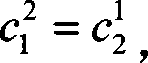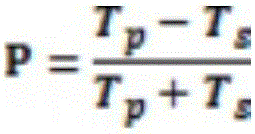Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Periodic boundary conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Periodic boundary conditions (PBCs) are a set of boundary conditions which are often chosen for approximating a large (infinite) system by using a small part called a unit cell. PBCs are often used in computer simulations and mathematical models. The topology of two-dimensional PBC is equal to that of a world map of some video games; the geometry of the unit cell satisfies perfect two-dimensional tiling, and when an object passes through one side of the unit cell, it re-appears on the opposite side with the same velocity.
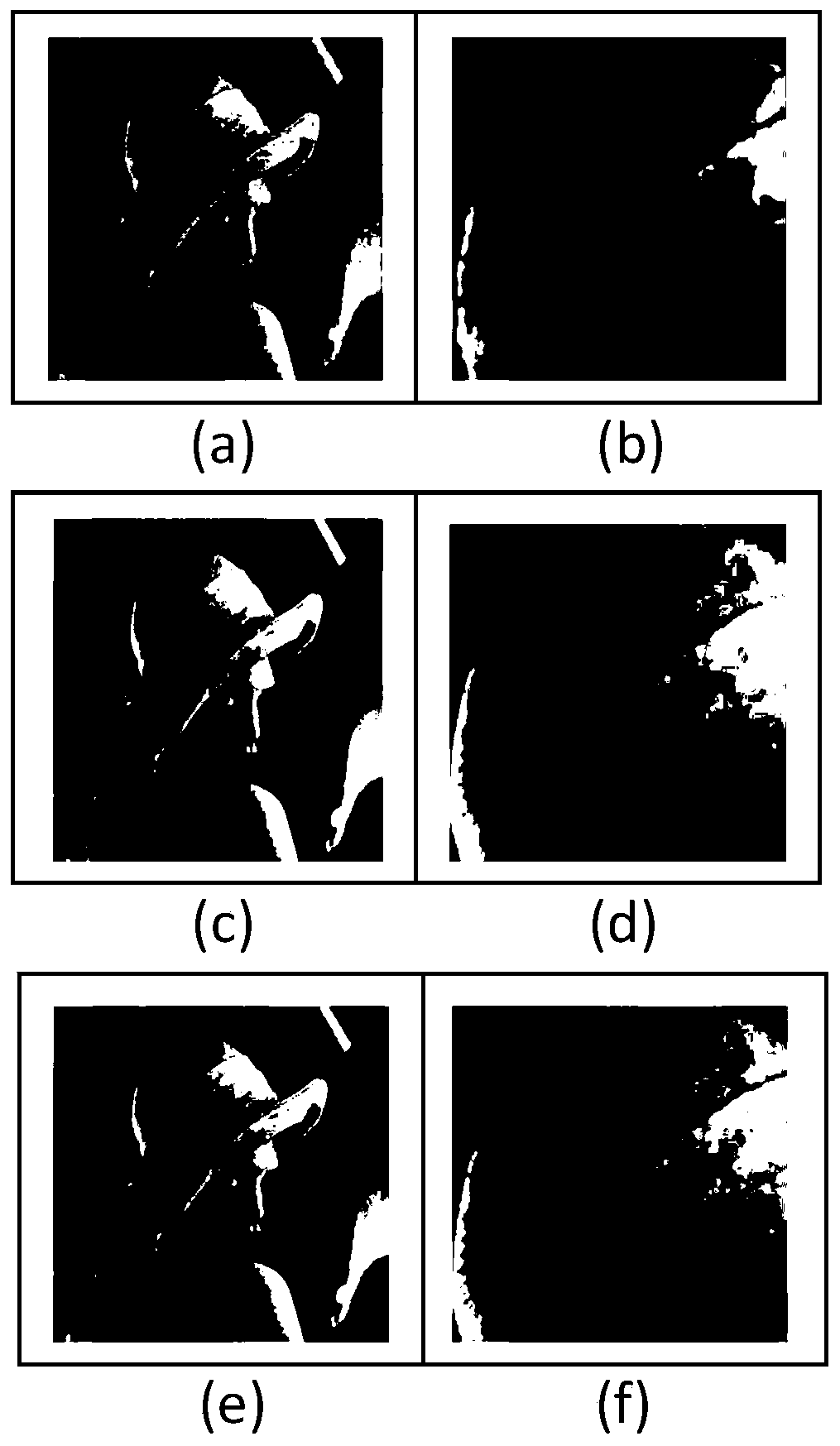
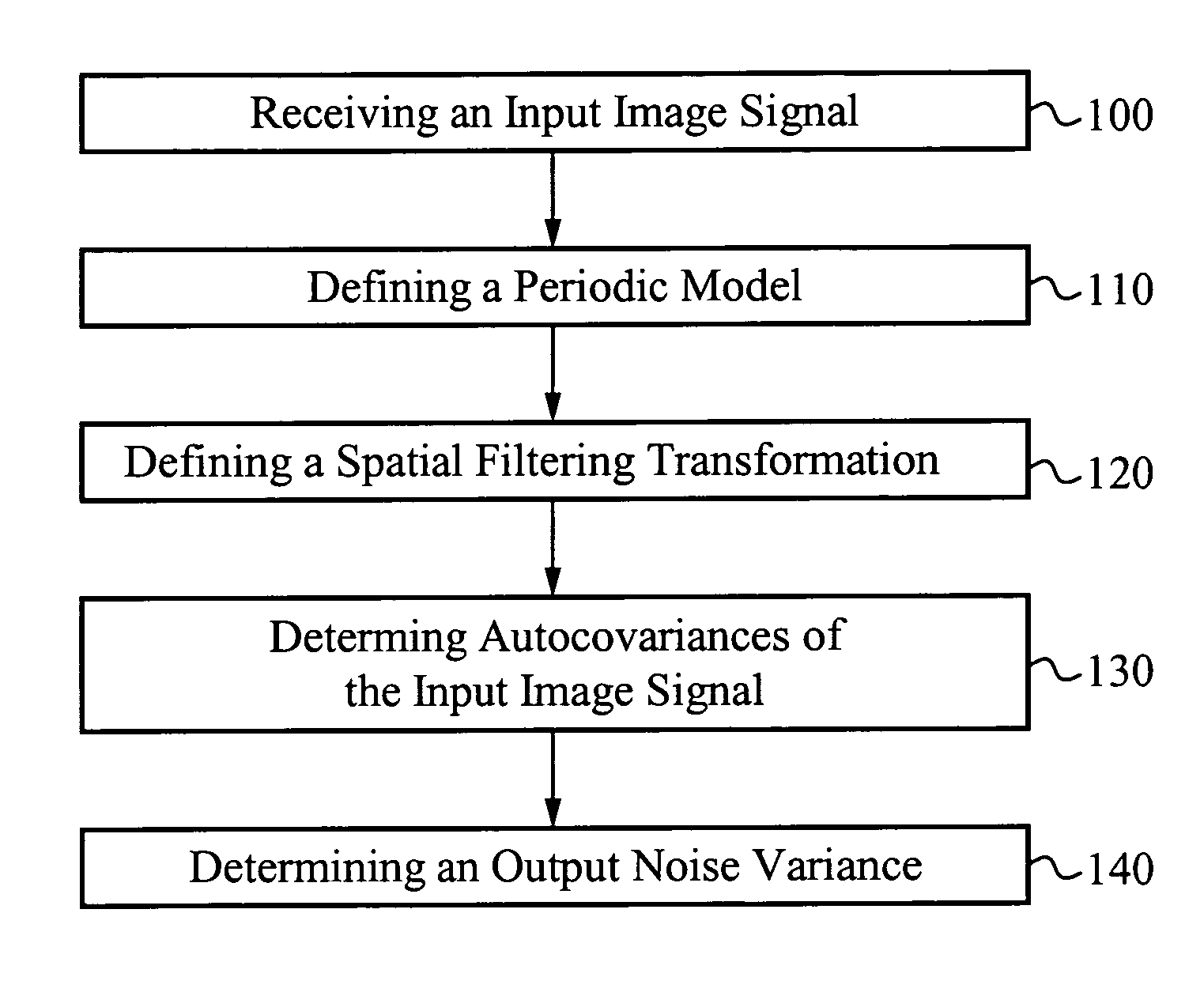
Method of estimating noise in spatial filtering of images
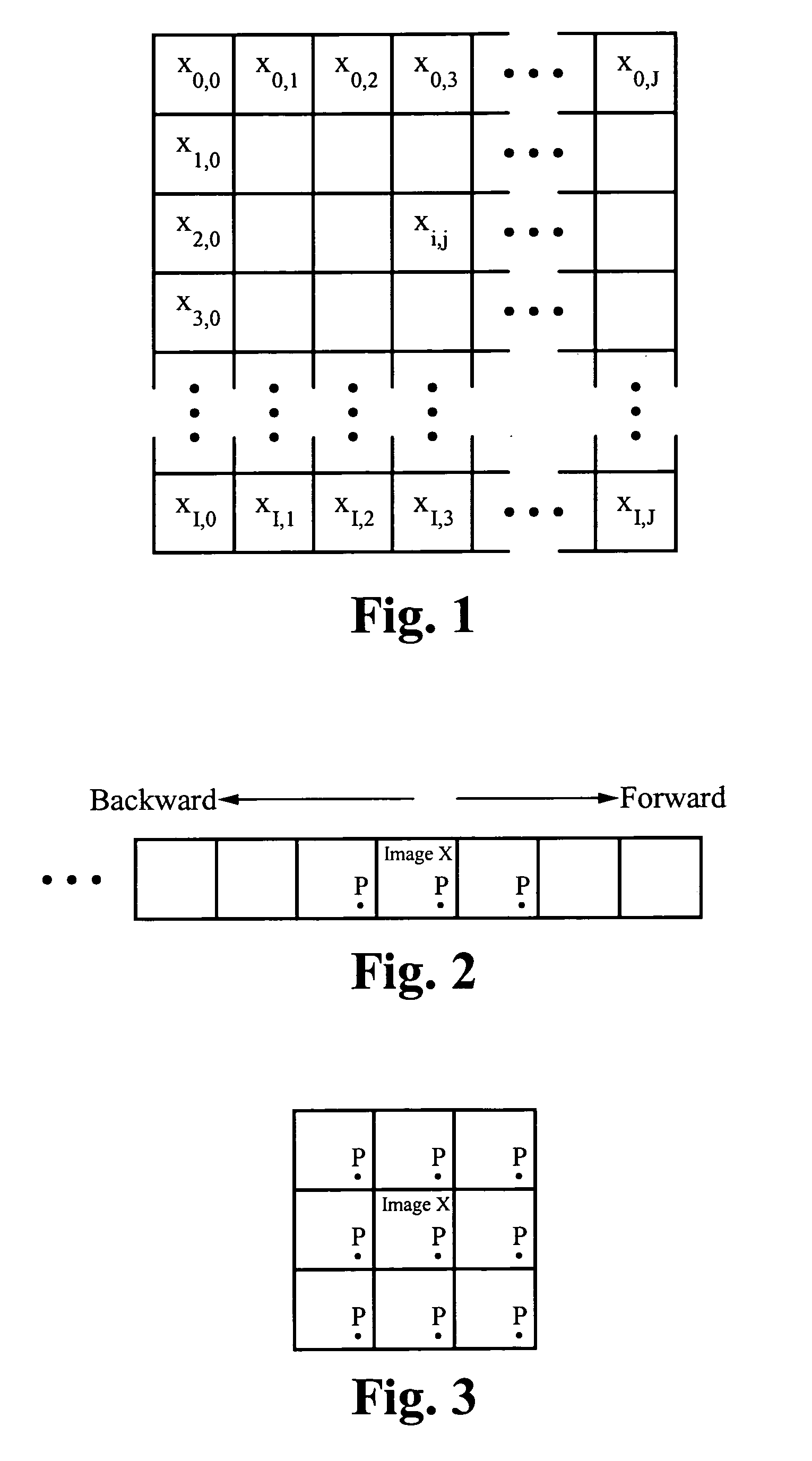
A noise prediction scheme provides a method of predicting an output noise variance resulting from a spatial filtering transformation. For a given input image signal with a known input noise variance, a periodic model is developed. The periodic model defines periodic boundary conditions for the input image signal based on the principal that the input image signal is repeated in each direction. In this manner, pixel values are defined about either side of the input image signal boundaries in either one, two, or three dimensions. A spatial filtering transformation includes convoluting the input image signal with an impulse response of a filter. Autocavariances at different points in time or lags of the input image signal are also determined. The number of autocovariances is determined by the nature of the spatial filtering transformation. The noise prediction scheme predicts an output noise variance resulting from the spatial filtering transformation based on the input noise variance, the autocovariances, and the periodic boundary conditions of the input image signal.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Multi-GPU molecular dynamics simulation method for structural material radiation damage
ActiveCN105787227AReduce energy costsReduce maintenance costsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTime evolution
The invention discloses a multi-GPU molecular dynamics simulation method for structural material radiation damage. The method comprises the following steps: initializing; dynamically dividing grids for each node; performing inter-node communication; establishing a sorting cellular list on GPU; updating time step; finding the corresponding relationship between particle and grid number according to the coordinate of the particle; forecasting the displacement, speed and accelerated speed of the particle; calculating the stress of each particle; utilizing the stress to rectify the displacement, speed and accelerated speed of the particle; ensuring the constant temperature of the system according to the ensemble correcting speed; utilizing a periodic boundary condition to correct the position of the particle; storing a current calculation result; and iteratively executing the above steps till reaching preset step number. The method can be utilized to high-efficiently and conveniently simulate the material radiation damage process on larger spatial and temporal scale and to explain the long-time evolution law of the radiation damage at micro-scale.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Design method for large-bandwidth strong-absorption metamaterial near-infrared wave-absorbing material
InactiveCN104181622AAbsorption BandwidthImprove conversion efficiencyOptical elementsCircular discUnit structure
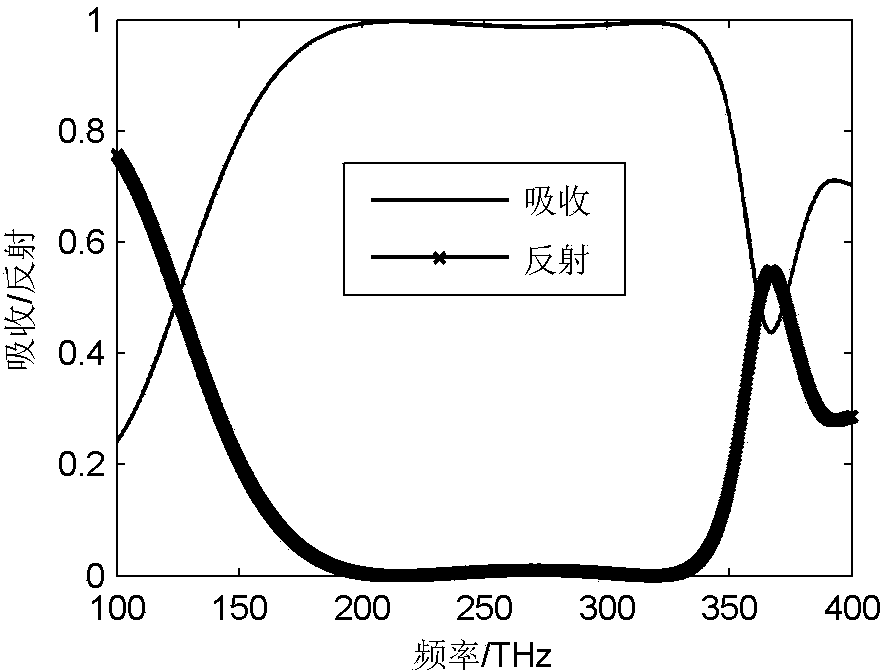
The invention discloses a design method for a large-bandwidth strong-absorption metamaterial near-infrared wave-absorbing material. The method includes the following steps: 1. according to an effective medium theory and through simulation of a CST microwave studio, S parameters are obtained, wherein a frequency domain calculation mode is adopted during the simulation; periodic unit structures are periodically distributed in x and y directions and the periodic distribution is set as a periodic boundary condition; and according to parameters S11 (Omega) and S21(Omega) obtained through scanning, a resistance value is calculated. 2. through change of the period of the unit structures and the sizes of titanium resonant plates, corresponding absorption frequencies are adjusted and then the plurality of resonant plates of different sizes are horizontally placed in one unit so that absorption spectral lines corresponding to the different resonant plates are overlapped. The method adopts a high-loss metal so that a wideband wave-absorbing effect can be achieved through a simple structure. Resonant units of one size are replaced by the resonant units of different sizes so that a resonance mode of adjacent frequencies can be triggered and an absorption bandwidth can be further expanded.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for predicting residual stiffness of two-dimensional braided ceramic matrix composite material after oxidation
