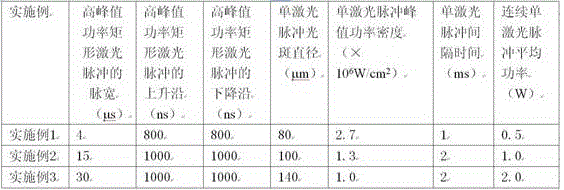
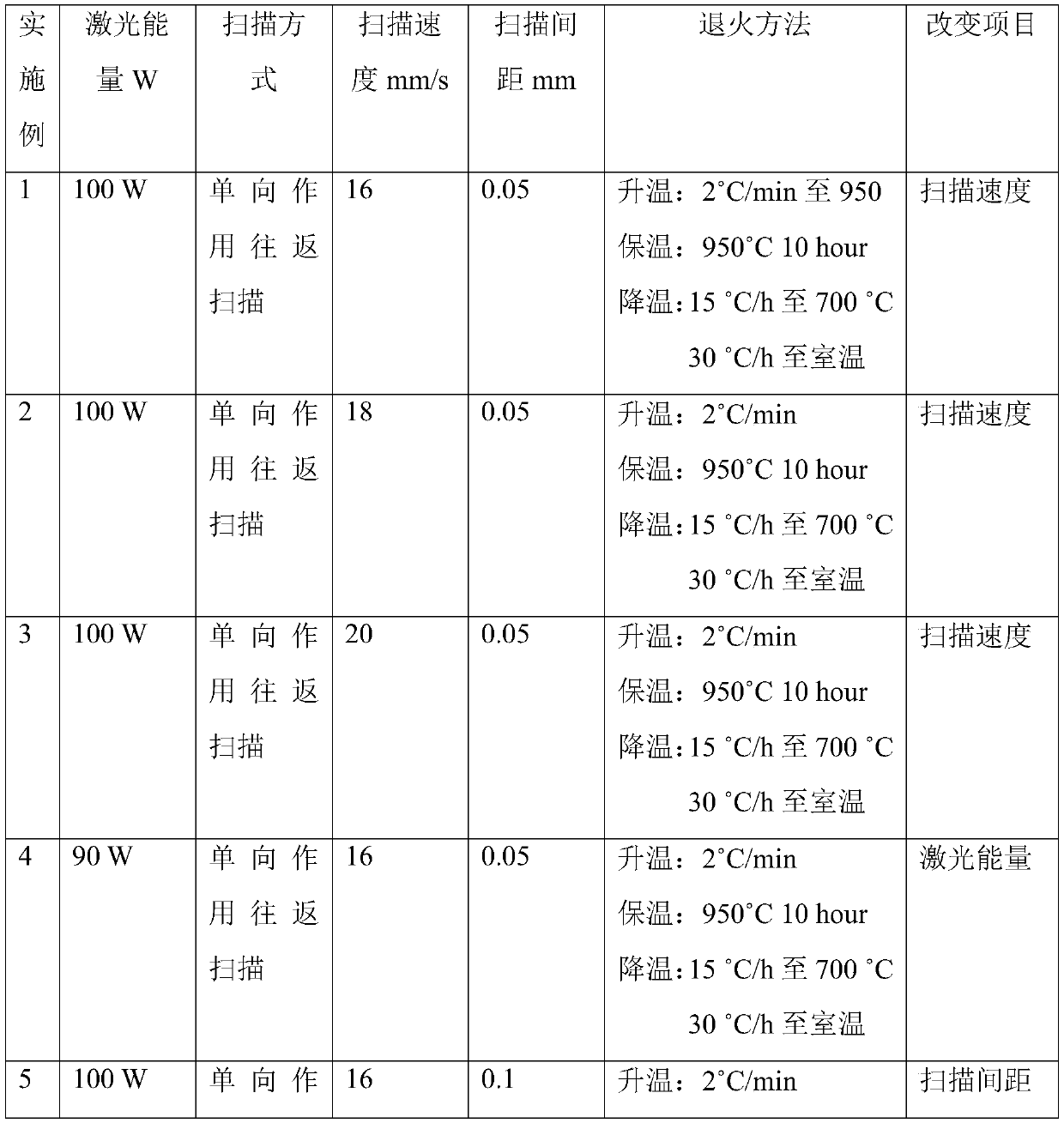
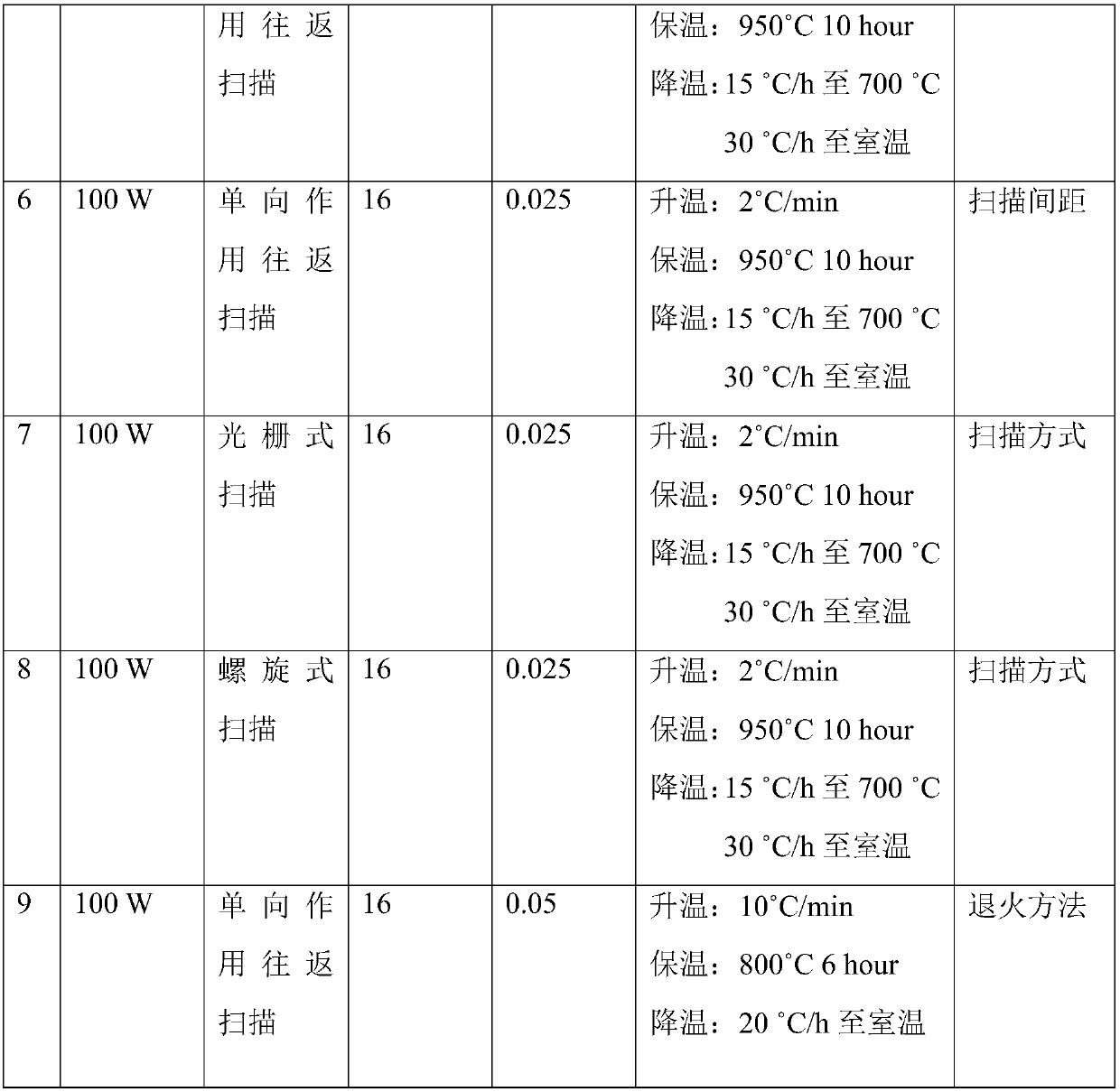
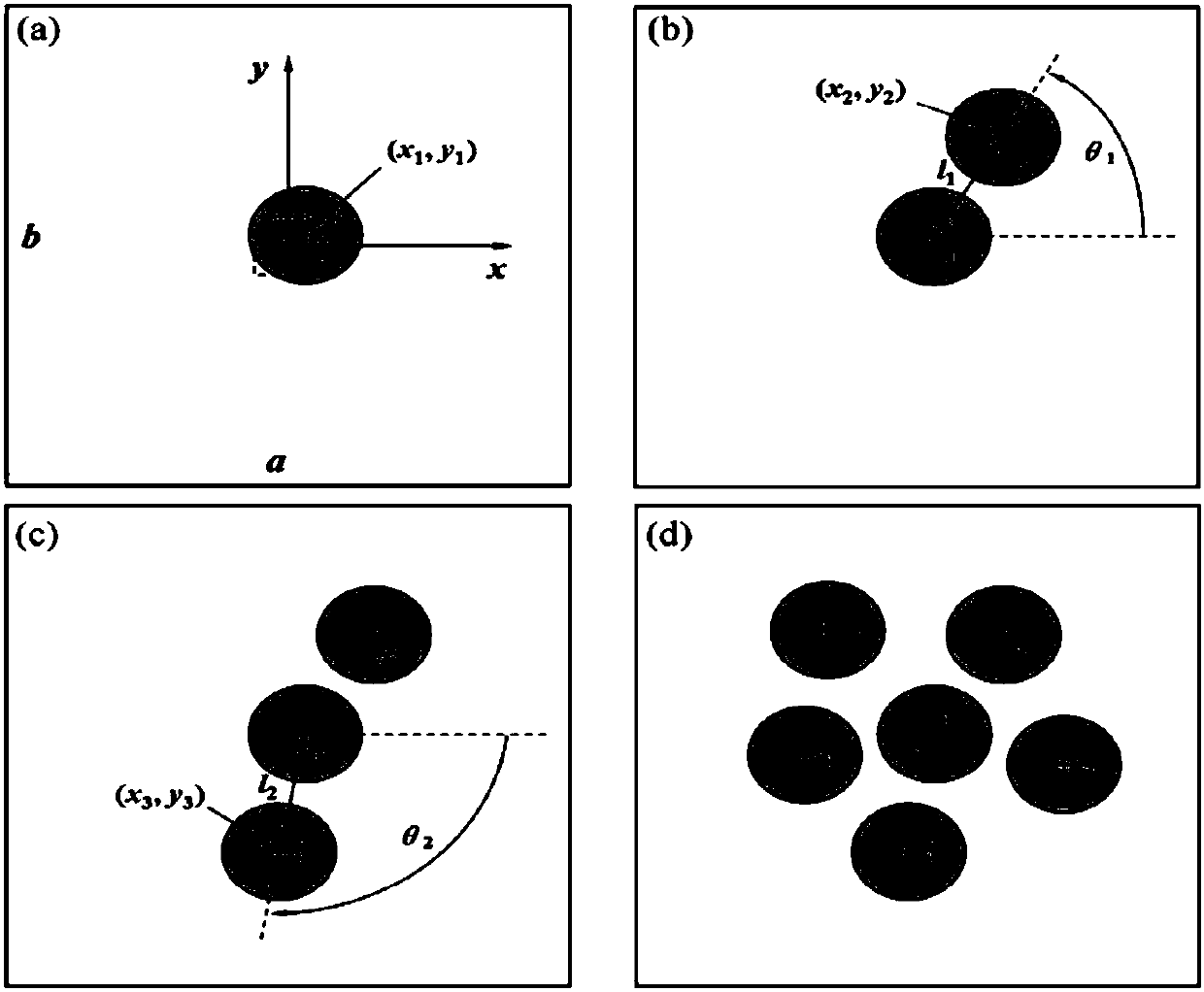
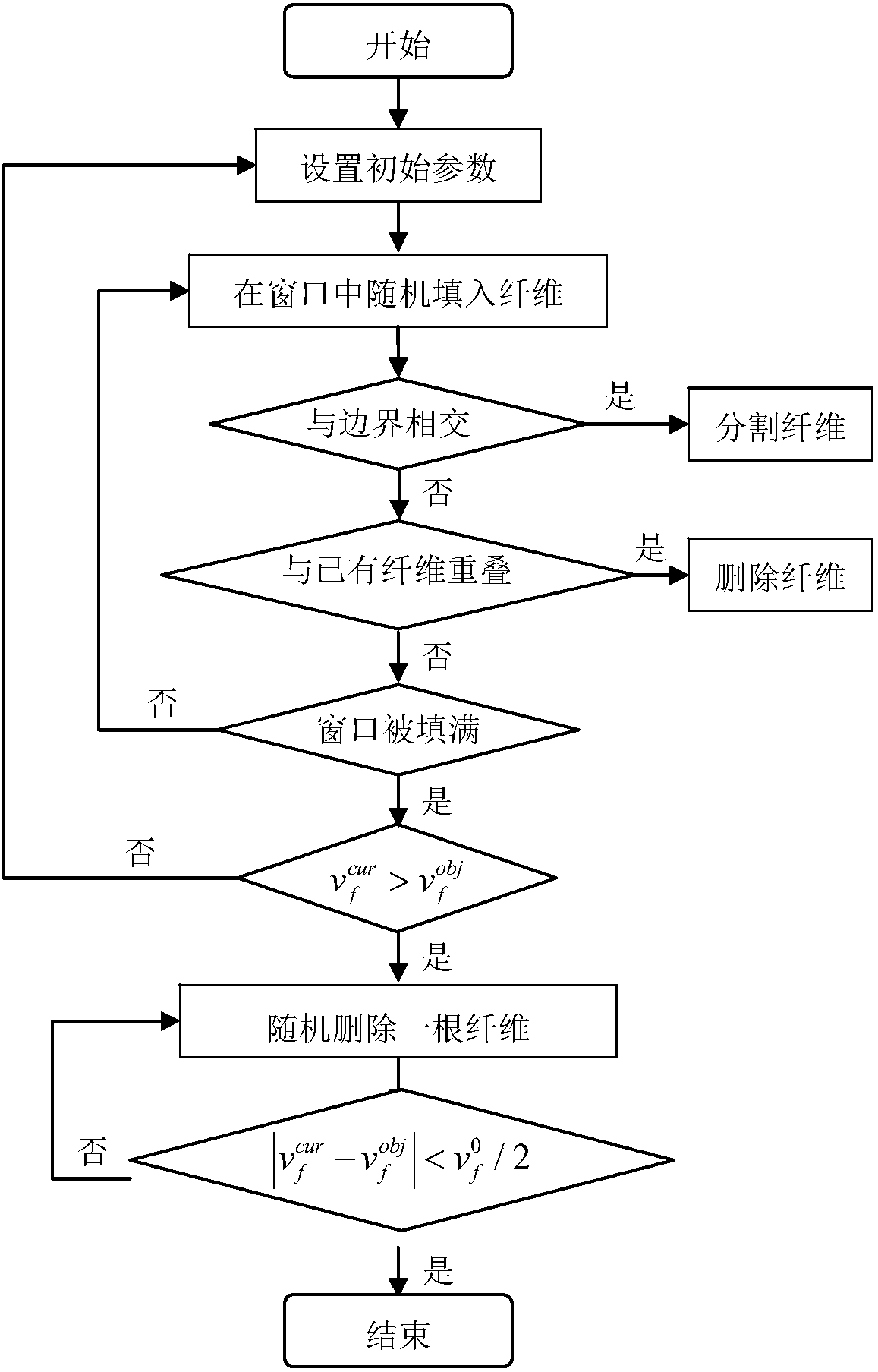
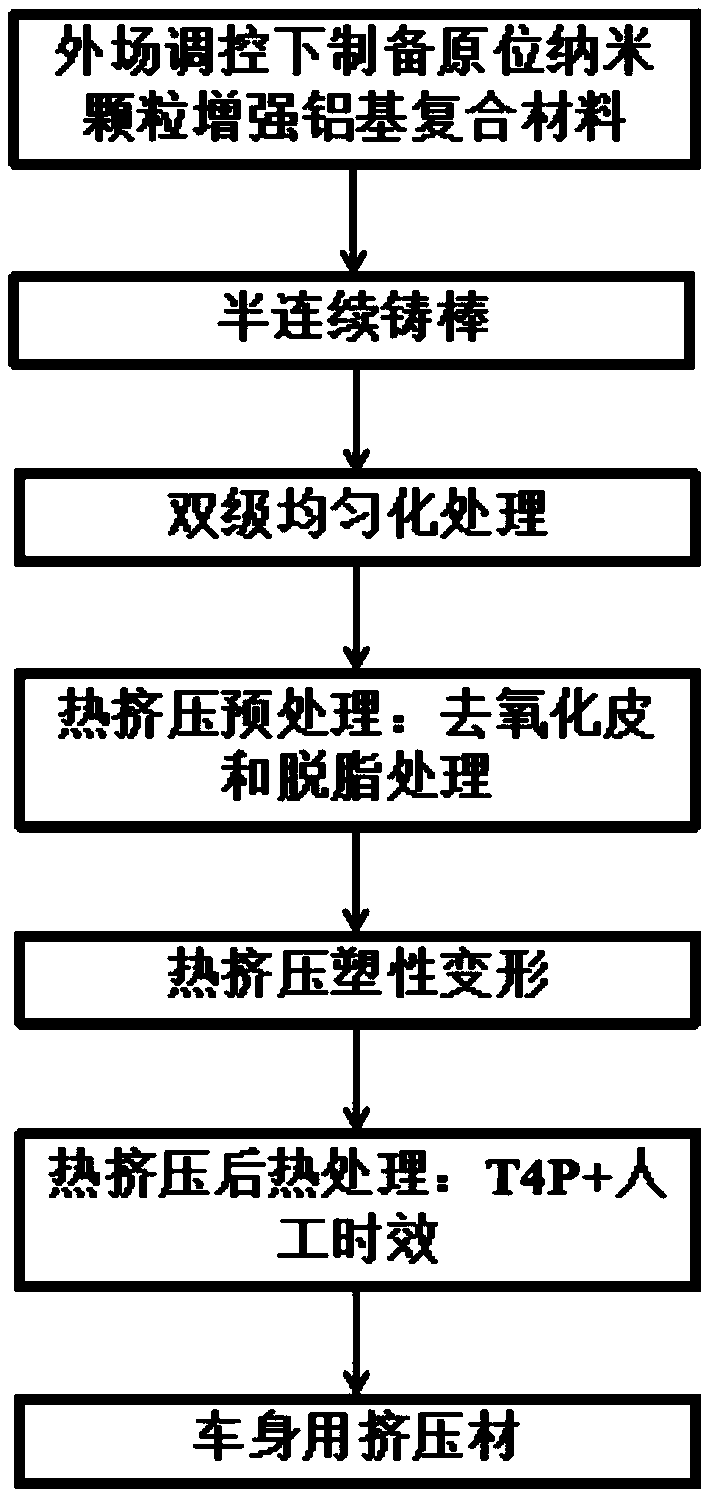
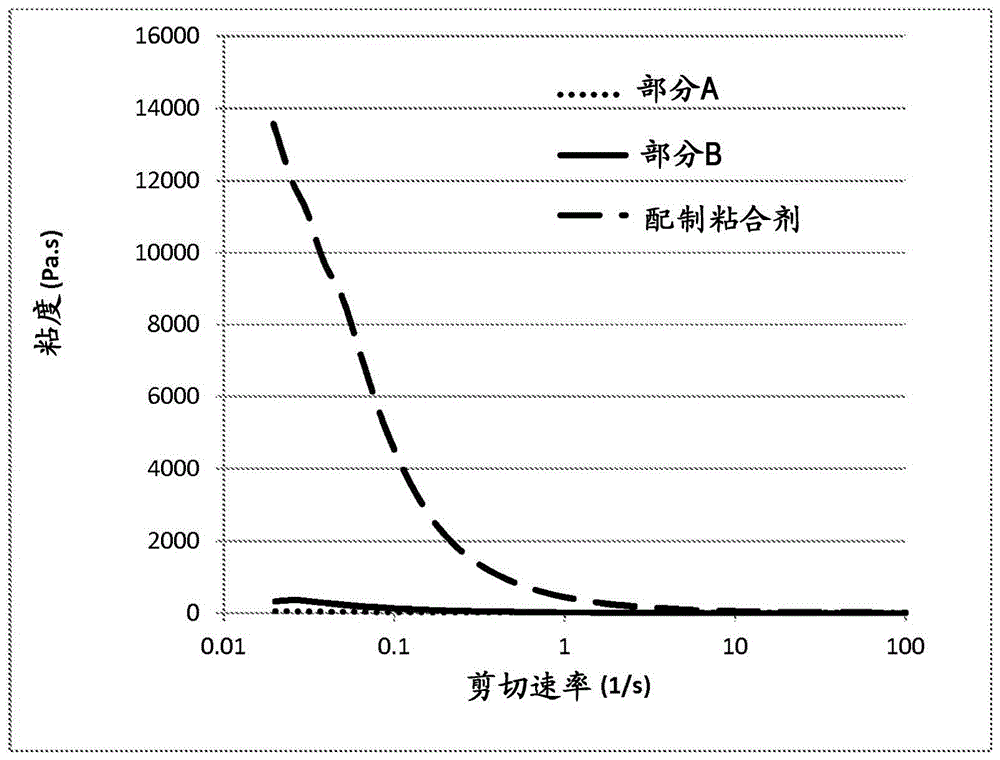
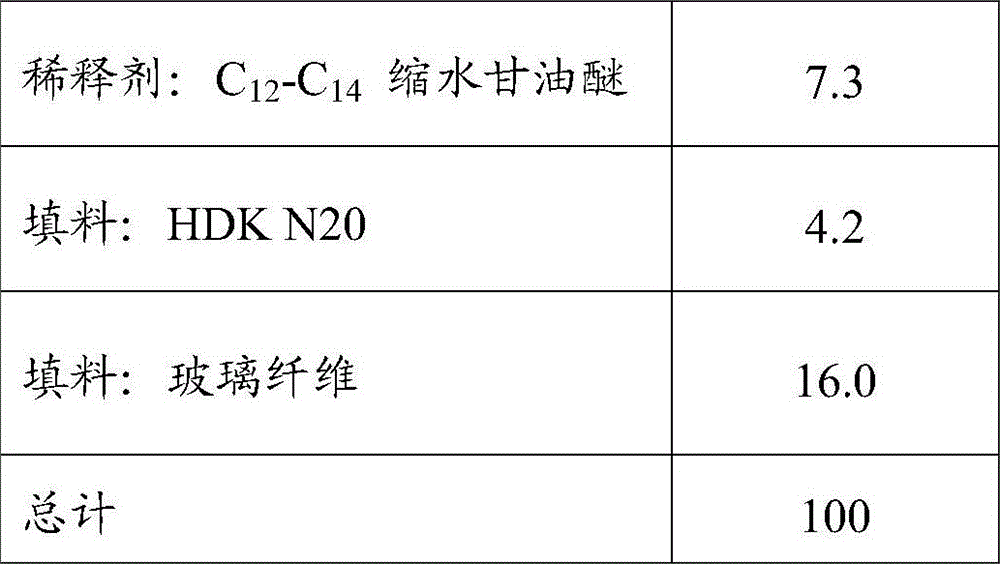
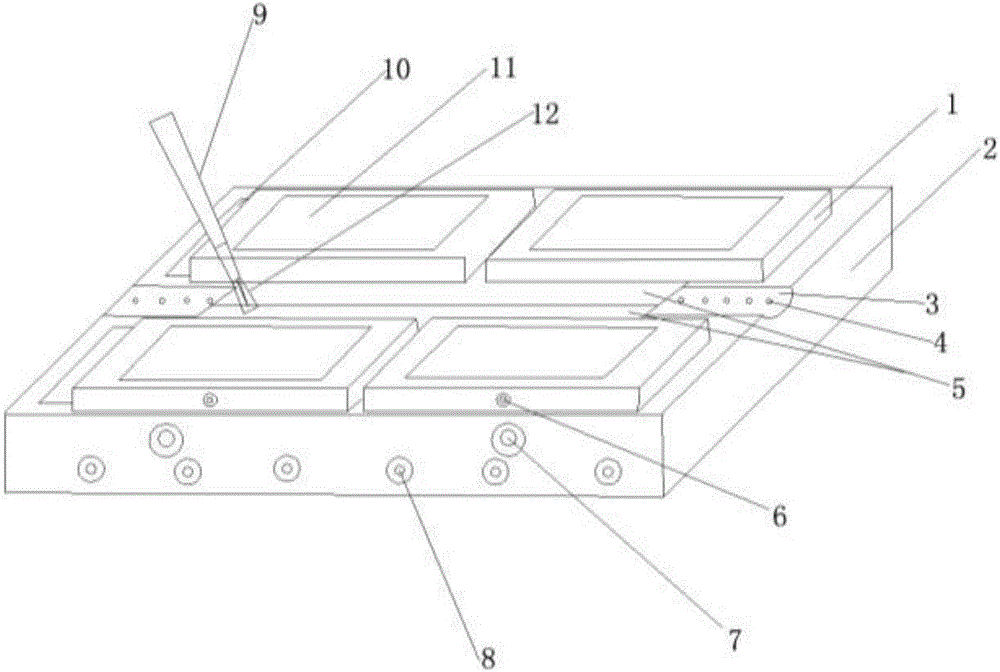
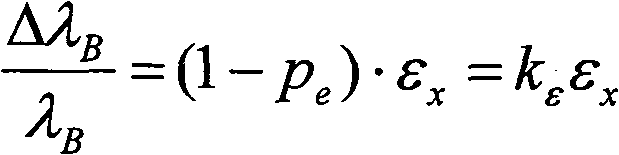Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Thermal residual stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This kind of stress is often referred to as flow induced residual stress. Another is thermal induced residual stress which arises during the cooling stage. An important fact is polymer shrinks as it cools. During the cooling stage, the polymer cools at different rates from the mold wall to the center.
