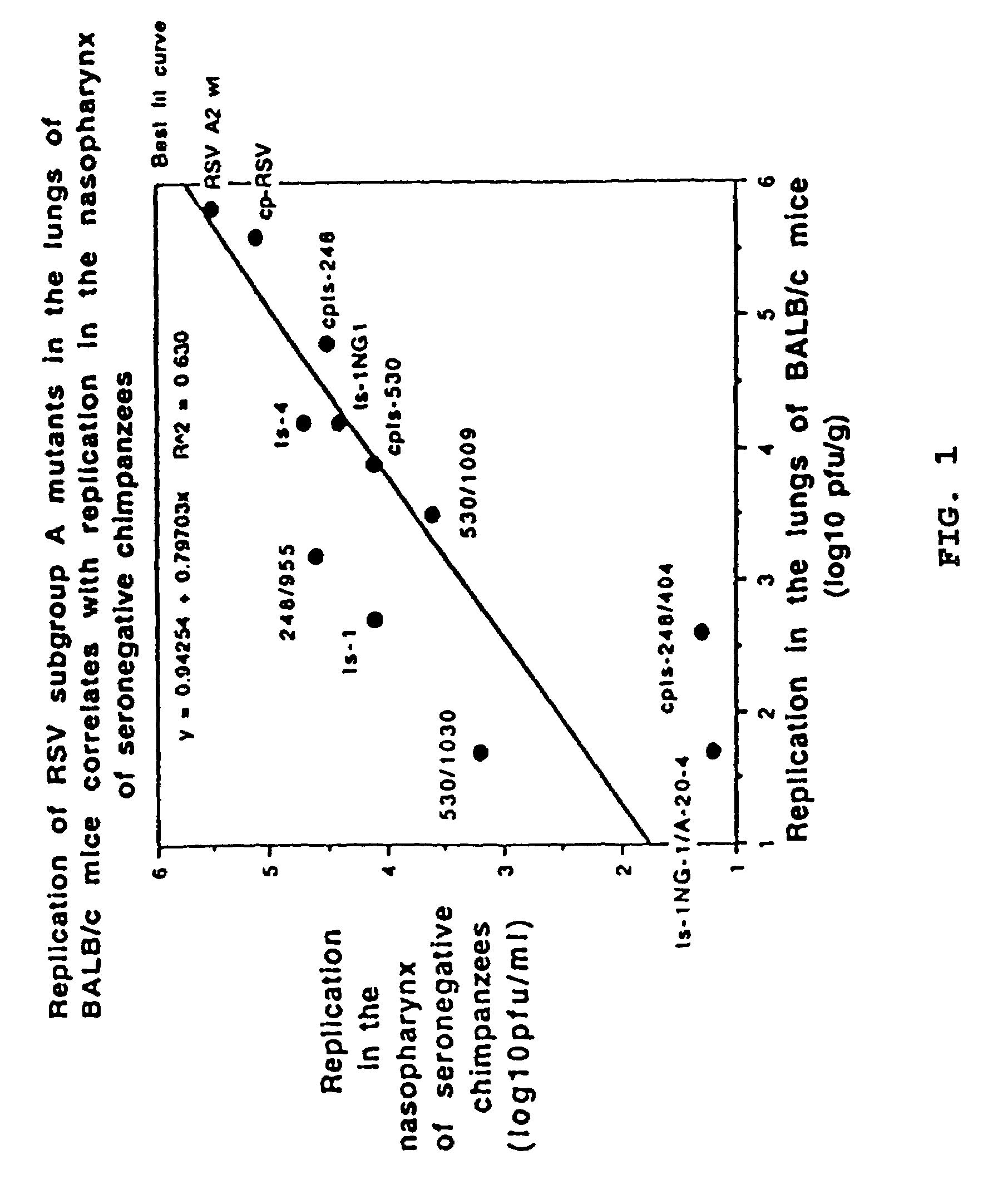
Chimeric respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and vaccine compositions thereof are produced by introducing one or more heterologous gene(s) or gene segment(s) from one RSV subgroup or strain into a recipient RSV backround of a different subgroup or strain. The resulting chimeric RSV virus or subviral particle is infectious and attenuated, preferably by introduction of selected mutations specifying attenuated phenotypes into a chimeric genome or antigenome to yield, for example, temperature sensitive (ts) and / or cold adapted (ca) vaccine strains. Alternatively, chimeric RSV and vaccine compositions thereof incorporate other mutations specifying desired structural and / or phenotypic characteristics in an infectious chimeric RSV. Such chimeric RSV incorporate desired mutations specified by insertion, deletion, substitution or rearrangement of one or more selected nucleotide sequence(s), gene(s), or gene segment(s) in a chimeric RSV clone. This provides a method for development of novel vaccines against diverse RSV strains by using a common attenuated backbone as a vector to express protective antigens of heterologous strains. The immune system of an individual is stimulated to induce protection against natural RSV infection, preferably in a multivalent manner to achieve protection against multiple RSV strains and / or subgroups.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Respiratory syncytial virus sub-units vaccine, preparation and application
InactiveCN101264323ALimit developmentEnhance cellular immune responseDepsipeptidesAntiinfectivesEscherichia coliCtl epitope
The invention relates to a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine, and the preparation method and application, in particular to an application of escherichia coli to express and recombinant respiratory syncytial virus G protein and mutation G protein, and preparation vaccine with nontoxic typed escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin, for human or animal preventive inoculation, and for respiratory syncytial virus resistance, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The respiratory syncytial virus vaccine is characterized in that: the respiratory syncytial virus subunits vaccine comprises lopped respiratory syncytial virus RSV protein G, and further comprises nontoxic typed escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin LT adjuvant. The vaccines are lopped respiratory syncytial virus RSV protein G containing amino acid between aa130 and 230 of the original G protein, and substitutes the amino acid CAWIC (CX3C module ordered) between aa182 and 186 with the amino acid YLEKESIYY (CTL epitope) on the RSV M protein, forming the GCIL protein. The respiratory syncytial virus vaccine has the advantages of remarkable practical significance for preventing human respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Production of attenuated respiratory syncytial virus vaccines from cloned nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS7709007B2Reduce the possibilityStabilizing mutationSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiNucleotideWild type
Attenuated respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and vaccine compositions thereof are produced by introducing specific mutations associated with attenuating phenotypes into wild-type or RSV which is incompletely attenuated by cold-passage or introduction of mutations which produce virus having a temperature sensitive (ts) or cold adapted (ca) phenotype. Alternatively, recombinant RSV and vaccine compositions thereof incorporate attenuating and other mutations specifying desired structural and or phenotypic characteristics in an infectious RSV. Recombinant RSV incorporate desired mutations specified by insertion, deletion, substitution or rearrangement of a selected nucleotide sequence, gene, or gene segment in an infectious RSV clone. The immune system of an individual is stimulated to induce protection against natural RSV infection, or multivalently against infection by RSV and another pathogen, such as PIV, by administration of attenuated, biologically derived or recombinant RSV.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Nucleic acid respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6017897AGood immune protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsF proteinEukaryotic plasmids
Non-replicating vectors containing a nucleotide sequence coding for an F protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and a promoter for such sequence, preferably a cytomegalovirus promoter, are described for in vivo immunization. Such non-replicating vectors, including plasmids, also may contain a further nucleotide sequence located adjacent to the RSV F protein encoding sequence to enhance the immunoprotective ability of the RSV F protein when expressed in vivo. Such non-replicating vectors may be used to immunize a host against disease caused by infection with RSV, including a human host, by administration thereto, and may be formulated as immunogenic compositions with pharmaceutically-acceptable carriers for such purpose. Such vectors also may be used to produce antibodies for detection of RSV infection in a sample.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