ActiveCN105930579AResidual Stiffness PredictionStiffness PredictionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMetallurgyResidual stiffness
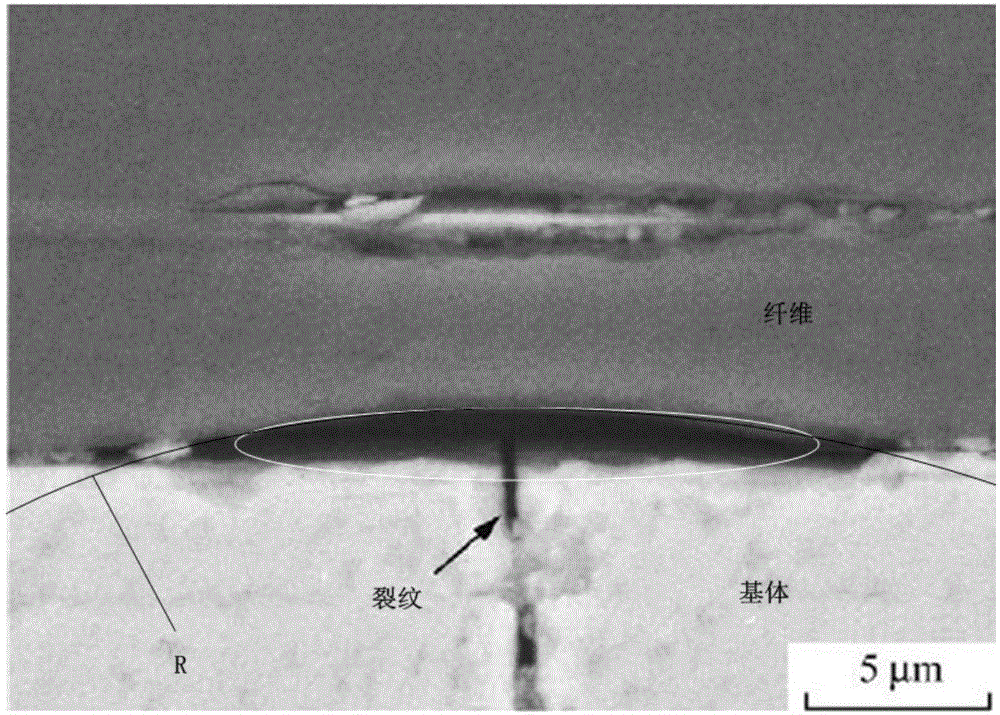
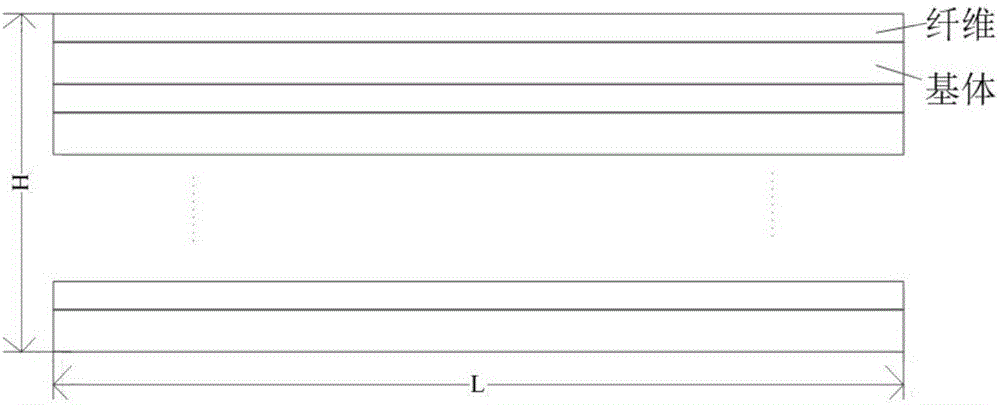
The invention relates to a method for predicting residual stiffness of a two-dimensional braided ceramic matrix composite material after oxidation. The stiffness refers to elastic deformation resistance ability of the material under stress. By analyzing the stiffness of each component of the material, stress and strain distribution in the material can be determined. Therefore, the invention provides the method capable of accurately predicting the residual stiffness of the two-dimensional braided ceramic matrix composite material after oxidation. A kinetic model considering fiber oxidation is proposed, and based on this, a microscale model considering fiber oxidation and a mesoscale model of the two-dimensional braided ceramic matrix composite material are established. With the adoption of a finite element method, the residual stiffness of the material after oxidation is calculated by applying a periodic boundary condition. According to the method, the residual stiffness of the material in different oxidation temperature intervals at different oxidation time can be accurately predicted and does not need to be tested by a large amount of manpower and material resources through tests, so that a large amount of test costs are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for generating random structure of continuous fiber composite material and predicting elastic performance of continuous fiber composite material
ActiveCN106815408AIncrease randomnessImprove production efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelThree-phase
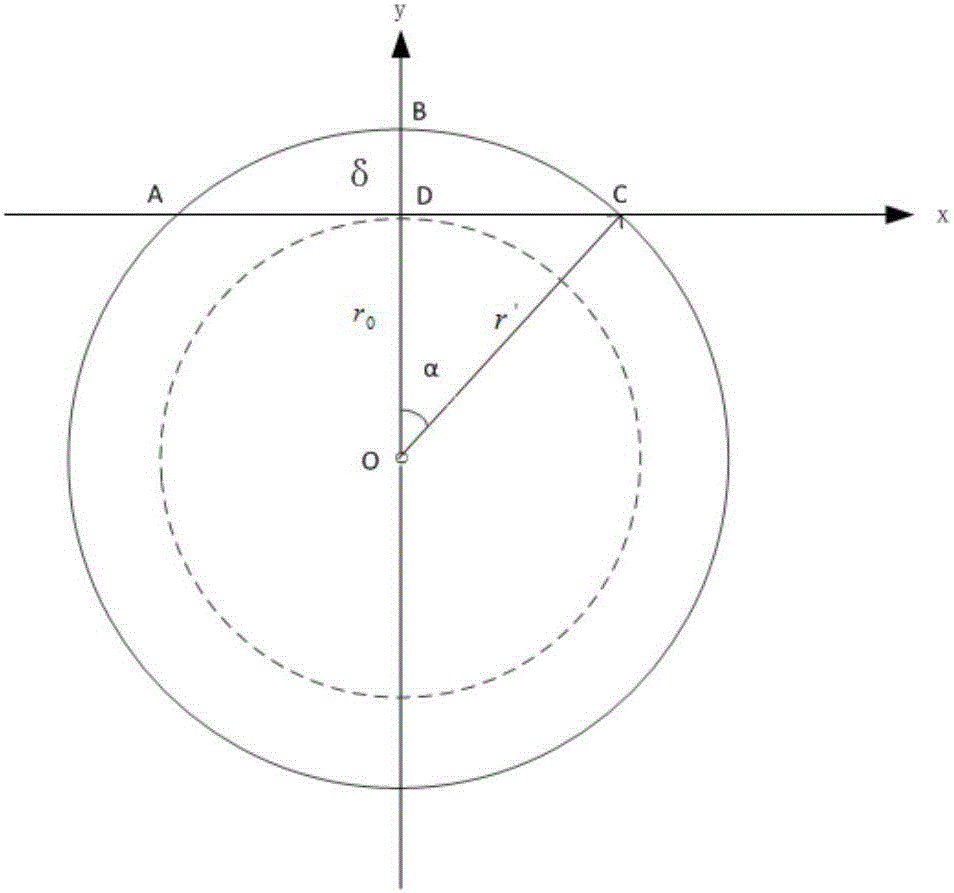
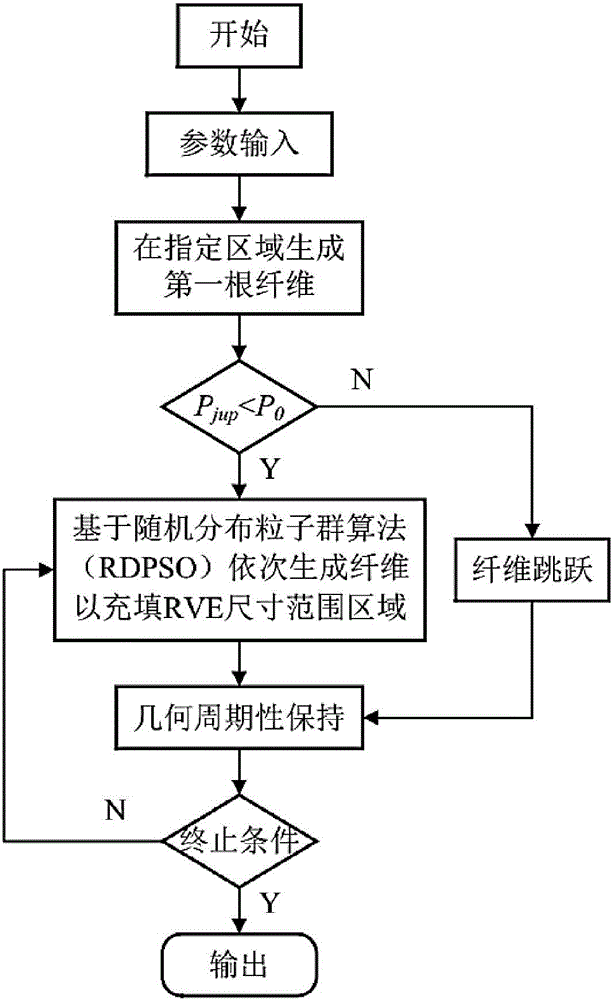
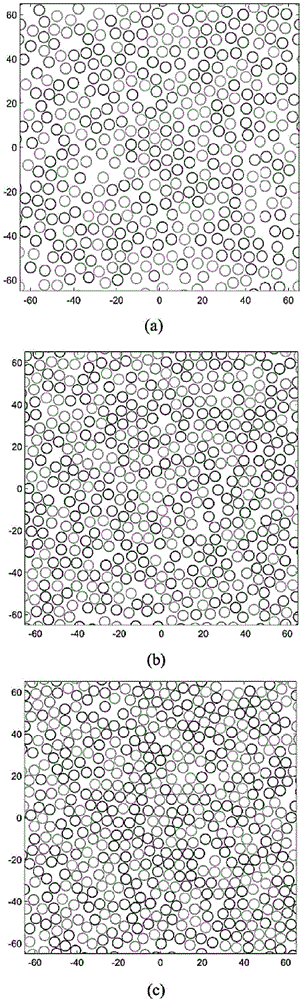
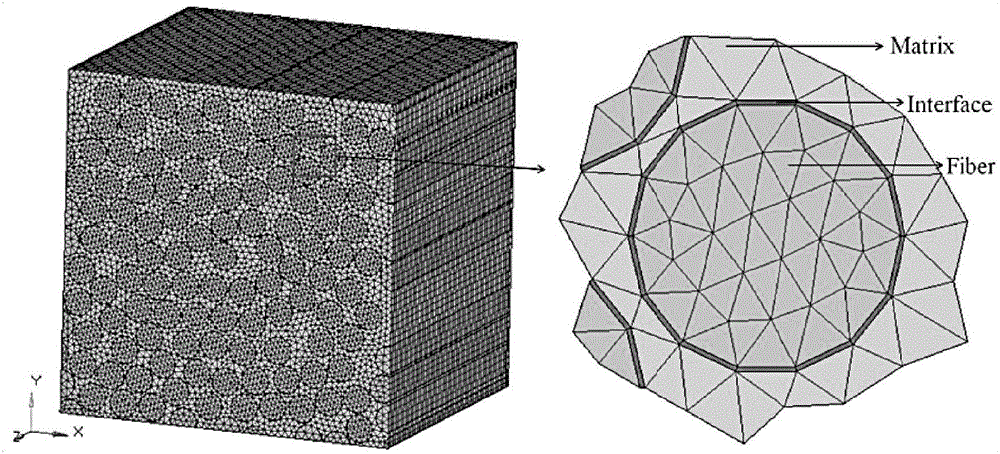
The invention provides a method for generating a random structure of a continuous fiber composite material and predicting the elastic performance of the continuous fiber composite material. The method comprises the following steps: generating a fiber model by a particle swarm algorithm, and optimizing the fiber model according to fiber jumping treatment to obtain particle space random distribution information for generating a three-phase RVE finite element model; and performing finite element simulation operation on the three-phase RVE finite element model to obtain a prediction result. Based on a representative volume element generation strategy of the particle swarm algorithm, the distance among fibers is controlled by the particle swarm algorithm in the process of generating the representative volume element, the requirement for the material volume percentage is fulfilled while fiber random distribution is ensured; and based on efficient generation of the representative volume unit and a homogenization theory, an elasticity prediction finite element model is established, a periodic boundary condition is applied, and the elasticity performance prediction result of the material can be obtained by microscomic finite element simulation, so that the efficiency of elasticity performance prediction is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Finite element simulation method capable of removing microwave tube high-frequency circuit in pseudo-DC mode
InactiveCN101944145AEfficient designFast and Efficient UWB Parametric SweepSpecial data processing applicationsMicrowave tubeClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a finite element simulation method capable of removing a microwave tube high-frequency circuit in a pseudo-DC mode, comprising the flowing steps: (A) using a zero electric displacement vector as an electric field constraint equation and acquiring an integrated form of the electric field constraint equation according to an boundary value problem of an electromagnetic field in a microwave tube high-frequency circuit and acquiring a functional equation of the boundary value problem of the electromagnetic field through a standard variation principle of a finite element method; and (B) necessarily ensuring the match between grids on a main surface and grids on a secondary surface on a peripheral boundary when solving a solution domain and considering a pseudo-periodic boundary condition by adopting a dissection solution domain of tetrahedral grids. The invention has the advantages that the finite element simulation method can greatly improve the accuracy, the efficiency and the robustness of microwave tube high-frequency system simulation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-dimensional predicting method for strength of braided ceramic base composite material