Method for scoring a sheet of brittle material
InactiveUS8245540B2Increase pressureImprove scoreGlass reforming apparatusGlass severing apparatusCutting glassMaterials science
A method of cutting glass that prevents uncontrolled crack propagation when high background stress is present, either in the form of thermal residual stress, external mechanical stress or a combination thereof. The method includes masking an edge of the glass by blocking the beam using highly reflective or absorptive material located near the glass surface, or deposited on the surface in a form of a thin film (or highly reflective paint) to prevent uncontrolled crack initiation and propagation starting from the glass edge. The initiation of the laser scoring is located at a predetermined distance from the glass edge. Yet another aspect of the invention embodies stopping propagation of the vent at the exiting end of the score line.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain
The invention provides a method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain. In order to solve the technical problems that as fiber grating sensors are bonded to the surface of a structure through polyimide resin or epoxy resin commonly used in the prior engineering, optic fiber in service is easily destroyed; the optic fiber can get encapsulation protection but cause the concentration of surrounding stress / strain thereof if the optic fiber is directly embedded in a composite-material structure; and thermal residual stress produced in a material-curing process can cause chirp phenomena of fiber grating reflection spectrum to affect the measurement accuracy of grating strain, and the like, the invention provides the method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain. In the method, the fiber grating sensors are embedded in composite-material layers to replace resistance strain gauges commonly used in the field of monitoring structural health; by applying prestress to embedded fiber gratings, the influence of the curing residual stress of composite material on the fiber grating reflection spectrum is reduced so as to avoid the chirp phenomena; and the stability and repeatability of the sensors are improved. In addition, the composite material plays a good role in encapsulating and protecting bare fiber gratings, and meets engineering construction requirement on sensor sensitivity.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AERONAUTICAL ENG +1
Method for scoring a sheet of brittle material
InactiveUS20100212361A1Increase pressureImprove scoreGlass reforming apparatusGlass severing apparatusCutting glassLight beam
A method of cutting glass that prevents uncontrolled crack propagation when high background stress is present, either in the form of thermal residual stress, external mechanical stress or a combination thereof. The method includes masking an edge of the glass by blocking the beam using highly reflective or absorptive material located near the glass surface, or deposited on the surface in a form of a thin film (or highly reflective paint) to prevent uncontrolled crack initiation and propagation starting from the glass edge. The initiation of the laser scoring is located at a predetermined distance from the glass edge. Yet another aspect of the invention embodies stopping propagation of the vent at the exiting end of the score line.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for repairing laser damage of fused quartz without thermal residual stress
ActiveCN105948519AControlling High Temperature Structural RelaxationThermal Residual Stress SuppressionRepair timeOptoelectronics
The invention provides a method for repairing laser damage of fused quartz without thermal residual stress. According to the method, rectangular laser pulses with high-peak power are acquired by intercepting peak segments of pulses output from a laser device; the rectangular laser pulses with high-peak power are focused, and single laser pulses with super-high-peak power density are acquired; the single laser pulses are used for peeling a material at a single point of a damaged part on a fused quartz substrate through transient gasification; the interval of the single laser pulses is controlled, so that the substrate is cooled sufficiently; gasification peeling is performed repeatedly through the single laser pulses until the material at the whole damaged part is removed. With the adoption of the method, high-temperature structural relaxation of the fused quartz substrate is effectively controlled, the damage of the fused quartz is repaired without thermal residual stress, the anti-damage capacity of damage points of a fused quartz optical element is improved, surface damage and development of surface damage of the fused quartz optical element are inhibited, the service life of the fused quartz optical element is prolonged, and the method has the advantages of short repair time, simple and efficient process, good process stability, high controllability and high repeatability.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Laser beam polishing method of fused quartz optical glass
InactiveCN109590603ASolve the problem of expensive and inefficient polishingOvercoming the problem of uneven heat accumulationLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsTemperature monitoring
The invention provides a polishing method of fused quartz optical glass. According to the method, the fused quartz optical glass is polished by continuous CO2 laser beams, laser beam polishing of thefused quartz optical glass with the surface of which the roughness RMS is less than 0.2 nm is realized by combining a nonfocusing light source with a temperature monitoring and feedback system, and almost no microdefect and scratch exist on the surface of the polished fused quartz optical glass. The method comprises an annealing step, and can eliminate the thermal residual stress caused by laser beam polishing. The invention provides a novel method for processing fused quartz optical glass with a nondestructive super-smooth surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Value calculating method of thermal residual stress of fiber reinforced composite material under low temperature
InactiveCN108090963AIncreased fiber volume contentImproved Hard-core model3D modellingElement modelFiber-reinforced composite
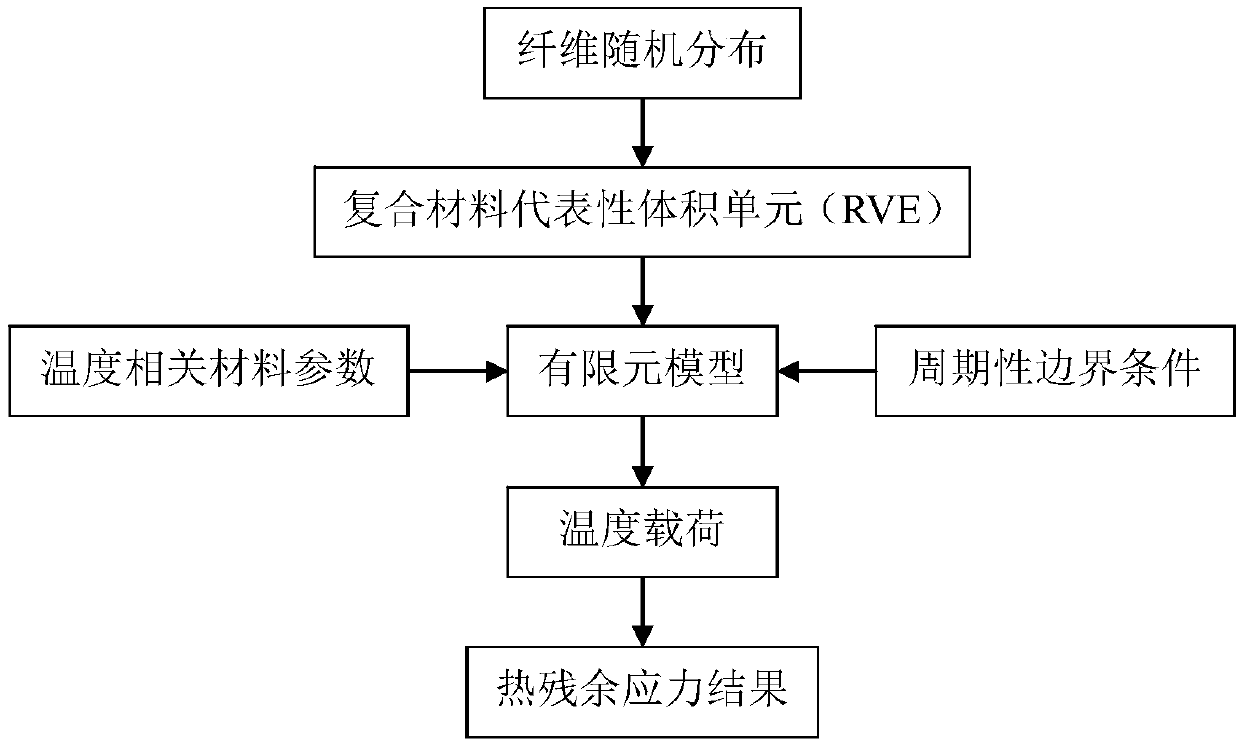
The invention discloses a value calculating method of a thermal residual stress of a fiber reinforced composite material under a low temperature. The method comprises the following steps of a, based on fiber random distribution, constructing a representative volume element (RVE) of a composite material; b, dividing a network for the composite material and acquiring a finite element model requiredby calculation; c, endowing the finite element model to thermal / mechanical performance parameters of a fiber and a matrix material which are related to a temperature; d, adding a periodic boundary condition for the finite element model; and e, applying a temperature load to the finite element model and calculating and acquiring the thermal residual stress. By using the method, operation is simpleand prediction precision is high; the method can play an important role in predicting the low temperature residual stress of the composite material so as to lay the foundation for the application of the composite material in a low temperature field.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Extrusion process for vehicle body in-situ nanoparticles enhancing aluminum base composite material
ActiveCN108796404AImprove tissue performance uniformityImprove strong plasticityResearch ObjectThermal expansion
The invention relates to the field of aluminum base composite material processing, in particular to an extrusion process for a vehicle body in-situ nanoparticles enhancing aluminum base composite material. The vehicle body in-situ nanoparticles enhancing aluminum base composite material synthesized in situ under the outer field control is used as a research object, the casting defects such as holes and loosening are eliminated by adopting the hot extrusion plasticity, so that the texture is refined and dense, the extruded grains are uniform and small, and the mechanical properties are obviously improved; meanwhile, under the action of the extrusion pressure, the agglomeration particles are dispersed and dispersed in a matrix, the bonding force with the matrix is higher, a lot of dislocation is generated, a high-density dislocation mesh is formed, and dislocation enhancement is produced accordingly. The T4P+ artificial aging heat treatment of the follow-up extrusion material can eliminate the thermal residual stress caused by the different thermal expansion coefficients of nanoparticles and matrix in the process of the hot extrusion, the plasticity of the vehicle body extrusion material is further improved, and the vehicle body in-situ nanoparticles enhancing aluminum base composite material extrusion material which can replace the steel plate is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Mould core insert part containing conformal cooling water channel
The invention discloses a mould core insert part containing a conformal cooling water channel. The mould core insert part comprises a core body and a conformal cooling water channel arranged in the core body, wherein the core body and the conformal cooling water channel are integrally formed by a selective laser sintered material, the conformal cooling water channel comprises a plurality of parallel V-shaped water channel bodies, a pipe opening of the V-shaped water channel body at the head end is set as a water inlet, a pipe opening of the V-shaped water channel body at the tail end is set asa water outlet, the pipe openings of the two adjacent V-shaped water channel bodies are connected through U-shaped water channels, a tip part at the bottom of each V-shaped water channel body is setas a transition fillet, and a plurality of centre holes are further arranged in the core body. The mould core insert part disclosed by the invention not only can improve a cooling efficiency of a mould and shorten product cooling time, but also shortens a product forming period, improves a product production efficiency and reduces thermal residual stress of injection molded parts; furthermore, themould core insert part can improve dimensional accuracy of injection molded products and improve product quality.