RNA respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
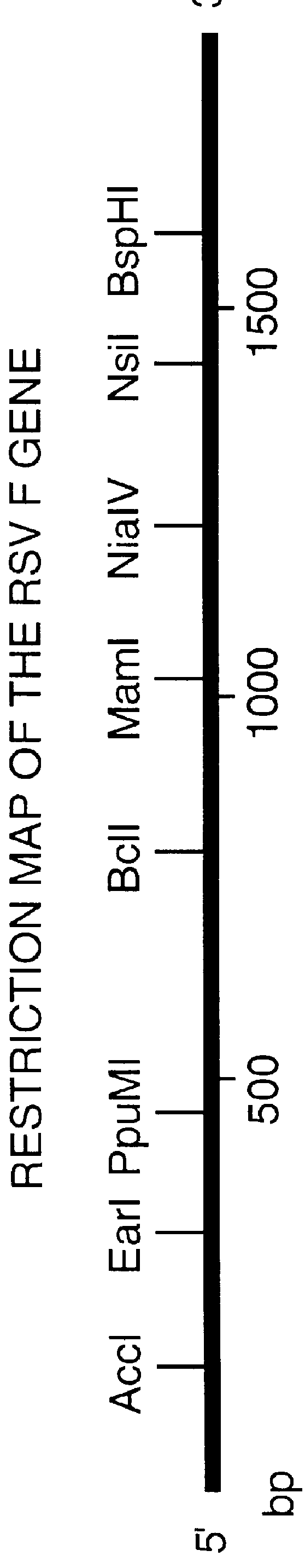
InactiveUS6428324B1Faster replicationImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsF proteinRestriction site
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Production of attenuated, human-bovine chimeric respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS20070184069A1Simple designAltered immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousBovine RSV
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Subunit respiratory syncytial virus vaccine preparation
InactiveUS20050089525A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIon exchangeViral Vaccine
The fusion (F) protein, attachment (G) protein and matrix (M) protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are isolated and purified from respiratory syncytial virus by mild detergent extraction of the proteins from concentrated virus, loading the protein onto a hydroxyapatite or other ion-exchange matrix column and eluting the protein using mild salt treatment. The F, G and M proteins, formulated as immunogenic compositions, are safe and highly immunogenic and protect relevant animal models against decreased caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Owner:CATES GEORGE +3
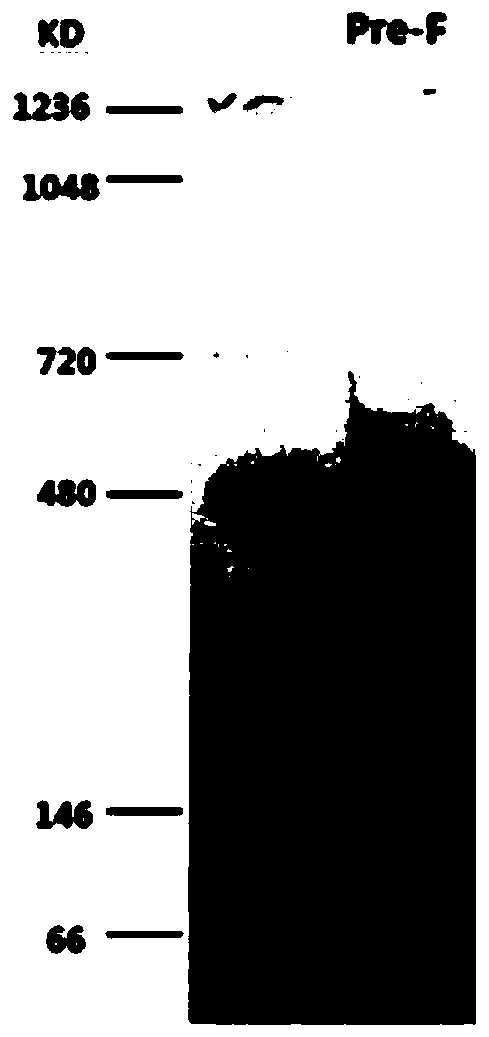
Respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion F protein and application thereof
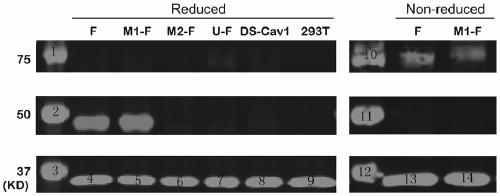
ActiveCN110054668AStable structureExpression did not decreaseSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesF proteinWild type
The invention provides a respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion F protein and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines. The pre-fusion F proteinis formed in the way that the 106th, 108th and 109th amino acids of a wild-type F protein are mutated from Arg to Asn, the 104th amino acid is mutated from Asn to Cys, the 155th amino acid is mutatedfrom Ser to Cys, or the 58th amino acid is mutated from Thr to Cys, and the 190th amino acid is mutated from Ser to Cys. A first furin cleavage site of the mutant wild-type F protein makes the structure of Pre-F more stable, the expression amount is not decreased, and the pre-fusion epitope of M1-F expression in 293T cells is significantly increased. The second mutation of the amino acid site of the F protein forms a disulfide bond, achieves the more stable pre-fusion epitope compared to the wild type, and is suitable for other strains of human RSV. The protein is suitable for various vaccineforms with the RSV F protein as the antigen, such as nucleic acid vaccines, protein vaccines, vector vaccines and recombinant virus particle vaccines.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Nucleic acid respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6677127B1Good immune protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideF protein
Vectors containing a nucleotide sequence coding for an F protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and a promoter for such sequence, preferably a cytomegalovirus promoter, are described. Such vectors also may contain a further nucleotide sequence located adjacent to the RSV F protein encoding sequence to enhance the immunoprotective ability of the RSV F protein when expressed in vivo. Such vectors may be used to immunize a host, including a human host, by administration thereto. Such vectors also may be used to produce antibodies for detection of RSV infection in a sample.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Subunit respiratory syncytial virus vaccine preparation
InactiveUS6309649B1Slow and sustained releaseImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsIon exchangeViral Vaccine
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Neutralizing antibody against respiratory syncytial viruses and application thereof
ActiveCN110016079ABiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesHeavy chainRespiratory syncytial virus B
The present invention relates to the field of medicine and immunology, and specifically discloses a neutralizing antibody against respiratory syncytial viruses and an application thereof. The neutralizing antibody comprises a heavy chain variable region of VH CDR1, VH CDR2 and VH CDR3 and a light chain variable region (or named as a variable light chain domain) of VL CDR1, VL CDR2 and VL CDR3; wherein amino acid sequences of the VH CDR1, VH CDR2 and VH CDR3 in the heavy chain variable region are shown in SEQ ID NO.1, 2 and 3, the amino acid sequences of the VL CDR1, VL CDR2 and VL CDR3 in thelight chain variable region are shown in SEQ ID NO.4, 5 and 6. Based on research results, the present invention also provides a nucleic acid molecule encoding the neutralizing antibody, and applications of the neutralizing antibody in preparing a pre-fusion protein product specifically binding the respiratory syncytial viruses, preparing respiratory syncytial virus vaccines, etc.
