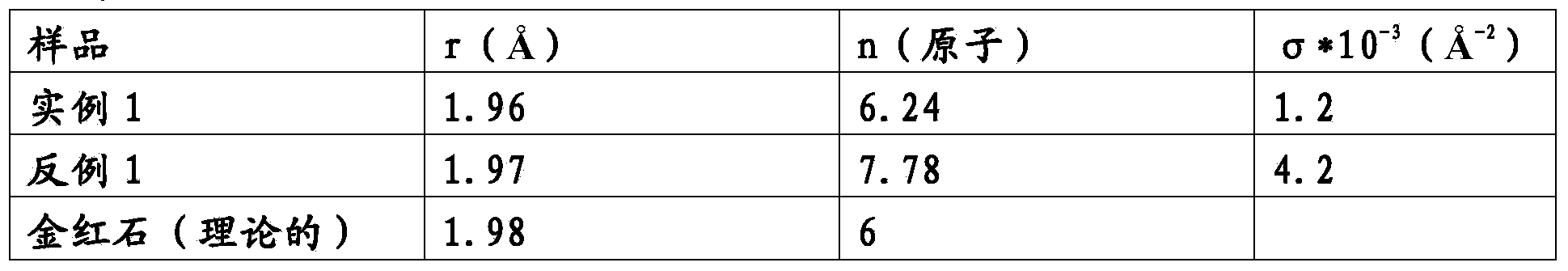Electrode for electrolytic processes and method of manufacturing thereof
An electrode and process technology, applied in the electrode field of electrolysis process, can solve problems such as high cathode overvoltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
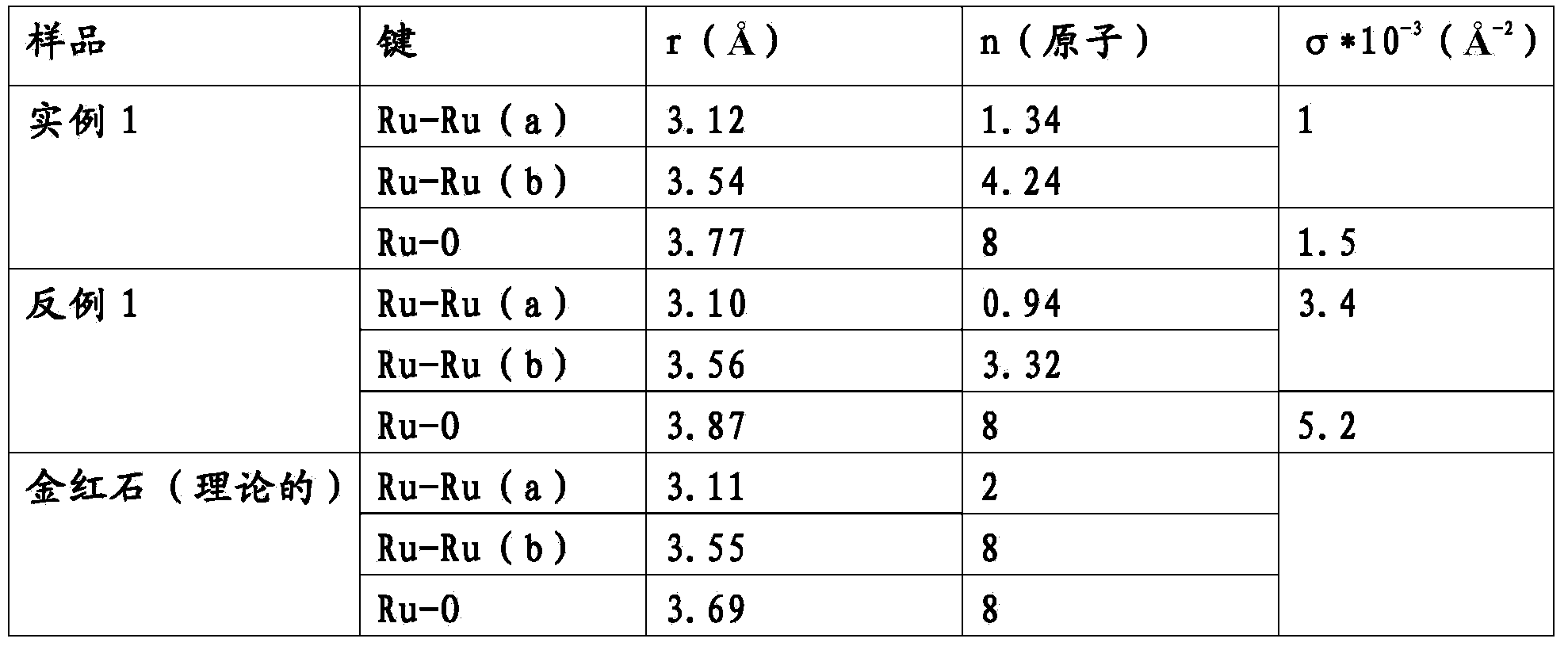
example 1
[0016] Put the amount corresponding to 100g Ru of Ru(NO)(NO 3 ) 3 Dissolve in 300 ml of glacial acetic acid to which a few ml of concentrated nitric acid have been added. The solution was stirred for three hours, keeping its temperature at 50°C. This solution was then poured into 500 ml volume of 10% by weight acetic acid (ruthenium solution).
[0017] Separately, the amount of Pr(NO 3 ) 2 Dissolve in 300 ml of glacial acetic acid to which a few ml of concentrated nitric acid have been added. The solution was stirred for three hours, keeping its temperature at 50°C. This solution was then poured into 500 ml volume of 10% by weight acetic acid (rare earth element solution).
[0018] 480 ml of the ruthenium solution were mixed into 120 ml of the rare earth element solution and stirred for five minutes. The solution thus obtained was poured into 1 liter of 10% by weight acetic acid (precursor).
[0019] A nickel mesh 200 of size 100mm x 100mm x 0.89mm was subjected to the...
example 2
[0023] Put the amount corresponding to 100g Ru of Ru(NO)(NO 3 ) 3 Dissolve in 300 ml of glacial acetic acid to which a few ml of concentrated nitric acid have been added. The solution was stirred for three hours, keeping its temperature at 50°C. This solution was then poured into 1 liter volume of 10% by weight acetic acid (precursor).