Owner:SUZHOU HUANA PRECISE TOOLING
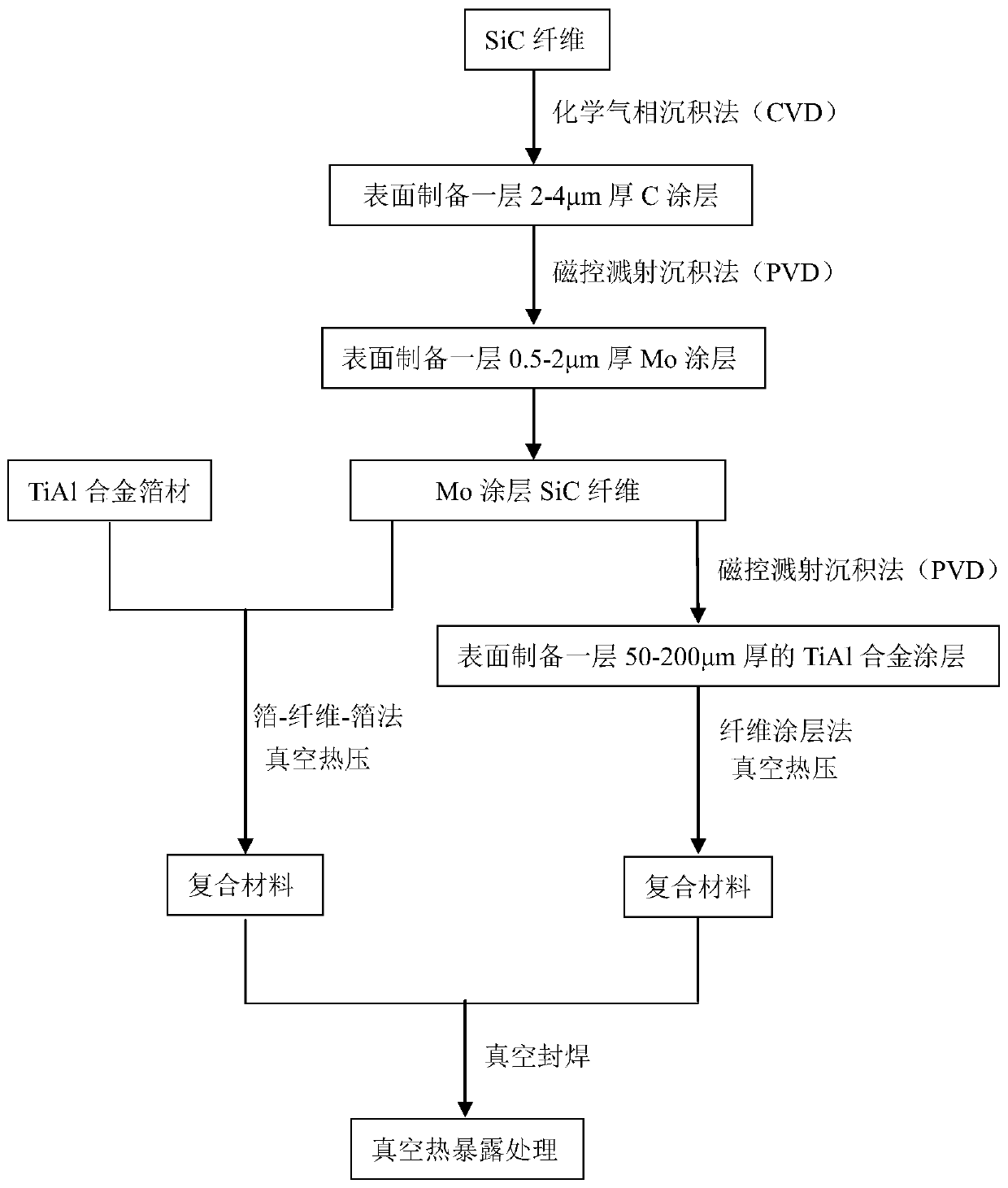
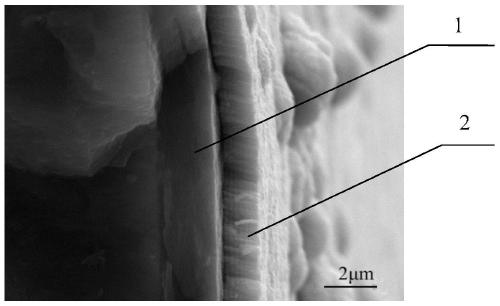
SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite with Mo coating and preparation method of SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite
The invention provides an SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite with an Mo coating and a preparation method of the SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite. The preparation method comprises the steps of firstly, preparing a layer of C coating with the thickness of 2-4[mu]m on the surface of SiC fiber by using a chemical vapor deposition process; then, uniformly depositing an Mo metal coating with the thickness of 0.5-2[mu]m on the surface of the SiC fiber with the C coating by using a magnetron sputtering deposition process; and finally, preparing the SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite with the Mo coating by using a foil-fiber-foil process or a fiber coating process. The interface reaction speed of the fiber and a matrix and the consumption speed of the C coating of the fiber under a high-temperature condition are effectively reduced, and the Mo coating is excellent in thermal stability, does not participate in the interface reaction, is not diffused and can be used for effectively relieving the thermal residual stress at the interface of the composite.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Epoxy adhesive composition
A curable epoxy adhesive composition including (a) at least one first epoxy resin; (b) at least one first diluent; (c) at least one first hardener; (d) at least a first hydrophilic filler that has a predetermined aspect ratio; (e) at least a second hydrophobic filler that is different from the first filler and that has a predetermined aspect ratio; and (f) at least a third filler that is different from the first and second fillers; wherein the third filler has a predetermined aspect ratio higher than the first filler and the second filer; and wherein the volume ratio of the third filler to the combination of the first filler and second filler is in the range of from 1:1 to 10: 1 such as to minimize the thermal residual stresses of the cured product made from the curable composition.
Owner:BLUE CUBE IP
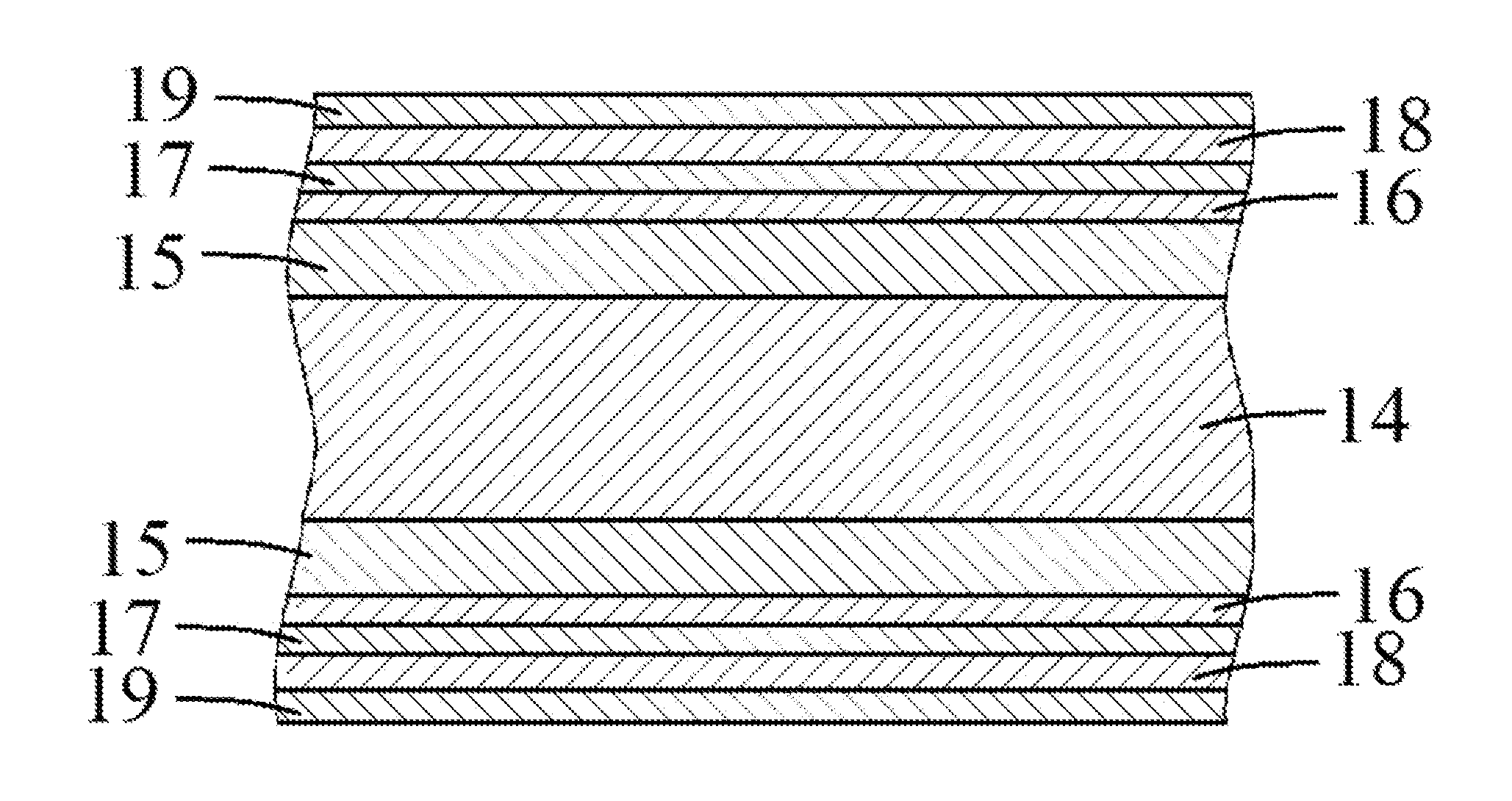
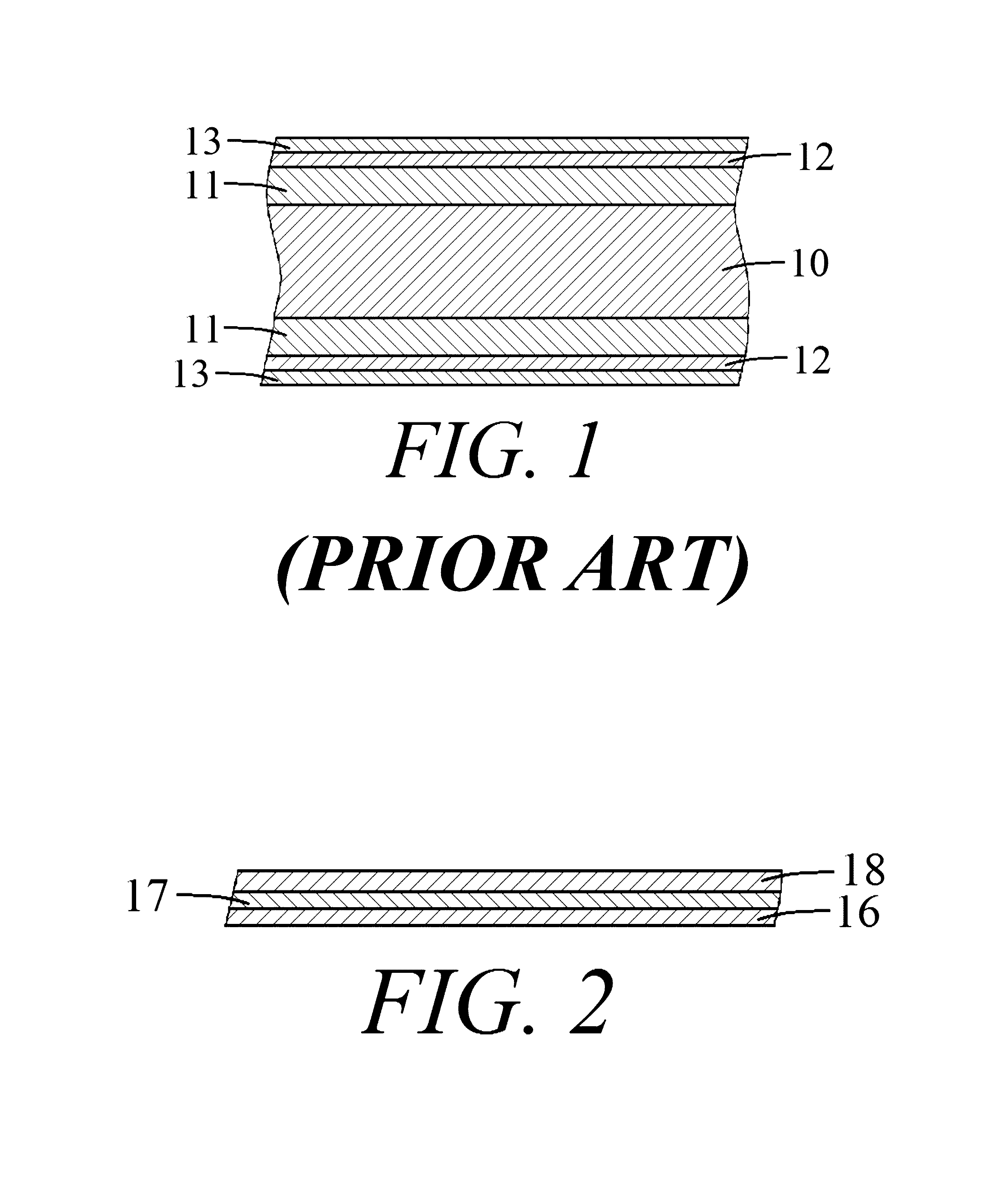
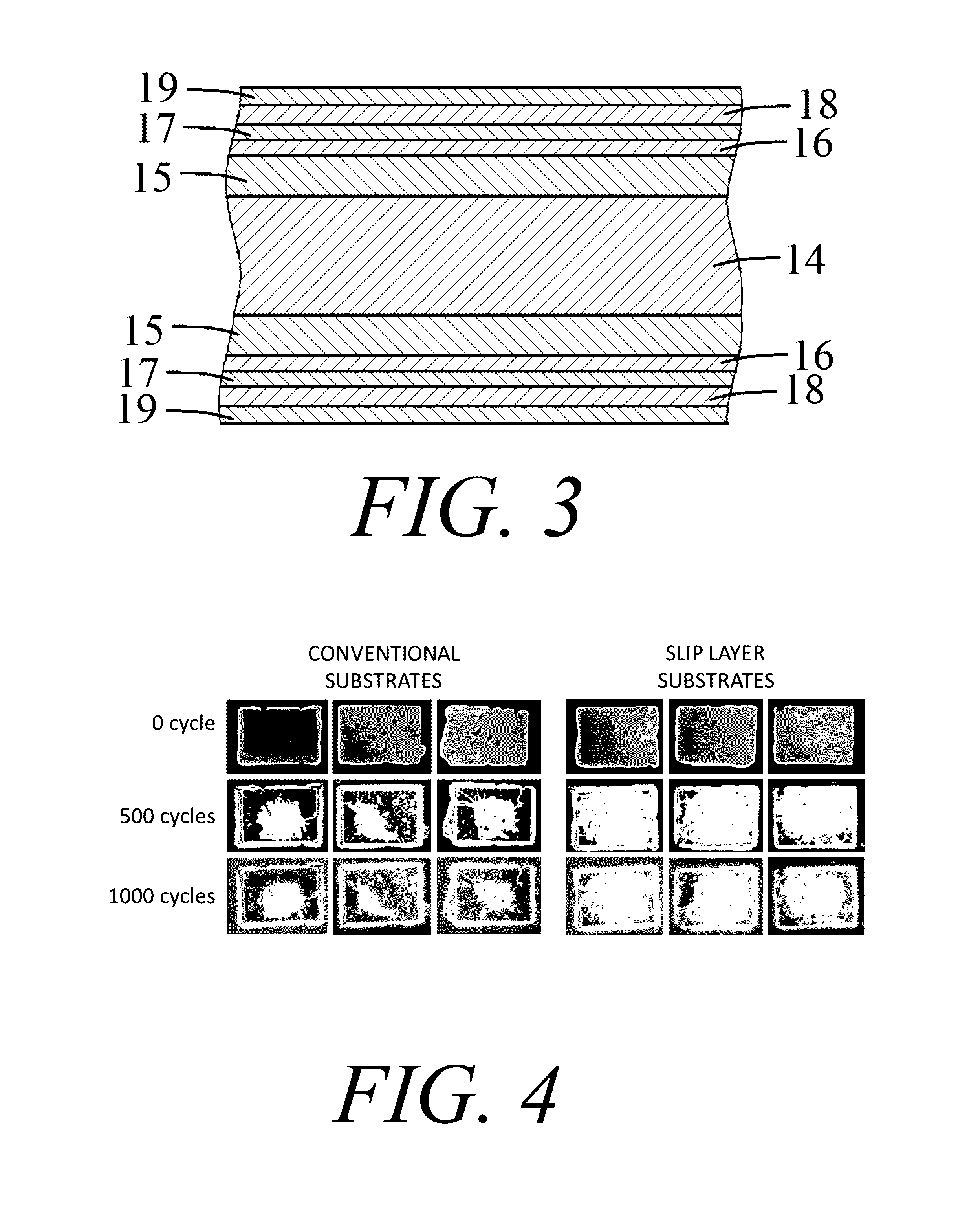
Multilayer substrate and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20150237724A1Improve reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsThermal expansionDiffusion barrier
The invention provides a slip layer substrate which can reduce the thermal residual stresses between components induced by their mismatch of thermal expansion, thus greatly improve the reliability of electronic packages. The slip layer substrate comprises: a base material; a first metallization layer formed on the base material; a first diffusion barrier layer formed on the first metallization layer; a slip layer formed on the first diffusion barrier layer; a second diffusion barrier layer formed on the slip layer; and a second metallization layer formed on the second diffusion barrier layer.
Owner:RSM ELECTRON POWER
Hard alloy matrix and polycrystalline diamond composite sheet