Owner:ZHUHAI TRINOMAB BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Production of attenuated chimeric respiratory syncytial virus vaccines from cloned nucleotide sequences
InactiveCN101012454ARecycling Mutations EffectiveEasy to operateSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiWild typeRSV Infections
Attenuated respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and vaccine compositions thereof are produced by introducing specific mutations associated with attenuating phenotypes into wild-type or RSV which is incompletely attenuated by cold-passage or introduction of mutations which produce virus having a temperature sensitive (ts) or cold adapted (ca) phenotype. Alternatively, recombinant RSV and vaccine compositions thereof incorporate attenuating and other mutations specifying desired structural and or phenotypic characteristics in an infectious RSV. Recombinant RSV incorporate desired mutations specified by insertion, deletion, substitution or rearrangement of a selected nucleotide sequence, gene, or gene segment in an infectious RSV clone. The immune system of an individual is stimulated to induce protection against natural RSV infection, or multivalently against infection by RSV and another pathogen, such as PIV, by administration of attenuated, biologically derived or recombinant RSV.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promotor-proximal genes
InactiveUS7744902B2Altered immunogenicitySmall sizeSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesProtective antigenMammal
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals. Gene shifted RSV are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome wherein a gene or gene segment is shifted to a more promoter-proximal or promoter-distal position within the genome or antigenome compared to a wild type position of the gene in the RSV gene map. