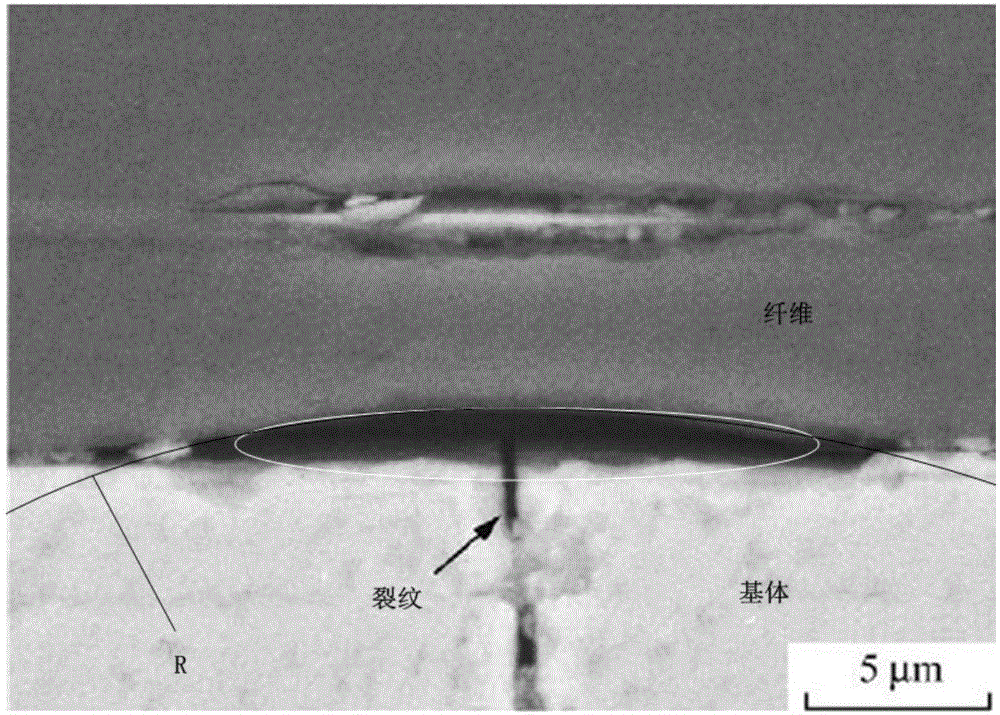
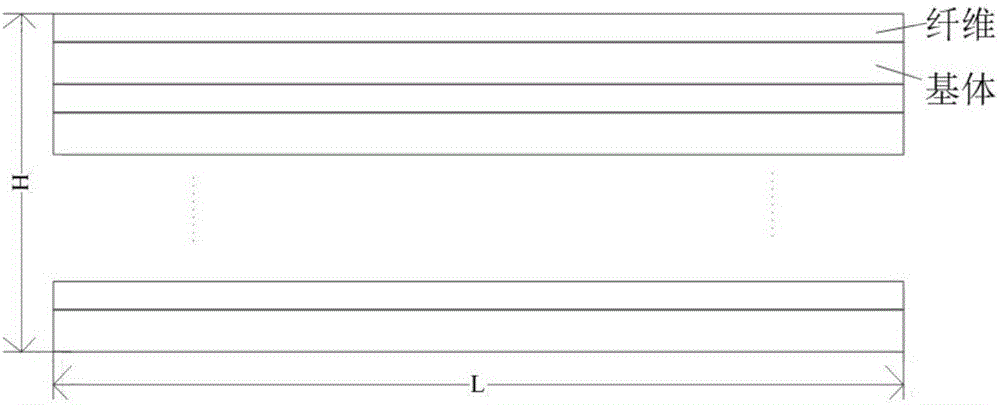
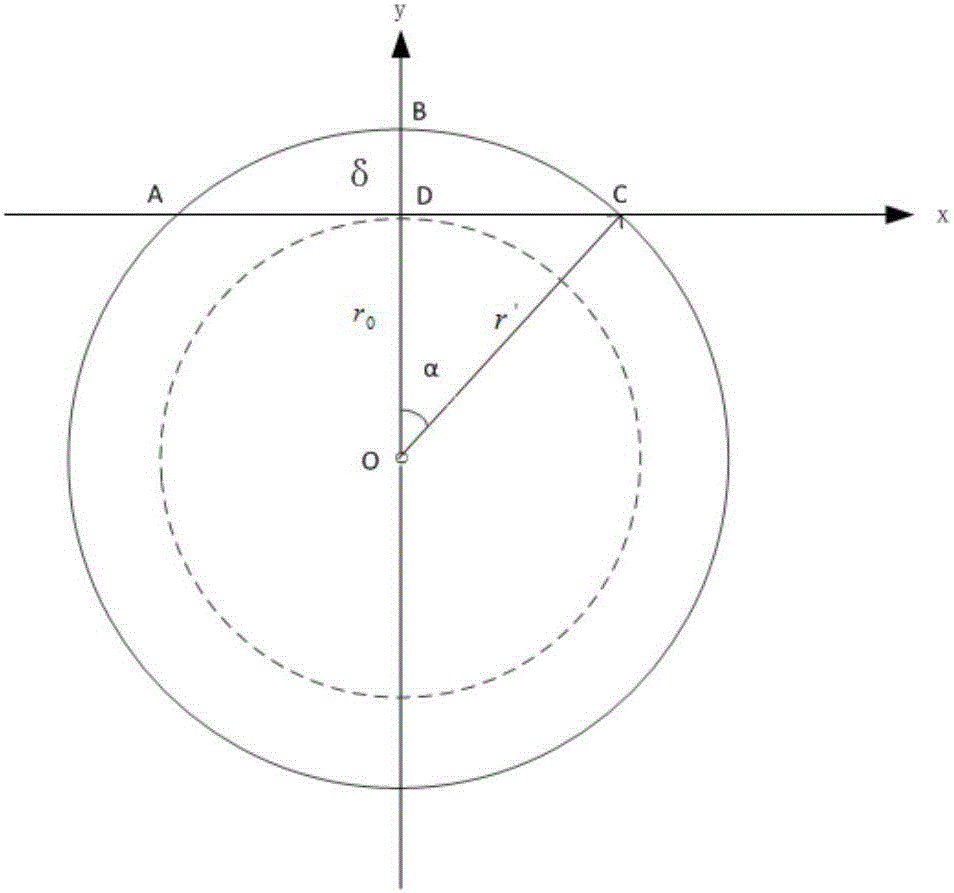
Method for predicting residual stiffness of two-dimensional braided ceramic matrix composite material after oxidation
A technology of composite materials and prediction methods, applied in design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as consuming large experimental funds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The present invention will be further explained below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0058] In this example, the two-dimensional plain weave C / SiC composite material is taken as an example to predict the residual stiffness of the material after oxidation in the range of 700°C to 900°C. The material performance parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0059] Table 1
[0060]
[0061] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the specific steps of this method are as follows:
[0062] (1), based on the theory of mass loss rate and the assumption of fiber degradation law, an oxidation kinetic model is established. Among them, the mass loss rate theory is divided into two temperature ranges:
[0063] 1) When the temperature is in the range of 400 °C to 700 °C, the formula for the mass loss rate of the composite material is as follows:
[0064] λ r = Δ W W ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com