InactiveCN105215388AImprove the interface binding forceWith impact resistanceWorkpiecesTurning toolsPolycrystalline diamondAlloy
The invention provides a hard alloy matrix for a polycrystalline diamond composite sheet. A plurality of evenly-arranged protrusions and a plurality of depressions are arranged on the combination interface of the hard alloy matrix and a diamond layer. Optimized design is carried out on the combination interface of the hard alloy matrix and the diamond layer, the thermal residual stress between the combination face is reduced, and therefore the impact toughness of polycrystalline diamond is improved, and the quality of the polycrystalline diamond is improved.
Owner:HENAN JINGRUI SUPERHARD MATERIAL
Annular laser device with electrode group and manufacture method for electrode group
ActiveCN103236634AAchieving a hermetic sealGood technical effectLaser constructional detailsReaction layerElectrical conductor
The invention relates to an annular laser device with an electrode group and a manufacture method for the electrode group. The annular laser device comprises a resonance cavity, wherein the resonance cavity is provided with the electrode group, an optical mirror and a plurality of clear aperture channels; helium-neon mixed gas is filled inside the resonance cavity; and the electrode group is formed by connection of an electrode conductor and a glass segment through a connecting layer in a thermocompression manner. The manufacture method for the electrode group comprises the following steps of depositing a seed layer and a transition layer, manufacturing an activated reaction layer, exciting the activated reaction layer, and welding the electrode conductor and the glass segment in a thermocompression way. The annular laser device and the manufacture method have the main advantages that 1, the electrode group is connected with the resonance cavity through the glass segment of the electrode group in a sealing manner, so that instant airtight sealing connection of local heating is realized, and the affect of thermal residual stress generated in integral heating and sealing is effectively eliminated; 2, the glass segment is clung to the resonance cavity through optical cement, and the disassembly and the replacement of the electrode group are convenient; and 3, the glass segment and the resonance cavity adopt the same material, and the sealing connection stress generated in direct sealing connection of the electrode group and the resonance cavity is avoided.
Owner:NO 717 INST CHINA MARINE HEAVY IND GRP
Kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method
The invention relates to a kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method. The kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method comprises the following steps of cleaning, filling welding flux, preheating, pressurizing and heating. The kovar alloy and tungsten copper alloy connecting method has the advantages of simple process, time saving, low production cost and high production efficiency, and additionally, the thermal residual stress of a joint is small, so that the performance of the joint is good, the joint is reliable, and the application requirement of the kovar alloy andtungsten copper alloy connecting joint can be met.