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene, depending on the nature and degree of the positional shift. In one embodiment, RSV glycoproteins are upregulated by shifting one or more glycoprotein-encoding genes to a more promoter-proximal position. Genes of interest for manipulation to create gene position-shifted RSV include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment that may be part of a gene or extragenic. A variety of additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within the gene position-shifted RSV of the invention to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccine
ActiveUS9409973B2Efficiently presentedEnhancement of disease symptomSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsRSV InfectionsTGE VACCINE
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Production of attenuated respiratory syncytial virus vaccines involving modification of M2 ORF2
InactiveUS7485440B2Slow kineticsIncrease synthesisSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesOpen reading frameADAMTS Proteins
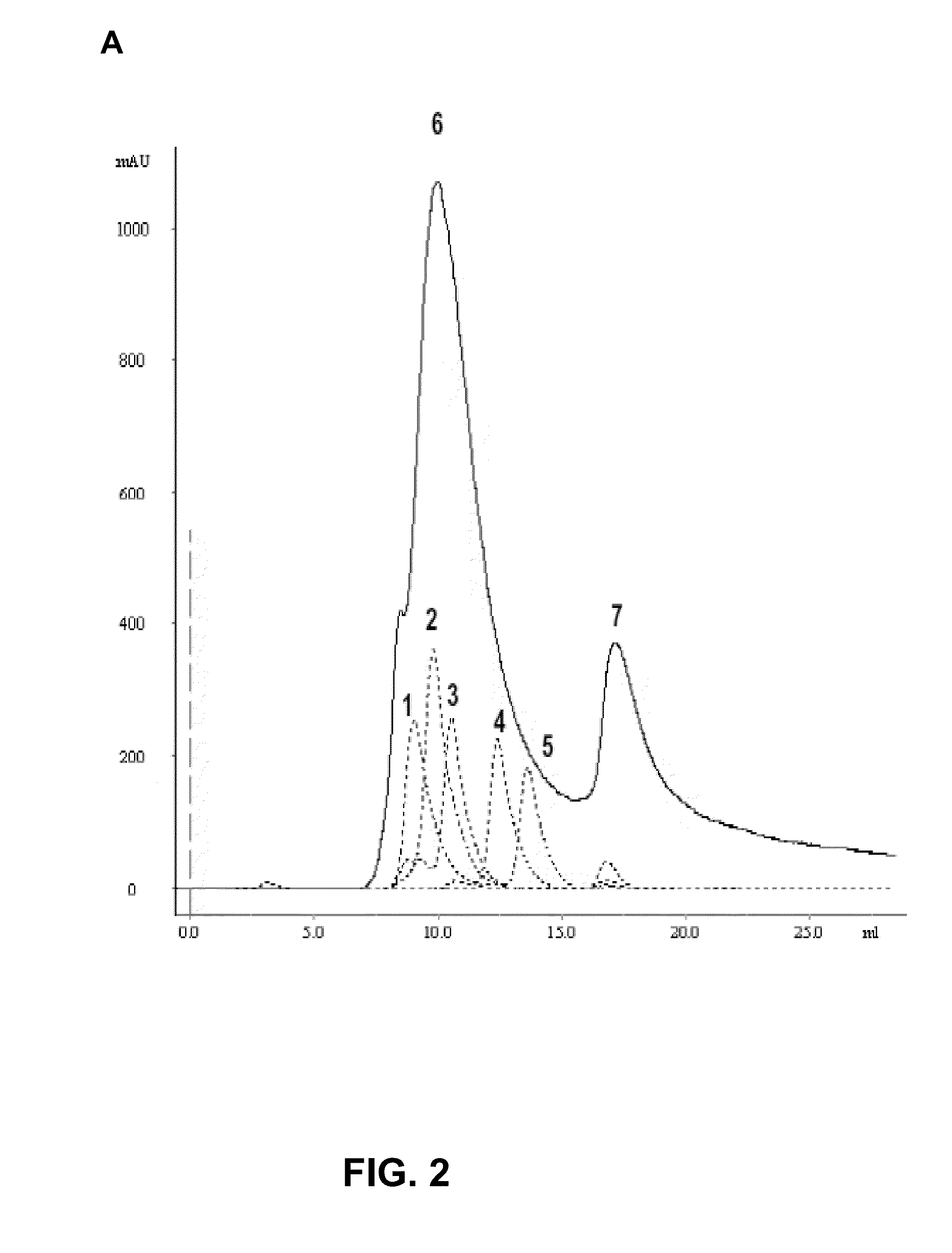
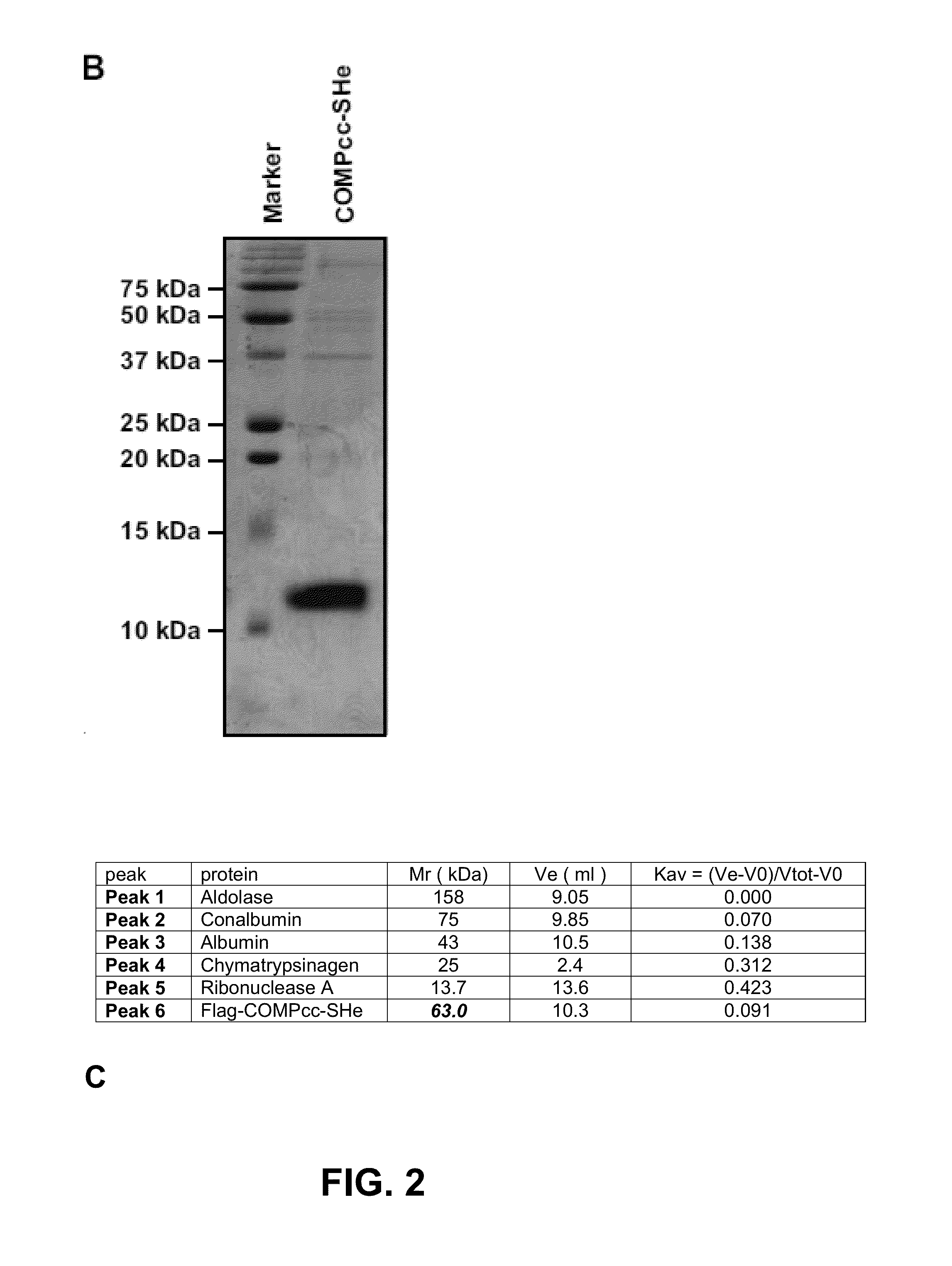
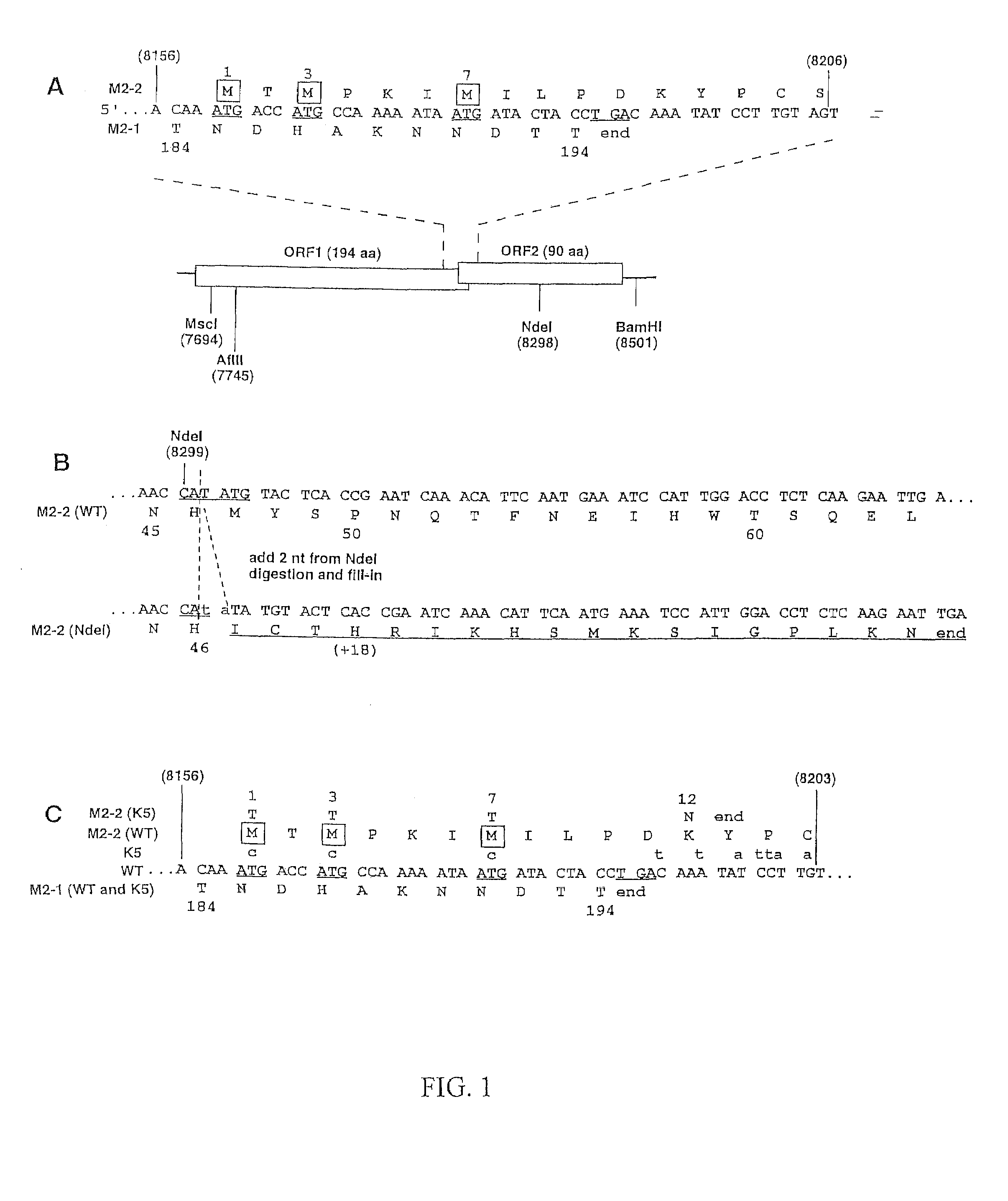
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are provided in which expression of the second translational open reading frame encoded by the M2 gene (M2ORF2) is reduced or ablated to yield novel RSV vaccine candidates. Expression of M2 ORF2 is reduced or ablated by modifying a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome to incorporate a frame shift mutation, or one or more stop codons in M2 ORF2. Alternatively, M2 ORF2 is deleted in whole or in part to render the M2-2 protein partially or entirely non-functional or to disrupt its expression altogether. M2 ORF2 deletion and knock out mutants possess highly desirable phenotypic characteristics for vaccine development. These