Seven point frequency domain finite difference method for analyzing periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide characteristic modes
A non-homogeneous medium and finite difference technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as lack of characteristic modes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
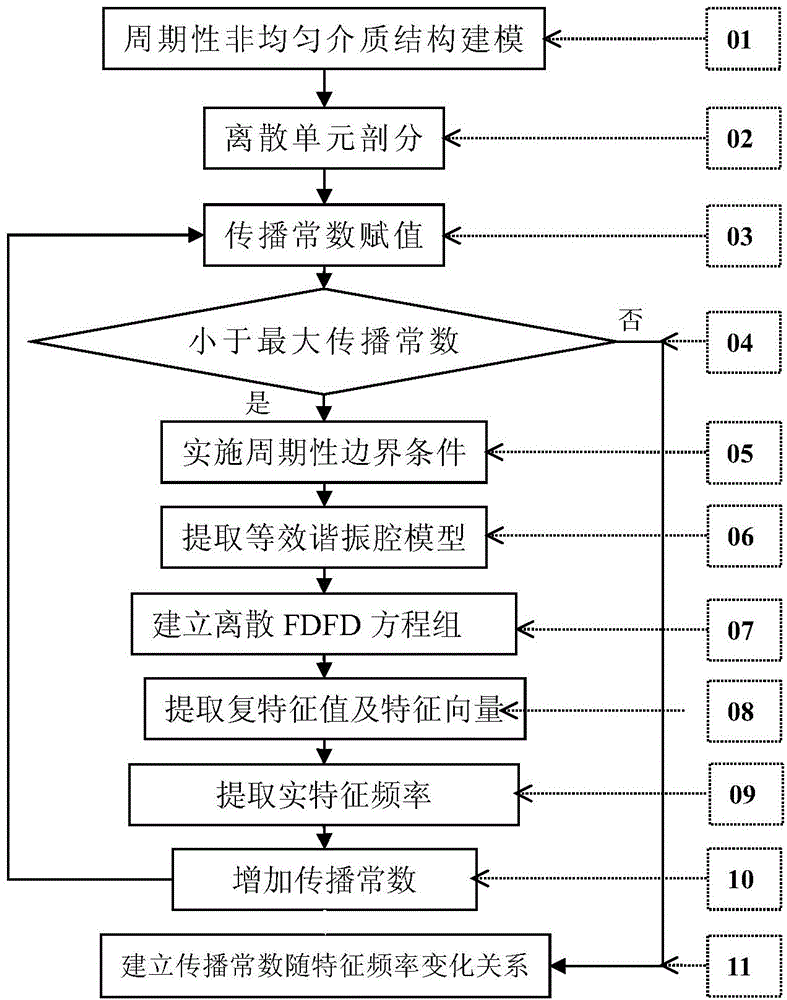
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a seven-point frequency-domain finite difference method for periodic inhomogeneous dielectric waveguide eigenmode analysis, and its specific steps are as follows:
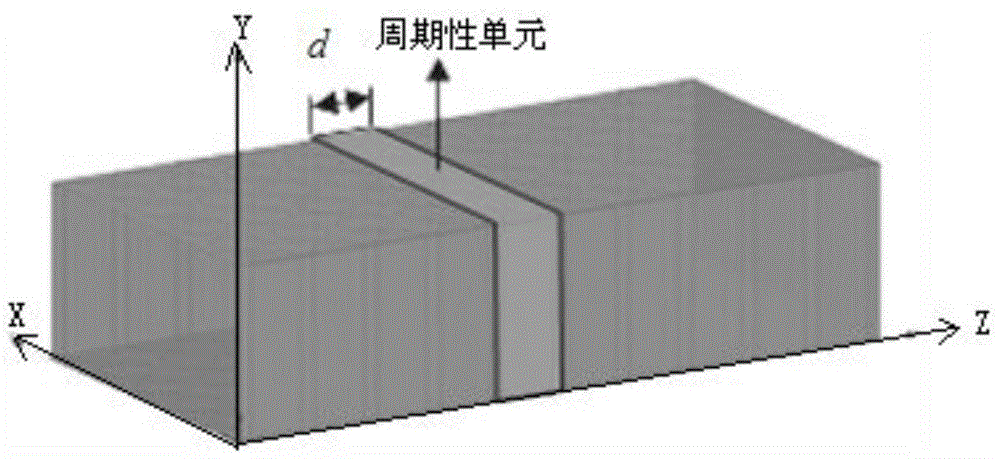
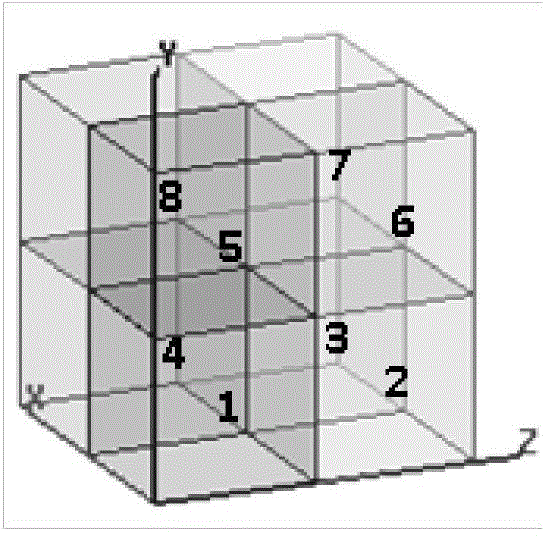
[0047] 01) Electromagnetic modeling of the periodic non-uniform dielectric waveguide structure is carried out in the computer, and the data entry of the shape parameters and the distribution of the dielectric constant of the structure is realized in the computer: the waveguide is placed in the rectangular coordinate system, so that the waveguide wall Parallel to the coordinate plane, and the medium filled in the waveguide is periodic along the z-axis direction, with a period of d, a three-dimensional coordinate array is established to record the shape and three-dimensional coordinate parameters of the non-uniform medium distribution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com