Owner:SUZHOU SAITERUI PRECISION MACHINERY PARTS CO LTD
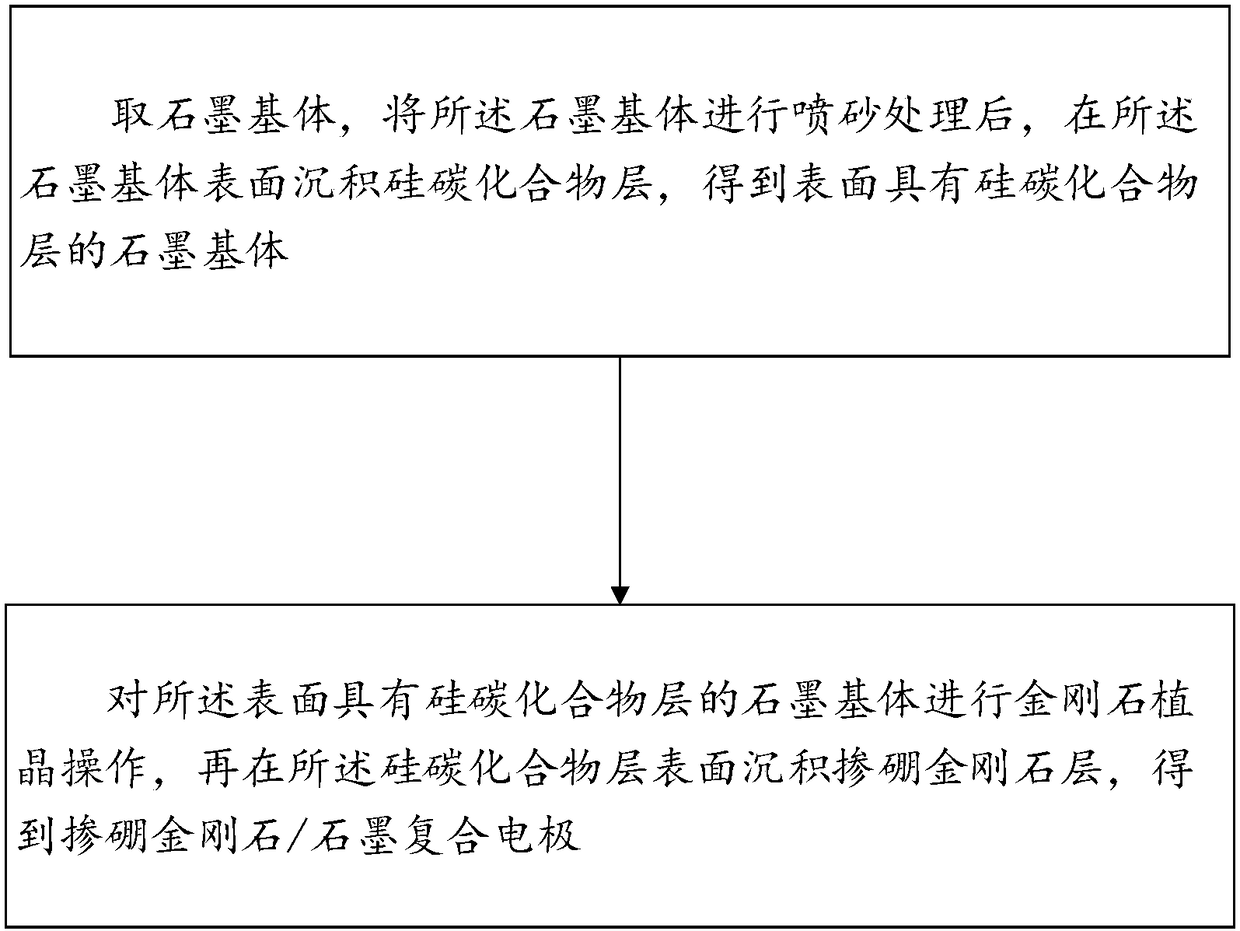
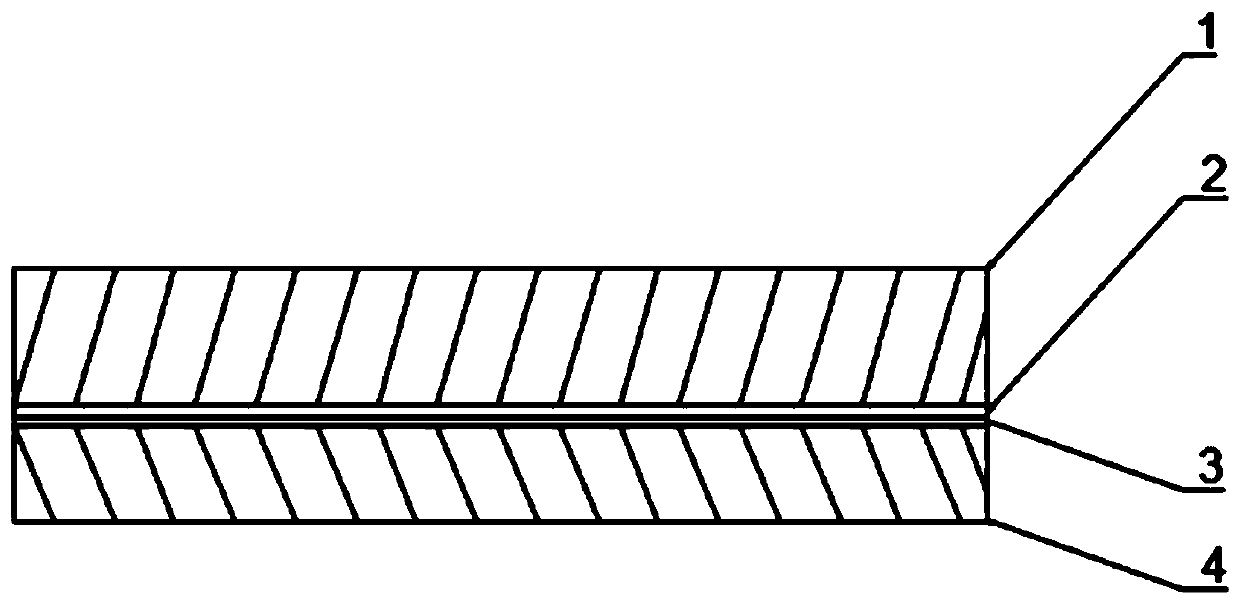
Boron-doped diamond/graphite composite electrode as well as manufacturing method thereof and double-battery reactor
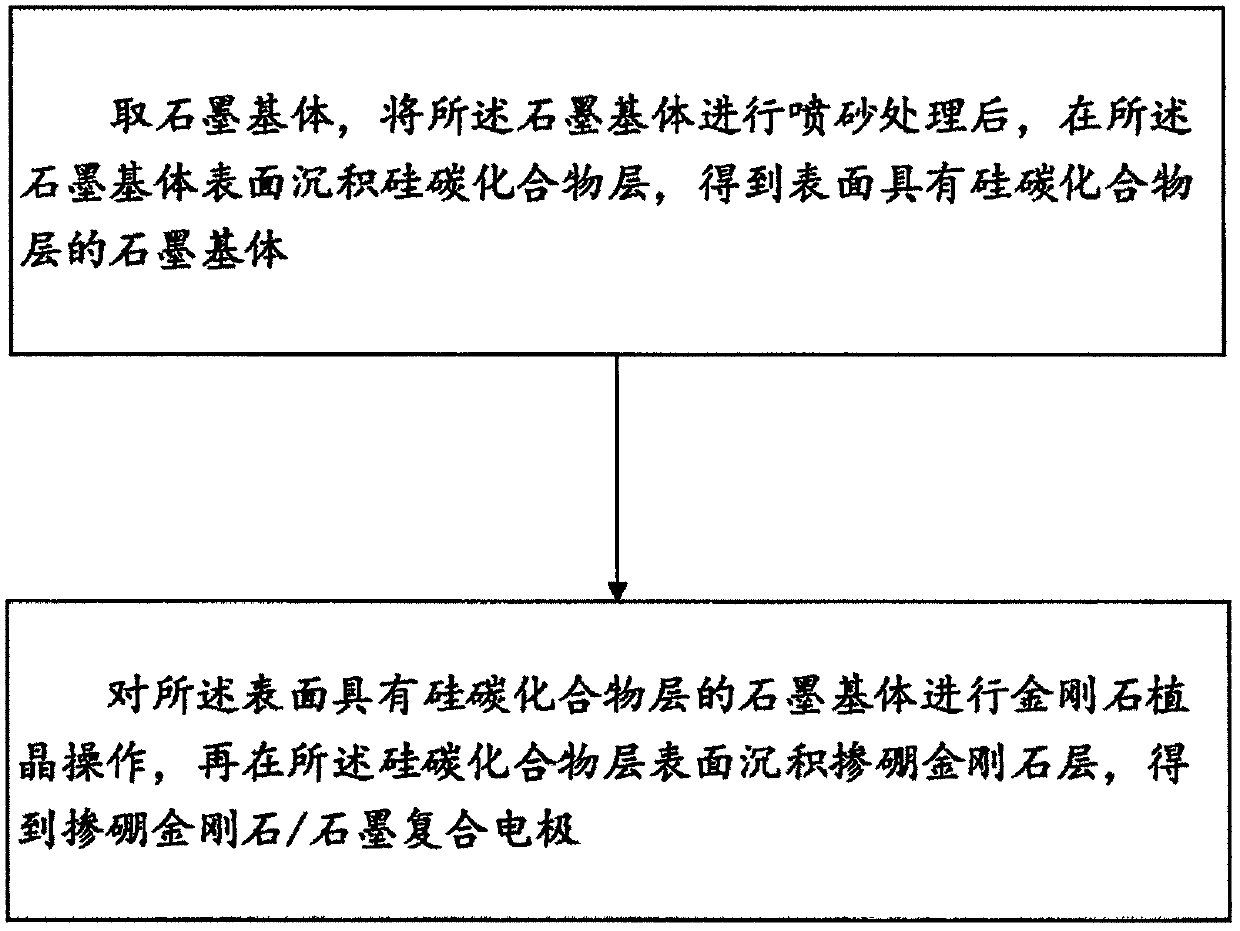
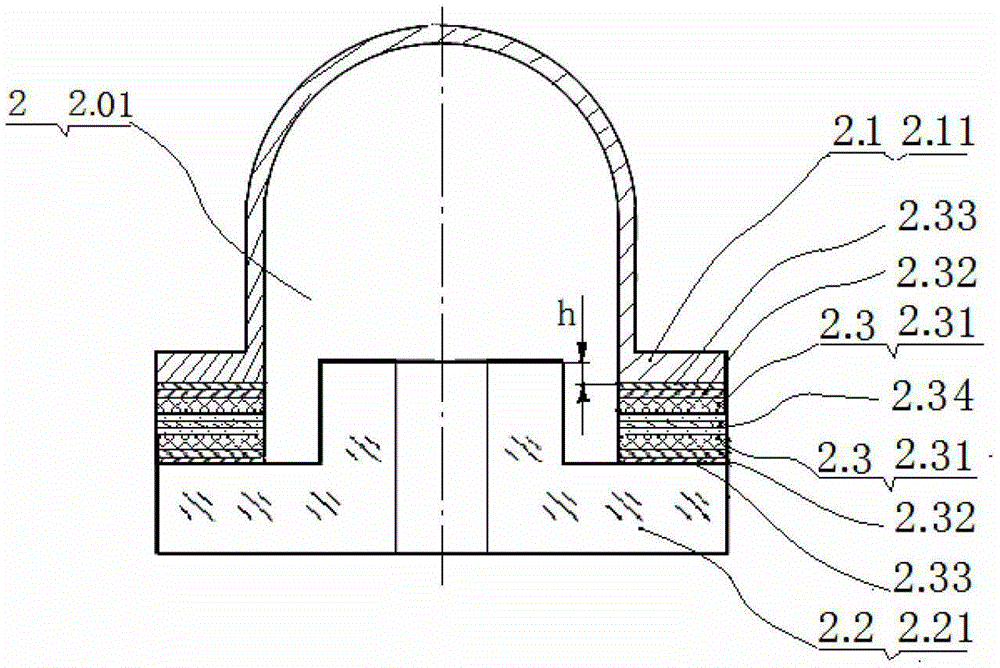
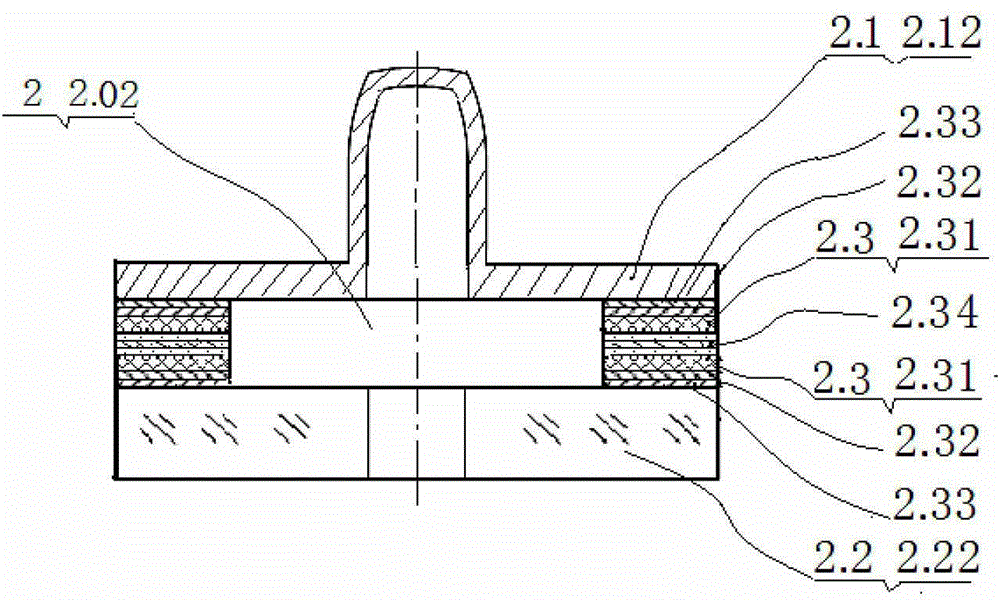
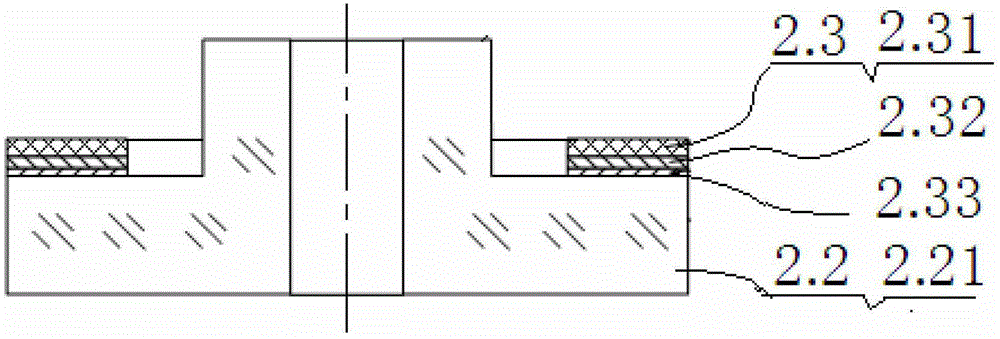
PendingCN108408848AImprove mechanical propertiesGood effectWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processWater/sewage treatment apparatusComposite electrodeThermal expansion
The invention provides a boron-doped diamond / graphite composite electrode. The boron-doped diamond / graphite composite electrode comprises a graphite base body as well as a silicon-carbon compound layer and a boron-doped diamond layer which are sequentially stacked on the graphite base body. A thermal expansion coefficient of the silicon-carbon compound is within an intermediate value range of thethermal expansion coefficient of graphite and boron-doped diamond, and therefore, the silicon-carbon compound is taken as an intermediate transition layer, and difference of thermal expansion coefficients of layers of the boron-doped diamond / graphite composite electrode is reduced. Influences, on film-based binding force, of thermal residual stress are finally reduced, and film-based binding forceof the boron-doped diamond / graphite composite electrode is improved. The invention further provides a manufacturing method for the composite electrode, and the manufacturing method is simple in process, and is low in cost; and the silicon-carbon compound layer is deposited for avoiding pollution on a chamber, so that the industrial applicability is very great.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for carbon fiber composite material and aluminum alloy interface treatment
InactiveCN109749637AReduce the differenceReduce interface thermal residual stressNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentEpoxyFiber
The invention relates to a method for carbon fiber composite material and aluminum alloy interface treatment. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing surface treatment on an aluminum alloy by using hydrochloric acid, and coating on the surface of the aluminum alloy by epoxy resin mixed with carbon nano tubes, enabling the carbon nano tubes to be directionally arranged by usingan externally applied magnetic field, and curing; coating by epoxy acrylic resin and curing; laying a layer of one-way carbon fiber cloth, wherein a laying angle is the same as a directional arrangement direction of the above carbon nano tubes, then laying the carbon fiber cloth, finally curing and forming. Because a longitudinal thermal expansion coefficient of the directionally arranged epoxy resin mixed with the carbon nano tubes is between the aluminum alloy and the one-way carbon fiber cloth, and the epoxy acrylic resin is positioned in a high-elastic state in a temperature above a glass-transition temperature, and serves as a stress buffer layer for absorbing partial stress, an interface heat residual stress caused by a larger difference of the longitudinal thermal expansion coefficients of two parties can be effectively reduced in a cooling process of the carbon fiber composite material and the aluminum alloy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain
The invention provides a method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain. In order to solve the technical problems that as fiber grating sensors are bonded to the surface of a structure through polyimide resin or epoxy resin commonly used in the prior engineering, optic fiber in service is easily destroyed; the optic fiber can get encapsulation protection but cause the concentration of surrounding stress / strain thereof if the optic fiber is directly embedded in a composite-material structure; and thermal residual stress produced in a material-curing process can cause chirp phenomena of fiber grating reflection spectrum to affect the measurement accuracy of grating strain, and the like, the invention provides the method for manufacturing intelligent composite-material laminates used for monitoring structural longitudinal strain. In the method, the fiber grating sensors are embedded in composite-material layers to replace resistance strain gauges commonly used in the field of monitoring structural health; by applying prestress to embedded fiber gratings, the influence of the curing residual stress of composite material on the fiber grating reflection spectrum is reduced so as to avoid the chirp phenomena; and the stability and repeatability of the sensors are improved. In addition, the composite material plays agood role in encapsulating and protecting bare fiber gratings, and meets engineering construction requirement on sensor sensitivity.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AERONAUTICAL ENG +1
Preparation process of wear-resistant stainless steel alloy coating
InactiveCN109622973AIncreased friction and wear resistanceSmall thermal residual stressVacuum evaporation coatingSurface reaction electrolytic coatingWear resistantBraze alloy