changes specify one or more desired phenotypic changes in the resulting virus or subviral particle. Vaccine candidates are generated that show a change in mRNA transcription, genomic or antigenomic RNA replication, viral growth characteristics, viral antigen expression, viral plaque size, and / or a change in cytopathogenicity. In addition, M2-2 knock out or deletion virus exhibits increased levels of synthesis of viral proteins in cell culture, providing an enriched source of viral antigen or protein for purification and use as a noninfectious subunit vaccine.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Vaccine against rsv
ActiveUS20180200360A1Reduce infectionReducing replicationSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWild typeTGE VACCINE
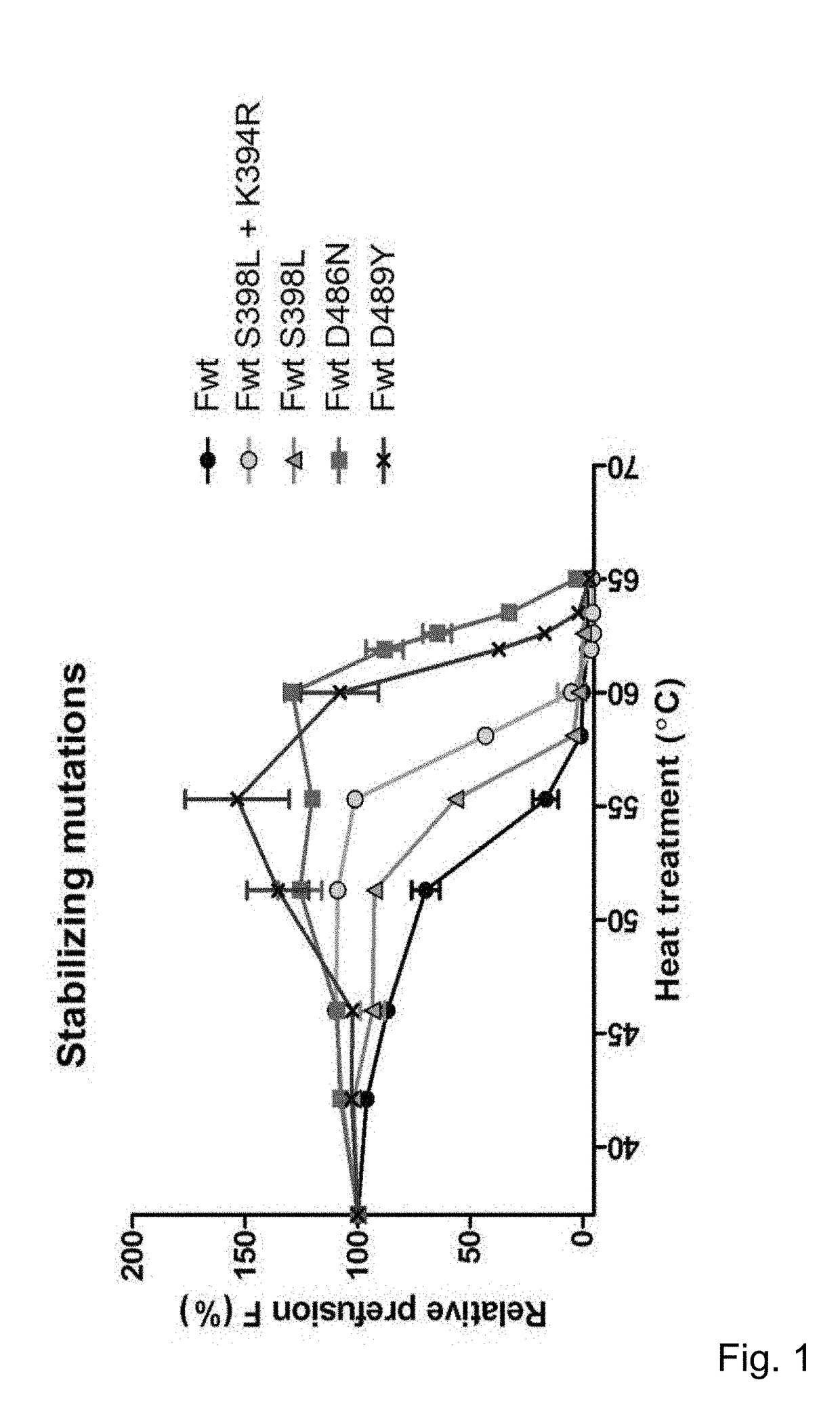
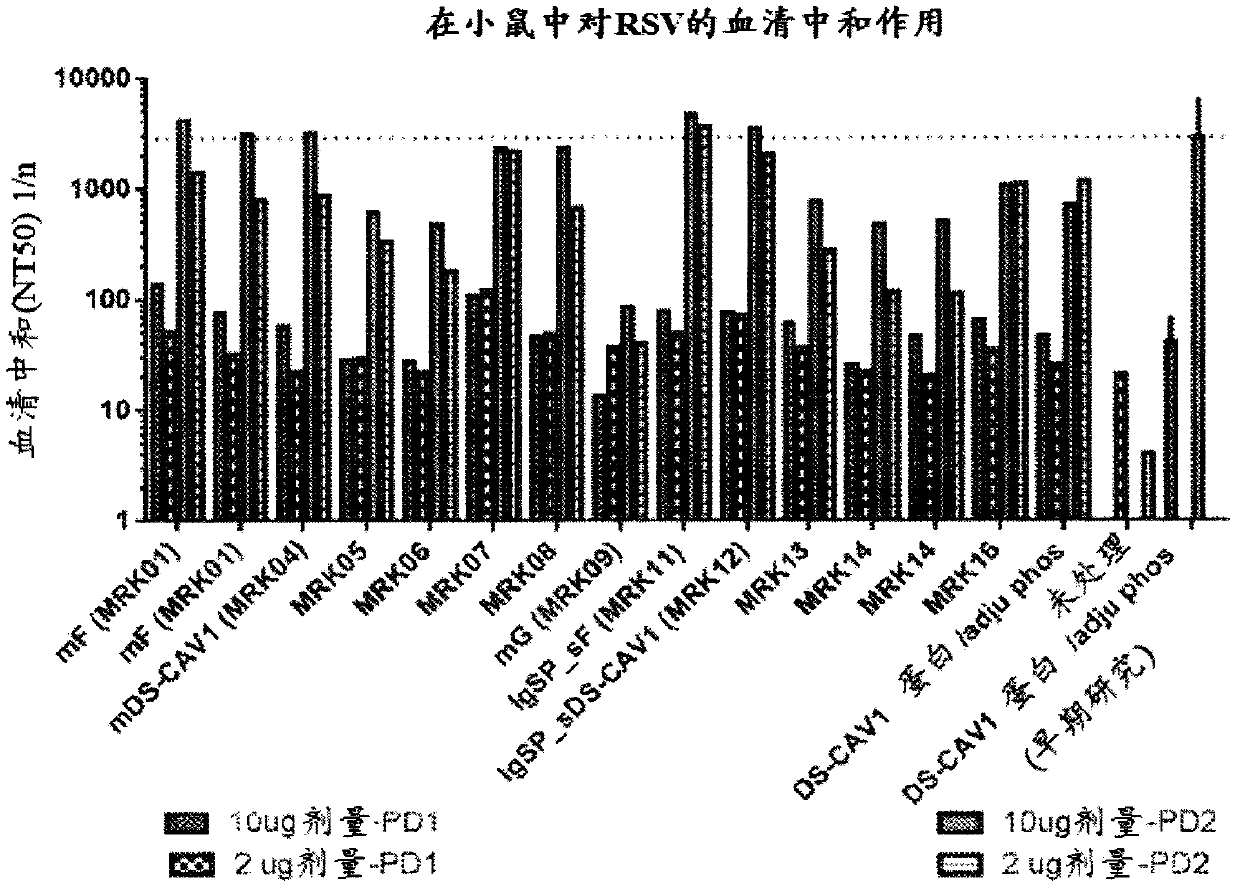
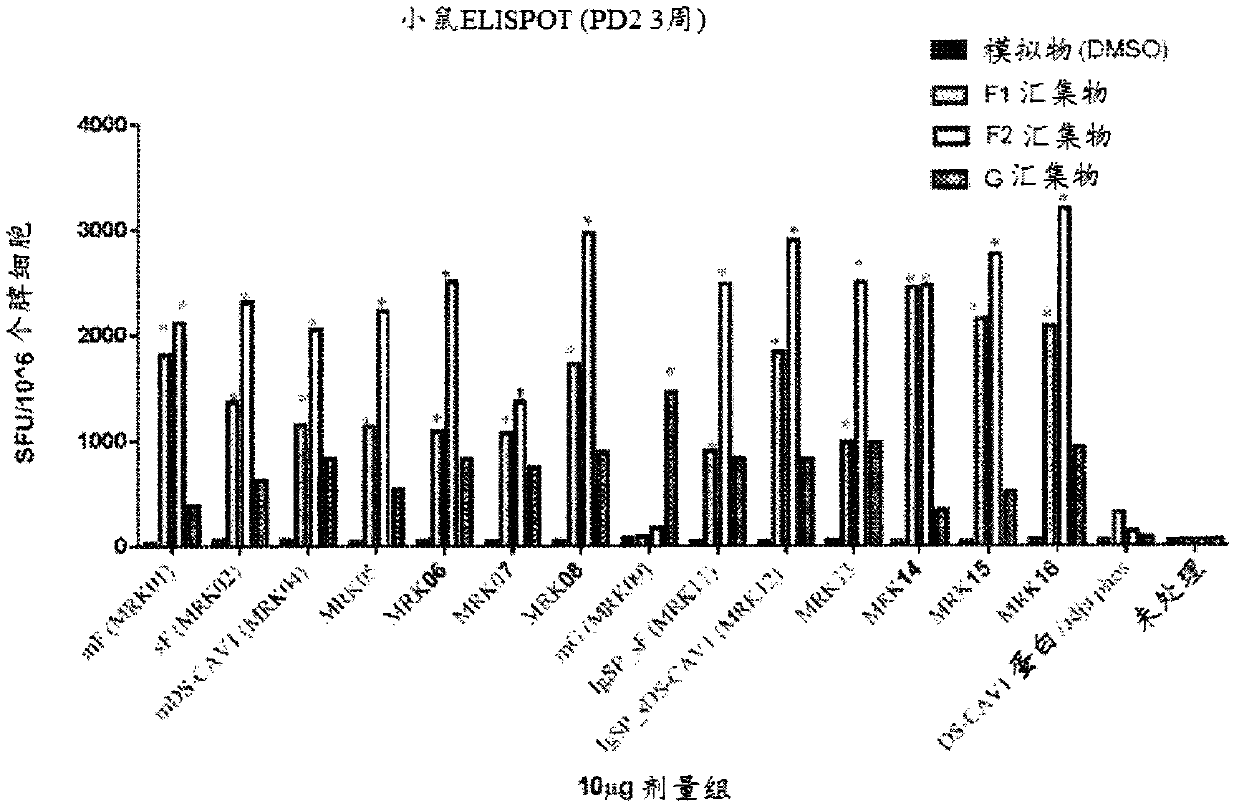
Compositions including a recombinant respiratory syncitial virus (RSV) Fusion (F) polypeptide that is stabilized in the pre-fusion conformation are described. The RSV F polypeptide includes at least one mutation as compared to a wild type RSV F polypeptide and the at least one mutation is a) a mutation of the amino acid aspartic acid (D) on position 486, b) a mutation of the amino acid aspartic acid (D) on position 489, or c) a mutation of the amino acid serine (S) on position 398 and / or the amino acid lysine (K) on position 394. Compositions including an isolated nucleic acid molecule encoding the stable RSV F polypeptides are also described.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Production of attenuated, human-bovine chimeric respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS20060057158A1Promote growthImprove the attenuation effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsHeterologousGenomic Segment