ActiveCN109920495AAccurately predict strengthChemical data visualisationComputational theoretical chemistryYarnMultiple-scale analysis
The invention provides a multi-dimensional predicting method for strength of a braided ceramic base composite material. Firstly a parameterization method is used for establishing a braided ceramic base composite material single-cell model which comprises yarns and a matrix, and then period grid dividing is performed. Afterwards a mesomechanics method is used for simulating the mechanics behavior of the yarn unit. Furthermore a strain conversion matrix is used for converting a yarn element stiffness matrix from a local coordinate system to an integral coordinate system. Finally through applyingan increment type periodic boundary condition, a micro-stress and a strain field of a single cell are calculated. A volume averaging method is used for obtaining a microscopic stress and strain of the braided ceramic base composite material. If a failure unit band which penetrates through the single cell is formed, failure of the braided ceramic base composite material is determined, and the single-cell average stress is the strength of the braided ceramic base composite material. According to the multi-dimensional predicting method, the multidimensional analysis method in which macrography and mesography are combined is utilized. The strength of the braided ceramic base composite material can be accurately predicted without dependence to a large number of experiments with time consumption and high cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for comparison test of thermal performance of two walls and test device
InactiveCN109187626AReduce experimental errorImprove the accuracy of comparative analysisMaterial heat developmentData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for comparison test of thermal performance of two walls and a test device. The test device comprises a test frame, two walls with different properties, temperature sensors, heat flow sensors and a data collecting and recording terminal. The method comprises the steps of collecting parameters of internal temperature distribution and surface heat flow transfer and the like under same heat transfer boundary conditions, of the two walls with different properties in the test frame, by utilizing the temperature sensors and the heat flow sensors; and carrying out comparative analysis on difference between the two walls on the aspects of the attenuation and the delay of temperature waves, heat transfer coefficient thermal performance parameters according to test data, wherein by applying the alternating temperature waves, specific values of the attenuation coefficients and the delay time of the two test walls can also be obtained respectively under periodic boundary conditions. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that not only can the advantages and the disadvantages of the thermal performance of the two walls be directly compared, butalso the test error can be reduced and the accuracy of the comparative analysis is improved. The device has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost and convenient to install.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
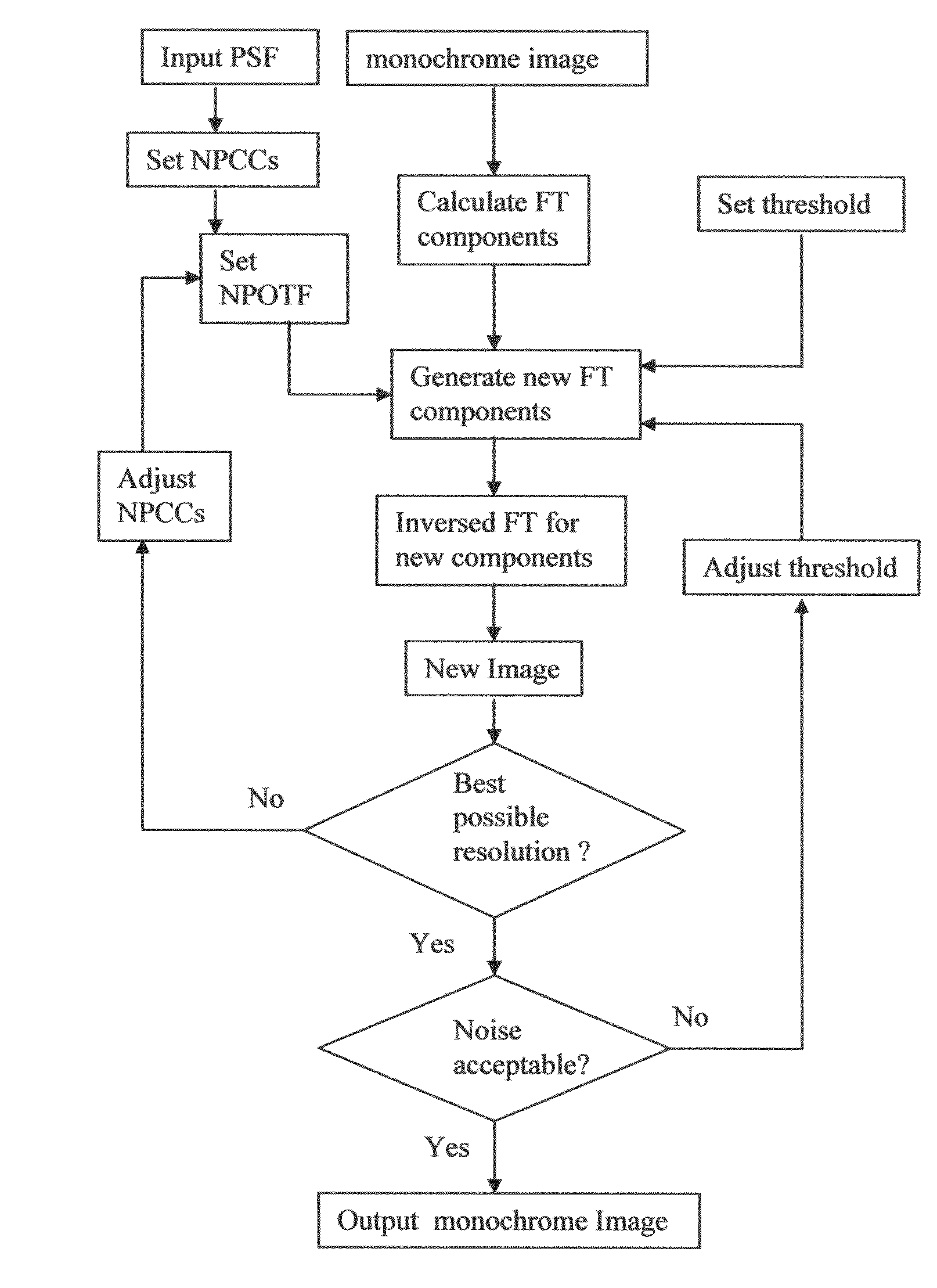
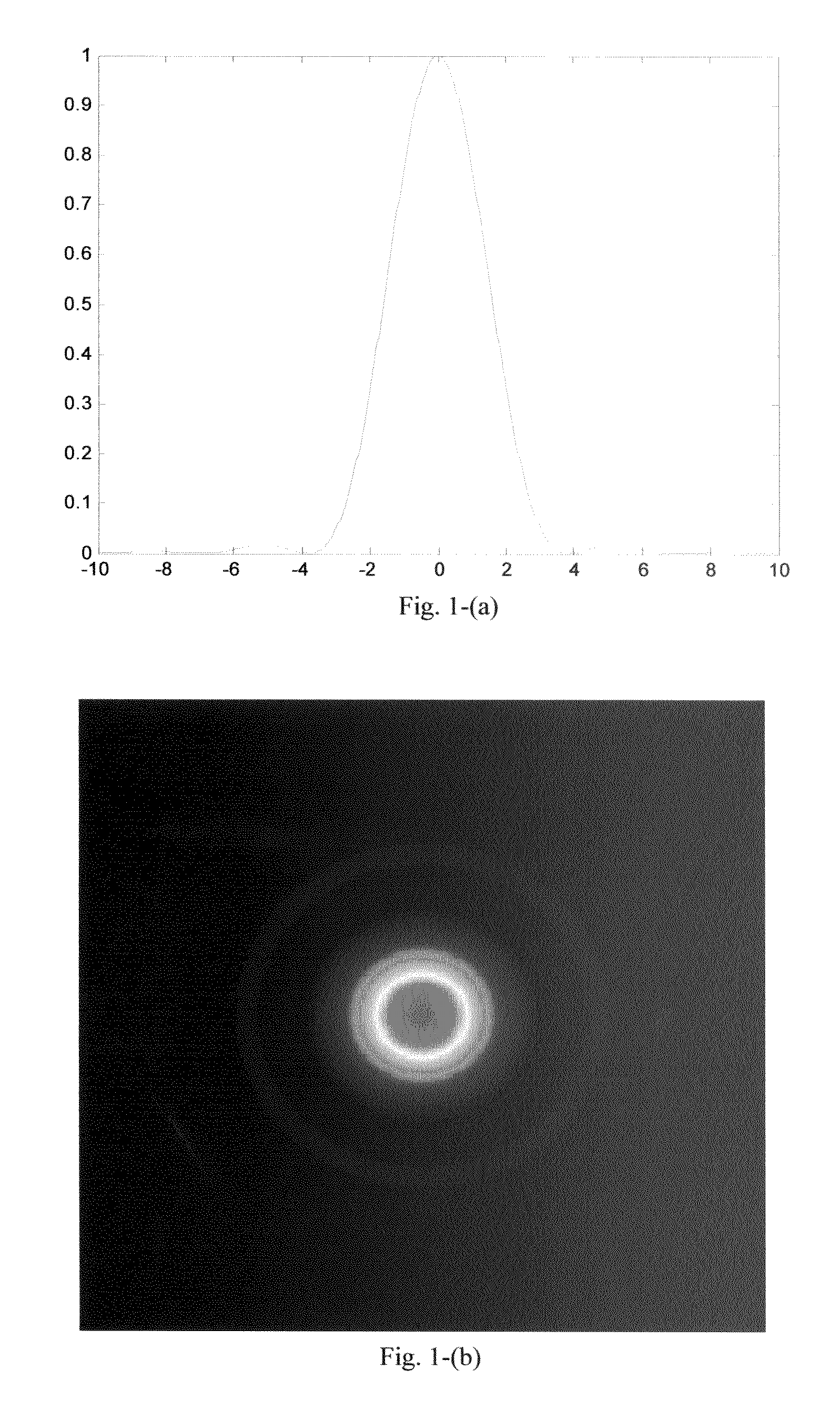
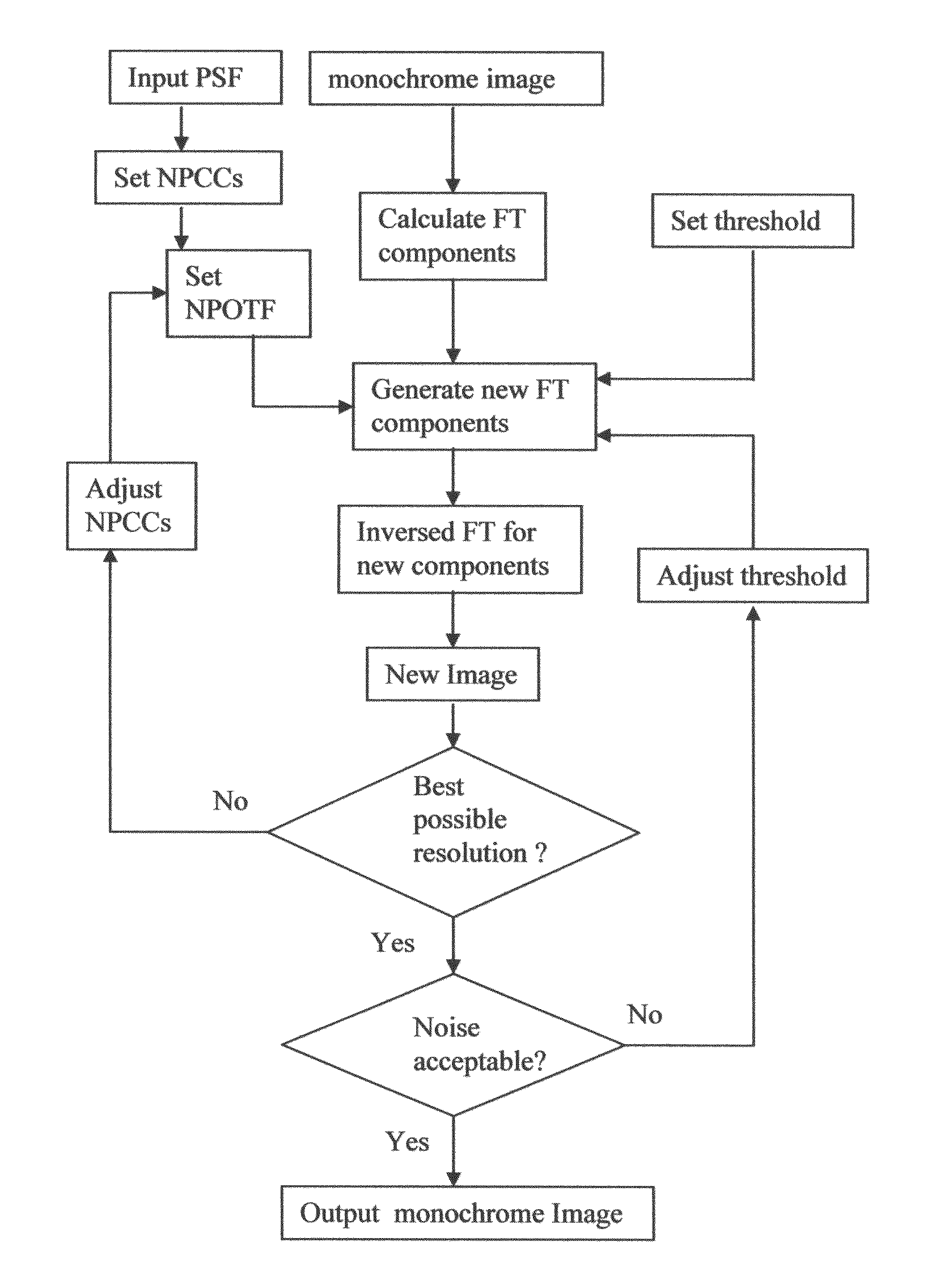
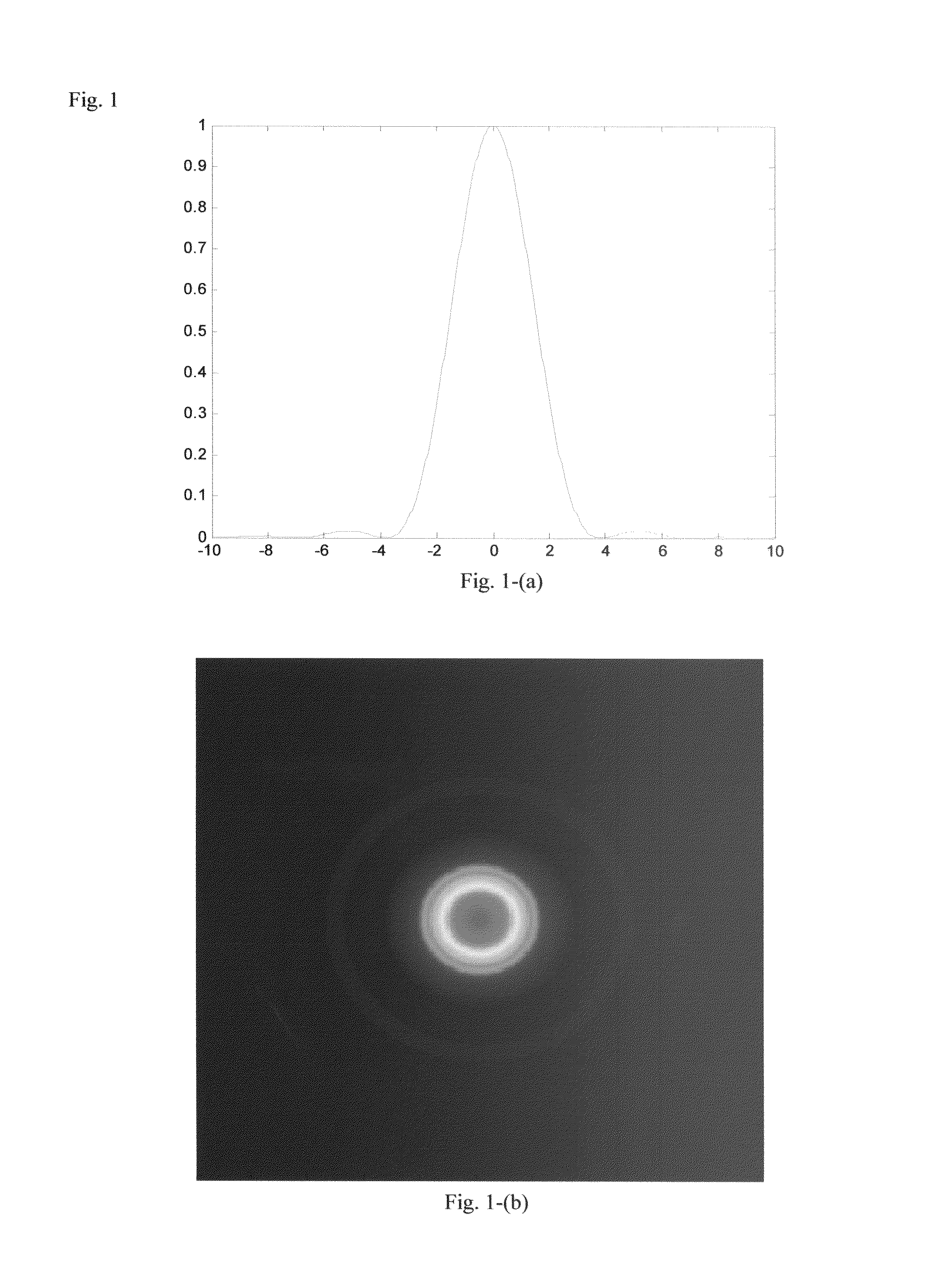
Deconvolution method using neighboring-pixel-optical-transfer-function in fourier domain
ActiveUS20080193034A1High resolutionImprove imaging resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingImage resolution
The present disclosure includes an image processing technique that is capable to increase spatial resolution of single frame images beyond diffraction limit. If an image is taken by diffraction limited optical system with regularly spaced pixel detectors, and if the spacing of pixels of the detectors is much small than the diffraction pattern, then the spatial resolution of the image can be increased beyond the diffraction limit by using neighboring-pixel-optical-transfer-function (NPOTF) in Fourier Domain with periodical boundary conditions.