The invention discloses a preparation process of a wear-resistant stainless steel alloy coating. The preparation process comprises the following steps of S1, selection of raw materials, S2, embedmentof polytetrafluoroethylene in alloy powder, S3, preparation and stacking of metal cloth, S4, brazing, and S5, coating of the alloy coating on the stainless steel surface. Tungsten carbide hard alloy powder and NiCrBSi self-fluxing brazing alloy powder are used as a hard phase and subjected to rolling with polytetrafluoroethylene into the cloth, then the cloth adheres to the surface of stainless steel and then brazed into a metallurgical bonding composite coating, and the flexible metal cloth can adhere to the surface of a complex structural part; when brazing, the metal cloth and a substrate are simultaneously heated, the thermal residual stress of the coating is small, the thickness variation range of the coating is wide, and the surface roughness is small, so that the stainless steel surface has high wear resistance and erosion resistance; and the anti-abrasive wear performance of the obtained coating is much higher than the anti-abrasive wear performance of a flame surfacing coating, and the wear resistance and tensile strength of a stainless steel substrate are significantly improved.
Owner:淮北市菲美得环保科技有限公司
Preparation technology of abrasion-resistant stainless steel alloy coating
InactiveCN109692957ASmall thermal residual stressWide range of thickness variationMetallic material coating processesBraze alloyAlloy coating
The invention discloses a preparation technology of an abrasion-resistant stainless steel alloy coating. The preparation technology includes the following steps that S1, raw materials are selected; S2, alloy powder is embedded into polytef; S3, a metal cloth is prepared and stacked; S4, brazing is conducted; and S5, the stainless steel surface is covered with the alloy coating. According to the preparation technology of the abrasion-resistant stainless steel alloy coating, tungsten carbide hard alloy powder and NiCrBSi self-fluxing brazing alloy powder are treated as hard phases and are rolledinto the cloth with the polytef, then the cloth adheres to the surface of stainless steel, then brazing is conducted to form a metallurgical bonded complex coating, and the flexible metal cloth can be adhered to the surface of a part of a complex structure; and thermal residual stress of the coating is small due to the fact that the metal cloth and a substrate are heated at the same time during brazing, the variation range of the thickness of the coating is large, surface roughness of the coating is small, thus the surface of the stainless steel has high abrasion resistance and erosion resistance, the grinding material abrasion resistant performance of the obtained coating is much higher than the grinding material abrasion resistant performance of a flame surfacing coating, and abrasion resistance and strength of extension of the stainless steel substrate are remarkably improved.
Owner:淮北市菲美得环保科技有限公司
epoxy adhesive composition
A curable epoxy adhesive composition comprising (a) at least one first epoxy resin; (b) at least one first diluent; (c) at least one first hardener; (d) having at least a first hydrophilic filler of a predetermined aspect ratio; (e) at least a second hydrophobic filler different from the first filler and having a predetermined aspect ratio; and (f) at least one hydrophobic filler different from said first and second fillers. A third filler; wherein the third filler has a predetermined aspect ratio higher than that of the first filler and the second filler; and wherein the volume ratio of the third filler to the combination of the first filler and the second filler In the range of 1:1 to 10:1, thereby minimizing the thermal residual stress of the cured product prepared from the cured composition.
Owner:BLUE CUBE IP
Welding base plate and application of welding base plate to magnesium/aluminum dissimilar metal welding
ActiveCN106425020APrevent thermal deformationReduce build timeArc welding apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesWelding residual stressThermal deformation
The invention discloses a welding base plate and application of the welding base plate to magnesium / aluminum dissimilar metal welding. According to the welding base plate, a to-be-welded plate is clamped and fixed by adopting the hollow welding base plate which is filled with a cooling agent. Generation time of a hard brittle intermetallic compound Mg17Al12 is effectively shortened; mechanical strength of a dissimilar welding connector is improved; thermal deformation of the plate during a welding process is effectively avoided; and thermal residual stress of welding is reduced. Meanwhile, during the welding process, a proper air flow is adopted for a welding area at the lower surface of the to-be-welded plate; argon is blown for protection; and the phenomenon that molten metal is in contact with air for reaction during the welding process, so that welding joint inclusions are generated can be avoided. According to the welding base plate, through double effects of thermal control during the welding process and post-welding thermal treatment, the amount of the hard brittle intermetallic compound Mg17Al12 and the welding residual stress are greatly reduced; and welding quality of the welding connector is effectively improved.