Chimeric human-bovine respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals and useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a chimeric RSV genome or antigenome which includes a partial or complete human or bovine RSV “background” genome or antigenome combined or integrated with one or more heterologous gene(s) or genome segment(s) of a different RSV strain. Chimeric human-bovine RSV of the invention include a partial or complete “background” RSV genome or antigenome derived from or patterned after a human or bovine RSV strain or subgroup virus combined with one or more heterologous gene(s) or genome segment(s) of a different RSV strain or subgroup virus to form the human-bovine chimeric RSV genome or antigenome. In preferred aspects of the invention, chimeric RSV incorporate a partial or complete bovine RSV background genome or antigenome combined with one or more heterologous gene(s) or genome segment(s) from a human RSV. Genes of interest include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment including a protein or portion thereof. A variety of additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within the human-bovine chimeric RSV of the invention to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promoter-proximal genes
InactiveUS7662397B2Altered immunogenicitySmall sizeSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsProtective antigenNucleotide
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals. Gene shifted RSV are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome wherein a gene or gene segment is shifted to a more promoter-proximal or promoter-distal position within the genome or antigenome compared to a wild type position of the gene in the RSV gene map. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene, depending on the nature and degree of the positional shift.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Subunit respiratory syncytial virus vaccine preparation