Owner:WANG YU
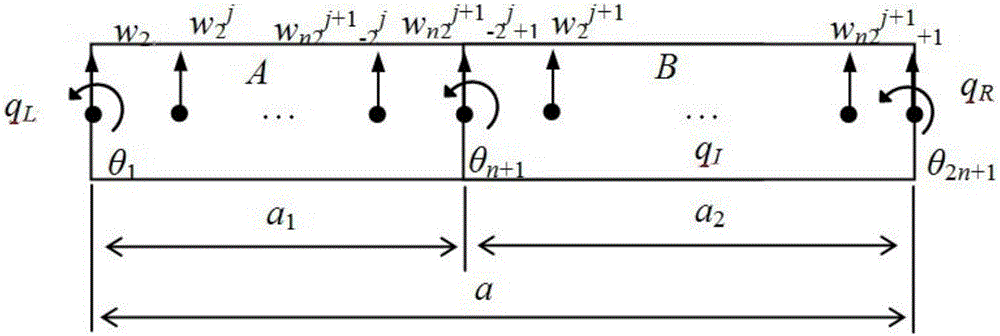
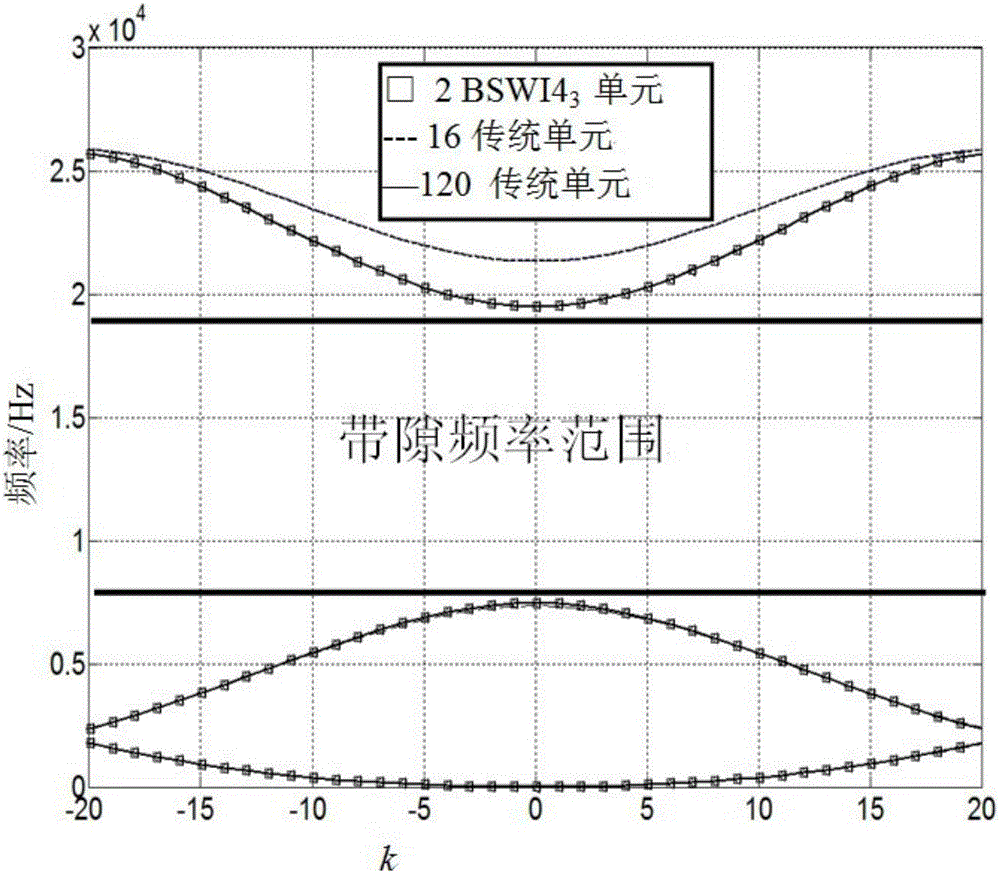
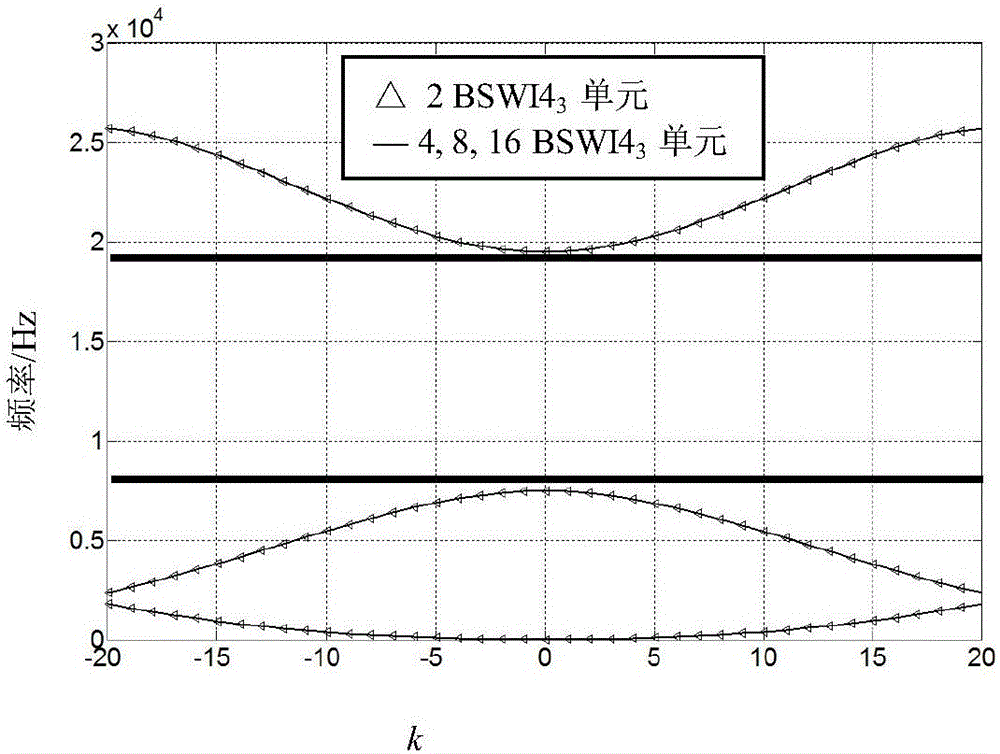
One-dimensional photonic crystal beam structure band gap designing method based on wavelet finite element model
InactiveCN106709202AGuaranteed accuracyImprove stabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelMixed finite element method
The invention provides a one-dimensional photonic crystal beam structure band gap designing method based on a wavelet finite element model. The wavelet finite element model uses the section B sample wavelet to be combined with a finite element method, a BSWI scaling function is used for replacing the polynomial interpolation of the traditional finite element, and the unit cell technology and periodic boundary condition PBCs are combined to build a real symmetrical feature value problem about the one-dimensional photonic crystal dispersing structure, so the band gap feature of the photonic crystal is obtained by calculating. The wavelet finite element model of the one-dimensional photonic crystal beam structure band gap calculation is capable of absorbing the advantages of the wavelet multi-scale approach feature and the complex solution domain of the finite element method, and obtaining a numerical calculation model with high precision and rapid convergence. The provided wavelet finite element model of the one-dimensional photonic crystal beam structure band gap design has the advantages of high precision and rapid convergence, and is suitable for the one-dimensional photonic crystal beam structure band gap design.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Image denoising method based on high-order overlapping group sparse total variation
InactiveCN110084756AIncrease differentiationImprove protectionImage enhancementFast Fourier transformImage denoising
The invention provides an image denoising method based on high-order overlapping group sparse total variation, and provides an overlapping group sparse total variation image recovery method based on high-order regularization term constraint on the basis of a traditional first-order overlapping group sparse total variation technology. According to the first-order overlapping combination technology,a total variation gradient of each conventional pixel is popularized into a combination gradient, so that the difference between a smooth region and an edge region is improved, and a high-order regular term can more effectively alleviate a'step effect 'from second-order or higher-order gradient information, so that the protection on the edge of the image is improved. In order to improve the operation speed of image restoration, transverse and longitudinal differential matrix operation of an image is modeled as convolution operation, periodic boundary conditions are combined, so that two-dimensional fast Fourier transform is skillfully applied to an image restoration problem, and point multiplication operation on a frequency domain is used for replacing large matrix operation on an airspace.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
Value calculating method of thermal residual stress of fiber reinforced composite material under low temperature
InactiveCN108090963AIncreased fiber volume contentImproved Hard-core model3D modellingElement modelFiber-reinforced composite
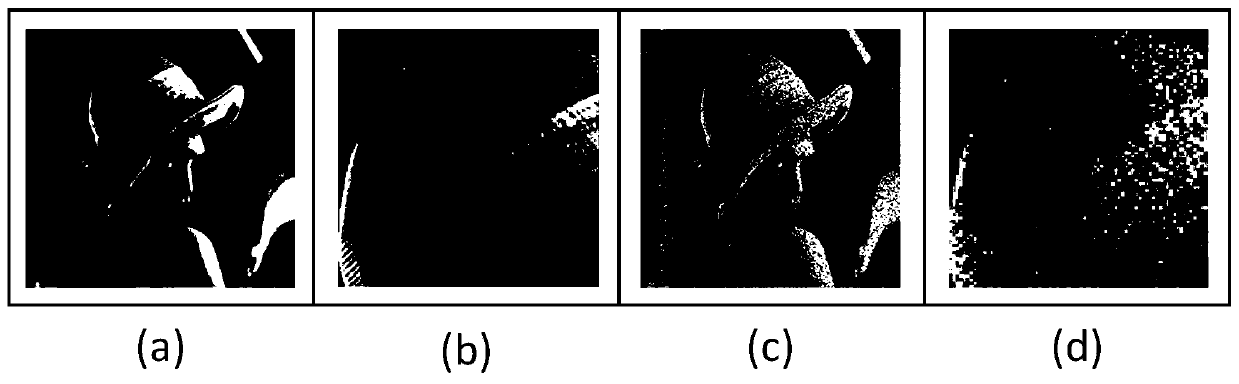
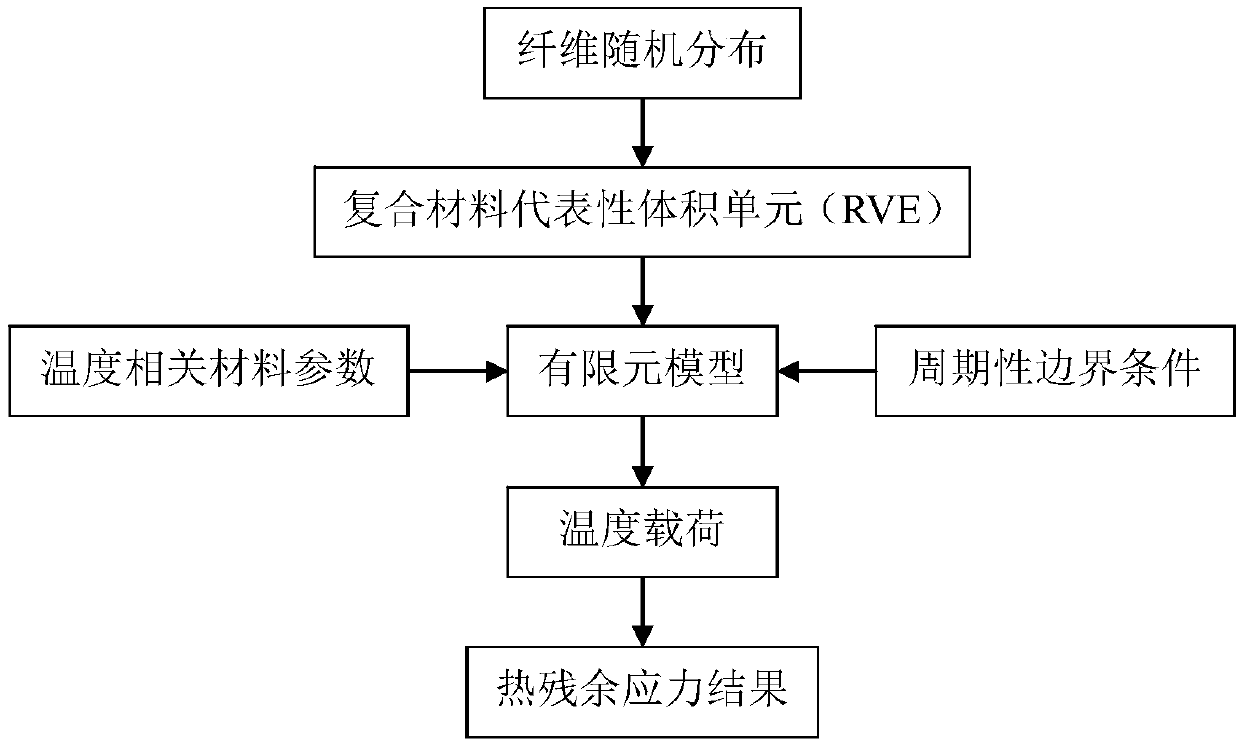
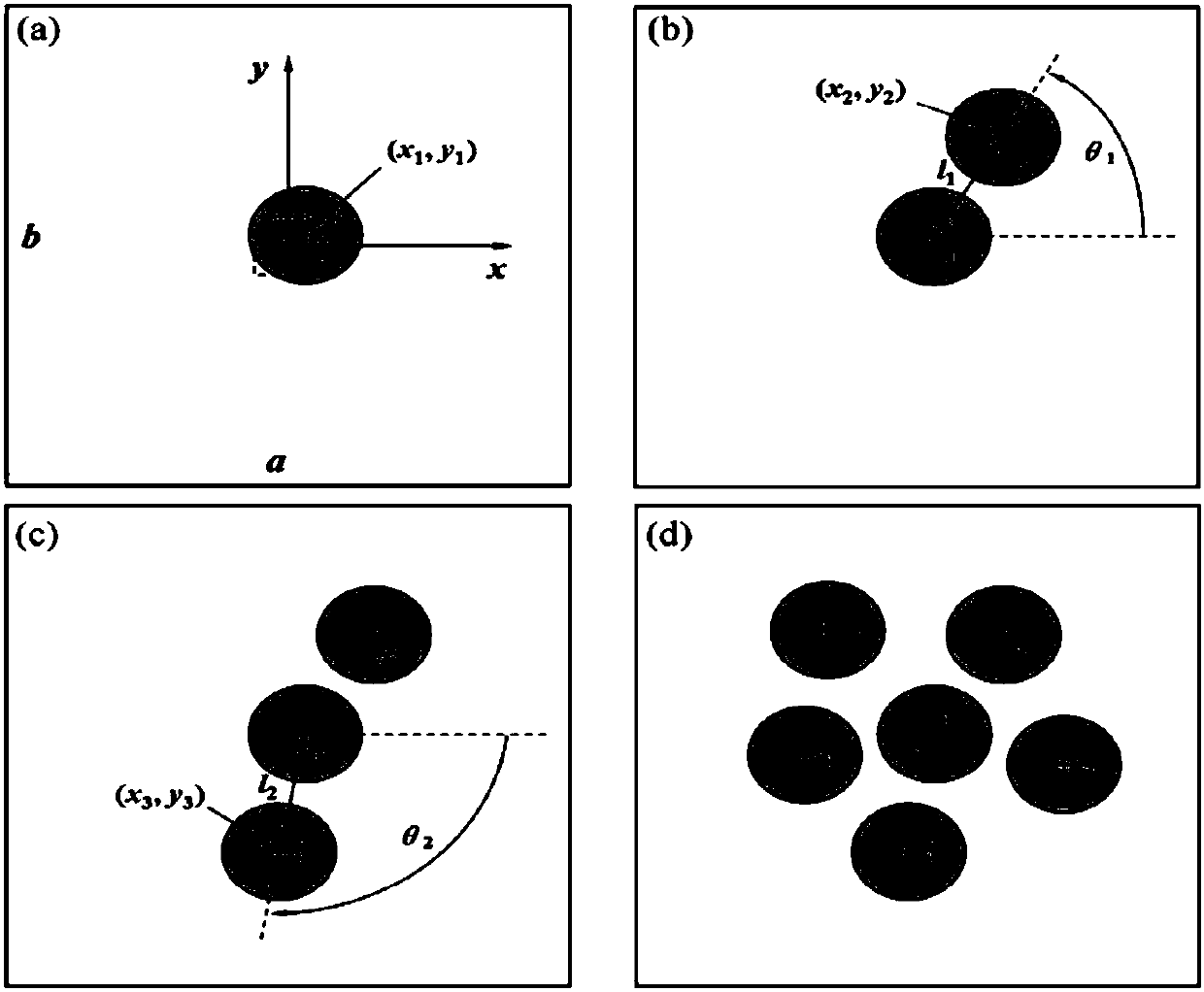
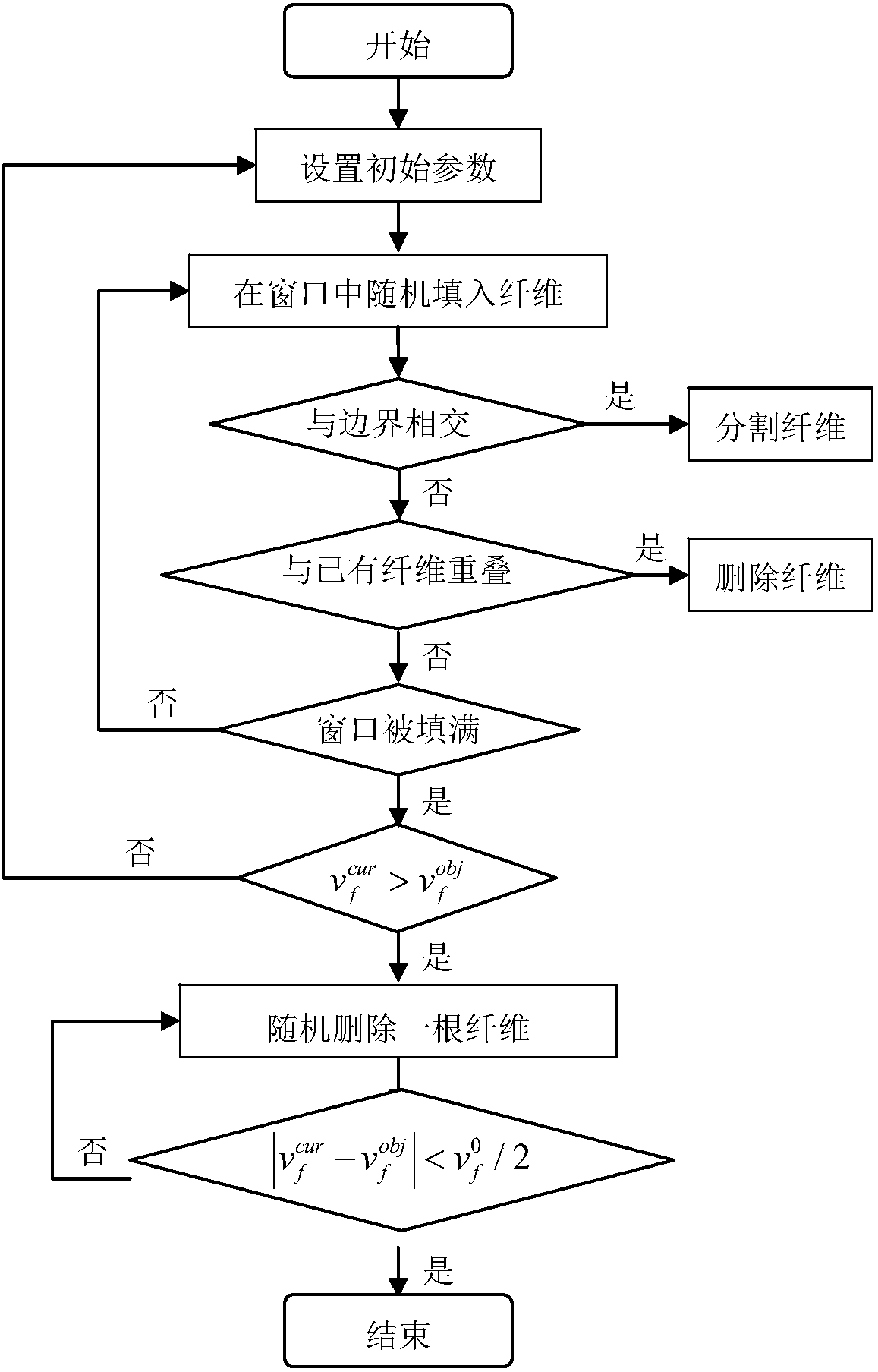
The invention discloses a value calculating method of a thermal residual stress of a fiber reinforced composite material under a low temperature. The method comprises the following steps of a, based on fiber random distribution, constructing a representative volume element (RVE) of a composite material; b, dividing a network for the composite material and acquiring a finite element model requiredby calculation; c, endowing the finite element model to thermal / mechanical performance parameters of a fiber and a matrix material which are related to a temperature; d, adding a periodic boundary condition for the finite element model; and e, applying a temperature load to the finite element model and calculating and acquiring the thermal residual stress. By using the method, operation is simpleand prediction precision is high; the method can play an important role in predicting the low temperature residual stress of the composite material so as to lay the foundation for the application of the composite material in a low temperature field.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Two-dimensional photonic crystal plate structure band gap design method based on wavelet finite element model
ActiveCN106777771AEasy to calculateImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelPhotonics
The invention discloses a two-dimensional photonic crystal plate structure band gap design method based on a wavelet finite element model. The wavelet finite element model combines interval B-spline wavelets and a finite element method, uses a BSWI scaling function to replace the polynomial interpolation of a traditional finite element and combines the unit cell technology and periodic boundary conditions PBCs to build the real symmetric eigenvalue problem of a two-dimensional photonic crystal discrete structure so as to calculate to obtain the band gap features of photonic crystals. The wavelet finite element model for calculating the two-dimensional photonic crystal plate structure band gap has the advantages of capability of processing complex solution domains and wavelet multi-dimensional approximation properties of the finite element method and can obtain the numerical calculation model high in precision and fast in convergence. The wavelet finite element model for designing the two-dimensional photonic crystal plate structure band gap is high in calculation precision, fast in convergence and suitable for the designing of the two-dimensional photonic crystal plate structure band gap.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for analyzing microscomic mechanical damage evolution of fan blade composite material