Owner:NEW MATERIAL INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF SCI
Mo coating SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a Mo coating SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of, first preparing a layer of C coating with the thickness of 2-4 micrometers on the SiC fiber surface through a chemical vapor deposition method; and then preparing a layer of Mo metal coating with the thickness is 0.5-2 micrometers on the SiC fiber surface with the C coating through uniform deposition; and finally preparing the Mo coating SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite material through a foil-fiber-foil method and a fiber coating method. According to the Mo coating SiC fiber-reinforced TiAl-based composite material, the interface reaction between a fiber and a matrix as well as the consumption speed of the C coating of the fiber at a high temperature are effectively reduced, and the Mo coating has excellent thermal stability, does not get involved in an interface reaction and does not diffuse, so that the thermal residual stress at the interface of the composite material can be effectively relieved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A Method for Measuring the Shrinkage of Injection Molded Products Using Three-dimensional Digital Image Technology
ActiveCN112945120BMonitor changes in real timeContinuityUsing optical meansShrinkage rateSpeckle pattern
The invention belongs to the technical field of injection molding, and specifically relates to a method for measuring the shrinkage rate of injection molded products using three-dimensional digital image technology. The invention adds black solid particles into the melt as marks on the basis of visual mold, and the added black Solid particles have the function of speckle in two-dimensional image measurement. After fixing the optical path, preparing random speckle, image information acquisition, image data storage, image matching, and calculating shrinkage, etc., the thermal residual stress change of the injection molded product to be tested can be realized. real-time monitoring.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU CRAFTSMAN MACHINERY EQUIP CO LTD
Device and method for removing white patches on surface of material
ActiveCN108994446ADoes not induce other residual stressesTo achieve the purpose of removing white spotsLaser beam welding apparatusGalvanometerLaser light
The invention provides a device for removing white patches on the surface of a material caused by the thermal residual stress. The device comprises a laser, an X galvanometer, a Y galvanometer and a focus lens, wherein the X galvanometer is used for reversing a laser light from the laser; the Y galvanometer is used for reversing the laser light processed through the X galvanometer; and the focus lens is used for adjusting the light intensity of the laser light processed through the Y galvanometer and guiding the laser subjected to light intensity adjustment to the surface of the material, so that the white patches on the surface of the material are removed. The laser light emitted by the device provided by the invention can be used for melting the white patches on the surface of the material, and the material around the white patches can be fuzzified through the cooperation of the focus lens in the device, so that the crystalline state is recovered to the amorphous state, the aim of removing the white patches is achieved, and the generation of other residual stresses cannot be triggered.
Owner:HEFEI LCFC INFORMATION TECH
Method for measuring shrinkage rate of injection molding product by using three-dimensional digital image technology
ActiveCN112945120AMonitor changes in real timeContinuityUsing optical meansShrinkage rateSpeckle pattern
The invention belongs to the technical field of injection molding, and particularly relates to a method for measuring the shrinkage rate of an injection molding product by using a three-dimensional digital image technology, black solid particles are added into a melt as a mark on the basis of a visual mold, and the added black solid particles have a speckle function in two-dimensional image measurement, and real-time monitoring of the thermal residual stress change of the injection molding product to be detected is realized through the steps of optical path fixing, random speckle preparation, image information acquisition, image data storage, image matching, shrinkage rate calculation and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Boron-doped diamond/graphite composite electrode, preparation method, and double-cell reactor
InactiveCN110872142AImprove mechanical propertiesGood effectWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processThermal dilatationComposite electrode
The invention provides a boron-doped diamond / graphite composite electrode including a graphite substrate and a silicon-carbon compound layer and a boron-doped diamond layer that are successively laminated on the graphite substrate; since the thermal expansion coefficient of the silicon-carbon compound is located between the thermal expansion coefficients of the graphite and the boron-doped diamond, the silicon-carbon compound, as a transition layer, can reduce the difference of the thermal expansion coefficients between the layers of the boron-doped diamond / graphite composite electrode, so that the influence on the film-substrate binding force due to thermal residual stress is finally reduced and the film-substrate binding force of the composite electrode is enhanced. The invention also provides a preparation method of the composite electrode, which is simple in process and low in cost; deposition of the silicon-carbon compound layer avoids pollution on the chamber, so that the processis great in industrial applicability.
Owner:EZHOU JINFENG SUPERHARD MATERIALS CO LTD
Annular laser device with electrode group and manufacture method for electrode group
ActiveCN103236634BAchieving a hermetic sealAvoid stressLaser constructional detailsReaction layerElectrical conductor
The invention relates to an annular laser device with an electrode group and a manufacture method for the electrode group. The annular laser device comprises a resonance cavity, wherein the resonance cavity is provided with the electrode group, an optical mirror and a plurality of clear aperture channels; helium-neon mixed gas is filled inside the resonance cavity; and the electrode group is formed by connection of an electrode conductor and a glass segment through a connecting layer in a thermocompression manner. The manufacture method for the electrode group comprises the following steps of depositing a seed layer and a transition layer, manufacturing an activated reaction layer, exciting the activated reaction layer, and welding the electrode conductor and the glass segment in a thermocompression way. The annular laser device and the manufacture method have the main advantages that 1, the electrode group is connected with the resonance cavity through the glass segment of the electrode group in a sealing manner, so that instant airtight sealing connection of local heating is realized, and the affect of thermal residual stress generated in integral heating and sealing is effectively eliminated; 2, the glass segment is clung to the resonance cavity through optical cement, and the disassembly and the replacement of the electrode group are convenient; and 3, the glass segment and the resonance cavity adopt the same material, and the sealing connection stress generated in direct sealing connection of the electrode group and the resonance cavity is avoided.
Owner:NO 717 INST CHINA MARINE HEAVY IND GRP
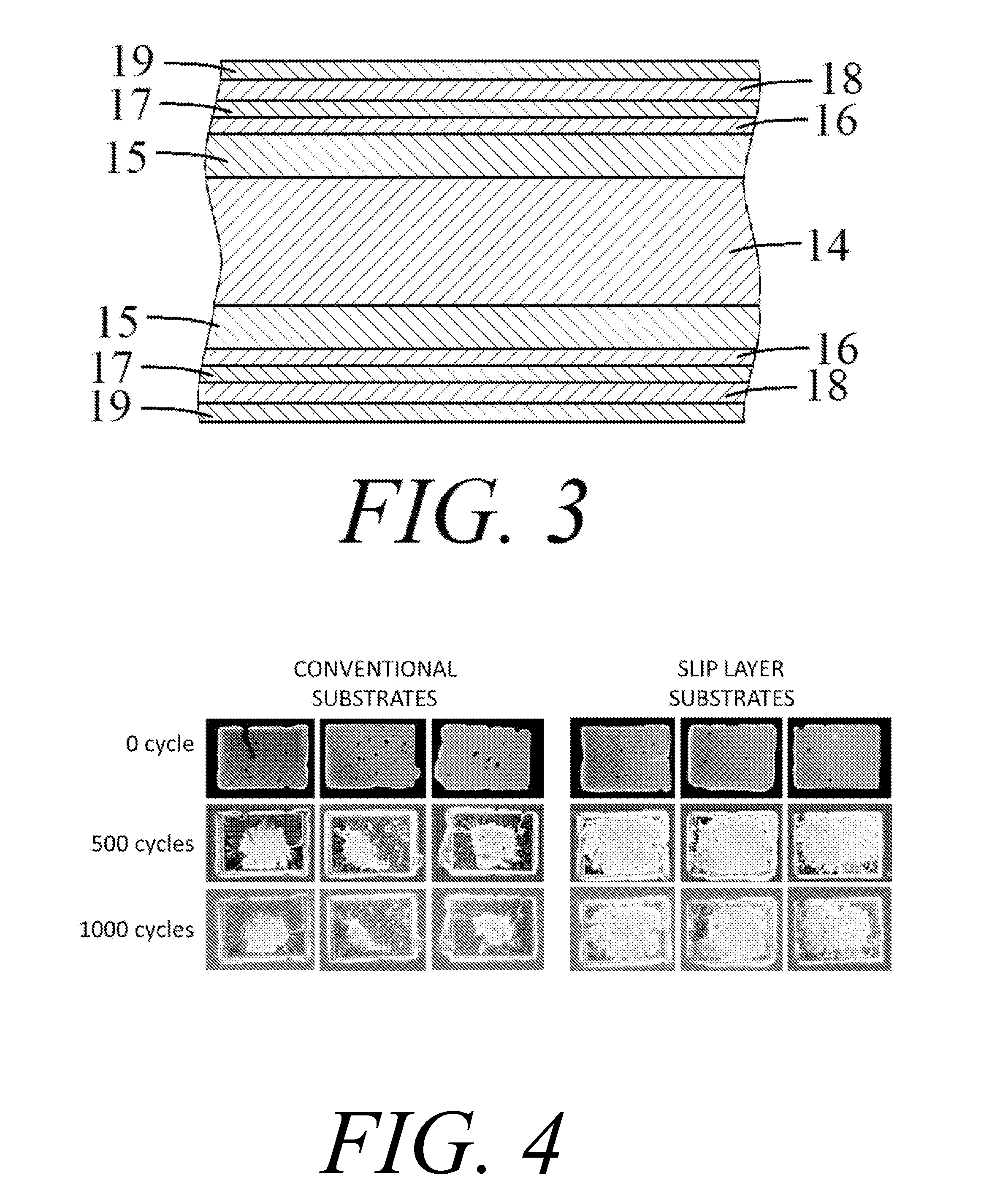
Multilayer substrate and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS9558859B2Improve reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsThermal expansionDiffusion barrier
The invention provides a slip layer substrate which can reduce the thermal residual stresses between components induced by their mismatch of thermal expansion, thus greatly improve the reliability of electronic packages. The slip layer substrate comprises: a base material; a first metallization layer formed on the base material; a first diffusion barrier layer formed on the first metallization layer; a slip layer formed on the first diffusion barrier layer; a second diffusion barrier layer formed on the slip layer; and a second metallization layer formed on the second diffusion barrier layer.
Owner:RSM ELECTRON POWER
A device and method for removing white spots on the surface of materials
ActiveCN108994446BTo achieve the purpose of removing white spotsDoes not induce other residual stressesLaser beam welding apparatusGalvanometerLaser light
The invention provides a device for removing white spots caused by thermal residual stress on the surface of a material, including a laser; an X oscillating mirror for reversing the laser light from the laser; The laser of the X galvanometer is reversing; the focusing lens is used to adjust the light intensity of the laser passing through the Y galvanometer, and guide the laser light after adjusting the light intensity to the surface of the material to remove white spots on the surface of the material. The laser emitted by the device provided by the invention can melt the white spots on the surface of the material, and cooperate with the focusing lens in the device to blur the material around the white spot, so that it can be restored from the crystalline state to the amorphous state, so as to achieve the removal of the white spot The purpose, and will not cause other residual stress generation.
Owner:HEFEI LCFC INFORMATION TECH
Energy-saving composite plate pressing device
InactiveCN107724963AImprove impact resistanceEnhanced ability to eat into the groundDrill bitsHeat resistancePolycrystalline diamond
The invention discloses an energy-saving composite sheet pressing device, which comprises a main body of a polycrystalline diamond composite sheet, a connection part is arranged under the main body of the polycrystalline diamond composite sheet, and convex ribs are arranged on the top of the main body of the polycrystalline diamond composite sheet , the surface of the polycrystalline diamond compact body is provided with an impact-resistant alloy layer, the lower layer of the impact-resistant alloy layer is provided with high heat-resistant polycrystalline diamond, and the lower layer of the high heat-resistant polycrystalline diamond is provided There is polycrystalline diamond, the polycrystalline diamond inner layer is provided with a transition layer. The invention is beneficial to enhance the ability of the composite sheet to penetrate into the formation, and the convex ribs make the cutting surface have a strong plowing effect, which reduces the drilling and cutting resistance, thereby increasing the ROP of the diamond drill bit, and the transition layer reduces the heat between the bonding surfaces. Residual stress, thereby improving the impact toughness of polycrystalline diamond, improving the quality of polycrystalline diamond, prolonging the service life, eliminating the need for frequent replacement, and being more energy-saving and environmentally friendly.
Owner:成都骏铭圭科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com