InactiveUS20040265326A1Slow and sustained releaseImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIon exchangeViral Vaccine
The fusion (F) protein, attachment (G) protein and matrix (M) protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are isolated and purified from respiratory syncytial virus by mild detergent extraction of the proteins from concentrated virus, loading the protein onto a hydroxyapatite or other ion-exchange matrix column and eluting the protein using mild salt treatment. The F, G and M proteins, formulated as immunogenic compositions, are safe and highly immunogenic and protect relevant animal models against decreased caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Owner:CATES GEORGE A +3
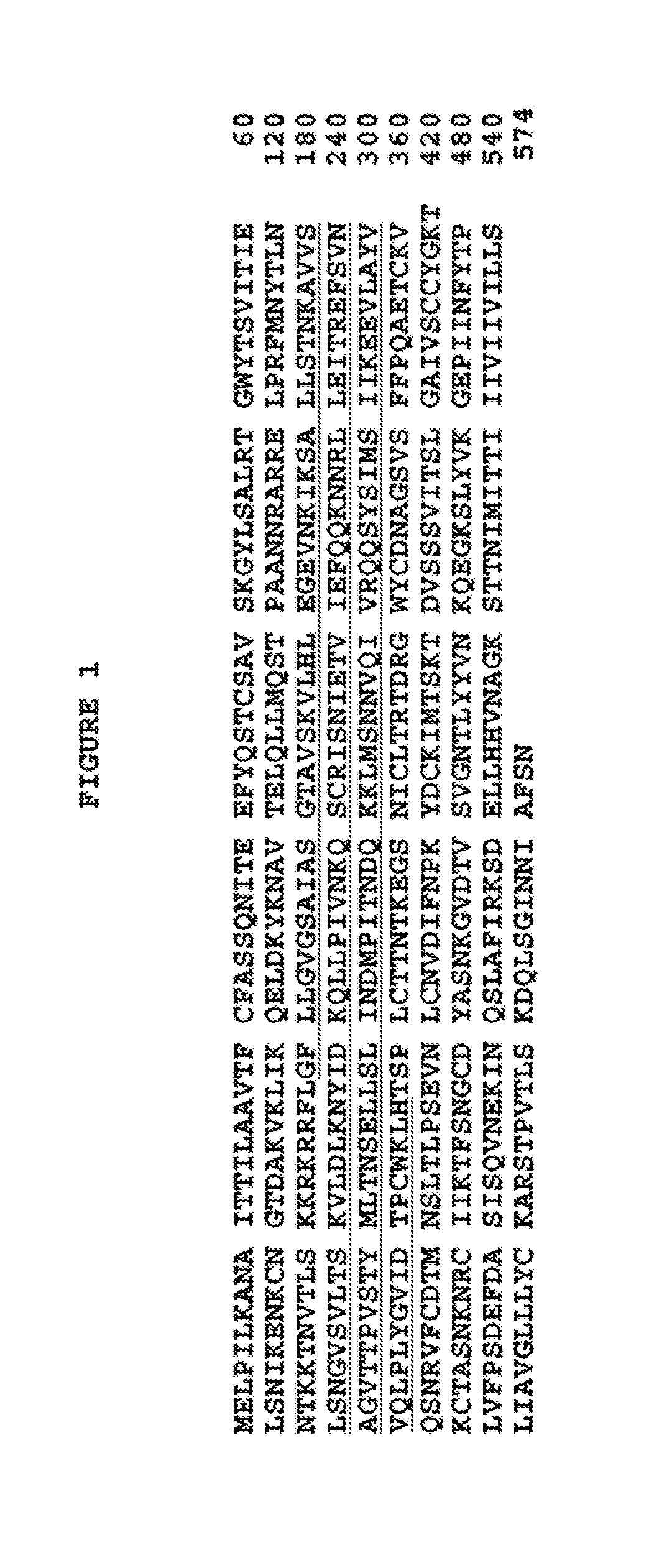
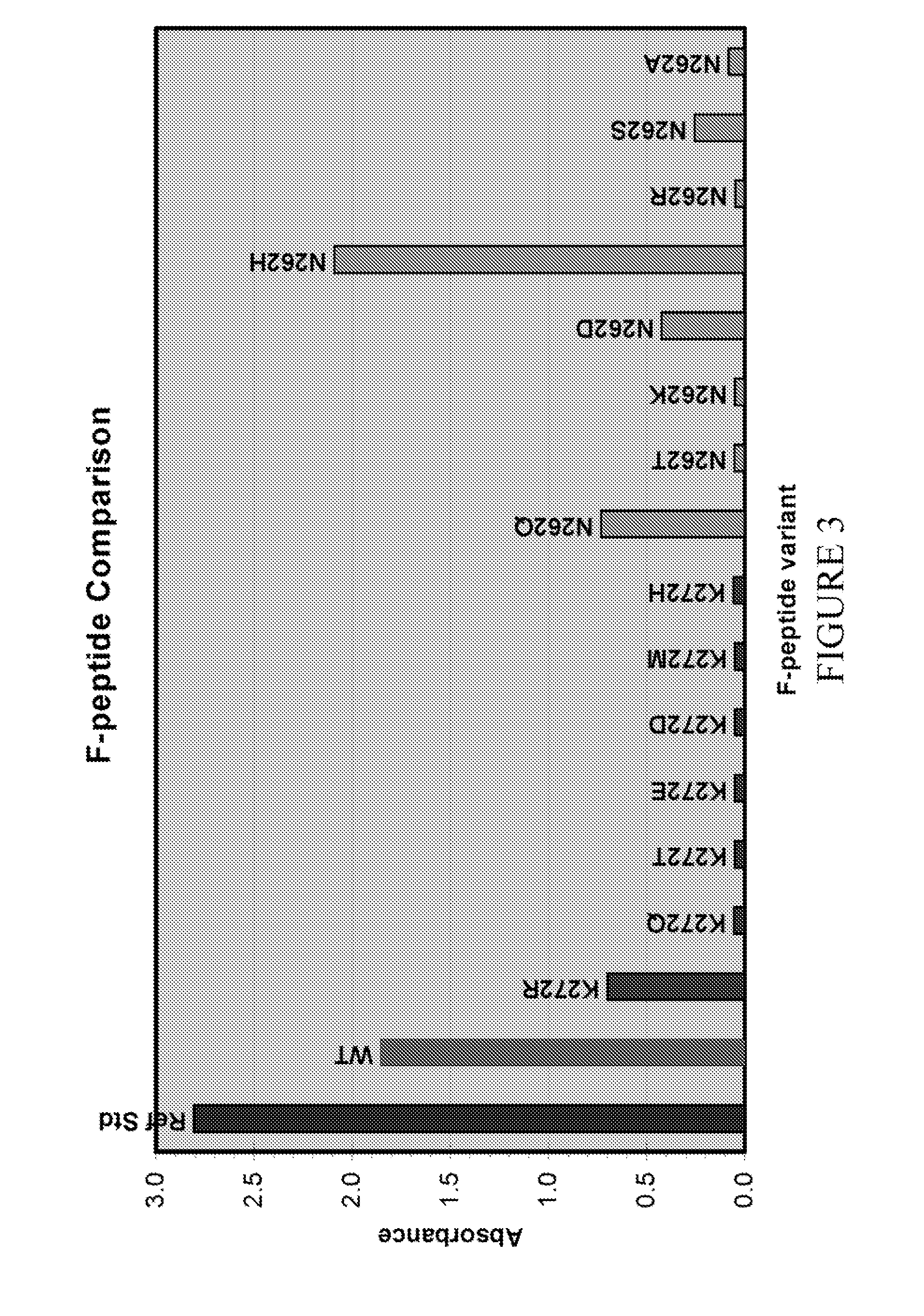
Antibodies Against And Methods For Producing Vaccines For Respiratory Syncytial Virus
ActiveUS20120156235A1Reduce morbidityShorten the durationSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptideRespiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines
The present invention relates to novel respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) F peptides and compositions comprising them. The present invention also relates to methods of evaluating anti-RSV antibody binding to F peptides. The present invention also relates to antibodies that immunospecifically bind to an F peptide of the present invention. The invention further provides methods and protocols for the administration of F peptides and / or antibodies that immunospecifically bind to F peptides for the prevention, neutralization, treatment of RSV infection. Additionally, the methods of the invention may be useful for the treatment, prevention and the amelioration of symptoms associated with RSV infection.