PendingCN110175419AGuaranteed randomnessGuaranteed accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringFan blade
The invention discloses a method for analyzing microscomic mechanical damage evolution of a fan blade composite material. Parametric modeling of the RVE structure model of the representative volume unit is achieved, the accuracy of damage initiation and crack generation of the described composite material component phase and the accuracy of the expansion evolution process are ensured, and for theboundary condition of the RVE model, an Abaqus-Python interface is utilized, periodic boundary conditions of the RVE model are quickly and smoothly applied, and a reasonable microscopic field quantityis obtained; according to the invention, isotropic damage of the matrix is considered; a single damage variable influencing the material rigidity is used; an interface phase is introduced into microscopic damage analysis of a composite material, a damage model is compiled into a UMAT material subprogram in combination with a subprogram interface of Abaqus finite element software, and simulation verification is carried out on the damage process of the blade material under the transverse stretching effect in Abaqus / Standard. The trend and expansion condition of microscopical volume unit interface cracks under the action of transverse tensile load and the influence of periodic temperature on the mechanical response are simulated.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
A method for automatic modeling of twisted and tilted grain boundaries based on repeated lattice searching
ActiveCN109002639ARealize the effect automaticallyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMetallic materialsMicroscopic scale
The invention discloses a method for automatic modeling of twisted and tilted grain boundaries based on repeated lattice searching, belonging to the technical field of metal materials. The method consists of four parts, namely, automatic searching of heavy site lattices, automatic construction of a twisted grain boundary model, automatic construction of a tilted grain boundary model and automaticcalculation of coincidence degree of lattice. The method of the invention can construct twisted and inclined grain boundaries conforming to periodic boundary conditions in batch, so as to realize high-throughput material interface computational simulation, facilitate users to construct a large number of models to analyze material failure mechanism, and can understand the relationship between grainboundaries and dislocations on the microscopic scale, thereby providing favorable assistance to the design of new materials.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
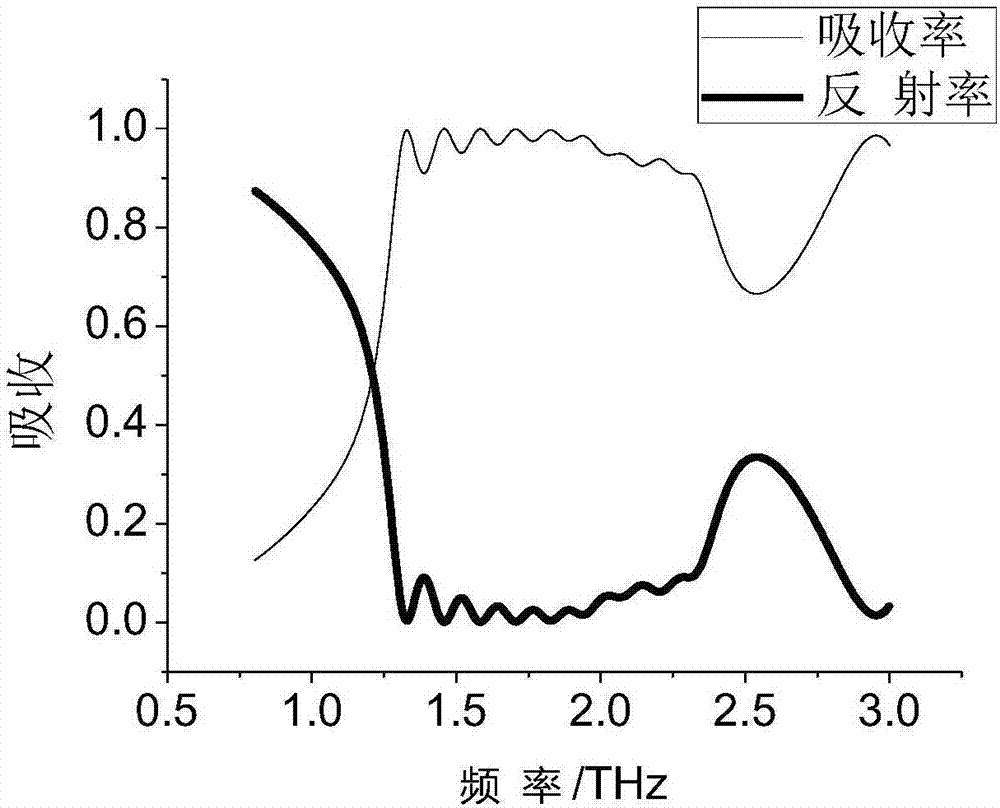
Design method of terahertz broadband absorption metamaterial
InactiveCN107093805ABroaden the absorption spectrumGuaranteed Relative Absorption BandwidthAntennasOptical elementsDielectricBroadband absorption
The invention belongs to the field of electromagnetic wave absorption and radiation control, and in particular relates to a design method of a terahertz broadband absorbing metamaterial. According to the effective medium theory, and using CST microwave studio to obtain S parameters through frequency domain simulation, the periodic unit structure is at x Both the and y directions are periodically distributed, and are set as periodic boundary conditions. Combining the parameters S11 and S21 obtained by scanning, the impedance value is calculated. By changing the period of the unit structure and the size of the metal thin film and dielectric material, the corresponding absorption frequency is adjusted, and multiple metal thin films and dielectric materials are cross-stacked in one unit period, so that the absorption lines corresponding to different resonant circular frustums are superimposed. The invention can effectively broaden the absorption spectrum of the terahertz frequency band, so that the frequency band with an absorption rate exceeding 90% can be widened, and meanwhile, a certain high relative absorption bandwidth can be guaranteed. And the first 9 absorption peaks are caused by the interior of the unit structure, so they are not affected by the period.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
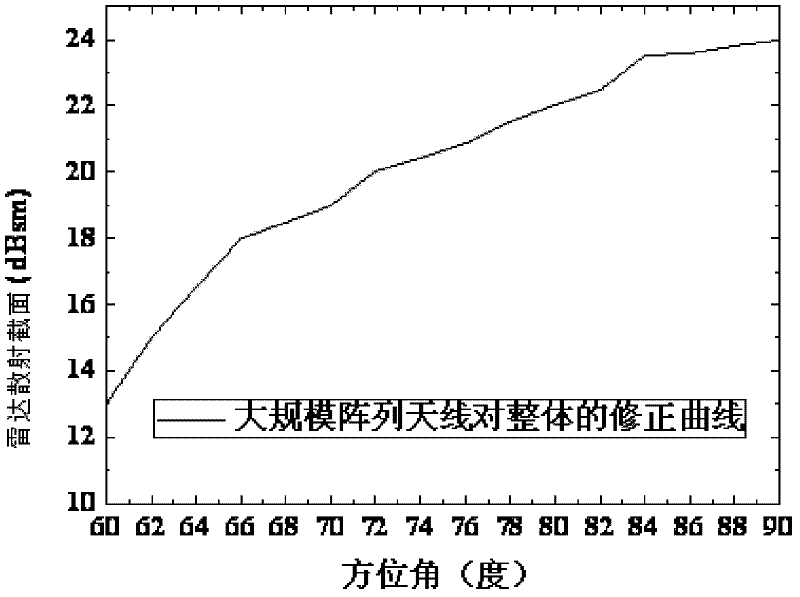
Whole-ship electromagnetic scattering prediction method of large-scale shipboard array antenna
InactiveCN102353850AIt is feasible to predict the scattering characteristics of the whole shipAvoid computationElectromagentic field characteristicsGlobal modelingEngineering