[0024] A nickel mesh 200 of size 100mm x 100mm x 0.89mm was subjected to the following process: blasting with corundum, etching in 20% HCl at 85°C for 2 minutes and thermal annealing at 500°C for 1 hour. The previously obtained precursor was then applied by brushing in 7 successive coats, followed by a drying treatment at 80°C-90°C for 10 minutes and thermal decomposition at 500°C for 10 minutes after each coat, until 12g / m 2 Deposition of Ru.
[0025] The sample was subjected to a performance test showing that at 3kA / m 2Under hydrogen evolution in 33% NaOH at a temperature of 90 °C, the ohmic drop-corrected initial cathodic potential of...
example 3
[0028] Pt(NH 3 ) 2 (NO 3 ) 2 Dissolve in 200ml glacial acetic acid. The solution was stirred for 3 hours, keeping its temperature at 50°C, and then poured into a volume of 500 ml of 10% by weight acetic acid (platinum solution).
[0029] Put the amount corresponding to 100g Ru of Ru(NO)(NO 3 ) 3 Dissolve in 300 ml of glacial acetic acid to which a few ml of concentrated nitric acid have been added. The solution was stirred for three hours, keeping its temperature at 50°C. This solution was then poured into 500 ml volume of 10% by weight acetic acid (ruthenium solution).
[0030] Separately, the amount of Pr(NO 3 ) 2 Dissolve in 300 ml of glacial acetic acid to which a few ml of concentrated nitric acid have been added. The solution was stirred for three hours, keeping its temperature at 50°C. This solution was then poured into a volume of 500 ml of 10% by weight acetic acid (rare earth element solution). 480 ml of the ruthenium solution were mixed into 120 ml of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com