Owner:AREXIS
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccine
PendingCN108472354ASsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsRNA - Ribonucleic acidTGE VACCINE
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Production of attenuated respiratory syncytial virus vaccines from cloned nucleotide sequences
InactiveUS20060159703A1Stabilizing mutationImprove scalabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiNucleotideWild type
Attenuated respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and vaccine compositions thereof are produced by introducing specific mutations associated with attenuating phenotypes into wild-type or RSV which is incompletely attenuated by cold-passage or introduction of mutations which produce virus having a temperature sensitive (ts) or cold adapted (ca) phenotype. Alternatively, recombinant RSV and vaccine compositions thereof incorporate attenuating and other mutations specifying desired structural and or phenotypic characteristics in an infectious RSV. Recombinant RSV incorporate desired mutations specified by insertion, deletion, substitution or rearrangement of a selected nucleotide sequence, gene, or gene segment in an infectious RSV clone. The immune system of an individual is stimulated to induce protection against natural RSV infection, or multivalently against infection by RSV and another pathogen, such as PIV, by administration of attenuated, biologically derived or recombinant RSV.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Replication-defective adenovirus vector vaccine for co-expressing respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion protein and adhesion glycoprotein
ActiveCN112226450ARapid immune responseStrong immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideVector vaccine
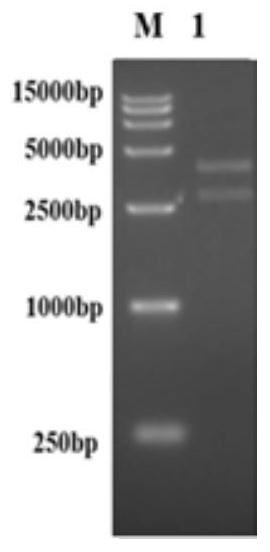
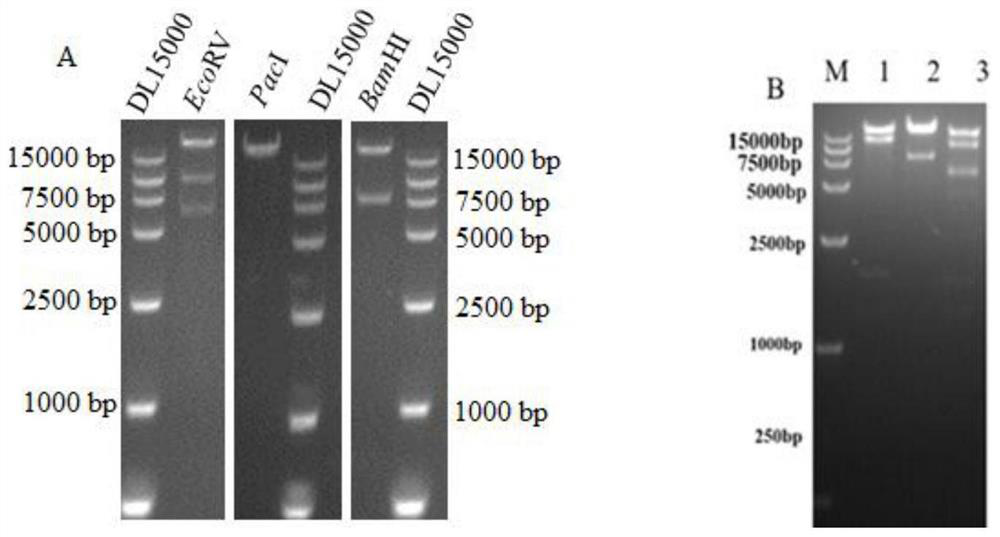
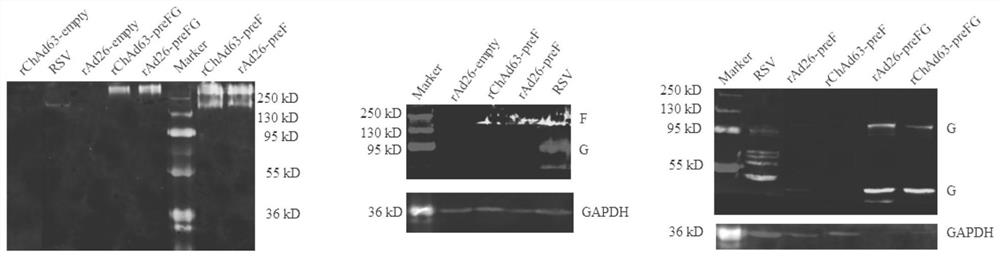
The invention provides a nucleotide sequence for co-expressing a respiratory syncytial virus pre-fusion glycoprotein (preF) and an adhesion glycoprotein 130-230aa (G130-230) and a preparation method of the nucleotide sequence. The sequence comprises nucleotide sequences of preF and G130-230, wherein the nucleotide sequences of preF and G130-230 are connected together by a T2A sequence; the nucleotide sequence contains a coding sequence shown as a preF2A3G sequence; the nucleotide sequence for coding preF is located at the 5' end of the preF2A3G sequence; the nucleotide sequence for coding G130-230 is located at the 3' end of the preF2A3G sequence; the nucleotide sequence is expressed by a chimpanzee 63-type replication-defective recombinant adenovirus vector or a human 26-type replication-defective recombinant adenovirus vector; the recombinant adenovirus is rChAd63 / preF2A3G or rAd26 / preF2A3G; after the recombinant adenovirus is used for immunizing an animal, a serum antibody aiming atthe fusion glycoprotein and the adhesion glycoprotein can be induced and generated simultaneously; and the induced and generated serum antibody is an antibody aiming at preF mainly and can be appliedto a vaccine for preventing the respiratory syncytial virus. The recombinant adenovirus vaccine can be prepared in a large scale and is used for preventing RSV infection.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promotor-proximal genes
InactiveUS20060024797A1Promote growthImprove the attenuation effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesAntigenGenomic Segment
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals. Gene shifted RSV are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome wherein a gene or gene segment is shifted to a more promoter-proximal or promoter-distal position within the genome or antigenome compared to a wild type position of the gene in the RSV gene map. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene, depending on the nature and degree of the positional shift. In one embodiment, RSV glycoproteins are upregulated by shifting one or more glycoprotein-encoding genes to a more promoter-proximal position. Genes of interest for manipulation to create gene position-shifted RSV include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment that may be part of a gene or extragenic. A variety of additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within the gene position-shifted RSV of the invention to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Plant-derived vaccines against respiratory syncytial virus
A plant-derived vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is disclosed. The vaccine includes an immunogenic complex that includes plant cells transformed with a chimeric gene containing a nucleotide sequence adapted for protein expression in plants and an RSV coding sequence that encodes an antigenic protein of RSV. Also disclosed are methods of making the plant-derived vaccine of the invention, as well as transgenic plants, transgenic plant cells, and nucleic acid constructs useful in immunizing a mammal against RSV.
Owner:KRASNYANSKI SERGEI F +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com