The invention provides a whole-ship electromagnetic scattering prediction method of a large-scale shipboard array antenna, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) modeling based on single array element of the large-scale array antenna based on a period moment method; 2) supplementing a model obtained in the step 1) according to periodic boundary conditions and an array element permutation number to obtain a model of the whole array; 3) carrying out simulation calculation on the set model by using the period moment method to obtain the scattering properties of the large-scale shipboard array antenna; and 4) comparing the scattering properties of the large-scale shipboard array antenna with a result of a ship load part to obtain a correction of the large-scale shipboard array antenna to whole-ship scattering properties. Compared with the whole-ship electromagnetic scattering prediction method of the traditional shipboard array antenna, the method provided by the invention has the advantage that a large amount of the calculation which is caused by modeling entirely is avoided so that the large-scale shipboard array antenna and whole-ship electromagnetic scattering prediction become feasible.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
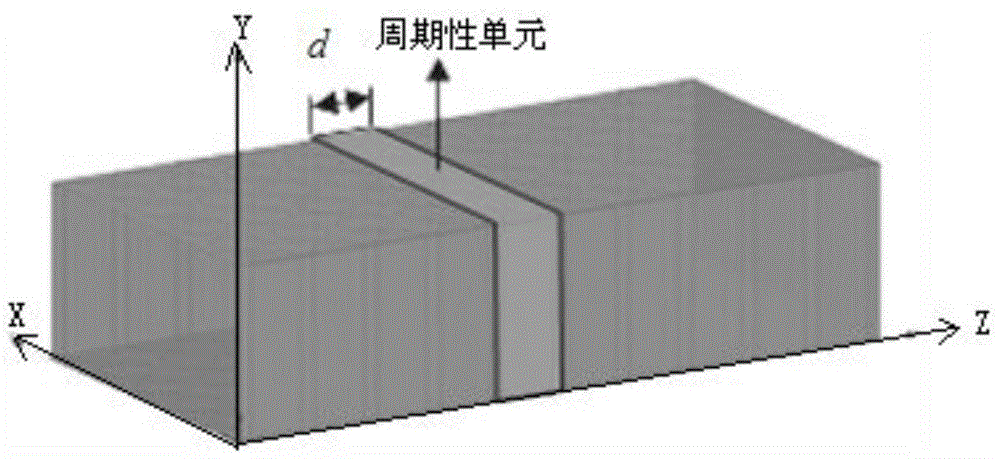
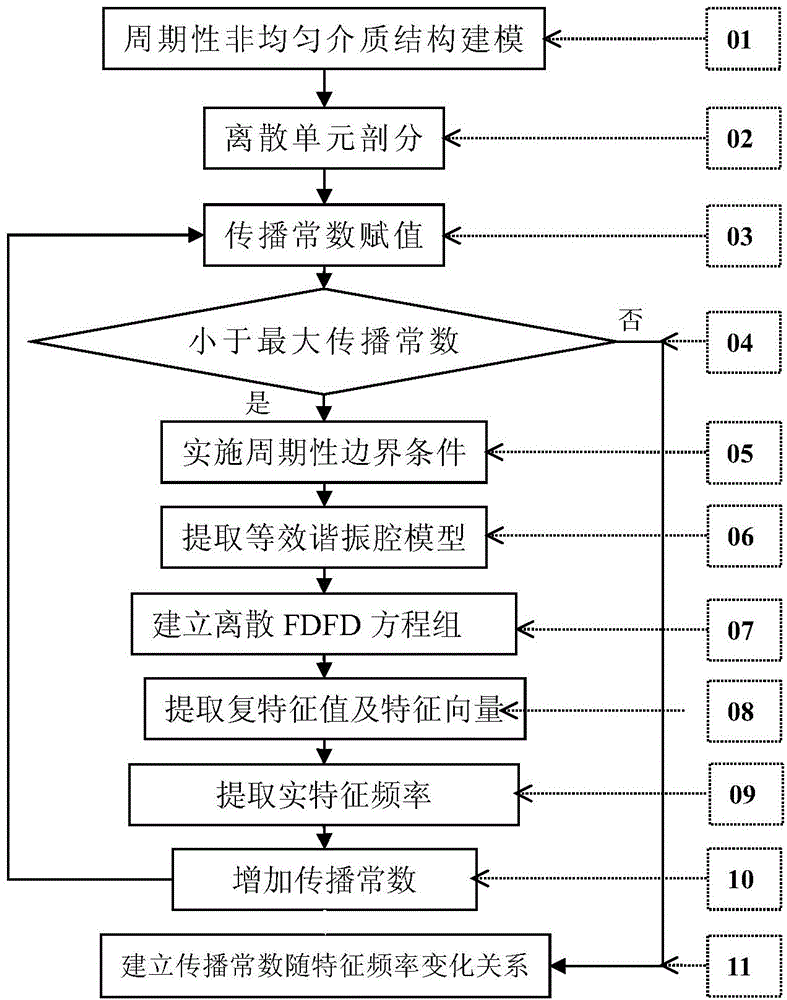
Seven point frequency domain finite difference method for analyzing periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide characteristic modes
ActiveCN104573240ASolve the problem that the non-uniform distribution of the medium along the propagation direction cannot be achievedSolve the problem of non-uniform distribution of mediaSpecial data processing applicationsDielectricDecomposition
The invention discloses a seven point frequency domain finite difference method for analyzing periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide characteristic modes. The seven point frequency domain finite difference method for analyzing the periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide characteristic modes mainly includes steps: firstly, performing finite difference mesh dissection, enabling an interface of inhomogeneous dielectric to coincide with a dissection unit, and using a computational node as a dissection unit peak; then, converting a field equation of an electromagnetic field real frequency domain in the inhomogeneous dielectric into a field equation of a complex frequency domain by using periodic boundary conditions and an equivalent resonant cavity theory; achieving dispersion for the field equation of the inhomogeneous dielectric by using tangential continuity boundary conditions of a field on eight dissection unit interfaces adjacent to the computational node and using seven computational node interpolation values adjacent to the computational node; obtaining frequency and field distribution of the characteristic modes by using a characteristic value decomposition technology through the dispersed field equation; establishing a function relationship between a propagation constant of each waveguide mode and working frequency, and thereby guiding design of a periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide. The seven point frequency domain finite difference method for analyzing the periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide characteristic modes solves the problem that uneven dielectric distribution in the propagation direction can not be achieved in the prior art.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and device for calculating shielding effectiveness of electromagnetic shielding net and a storage medium
PendingCN110348068AEliminate theoretical errorsThe calculation result is accurateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical field strengthObservation point
The invention discloses a method and device for calculating the shielding effectiveness of an electromagnetic shielding net and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a distribution model diagram of the electromagnetic shielding net with periodic distribution characteristics and uniform plane electromagnetic waves, and obtaining subunits of the electromagnetic shielding net; establishing a geometric model containing continuous periodic boundary conditions according to the subunits; dividing the geometric model into an electromagnetic shielding net space, an external space and a shielded space; placing the subunits in an electromagnetic shielding net space, placing the uniform planar electromagnetic waves in an external space, and presetting an observation point ina shielded space; setting simulation model parameters according to the geometric model and the electromagnetic shielding net to obtain a simulation model; performing numerical calculation on the simulation model to obtain the electric field intensity at the observation point; and obtaining the shielding effectiveness of the electromagnetic shielding net according to a shielding effectiveness calculation formula. The shielding effectiveness of the electromagnetic shielding net with the periodic distribution characteristic and any shape can be calculated, and the calculation result is more accurate.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Compound material liquid storage container performance multi-dimension testing method
InactiveCN101178341AReliable macro performance test resultsGuaranteed accuracyComplex mathematical operationsStrength propertiesImaging processingDrop tests
The invention relates to a method for multi-scale detection of a composite material liquid storage container. The steps are: obtaining the mesoscopic geometric shape of the material through optical equipment, using image processing technology to extract the mesoscopic geometric parameters of the material; The three-dimensional reconstruction method is used to establish the material unit cell, and the comprehensive performance parameters of the material are predicted by loading the periodic boundary conditions; the composite material liquid storage container model is established by using the material comprehensive performance parameters and the design size of the liquid storage container. The fluid-solid coupling is realized in the form of a function, and the safety detection of the collision impact of the liquid storage container is carried out with the numerical reproduction of the airdrop test; for the damaged area of the liquid storage container, the microscopic damage behavior of the material is detected through the unit cell model, and the macroscopic damage behavior of the composite material is obtained. performance parameters. The invention solves the performance detection problem of the composite material liquid storage container, greatly shortens the equipment development time, and reduces the randomness of experiments and capital investment.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Image deblurring method
InactiveCN108198149AImprove robustnessIncrease differentiationImage enhancementImage analysisFast Fourier transformDeblurring
The invention relates to an image deblurring method, in particular to a total variation image deblurring method based on a four-direction overlapping group technique. The gradients of each of pixels in each direction are combined to form a non-separable combined gradient, so that the difference between a smooth region and an edge region is further improved, and the quality of image reconstructionis improved. In order to improve the computing speed of image restoration, the horizontal and vertical difference matrix operation of an image is modeled as convolution operation, and periodic boundary conditions are combined, so that the two-dimensional fast Fourier transform can be ingeniously applied to the image restoration problem, and the point multiplication operation on a frequency domainreplaces the large-scale matrix operation on the airspace.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
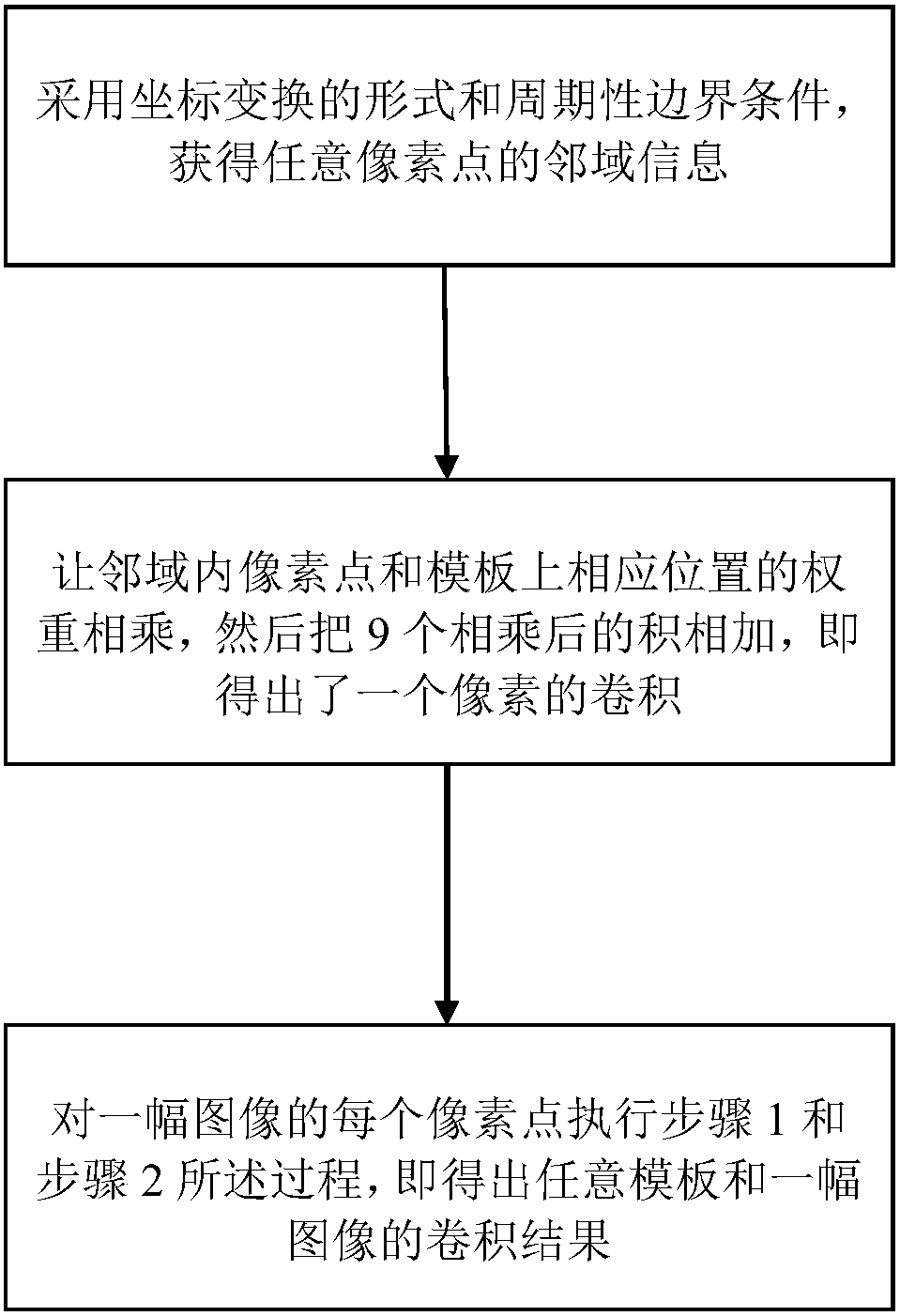
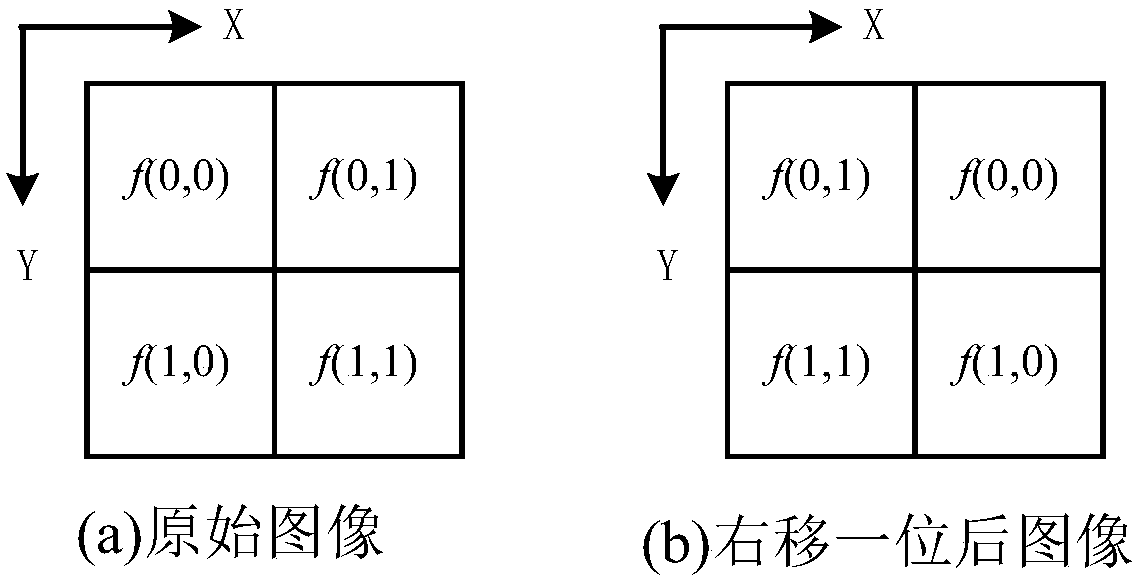
Quantum image convolution method
InactiveCN108280800AImplement convolutionGreat advantageQuantum computersProcessor architectures/configurationQuantum image processingComputer vision
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum image processing and relates to a quantum image convolution method. The method includes steps: S1, changing transverse or vertical coordinates of a pixel point of an original image by adoption of a coordination transformation mode and periodic boundary conditions to obtain information of the pixel point in neighborhood pixel points; S2, multiplying the neighborhood pixel points with corresponding weights on a template to obtain corresponding weight products, and adding all weight products to obtain convolution of the pixel point; S3, repeatedly executing the step S1-S2 on each pixel point of the image to obtain convolution results of any templates and images. By a quantum adder and a quantum multiplier, convolution of any templates and images on a quantum computer is realized, and the quantum image convolution method is greatly superior to a classical algorithm.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
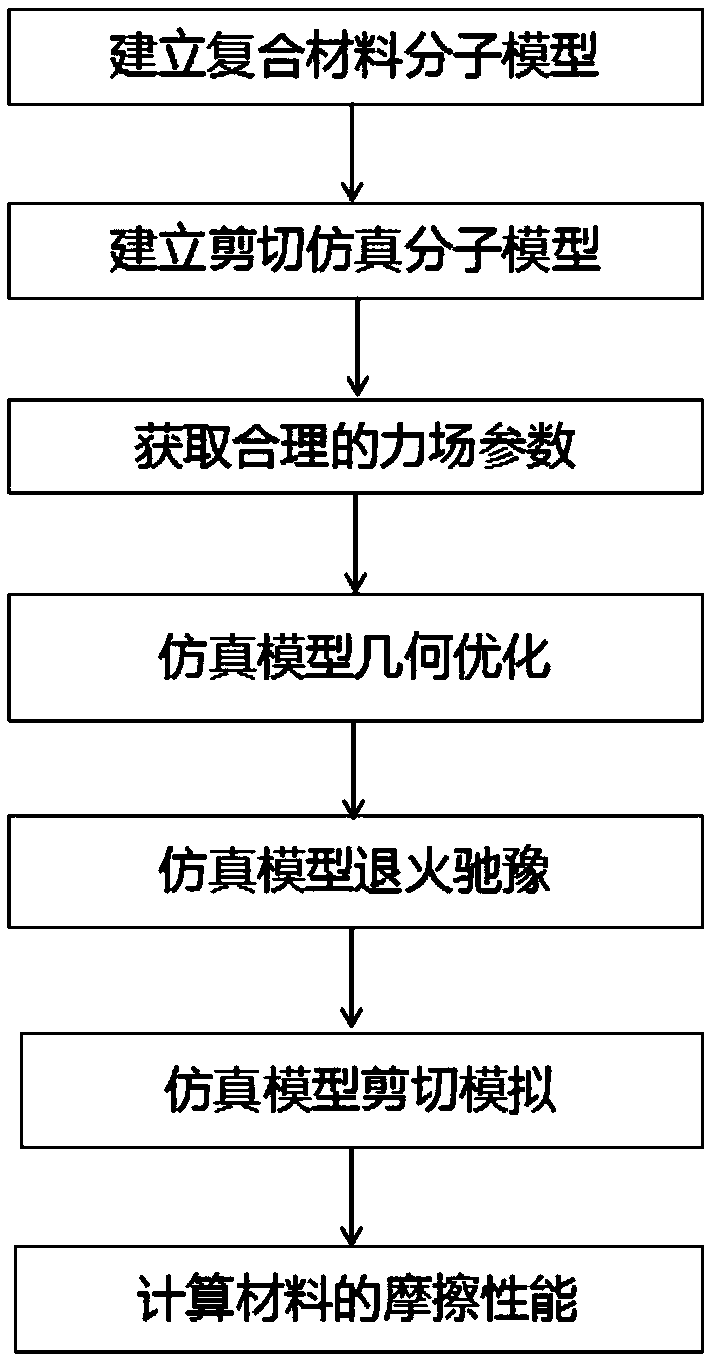
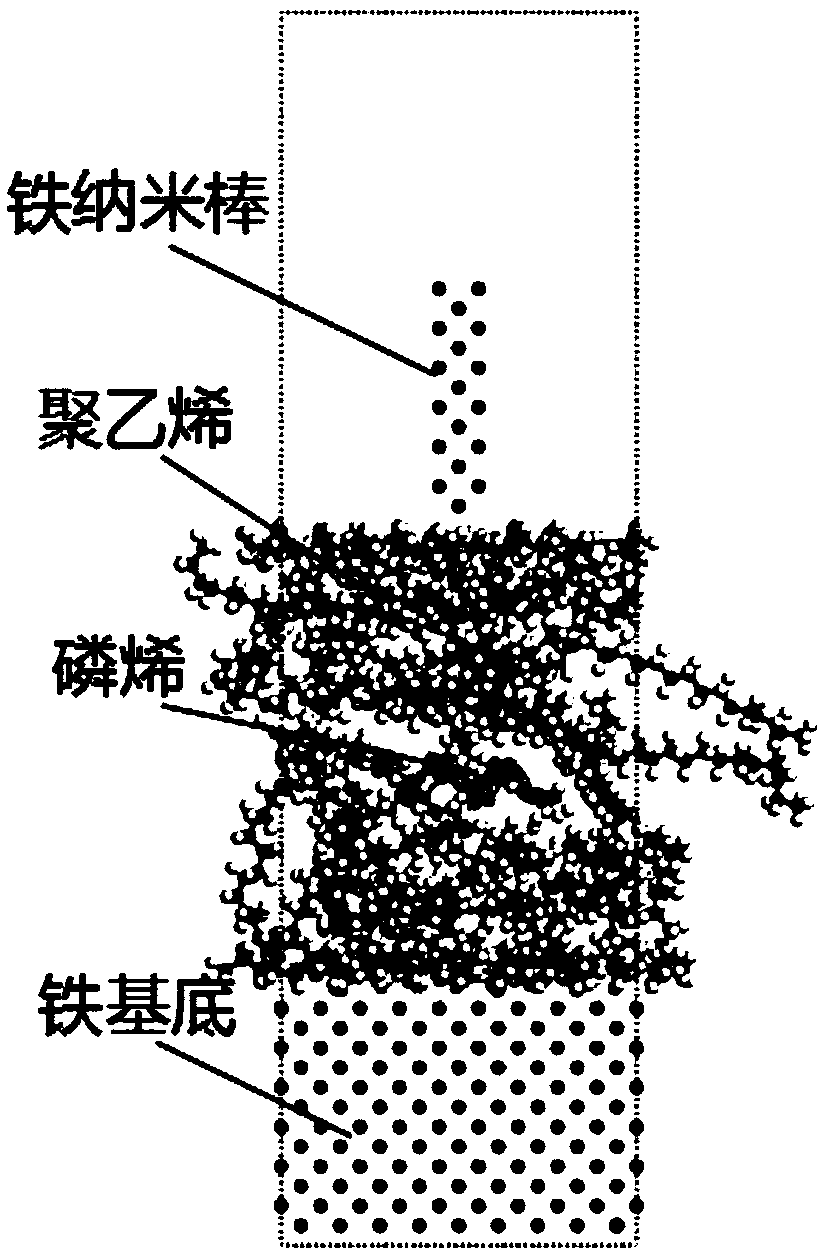
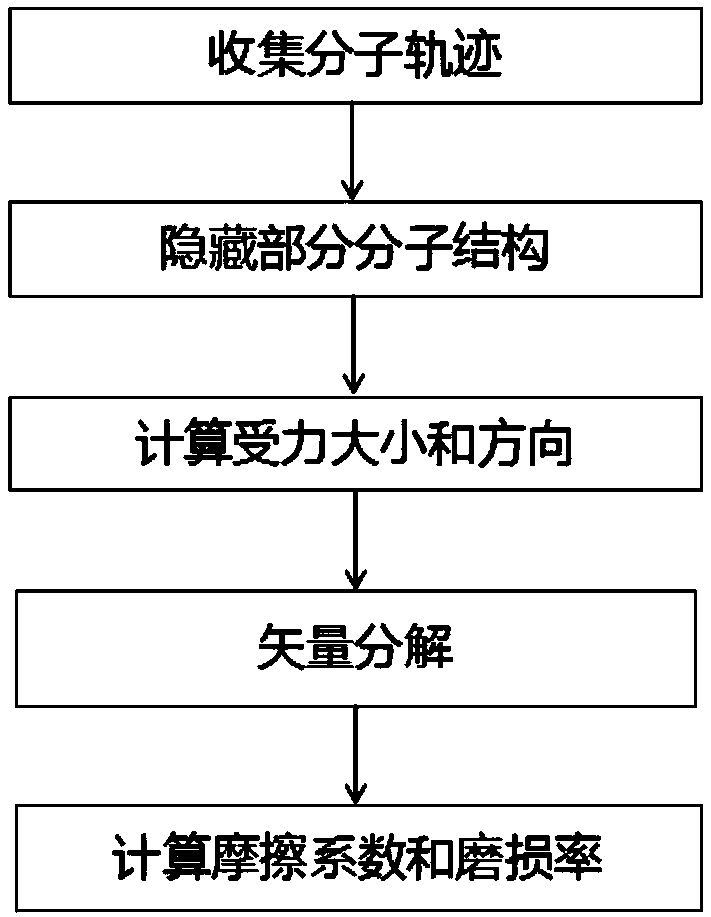
A composite material friction performance prediction method based on molecular dynamics
PendingCN109543272AExplore the loss mechanismLow costDesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryTangential forceAtomic motion
The invention discloses a composite material friction performance prediction method based on molecular dynamics, which comprises the following steps: establishing a molecular model of the material byusing Material Studio software; The composites were used as the intermediate layer, iron nanorods and iron substrates were added up and down respectively, the shear simulation molecular model was constructed, and the periodic boundary conditions were applied. Obtaining force field parameters of the model; Geometric optimization, annealing relaxation and shear simulation were carried out by using force field parameters, and the atomic motion trajectory was recorded during the shear simulation. According to the atomic motion trajectory, based on the secondary development of Material Studio software, the average tangential force and the average normal force of the composite material in the sliding process are calculated, and the friction coefficient and wear rate are calculated. This prediction method has low cost and high efficiency. It can explore the wear mechanism of composites in the friction process and provide theoretical guidance for the preparation and practical application of composites.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Deconvolution method using neighboring-pixel-optical-transfer-function in fourier domain
ActiveUS7912307B2High resolutionImprove imaging resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionOptical transfer function
The present disclosure includes an image processing technique that is capable to increase spatial resolution of single frame images beyond diffraction limit. If an image is taken by diffraction limited optical system with regularly spaced pixel detectors, and if the spacing of pixels of the detectors is much small than the diffraction pattern, then the spatial resolution of the image can be increased beyond the diffraction limit by using neighboring-pixel-optical-transfer-function (NPOTF) in Fourier Domain with periodical boundary conditions.
Owner:WANG YU
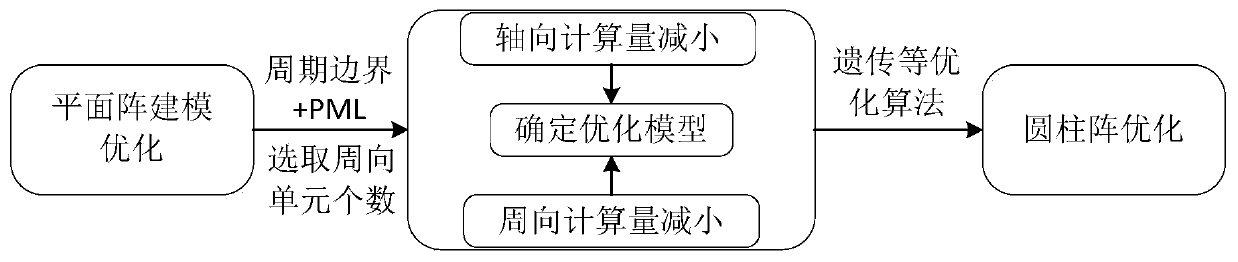
Rapid optimization design method and system based on cylindrical surface conformal array
ActiveCN110059376ASimple designReduce complexityInternal combustion piston enginesDesign optimisation/simulationMicrowaveFast optimization
The invention discloses a rapid optimization design method and system based on a cylindrical surface conformal array, and belongs to the technical field of microwaves, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, setting modeling conditions; S2, selecting the number of optimization units; S3, optimizing the model by using an algorithm. According to the method, the cylinder array model is built by combining the periodic boundary condition and PML. The minimum number of units needed for optimization is found by utilizing the mutual coupling relation of the circumference of the cylinder, andthen optimization is carried out through algorithms such as heredity and the like. The cylinder array is modeled in a mode of combining the periodic boundary condition and the PML. The complexity ofthe model can be greatly reduced, the modeling efficiency is effectively improved. Mutual coupling strength relationship between the antenna units is utilized. The minimum number of units is selectedto optimize the central active standing wave. The time required by simulation can be greatly reduced, optimization design can be conveniently carried out on the antenna through algorithms such as heredity, and the method is worthy of being popularized and used.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Active brightness enhancement film, preparation method thereof and method for analyzing polarization of active brightness enhancement film based on FDTD
PendingCN106773285AStrong fluorescenceImprove light resistanceNon-linear opticsFilm baseFluorescence
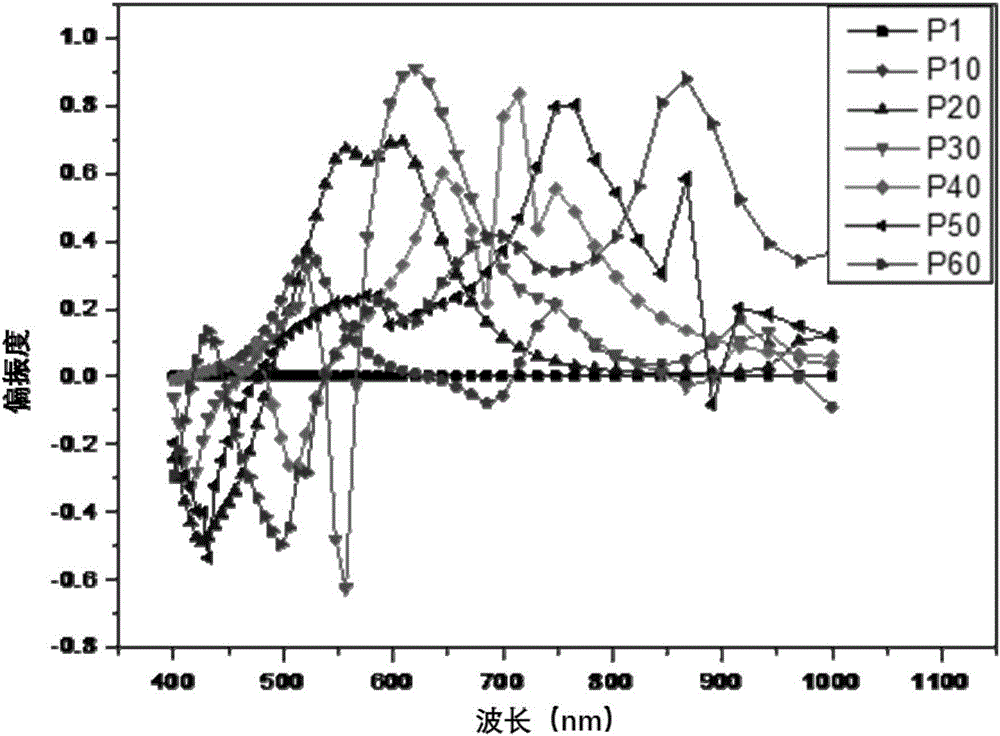
The invention discloses an active brightness enhancement film, a preparation method thereof and a method for analyzing the polarization of the active brightness enhancement film based on FDTD. The active brightness enhancement film comprises at least one layer of quantum dot doped polymer film and at least one layer of metal nanorod containing polymer film, wherein metal nanorods in the metal nanorod containing polymer film are uniform in orientation and are periodically arranged. The brightness enhancement film is unique in structure, efficient red and green fluorescence emitted by quantum dots can be obtained, and high-efficiency polarized light in a light source wave band can also be obtained. The active brightness enhancement film is economical in cost and excellent in performance, and the market monopoly formed by dual brightness enhancement films (DBEF) of 3M radicals is broken through. The invention also provides the method for analyzing the polarization of the active brightness enhancement film based on FDTD, and 3D-FDTD periodic boundary conditions are used, so that a great deal of computing time is reduced, and the method is an effective tool applicable for analyzing polarization behaviors of the nanorods.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Ceramic matrix composite mesoscopic modeling and mechanical calculation method based on structural grid
ActiveCN110348165AReduce dependenceReduce difficultyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial typeGeometric modeling
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite material modeling and mechanical calculation, and particularly relates to a ceramic matrix composite material microscopic modeling and mechanical calculation method based on a structural grid. According to the method, based on the structure grid, the material types to which the pixel units belong are distinguished through several given independent mesoscopic geometrical parameters, and therefore mesoscopic modeling of the ceramic matrix composite is achieved. A homogenization theory is adopted, a flexibility matrix is obtained accordingto six groups of stress-strain relations under different periodic boundary conditions, and finally elastic parameter calculation is achieved. According to the method, parameterized modeling of the ceramic matrix composite mesoscopic geometric model and automatic hexahedral mesh division are realized in a parameterized manner, and mechanical calculation is realized. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages that the difficulty is greatly reduced, the dependence on people is reduced, and the modeling and calculation time is shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for generating two-dimensional high-volume-fraction earth-rock mixed material geometric model
PendingCN114048663ARaise the upper limitImprove production efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationComputational physicsContact model
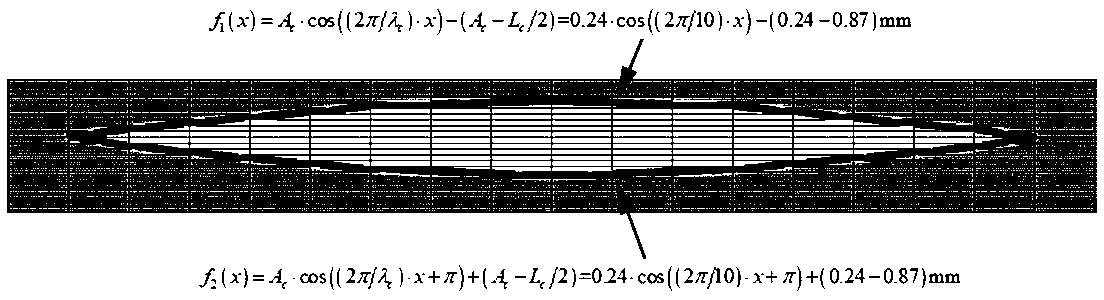
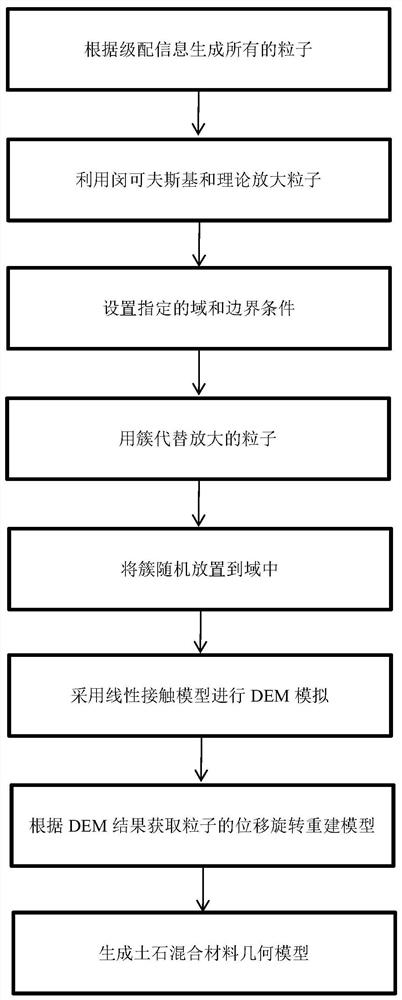
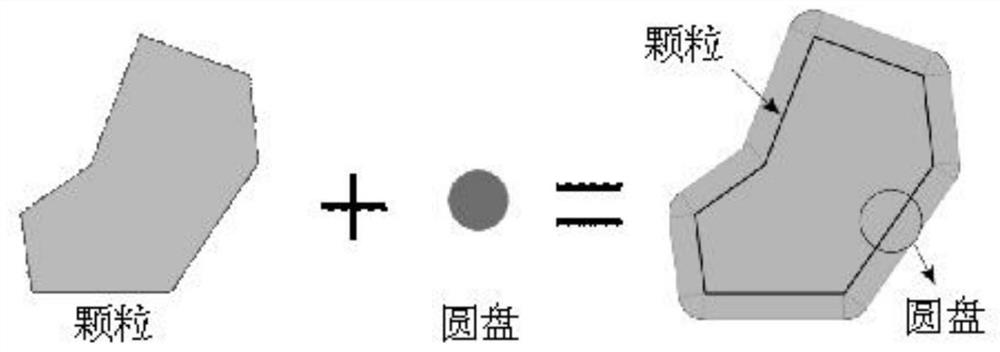
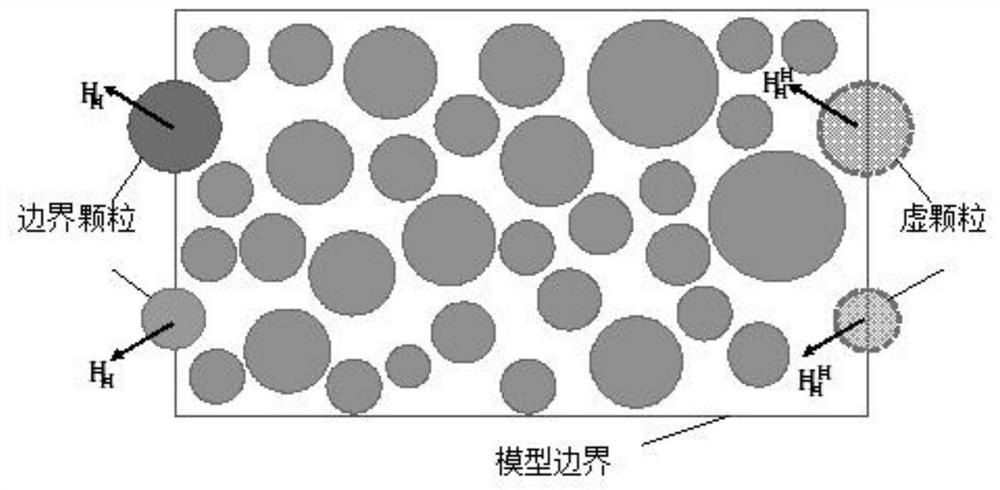
The invention discloses a method for generating a geometric model of a two-dimensional high-volume-fraction earth-rock mixed material, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, generating randomly distributed particles in any shape according to a grading curve; performing Minkowski sum operation on the particles, and controlling the minimum gap between the adjacent particles; achieving transition from particles to clusters by an overlapped discrete element cluster method, and randomly placing the particles in a certain area; assigning a linear contact model, performing DEM simulation, separating overlapped clusters, and recording initial positions, displacement and rotation of the clusters; and finally, reconstructing the model based on the displacement and rotation information. The theoretical maximum volume fraction of any particle shape is easy to obtain, meanwhile, the boundary distribution problem of the particles and the contact problem between the particles are solved, in addition, the periodic boundary condition in the DEM provides a simple implementation method for the periodic microstructure, the generated model better conforms to the actual situation. Reliability of a subsequent numerical method test research result can be improved, and the method has relatively high application significance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Frequency response characteristic analysis method of surface acoustic wave resonator based on dimensionality reduction PDE model
PendingCN113962084AEliminate degrees of freedomUniform residual sound fieldDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSystem matrixDimensionality reduction
The invention belongs to the technical field of numerical calculation of surface acoustic wave filters, and particularly relates to a frequency response characteristic analysis method of a surface acoustic wave resonator based on a dimensionality reduction PDE model. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining the structural data of a surface acoustic wave resonator; inputting the data into a dimension reduction PDF model to obtain a partial differential equation set representing the surface acoustic wave resonator; solving the partial differential equation set by adopting a finite element method to obtain a system matrix representing the surface acoustic wave resonator; adopting a finite element degree-of-freedom compression method and an order reduction technology to eliminate the degree-of-freedom needing no attention on the system matrix, and adopting periodic boundary conditions to eliminate the degree-of-freedom of left and right boundaries to obtain a system matrix equation after the degree-of-freedom is eliminated; solving the system matrix equation to obtain frequency response characteristics of the surface acoustic wave resonator. According to the method, irrelevant degree-of-freedom are eliminated by adopting the finite element degree-of-freedom compression method and the order reduction technology, and a uniform residual sound field can be realized in a directivity area.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 26 RES INST
Method for simulating linear polymer crystallization
The invention discloses a method for simulating linear polymer crystallization. The method comprises the following steps of building a polymer model, simulating crystallization, building a polymer coarse-grained model, and setting particle position, particle initial velocity, bond length and bond angle; setting a corresponding force field for the polymer model, i.e. adopting LJ-96 potential for intermolecular forces, and adopting corresponding energy potential for bond length and bond angle; initially setting corresponding periodic boundary conditions for the model; sequentially performing down balance when T* is equal to 0.1, temperature raising NPT movement from T* which is equal to 0.1 to T* which is equal to 1.6, NPT balance movement when T* is equal to 1.6, temperature reducing NPT movement from T* which is equal to 1.6 to T* which is equal to 0.4 under the experiment temperature, and NPT balance movement when T* is equal to 0.4 on the model. According to the computer simulation method provided by the invention, the defect of the traditional observation experiment method is overcome; integral and real-time observation can be performed, and the result shows that computer simulated data can be well identical to the traditional experiment data.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com